⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-05-14 更新
Beyond CLIP Generalization: Against Forward&Backward Forgetting Adapter for Continual Learning of Vision-Language Models
Authors:Songlin Dong, Chenhao Ding, Jiangyang Li, Jizhou Han, Qiang Wang, Yuhang He, Yihong Gong
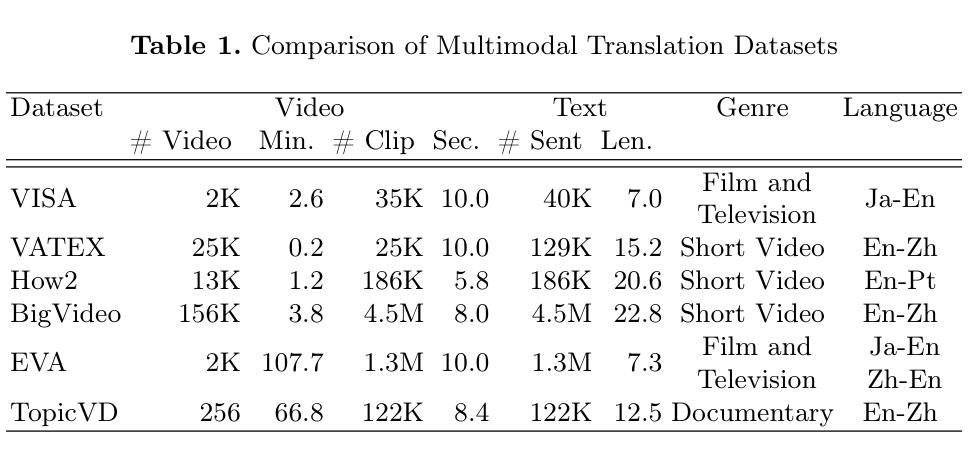
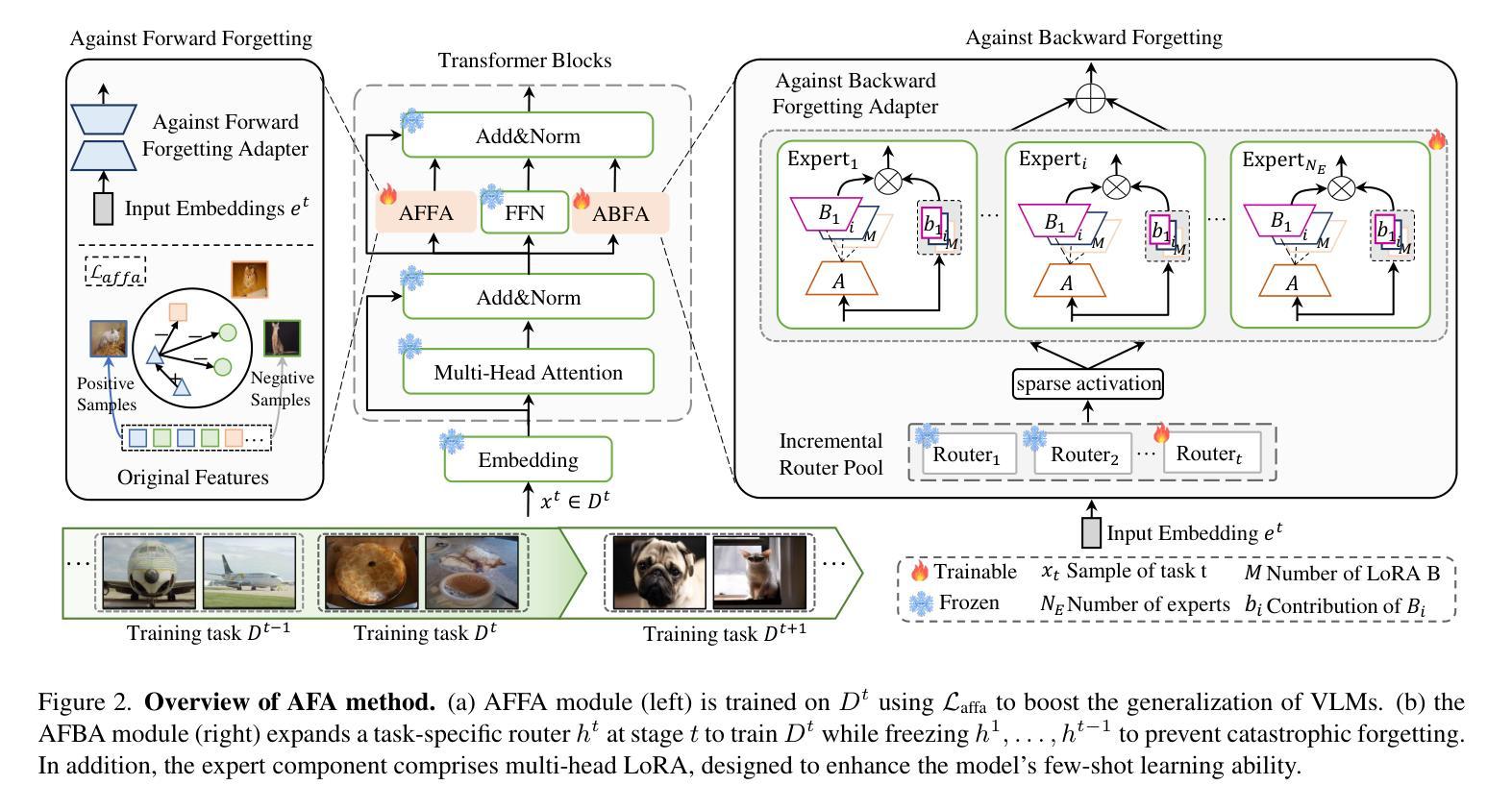
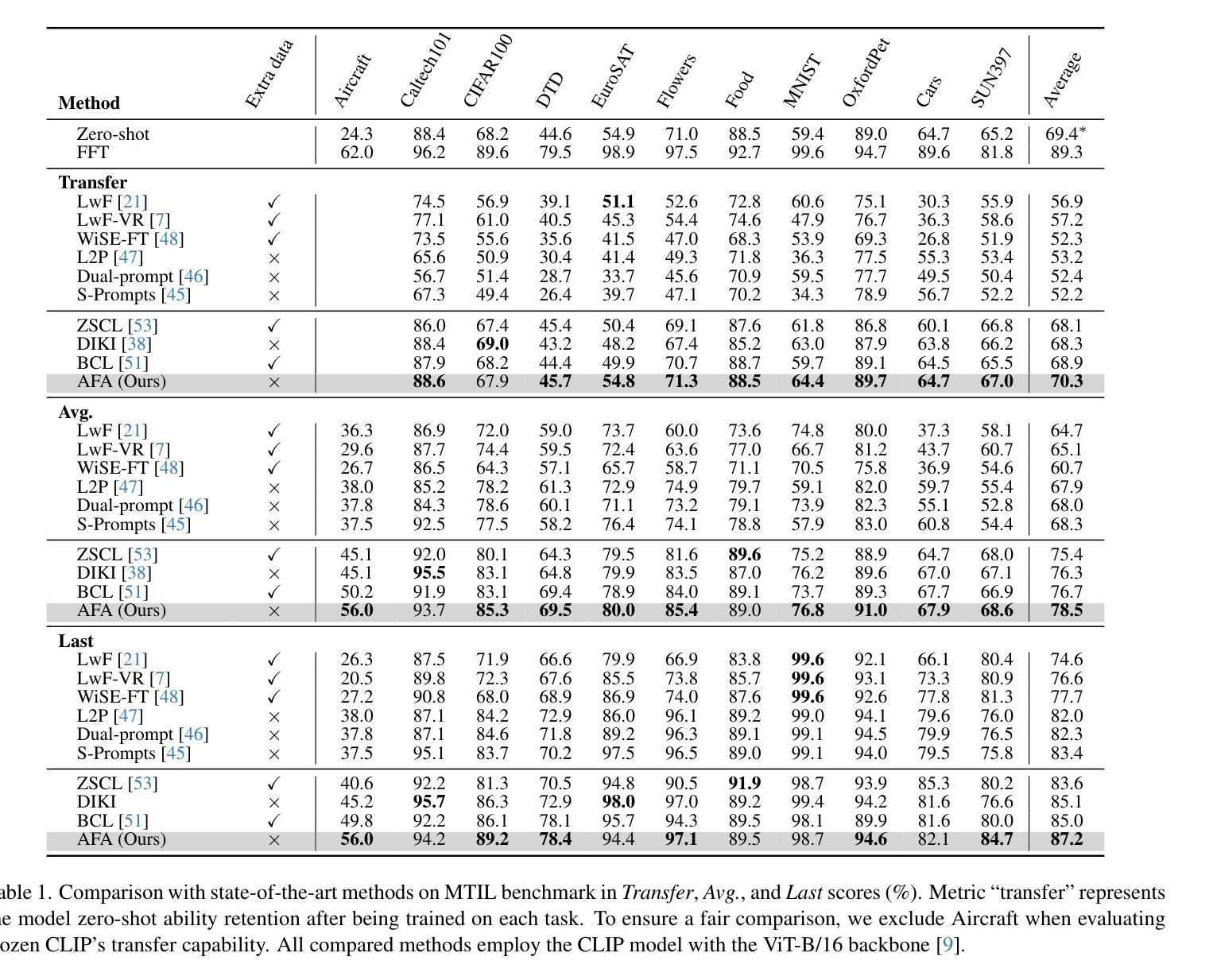
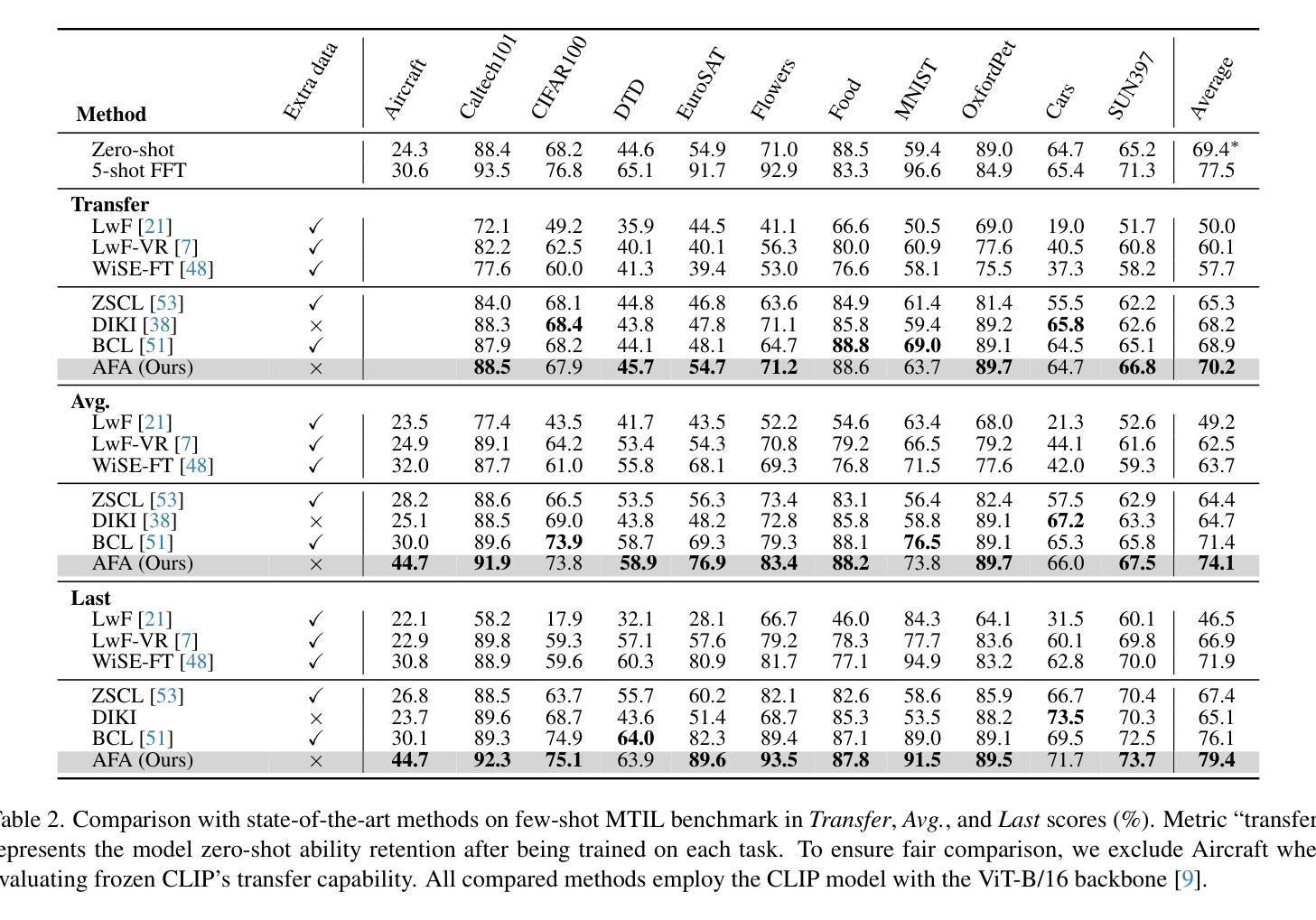
This study aims to address the problem of multi-domain task incremental learning(MTIL), which requires that vision-language models(VLMs) continuously acquire new knowledge while maintaining their inherent zero-shot recognition capability. Existing paradigms delegate the testing of unseen-domain samples to the original CLIP, which only prevents the degradation of the model’s zero-shot capability but fails to enhance the generalization of the VLM further. To this end, we propose a novel MTIL framework, named AFA, which comprises two core modules: (1) an against forward-forgetting adapter that learns task-invariant information for each dataset in the incremental tasks to enhance the zero-shot recognition ability of VLMs; (2) an against backward-forgetting adapter that strengthens the few-shot learning capability of VLMs while supporting incremental learning. Extensive experiments demonstrate that the AFA method significantly outperforms existing state-of-the-art approaches, especially in few-shot MTIL tasks, and surpasses the inherent zero-shot performance of CLIP in terms of transferability. The code is provided in the Supplementary Material.
本研究旨在解决多域任务增量学习(MTIL)的问题,这要求视觉语言模型(VLM)在持续获取新知识的同时,保持其固有的零样本识别能力。现有范式将未见域样本的测试委托给原始CLIP,这只能防止模型零样本能力的退化,但未能进一步提高VLM的泛化能力。为此,我们提出了一种新型的MTIL框架,名为AFA,它包括两个核心模块:(1)一种对抗前向遗忘适配器,用于学习增量任务中每个数据集的任务不变信息,以提高VLM的零样本识别能力;(2)一种对抗后向遗忘适配器,旨在加强VLM的小样本学习能力,同时支持增量学习。大量实验表明,AFA方法显著优于现有最先进的方法,尤其在少样本MTIL任务中表现突出,并且在可迁移性方面超越了CLIP的固有零样本性能。代码已作为补充材料提供。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
多域任务增量学习(MTIL)问题要求视觉语言模型(VLM)在持续获取新知识的同时保持其固有的零样本识别能力。现有模式将未见域样本的测试委托给原始CLIP,这只能防止模型零样本能力的退化,但未能进一步提高VLM的泛化能力。为此,我们提出了一种新的MTIL框架,名为AFA,它包括两个核心模块:(1)一种防止知识遗忘的适配器,用于学习增量任务中每个数据集的任务不变信息,以提高VLM的零样本识别能力;(2)另一种强化VLM的少样本学习能力并支持增量学习的防止反向遗忘的适配器。实验表明,AFA方法在少样本MTIL任务上显著优于现有先进技术,并且在可迁移性方面超越了CLIP的固有零样本性能。
Key Takeaways
- 该研究关注多域任务增量学习(MTIL),旨在让视觉语言模型(VLM)在持续学习新知识的同时保持零样本识别能力。
- 现有模式测试未见域样本时存在局限性,仅防止模型零样本能力退化,未进一步提高VLM泛化能力。
- 提出的AFA框架包含两个核心模块:防止正向遗忘的适配器和防止反向遗忘的适配器。
- 防止正向遗忘的适配器通过学习任务不变信息来提高VLM的零样本识别能力。
- 防止反向遗忘的适配器强化VLM的少样本学习能力,并支持增量学习。
- 实验表明,AFA方法在少样本MTIL任务上表现优异,超越现有技术。
点此查看论文截图

ShotAdapter: Text-to-Multi-Shot Video Generation with Diffusion Models
Authors:Ozgur Kara, Krishna Kumar Singh, Feng Liu, Duygu Ceylan, James M. Rehg, Tobias Hinz
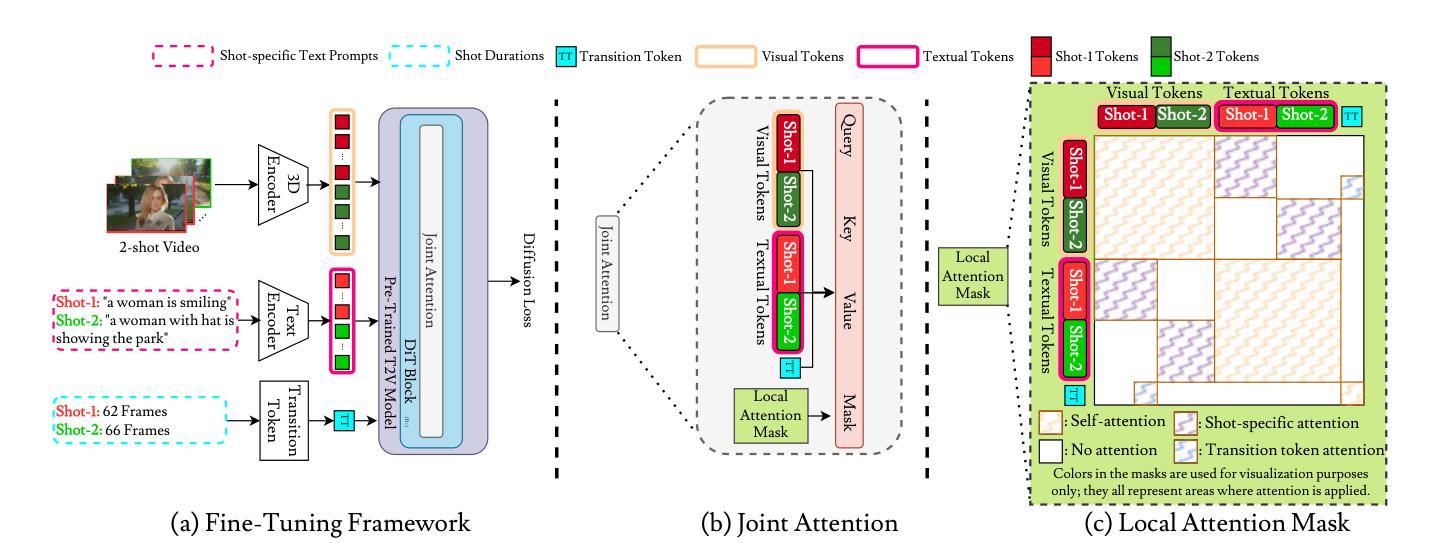
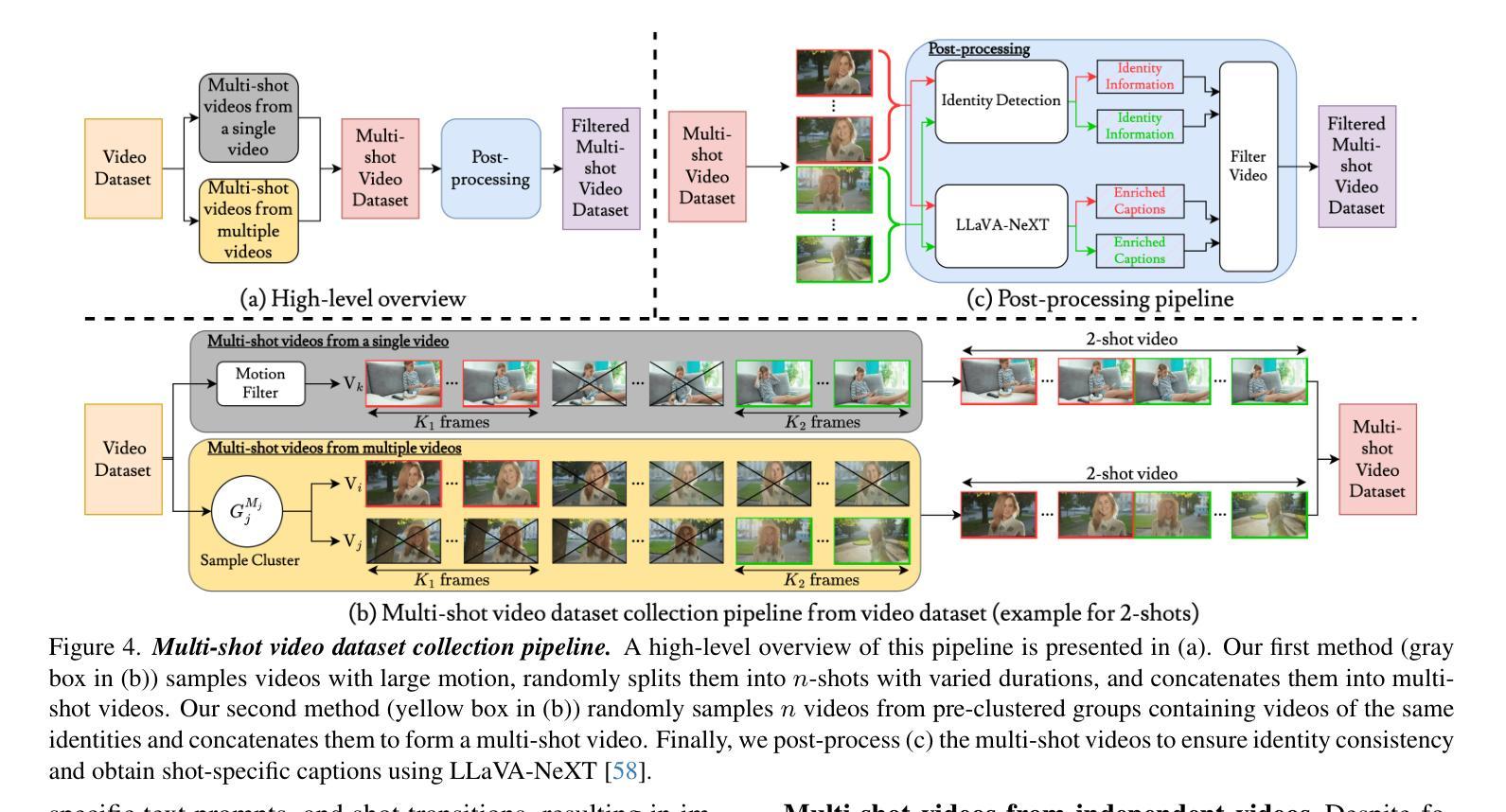
Current diffusion-based text-to-video methods are limited to producing short video clips of a single shot and lack the capability to generate multi-shot videos with discrete transitions where the same character performs distinct activities across the same or different backgrounds. To address this limitation we propose a framework that includes a dataset collection pipeline and architectural extensions to video diffusion models to enable text-to-multi-shot video generation. Our approach enables generation of multi-shot videos as a single video with full attention across all frames of all shots, ensuring character and background consistency, and allows users to control the number, duration, and content of shots through shot-specific conditioning. This is achieved by incorporating a transition token into the text-to-video model to control at which frames a new shot begins and a local attention masking strategy which controls the transition token’s effect and allows shot-specific prompting. To obtain training data we propose a novel data collection pipeline to construct a multi-shot video dataset from existing single-shot video datasets. Extensive experiments demonstrate that fine-tuning a pre-trained text-to-video model for a few thousand iterations is enough for the model to subsequently be able to generate multi-shot videos with shot-specific control, outperforming the baselines. You can find more details in https://shotadapter.github.io/
当前基于扩散的文本到视频转换方法仅限于生成单镜头的简短视频片段,缺乏生成具有离散过渡的多镜头视频的能力,其中同一角色在同一或不同背景下执行不同的活动。为了解决这个问题,我们提出了一种框架,包括数据集收集管道和视频扩散模型的架构扩展,以实现文本到多镜头视频的生成。我们的方法能够将多镜头视频生成为一个单一视频,全面关注所有镜头的所有帧,确保角色和背景的一致性,并允许用户通过镜头特定的条件控制镜头的数量、持续时间和内容。这是通过向文本到视频模型中融入过渡令牌来实现的,该令牌控制新镜头在哪些帧开始,以及局部注意力掩码策略,该策略控制过渡令牌的影响,并允许针对镜头进行特定提示。为了获取训练数据,我们提出了一种新的数据收集管道,用于从现有的单镜头视频数据集中构建多镜头视频数据集。大量实验表明,对预训练的文本到视频模型进行数千次迭代的微调足以使模型随后能够具有针对镜头的控制生成多镜头视频,并且表现优于基线。更多细节可在https://shotadapter.github.io/找到。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF CVPR 2025
Summary
本文提出了一种能够生成文本到多镜头视频的框架,包括数据集收集管道和架构扩展的视频扩散模型。该框架解决了现有文本转视频方法仅限于生成单镜头短视频的问题,并实现了在多镜头视频生成中跨越相同或不同背景的相同角色执行不同活动的功能。用户可以通过镜头特定的条件控制镜头的数量、持续时间和内容。通过引入过渡令牌来控制新镜头开始的位置和局部注意力掩码策略来实现这一点。为了获取训练数据,我们提出了一种新的数据收集管道,从现有的单镜头视频数据集中构建多镜头视频数据集。实验表明,对预训练的文本到视频模型进行数千次迭代的微调足以使模型能够生成具有镜头特定控制的多镜头视频,超越了基线方法。
Key Takeaways
- 提出了一个能够生成文本到多镜头视频的框架,解决了现有方法仅限于单镜头视频的局限性。
- 框架包括数据集收集管道和视频扩散模型的架构扩展。
- 用户可以通过镜头特定的条件控制镜头的数量、持续时间和内容。
- 通过引入过渡令牌和局部注意力掩码策略实现多镜头视频的生成。
- 提出了一种新的数据收集管道,用于从现有的单镜头视频数据集中构建多镜头视频数据集。
- 实验表明,对预训练模型进行微调能够生成具有镜头特定控制的多镜头视频。
点此查看论文截图



ReinboT: Amplifying Robot Visual-Language Manipulation with Reinforcement Learning
Authors:Hongyin Zhang, Zifeng Zhuang, Han Zhao, Pengxiang Ding, Hongchao Lu, Donglin Wang
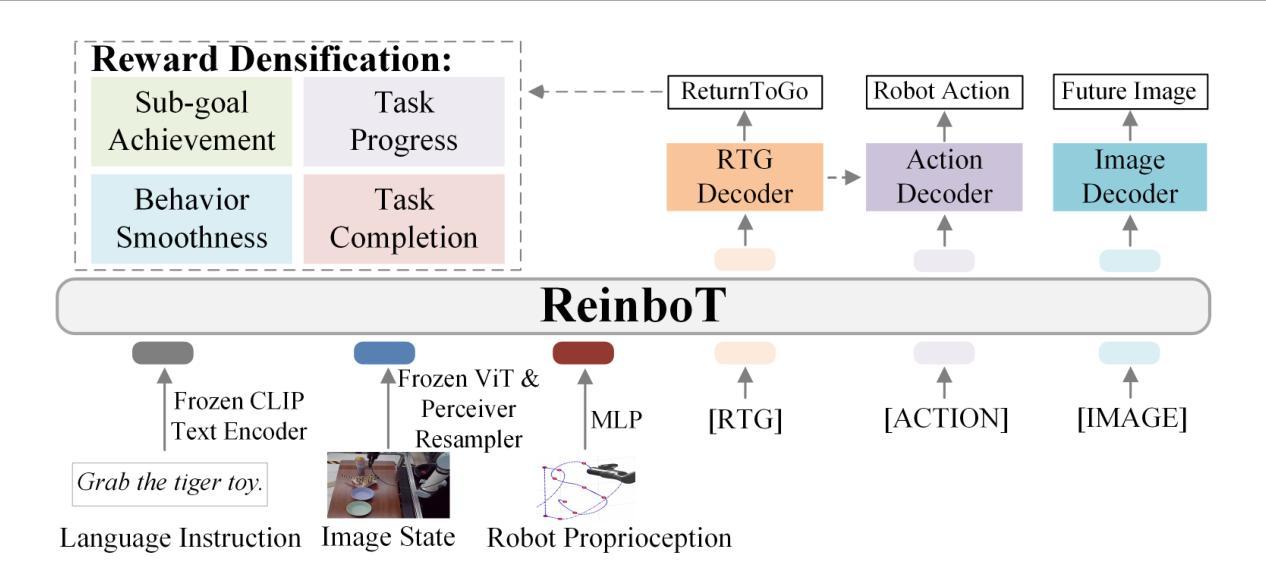
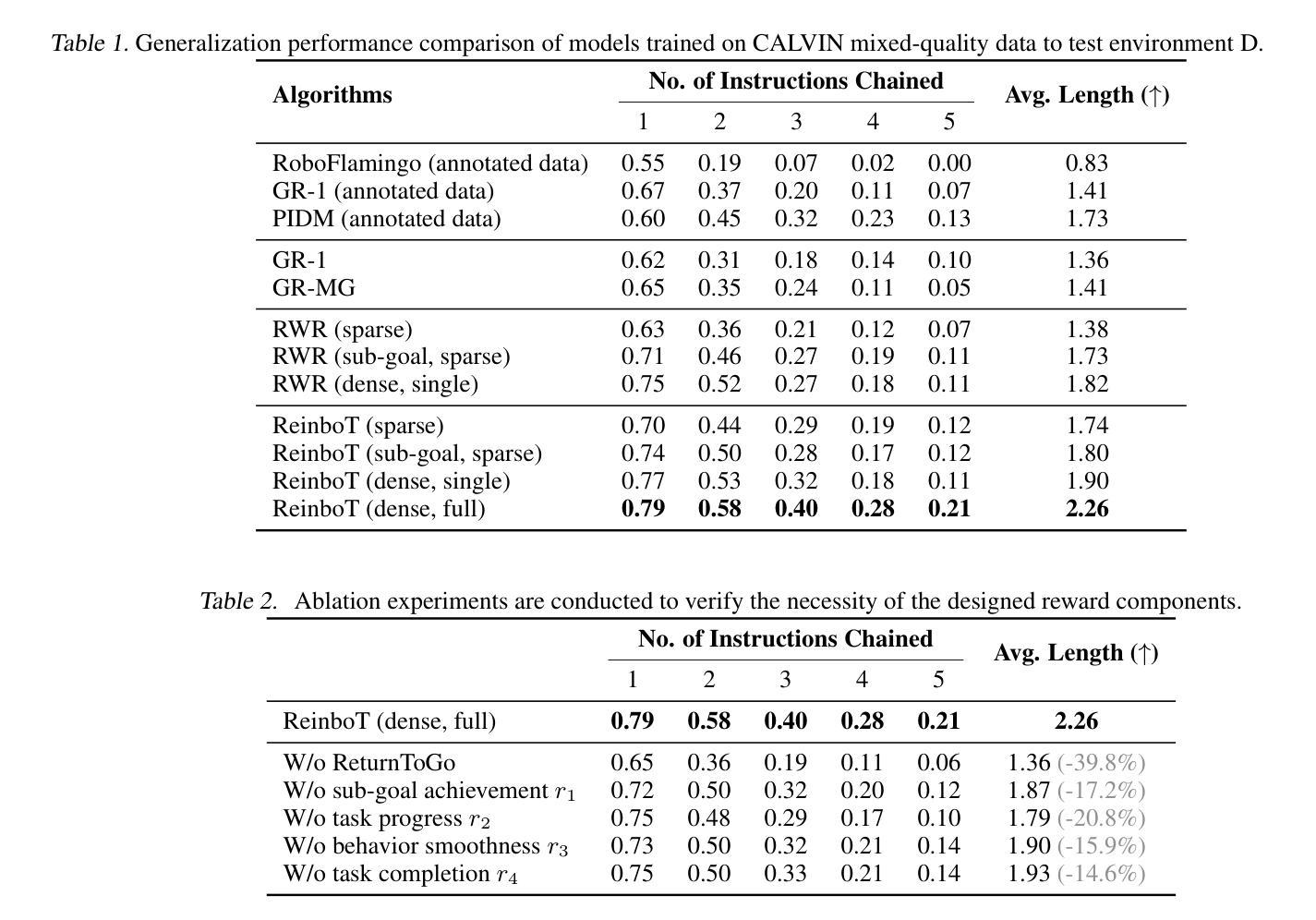
Vision-Language-Action (VLA) models have shown great potential in general robotic decision-making tasks via imitation learning. However, the variable quality of training data often constrains the performance of these models. On the other hand, offline Reinforcement Learning (RL) excels at learning robust policy models from mixed-quality data. In this paper, we introduce Reinforced robot GPT (ReinboT), a novel end-to-end VLA model that integrates the RL principle of maximizing cumulative reward. ReinboT achieves a deeper understanding of the data quality distribution by predicting dense returns that capture the nuances of manipulation tasks. The dense return prediction capability enables the robot to generate more robust decision-making actions, oriented towards maximizing future benefits. Extensive experiments show that ReinboT achieves state-of-the-art performance on the CALVIN mixed-quality dataset and exhibits superior few-shot learning and out-of-distribution generalization capabilities in real-world tasks.
视觉-语言-动作(VLA)模型在通过模仿学习进行一般的机器人决策任务中表现出了巨大的潜力。然而,训练数据质量的不稳定经常限制这些模型的性能。另一方面,离线强化学习(RL)擅长从混合质量数据中学习稳健的策略模型。在本文中,我们介绍了强化机器人GPT(ReinboT),这是一种新型端到端的VLA模型,集成了强化学习的最大化累积回报原则。ReinboT通过预测密集回报来实现对数据质量分布的深入理解,这些密集回报捕捉到了操作任务的细微差别。密集回报预测能力使机器人能够生成更稳健的决策行动,致力于最大化未来收益。大量实验表明,ReinboT在CALVIN混合质量数据集上达到了最新性能,并在现实任务中表现出了卓越的小样本学习和跨分布泛化能力。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
基于视觉、语言和动作的VLA模型在机器人决策任务中展现出了巨大潜力,但它们常常受限于训练数据的质量问题。而离线强化学习擅长从混合质量数据中学习稳健的策略模型。本文介绍了融合强化学习原理的机器人GPT(ReinboT),一种新型端到端的VLA模型。ReinboT通过预测密集回报来理解数据质量分布,从而实现在操作任务中的细微差别。这种密集回报预测能力使机器人能够生成更稳健的决策行动,致力于最大化未来收益。实验表明,ReinboT在CALVIN混合质量数据集上达到了最新技术水平,并在现实任务中展现出卓越的小样本学习和跨分布泛化能力。
Key Takeaways
- VLA模型在机器人决策任务中有巨大潜力,但受限于训练数据质量。
- 离线强化学习擅长从混合质量数据中学习稳健策略模型。
- ReinboT是结合强化学习原理的新型VLA模型,能预测密集回报以理解数据质量分布。
- 密集回报预测能力有助于机器人生成更稳健的决策行动,致力于最大化未来收益。
- ReinboT在CALVIN混合质量数据集上实现了最新技术水平。
- ReinboT展现出卓越的小样本学习能力。
点此查看论文截图

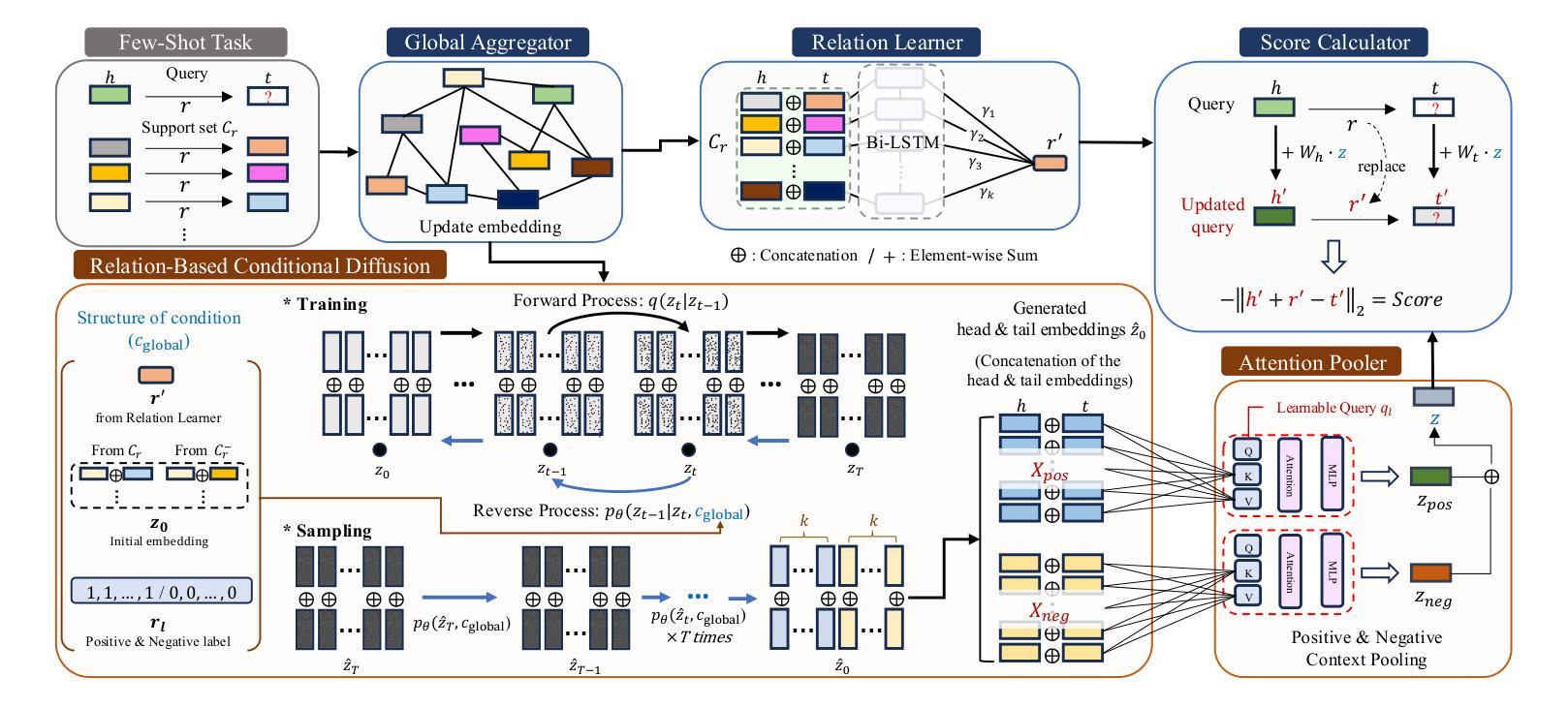
ReCDAP: Relation-Based Conditional Diffusion with Attention Pooling for Few-Shot Knowledge Graph Completion
Authors:Jeongho Kim, Chanyeong Heo, Jaehee Jung
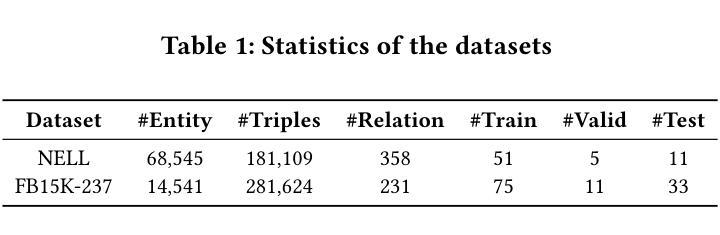
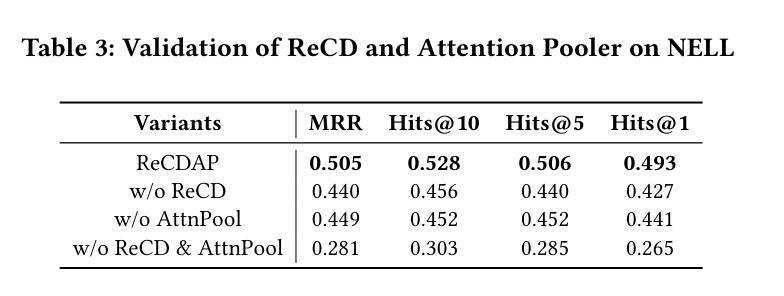
Knowledge Graphs (KGs), composed of triples in the form of (head, relation, tail) and consisting of entities and relations, play a key role in information retrieval systems such as question answering, entity search, and recommendation. In real-world KGs, although many entities exist, the relations exhibit a long-tail distribution, which can hinder information retrieval performance. Previous few-shot knowledge graph completion studies focused exclusively on the positive triple information that exists in the graph or, when negative triples were incorporated, used them merely as a signal to indicate incorrect triples. To overcome this limitation, we propose Relation-Based Conditional Diffusion with Attention Pooling (ReCDAP). First, negative triples are generated by randomly replacing the tail entity in the support set. By conditionally incorporating positive information in the KG and non-existent negative information into the diffusion process, the model separately estimates the latent distributions for positive and negative relations. Moreover, including an attention pooler enables the model to leverage the differences between positive and negative cases explicitly. Experiments on two widely used datasets demonstrate that our method outperforms existing approaches, achieving state-of-the-art performance. The code is available at https://github.com/hou27/ReCDAP-FKGC.
知识图谱(KGs)由(头实体,关系,尾实体)形式的三元组构成,包含实体和关系,在问答、实体搜索和推荐等信息系统检索中扮演着关键角色。在现实世界的知识图谱中,尽管存在许多实体,但关系呈现出长尾分布,可能会阻碍信息检索性能。以前关于知识图谱补全的研究主要集中在图中存在的正三元组信息上,或者当引入负三元组时,仅仅将它们作为表示错误三元组的信号。为了克服这一局限性,我们提出了基于关系的条件扩散与注意力池化(ReCDAP)。首先,通过随机替换支持集中的尾实体来生成负三元组。通过有条件地融入知识图谱中的正信息和不存在的负信息到扩散过程中,该模型分别估计正关系和负关系的潜在分布。此外,加入注意力池化器使模型能够明确利用正负案例之间的差异。在两个广泛使用的数据集上的实验表明,我们的方法优于现有方法,达到了最先进的性能。代码可访问https://github.com/hou27/ReCDAP-FKGC。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by SIGIR 2025, 5 pages, 1 figure
Summary
本文介绍了知识图谱在信息检索系统中的作用,如问答、实体搜索和推荐等。针对知识图谱补全中的长尾分布问题,提出了一种基于关系条件扩散与注意力池化的方法(ReCDAP)。该方法通过生成负三元组,结合正三元组信息,分别估计正负关系的潜在分布。实验表明,该方法在常用数据集上取得了最佳性能。
Key Takeaways
- 知识图谱在信息检索系统中扮演重要角色,如问答、实体搜索和推荐。
- 现实世界中知识图谱的实体关系呈现长尾分布,影响信息检索性能。
- 现有研究主要关注正三元组信息,忽视了负三元组在信息检索中的作用。
- ReCDAP方法通过生成负三元组,结合正三元组信息,进行知识图谱补全。
- ReCDAP方法估计正负关系的潜在分布,提高知识图谱补全的性能。
- 实验表明,ReCDAP方法在常用数据集上取得了最佳性能。
点此查看论文截图

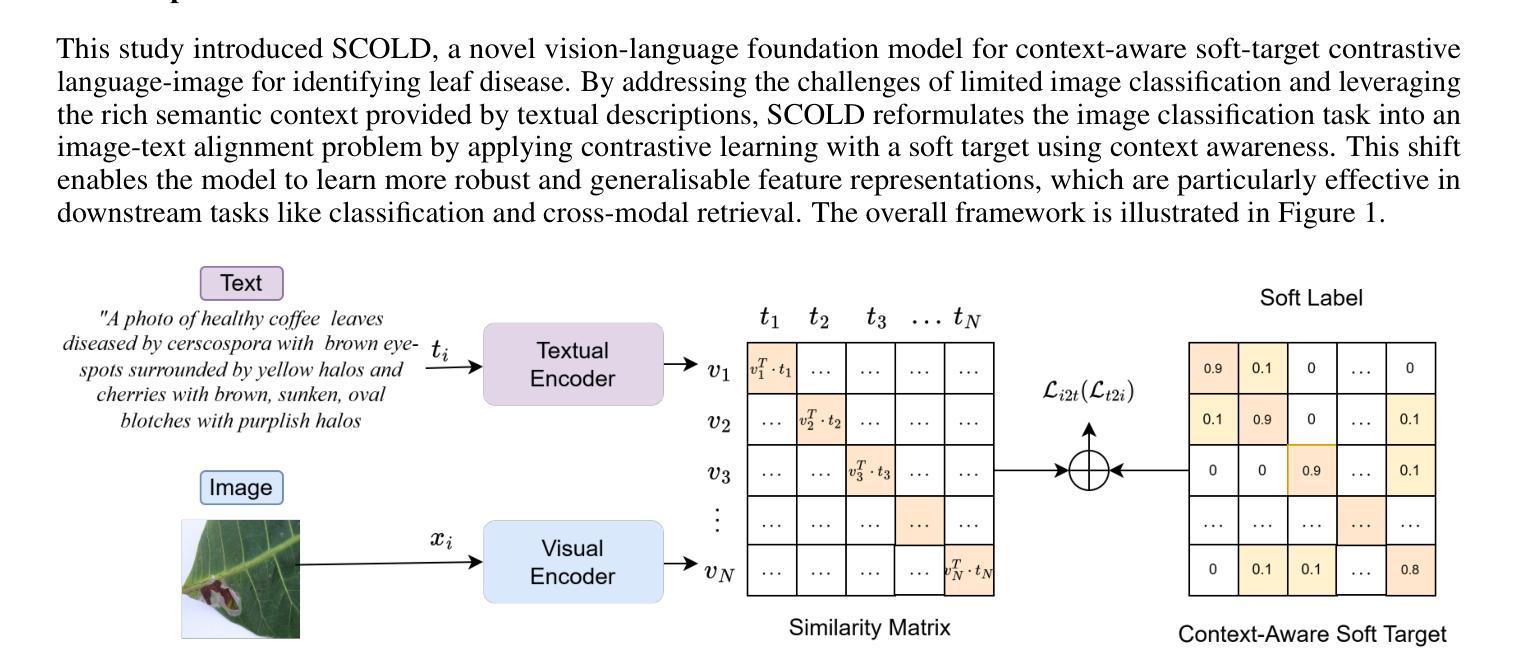
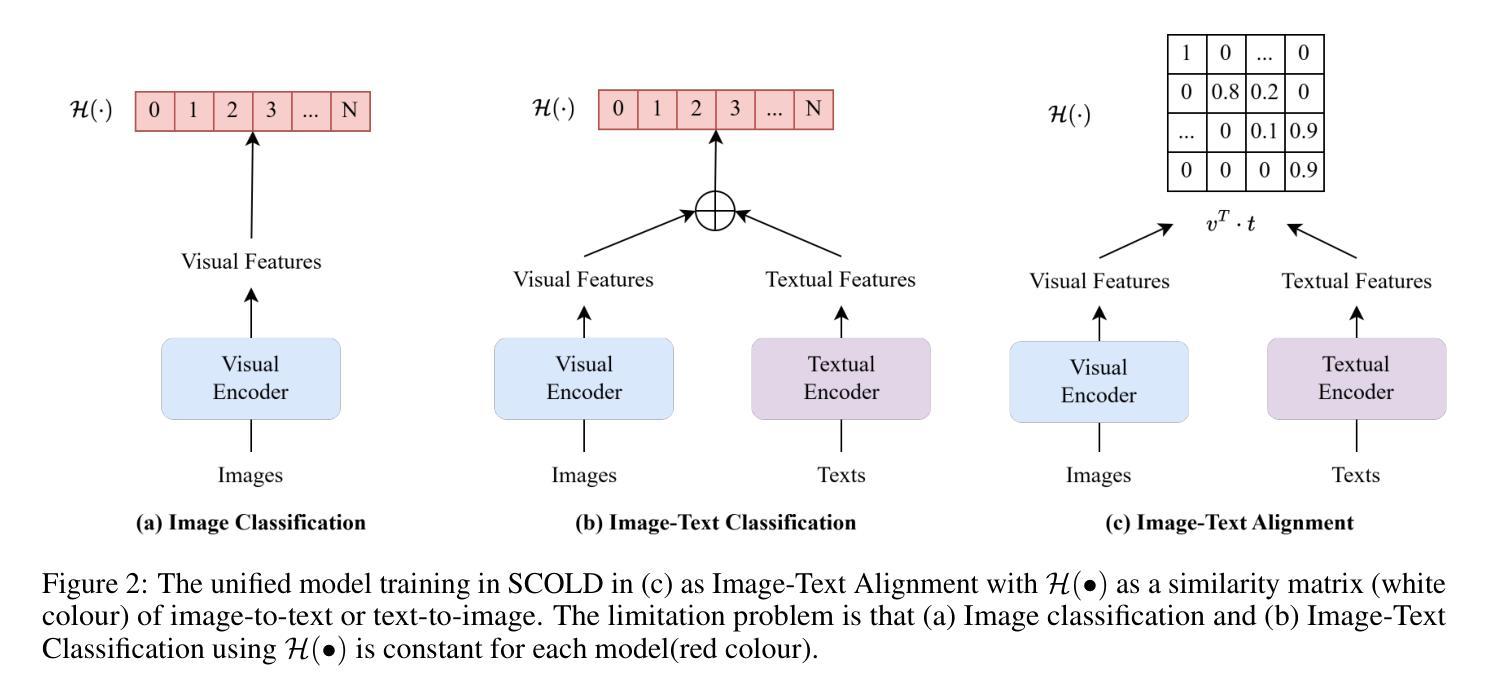
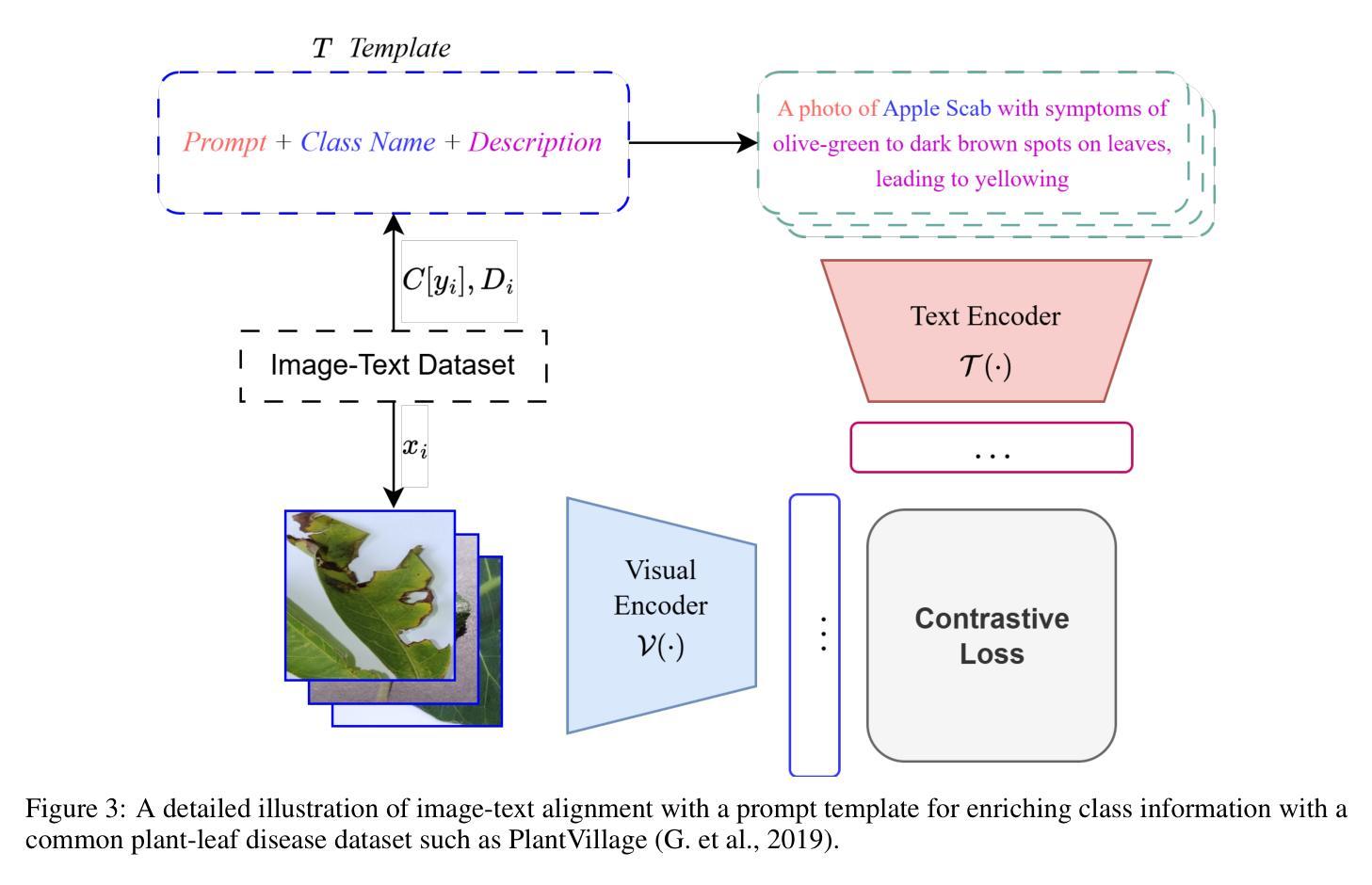
A Vision-Language Foundation Model for Leaf Disease Identification
Authors:Khang Nguyen Quoc, Lan Le Thi Thu, Luyl-Da Quach
Leaf disease identification plays a pivotal role in smart agriculture. However, many existing studies still struggle to integrate image and textual modalities to compensate for each other’s limitations. Furthermore, many of these approaches rely on pretraining with constrained datasets such as ImageNet, which lack domain-specific information. We propose SCOLD (Soft-target COntrastive learning for Leaf Disease identification), a context-aware vision-language foundation model tailored to address these challenges for agricultural tasks. SCOLD is developed using a diverse corpus of plant leaf images and corresponding symptom descriptions, comprising over 186,000 image-caption pairs aligned with 97 unique concepts. Through task-agnostic pretraining, SCOLD leverages contextual soft targets to mitigate overconfidence in contrastive learning by smoothing labels, thereby improving model generalization and robustness on fine-grained classification tasks. Experimental results demonstrate that SCOLD outperforms existing vision-language models such as OpenAI-CLIP-L, BioCLIP, and SigLIP2 across several benchmarks, including zero-shot and few-shot classification, image-text retrieval, and image classification, while maintaining a competitive parameter footprint. Ablation studies further highlight SCOLD’s effectiveness in contrast to its counterparts. The proposed approach significantly advances the agricultural vision-language foundation model, offering strong performance with minimal or no supervised fine-tuning. This work lays a solid groundwork for future research on models trained with long-form and simplified contexts, tasks involving class ambiguity, and multi-modal systems for intelligent plant disease diagnostics. The code for this study is available at https://huggingface.co/enalis/scold
叶片疾病识别在智能农业中扮演着至关重要的角色。然而,许多现有的研究仍难以整合图像和文本模态以相互弥补彼此的局限性。此外,这些方法中许多依赖于使用受限数据集(如ImageNet)进行预训练,这些数据集缺乏特定领域的详细信息。我们提出了SCOLD(针对叶片疾病识别的软目标对比学习法),这是一种面向农业任务挑战的上下文感知视觉语言基础模型。SCOLD使用包含超过18.6万张与97个独特概念对齐的图像标题对构成的多样化植物叶片图像和相应的症状描述来开发。通过任务无关的预训练,SCOLD利用上下文软目标来缓解对比学习中标签平滑导致的过度自信问题,从而提高模型在细粒度分类任务上的泛化和稳健性。实验结果表明,SCOLD在多个基准测试中均优于现有的视觉语言模型,如OpenAI-CLIP-L、BioCLIP和SigLIP2,包括零样本和少样本分类、图像文本检索和图像分类等任务,同时保持竞争性的参数占用空间。消融研究进一步突出了SCOLD与竞争对手的有效性。所提出的方法显著地推进了农业视觉语言基础模型的发展,以最小的或无需监督微调就能实现强劲的性能。这项工作为未来在模型使用长形式简化语境、涉及类别模糊性的任务和多模态系统智能植物疾病诊断等领域的研究奠定了坚实的基础。这项研究的代码可在https://huggingface.co/enalis/scold 获得。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文提出了针对农业任务中的叶病识别挑战的解决方案。通过开发一种名为SCOLD的上下文感知视觉语言基础模型,该模型能够融合图像和文本模态,克服单一模态的局限性。SCOLD模型使用包含超过18.6万张植物叶片图像和相应症状描述的多样语料库进行训练,涵盖97个独特概念。实验结果表明,SCOLD在零样本和少样本分类、图像文本检索和图像分类等多个基准测试中优于现有视觉语言模型,如OpenAI-CLIP-L、BioCLIP和SigLIP2,同时保持竞争性的参数占用。该模型为提高农业视觉语言基础模型的性能提供了新的方向。
Key Takeaways
- 叶病识别在智能农业中至关重要,但现有研究在整合图像和文本模态方面仍存在挑战。
- SCOLD模型是一种上下文感知的视觉语言基础模型,旨在解决这些挑战,特别针对农业任务。
- SCOLD模型使用包含大量植物叶片图像和症状描述的语料库进行训练,涵盖多种概念和任务。
- SCOLD通过任务无关预训练和上下文软目标,利用标签平滑来提高模型的泛化和鲁棒性。
- 实验结果表明,SCOLD在多个基准测试中优于其他视觉语言模型。
- SCOLD模型在零样本和少样本分类、图像文本检索和图像分类等任务上表现出色。
点此查看论文截图

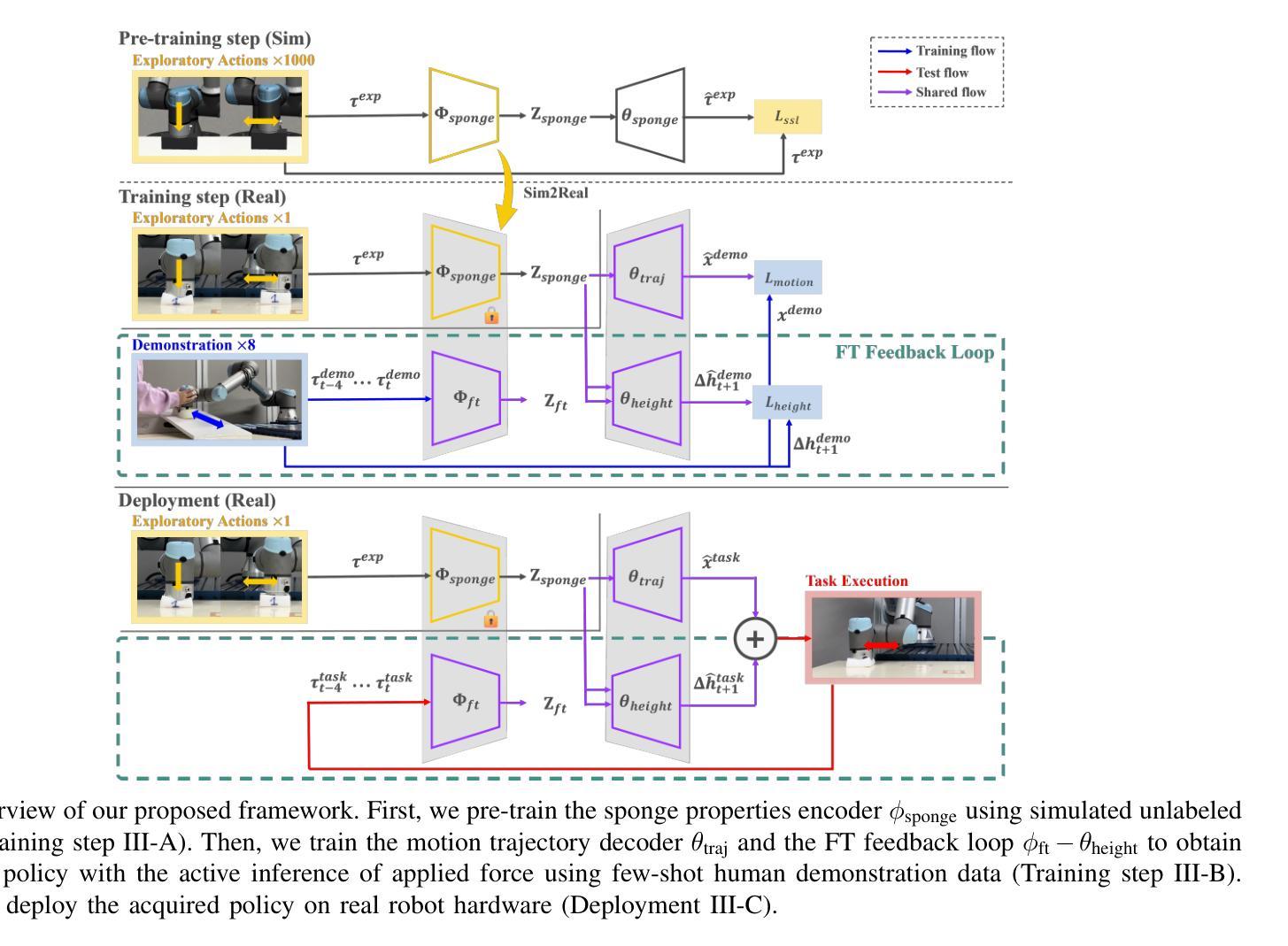
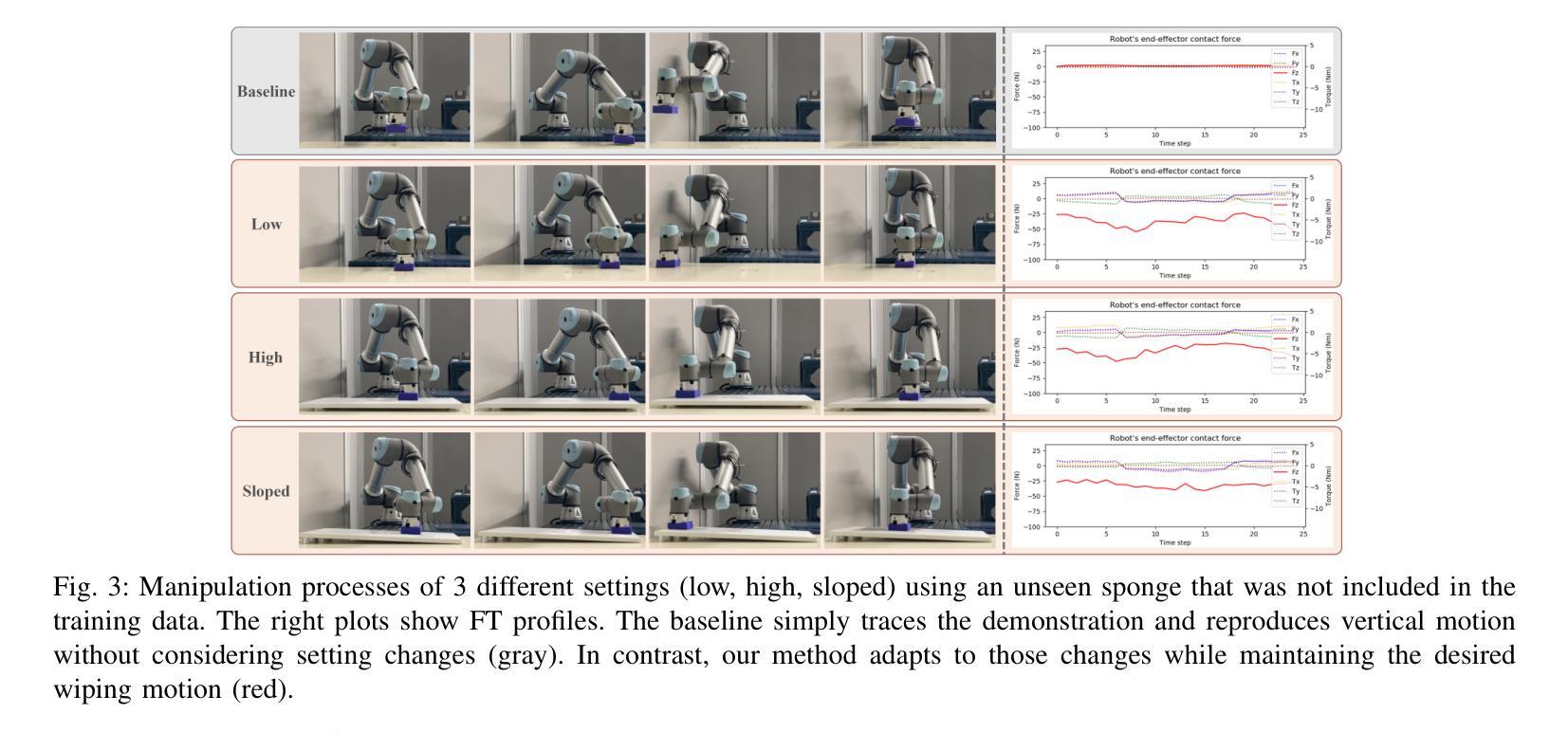
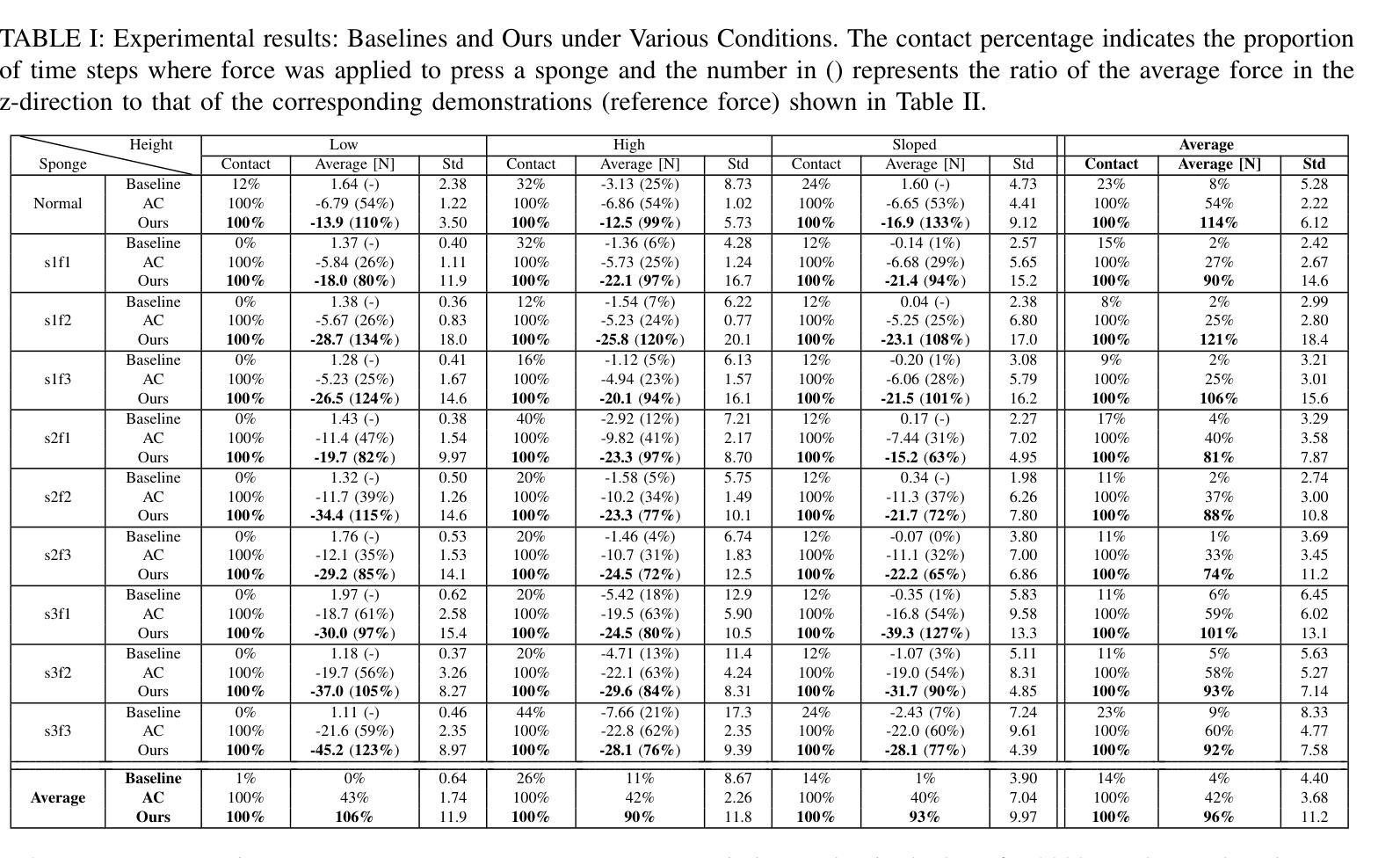
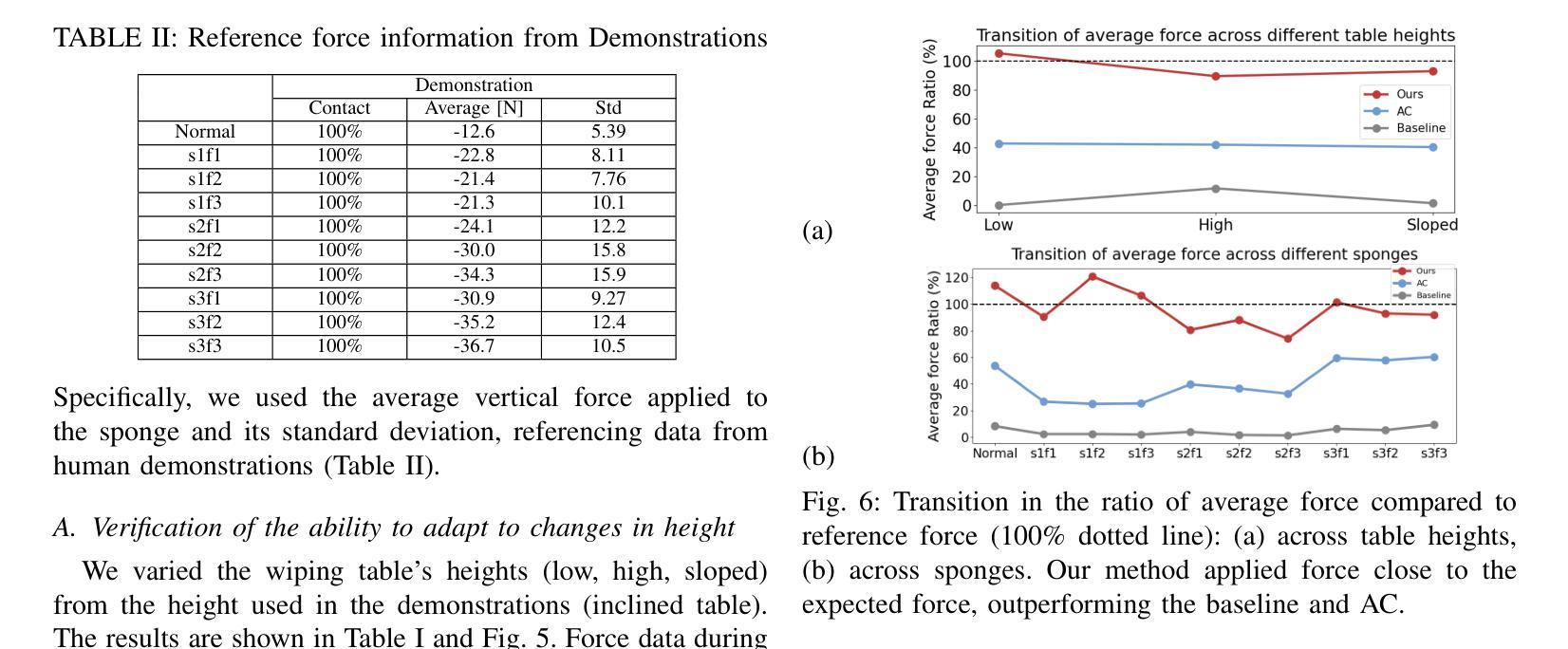
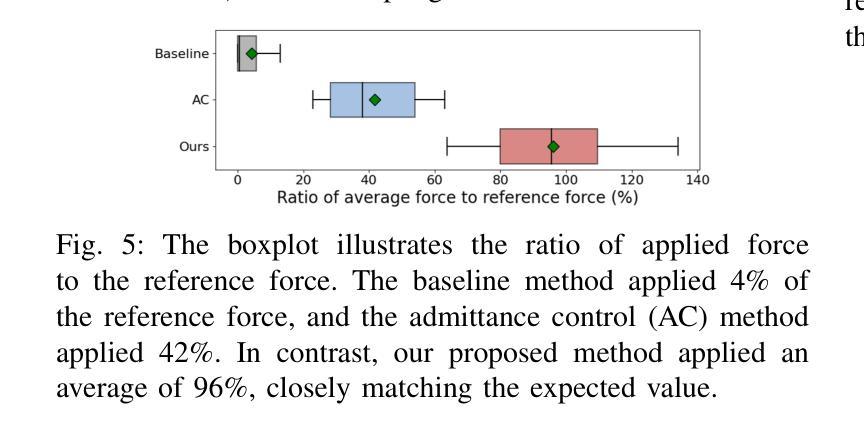
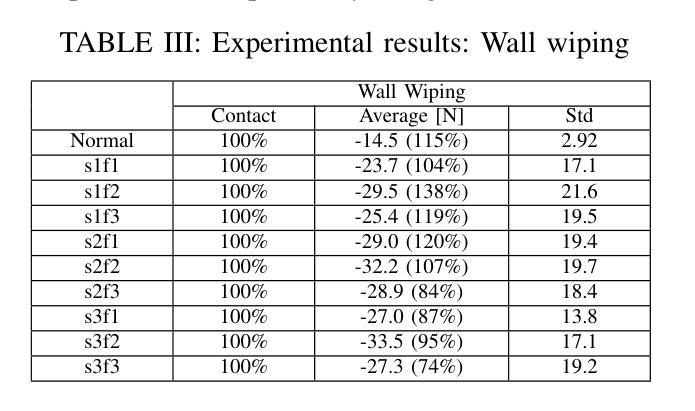
Adaptive Wiping: Adaptive contact-rich manipulation through few-shot imitation learning with Force-Torque feedback and pre-trained object representations
Authors:Chikaha Tsuji, Enrique Coronado, Pablo Osorio, Gentiane Venture
Imitation learning offers a pathway for robots to perform repetitive tasks, allowing humans to focus on more engaging and meaningful activities. However, challenges arise from the need for extensive demonstrations and the disparity between training and real-world environments. This paper focuses on contact-rich tasks like wiping with soft and deformable objects, requiring adaptive force control to handle variations in wiping surface height and the sponge’s physical properties. To address these challenges, we propose a novel method that integrates real-time force-torque (FT) feedback with pre-trained object representations. This approach allows robots to dynamically adjust to previously unseen changes in surface heights and sponges’ physical properties. In real-world experiments, our method achieved 96% accuracy in applying reference forces, significantly outperforming the previous method that lacked an FT feedback loop, which only achieved 4% accuracy. To evaluate the adaptability of our approach, we conducted experiments under different conditions from the training setup, involving 40 scenarios using 10 sponges with varying physical properties and 4 types of wiping surface heights, demonstrating significant improvements in the robot’s adaptability by analyzing force trajectories. The video of our work is available at: https://sites.google.com/view/adaptive-wiping
模仿学习为机器人执行重复性任务提供了途径,使人类能够专注于更具吸引力和有意义的活动。然而,挑战来自于需要大量的演示以及训练环境与真实环境之间的差异。本文聚焦于擦拭类任务,如使用柔软且可变形物体的擦拭操作,需要自适应力控制来处理擦拭表面高度和海绵的物理属性变化。为了应对这些挑战,我们提出了一种新方法,该方法将实时力扭矩(FT)反馈与预训练的对象表示相结合。这种方法使机器人能够动态适应以前未见过的表面高度和海绵物理属性的变化。在真实世界的实验中,我们的方法在应用参考力方面达到了96%的准确率,显著优于缺乏FT反馈回路的方法,后者仅达到4%的准确率。为了评估我们方法的适应性,我们在不同于训练环境的条件下进行了实验,涉及使用具有不同物理属性的10种海绵和4种擦拭表面高度的40个场景,通过分析力轨迹,显示出机器人在适应性方面的显著改善。我们工作的视频可在以下网址观看:https://sites.google.com/view/adaptive-wiping 。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
机器人通过模仿学习执行重复任务,使人类能够专注于更有意义和吸引力的活动。然而,该方法面临需要海量演示数据和训练环境与真实环境存在差异的挑战。针对擦拭等接触丰富的任务,本文提出一种结合实时力扭矩反馈与预训练物体表征的新方法,机器人可根据表面高度和海绵物理属性的变化动态调整。在真实场景中,新方法在施加参考力方面实现了96%的准确率,显著优于缺乏力扭矩反馈的以往方法(仅4%的准确率)。通过在不同条件下进行实验,验证了方法在不同海绵物理属性和表面高度下的适应性。
Key Takeaways
- 模仿学习允许机器人执行重复任务,使人类专注于更有意义的活动。
- 模仿学习面临的挑战包括需要大量演示数据和训练环境与真实环境的差异。
- 针对擦拭等接触丰富的任务,需要适应力控制来处理表面高度和海绵物理属性的变化。
- 提出了一种结合实时力扭矩反馈与预训练物体表征的新方法,以应对这些挑战。
- 新方法在真实场景中实现了高准确率,显著优于以往方法。
- 通过实验验证了方法在不同海绵物理属性和表面高度下的适应性。
点此查看论文截图


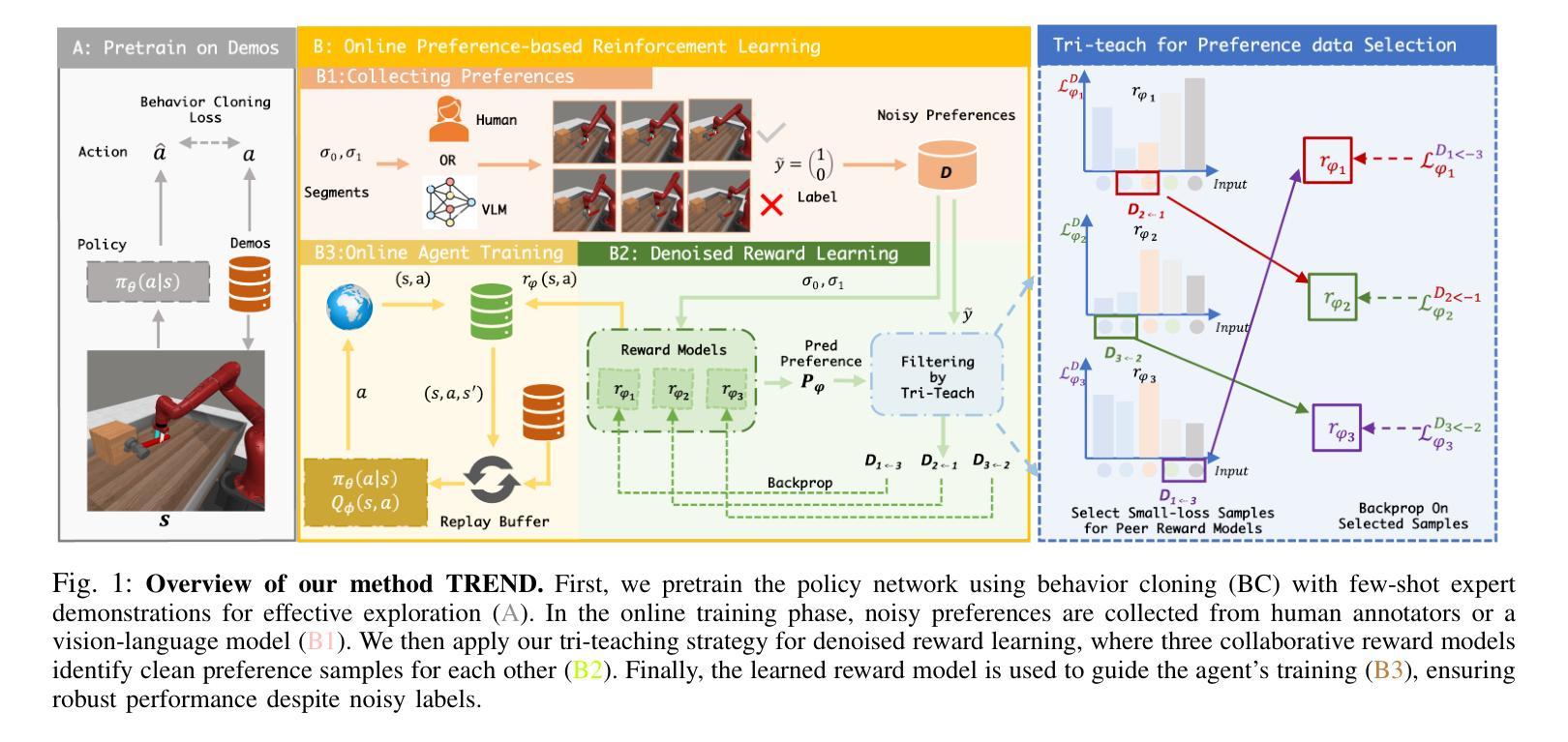
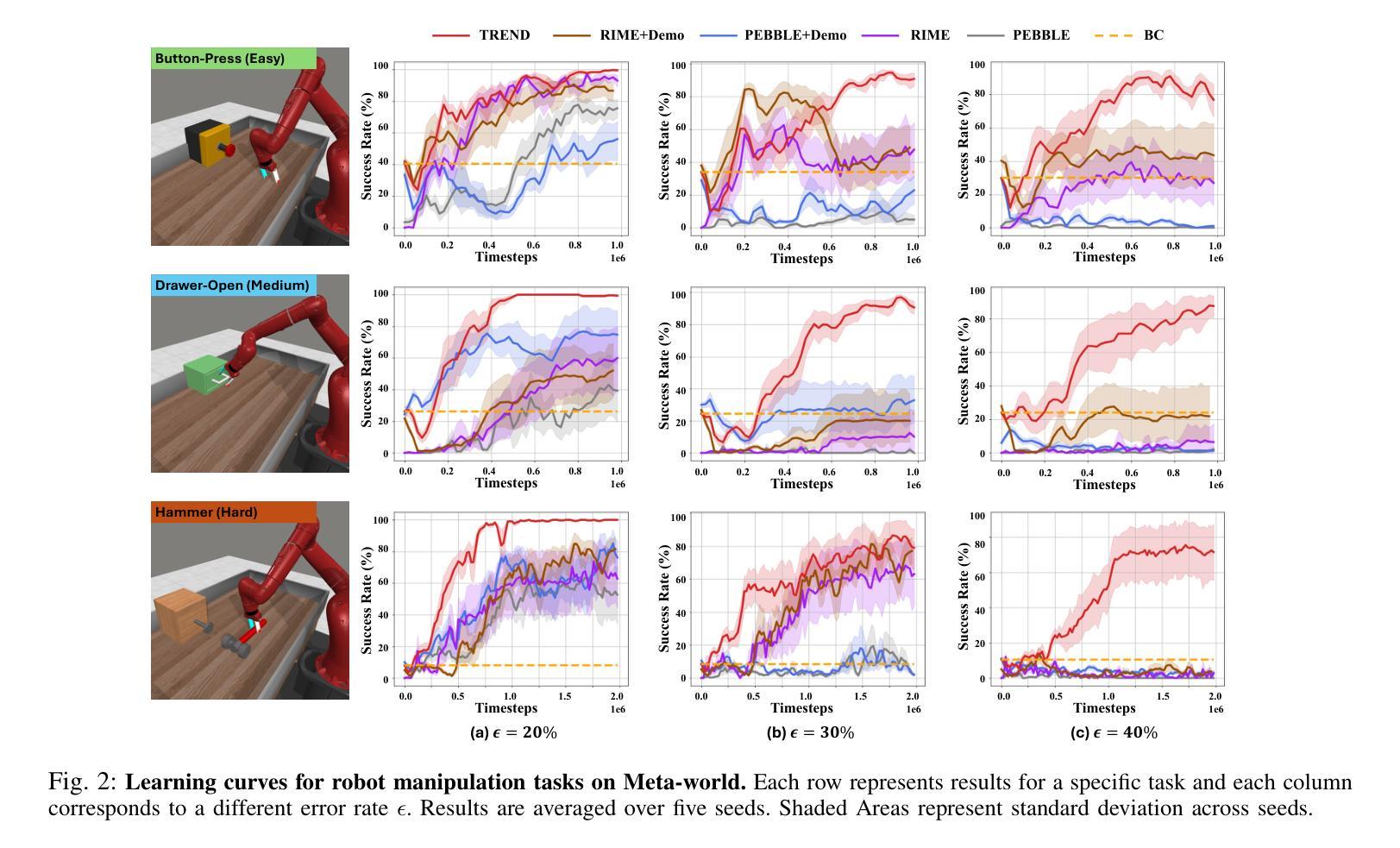
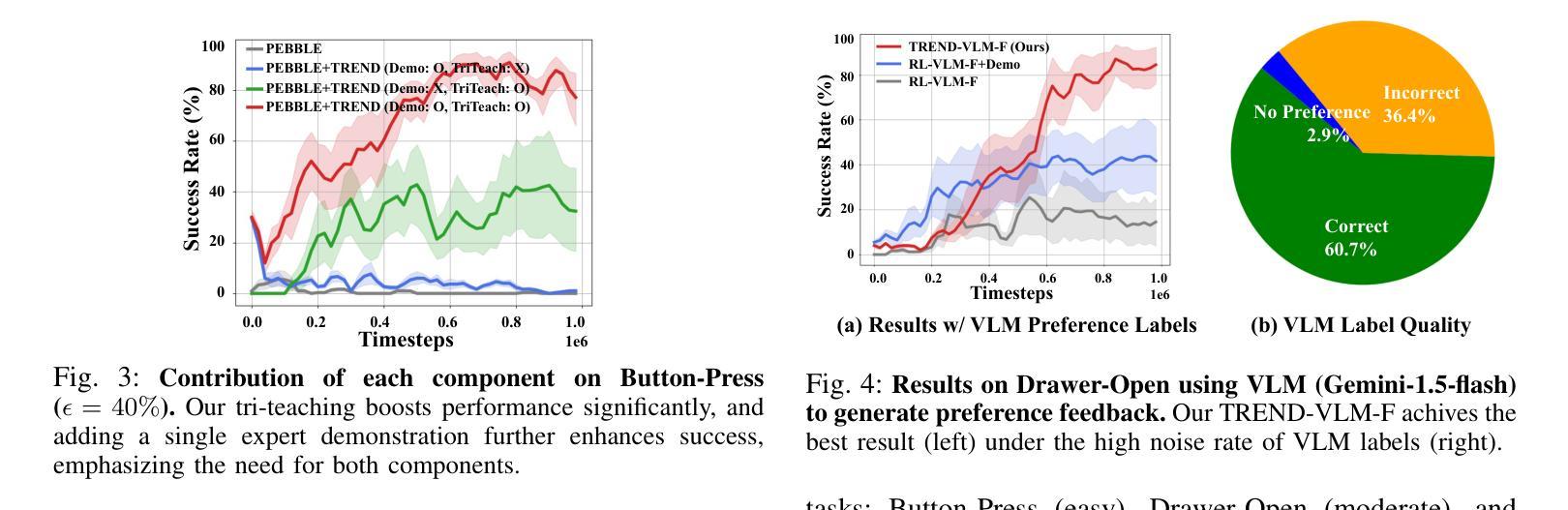
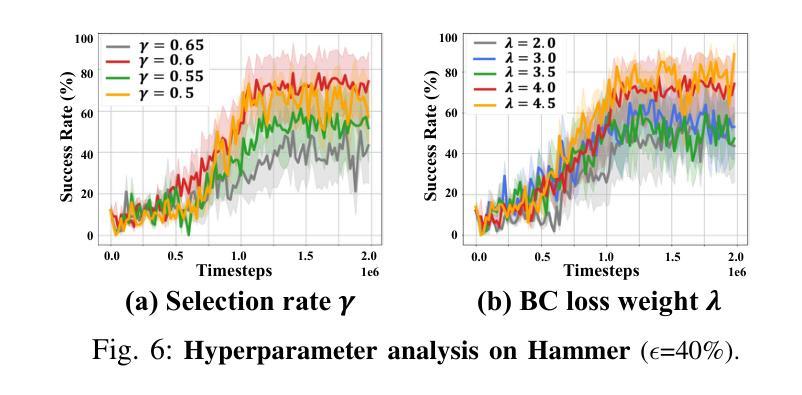
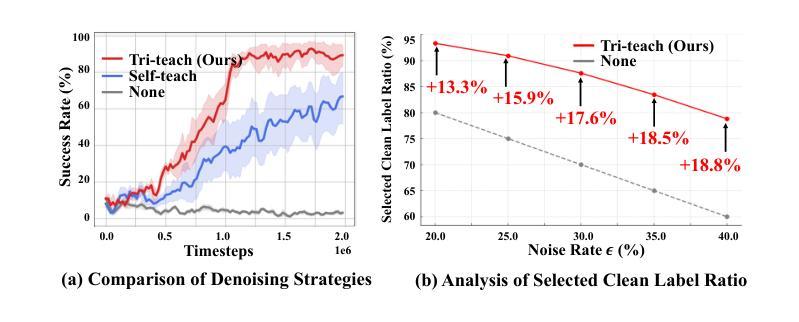
TREND: Tri-teaching for Robust Preference-based Reinforcement Learning with Demonstrations
Authors:Shuaiyi Huang, Mara Levy, Anubhav Gupta, Daniel Ekpo, Ruijie Zheng, Abhinav Shrivastava
Preference feedback collected by human or VLM annotators is often noisy, presenting a significant challenge for preference-based reinforcement learning that relies on accurate preference labels. To address this challenge, we propose TREND, a novel framework that integrates few-shot expert demonstrations with a tri-teaching strategy for effective noise mitigation. Our method trains three reward models simultaneously, where each model views its small-loss preference pairs as useful knowledge and teaches such useful pairs to its peer network for updating the parameters. Remarkably, our approach requires as few as one to three expert demonstrations to achieve high performance. We evaluate TREND on various robotic manipulation tasks, achieving up to 90% success rates even with noise levels as high as 40%, highlighting its effective robustness in handling noisy preference feedback. Project page: https://shuaiyihuang.github.io/publications/TREND.
通过人类或VLM注释器收集的偏好反馈往往存在噪声,这为基于准确偏好标签的基于偏好的强化学习带来了重大挑战。为了应对这一挑战,我们提出了TREND,这是一个将少量专家演示与三教学习策略相结合的新型框架,以实现有效的噪声缓解。我们的方法同时训练三个奖励模型,每个模型将其低损失偏好对视为有用知识,并将其教给同行网络以更新参数。值得注意的是,我们的方法只需要一到三个专家演示即可实现高性能。我们在各种机器人操作任务上评估TREND,即使在高达40%的噪声水平下,也能达到高达90%的成功率,从而突出了其在处理噪声偏好反馈方面的有效稳健性。项目页面:https://shuaiyihuang.github.io/publications/TREND。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF ICRA 2025
Summary
本文提出一种名为TREND的新框架,通过整合少量专家演示和三重教学策略来解决基于噪声偏好的强化学习问题。该框架同时训练三个奖励模型,每个模型将其低损失偏好对视为有用知识并传授给同行网络进行参数更新。该方法只需要一到三次专家演示即可实现高性能,在机器人操作任务上取得高达90%的成功率,即使在高达40%的噪声水平下也能有效应对噪声偏好反馈。
Key Takeaways
- TREND框架解决了基于噪声偏好的强化学习挑战。
- 通过整合少量专家演示和三重教学策略实现有效噪声缓解。
- 同时训练三个奖励模型,利用低损失偏好对更新参数。
- 仅需一至三次专家演示即可实现高性能。
- 在机器人操作任务上取得了高达90%的成功率。
- 在高噪声水平下仍能保持稳健性。
点此查看论文截图

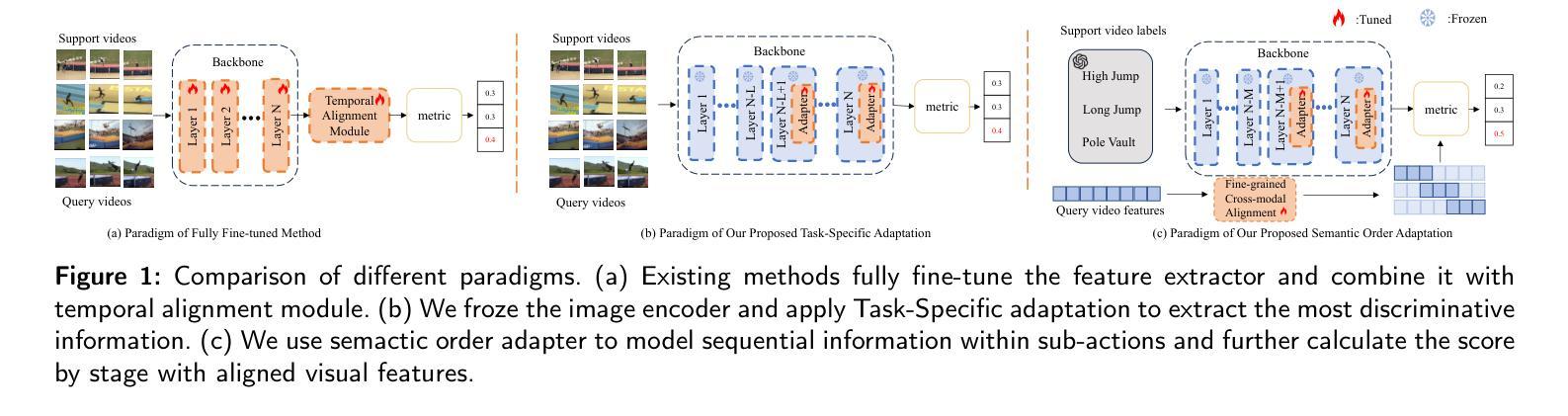
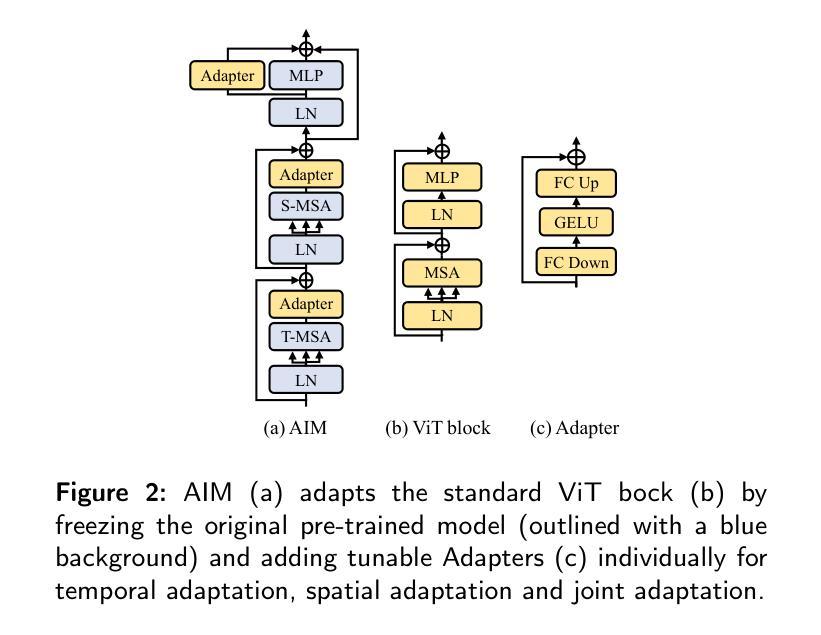
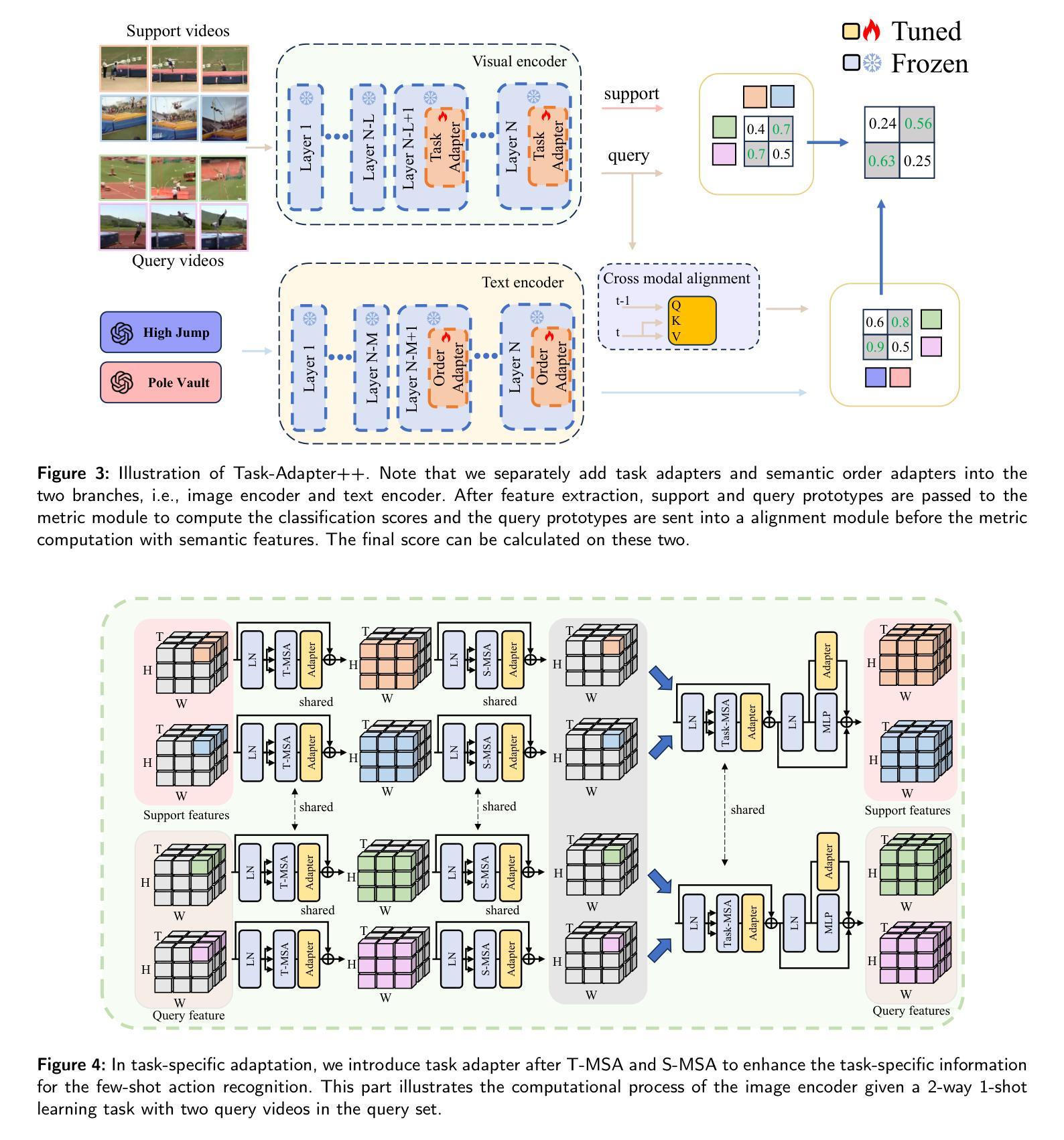
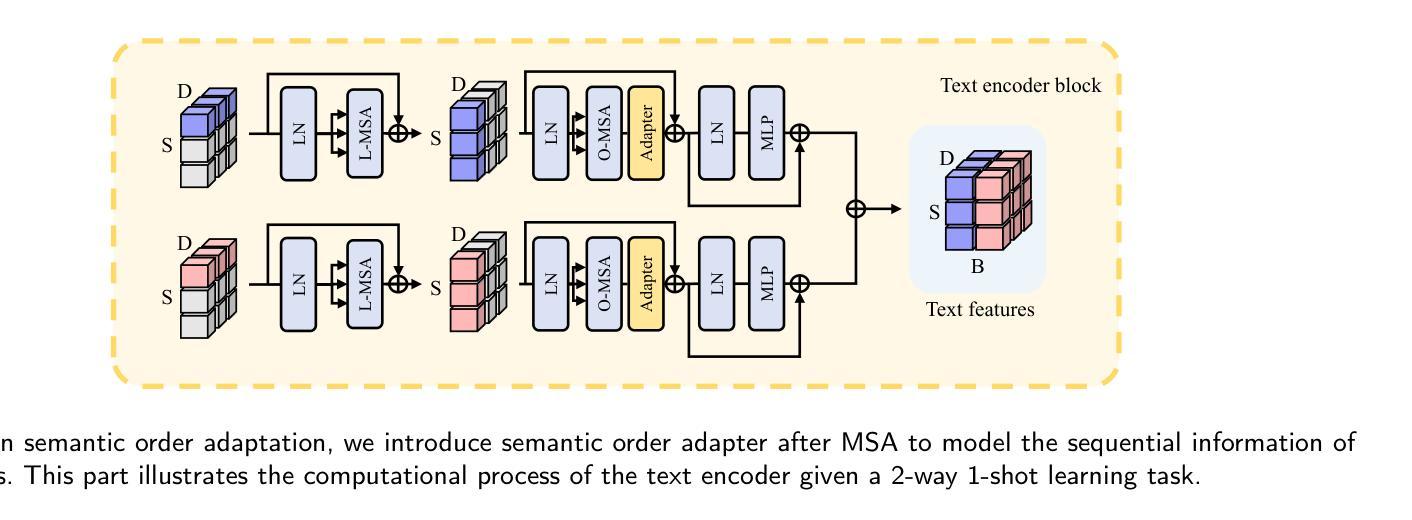
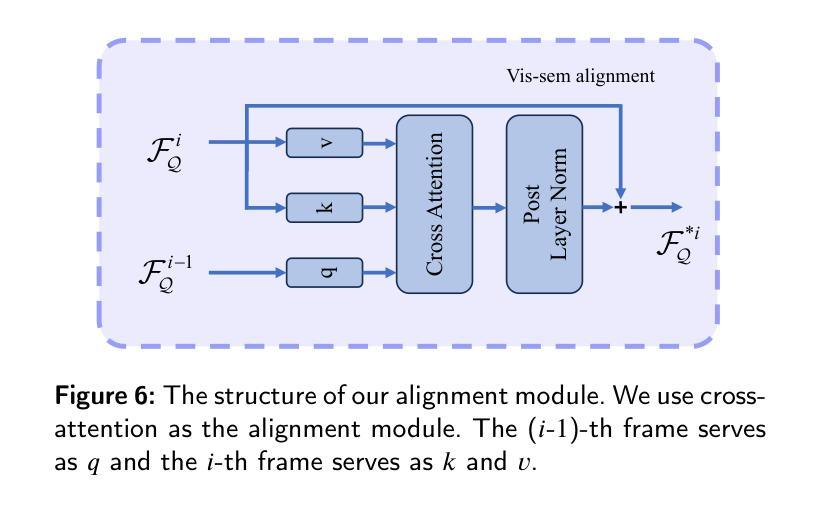
Task-Adapter++: Task-specific Adaptation with Order-aware Alignment for Few-shot Action Recognition
Authors:Congqi Cao, Peiheng Han, Yueran zhang, Yating Yu, Qinyi Lv, Lingtong Min, Yanning zhang
Large-scale pre-trained models have achieved remarkable success in language and image tasks, leading an increasing number of studies to explore the application of pre-trained image models, such as CLIP, in the domain of few-shot action recognition (FSAR). However, current methods generally suffer from several problems: 1) Direct fine-tuning often undermines the generalization capability of the pre-trained model; 2) The exploration of task-specific information is insufficient in the visual tasks; 3) The semantic order information is typically overlooked during text modeling; 4) Existing cross-modal alignment techniques ignore the temporal coupling of multimodal information. To address these, we propose Task-Adapter++, a parameter-efficient dual adaptation method for both image and text encoders. Specifically, to make full use of the variations across different few-shot learning tasks, we design a task-specific adaptation for the image encoder so that the most discriminative information can be well noticed during feature extraction. Furthermore, we leverage large language models (LLMs) to generate detailed sequential sub-action descriptions for each action class, and introduce semantic order adapters into the text encoder to effectively model the sequential relationships between these sub-actions. Finally, we develop an innovative fine-grained cross-modal alignment strategy that actively maps visual features to reside in the same temporal stage as semantic descriptions. Extensive experiments fully demonstrate the effectiveness and superiority of the proposed method, which achieves state-of-the-art performance on 5 benchmarks consistently. The code is open-sourced at https://github.com/Jaulin-Bage/Task-Adapter-pp.
大规模预训练模型在语言和图像任务中取得了显著的成功,引发了越来越多的研究探索预训练图像模型(如CLIP)在少样本动作识别(FSAR)领域的应用。然而,当前的方法普遍存在一些问题:1)直接微调往往会削弱预训练模型的泛化能力;2)视觉任务中特定任务信息的探索不足;3)文本建模时忽略了语义顺序信息;4)现有的跨模态对齐技术忽略了多模态信息的时序耦合。为了解决这些问题,我们提出了Task-Adapter++,这是一种参数高效的图像和文本编码器的双重适应方法。具体来说,为了充分利用不同少样本学习任务之间的差异,我们为图像编码器设计了特定任务的适应方法,以便在特征提取过程中能够充分注意到最具区分性的信息。此外,我们利用大型语言模型(LLM)为每个动作类别生成详细的序列子动作描述,并在文本编码器中引入语义顺序适配器,以有效地建模这些子动作之间的序列关系。最后,我们开发了一种创新的精细跨模态对齐策略,该策略能积极地将视觉特征映射到与语义描述相同的时序阶段。大量的实验充分证明了所提方法的有效性和优越性,该方法在5个基准测试上均达到了最新技术水平。代码已开源在https://github.com/Jaulin-Bage/Task-Adapter-pp。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF arXiv admin note: substantial text overlap with arXiv:2408.00249
Summary
本文探讨了大规模预训练模型在语言和图像任务中的出色表现,特别是在少样本动作识别(FSAR)领域的应用。针对现有方法存在的问题,如直接微调影响模型泛化能力、视觉任务中任务特定信息探索不足、文本建模中语义顺序信息被忽视以及现有跨模态对齐技术忽略多模态信息的时序耦合等,本文提出了Task-Adapter++,一种参数高效的图像和文本编码器的双重适应方法。该方法通过设计任务特定适应的图像编码器、利用大型语言模型生成详细顺序子动作描述以及引入语义顺序适配器到文本编码器和精细跨模态对齐策略,实现了在五个基准测试上的卓越表现。
Key Takeaways
- 大规模预训练模型在语言和图像任务中表现卓越,特别是在少样本动作识别(FSAR)领域。
- 当前方法存在的问题包括直接微调影响模型泛化能力、视觉任务中任务特定信息探索不足等。
- Task-Adapter++是一种参数高效的图像和文本编码器的双重适应方法,旨在解决上述问题。
- 该方法通过设计任务特定适应的图像编码器以利用不同少样本学习任务中的变化。
- 利用大型语言模型生成详细顺序子动作描述,并引入语义顺序适配器到文本编码器。
- 开发出一种创新的精细跨模态对齐策略,积极将视觉特征与语义描述映射到同一时间阶段。
- Task-Adapter++在五个基准测试上实现了卓越表现,并公开了源代码。
点此查看论文截图

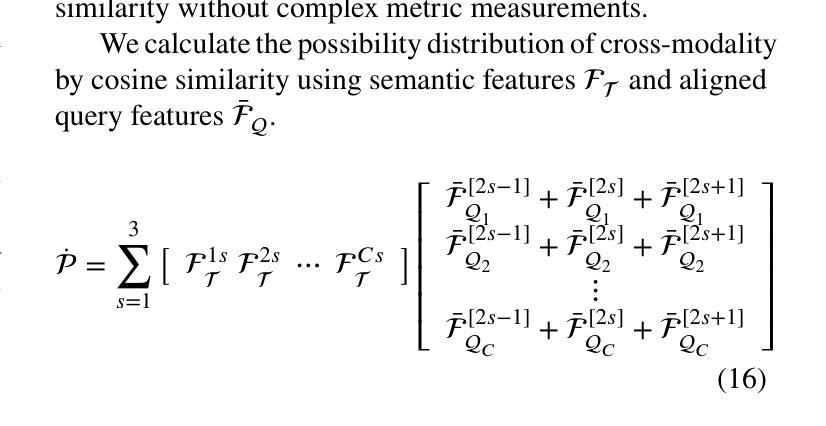
Can open source large language models be used for tumor documentation in Germany? – An evaluation on urological doctors’ notes
Authors:Stefan Lenz, Arsenij Ustjanzew, Marco Jeray, Meike Ressing, Torsten Panholzer
Tumor documentation in Germany is largely done manually, requiring reading patient records and entering data into structured databases. Large language models (LLMs) could potentially enhance this process by improving efficiency and reliability. This evaluation tests eleven different open source LLMs with sizes ranging from 1-70 billion model parameters on three basic tasks of the tumor documentation process: identifying tumor diagnoses, assigning ICD-10 codes, and extracting the date of first diagnosis. For evaluating the LLMs on these tasks, a dataset of annotated text snippets based on anonymized doctors’ notes from urology was prepared. Different prompting strategies were used to investigate the effect of the number of examples in few-shot prompting and to explore the capabilities of the LLMs in general. The models Llama 3.1 8B, Mistral 7B, and Mistral NeMo 12 B performed comparably well in the tasks. Models with less extensive training data or having fewer than 7 billion parameters showed notably lower performance, while larger models did not display performance gains. Examples from a different medical domain than urology could also improve the outcome in few-shot prompting, which demonstrates the ability of LLMs to handle tasks needed for tumor documentation. Open source LLMs show a strong potential for automating tumor documentation. Models from 7-12 billion parameters could offer an optimal balance between performance and resource efficiency. With tailored fine-tuning and well-designed prompting, these models might become important tools for clinical documentation in the future. The code for the evaluation is available from https://github.com/stefan-m-lenz/UroLlmEval. We also release the dataset as a new valuable resource that addresses the shortage of authentic and easily accessible benchmarks in German-language medical NLP.
在德国,肿瘤记录工作大多以手动方式进行,需要阅读患者病历并将数据录入结构化数据库。大型语言模型(LLM)有潜力通过提高效率和可靠性来改进这一过程。本次评估对三种肿瘤记录基本任务(识别肿瘤诊断、分配ICD-10代码和提取首次诊断日期)上,测试了规模从1亿至70亿模型参数的11个不同开源LLM。为了评估这些任务上的LLM性能,准备了一个基于泌尿外科匿名医生笔记的标注文本片段数据集。使用了不同的提示策略来研究少量示例提示中示例数量对LLM性能的影响,并探索LLM的一般能力。模型Llama 3.1 8B、Mistral 7B和Mistral NeMo 12B在任务中表现相当出色。拥有较少训练数据或参数少于7亿的模型表现明显较差,而更大的模型并没有显示出性能提升。来自泌尿学以外的医学领域的例子也可以在少量提示中改善结果,这证明了LLM处理肿瘤记录所需任务的能力。开源LLM在自动进行肿瘤记录方面显示出巨大潜力。参数在7亿至12亿之间的模型可能在性能和资源效率之间达到最佳平衡。通过有针对性的微调以及精心设计提示,这些模型可能会成为未来临床记录的重要工具。评估的代码可从https://github.com/stefan-m-lenz/UroLlmEval获取。我们还公开了数据集,作为解决德国医学NLP中真实、易于访问的基准测试资源短缺问题的一个新有价值资源。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 53 pages, 5 figures
Summary
大型语言模型(LLMs)在肿瘤文档处理中展现出潜在的应用价值,能提高效率和可靠性。通过对11种不同规模(从1亿到70亿参数)的开源LLMs进行评价,发现它们在肿瘤诊断确认、ICD-10代码分配和首次诊断日期提取等任务中表现良好。模型性能随参数增加而提高,但不是线性关系。特定医疗领域的样本在few-shot prompting下能够提高表现,说明LLMs有能力处理肿瘤文档相关的任务。推荐模型参数在7-12亿范围内以达到性能和资源效率的平衡。适当微调并设计提示可使其在未来成为临床文档的重要工具。相关代码和数据集已发布供研究使用。
Key Takeaways
- 大型语言模型(LLMs)可应用于肿瘤文档处理,提高效率和可靠性。
- 通过评价11种不同规模和类型的LLMs在三个基本任务上的表现,发现良好性能。
- 模型性能与参数规模有关,但不是线性关系,参数规模过大不一定带来性能提升。
- Few-shot prompting效果受样本领域影响,表明LLMs具备处理不同医疗领域任务的能力。
- 推荐模型参数范围在7-12亿,以实现性能和资源效率之间的平衡。
- 适当微调和优化提示设计可以使这些模型成为未来临床文档处理的重要工具。
点此查看论文截图

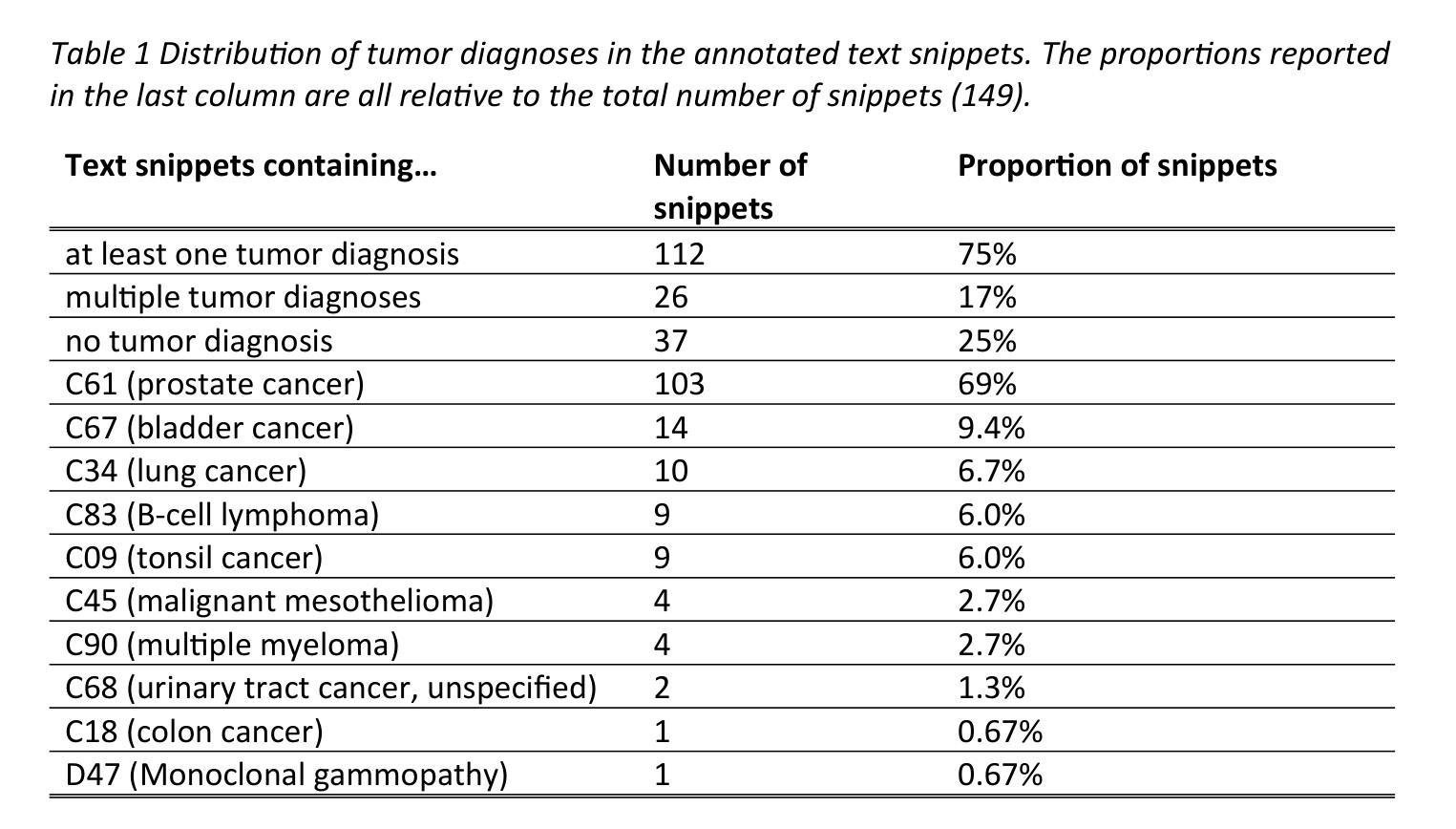
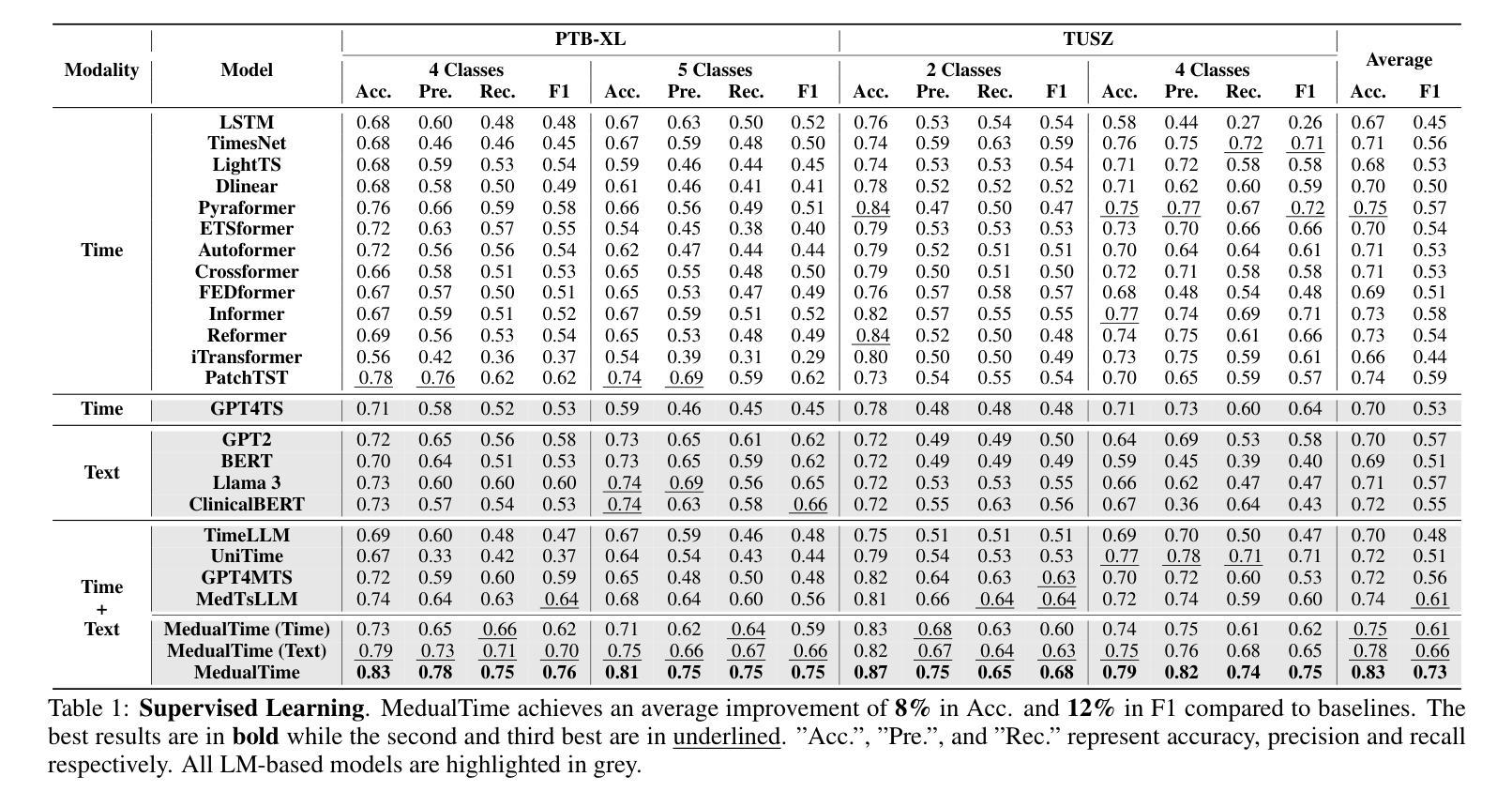
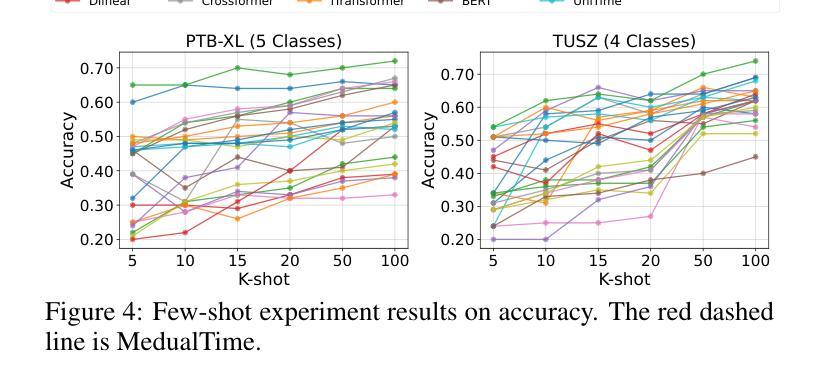
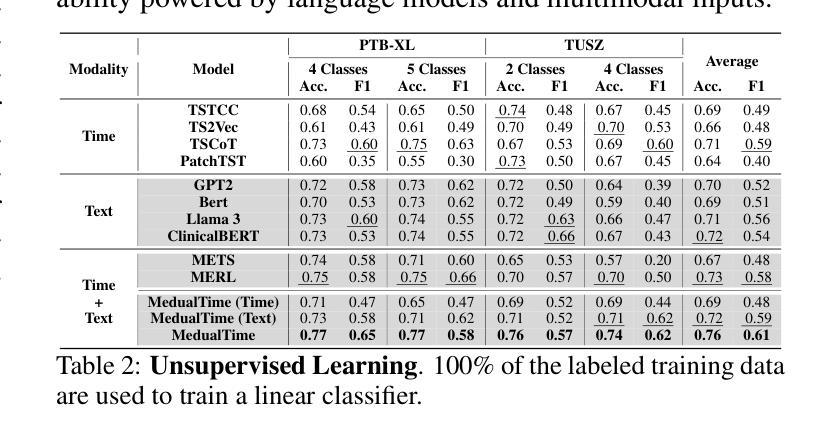
MedualTime: A Dual-Adapter Language Model for Medical Time Series-Text Multimodal Learning
Authors:Jiexia Ye, Weiqi Zhang, Ziyue Li, Jia Li, Meng Zhao, Fugee Tsung
The recent rapid advancements in language models (LMs) have garnered attention in medical time series-text multimodal learning. However, existing contrastive learning-based and prompt-based LM approaches tend to be biased, often assigning a primary role to time series modality while treating text modality as secondary. We classify these approaches under a temporal-primary paradigm, which may overlook the unique and critical task-relevant information embedded in text modality like clinical reports, thus failing to fully leverage mutual benefits and complementarity of different modalities. To fill this gap, we propose a novel textual-temporal multimodal learning paradigm that enables either modality to serve as the primary while being enhanced by the other, thereby effectively capturing modality-specific information and fostering cross-modal interaction. In specific, we design MedualTime, a language model composed of dual adapters to implement temporal-primary and textual-primary modeling simultaneously. Within each adapter, lightweight adaptation tokens are injected into the top layers of LM to encourage high-level modality fusion. The shared LM pipeline by dual adapters not only achieves adapter alignment but also enables efficient fine-tuning, reducing computational resources. Empirically, MedualTime demonstrates superior performance on medical data, achieving notable improvements of 8% accuracy and 12% F1 in supervised settings. Furthermore, MedualTime’s transferability is validated by few-shot label transfer experiments from coarse-grained to fine-grained medical data. https://github.com/start2020/MedualTime
近期的语言模型(LMs)迅速进展引起了医学时间序列文本多模态学习的关注。然而,现有的基于对比学习和基于提示的语言模型方法往往存在偏见,通常将时间序列模态视为主要模态,而将文本模态视为次要模态。我们将这些方法归类为时间主导范式,这可能会忽视文本模态中嵌入的独特且关键的任务相关信息,如临床报告,从而未能充分利用不同模态的相互优势和互补性。为了填补这一空白,我们提出了一种新的文本时间多模态学习范式,使任一模态都可以作为主要模态,同时受到另一模态的增强,从而有效地捕获特定于模态的信息并促进跨模态交互。具体来说,我们设计了MedualTime,一个由双适配器组成的语言模型,可同时实现时间主导和文本主导建模。在每个适配器中,将轻量级适配令牌注入语言模型顶层,以鼓励高级模态融合。双适配器共享的LM管道不仅实现了适配器对齐,还实现了高效的微调,减少了计算资源。实际上,MedualTime在医疗数据上表现出卓越的性能,在监督设置中的准确率和F1得分分别提高了8%和12%。此外,通过从粗粒度到细粒度的医学数据的少量标签转移实验,验证了MedualTime的可迁移性。https://github.com/start2020/MedualTime
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 9 pages, 6 figure, 3 tables
Summary
本文关注语言模型在医学时间序列文本多模态学习中的最新进展。针对现有对比学习和提示语言模型中的时间序列为主要模态、文本为次要模态的问题,提出了一种新的文本时序多模态学习范式。通过设计MedualTime模型,实现了时序为主和文本为主的建模同时进行。该模型通过轻量级适配器注入高层模态融合信息,达到优异性能。此外,该模型在医学数据上表现出卓越性能,并在粗粒度到细粒度的医学数据迁移实验中验证了其迁移能力。有关更多详细信息,请访问GitHub仓库以获取更多资源。
Key Takeaways
- 语言模型在医学时间序列文本多模态学习中取得进展。
- 现有方法倾向于将时间序列作为主模态,而文本为次要模态,这可能导致任务相关的关键信息被忽视。
- 提出了一种新的文本时序多模态学习范式,使任一模态都可以作为主要模态,同时得到另一模态的增强。
- MedualTime模型实现了时序为主和文本为主的建模同时进行,通过双适配器实现模态对齐和高效微调。
- MedualTime模型在医学数据上表现优越,监督设置下准确率和F1得分有显著提高。
点此查看论文截图

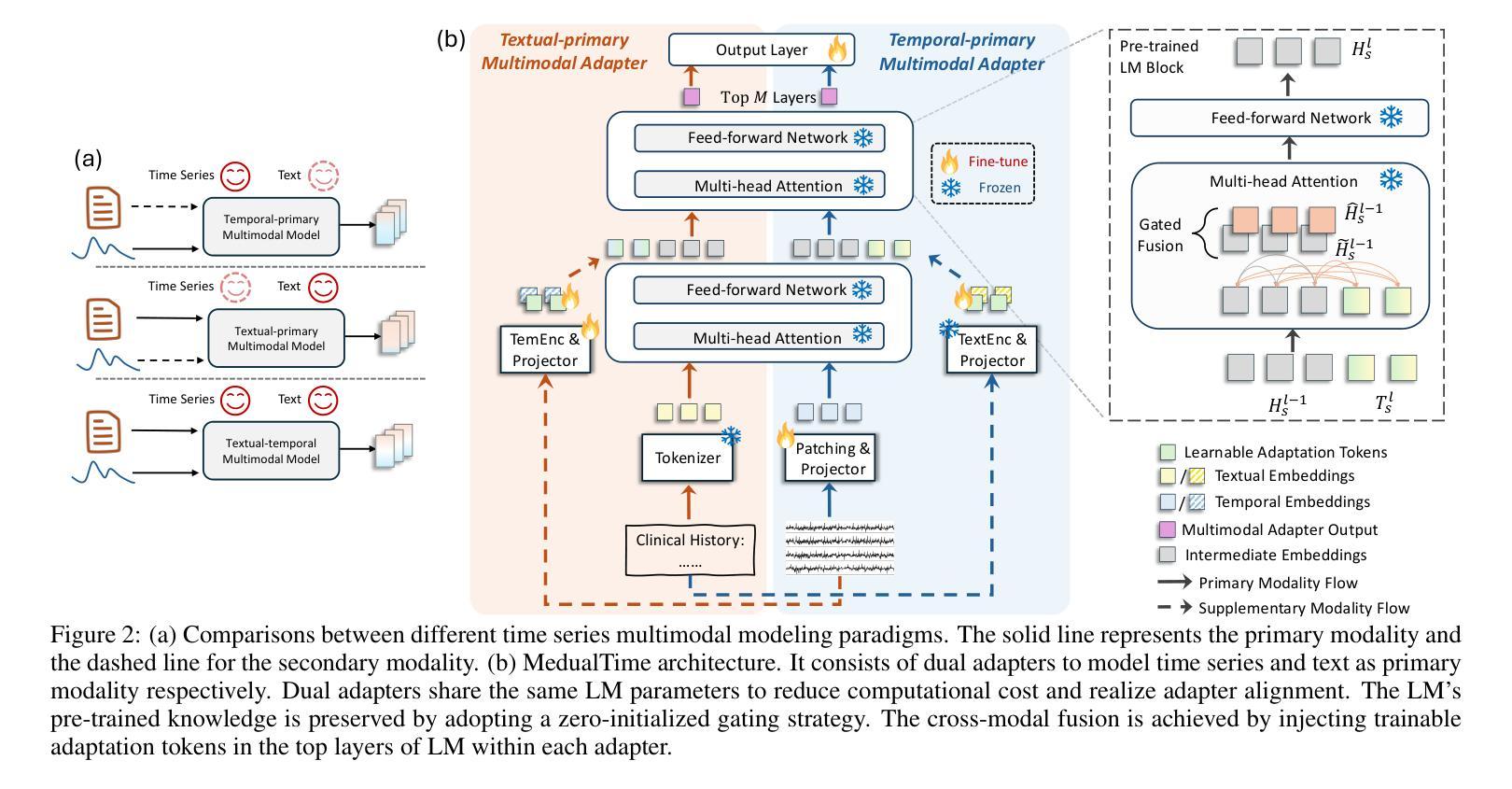
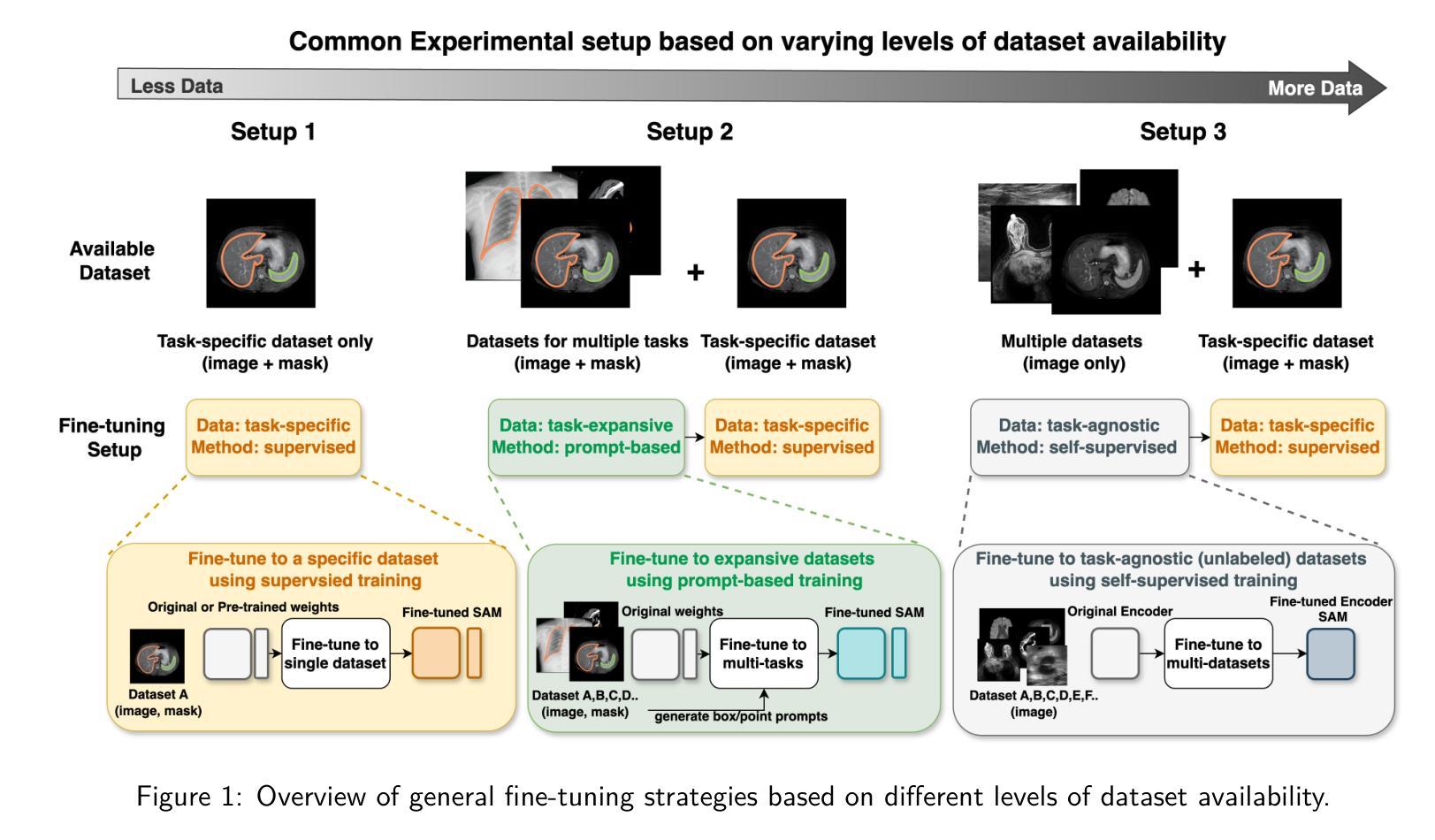
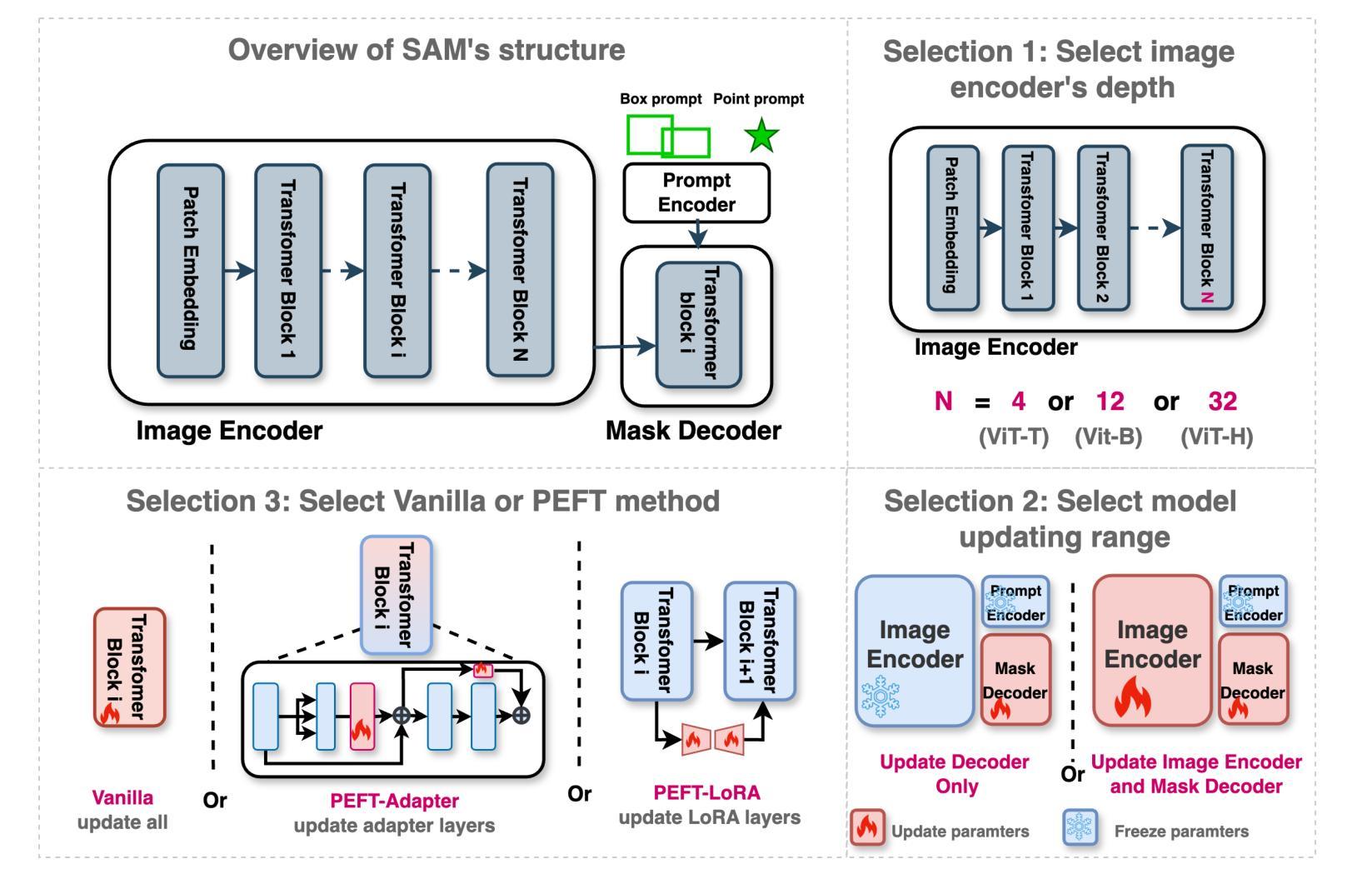
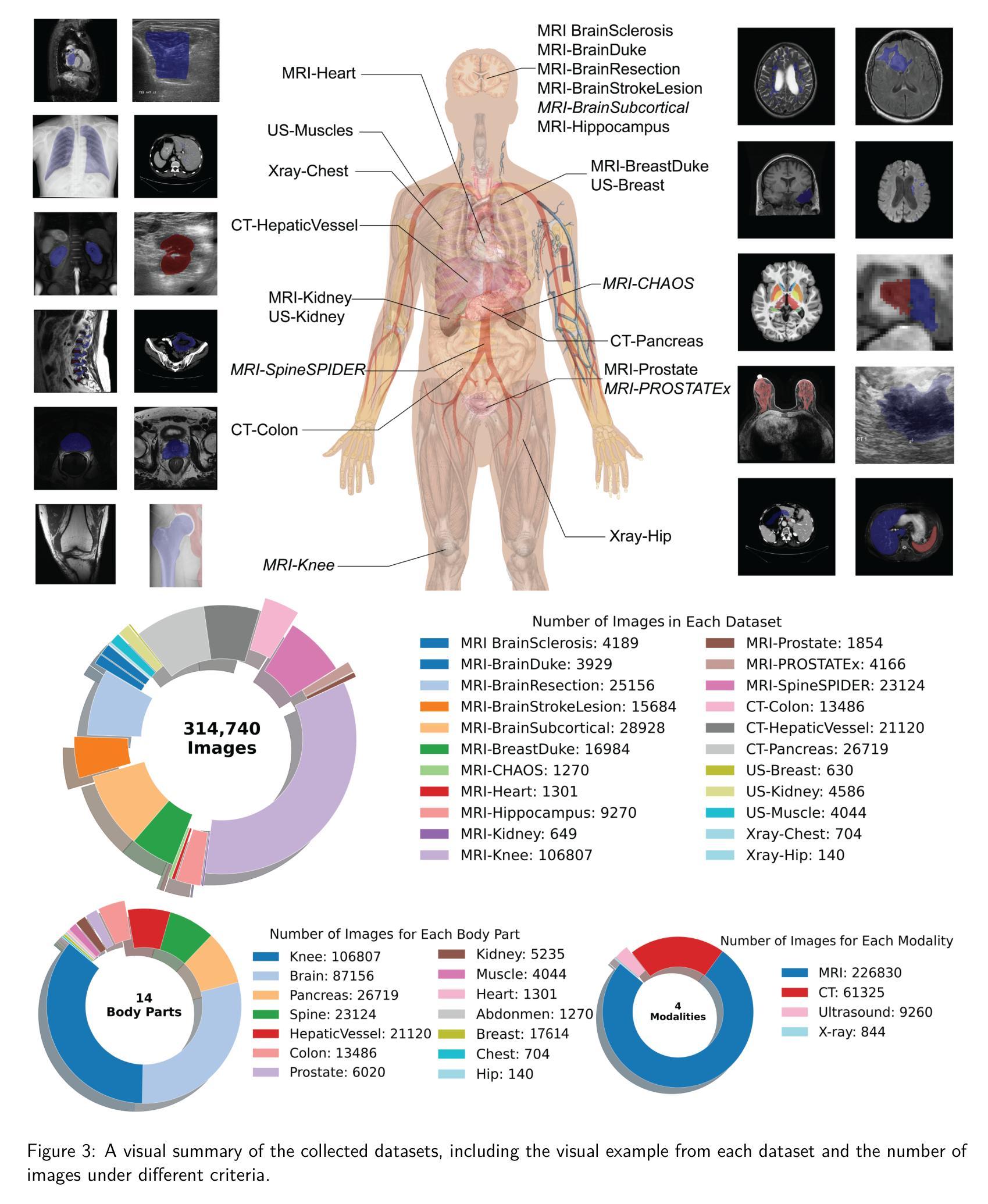
How to build the best medical image segmentation algorithm using foundation models: a comprehensive empirical study with Segment Anything Model
Authors:Hanxue Gu, Haoyu Dong, Jichen Yang, Maciej A. Mazurowski
Automated segmentation is a fundamental medical image analysis task, which enjoys significant advances due to the advent of deep learning. While foundation models have been useful in natural language processing and some vision tasks for some time, the foundation model developed with image segmentation in mind - Segment Anything Model (SAM) - has been developed only recently and has shown similar promise. However, there are still no systematic analyses or “best-practice” guidelines for optimal fine-tuning of SAM for medical image segmentation. This work summarizes existing fine-tuning strategies with various backbone architectures, model components, and fine-tuning algorithms across 18 combinations, and evaluates them on 17 datasets covering all common radiology modalities. Our study reveals that (1) fine-tuning SAM leads to slightly better performance than previous segmentation methods, (2) fine-tuning strategies that use parameter-efficient learning in both the encoder and decoder are superior to other strategies, (3) network architecture has a small impact on final performance, (4) further training SAM with self-supervised learning can improve final model performance. We also demonstrate the ineffectiveness of some methods popular in the literature and further expand our experiments into few-shot and prompt-based settings. Lastly, we released our code and MRI-specific fine-tuned weights, which consistently obtained superior performance over the original SAM, at https://github.com/mazurowski-lab/finetune-SAM.
自动分割是医学图像分析中的一项基本任务,得益于深度学习的进步,该任务取得了重大进展。虽然基础模型在自然语言处理和某些视觉任务中已有一段时间的应用,但以图像分割为中心开发的基础模型——任意分割模型(SAM)——是最近才开发的,并显示出同样的潜力。然而,对于SAM在医学图像分割中的最佳微调,仍然没有系统的分析或“最佳实践”指南。这项工作总结了使用各种主干架构、模型组件和微调算法的现有微调策略,跨越了18种组合,并在涵盖所有常见放射学模态的17个数据集上进行了评估。我们的研究表明:(1)微调SAM略微优于以前的分割方法;(2)在编码器和解码器中都使用参数有效学习的微调策略优于其他策略;(3)网络架构对最终性能的影响较小;(4)使用自监督学习进一步训练SAM可以提高最终模型性能。我们还证明了文献中一些流行方法的无效性,并将我们的实验进一步扩展到小样本和基于提示的设置中。最后,我们在https://github.com/mazurowski-lab/finetune-SAM上发布了我们的代码和针对MRI的特定微调权重,这些权重在原始SAM上始终获得了更好的性能。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted for publication at the Journal of Machine Learning for Biomedical Imaging (MELBA)
Summary
深度学习的发展推动了医学图像分析中的自动化分割任务取得显著进展。最近开发的以图像分割为重点的Segment Anything Model(SAM)显示出巨大的潜力。然而,关于如何对SAM进行最佳微调以优化医学图像分割,尚无系统分析和“最佳实践”指南。本研究总结了使用不同主干架构、模型组件和微调算法的现有微调策略,并在涵盖所有常见放射学模态的17个数据集上进行了评估。研究发现,微调SAM略优于以前的方法,使用参数高效学习的微调策略优于其他策略,网络架构对最终性能的影响较小,使用自监督学习进一步训练SAM可以提高最终模型性能。此外,还展示了文献中一些流行方法的有效性不足,并将实验进一步扩展到小样本和基于提示的环境中。最后,发布了代码和针对MRI的微调权重,性能优于原始SAM模型。
Key Takeaways
- 自动化分割是医学图像分析中的基本任务,深度学习的发展显著推动了其进展。
- Segment Anything Model (SAM)是针对图像分割而开发的,显示出巨大潜力。
- 目前针对SAM的最佳微调策略尚无系统分析和指南。
- 研究总结了多种微调策略,包括使用不同的主干架构、模型组件和微调算法。
- 微调SAM的性能略优于以前的方法。
- 使用参数高效学习的微调策略在网络架构对最终性能影响较小的情况下表现更佳。
点此查看论文截图