⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-05-11 更新
Communicating Activations Between Language Model Agents
Authors:Vignav Ramesh, Kenneth Li
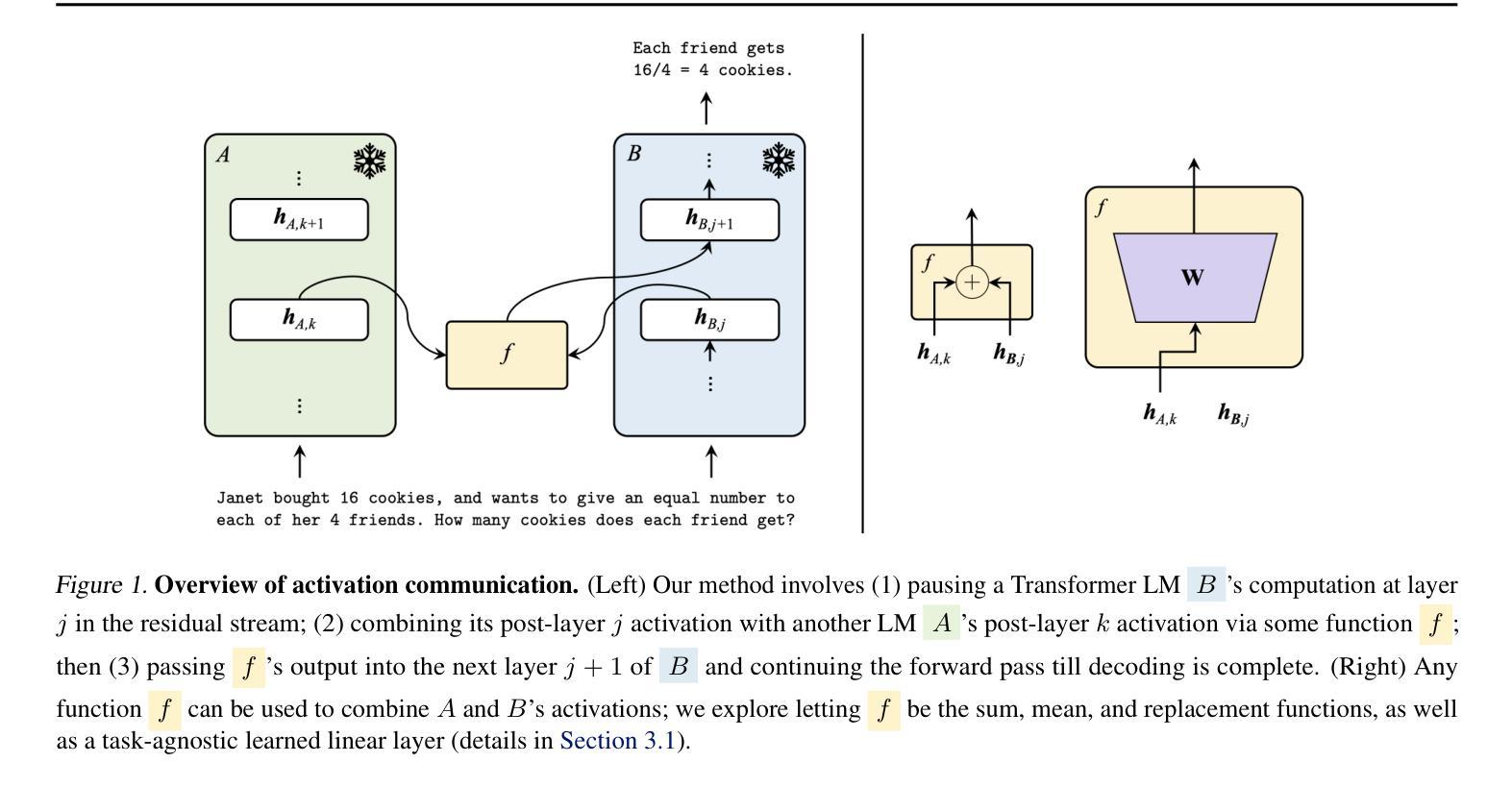
Communication between multiple language model (LM) agents has been shown to scale up the reasoning ability of LMs. While natural language has been the dominant medium for inter-LM communication, it is not obvious this should be the standard: not only does natural language communication incur high inference costs that scale quickly with the number of both agents and messages, but also the decoding process abstracts away too much rich information that could be otherwise accessed from the internal activations. In this work, we propose a simple technique whereby LMs communicate via activations; concretely, we pause an LM $\textit{B}$’s computation at an intermediate layer, combine its current activation with another LM $\textit{A}$’s intermediate activation via some function $\textit{f}$, then pass $\textit{f}$’s output into the next layer of $\textit{B}$ and continue the forward pass till decoding is complete. This approach scales up LMs on new tasks with zero additional parameters and data, and saves a substantial amount of compute over natural language communication. We test our method with various functional forms $\textit{f}$ on two experimental setups–multi-player coordination games and reasoning benchmarks–and find that it achieves up to $27.0%$ improvement over natural language communication across datasets with $<$$1/4$ the compute, illustrating the superiority and robustness of activations as an alternative “language” for communication between LMs.
多语言模型(LM)代理之间的通信已经证明可以扩展LM的推理能力。虽然自然语言一直是LM间通信的主要媒介,但显然这并不应该是标准方式:自然语言通信不仅会产生与代理数量和消息数量迅速增长的高推理成本,而且解码过程会抽象掉许多可以从内部激活中获得的其他丰富信息。在这项工作中,我们提出了一种简单的技术,即LM通过激活进行通信;具体地说,我们在LM B的中间层暂停计算,通过某个函数f将其当前激活与另一个LM A的中间激活相结合,然后将f的输出传递给B的下一层,并继续向前传递直至解码完成。这种方法在新的任务上扩展了LM,无需添加任何参数和数据,与基于自然语言通信相比,可以节省大量的计算量。我们在两种实验设置——多人协作游戏和推理基准测试上,使用各种形式的函数f进行测试,发现与基于自然语言通信相比,在不同的数据集上,我们的方法可以实现高达27.0%的改进,并且计算量不到四分之一,这表明激活作为一种替代的“语言”在LM之间进行通信具有优越性和稳健性。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF ICML 2025
Summary
在多项语言模型(LM)代理之间的通信中,通过激活进行通信的方法被提出。该方法通过暂停LM B的中间层计算,通过某种函数f将其当前激活与LM A的中间激活相结合,然后将f的输出传递给B的下一层并继续前向传递直至解码完成。这种方法无需添加额外的参数和数据即可扩展LMs的新任务,与基于自然语言通信相比,可以节省大量的计算量。实验表明,该方法在多人协调游戏和推理基准测试中实现了高达27.0%的改进,且使用激活作为LM之间通信的替代语言具有优越性和稳健性。
Key Takeaways
- 语言模型(LM)之间的通信可以通过激活来进行,这是一种新的方法。
- 通过暂停LM的中间层计算,将两个LM的激活结合,再继续前向传递至解码完成。
- 此方法无需添加新的参数和数据即可扩展LMs的新任务。
- 与自然语言通信相比,该方法可以节省大量计算量。
- 实验表明,该方法在多人协调游戏和推理基准测试中表现优越。
- 通过激活进行通信的方法具有稳健性。
点此查看论文截图