⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-05-14 更新
GIFStream: 4D Gaussian-based Immersive Video with Feature Stream
Authors:Hao Li, Sicheng Li, Xiang Gao, Abudouaihati Batuer, Lu Yu, Yiyi Liao
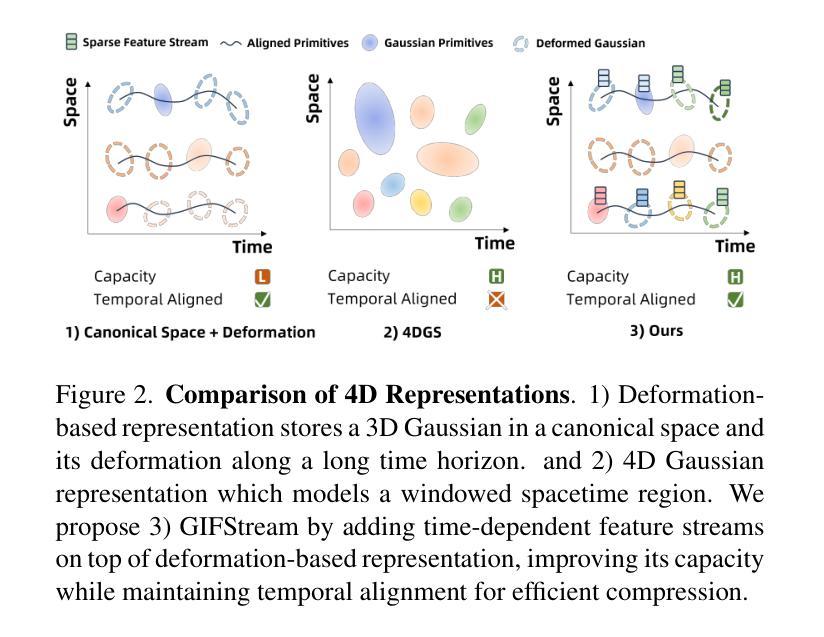
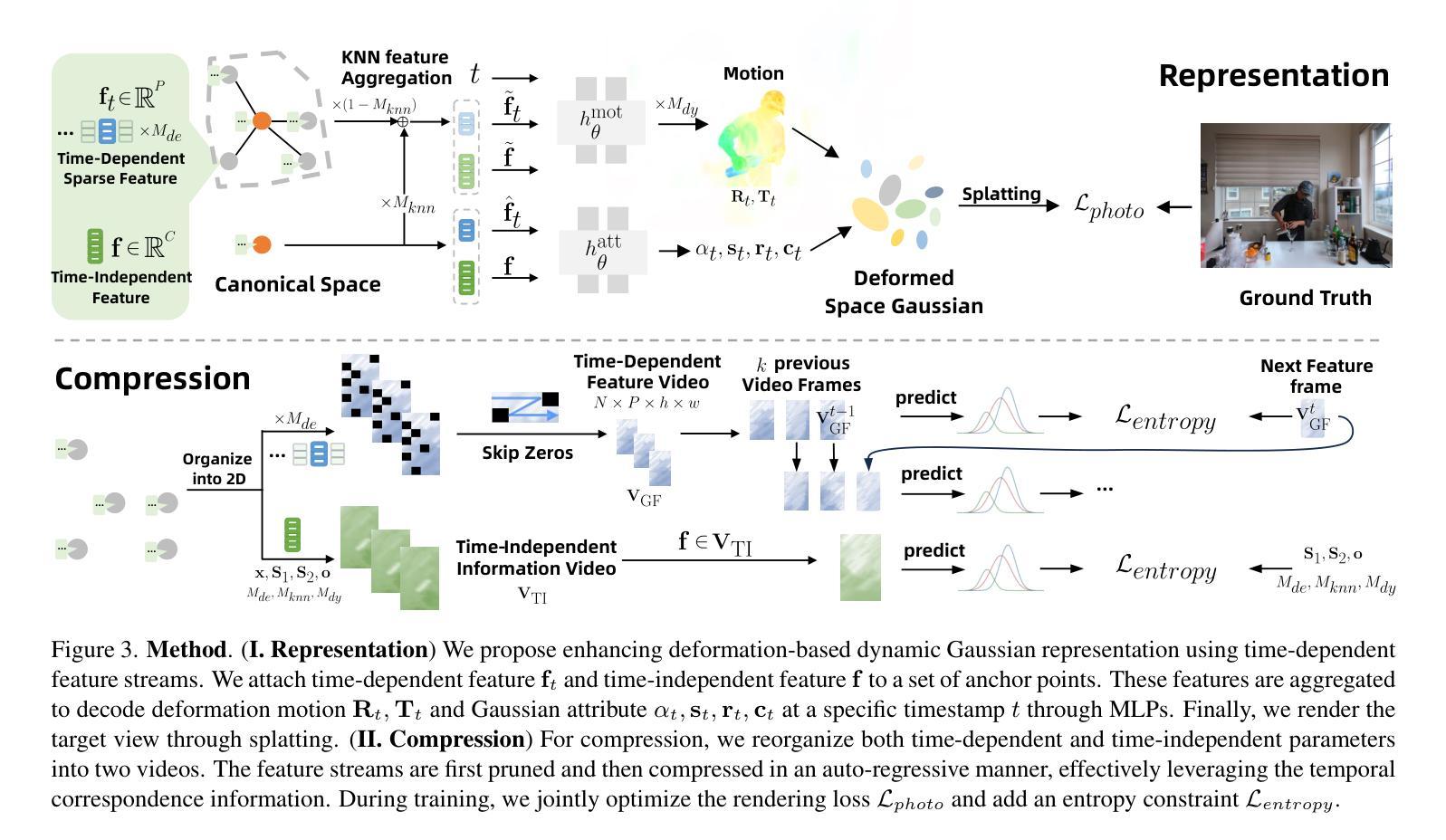
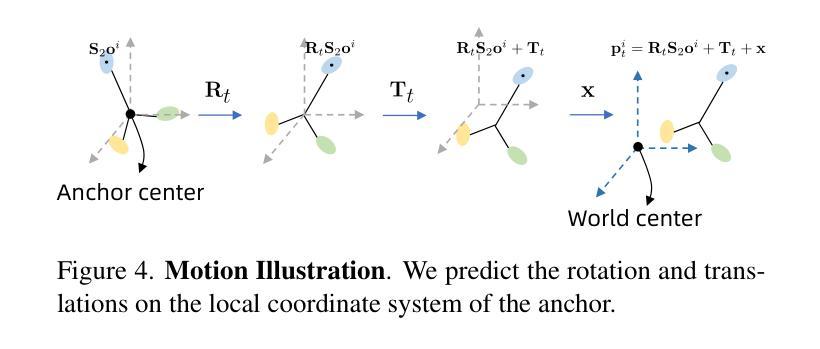
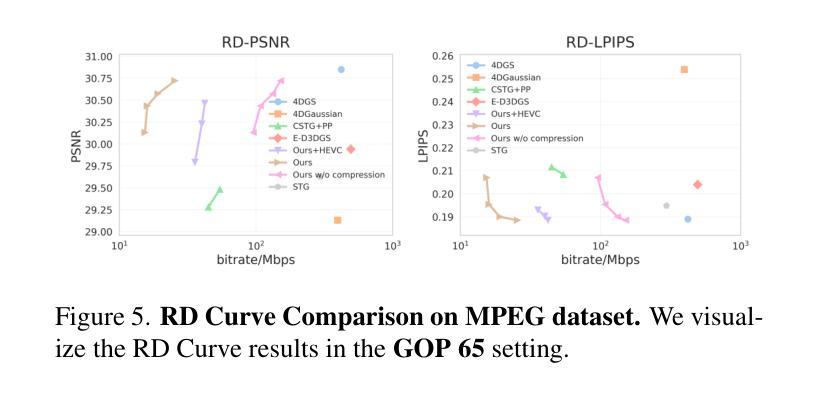
Immersive video offers a 6-Dof-free viewing experience, potentially playing a key role in future video technology. Recently, 4D Gaussian Splatting has gained attention as an effective approach for immersive video due to its high rendering efficiency and quality, though maintaining quality with manageable storage remains challenging. To address this, we introduce GIFStream, a novel 4D Gaussian representation using a canonical space and a deformation field enhanced with time-dependent feature streams. These feature streams enable complex motion modeling and allow efficient compression by leveraging temporal correspondence and motion-aware pruning. Additionally, we incorporate both temporal and spatial compression networks for end-to-end compression. Experimental results show that GIFStream delivers high-quality immersive video at 30 Mbps, with real-time rendering and fast decoding on an RTX 4090. Project page: https://xdimlab.github.io/GIFStream
沉浸式视频提供了六自由度(6DoF)的观看体验,在未来视频技术中可能发挥关键作用。最近,由于具有较高的渲染效率和质量,4D高斯贴图技术受到了关注。然而,如何在可管理的存储条件下保持质量仍然是一个挑战。为了解决这个问题,我们引入了GIFStream,这是一种新的4D高斯表示方法,使用标准空间和增强变形场的时间相关特征流。这些特征流能够进行复杂的运动建模,并利用时间对应和运动感知修剪实现有效的压缩。此外,我们结合了时间和空域压缩网络进行端到端的压缩。实验结果表明,GIFStream在RTX 4090上以30 Mbps的速度提供高质量的沉浸式视频,具有实时渲染和快速解码功能。项目页面:https://xdimlab.github.io/GIFStream
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 14 pages, 10 figures
Summary
一种名为GIFStream的新型4D高斯表示方法,利用规范空间和增强变形场以及时间相关特性流,为沉浸式视频提供了高效渲染和压缩方案,可支持复杂运动建模,能在RTX 4090上实现实时渲染和快速解码,为未来的视频技术带来关键性影响。
Key Takeaways
- GIFStream是一种新型的4D高斯表示方法,利用规范空间和增强变形场技术。
- GIFStream通过引入时间相关特性流,支持复杂运动建模。
- GIFStream能实现在保持高质量沉浸式视频的同时,对视频进行高效压缩。
- GIFStream解决了在存储和管理质量方面的挑战。
- GIFStream能在RTX 4090上实现实时渲染和快速解码。
- GIFStream的实时渲染性能为其在未来视频技术中的应用提供了可能性。
点此查看论文截图

TUM2TWIN: Introducing the Large-Scale Multimodal Urban Digital Twin Benchmark Dataset
Authors:Olaf Wysocki, Benedikt Schwab, Manoj Kumar Biswanath, Qilin Zhang, Jingwei Zhu, Thomas Froech, Medhini Heeramaglore, Ihab Hijazi, Khaoula Kanna, Mathias Pechinger, Zhaiyu Chen, Yao Sun, Alejandro Rueda Segura, Ziyang Xu, Omar AbdelGafar, Mansour Mehranfar, Chandan Yeshwanth, Yueh-Cheng Liu, Hadi Yazdi, Jiapan Wang, Stefan Auer, Katharina Anders, Klaus Bogenberger, Andre Borrmann, Angela Dai, Ludwig Hoegner, Christoph Holst, Thomas H. Kolbe, Ferdinand Ludwig, Matthias Nießner, Frank Petzold, Xiao Xiang Zhu, Boris Jutzi
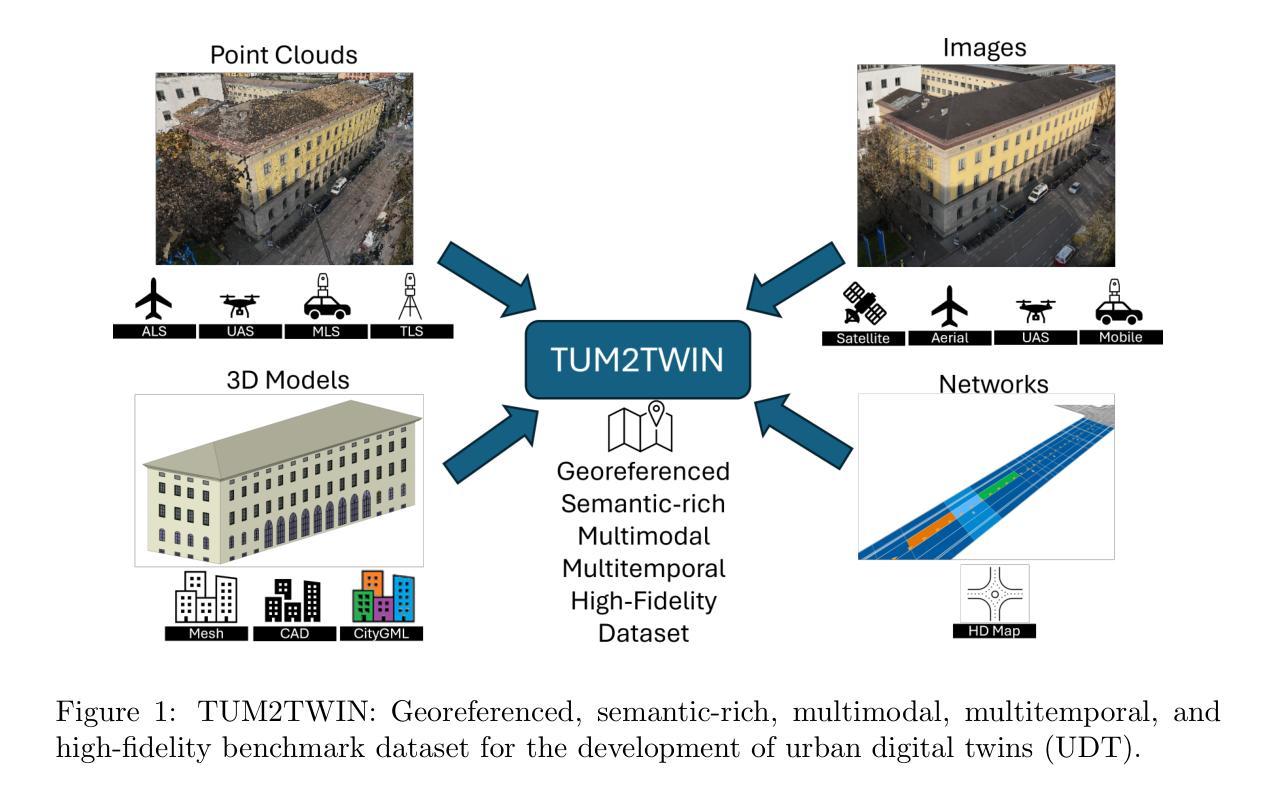
Urban Digital Twins (UDTs) have become essential for managing cities and integrating complex, heterogeneous data from diverse sources. Creating UDTs involves challenges at multiple process stages, including acquiring accurate 3D source data, reconstructing high-fidelity 3D models, maintaining models’ updates, and ensuring seamless interoperability to downstream tasks. Current datasets are usually limited to one part of the processing chain, hampering comprehensive UDTs validation. To address these challenges, we introduce the first comprehensive multimodal Urban Digital Twin benchmark dataset: TUM2TWIN. This dataset includes georeferenced, semantically aligned 3D models and networks along with various terrestrial, mobile, aerial, and satellite observations boasting 32 data subsets over roughly 100,000 $m^2$ and currently 767 GB of data. By ensuring georeferenced indoor-outdoor acquisition, high accuracy, and multimodal data integration, the benchmark supports robust analysis of sensors and the development of advanced reconstruction methods. Additionally, we explore downstream tasks demonstrating the potential of TUM2TWIN, including novel view synthesis of NeRF and Gaussian Splatting, solar potential analysis, point cloud semantic segmentation, and LoD3 building reconstruction. We are convinced this contribution lays a foundation for overcoming current limitations in UDT creation, fostering new research directions and practical solutions for smarter, data-driven urban environments. The project is available under: https://tum2t.win
城市数字双胞胎(UDTs)对于管理城市以及整合来自不同源的复杂、异构数据已经变得至关重要。创建UDTs涉及多个流程阶段的挑战,包括获取准确的3D源数据、重建高保真3D模型、保持模型的更新以及确保无缝地衔接下游任务。当前的数据集通常仅限于处理链的一部分,阻碍了全面的UDTs验证。为了应对这些挑战,我们引入了第一个综合多模式城市数字双胞胎基准数据集:TUM2TWIN。该数据集包括地理参照的、语义对齐的3D模型和网络,以及各种地面、移动、空中和卫星观测数据,拥有超过约10万$m^2$的32个数据集和目前总计767GB的数据。通过确保地理参照的室内外采集、高精度和多模式数据整合,该基准数据集支持对传感器的稳健分析以及先进重建方法的发展。此外,我们还探索了下游任务,展示了TUM2TWIN的潜力,包括NeRF和高斯贴图的全新视图合成、太阳能潜力分析、点云语义分割和LOD3建筑重建。我们相信这一贡献为克服UDTs创建中的当前局限性奠定了基础,并促进了智能、数据驱动的城市环境的新研究方向和实际解决方案的发展。该项目网址为:[https://tum2t.win/]
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Submitted to the ISPRS Journal of Photogrammetry and Remote Sensing
Summary
本文介绍了城市数字双胞胎(UDTs)在管理城市和整合复杂、异构数据方面的作用。针对创建UDTs所面临的挑战,如获取准确的3D源数据、重建高保真3D模型等,研究者引入了首个多模式城市数字双胞胎基准数据集TUM2TWIN。该数据集包含地理参考的语义对齐的3D模型和网络,以及各种地面、移动、空中和卫星观测数据,包含约10万平米的约含超过数据子集高达32个的共767GB的数据。该基准数据集支持传感器稳健性分析和发展高级重建方法的研究。此数据集对城市数字双胞胎的下游任务具有潜力,包括新型视图合成和太阳能潜力分析等。本项目的贡献为克服UDT创建中的现有局限性奠定了基石,并为更智能的数据驱动城市环境的研究和实际应用提供了方向。
Key Takeaways
- 城市数字双胞胎(UDTs)对于城市管理和整合复杂数据至关重要。
- 创建UDTs面临多个挑战,如获取准确数据、模型重建等。
- TUM2TWIN是首个多模式城市数字双胞胎基准数据集,包含丰富的地理参考数据。
- TUM2TWIN包含地面、移动、空中和卫星等多种观测数据,并支持传感器稳健性分析和高级重建方法的发展。
- 该数据集有助于多种下游任务,如新型视图合成和太阳能潜力分析。
- TUM2TWIN为克服UDT创建中的局限性提供了基础。
点此查看论文截图


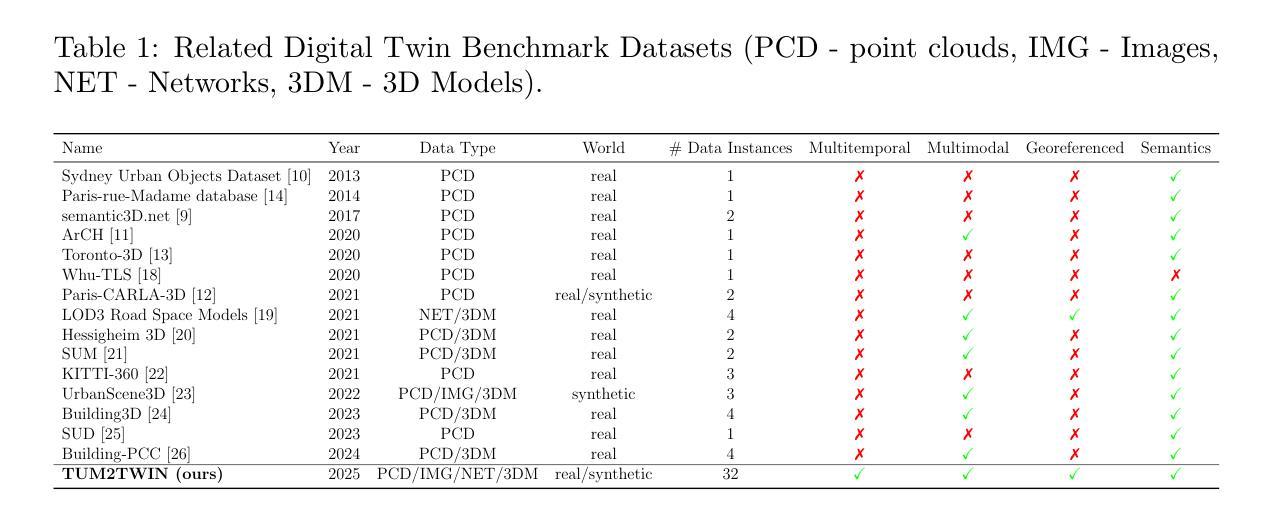
TeGA: Texture Space Gaussian Avatars for High-Resolution Dynamic Head Modeling
Authors:Gengyan Li, Paulo Gotardo, Timo Bolkart, Stephan Garbin, Kripasindhu Sarkar, Abhimitra Meka, Alexandros Lattas, Thabo Beeler
Sparse volumetric reconstruction and rendering via 3D Gaussian splatting have recently enabled animatable 3D head avatars that are rendered under arbitrary viewpoints with impressive photorealism. Today, such photoreal avatars are seen as a key component in emerging applications in telepresence, extended reality, and entertainment. Building a photoreal avatar requires estimating the complex non-rigid motion of different facial components as seen in input video images; due to inaccurate motion estimation, animatable models typically present a loss of fidelity and detail when compared to their non-animatable counterparts, built from an individual facial expression. Also, recent state-of-the-art models are often affected by memory limitations that reduce the number of 3D Gaussians used for modeling, leading to lower detail and quality. To address these problems, we present a new high-detail 3D head avatar model that improves upon the state of the art, largely increasing the number of 3D Gaussians and modeling quality for rendering at 4K resolution. Our high-quality model is reconstructed from multiview input video and builds on top of a mesh-based 3D morphable model, which provides a coarse deformation layer for the head. Photoreal appearance is modelled by 3D Gaussians embedded within the continuous UVD tangent space of this mesh, allowing for more effective densification where most needed. Additionally, these Gaussians are warped by a novel UVD deformation field to capture subtle, localized motion. Our key contribution is the novel deformable Gaussian encoding and overall fitting procedure that allows our head model to preserve appearance detail, while capturing facial motion and other transient high-frequency features such as skin wrinkling.
通过3D高斯贴图(Gaussian Splatting)进行稀疏体积重建和渲染,最近已经能够实现可动画的3D头像,这些头像可在任意视点以令人印象深刻的逼真度进行渲染。如今,这种逼真的头像被视为远程存在、扩展现实和娱乐等新兴应用中的关键组成部分。构建逼真的头像需要估计输入视频图像中不同面部组件的复杂非刚性运动;由于运动估计不准确,与不可动画的同行相比,可动画模型在细节和保真度方面通常会损失。此外,最新技术模型通常受到内存限制的影响,减少了用于建模的3D高斯数量,导致细节和质量下降。为了解决这些问题,我们提出了一种新的高细节3D头像模型,该模型改进了现有技术,大大提高了用于以4K分辨率渲染的3D高斯数量和建模质量。我们的高质量模型是从多视角输入视频重建的,并基于网格化的3D可变形模型进行构建,该模型为头部提供了一个粗略的变形层。通过嵌入到此网格的连续UVD切线空间中的3D高斯来模拟逼真的外观,允许在需要的地方更有效地密集化。此外,这些高斯被一个新型的UVD变形场扭曲以捕捉微妙的局部运动。我们的主要贡献是可变形的高斯编码和整体拟合程序,这使我们能够保留头像的细节,同时捕捉面部运动和其他瞬态高频特征,如皮肤皱纹。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 10 pages, 9 figures, supplementary results found at: https://syntec-research.github.io/UVGA/, to be published in SIGGRAPH 2025
Summary
本文介绍了通过3D高斯贴图技术实现的高细节三维头像模型。该模型能够从多角度视频输入中重建和渲染,具有动画功能,并在4K分辨率下呈现出令人印象深刻的逼真度。模型基于网格的3D可变形模型提供粗糙的头部变形层,而真实感的外观则是通过嵌入到此网格的连续UVD切线空间的3D高斯实现的。此外,通过新颖的UVD变形场对高斯进行变形,以捕捉细微的局部运动。主要贡献在于可变形的高斯编码和整体拟合程序,允许头像模型在捕捉面部运动和其他短暂的高频特征(如皮肤皱纹)的同时保留外观细节。
Key Takeaways
- 3D高斯贴图技术用于创建高细节三维头像模型。
- 模型能够从多角度视频输入中重建和渲染,具有动画功能。
- 模型在4K分辨率下呈现逼真的效果。
- 网格的3D可变形模型提供头部的粗糙变形层。
- 真实感的外观通过嵌入到网格UVD切线空间的3D高斯实现。
- 通过UVD变形场捕捉细微的局部运动。
点此查看论文截图
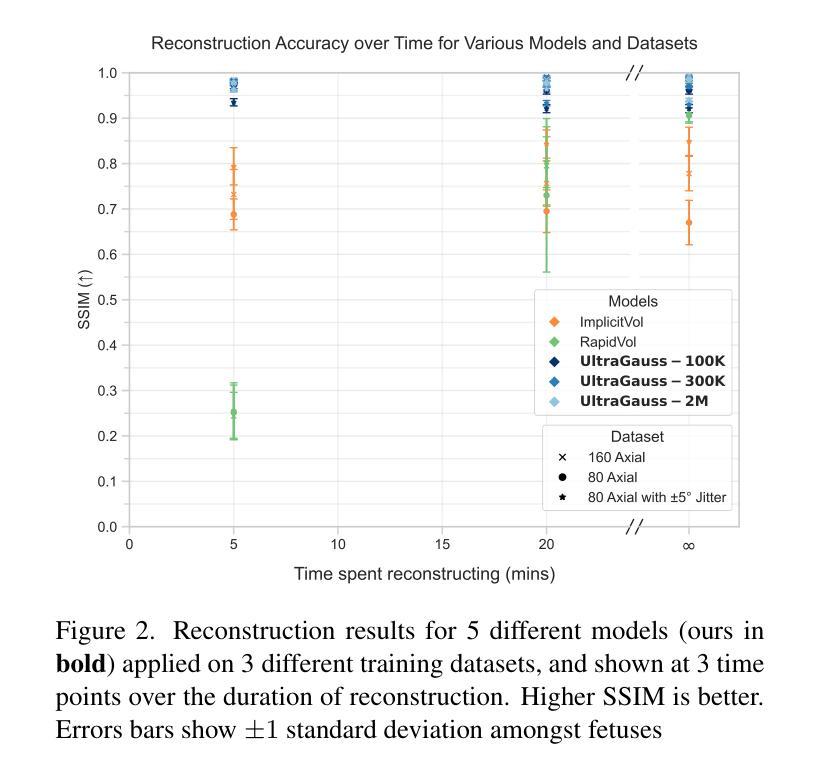
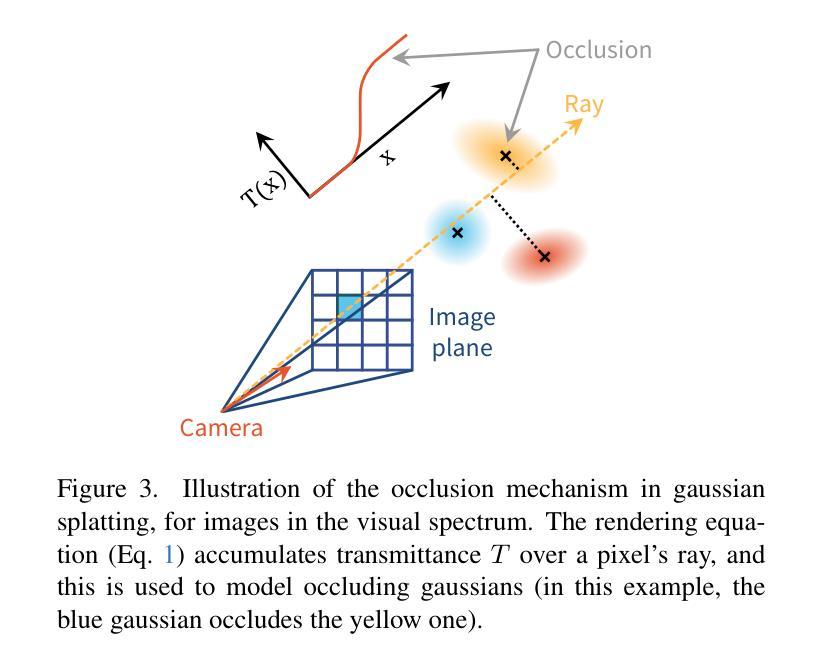
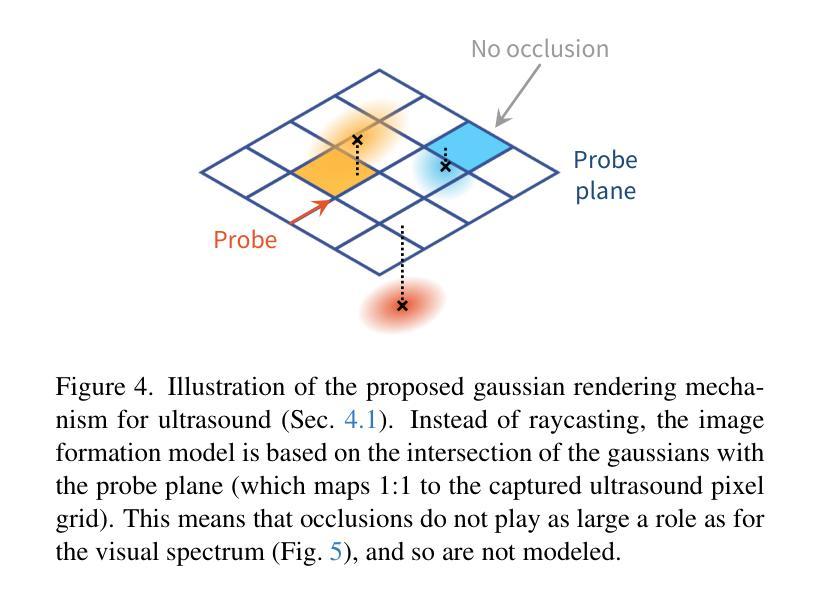
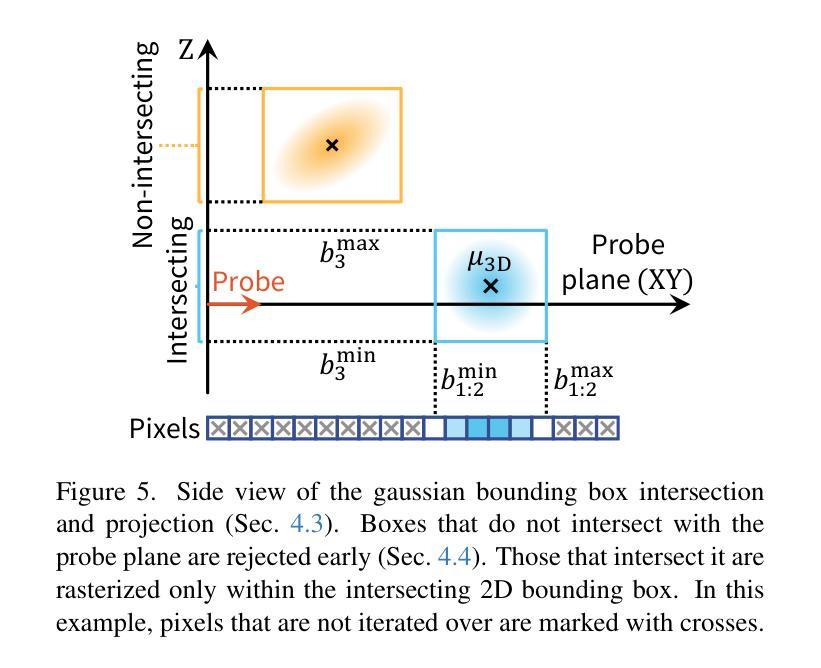
UltraGauss: Ultrafast Gaussian Reconstruction of 3D Ultrasound Volumes
Authors:Mark C. Eid, Ana I. L. Namburete, João F. Henriques
Ultrasound imaging is widely used due to its safety, affordability, and real-time capabilities, but its 2D interpretation is highly operator-dependent, leading to variability and increased cognitive demand. 2D-to-3D reconstruction mitigates these challenges by providing standardized volumetric views, yet existing methods are often computationally expensive, memory-intensive, or incompatible with ultrasound physics. We introduce UltraGauss: the first ultrasound-specific Gaussian Splatting framework, extending view synthesis techniques to ultrasound wave propagation. Unlike conventional perspective-based splatting, UltraGauss models probe-plane intersections in 3D, aligning with acoustic image formation. We derive an efficient rasterization boundary formulation for GPU parallelization and introduce a numerically stable covariance parametrization, improving computational efficiency and reconstruction accuracy. On real clinical ultrasound data, UltraGauss achieves state-of-the-art reconstructions in 5 minutes, and reaching 0.99 SSIM within 20 minutes on a single GPU. A survey of expert clinicians confirms UltraGauss’ reconstructions are the most realistic among competing methods. Our CUDA implementation will be released upon publication.
超声波成像因其安全性、可负担性和实时功能而得到广泛应用,但其二维解读高度依赖于操作人员,导致可变性和认知需求增加。二维到三维重建通过提供标准化体积视图来缓解这些挑战,但现有方法往往计算量大、内存密集,或与超声物理不兼容。我们推出了UltraGauss:首个专门针对超声的高斯喷绘框架,将视图合成技术扩展到超声波传播。与基于传统透视的喷绘不同,UltraGauss在三维空间中模拟探针平面交点,与声成像形成对齐。我们为GPU并行化推导了高效的栅格化边界公式,并引入数值稳定的协方差参数化,提高了计算效率和重建精度。在真实的临床超声数据上,UltraGauss在5分钟内实现了最先进的重建效果,并在单个GPU上20分钟内达到0.99的结构相似性度量指数。专家医生的调查证实,UltraGauss的重建效果在竞争方法中最为现实。我们的CUDA实现将在发表时发布。
论文及项目相关链接
摘要
超声成像因其安全性、经济性和实时性能而得到广泛应用,但其二维解释高度依赖于操作者,导致差异性和认知需求增加。二维到三维重建通过提供标准化体积视图来缓解这些挑战,但现有方法往往计算量大、内存密集或与超声物理不兼容。本文介绍UltraGauss:首个超声专用高斯Splatting框架,将视图合成技术扩展到超声波传播。与传统的基于透视的Splatting不同,UltraGauss在三维空间中模拟探针平面交点,与声学图像形成相一致。我们推导了一种高效的栅格化边界公式,用于GPU并行化,并引入了一种数值稳定的协方差参数化,提高了计算效率和重建精度。在真实临床超声数据上,UltraGauss在5分钟内实现最先进的重建效果,在单个GPU上20分钟内结构相似性度量(SSIM)达到0.99。专家医生的调查显示,UltraGauss的重建效果在竞品方法中最为真实。我们的CUDA实现将在发表时发布。
要点提炼
- 超声成像虽然广泛应用,但其二维解释存在操作者依赖性问题,导致差异和认知需求增加。
- 二维到三维重建是解决此问题的一种方法,但现有方法存在计算量大、内存密集或与超声物理不兼容的问题。
- UltraGauss是首个超声专用高斯Splatting框架,将视图合成技术扩展到超声波传播,实现三维重建。
- UltraGauss采用高效的栅格化边界公式和数值稳定的协方差参数化,提高计算效率和重建精度。
- 在真实临床数据测试中,UltraGauss达到先进的重建效果,结构相似性度量(SSIM)高。
- 专家医生评价UltraGauss的重建效果最为真实。
点此查看论文截图

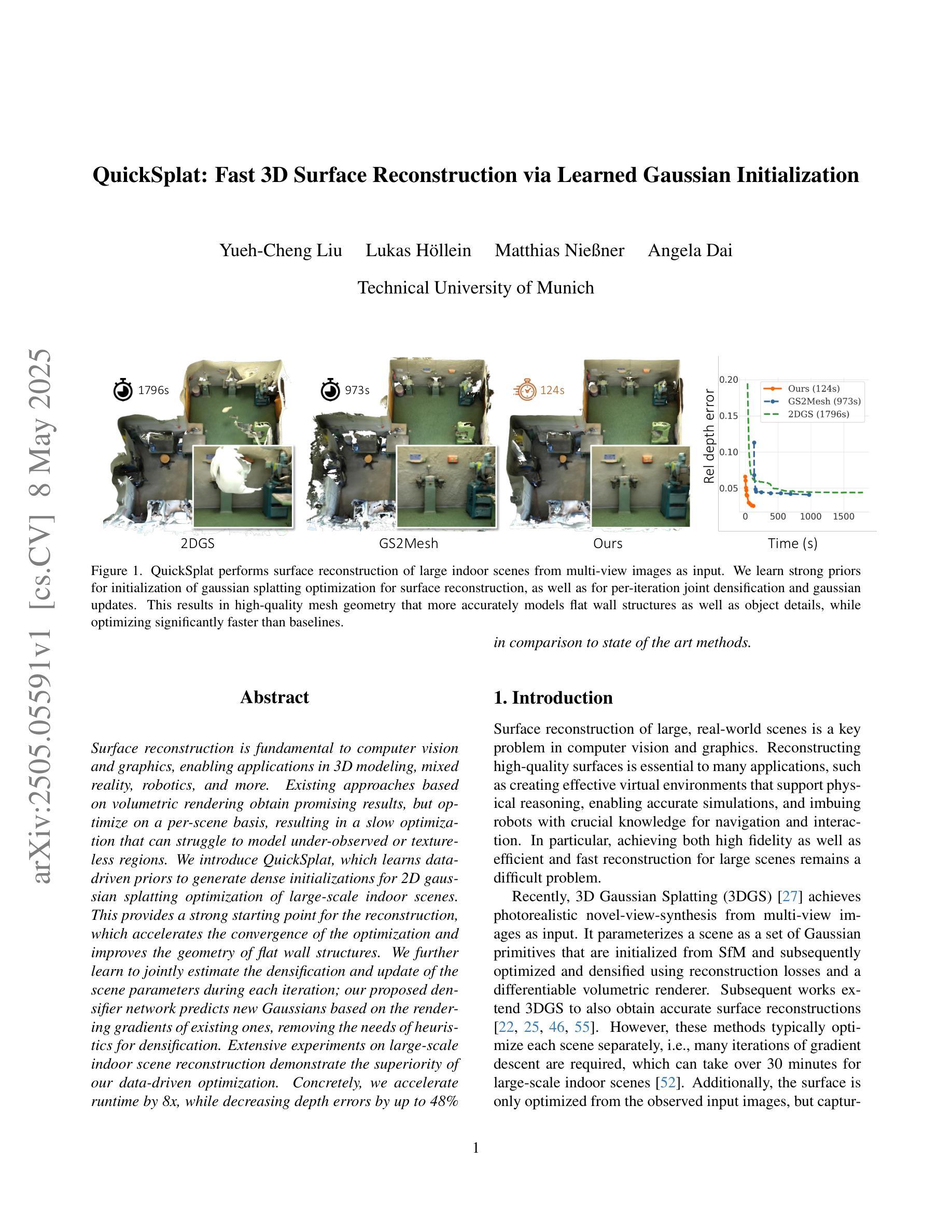
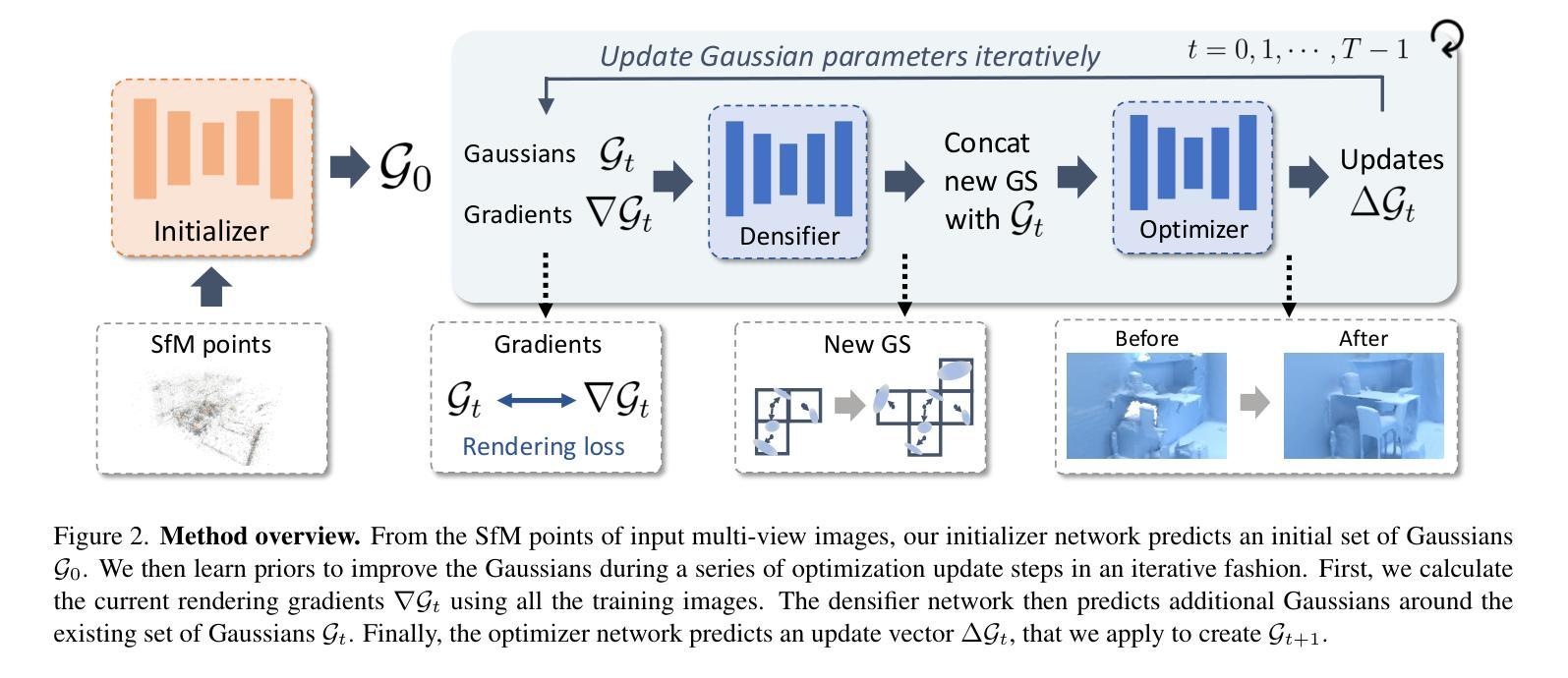
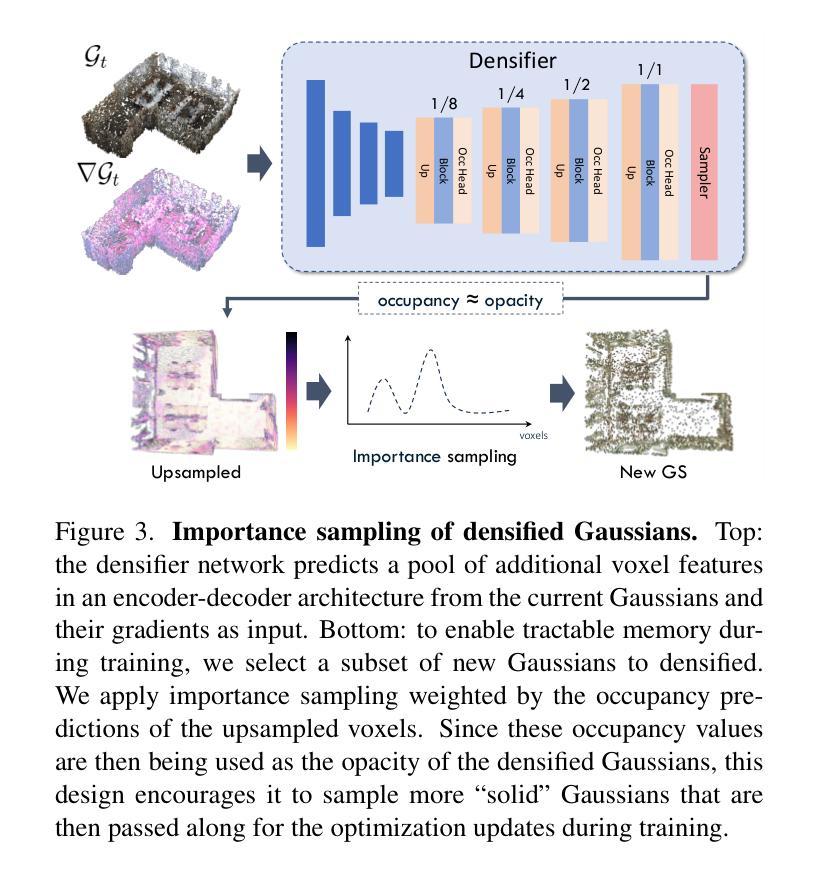
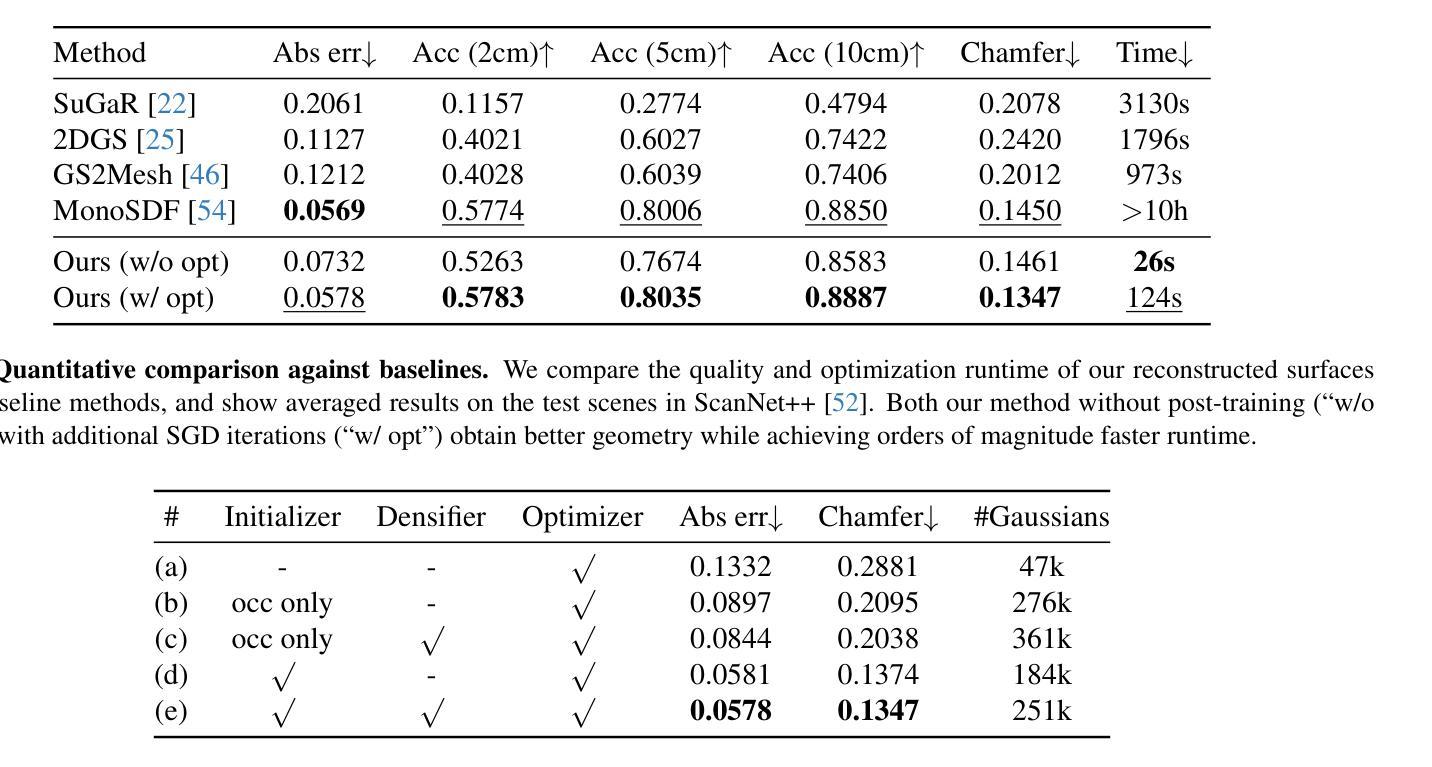
QuickSplat: Fast 3D Surface Reconstruction via Learned Gaussian Initialization
Authors:Yueh-Cheng Liu, Lukas Höllein, Matthias Nießner, Angela Dai
Surface reconstruction is fundamental to computer vision and graphics, enabling applications in 3D modeling, mixed reality, robotics, and more. Existing approaches based on volumetric rendering obtain promising results, but optimize on a per-scene basis, resulting in a slow optimization that can struggle to model under-observed or textureless regions. We introduce QuickSplat, which learns data-driven priors to generate dense initializations for 2D gaussian splatting optimization of large-scale indoor scenes. This provides a strong starting point for the reconstruction, which accelerates the convergence of the optimization and improves the geometry of flat wall structures. We further learn to jointly estimate the densification and update of the scene parameters during each iteration; our proposed densifier network predicts new Gaussians based on the rendering gradients of existing ones, removing the needs of heuristics for densification. Extensive experiments on large-scale indoor scene reconstruction demonstrate the superiority of our data-driven optimization. Concretely, we accelerate runtime by 8x, while decreasing depth errors by up to 48% in comparison to state of the art methods.
表面重建是计算机视觉和图形学的基础,在3D建模、混合现实、机器人技术等领域有着广泛的应用。现有的基于体积渲染的方法虽然取得了有前景的结果,但它们是针对每个场景进行优化,导致优化过程缓慢,并且在观测不足或无纹理区域建模时遇到困难。我们引入了QuickSplat方法,该方法学习数据驱动先验知识,为大规模室内场景的2D高斯绘制优化生成密集初始化。这为重建提供了一个强有力的起点,加速了优化的收敛,并改善了平面墙结构的几何形状。我们进一步学习在每次迭代中联合估计场景的参数密集化和更新;我们提出的稠密网络根据现有渲染梯度预测新的高斯分布,无需启发式方法进行密集化。大规模室内场景重建的广泛实验表明,我们的数据驱动优化具有优越性。具体来说,我们的方法将运行时速度提高了8倍,与最新技术相比,深度误差减少了高达48%。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Project page: https://liu115.github.io/quicksplat, Video: https://youtu.be/2IA_gnFvFG8
Summary
本文介绍了QuickSplat方法,该方法利用数据驱动先验生成大规模室内场景的密集初始化,用于二维高斯涂抹优化。此方法为重建提供了一个良好的起点,加速了优化的收敛,并改进了平面墙结构的几何形状。通过联合估计场景参数的密集化和更新,提出了一个预测高斯密度的新网络,提高了渲染效果并提升了运行效率。实验结果表明,相较于当前先进方法,QuickSplat具有显著优势,运行时速提高了8倍,深度误差降低了高达48%。
Key Takeaways
- QuickSplat是一种用于大规模室内场景重建的方法,利用数据驱动先验生成密集初始化进行二维高斯涂抹优化。
- 提供了良好的起点用于重建,从而加速了优化的收敛并改善了平面墙结构的几何形状。
- 通过联合估计场景参数的密集化和更新,提高了渲染效果。
- 提出了一种新的网络结构来预测高斯密度,基于现有渲染梯度的学习来消除密集化的启发式需求。
- QuickSplat方法在运行时速度方面显著提高,相对于现有技术,其速度提高了8倍。
- 与当前先进方法相比,QuickSplat在深度误差方面表现出显著优势,降低了高达48%的深度误差。
点此查看论文截图
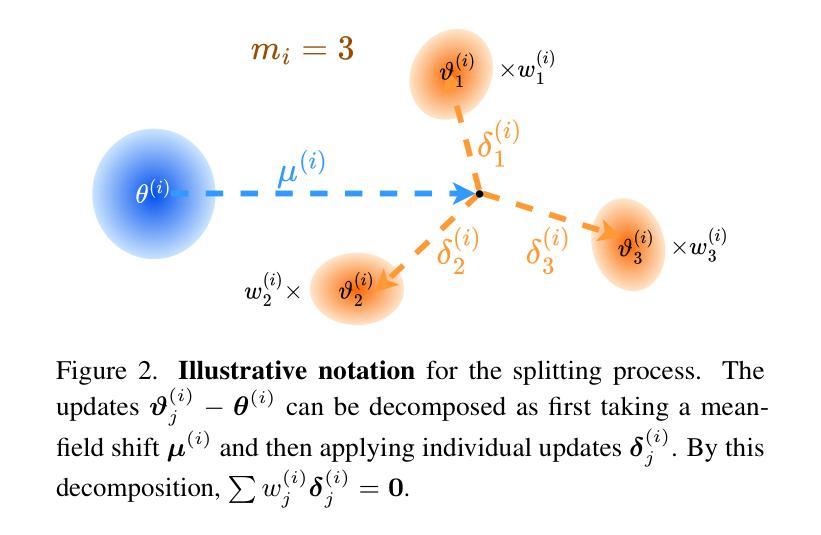
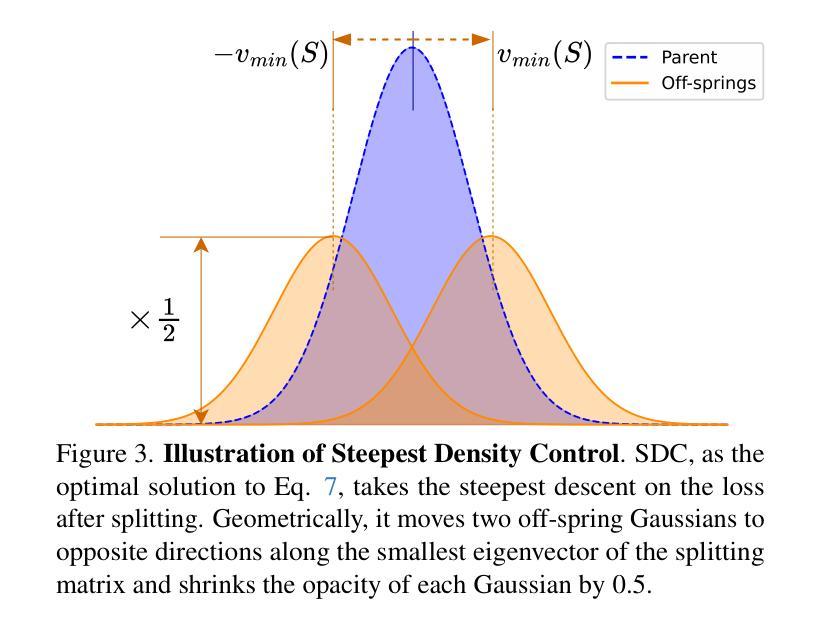
Steepest Descent Density Control for Compact 3D Gaussian Splatting
Authors:Peihao Wang, Yuehao Wang, Dilin Wang, Sreyas Mohan, Zhiwen Fan, Lemeng Wu, Ruisi Cai, Yu-Ying Yeh, Zhangyang Wang, Qiang Liu, Rakesh Ranjan
3D Gaussian Splatting (3DGS) has emerged as a powerful technique for real-time, high-resolution novel view synthesis. By representing scenes as a mixture of Gaussian primitives, 3DGS leverages GPU rasterization pipelines for efficient rendering and reconstruction. To optimize scene coverage and capture fine details, 3DGS employs a densification algorithm to generate additional points. However, this process often leads to redundant point clouds, resulting in excessive memory usage, slower performance, and substantial storage demands - posing significant challenges for deployment on resource-constrained devices. To address this limitation, we propose a theoretical framework that demystifies and improves density control in 3DGS. Our analysis reveals that splitting is crucial for escaping saddle points. Through an optimization-theoretic approach, we establish the necessary conditions for densification, determine the minimal number of offspring Gaussians, identify the optimal parameter update direction, and provide an analytical solution for normalizing off-spring opacity. Building on these insights, we introduce SteepGS, incorporating steepest density control, a principled strategy that minimizes loss while maintaining a compact point cloud. SteepGS achieves a ~50% reduction in Gaussian points without compromising rendering quality, significantly enhancing both efficiency and scalability.
3D高斯展平(3DGS)作为一种强大的实时高分辨率新视角合成技术已崭露头角。通过将场景表示为高斯原始数据的混合物,3DGS利用GPU光栅化管道进行高效渲染和重建。为了优化场景覆盖并捕捉细节,3DGS采用致密化算法生成额外的点。然而,这一过程通常会导致冗余的点云,从而导致内存使用过多、性能下降和存储需求巨大,对资源受限设备的部署构成了重大挑战。为了解决这一局限性,我们提出了一个理论框架,揭秘并改进了3DGS中的密度控制。我们的分析表明,分裂对于逃避鞍点至关重要。通过优化理论方法,我们确定了致密化的必要条件,确定了子代高斯的最小数量,确定了参数更新的最优方向,并为子代不透明度的归一化提供了分析解决方案。基于这些见解,我们引入了SteepGS,结合了最陡密度控制策略,该策略在保持紧凑点云的同时最小化损失。SteepGS在不损害渲染质量的情况下实现了高斯点约50%的减少,显著提高了效率和可扩展性。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF CVPR 2025, Project page: https://vita-group.github.io/SteepGS/
Summary
实时高保真视角合成中的三维高斯融合技术(3DGS)通过高斯原始混合表示场景,利用GPU光栅化管道实现高效渲染与重建。为提高场景覆盖率和精细细节捕捉,3DGS采用稠密化算法生成额外点,但易产生冗余点云,导致内存使用过度、性能下降及存储需求增大,给资源受限设备带来挑战。本研究提出理论框架解析并优化密度控制问题,建立必要稠密化条件,确定最小高斯子代数量,提供子代透明度分析解决方案。基于这些见解,引入SteepGS技术,采用最陡密度控制策略,在减少损失的同时维持紧凑点云,实现高斯点数减少约50%,提升效率和可扩展性而不损失渲染质量。
Key Takeaways
- 3DGS是实时高保真视角合成中的强大技术,通过高斯原始混合表示场景。
- 3DGS利用GPU进行高效渲染和重建,并采用稠密化算法捕捉场景细节。
- 冗余点云问题导致内存消耗大、性能下降和存储需求增加。
- 本研究提出了理论框架改善密度控制问题并建立必要的稠密化条件。
点此查看论文截图

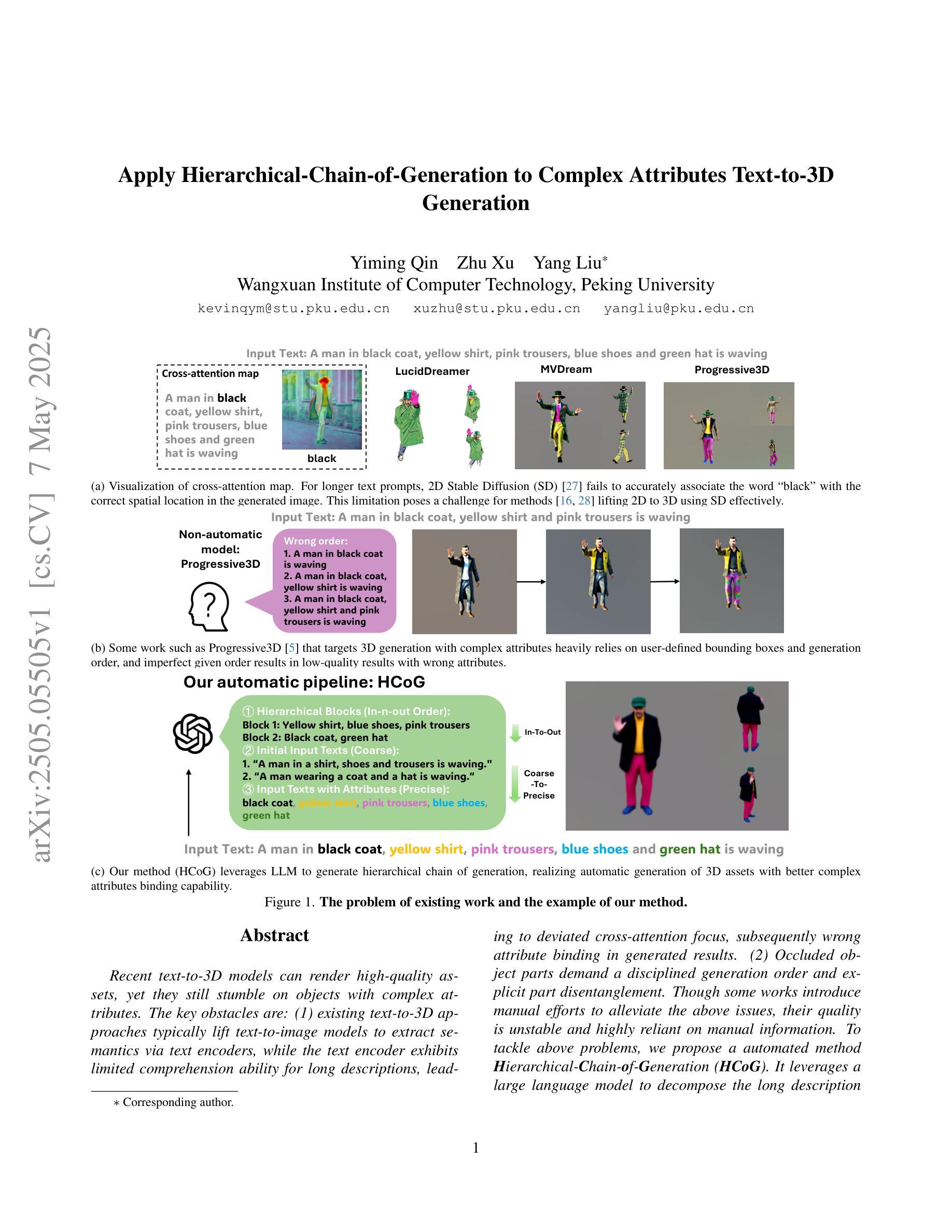
Apply Hierarchical-Chain-of-Generation to Complex Attributes Text-to-3D Generation
Authors:Yiming Qin, Zhu Xu, Yang Liu
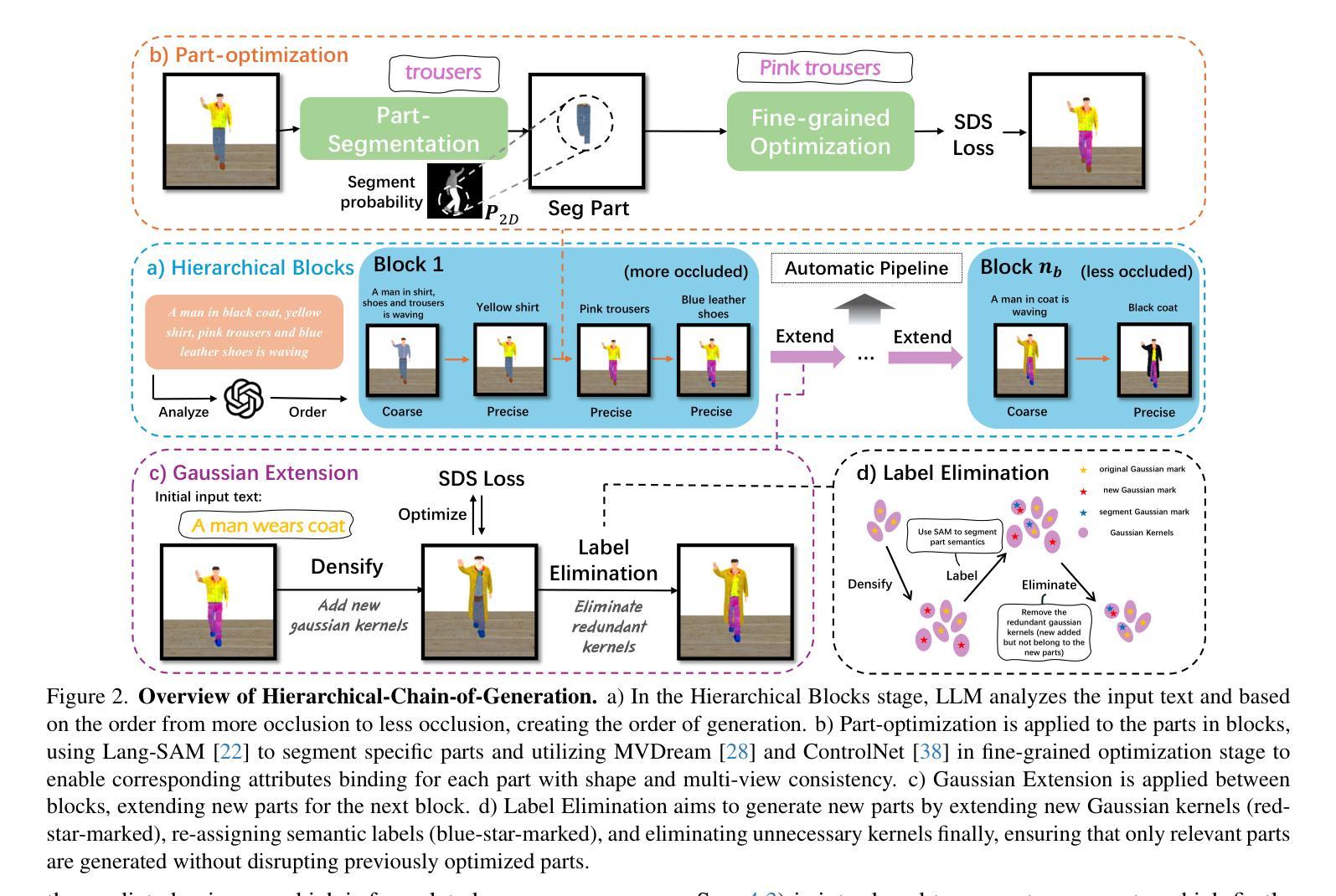
Recent text-to-3D models can render high-quality assets, yet they still stumble on objects with complex attributes. The key obstacles are: (1) existing text-to-3D approaches typically lift text-to-image models to extract semantics via text encoders, while the text encoder exhibits limited comprehension ability for long descriptions, leading to deviated cross-attention focus, subsequently wrong attribute binding in generated results. (2) Occluded object parts demand a disciplined generation order and explicit part disentanglement. Though some works introduce manual efforts to alleviate the above issues, their quality is unstable and highly reliant on manual information. To tackle above problems, we propose a automated method Hierarchical-Chain-of-Generation (HCoG). It leverages a large language model to decompose the long description into blocks representing different object parts, and orders them from inside out according to occlusions, forming a hierarchical chain. Within each block we first coarsely create components, then precisely bind attributes via target-region localization and corresponding 3D Gaussian kernel optimization. Between blocks, we introduce Gaussian Extension and Label Elimination to seamlessly generate new parts by extending new Gaussian kernels, re-assigning semantic labels, and eliminating unnecessary kernels, ensuring that only relevant parts are added without disrupting previously optimized parts. Experiments confirm that HCoG yields structurally coherent, attribute-faithful 3D objects with complex attributes. The code is available at https://github.com/Wakals/GASCOL .
虽然最近的文本到3D模型可以呈现高质量的资产,但它们在处理具有复杂属性的对象时仍然会遇到困难。主要障碍是:(1)现有的文本到3D的方法通常将文本到图像模型提升为通过文本编码器提取语义,而文本编码器对于长描述的理解能力有限,导致交叉注意力焦点偏离,进而在生成结果中出现错误的属性绑定。(2)被遮挡的对象部分需要有序的生成顺序和明确的部件分离。虽然一些工作引入了手动努力来缓解上述问题,但其质量不稳定,高度依赖于手动信息。为了解决上述问题,我们提出了一种自动方法——分层生成链(HCoG)。它利用大型语言模型将长描述分解为表示不同对象部分的块,并根据遮挡情况从内到外进行排序,形成分层链。在每个块内,我们首先粗略地创建组件,然后通过目标区域定位和相应的3D高斯核优化精确地绑定属性。在块之间,我们引入了高斯扩展和标签消除,通过扩展新的高斯核、重新分配语义标签和消除不必要的核,无缝地生成新的部分,确保只添加相关的部分,而不破坏之前优化过的部分。实验证实,HCoG能够生成结构连贯、属性忠实的具有复杂属性的3D对象。代码可在https://github.com/Wakals/GASCOL中找到。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Project page here: https://hierarchical-chain-of-generation.github.io/
Summary
该文指出当前文本到3D模型的转换技术在处理具有复杂属性的对象时存在挑战。主要障碍包括:文本编码器对长描述的理解能力有限,导致跨注意力焦点偏差,进而在生成结果中出现属性绑定错误;对于被遮挡的对象部分,需要有序生成和明确的部件分解。针对这些问题,提出了Hierarchical-Chain-of-Generation(HCoG)方法,利用大型语言模型将长描述分解为表示不同对象部分的块,并根据遮挡情况从内到外进行排序,形成层次链。在每个块内,首先粗略创建组件,然后通过目标区域定位和相应的3D高斯核优化来精确绑定属性。实验证实,HCoG能够生成结构连贯、属性真实的具有复杂属性的3D对象。
Key Takeaways
- 当前文本到3D模型的转换技术在处理复杂属性对象时存在挑战。
- 主要障碍包括文本编码器对长描述理解有限,导致属性绑定错误,以及被遮挡对象部分的处理问题。
- HCoG方法利用大型语言模型将描述分解为表示不同对象部分的块,并根据遮挡情况排序。
- HCoG在每个块内先粗略创建组件,再通过定位和目标区域优化精确绑定属性。
- HCoG通过Gaussian Extension和Label Elimination在不同块之间生成新部分,通过扩展高斯核、重新分配语义标签和消除不必要的核,确保只添加相关部分而不会破坏已优化的部分。
- 实验证实HCoG能够生成结构连贯、属性真实的3D对象。
点此查看论文截图