⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-05-14 更新
Anatomical Attention Alignment representation for Radiology Report Generation
Authors:Quang Vinh Nguyen, Minh Duc Nguyen, Thanh Hoang Son Vo, Hyung-Jeong Yang, Soo-Hyung Kim
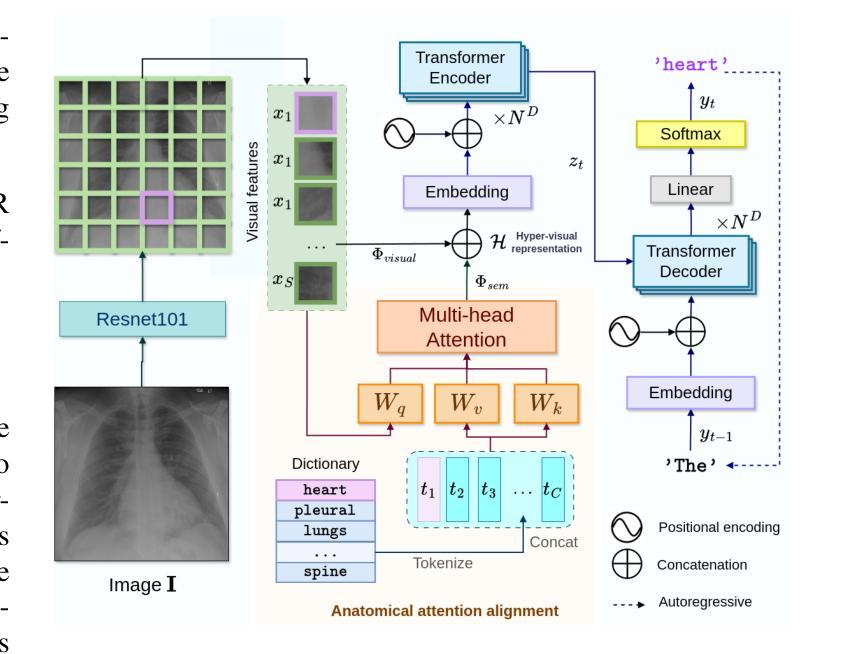
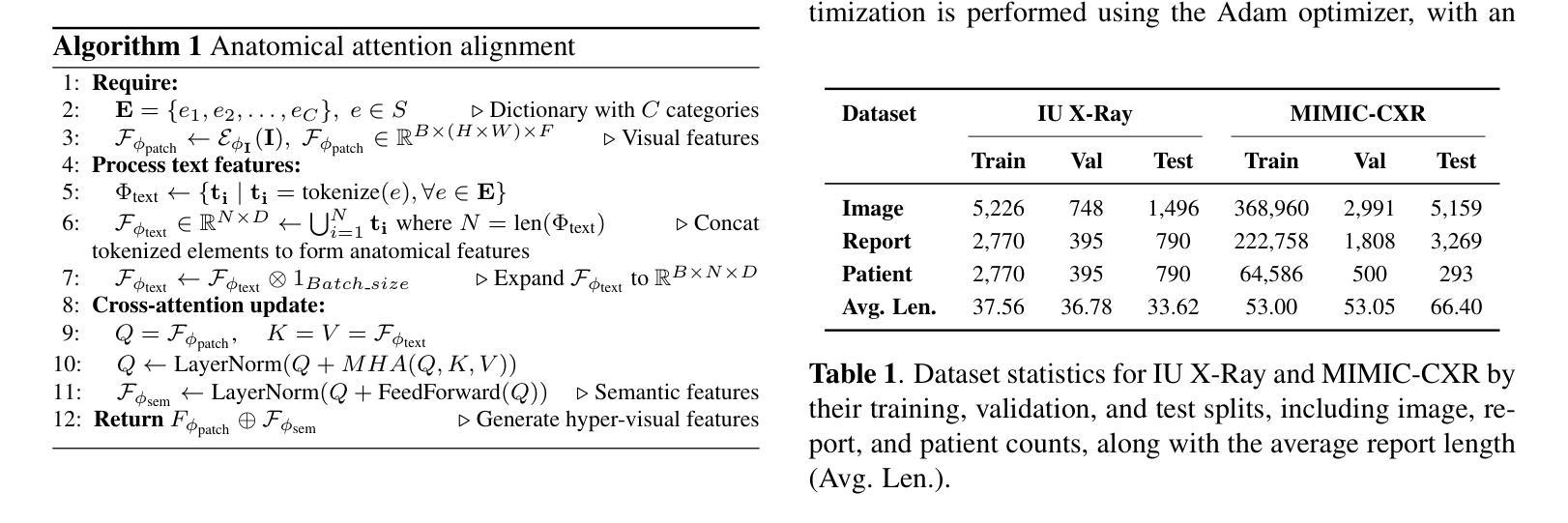
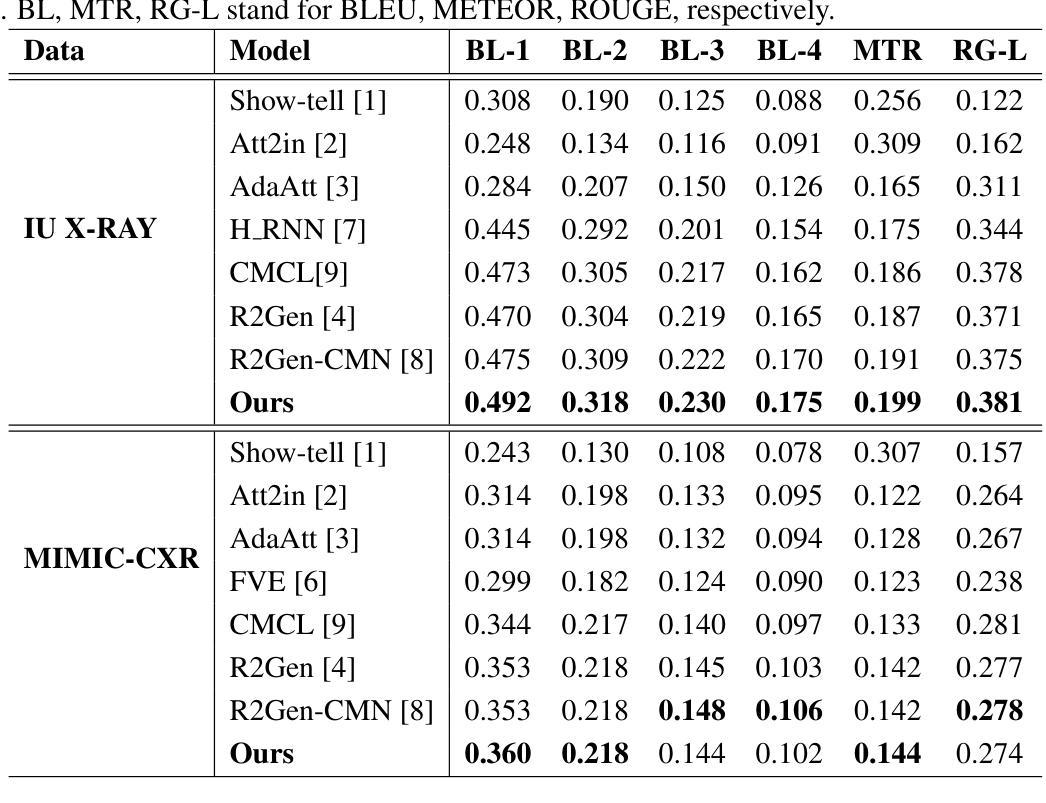
Automated Radiology report generation (RRG) aims at producing detailed descriptions of medical images, reducing radiologists’ workload and improving access to high-quality diagnostic services. Existing encoder-decoder models only rely on visual features extracted from raw input images, which can limit the understanding of spatial structures and semantic relationships, often resulting in suboptimal text generation. To address this, we propose Anatomical Attention Alignment Network (A3Net), a framework that enhance visual-textual understanding by constructing hyper-visual representations. Our approach integrates a knowledge dictionary of anatomical structures with patch-level visual features, enabling the model to effectively associate image regions with their corresponding anatomical entities. This structured representation improves semantic reasoning, interpretability, and cross-modal alignment, ultimately enhancing the accuracy and clinical relevance of generated reports. Experimental results on IU X-Ray and MIMIC-CXR datasets demonstrate that A3Net significantly improves both visual perception and text generation quality. Our code is available at \href{https://github.com/Vinh-AI/A3Net}{GitHub}.
自动放射学报告生成(RRG)旨在生成医学图像的详细描述,减轻放射科医生的工作量,改善高质量诊断服务的获取途径。现有的编码器-解码器模型仅依赖于从原始输入图像中提取的视觉特征,这可能会限制对空间结构和语义关系的理解,通常导致文本生成效果不佳。为了解决这一问题,我们提出了“解剖注意力对齐网络(A3Net)”,这是一个通过构建超视觉表征增强视觉文本理解的框架。我们的方法整合了解剖结构的知识词典和补丁级别的视觉特征,使模型能够有效地将图像区域与相应的解剖实体相关联。这种结构化表示提高了语义推理、解释性和跨模态对齐,最终提高了生成报告准确性和临床相关性。在IU X光片和MIMIC-CXR数据集上的实验结果表明,A3Net显著提高了视觉感知和文本生成质量。我们的代码可在GitHub上获得:https://github.com/Vinh-AI/A3Net。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
医学图像报告自动生成(RRG)旨在减轻放射科医生的工作量并改善高质量诊断服务的获取。现有模型主要依赖从原始图像中提取的视觉特征,这限制了空间结构和语义关系的理解,导致文本生成效果常不理想。为解决这一问题,我们提出了Anatomical Attention Alignment Network(A3Net)框架,通过构建超视觉表征增强视觉与文本的理解。该方法结合了结构知识字典与补丁级别的视觉特征,使模型能够有效地将图像区域与相应的解剖实体相关联。这种结构化表示提高了语义推理、可解释性和跨模态对齐,最终提高了报告生成的准确性和临床相关性。在IU X光片和MIMIC-CXR数据集上的实验结果表明,A3Net显著提高了视觉感知和文本生成质量。
Key Takeaways
- 医学图像报告自动生成(RRG)有助于减轻放射科医生的工作负担,提高高质量诊断服务的可及性。
- 现有模型主要依赖视觉特征,限制了空间结构和语义关系的理解。
- A3Net框架通过构建超视觉表征增强视觉与文本的理解。
- A3Net结合结构知识字典与补丁级别的视觉特征,提高模型对图像区域与解剖实体的关联能力。
- 结构化表示提高了语义推理、可解释性和跨模态对齐。
- A3Net显著提高了报告生成的准确性和临床相关性。
点此查看论文截图


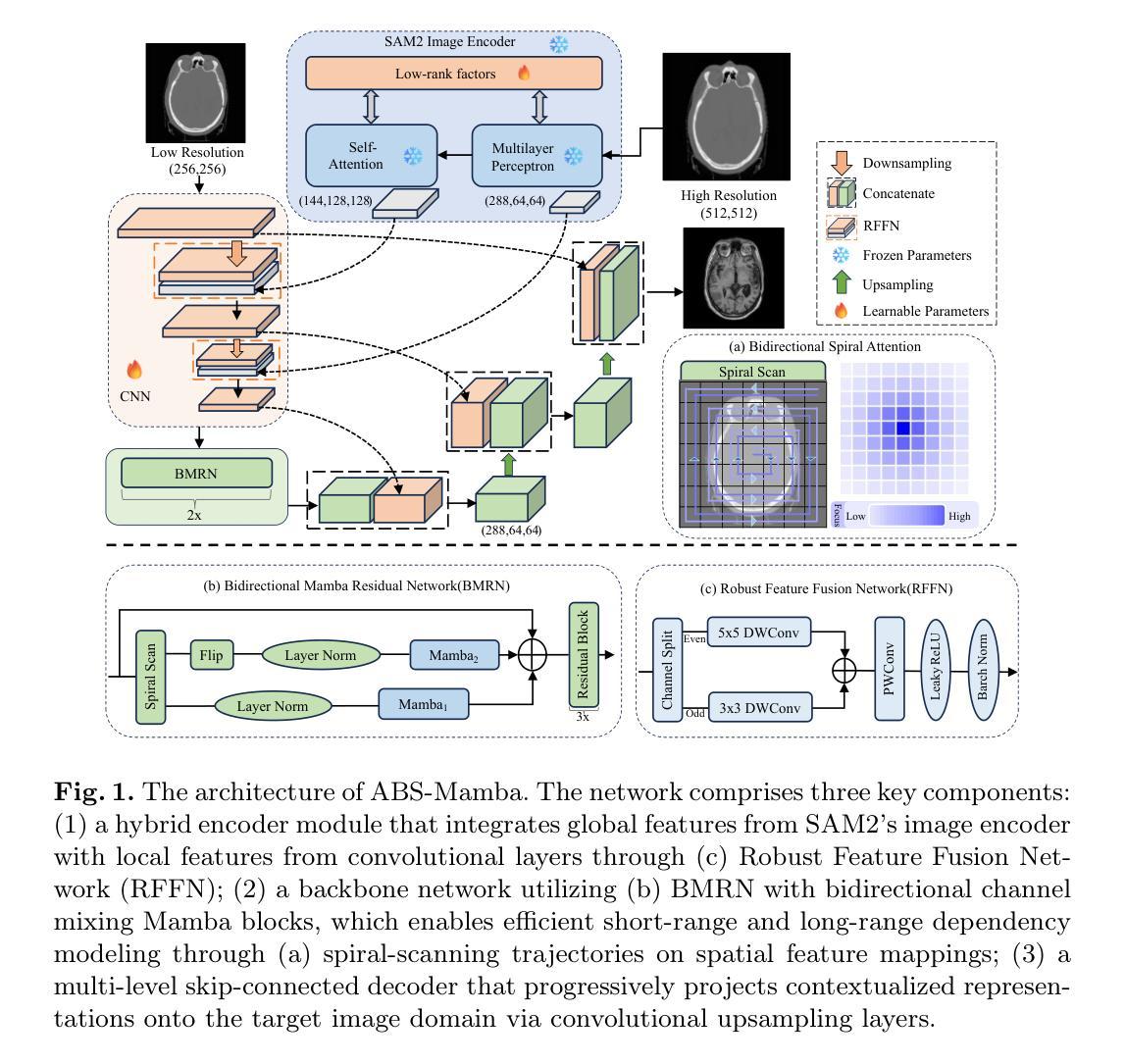
ABS-Mamba: SAM2-Driven Bidirectional Spiral Mamba Network for Medical Image Translation
Authors:Feng Yuan, Yifan Gao, Wenbin Wu, Keqing Wu, Xiaotong Guo, Jie Jiang, Xin Gao
Accurate multi-modal medical image translation requires ha-rmonizing global anatomical semantics and local structural fidelity, a challenge complicated by intermodality information loss and structural distortion. We propose ABS-Mamba, a novel architecture integrating the Segment Anything Model 2 (SAM2) for organ-aware semantic representation, specialized convolutional neural networks (CNNs) for preserving modality-specific edge and texture details, and Mamba’s selective state-space modeling for efficient long- and short-range feature dependencies. Structurally, our dual-resolution framework leverages SAM2’s image encoder to capture organ-scale semantics from high-resolution inputs, while a parallel CNNs branch extracts fine-grained local features. The Robust Feature Fusion Network (RFFN) integrates these epresentations, and the Bidirectional Mamba Residual Network (BMRN) models spatial dependencies using spiral scanning and bidirectional state-space dynamics. A three-stage skip fusion decoder enhances edge and texture fidelity. We employ Efficient Low-Rank Adaptation (LoRA+) fine-tuning to enable precise domain specialization while maintaining the foundational capabilities of the pre-trained components. Extensive experimental validation on the SynthRAD2023 and BraTS2019 datasets demonstrates that ABS-Mamba outperforms state-of-the-art methods, delivering high-fidelity cross-modal synthesis that preserves anatomical semantics and structural details to enhance diagnostic accuracy in clinical applications. The code is available at https://github.com/gatina-yone/ABS-Mamba
准确的多模态医学图像翻译需要协调全局解剖语义和局部结构忠实性,这一挑战因模态间信息丢失和结构失真而复杂化。我们提出了ABS-Mamba,这是一种新型架构,它集成了Segment Anything Model 2(SAM2)用于器官感知语义表示,专门设计的卷积神经网络(CNN)用于保留模态特定的边缘和纹理细节,以及Mamba的选择状态空间建模,以实现高效的长短程特征依赖性。结构上,我们的双分辨率框架利用SAM2的图像编码器从高分辨率输入中捕获器官级语义,而并行CNN分支则提取精细的局部特征。鲁棒特征融合网络(RFFN)集成了这些表示,双向Mamba残差网络(BMRN)使用螺旋扫描和双向状态空间动力学对空间依赖性进行建模。三阶段跳过融合解码器增强了边缘和纹理的忠实性。我们采用有效的低秩适应(LoRA+)微调方法,在保持预训练组件基础能力的同时,实现精确的领域专业化。在SynthRAD2023和BraTS2019数据集上的广泛实验验证表明,ABS-Mamba优于最先进的方法,实现了高保真跨模态合成,保留了解剖语义和结构细节,提高了临床应用中诊断的准确性。代码可在https://github.com/gatina-yone/ABS-Mamba找到。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF MICCAI 2025(under view)
Summary
本文提出一种新型医学图像翻译架构ABS-Mamba,该架构融合了Segment Anything Model 2(SAM2)进行器官感知语义表示,专业卷积神经网络(CNNs)保留模态特定的边缘和纹理细节,以及Mamba的选择状态空间建模,以高效实现长短程特征依赖。其双分辨率框架捕捉器官规模语义和高分辨率输入,同时并行CNN分支提取精细局部特征。通过Robust Feature Fusion Network(RFFN)整合这些表示,并通过Bidirectional Mamba Residual Network(BMRN)进行空间依赖性建模。经过在SynthRAD2023和BraTS2019数据集上的广泛实验验证,ABS-Mamba表现出优异性能,实现了高保真跨模态合成,保留解剖学语义和结构细节,提高临床诊断准确性。
Key Takeaways
- ABS-Mamba架构融合了SAM2进行器官感知语义表示,以捕捉全局解剖学语义。
- CNNs用于保留模态特定的边缘和纹理细节,以维持局部结构完整性。
- Mamba的选择状态空间建模实现高效长短程特征依赖。
- 双分辨率框架同时捕捉器官规模语义和高分辨率信息。
- RFFN整合不同特征表示,BMRN进行空间依赖性建模以提高性能。
- 通过Efficient Low-Rank Adaptation(LoRA+)精细调整,实现精确域专业化,同时保持预训练组件的基础能力。
点此查看论文截图

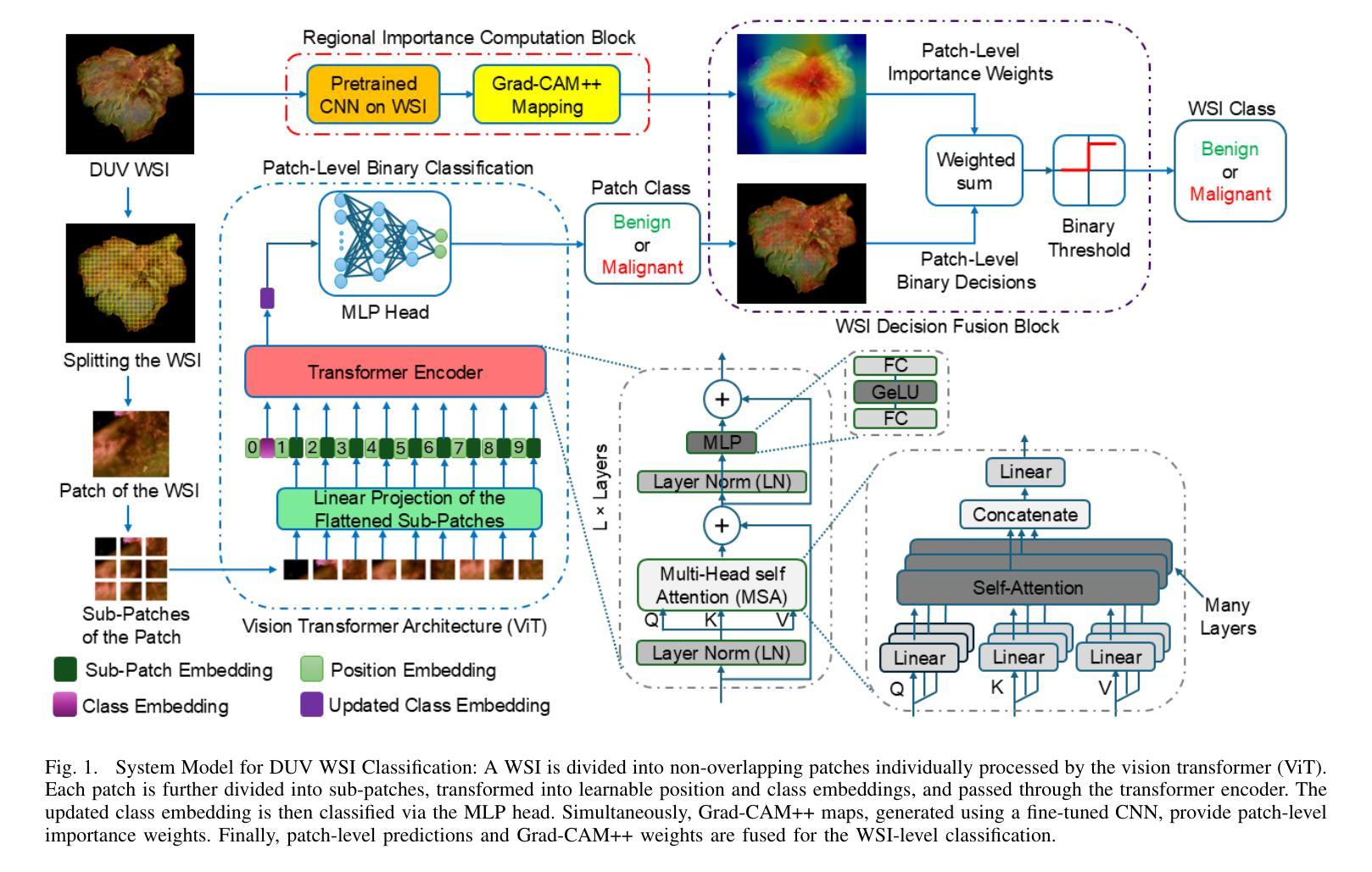
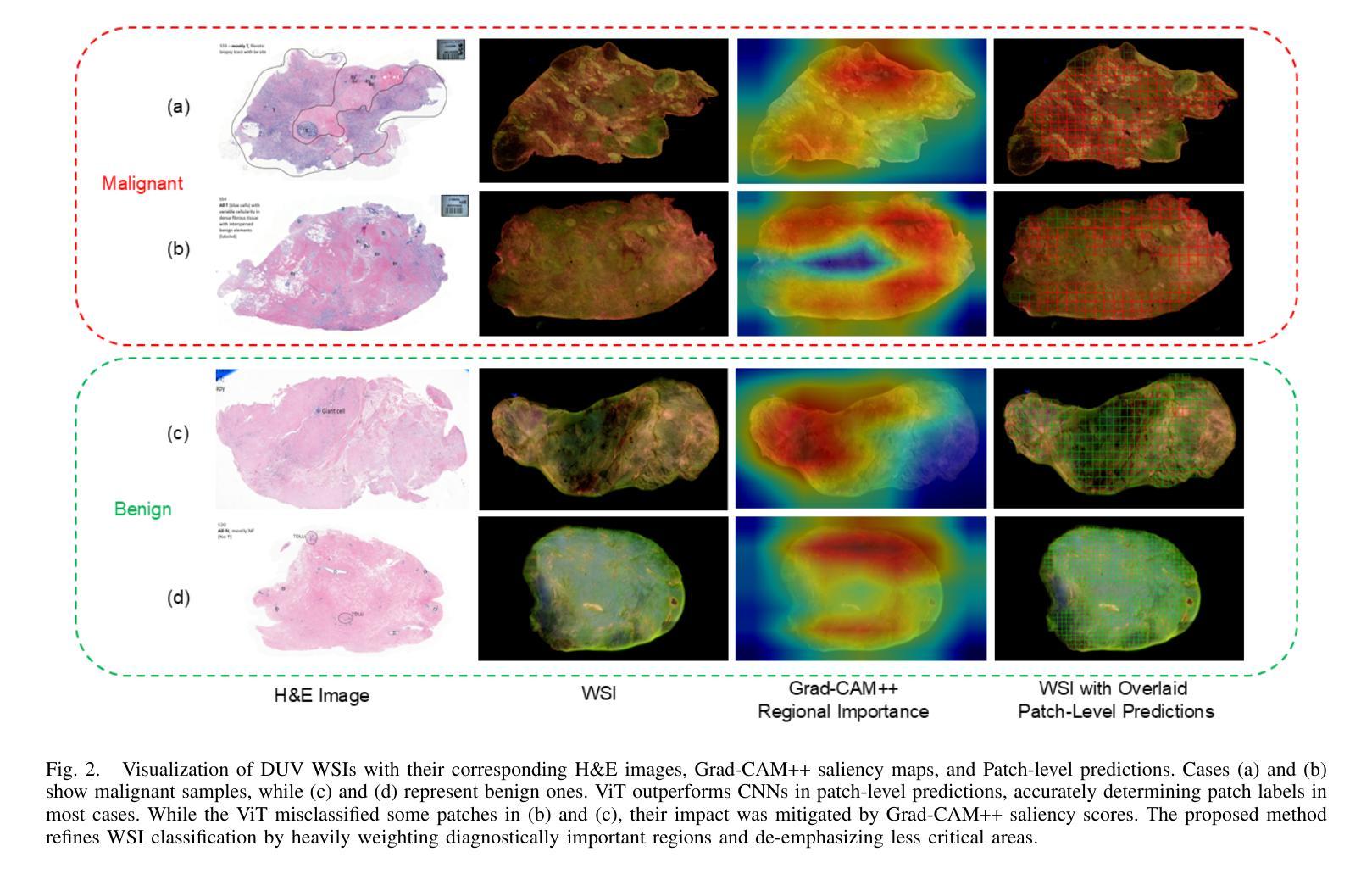
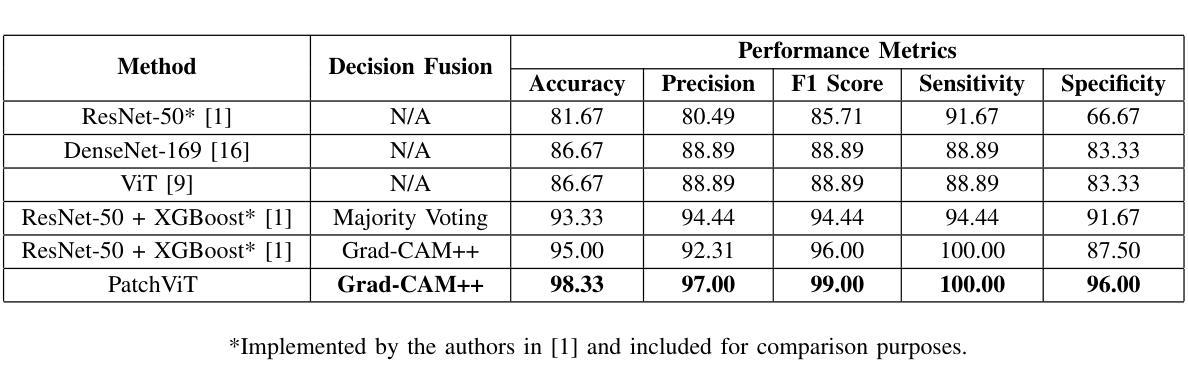
Breast Cancer Classification in Deep Ultraviolet Fluorescence Images Using a Patch-Level Vision Transformer Framework
Authors:Pouya Afshin, David Helminiak, Tongtong Lu, Tina Yen, Julie M. Jorns, Mollie Patton, Bing Yu, Dong Hye Ye
Breast-conserving surgery (BCS) aims to completely remove malignant lesions while maximizing healthy tissue preservation. Intraoperative margin assessment is essential to achieve a balance between thorough cancer resection and tissue conservation. A deep ultraviolet fluorescence scanning microscope (DUV-FSM) enables rapid acquisition of whole surface images (WSIs) for excised tissue, providing contrast between malignant and normal tissues. However, breast cancer classification with DUV WSIs is challenged by high resolutions and complex histopathological features. This study introduces a DUV WSI classification framework using a patch-level vision transformer (ViT) model, capturing local and global features. Grad-CAM++ saliency weighting highlights relevant spatial regions, enhances result interpretability, and improves diagnostic accuracy for benign and malignant tissue classification. A comprehensive 5-fold cross-validation demonstrates the proposed approach significantly outperforms conventional deep learning methods, achieving a classification accuracy of 98.33%.
保留乳房手术(BCS)旨在彻底清除恶性病变,同时最大限度地保留健康组织。术中边缘评估对于在彻底切除癌症与保留组织之间取得平衡至关重要。深紫外线荧光扫描显微镜(DUV-FSM)可以快速获取已切除组织的全表面图像(WSI),为恶性组织和正常组织提供对比。然而,使用DUV WSI进行乳腺癌分类面临着高分辨率和复杂组织病理特征的挑战。本研究引入了一种基于补丁级视觉转换器(ViT)模型的DUV WSI分类框架,能够捕捉局部和全局特征。Grad-CAM++显著性加权能够突出相关的空间区域,提高结果的可解释性,并增强对良性和恶性组织分类的诊断准确性。经过全面的五折交叉验证,结果表明该方法明显优于传统的深度学习方法,达到了98.33%的分类准确率。
论文及项目相关链接
摘要
本文介绍了采用深紫外线荧光扫描显微镜(DUV-FSM)对乳腺癌切除组织进行术中边缘评估的方法。通过获取全表面图像(WSI),该方法能够迅速识别恶性与正常组织之间的对比。研究引入了一种基于patch级视觉转换器(ViT)模型的DUV WSI分类框架,能够捕捉局部和全局特征。Grad-CAM++显著性加权技术突出了关键的空间区域,提高了分类结果的解释性和诊断准确性。经过综合的5倍交叉验证,该方法显著优于传统的深度学习方法,实现了高达98.33%的分类准确率。
关键见解
- 乳腺癌手术中,完全切除恶性病灶并尽可能保留健康组织是关键。
- 深紫外线荧光扫描显微镜(DUV-FSM)能快速获取切除组织的全表面图像(WSI)。
- 通过对比恶性与正常组织,有助于进行术中边缘评估。
- 采用基于patch级视觉转换器(ViT)模型的DUV WSI分类框架能够捕捉局部和全局特征。
- Grad-CAM++技术能够突出关键的空间区域,提高诊断的准确性。
- 与传统深度学习模型相比,新方法在分类准确率上表现出显著优势。
点此查看论文截图

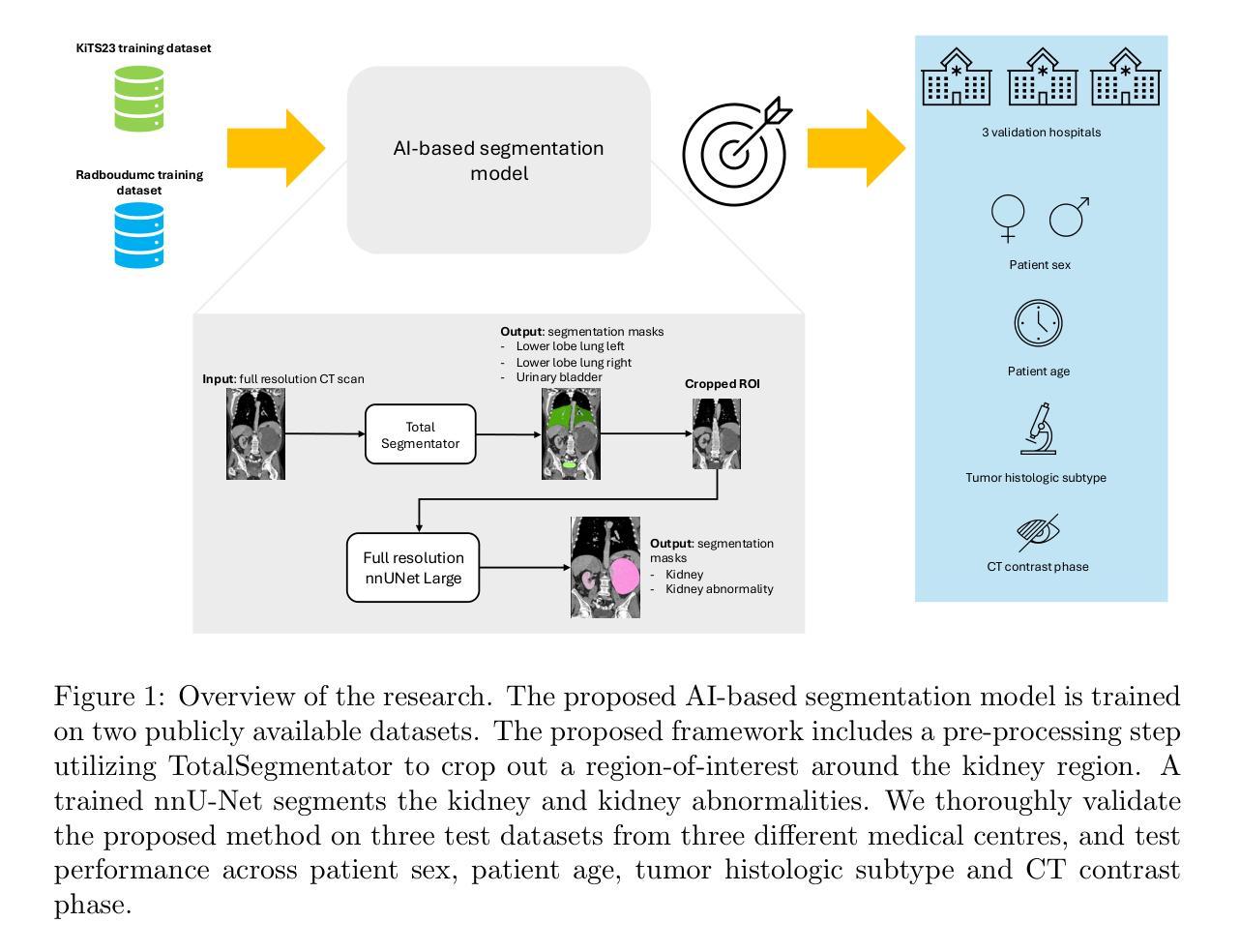
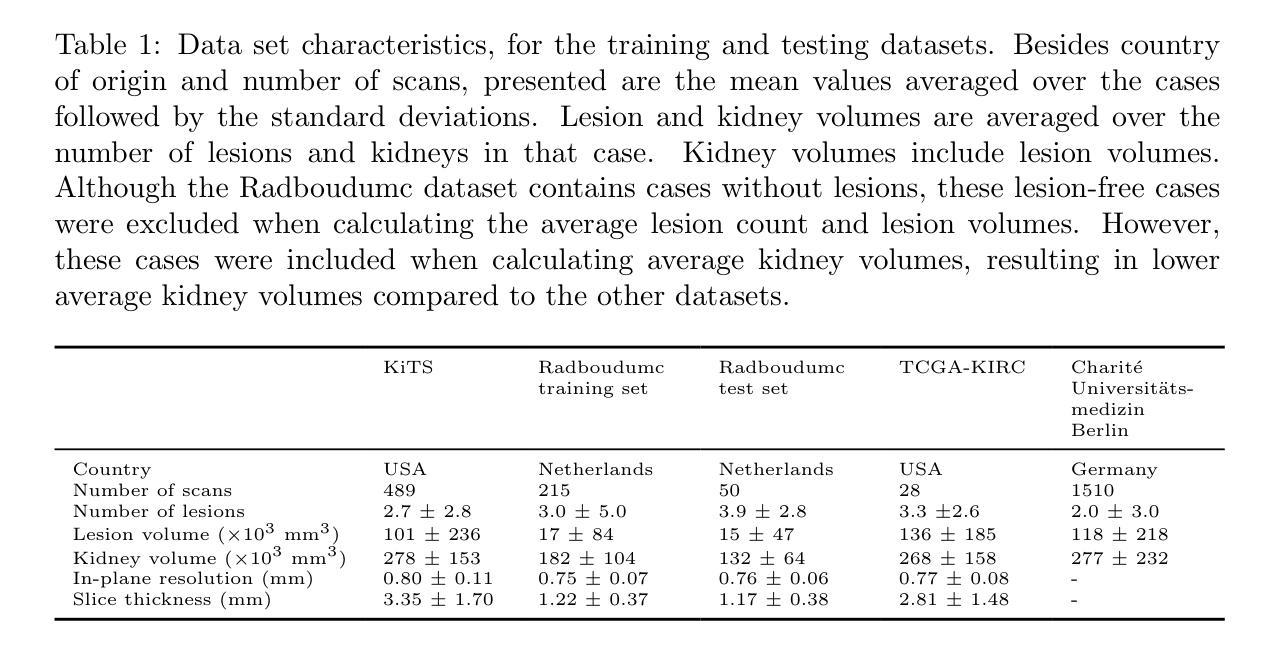
Robust Kidney Abnormality Segmentation: A Validation Study of an AI-Based Framework
Authors:Sarah de Boer, Hartmut Häntze, Kiran Vaidhya Venkadesh, Myrthe A. D. Buser, Gabriel E. Humpire Mamani, Lina Xu, Lisa C. Adams, Jawed Nawabi, Keno K. Bressem, Bram van Ginneken, Mathias Prokop, Alessa Hering
Kidney abnormality segmentation has important potential to enhance the clinical workflow, especially in settings requiring quantitative assessments. Kidney volume could serve as an important biomarker for renal diseases, with changes in volume correlating directly with kidney function. Currently, clinical practice often relies on subjective visual assessment for evaluating kidney size and abnormalities, including tumors and cysts, which are typically staged based on diameter, volume, and anatomical location. To support a more objective and reproducible approach, this research aims to develop a robust, thoroughly validated kidney abnormality segmentation algorithm, made publicly available for clinical and research use. We employ publicly available training datasets and leverage the state-of-the-art medical image segmentation framework nnU-Net. Validation is conducted using both proprietary and public test datasets, with segmentation performance quantified by Dice coefficient and the 95th percentile Hausdorff distance. Furthermore, we analyze robustness across subgroups based on patient sex, age, CT contrast phases, and tumor histologic subtypes. Our findings demonstrate that our segmentation algorithm, trained exclusively on publicly available data, generalizes effectively to external test sets and outperforms existing state-of-the-art models across all tested datasets. Subgroup analyses reveal consistent high performance, indicating strong robustness and reliability. The developed algorithm and associated code are publicly accessible at https://github.com/DIAGNijmegen/oncology-kidney-abnormality-segmentation.
肾脏异常分割在临床工作流程中具有重要潜力,特别是在需要进行定量评估的情况下。肾脏体积可作为肾脏疾病的重要生物标志物,体积的变化直接与肾脏功能相关。目前,临床上通常依赖于主观视觉评估来评估肾脏大小和异常,包括肿瘤和囊肿等,这些通常基于直径、体积和解剖位置进行分期。为了支持更客观和可重复的方法,本研究旨在开发一种稳健且经过充分验证的肾脏异常分割算法,该算法可公开用于临床和研究。我们采用公开可用的训练数据集,并利用最先进的医学图像分割框架nnU-Net。验证使用专有和公共测试数据集进行,通过Dice系数和95th百分位Hausdorff距离量化分割性能。此外,我们分析了基于患者性别、年龄、CT对比阶段和肿瘤组织学亚型的子组稳健性。我们的研究结果表明,仅使用公开数据训练的分割算法有效地推广到外部测试集,并且在所有测试数据集上的表现优于现有最先进的模型。子组分析显示性能一致较高,表明其具有较强的稳健性和可靠性。所开发的算法和相关代码可在https://github.com/DIAGNijmegen/oncology-kidney-abnormality-segmentation上公开访问。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 35 pages, 11 figures
Summary
本文介绍了一种用于肾脏异常分割的算法,该算法可提高临床工作流程效率,尤其在需要定量评估的情境下。肾脏体积作为肾脏疾病的重要生物标志物,其变化可直接反映肾脏功能。研究旨在开发一种稳健且经过充分验证的肾脏异常分割算法,用于临床和研究使用,并公开可用。该研究采用公开的训练数据集和最新的医学图像分割框架nnU-Net,并在专有和公共测试数据集上进行验证,通过Dice系数和95th百分位Hausdorff距离量化分割性能。此外,还分析了算法在不同患者性别、年龄、CT对比阶段和肿瘤组织学亚型下的稳健性。结果表明,该算法在外部测试集上的表现优于现有最先进的模型,且性能稳定可靠。
Key Takeaways
- 肾脏异常分割在临床工作流程中具有重要意义,尤其在需要定量评估的情况下。
- 肾脏体积是反映肾脏功能的重要生物标志物。
- 研究旨在开发一种稳健、经过验证的肾脏异常分割算法,用于临床和研究使用。
- 该研究采用公开的训练数据集和最新的医学图像分割框架nnU-Net。
- 算法在专有和公共测试数据集上进行了验证,表现出优异的性能。
- 算法在不同患者特征(如性别、年龄)和不同的CT对比阶段下具有稳健性。
点此查看论文截图

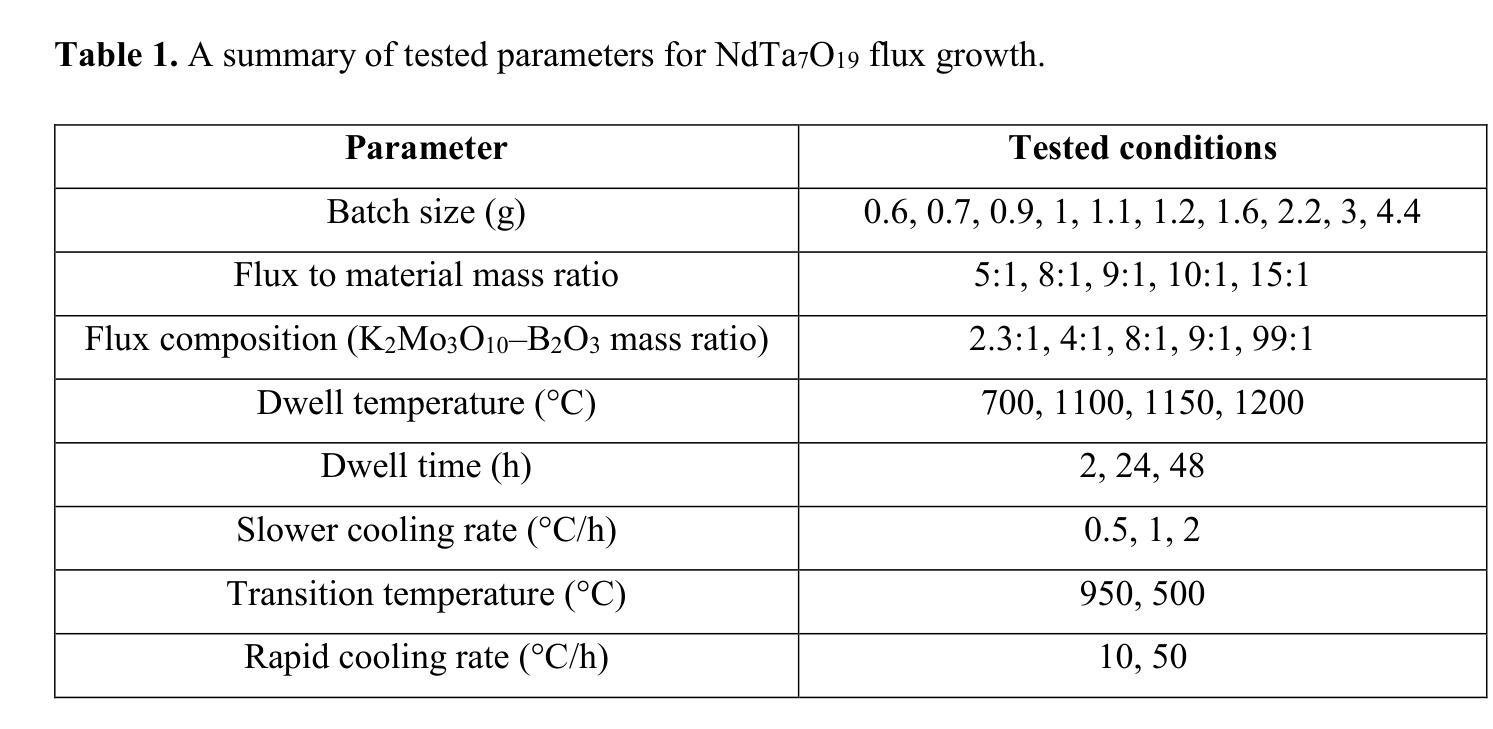
Optimized flux single-crystal growth of the quantum spin liquid candidate NdTa$7$O${19}$ and other rare-earth heptatantalates, ErTa$7$O${19}$ and GdTa$7$O${19}$
Authors:Lia Šibav, Matic Lozinšek, Zvonko Jagličić, Tina Arh, Panchanana Khuntia, Andrej Zorko, Mirela Dragomir
Single crystals are essential for characterizing a wide range of magnetic states, including exotic ones such as quantum spin liquids. This study reports a flux method for growing single crystals of NdTa$7$O${19}$, the first quantum spin liquid candidate on a triangular spin lattice with dominant Ising like spin correlations. Purple NdTa$7$O${19}$ single crystals with hexagonal morphology were successfully grown using a K$_2$Mo$3$O${10}$-B$_2$O$_3$ flux. With lateral sizes up to 3.5 mm and a thickness up to 2 mm, these are the largest dimensions reported to date. The chemical composition was confirmed by powder and single-crystal X-ray diffraction along with scanning electron microscopy with energy dispersive X-ray spectroscopy. Aiming for an accurate determination of the magnetic anisotropy and its effect on the magnetic properties, NdTa$7$O${19}$ crystals were additionally analyzed by magnetic susceptibility, revealing a substantial anisotropy without long-range magnetic ordering down to 2 K. Single crystals of two novel rare-earth heptatantalates, ErTa$7$O${19}$ and GdTa$7$O${19}$, were also grown and their magnetic properties investigated. The magnetic anisotropy of ErTa$7$O${19}$ closely resembles that of isostructural NdTa$7$O${19}$, indicating a possibility of a similar exotic magnetic ground state. In contrast, GdTa$7$O${19}$ shows paramagnetic behavior, consistent with previous results obtained for polycrystalline samples.
单晶对于表征各种磁态,包括量子自旋液体等奇异状态至关重要。本研究报告了一种生长NdTa7O19单晶的通量方法,这是一种在三角自旋晶格上具有主导伊辛型自旋关联的首个量子自旋液体候选材料。使用K2Mo3O10-B2O3通量成功生长了具有六边形形态的紫色NdTa7O19单晶,其横向尺寸达3.5毫米,厚度达2毫米,是目前报道的最大尺寸。通过粉末和单晶X射线衍射以及带有能量色散X射线光谱的扫描电子显微镜确认了其化学成分。为了准确确定磁各向异性及其对磁性的影响,还通过磁化率对NdTa7O19晶体进行了分析,发现其在低至2K时没有长程磁序,表现出显著的各向异性。还生长了两种新型稀土七钽酸盐ErTa7O19和GdTa7O19的单晶,并研究了它们的磁性能。ErTa7O19的磁各向异性与具有同构的NdTa7O19非常相似,表明可能存在类似的奇异磁基态。相反,GdTa7O19表现出顺磁性行为,这与多晶样品的先前结果一致。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 24 pages, 11 figures, supplementary material
摘要
本文报道了一种生长$NdTa_7O_{19}$单晶的通量方法,该物质成为首个在三角自旋晶格上具有主导Ising类自旋关联的量子自旋液体候选材料。成功使用$K_2Mo_3O_{10}-B_2O_3$通量生长出具有六角形态的紫色$NdTa_7O_{19}$单晶,其横向尺寸最大可达3.5毫米,厚度最大为2毫米。通过粉末和单晶X射线衍射以及扫描电子显微镜与能量色散X射线光谱学确认其化学成分。为准确确定磁各向异性及其对磁性能的影响,还通过磁化率分析了$NdTa_7O_{19}$晶体,揭示出显著的磁各向异性以及在2K以下无远程磁序的现象。此外,还生长了两种新型稀土七钽酸盐$ErTa_7O_{19}$和$GdTa_7O_{19}$的单晶,并研究了它们的磁性能。$ErTa_7O_{19}$的磁各向异性类似于同构的$NdTa_7O_{19}$,可能具有类似的奇异磁基态。而$GdTa_7O_{19}$则表现出与多晶样品结果一致的顺磁性行为。
关键见解
- 报道了一种生长$NdTa_7O_{19}$单晶的通量方法,这种材料是首个在三角自旋晶格上的量子自旋液体候选。
- 成功生长出大尺寸的$NdTa_7O_{19}$单晶,最大横向尺寸达3.5毫米,厚度达2毫米。
- 通过多种技术确认了$NdTa_7O_{19}$、$ErTa_7O_{19}$和$GdTa_7O_{19}$的化学成分。
- $NdTa_7O_{19}$显示出显著的磁各向异性及低温下无远程磁序的现象。
- $ErTa_7O_{19}$的磁各向异性类似于$NdTa_7O_{19}$,暗示其可能有类似的特殊磁基态。
- $GdTa_7O_{19}$表现出顺磁性行为,这与之前的多晶样品研究结果一致。
点此查看论文截图

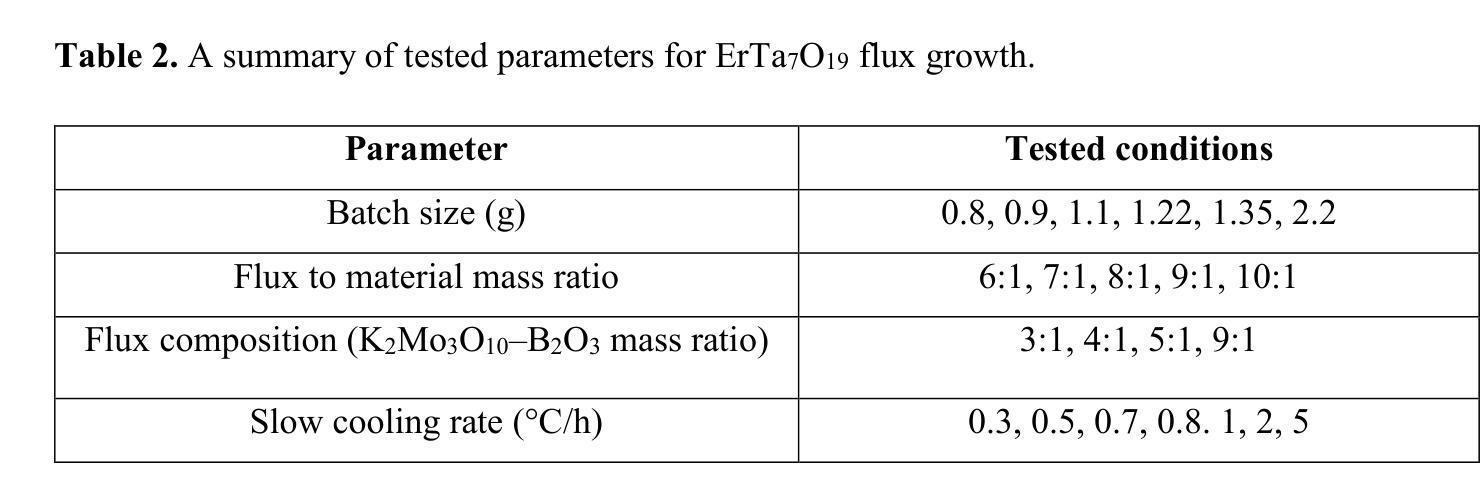
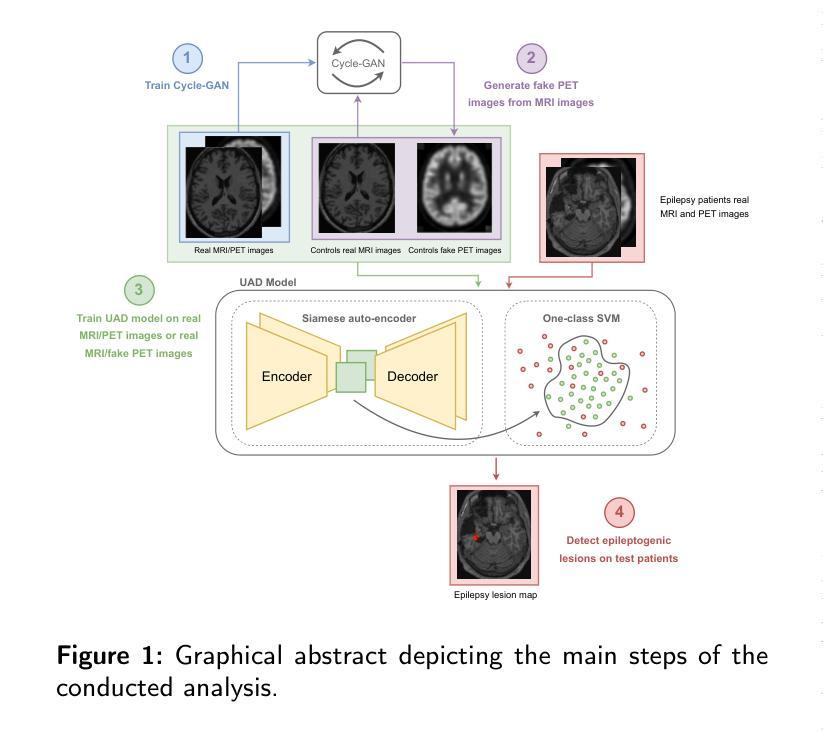
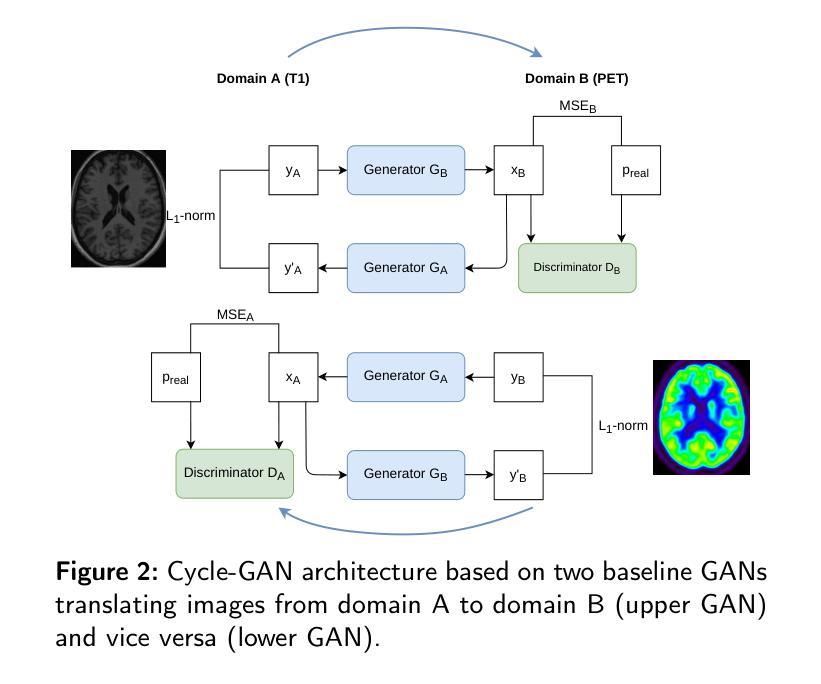
GAN-based synthetic FDG PET images from T1 brain MRI can serve to improve performance of deep unsupervised anomaly detection models
Authors:Daria Zotova, Nicolas Pinon, Robin Trombetta, Romain Bouet, Julien Jung, Carole Lartizien
Background and Objective. Research in the cross-modal medical image translation domain has been very productive over the past few years in tackling the scarce availability of large curated multimodality datasets with the promising performance of GAN-based architectures. However, only a few of these studies assessed task-based related performance of these synthetic data, especially for the training of deep models. Method. We design and compare different GAN-based frameworks for generating synthetic brain [18F]fluorodeoxyglucose (FDG) PET images from T1 weighted MRI data. We first perform standard qualitative and quantitative visual quality evaluation. Then, we explore further impact of using these fake PET data in the training of a deep unsupervised anomaly detection (UAD) model designed to detect subtle epilepsy lesions in T1 MRI and FDG PET images. We introduce novel diagnostic task-oriented quality metrics of the synthetic FDG PET data tailored to our unsupervised detection task, then use these fake data to train a use case UAD model combining a deep representation learning based on siamese autoencoders with a OC-SVM density support estimation model. This model is trained on normal subjects only and allows the detection of any variation from the pattern of the normal population. We compare the detection performance of models trained on 35 paired real MR T1 of normal subjects paired either on 35 true PET images or on 35 synthetic PET images generated from the best performing generative models. Performance analysis is conducted on 17 exams of epilepsy patients undergoing surgery. Results. The best performing GAN-based models allow generating realistic fake PET images of control subject with SSIM and PSNR values around 0.9 and 23.8, respectively and in distribution (ID) with regard to the true control dataset. The best UAD model trained on these synthetic normative PET data allows reaching 74% sensitivity. Conclusion. Our results confirm that GAN-based models are the best suited for MR T1 to FDG PET translation, outperforming transformer or diffusion models. We also demonstrate the diagnostic value of these synthetic data for the training of UAD models and evaluation on clinical exams of epilepsy patients. Our code and the normative image dataset are available.
背景与目的。近年来,基于GAN架构的跨模态医学图像翻译领域的研究已经取得了丰硕的成果,解决了大型整理多模态数据集稀缺的问题。然而,只有少数研究评估了这些合成数据在任务相关性能方面的表现,尤其是用于训练深度模型方面。
方法。我们设计并比较了基于不同GAN的框架,用于从T1加权MRI数据生成合成的大脑[18F]氟脱氧葡萄糖(FDG)PET图像。我们首先进行标准的主观和客观视觉质量评估。然后,我们进一步探索使用这些假PET数据在训练深度无监督异常检测(UAD)模型中的影响,该模型旨在检测T1 MRI和FDG PET图像中的细微癫痫病灶。我们引入针对我们的无监督检测任务的新型诊断任务导向型质量指标,以评估合成FDG PET数据,然后使用这些假数据来训练一个用例UAD模型,该模型结合了基于孪生自编码器的深度表示学习和OC-SVM密度支持估计模型。该模型仅对正常主体进行训练,可检测出任何与正常人群模式的偏差。我们比较了在真实MR T1图像(来自35名正常受试者)配对中,使用真实PET图像或最佳性能生成模型的合成PET图像训练的模型的检测性能。性能分析是在接受手术的17名癫痫患者身上进行的。
结果。表现最佳的基于GAN的模型能够生成逼真的假PET图像,对照组的SSIM和PSNR值分别约为0.9和23.8,与真实对照组数据在分布上相符。使用这些合成规范性PET数据训练的最佳UAD模型的敏感性达到74%。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
医学图像跨模态转换领域的研究在过去几年中取得了显著进展,特别是基于GAN的架构在生成合成数据方面表现出色。本研究设计并比较了不同的GAN框架,用于从T1加权MRI数据生成合成的大脑[18F]氟脱氧葡萄糖(FDG)PET图像。研究发现,最佳GAN模型生成的合成PET图像与现实图像相似度高,且对于训练无监督异常检测模型具有诊断价值。该模型在癫痫病灶检测方面的敏感度达到74%。
Key Takeaways
- 基于GAN的架构在医学图像跨模态转换领域表现优异,特别是在生成合成数据方面。
- 设计并比较了多种GAN框架,用于从T1加权MRI数据生成大脑FDG PET图像。
- 最佳GAN模型生成的合成PET图像与现实图像相似度高,具有现实性评估指标如SSIM和PSNR值。
- 合成数据对于训练无监督异常检测模型具有诊断价值。
- 在癫痫病灶检测方面,使用合成数据训练的模型的敏感度达到74%。
- 最佳UAD模型在手术中的癫痫患者考试上表现出良好的检测性能。
- 研究代码和标准化图像数据集可供使用。
点此查看论文截图

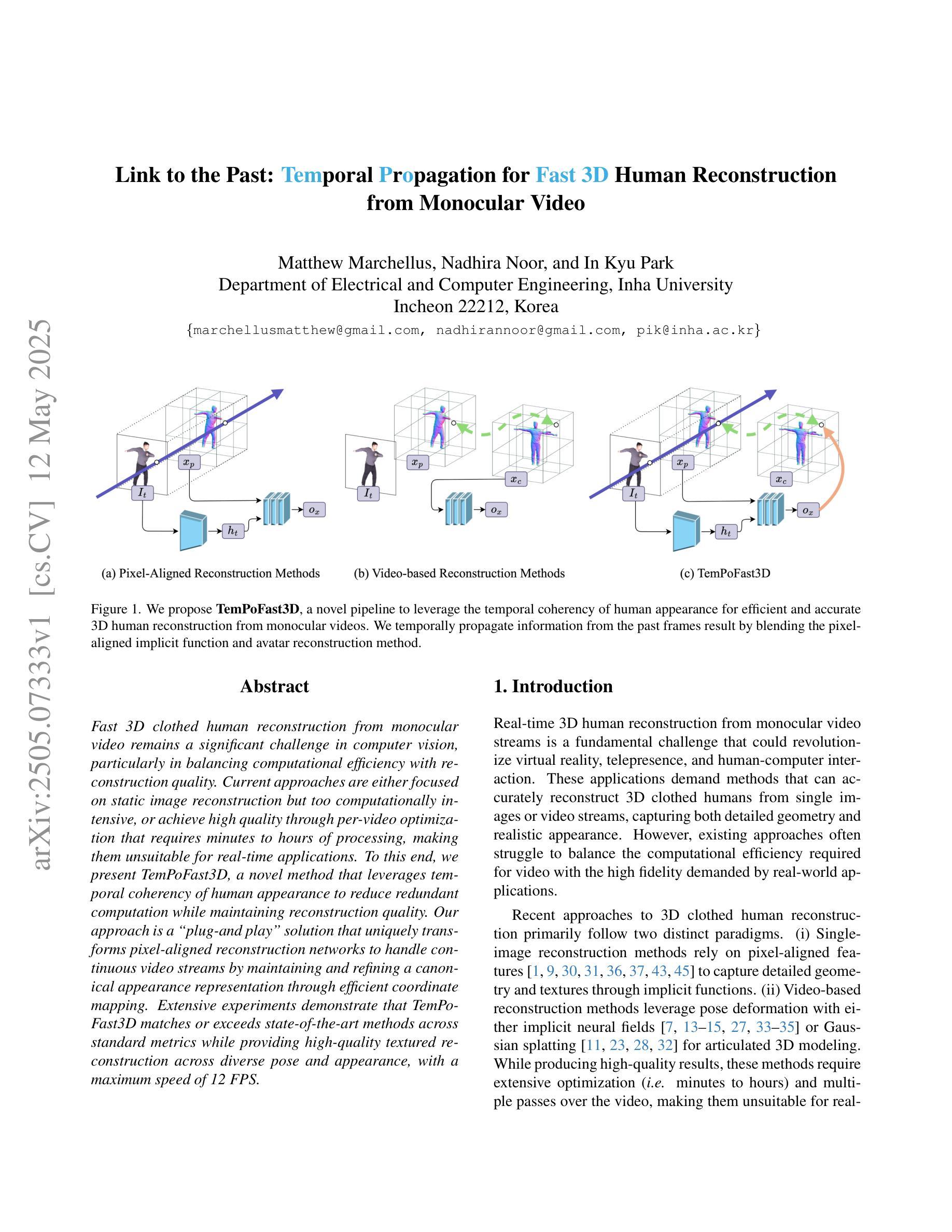
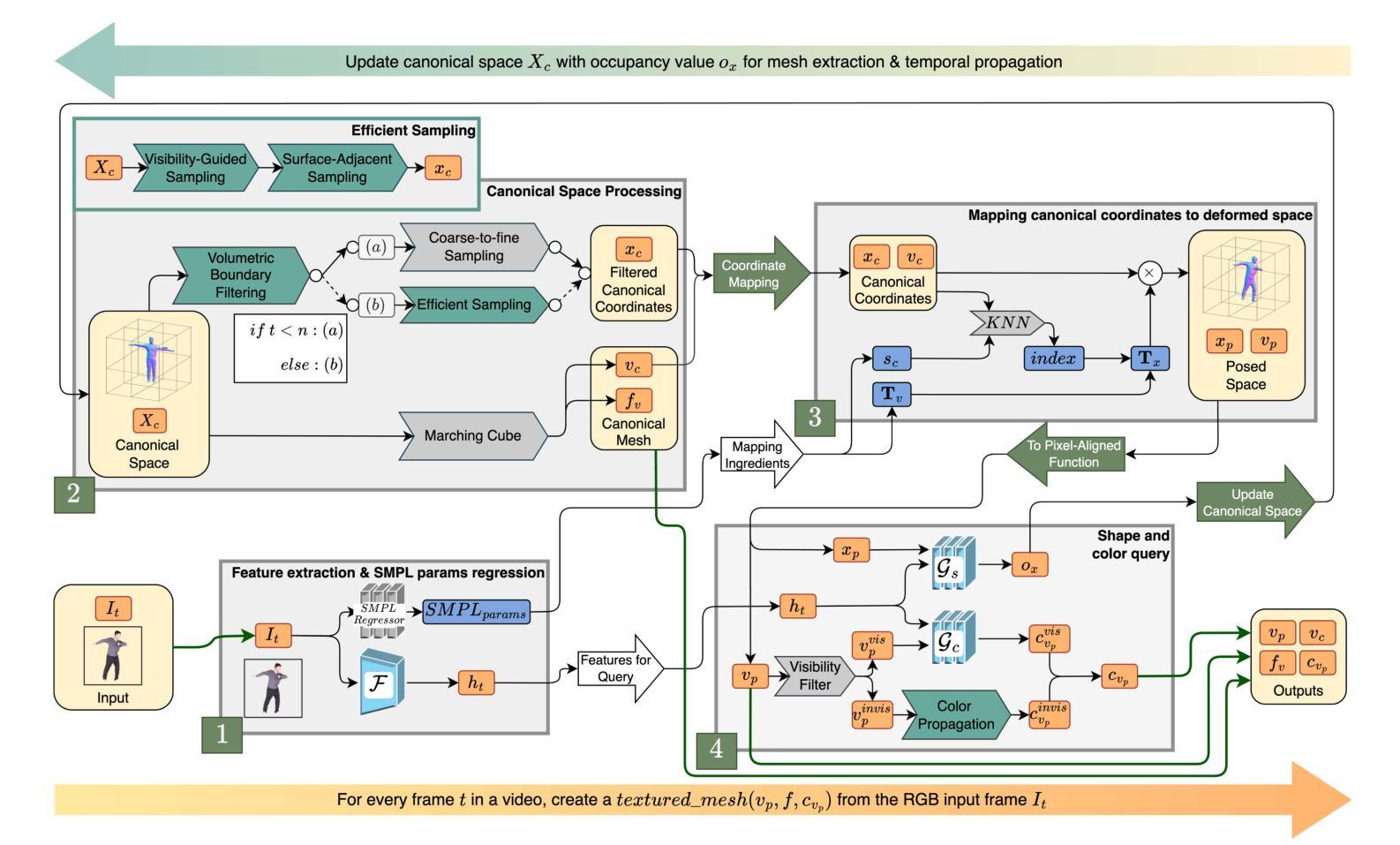
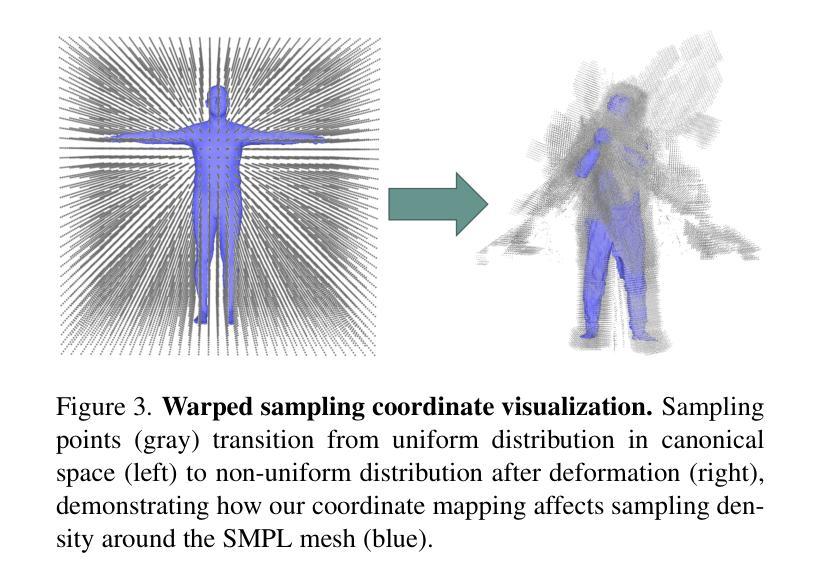
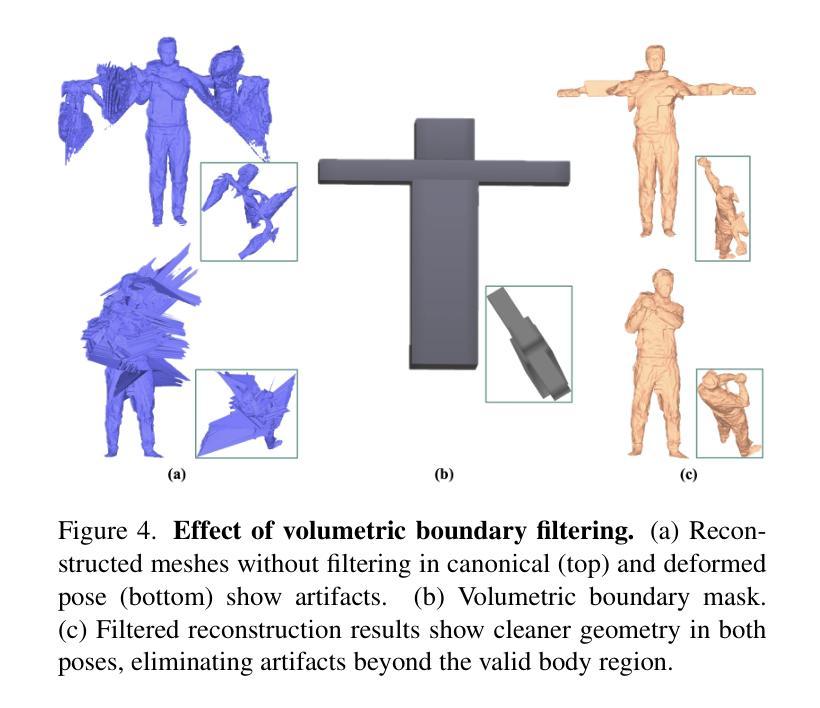
Link to the Past: Temporal Propagation for Fast 3D Human Reconstruction from Monocular Video
Authors:Matthew Marchellus, Nadhira Noor, In Kyu Park
Fast 3D clothed human reconstruction from monocular video remains a significant challenge in computer vision, particularly in balancing computational efficiency with reconstruction quality. Current approaches are either focused on static image reconstruction but too computationally intensive, or achieve high quality through per-video optimization that requires minutes to hours of processing, making them unsuitable for real-time applications. To this end, we present TemPoFast3D, a novel method that leverages temporal coherency of human appearance to reduce redundant computation while maintaining reconstruction quality. Our approach is a “plug-and play” solution that uniquely transforms pixel-aligned reconstruction networks to handle continuous video streams by maintaining and refining a canonical appearance representation through efficient coordinate mapping. Extensive experiments demonstrate that TemPoFast3D matches or exceeds state-of-the-art methods across standard metrics while providing high-quality textured reconstruction across diverse pose and appearance, with a maximum speed of 12 FPS.
从单目视频中快速进行三维服装人体重建仍然是计算机视觉领域的一个重要挑战,尤其是在计算效率和重建质量之间取得平衡。当前的方法要么专注于静态图像的重建,但计算过于密集,要么通过视频优化实现高质量重建,这需要数分钟到数小时的处理时间,使其不适合实时应用。为此,我们提出了TemPoFast3D,这是一种利用人体外观的时间连贯性来减少冗余计算并保持重建质量的新方法。我们的方法是一种“即插即用”的解决方案,它通过保持和细化规范外观表示,并通过有效的坐标映射来转换像素对齐重建网络,以处理连续的视频流。大量实验表明,TemPoFast3D在标准指标上的表现与现有技术方法相当或更优,在不同姿态和外观下都能实现高质量纹理重建,最高速度为每秒处理十二帧图像。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted in CVPR 2025
Summary
提出了一种基于时序一致性的快速三维服装重建方法,实现了高效计算与高质量重建的平衡。利用像素对齐重建网络处理连续视频流,通过维护并优化标准外观表示,实现高质量纹理重建。最高处理速度可达每秒12帧。
Key Takeaways
- TemPoFast3D是一种利用人体外观时序一致性进行快速三维服装重建的方法。
- 该方法实现了计算效率和重建质量的平衡。
- TemPoFast3D采用“即插即用”的解决方案,能够处理连续的视频流。
- 通过维护并优化标准外观表示,实现了高效的坐标映射。
- 该方法在多种姿势和外观下的重建质量达到或超过了现有技术。
- TemPoFast3D具有每秒最高可达12帧的处理速度。
点此查看论文截图
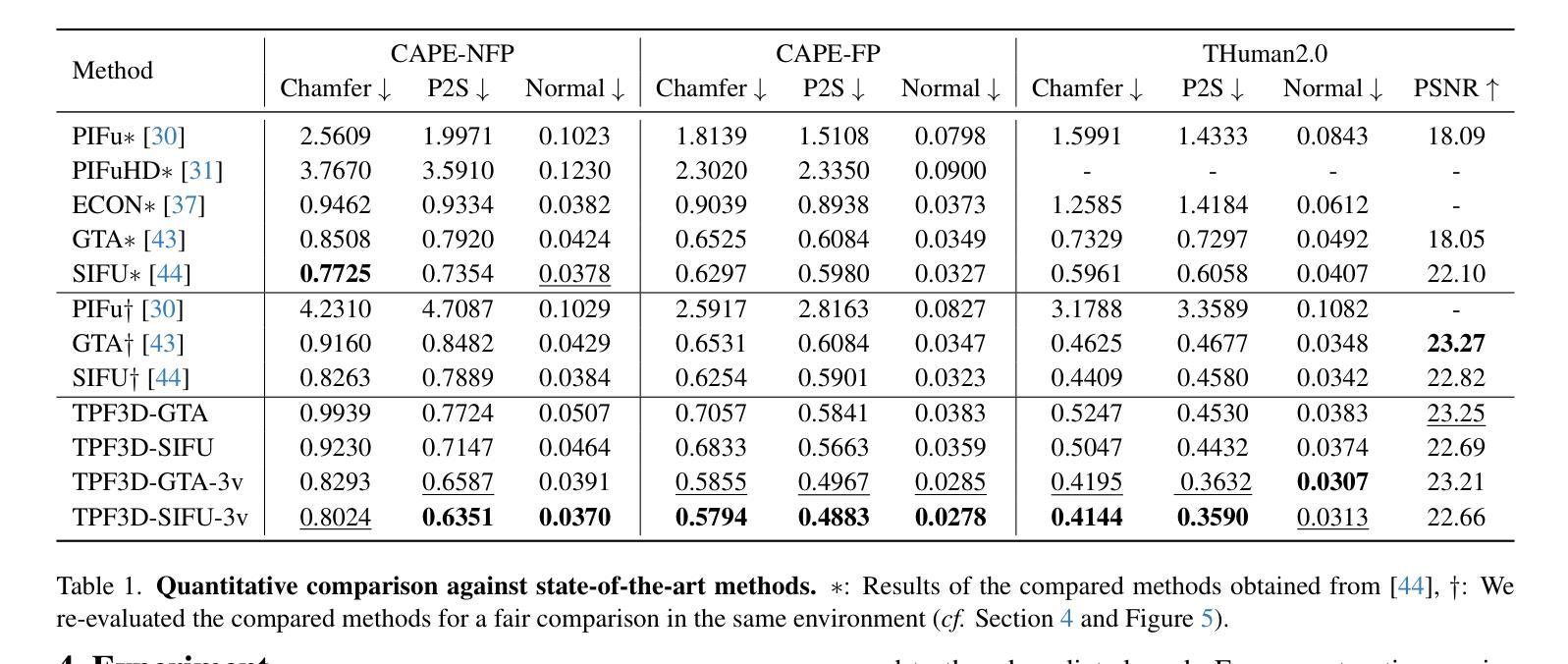
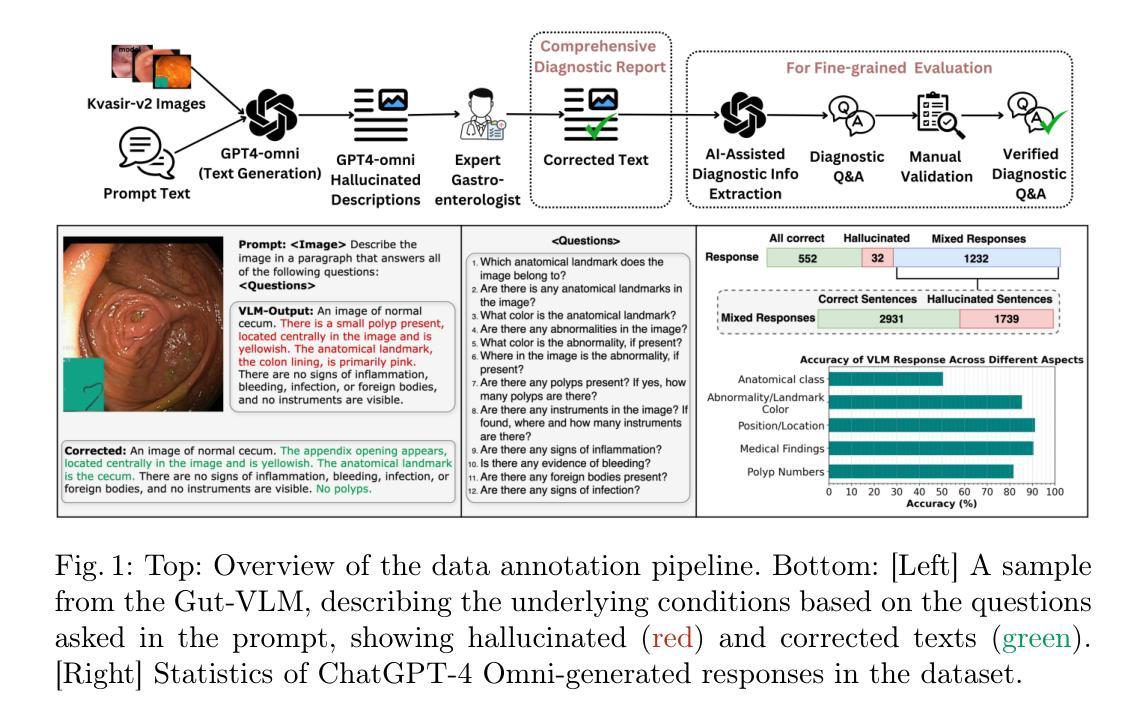
Hallucination-Aware Multimodal Benchmark for Gastrointestinal Image Analysis with Large Vision-Language Models
Authors:Bidur Khanal, Sandesh Pokhrel, Sanjay Bhandari, Ramesh Rana, Nikesh Shrestha, Ram Bahadur Gurung, Cristian Linte, Angus Watson, Yash Raj Shrestha, Binod Bhattarai
Vision-Language Models (VLMs) are becoming increasingly popular in the medical domain, bridging the gap between medical images and clinical language. Existing VLMs demonstrate an impressive ability to comprehend medical images and text queries to generate detailed, descriptive diagnostic medical reports. However, hallucination–the tendency to generate descriptions that are inconsistent with the visual content–remains a significant issue in VLMs, with particularly severe implications in the medical field. To facilitate VLM research on gastrointestinal (GI) image analysis and study hallucination, we curate a multimodal image-text GI dataset: Gut-VLM. This dataset is created using a two-stage pipeline: first, descriptive medical reports of Kvasir-v2 images are generated using ChatGPT, which introduces some hallucinated or incorrect texts. In the second stage, medical experts systematically review these reports, and identify and correct potential inaccuracies to ensure high-quality, clinically reliable annotations. Unlike traditional datasets that contain only descriptive texts, our dataset also features tags identifying hallucinated sentences and their corresponding corrections. A common approach to reducing hallucination in VLM is to finetune the model on a small-scale, problem-specific dataset. However, we take a different strategy using our dataset. Instead of finetuning the VLM solely for generating textual reports, we finetune it to detect and correct hallucinations, an approach we call hallucination-aware finetuning. Our results show that this approach is better than simply finetuning for descriptive report generation. Additionally, we conduct an extensive evaluation of state-of-the-art VLMs across several metrics, establishing a benchmark. GitHub Repo: https://github.com/bhattarailab/Hallucination-Aware-VLM.
视觉语言模型(VLMs)在医疗领域越来越受欢迎,它们填补了医疗图像和临床语言之间的空白。现有的VLMs表现出令人印象深刻的理解医疗图像和文本查询的能力,能够生成详细、描述性的诊断医疗报告。然而,幻觉——生成与视觉内容不一致描述的倾向——仍然是VLMs中的一个重大问题,在医疗领域具有尤其严重的后果。为了促进胃肠道(GI)图像分析和幻觉研究的VLM研究,我们创建了一个多模态图像文本胃肠道数据集:肠道VLM。该数据集使用两阶段管道创建:首先,使用ChatGPT生成Kvasir-v2图像的描述性医疗报告,这引入了一些幻觉或错误的文本。在第二阶段,医学专家系统地对这些报告进行审查,并识别并纠正潜在的不准确之处,以确保高质量、临床可靠的注释。与传统的仅包含描述性文本的数据集不同,我们的数据集还包含标识幻觉句子及其相应修正的标签。减少VLM中幻觉的一种常见方法是使用小规模、特定问题的数据集对模型进行微调。然而,我们采用了不同的策略使用我们的数据集。我们不是仅针对生成文本报告对VLM进行微调,而是对其进行调整和修正幻觉的微调,我们称这种方法为“幻觉感知微调”。我们的结果表明,这种方法优于仅用于生成描述性报告的微调。此外,我们对最先进的VLMs进行了广泛评估,建立了基准测试。GitHub仓库链接:https://github.com/bhattarailab/Hallucination-Aware-VLM。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了在医学领域日益流行的跨视觉语言模型(VLMs),这些模型能够在医学图像和临床语言之间建立联系。现有的VLM能够生成详细的诊断报告,但图像描述中的幻觉问题仍然严重。为了研究胃肠道图像分析和幻觉问题,创建了一个多模态图像文本胃肠道数据集:肠道视界模型。此数据集采用两阶段流程生成,第一阶段使用ChatGPT生成Kvasir-v2图像的医学报告,可能包含幻觉或错误文本。第二阶段由医学专家审查并纠正潜在错误,确保高质量的临床可靠注释。不同于仅包含描述性文本的传统数据集,该数据集还包含识别幻觉句子的标签及其相应更正。本文采用了一种不同于传统减少幻觉的方法,不是通过小规模特定问题的数据集微调视觉语言模型,而是对其进行微调以检测和纠正幻觉,称为幻觉感知微调。实验结果表明,这种方法优于仅用于生成描述性报告的微调方法。此外,对最先进的VLM进行了全面的评估,建立了基准测试。
Key Takeaways
- 视觉语言模型(VLMs)在医学领域受到广泛关注,能够在医学图像和临床文本之间建立联系。
- 现有VLM在生成医学图像描述时存在幻觉问题,即生成与图像内容不一致的描述。
- 为了研究和解决胃肠道图像分析中的幻觉问题,创建了一个多模态图像文本胃肠道数据集:肠道视界模型。
- 该数据集包含由ChatGPT生成的医学报告以及由医学专家进行的审查和更正,以确保高质量和临床可靠性。
- 与传统减少幻觉的方法不同,采用幻觉感知微调的方法对VLM进行微调,以检测和纠正幻觉。
- 幻觉感知微调方法优于仅用于生成描述性报告的微调方法。
点此查看论文截图

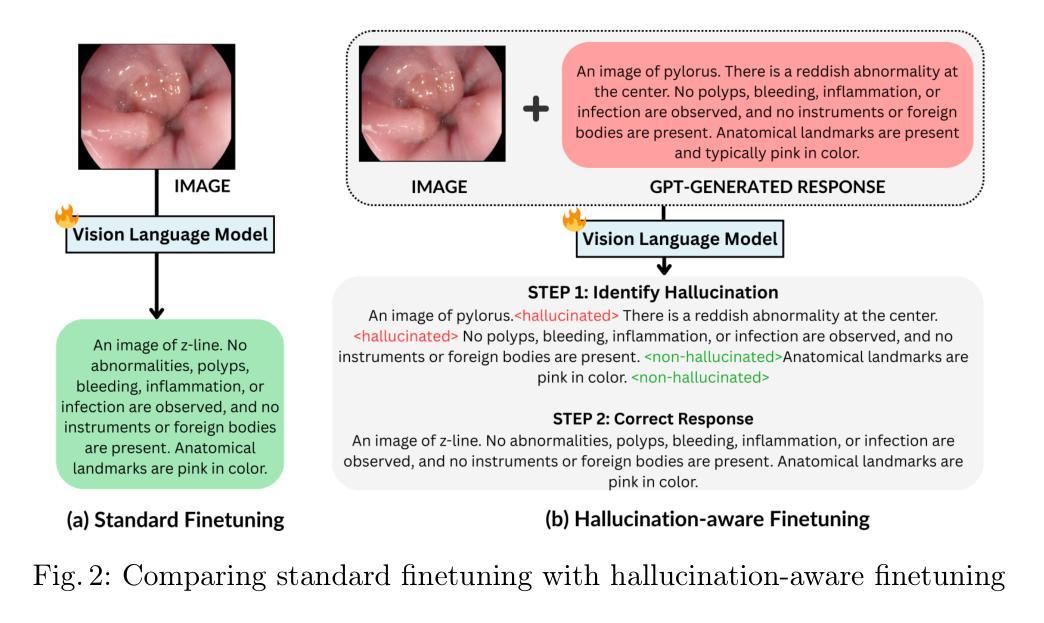
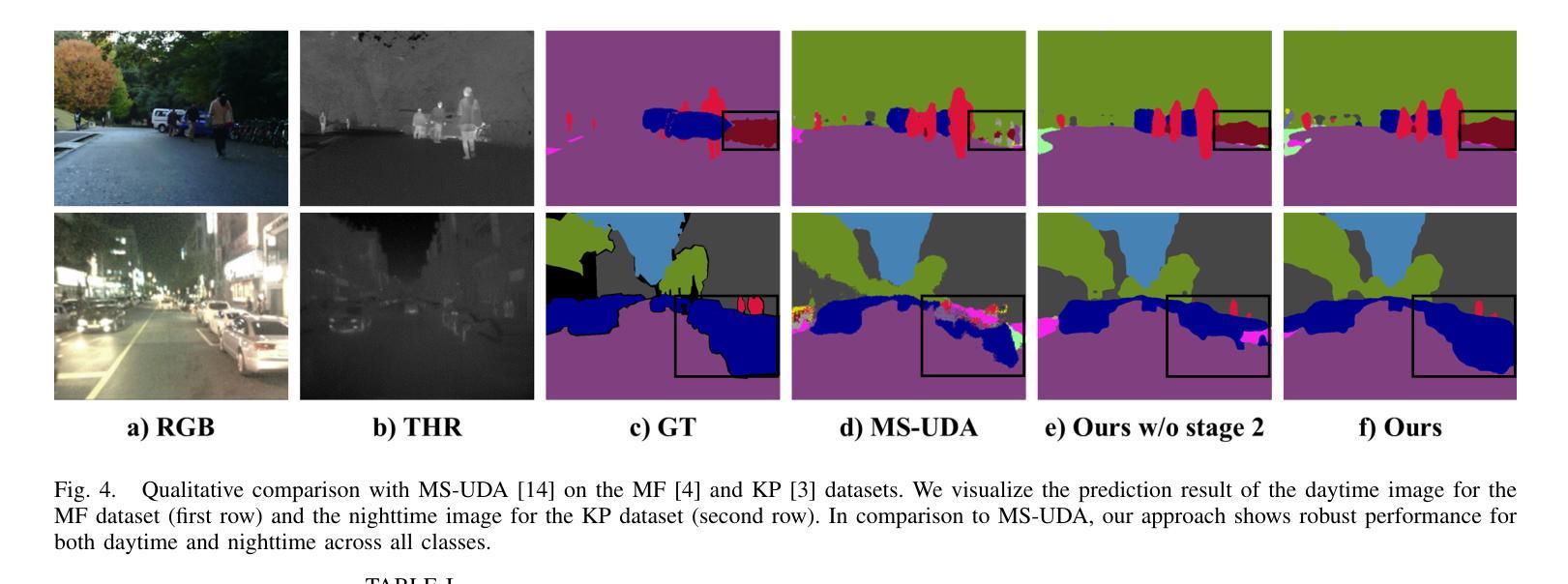
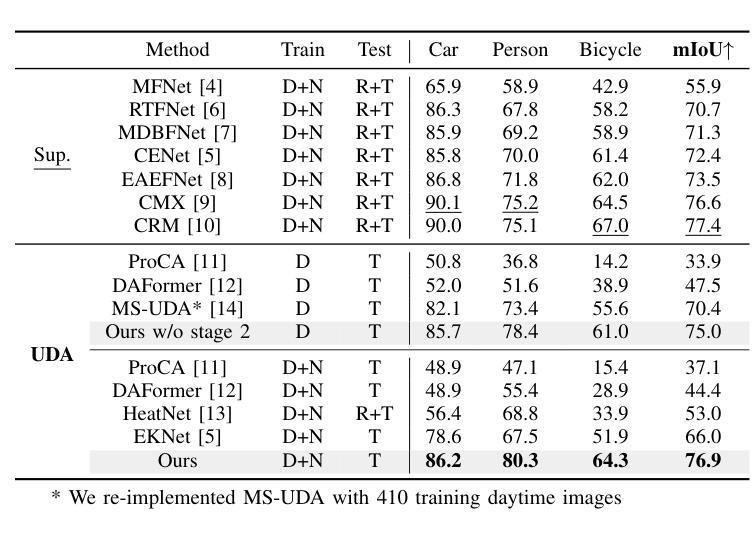
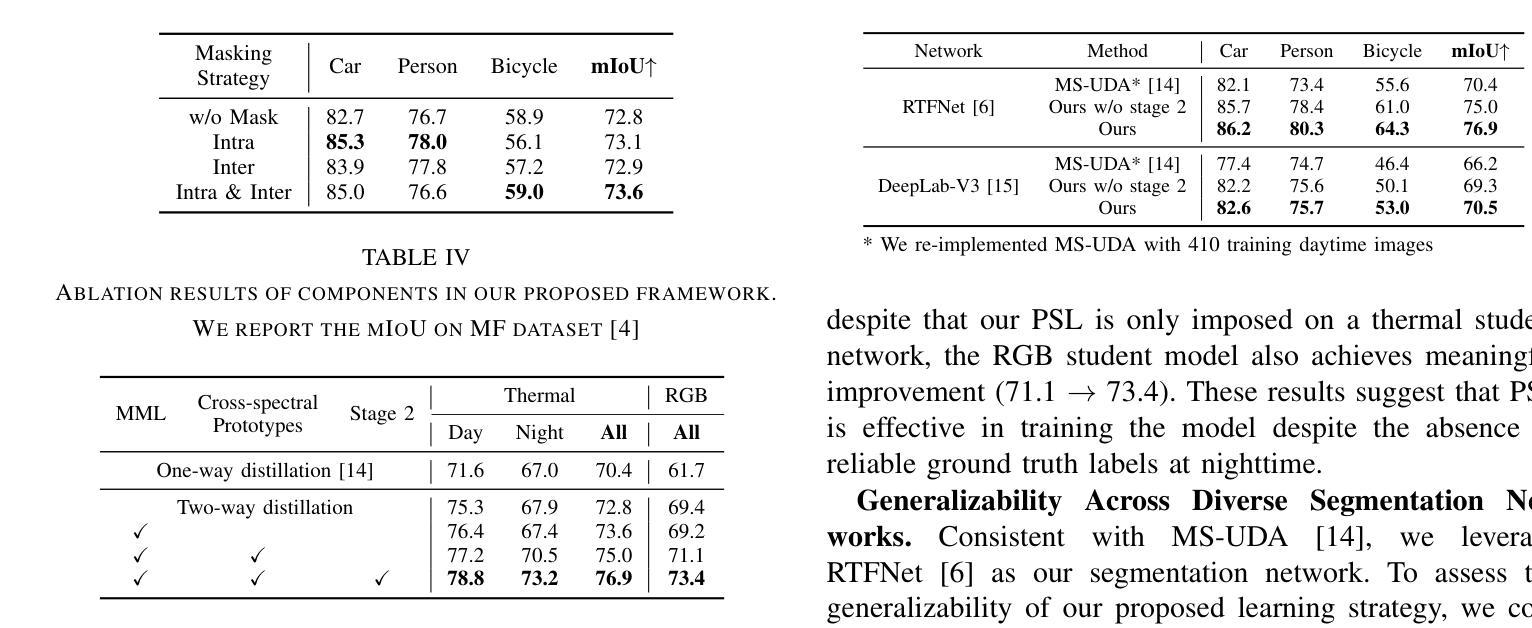
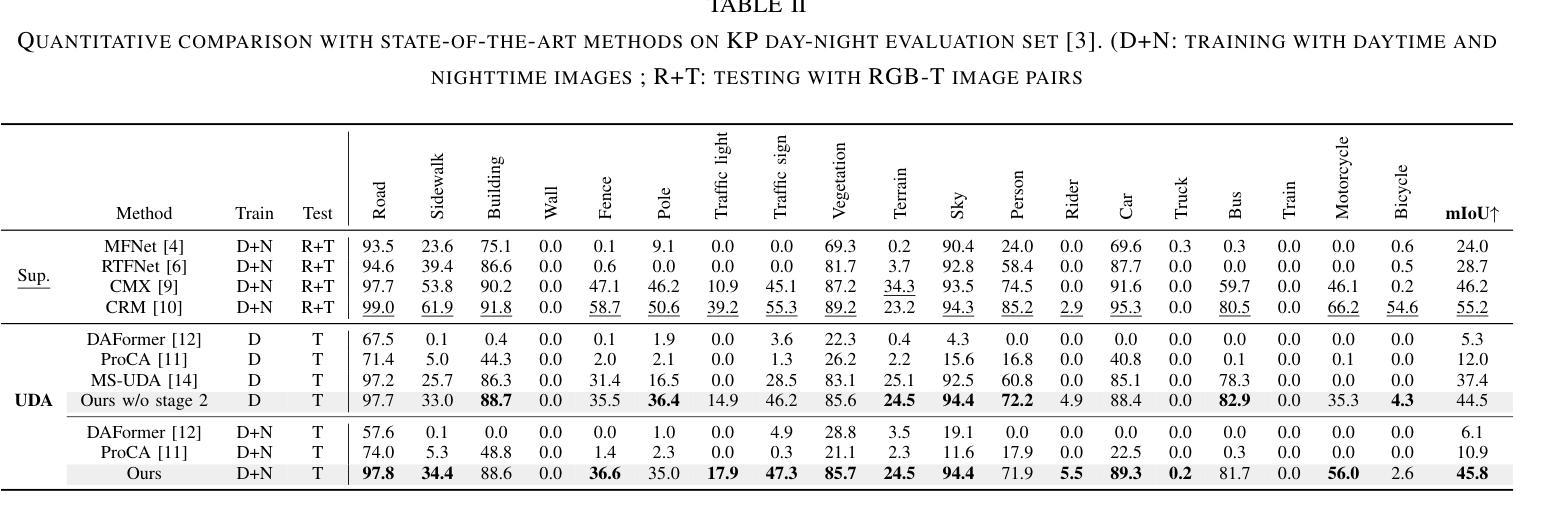
Boosting Cross-spectral Unsupervised Domain Adaptation for Thermal Semantic Segmentation
Authors:Seokjun Kwon, Jeongmin Shin, Namil Kim, Soonmin Hwang, Yukyung Choi
In autonomous driving, thermal image semantic segmentation has emerged as a critical research area, owing to its ability to provide robust scene understanding under adverse visual conditions. In particular, unsupervised domain adaptation (UDA) for thermal image segmentation can be an efficient solution to address the lack of labeled thermal datasets. Nevertheless, since these methods do not effectively utilize the complementary information between RGB and thermal images, they significantly decrease performance during domain adaptation. In this paper, we present a comprehensive study on cross-spectral UDA for thermal image semantic segmentation. We first propose a novel masked mutual learning strategy that promotes complementary information exchange by selectively transferring results between each spectral model while masking out uncertain regions. Additionally, we introduce a novel prototypical self-supervised loss designed to enhance the performance of the thermal segmentation model in nighttime scenarios. This approach addresses the limitations of RGB pre-trained networks, which cannot effectively transfer knowledge under low illumination due to the inherent constraints of RGB sensors. In experiments, our method achieves higher performance over previous UDA methods and comparable performance to state-of-the-art supervised methods.
在自动驾驶领域,热图像语义分割已成为一个关键研究领域,因为它能在恶劣的视觉条件下提供稳健的场景理解。特别是,用于热图像分割的无监督域自适应(UDA)可以是有效解决缺乏标记热数据集的方法。然而,由于这些方法没有有效地利用RGB和热图像之间的互补信息,它们在域自适应过程中会降低性能。在本文中,我们对用于热图像语义分割的跨光谱UDA进行了深入研究。我们首先提出了一种新颖的掩模互学习策略,通过选择性地在各光谱模型之间转移结果并屏蔽不确定区域,以促进互补信息的交换。此外,我们还引入了一种新型的原型自监督损失,旨在提高夜间场景中的热分割模型性能。该方法解决了RGB预训练网络的局限性,由于RGB传感器的固有约束,这些网络在低光照条件下无法有效地转移知识。在实验中,我们的方法较之前的UDA方法实现了更高的性能,并与最新的有监督方法达到了相当的性能水平。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 7 pages, 4 figures, International Conference on Robotics and Automation(ICRA) 2025
摘要
在自动驾驶领域,热图像语义分割已成为一项重要的研究领域,因其能够在恶劣的视觉条件下提供稳健的场景理解。针对热图像分割的无监督域自适应(UDA)方法可以有效解决标记热数据集缺乏的问题。然而,由于这些方法未能有效利用RGB和热图像之间的互补信息,它们在域自适应过程中的性能有所降低。本文全面研究了用于热图像语义分割的跨光谱UDA。我们首先提出了一种新颖的掩模互学习策略,通过选择性地在各光谱模型之间转移结果并掩盖不确定区域,以促进互补信息的交换。此外,我们还引入了一种新型的原型自监督损失,旨在提高夜间场景中的热分割模型性能。该方法解决了RGB预训练网络在夜间无法有效转移知识的局限性,这是由于RGB传感器的固有约束造成的。在实验中,我们的方法相较于之前的UDA方法表现出更高的性能,并与最新的监督方法相当。
关键见解
- 热图像语义分割在自动驾驶中是关键研究领域,能在恶劣视觉条件下提供稳健的场景理解。
- 无监督域自适应(UDA)是解决热图像分割中标记数据集缺乏的有效方法。
- 现有UDA方法未能充分利用RGB和热图像之间的互补信息,导致性能下降。
- 提出了掩模互学习策略,通过选择性转移结果并掩盖不确定区域,促进互补信息交换。
- 引入原型自监督损失,提高夜间场景中的热分割模型性能。
- 该方法解决了RGB预训练网络在夜间无法有效转移知识的局限性。
点此查看论文截图

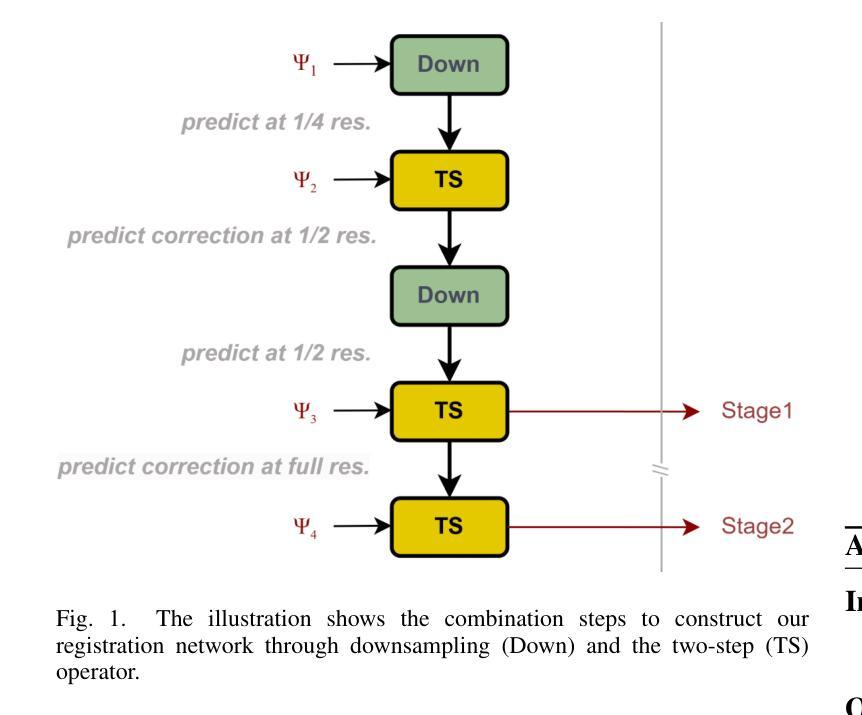
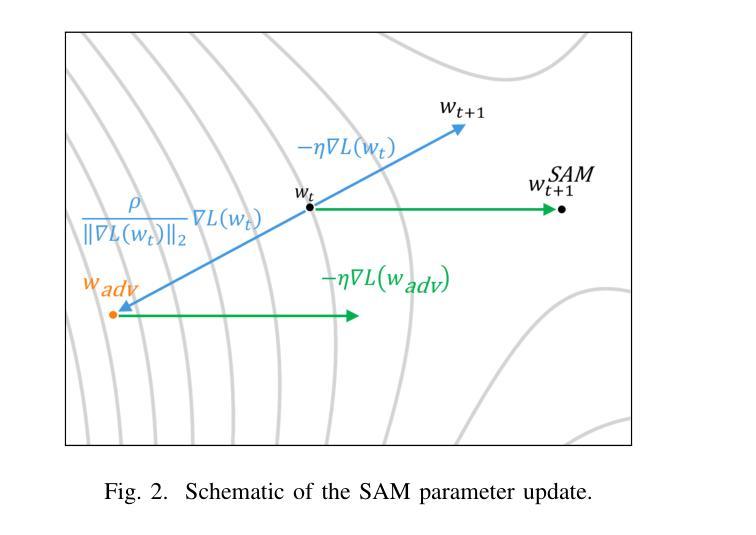
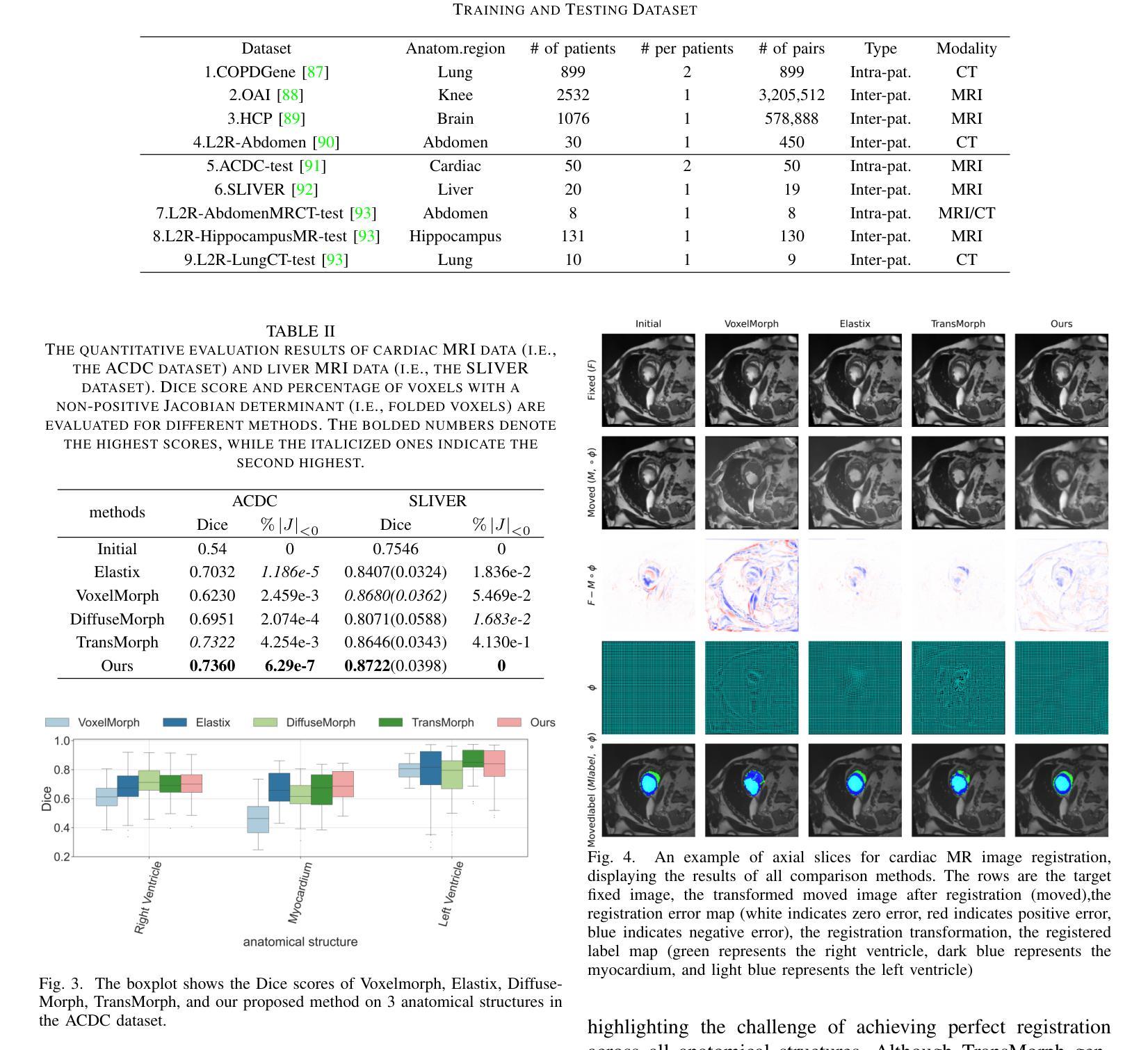
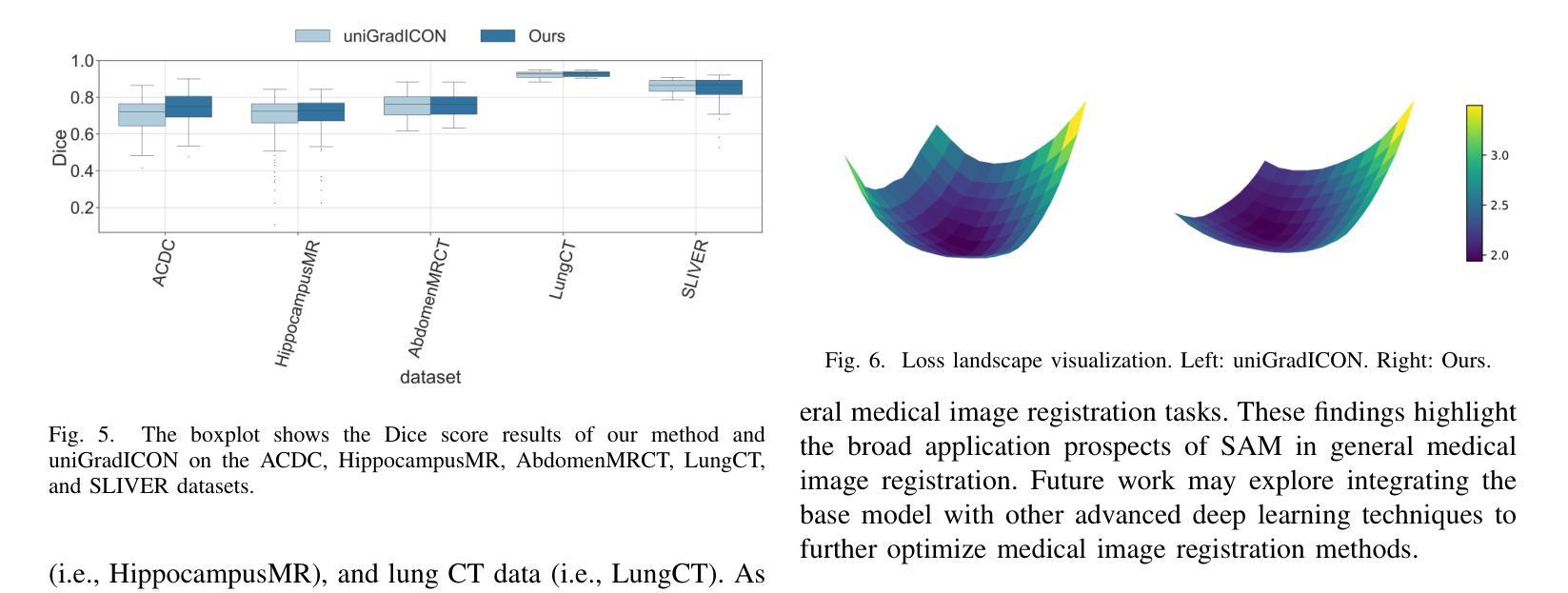
Improving Generalization of Medical Image Registration Foundation Model
Authors:Jing Hu, Kaiwei Yu, Hongjiang Xian, Shu Hu, Xin Wang
Deformable registration is a fundamental task in medical image processing, aiming to achieve precise alignment by establishing nonlinear correspondences between images. Traditional methods offer good adaptability and interpretability but are limited by computational efficiency. Although deep learning approaches have significantly improved registration speed and accuracy, they often lack flexibility and generalizability across different datasets and tasks. In recent years, foundation models have emerged as a promising direction, leveraging large and diverse datasets to learn universal features and transformation patterns for image registration, thus demonstrating strong cross-task transferability. However, these models still face challenges in generalization and robustness when encountering novel anatomical structures, varying imaging conditions, or unseen modalities. To address these limitations, this paper incorporates Sharpness-Aware Minimization (SAM) into foundation models to enhance their generalization and robustness in medical image registration. By optimizing the flatness of the loss landscape, SAM improves model stability across diverse data distributions and strengthens its ability to handle complex clinical scenarios. Experimental results show that foundation models integrated with SAM achieve significant improvements in cross-dataset registration performance, offering new insights for the advancement of medical image registration technology. Our code is available at https://github.com/Promise13/fm_sam}{https://github.com/Promise13/fm\_sam.
可变形的图像配准是一个基本的医学图像处理任务,目的是通过在不同的图像之间建立非线性对应关系来实现精确的配准。传统的方法具有良好的适应性和可解释性,但在计算效率上有所局限。尽管深度学习方法大大提高了配准的速度和准确性,但它们往往在跨越不同的数据集和任务时缺乏灵活性和泛化能力。近年来,基础模型作为一个有前景的方向崭露头角,它们利用大规模和多样化的数据集来学习图像配准中的通用特征和转换模式,从而表现出强大的跨任务迁移能力。然而,当遇到新的解剖结构、不同的成像条件或未见的模态时,这些模型在泛化和稳健性方面仍面临挑战。为了解决这些局限性,本文引入了Sharpness-Aware Minimization(SAM)技术到基础模型中,以增强其在医学图像配准中的泛化和稳健性。通过优化损失景观的尖锐度,SAM提高了模型在不同数据分布上的稳定性,并加强了其处理复杂临床场景的能力。实验结果表明,集成SAM的基础模型在跨数据集配准性能方面取得了显著改进,为医学图像配准技术的发展提供了新的见解。我们的代码可通过https://github.com/Promise13/fm_sam访问。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF IJCNN
Summary
本文探讨了医学图像处理中的可变形注册问题,介绍了传统方法和深度学习方法在该领域的局限和挑战。为解决这些问题,文章将Sharpness-Aware Minimization(SAM)技术引入基础模型,提高了模型在医学图像注册中的泛化和稳健性。实验结果显示,结合SAM的基础模型在跨数据集注册性能上取得了显著改进。
Key Takeaways
- 可变形注册是医学图像处理中的基础任务,旨在通过图像间的非线性对应关系实现精确对齐。
- 传统方法具有良好的适应性和可解释性,但计算效率有限。
- 深度学习方法的注册速度和准确性得到了显著提升,但缺乏灵活性和跨数据集的泛化能力。
- 基础模型利用大规模多样数据集学习图像注册的通用特征和转换模式,表现出强大的跨任务迁移能力。
- 引入Sharpness-Aware Minimization(SAM)技术增强基础模型的泛化和稳健性。
- SAM通过优化损失景观的平坦度,提高了模型在多样化数据分布下的稳定性,并增强了处理复杂临床场景的能力。
点此查看论文截图

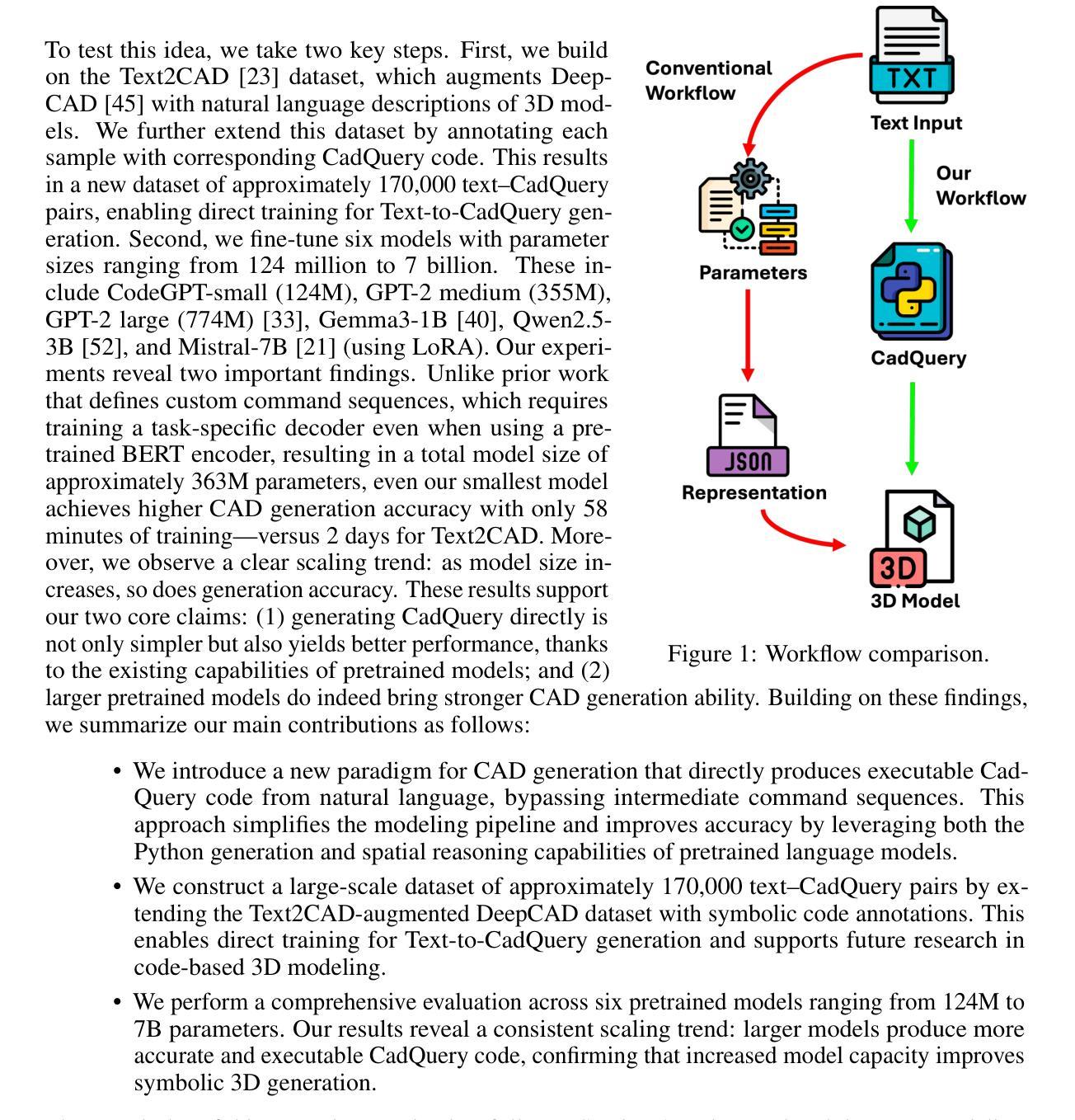
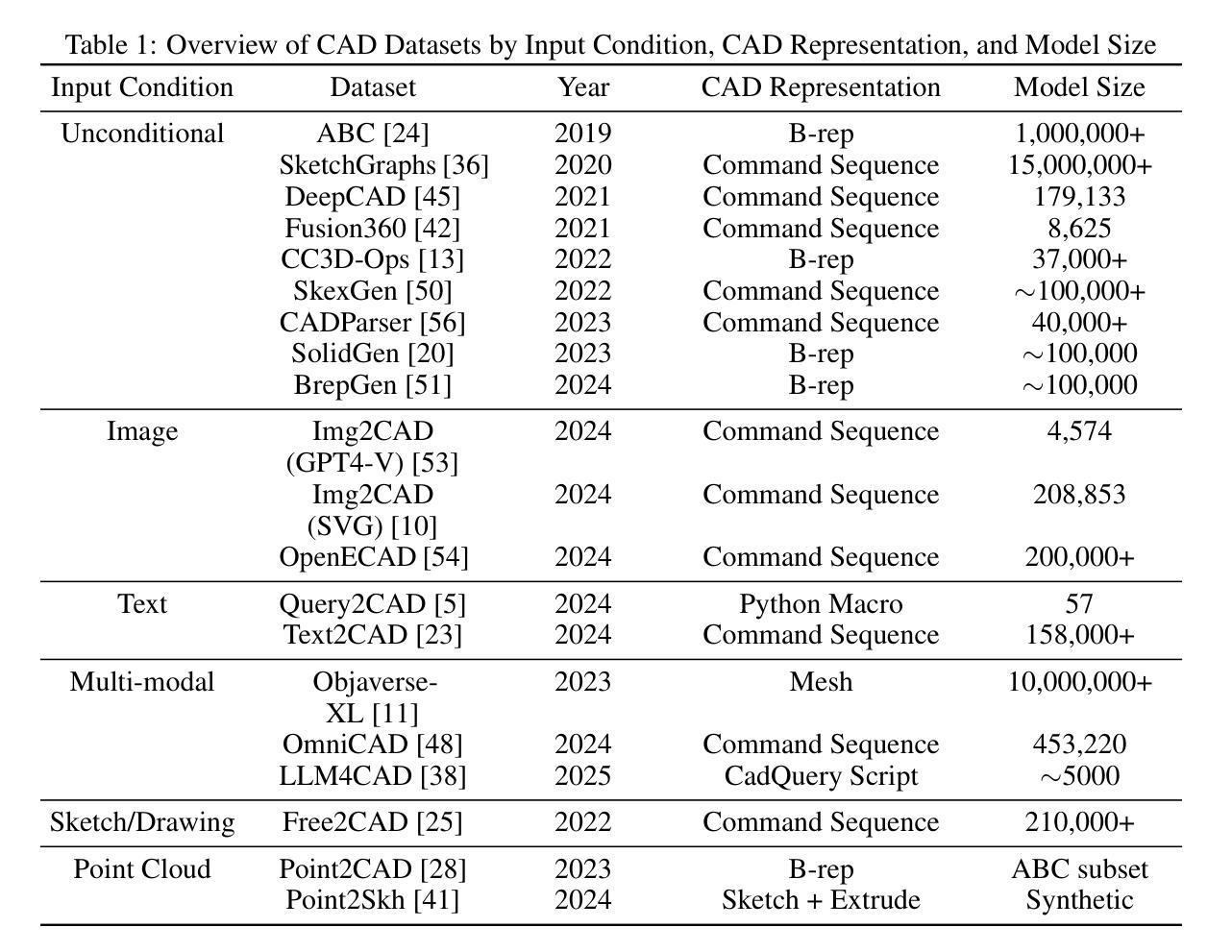
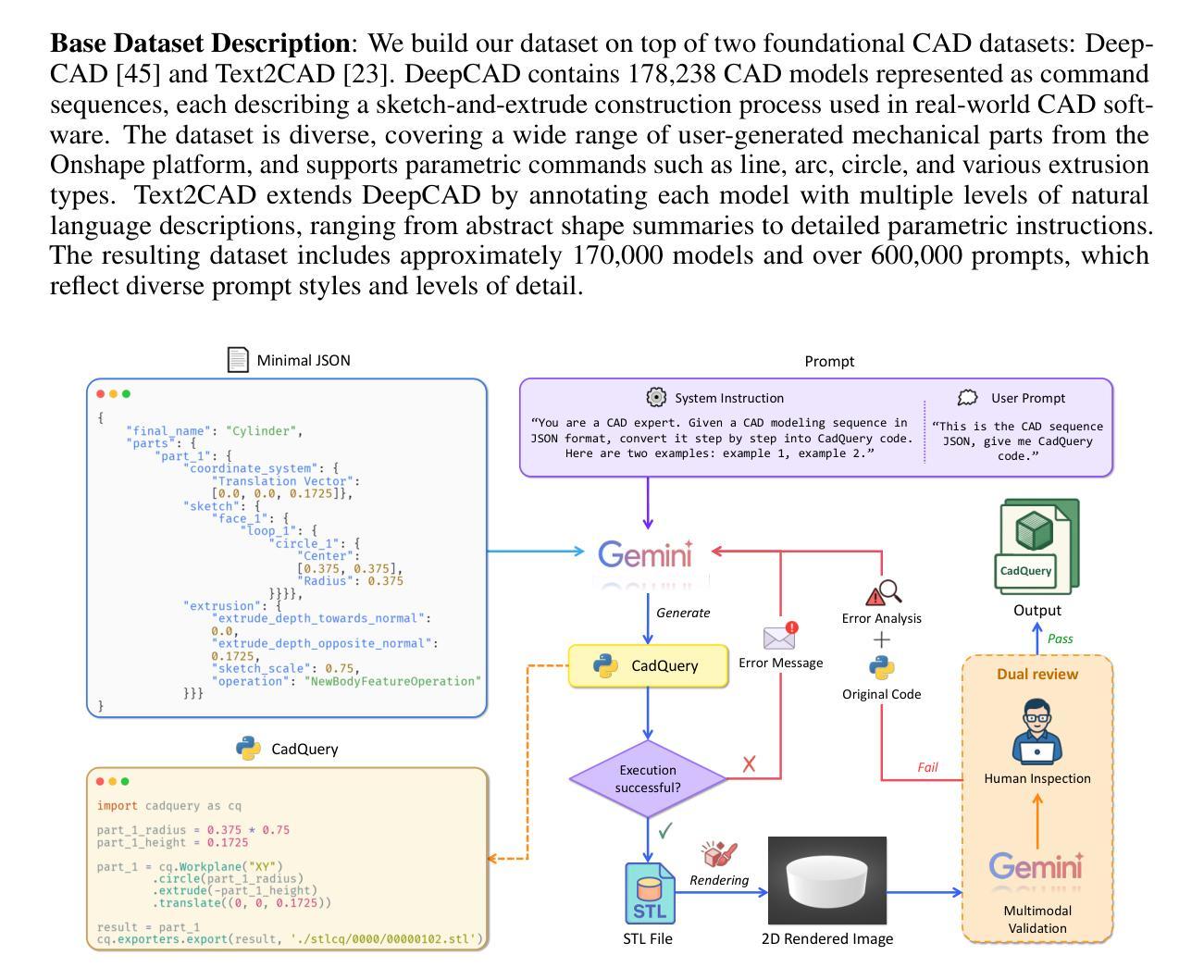
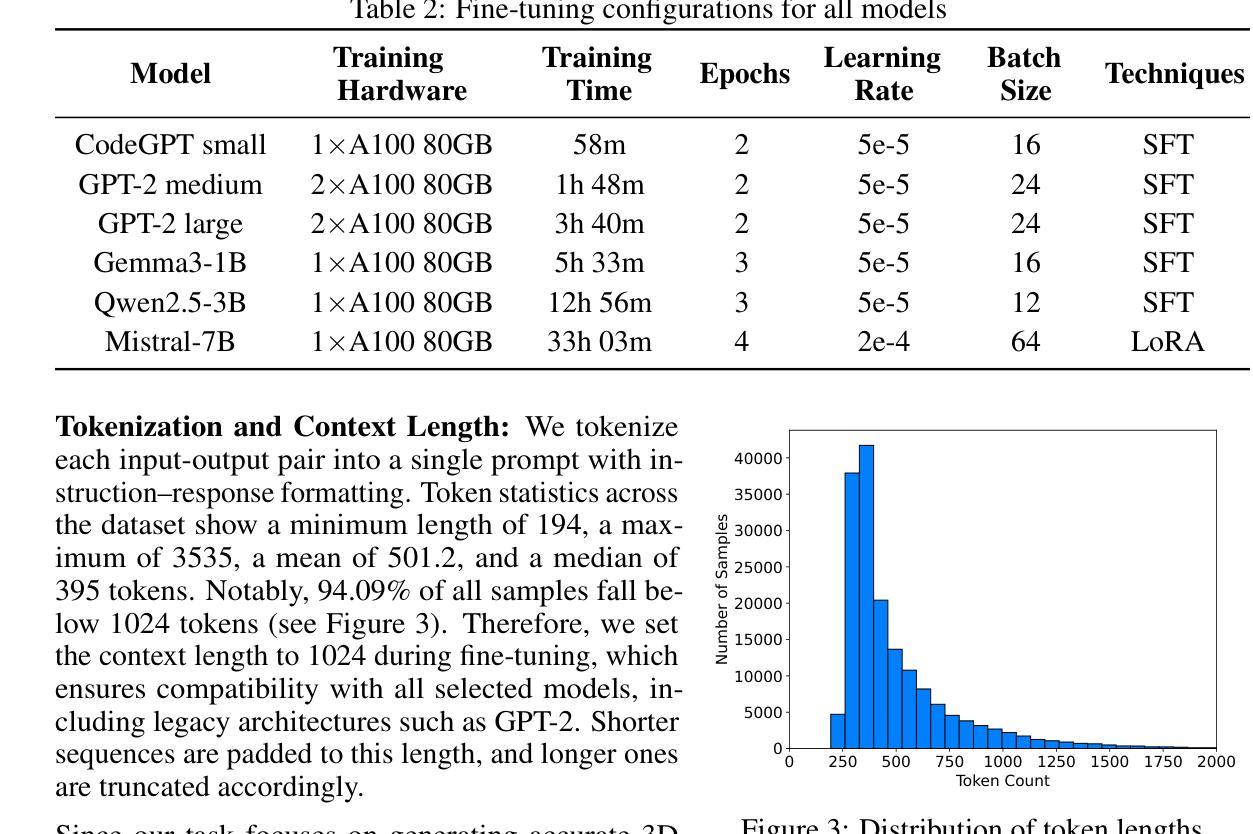
Text-to-CadQuery: A New Paradigm for CAD Generation with Scalable Large Model Capabilities
Authors:Haoyang Xie, Feng Ju
Computer-aided design (CAD) is fundamental to modern engineering and manufacturing, but creating CAD models still requires expert knowledge and specialized software. Recent advances in large language models (LLMs) open up the possibility of generative CAD, where natural language is directly translated into parametric 3D models. However, most existing methods generate task-specific command sequences that pretrained models cannot directly handle. These sequences must be converted into CAD representations such as CAD vectors before a 3D model can be produced, which requires training models from scratch and adds unnecessary complexity. To tackle this issue, we propose generating CadQuery code directly from text, leveraging the strengths of pretrained LLMs to produce 3D models without intermediate representations, using this Python-based scripting language. Since LLMs already excel at Python generation and spatial reasoning, fine-tuning them on Text-to-CadQuery data proves highly effective. Given that these capabilities typically improve with scale, we hypothesize that larger models will perform better after fine-tuning. To enable this, we augment the Text2CAD dataset with 170,000 CadQuery annotations. We fine-tune six open-source LLMs of varying sizes and observe consistent improvements. Our best model achieves a top-1 exact match of 69.3%, up from 58.8%, and reduces Chamfer Distance by 48.6%. Project page: https://github.com/Text-to-CadQuery/Text-to-CadQuery.
计算机辅助设计(CAD)是现代工程和制造业的基础,但创建CAD模型仍然需要专业知识和专用软件。大型语言模型(LLM)的最新进展为生成式CAD提供了可能性,其中自然语言直接翻译为参数化3D模型。然而,大多数现有方法生成特定任务的命令序列,这些序列不能直接由预训练模型处理。这些序列必须转换为CAD表示(如CAD矢量),然后才能生成3D模型,这需要从头开始训练模型,增加了不必要的复杂性。为了解决这个问题,我们提出直接从文本生成CadQuery代码,利用预训练LLM的优势,通过基于Python的脚本语言生成3D模型,无需中间表示。由于LLM已经在Python生成和空间推理方面表现出色,因此在Text-to-CadQuery数据上进行微调证明是非常有效的。考虑到这些能力通常随着规模而提高,我们假设更大的模型在微调后会有更好的表现。为此,我们增加了17万个CadQuery注释来增强Text2CAD数据集。我们微调了六个不同大小的开源LLM,并观察到了一致的改进。我们的最佳模型将top-1精确匹配度从58.8%提高到69.3%,并减少了Chamfer距离48.6%。项目页面:https://github.com/Text-to-CadQuery/Text-to-CadQuery。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
基于计算机辅助设计(CAD)在现代工程和制造中的重要性,研究团队尝试将自然语言直接转化为参数化三维模型,实现生成式CAD。然而,现有方法需将自然语言转化为特定任务命令序列,再转换为CAD表示形式,如CAD矢量,才能生成三维模型。为解决这一问题,研究团队提出通过文本直接生成CadQuery代码的方法,利用预训练的语言模型产生三维模型,跳过中间表示形式。经过在Text-to-CadQuery数据集上的微调,大型模型表现出更高的性能。
Key Takeaways
- 计算机辅助设计(CAD)在现代工程制造中仍需要专业知识和专门软件。
- 自然语言直接转化为参数化三维模型是生成式CAD的新趋势。
- 当前方法需将自然语言转化为任务特定命令序列再生成CAD模型,这增加了复杂性和时间成本。
- 通过文本直接生成CadQuery代码可跳过中间表示形式,简化流程。
- 利用预训练的语言模型进行微调可有效提高模型性能。
- 项目通过使用更大规模数据集提升了模型的性能表现。
点此查看论文截图

Robust & Precise Knowledge Distillation-based Novel Context-Aware Predictor for Disease Detection in Brain and Gastrointestinal
Authors:Saif Ur Rehman Khan, Muhammad Nabeel Asim, Sebastian Vollmer, Andreas Dengel
Medical disease prediction, particularly through imaging, remains a challenging task due to the complexity and variability of medical data, including noise, ambiguity, and differing image quality. Recent deep learning models, including Knowledge Distillation (KD) methods, have shown promising results in brain tumor image identification but still face limitations in handling uncertainty and generalizing across diverse medical conditions. Traditional KD methods often rely on a context-unaware temperature parameter to soften teacher model predictions, which does not adapt effectively to varying uncertainty levels present in medical images. To address this issue, we propose a novel framework that integrates Ant Colony Optimization (ACO) for optimal teacher-student model selection and a novel context-aware predictor approach for temperature scaling. The proposed context-aware framework adjusts the temperature based on factors such as image quality, disease complexity, and teacher model confidence, allowing for more robust knowledge transfer. Additionally, ACO efficiently selects the most appropriate teacher-student model pair from a set of pre-trained models, outperforming current optimization methods by exploring a broader solution space and better handling complex, non-linear relationships within the data. The proposed framework is evaluated using three publicly available benchmark datasets, each corresponding to a distinct medical imaging task. The results demonstrate that the proposed framework significantly outperforms current state-of-the-art methods, achieving top accuracy rates: 98.01% on the MRI brain tumor (Kaggle) dataset, 92.81% on the Figshare MRI dataset, and 96.20% on the GastroNet dataset. This enhanced performance is further evidenced by the improved results, surpassing existing benchmarks of 97.24% (Kaggle), 91.43% (Figshare), and 95.00% (GastroNet).
医疗疾病预测,尤其是通过成像进行预测,仍然是一项具有挑战性的任务,因为医疗数据具有复杂性和多样性,包括噪声、模糊和不同图像质量等问题。最近的深度学习模型,包括知识蒸馏(KD)方法,在脑肿瘤图像识别方面已显示出有前景的结果,但在处理不确定性和跨不同医疗条件推广方面仍存在局限性。传统知识蒸馏方法通常依赖于上下文无关的温度参数来软化教师模型的预测,这不能有效地适应医学图像中存在的不同不确定性水平。为了解决这一问题,我们提出了一种新的框架,融合了蚁群优化(ACO)来进行最佳教师-学生模型选择以及一种新型上下文感知预测方法进行温度标定。所提出的上下文感知框架根据图像质量、疾病复杂性和教师模型信心等因素调整温度,从而实现更稳健的知识转移。此外,蚁群优化能够高效地从一组预训练模型中选择最合适的教学模型对学生模型进行知识蒸馏,通过探索更广泛的解决方案空间和更好地处理数据中的复杂非线性关系,超越了当前优化方法。该框架使用三个公开可用的基准数据集进行了评估,每个数据集都对应一个独特的医学成像任务。结果表明,所提出的框架显著优于当前最先进的方法,在MRI脑肿瘤(Kaggle)数据集上达到98.01%的准确率,在Figshare MRI数据集上达到92.8r%的准确率,以及在GastroNet数据集上达到96.20%的准确率。这一改进的性能进一步体现在超越现有基准的结果中,分别为Kaggle的97.24%、Figshare的91.43%和GastroNet的95.00%。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
医学疾病预测,尤其是通过医学影像预测,因医学数据复杂性及多变性(如噪声、模糊、图像质量不一等)而充满挑战。深度学习模型,如知识蒸馏(KD)方法,在脑肿瘤图像识别方面展现出良好前景,但在处理不确定性和跨不同医学状况推广时仍有限制。针对传统KD方法在处理医学图像中的不同不确定性时不够灵活的问题,提出一种结合蚁群优化(ACO)进行最优教师-学生模型选择和上下文感知预测器进行温度调节的新框架。该框架根据图像质量、疾病复杂性和教师模型信心等因素调整温度,实现更稳健的知识转移。同时,ACO能从预训练模型中高效选择最合适的教学模型,在数据处理方面表现更优秀。新框架在三个公开基准数据集上的评估结果显示,其显著优于当前最先进的方法,准确率分别达到了Kaggle的MRI脑肿瘤数据集的98.01%、Figshare的MRI数据集的92.81%,以及GastroNet数据集的96.20%。与原基准相比有所改进。
Key Takeaways
- 医学疾病预测通过医学影像存在复杂性及挑战,包括数据噪声、模糊和图像质量不一等问题。
- 深度学习模型,如知识蒸馏(KD)方法,在脑肿瘤图像识别方面有所成就,但处理不确定性和跨不同医学状况推广时存在局限。
- 传统KD方法在处理医学图像中的不同不确定性时缺乏灵活性。
- 提出的结合蚁群优化(ACO)和上下文感知预测器的新框架能够更稳健地进行知识转移,并根据图像质量、疾病复杂性和教师模型信心调整温度。
- ACO能够高效选择最优教师-学生模型,在数据处理方面表现优异。
- 新框架在三个公开数据集上的评估结果显著优于当前最先进的方法。
- 新框架的准确率在Kaggle的MRI脑肿瘤数据集上达到98.01%,在Figshare的MRI数据集上达到92.81%,在GastroNet数据集上达到96.2%。
点此查看论文截图

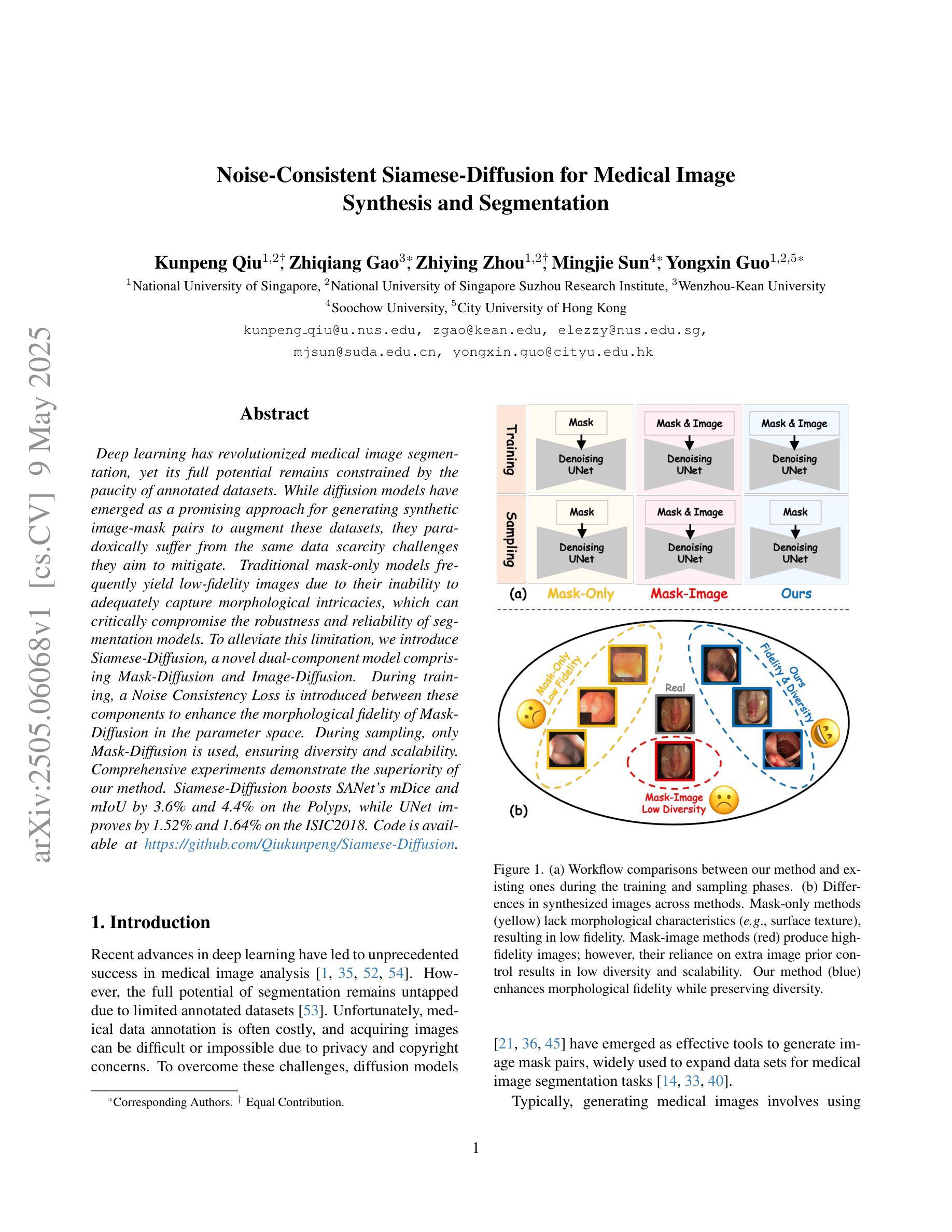
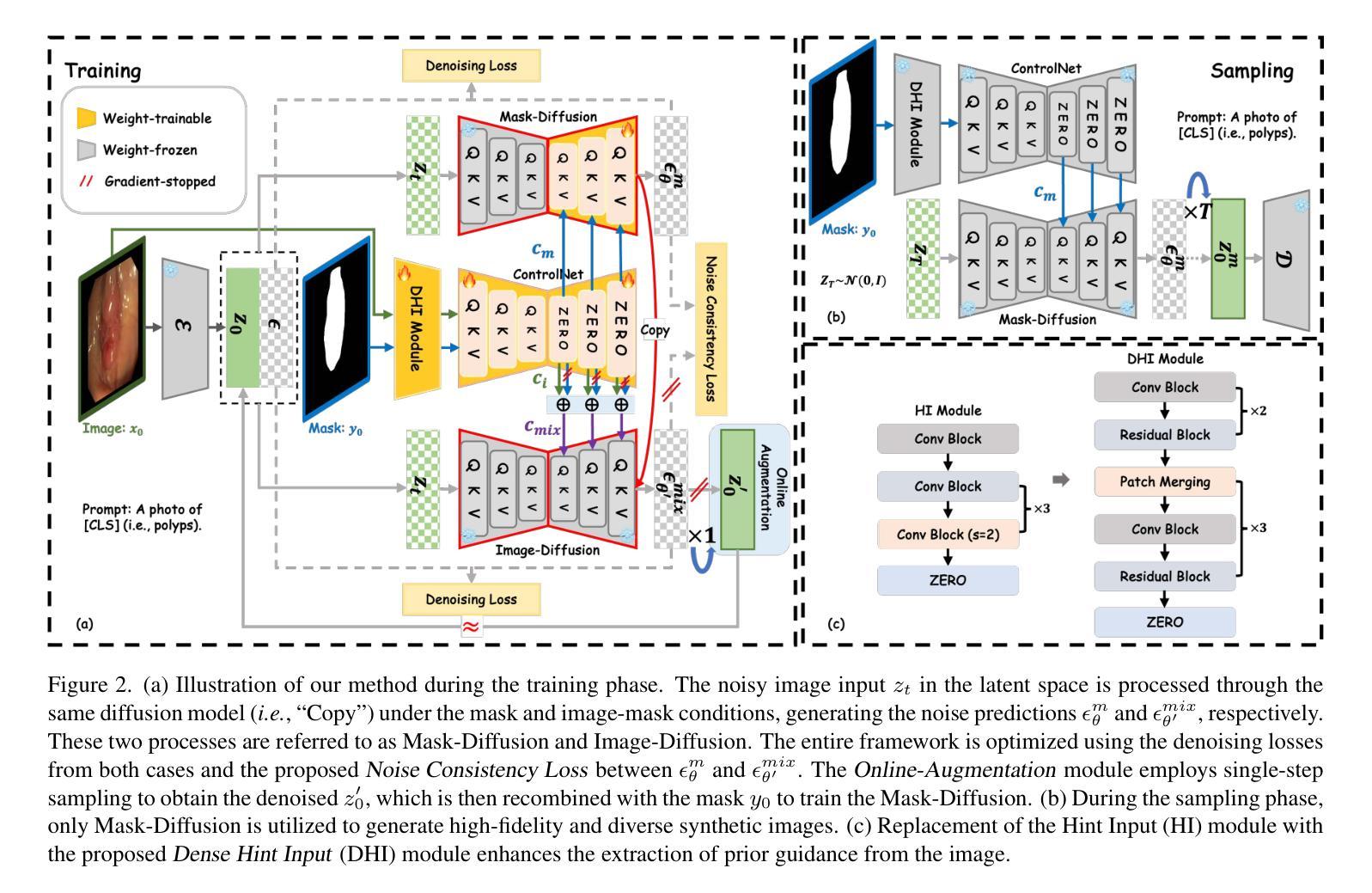
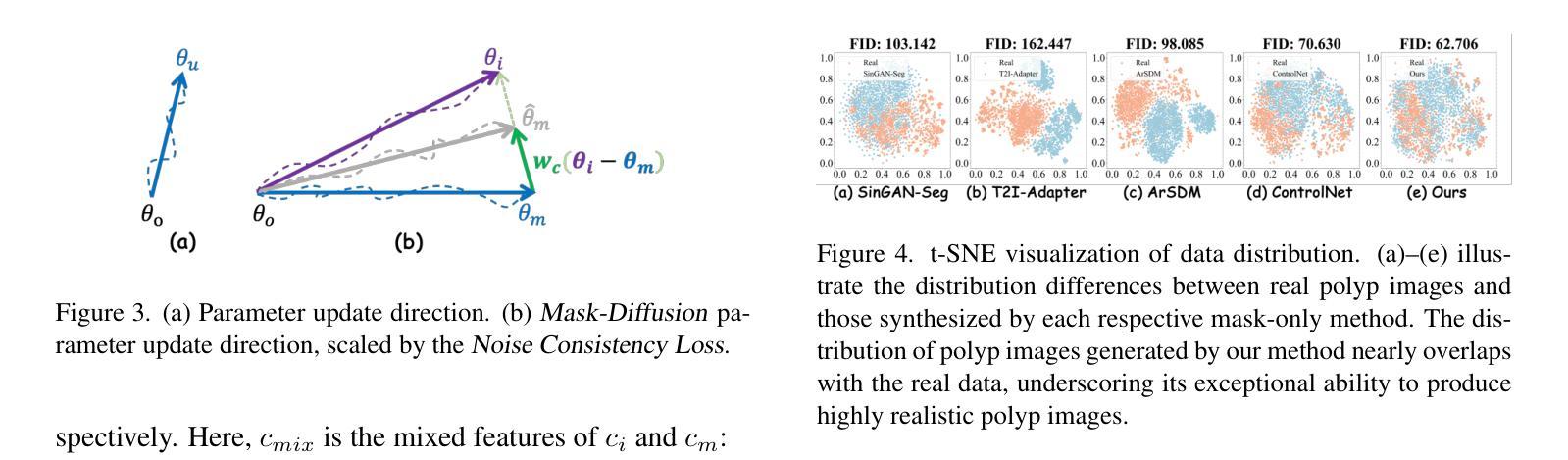
Noise-Consistent Siamese-Diffusion for Medical Image Synthesis and Segmentation
Authors:Kunpeng Qiu, Zhiqiang Gao, Zhiying Zhou, Mingjie Sun, Yongxin Guo
Deep learning has revolutionized medical image segmentation, yet its full potential remains constrained by the paucity of annotated datasets. While diffusion models have emerged as a promising approach for generating synthetic image-mask pairs to augment these datasets, they paradoxically suffer from the same data scarcity challenges they aim to mitigate. Traditional mask-only models frequently yield low-fidelity images due to their inability to adequately capture morphological intricacies, which can critically compromise the robustness and reliability of segmentation models. To alleviate this limitation, we introduce Siamese-Diffusion, a novel dual-component model comprising Mask-Diffusion and Image-Diffusion. During training, a Noise Consistency Loss is introduced between these components to enhance the morphological fidelity of Mask-Diffusion in the parameter space. During sampling, only Mask-Diffusion is used, ensuring diversity and scalability. Comprehensive experiments demonstrate the superiority of our method. Siamese-Diffusion boosts SANet’s mDice and mIoU by 3.6% and 4.4% on the Polyps, while UNet improves by 1.52% and 1.64% on the ISIC2018. Code is available at GitHub.
深度学习已经彻底改变了医学图像分割领域,但其潜力仍然受到标注数据集缺乏的限制。尽管扩散模型已成为生成合成图像-掩膜对以增强这些数据集的很有前途的方法,但它们却面临着自身想要缓解的数据稀缺挑战。传统的仅掩膜模型经常产生低保真度的图像,因为它们无法充分捕捉形态细节,这可能会严重损害分割模型的稳健性和可靠性。为了缓解这一局限性,我们引入了Siamese-Diffusion,这是一种新型的双组分模型,包括Mask-Diffusion和Image-Diffusion。在训练过程中,在这两个组件之间引入了噪声一致性损失,以增强Mask-Diffusion在参数空间中的形态保真度。在采样过程中,只使用Mask-Diffusion,以确保多样性和可扩展性。综合实验证明了我们方法的优越性。Siamese-Diffusion提高了Polyps上的SANet的mDice和mIoU分别为3.6%和4.4%,而UNet在ISIC2018上的改进分别为1.52%和1.64%。代码已在GitHub上提供。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by CVPR2025
Summary
深度学习在医学图像分割领域引发了革命性的变革,但受限于标注数据集的匮乏。尽管扩散模型在生成合成图像-掩膜对以扩充数据集方面展现出巨大潜力,但它们同样面临数据稀缺的挑战。传统仅使用掩膜模型因无法充分捕捉形态细节,常导致图像保真度低,从而严重影响分割模型的稳健性和可靠性。为缓解这一问题,我们提出Siamese-Diffusion,一种包含Mask-Diffusion和Image-Diffusion的双组分新型模型。训练过程中,引入噪声一致性损失,增强Mask-Diffusion的形态保真度。采样过程中仅使用Mask-Diffusion,确保多样性和可扩展性。实验证明,该方法具有优越性,Siamese-Diffusion提升Polyps上的SANet的mDice和mIoU分别为3.6%和4.4%,ISIC2018上的UNet分别提升1.52%和1.64%。代码已上传至GitHub。
Key Takeaways
- 深度学习在医学图像分割中的应用受到标注数据集缺乏的限制。
- 扩散模型是一种生成合成图像-掩膜对的潜力方法,用于扩充数据集,但也面临数据稀缺的挑战。
- 传统仅使用掩膜模型的图像保真度低,因无法充分捕捉形态细节,影响分割模型的稳健性和可靠性。
- 提出的Siamese-Diffusion模型包含Mask-Diffusion和Image-Diffusion双组分,旨在解决上述问题。
- 训练过程中引入噪声一致性损失,以提高Mask-Diffusion的形态保真度。
- Siamese-Diffusion模型在Polyps和ISIC2018数据集上的实验表现优异,相比传统方法有所提升。
点此查看论文截图
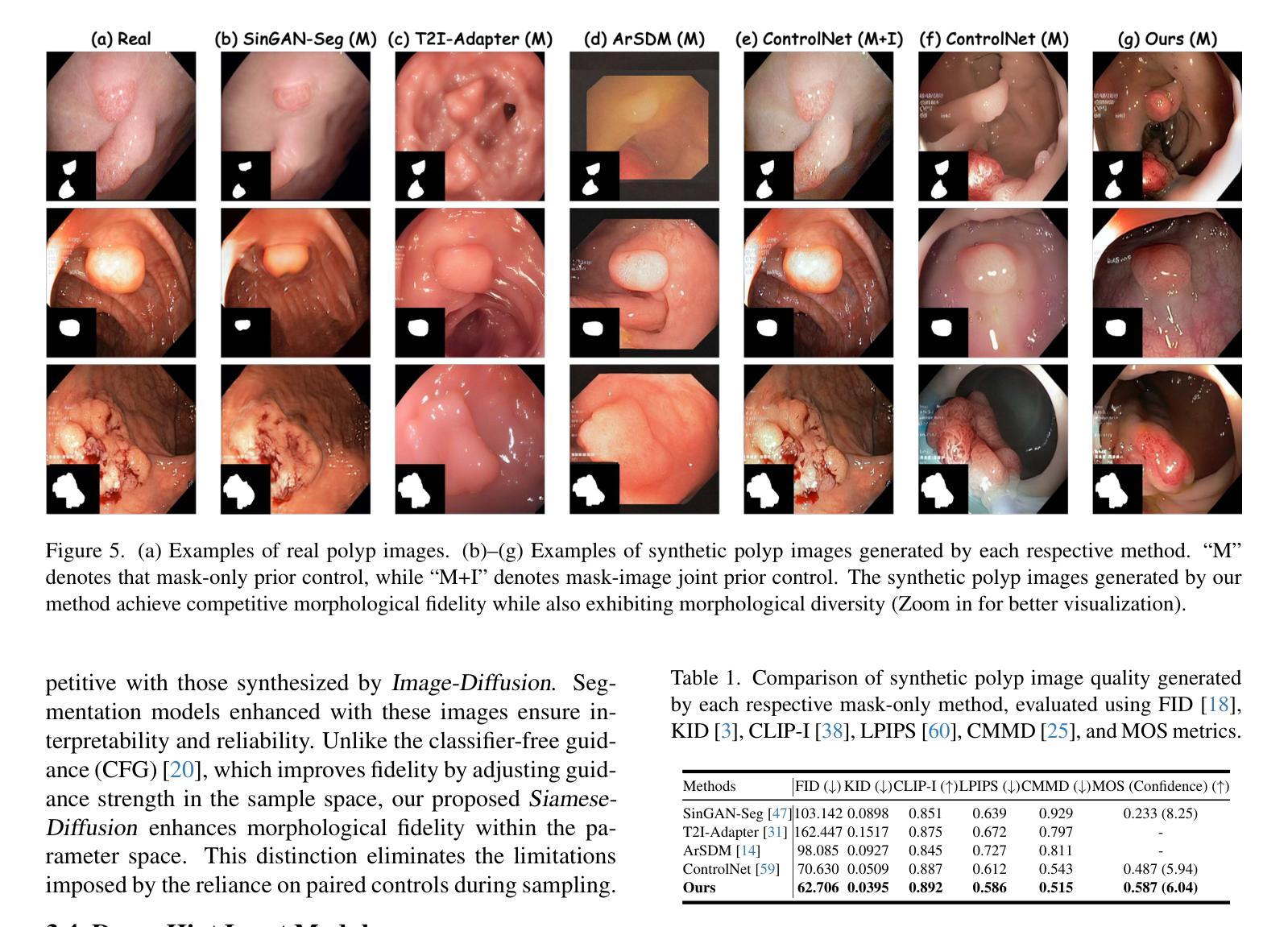
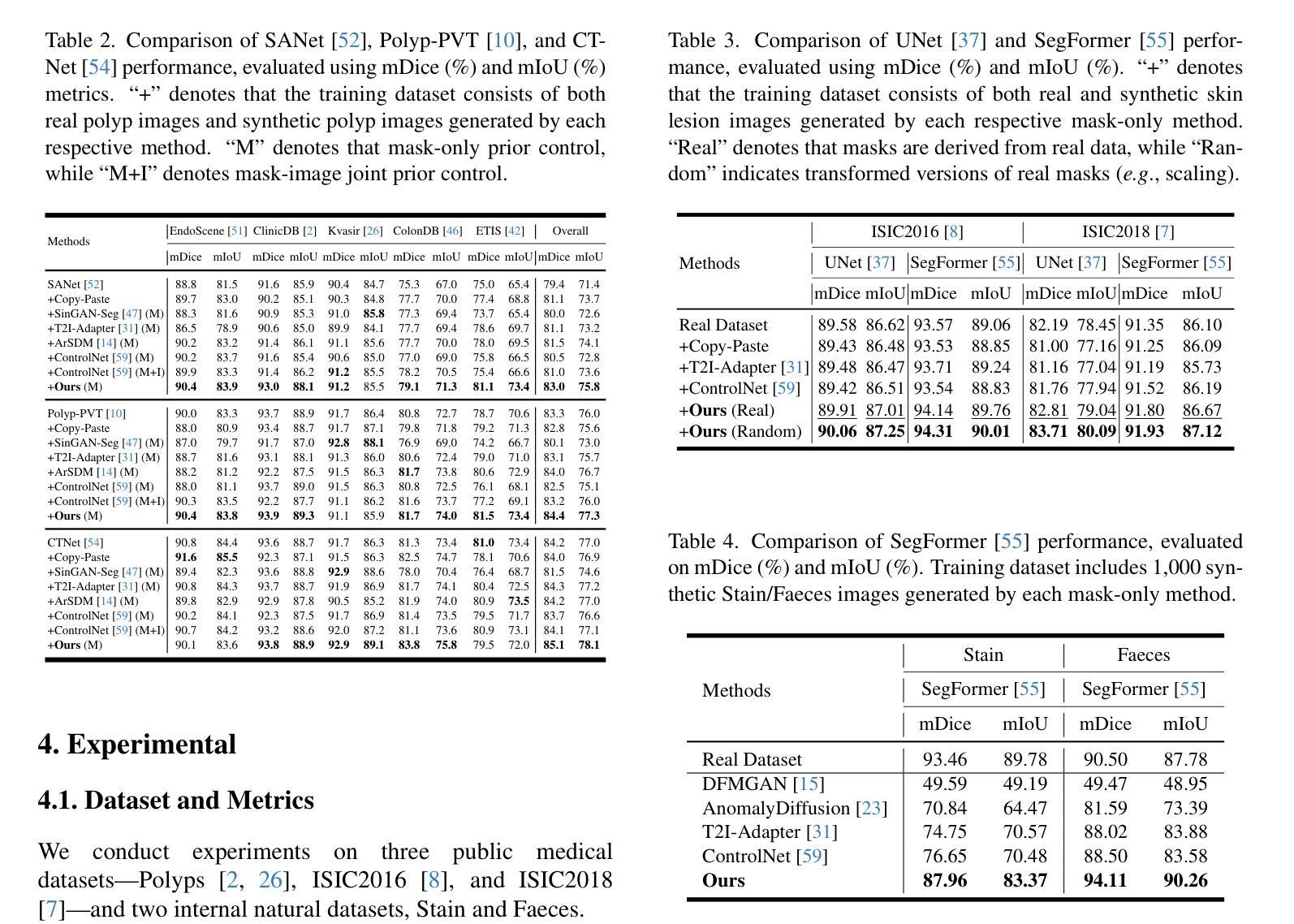
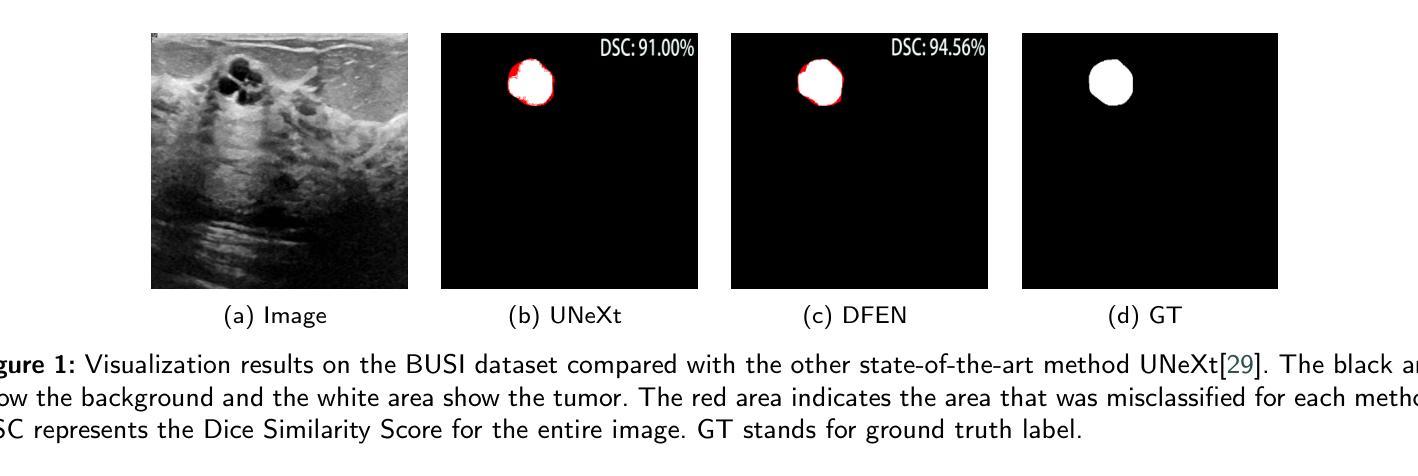
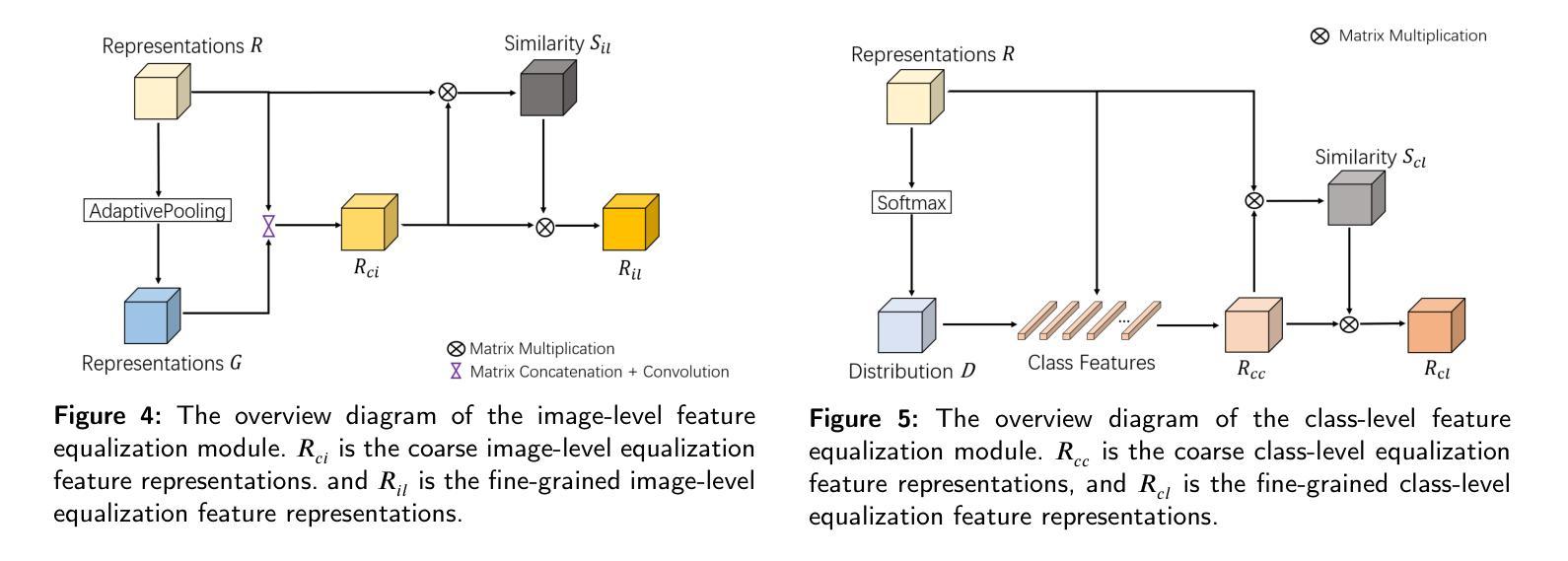
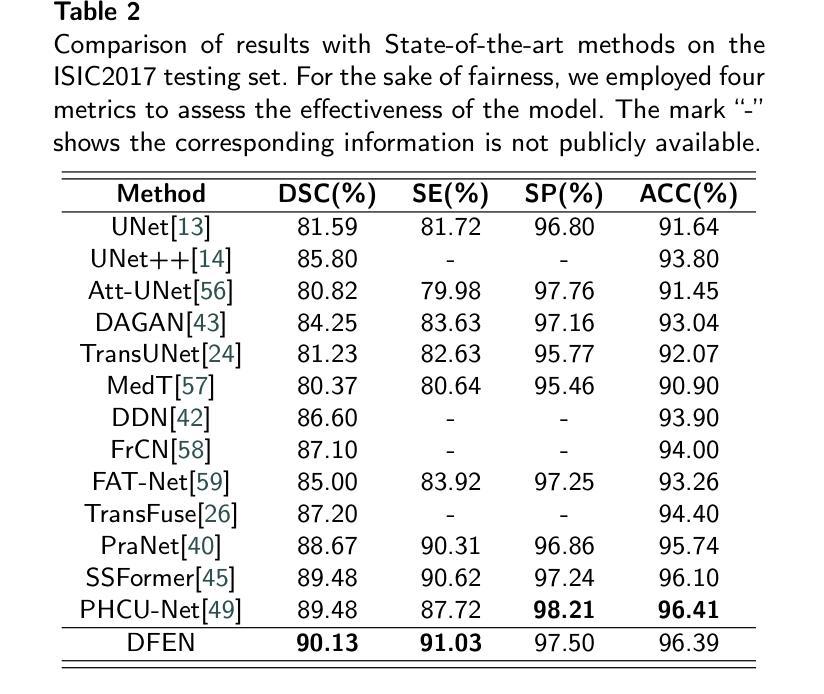
DFEN: Dual Feature Equalization Network for Medical Image Segmentation
Authors:Jianjian Yin, Yi Chen, Chengyu Li, Zhichao Zheng, Yanhui Gu, Junsheng Zhou
Current methods for medical image segmentation primarily focus on extracting contextual feature information from the perspective of the whole image. While these methods have shown effective performance, none of them take into account the fact that pixels at the boundary and regions with a low number of class pixels capture more contextual feature information from other classes, leading to misclassification of pixels by unequal contextual feature information. In this paper, we propose a dual feature equalization network based on the hybrid architecture of Swin Transformer and Convolutional Neural Network, aiming to augment the pixel feature representations by image-level equalization feature information and class-level equalization feature information. Firstly, the image-level feature equalization module is designed to equalize the contextual information of pixels within the image. Secondly, we aggregate regions of the same class to equalize the pixel feature representations of the corresponding class by class-level feature equalization module. Finally, the pixel feature representations are enhanced by learning weights for image-level equalization feature information and class-level equalization feature information. In addition, Swin Transformer is utilized as both the encoder and decoder, thereby bolstering the ability of the model to capture long-range dependencies and spatial correlations. We conducted extensive experiments on Breast Ultrasound Images (BUSI), International Skin Imaging Collaboration (ISIC2017), Automated Cardiac Diagnosis Challenge (ACDC) and PH$^2$ datasets. The experimental results demonstrate that our method have achieved state-of-the-art performance. Our code is publicly available at https://github.com/JianJianYin/DFEN.
当前医学图像分割的方法主要从整个图像的角度提取上下文特征信息。虽然这些方法已经展现出有效的性能,但它们都没有考虑到边界处的像素以及具有少量类别像素的区域能够从其他类别中获取更多的上下文特征信息,从而导致像素误分类,因为上下文特征信息是不平等的。在本文中,我们提出了一种基于Swin Transformer和卷积神经网络混合架构的双特征均衡网络,旨在通过图像级均衡特征信息和类别级均衡特征信息来增强像素特征表示。首先,设计了图像级特征均衡模块,以均衡图像内像素的上下文信息。其次,我们通过类别级特征均衡模块聚合同一类别的区域,以均衡相应类别的像素特征表示。最后,通过图像级均衡特征信息和类别级均衡特征信息的学习权重来增强像素特征表示。此外,Swin Transformer同时作为编码器和解码器,增强了模型捕捉长距离依赖性和空间关联性的能力。我们在乳腺超声图像(BUSI)、国际皮肤影像协作(ISIC2017)、自动心脏诊断挑战(ACDC)和PH数据集上进行了大量实验。实验结果表明,我们的方法达到了最先进的性能。我们的代码可在https://github.com/JianJianYin/DFEN公开获取。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
该文本提出了一种基于Swin Transformer和卷积神经网络混合架构的双特征均衡网络,用于增强像素特征表示。该网络通过图像级特征均衡模块和类别级特征均衡模块,均衡图像内像素的上下文信息和同类像素的特征表示。此外,Swin Transformer同时作为编码器和解码器,提高了模型捕捉长距离依赖和空间关联的能力。在多个数据集上的实验结果表明,该方法达到了最先进的性能。
Key Takeaways
- 当前医学图像分割方法主要关注从整个图像的角度提取上下文特征信息。
- 现有方法忽略了边界像素和具有较少类别像素的区域,这些区域从其他类别捕获更多的上下文特征信息,导致像素误分类。
- 提出的双特征均衡网络旨在通过图像级和类别级的特征均衡信息来增强像素特征表示。
- 网络设计包括图像级特征均衡模块,用于均衡图像内像素的上下文信息。
- 通过类别级特征均衡模块,网络聚合同一类别的区域,均衡相应类别的像素特征表示。
- Swin Transformer作为编码器和解码器,提高了模型捕捉长距离依赖和空间关联的能力。
点此查看论文截图


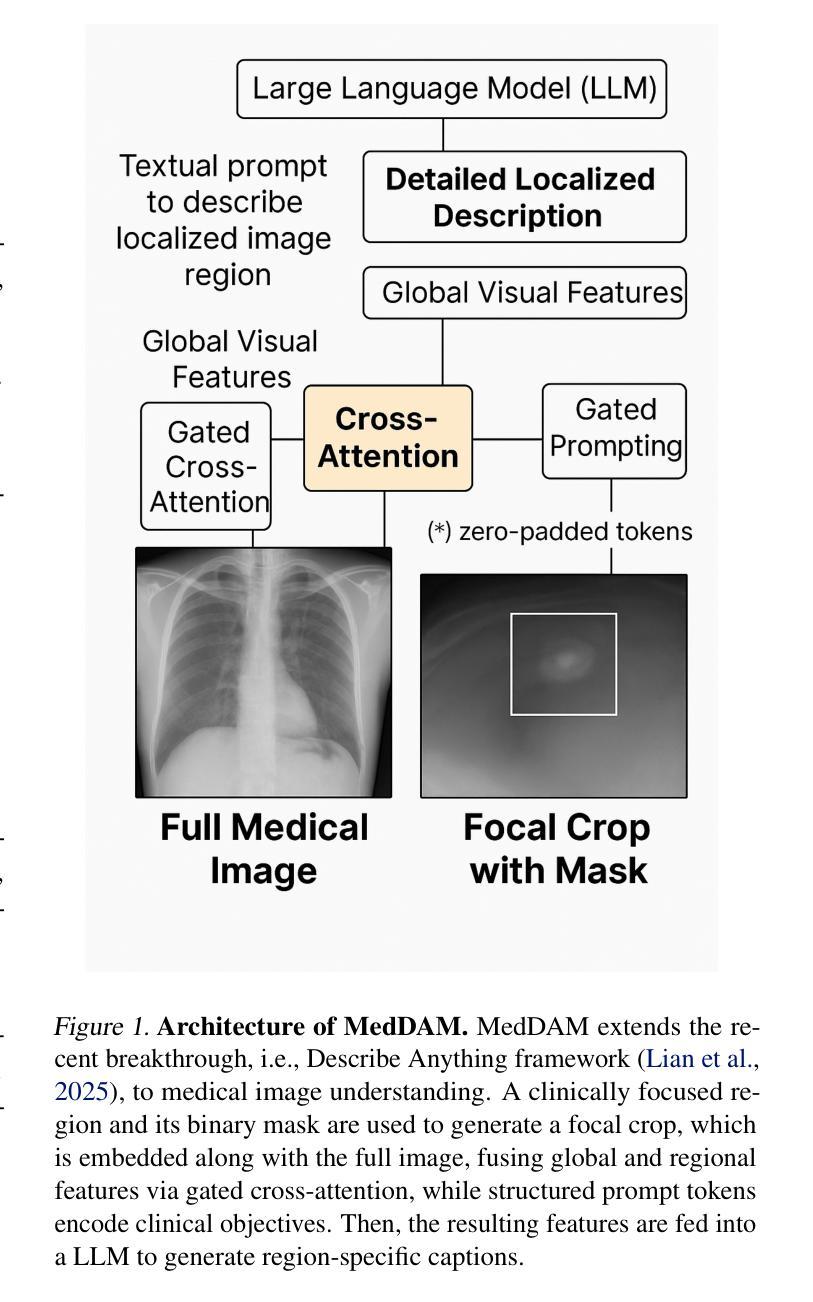
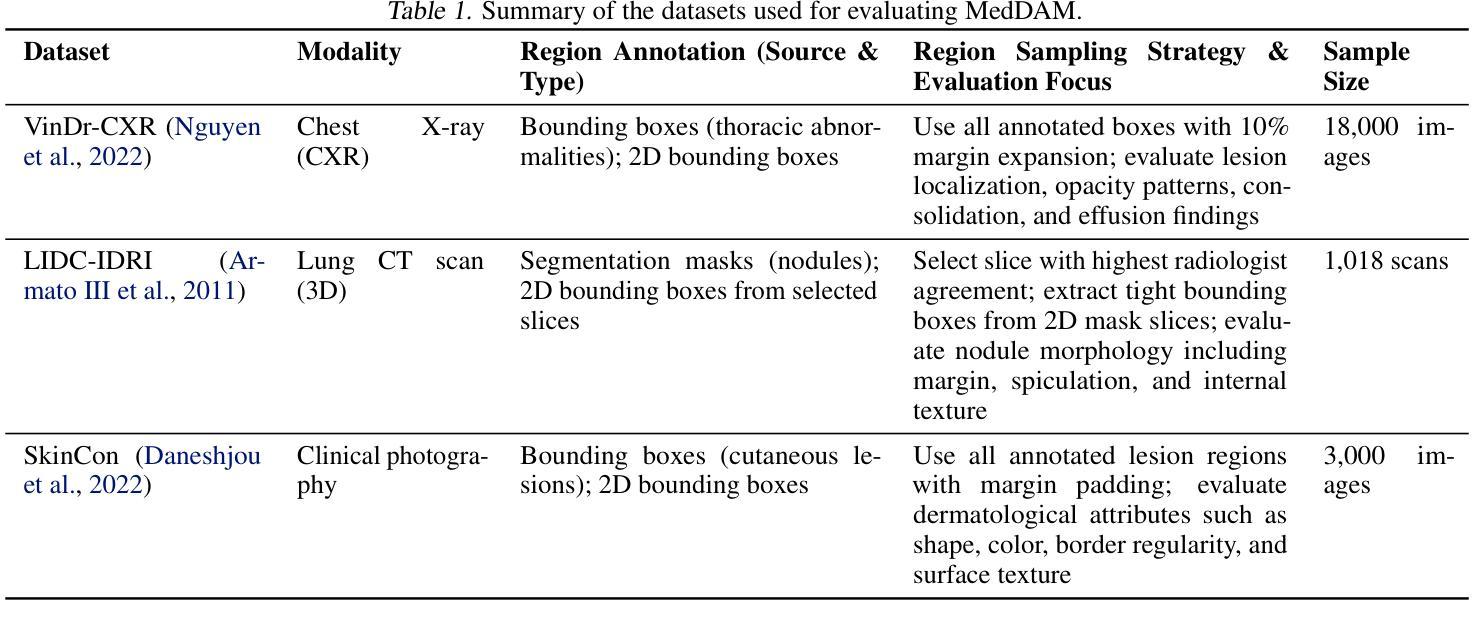
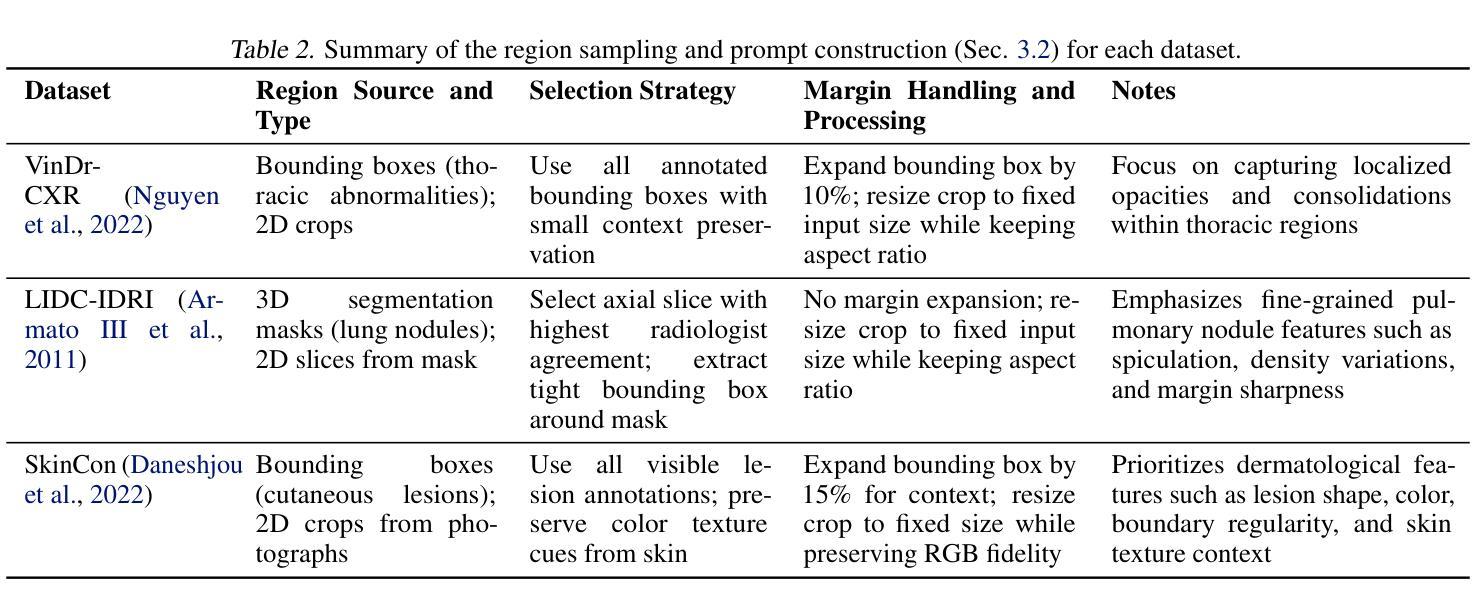
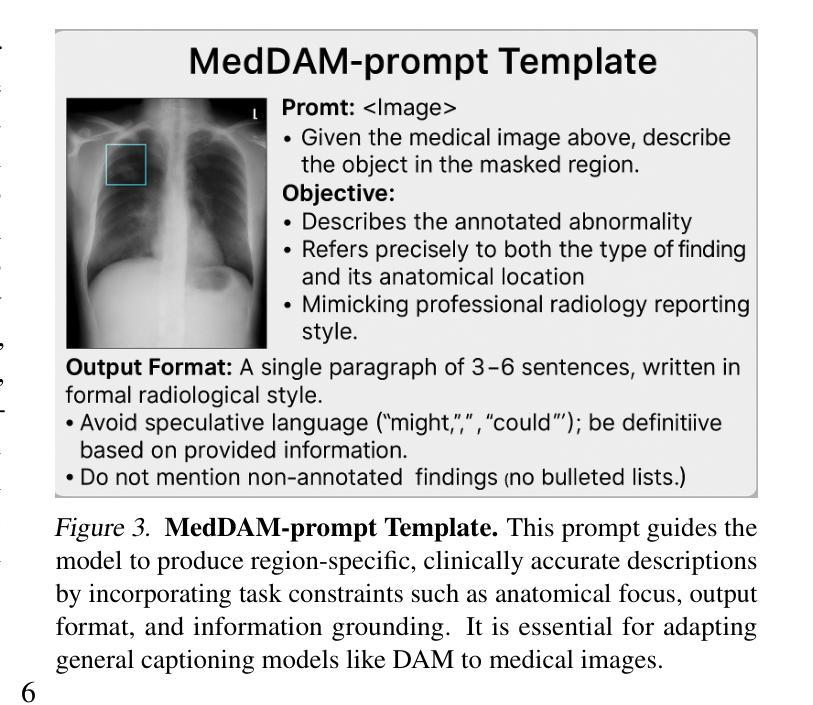
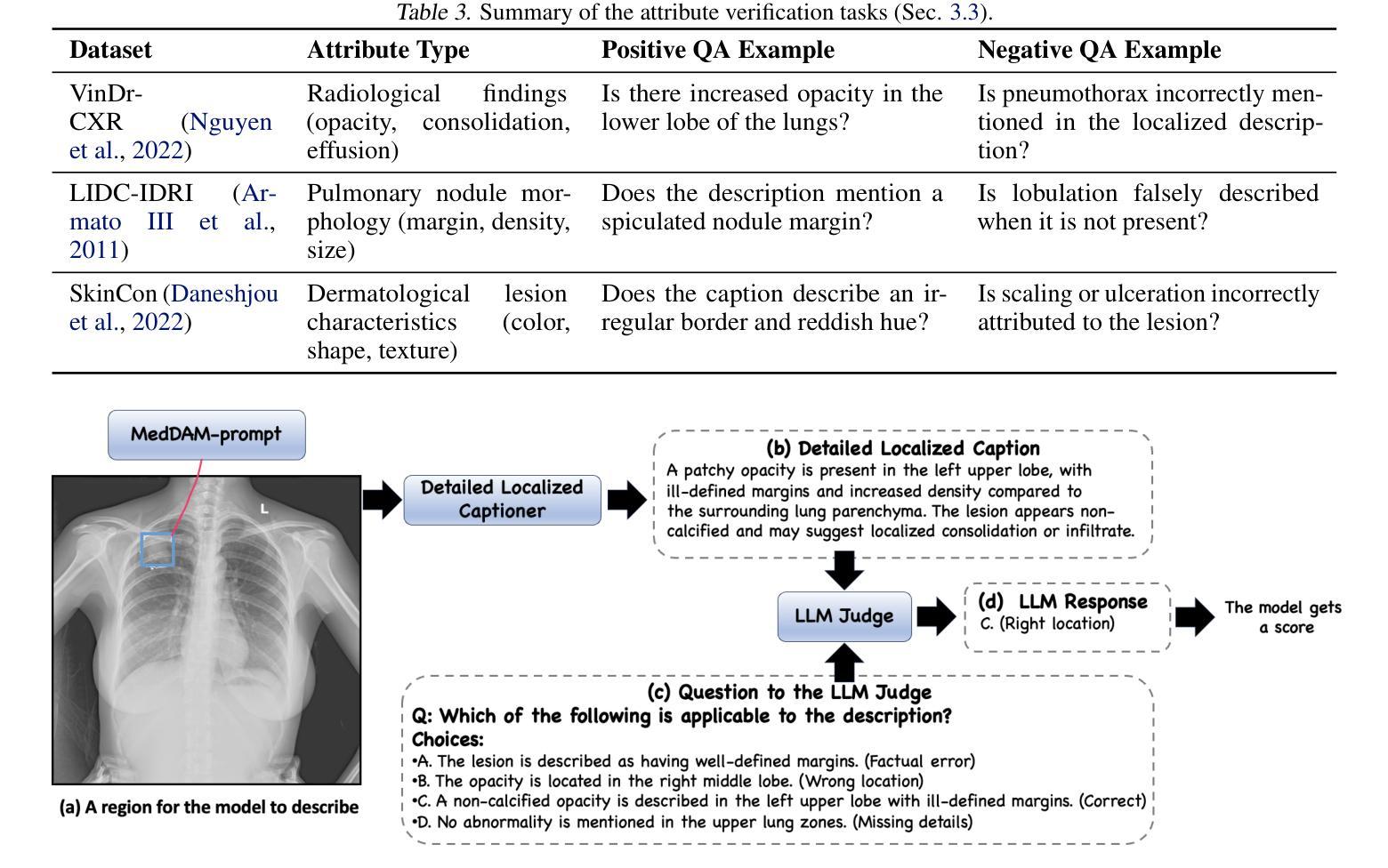
Describe Anything in Medical Images
Authors:Xi Xiao, Yunbei Zhang, Thanh-Huy Nguyen, Ba-Thinh Lam, Janet Wang, Jihun Hamm, Tianyang Wang, Xingjian Li, Xiao Wang, Hao Xu, Tianming Liu, Min Xu
Localized image captioning has made significant progress with models like the Describe Anything Model (DAM), which can generate detailed region-specific descriptions without explicit region-text supervision. However, such capabilities have yet to be widely applied to specialized domains like medical imaging, where diagnostic interpretation relies on subtle regional findings rather than global understanding. To mitigate this gap, we propose MedDAM, the first comprehensive framework leveraging large vision-language models for region-specific captioning in medical images. MedDAM employs medical expert-designed prompts tailored to specific imaging modalities and establishes a robust evaluation benchmark comprising a customized assessment protocol, data pre-processing pipeline, and specialized QA template library. This benchmark evaluates both MedDAM and other adaptable large vision-language models, focusing on clinical factuality through attribute-level verification tasks, thereby circumventing the absence of ground-truth region-caption pairs in medical datasets. Extensive experiments on the VinDr-CXR, LIDC-IDRI, and SkinCon datasets demonstrate MedDAM’s superiority over leading peers (including GPT-4o, Claude 3.7 Sonnet, LLaMA-3.2 Vision, Qwen2.5-VL, GPT-4Rol, and OMG-LLaVA) in the task, revealing the importance of region-level semantic alignment in medical image understanding and establishing MedDAM as a promising foundation for clinical vision-language integration.
局部图像描述在诸如Describe Anything Model(DAM)等模型的推动下取得了显著进展,这些模型能够在没有明确的区域文本监督的情况下生成详细的区域特定描述。然而,这种能力尚未广泛应用于医学成像等特定领域,诊断解读依赖于细微的区域发现而非全局理解。为了弥补这一差距,我们提出了MedDAM,这是第一个利用大型视觉语言模型进行医学图像区域特定描述的全面框架。MedDAM采用针对特定成像模式设计的医学专家提示,并建立了一个稳健的评估基准,包括定制评估协议、数据预处理管道和专用问答模板库。该基准不仅评估MedDAM的性能,还评估其他可适应的大型视觉语言模型,通过属性级别验证任务关注临床事实性,从而规避医学数据集中缺乏地面真实区域标题对的问题。在VinDr-CXR、LIDC-IDRI和SkinCon数据集上的大量实验表明,MedDAM在任务中优于领先的对标模型(包括GPT-4o、Claude 3.7 Sonnet、LLaMA-3.2 Vision、Qwen2.5-VL、GPT-4Rol和OMG-LLaVA),揭示了医学图像理解中区域级语义对齐的重要性,并确立了MedDAM作为临床视觉语言集成的有前途的基础。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文主要介绍了针对医学图像区域特定的描述模型MedDAM的发展和应用。MedDAM利用大型视觉语言模型,能够在医学图像中进行区域特定的描述,并建立了包含自定义评估协议、数据预处理管道和专门的质量保证模板库的综合评估基准。在多个数据集上的实验证明了MedDAM在医学图像理解中的优越性。
Key Takeaways
- MedDAM是首个针对医学图像区域特定描述的综合框架,利用大型视觉语言模型进行描述。
- MedDAM采用医学专家设计的针对特定成像模式的提示。
- 建立了包含自定义评估协议、数据预处理管道和专门质量保证模板库的综合评估基准。
- MedDAM重点评估临床事实性,通过属性级别的验证任务来克服医学数据集中缺乏真实区域标题对的问题。
- 在多个数据集上的实验表明,MedDAM在医学图像理解任务中优于其他大型视觉语言模型。
- MedDAM的重要性在于其在医学图像理解中的区域级语义对齐。
点此查看论文截图

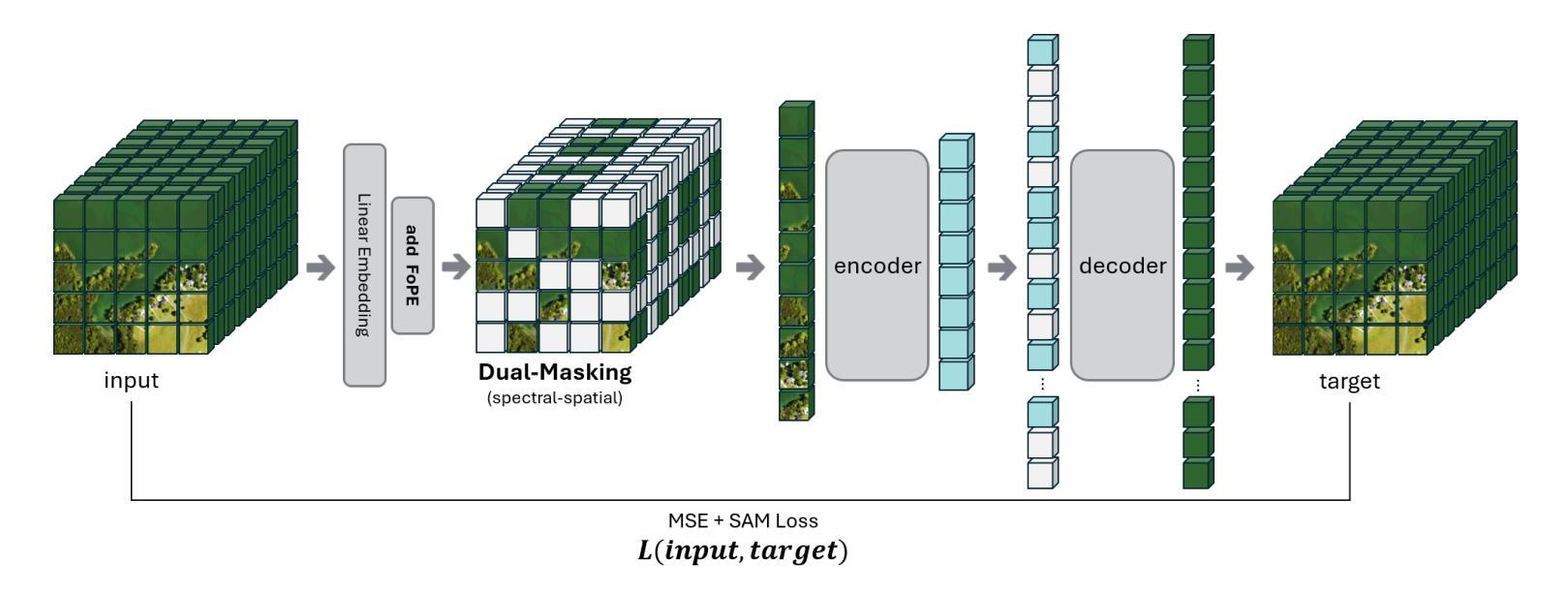
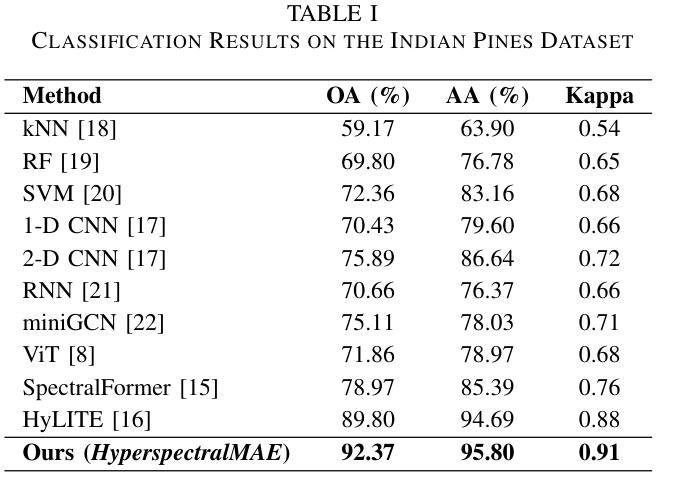
HyperspectralMAE: The Hyperspectral Imagery Classification Model using Fourier-Encoded Dual-Branch Masked Autoencoder
Authors:Wooyoung Jeong, Hyun Jae Park, Seonghun Jeong, Jong Wook Jang, Tae Hoon Lim, Dae Seoung Kim
Hyperspectral imagery provides rich spectral detail but poses unique challenges because of its high dimensionality in both spatial and spectral domains. We propose \textit{HyperspectralMAE}, a Transformer-based foundation model for hyperspectral data that employs a \textit{dual masking} strategy: during pre-training we randomly occlude 50% of spatial patches and 50% of spectral bands. This forces the model to learn representations capable of reconstructing missing information across both dimensions. To encode spectral order, we introduce learnable harmonic Fourier positional embeddings based on wavelength. The reconstruction objective combines mean-squared error (MSE) with the spectral angle mapper (SAM) to balance pixel-level accuracy and spectral-shape fidelity. The resulting model contains about $1.8\times10^{8}$ parameters and produces 768-dimensional embeddings, giving it sufficient capacity for transfer learning. We pre-trained HyperspectralMAE on two large hyperspectral corpora – NASA EO-1 Hyperion ($\sim$1,600 scenes, $\sim$$3\times10^{11}$ pixel spectra) and DLR EnMAP Level-0 ($\sim$1,300 scenes, $\sim$$3\times10^{11}$ pixel spectra) – and fine-tuned it for land-cover classification on the Indian Pines benchmark. HyperspectralMAE achieves state-of-the-art transfer-learning accuracy on Indian Pines, confirming that masked dual-dimensional pre-training yields robust spectral-spatial representations. These results demonstrate that dual masking and wavelength-aware embeddings advance hyperspectral image reconstruction and downstream analysis.
高光谱成像提供了丰富的光谱细节,但同时也因其空间与光谱域的高维度特性带来了独特的挑战。我们提出了基于Transformer的高光谱数据基础模型——HyperspectralMAE。该模型采用双重掩蔽策略:在预训练过程中,我们随机遮挡50%的空间斑块和50%的光谱波段。这迫使模型学习能够在两个维度上重建缺失信息的能力。为了编码光谱顺序,我们基于波长引入了可学习的谐波傅里叶位置嵌入。重建目标结合了均方误差(MSE)与光谱角度映射器(SAM),以平衡像素级精度和光谱形状保真度。所得模型包含约1.8×10^8个参数,生成768维嵌入,为迁移学习提供了足够的容量。我们在两个大型高光谱语料库——NASA EO-1 Hyperion(约1600个场景,约3×10^11像素光谱)和DLR EnMAP Level-0(约1300个场景,约3×10^11像素光谱)上预训练了HyperspectralMAE模型,并在印度松树土地覆盖分类任务上进行了微调。HyperspectralMAE在Indian Pines基准测试上达到了最先进的迁移学习精度,证实了掩蔽双重维度预训练能够产生稳健的光谱空间表示。这些结果表明,双重掩蔽和波长感知嵌入在推进高光谱图像重建和下游分析方面具有重要意义。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文提出一种名为HyperspectralMAE的基于Transformer的用于高光谱数据的模型。它采用双重掩码策略进行预训练,能够学习在空间和光谱两个维度上重建缺失信息的能力。引入基于波长的可学习谐波傅里叶位置嵌入来编码光谱顺序。重建目标结合了均方误差(MSE)和光谱角度映射器(SAM),以实现像素级精度和光谱形状保真度的平衡。模型在大型高光谱数据集上进行预训练,并在印度松树基准测试上进行微调,实现了最先进的迁移学习精度。
Key Takeaways
模型引入双重掩码策略,在空间和光谱两个维度上训练模型重建缺失信息的能力。
模型采用可学习谐波傅里叶位置嵌入,基于波长编码光谱顺序。
重建目标结合了均方误差和光谱角度映射器,实现像素级和光谱级的准确性平衡。
模型预训练在两个大型高光谱数据集上进行,包含约一亿八千万参数和768维嵌入,具有足够的迁移学习能力。
模型在印度松树基准测试上实现了最先进的迁移学习精度。
实验结果表明双重掩码和波长感知嵌入能够推进高光谱图像重建和下游分析。
点此查看论文截图

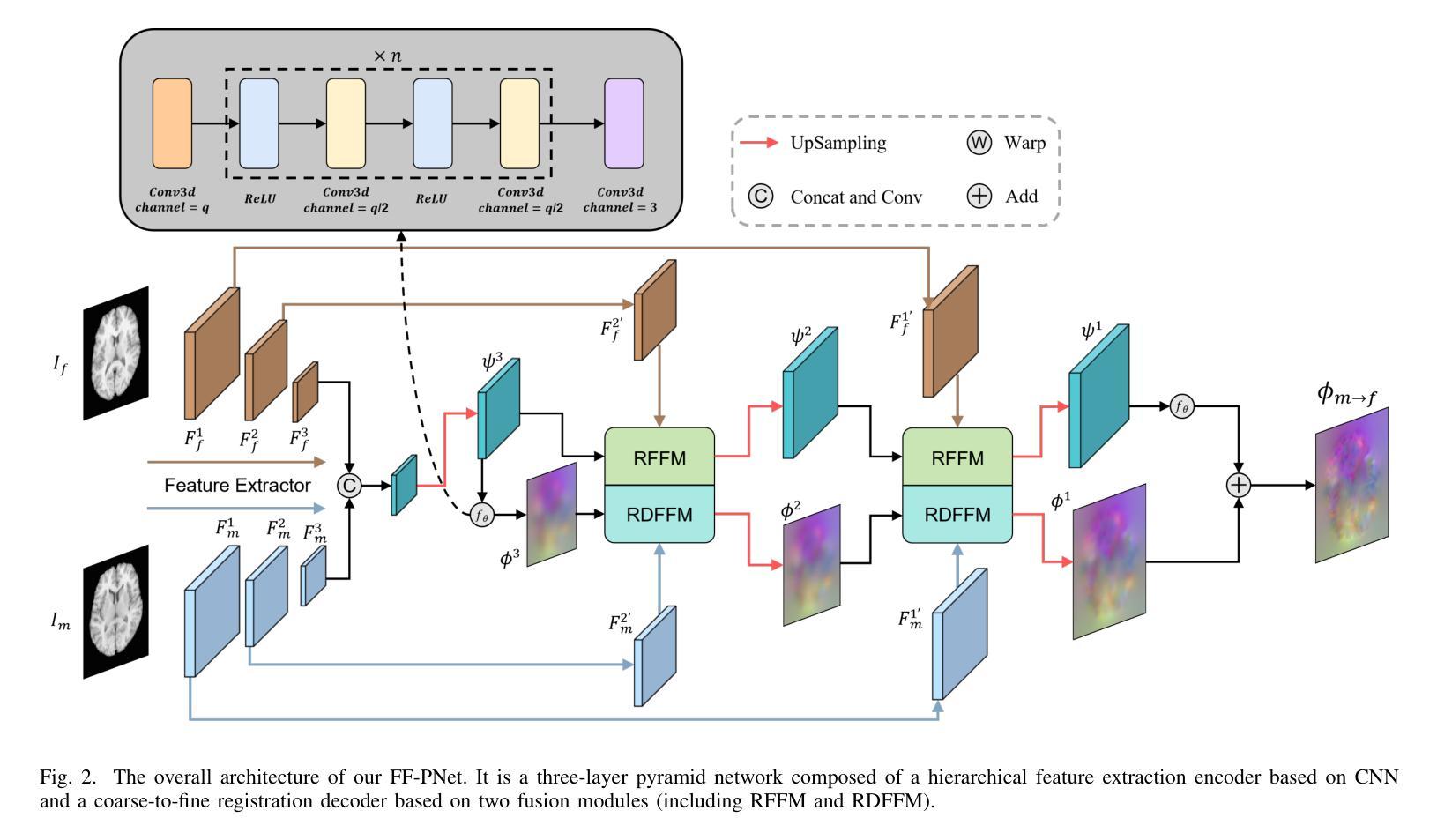
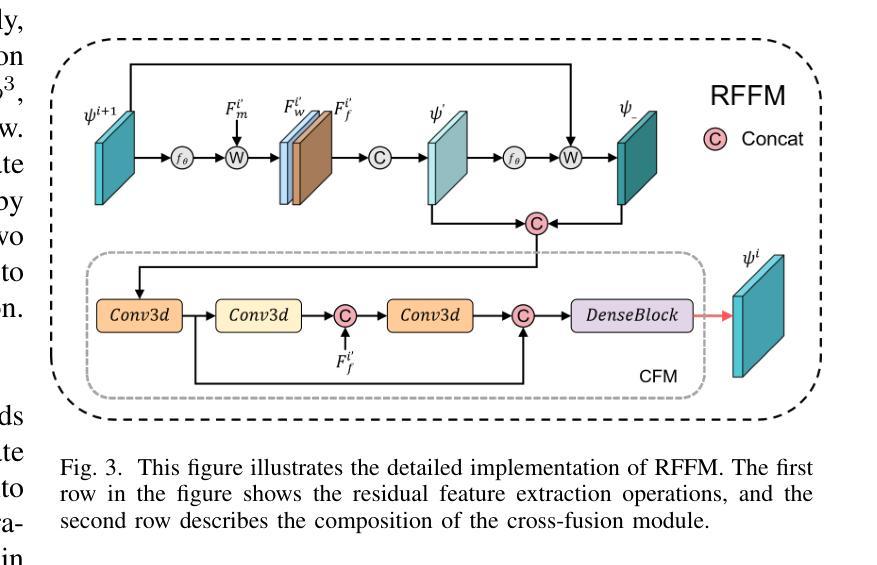
FF-PNet: A Pyramid Network Based on Feature and Field for Brain Image Registration
Authors:Ying Zhang, Shuai Guo, Chenxi Sun, Yuchen Zhu, Jinhai Xiang
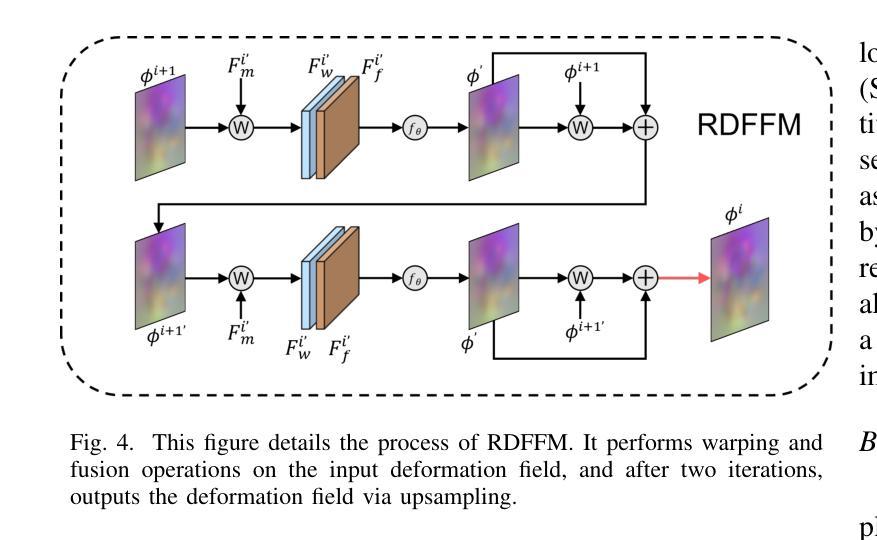
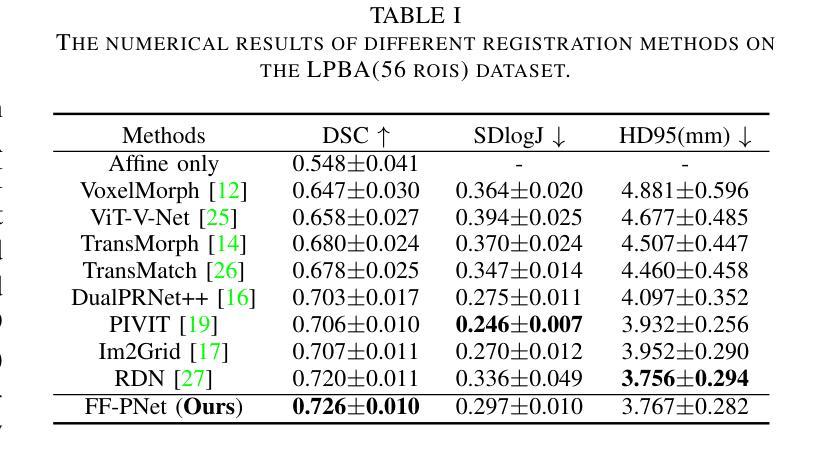
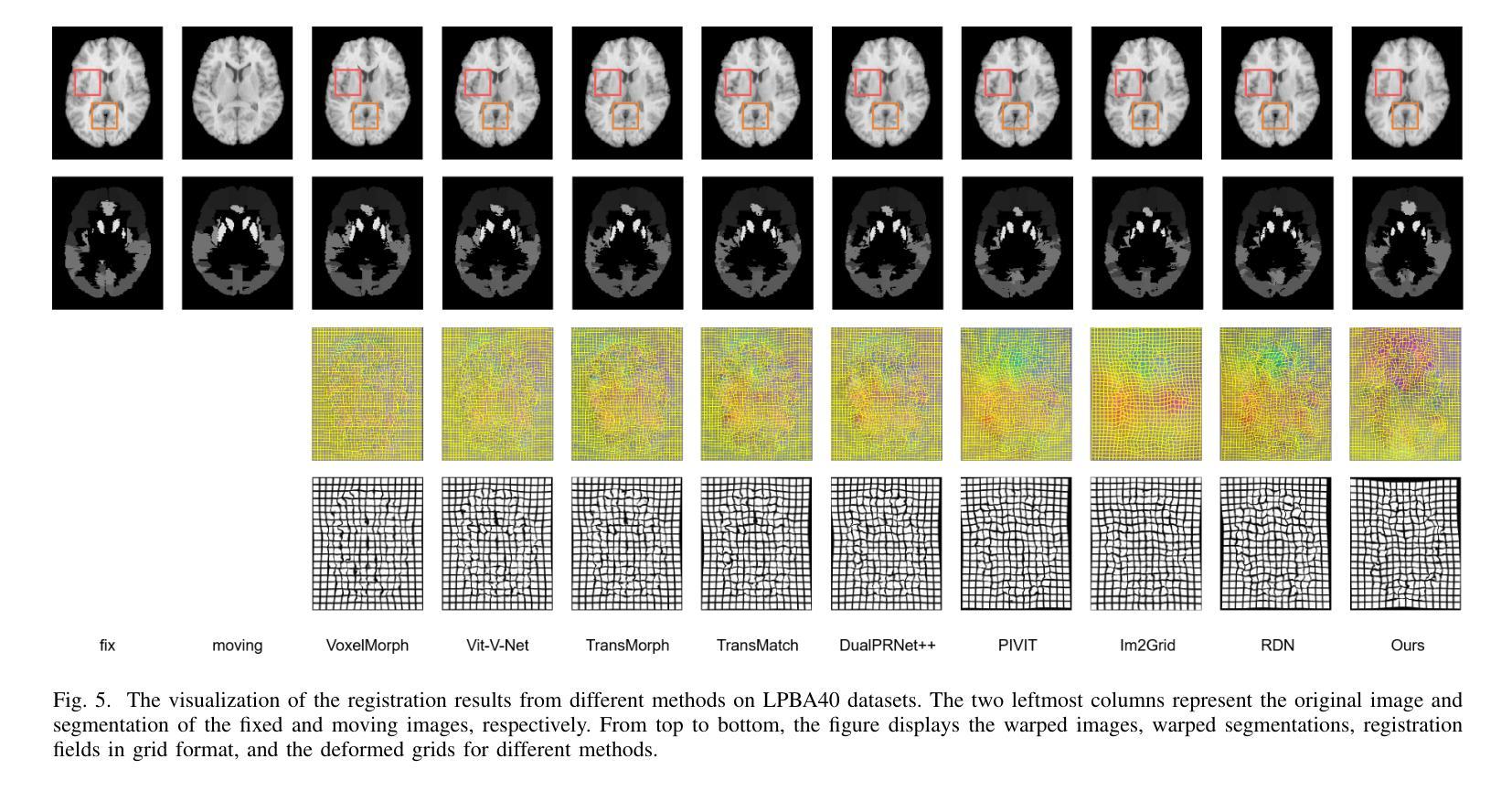
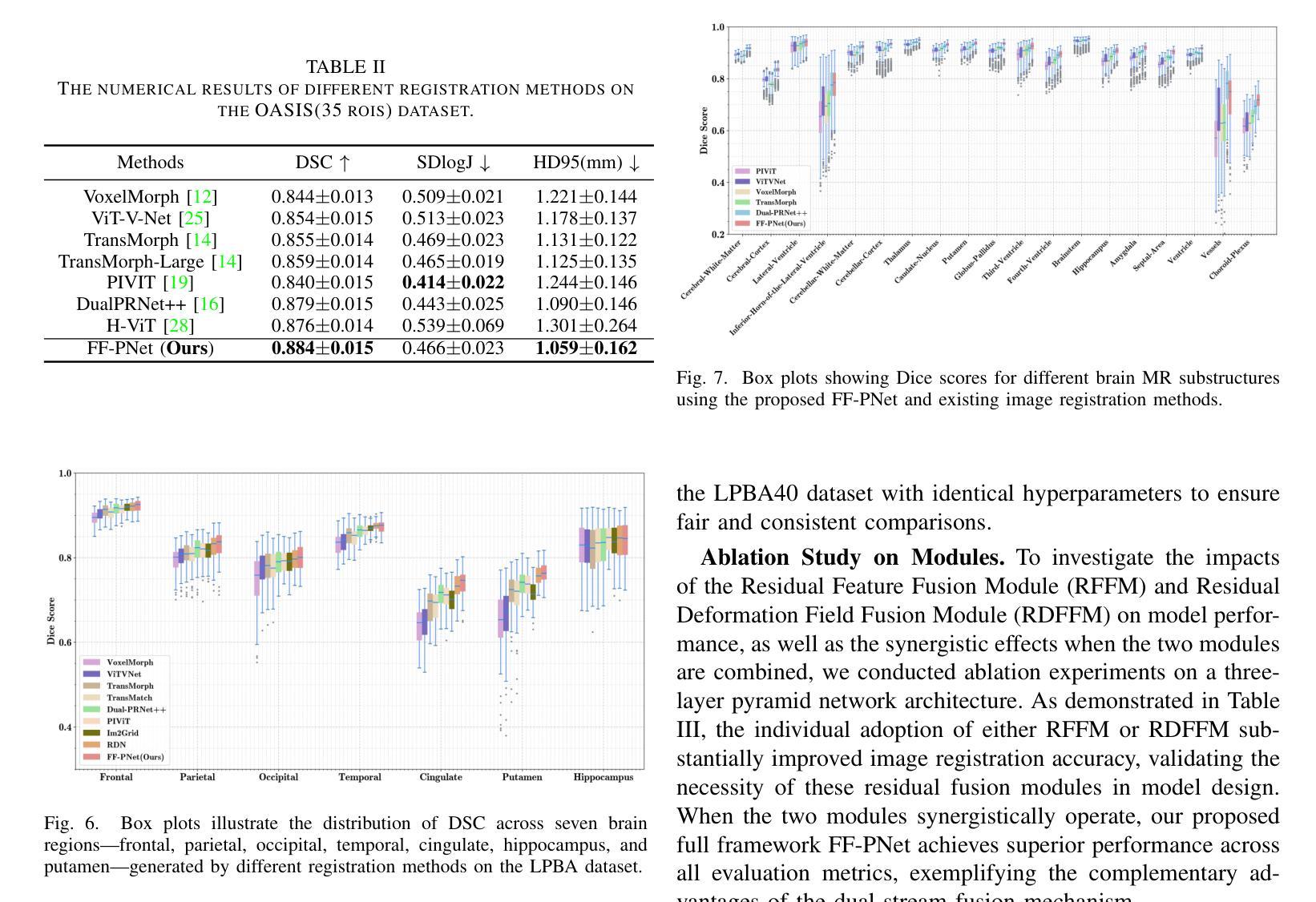
In recent years, deformable medical image registration techniques have made significant progress. However, existing models still lack efficiency in parallel extraction of coarse and fine-grained features. To address this, we construct a new pyramid registration network based on feature and deformation field (FF-PNet). For coarse-grained feature extraction, we design a Residual Feature Fusion Module (RFFM), for fine-grained image deformation, we propose a Residual Deformation Field Fusion Module (RDFFM). Through the parallel operation of these two modules, the model can effectively handle complex image deformations. It is worth emphasizing that the encoding stage of FF-PNet only employs traditional convolutional neural networks without any attention mechanisms or multilayer perceptrons, yet it still achieves remarkable improvements in registration accuracy, fully demonstrating the superior feature decoding capabilities of RFFM and RDFFM. We conducted extensive experiments on the LPBA and OASIS datasets. The results show our network consistently outperforms popular methods in metrics like the Dice Similarity Coefficient.
近年来,可变形医学图像配准技术取得了重大进展。然而,现有模型在粗粒度和细粒度特征的并行提取方面仍缺乏效率。为解决这一问题,我们构建了一个基于特征和变形场(FF-PNet)的新金字塔配准网络。对于粗粒度特征提取,我们设计了残差特征融合模块(RFFM),对于细粒度图像变形,我们提出了残差变形场融合模块(RDFFM)。这两个模块的并行操作使模型能够有效地处理复杂的图像变形。值得一提的是,FF-PNet的编码阶段仅采用传统的卷积神经网络,没有任何注意力机制或多层感知器,但在配准精度上仍实现了显著的改进,充分展示了RFFM和RDFFM的优秀特征解码能力。我们在LPBA和OASIS数据集上进行了大量实验。结果表明,我们的网络在Dice相似系数等指标上始终优于流行的方法。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
医学图像配准技术近年来取得显著进展,但仍存在粗粒度和细粒度特征并行提取效率不足的问题。为此,我们构建了基于特征和变形场的新型金字塔配准网络(FF-PNet)。为提取粗粒度特征,设计了Residual Feature Fusion Module(RFFM);为处理图像精细变形,提出了Residual Deformation Field Fusion Module(RDFFM)。这两个模块的并行操作使得模型能更有效地处理复杂的图像变形。该网络在LPBA和OASIS数据集上的实验结果证明,即使在无注意力机制或多层感知器的情况下,仅使用传统的卷积神经网络,我们的网络在配准精度上仍有显著提升,充分展示了RFFM和RDFFM的特征解码优势。
Key Takeaways
- 现有医学图像配准技术仍存在粗粒度和细粒度特征并行提取效率问题。
- 提出了一种新的金字塔配准网络(FF-PNet),融合了特征和变形场。
- 设计了Residual Feature Fusion Module(RFFM)用于粗粒度特征提取。
- 提出了Residual Deformation Field Fusion Module(RDFFM)处理图像精细变形。
- FF-PNet通过并行操作这两个模块,更有效地处理复杂图像变形。
- 实验结果表明,FF-PNet在配准精度上显著优于其他方法。
点此查看论文截图

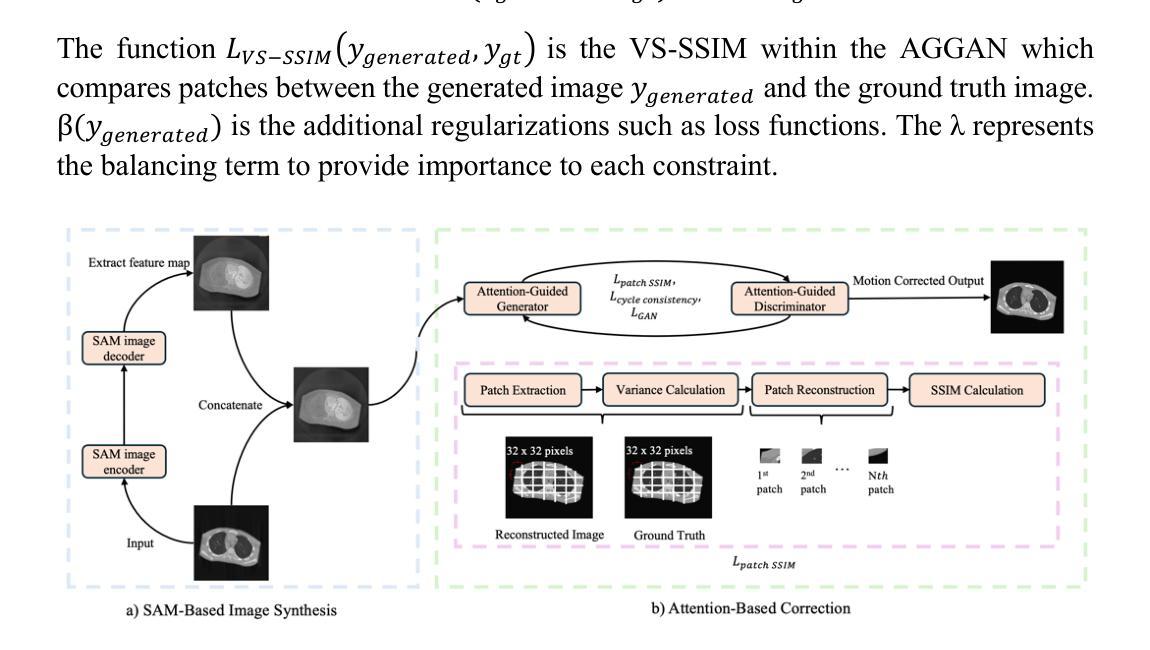
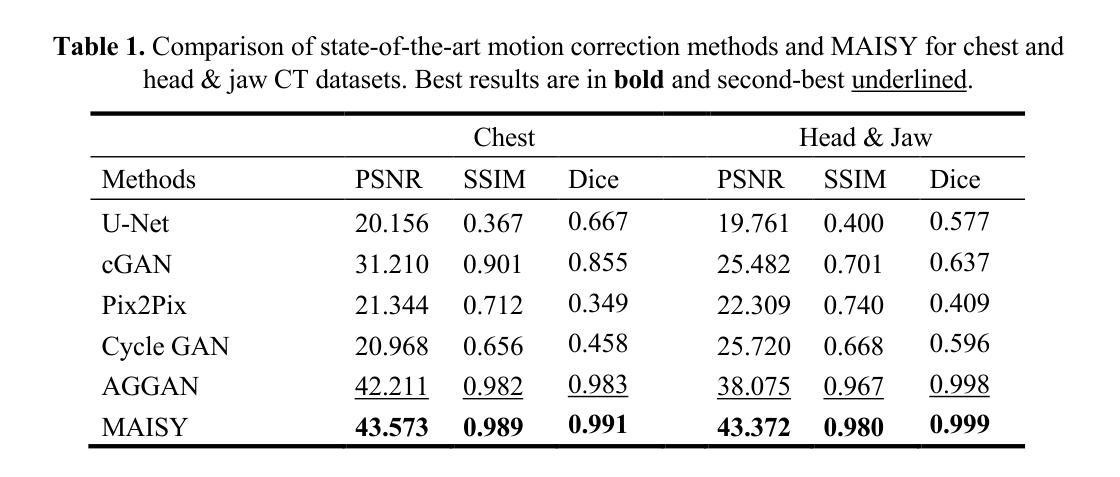
MAISY: Motion-Aware Image SYnthesis for Medical Image Motion Correction
Authors:Andrew Zhang, Hao Wang, Shuchang Ye, Michael Fulham, Jinman Kim
Patient motion during medical image acquisition causes blurring, ghosting, and distorts organs, which makes image interpretation challenging. Current state-of-the-art algorithms using Generative Adversarial Network (GAN)-based methods with their ability to learn the mappings between corrupted images and their ground truth via Structural Similarity Index Measure (SSIM) loss effectively generate motion-free images. However, we identified the following limitations: (i) they mainly focus on global structural characteristics and therefore overlook localized features that often carry critical pathological information, and (ii) the SSIM loss function struggles to handle images with varying pixel intensities, luminance factors, and variance. In this study, we propose Motion-Aware Image SYnthesis (MAISY) which initially characterize motion and then uses it for correction by: (a) leveraging the foundation model Segment Anything Model (SAM), to dynamically learn spatial patterns along anatomical boundaries where motion artifacts are most pronounced and, (b) introducing the Variance-Selective SSIM (VS-SSIM) loss which adaptively emphasizes spatial regions with high pixel variance to preserve essential anatomical details during artifact correction. Experiments on chest and head CT datasets demonstrate that our model outperformed the state-of-the-art counterparts, with Peak Signal-to-Noise Ratio (PSNR) increasing by 40%, SSIM by 10%, and Dice by 16%.
患者在医学图像采集过程中的运动会导致图像模糊、出现残影和器官扭曲,这使得图像解读具有挑战性。当前最先进的算法使用基于生成对抗网络(GAN)的方法,它们能够通过结构相似性指数度量(SSIM)损失来学习失真图像与真实图像之间的映射,从而有效地生成无运动图像。然而,我们发现了以下局限性:(i)它们主要关注全局结构特征,因此忽略了通常携带关键病理信息的局部特征;(ii)SSIM损失函数在处理像素强度、亮度因素和方差各异的图像时遇到困难。在这项研究中,我们提出了运动感知图像合成(MAISY),它首先表征运动,然后利用运动进行修正:(a)通过利用“任何内容分割模型”(SAM)的基础,动态学习解剖边界处的空间模式,这些边界是运动伪影最明显的区域;(b)引入方差选择性SSIM(VS-SSIM)损失,该损失能够自适应地强调具有高像素方差的区域,从而在纠正伪影时保留关键的解剖细节。对胸部和头部CT数据集的实验表明,我们的模型优于当前最先进的模型,峰值信噪比(PSNR)提高了40%,结构相似性指数度量(SSIM)提高了10%,迪杰斯特拉系数提高了16%。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文探讨了医学图像获取过程中患者运动导致的图像模糊、鬼影和器官扭曲问题,使得图像解读具有挑战性。现有算法虽可使用生成对抗网络(GAN)基于结构相似性指数(SSIM)损失生成无运动图像,但仍存在忽略局部特征和SSIM损失函数处理像素强度、亮度因素和方差差异较大的图像时表现不佳的局限性。本研究提出Motion-Aware Image SYnthesis(MAISY),首先表征运动,然后利用运动信息进行校正:通过利用Segment Anything Model(SAM)基础模型动态学习解剖边界的空间模式来突出运动伪影,并引入Variance-Selective SSIM(VS-SSIM)损失,以在伪影校正过程中自适应强调高像素方差的区域,保留关键的解剖细节。实验表明,该模型在胸部和头部CT数据集上的表现优于现有技术,峰值信噪比(PSNR)提高40%,结构相似性指数(SSIM)提高10%,狄氏系数提高16%。
Key Takeaways
- 患者运动在医学图像获取中导致图像模糊、鬼影和器官扭曲,使得解读困难。
- 当前算法使用GAN和SSIM损失处理运动伪影,但主要关注全局结构特征,忽视包含重要病理信息的局部特征。
- SSIM损失在处理像素强度、亮度因素和方差不同的图像时存在困难。
- 提出Motion-Aware Image SYnthesis(MAISY)模型,通过Segment Anything Model(SAM)动态学习解剖边界的空间模式来识别运动伪影。
- MAISY引入Variance-Selective SSIM(VS-SSIM)损失,自适应强调像素方差高的区域,以保留关键解剖细节。
- 实验表明,MAISY在胸部和头部CT数据集上的表现优于现有技术。
点此查看论文截图

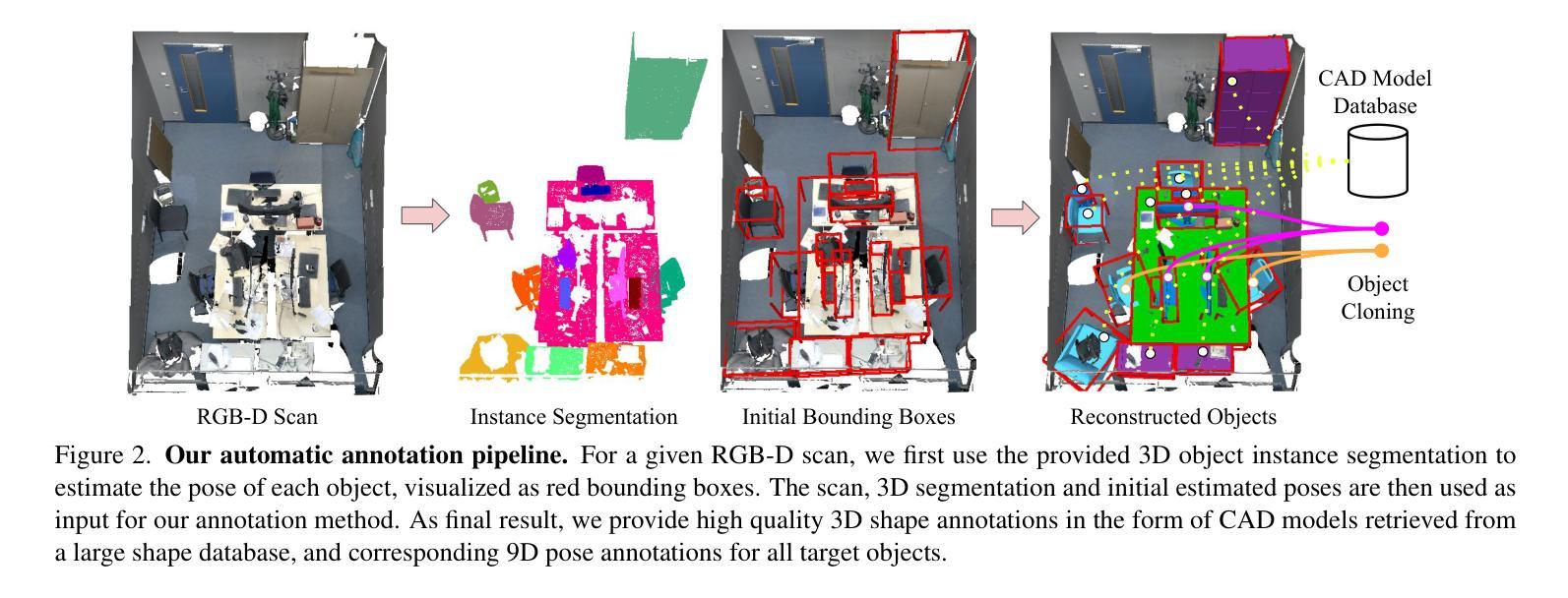
Leveraging Automatic CAD Annotations for Supervised Learning in 3D Scene Understanding
Authors:Yuchen Rao, Stefan Ainetter, Sinisa Stekovic, Vincent Lepetit, Friedrich Fraundorfer
High-level 3D scene understanding is essential in many applications. However, the challenges of generating accurate 3D annotations make development of deep learning models difficult. We turn to recent advancements in automatic retrieval of synthetic CAD models, and show that data generated by such methods can be used as high-quality ground truth for training supervised deep learning models. More exactly, we employ a pipeline akin to the one previously used to automatically annotate objects in ScanNet scenes with their 9D poses and CAD models. This time, we apply it to the recent ScanNet++ v1 dataset, which previously lacked such annotations. Our findings demonstrate that it is not only possible to train deep learning models on these automatically-obtained annotations but that the resulting models outperform those trained on manually annotated data. We validate this on two distinct tasks: point cloud completion and single-view CAD model retrieval and alignment. Our results underscore the potential of automatic 3D annotations to enhance model performance while significantly reducing annotation costs. To support future research in 3D scene understanding, we will release our annotations, which we call SCANnotate++, along with our trained models.
高级三维场景理解在许多应用中至关重要。然而,生成精确三维注释的挑战使得深度学习模型的开发变得困难。我们转向最近自动检索合成CAD模型的进展,并证明通过此类方法生成的数据可以用作训练有监督深度学习模型的高质量真实标注。更具体地说,我们采用了一条类似于之前用于ScanNet场景中自动标注对象与其九维姿态和CAD模型的管道。这次,我们将其应用于最新的ScanNet++ v1数据集,该数据集之前缺乏此类注释。我们的研究结果表明,不仅可以在这些自动获得的注释上训练深度学习模型,而且得到的模型的性能超过了在手动注释数据上训练的模型。我们通过两个独立的任务验证了这一点:点云补全和单视图CAD模型检索与对齐。我们的结果突出了自动三维注释在提高模型性能的同时显著降低标注成本的潜力。为了支持未来的三维场景理解研究,我们将发布我们的注释(我们称之为SCANnotate++),以及我们训练的模型。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Project page: https://stefan-ainetter.github.io/SCANnotatepp; CVPR’25 Workshop
Summary
本文利用自动检索合成CAD模型的新技术,解决了生成准确3D注释的挑战性问题。文章通过类似ScanNet场景对象自动标注的管道,对缺乏此类标注的ScanNet++ v1数据集进行标注。实验表明,不仅可以在这些自动获得的标注上训练深度学习模型,而且所得模型的性能还优于手动标注数据训练的模型。这为自动3D注释在增强模型性能的同时显著降低标注成本提供了可能。文章最后发布了名为SCANnotate++的标注及训练模型,以支持未来的3D场景理解研究。
Key Takeaways
- 文中探讨了在许多应用中,高级三维场景理解的重要性及其所面临的挑战。特别是在生成准确三维注释方面存在的困难对深度学习模型的开发造成了影响。
- 最近在自动检索合成CAD模型方面的进展被应用于文章中讨论的问题,这些技术进步能解决深度学习中训练样本注释的难题。
- 文章通过使用类似ScanNet场景的管道,成功对缺乏此类标注的ScanNet++ v1数据集进行了自动标注。这一方法利用先前用于对象自动标注的技术,但这次应用到了新的数据集上。
- 实验证明,使用自动获取的注释训练深度学习模型不仅可行,而且结果模型的表现超越了手动注释数据训练的模型。这一发现体现在点云补全和单视图CAD模型检索与对齐两个任务上。
- 自动三维注释技术具有提高模型性能同时显著降低标注成本的潜力。这一技术的实际应用价值得到了验证。
- 为了支持未来的研究,文章发布了名为SCANnotate++的注释以及训练好的模型。这将为三维场景理解研究提供新的资源。
点此查看论文截图


Comprehensive Analysis of Relative Pressure Estimation Methods Utilizing 4D Flow MRI
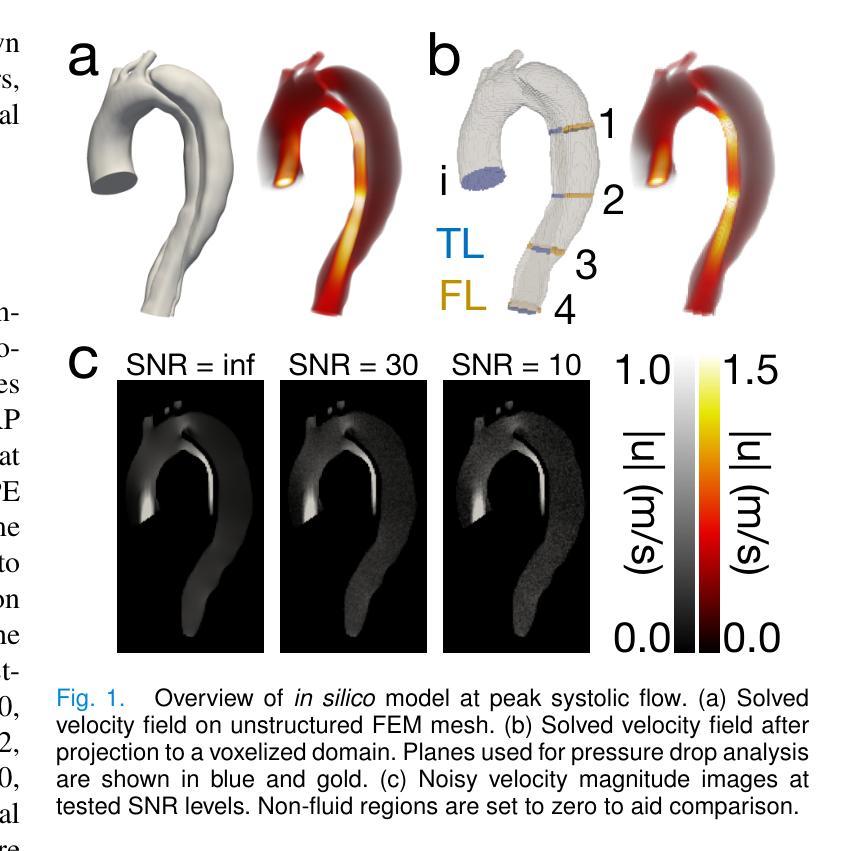
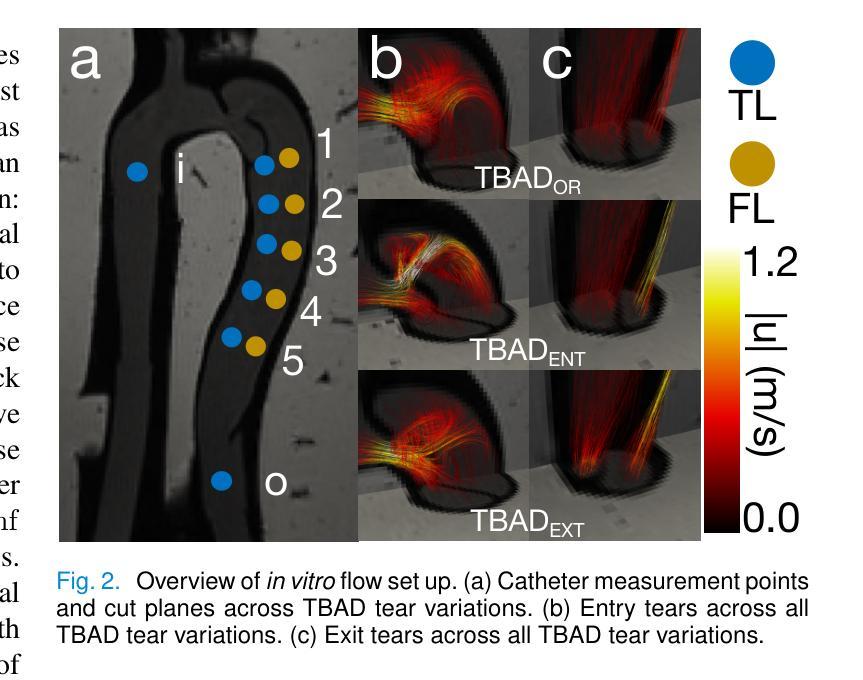
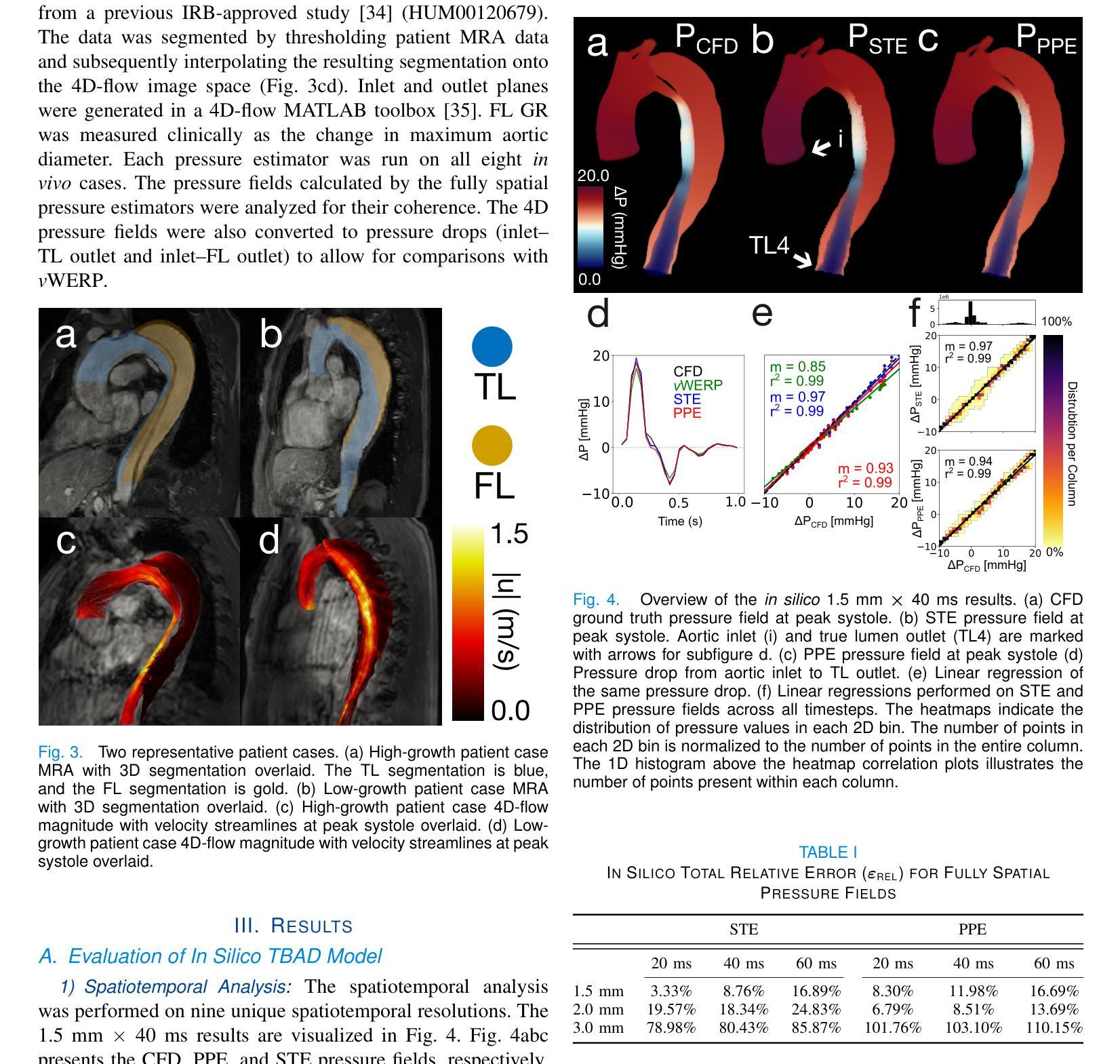
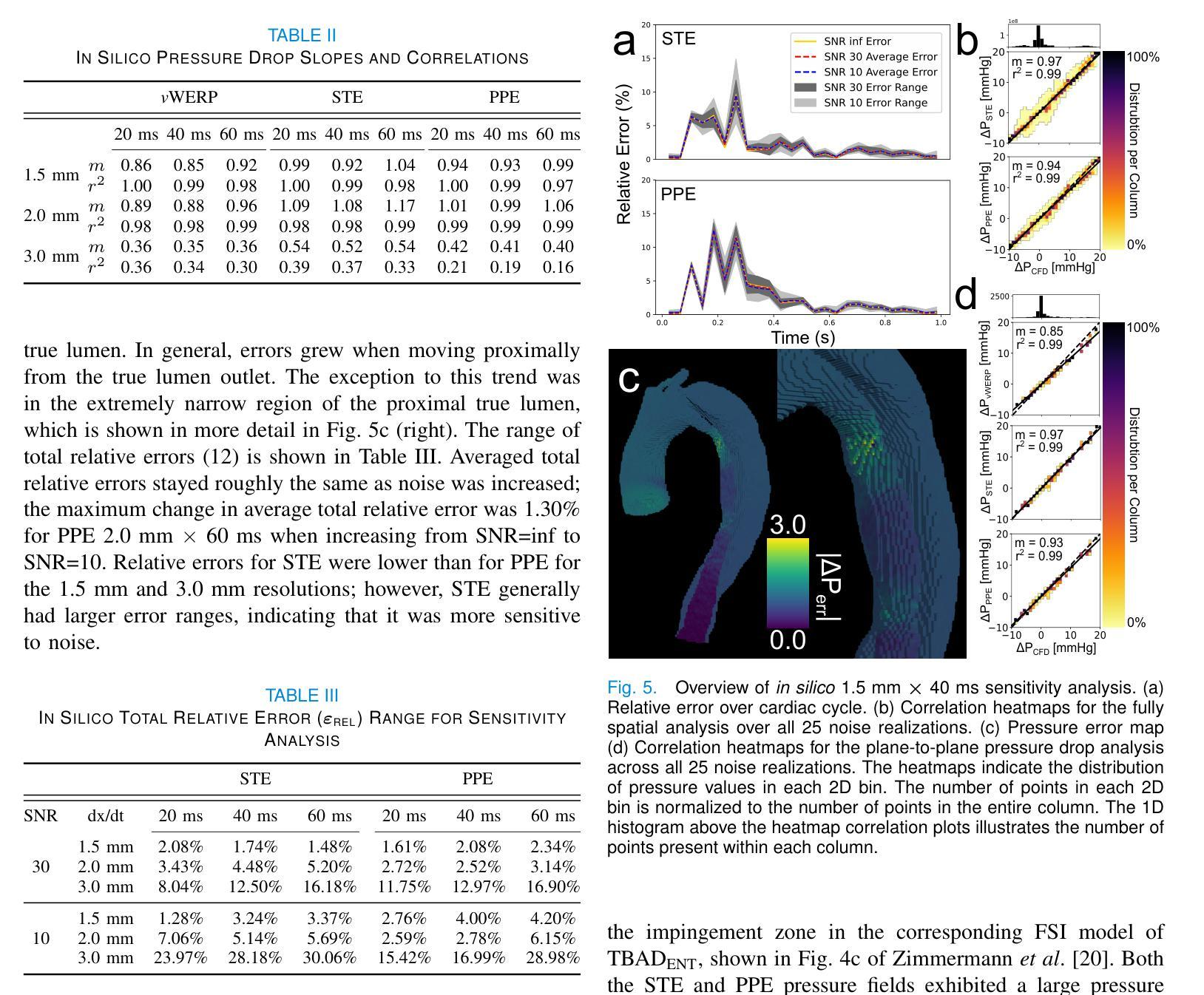
Authors:Brandon Hardy, Judith Zimmermann, Vincent Lechner, Mia Bonini, Julio A. Sotelo, Nicholas S. Burris, Daniel B. Ennis, David Marlevi, David A. Nordsletten
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) can estimate three-dimensional (3D) time-resolved relative pressure fields using 4D-flow MRI, thereby providing rich pressure field information. Clinical alternatives include catheterization and Doppler echocardiography, which only provide one-dimensional pressure drops. The accuracy of one-dimensional pressure drops derived from 4D-flow has been explored previously, but additional work is needed to evaluate the accuracy of 3D relative pressure field estimates. This work presents an analysis of three state-of-the-art relative pressure estimators: virtual Work-Energy Relative Pressure (vWERP), the Pressure Poisson Estimator (PPE), and the Stokes Estimator (STE). The spatiotemporal characteristics and sensitivity to noise were determined in silico. Estimators were then validated using a type B aortic dissection (TBAD) flow phantom with varying tear geometry and twelve catheter pressure measurements. Finally, the performance of each estimator was evaluated across eight patient cases. In silico pressure field errors were lower in STE compared to PPE, although PPE pressures were less noise sensitive. High velocity gradients and low spatial resolution contributed most significantly to local variations in 3D pressure field errors. Low temporal resolution lead to systematic underestimation of highly transient peak pressure events. In the flow phantom analysis, vWERP was the most accurate method, followed by STE and PPE. Each pressure estimator was strongly correlated with ground truth pressure values, despite the tendency to underestimate peak pressures. Patient case results demonstrated that each pressure estimator could be feasibly integrated into a clinical workflow.
利用磁共振成像(MRI)的4D流技术可以估计三维(3D)时间分辨的相对压力场,从而提供丰富的压力场信息。临床上可选择的方法包括导管插入法和多普勒超声心动图法,但这两者仅能提供一维的压力下降信息。以前已经探索过从四维流中提取一维压力下降的准确性,但还需要更多的工作来评估三维相对压力场估计的准确性。本文介绍了三种最先进的相对压力估计器:虚拟工作能量相对压力(vWERP)、压力泊松估计器(PPE)和斯托克斯估计器(STE)。这些估计器的时空特性和对噪声的敏感性都是通过计算机模拟确定的。然后利用B型主动脉夹层(TBAD)流动模型进行验证,该模型具有不同的撕裂几何形状和十二次导管压力测量值。最后,对每种估计器在八例患者中的表现进行了评估。模拟的压力场误差在STE中低于PPE,但PPE对噪声的敏感性较低。高速梯度和低空间分辨率对三维压力场误差的局部变化贡献最大。低时间分辨率导致高度瞬态峰值压力事件的系统性低估。在流动模型分析中,vWERP是最准确的方法,其次是STE和PPE。尽管有低估峰值压力的趋势,但每个压力估计值与真实压力值都有很强的相关性。患者案例结果表明,每个压力估计器都可以合理地集成到临床工作流程中。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 10 pages, 8 figures. Planned submission to IEEE Transactions on Medical Imaging
Summary
基于磁共振成像(MRI)的4D-流MRI技术可估计三维时间解析的相对压力场,提供丰富的压力场信息。本研究对三种先进的相对压力估计器进行分析,包括虚拟工作能量相对压力(vWERP)、压力泊松估计器(PPE)和斯托克斯估计器(STE)。研究确定了这些估计器的时空特性和对噪声的敏感性,并使用B型主动脉夹层(TBAD)流模型和导管压力测量进行验证。尽管存在局限性,但各估计器与患者压力值高度相关。
Key Takeaways
- 4D-flow MRI可估计三维时间解析的相对压力场,提供丰富的压力信息。
- 三种相对压力估计器(vWERP、PPE、STE)的分析表明,它们在模拟压力场误差和噪声敏感性方面有所不同。
- 在模拟和真实模型中,vWERP在压力估计方面表现最为准确。
- 压力估计器与真实压力值高度相关,但可能低估峰值压力。
- 这些压力估计器可以整合到临床工作流程中,为临床应用提供有价值的工具。
点此查看论文截图