⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-05-14 更新
DanceGRPO: Unleashing GRPO on Visual Generation
Authors:Zeyue Xue, Jie Wu, Yu Gao, Fangyuan Kong, Lingting Zhu, Mengzhao Chen, Zhiheng Liu, Wei Liu, Qiushan Guo, Weilin Huang, Ping Luo
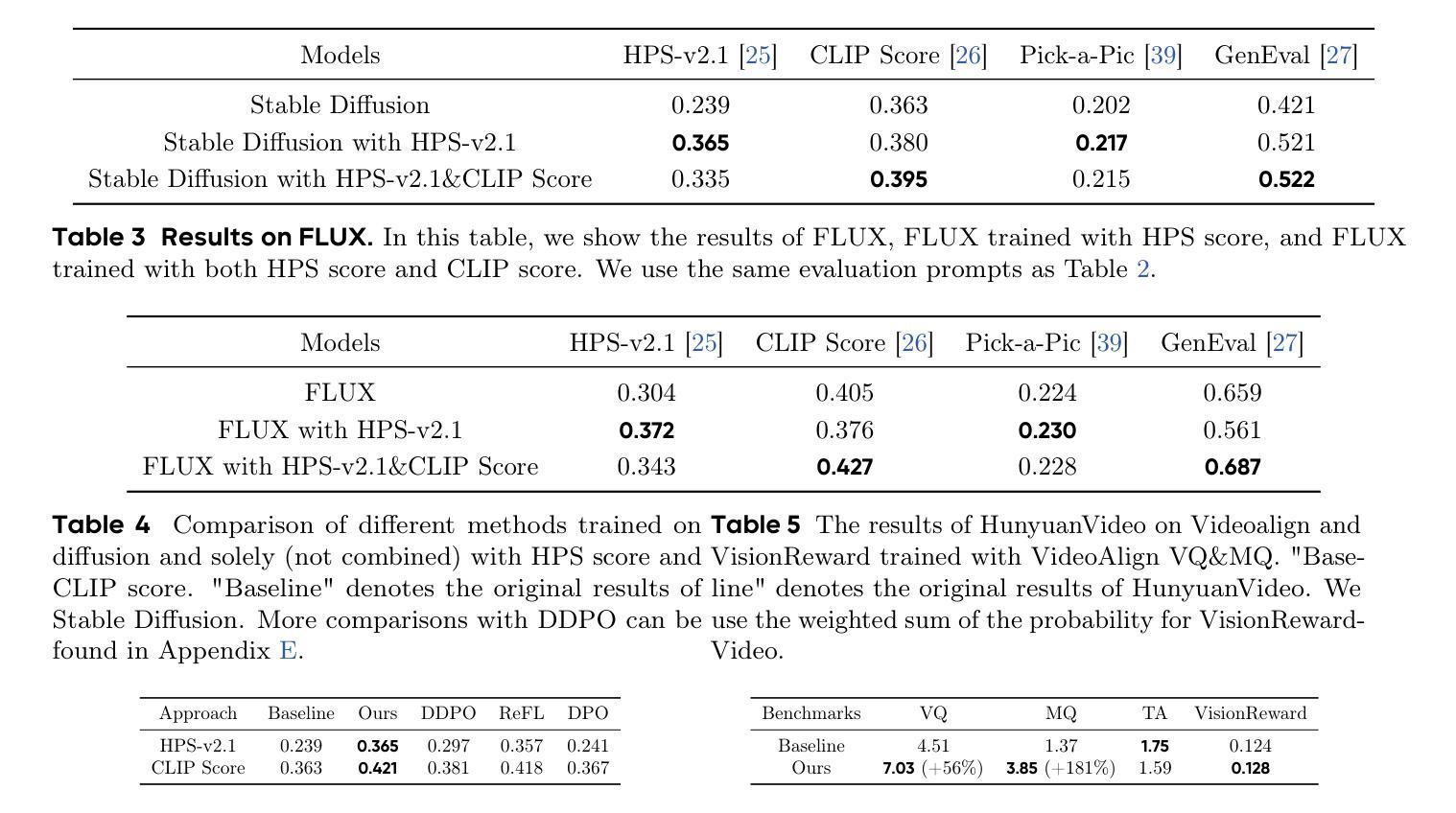
Recent breakthroughs in generative models-particularly diffusion models and rectified flows-have revolutionized visual content creation, yet aligning model outputs with human preferences remains a critical challenge. Existing reinforcement learning (RL)-based methods for visual generation face critical limitations: incompatibility with modern Ordinary Differential Equations (ODEs)-based sampling paradigms, instability in large-scale training, and lack of validation for video generation. This paper introduces DanceGRPO, the first unified framework to adapt Group Relative Policy Optimization (GRPO) to visual generation paradigms, unleashing one unified RL algorithm across two generative paradigms (diffusion models and rectified flows), three tasks (text-to-image, text-to-video, image-to-video), four foundation models (Stable Diffusion, HunyuanVideo, FLUX, SkyReel-I2V), and five reward models (image/video aesthetics, text-image alignment, video motion quality, and binary reward). To our knowledge, DanceGRPO is the first RL-based unified framework capable of seamless adaptation across diverse generative paradigms, tasks, foundational models, and reward models. DanceGRPO demonstrates consistent and substantial improvements, which outperform baselines by up to 181% on benchmarks such as HPS-v2.1, CLIP Score, VideoAlign, and GenEval. Notably, DanceGRPO not only can stabilize policy optimization for complex video generation, but also enables generative policy to better capture denoising trajectories for Best-of-N inference scaling and learn from sparse binary feedback. Our results establish DanceGRPO as a robust and versatile solution for scaling Reinforcement Learning from Human Feedback (RLHF) tasks in visual generation, offering new insights into harmonizing reinforcement learning and visual synthesis. The code will be released.
最近生成模型——尤其是扩散模型和校正流——的突破为视觉内容创作带来了革命性的变革,但将模型输出与人的偏好对齐仍然是一个巨大的挑战。现有的基于强化学习(RL)的视觉生成方法面临重要局限:与现代基于常微分方程(ODE)的采样范式不兼容、大规模训练不稳定、以及视频生成的验证缺乏。本文介绍了DanceGRPO,这是第一个将Group Relative Policy Optimization (GRPO)适应视觉生成范式的统一框架,释放了一种统一的强化学习算法,涵盖两种生成范式(扩散模型和校正流)、三种任务(文本到图像、文本到视频、图像到视频)、四种基础模型(Stable Diffusion、HunyuanVideo、FLUX、SkyReel-I2V),以及五种奖励模型(图像/视频美学、文本-图像对齐、视频运动质量、二元奖励)。据我们所知,DanceGRPO是第一个基于强化学习的统一框架,能够在不同的生成范式、任务、基础模型和奖励模型之间进行无缝适应。DanceGRPO表现出了持续而显著的改进,在HPS-v2.1、CLIP Score、VideoAlign和GenEval等基准测试上的表现优于基线高达181%。值得一提的是,DanceGRPO不仅可稳定复杂视频生成的策略优化,还能够使生成策略更好地捕捉去噪轨迹,用于Best-of-N推理扩展并从稀疏的二元反馈中学习。我们的结果确立了DanceGRPO在视觉生成中扩展强化学习从人类反馈(RLHF)任务的稳健性和通用性解决方案,为强化学习与合成视觉的和谐融合提供了新的见解。代码将被公开发布。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Project Page: https://dancegrpo.github.io/
摘要
近期生成模型(如扩散模型和校正流)的突破为视觉内容创作带来革命性变化,但如何使模型输出符合人类偏好仍是关键挑战。现有基于强化学习(RL)的视觉生成方法存在与现代基于常微分方程(ODEs)的采样范式不兼容、大规模训练不稳定以及视频生成验证缺乏等问题。本文引入DanceGRPO,这是第一个将Group Relative Policy Optimization (GRPO)适应于视觉生成范式的统一框架,使用一个统一的RL算法,跨越两种生成范式(扩散模型和校正流),三项任务(文本转图像、文本转视频、图像转视频),四种基础模型(Stable Diffusion、HunyuanVideo、FLUX、SkyReel-I2V)和五种奖励模型(图像/视频美学、文本-图像对齐、视频运动质量、二元奖励)。据我们所知,DanceGRPO是首个能够在多种生成范式、任务、基础模型和奖励模型之间无缝适应的RL统一框架。DanceGRPO在HPS-v2.1、CLIP Score、VideoAlign和GenEval等基准测试上实现了持续且显著的改进,相较于基线方法最高提升了181%。DanceGRPO不仅能稳定复杂视频生成的策略优化,还能使生成策略更好地捕捉去噪轨迹,支持Best-of-N推理扩展并从稀疏二元反馈中学习。研究结果确立了DanceGRPO在视觉生成领域强化学习从人类反馈(RLHF)任务的稳健性和通用性,为强化学习与合成视觉的和谐结合提供了新的见解。代码将公开发布。
关键见解
- 扩散模型和校正流等生成模型的突破为视觉内容创作带来进步,但仍有模型输出与人类偏好对齐的挑战。
- 现有基于强化学习(RL)的视觉生成方法存在诸多限制,如与现代采样范式不兼容、训练不稳定以及视频生成验证缺乏。
- DanceGRPO是首个统一框架,将Group Relative Policy Optimization (GRPO)应用于视觉生成,支持多种生成范式、任务、基础模型和奖励模型。
- DanceGRPO实现了在各项基准测试上的显著改进,最高提升达181%。
- DanceGRPO能稳定复杂视频生成的策略优化,并捕捉去噪轨迹,支持Best-of-N推理扩展。
- DanceGRPO能从稀疏二元反馈中学习,为强化学习与视觉合成的结合提供了新的见解。
点此查看论文截图
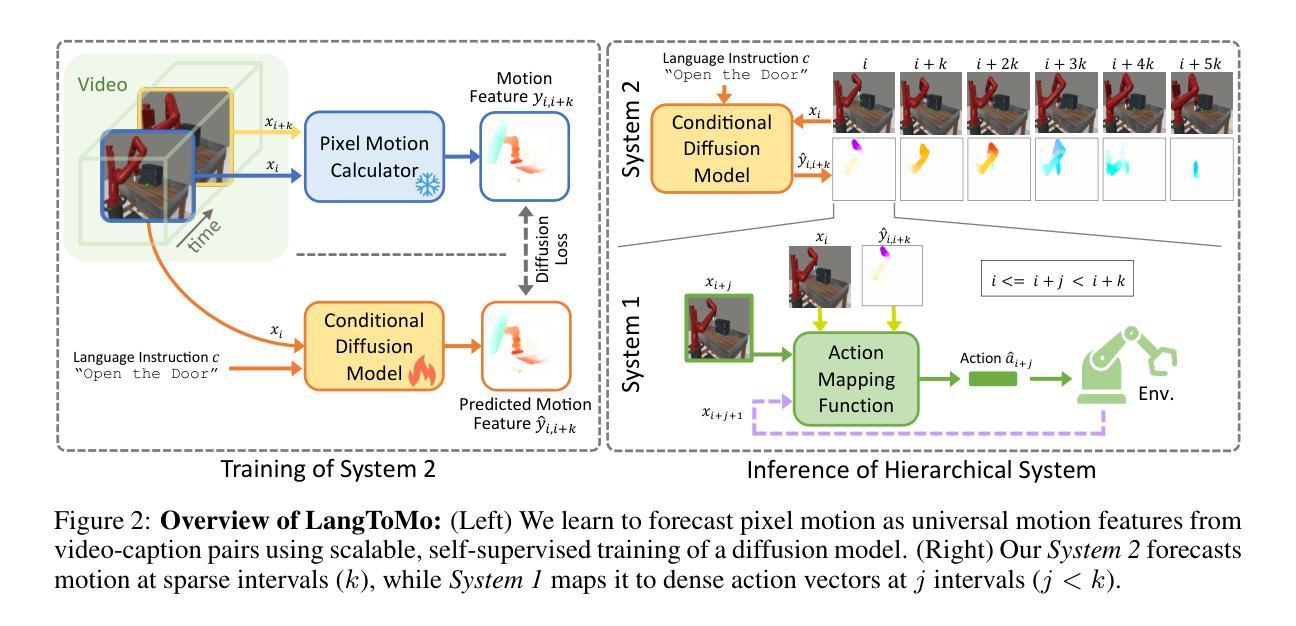
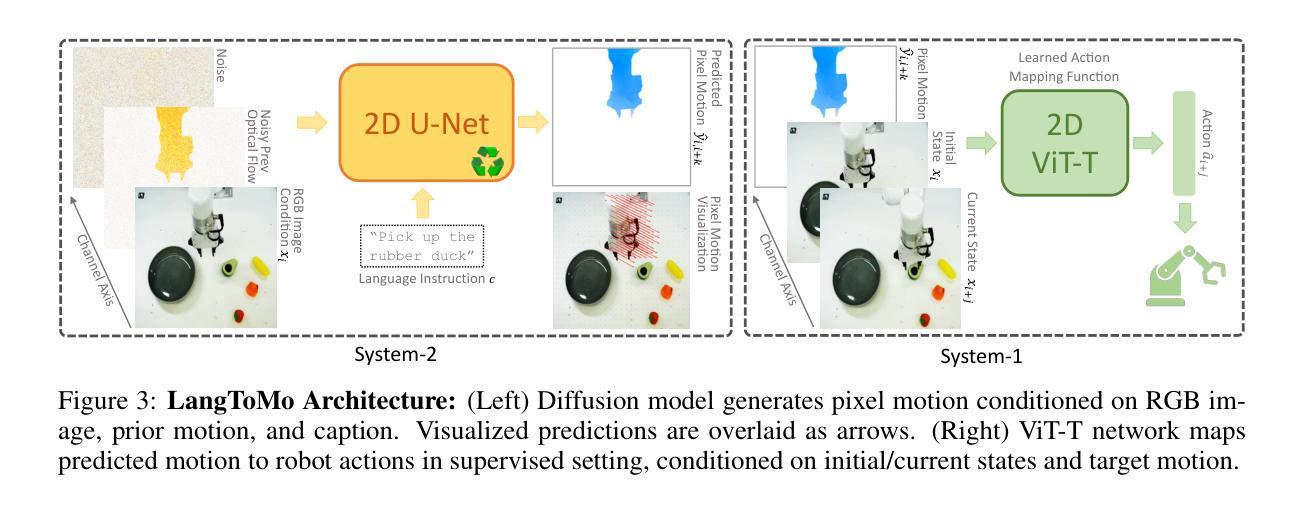
Pixel Motion as Universal Representation for Robot Control
Authors:Kanchana Ranasinghe, Xiang Li, Cristina Mata, Jongwoo Park, Michael S Ryoo
We present LangToMo, a vision-language-action framework structured as a dual-system architecture that uses pixel motion forecasts as intermediate representations. Our high-level System 2, an image diffusion model, generates text-conditioned pixel motion sequences from a single frame to guide robot control. Pixel motion-a universal, interpretable, and motion-centric representation-can be extracted from videos in a self-supervised manner, enabling diffusion model training on web-scale video-caption data. Treating generated pixel motion as learned universal representations, our low level System 1 module translates these into robot actions via motion-to-action mapping functions, which can be either hand-crafted or learned with minimal supervision. System 2 operates as a high-level policy applied at sparse temporal intervals, while System 1 acts as a low-level policy at dense temporal intervals. This hierarchical decoupling enables flexible, scalable, and generalizable robot control under both unsupervised and supervised settings, bridging the gap between language, motion, and action. Checkout https://kahnchana.github.io/LangToMo for visualizations.
我们提出了LangToMo,这是一个视觉语言行动框架,采用双重系统架构,以像素运动预测作为中间表示形式。我们的高级系统2是一个图像扩散模型,从单帧生成文本控制的像素运动序列,以指导机器人控制。像素运动是一种通用、可解释、以运动为中心的表现形式,可以以自我监督的方式从视频中提取,从而实现扩散模型在网页规模视频字幕数据上的训练。将生成的像素运动视为学习的通用表示,我们的低级系统1模块通过运动到动作的映射函数将这些表示转换为机器人动作,这些映射函数可以是手工制作的,也可以在最少的监督下学习。系统2作为高级策略,在稀疏的时间间隔内运行,而系统1则在密集的时间间隔内作为低级策略运行。这种层次化的解耦使机器人在无监督和监督的环境下都能实现灵活、可扩展和通用的控制,从而缩小了语言、动作和行动之间的差距。想了解更多可视化内容,请访问:[https://kahnchana.github.io/LangToMo/] 。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
LangToMo是一个结合视觉、语言和动作的框架,采用双系统架构并利用像素运动预测作为中间表示。其高级系统2采用图像扩散模型,从单帧生成文本调节的像素运动序列,指导机器人控制。像素运动是一种通用、可解释、以运动为中心的表现形式,可从视频中自我监督提取,使扩散模型能够在网页规模的视频字幕数据上进行训练。将生成的像素运动视为学习到的通用表示,低级系统1模块通过运动到动作的映射函数将这些表示转化为机器人动作,这些映射函数可以是手工制作的,也可以是最少监督学习的。系统2作为高级策略在稀疏时间间隔内运行,而系统1作为低级策略在密集时间间隔内运行。这种分层解耦实现了灵活的、可扩展的和通用的机器人控制,无论是在无监督还是监督设置下都能缩小语言、运动和动作之间的差距。更多可视化内容请访问:链接地址。
Key Takeaways
- LangToMo是一个融合视觉、语言和动作的框架,具有双系统架构。
- 框架利用像素运动预测作为中间表示形式。
- 高级系统2采用图像扩散模型生成文本调节的像素运动序列,指导机器人控制。
- 像素运动可从视频中自我监督提取,并用于训练扩散模型。
- 低级系统1模块将像素运动转化为机器人动作。
- 系统2和系统1分别作为高级和低级策略运行,实现灵活的机器人控制。
点此查看论文截图

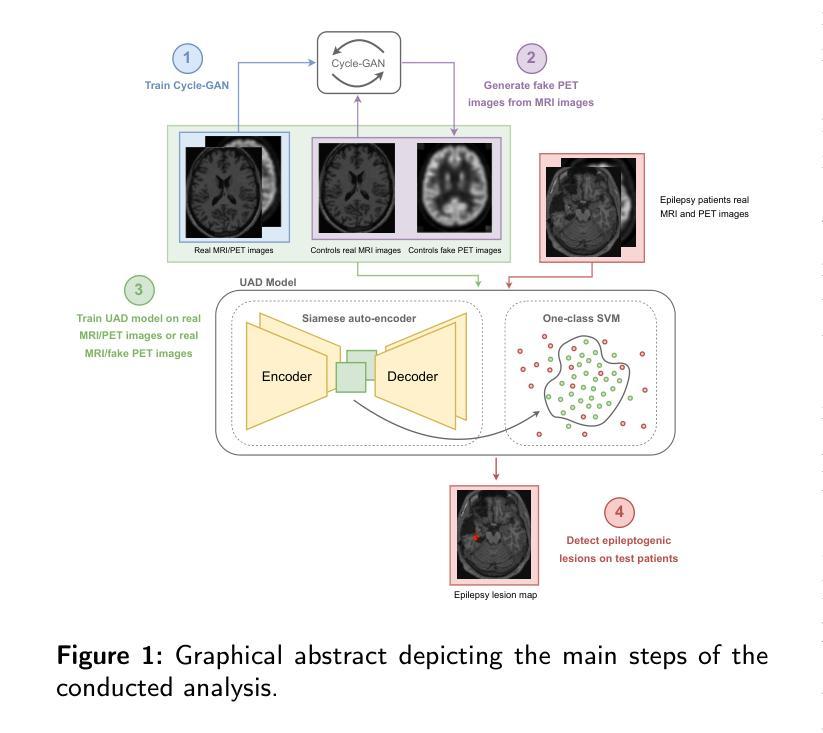
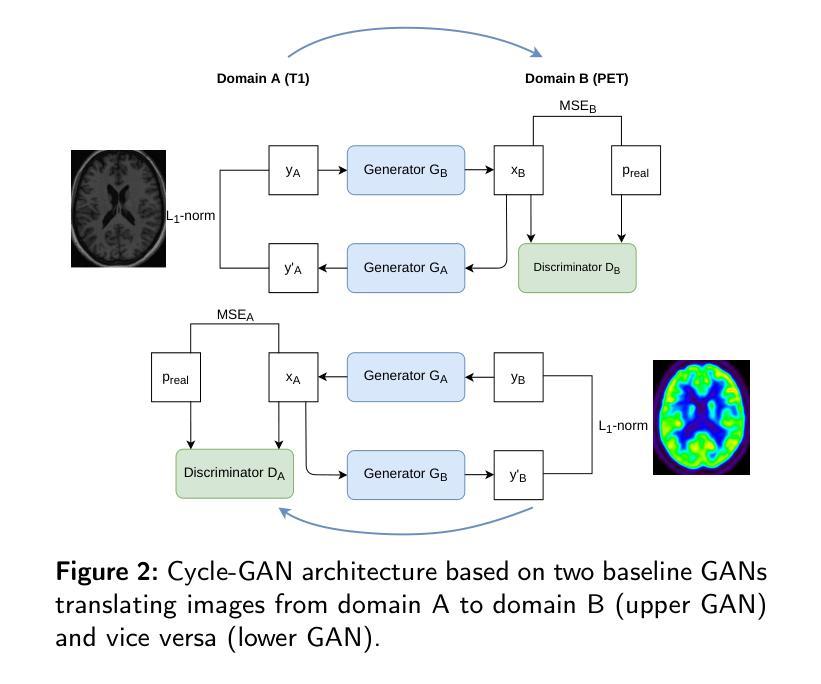
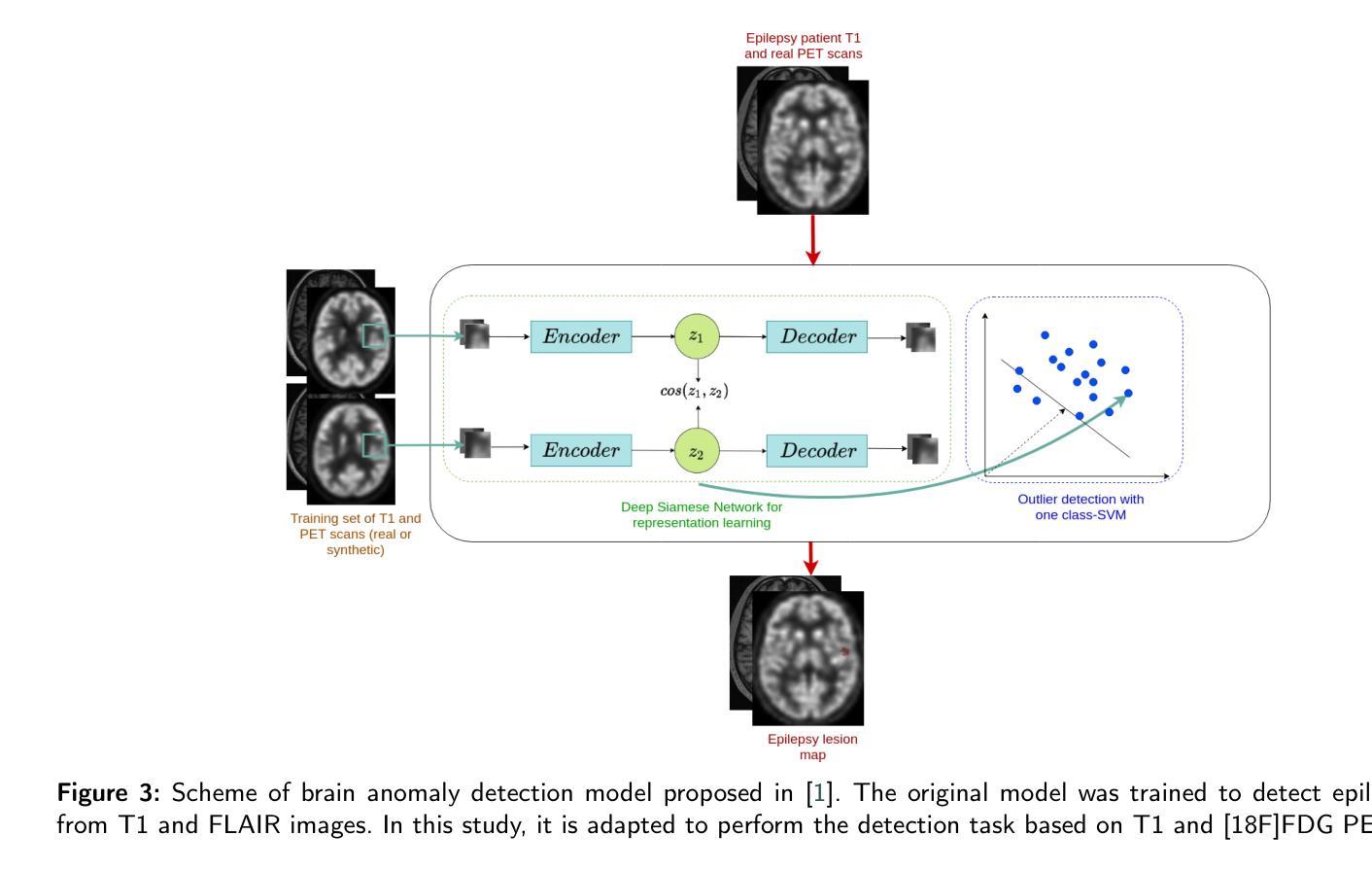
GAN-based synthetic FDG PET images from T1 brain MRI can serve to improve performance of deep unsupervised anomaly detection models
Authors:Daria Zotova, Nicolas Pinon, Robin Trombetta, Romain Bouet, Julien Jung, Carole Lartizien
Background and Objective. Research in the cross-modal medical image translation domain has been very productive over the past few years in tackling the scarce availability of large curated multimodality datasets with the promising performance of GAN-based architectures. However, only a few of these studies assessed task-based related performance of these synthetic data, especially for the training of deep models. Method. We design and compare different GAN-based frameworks for generating synthetic brain [18F]fluorodeoxyglucose (FDG) PET images from T1 weighted MRI data. We first perform standard qualitative and quantitative visual quality evaluation. Then, we explore further impact of using these fake PET data in the training of a deep unsupervised anomaly detection (UAD) model designed to detect subtle epilepsy lesions in T1 MRI and FDG PET images. We introduce novel diagnostic task-oriented quality metrics of the synthetic FDG PET data tailored to our unsupervised detection task, then use these fake data to train a use case UAD model combining a deep representation learning based on siamese autoencoders with a OC-SVM density support estimation model. This model is trained on normal subjects only and allows the detection of any variation from the pattern of the normal population. We compare the detection performance of models trained on 35 paired real MR T1 of normal subjects paired either on 35 true PET images or on 35 synthetic PET images generated from the best performing generative models. Performance analysis is conducted on 17 exams of epilepsy patients undergoing surgery. Results. The best performing GAN-based models allow generating realistic fake PET images of control subject with SSIM and PSNR values around 0.9 and 23.8, respectively and in distribution (ID) with regard to the true control dataset. The best UAD model trained on these synthetic normative PET data allows reaching 74% sensitivity. Conclusion. Our results confirm that GAN-based models are the best suited for MR T1 to FDG PET translation, outperforming transformer or diffusion models. We also demonstrate the diagnostic value of these synthetic data for the training of UAD models and evaluation on clinical exams of epilepsy patients. Our code and the normative image dataset are available.
背景与目的:近年来,在解决大型精选多模态数据集稀缺的问题方面,跨模态医学图像翻译领域的研究取得了显著成果,基于GAN的架构表现出巨大潜力。然而,只有少数研究评估了这些合成数据在任务相关的性能表现,尤其是在深度模型的训练方面。方法:我们设计并比较了基于不同GAN的框架,用于从T1加权MRI数据生成合成脑[18F]氟脱氧葡萄糖(FDG)PET图像。我们首先进行标准的定性和定量视觉质量评估。然后,我们进一步探讨了使用这些假PET数据在训练深度无监督异常检测(UAD)模型中的影响,该模型旨在检测T1 MRI和FDG PET图像中的微妙癫痫病灶。我们引入了针对我们的无监督检测任务的新型诊断任务导向型质量指标,然后使用这些假数据来训练一个用例UAD模型,该模型结合了基于孪生自编码器的深度表示学习与OC-SVM密度支持估计模型。该模型仅在正常受试者上进行训练,可检测任何与正常人群模式的偏差。我们比较了在真实MR T1图像(正常受试者配对)的35对图像上训练的模型性能,这些图像要么与真实的PET图像配对,要么与由表现最佳的生成模型生成的合成PET图像配对。在接受手术的17例癫痫患者考试上进行性能分析。结果:表现最佳的基于GAN的模型能够生成逼真的假PET图像,控制对象的结构相似性度量(SSIM)和峰值信噪比(PSNR)值分别为约0.9和23.8,在真实控制数据集方面表现出身份分布(ID)。使用这些合成规范性PET数据训练的最佳UAD模型的敏感性达到74%。结论:我们的结果证实,基于GAN的模型最适合于从MR T1到FDG PET的翻译任务,优于转换器或扩散模型。我们还证明了这些合成数据在训练UAD模型和评估癫痫患者临床考试中的诊断价值。我们的代码和规范图像数据集可供使用。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本研究利用GAN架构生成合成脑[18F]氟脱氧葡萄糖(FDG)PET图像,从T1加权MRI数据中生成。研究不仅评估了生成图像的质量,还探索了这些合成数据在训练深度无监督异常检测模型中的应用,该模型旨在检测T1 MRI和FDG PET图像中的细微癫痫病灶。研究确认GAN模型最适合MR T1到FDG PET的翻译,且合成数据对训练无监督检测模型具有诊断价值。
Key Takeaways
- GAN架构被用于生成合成脑FDG PET图像,从T1加权MRI数据中生成。
- 不仅评估了图像生成的质量,还研究了这些合成数据在训练无监督异常检测模型中的应用。
- 最佳GAN模型生成的合成PET图像具有高度的现实性,与真实控制数据集分布一致。
- 使用合成规范性PET数据训练的最佳UAD模型达到74%的敏感性。
- GAN模型最适合于MR T1到FDG PET的翻译。
- 合成数据对训练无监督检测模型具有诊断价值。
- 研究代码和规范图像数据集可供使用。
点此查看论文截图

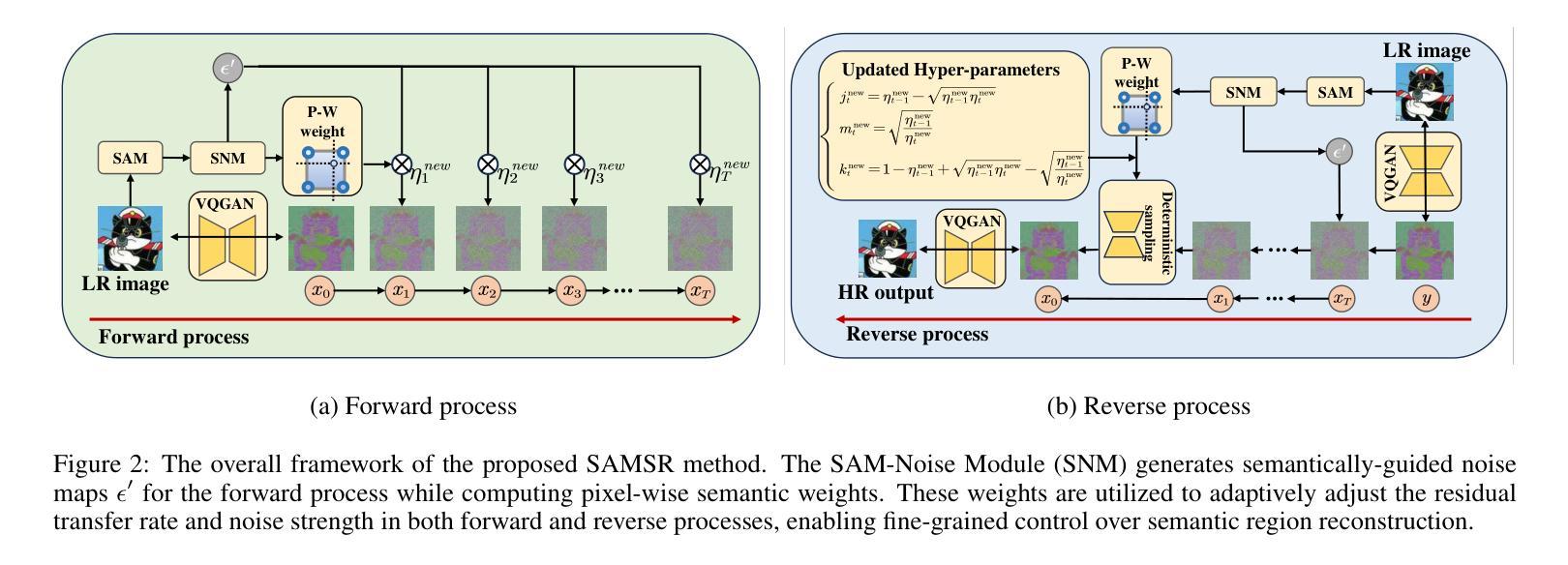
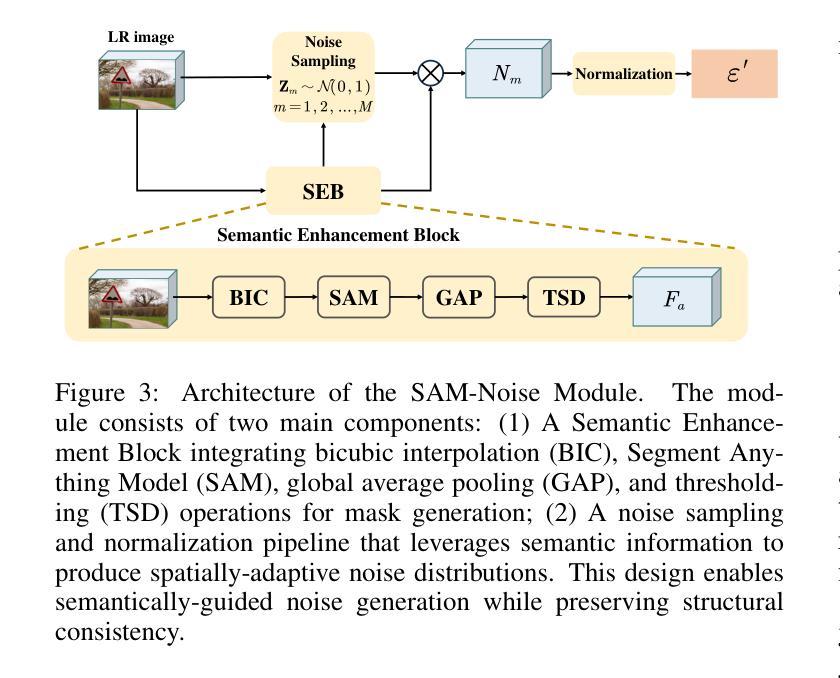
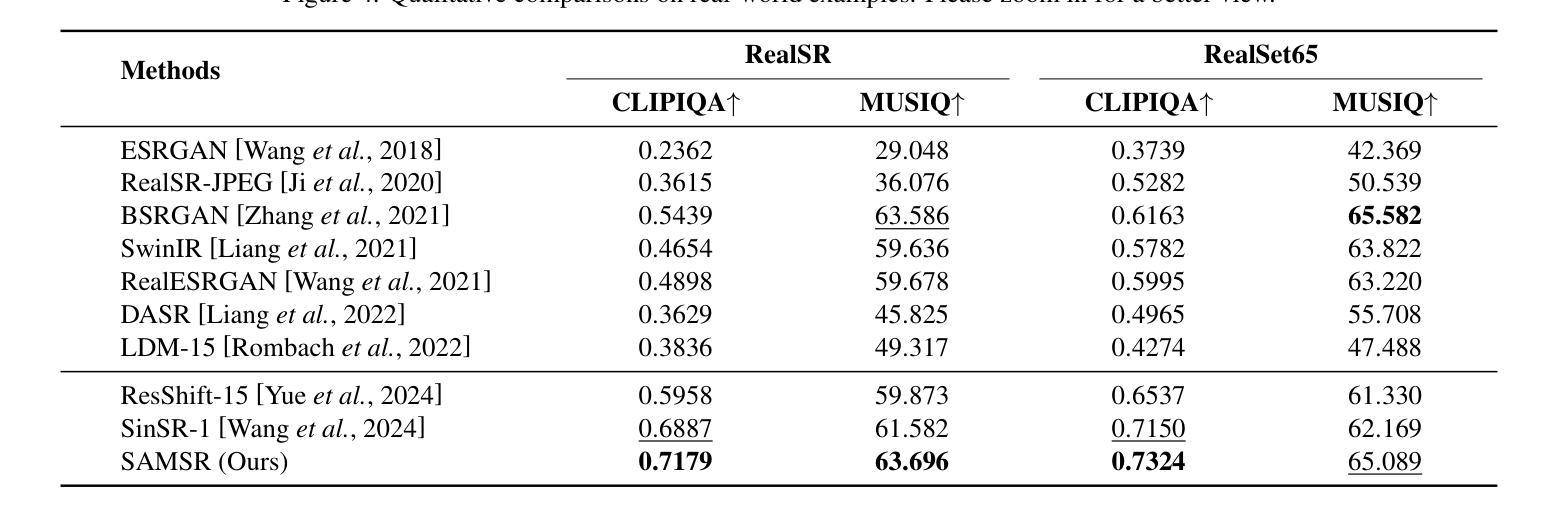
Semantic-Guided Diffusion Model for Single-Step Image Super-Resolution
Authors:Zihang Liu, Zhenyu Zhang, Hao Tang
Diffusion-based image super-resolution (SR) methods have demonstrated remarkable performance. Recent advancements have introduced deterministic sampling processes that reduce inference from 15 iterative steps to a single step, thereby significantly improving the inference speed of existing diffusion models. However, their efficiency remains limited when handling complex semantic regions due to the single-step inference. To address this limitation, we propose SAMSR, a semantic-guided diffusion framework that incorporates semantic segmentation masks into the sampling process. Specifically, we introduce the SAM-Noise Module, which refines Gaussian noise using segmentation masks to preserve spatial and semantic features. Furthermore, we develop a pixel-wise sampling strategy that dynamically adjusts the residual transfer rate and noise strength based on pixel-level semantic weights, prioritizing semantically rich regions during the diffusion process. To enhance model training, we also propose a semantic consistency loss, which aligns pixel-wise semantic weights between predictions and ground truth. Extensive experiments on both real-world and synthetic datasets demonstrate that SAMSR significantly improves perceptual quality and detail recovery, particularly in semantically complex images. Our code is released at https://github.com/Liu-Zihang/SAMSR.
基于扩散的图像超分辨率(SR)方法已显示出卓越的性能。最近的进展引入了确定性采样过程,将推理从15个迭代步骤减少到单个步骤,从而显著提高了现有扩散模型的推理速度。然而,由于单步推理的限制,它们在处理复杂语义区域时的效率仍然有限。为了解决这一局限性,我们提出了SAMSR,一个语义引导的扩散框架,将语义分割掩膜融入到采样过程中。具体来说,我们引入了SAM-Noise模块,该模块使用分割掩膜对高斯噪声进行精炼,以保留空间和语义特征。此外,我们开发了一种像素级采样策略,根据像素级语义权重动态调整残差传输率和噪声强度,在扩散过程中优先处理语义丰富的区域。为了提高模型训练效果,我们还提出了一种语义一致性损失,该损失可以对齐预测和真实值之间的像素级语义权重。在真实和合成数据集上的大量实验表明,SAMSR显著提高了感知质量和细节恢复,特别是在语义复杂的图像中。我们的代码已发布在https://github.com/Liu-Zihang/SAMSR。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了基于扩散的图像超分辨率(SR)方法的新进展。为了提高效率,研究者提出了一种新的语义引导扩散框架SAMSR,结合语义分割掩膜进行采样过程。该框架通过SAM-Noise模块使用分割掩膜优化高斯噪声,以保留空间语义特征。此外,还提出了像素级采样策略,根据像素级语义权重动态调整残留传输率和噪声强度。为改进模型训练,引入语义一致性损失,对齐预测和真实标签的像素级语义权重。实验表明,SAMSR显著提高感知质量和细节恢复能力,特别是在语义复杂的图像中。
Key Takeaways
- 扩散模型在图像超分辨率领域展现出显著性能。
- 近期发展引入了确定性采样过程,将推理步骤从15次迭代减少到一次,提高了现有扩散模型的推理速度。
- 提出的SAMSR框架结合语义分割掩膜进行采样,旨在解决处理复杂语义区域时的效率限制。
- SAMSR通过SAM-Noise模块利用分割掩膜优化高斯噪声,保留空间和语义特征。
- 像素级采样策略根据像素级语义权重调整残留传输率和噪声强度,优先处理语义丰富的区域。
- 引入语义一致性损失以改进模型训练,对齐预测和真实标签的像素级语义权重。
点此查看论文截图



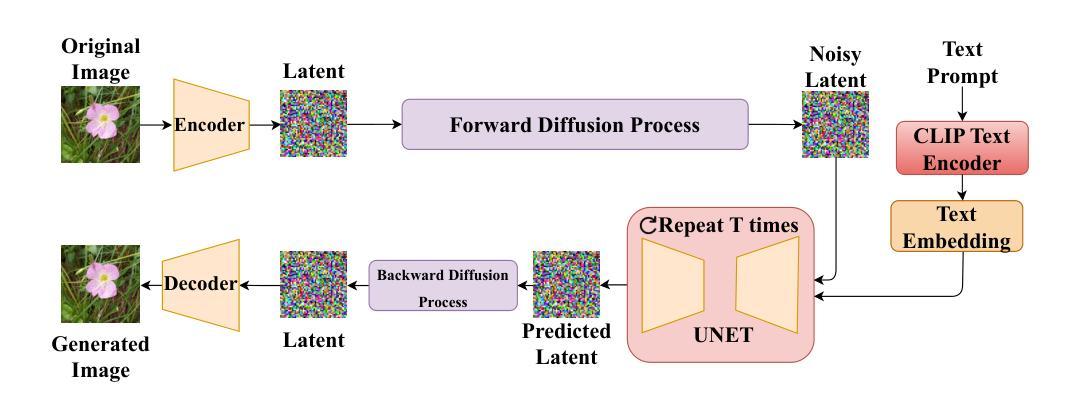
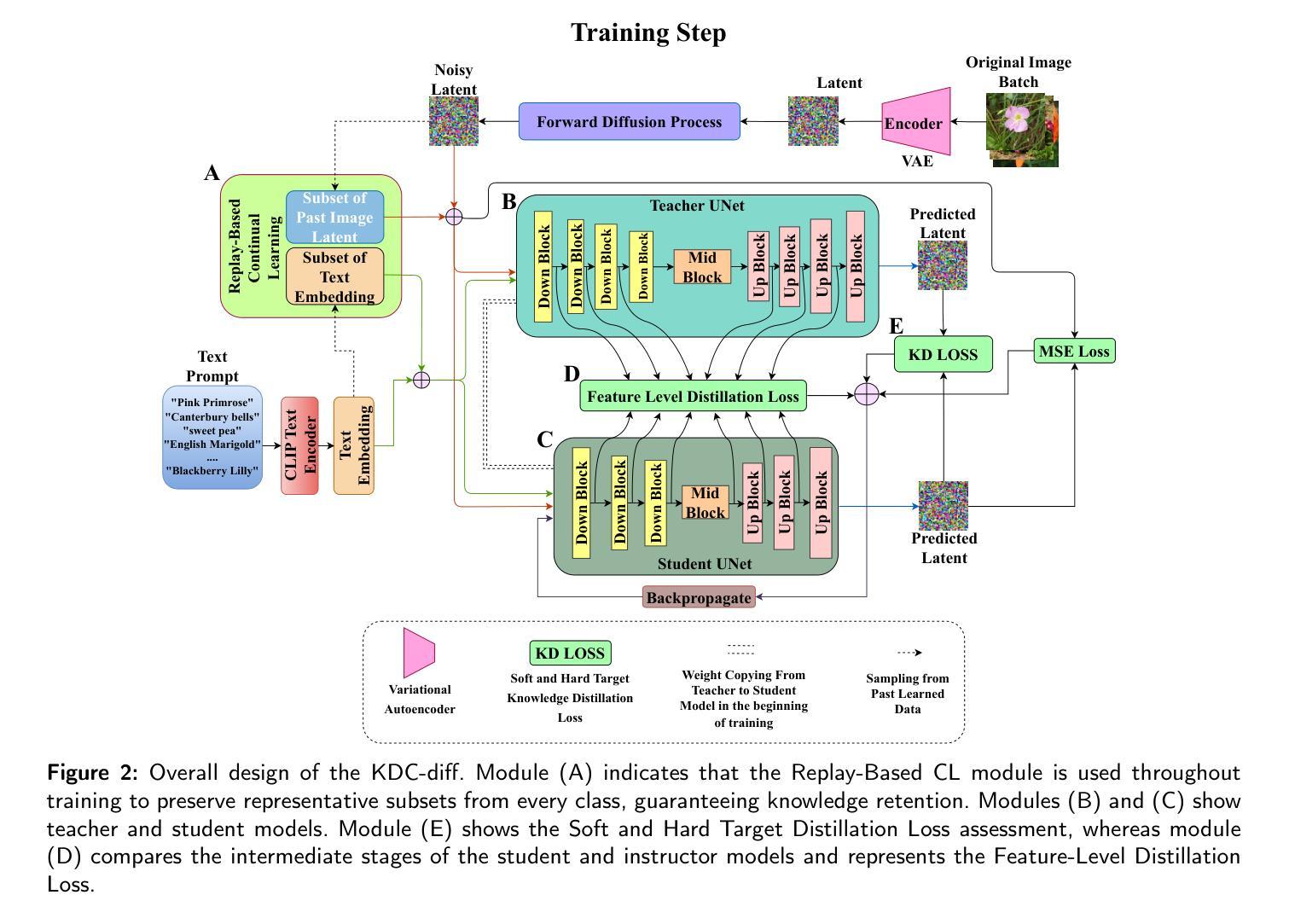
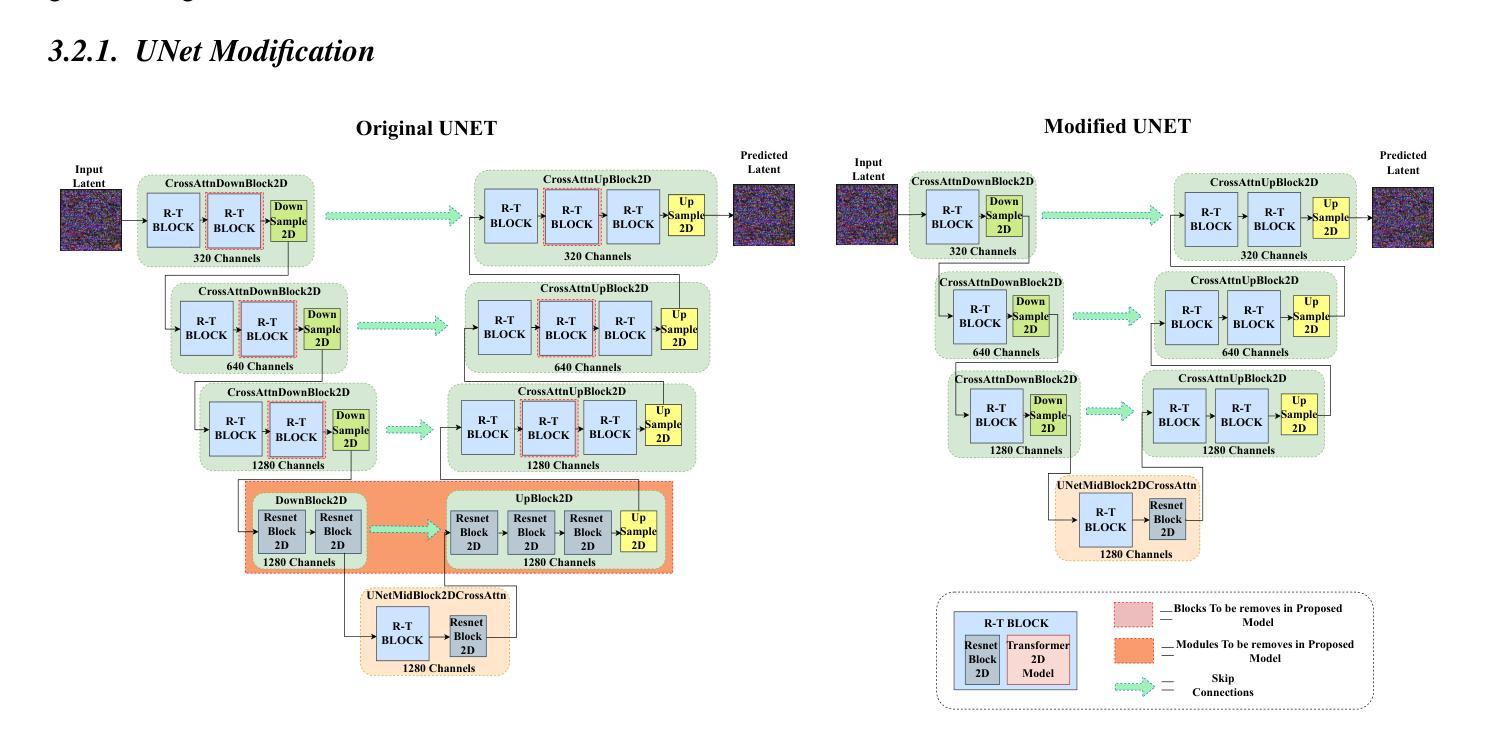
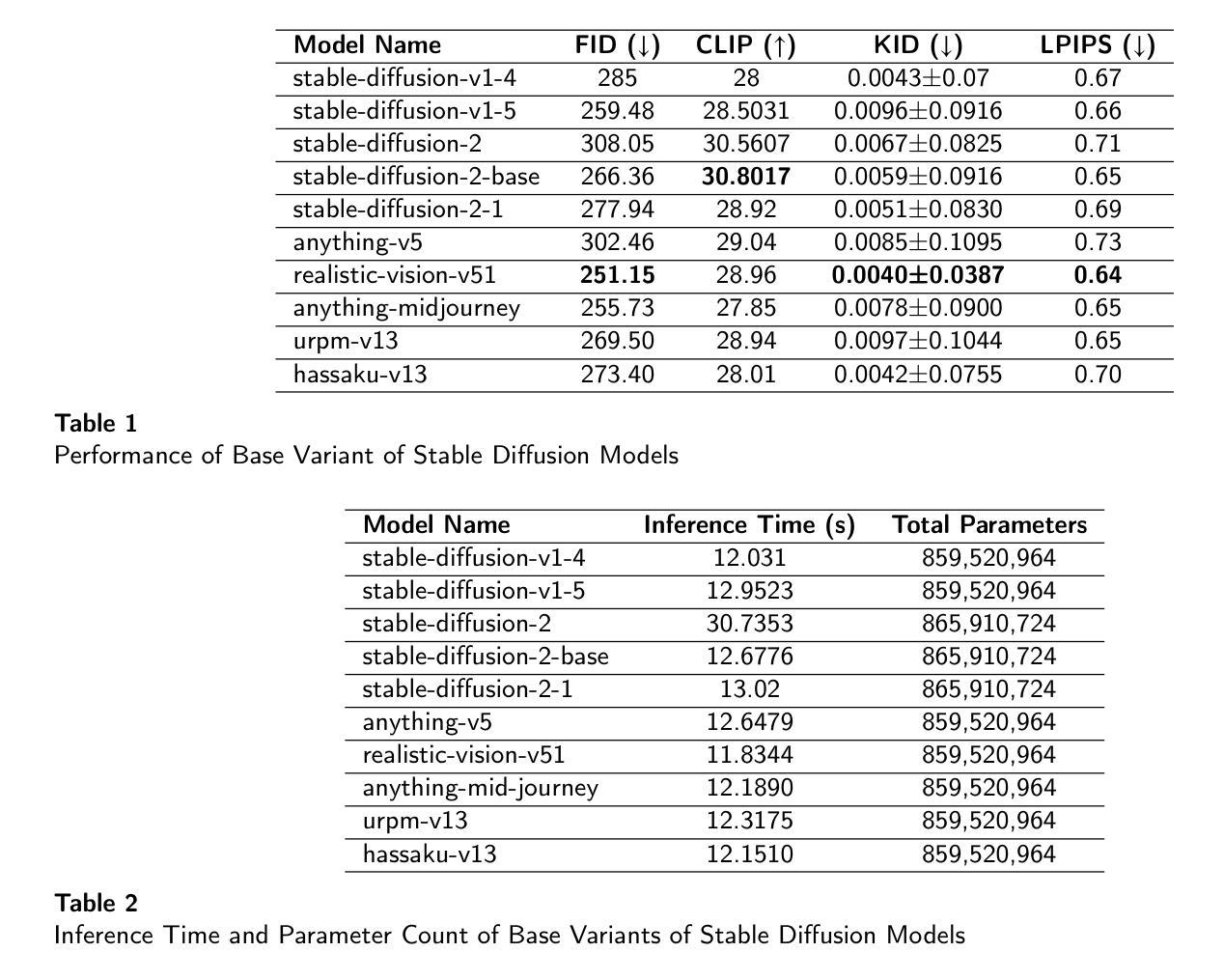
Replay-Based Continual Learning with Dual-Layered Distillation and a Streamlined U-Net for Efficient Text-to-Image Generation
Authors:Md. Naimur Asif Borno, Md Sakib Hossain Shovon, Asmaa Soliman Al-Moisheer, Mohammad Ali Moni
Recent advancements in text-to-image diffusion models are hindered by high computational demands, limiting accessibility and scalability. This paper introduces KDC-Diff, a novel stable diffusion framework that enhances efficiency while maintaining image quality. KDC-Diff features a streamlined U-Net architecture with nearly half the parameters of the original U-Net (482M), significantly reducing model complexity. We propose a dual-layered distillation strategy to ensure high-fidelity generation, transferring semantic and structural insights from a teacher to a compact student model while minimizing quality degradation. Additionally, replay-based continual learning is integrated to mitigate catastrophic forgetting, allowing the model to retain prior knowledge while adapting to new data. Despite operating under extremely low computational resources, KDC-Diff achieves state-of-the-art performance on the Oxford Flowers and Butterflies & Moths 100 Species datasets, demonstrating competitive metrics such as FID, CLIP, and LPIPS. Moreover, it significantly reduces inference time compared to existing models. These results establish KDC-Diff as a highly efficient and adaptable solution for text-to-image generation, particularly in computationally constrained environments.
近期文本到图像扩散模型的进展受到高计算需求的阻碍,这限制了其可访问性和可扩展性。本文介绍了KDC-Diff,这是一种新型稳定的扩散框架,提高了效率同时保持了图像质量。KDC-Diff采用简化的U-Net架构,参数数量几乎为原始U-Net的一半(482M),显著降低了模型复杂性。我们提出了一种双层蒸馏策略,以确保高保真生成,将教师和学生的紧凑模型之间的语义和结构见解进行转移,同时最小化质量下降。此外,还集成了基于重放的持续学习,以减轻灾难性遗忘,使模型在适应新数据的同时保留先前知识。尽管在极低的计算资源下运行,KDC-Diff在Oxford Flowers和Butterflies & Moths 100 Species数据集上实现了最先进的性能,显示出具有竞争力的指标,如FID、CLIP和LPIPS。而且,与现有模型相比,它大大减少了推理时间。这些结果使KDC-Diff成为文本到图像生成的高效且可适应的解决方案,特别是在计算受限的环境中。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文提出了一种高效稳定的文本到图像扩散模型KDC-Diff,它能够在保持图像质量的同时提高计算效率。该模型通过简化U-Net架构和引入双层次蒸馏策略以及回放式持续学习,显著降低了模型复杂度和计算需求。在牛津花卉和蝴蝶与飞蛾等数据集上,KDC-Diff取得了先进的表现,展示了其高效的文本到图像生成能力。
Key Takeaways
- KDC-Diff是一种新的文本到图像扩散模型,旨在解决现有模型的高计算需求问题。
- KDC-Diff采用简化的U-Net架构,参数数量接近原始U-Net的一半,降低了模型复杂度。
- 提出双层次蒸馏策略,确保从教师模型到学生模型的语义和结构知识转移,同时最小化质量损失。
- 集成回放式持续学习,缓解灾难性遗忘问题,使模型能够适应新数据的同时保留先前知识。
- KDC-Diff在牛津花卉和蝴蝶与飞蛾等数据集上取得了卓越表现,显示其在FID、CLIP和LPIPS等评估指标上的竞争力。
- 与现有模型相比,KDC-Diff显著减少了推理时间。
点此查看论文截图

Unsupervised Learning for Class Distribution Mismatch
Authors:Pan Du, Wangbo Zhao, Xinai Lu, Nian Liu, Zhikai Li, Chaoyu Gong, Suyun Zhao, Hong Chen, Cuiping Li, Kai Wang, Yang You
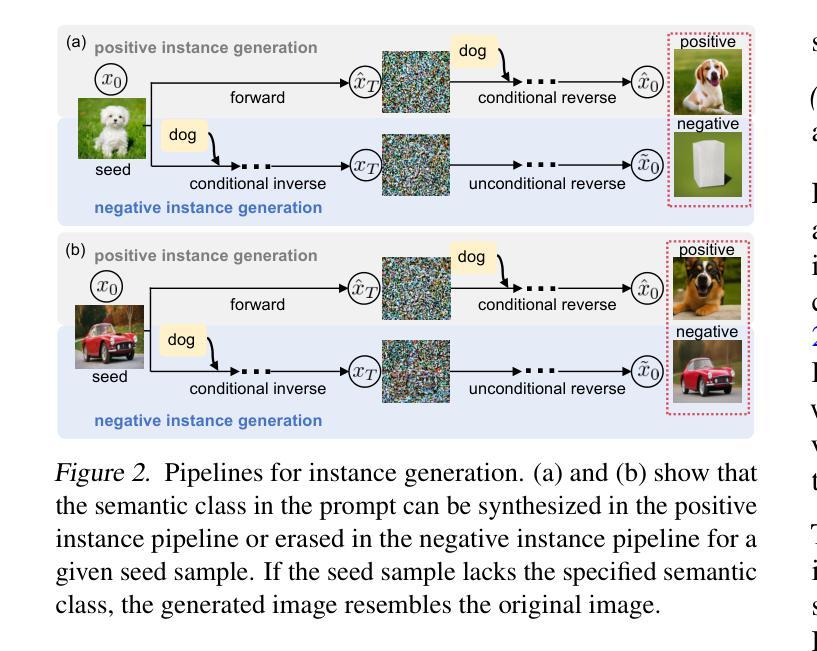
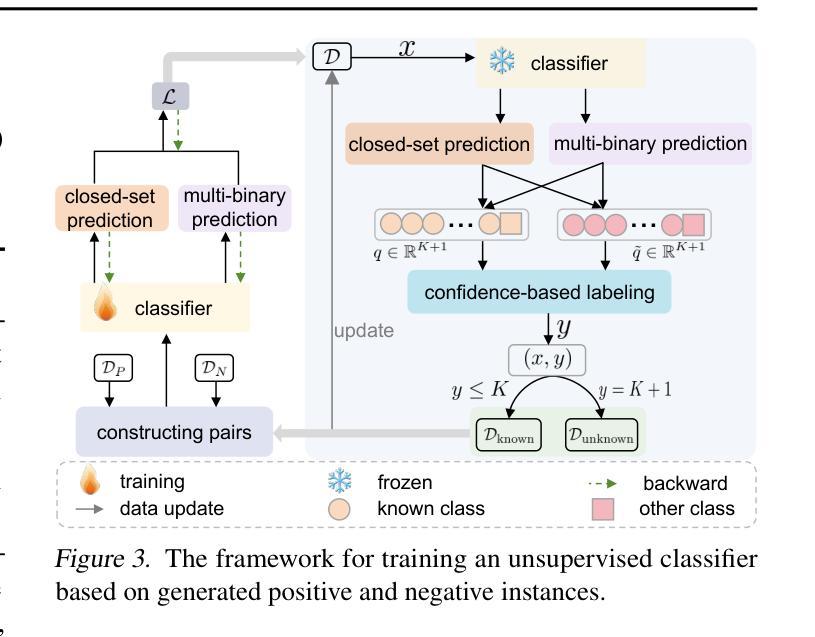
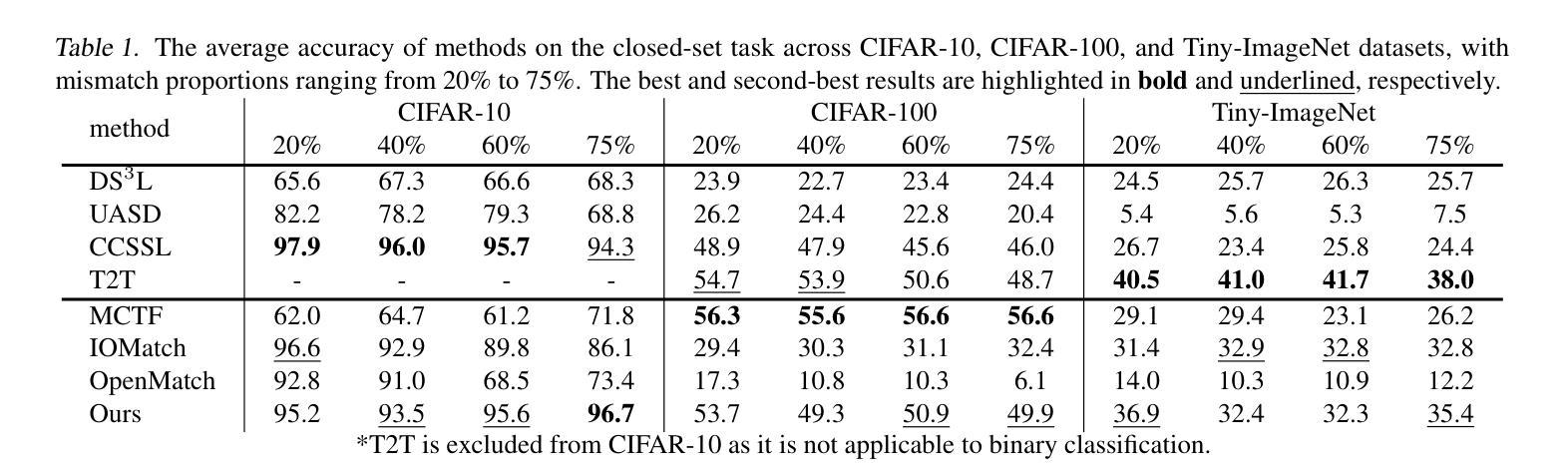
Class distribution mismatch (CDM) refers to the discrepancy between class distributions in training data and target tasks. Previous methods address this by designing classifiers to categorize classes known during training, while grouping unknown or new classes into an “other” category. However, they focus on semi-supervised scenarios and heavily rely on labeled data, limiting their applicability and performance. To address this, we propose Unsupervised Learning for Class Distribution Mismatch (UCDM), which constructs positive-negative pairs from unlabeled data for classifier training. Our approach randomly samples images and uses a diffusion model to add or erase semantic classes, synthesizing diverse training pairs. Additionally, we introduce a confidence-based labeling mechanism that iteratively assigns pseudo-labels to valuable real-world data and incorporates them into the training process. Extensive experiments on three datasets demonstrate UCDM’s superiority over previous semi-supervised methods. Specifically, with a 60% mismatch proportion on Tiny-ImageNet dataset, our approach, without relying on labeled data, surpasses OpenMatch (with 40 labels per class) by 35.1%, 63.7%, and 72.5% in classifying known, unknown, and new classes.
类别分布不匹配(CDM)指的是训练数据与目标任务中类别分布的差异。之前的方法是通过设计分类器来应对这一差异,对训练期间已知的类别进行分类,同时将未知或新类别归为“其他”类别。然而,它们主要关注半监督场景,并严重依赖有标签数据,从而限制了其适用性和性能。为了解决这一问题,我们提出了用于类别分布不匹配的无监督学习(UCDM),它通过无标签数据构建正负面对来进行分类器训练。我们的方法随机采样图像,并使用扩散模型添加或删除语义类别,合成多样化的训练对。此外,我们还引入了一种基于置信度的标记机制,该机制可以迭代地对有价值的真实数据进行伪标签分配并将其纳入训练过程。在三个数据集上的大量实验表明,UCDM在之前半监督方法上的优越性。特别是在Tiny-ImageNet数据集上,在高达60%的类别分布不匹配比例下,我们的方法在不依赖有标签数据的情况下,对已知类别、未知类别和新类别的分类超过了OpenMatch(每类有40个标签)的准确率分别为:提升了35.1%、63.7%和72.5%。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by ICML 2025
Summary
本文提出了针对类别分布不匹配(CDM)问题的无监督学习方法UCDM。该方法利用无标签数据构建正负样本对进行分类器训练,通过随机采样图像并运用扩散模型增加或删除语义类别,合成多样的训练样本对。此外,还引入了一种基于置信度的标签机制,迭代地为有价值的真实数据分配伪标签并将其纳入训练过程。在三个数据集上的实验表明,UCDM在类别分布高度不匹配的情况下,性能优于传统的半监督方法。
Key Takeaways
- 类分布不匹配(CDM)指的是训练数据与目标任务中类别分布的不一致性。
- 现有方法主要通过设计分类器来识别训练期间已知的类别,将未知或新类别归为“其他”类别,但这种方法主要应用于半监督场景,严重依赖标记数据,限制了其应用性和性能。
- UCDM方法利用无标签数据构建正负样本对进行训练,解决了对标记数据的依赖问题。
- UCDM通过随机采样图像并运用扩散模型,实现了语义类别的增加或删除,合成了多样的训练样本。
- 引入了一种基于置信度的标签机制,该机制能够迭代地为真实数据分配伪标签,并将其纳入训练过程。
- 在Tiny-ImageNet数据集上,当类别不匹配比例为60%时,UCDM方法在识别已知、未知和新类别上的性能均超过了传统的半监督方法OpenMatch。
点此查看论文截图

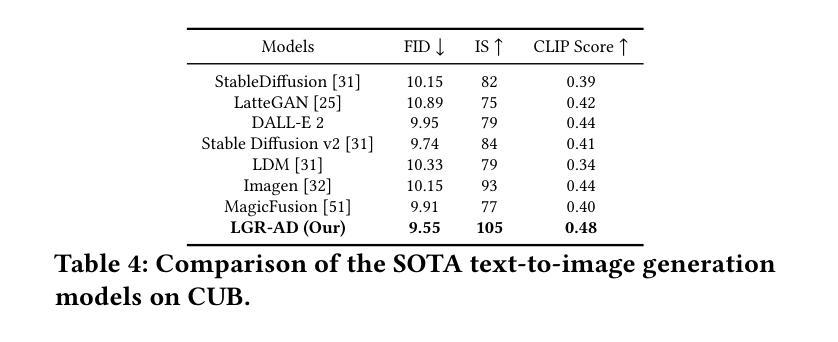
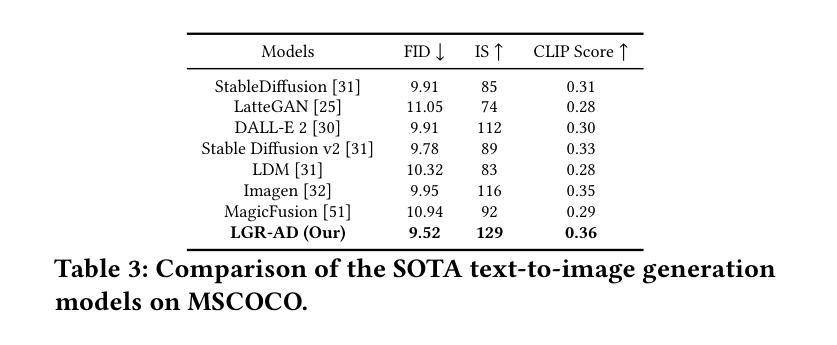
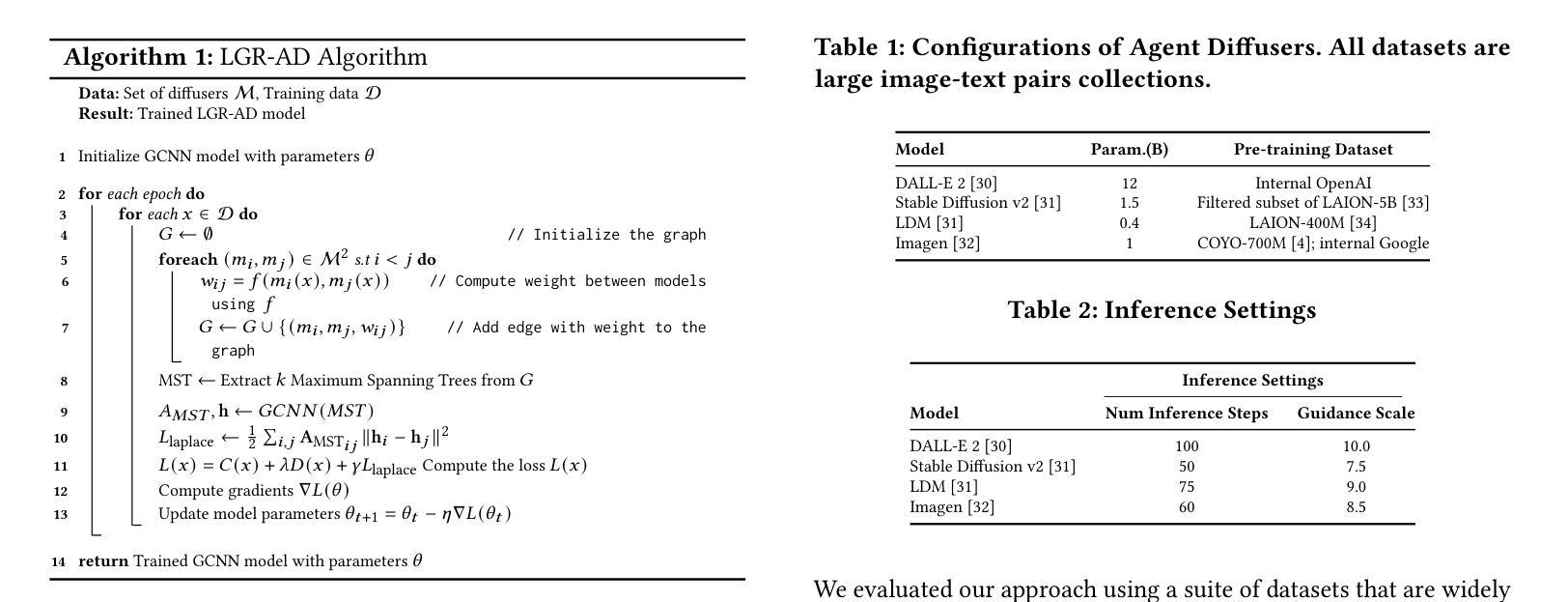
Learning Graph Representation of Agent Diffuser
Authors:Youcef Djenouri, Nassim Belmecheri, Tomasz Michalak, Jan Dubiński, Ahmed Nabil Belbachir, Anis Yazidi
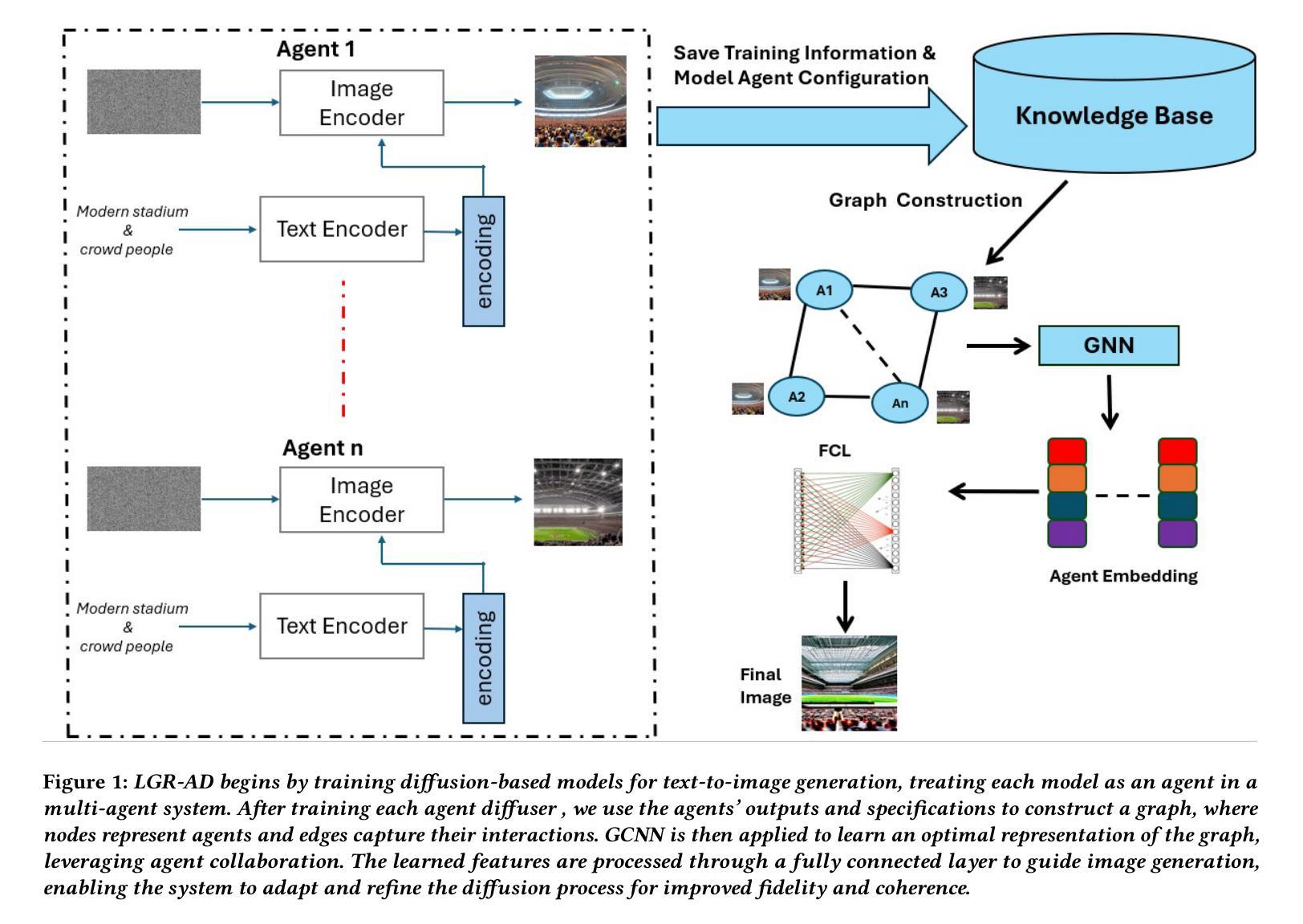
Diffusion-based generative models have significantly advanced text-to-image synthesis, demonstrating impressive text comprehension and zero-shot generalization. These models refine images from random noise based on textual prompts, with initial reliance on text input shifting towards enhanced visual fidelity over time. This transition suggests that static model parameters might not optimally address the distinct phases of generation. We introduce LGR-AD (Learning Graph Representation of Agent Diffusers), a novel multi-agent system designed to improve adaptability in dynamic computer vision tasks. LGR-AD models the generation process as a distributed system of interacting agents, each representing an expert sub-model. These agents dynamically adapt to varying conditions and collaborate through a graph neural network that encodes their relationships and performance metrics. Our approach employs a coordination mechanism based on top-$k$ maximum spanning trees, optimizing the generation process. Each agent’s decision-making is guided by a meta-model that minimizes a novel loss function, balancing accuracy and diversity. Theoretical analysis and extensive empirical evaluations show that LGR-AD outperforms traditional diffusion models across various benchmarks, highlighting its potential for scalable and flexible solutions in complex image generation tasks. Code is available at: https://github.com/YousIA/LGR_AD
基于扩散的生成模型在文本到图像合成方面取得了重大进展,展示了令人印象深刻的文本理解和零样本泛化能力。这些模型根据文本提示从随机噪声中细化图像,最初依赖文本输入,随着时间的推移,对视觉逼真度的关注逐渐增强。这种转变表明,静态模型参数可能无法最佳地处理生成的不同阶段。我们引入了LGR-AD(学习代理扩散图表示),这是一种新型多代理系统,旨在提高动态计算机视觉任务的适应性。LGR-AD将生成过程建模为相互作用的代理的分布式系统,每个代理代表一个专家子模型。这些代理能够动态适应各种条件,并通过编码其关系和性能指标的图神经网络进行协作。我们的方法采用基于top-k最大生成树的协调机制,以优化生成过程。每个代理的决策由元模型引导,该元模型最小化新型损失函数,平衡准确性和多样性。理论分析和广泛的实证评估表明,在各种基准测试中,LGR-AD的表现优于传统扩散模型,突显其在复杂图像生成任务中可扩展和灵活解决方案的潜力。相关代码可在:https://github.com/YousIA/LGR_AD找到。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted at AAMAS2025 International Conference on Autonomous Agents and Multiagent Systems
Summary
本文介绍了基于扩散的生成模型在文本到图像合成方面的显著进展,以及这些模型如何实现对文本理解的显著进步和零样本泛化能力的提升。为改善动态计算机视觉任务中的适应性,文章提出了一种新型的多代理系统LGR-AD。该系统将生成过程模拟为交互代理的分布式系统,每个代理代表一个专家子模型,通过图神经网络进行协作与适应。LGR-AD通过top-k最大生成树优化生成过程,同时引入新型损失函数平衡精度与多样性。理论与大量实证评估显示,LGR-AD在多个基准测试中优于传统扩散模型,为复杂图像生成任务提供了可扩展且灵活的解决方案。
Key Takeaways
- 扩散生成模型在文本到图像合成方面取得显著进展,展示了良好的文本理解和零样本泛化能力。
- LGR-AD是一种新型多代理系统,旨在改善动态计算机视觉任务的适应性。
- LGR-AD将生成过程模拟为交互代理的分布式系统,每个代理代表一个专家子模型。
- 通过图神经网络进行协作与适应,实现了代理间的动态调整和互动。
- LGR-AD采用top-k最大生成树优化生成过程。
- 引入新型损失函数以平衡生成的精度和多样性。
- 理论与大量实证评估证明LGR-AD在多个基准测试中优于传统扩散模型。
点此查看论文截图

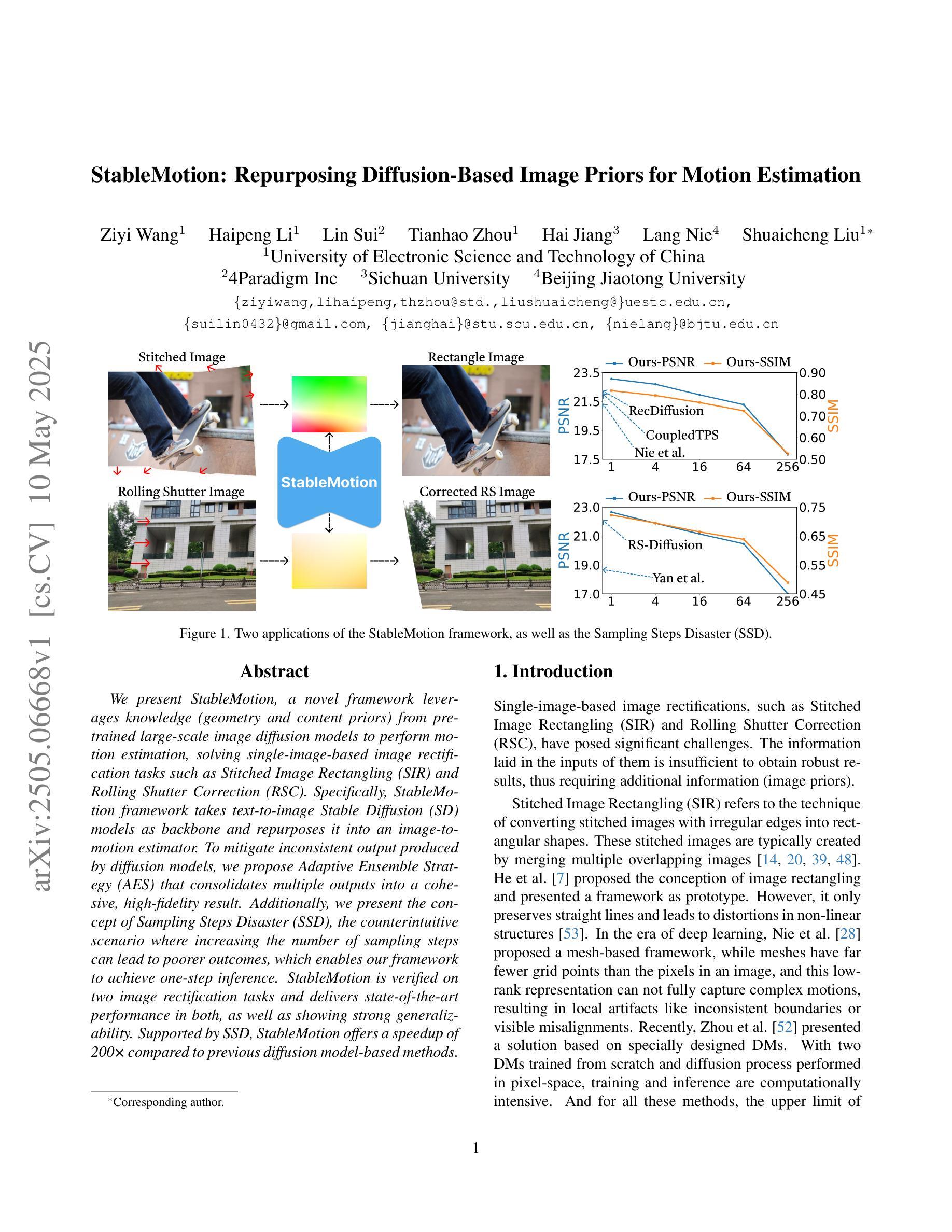
StableMotion: Repurposing Diffusion-Based Image Priors for Motion Estimation
Authors:Ziyi Wang, Haipeng Li, Lin Sui, Tianhao Zhou, Hai Jiang, Lang Nie, Shuaicheng Liu
We present StableMotion, a novel framework leverages knowledge (geometry and content priors) from pretrained large-scale image diffusion models to perform motion estimation, solving single-image-based image rectification tasks such as Stitched Image Rectangling (SIR) and Rolling Shutter Correction (RSC). Specifically, StableMotion framework takes text-to-image Stable Diffusion (SD) models as backbone and repurposes it into an image-to-motion estimator. To mitigate inconsistent output produced by diffusion models, we propose Adaptive Ensemble Strategy (AES) that consolidates multiple outputs into a cohesive, high-fidelity result. Additionally, we present the concept of Sampling Steps Disaster (SSD), the counterintuitive scenario where increasing the number of sampling steps can lead to poorer outcomes, which enables our framework to achieve one-step inference. StableMotion is verified on two image rectification tasks and delivers state-of-the-art performance in both, as well as showing strong generalizability. Supported by SSD, StableMotion offers a speedup of 200 times compared to previous diffusion model-based methods.
我们提出了StableMotion框架,它利用预训练的大规模图像扩散模型的知识(几何和先验内容)来进行运动估计,解决基于单图像的图像校正任务,如拼接图像矩形化(SIR)和滚动快门校正(RSC)。具体来说,StableMotion框架以文本到图像的Stable Diffusion(SD)模型作为骨干,并将其重新定位为图像到运动估计器。为了减轻扩散模型产生的输出不一致问题,我们提出了自适应集成策略(AES),它将多个输出合并为一个连贯、高保真度的结果。此外,我们还提出了采样步骤灾难(SSD)的概念,即增加采样步骤的数量可能导致结果更差的反直觉场景,这使我们的框架能够实现一步推断。StableMotion在两项图像校正任务上得到了验证,并在两项任务上都达到了最先进的性能,并表现出了强大的泛化能力。得益于SSD,StableMotion与之前的扩散模型方法相比实现了200倍的速度提升。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
稳定运动框架利用预训练的大规模图像扩散模型的知识,进行运动估计,解决基于单图像的任务,如图像校正和滚动快门校正。它采用文本到图像的Stable Diffusion模型作为骨干,并将其转化为图像到运动估计器。通过自适应集成策略,减轻扩散模型产生的不一致输出问题。此外,还介绍了采样步骤灾难的概念,使框架实现一步推断。StableMotion在两种图像校正任务上表现出卓越的性能和强大的泛化能力,与之前的扩散模型方法相比,速度提高了200倍。
Key Takeaways
- StableMotion框架利用预训练的大型图像扩散模型进行运动估计。
- 它解决了基于单图像的任务,如图像校正和滚动快门校正。
- 采用文本到图像的Stable Diffusion模型作为骨干,转化用于图像到运动估计。
- 通过自适应集成策略(AES)减轻扩散模型的不一致输出问题。
- 引入采样步骤灾难(SSD)概念,说明增加采样步骤数量可能导致性能下降。
- StableMotion在图像校正任务上实现了一流性能。
点此查看论文截图
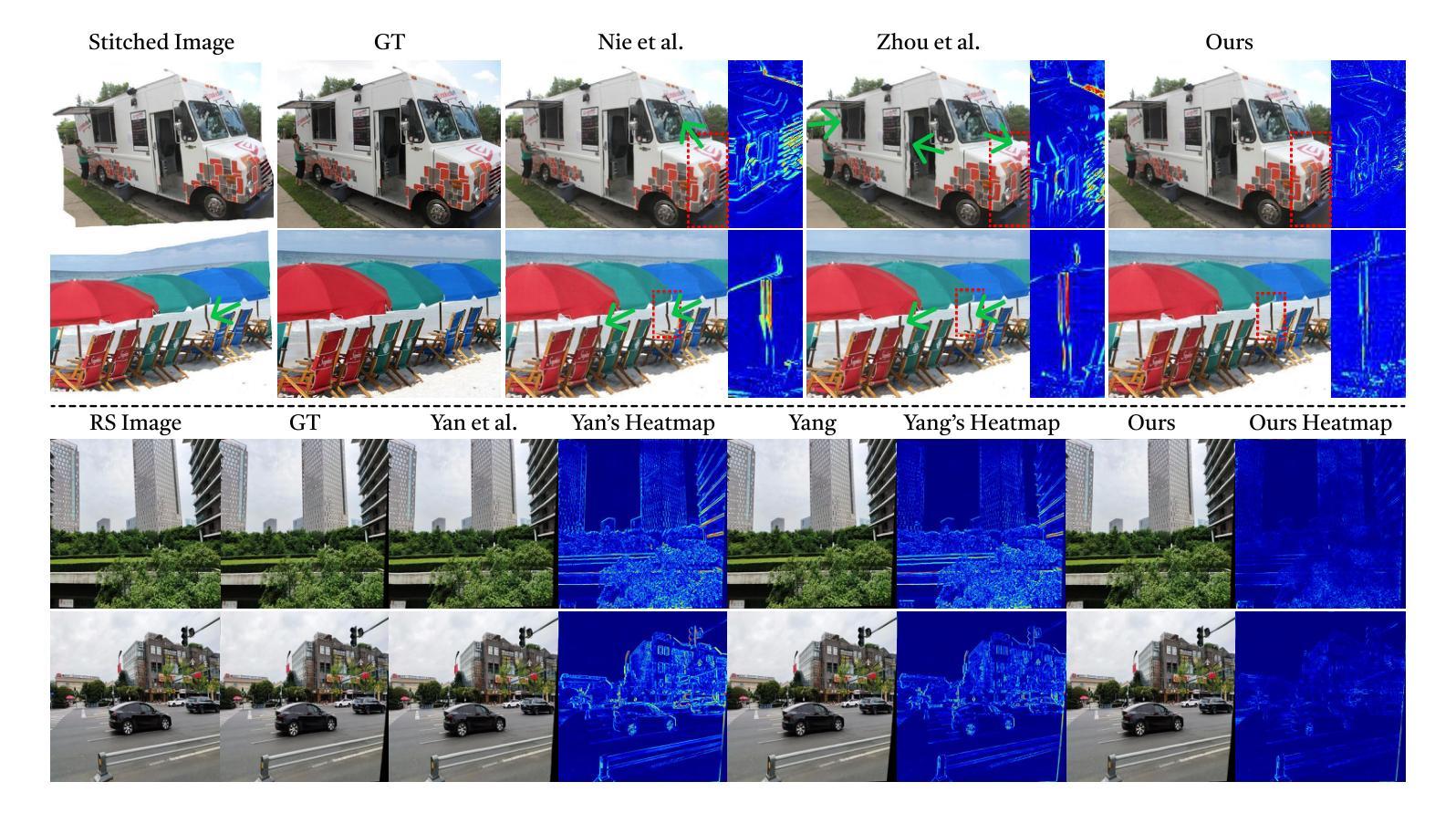
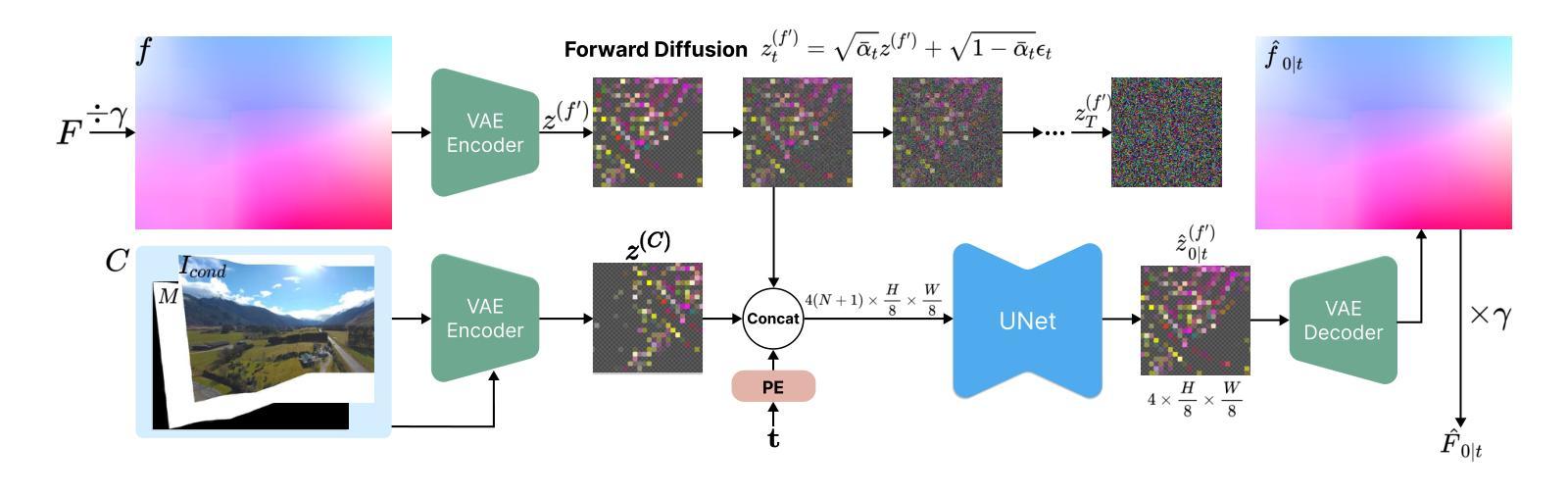
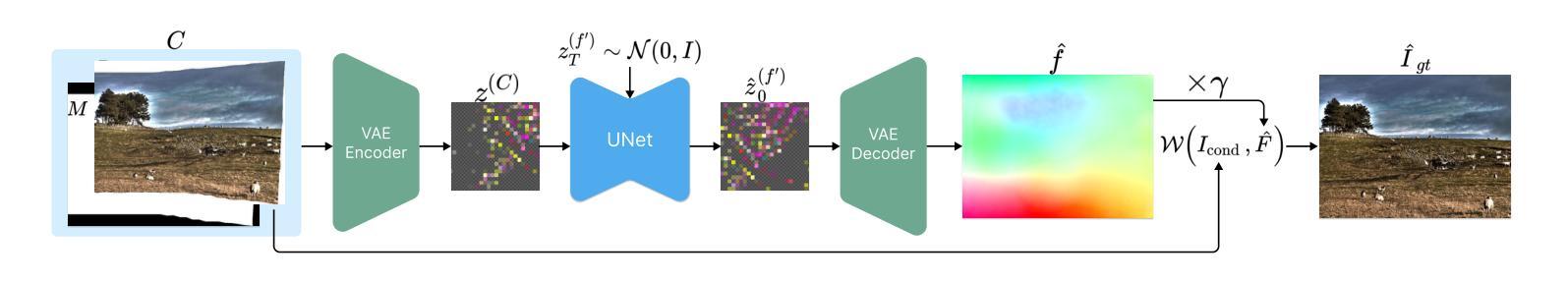
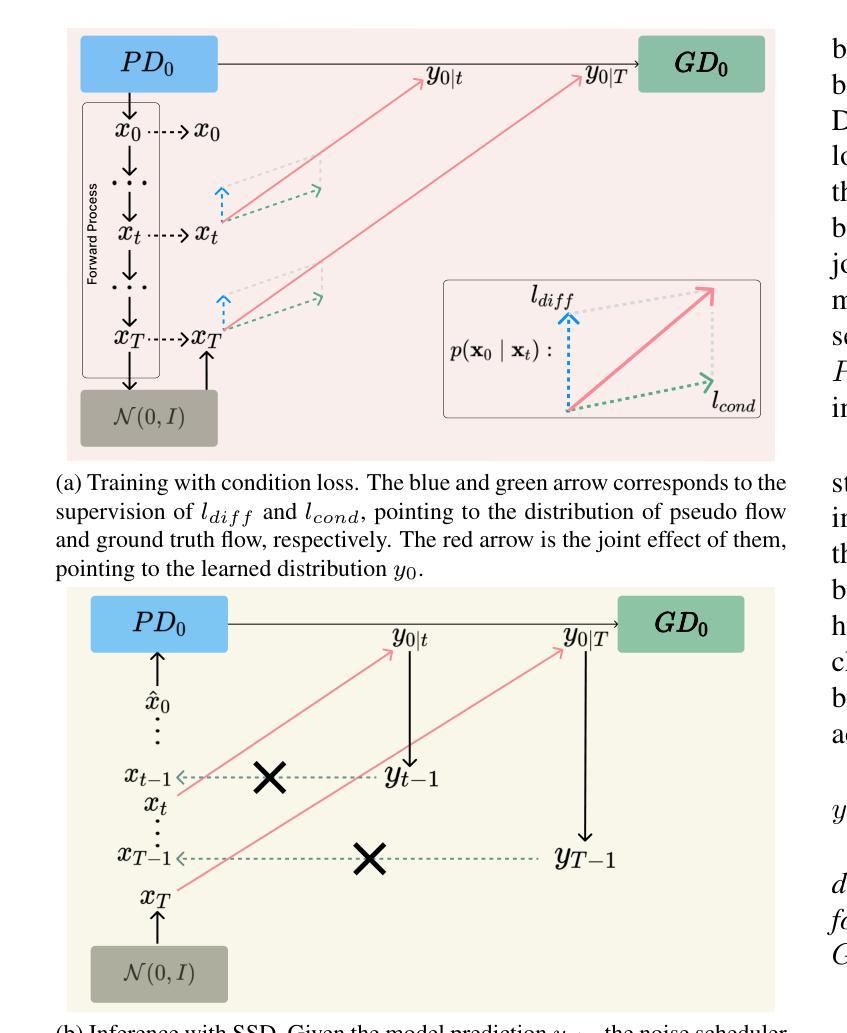

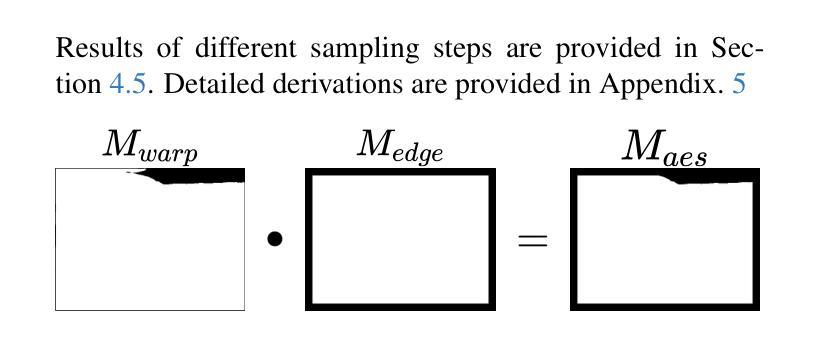
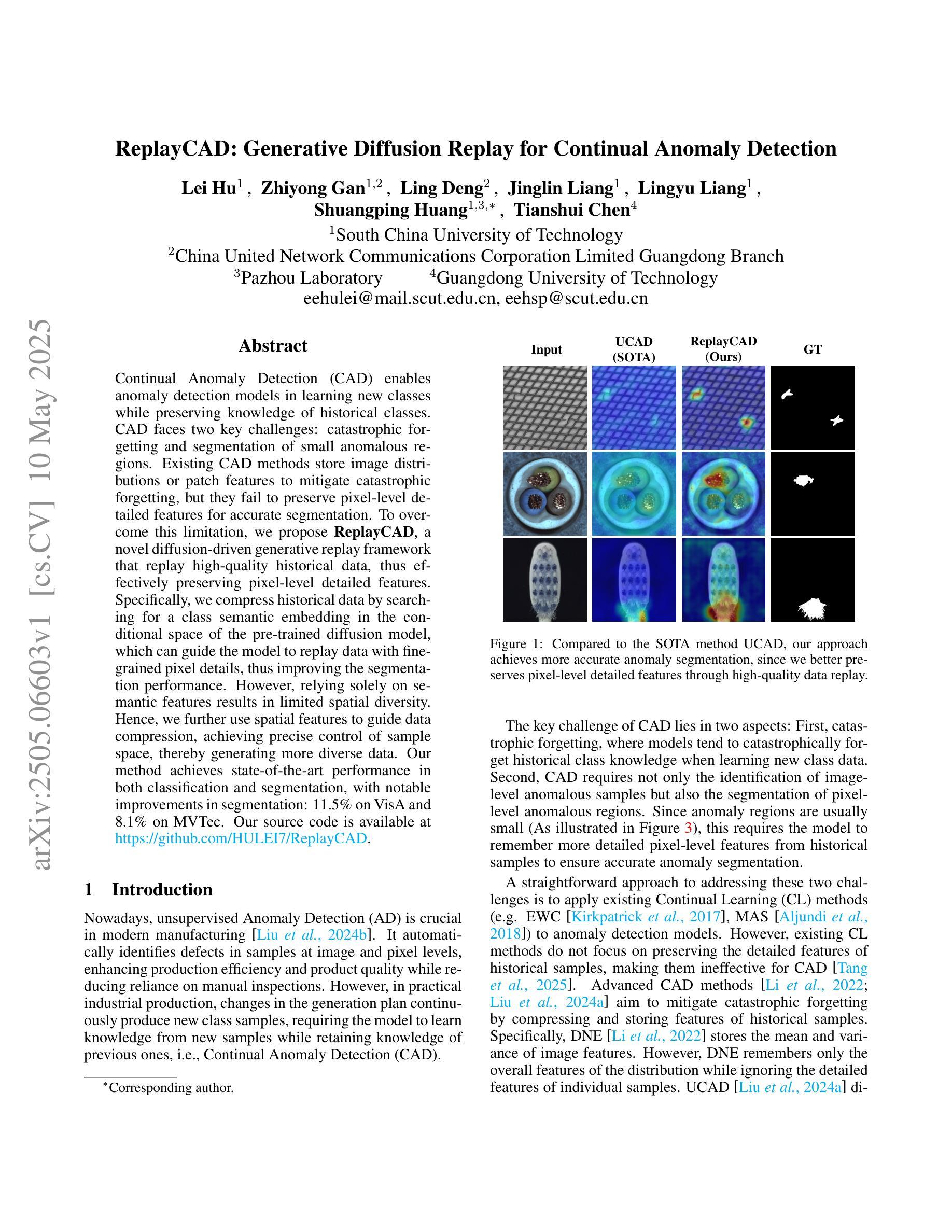
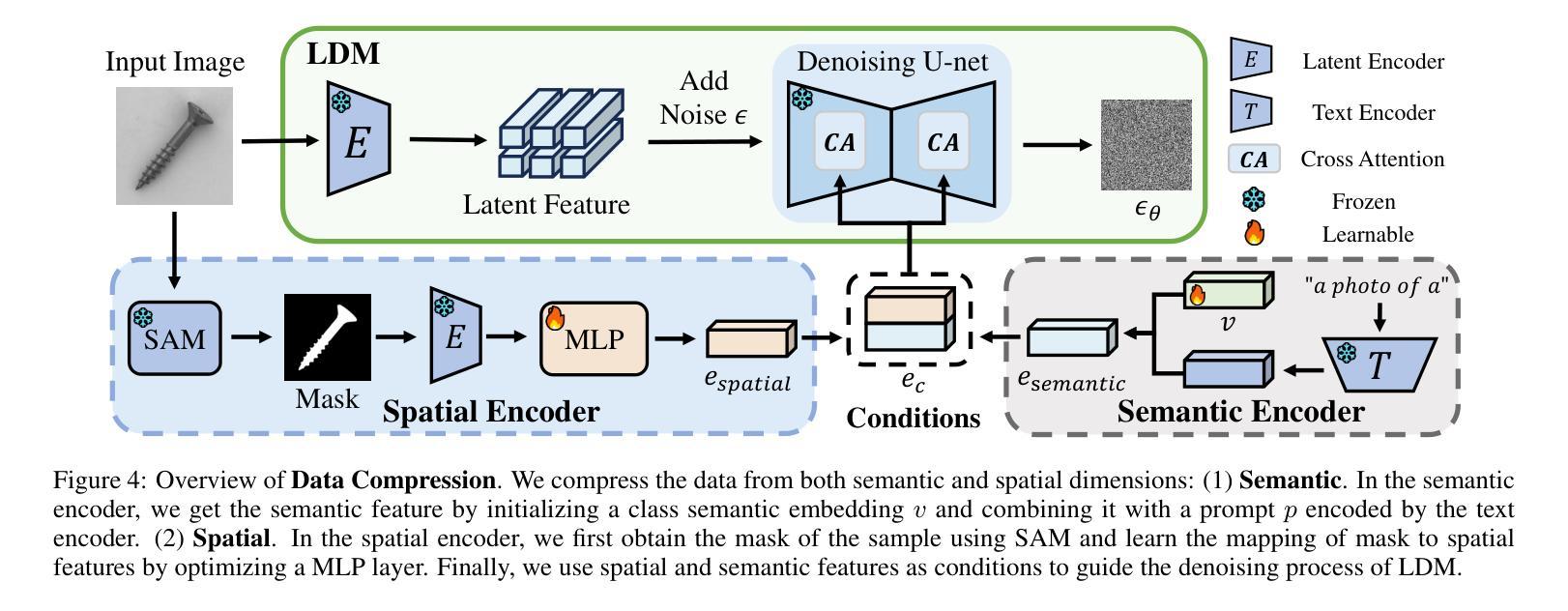
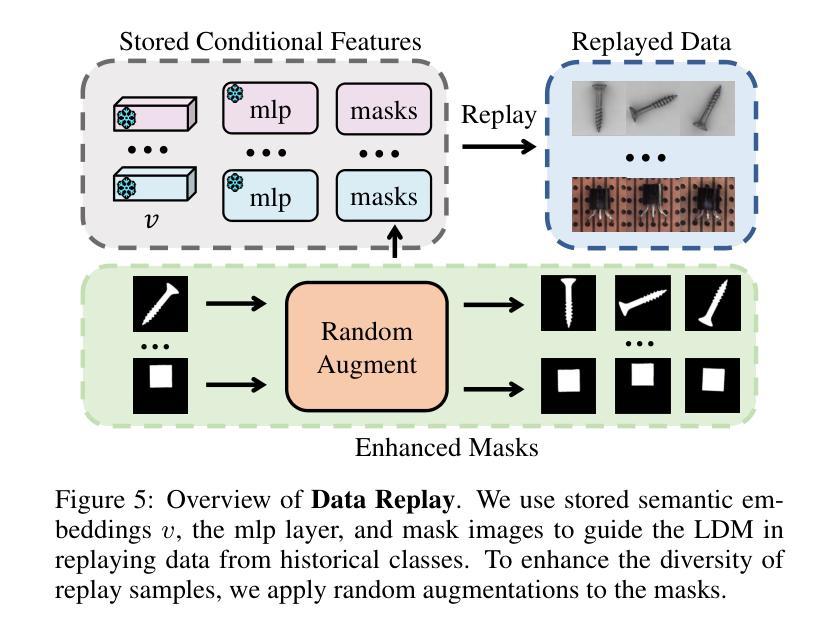
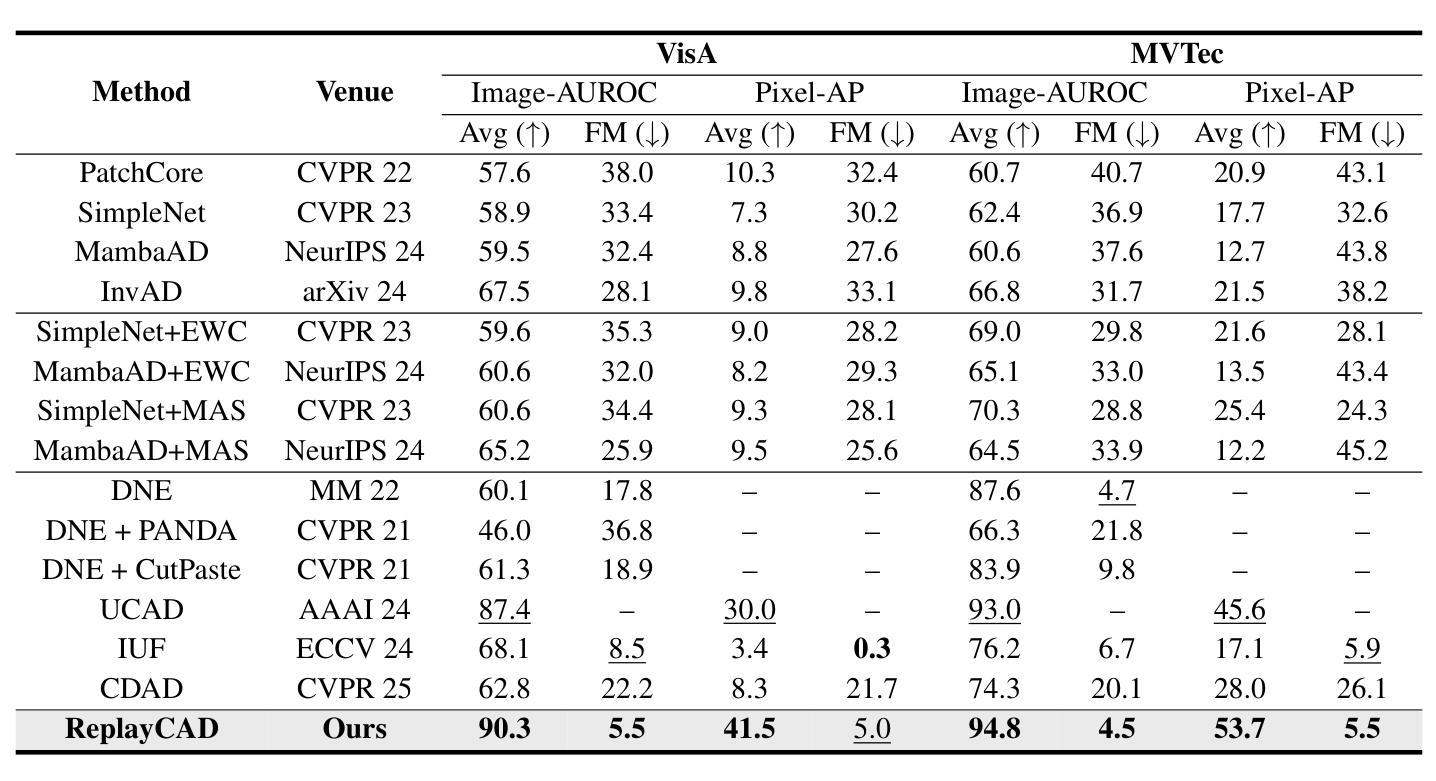
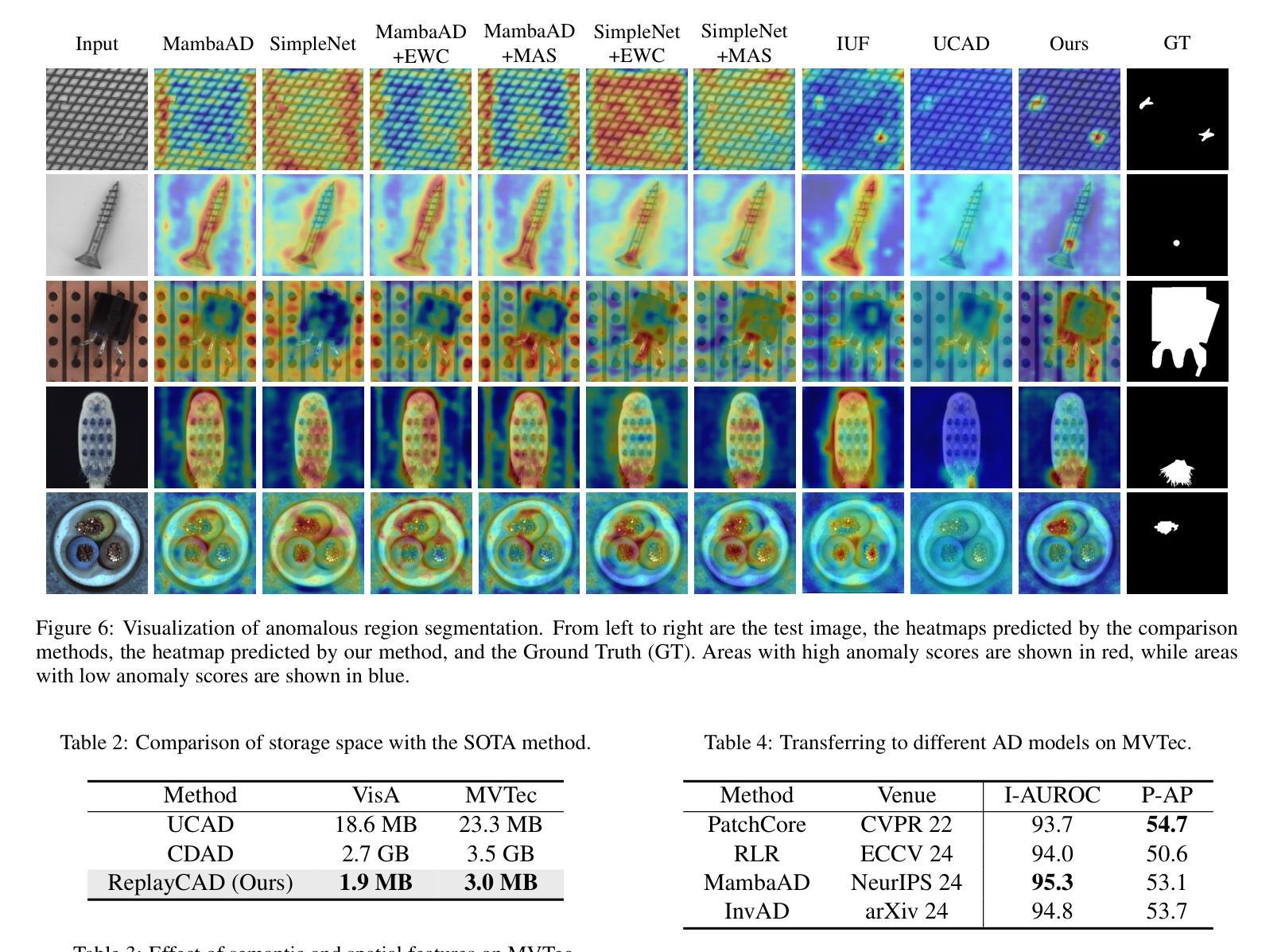
ReplayCAD: Generative Diffusion Replay for Continual Anomaly Detection
Authors:Lei Hu, Zhiyong Gan, Ling Deng, Jinglin Liang, Lingyu Liang, Shuangping Huang, Tianshui Chen
Continual Anomaly Detection (CAD) enables anomaly detection models in learning new classes while preserving knowledge of historical classes. CAD faces two key challenges: catastrophic forgetting and segmentation of small anomalous regions. Existing CAD methods store image distributions or patch features to mitigate catastrophic forgetting, but they fail to preserve pixel-level detailed features for accurate segmentation. To overcome this limitation, we propose ReplayCAD, a novel diffusion-driven generative replay framework that replay high-quality historical data, thus effectively preserving pixel-level detailed features. Specifically, we compress historical data by searching for a class semantic embedding in the conditional space of the pre-trained diffusion model, which can guide the model to replay data with fine-grained pixel details, thus improving the segmentation performance. However, relying solely on semantic features results in limited spatial diversity. Hence, we further use spatial features to guide data compression, achieving precise control of sample space, thereby generating more diverse data. Our method achieves state-of-the-art performance in both classification and segmentation, with notable improvements in segmentation: 11.5% on VisA and 8.1% on MVTec. Our source code is available at https://github.com/HULEI7/ReplayCAD.
持续异常检测(CAD)能够使异常检测模型在学习新类别时保留对历史类别的知识。CAD面临两个主要挑战:灾难性遗忘和小区域异常的分割。现有的CAD方法通过存储图像分布或补丁特征来缓解灾难性遗忘的问题,但它们无法保留像素级别的详细特征以实现准确分割。为了克服这一局限性,我们提出了ReplayCAD,这是一种新型扩散驱动生成回放框架,可以回放高质量的历史数据,从而有效地保留像素级别的详细特征。具体来说,我们通过搜索预训练扩散模型的条件空间中的类语义嵌入来压缩历史数据,这可以引导模型以精细的像素细节回放数据,从而提高分割性能。然而,仅依赖语义特征会导致空间多样性有限。因此,我们进一步使用空间特征来指导数据压缩,实现对样本空间的精确控制,从而生成更多样化的数据。我们的方法在分类和分割方面都达到了最新技术水平,在分割方面的改进尤为显著:VisA上提高了11.5%,MVTec上提高了8.1%。我们的源代码可在https://github.com/HULEI7/ReplayCAD找到。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by IJCAI 2025
Summary
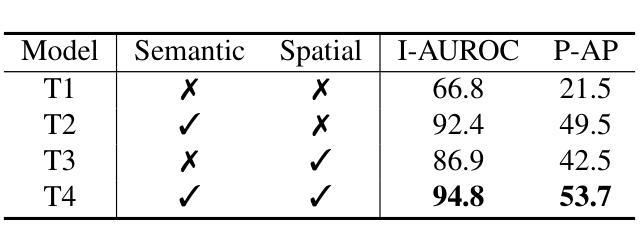
本文介绍了Continual Anomaly Detection (CAD)面临的挑战,包括灾难性遗忘和微小异常区域分割问题。现有CAD方法通过存储图像分布或补丁特征来减轻灾难性遗忘,但无法保留像素级详细特征以实现准确分割。针对此限制,本文提出ReplayCAD,一种新型扩散驱动生成回放框架,通过回放高质量历史数据有效保留像素级详细特征。该方法通过搜索预训练扩散模型的条件空间中的类语义嵌入来压缩历史数据,可指导模型以精细的像素细节回放数据,从而提高分割性能。同时,结合空间特征指导数据压缩,实现样本空间的精确控制,生成更多样化的数据。该方法在分类和分割方面都取得了最新性能,特别是在分割方面:VisA上提高了11.5%,MVTec上提高了8.1%。
Key Takeaways
- Continual Anomaly Detection (CAD) 面临灾难性遗忘和微小异常区域分割的挑战。
- 现有CAD方法主要依赖存储图像分布或补丁特征来应对灾难性遗忘问题,但无法实现准确分割。
- ReplayCAD是一个新型的扩散驱动生成回放框架,旨在通过回放高质量历史数据来解决上述问题。
- ReplayCAD通过搜索预训练扩散模型的条件空间中的类语义嵌入来压缩历史数据。
- ReplayCAD结合了语义特征,提高了像素级别的精细回放能力,进而提高分割性能。
- 除了语义特征外,ReplayCAD还使用空间特征来指导数据压缩,实现样本空间的精确控制并生成更多样化的数据。
点此查看论文截图

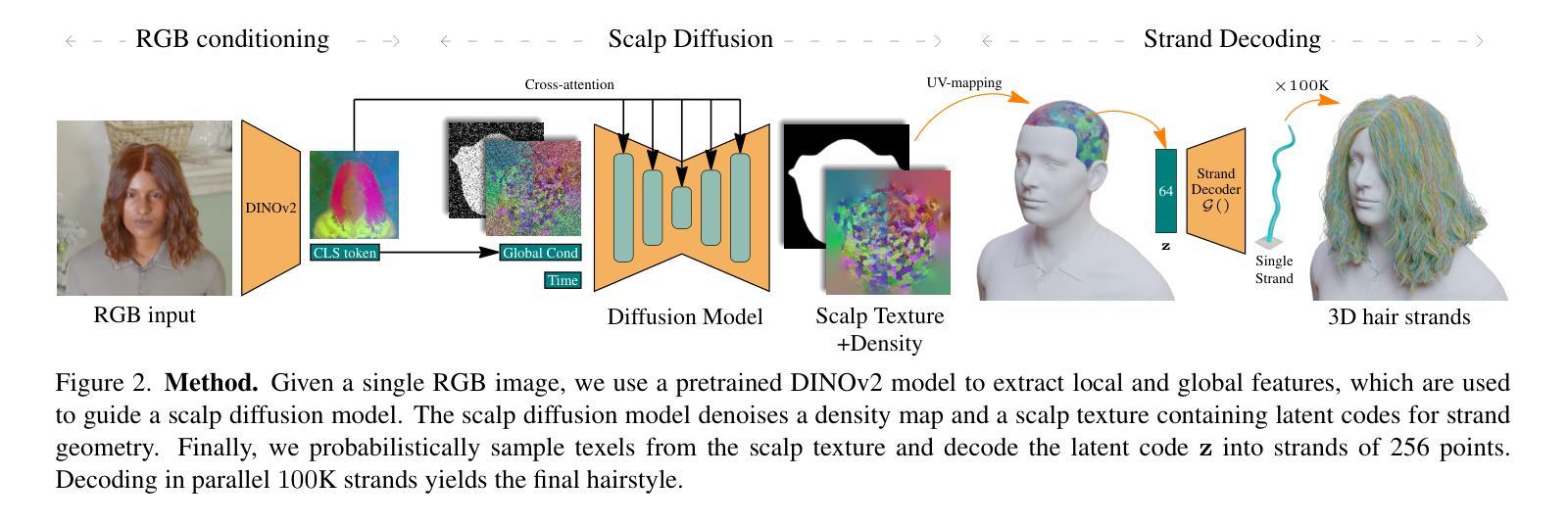
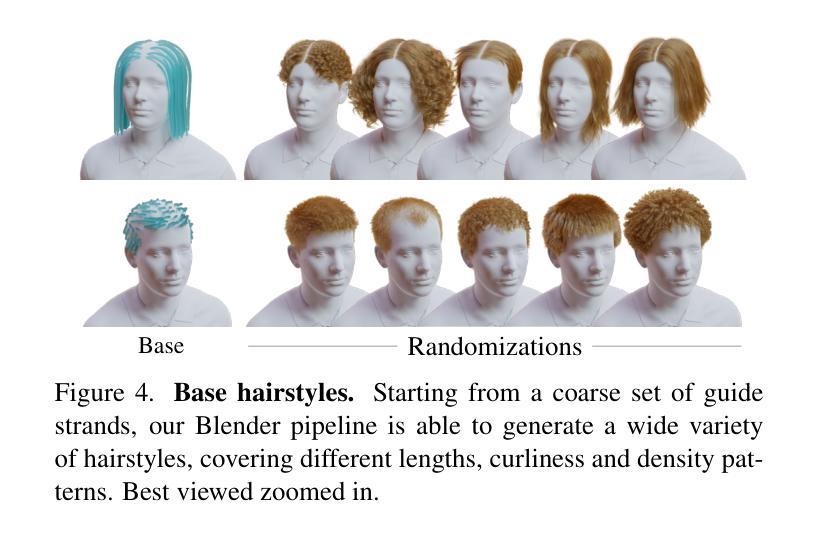
DiffLocks: Generating 3D Hair from a Single Image using Diffusion Models
Authors:Radu Alexandru Rosu, Keyu Wu, Yao Feng, Youyi Zheng, Michael J. Black
We address the task of generating 3D hair geometry from a single image, which is challenging due to the diversity of hairstyles and the lack of paired image-to-3D hair data. Previous methods are primarily trained on synthetic data and cope with the limited amount of such data by using low-dimensional intermediate representations, such as guide strands and scalp-level embeddings, that require post-processing to decode, upsample, and add realism. These approaches fail to reconstruct detailed hair, struggle with curly hair, or are limited to handling only a few hairstyles. To overcome these limitations, we propose DiffLocks, a novel framework that enables detailed reconstruction of a wide variety of hairstyles directly from a single image. First, we address the lack of 3D hair data by automating the creation of the largest synthetic hair dataset to date, containing 40K hairstyles. Second, we leverage the synthetic hair dataset to learn an image-conditioned diffusion-transfomer model that generates accurate 3D strands from a single frontal image. By using a pretrained image backbone, our method generalizes to in-the-wild images despite being trained only on synthetic data. Our diffusion model predicts a scalp texture map in which any point in the map contains the latent code for an individual hair strand. These codes are directly decoded to 3D strands without post-processing techniques. Representing individual strands, instead of guide strands, enables the transformer to model the detailed spatial structure of complex hairstyles. With this, DiffLocks can recover highly curled hair, like afro hairstyles, from a single image for the first time. Data and code is available at https://radualexandru.github.io/difflocks/
我们解决了从单张图像生成3D头发几何形状的任务,这是一个挑战,因为发型多样,并且缺乏成对的图像到3D头发数据。之前的方法主要是在合成数据上进行训练,并通过使用低维中间表示(如引导发丝和头皮级嵌入)来处理此类数据的有限量,这些表示需要后处理来进行解码、上采样和增加真实感。这些方法无法重建详细的头发,难以处理卷发,或者仅限于处理几种发型。为了克服这些局限性,我们提出了DiffLocks,这是一个能够从单张图像直接重建各种发型细节的新框架。首先,我们通过自动化创建迄今为止最大的合成头发数据集来解决3D头发数据的缺乏问题,该数据集包含4万种发型。其次,我们利用合成头发数据集来学习一个受图像条件扩散的变压器模型,该模型可以从单张正面图像生成准确的3D发丝。通过使用预训练的图像主干,我们的方法能够推广到野生图像,尽管它只在合成数据上进行训练。我们的扩散模型预测了一个头皮纹理图,该图中的任何点都包含单个发丝的潜在代码。这些代码直接被解码为3D发丝,无需后处理技巧。通过表示单个发丝而不是引导发丝,变压器能够模拟复杂发型的详细空间结构。因此,DiffLocks能够首次从单张图像中恢复高度卷曲的头发,如非洲式发型。数据和代码可在https://radualexandru.github.io/difflocks/上找到。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted to CVPR 2025
Summary
本文解决了从单张图像生成3D头发几何结构的问题。针对发型多样性和缺乏配对图像到3D头发数据的问题,提出了DiffLocks框架。该框架通过自动化创建迄今为止最大的合成头发数据集,其中包含4万多种发型来解决数据缺乏的问题。此外,利用合成头发数据集学习图像条件扩散转移模型,直接从单张正面图像生成准确的3D发丝。通过使用预训练的图像主干,该方法能够推广到野外图像,尽管只接受合成数据训练。扩散模型预测头皮纹理图,图中的每个点都包含单个发丝潜代码,可直接解码为3D发丝,无需后处理。这代表单个发丝,而不是引导发丝,使转换器能够模拟复杂发型的详细空间结构。DiffLocks能首次从单一图像中恢复高度卷曲的头发,如非洲发型。
Key Takeaways
- DiffLocks框架解决了从单张图像生成3D头发几何结构的问题,能够处理多种发型。
- 自动化创建了迄今为止最大的合成头发数据集,包含4万多种发型。
- 利用合成头发数据集学习图像条件扩散转移模型,直接生成3D发丝。
- 扩散模型预测头皮纹理图,每个点包含发丝潜代码,可直接解码为3D发丝。
- 方法通过预训练的图像主干实现推广,适用于野外图像。
- 代表单个发丝而不是引导发丝,使模型能够模拟复杂发型的详细空间结构。
点此查看论文截图


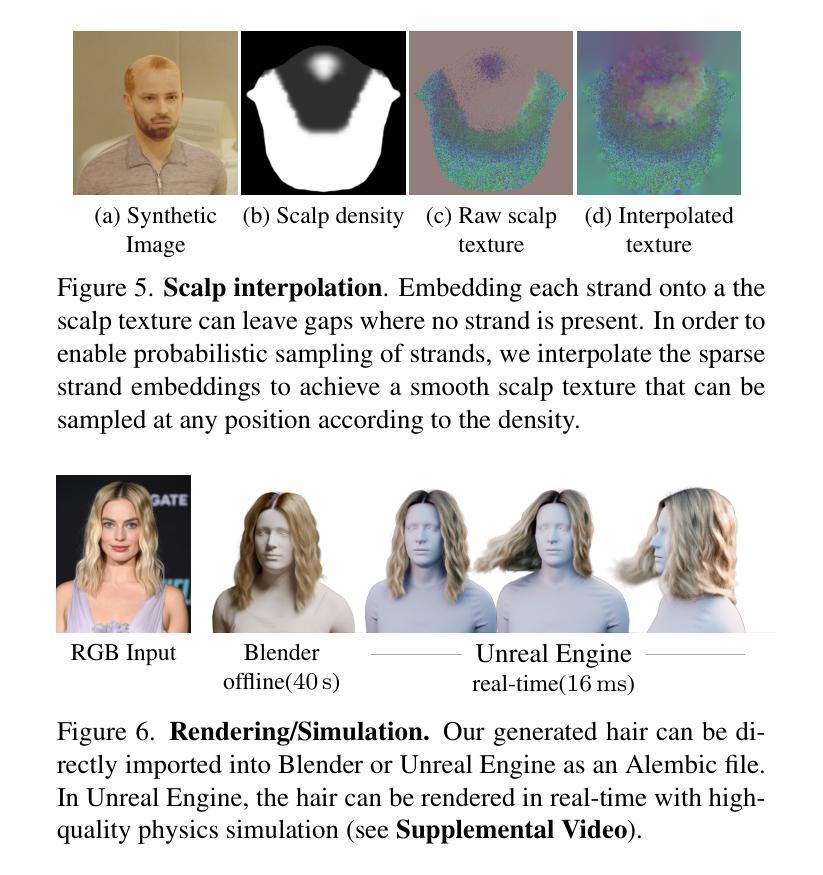
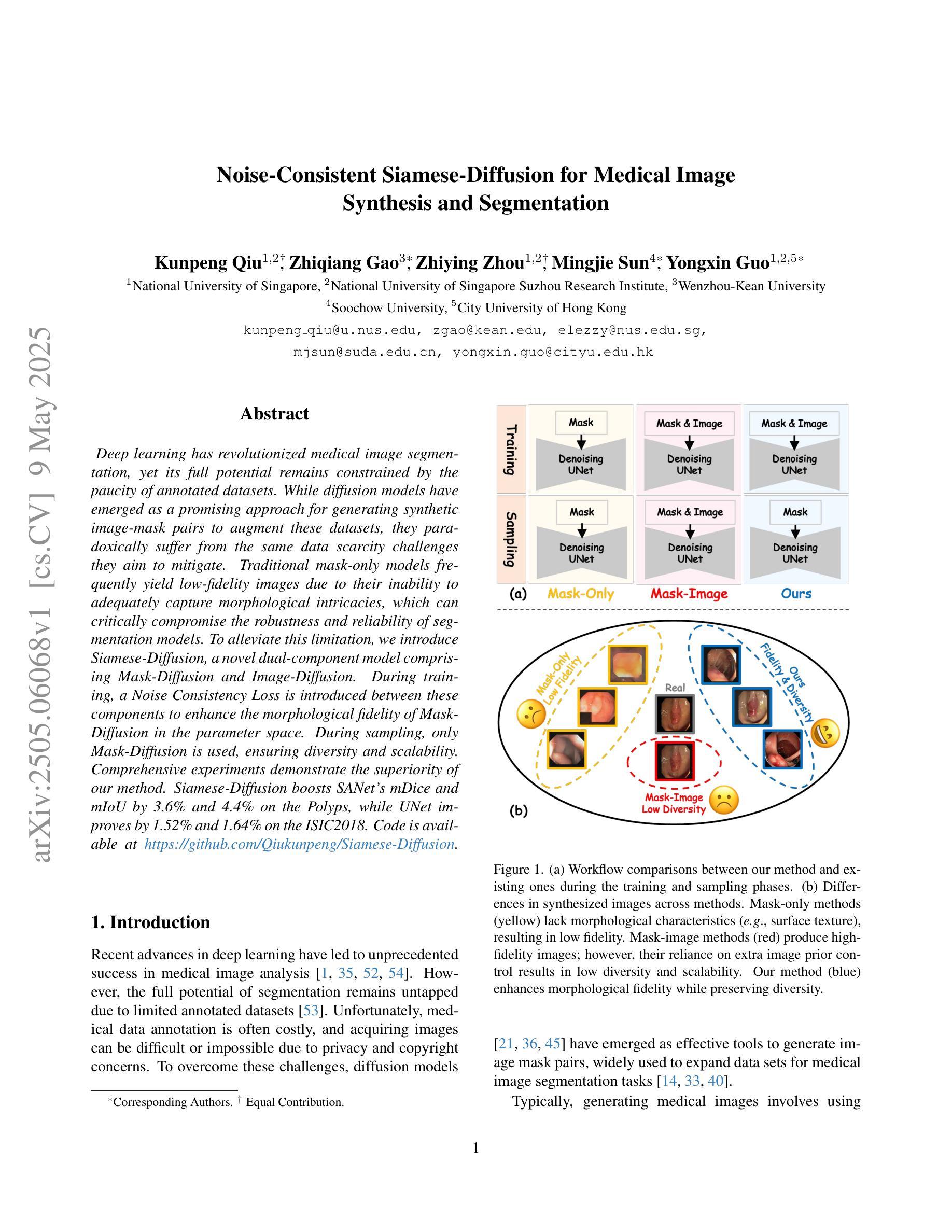
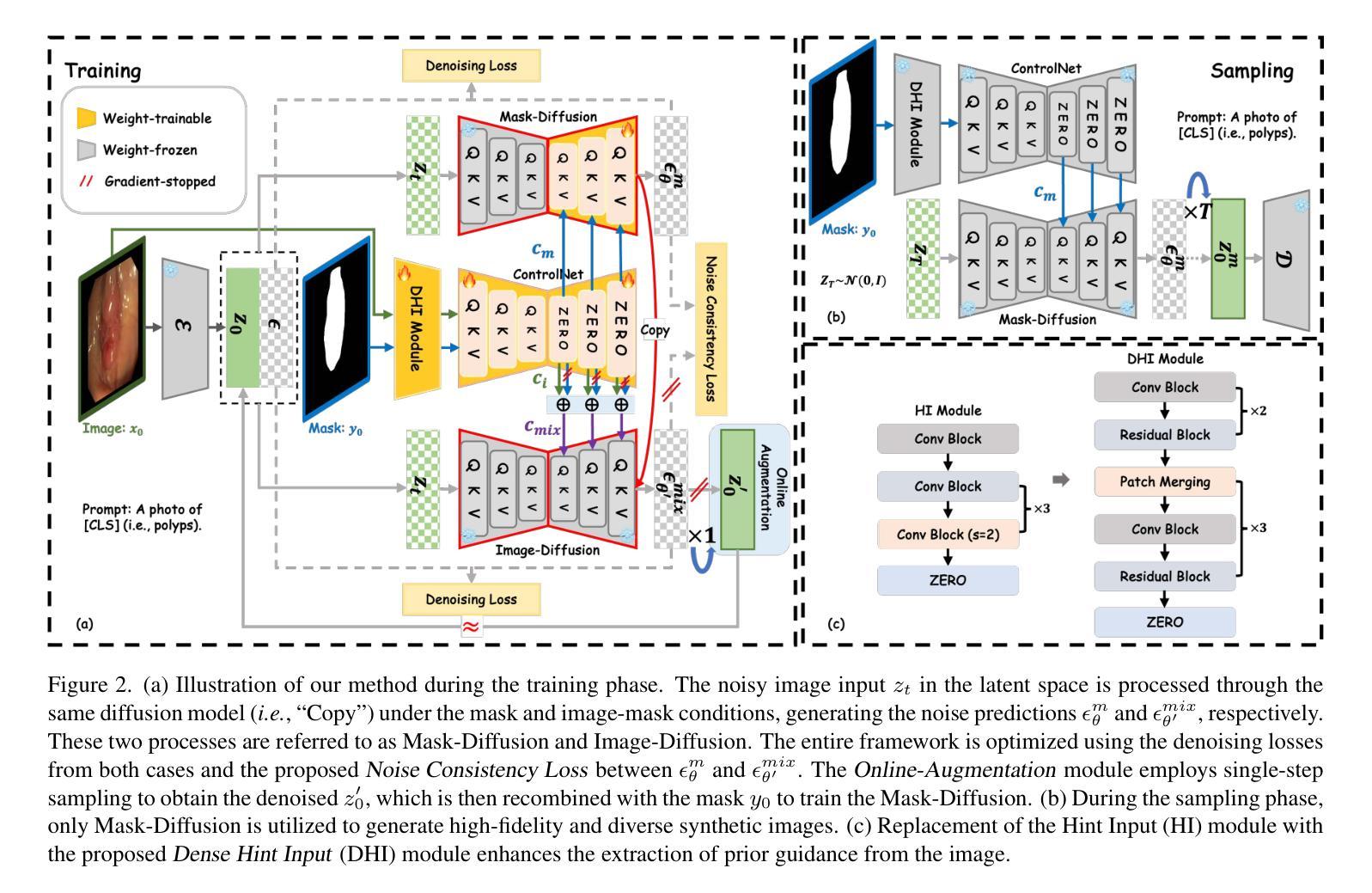
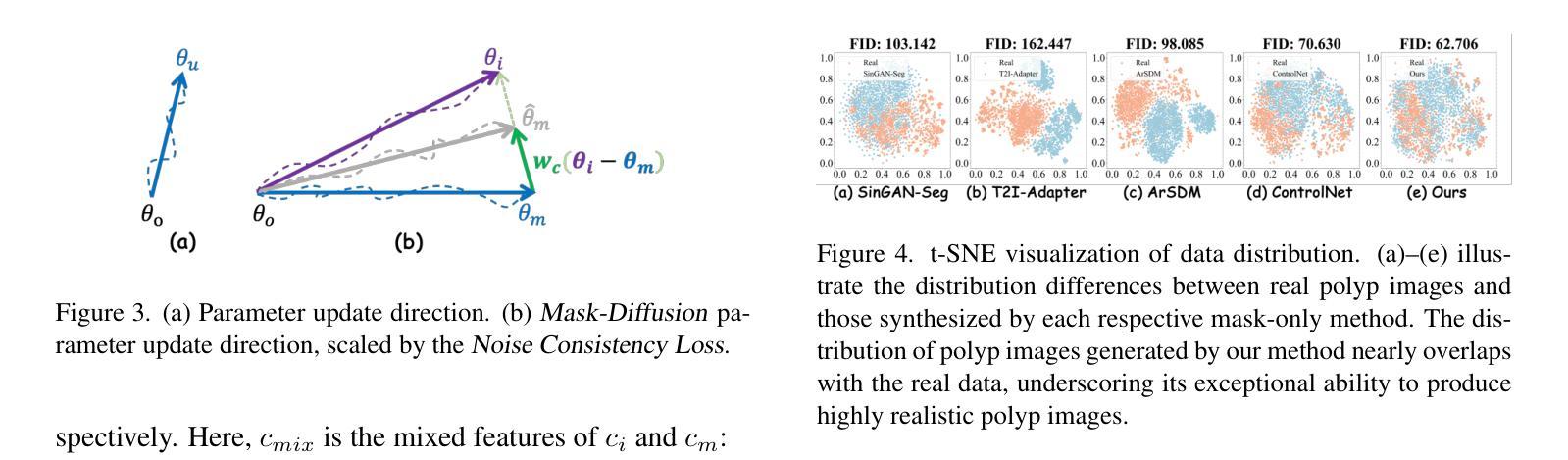
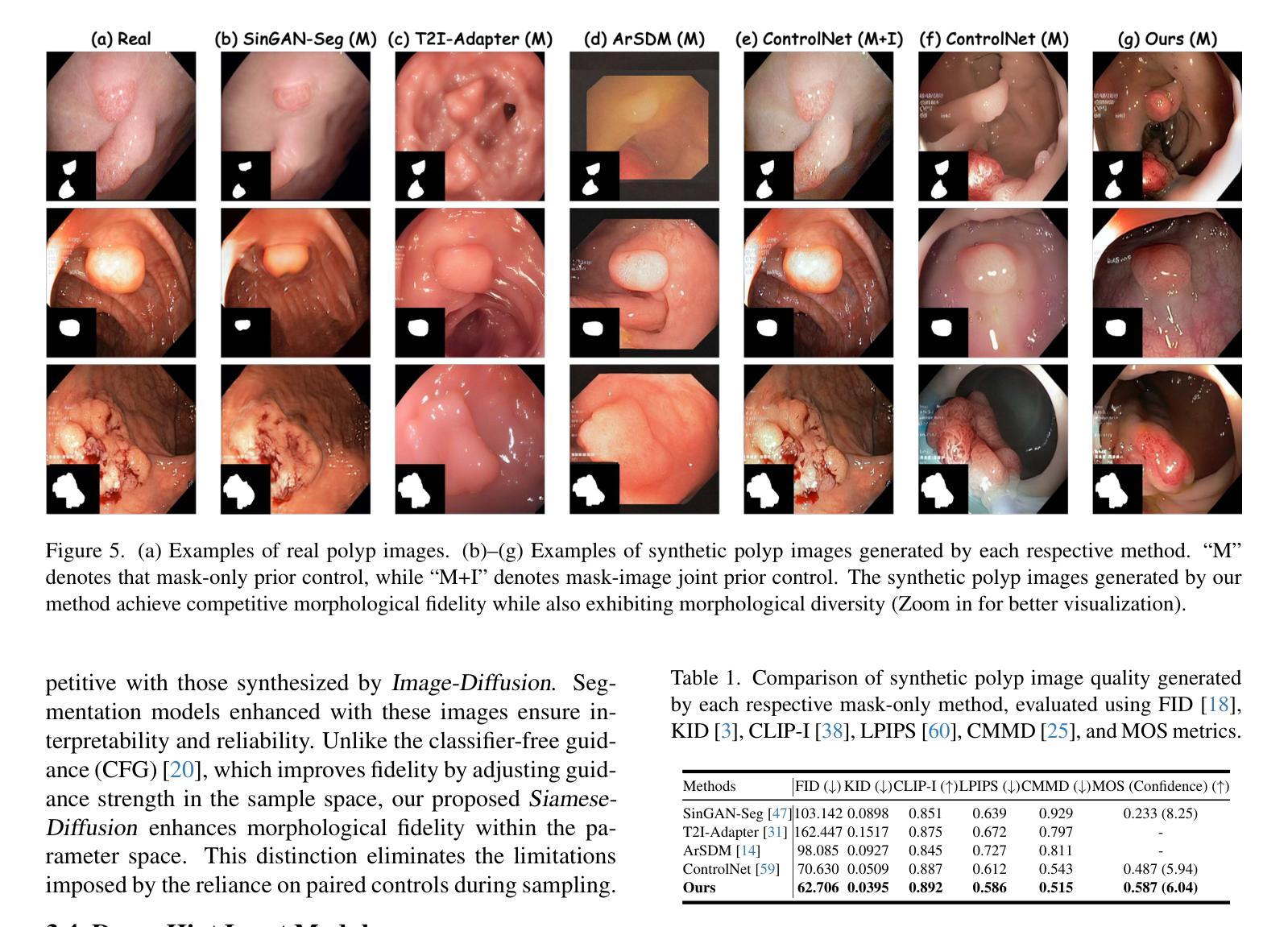
Noise-Consistent Siamese-Diffusion for Medical Image Synthesis and Segmentation
Authors:Kunpeng Qiu, Zhiqiang Gao, Zhiying Zhou, Mingjie Sun, Yongxin Guo
Deep learning has revolutionized medical image segmentation, yet its full potential remains constrained by the paucity of annotated datasets. While diffusion models have emerged as a promising approach for generating synthetic image-mask pairs to augment these datasets, they paradoxically suffer from the same data scarcity challenges they aim to mitigate. Traditional mask-only models frequently yield low-fidelity images due to their inability to adequately capture morphological intricacies, which can critically compromise the robustness and reliability of segmentation models. To alleviate this limitation, we introduce Siamese-Diffusion, a novel dual-component model comprising Mask-Diffusion and Image-Diffusion. During training, a Noise Consistency Loss is introduced between these components to enhance the morphological fidelity of Mask-Diffusion in the parameter space. During sampling, only Mask-Diffusion is used, ensuring diversity and scalability. Comprehensive experiments demonstrate the superiority of our method. Siamese-Diffusion boosts SANet’s mDice and mIoU by 3.6% and 4.4% on the Polyps, while UNet improves by 1.52% and 1.64% on the ISIC2018. Code is available at GitHub.
深度学习已经彻底改变了医学图像分割领域,但其潜力仍然受到标注数据集缺乏的限制。尽管扩散模型作为一种生成合成图像-掩膜对以增强这些数据集的方法展现出巨大潜力,但它们却面临着相同的数据稀缺挑战,即它们试图缓解的问题。传统的仅使用掩膜模型由于无法充分捕捉形态细节,经常产生低保真度的图像,这可能会严重损害分割模型的稳健性和可靠性。为了缓解这一局限性,我们引入了Siamese-Diffusion,这是一种新型的双组分模型,包括Mask-Diffusion和Image-Diffusion。在训练过程中,我们在这些组件之间引入了噪声一致性损失,以增强Mask-Diffusion在参数空间中的形态保真度。在采样过程中,只使用Mask-Diffusion,以确保多样性和可扩展性。综合实验证明了我们方法的优越性。Siamese-Diffusion提高了Polyps上的SANet的mDice和mIoU分别为3.6%和4.4%,而UNet在ISIC2018上的改进分别为1.52%和1.64%。代码已在GitHub上提供。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by CVPR2025
Summary
深度学习在医疗图像分割领域引起了革命性的变革,但仍受到标注数据集缺乏的限制。扩散模型作为一种生成合成图像-掩膜对以增强数据集的方法有潜力,但它们同样面临数据缺乏的挑战。传统的仅掩膜模型因无法充分捕捉形态细节,常产生低质量图像,这会严重影响分割模型的稳健性和可靠性。为解决此问题,我们提出了Siamese-Diffusion,一种包含Mask-Diffusion和Image-Diffusion的新型双组件模型。训练过程中,我们在组件间引入噪声一致性损失,以在参数空间中提升Mask-Diffusion的形态保真度。采样时仅使用Mask-Diffusion,以确保多样性和可扩展性。实验证明我们的方法表现卓越,Siamese-Diffusion提升了Polyps上的SANet的mDice和mIoU分别为3.6%和4.4%,而UNet在ISIC2018上的改进分别为1.52%和1.64%。代码已上传至GitHub。
Key Takeaways
- 深度学习在医疗图像分割中应用广泛,但标注数据集的缺乏限制了其潜力。
- 扩散模型可生成合成图像-掩膜对以增强数据集,但面临数据缺乏的挑战。
- 传统仅掩膜模型产生的图像质量较低,因无法充分捕捉形态细节,影响模型稳健性和可靠性。
- 提出的Siamese-Diffusion模型包含Mask-Diffusion和Image-Diffusion两个组件。
- 训练过程中引入噪声一致性损失,以提升Mask-Diffusion的形态保真度。
- 采样时仅使用Mask-Diffusion,以实现多样性和可扩展性。
- 实验证明Siamese-Diffusion表现卓越,对SANet和UNet的性能有显著提升。
点此查看论文截图
Mogao: An Omni Foundation Model for Interleaved Multi-Modal Generation
Authors:Chao Liao, Liyang Liu, Xun Wang, Zhengxiong Luo, Xinyu Zhang, Wenliang Zhao, Jie Wu, Liang Li, Zhi Tian, Weilin Huang
Recent progress in unified models for image understanding and generation has been impressive, yet most approaches remain limited to single-modal generation conditioned on multiple modalities. In this paper, we present Mogao, a unified framework that advances this paradigm by enabling interleaved multi-modal generation through a causal approach. Mogao integrates a set of key technical improvements in architecture design, including a deep-fusion design, dual vision encoders, interleaved rotary position embeddings, and multi-modal classifier-free guidance, which allow it to harness the strengths of both autoregressive models for text generation and diffusion models for high-quality image synthesis. These practical improvements also make Mogao particularly effective to process interleaved sequences of text and images arbitrarily. To further unlock the potential of unified models, we introduce an efficient training strategy on a large-scale, in-house dataset specifically curated for joint text and image generation. Extensive experiments show that Mogao not only achieves state-of-the-art performance in multi-modal understanding and text-to-image generation, but also excels in producing high-quality, coherent interleaved outputs. Its emergent capabilities in zero-shot image editing and compositional generation highlight Mogao as a practical omni-modal foundation model, paving the way for future development and scaling the unified multi-modal systems.
关于图像理解和生成的综合模型,近期进展令人印象深刻。然而,大多数方法仍然局限于多模态条件下的单模态生成。在本文中,我们介绍了Mogao,这是一个推进这一范式的一体化框架,它通过因果方法实现了交错多模态生成。Mogao在架构设计上进行了一系列关键技术改进,包括深度融合设计、双视编码器、交错旋转位置嵌入和无多模态分类引导,使其结合了自回归文本生成模型和扩散模型进行高质量图像合成的优势。这些实际改进也使得Mogao在处理任意文本和图像的交错序列时特别有效。为了充分发挥统一模型的潜力,我们在专门用于联合文本和图像生成的大规模内部数据集上引入了一种有效的训练策略。大量实验表明,Mogao不仅在多模态理解和文本到图像生成方面达到了最先进的性能,而且在生成高质量、连贯的交错输出方面也表现出色。其在零样本图像编辑和组合生成方面的能力突显了Mogao作为一个实用的全模态基础模型的优势,为未来的发展和扩大统一多模态系统铺平了道路。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Mogao Technical Report
Summary
多模态生成是图像理解和生成领域的一个热门话题。本文提出了一种名为Mogao的统一框架,通过一系列关键技术改进,实现了多模态生成模式的突破。Mogao框架采用深度融合设计、双重视觉编码器、交错旋转位置嵌入和无分类器多模态指导等技术,能够充分利用自回归文本生成模型和扩散模型的优势进行高质量图像合成。此外,本文还提出了一种在大规模内部数据集上训练统一模型的策略,该策略特别适用于文本和图像的任意交错序列处理。实验表明,Mogao在多模态理解和文本到图像生成方面达到了最先进的性能,并在零样本图像编辑和组合生成方面表现出卓越的能力,成为了一个实用的多模态基础模型。
Key Takeaways
- Mogao是一个统一框架,实现了多模态生成模式的突破。
- 通过深度融合设计等技术改进,Mogao能够综合利用自回归文本生成模型和扩散模型的优势。
- Mogao具有处理文本和图像任意交错序列的能力。
- Mogao在大规模内部数据集上的训练策略特别有效。
- Mogao在多模态理解和文本到图像生成方面达到了最先进的性能。
- Mogao在零样本图像编辑和组合生成方面表现出卓越的能力。
点此查看论文截图



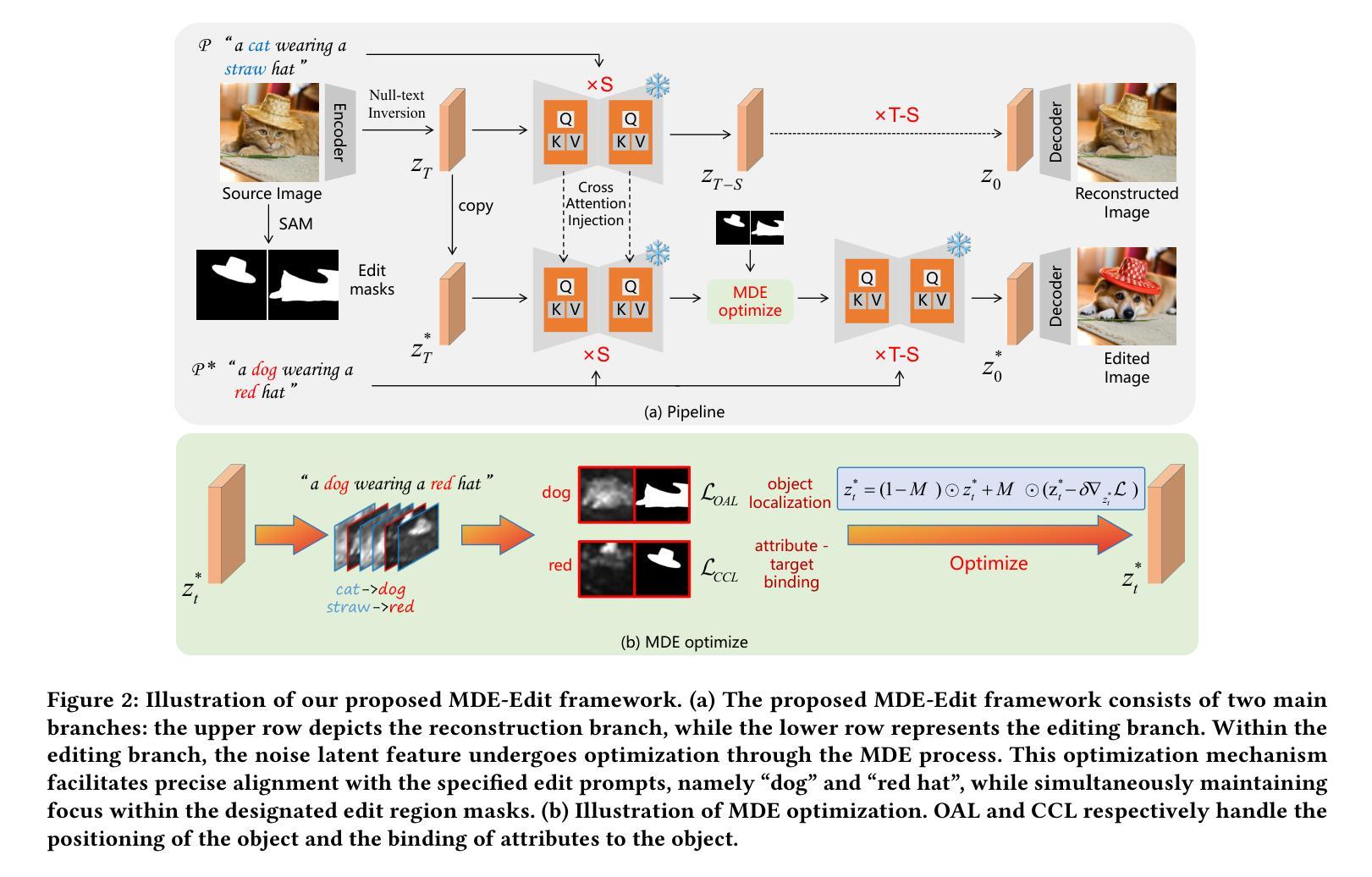
MDE-Edit: Masked Dual-Editing for Multi-Object Image Editing via Diffusion Models
Authors:Hongyang Zhu, Haipeng Liu, Bo Fu, Yang Wang
Multi-object editing aims to modify multiple objects or regions in complex scenes while preserving structural coherence. This task faces significant challenges in scenarios involving overlapping or interacting objects: (1) Inaccurate localization of target objects due to attention misalignment, leading to incomplete or misplaced edits; (2) Attribute-object mismatch, where color or texture changes fail to align with intended regions due to cross-attention leakage, creating semantic conflicts (\textit{e.g.}, color bleeding into non-target areas). Existing methods struggle with these challenges: approaches relying on global cross-attention mechanisms suffer from attention dilution and spatial interference between objects, while mask-based methods fail to bind attributes to geometrically accurate regions due to feature entanglement in multi-object scenarios. To address these limitations, we propose a training-free, inference-stage optimization approach that enables precise localized image manipulation in complex multi-object scenes, named MDE-Edit. MDE-Edit optimizes the noise latent feature in diffusion models via two key losses: Object Alignment Loss (OAL) aligns multi-layer cross-attention with segmentation masks for precise object positioning, and Color Consistency Loss (CCL) amplifies target attribute attention within masks while suppressing leakage to adjacent regions. This dual-loss design ensures localized and coherent multi-object edits. Extensive experiments demonstrate that MDE-Edit outperforms state-of-the-art methods in editing accuracy and visual quality, offering a robust solution for complex multi-object image manipulation tasks.
多对象编辑旨在在复杂的场景中修改多个对象或区域,同时保持结构连贯性。在涉及重叠或交互对象的场景中,此任务面临重大挑战:(1)由于注意力错位导致目标对象定位不准确,从而导致编辑不完整或错位;(2)属性对象不匹配,由于跨注意力泄漏,颜色或纹理变化未能与意图区域对齐,从而产生语义冲突(例如,颜色渗入非目标区域)。现有方法难以应对这些挑战:依赖全局跨注意力机制的方法受到注意力稀释和对象间空间干扰的影响,而基于掩膜的方法由于在多对象场景中的特征纠缠而无法将属性绑定到几何精确的区域。为了解决这些局限性,我们提出了一种无需训练、在推理阶段进行优化的方法,能够在复杂的多对象场景中实现精确的定位图像操作,名为MDE-Edit。MDE-Edit通过两个关键损失优化扩散模型中的噪声潜在特征:对象对齐损失(OAL)将多层跨注意力与分割掩膜对齐,以实现精确的对象定位;颜色一致性损失(CCL)在掩膜内放大目标属性注意力,同时抑制对相邻区域的泄漏。这种双重损失设计确保局部化和连贯的多对象编辑。大量实验表明,MDE-Edit在编辑准确性和视觉质量方面优于最新方法,为复杂的多对象图像操作任务提供了稳健的解决方案。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 9 pages, 7 figures
Summary
文本介绍了一种名为MDE-Edit的方法,它可以在复杂的多对象场景中实现精确的局部图像操作。MDE-Edit通过在扩散模型中优化噪声潜在特征,采用两种关键损失:对象对齐损失(OAL)和颜色一致性损失(CCL),实现对多对象进行精确定位和对目标属性进行一致编辑。该方法在编辑准确性和视觉质量方面优于现有技术,为复杂的多对象图像操作任务提供了稳健的解决方案。
Key Takeaways
- 多对象编辑面临挑战:目标对象定位不准确,导致编辑不完整或错位;属性与对象不匹配,由于跨注意力泄漏导致语义冲突。
- 现有方法在处理这些挑战时存在困难,全球跨注意力机制和基于遮罩的方法都有局限性。
- MDE-Edit采用训练外、推理阶段优化的方法,可在复杂的多对象场景中实现精确局部图像操作。
- MDE-Edit通过两种关键损失实现:对象对齐损失(OAL)用于精确对象定位,颜色一致性损失(CCL)确保目标属性在遮罩内一致,同时抑制泄漏到相邻区域。
- MDE-Edit通过优化扩散模型中的噪声潜在特征来实现精确编辑。
- MDE-Edit在编辑准确性和视觉质量方面表现出优于现有技术。
点此查看论文截图


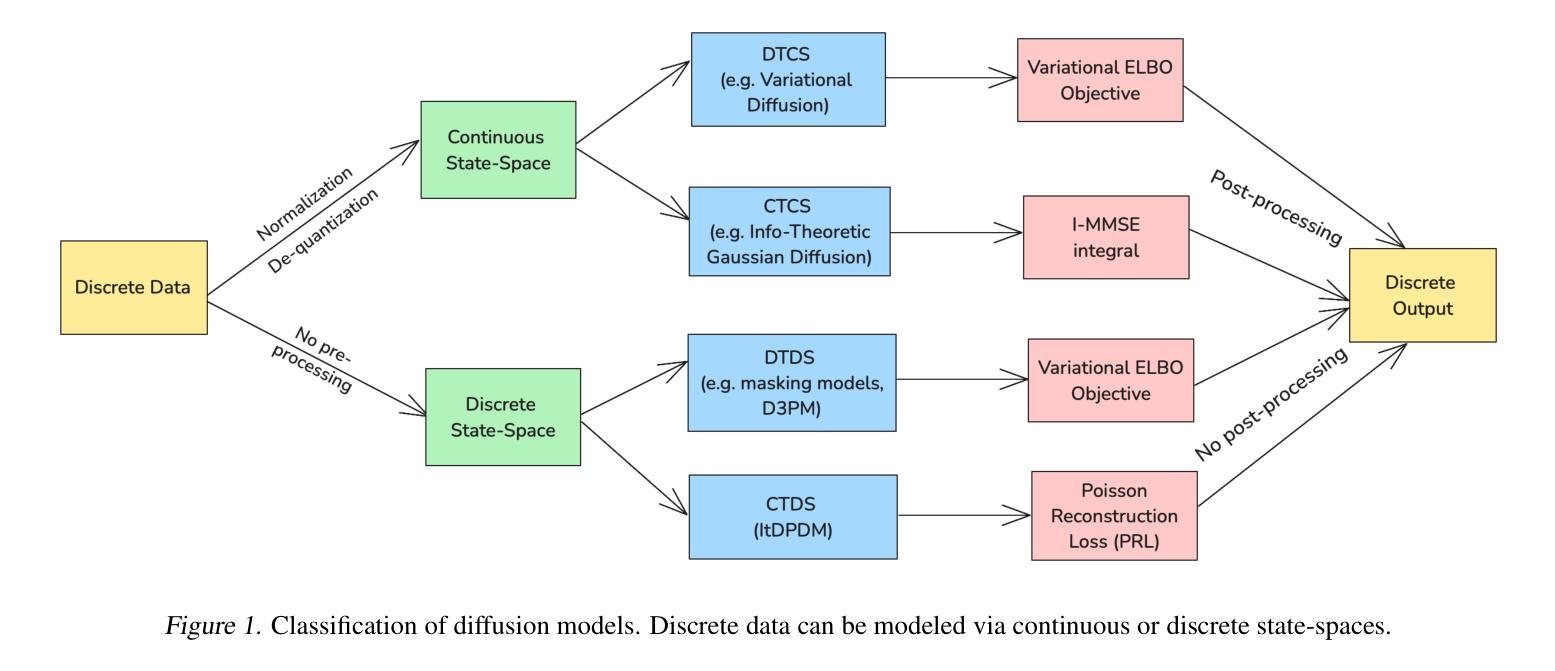
ItDPDM: Information-Theoretic Discrete Poisson Diffusion Model
Authors:Sagnik Bhattacharya, Abhiram Gorle, Ahmed Mohsin, Ahsan Bilal, Connor Ding, Amit Kumar Singh Yadav, Tsachy Weissman
Existing methods for generative modeling of discrete data, such as symbolic music tokens, face two primary challenges: (1) they either embed discrete inputs into continuous state-spaces or (2) rely on variational losses that only approximate the true negative log-likelihood. Previous efforts have individually targeted these limitations. While information-theoretic Gaussian diffusion models alleviate the suboptimality of variational losses, they still perform modeling in continuous domains. In this work, we introduce the Information-Theoretic Discrete Poisson Diffusion Model (ItDPDM), which simultaneously addresses both limitations by directly operating in a discrete state-space via a Poisson diffusion process inspired by photon arrival processes in camera sensors. We introduce a novel Poisson Reconstruction Loss (PRL) and derive an exact relationship between PRL and the true negative log-likelihood, thereby eliminating the need for approximate evidence lower bounds. Experiments conducted on the Lakh MIDI symbolic music dataset and the CIFAR-10 image benchmark demonstrate that ItDPDM delivers significant improvements, reducing test NLL by up to 80% compared to prior baselines, while also achieving faster convergence.
现有的离散数据生成模型方法,如符号音乐令牌,面临两个主要挑战:一是将离散输入嵌入连续状态空间,二是依赖于仅近似真实负对数似然的变化损失。之前的努力已经分别针对这些局限性进行了改进。虽然信息理论高斯扩散模型缓解了变化损失的次优性,但它们仍然在连续域中进行建模。在这项工作中,我们引入了信息理论离散泊松扩散模型(ItDPDM),该模型通过受相机传感器中光子到达过程启发的泊松扩散过程,直接在离散状态空间中解决这两个局限性。我们引入了一种新型的泊松重建损失(PRL)并推导出PRL与真实负对数似然之间的精确关系,从而消除了对近似证据下限的需求。在Lakh MIDI符号音乐数据集和CIFAR-10图像基准测试上进行的实验表明,ItDPDM提供了显著的改进,与先前的基础相比,测试NLL降低了高达80%,同时实现了更快的收敛速度。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Pre-print
Summary
本文介绍了信息理论离散泊松扩散模型(ItDPDM),该模型通过泊松扩散过程直接在离散状态空间中进行操作,解决了当前生成离散数据建模的两个主要挑战。ItDPDM引入了一种新的泊松重建损失(PRL),并与真正的负对数似然建立了精确的关系,从而不需要使用近似的证据下界。实验结果表明,ItDPDM在Lakh MIDI符号音乐数据集和CIFAR-10图像基准测试上实现了显著改进,与先前的基础相比,测试NLL降低了高达80%,同时实现了更快的收敛速度。
Key Takeaways
- ItDPDM解决了现有生成离散数据建模方法面临的主要挑战。
- ItDPDM通过泊松扩散过程直接在离散状态空间中进行操作。
- 引入了新的泊松重建损失(PRL)。
- PRL与真正的负对数似然之间建立了精确的关系。
- 无需使用近似的证据下界。
- ItDPDM在符号音乐数据集和图像基准测试上实现了显著的性能改进。
点此查看论文截图


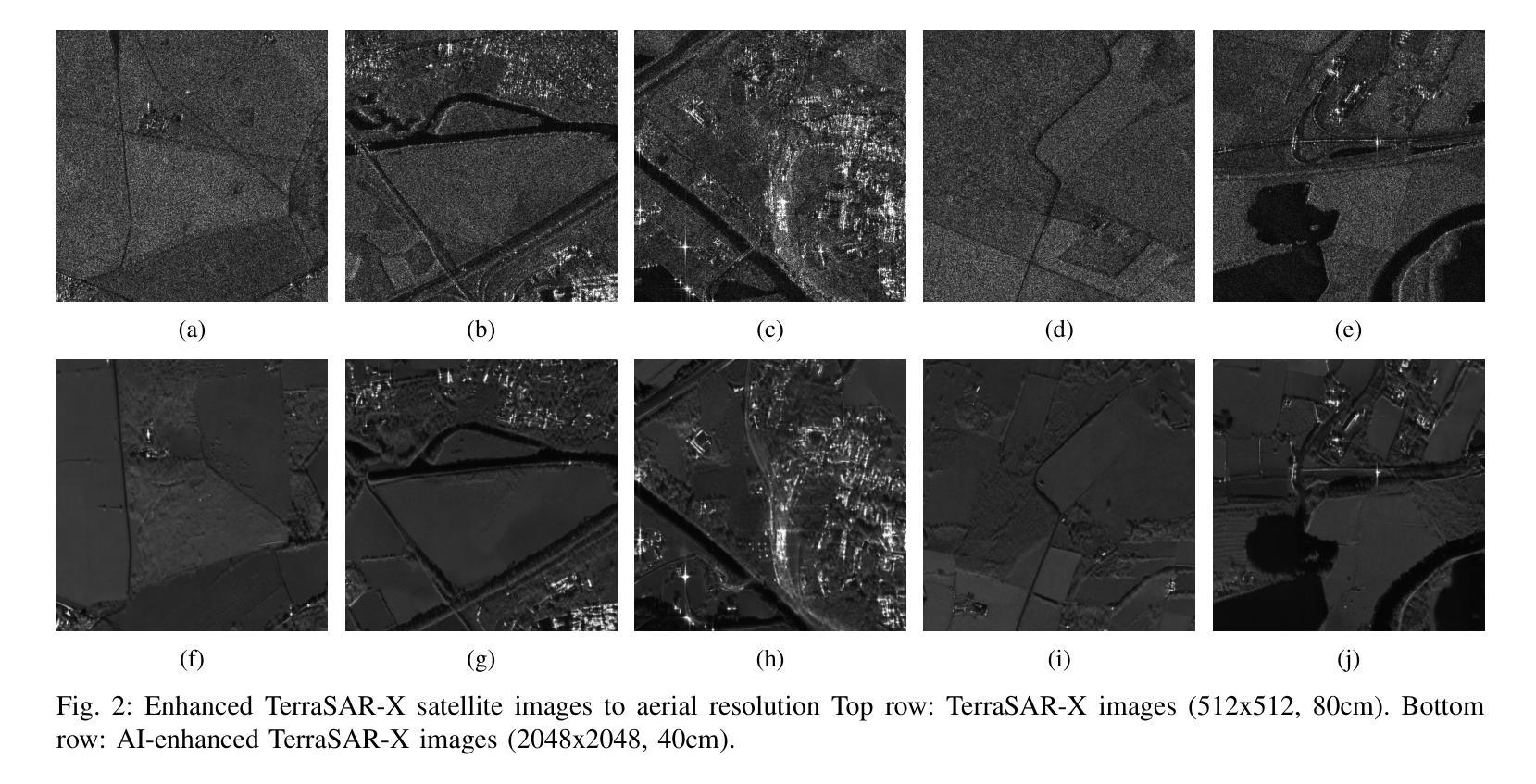
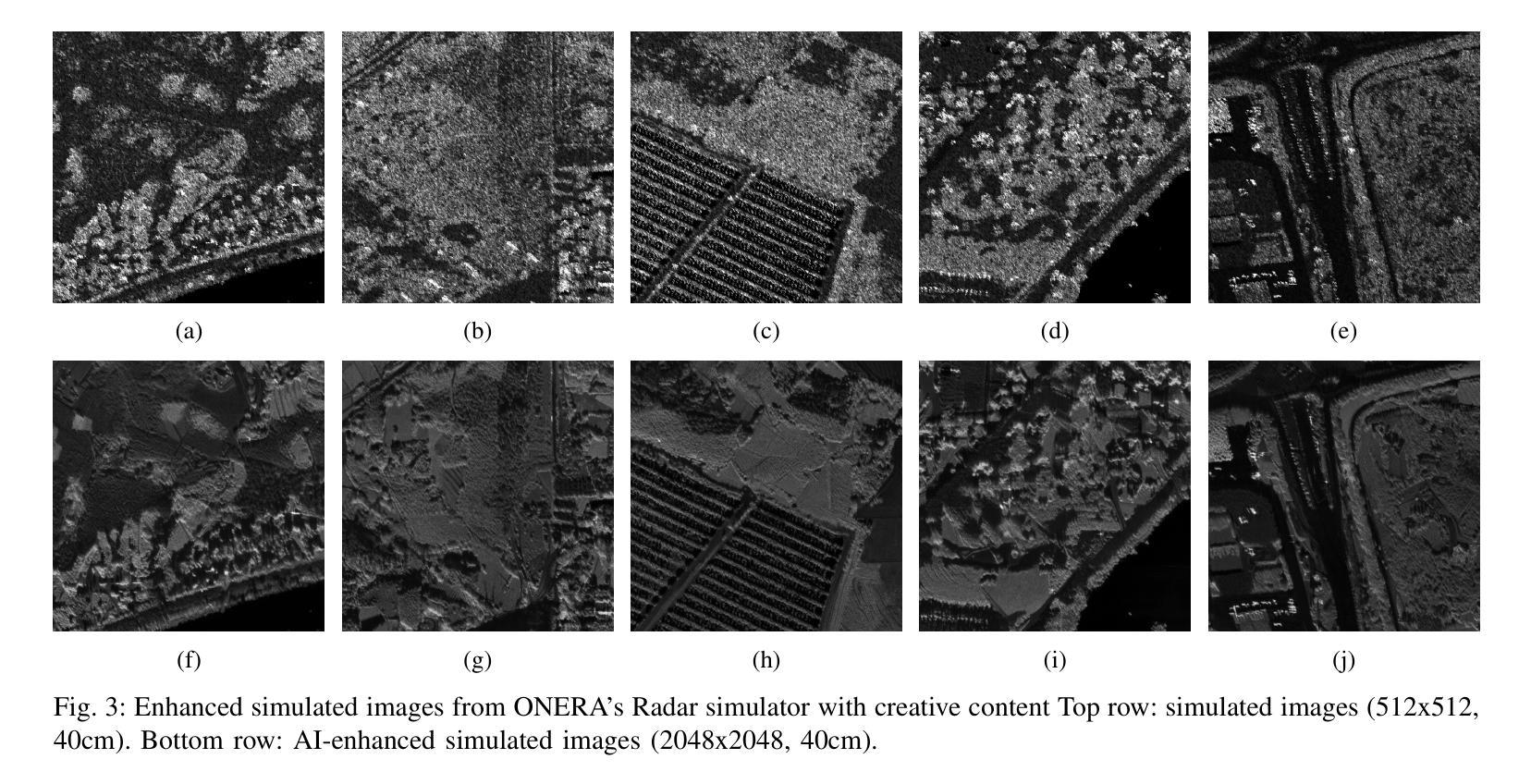
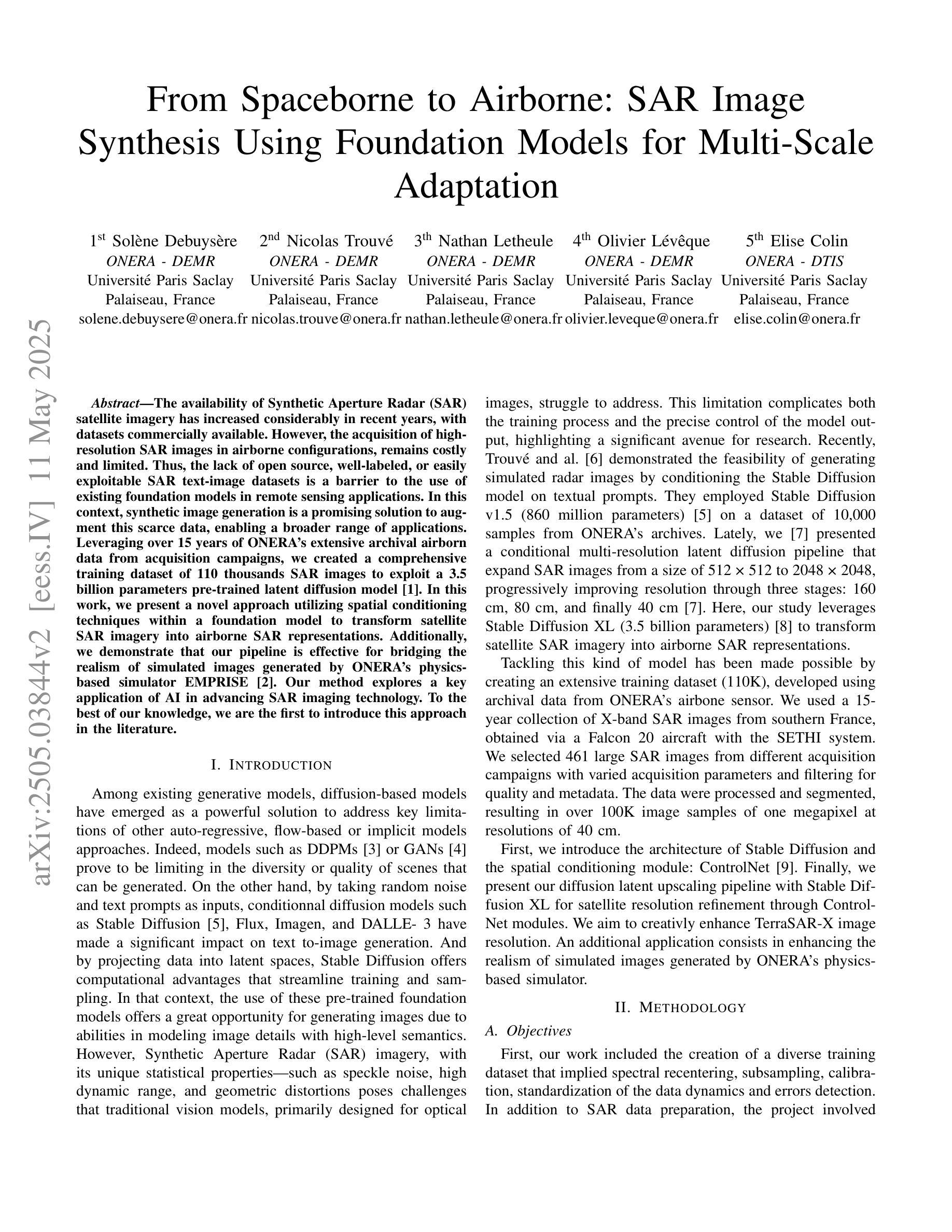
From Spaceborne to Airborne: SAR Image Synthesis Using Foundation Models for Multi-Scale Adaptation
Authors:Solene Debuysere, Nicolas Trouve, Nathan Letheule, Olivier Leveque, Elise Colin
The availability of Synthetic Aperture Radar (SAR) satellite imagery has increased considerably in recent years, with datasets commercially available. However, the acquisition of high-resolution SAR images in airborne configurations, remains costly and limited. Thus, the lack of open source, well-labeled, or easily exploitable SAR text-image datasets is a barrier to the use of existing foundation models in remote sensing applications. In this context, synthetic image generation is a promising solution to augment this scarce data, enabling a broader range of applications. Leveraging over 15 years of ONERA’s extensive archival airborn data from acquisition campaigns, we created a comprehensive training dataset of 110 thousands SAR images to exploit a 3.5 billion parameters pre-trained latent diffusion model \cite{Baqu2019SethiR}. In this work, we present a novel approach utilizing spatial conditioning techniques within a foundation model to transform satellite SAR imagery into airborne SAR representations. Additionally, we demonstrate that our pipeline is effective for bridging the realism of simulated images generated by ONERA’s physics-based simulator EMPRISE \cite{empriseem_ai_images}. Our method explores a key application of AI in advancing SAR imaging technology. To the best of our knowledge, we are the first to introduce this approach in the literature.
近年来,合成孔径雷达(SAR)卫星图像的可获取性大幅增加,并且数据集已实现商业化。然而,获取空中配置的SAR高分辨率图像成本仍然高昂且资源有限。因此,缺乏开放源代码、带有明确标签或易于开发的SAR文本图像数据集是阻碍现有基础模型在遥感应用中使用的一个障碍。在这种情况下,合成图像生成是解决数据稀缺的有前途的解决方案,能够支持更广泛的应用。利用法国航空航天研究院(ONERA)多年来收集的15万余张从多个收集任务收集的数据构建的航空和图像数据库数据集资源,我们创建了一个包含百万SAR图像的综合训练数据集来开发拥有3.5亿参数的预训练扩散模型(Baqu等人在其著作《利用深度学习在超宽带谱合成孔径雷达上进行特征识别和定量成像分析》中提到)。在这项工作中,我们提出了一种新的方法,使用基础模型中的空间条件技术将卫星SAR图像转换为空中SAR表示。此外,我们证明了我们的管道可以有效地将仿真图像的逼真度提高到由ONERA基于物理的模拟器EMPRISE生成的图像水平(empriseem在其著作中提到)。我们的方法探索了人工智能在推动SAR成像技术方面的一项关键应用。据我们所知,我们是第一个在文献中介绍这种方法的人。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
SAR卫星图像数据日益丰富,但高分辨率的SAR图像获取成本高昂且有限。缺乏开源、标注良好或易于利用的SAR文本图像数据集成为使用现有遥感应用基础模型的障碍。利用ONERA长达15年的大量存档飞行数据,创建了一个包含11万张SAR图像的综合训练数据集,利用含有3.5亿参数的预训练潜在扩散模型进行利用。本研究采用一种新方法,利用基础模型中的空间条件技术,将卫星SAR图像转换为飞行SAR表示形式。此外,展示了该管道能有效弥合由ONERA的物理模拟器EMPRISE生成的模拟图像的现实感差距。本研究探索了AI在推动SAR成像技术方面的重要应用。我们是文献中首次引入这种方法的研究者。
Key Takeaways
- SAR卫星图像数据日益丰富,但高质量数据获取仍然受限且成本高。
- 缺乏开源、标注良好的SAR文本图像数据集限制了基础模型在遥感应用中的使用。
- 利用ONERA存档的飞行数据创建了包含大量SAR图像的综合训练数据集。
- 采用空间条件技术的基础模型能将卫星SAR图像转化为飞行SAR表示形式。
- 成功弥合模拟图像与现实之间的差距,利用ONERA的物理模拟器EMPRISE生成的模拟图像进行验证。
- 该方法首次在文献中引入,展现了AI在推动SAR成像技术方面的重要应用。
点此查看论文截图


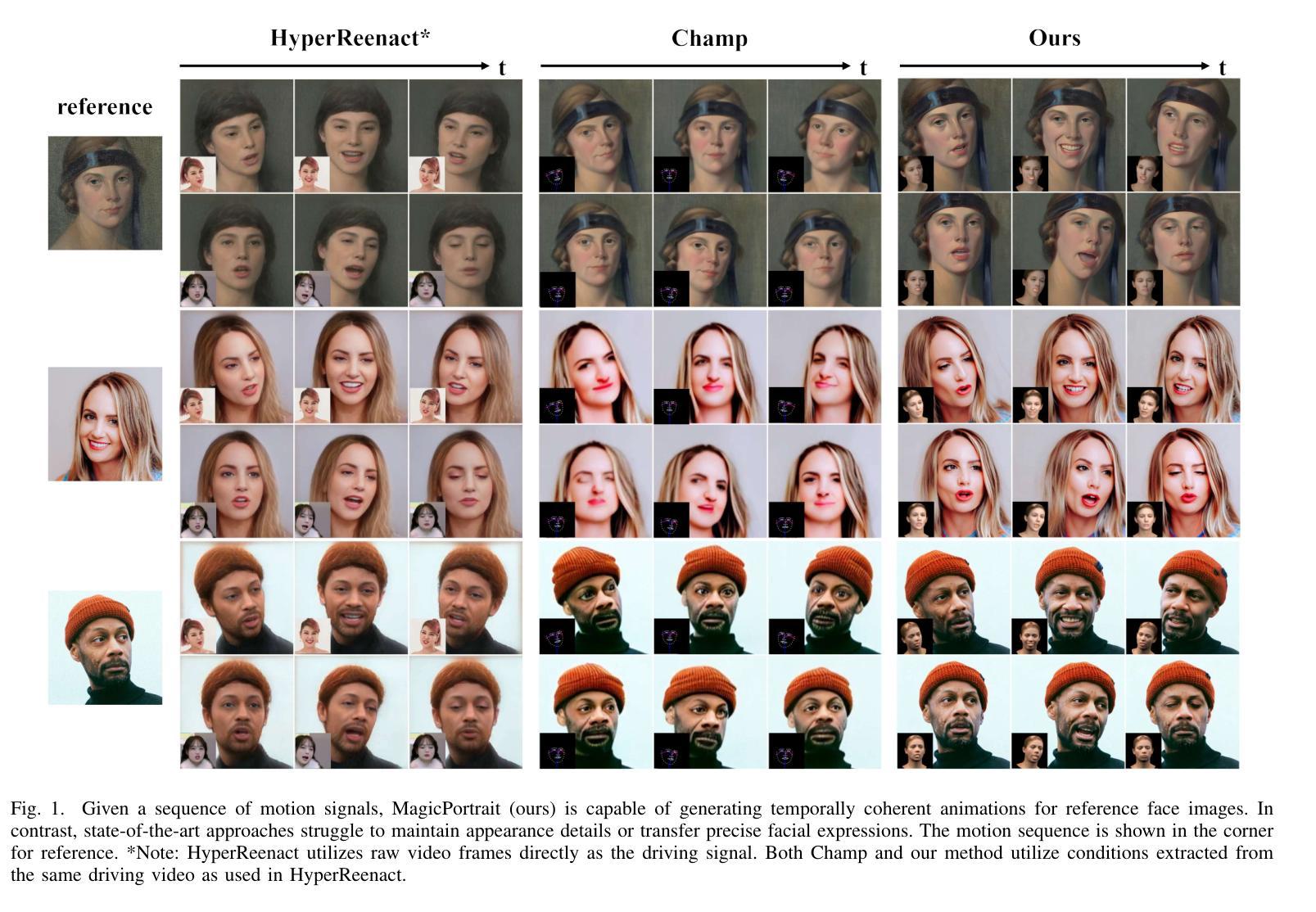
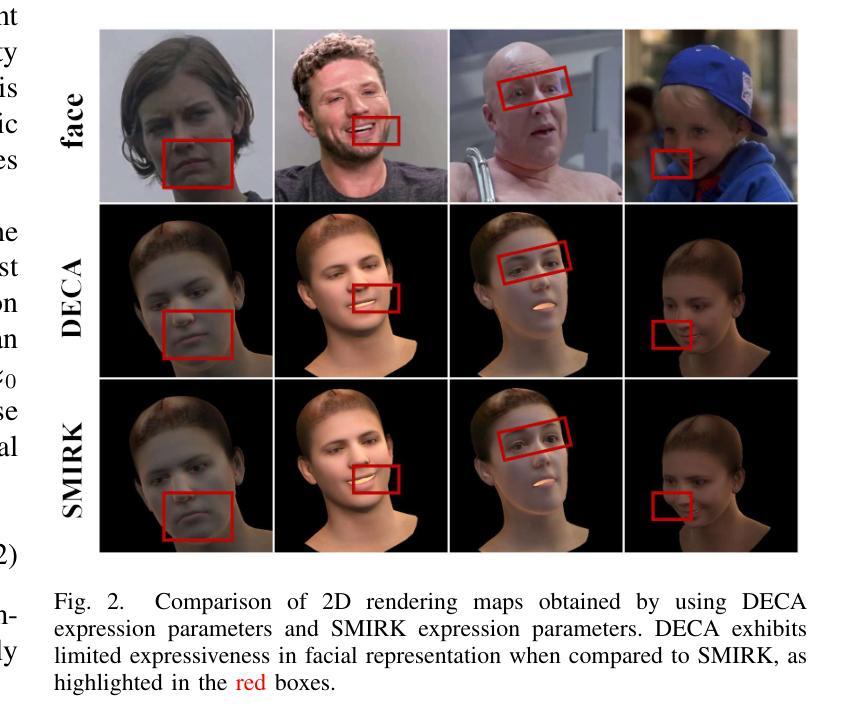
MagicPortrait: Temporally Consistent Face Reenactment with 3D Geometric Guidance
Authors:Mengting Wei, Yante Li, Tuomas Varanka, Yan Jiang, Guoying Zhao
In this study, we propose a method for video face reenactment that integrates a 3D face parametric model into a latent diffusion framework, aiming to improve shape consistency and motion control in existing video-based face generation approaches. Our approach employs the FLAME (Faces Learned with an Articulated Model and Expressions) model as the 3D face parametric representation, providing a unified framework for modeling face expressions and head pose. This not only enables precise extraction of motion features from driving videos, but also contributes to the faithful preservation of face shape and geometry. Specifically, we enhance the latent diffusion model with rich 3D expression and detailed pose information by incorporating depth maps, normal maps, and rendering maps derived from FLAME sequences. These maps serve as motion guidance and are encoded into the denoising UNet through a specifically designed Geometric Guidance Encoder (GGE). A multi-layer feature fusion module with integrated self-attention mechanisms is used to combine facial appearance and motion latent features within the spatial domain. By utilizing the 3D face parametric model as motion guidance, our method enables parametric alignment of face identity between the reference image and the motion captured from the driving video. Experimental results on benchmark datasets show that our method excels at generating high-quality face animations with precise expression and head pose variation modeling. In addition, it demonstrates strong generalization performance on out-of-domain images. Code is publicly available at https://github.com/weimengting/MagicPortrait.
本研究提出了一种将3D人脸参数模型集成到潜在扩散框架中的视频人脸再演绎方法。该方法旨在提高现有视频人脸生成方法中的形状一致性和运动控制。我们的方法采用FLAME(用关节模型和表情学习的面部模型)作为3D人脸参数表示,为面部表达和头部姿态建模提供了统一框架。这不仅能够实现从驱动视频中精确提取运动特征,还有助于保留面部形状和几何结构。具体来说,我们通过融入从FLAME序列中得到的深度图、法线图以及渲染图,增强潜在扩散模型的丰富3D表达和详细姿态信息。这些图作为运动指导,通过专门设计的几何指导编码器(GGE)被编码到去噪UNet中。利用具有集成自注意力机制的多层特征融合模块,在空间域内组合面部外观和运动潜在特征。通过利用3D人脸参数模型作为运动指导,我们的方法能够实现参考图像与从驱动视频中捕获的运动之间的参数对齐。在基准数据集上的实验结果表明,我们的方法在生成高质量人脸动画方面表现出色,具有精确的表情和头部姿态变化建模能力。此外,它在域外图像上表现出强大的泛化性能。代码公开在:https://github.com/weimengting/MagicPortrait。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
该研究将3D人脸参数模型融入潜在扩散框架,提出一种视频人脸再演绎方法,旨在提高现有视频人脸生成方法中的形状一致性和运动控制效果。使用FLAME模型作为3D人脸参数表示,为面部表情和头部姿态建模提供统一框架,可精确提取驱动视频中的运动特征,并忠实保留人脸形状和几何特征。
Key Takeaways
- 研究将3D人脸参数模型融入潜在扩散框架,旨在提升视频人脸生成的质量。
- 采用FLAME模型作为3D人脸参数表示,统一建模面部表情和头部姿态。
- 通过深度图、法线图、渲染图等,增强潜在扩散模型的3D表情和姿态细节。
- 设计的Geometric Guidance Encoder (GGE)将运动指导信息编码进去噪UNet。
- 利用多层特征融合模块结合自注意力机制,在空域内结合面部外观和运动潜在特征。
- 使用3D人脸参数模型作为运动指导,实现参考图像与驱动视频中捕捉到的运动的参数对齐。
- 实验结果表明,该方法在基准数据集上表现优异,能生成高质量的人脸动画,具有强大的泛化性能。
点此查看论文截图



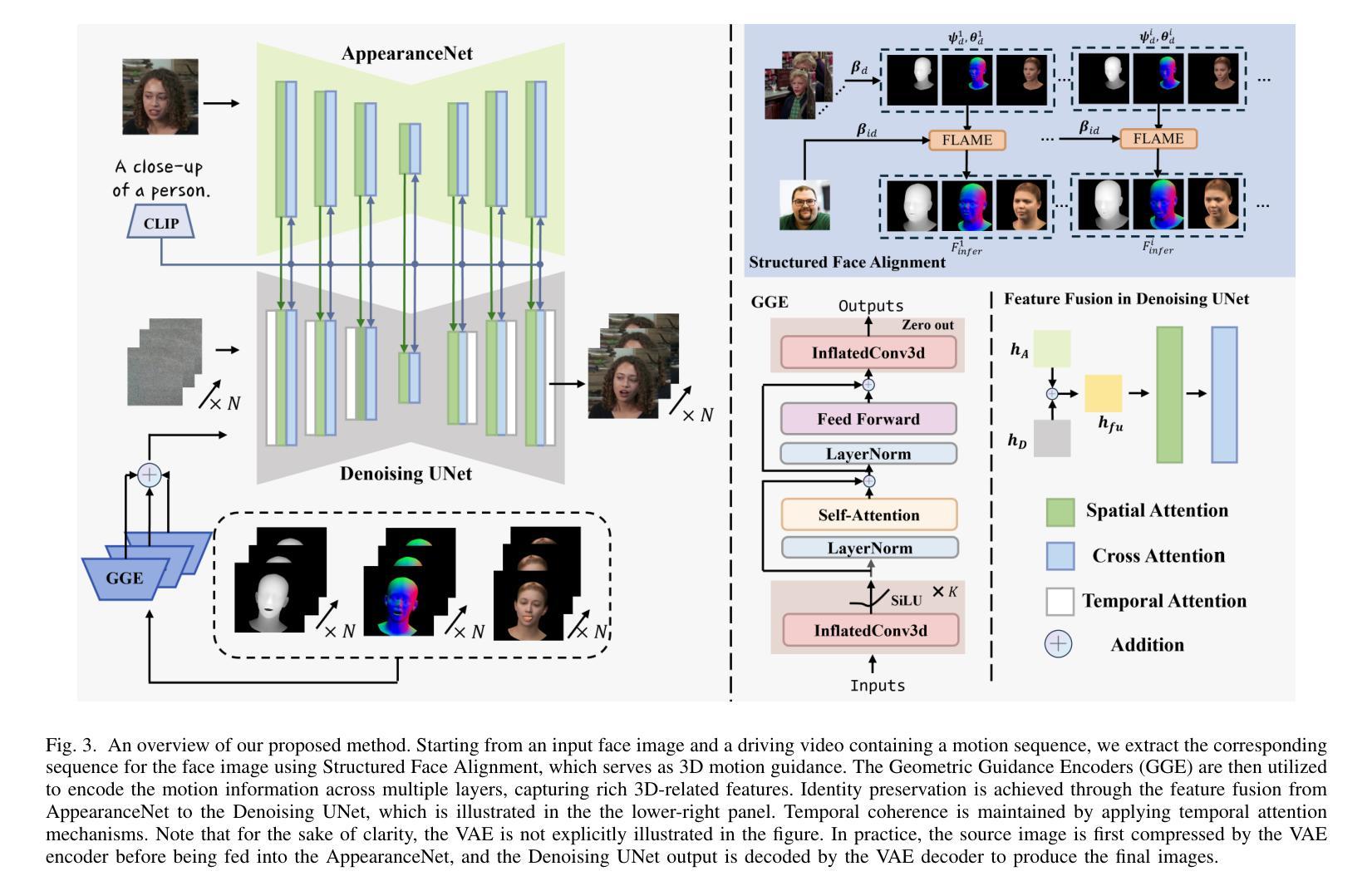
DiffServe: Efficiently Serving Text-to-Image Diffusion Models with Query-Aware Model Scaling
Authors:Sohaib Ahmad, Qizheng Yang, Haoliang Wang, Ramesh K. Sitaraman, Hui Guan
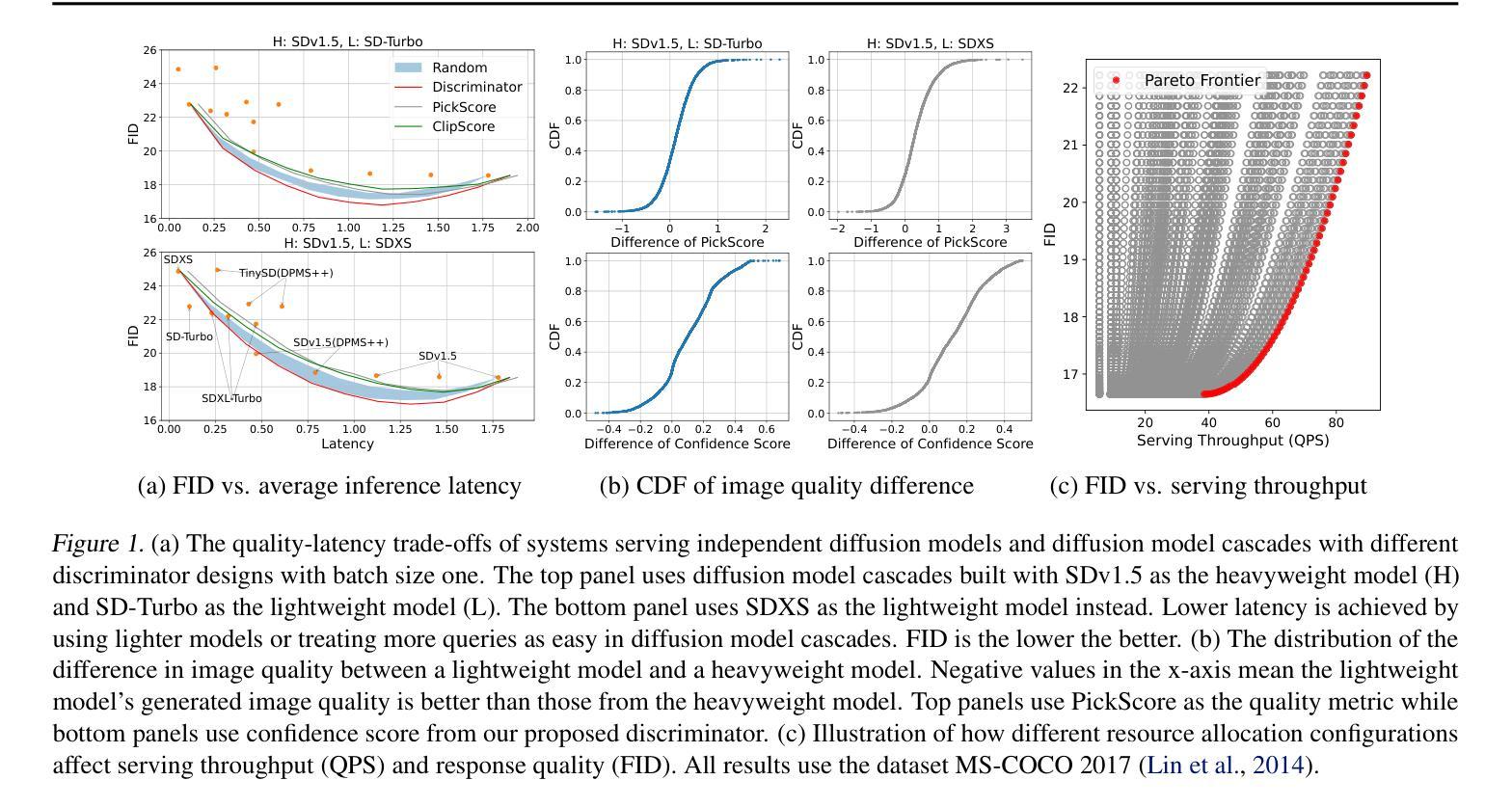
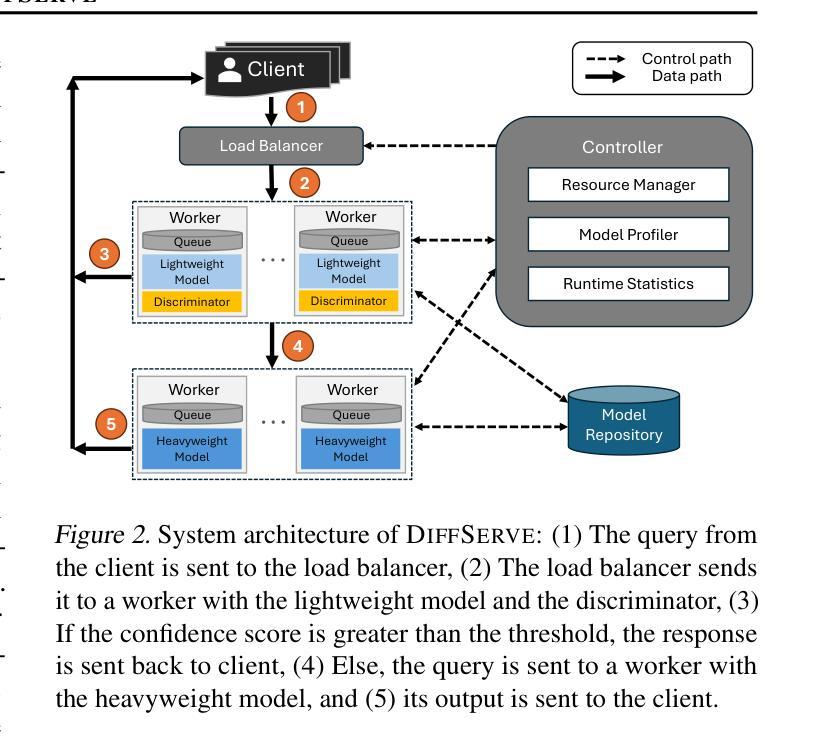
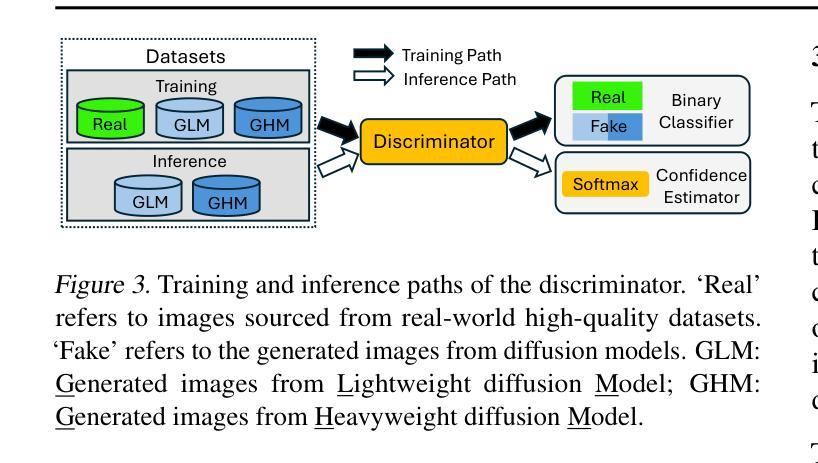
Text-to-image generation using diffusion models has gained increasing popularity due to their ability to produce high-quality, realistic images based on text prompts. However, efficiently serving these models is challenging due to their computation-intensive nature and the variation in query demands. In this paper, we aim to address both problems simultaneously through query-aware model scaling. The core idea is to construct model cascades so that easy queries can be processed by more lightweight diffusion models without compromising image generation quality. Based on this concept, we develop an end-to-end text-to-image diffusion model serving system, DiffServe, which automatically constructs model cascades from available diffusion model variants and allocates resources dynamically in response to demand fluctuations. Our empirical evaluations demonstrate that DiffServe achieves up to 24% improvement in response quality while maintaining 19-70% lower latency violation rates compared to state-of-the-art model serving systems.
使用扩散模型进行文本到图像生成因能根据文本提示产生高质量、逼真的图像而越来越受欢迎。然而,由于这些模型的计算密集型和查询需求的多样性,有效地提供服务是一个挑战。本文旨在通过查询感知模型缩放同时解决这两个问题。核心思想是构建模型级联,使简单查询可以由更轻量级的扩散模型处理,而不会损害图像生成质量。基于此概念,我们开发了一种端到端的文本到图像扩散模型服务系统DiffServe,它自动根据可用的扩散模型变体构建模型级联,并动态分配资源以应对需求波动。我们的经验评估表明,与最新的模型服务系统相比,DiffServe在保持19-70%较低延迟违规率的同时,实现了高达24%的响应质量提升。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 16 pages, 9 figures
Summary
扩散模型在文本转图像生成方面表现出强大的能力,能生成高质量、逼真的图像。然而,高效服务这些模型具有挑战性,因为它们计算密集且查询需求多变。本文旨在通过查询感知模型缩放同时解决这两个问题,构建模型级联,使简单查询可以由更轻量级的扩散模型处理,而不影响图像生成质量。基于这一理念,我们开发了一个端到端的文本到图像扩散模型服务系统DiffServe,它自动构建模型级联,并根据需求波动动态分配资源。实证评估表明,DiffServe在提高响应质量的同时,将延迟违规率降低了19-70%,达到了业界领先水平。
Key Takeaways
- 扩散模型能够生成高质量、逼真的文本转图像。
- 高效服务扩散模型具有挑战性,因为它们计算密集且查询需求多变。
- 本文通过查询感知模型缩放解决计算密集和查询需求多变的问题。
- 构建模型级联可以处理简单查询,同时保持图像生成质量。
- 开发了一个端到端的文本到图像扩散模型服务系统DiffServe。
- DiffServe自动构建模型级联并根据需求波动动态分配资源。
点此查看论文截图

Enhanced Generative Data Augmentation for Semantic Segmentation via Stronger Guidance
Authors:Quang-Huy Che, Duc-Tri Le, Bich-Nga Pham, Duc-Khai Lam, Vinh-Tiep Nguyen
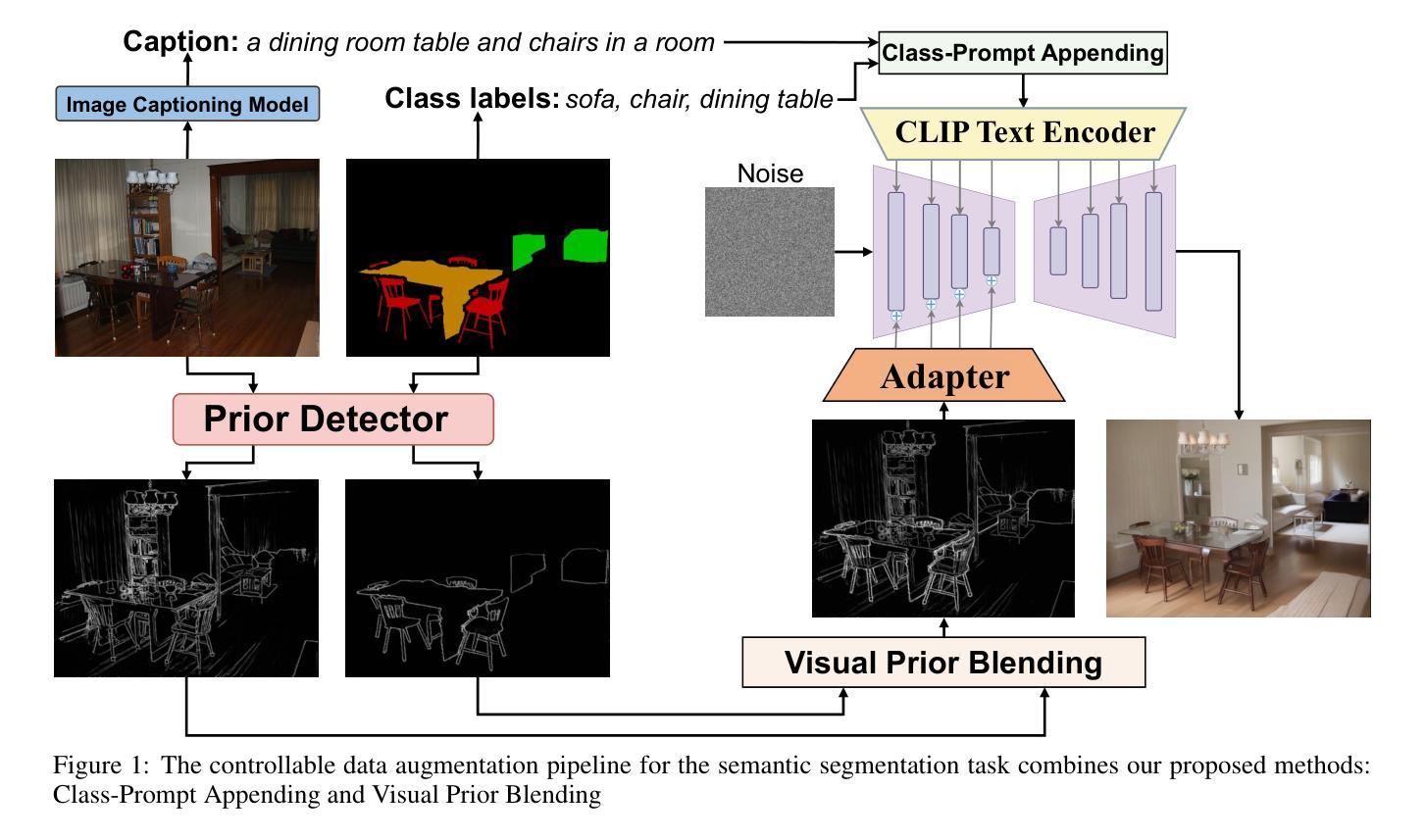
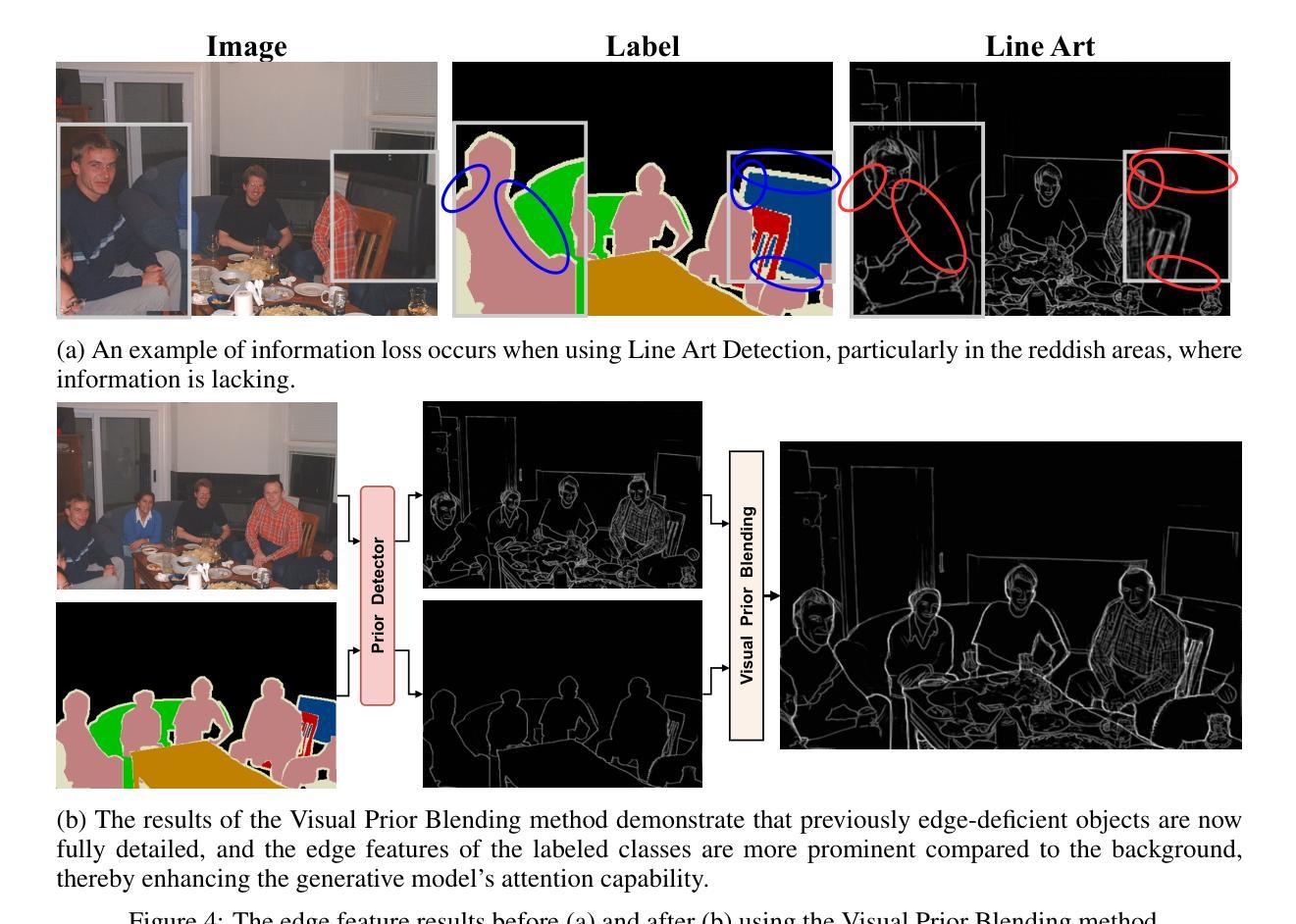
Data augmentation is crucial for pixel-wise annotation tasks like semantic segmentation, where labeling requires significant effort and intensive labor. Traditional methods, involving simple transformations such as rotations and flips, create new images but often lack diversity along key semantic dimensions and fail to alter high-level semantic properties. To address this issue, generative models have emerged as an effective solution for augmenting data by generating synthetic images. Controllable Generative models offer data augmentation methods for semantic segmentation tasks by using prompts and visual references from the original image. However, these models face challenges in generating synthetic images that accurately reflect the content and structure of the original image due to difficulties in creating effective prompts and visual references. In this work, we introduce an effective data augmentation pipeline for semantic segmentation using Controllable Diffusion model. Our proposed method includes efficient prompt generation using \textit{Class-Prompt Appending} and \textit{Visual Prior Blending} to enhance attention to labeled classes in real images, allowing the pipeline to generate a precise number of augmented images while preserving the structure of segmentation-labeled classes. In addition, we implement a \textit{class balancing algorithm} to ensure a balanced training dataset when merging the synthetic and original images. Evaluation on PASCAL VOC datasets, our pipeline demonstrates its effectiveness in generating high-quality synthetic images for semantic segmentation. Our code is available at \href{https://github.com/chequanghuy/Enhanced-Generative-Data-Augmentation-for-Semantic-Segmentation-via-Stronger-Guidance}{this https URL}.
数据增强对于像素级标注任务(如语义分割)至关重要,这些任务需要投入大量精力和劳力进行标注。传统的方法虽然可以通过旋转、翻转等简单变换来创建新图像,但它们往往在关键的语义维度上缺乏多样性,并且无法改变高级语义属性。为了解决这一问题,生成模型作为一种有效的数据增强解决方案已经出现,通过生成合成图像来增强数据。可控生成模型通过使用原始图像的提示和视觉参考来为语义分割任务提供数据增强方法。然而,这些模型在生成准确反映原始图像内容和结构的合成图像时面临挑战,因为创建有效的提示和视觉参考具有难度。在这项工作中,我们引入了一种使用可控扩散模型的有效数据增强管道,用于语义分割。我们提出的方法包括使用“类提示附加”和“视觉先验混合”进行高效提示生成,以提高对真实图像中标记类的注意力,使管道能够在保留分割标记类结构的同时生成精确数量的增强图像。此外,我们实现了一种“类别平衡算法”,以确保在合并合成图像和原始图像时获得平衡的训练数据集。在PASCAL VOC数据集上的评估表明,我们的管道在生成高质量合成图像进行语义分割方面非常有效。我们的代码可在此https URL找到。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了一种利用可控扩散模型进行语义分割的有效数据增强管道。通过采用类提示附加和视觉先验融合等方法,该管道能够在生成增强图像时重点关注真实图像中的标记类,同时保持分割标记类的结构。此外,还实现了一种类平衡算法,以确保在合并合成图像和原始图像时训练数据集平衡。在PASCAL VOC数据集上的评估证明了该管道在生成高质量合成图像进行语义分割方面的有效性。
Key Takeaways
- 数据增强在像素级注释任务(如语义分割)中非常重要,因为标注需要大量劳动。
- 传统的数据增强方法(如旋转和翻转)缺乏语义维度上的多样性,无法改变高级语义属性。
- 生成模型是解决数据增强问题的有效方法,可以通过生成合成图像来增加数据多样性。
- 可控生成模型使用提示和原始图像的视觉参考,为语义分割任务提供数据增强方法。
- 引入了一种新的数据增强管道,包括高效的提示生成和视觉先验融合,以在真实图像中增强对标记类的关注。
- 该管道实施了一种类平衡算法,以确保在合并合成和原始图像时训练数据集的平衡。
- 在PASCAL VOC数据集上的评估证明了该管道生成高质量合成图像进行语义分割的有效性。
点此查看论文截图




Speed-accuracy relations for diffusion models: Wisdom from nonequilibrium thermodynamics and optimal transport
Authors:Kotaro Ikeda, Tomoya Uda, Daisuke Okanohara, Sosuke Ito
We discuss a connection between a generative model, called the diffusion model, and nonequilibrium thermodynamics for the Fokker-Planck equation, called stochastic thermodynamics. Using techniques from stochastic thermodynamics, we derive the speed-accuracy relations for diffusion models, which are inequalities that relate the accuracy of data generation to the entropy production rate. This relation can be interpreted as the speed of the diffusion dynamics in the absence of the non-conservative force. From a stochastic thermodynamic perspective, our results provide quantitative insight into how best to generate data in diffusion models. The optimal learning protocol is introduced by the geodesic of space of the 2-Wasserstein distance in optimal transport theory. We numerically illustrate the validity of the speed-accuracy relations for diffusion models with different noise schedules and different data. We numerically discuss our results for optimal and suboptimal learning protocols. We also demonstrate the applicability of our results to data generation from the real-world image datasets.
我们探讨了一种生成模型——扩散模型与非平衡态热力学之间的关联,对于福克-普朗克方程,我们称之为随机热力学。利用随机热力学的技术,我们推导出扩散模型的速度-精度关系,这些关系是不等式,描述了数据生成的精度与熵产生率之间的联系。这种关系可以被解释为在没有非保守力的情况下扩散动力学的速度。从随机热力学的角度来看,我们的结果提供了在扩散模型中如何最佳生成数据的定量见解。最佳学习协议是通过最优传输理论中的2-Wasserstein距离的空间测地线引入的。我们通过数值方法说明了不同噪声计划和不同数据的扩散模型的速度-精度关系的有效性。我们数值讨论了我们针对最佳和次优学习协议的结果。我们还展示了我们的结果在现实图像数据集的数据生成中的应用。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 37 pages, 9 figures
Summary
扩散模型与Fokker-Planck方程的随机热力学之间的联系。通过随机热力学技术,我们推导出扩散模型的速度-精度关系,这些关系是不等式,将数据生成的精度与熵产生率相关联。结果从随机热力学的角度为如何在扩散模型中最佳生成数据提供了定量见解。引入最优学习协议,通过最优传输理论中的2-Wasserstein距离的空间测地线实现。
Key Takeaways
- 扩散模型与Fokker-Planck方程的随机热力学存在联系。
- 通过随机热力学技术,推导出扩散模型的速度-精度关系。
- 速度-精度关系可以解释为非保守力不存在情况下扩散动力学的速度。
- 结果从随机热力学角度提供了在扩散模型中最佳生成数据的定量见解。
- 引入最优学习协议,该协议通过最优传输理论中的2-Wasserstein距离的测地线实现。
- 对不同噪声安排和数据集的扩散模型的速度-精度关系进行了数值验证。
点此查看论文截图


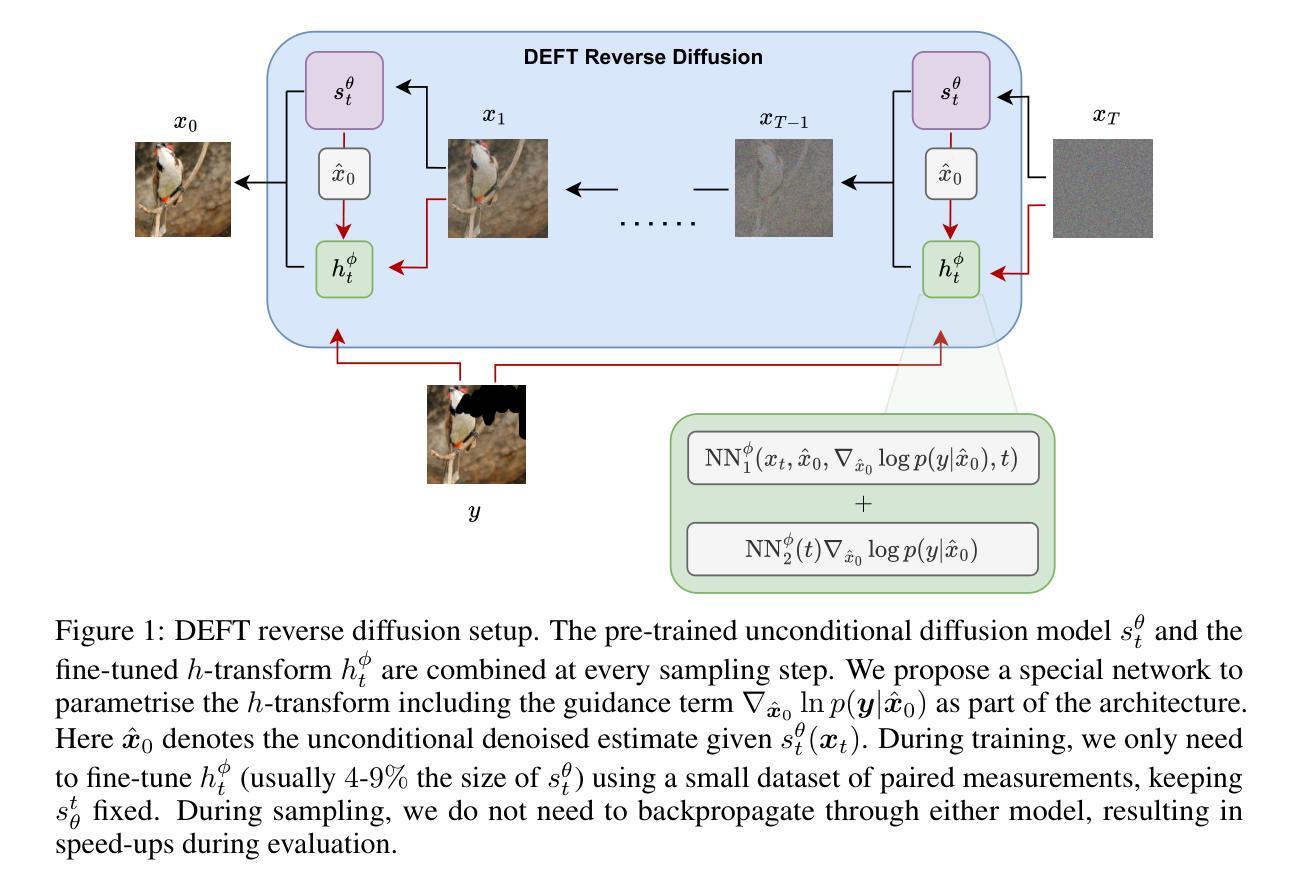
DEFT: Efficient Fine-Tuning of Diffusion Models by Learning the Generalised $h$-transform
Authors:Alexander Denker, Francisco Vargas, Shreyas Padhy, Kieran Didi, Simon Mathis, Vincent Dutordoir, Riccardo Barbano, Emile Mathieu, Urszula Julia Komorowska, Pietro Lio
Generative modelling paradigms based on denoising diffusion processes have emerged as a leading candidate for conditional sampling in inverse problems. In many real-world applications, we often have access to large, expensively trained unconditional diffusion models, which we aim to exploit for improving conditional sampling. Most recent approaches are motivated heuristically and lack a unifying framework, obscuring connections between them. Further, they often suffer from issues such as being very sensitive to hyperparameters, being expensive to train or needing access to weights hidden behind a closed API. In this work, we unify conditional training and sampling using the mathematically well-understood Doob’s h-transform. This new perspective allows us to unify many existing methods under a common umbrella. Under this framework, we propose DEFT (Doob’s h-transform Efficient FineTuning), a new approach for conditional generation that simply fine-tunes a very small network to quickly learn the conditional $h$-transform, while keeping the larger unconditional network unchanged. DEFT is much faster than existing baselines while achieving state-of-the-art performance across a variety of linear and non-linear benchmarks. On image reconstruction tasks, we achieve speedups of up to 1.6$\times$, while having the best perceptual quality on natural images and reconstruction performance on medical images. Further, we also provide initial experiments on protein motif scaffolding and outperform reconstruction guidance methods.
基于去噪扩散过程的生成建模范式已成为逆问题中条件采样的领先候选方法。在许多真实世界应用中,我们通常可以访问大型且经过昂贵训练的无条件扩散模型,我们旨在利用这些模型来改善条件采样。最近的方法大多是启发式且缺乏统一框架,导致它们之间的联系模糊不清。此外,它们经常面临诸如对超参数非常敏感、训练成本高昂或需要访问封闭API中的权重等问题。在这项工作中,我们使用数学上易于理解的Doob的h转换来统一条件训练和采样。这个新视角使我们能够在共同的基础上统一许多现有方法。在这个框架下,我们提出了DEFT(Doob的h转换高效微调),这是一种新的条件生成方法,只需微调一个非常小的网络即可快速学习条件h转换,同时保持较大的无条件网络不变。DEFT相较于现有基准测试,速度更快,同时在各种线性和非线性基准测试中实现了最先进的性能。在图像重建任务上,我们实现了高达1.6倍的加速,同时在自然图像上拥有最佳的感知质量和医疗图像的重建性能。此外,我们还对蛋白质基序支架进行了初步实验,并超越了重建指导方法。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF arXiv admin note: text overlap with arXiv:2312.09236
Summary
基于去噪扩散过程生成建模范式已成为解决逆向问题中条件采样的领先候选方法。本文利用数学上理解良好的Doob的h-变换来统一条件训练和采样。在此基础上,我们提出DEFT(Doob的h变换高效微调),这是一种新的条件生成方法,只需微调一个非常小的网络即可快速学习条件h变换,同时保持更大的无条件网络不变。DEFT相比现有基线方法更快,同时在各种线性和非线性基准测试中实现了最先进的性能。在图像重建任务上,我们实现了最高达1.6倍的加速,同时在自然图像上具有最佳的感知质量和医疗图像的重建性能。此外,我们还进行了蛋白质基序支架的初步实验,并超越了重建指导方法。
Key Takeaways
- 扩散模型在条件采样领域具有领先地位,特别是在解决逆向问题中。
- 现有方法缺乏统一框架,本文利用Doob的h-变换来统一条件训练和采样。
- 提出DEFT方法,通过微调小网络快速学习条件h变换,保持大网络不变。
- DEFT在多种基准测试中表现优异,图像重建任务加速效果显著。
- DEFT在自然图像和医疗图像上分别表现出最佳感知质量和重建性能。
- 初步实验显示,DEFT在蛋白质基序支架方面表现优越。
点此查看论文截图