⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-05-10 更新
ReAlign: Bilingual Text-to-Motion Generation via Step-Aware Reward-Guided Alignment
Authors:Wanjiang Weng, Xiaofeng Tan, Hongsong Wang, Pan Zhou
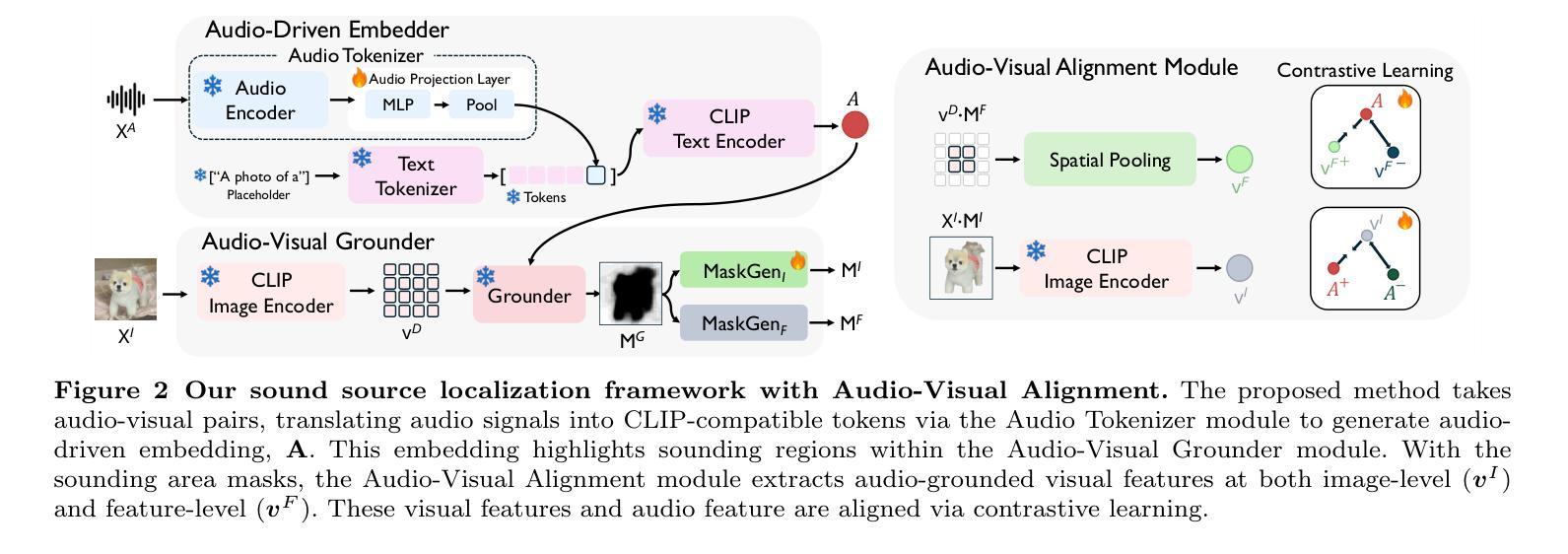
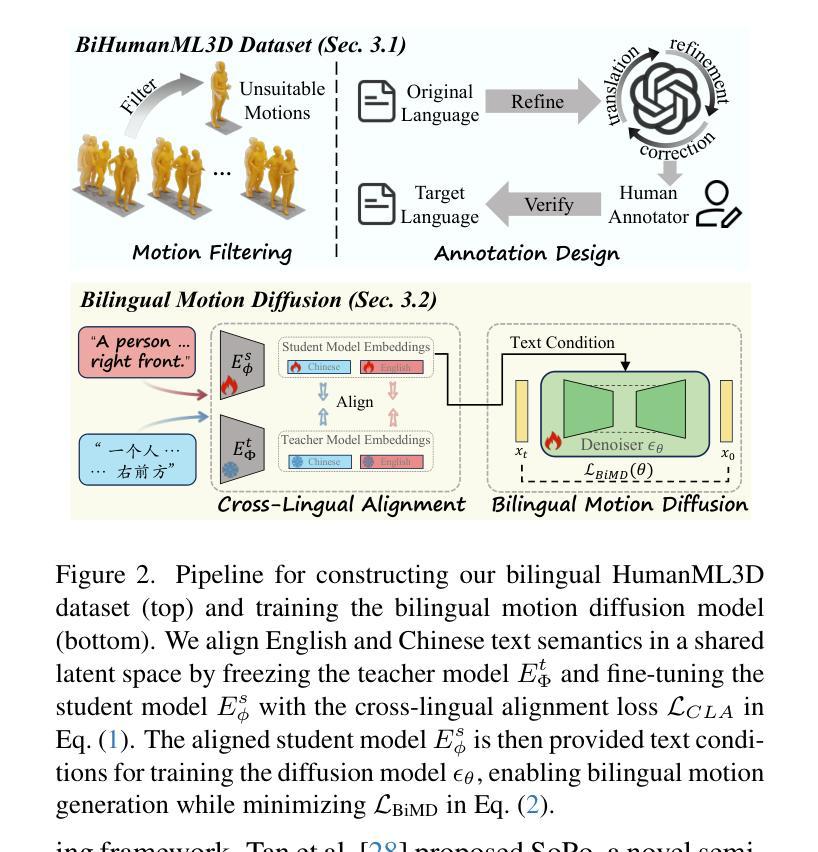
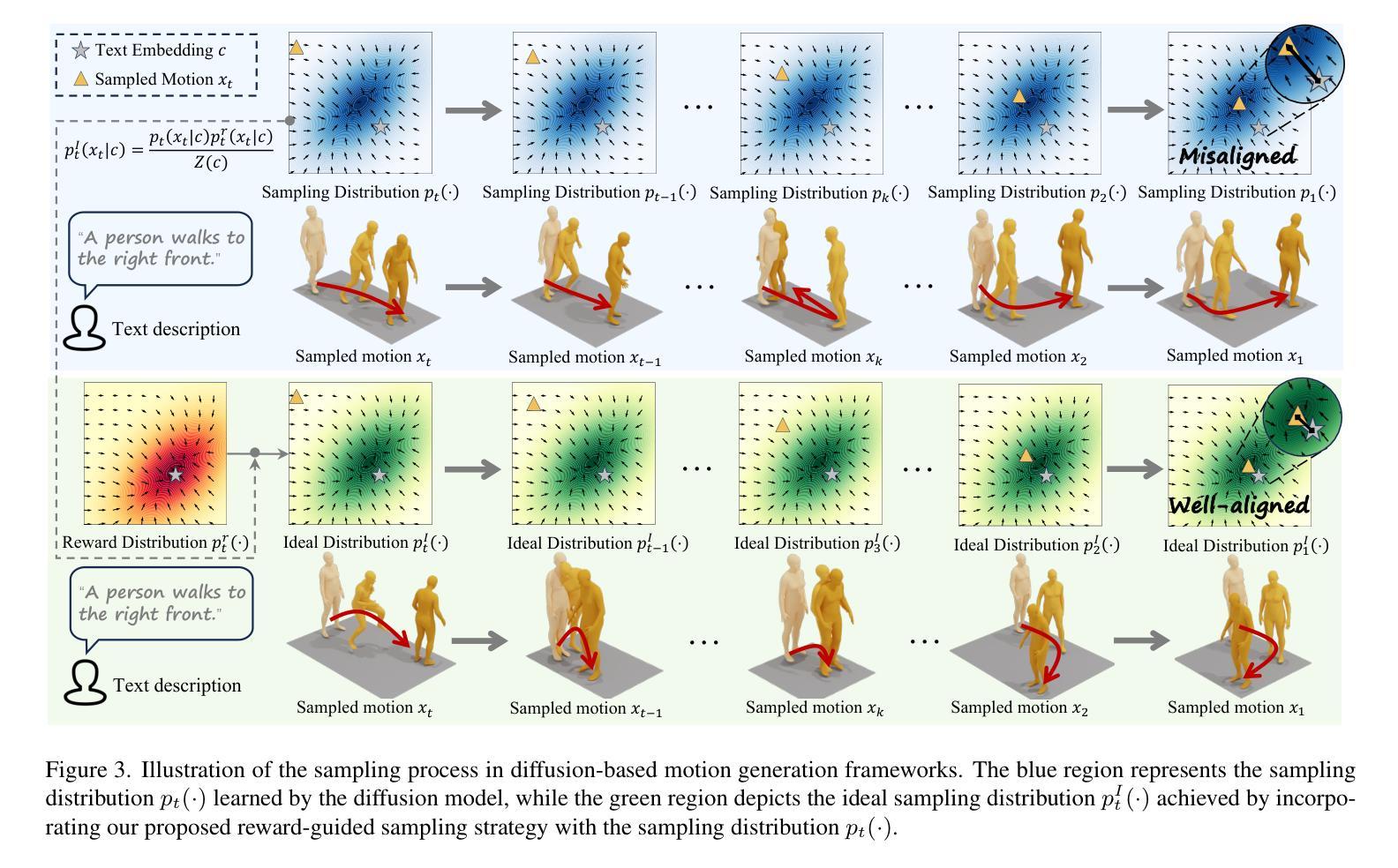
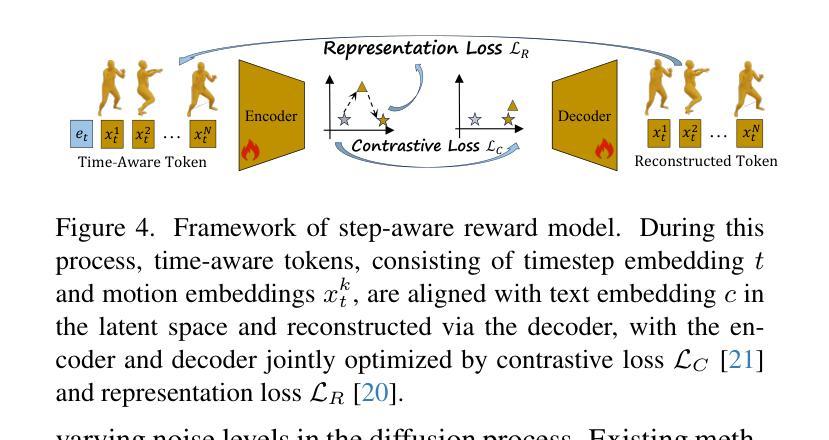
Bilingual text-to-motion generation, which synthesizes 3D human motions from bilingual text inputs, holds immense potential for cross-linguistic applications in gaming, film, and robotics. However, this task faces critical challenges: the absence of bilingual motion-language datasets and the misalignment between text and motion distributions in diffusion models, leading to semantically inconsistent or low-quality motions. To address these challenges, we propose BiHumanML3D, a novel bilingual human motion dataset, which establishes a crucial benchmark for bilingual text-to-motion generation models. Furthermore, we propose a Bilingual Motion Diffusion model (BiMD), which leverages cross-lingual aligned representations to capture semantics, thereby achieving a unified bilingual model. Building upon this, we propose Reward-guided sampling Alignment (ReAlign) method, comprising a step-aware reward model to assess alignment quality during sampling and a reward-guided strategy that directs the diffusion process toward an optimally aligned distribution. This reward model integrates step-aware tokens and combines a text-aligned module for semantic consistency and a motion-aligned module for realism, refining noisy motions at each timestep to balance probability density and alignment. Experiments demonstrate that our approach significantly improves text-motion alignment and motion quality compared to existing state-of-the-art methods. Project page: https://wengwanjiang.github.io/ReAlign-page/.
双语文本到动作生成技术能够从双语文本输入中合成3D人类动作,为游戏、电影和机器人等领域的跨语言应用提供了巨大潜力。然而,这一任务面临着关键挑战:缺乏双语运动语言数据集以及扩散模型中文本和运动分布之间的不匹配,这可能导致语义不一致或质量较低的动作。为了应对这些挑战,我们提出了BiHumanML3D,这是一个新的双语人类运动数据集,为双语文本到动作生成模型建立了关键基准。此外,我们提出了双语运动扩散模型(BiMD),该模型利用跨语言对齐表示来捕捉语义,从而实现统一的双语模型。在此基础上,我们提出了奖励引导采样对齐(ReAlign)方法,包括一个步骤感知奖励模型,在采样过程中评估对齐质量,以及一个奖励引导策略,将扩散过程导向最佳对齐分布。该奖励模型结合了步骤感知令牌,并融合了文本对齐模块以确保语义一致性,以及运动对齐模块以确保真实性,在每个时间步长精细调整噪声动作,以平衡概率密度和对齐。实验表明,我们的方法在文本动作对齐和运动质量方面显著优于现有最先进的方法。项目页面:https://wengwanjiang.github.io/ReAlign-page/。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 17 pages, 9 figures
Summary:提出一种双语运动扩散模型(BiMD),利用跨语言对齐表示来捕捉语义,实现统一双语模型。为应对双语文本到运动生成中的挑战,构建了一个双语人类运动数据集BiHumanML3D,并提出了一种奖励引导采样对齐(ReAlign)方法,包括一个步骤感知奖励模型,用于在采样过程中评估对齐质量,以及一个奖励引导策略,引导扩散过程朝最优对齐分布进行。
Key Takeaways:
- 双语文本到运动生成具有巨大的潜力,但缺乏双语运动语言数据集和对齐挑战。
- 介绍了BiHumanML3D双语人类运动数据集,为双语文本到运动生成模型提供了关键基准。
- 提出了双语运动扩散模型(BiMD),利用跨语言对齐表示捕捉语义。
- 提出了奖励引导采样对齐(ReAlign)方法,包括步骤感知奖励模型和奖励引导策略。
- ReAlign方法通过评估对齐质量和引导扩散过程,显著提高了文本与运动的对齐度和运动质量。
- 实验证明,该方法与现有先进技术相比,具有更好的文本运动对齐和运动质量。
点此查看论文截图

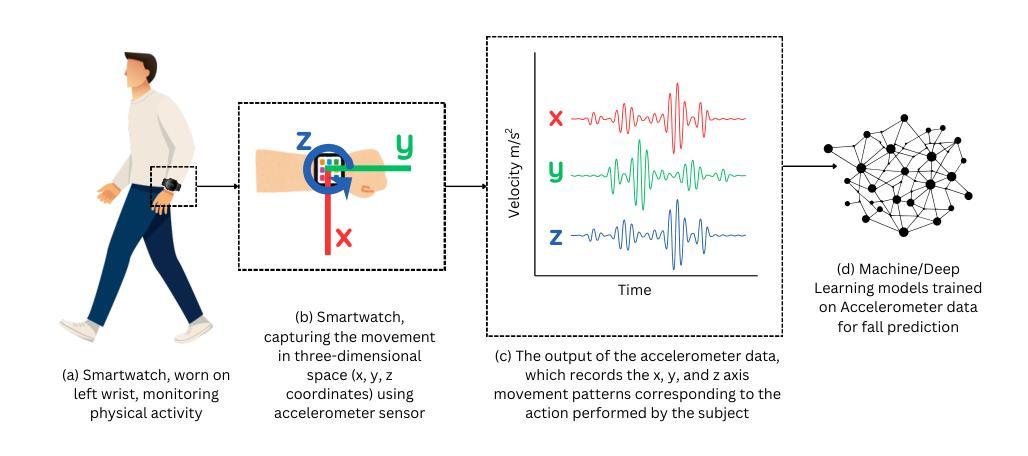
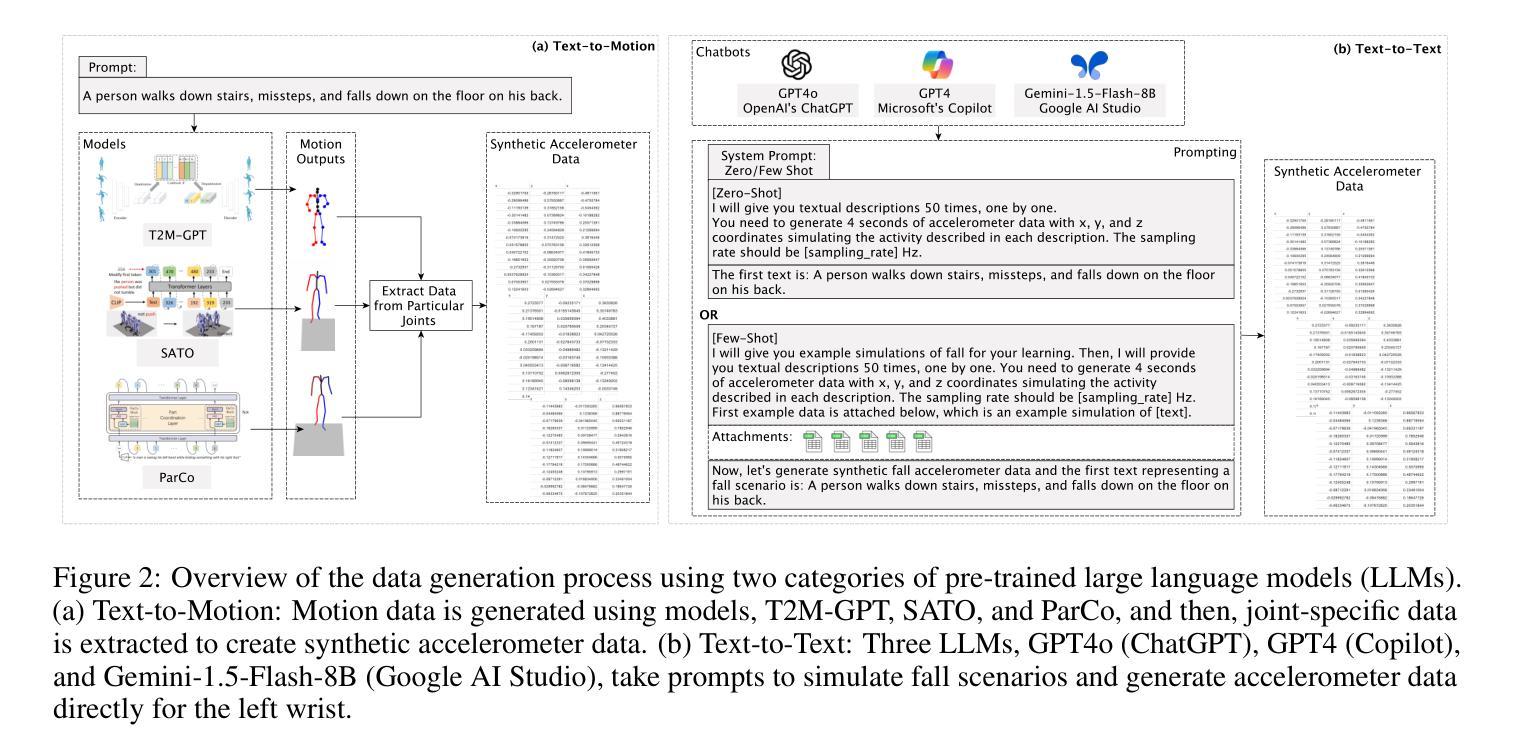
AI-Generated Fall Data: Assessing LLMs and Diffusion Model for Wearable Fall Detection
Authors:Sana Alamgeer, Yasine Souissi, Anne H. H. Ngu
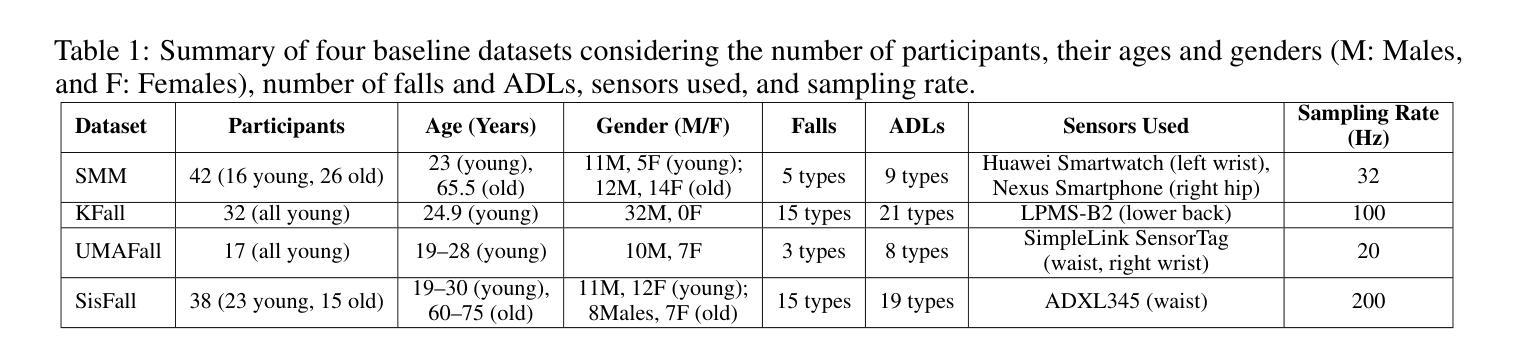
Training fall detection systems is challenging due to the scarcity of real-world fall data, particularly from elderly individuals. To address this, we explore the potential of Large Language Models (LLMs) for generating synthetic fall data. This study evaluates text-to-motion (T2M, SATO, ParCo) and text-to-text models (GPT4o, GPT4, Gemini) in simulating realistic fall scenarios. We generate synthetic datasets and integrate them with four real-world baseline datasets to assess their impact on fall detection performance using a Long Short-Term Memory (LSTM) model. Additionally, we compare LLM-generated synthetic data with a diffusion-based method to evaluate their alignment with real accelerometer distributions. Results indicate that dataset characteristics significantly influence the effectiveness of synthetic data, with LLM-generated data performing best in low-frequency settings (e.g., 20Hz) while showing instability in high-frequency datasets (e.g., 200Hz). While text-to-motion models produce more realistic biomechanical data than text-to-text models, their impact on fall detection varies. Diffusion-based synthetic data demonstrates the closest alignment to real data but does not consistently enhance model performance. An ablation study further confirms that the effectiveness of synthetic data depends on sensor placement and fall representation. These findings provide insights into optimizing synthetic data generation for fall detection models.
训练摔倒检测系统面临的一个挑战是缺乏真实世界的摔倒数据,特别是来自老年人的数据。为了解决这一问题,我们探索了大型语言模型(LLM)在生成合成摔倒数据方面的潜力。本研究评估了文本到运动(T2M、SATO、ParCo)和文本到文本模型(GPT4o、GPT4、Gemini)在模拟现实摔倒场景方面的表现。我们生成了合成数据集,并将其与四个真实世界的基础数据集相结合,使用长短期记忆(LSTM)模型评估它们对摔倒检测性能的影响。此外,我们还比较了LLM生成的合成数据与基于扩散的方法,以评估它们与真实加速度计分布的对齐程度。结果表明,数据集特性对合成数据的有效性有显著影响,LLM生成的数据在低频率设置(例如20Hz)中表现最佳,而在高频率数据集(例如200Hz)中表现出不稳定。虽然文本到运动模型产生的生物力学数据比文本到文本模型更真实,但它们对摔倒检测的影响各不相同。基于扩散的合成数据最接近于真实数据,但并不总能提高模型性能。一项消融研究进一步证实,合成数据的有效性取决于传感器的放置和摔倒的表示。这些发现为优化合成数据生成以支持摔倒检测模型提供了见解。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
该文探讨了在缺乏真实坠落数据的情况下,如何训练坠落检测系统的问题。为了解决这个问题,文章探索了大型语言模型(LLMs)在生成合成坠落数据方面的潜力。文章评估了文本到运动(T2M、SATO、ParCo)和文本到文本模型(GPT4o、GPT4、Gemini)在模拟真实坠落场景中的表现。通过生成合成数据集并将其与四个真实世界基线数据集相结合,使用长短时记忆(LSTM)模型评估它们对坠落检测性能的影响。文章还对比了LLM生成的合成数据与基于扩散的方法,以评估其与真实加速度计分布的契合度。研究结果表明,数据集特性对合成数据的有效性有显著影响,LLM生成的数据在低频率设置下表现最佳,而在高频率数据集中表现不稳定。虽然文本到运动模型产生的生物力学数据比文本到文本模型更真实,但它们对坠落检测的影响是变化的。基于扩散的合成数据在真实数据方面表现出最紧密的契合度,但并不总是能提高模型性能。此外,一项消融研究进一步证实了合成数据的有效性取决于传感器放置和坠落表示。这些发现有助于优化合成数据的生成,以改进坠落检测模型。
Key Takeaways
- 缺乏真实坠落数据是训练坠落检测系统的挑战。
- 大型语言模型(LLMs)在生成合成坠落数据方面展现出潜力。
- 文本到运动(T2M)和文本到文本模型在模拟真实坠落场景中有不同表现。
- 合成数据集与真实世界数据集结合,有助于评估坠落检测性能。
- LLM生成的数据在低频率设置下表现最佳,高频率数据集中表现不稳定。
- 文本到运动模型产生的生物力学数据较为真实,但对坠落检测影响不一。
点此查看论文截图