⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-05-14 更新
DepthFusion: Depth-Aware Hybrid Feature Fusion for LiDAR-Camera 3D Object Detection
Authors:Mingqian Ji, Jian Yang, Shanshan Zhang
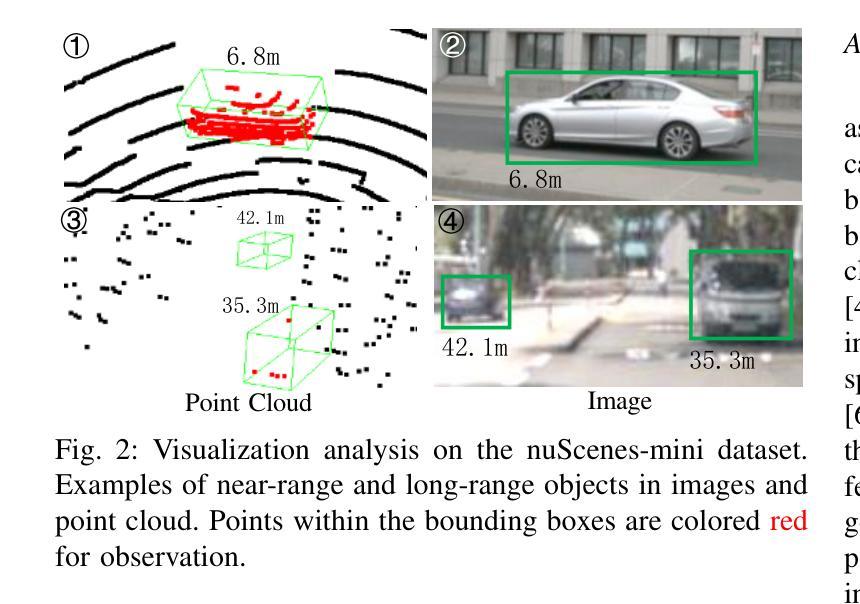
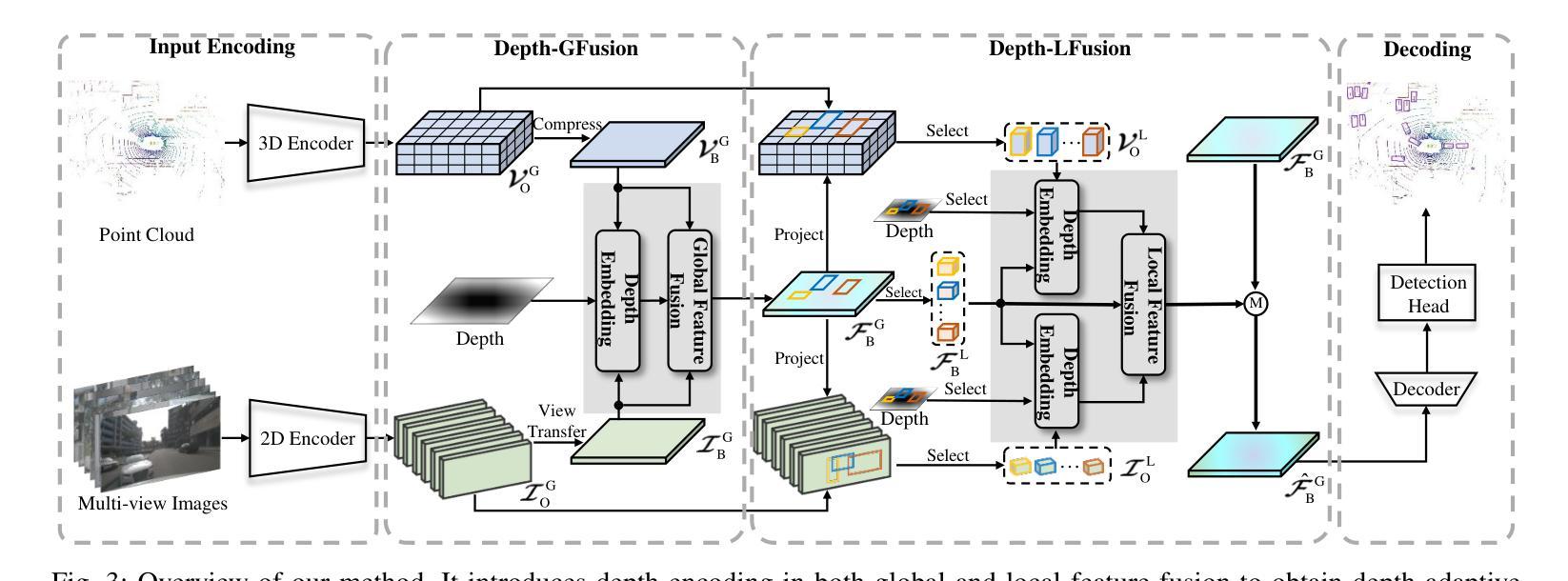
State-of-the-art LiDAR-camera 3D object detectors usually focus on feature fusion. However, they neglect the factor of depth while designing the fusion strategy. In this work, we are the first to observe that different modalities play different roles as depth varies via statistical analysis and visualization. Based on this finding, we propose a Depth-Aware Hybrid Feature Fusion (DepthFusion) strategy that guides the weights of point cloud and RGB image modalities by introducing depth encoding at both global and local levels. Specifically, the Depth-GFusion module adaptively adjusts the weights of image Bird’s-Eye-View (BEV) features in multi-modal global features via depth encoding. Furthermore, to compensate for the information lost when transferring raw features to the BEV space, we propose a Depth-LFusion module, which adaptively adjusts the weights of original voxel features and multi-view image features in multi-modal local features via depth encoding. Extensive experiments on the nuScenes and KITTI datasets demonstrate that our DepthFusion method surpasses previous state-of-the-art methods. Moreover, our DepthFusion is more robust to various kinds of corruptions, outperforming previous methods on the nuScenes-C dataset.
前沿的激光雷达相机3D目标检测器通常关注特征融合。然而,在设计融合策略时,它们忽略了深度因素。在这项工作中,我们首次通过统计分析和可视化观察到,随着深度的变化,不同模式起着不同的作用。基于这一发现,我们提出了一种深度感知混合特征融合(DepthFusion)策略,通过在全球和局部层面引入深度编码,来指导点云和RGB图像模式的权重。具体来说,Depth-GFusion模块通过深度编码自适应调整多模态全局特征中图像鸟瞰图(BEV)特征的权重。此外,为了弥补将原始特征转移到BEV空间时丢失的信息,我们提出了Depth-LFusion模块,它通过深度编码自适应调整多模态局部特征中原始体素特征和多视角图像特征的权重。在nuScenes和KITTI数据集上的大量实验表明,我们的DepthFusion方法超越了之前的最先进方法。此外,我们的DepthFusion对各种腐败现象具有更强的鲁棒性,在nuScenes-C数据集上的表现优于以前的方法。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
基于激光雷达和摄像头的三维物体检测中,现有技术主要聚焦于特征融合,但忽略了深度因素在设计融合策略中的重要性。本文通过统计分析和可视化发现不同模态在不同深度下扮演着不同的角色。因此,本文提出了一种深度感知混合特征融合策略(DepthFusion),通过引入深度编码,在全局和局部层面指导点云和RGB图像模态的权重。实验证明,本文提出的DepthFusion方法超越了现有技术,对各类失真具有更强的鲁棒性。
Key Takeaways
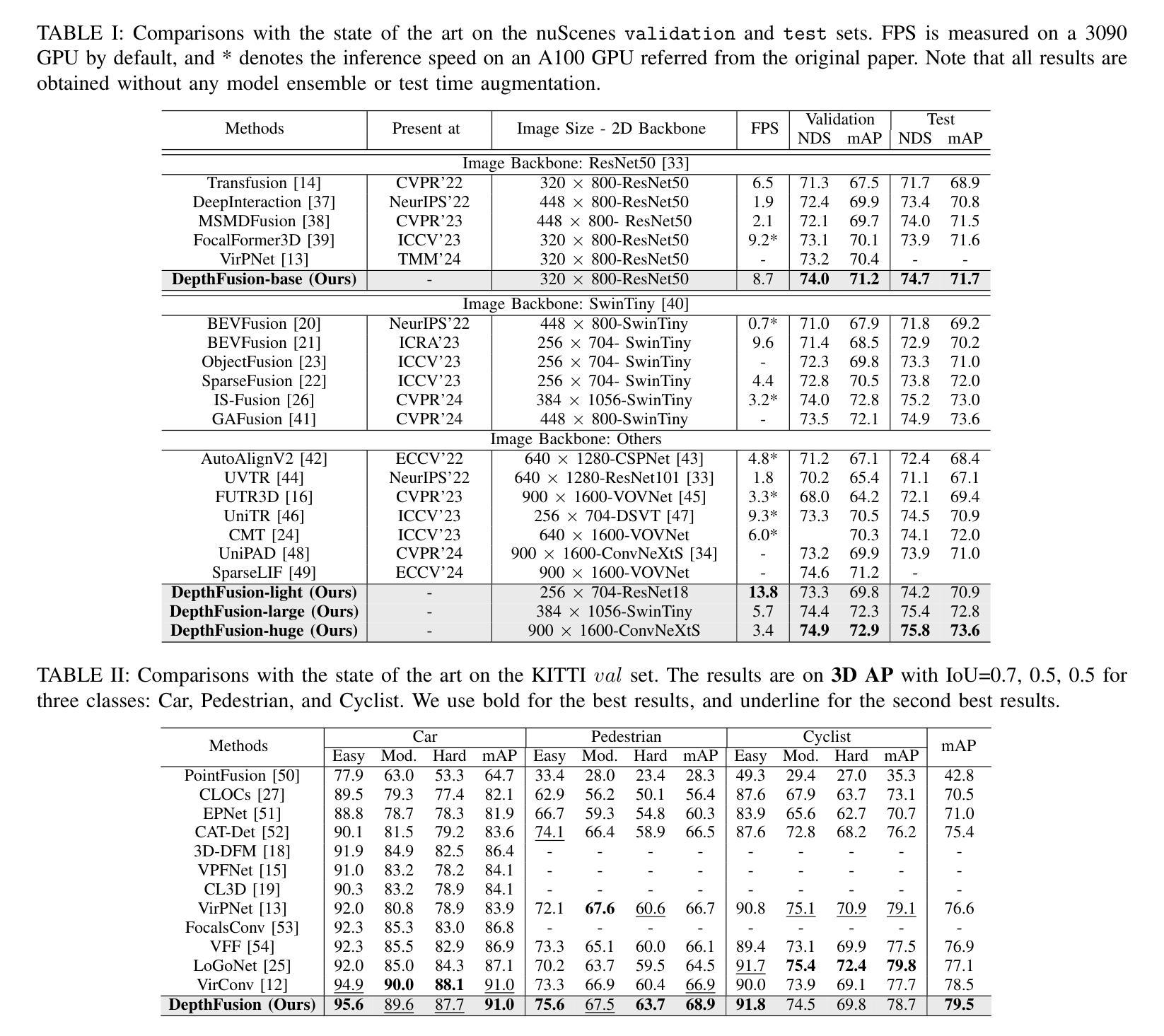
- 当前先进的激光雷达-摄像头3D物体检测主要关注特征融合,但忽略了深度因素。
- 本文首次通过统计分析和可视化发现不同模态在不同深度下的不同作用。
- 提出了一种新的深度感知混合特征融合策略(DepthFusion)。
- DepthFusion通过引入深度编码,在全局和局部层面调整点云和RGB图像模态的权重。
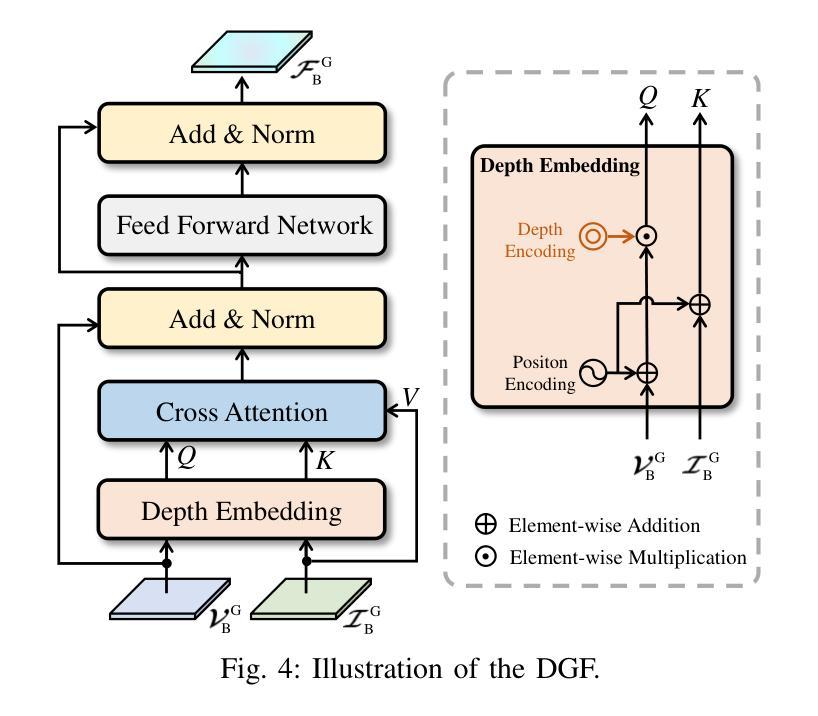
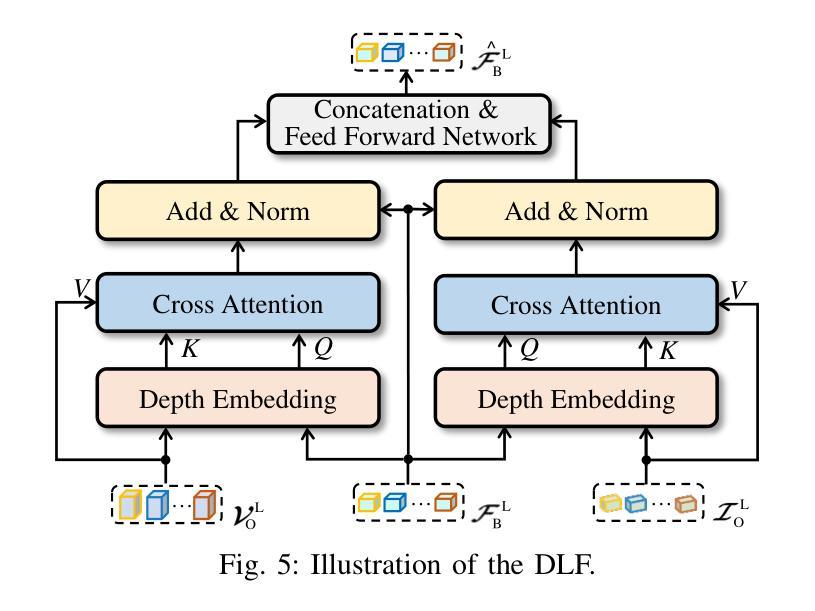
- Depth-GFusion模块自适应调整图像鸟瞰图特征的权重。
- Depth-LFusion模块用于补偿特征从原始空间转移到鸟瞰图空间时的信息损失。
点此查看论文截图

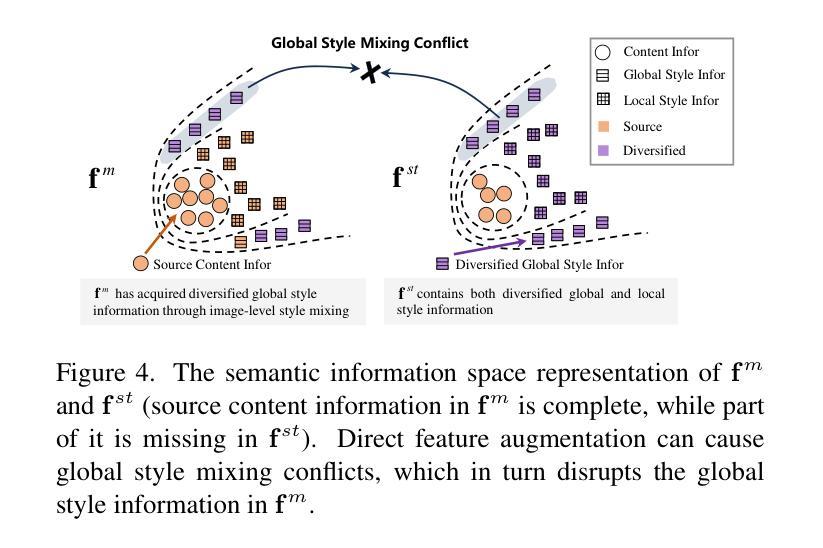
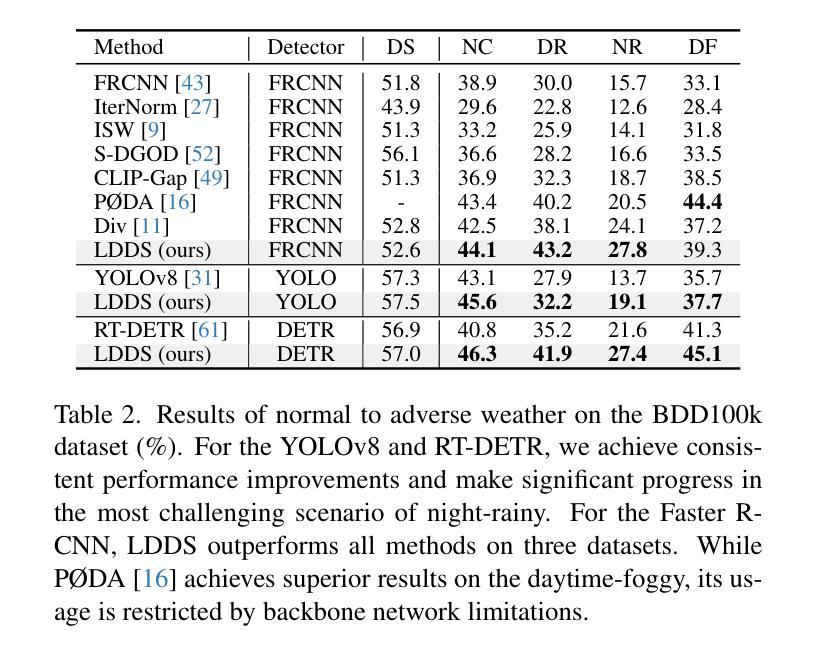
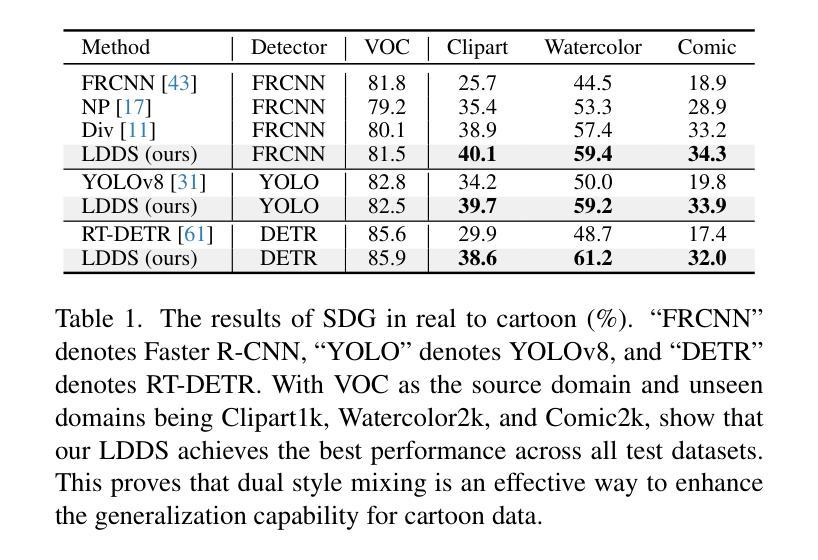
Language-Driven Dual Style Mixing for Single-Domain Generalized Object Detection
Authors:Hongda Qin, Xiao Lu, Zhiyong Wei, Yihong Cao, Kailun Yang, Ningjiang Chen
Generalizing an object detector trained on a single domain to multiple unseen domains is a challenging task. Existing methods typically introduce image or feature augmentation to diversify the source domain to raise the robustness of the detector. Vision-Language Model (VLM)-based augmentation techniques have been proven to be effective, but they require that the detector’s backbone has the same structure as the image encoder of VLM, limiting the detector framework selection. To address this problem, we propose Language-Driven Dual Style Mixing (LDDS) for single-domain generalization, which diversifies the source domain by fully utilizing the semantic information of the VLM. Specifically, we first construct prompts to transfer style semantics embedded in the VLM to an image translation network. This facilitates the generation of style diversified images with explicit semantic information. Then, we propose image-level style mixing between the diversified images and source domain images. This effectively mines the semantic information for image augmentation without relying on specific augmentation selections. Finally, we propose feature-level style mixing in a double-pipeline manner, allowing feature augmentation to be model-agnostic and can work seamlessly with the mainstream detector frameworks, including the one-stage, two-stage, and transformer-based detectors. Extensive experiments demonstrate the effectiveness of our approach across various benchmark datasets, including real to cartoon and normal to adverse weather tasks. The source code and pre-trained models will be publicly available at https://github.com/qinhongda8/LDDS.
将单一领域训练的物体检测器推广到多个未见领域是一项具有挑战性的任务。现有方法通常通过图像或特征增强来使源领域多样化,以提高检测器的稳健性。基于视觉语言模型(VLM)的增强技术已被证明是有效的,但它们要求检测器的骨干结构与VLM的图像编码器相同,从而限制了检测器框架的选择。为了解决这一问题,我们提出了用于单一领域推广的语言驱动双重风格混合(LDDS)方法,该方法通过充分利用VLM的语义信息来使源领域多样化。具体来说,我们首先构建提示,将嵌入在VLM中的风格语义信息转移到图像翻译网络中。这有助于生成具有明确语义信息的风格多样化图像。然后,我们提出了多样化图像和源域图像之间的图像级风格混合。这有效地挖掘了用于图像增强的语义信息,而不依赖于特定的增强选择。最后,我们采用双管道方式提出了特征级风格混合,使特征增强成为模型无关,并能无缝地与主流检测器框架协同工作,包括一阶、二阶和基于变压器的检测器。大量实验表明,我们的方法在各种基准数据集上都是有效的,包括从现实到卡通和从正常到恶劣天气任务。源代码和预训练模型将在https://github.com/qinhongda8/LDDS上公开提供。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF The source code and pre-trained models will be publicly available at https://github.com/qinhongda8/LDDS
摘要
利用视觉语言模型(VLM)的语义信息提升单域目标检测器在多域中的通用化性能是一大挑战。当前方法主要通过图像或特征增强技术丰富源域数据来提升检测器鲁棒性。尽管基于VLM的增强技术已证明有效,但受限于检测器架构必须与图像编码器的结构相同。为解决此问题,我们提出语言驱动的双风格混合(LDDS)方法用于单域通用化,通过充分利用VLM的语义信息丰富源域数据。首先构建提示以将VLM中的风格语义转移到图像翻译网络中,生成具有明确语义信息的风格多样化图像。接着提出图像级别的风格混合技术,有效挖掘多样化图像的语义信息,无需特定增强选择。最后,采用双管道方式进行特征级别的风格混合,使特征增强具有模型无关性,并能无缝配合主流检测器框架。大量实验证明我们的方法在各种基准数据集上的有效性,包括真实到卡通和正常到恶劣天气任务。相关源代码和预训练模型将在https://github.com/qinhongda8/LDDS公开提供。
关键发现
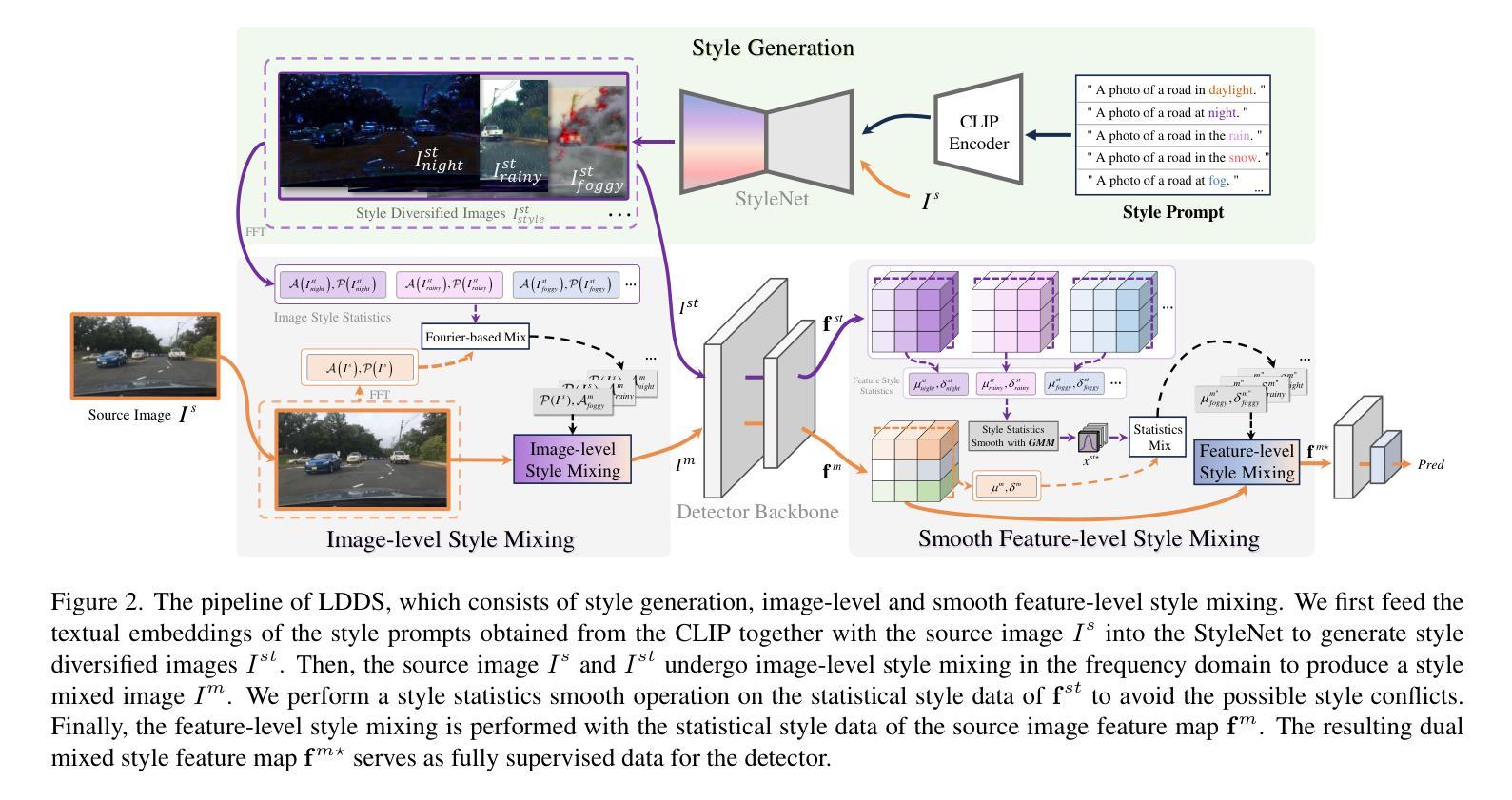
- 提出了一种新的单域通用化方法——语言驱动的双风格混合(LDDS),以解决将单一域训练的检测器推广到多个未见域的挑战。
- 通过利用视觉语言模型(VLM)的语义信息丰富源域数据,提高了检测器的鲁棒性。
- 提出构建提示以转移VLM中的风格语义到图像翻译网络,生成具有明确语义信息的风格多样化图像。
- 引入图像级别的风格混合技术,有效挖掘多样化图像的语义信息,无需特定增强选择。
- 采用双管道方式进行特征级别的风格混合,使得特征增强具有模型无关性,并适应主流检测器框架。
- 在多个基准数据集上进行了广泛实验,证明了方法的有效性,包括真实到卡通和正常到恶劣天气任务的应用。
点此查看论文截图


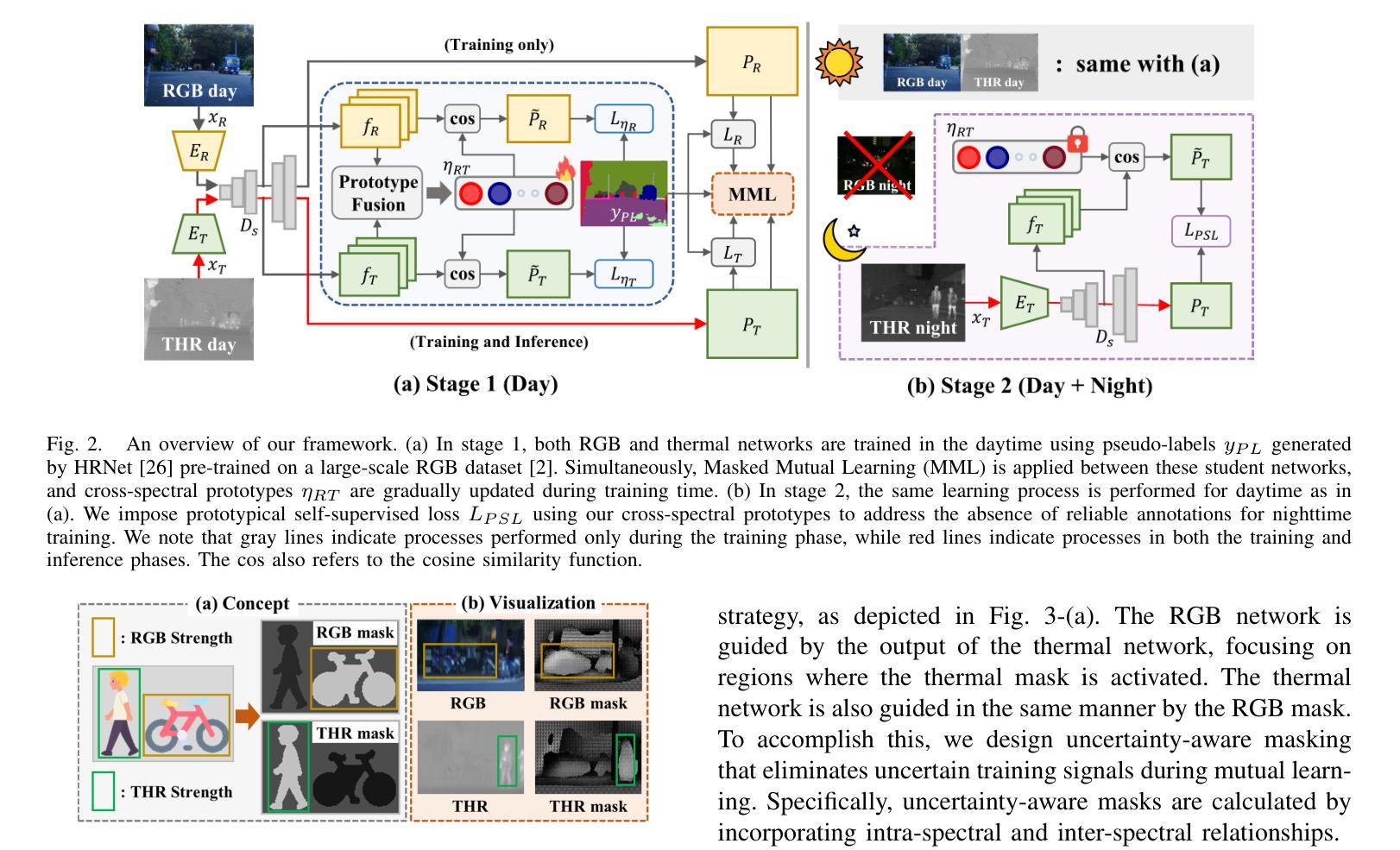
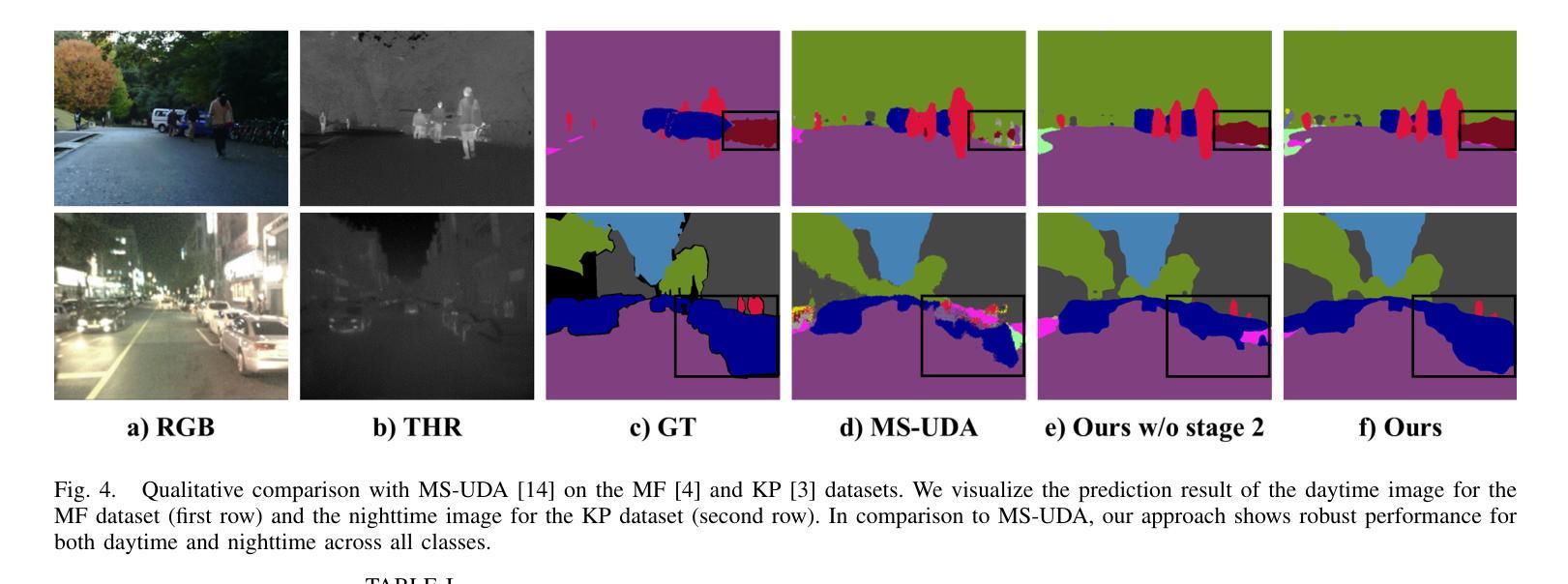
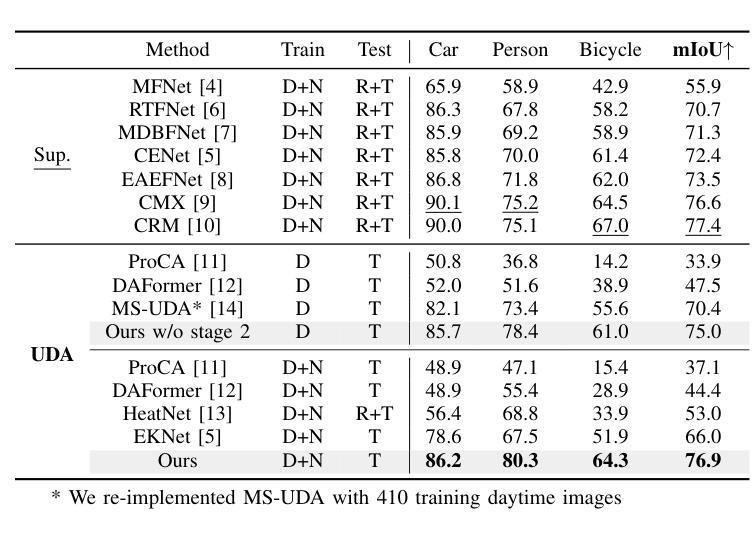
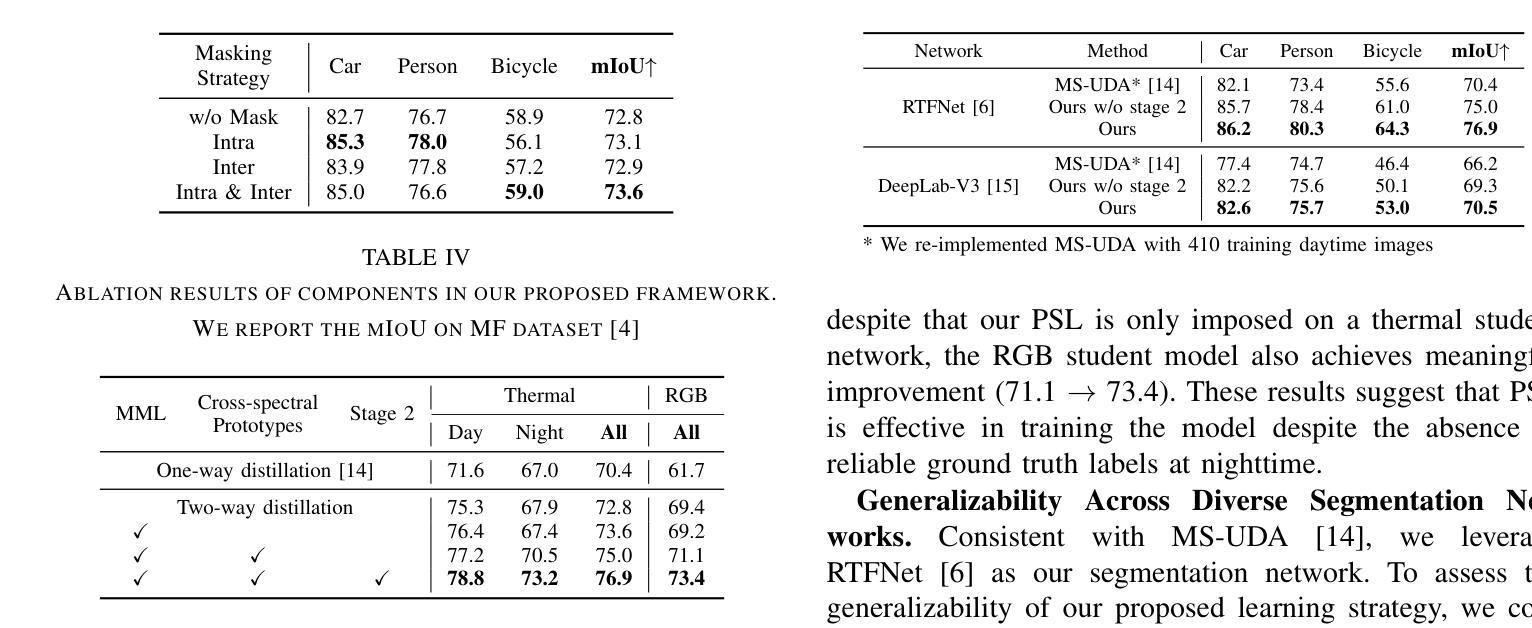
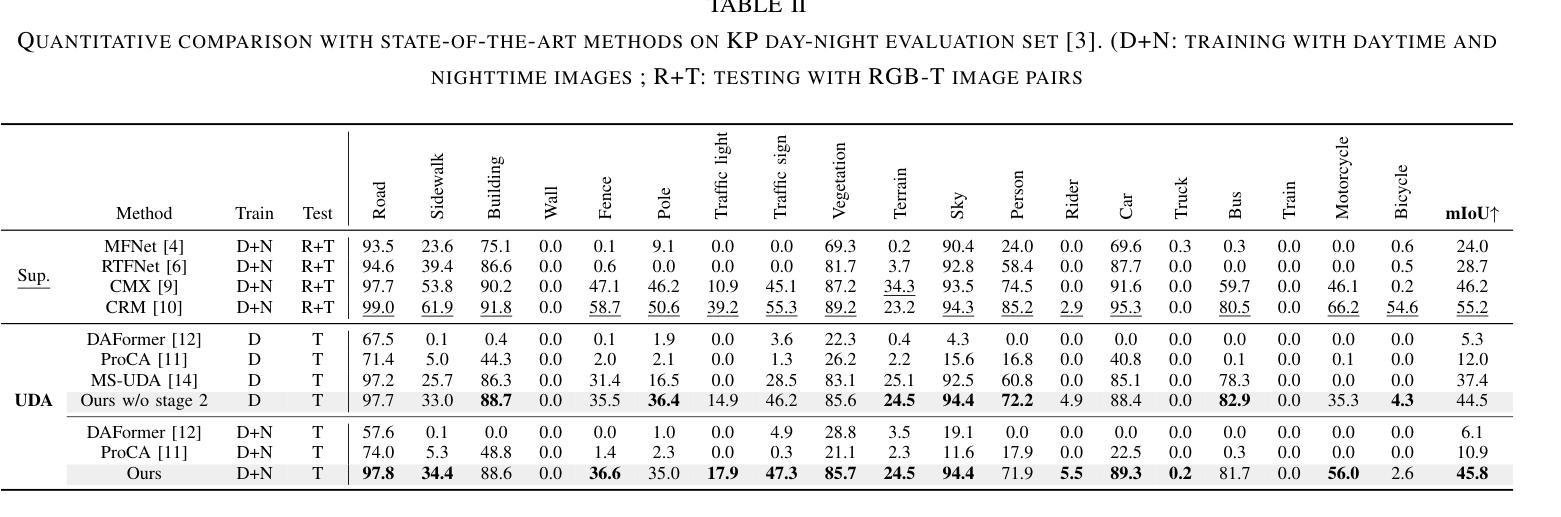
Boosting Cross-spectral Unsupervised Domain Adaptation for Thermal Semantic Segmentation
Authors:Seokjun Kwon, Jeongmin Shin, Namil Kim, Soonmin Hwang, Yukyung Choi
In autonomous driving, thermal image semantic segmentation has emerged as a critical research area, owing to its ability to provide robust scene understanding under adverse visual conditions. In particular, unsupervised domain adaptation (UDA) for thermal image segmentation can be an efficient solution to address the lack of labeled thermal datasets. Nevertheless, since these methods do not effectively utilize the complementary information between RGB and thermal images, they significantly decrease performance during domain adaptation. In this paper, we present a comprehensive study on cross-spectral UDA for thermal image semantic segmentation. We first propose a novel masked mutual learning strategy that promotes complementary information exchange by selectively transferring results between each spectral model while masking out uncertain regions. Additionally, we introduce a novel prototypical self-supervised loss designed to enhance the performance of the thermal segmentation model in nighttime scenarios. This approach addresses the limitations of RGB pre-trained networks, which cannot effectively transfer knowledge under low illumination due to the inherent constraints of RGB sensors. In experiments, our method achieves higher performance over previous UDA methods and comparable performance to state-of-the-art supervised methods.
在自动驾驶领域,热图像语义分割已成为一个关键的研究方向,因为它能在恶劣的视觉条件下提供稳健的场景理解。特别是,针对热图像分割的无监督域自适应(UDA)可以作为一种有效的解决方案来解决标记热数据集缺乏的问题。然而,由于这些方法不能有效地利用RGB和热图像之间的互补信息,它们在域自适应过程中会降低性能。在本文中,我们对跨光谱UDA在热图像语义分割方面进行了深入研究。首先,我们提出了一种新颖的掩模互学习策略,通过有选择地转移每个光谱模型之间的结果并掩盖不确定区域,从而促进互补信息的交换。此外,我们还引入了一种新型的原型自监督损失,旨在提高夜间场景中的热分割模型性能。该方法解决了RGB预训练网络的局限性,由于RGB传感器的固有约束,这些网络在低光照条件下无法有效地转移知识。在实验中,我们的方法取得了超过以前UDA方法的高性能和与最新监督方法的相当性能。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 7 pages, 4 figures, International Conference on Robotics and Automation(ICRA) 2025
Summary
基于无监督域自适应方法的优势,本研究探讨交叉光谱自适应语义分割技术对于热图像自主驾驶技术的影响。本研究提出一种新颖的掩膜互学习机制,促进RGB与热图像之间的互补信息交换,同时引入原型自监督损失以增强夜间场景下的热图像分割性能。该方法解决了基于RGB的预训练网络在低光照环境下的知识迁移难题。
Key Takeaways
- 研究聚焦于无监督域自适应(UDA)在热图像语义分割中的应用。
- 提出一种新颖的掩膜互学习机制,用于选择性地在光谱模型之间转移结果,同时掩盖不确定区域。这种机制促进RGB和热力图像的互补信息交换。
- 为提高夜间场景下的热图像分割性能,引入原型自监督损失。这一损失旨在增强模型在低光照环境下的性能表现。
点此查看论文截图

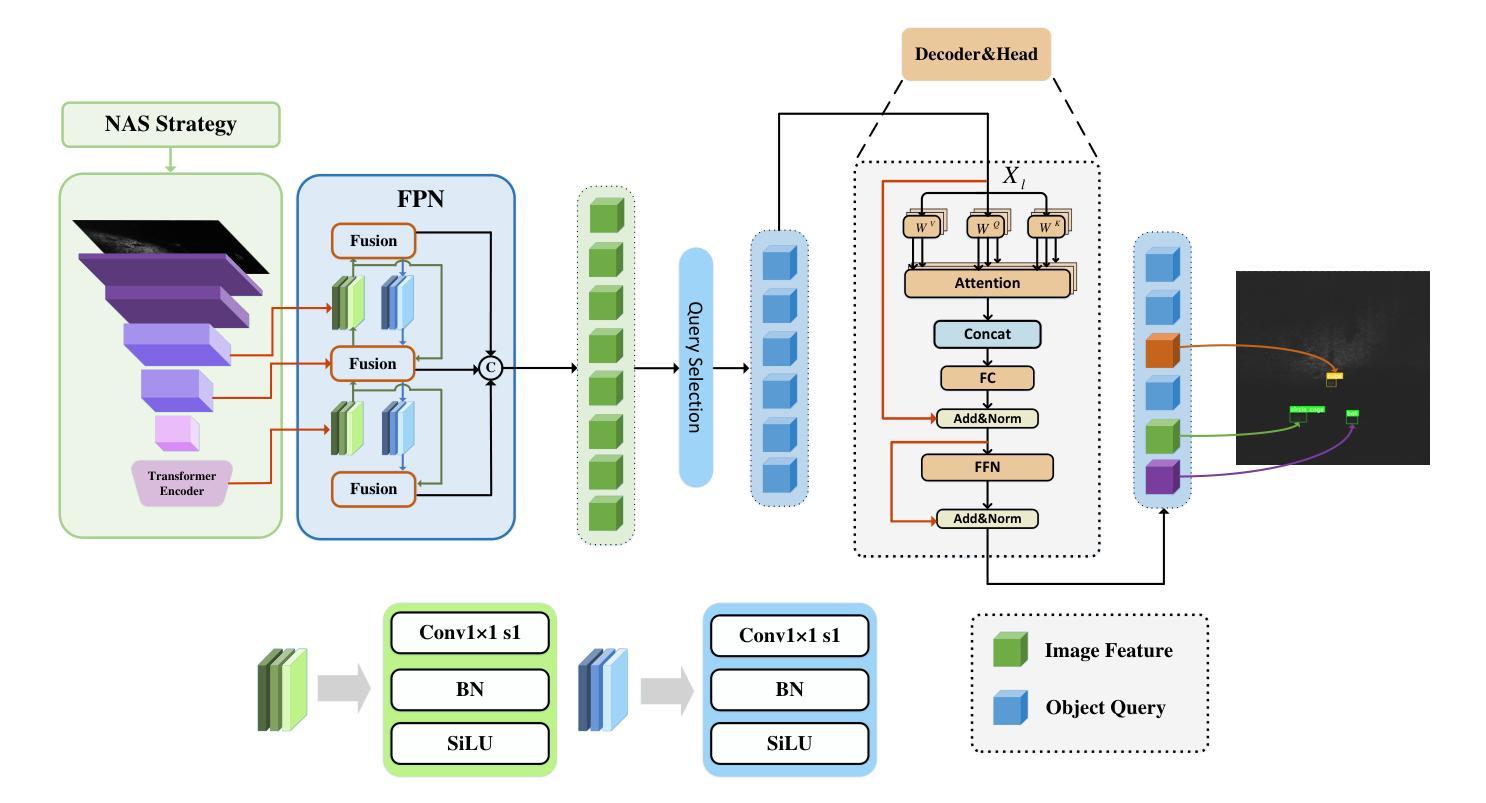
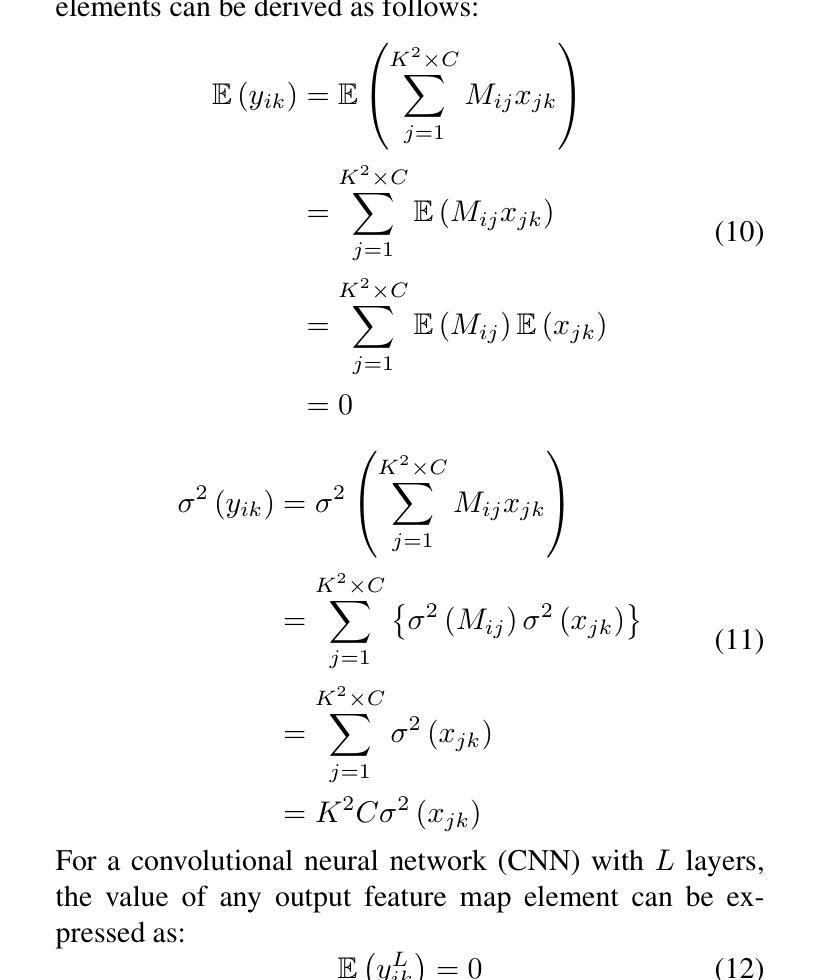
Underwater object detection in sonar imagery with detection transformer and Zero-shot neural architecture search
Authors:XiaoTong Gu, Shengyu Tang, Yiming Cao, Changdong Yu
Underwater object detection using sonar imagery has become a critical and rapidly evolving research domain within marine technology. However, sonar images are characterized by lower resolution and sparser features compared to optical images, which seriously degrades the performance of object detection.To address these challenges, we specifically propose a Detection Transformer (DETR) architecture optimized with a Neural Architecture Search (NAS) approach called NAS-DETR for object detection in sonar images. First, an improved Zero-shot Neural Architecture Search (NAS) method based on the maximum entropy principle is proposed to identify a real-time, high-representational-capacity CNN-Transformer backbone for sonar image detection. This method enables the efficient discovery of high-performance network architectures with low computational and time overhead. Subsequently, the backbone is combined with a Feature Pyramid Network (FPN) and a deformable attention-based Transformer decoder to construct a complete network architecture. This architecture integrates various advanced components and training schemes to enhance overall performance. Extensive experiments demonstrate that this architecture achieves state-of-the-art performance on two Representative datasets, while maintaining minimal overhead in real-time efficiency and computational complexity. Furthermore, correlation analysis between the key parameters and differential entropy-based fitness function is performed to enhance the interpretability of the proposed framework. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first work in the field of sonar object detection to integrate the DETR architecture with a NAS search mechanism.
使用声纳图像进行水下目标检测已成为海洋技术中一个关键且快速发展的研究领域。然而,与光学图像相比,声纳图像的特征分辨率较低、特征较稀疏,这严重降低了目标检测的性能。为了解决这些挑战,我们特地提出了一种使用神经网络架构搜索(NAS)方法优化的检测转换器(DETR)架构,称为NAS-DETR,用于声纳图像中的目标检测。首先,我们提出了一种基于最大熵原理的改进零镜头神经网络架构搜索(NAS)方法,用于识别适用于声纳图像检测的实时、高表征容量CNN-Transformer骨干网。该方法能够高效地发现具有低计算和时间开销的高性能网络架构。随后,将骨干网与特征金字塔网络(FPN)和基于可变形注意力的Transformer解码器相结合,构建完整的网络架构。该架构集成了各种先进组件和训练方案,以提高整体性能。大量实验表明,该架构在两个代表性数据集上实现了最先进的性能,同时保持了实时效率和计算复杂度的最低开销。此外,还对关键参数与基于差异熵的适应度函数进行了相关性分析,以提高所提出框架的可解释性。据我们所知,这是声纳目标检测领域首次将DETR架构与NAS搜索机制相结合的工作。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
针对水下物体检测的挑战,提出一种基于神经网络架构搜索(NAS)的优化检测转换器(DETR)架构,称为NAS-DETR。它采用改进的零镜头NAS方法,结合特征金字塔网络(FPN)和可变形注意力基础的转换器解码器,构建完整网络架构。在两项代表性数据集上实现最先进的性能,同时保持实时效率和计算复杂度的最小化。
Key Takeaways
- 水下物体检测是海洋技术中关键且快速演化的研究领域。
- 声纳图像具有较低分辨率和稀疏特征,给物体检测带来挑战。
- 提出基于神经网络架构搜索(NAS)的优化检测转换器(DETR)架构,称为NAS-DETR,用于声纳图像中的物体检测。
- 改进的零镜头NAS方法基于最大熵原则,能高效发现高性能网络架构,具有低计算和时间开销。
- 结合FPN和可变形注意力基础的转换器解码器,构建完整网络架构,提高整体性能。
- 在两个代表性数据集上实现最先进的性能,同时保持实时效率和计算复杂度的平衡。
- 通过关键参数与差异熵基于的适应度函数之间的相关性分析,提高框架的可解释性。
点此查看论文截图

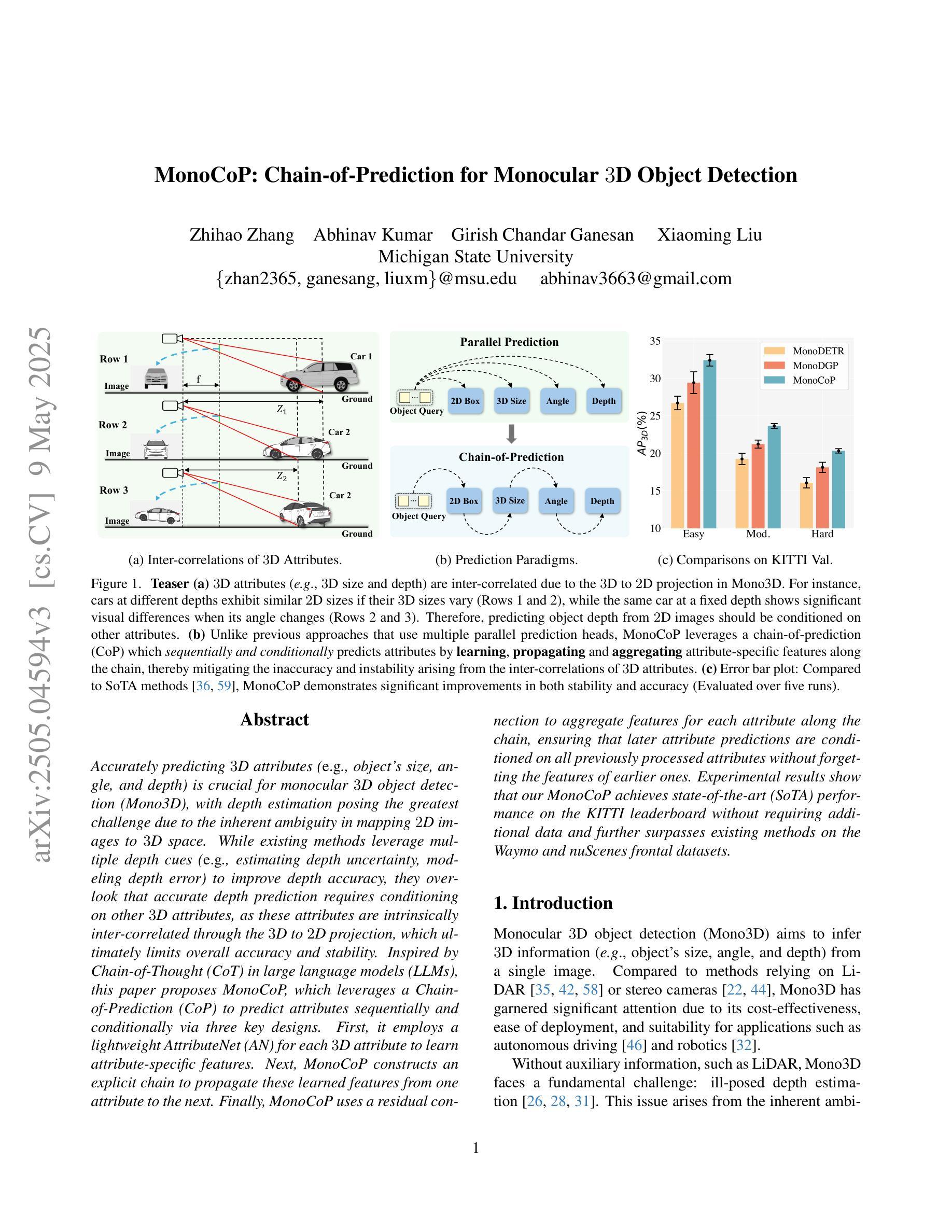
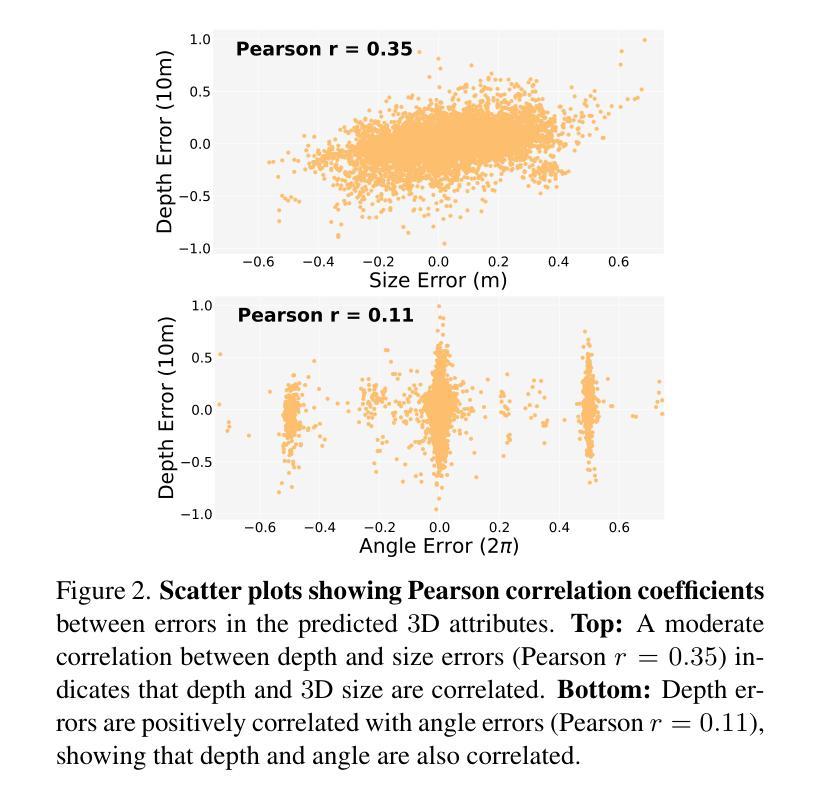
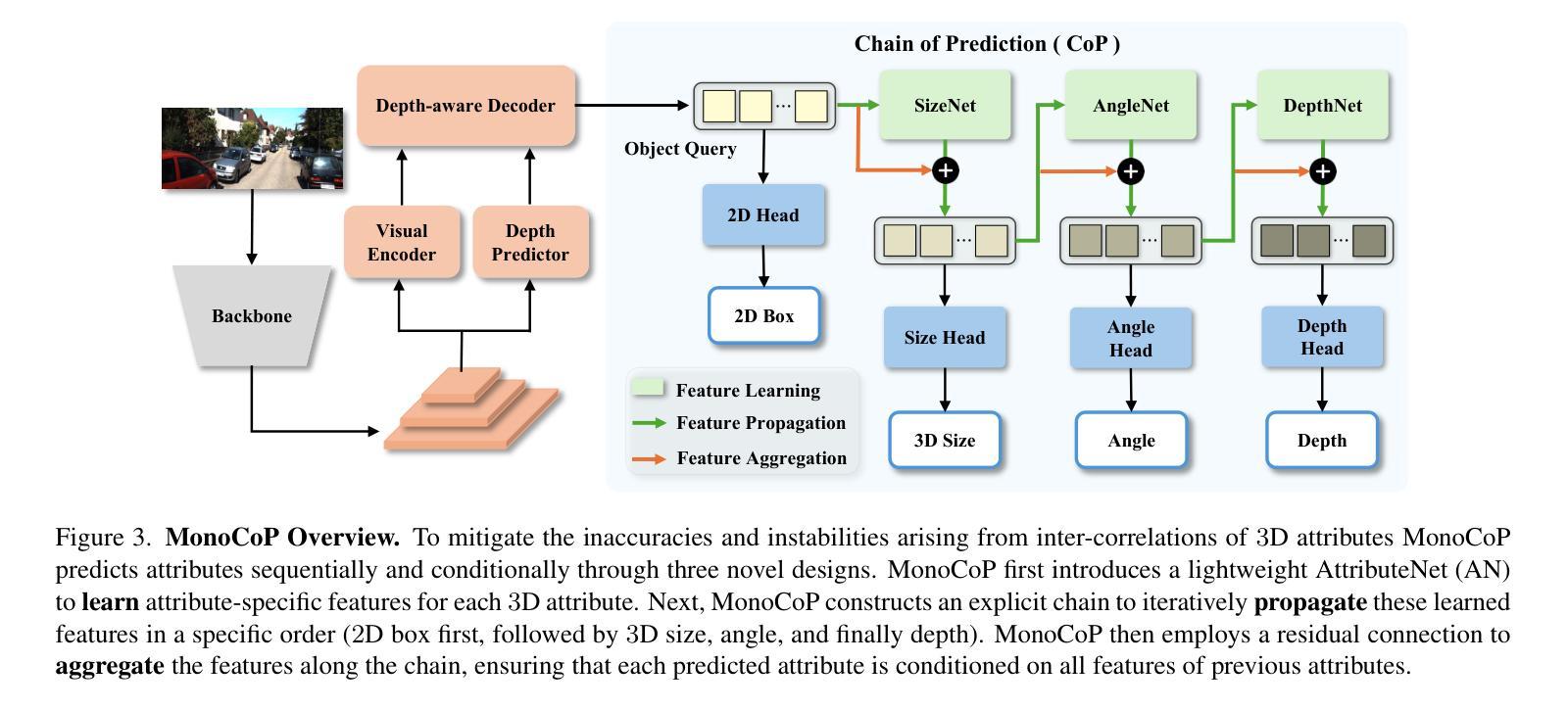
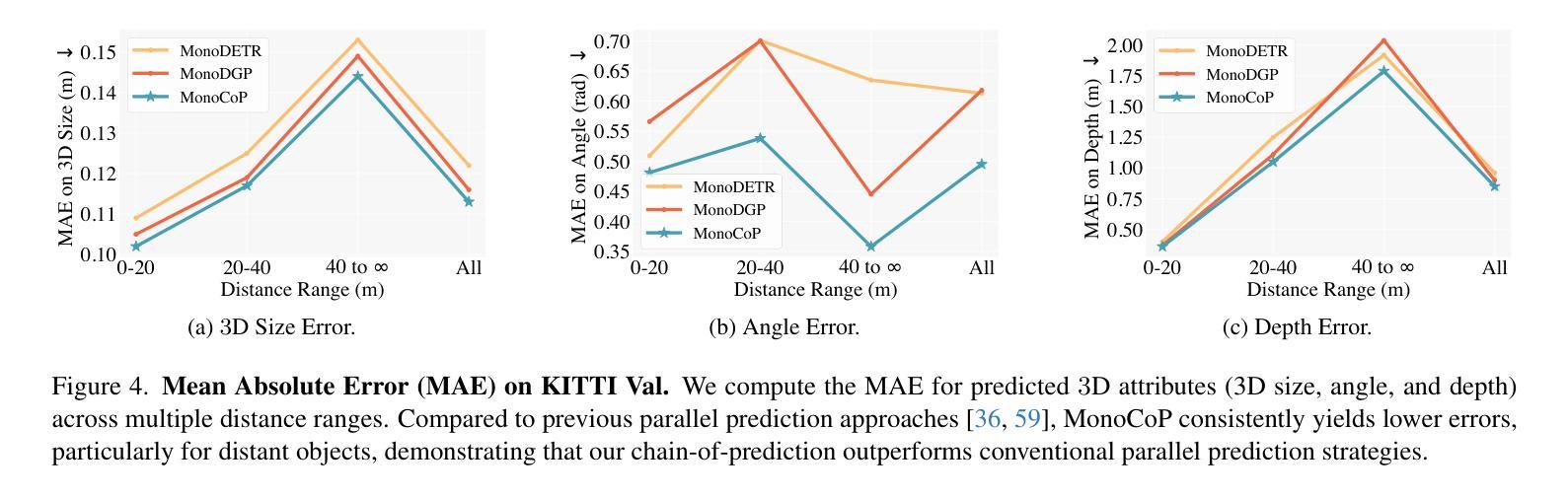
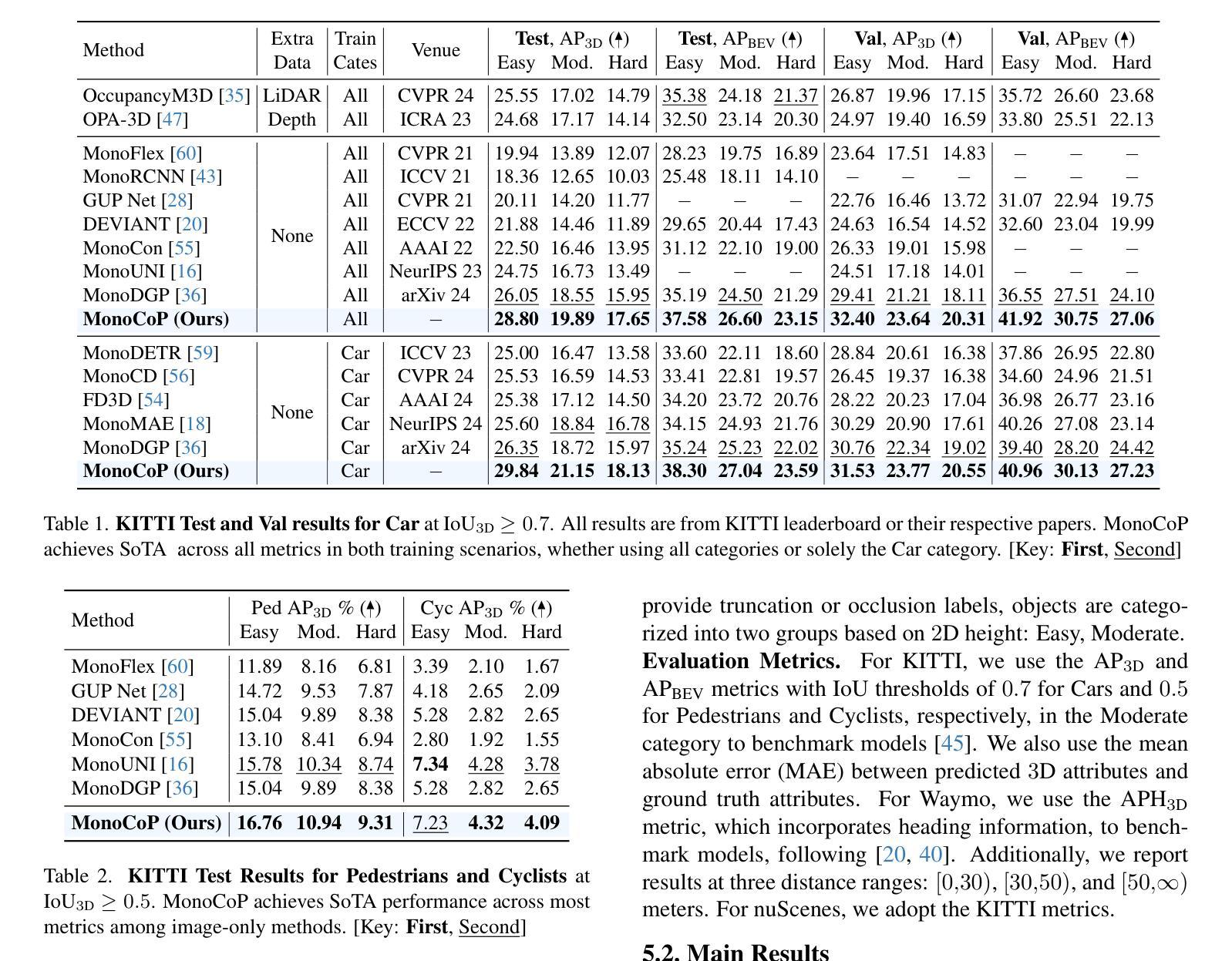
MonoCoP: Chain-of-Prediction for Monocular 3D Object Detection
Authors:Zhihao Zhang, Abhinav Kumar, Girish Chandar Ganesan, Xiaoming Liu
Accurately predicting 3D attributes is crucial for monocular 3D object detection (Mono3D), with depth estimation posing the greatest challenge due to the inherent ambiguity in mapping 2D images to 3D space. While existing methods leverage multiple depth cues (e.g., estimating depth uncertainty, modeling depth error) to improve depth accuracy, they overlook that accurate depth prediction requires conditioning on other 3D attributes, as these attributes are intrinsically inter-correlated through the 3D to 2D projection, which ultimately limits overall accuracy and stability. Inspired by Chain-of-Thought (CoT) in large language models (LLMs), this paper proposes MonoCoP, which leverages a Chain-of-Prediction (CoP) to predict attributes sequentially and conditionally via three key designs. First, it employs a lightweight AttributeNet (AN) for each 3D attribute to learn attribute-specific features. Next, MonoCoP constructs an explicit chain to propagate these learned features from one attribute to the next. Finally, MonoCoP uses a residual connection to aggregate features for each attribute along the chain, ensuring that later attribute predictions are conditioned on all previously processed attributes without forgetting the features of earlier ones. Experimental results show that our MonoCoP achieves state-of-the-art (SoTA) performance on the KITTI leaderboard without requiring additional data and further surpasses existing methods on the Waymo and nuScenes frontal datasets.
准确预测3D属性对于单目3D对象检测(Mono3D)至关重要,深度估计由于将2D图像映射到3D空间时固有的模糊性而面临最大挑战。尽管现有方法利用多种深度线索(例如估计深度不确定性、建模深度误差)来提高深度准确性,但它们忽略了准确的深度预测需要依赖于其他3D属性,因为这些属性通过3D到2D的投影本质上相互关联,这最终限制了总体准确性和稳定性。本文受到大型语言模型(LLM)中的思维链(Chain-of-Thought,CoT)的启发,提出了一种利用预测链(Chain-of-Prediction,CoP)进行属性顺序预测和条件预测的方法MonoCoP,其通过三个关键设计实现:首先,它为每个3D属性采用轻量级的AttributeNet(AN)来学习特定于属性的特征;其次,MonoCoP构建了一个明确的链条来传播从一个属性学到的特征到下一个属性;最后,MonoCoP使用残差连接来沿着链条聚合每个属性的特征,确保后续的属性预测依赖于所有先前处理的属性,同时不会忘记早期的属性特征。实验结果表明,我们的MonoCoP在KITTI排行榜上达到了最新技术水平,并且无需额外数据,在Waymo和nuScenes正面数据集上也超越了现有方法。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文提出一种基于Chain-of-Prediction(CoP)的单眼三维物体检测新方法MonoCoP。该方法通过构建预测链,顺序且条件地预测三维属性。它通过为每个三维属性设计轻量级的AttributeNet(AN)来学习特定属性特征,并通过显式链传播这些特征。此外,MonoCoP采用残差连接来汇聚各属性的特征,确保后续属性预测建立在所有先前处理过的属性之上。实验结果显示,MonoCoP在KITTI排行榜上达到最新技术水平,且在Waymo和nuScenes正面数据集上超越现有方法。
Key Takeaways
- MonoCoP利用Chain-of-Prediction(CoP)方法顺序且条件地预测三维属性,这与传统方法不同。
- 通过AttributeNet(AN)为每个三维属性学习特定特征。
- 通过显式预测链传播特征,增强属性间的关联性。
- 残差连接确保后续属性预测建立在所有先前处理过的属性之上,避免遗忘早期特征。
- MonoCoP在KITTI、Waymo和nuScenes数据集上实现先进性能。
点此查看论文截图
Enhanced Generative Data Augmentation for Semantic Segmentation via Stronger Guidance
Authors:Quang-Huy Che, Duc-Tri Le, Bich-Nga Pham, Duc-Khai Lam, Vinh-Tiep Nguyen
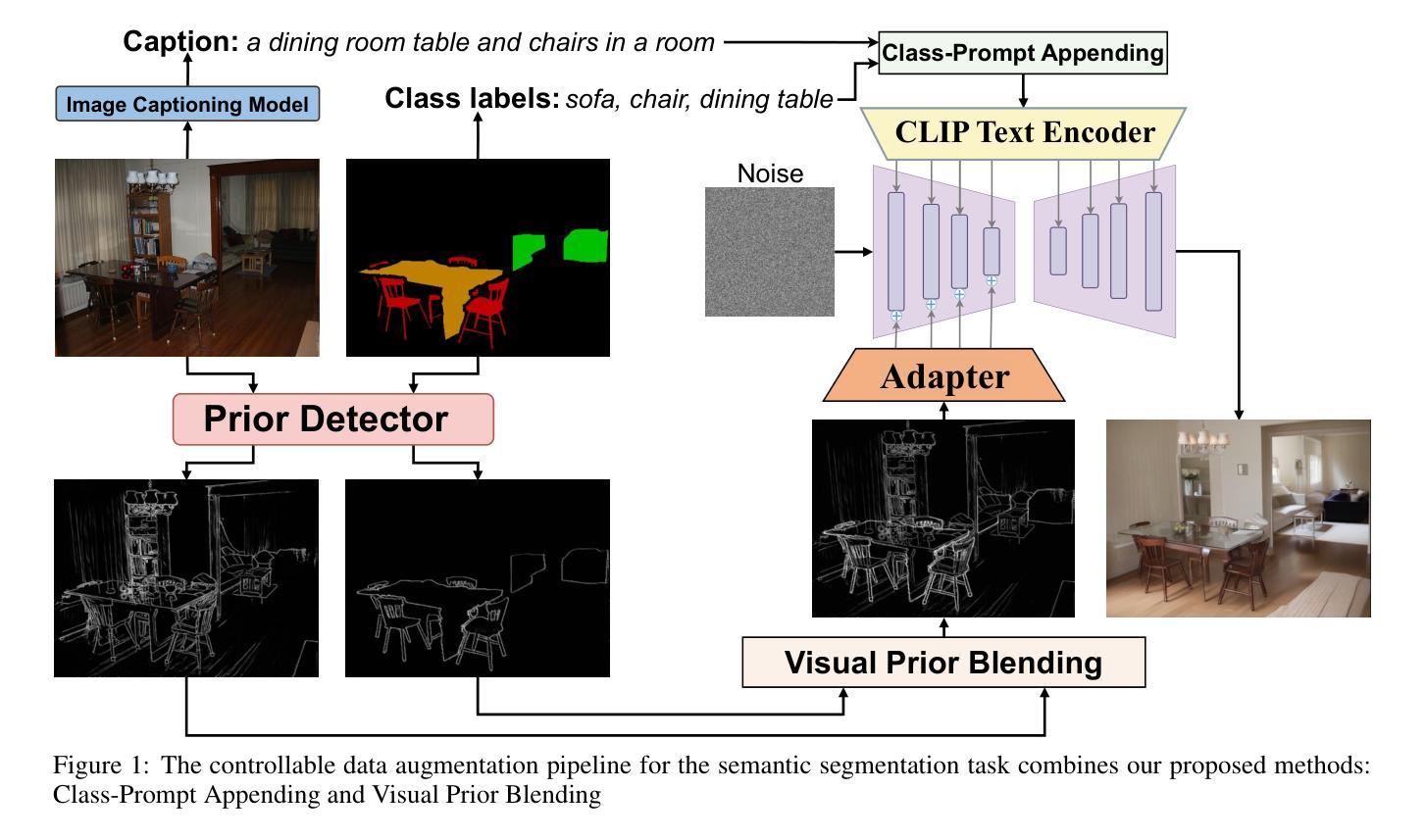
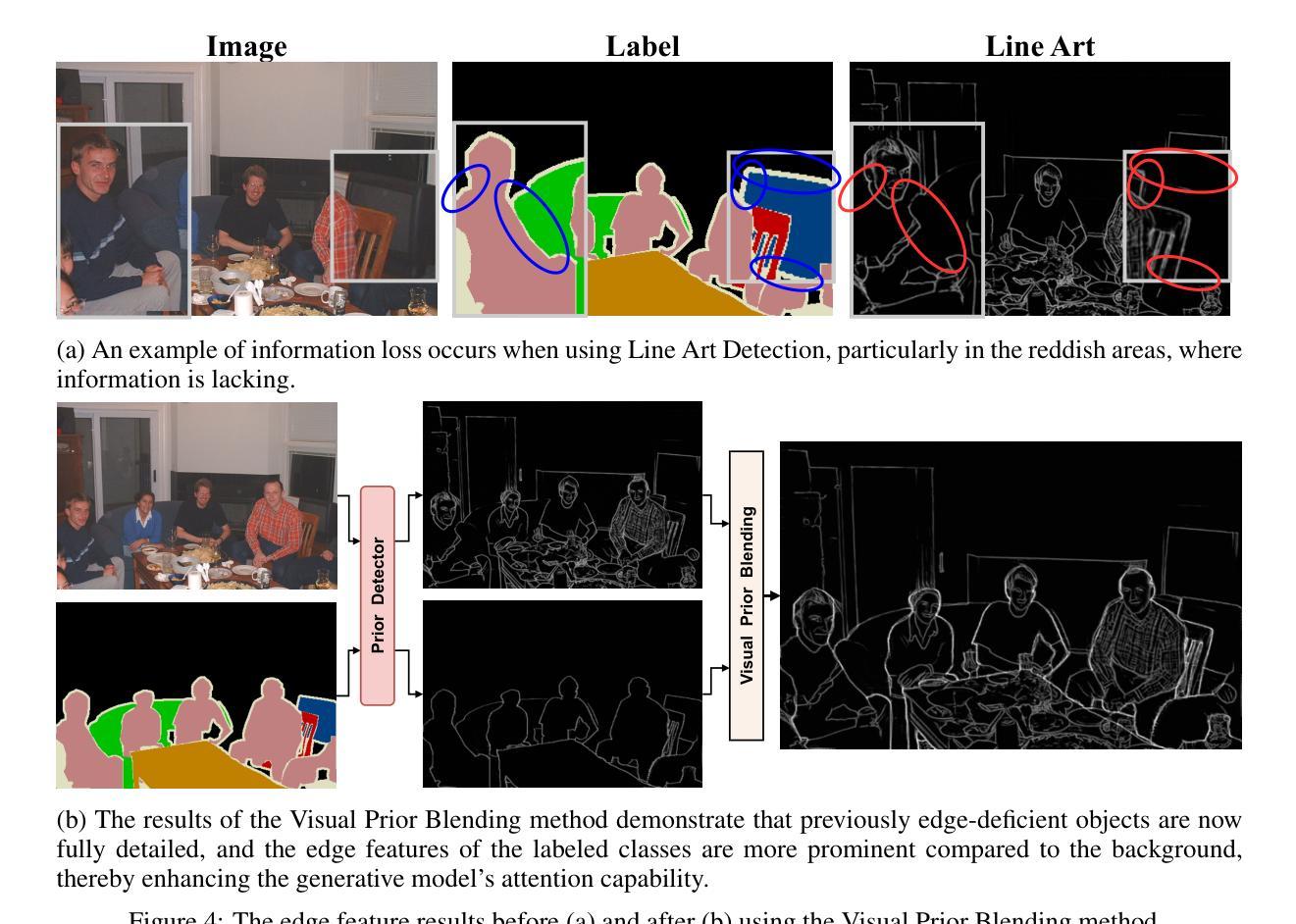
Data augmentation is crucial for pixel-wise annotation tasks like semantic segmentation, where labeling requires significant effort and intensive labor. Traditional methods, involving simple transformations such as rotations and flips, create new images but often lack diversity along key semantic dimensions and fail to alter high-level semantic properties. To address this issue, generative models have emerged as an effective solution for augmenting data by generating synthetic images. Controllable Generative models offer data augmentation methods for semantic segmentation tasks by using prompts and visual references from the original image. However, these models face challenges in generating synthetic images that accurately reflect the content and structure of the original image due to difficulties in creating effective prompts and visual references. In this work, we introduce an effective data augmentation pipeline for semantic segmentation using Controllable Diffusion model. Our proposed method includes efficient prompt generation using \textit{Class-Prompt Appending} and \textit{Visual Prior Blending} to enhance attention to labeled classes in real images, allowing the pipeline to generate a precise number of augmented images while preserving the structure of segmentation-labeled classes. In addition, we implement a \textit{class balancing algorithm} to ensure a balanced training dataset when merging the synthetic and original images. Evaluation on PASCAL VOC datasets, our pipeline demonstrates its effectiveness in generating high-quality synthetic images for semantic segmentation. Our code is available at \href{https://github.com/chequanghuy/Enhanced-Generative-Data-Augmentation-for-Semantic-Segmentation-via-Stronger-Guidance}{this https URL}.
数据增强对于像素级注释任务(如语义分割)至关重要,这些任务需要大量劳动和努力来进行标注。传统的方法,涉及简单的转换(如旋转和翻转),可以创建新的图像,但往往在关键的语义维度上缺乏多样性,并且无法改变高级语义属性。为了解决这个问题,生成模型已经出现为通过生成合成图像来增强数据的有效解决方案。可控生成模型通过使用原始图像的提示和视觉参考来为语义分割任务提供数据增强方法。然而,这些模型在生成准确反映原始图像内容和结构的合成图像时面临挑战,因为创建有效的提示和视觉参考存在困难。在这项工作中,我们引入了使用可控扩散模型对语义分割进行有效数据增强的管道。我们提出的方法包括使用“类提示追加”和“视觉先验混合”进行有效的提示生成,以提高对真实图像中标记类的关注,使管道能够在保留分割标记类结构的同时生成精确数量的增强图像。此外,我们实现了“类别平衡算法”,以确保在合并合成图像和原始图像时获得平衡的训练数据集。在PASCAL VOC数据集上的评估表明,我们的管道在生成用于语义分割的高质量合成图像方面非常有效。我们的代码可以在这个URL的网址找到:https://github.com/chequanghuy/Enhanced-Generative-Data-Augmentation-for-Semantic-Segmentation-via-Stronger-Guidance。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
数据增强对于像素级标注任务如语义分割至关重要,传统方法缺乏多样性。生成模型通过生成合成图像有效解决了数据增强问题,但可控生成模型面临准确反映原始图像内容和结构的挑战。本文引入了一种使用可控扩散模型的语义分割数据增强管道,通过高效提示生成和视觉先验融合,在真实图像中增强对标记类的注意力,同时保证合成图像的数量和质量。
Key Takeaways
- 数据增强在像素级标注任务中非常重要,尤其对于语义分割,能减少标注的劳动成本。
- 传统数据增强方法如旋转和翻转虽然能创建新图像,但缺乏关键语义维度上的多样性。
- 生成模型,特别是可控生成模型,已被证明是数据增强的有效解决方案。
- 可控生成模型面临准确反映原始图像内容和结构的挑战,需要有效的提示和视觉参考。
- 本文介绍了一种新的数据增强管道,结合类提示添加和视觉先验融合,用于语义分割任务。
- 该管道在PASCAL VOC数据集上的评估结果证明了其生成高质量合成图像的有效性。
点此查看论文截图




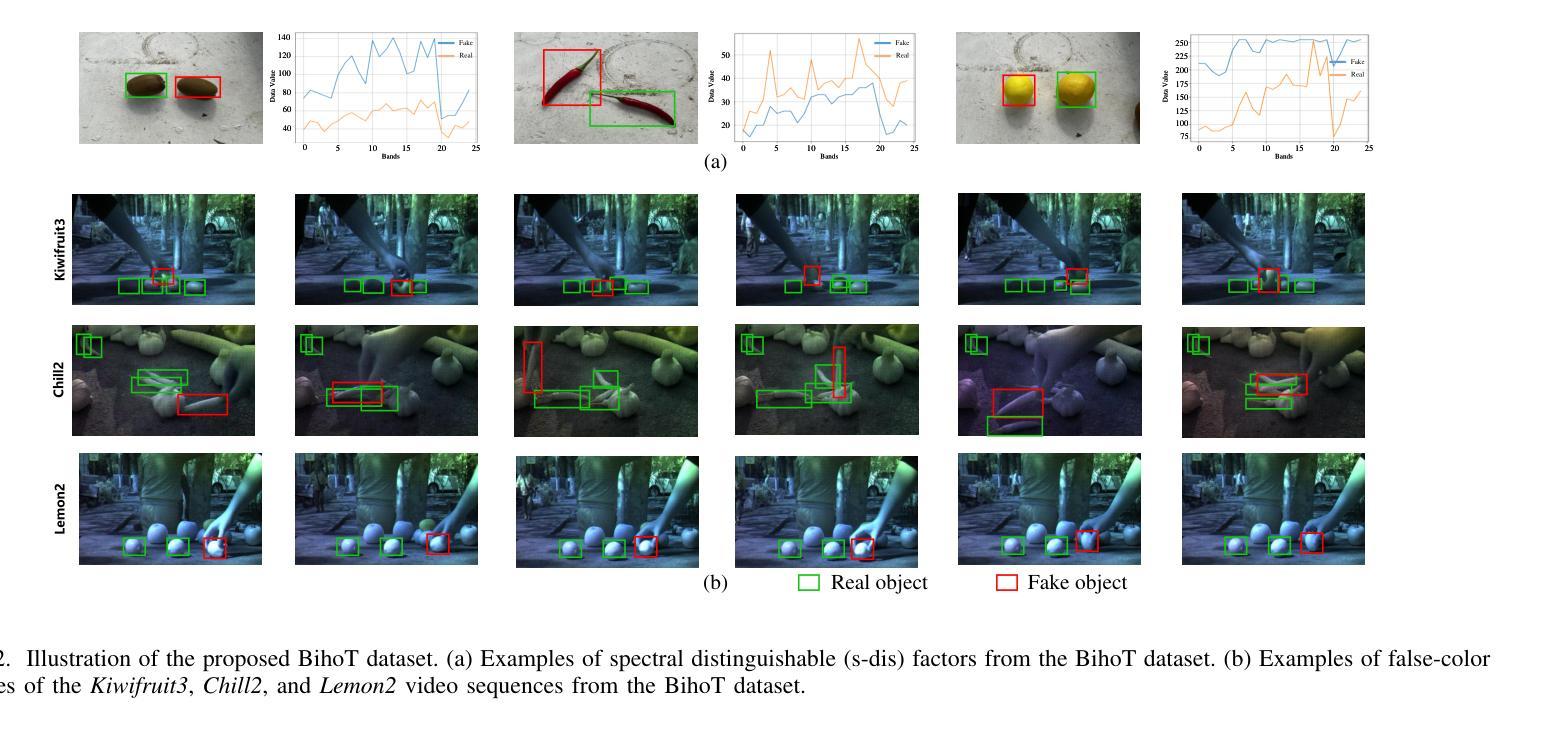
BihoT: A Large-Scale Dataset and Benchmark for Hyperspectral Camouflaged Object Tracking
Authors:Hanzheng Wang, Wei Li, Xiang-Gen Xia, Qian Du
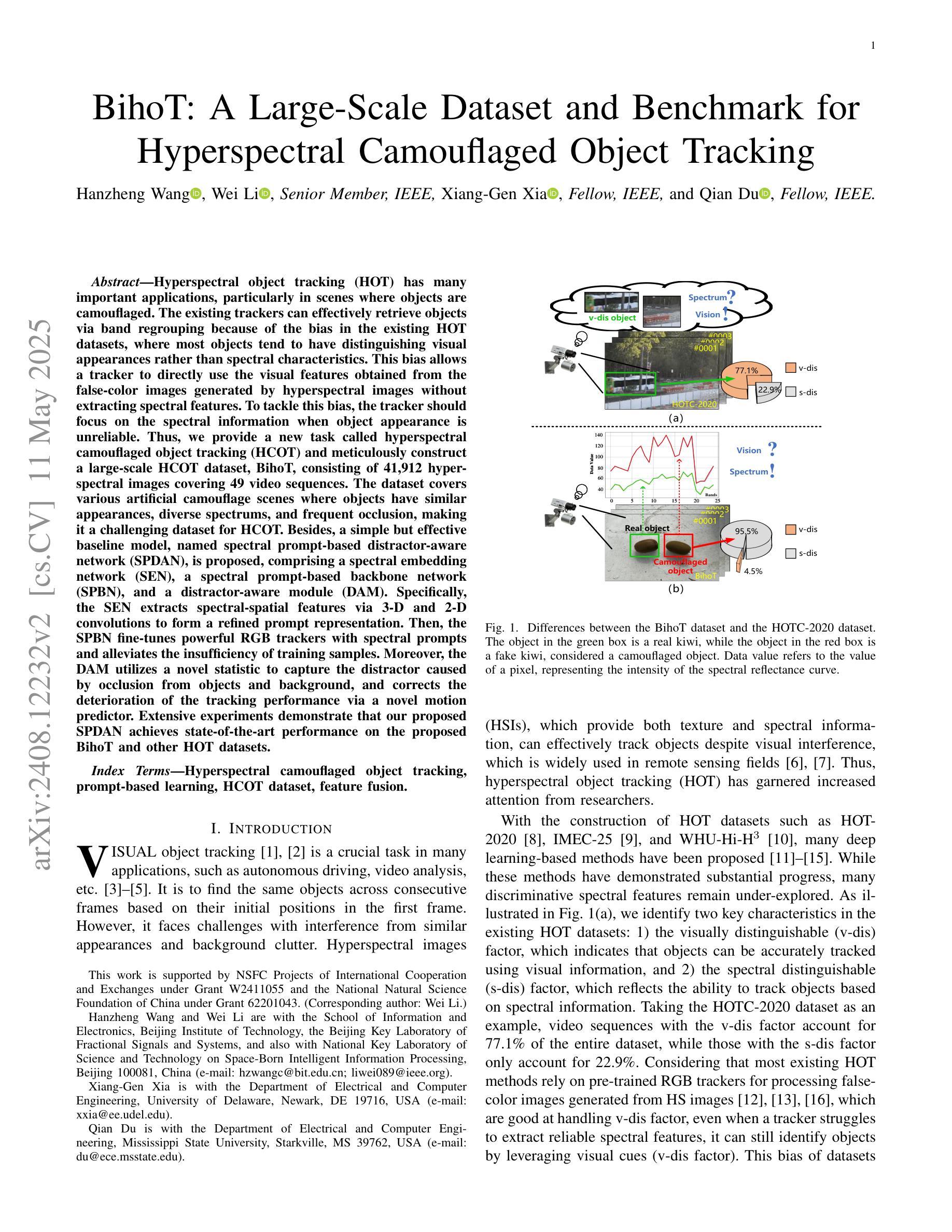
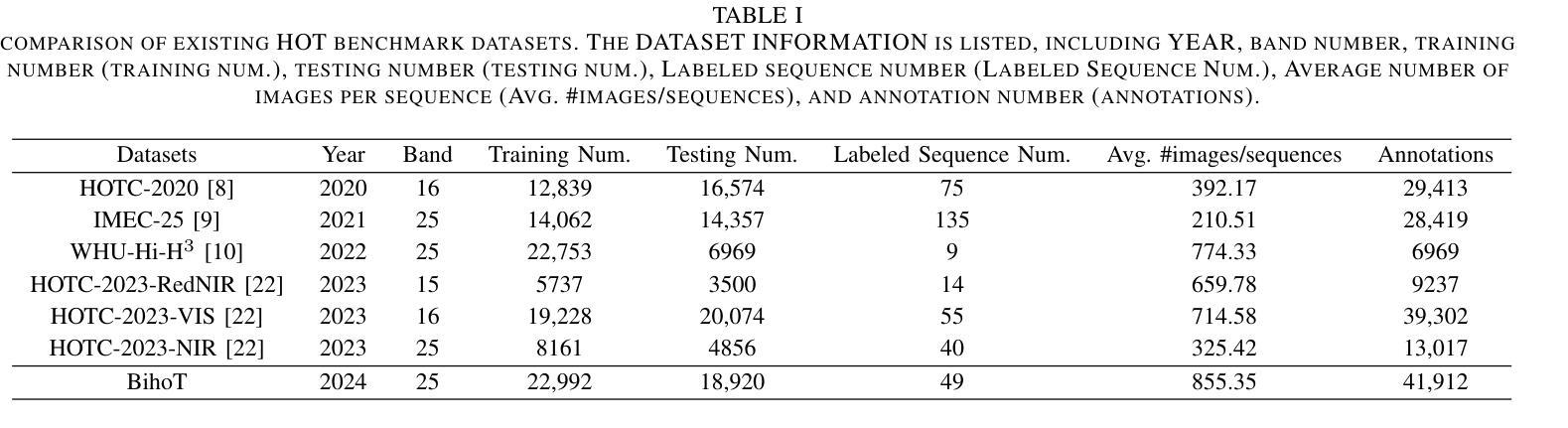
Hyperspectral object tracking (HOT) has exhibited potential in various applications, particularly in scenes where objects are camouflaged. Existing trackers can effectively retrieve objects via band regrouping because of the bias in existing HOT datasets, where most objects tend to have distinguishing visual appearances rather than spectral characteristics. This bias allows the tracker to directly use the visual features obtained from the false-color images generated by hyperspectral images without the need to extract spectral features. To tackle this bias, we find that the tracker should focus on the spectral information when object appearance is unreliable. Thus, we provide a new task called hyperspectral camouflaged object tracking (HCOT) and meticulously construct a large-scale HCOT dataset, termed BihoT, which consists of 41,912 hyperspectral images covering 49 video sequences. The dataset covers various artificial camouflage scenes where objects have similar appearances, diverse spectrums, and frequent occlusion, making it a very challenging dataset for HCOT. Besides, a simple but effective baseline model, named spectral prompt-based distractor-aware network (SPDAN), is proposed, comprising a spectral embedding network (SEN), a spectral prompt-based backbone network (SPBN), and a distractor-aware module (DAM). Specifically, the SEN extracts spectral-spatial features via 3-D and 2-D convolutions. Then, the SPBN fine-tunes powerful RGB trackers with spectral prompts and alleviates the insufficiency of training samples. Moreover, the DAM utilizes a novel statistic to capture the distractor caused by occlusion from objects and background. Extensive experiments demonstrate that our proposed SPDAN achieves state-of-the-art performance on the proposed BihoT and other HOT datasets.
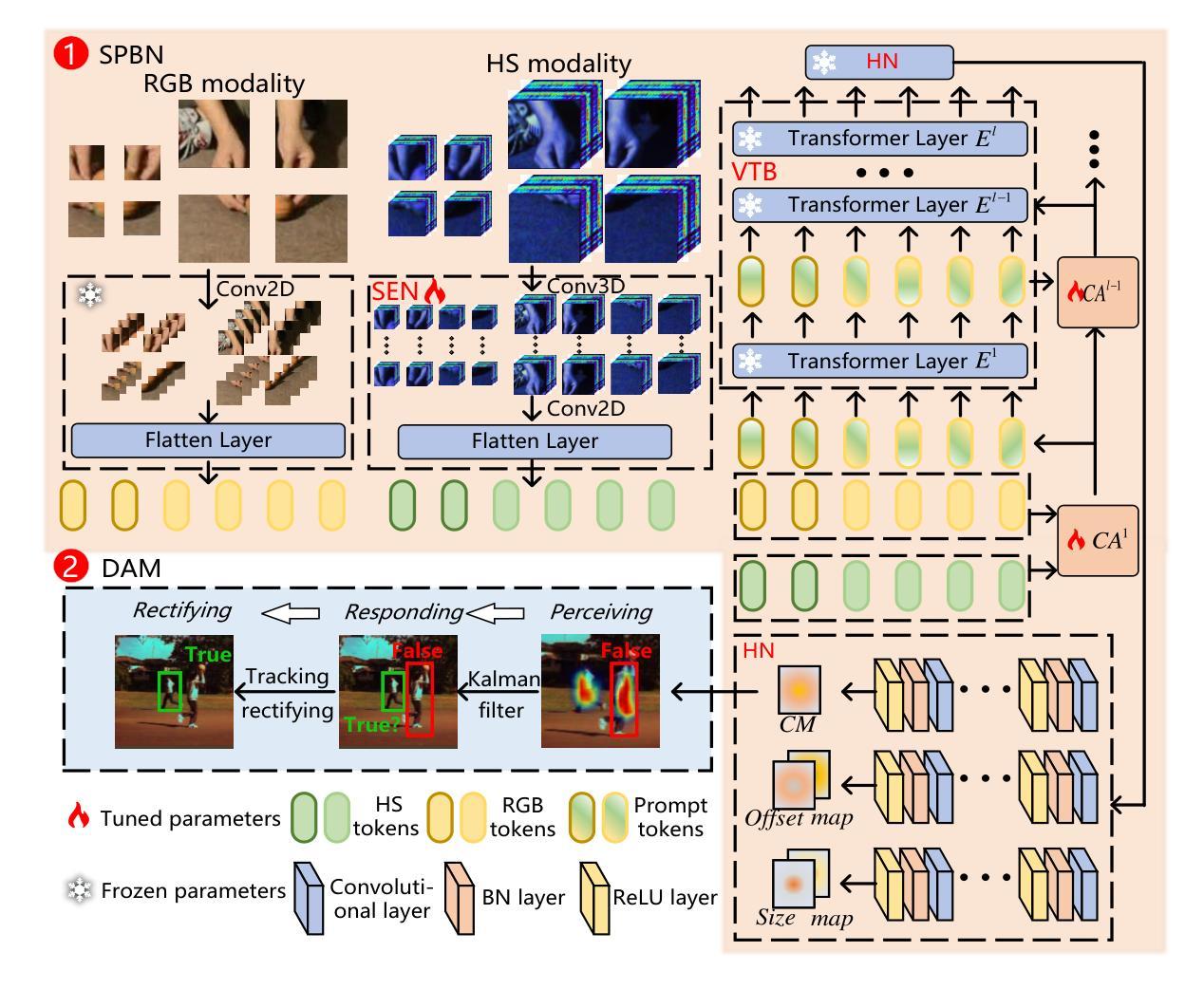
高光谱目标跟踪(HOT)在各种应用中已显示出潜力,特别是在目标伪装场景中。现有的跟踪器可以通过波段重组有效地检索目标,这是因为现有HOT数据集存在的偏见,大多数目标往往具有区分度的是视觉外观而不是光谱特征。这种偏见使得跟踪器能够直接使用从高光谱图像生成的假彩色图像获得的视觉特征,而无需提取光谱特征。为了解决这种偏见,我们发现当目标外观不可靠时,跟踪器应专注于光谱信息。因此,我们提供了一个新的任务,称为高光谱伪装目标跟踪(HCOT),并精心构建了一个大规模的HCOT数据集,名为BihoT,由覆盖49个视频序列的41912个高光谱图像组成。该数据集涵盖了各种人工伪装场景,其中目标具有相似的外观、多样的光谱和频繁遮挡,使其成为HCOT非常有挑战性的数据集。此外,提出了一个简单有效的基线模型,称为基于光谱提示的分心网络(SPDAN),它由光谱嵌入网络(SEN)、基于光谱提示的主干网络(SPBN)和分心模块(DAM)组成。具体而言,SEN通过3D和2D卷积提取光谱空间特征。然后,SPBN利用光谱提示微调功能强大的RGB跟踪器并缓解训练样本不足的问题。此外,DAM利用一种新型统计方法来捕捉由目标和背景遮挡造成的分心物。大量实验表明,我们提出的SPDAN在提出的BihoT和其他HOT数据集上达到了最先进的性能。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems, 2025
摘要
本文介绍了超光谱伪装目标跟踪(HCOT)的新任务及其挑战。针对现有超光谱目标跟踪(HOT)数据集的偏见问题,提出了大型HCOT数据集BihoT的构建方法,包含各种伪装场景下的复杂变化目标。同时,提出了一种简单有效的基线模型SPDAN,能够在数据集上取得一流性能。SPDAN包含光谱嵌入网络、光谱提示背景网络和干扰识别模块。其中,光谱嵌入网络通过三维和二维卷积提取光谱空间特征;光谱提示背景网络通过引入光谱提示优化RGB跟踪器;干扰识别模块能够捕捉遮挡引起的干扰。
关键发现
- 现有超光谱目标跟踪(HOT)数据集存在偏见,更关注目标视觉特征而非光谱特性。
- 提出新的任务:超光谱伪装目标跟踪(HCOT),以解决现有偏见问题。
- 构建大型HCOT数据集BihoT,包含复杂伪装场景下的目标图像和视频序列。
- SPDAN基线模型包括光谱嵌入网络(SEN)、光谱提示背景网络(SPBN)和干扰识别模块(DAM)。
- SEN通过三维和二维卷积提取光谱空间特征。
- SPBN通过引入光谱提示优化RGB跟踪器,缓解训练样本不足的问题。
- DAM能够捕捉遮挡引起的干扰,提高跟踪性能。
点此查看论文截图