⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-05-10 更新
Benchmarking Ophthalmology Foundation Models for Clinically Significant Age Macular Degeneration Detection
Authors:Benjamin A. Cohen, Jonathan Fhima, Meishar Meisel, Baskin Meital, Luis Filipe Nakayama, Eran Berkowitz, Joachim A. Behar
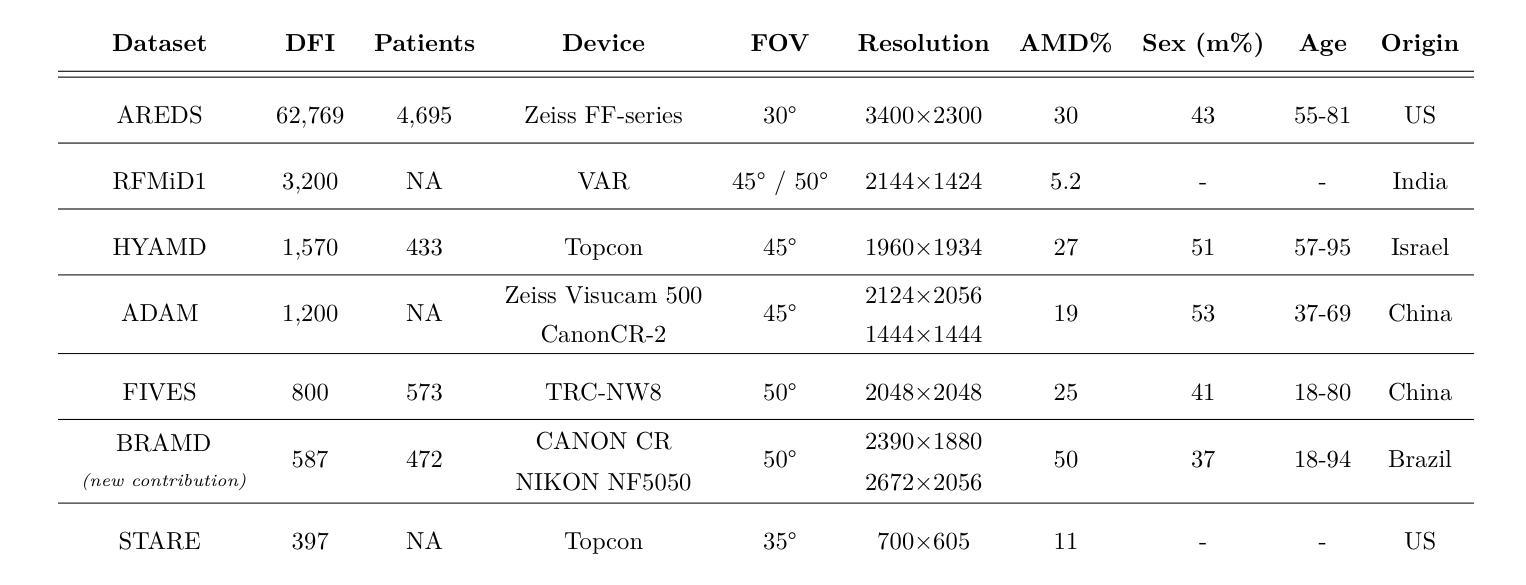
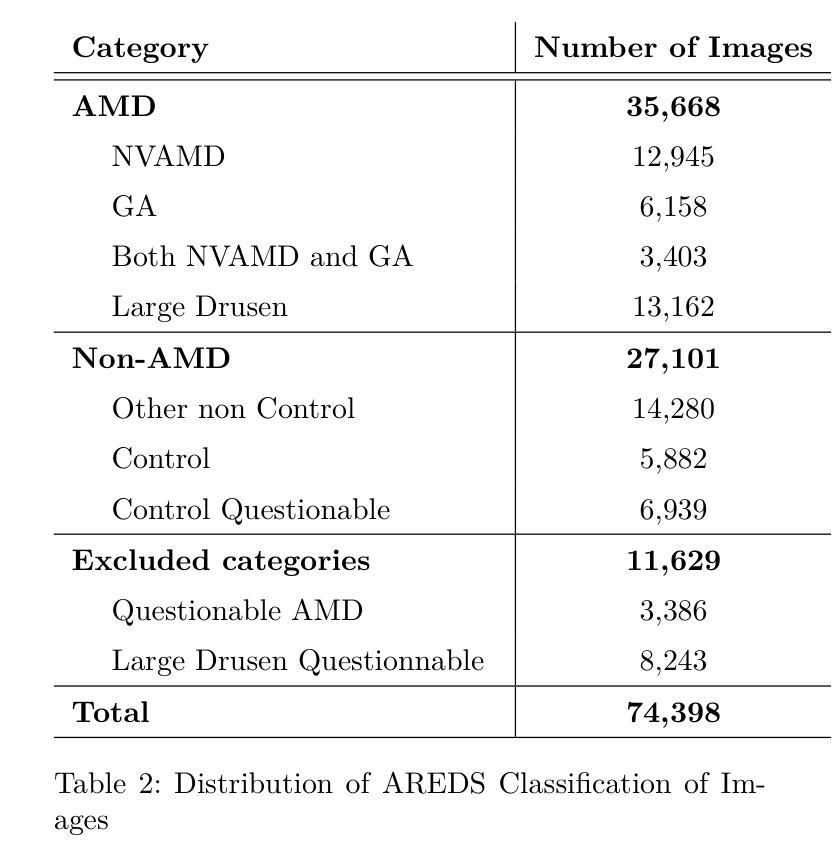
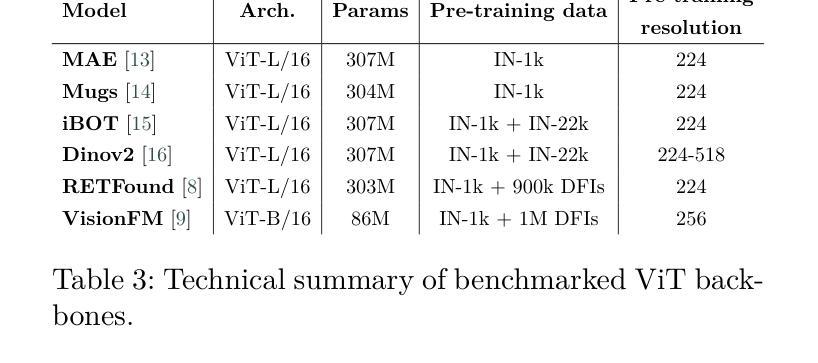
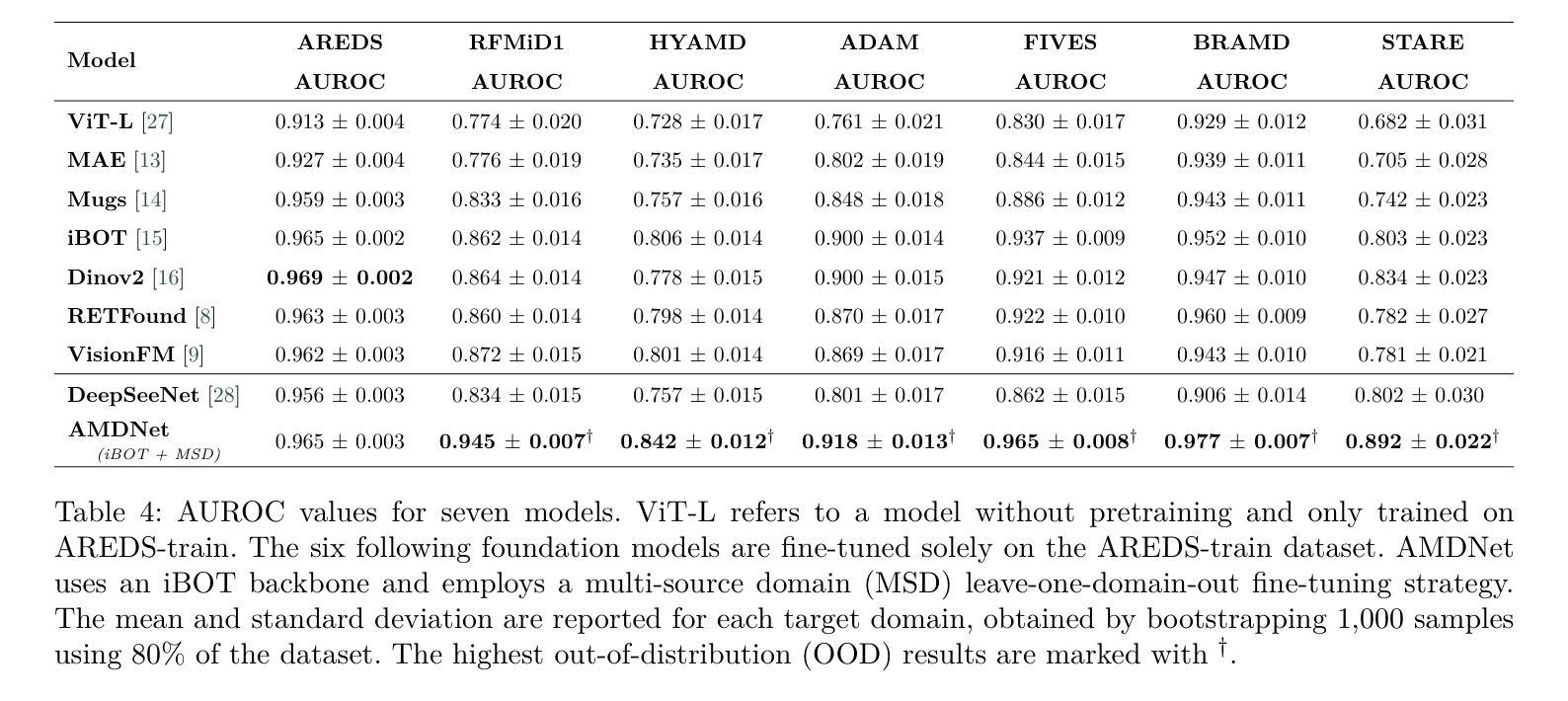
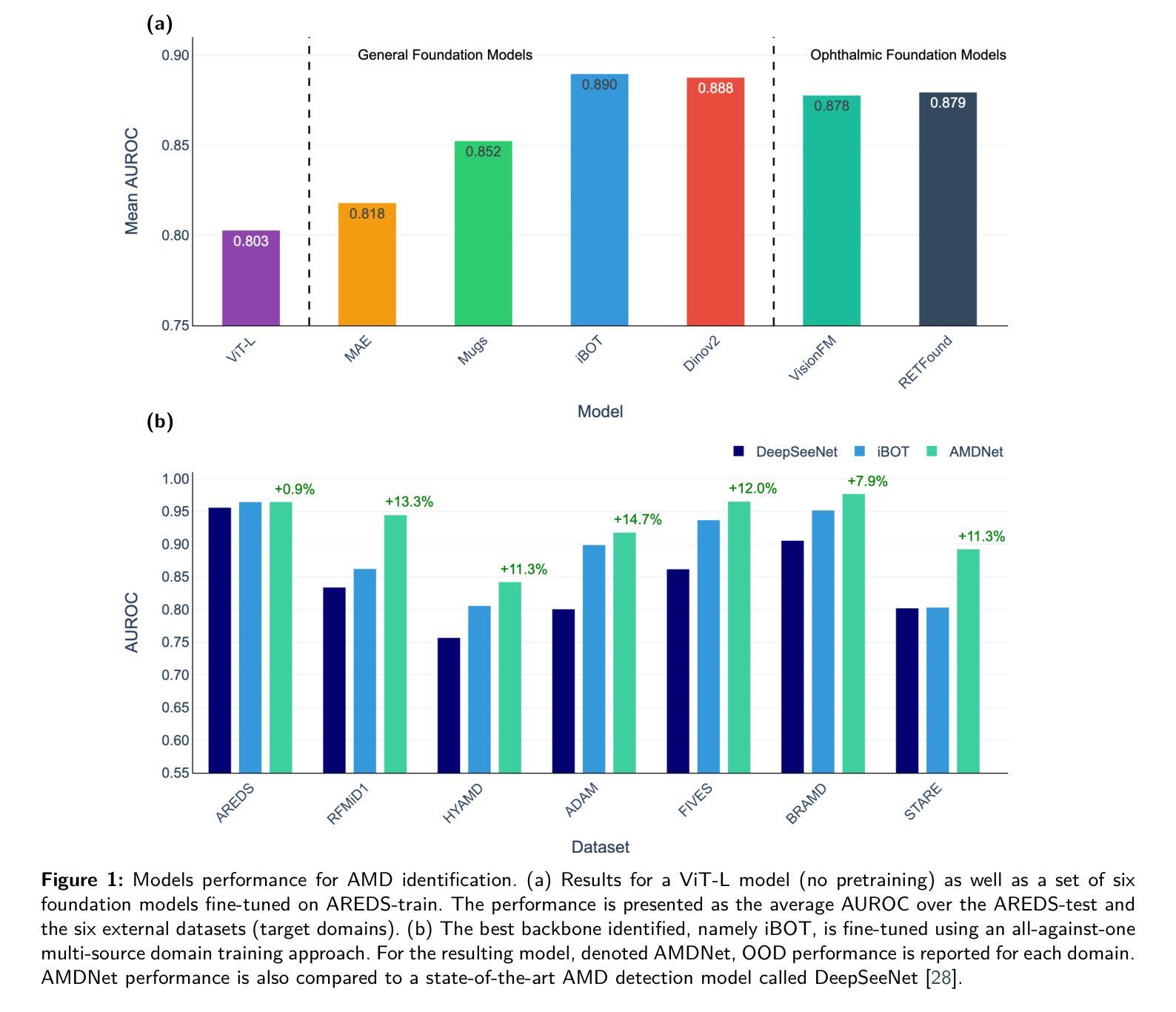
Self-supervised learning (SSL) has enabled Vision Transformers (ViTs) to learn robust representations from large-scale natural image datasets, enhancing their generalization across domains. In retinal imaging, foundation models pretrained on either natural or ophthalmic data have shown promise, but the benefits of in-domain pretraining remain uncertain. To investigate this, we benchmark six SSL-pretrained ViTs on seven digital fundus image (DFI) datasets totaling 70,000 expert-annotated images for the task of moderate-to-late age-related macular degeneration (AMD) identification. Our results show that iBOT pretrained on natural images achieves the highest out-of-distribution generalization, with AUROCs of 0.80-0.97, outperforming domain-specific models, which achieved AUROCs of 0.78-0.96 and a baseline ViT-L with no pretraining, which achieved AUROCs of 0.68-0.91. These findings highlight the value of foundation models in improving AMD identification and challenge the assumption that in-domain pretraining is necessary. Furthermore, we release BRAMD, an open-access dataset (n=587) of DFIs with AMD labels from Brazil.
自监督学习(SSL)使得视觉Transformer(ViT)能够从大规模的自然图像数据集中学习鲁棒性表示,增强了其在不同领域的泛化能力。在视网膜成像中,预训练在自然或眼科数据上的基础模型已经显示出潜力,但领域内预训练的好处仍不确定。为了研究这一点,我们在包含总计7万张专家标注图像的7个数字眼底图像(DFI)数据集上,对六个SSL预训练的ViT进行了基准测试,用于中度至晚期年龄相关性黄斑病变(AMD)的识别任务。我们的结果表明,在自然图像上预训练的iBOT具有最高的跨分布泛化能力,AUC值在0.80至0.97之间,优于特定领域的模型(AUC值在0.78至0.96之间)和未经预训练的基线ViT-L(AUC值在0.68至0.91之间)。这些发现凸显了基础模型在改进AMD识别方面的价值,并挑战了认为领域内预训练是必要的假设。此外,我们发布了BRAMD,这是一个开放访问的眼底图像数据集,包含来自巴西的AMD标签图像共计587张。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 10 pages, 3 figures
Summary
在视网膜成像领域,自监督学习(SSL)赋能Vision Transformers(ViTs)从大规模自然图像数据集中学习稳健表示,提升其在不同领域的泛化能力。本研究对比了六种SSL预训练ViTs在眼底图像(DFI)数据集中识别年龄相关性黄斑病变(AMD)的表现。结果显示,以自然图像预训练的iBOT模型表现出最佳泛化能力,领域相关模型的性能次之,无预训练的基础模型性能最低。这表明在AMD识别方面,基础模型具有改善潜力,挑战了领域特定预训练的必要假设。同时,本研究公开了巴西AMD标记眼底图像数据集BRAMD。
Key Takeaways
- 自监督学习使Vision Transformers能从大规模自然图像数据集中学习稳健表示,提升其在视网膜成像中的泛化能力。
- 在眼底图像数据集中识别年龄相关性黄斑病变的研究中,iBOT预训练模型表现出最佳泛化能力。
- 与领域特定预训练的模型相比,iBOT预训练模型性能更优,这挑战了领域特定预训练的必要假设。
- 公开了巴西的眼底图像数据集BRAMD,为未来的研究提供数据支持。
- 研究表明,基础模型在改善AMD识别方面具有潜力。
- 研究结果强调了预训练在提升模型性能中的重要性。
点此查看论文截图

Biomed-DPT: Dual Modality Prompt Tuning for Biomedical Vision-Language Models
Authors:Wei Peng, Kang Liu, Jianchen Hu, Meng Zhang
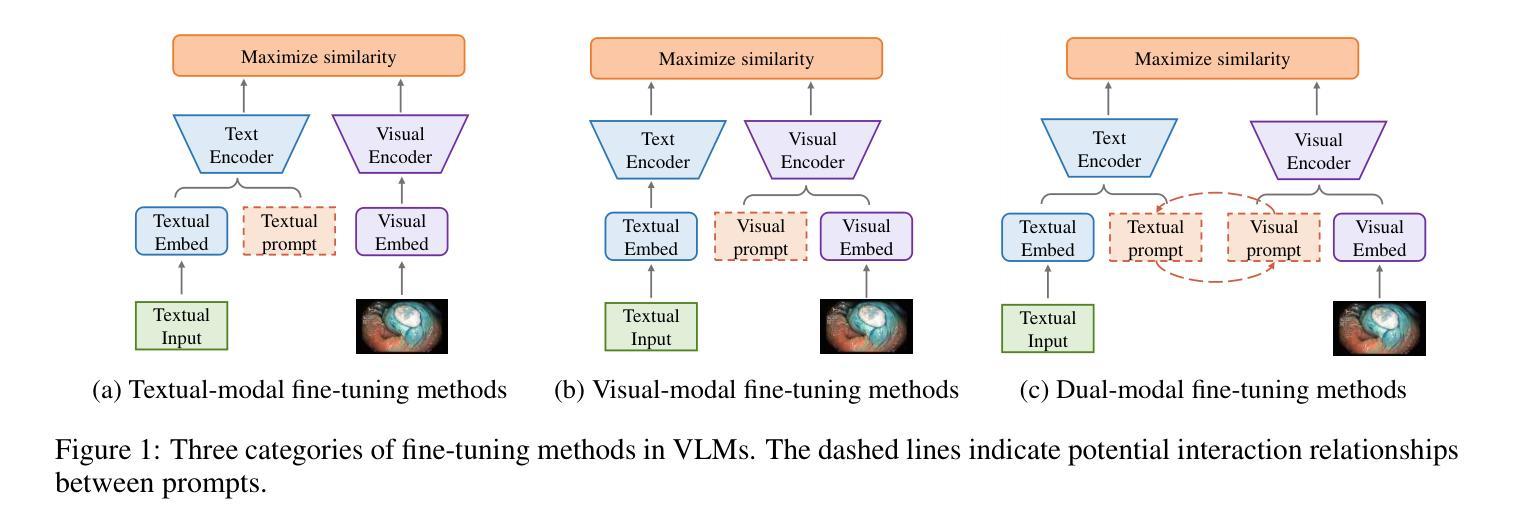
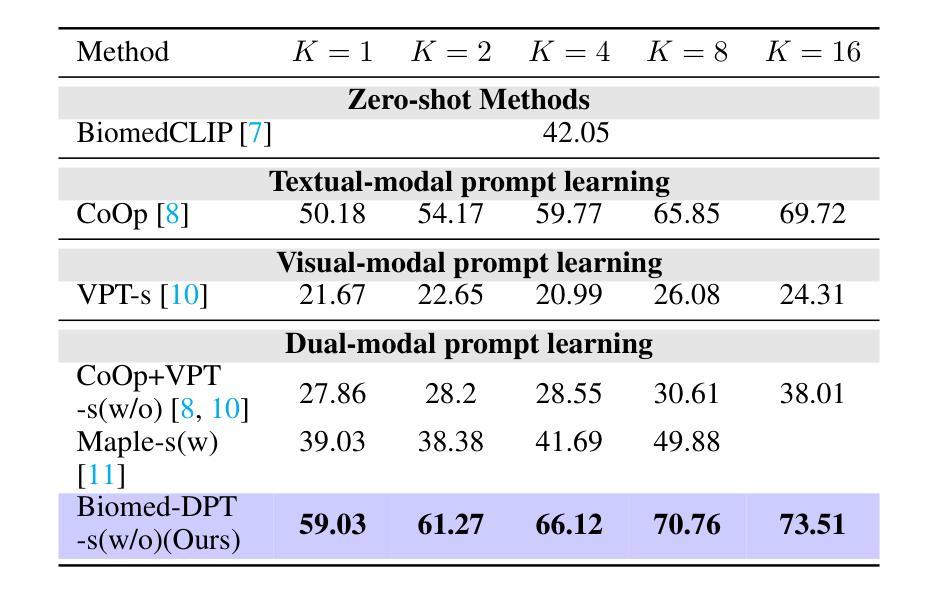
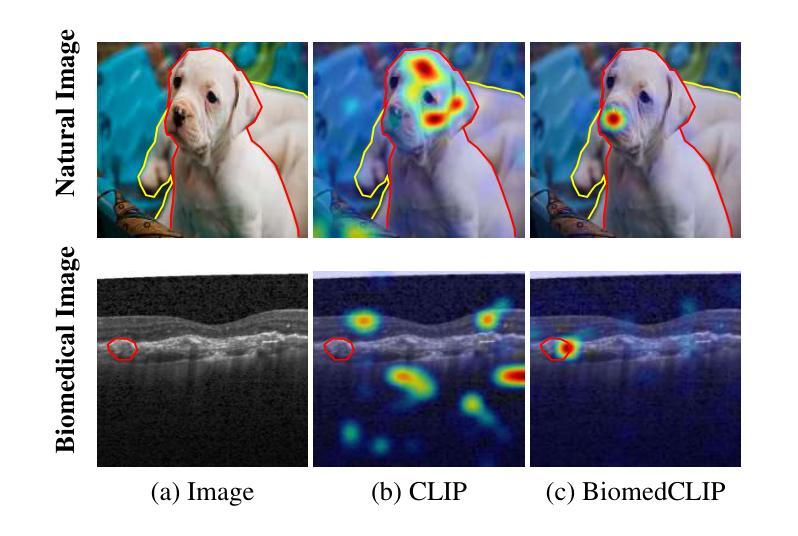
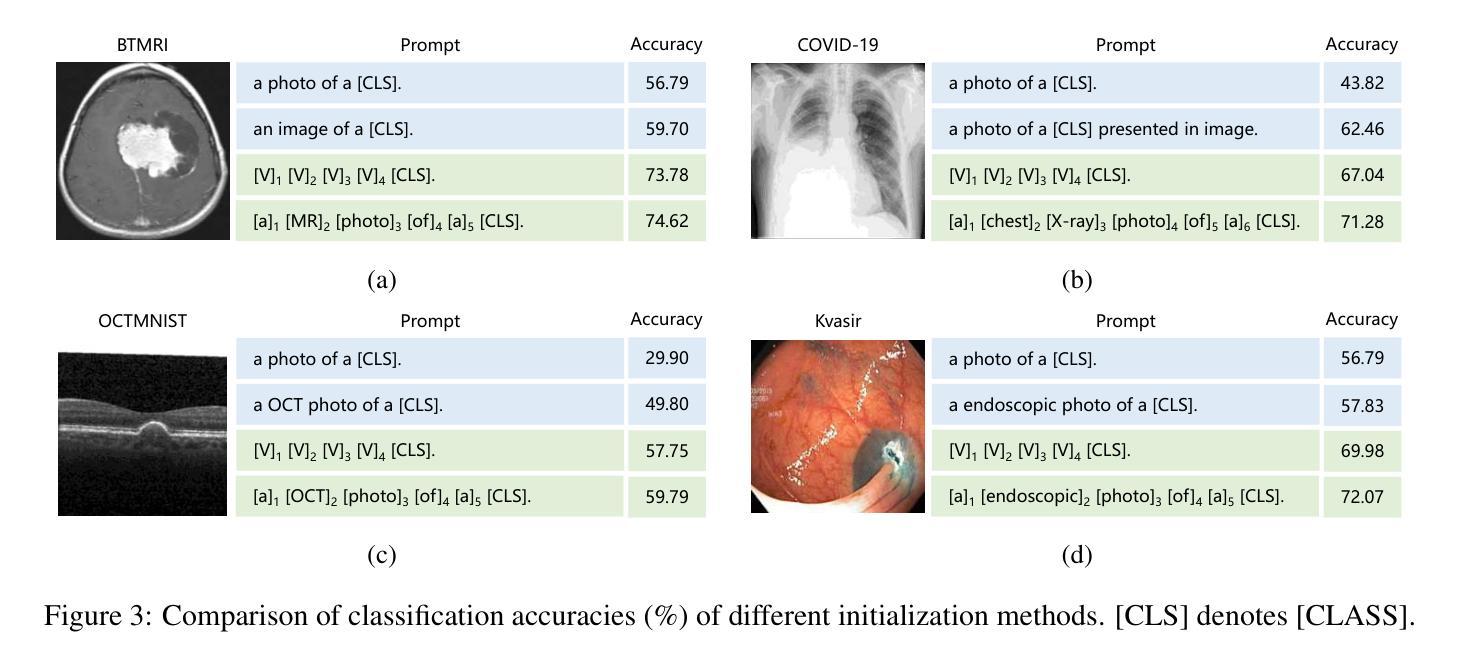
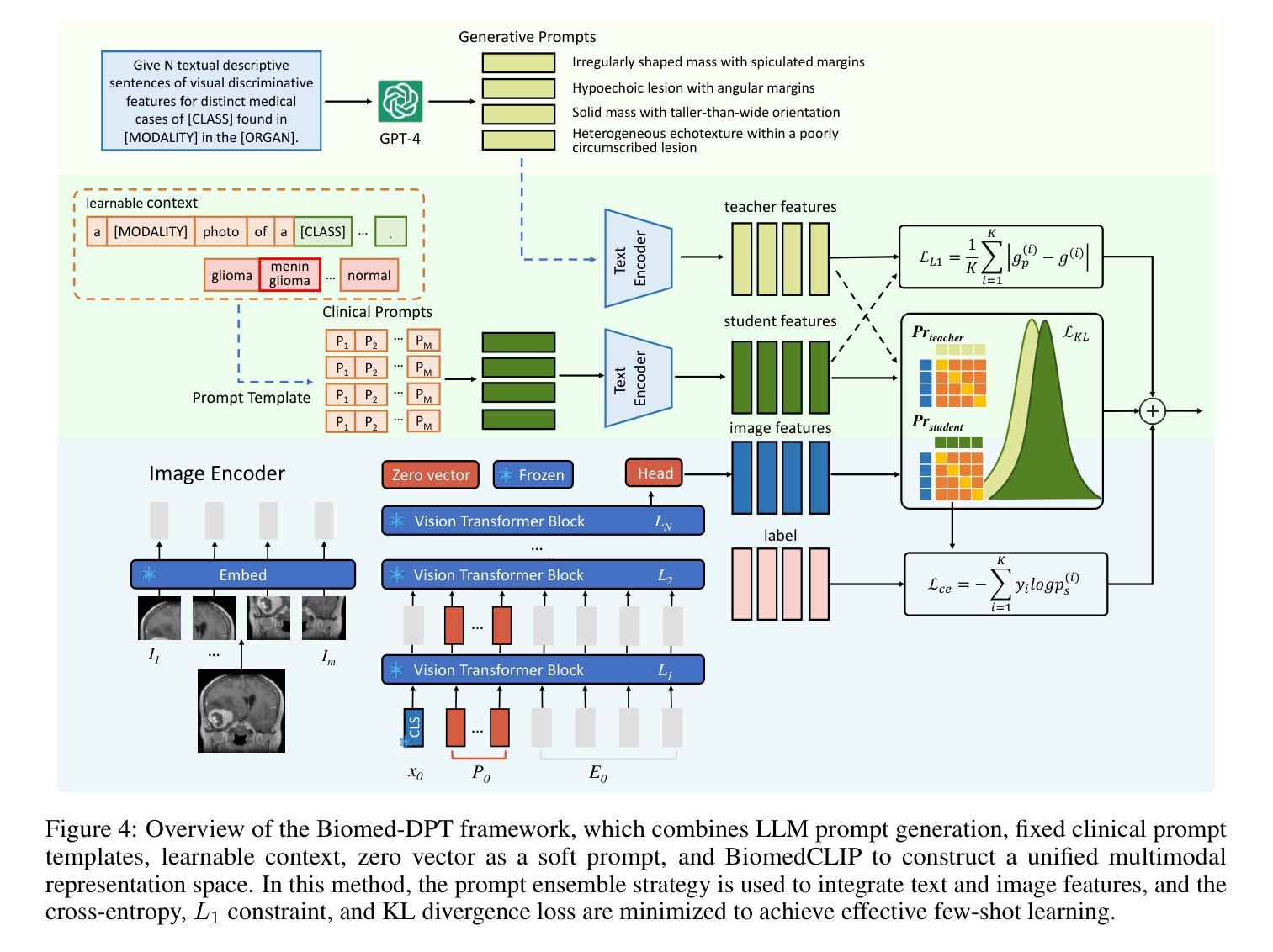
Prompt learning is one of the most effective paradigms for adapting pre-trained vision-language models (VLMs) to the biomedical image classification tasks in few shot scenarios. However, most of the current prompt learning methods only used the text prompts and ignored the particular structures (such as the complex anatomical structures and subtle pathological features) in the biomedical images. In this work, we propose Biomed-DPT, a knowledge-enhanced dual modality prompt tuning technique. In designing the text prompt, Biomed-DPT constructs a dual prompt including the template-driven clinical prompts and the large language model (LLM)-driven domain-adapted prompts, then extracts the clinical knowledge from the domain-adapted prompts through the knowledge distillation technique. In designing the vision prompt, Biomed-DPT introduces the zero vector as a soft prompt to leverage attention re-weighting so that the focus on non-diagnostic regions and the recognition of non-critical pathological features are avoided. Biomed-DPT achieves an average classification accuracy of 66.14% across 11 biomedical image datasets covering 9 modalities and 10 organs, with performance reaching 78.06% in base classes and 75.97% in novel classes, surpassing the Context Optimization (CoOp) method by 6.20%, 3.78%, and 8.04%, respectively. Our code are available at \underline{https://github.com/Kanyooo/Biomed-DPT}.
提示学习是在小样本场景中,将预训练的视觉语言模型(VLMs)适应生物医学图像分类任务的最有效范式之一。然而,当前大多数提示学习方法仅使用文本提示,而忽略了生物医学图像中的特定结构(如复杂的解剖结构和微妙的病理特征)。在我们的工作中,我们提出了生物医学领域知识增强的双模态提示调整技术——Biomed-DPT。在设计文本提示时,Biomed-DPT构建了一个双提示,包括模板驱动的临床提示和大语言模型(LLM)驱动的域适配提示,然后通过知识蒸馏技术从域适配提示中提取临床知识。在设计视觉提示时,Biomed-DPT引入了零向量作为软提示,以利用注意力重新加权,从而避免关注非诊断区域和识别非关键病理特征。Biomed-DPT在涵盖9种模态和10个器官的11个生物医学图像数据集上取得了平均分类准确率66.14%的成绩,其中基础类的性能达到78.06%,新型类的性能达到75.97%,分别超过了CoOp方法6.20%、3.78%和8.04%。我们的代码可在https://github.com/Kanyooo/Biomed-DPT找到。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文提出一种知识增强的双模态提示调整技术(Biomed-DPT),该技术针对生物医学图像分类任务进行预训练视语言模型(VLMs)的快速适应。通过设计文本提示和视觉提示,Biomed-DPT构建了一种双提示系统,包括模板驱动的临床提示和大型语言模型(LLM)驱动的领域自适应提示,并通过知识蒸馏技术提取领域自适应提示中的临床知识。同时,引入零向量作为软提示,避免对非诊断区域的关注和对非关键病理特征的识别。在跨越多个数据集的实验中,Biomed-DPT的分类准确度达到平均66.14%,并且在基准类和新型类中分别达到了78.06%和75.97%,超过了CoOp方法的性能。
Key Takeaways
- 当前大多数提示学习方法仅依赖文本提示,忽略了生物医学图像中的特定结构。
- Biomed-DPT是一种知识增强的双模态提示调整技术,旨在解决生物医学图像分类任务中的快速适应问题。
- 该技术通过构建双提示系统(包括临床提示和领域自适应提示)来优化文本提示设计。
- 通过知识蒸馏技术从领域自适应提示中提取临床知识。
- 引入零向量作为视觉软提示,避免对非诊断区域的关注和对非关键病理特征的识别。
- 实验结果显示,Biomed-DPT的分类准确度在多个生物医学图像数据集上平均达到66.14%,并且在基准类和新型类中都表现出优越性能。
点此查看论文截图

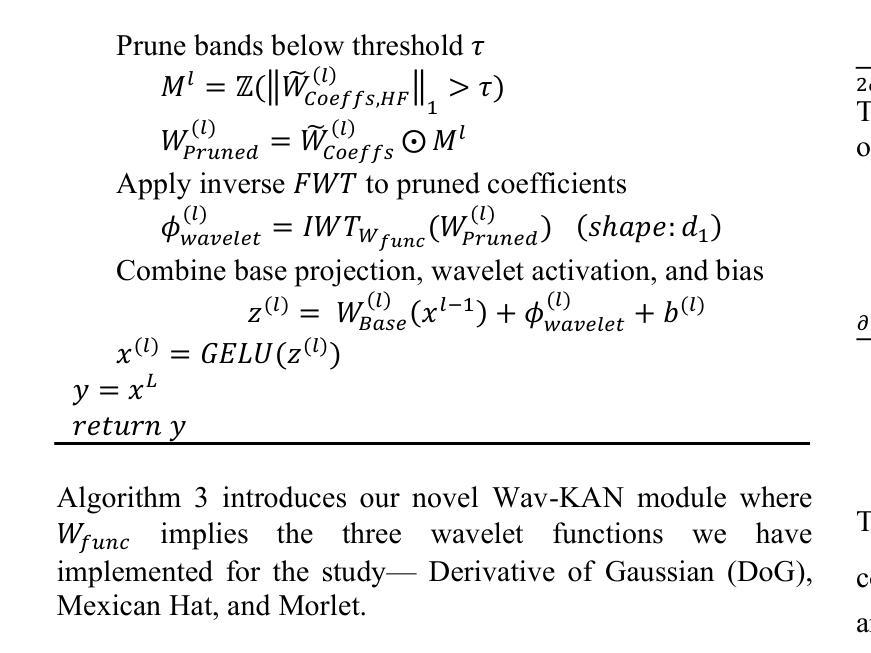
Hyb-KAN ViT: Hybrid Kolmogorov-Arnold Networks Augmented Vision Transformer
Authors:Sainath Dey, Mitul Goswami, Jashika Sethi, Prasant Kumar Pattnaik
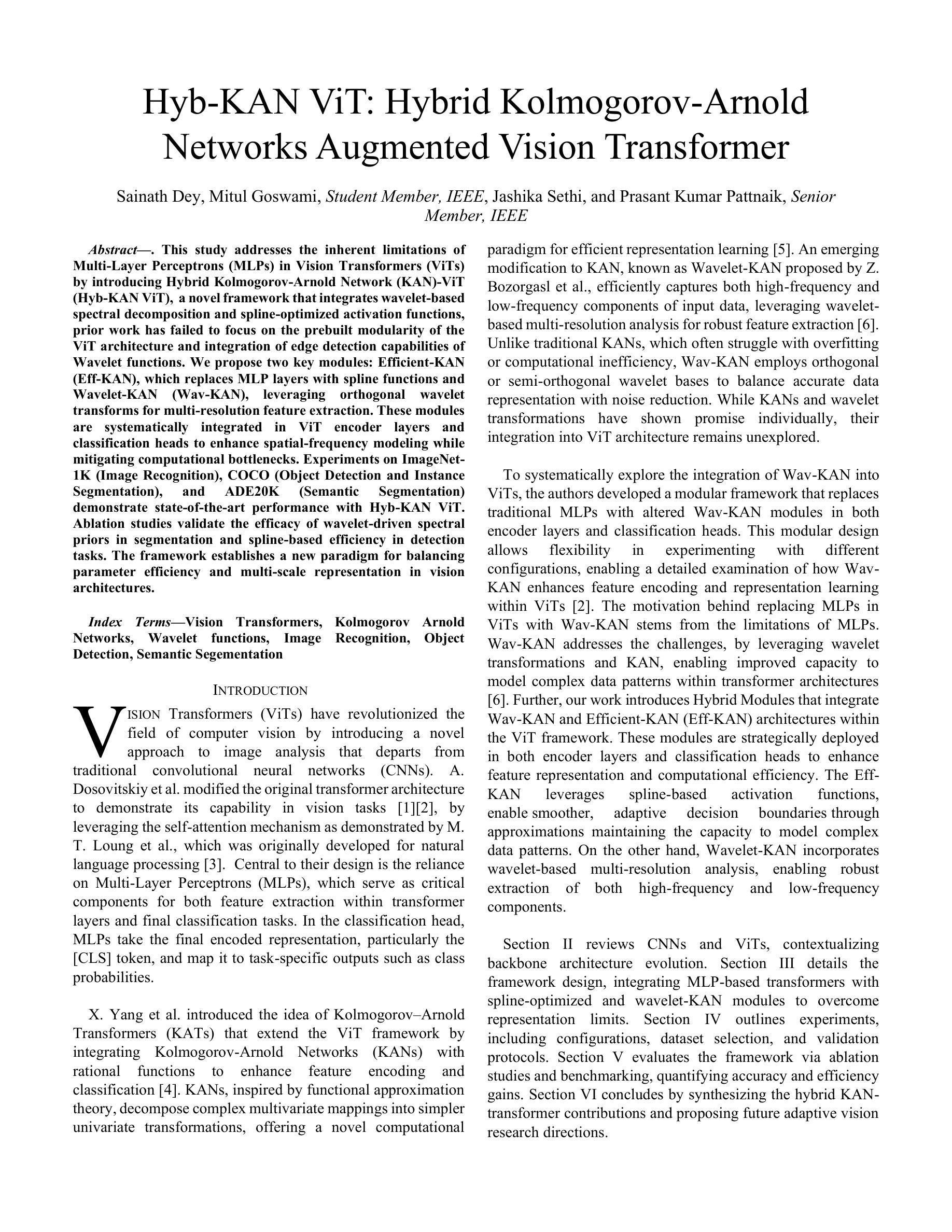
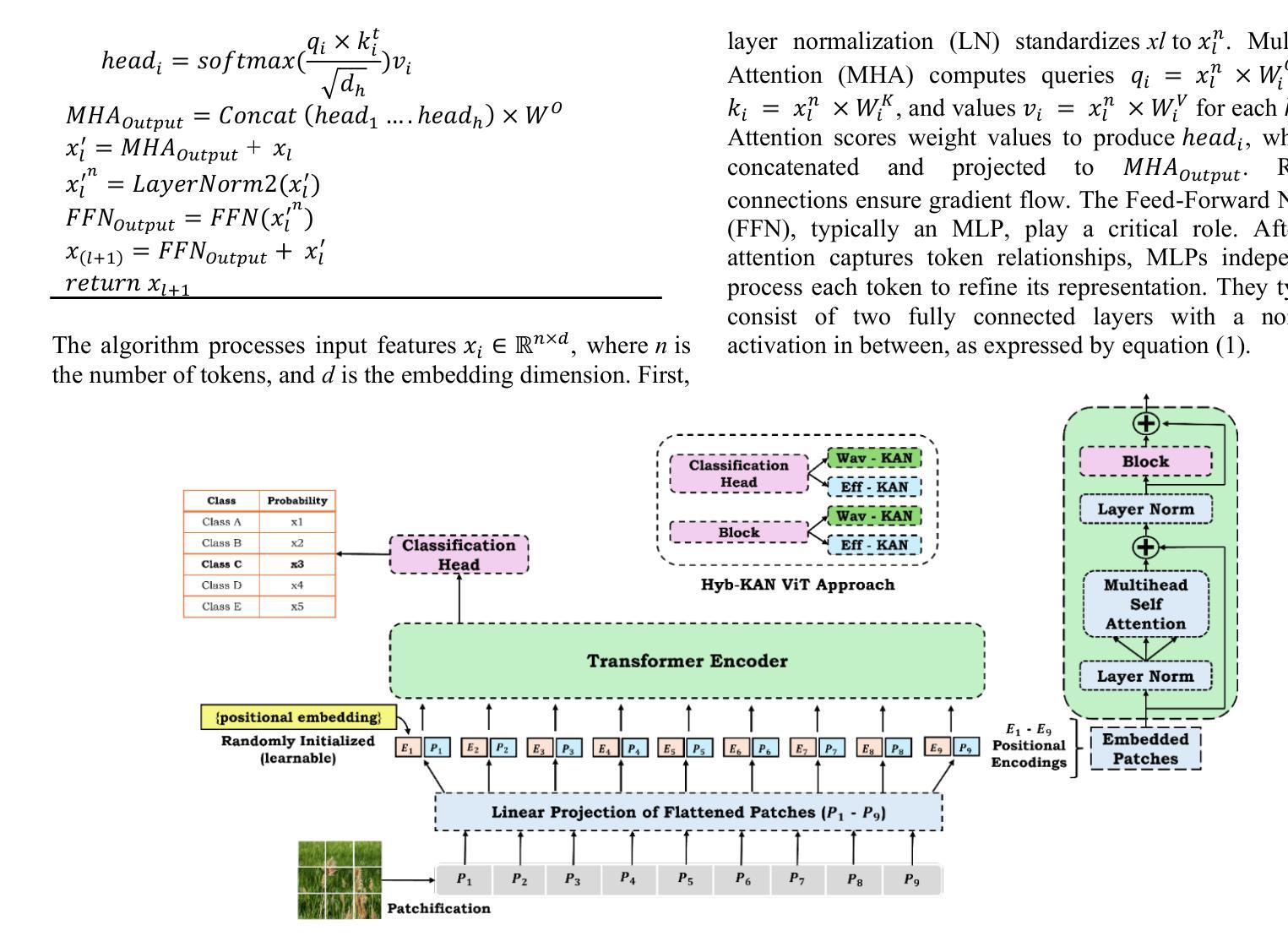
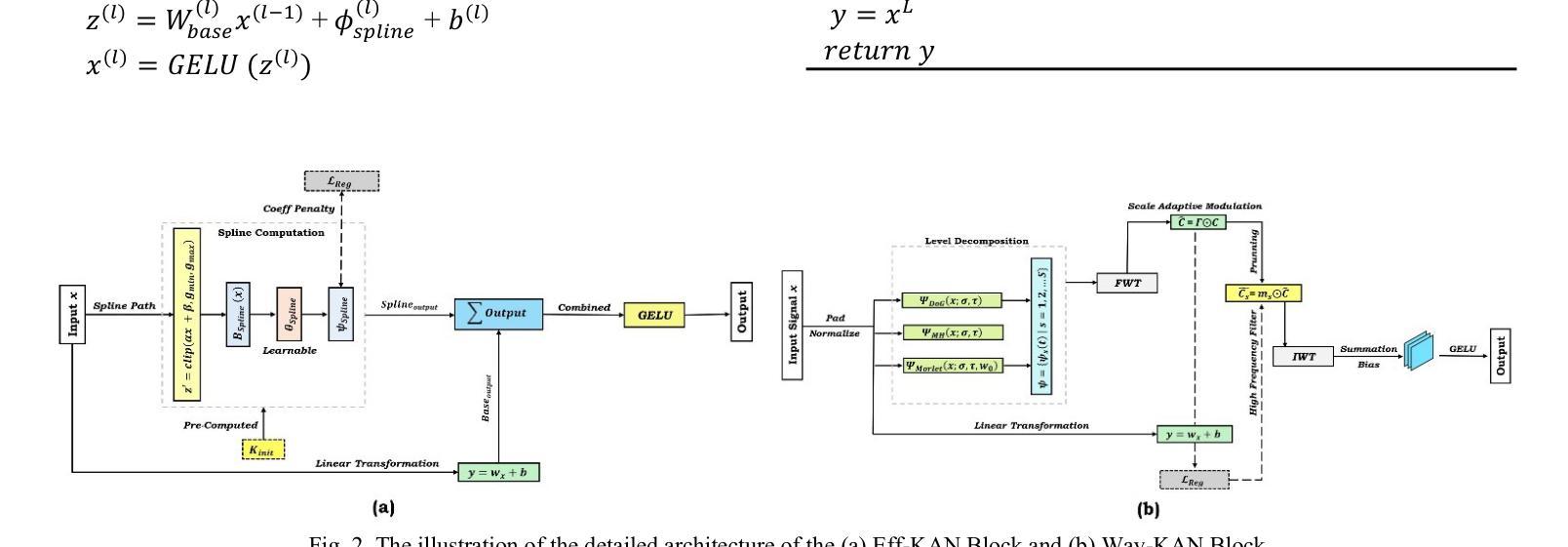
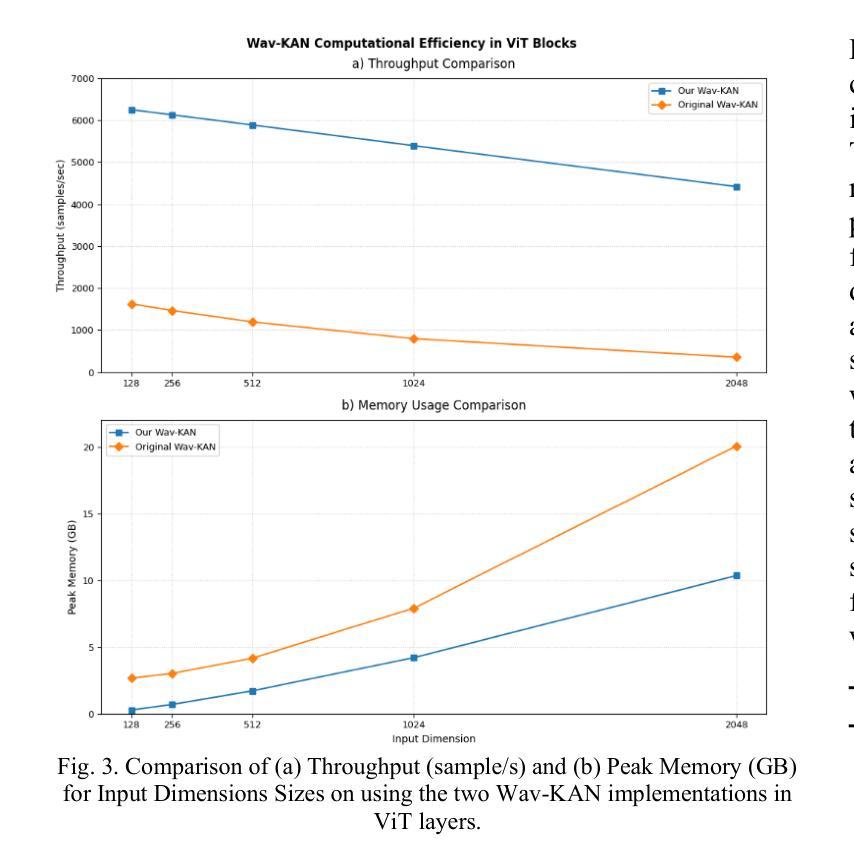
This study addresses the inherent limitations of Multi-Layer Perceptrons (MLPs) in Vision Transformers (ViTs) by introducing Hybrid Kolmogorov-Arnold Network (KAN)-ViT (Hyb-KAN ViT), a novel framework that integrates wavelet-based spectral decomposition and spline-optimized activation functions, prior work has failed to focus on the prebuilt modularity of the ViT architecture and integration of edge detection capabilities of Wavelet functions. We propose two key modules: Efficient-KAN (Eff-KAN), which replaces MLP layers with spline functions and Wavelet-KAN (Wav-KAN), leveraging orthogonal wavelet transforms for multi-resolution feature extraction. These modules are systematically integrated in ViT encoder layers and classification heads to enhance spatial-frequency modeling while mitigating computational bottlenecks. Experiments on ImageNet-1K (Image Recognition), COCO (Object Detection and Instance Segmentation), and ADE20K (Semantic Segmentation) demonstrate state-of-the-art performance with Hyb-KAN ViT. Ablation studies validate the efficacy of wavelet-driven spectral priors in segmentation and spline-based efficiency in detection tasks. The framework establishes a new paradigm for balancing parameter efficiency and multi-scale representation in vision architectures.
本研究通过引入混合Kolmogorov-Arnold网络(KAN)-ViT(Hyb-KAN ViT)这一新型框架,解决了多层感知器(MLP)在视觉转换器(ViT)中的固有局限性。该框架结合了基于小波谱分解和样条优化激活函数。先前的工作未能关注ViT架构的预构建模块性和小波功能的边缘检测能力的集成。我们提出了两个关键模块:Efficient-KAN(Eff-KAN),用样条函数替换MLP层;Wavelet-KAN(Wav-KAN),利用正交小波变换进行多分辨率特征提取。这些模块系统地集成在ViT编码器层和分类头中,以增强空间频率建模,同时缓解计算瓶颈。在ImageNet-1K(图像识别)、COCO(目标检测和实例分割)和ADE20K(语义分割)上的实验表明,Hyb-KAN ViT具有最先进的性能。消融研究验证了基于小波驱动的谱先验在分割中的有效性以及基于样条的检测任务效率。该框架为在视觉架构中平衡参数效率和多尺度表示建立了新范式。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文提出一种名为Hybrid Kolmogorov-Arnold Network(KAN)-ViT(Hyb-KAN ViT)的新型框架,解决了多层感知器(MLP)在视觉转换器(ViT)中的固有局限性。该框架结合了基于小波谱分解和样条优化激活函数。它提出了两个关键模块:Efficient-KAN(Eff-KAN)和Wavelet-KAN(Wav-KAN)。前者用样条函数替代MLP层,后者利用正交小波变换进行多分辨率特征提取。这些模块被系统地集成到ViT编码层和分类头中,以增强空间频率建模并缓解计算瓶颈。在ImageNet-1K(图像识别)、COCO(对象检测和实例分割)和ADE20K(语义分割)上的实验表明,Hyb-KAN ViT具有最先进的性能。消融研究验证了以波为驱动谱先验在分割中的有效性以及基于样条的效率在检测任务中的应用。该框架为平衡参数效率和多尺度表示在视觉架构中建立了新的范例。
Key Takeaways
- 介绍了Hybrid Kolmogorov-Arnold Network (KAN)-ViT框架,旨在解决多层感知器(MLP)在视觉转换器(ViT)中的局限性。
- 提出了Efficient-KAN和Wavelet-KAN两个关键模块,前者用样条函数替代MLP层以提高效率,后者利用小波变换进行多分辨率特征提取。
- 将这些模块系统地集成到ViT编码层和分类头中,以增强空间频率建模,并缓解计算瓶颈。
- 在多个数据集上的实验表明Hyb-KAN ViT具有最先进的性能,包括ImageNet-1K、COCO和ADE20K。
- 消融研究验证了以波为驱动谱先验在分割任务中的有效性以及基于样条的激活函数在检测任务中的效率。
- 该框架为平衡参数效率和多尺度表示在视觉架构中提供了新范例。
点此查看论文截图
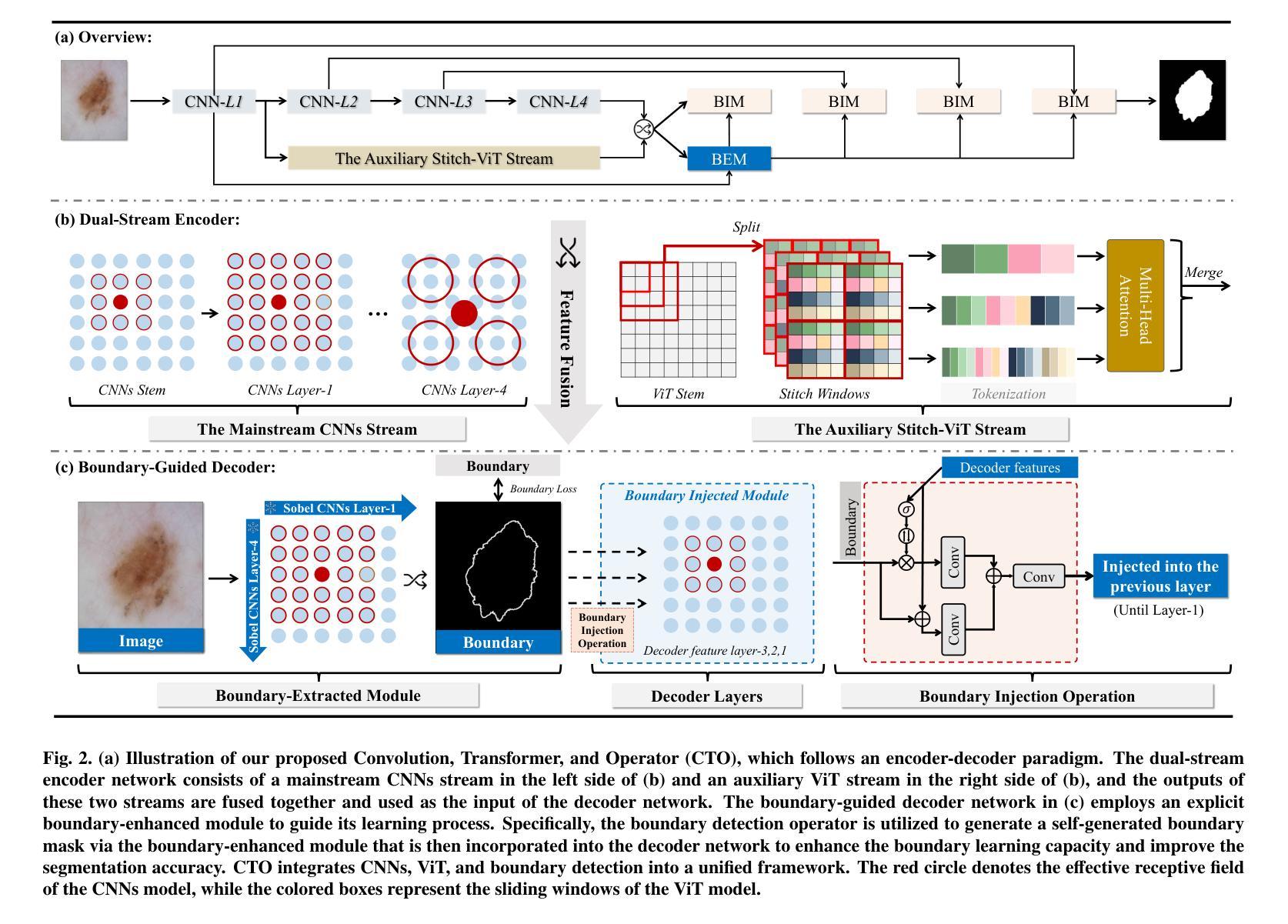
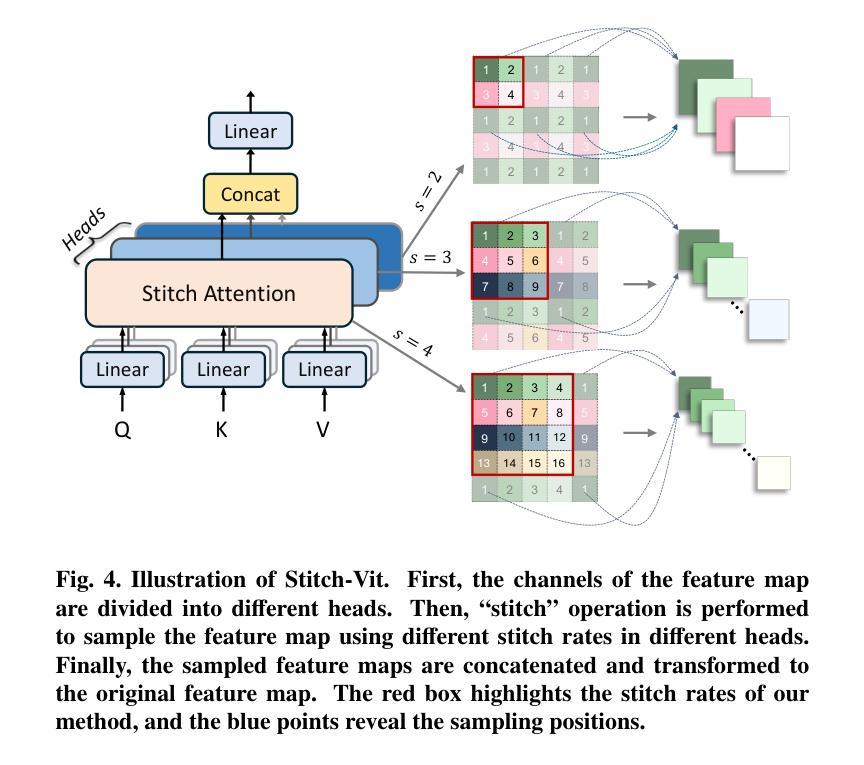
Rethinking Boundary Detection in Deep Learning-Based Medical Image Segmentation
Authors:Yi Lin, Dong Zhang, Xiao Fang, Yufan Chen, Kwang-Ting Cheng, Hao Chen
Medical image segmentation is a pivotal task within the realms of medical image analysis and computer vision. While current methods have shown promise in accurately segmenting major regions of interest, the precise segmentation of boundary areas remains challenging. In this study, we propose a novel network architecture named CTO, which combines Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs), Vision Transformer (ViT) models, and explicit edge detection operators to tackle this challenge. CTO surpasses existing methods in terms of segmentation accuracy and strikes a better balance between accuracy and efficiency, without the need for additional data inputs or label injections. Specifically, CTO adheres to the canonical encoder-decoder network paradigm, with a dual-stream encoder network comprising a mainstream CNN stream for capturing local features and an auxiliary StitchViT stream for integrating long-range dependencies. Furthermore, to enhance the model’s ability to learn boundary areas, we introduce a boundary-guided decoder network that employs binary boundary masks generated by dedicated edge detection operators to provide explicit guidance during the decoding process. We validate the performance of CTO through extensive experiments conducted on seven challenging medical image segmentation datasets, namely ISIC 2016, PH2, ISIC 2018, CoNIC, LiTS17, and BTCV. Our experimental results unequivocally demonstrate that CTO achieves state-of-the-art accuracy on these datasets while maintaining competitive model complexity. The codes have been released at: https://github.com/xiaofang007/CTO.
医学图像分割是医学图像分析和计算机视觉领域中的一项关键任务。虽然当前方法在准确分割主要感兴趣区域方面显示出潜力,但边界区域的精确分割仍然具有挑战性。本研究提出了一种名为CTO的新型网络架构,它结合了卷积神经网络(CNN)、视觉转换器(ViT)模型和明确的边缘检测算子,以应对这一挑战。CTO在分割精度上超越了现有方法,并在精度和效率之间达到了更好的平衡,无需额外的数据输入或标签注入。具体来说,CTO遵循典型的编码器-解码器网络范式,具有双流编码器网络,包括用于捕获局部特征的主流CNN流和用于集成远程依赖的辅助StitchViT流。此外,为了提高模型学习边界区域的能力,我们引入了一个边界引导解码器网络,该网络使用由专用边缘检测算子生成的二进制边界掩膜在解码过程中提供明确指导。我们在七个具有挑战性的医学图像分割数据集上进行了广泛实验,验证了CTO的性能,这些数据集分别是ISIC 2016、PH2、ISIC 2018、CoNIC、LiTS17和BTCV。我们的实验结果明确证明,CTO在这些数据集上实现了最先进的准确性,同时保持了竞争性的模型复杂度。代码已发布在:[https://github.com/xiaofang007/CTO。]
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by Medical Image Analysis
Summary
本文提出了一种新型网络架构CTO,融合了卷积神经网络(CNN)、视觉转换器(ViT)模型和边缘检测算子,以应对医疗图像分割中边界区域精确分割的挑战。CTO在分割精度上超越了现有方法,并在精度和效率之间达到了更好的平衡,无需额外的数据输入或标签注入。
Key Takeaways
- 医疗图像分割是医学图像分析和计算机视觉中的关键任务。
- 现有方法在精确分割边界区域时面临挑战。
- 本研究提出了一种新型网络架构CTO,结合了CNN、ViT模型和边缘检测算子来应对这一挑战。
- CTO超越了现有方法的分割精度,并在精度和效率之间取得了平衡。
- CTO采用典型的编码器-解码器网络范式,具有双流编码器网络,包括主流CNN流和辅助StitchViT流。
- 为提高模型对边界区域的学习能力,引入了边界引导解码器网络,采用专用边缘检测算子生成的二进制边界掩膜为解码过程提供明确指导。
点此查看论文截图


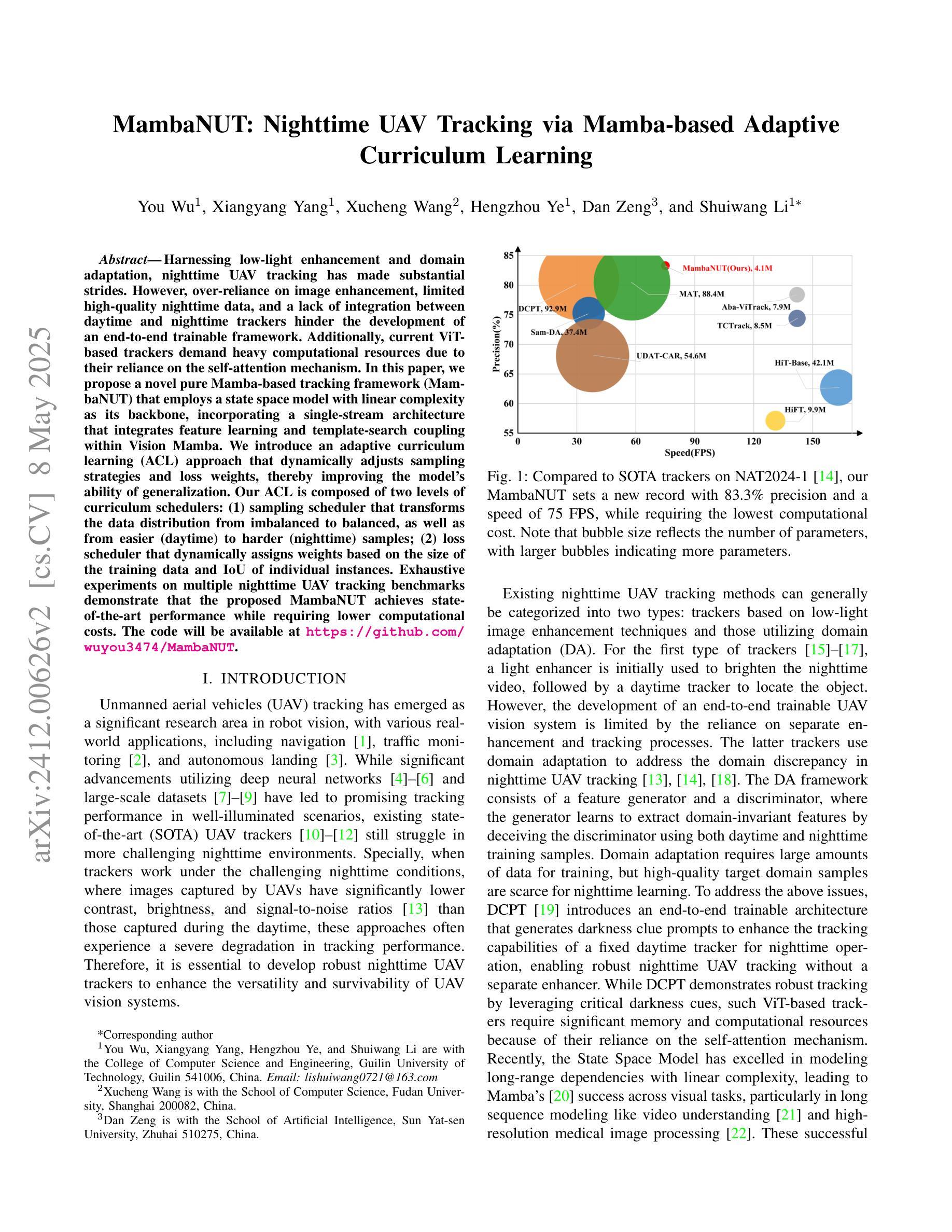
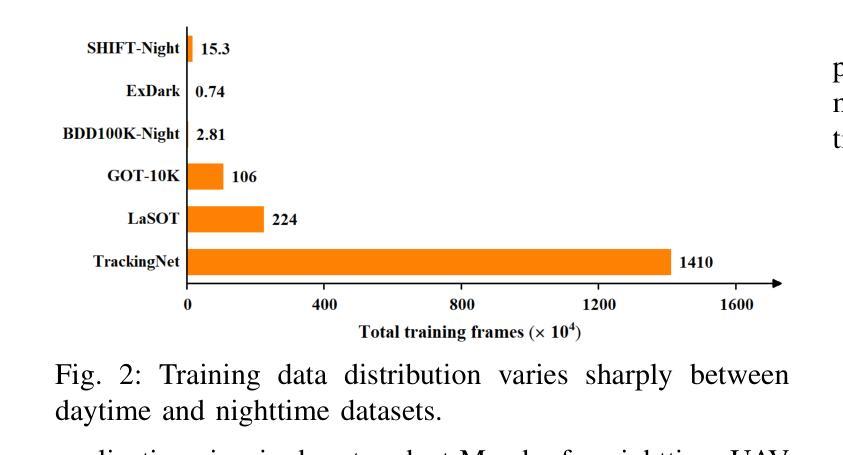
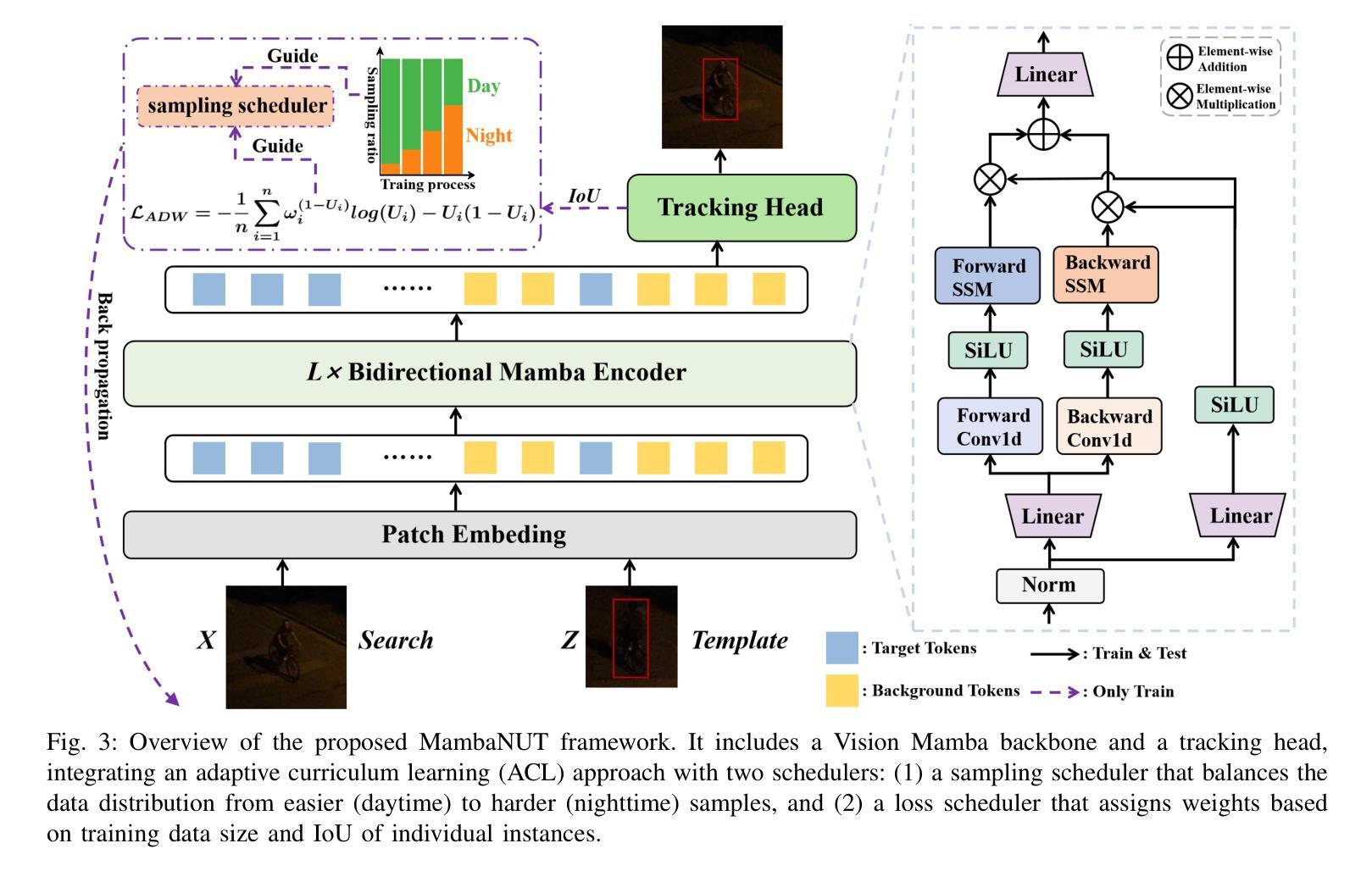
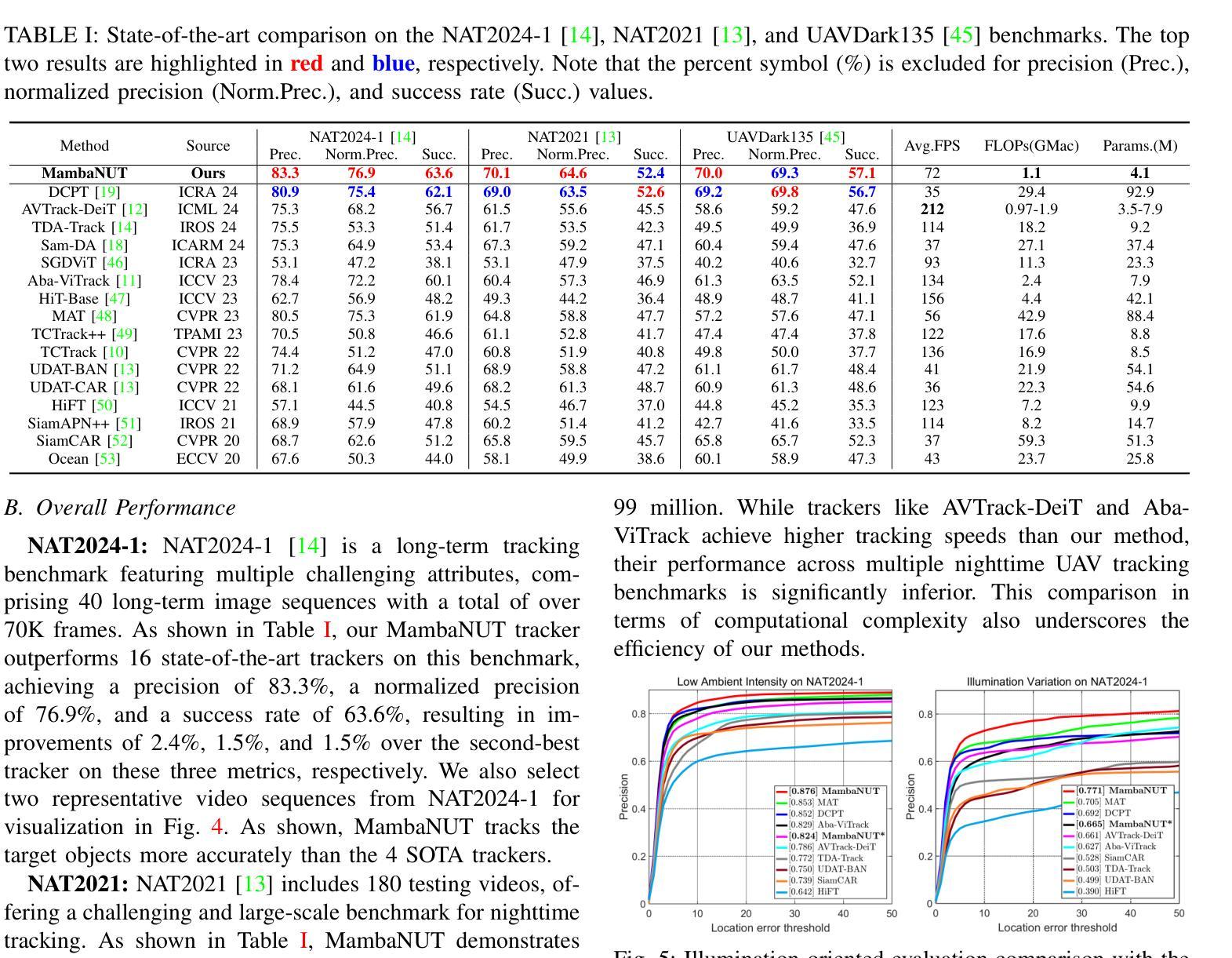
MambaNUT: Nighttime UAV Tracking via Mamba-based Adaptive Curriculum Learning
Authors:You Wu, Xiangyang Yang, Xucheng Wang, Hengzhou Ye, Dan Zeng, Shuiwang Li
Harnessing low-light enhancement and domain adaptation, nighttime UAV tracking has made substantial strides. However, over-reliance on image enhancement, limited high-quality nighttime data, and a lack of integration between daytime and nighttime trackers hinder the development of an end-to-end trainable framework. Additionally, current ViT-based trackers demand heavy computational resources due to their reliance on the self-attention mechanism. In this paper, we propose a novel pure Mamba-based tracking framework (MambaNUT) that employs a state space model with linear complexity as its backbone, incorporating a single-stream architecture that integrates feature learning and template-search coupling within Vision Mamba. We introduce an adaptive curriculum learning (ACL) approach that dynamically adjusts sampling strategies and loss weights, thereby improving the model’s ability of generalization. Our ACL is composed of two levels of curriculum schedulers: (1) sampling scheduler that transforms the data distribution from imbalanced to balanced, as well as from easier (daytime) to harder (nighttime) samples; (2) loss scheduler that dynamically assigns weights based on the size of the training data and IoU of individual instances. Exhaustive experiments on multiple nighttime UAV tracking benchmarks demonstrate that the proposed MambaNUT achieves state-of-the-art performance while requiring lower computational costs. The code will be available at https://github.com/wuyou3474/MambaNUT.
利用低光增强和领域自适应技术,夜间无人机跟踪已经取得了重大进展。然而,对图像增强的过度依赖、高质量夜间数据的有限性以及日间和夜间跟踪器之间缺乏整合,阻碍了端到端可训练框架的发展。此外,当前的基于ViT的跟踪器由于依赖于自注意力机制,需要大量的计算资源。在本文中,我们提出了一种基于纯Mamba的跟踪框架(MambaNUT),它采用具有线性复杂度的状态空间模型作为骨干,并采用了单流架构,该架构在Vision Mamba内集成了特征学习和模板搜索耦合。我们引入了一种自适应课程学习(ACL)方法,该方法可以动态调整采样策略和损失权重,从而提高模型的泛化能力。我们的ACL由两级课程调度器组成:(1)采样调度器,它改变数据分布,从不平衡到平衡,从简单的(日间)样本到复杂的(夜间)样本;(2)损失调度器,它根据训练数据的大小和各个实例的IoU动态分配权重。在多个夜间无人机跟踪基准测试上的大量实验表明,所提出的MambaNUT达到了最先进的性能,同时计算成本较低。代码将在https://github.com/wuyou3474/MambaNUT上提供。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文提出一种基于Mamba的纯跟踪框架(MambaNUT),采用线性复杂度的状态空间模型作为骨干。该框架结合了特征学习与模板搜索耦合的单流架构,并引入了自适应课程学习方法(ACL)以动态调整采样策略和损失权重,从而提高模型的泛化能力。实验证明,MambaNUT在夜间无人机跟踪方面达到了最新技术水平,并降低了计算成本。
Key Takeaways
- 夜间无人机跟踪领域取得了显著进展,但仍面临图像增强过度依赖、高质量夜间数据有限以及日夜跟踪器融合不足的问题。
- 提出了基于Mamba的纯跟踪框架(MambaNUT),结合特征学习与模板搜索耦合的单流架构。
- MambaNUT采用状态空间模型作为骨干,具有线性复杂度,降低了计算资源的消耗。
- 引入了自适应课程学习方法(ACL),动态调整采样策略和损失权重,提高了模型的泛化能力。
- ACL包含两个层次的课程调度器:采样调度器和损失调度器,分别对数据的分布和损失权重进行动态调整。
- 实验证明,MambaNUT在多个夜间无人机跟踪基准测试中达到了最佳性能。
点此查看论文截图

Evaluating Deep Learning Models for Breast Cancer Classification: A Comparative Study
Authors:Sania Eskandari, Ali Eslamian, Nusrat Munia, Amjad Alqarni, Qiang Cheng
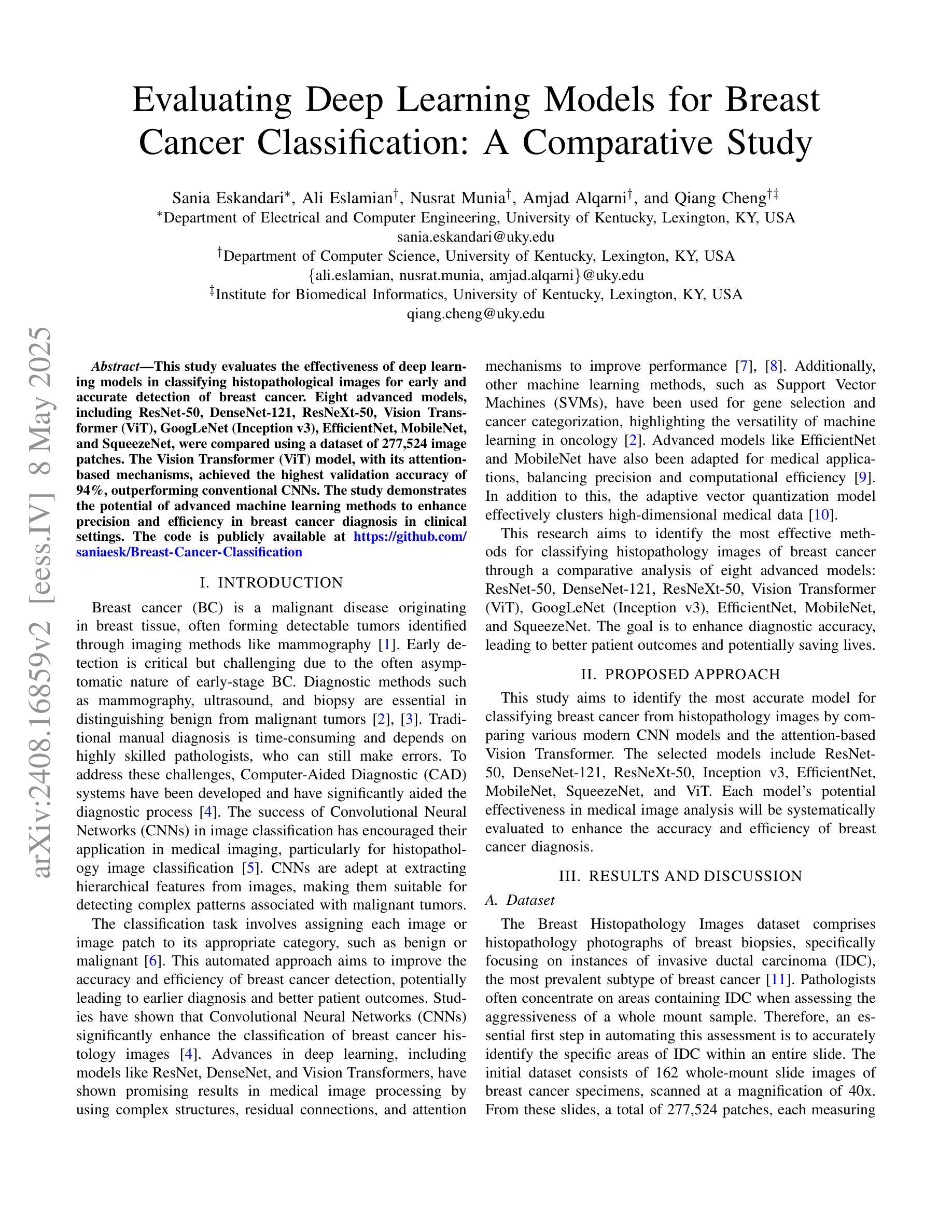
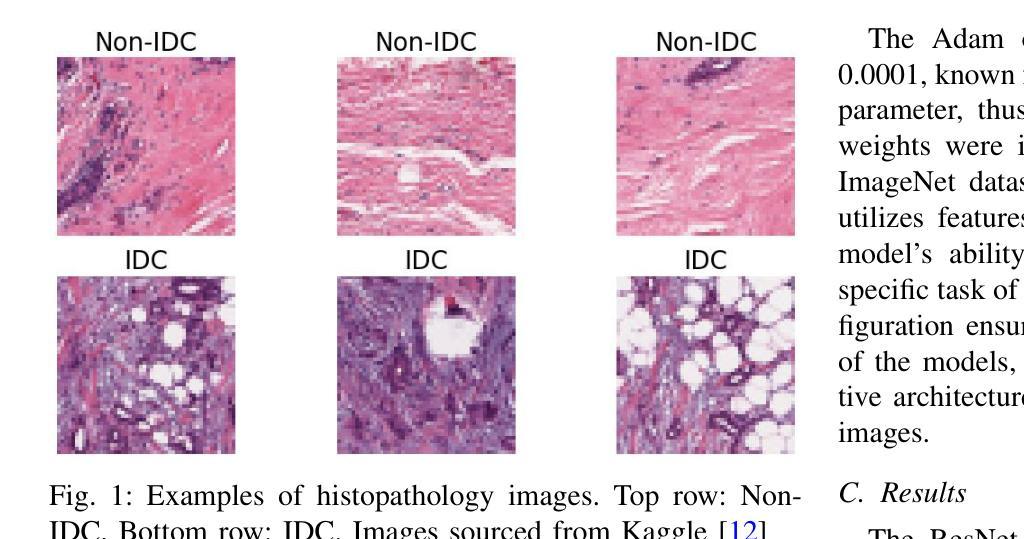
This study evaluates the effectiveness of deep learning models in classifying histopathological images for early and accurate detection of breast cancer. Eight advanced models, including ResNet-50, DenseNet-121, ResNeXt-50, Vision Transformer (ViT), GoogLeNet (Inception v3), EfficientNet, MobileNet, and SqueezeNet, were compared using a dataset of 277,524 image patches. The Vision Transformer (ViT) model, with its attention-based mechanisms, achieved the highest validation accuracy of 94%, outperforming conventional CNNs. The study demonstrates the potential of advanced machine learning methods to enhance precision and efficiency in breast cancer diagnosis in clinical settings.
本研究评估了深度学习模型在分类病理图像以早期和准确检测乳腺癌方面的有效性。使用包含277524个图像块的数据集,对比了ResNet-50、DenseNet-121、ResNeXt-50、Vision Transformer(ViT)、GoogLeNet(Inception v3)、EfficientNet、MobileNet和SqueezeNet等八种先进模型。其中,采用注意力机制的Vision Transformer(ViT)模型取得了最高的验证准确率,达到了94%,并优于传统的卷积神经网络(CNNs)。该研究证明了先进的机器学习方法在提高乳腺癌诊断的准确性和效率方面的潜力。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 4 pages, 2 figures, 2 tables
Summary
本研究评估了深度学习模型在分类病理图像以进行乳腺癌早期准确检测方面的有效性。研究比较了ResNet-50、DenseNet-121等八种先进模型,使用包含277,524个图像补丁的数据集进行测试。其中,Vision Transformer(ViT)模型凭借注意力机制实现了最高验证准确率94%,超过了传统CNN。此研究展示了先进机器学习方法在增强乳腺癌诊断精度和效率方面的潜力。
Key Takeaways
- 本研究使用深度学习模型进行病理图像分类,旨在早期准确检测乳腺癌。
- 评估了八种先进模型(ResNet-50等),通过对比验证模型效果。
- Vision Transformer(ViT)模型因具备注意力机制,取得了最高的验证准确率94%。
- Vision Transformer模型的性能优于传统的卷积神经网络(CNN)。
- 该研究为临床环境中的乳腺癌诊断提供了更为精确和高效的机器学习方法的潜力证据。
- 数据集包含大量的图像补丁(277,524个),有助于模型的训练和验证。
点此查看论文截图