⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-05-14 更新
Pixel Motion as Universal Representation for Robot Control
Authors:Kanchana Ranasinghe, Xiang Li, Cristina Mata, Jongwoo Park, Michael S Ryoo
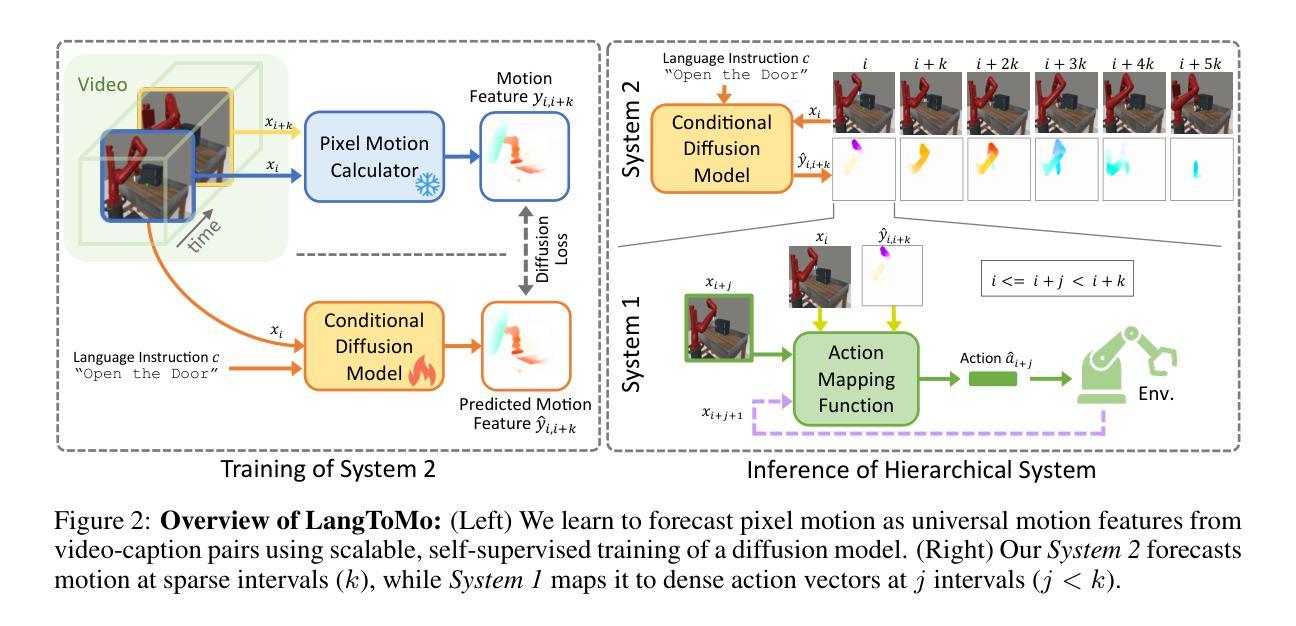
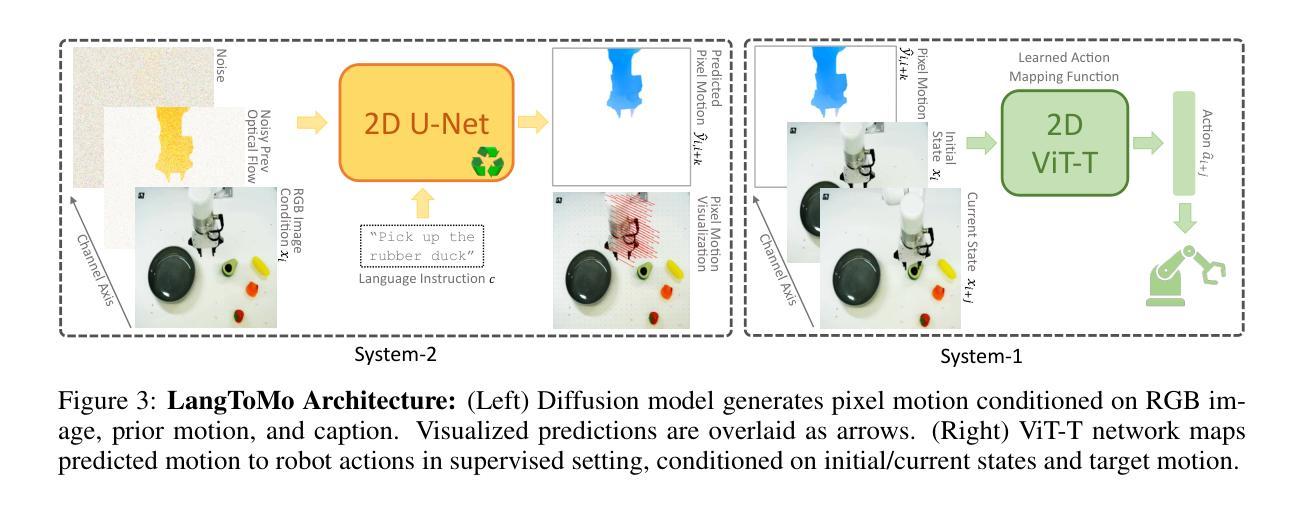
We present LangToMo, a vision-language-action framework structured as a dual-system architecture that uses pixel motion forecasts as intermediate representations. Our high-level System 2, an image diffusion model, generates text-conditioned pixel motion sequences from a single frame to guide robot control. Pixel motion-a universal, interpretable, and motion-centric representation-can be extracted from videos in a self-supervised manner, enabling diffusion model training on web-scale video-caption data. Treating generated pixel motion as learned universal representations, our low level System 1 module translates these into robot actions via motion-to-action mapping functions, which can be either hand-crafted or learned with minimal supervision. System 2 operates as a high-level policy applied at sparse temporal intervals, while System 1 acts as a low-level policy at dense temporal intervals. This hierarchical decoupling enables flexible, scalable, and generalizable robot control under both unsupervised and supervised settings, bridging the gap between language, motion, and action. Checkout https://kahnchana.github.io/LangToMo for visualizations.
我们推出了LangToMo,这是一个视觉-语言-行动框架,采用双系统架构,利用像素运动预测作为中间表示。我们的高级系统2是一个图像扩散模型,从单帧生成文本调节的像素运动序列,以指导机器人控制。像素运动是一种通用、可解释、以运动为中心的表示,可以以自我监督的方式从视频中提取,使得扩散模型能够在网页规模的视频字幕数据上进行训练。将生成的像素运动视为学习的通用表示,我们的低级系统1模块通过运动到动作的映射功能将这些表示转换为机器人动作,这些映射功能可以是手工制作的,或者通过最小的监督进行学习。系统2作为高级策略,在稀疏的时间间隔内应用,而系统1作为低级策略在密集的时间间隔内行动。这种分层解耦使得在无人监督和有人监督的环境下,机器人控制更加灵活、可扩展和通用,在语言、运动和动作之间搭建了桥梁。想了解更多可视化内容,请访问:https://kahnchana.github.io/LangToMo。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary:
LangToMo是一个视觉语言动作框架,采用双系统架构,以像素运动预测作为中间表示形式。其高级系统2采用图像扩散模型,通过单一帧生成文本控制的像素运动序列,指导机器人控制。该框架通过自我监督的方式从视频中提取像素运动,使扩散模型能够在网页规模的视频描述数据上进行训练。将生成的像素运动视为学习的通用表示,其低级系统1模块通过运动到动作的映射函数将这些表示转换为机器人动作,这些映射函数可以是手工制作的,也可以以最少的监督进行学习。系统2作为高级策略在稀疏时间间隔内运行,而系统1作为低级策略在密集时间间隔内运行。这种分层解耦实现了灵活的、可扩展的和通用的机器人控制,无论是在无监督还是监督设置下都能缩小语言、动作和行为之间的差距。更多可视化内容请访问:网站链接。
Key Takeaways:
- LangToMo是一个视觉语言动作框架,具有双系统架构。
- 该框架利用像素运动预测作为中间表示形式。
- 高级系统2采用图像扩散模型,生成文本控制的像素运动序列来指导机器人控制。
- 像素运动可以通过自我监督的方式从视频中提取。
- 低级系统1模块将像素运动转换为机器人动作。
- 该框架实现了灵活的、可扩展的和通用的机器人控制。
- 该框架缩小了语言、动作和行为之间的差距。
点此查看论文截图

ABS-Mamba: SAM2-Driven Bidirectional Spiral Mamba Network for Medical Image Translation
Authors:Feng Yuan, Yifan Gao, Wenbin Wu, Keqing Wu, Xiaotong Guo, Jie Jiang, Xin Gao
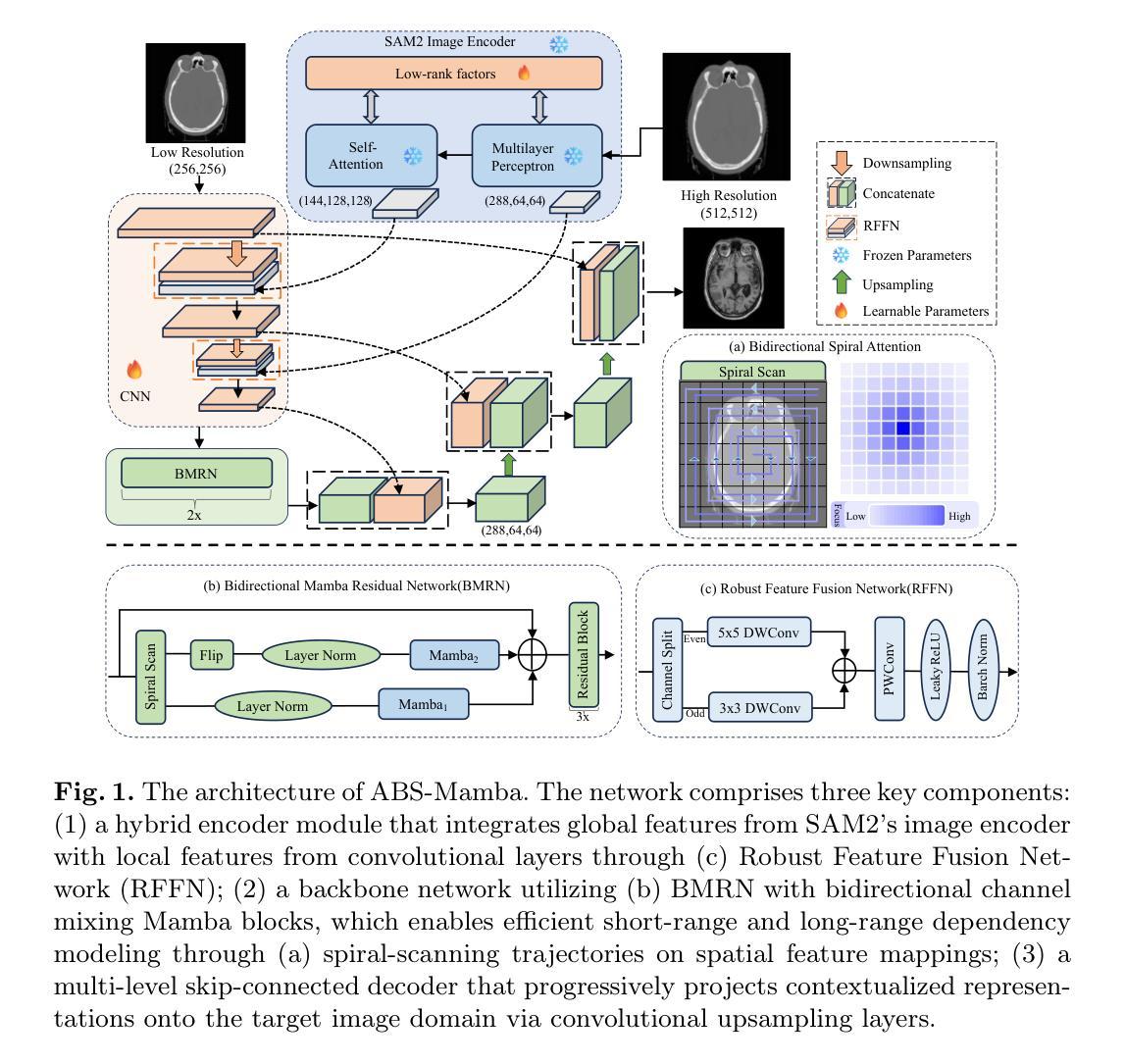
Accurate multi-modal medical image translation requires ha-rmonizing global anatomical semantics and local structural fidelity, a challenge complicated by intermodality information loss and structural distortion. We propose ABS-Mamba, a novel architecture integrating the Segment Anything Model 2 (SAM2) for organ-aware semantic representation, specialized convolutional neural networks (CNNs) for preserving modality-specific edge and texture details, and Mamba’s selective state-space modeling for efficient long- and short-range feature dependencies. Structurally, our dual-resolution framework leverages SAM2’s image encoder to capture organ-scale semantics from high-resolution inputs, while a parallel CNNs branch extracts fine-grained local features. The Robust Feature Fusion Network (RFFN) integrates these epresentations, and the Bidirectional Mamba Residual Network (BMRN) models spatial dependencies using spiral scanning and bidirectional state-space dynamics. A three-stage skip fusion decoder enhances edge and texture fidelity. We employ Efficient Low-Rank Adaptation (LoRA+) fine-tuning to enable precise domain specialization while maintaining the foundational capabilities of the pre-trained components. Extensive experimental validation on the SynthRAD2023 and BraTS2019 datasets demonstrates that ABS-Mamba outperforms state-of-the-art methods, delivering high-fidelity cross-modal synthesis that preserves anatomical semantics and structural details to enhance diagnostic accuracy in clinical applications. The code is available at https://github.com/gatina-yone/ABS-Mamba
精确的多模态医学图像翻译需要协调全局解剖语义和局部结构保真度,这一挑战因模态间信息丢失和结构失真而复杂化。我们提出了ABS-Mamba,这是一种新型架构,它集成了Segment Anything Model 2(SAM2)用于器官感知语义表示,专业化的卷积神经网络(CNN)用于保留模态特定的边缘和纹理细节,以及Mamba的选择性状态空间建模,以实现高效的长短程特征依赖性。结构上,我们的双分辨率框架利用SAM2的图像编码器捕获来自高分辨率输入的组织规模语义,而并行CNN分支则提取精细的局部特征。鲁棒的特征融合网络(RFFN)集成了这些表示,双向Mamba残差网络(BMRN)使用螺旋扫描和双向状态空间动力学对空间依赖性进行建模。三阶段跳过融合解码器增强了边缘和纹理的保真度。我们采用有效的低秩适应(LoRA+)微调方法,以实现精确的领域专业化,同时保持预训练组件的基本功能。在SynthRAD2023和BraTS2019数据集上的广泛实验验证表明,ABS-Mamba优于最新方法,实现了高保真度的跨模态合成,保留了解剖语义和结构细节,提高了临床应用中诊断的准确性。代码可用在https://github.com/gatina-yone/ABS-Mamba。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF MICCAI 2025(under view)
Summary
本文提出一种名为ABS-Mamba的新型多模态医学影像翻译架构,它融合了Segment Anything Model 2(SAM2)进行器官感知语义表示、卷积神经网络(CNN)保留模态边缘和纹理细节,以及Mamba的选择状态空间建模进行长短距离特征依赖。通过高效融合网络(RFFN)整合表示,采用双向Mamba残差网络(BMRN)进行空间依赖性建模。该架构在SynthRAD2023和BraTS2019数据集上的实验验证显示,ABS-Mamba在保持解剖语义和结构细节的同时,实现了高保真跨模态合成,提高了临床应用的诊断准确性。
Key Takeaways
- ABS-Mamba架构融合了SAM2进行器官感知语义表示,以捕捉全局解剖学语义。
- 专用CNN用于保留模态特定的边缘和纹理细节。
- Mamba的选择状态空间建模实现长短距离特征依赖的有效平衡。
- RFFN整合了不同特征表示,而BMRN通过螺旋扫描和双向状态空间动力学进行空间依赖性建模。
- 三阶段跳过融合解码器增强了边缘和纹理的保真度。
- 采用Efficient Low-Rank Adaptation(LoRA+)微调方法,可在精确领域专业化的同时保持预训练组件的基础能力。
点此查看论文截图

GAN-based synthetic FDG PET images from T1 brain MRI can serve to improve performance of deep unsupervised anomaly detection models
Authors:Daria Zotova, Nicolas Pinon, Robin Trombetta, Romain Bouet, Julien Jung, Carole Lartizien
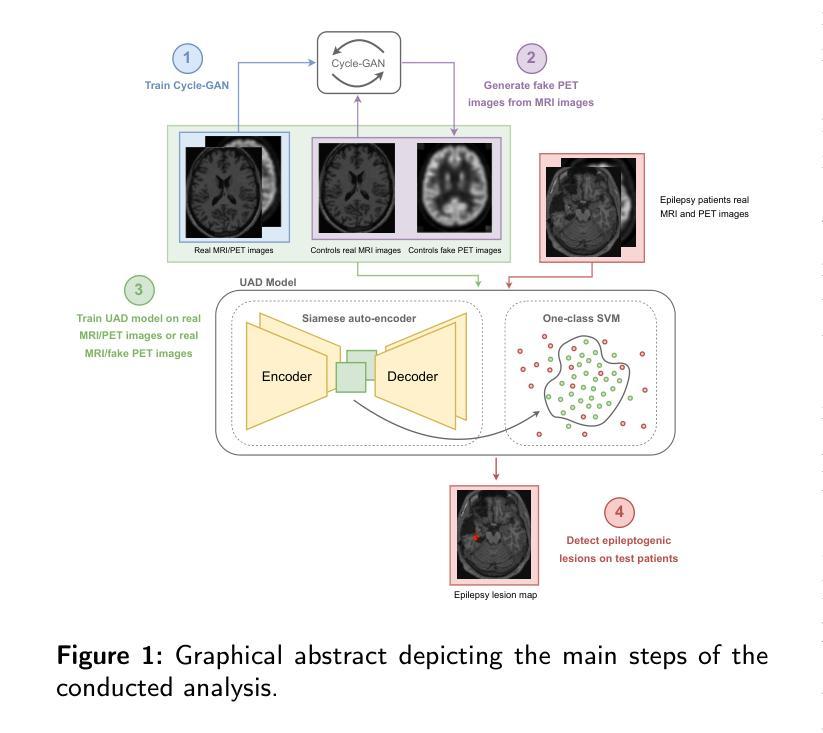
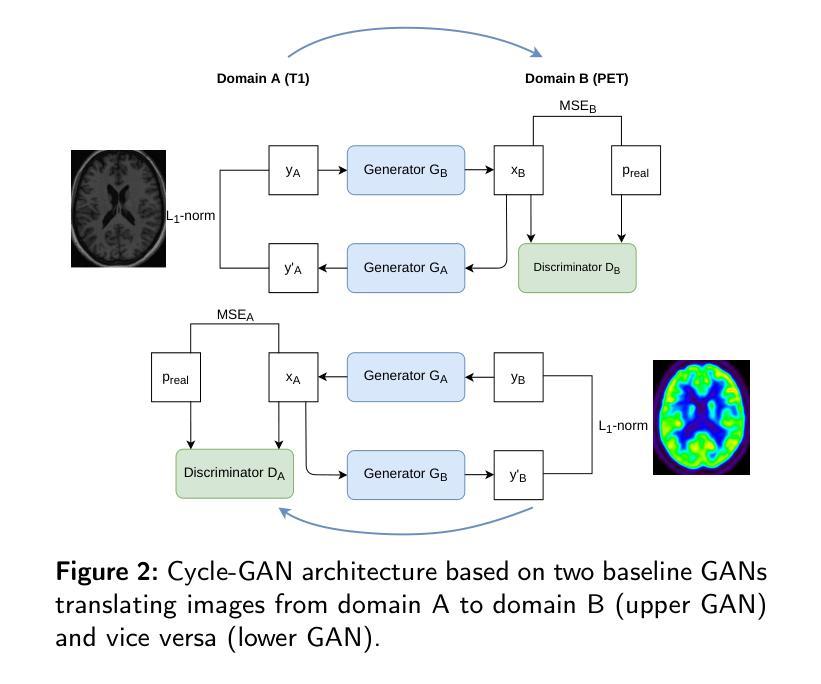
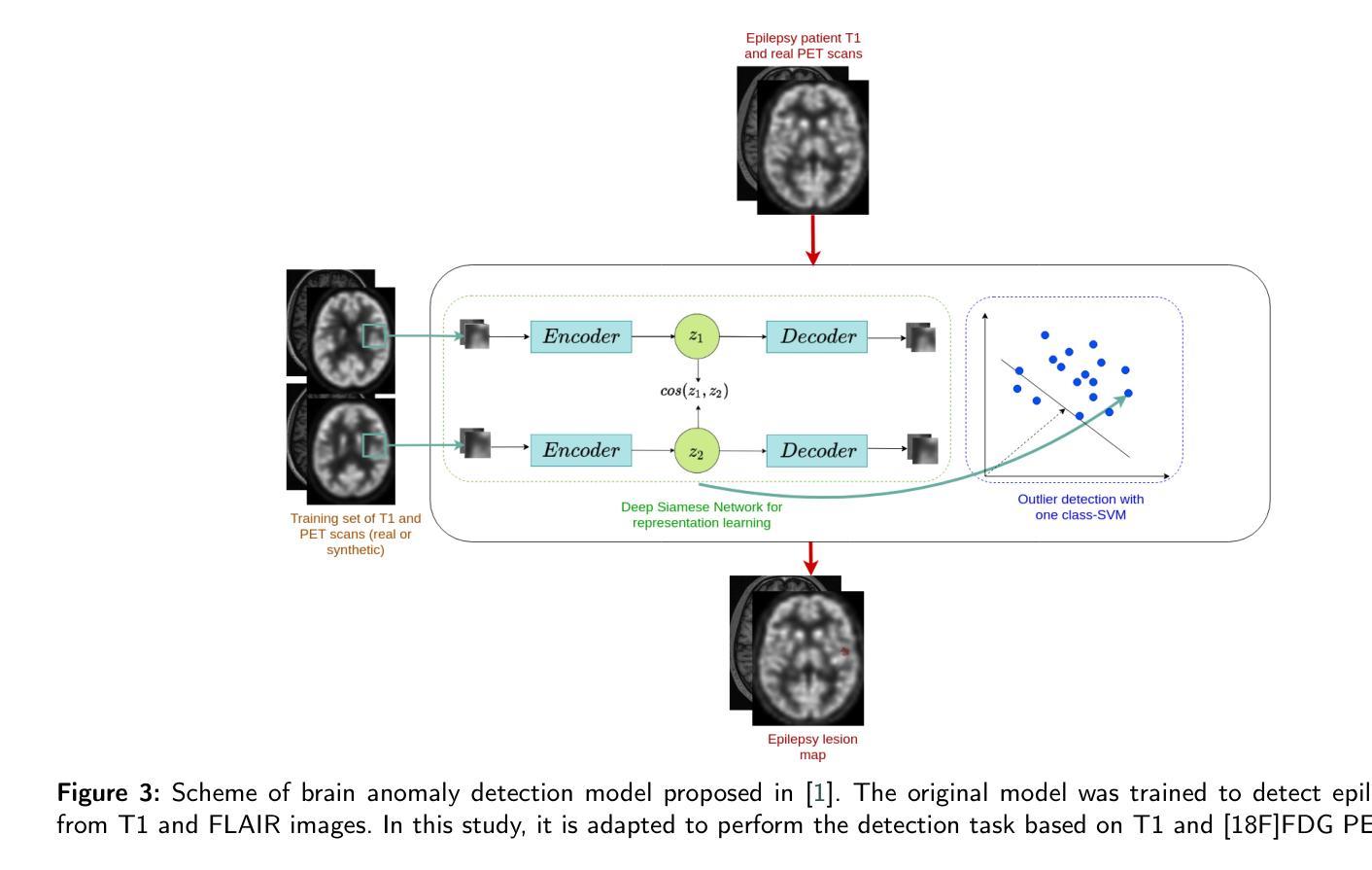
Background and Objective. Research in the cross-modal medical image translation domain has been very productive over the past few years in tackling the scarce availability of large curated multimodality datasets with the promising performance of GAN-based architectures. However, only a few of these studies assessed task-based related performance of these synthetic data, especially for the training of deep models. Method. We design and compare different GAN-based frameworks for generating synthetic brain [18F]fluorodeoxyglucose (FDG) PET images from T1 weighted MRI data. We first perform standard qualitative and quantitative visual quality evaluation. Then, we explore further impact of using these fake PET data in the training of a deep unsupervised anomaly detection (UAD) model designed to detect subtle epilepsy lesions in T1 MRI and FDG PET images. We introduce novel diagnostic task-oriented quality metrics of the synthetic FDG PET data tailored to our unsupervised detection task, then use these fake data to train a use case UAD model combining a deep representation learning based on siamese autoencoders with a OC-SVM density support estimation model. This model is trained on normal subjects only and allows the detection of any variation from the pattern of the normal population. We compare the detection performance of models trained on 35 paired real MR T1 of normal subjects paired either on 35 true PET images or on 35 synthetic PET images generated from the best performing generative models. Performance analysis is conducted on 17 exams of epilepsy patients undergoing surgery. Results. The best performing GAN-based models allow generating realistic fake PET images of control subject with SSIM and PSNR values around 0.9 and 23.8, respectively and in distribution (ID) with regard to the true control dataset. The best UAD model trained on these synthetic normative PET data allows reaching 74% sensitivity. Conclusion. Our results confirm that GAN-based models are the best suited for MR T1 to FDG PET translation, outperforming transformer or diffusion models. We also demonstrate the diagnostic value of these synthetic data for the training of UAD models and evaluation on clinical exams of epilepsy patients. Our code and the normative image dataset are available.
背景与目的:近年来,关于跨模态医学图像翻译领域的研究在解决大型整理多模态数据集稀缺的问题方面取得了丰硕的成果,基于GAN的架构表现出良好的性能。然而,只有少数研究评估了这些合成数据在任务相关方面的性能,尤其是用于训练深度学习模型方面。
方法:我们设计和比较了基于不同GAN的框架,用于从T1加权MRI数据生成合成的大脑氟代脱氧葡萄糖(FDG)PET图像。我们首先进行标准的定性和定量视觉质量评估。然后,我们进一步探索使用这些假PET数据在训练深度无监督异常检测(UAD)模型中的影响,该模型旨在检测T1 MRI和FDG PET图像中的微妙癫痫病灶。我们引入了针对我们的无监督检测任务的新型诊断任务导向型质量指标,用于评估合成FDG PET数据的质量。然后,我们使用这些假数据来训练一个用例UAD模型,该模型结合了基于孪生自编码器的深度表示学习与OC-SVM密度支持估计模型。该模型仅对正常主体进行训练,并允许检测任何与正常人群模式的偏差。我们比较了在35对真实MR T1图像(正常主体)与35张真实PET图像或来自表现最佳的生成模型的35张合成PET图像上训练的模型的检测性能。性能分析是在接受手术的17名癫痫患者身上进行的。
结果:表现最佳的基于GAN的模型能够生成逼真的假PET图像,控制对象的结构相似性度量(SSIM)和峰值信噪比(PSNR)值分别约为0.9和23.8,且在身份分布上与真实控制数据集相符。使用这些合成规范性PET数据训练的最佳UAD模型的敏感性达到74%。
结论:我们的结果证实,基于GAN的模型在MR T1到FDG PET翻译方面最适合,优于Transformer或扩散模型。我们还证明了这些合成数据对于训练UAD模型和评估癫痫患者的临床考试中的诊断价值。我们的代码和规范图像数据集可供使用。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary:
本文探讨了基于GAN架构的跨模态医学图像翻译在生成合成脑[¹⁸F]氟脱氧葡萄糖(FDG)PET图像方面的应用。研究设计并比较了不同GAN框架生成合成图像的效果,特别是在训练用于检测细微癫痫病灶的深度学习模型中的应用。结果表明,GAN模型最适合于生成与真实数据相近的合成PET图像,使用这些合成数据训练的模型在临床癫痫患者检查中显示出诊断价值。代码及数据集可供公开获取。
Key Takeaways:
- GAN模型适用于生成医学图像合成数据,尤其是用于跨模态医学图像翻译领域。
- 研究通过设计不同GAN框架生成合成脑FDG PET图像,从MR T1数据出发。
- 通过对合成图像进行视觉质量评估和定量评估,确定最佳性能的GAN模型。
- 研究探索了使用合成PET数据训练深度学习模型进行癫痫病灶检测的应用。
- 引入针对特定检测任务的新型诊断质量指标来评估合成数据的适用性。
- 使用最佳合成数据训练的UAD模型在癫痫患者检测中达到74%的敏感性。
点此查看论文截图

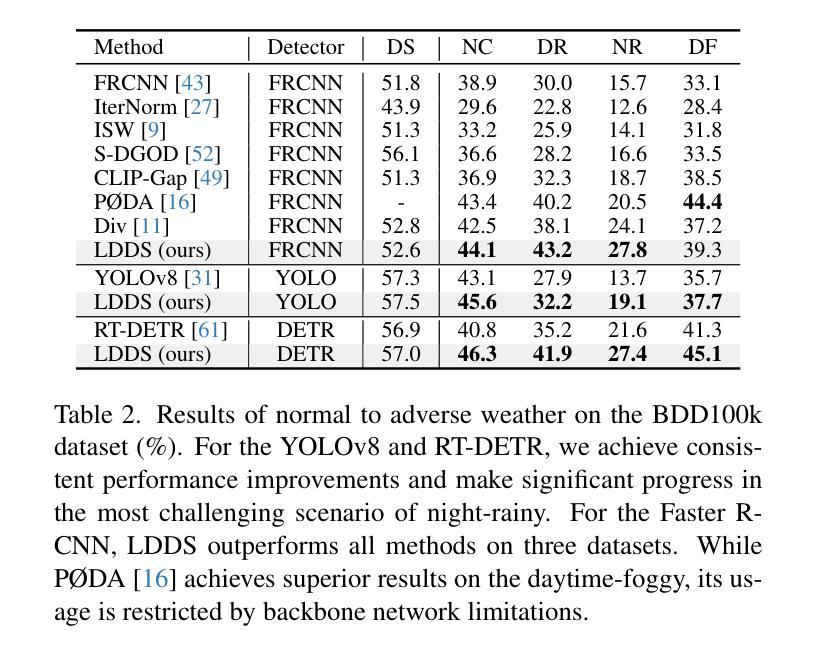
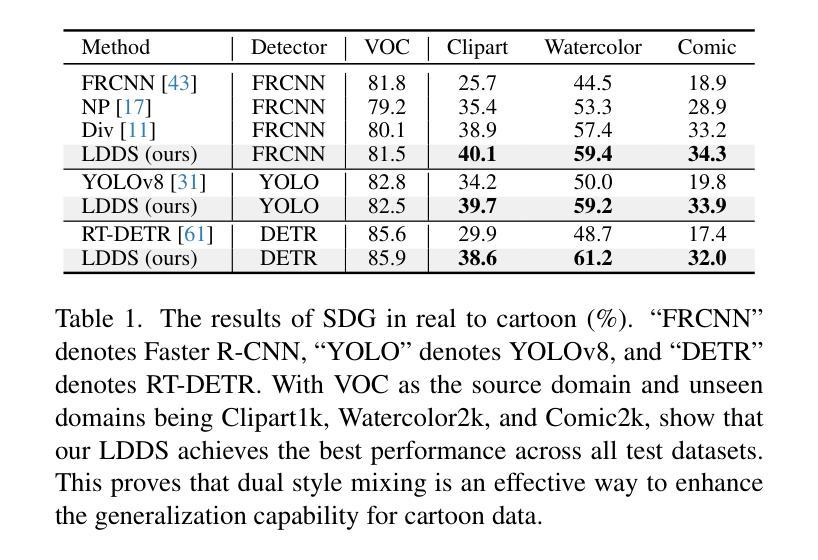
Language-Driven Dual Style Mixing for Single-Domain Generalized Object Detection
Authors:Hongda Qin, Xiao Lu, Zhiyong Wei, Yihong Cao, Kailun Yang, Ningjiang Chen
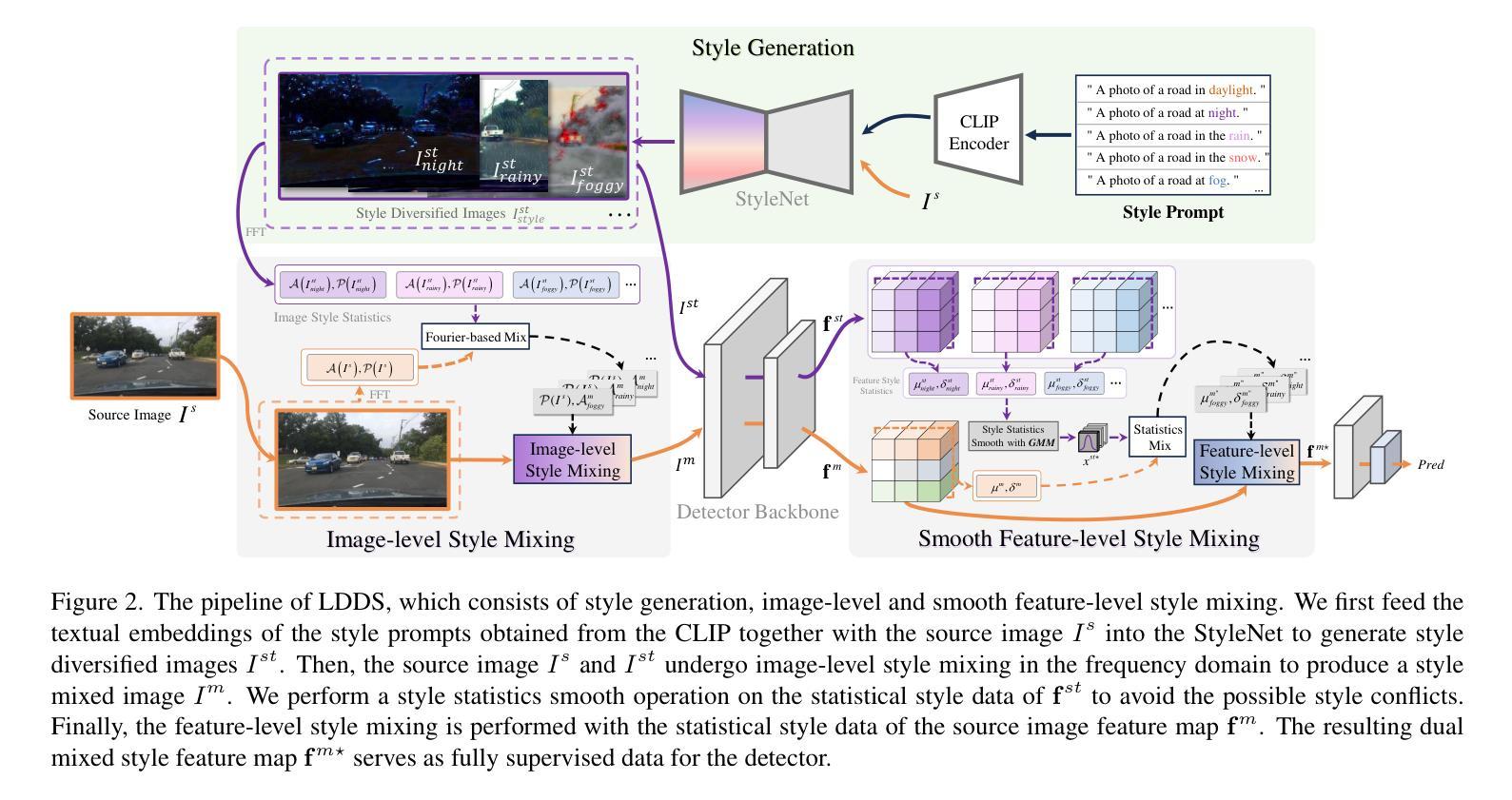
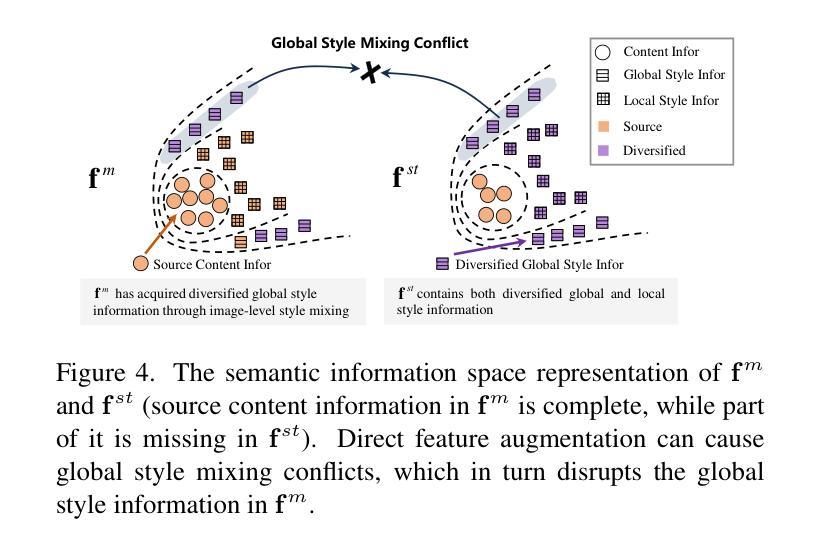
Generalizing an object detector trained on a single domain to multiple unseen domains is a challenging task. Existing methods typically introduce image or feature augmentation to diversify the source domain to raise the robustness of the detector. Vision-Language Model (VLM)-based augmentation techniques have been proven to be effective, but they require that the detector’s backbone has the same structure as the image encoder of VLM, limiting the detector framework selection. To address this problem, we propose Language-Driven Dual Style Mixing (LDDS) for single-domain generalization, which diversifies the source domain by fully utilizing the semantic information of the VLM. Specifically, we first construct prompts to transfer style semantics embedded in the VLM to an image translation network. This facilitates the generation of style diversified images with explicit semantic information. Then, we propose image-level style mixing between the diversified images and source domain images. This effectively mines the semantic information for image augmentation without relying on specific augmentation selections. Finally, we propose feature-level style mixing in a double-pipeline manner, allowing feature augmentation to be model-agnostic and can work seamlessly with the mainstream detector frameworks, including the one-stage, two-stage, and transformer-based detectors. Extensive experiments demonstrate the effectiveness of our approach across various benchmark datasets, including real to cartoon and normal to adverse weather tasks. The source code and pre-trained models will be publicly available at https://github.com/qinhongda8/LDDS.
将单一领域训练的物体检测器推广到多个未见领域是一项具有挑战性的任务。现有方法通常通过图像或特征增强来多样化源领域,以提高检测器的稳健性。基于视觉语言模型(VLM)的增强技术已被证明是有效的,但它们要求检测器的骨干结构与VLM的图像编码器相同,从而限制了检测器框架的选择。为了解决此问题,我们提出了用于单一领域推广的语言驱动双风格混合(LDDS)方法,该方法通过充分利用VLM中的语义信息来多样化源领域。具体来说,我们首先构建提示,将嵌入在VLM中的风格语义转移到图像翻译网络中。这有助于生成具有明确语义信息的风格多样化图像。然后,我们提出在多样化图像和源域图像之间进行图像级别的风格混合。这有效地挖掘了用于图像增强的语义信息,而无需依赖特定的增强选择。最后,我们采用双管道方式进行特征级别的风格混合,使特征增强成为模型无关,并能无缝地与主流检测器框架配合使用,包括单阶段、两阶段和基于变压器的检测器。大量实验证明,我们的方法在各种基准数据集上均有效,包括从现实到卡通和从正常到恶劣天气任务。源代码和预训练模型将在https://github.com/qinhongda8/LDDS上公开提供。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF The source code and pre-trained models will be publicly available at https://github.com/qinhongda8/LDDS
Summary
基于视觉语言模型(VLM)的单域泛化挑战可通过语言驱动双风格混合(LDDS)技术来解决。该方法充分利用VLM中的风格语义信息生成多样化图像,通过图像级风格混合和特征级风格混合,提高了检测器对未见域的泛化能力。实验证明,该方法在不同基准数据集上均有效。
Key Takeaways
- LDDS方法解决了将单一域训练的物体检测器推广到多个未见域的挑战。
- LDDS利用VLM中的风格语义信息生成多样化图像,提高检测器的泛化能力。
- LDDS通过图像级风格混合挖掘语义信息,不依赖于特定增强选择。
- LDDS采用双管道方式实现特征级风格混合,可与主流检测器框架无缝协作。
- LDDS方法在各种基准数据集上进行广泛实验验证,包括真实到卡通和正常到恶劣天气任务。
- LDDS的源代码和预训练模型将公开提供,便于其他研究者使用和改进。
点此查看论文截图


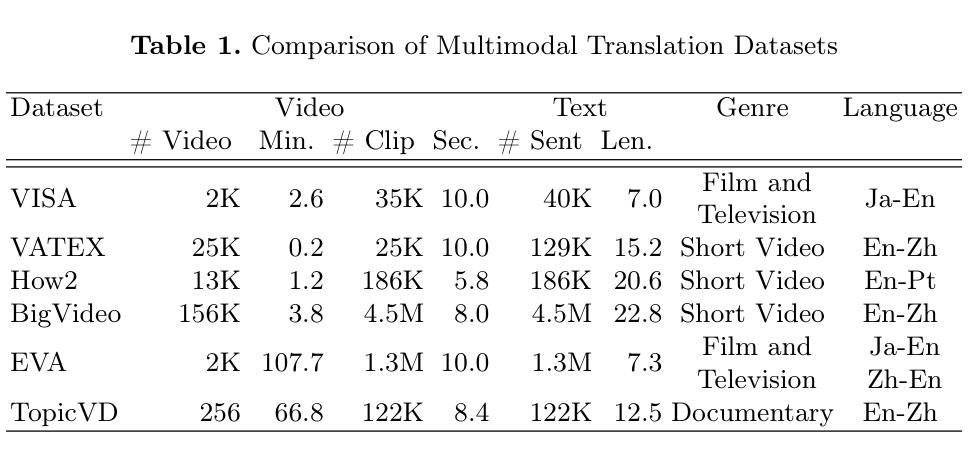
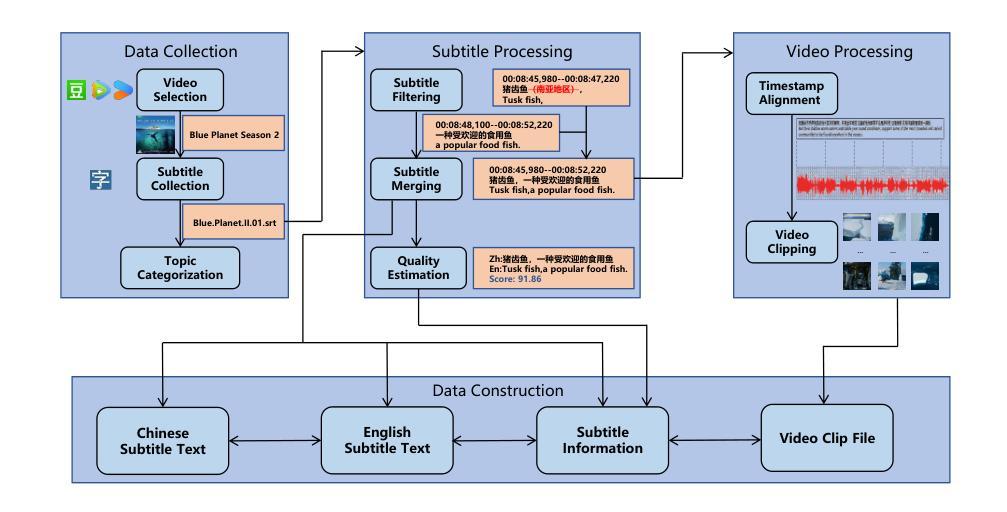
TopicVD: A Topic-Based Dataset of Video-Guided Multimodal Machine Translation for Documentaries
Authors:Jinze Lv, Jian Chen, Zi Long, Xianghua Fu, Yin Chen
Most existing multimodal machine translation (MMT) datasets are predominantly composed of static images or short video clips, lacking extensive video data across diverse domains and topics. As a result, they fail to meet the demands of real-world MMT tasks, such as documentary translation. In this study, we developed TopicVD, a topic-based dataset for video-supported multimodal machine translation of documentaries, aiming to advance research in this field. We collected video-subtitle pairs from documentaries and categorized them into eight topics, such as economy and nature, to facilitate research on domain adaptation in video-guided MMT. Additionally, we preserved their contextual information to support research on leveraging the global context of documentaries in video-guided MMT. To better capture the shared semantics between text and video, we propose an MMT model based on a cross-modal bidirectional attention module. Extensive experiments on the TopicVD dataset demonstrate that visual information consistently improves the performance of the NMT model in documentary translation. However, the MMT model’s performance significantly declines in out-of-domain scenarios, highlighting the need for effective domain adaptation methods. Additionally, experiments demonstrate that global context can effectively improve translation performance. % Dataset and our implementations are available at https://github.com/JinzeLv/TopicVD
目前大多数多模态机器翻译(MMT)数据集主要由静态图像或短视频片段组成,缺乏跨不同领域和主题的大量视频数据。因此,它们无法满足现实世界中的MMT任务需求,如纪录片翻译。本研究中,我们开发了TopicVD,这是一个基于视频支持的多模态机器翻译纪录片数据集,旨在推动该领域的研究。我们从纪录片中收集了视频字幕对,并将其分为经济、自然等八个主题,以促进视频指导的MMT中的领域自适应研究。此外,我们还保留了其上下文信息,以支持在视频指导的MMT中利用纪录片的全球语境的研究。为了更好地捕捉文本和视频之间的共享语义,我们提出了一种基于跨模态双向注意力模块的多模态翻译模型。在TopicVD数据集上的大量实验表明,视觉信息始终提高了神经机器翻译模型在纪录片翻译方面的性能。然而,在多模态翻译模型处理跨领域场景时性能显著下降,这凸显了有效领域自适应方法的必要性。此外,实验表明全局上下文可以有效地提高翻译性能。数据集及我们的实现可访问 https://github.com/JinzeLv/TopicVD 了解。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF NLDB 2025
Summary:
针对当前多媒体机器翻译(MMT)数据集缺乏涵盖广泛主题的视频数据的问题,本文提出TopicVD数据集,旨在推进视频辅助多媒体机器翻译领域的研究。通过收集纪录片视频字幕对,并按主题分类,同时保留上下文信息,研究视频与文本之间的共享语义。此外,引入基于跨模态双向注意力模块的多媒体机器翻译模型。实验表明,视频信息可提高翻译性能,但跨领域场景下性能下降,显示需要有效的领域适应方法。全球语境可有效提升翻译性能。数据集及相关实现已公开在GitHub上提供。
Key Takeaways:
- TopicVD数据集针对多媒体机器翻译设计,尤其适用于纪录片翻译研究。
- TopicVD包含多种主题的视频数据,有利于领域适应研究。
- 上下文信息得以保留以支持相关研究。
- 提出基于跨模态双向注意力模块的多媒体机器翻译模型。
- 视频信息能改善翻译性能。
- 在跨领域场景下,多媒体机器翻译模型性能显著下降,显示对有效领域适应方法的需求。
点此查看论文截图

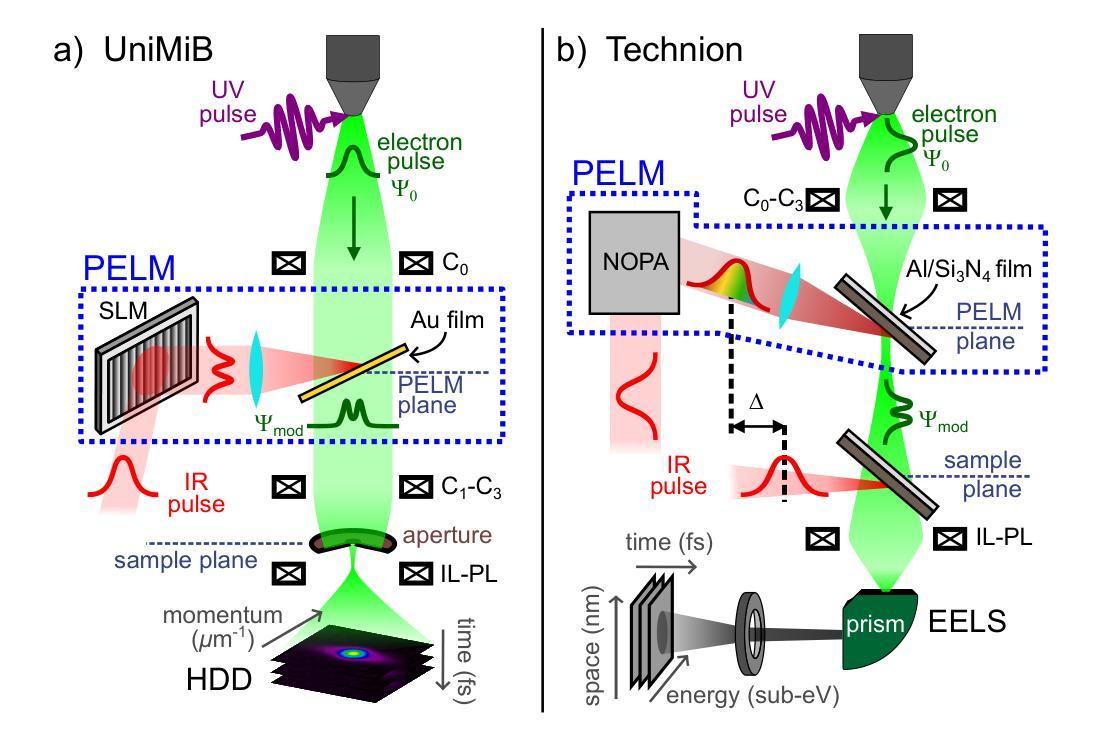
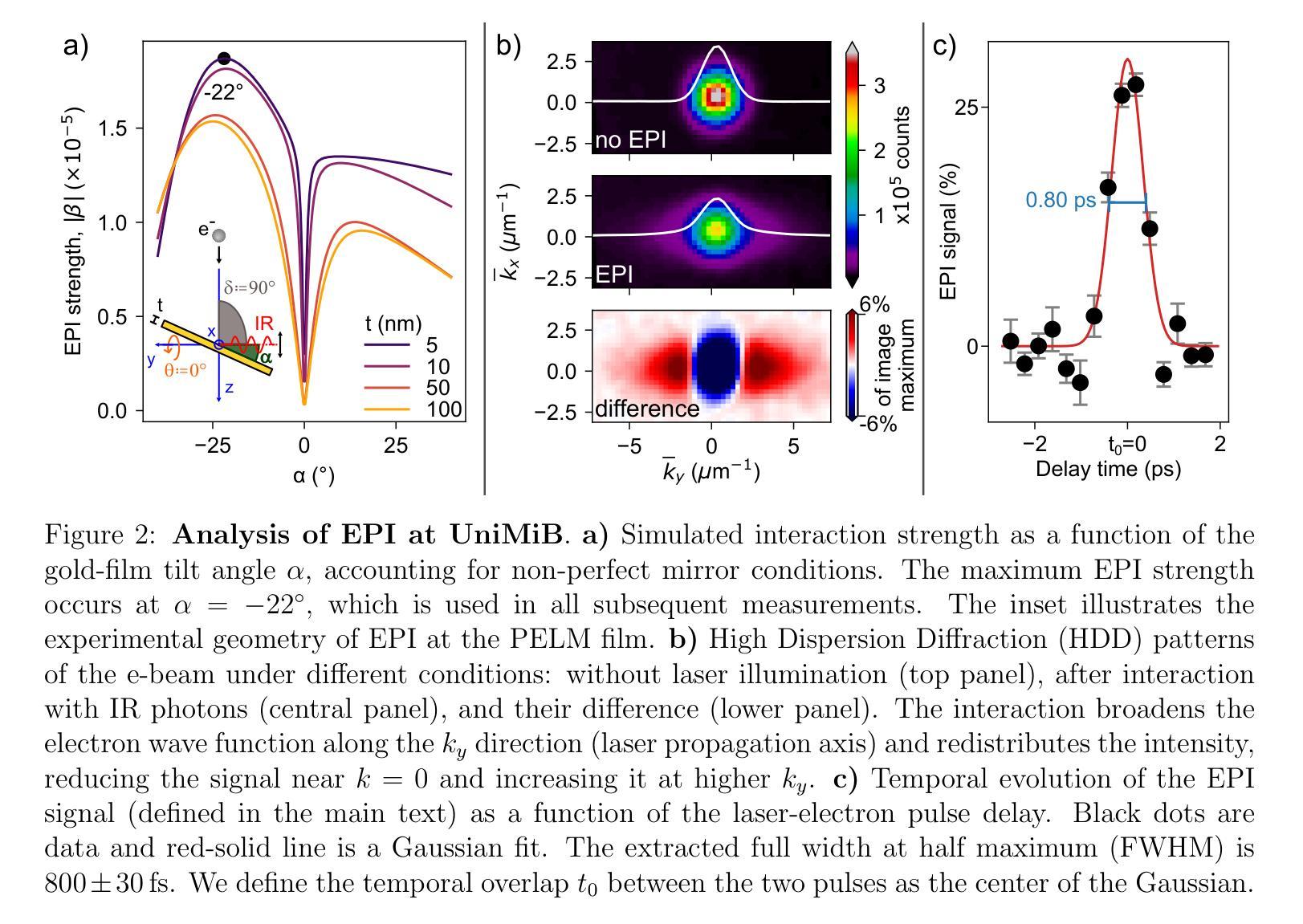
Realization of a Pre-Sample Photonic-based Free-Electron Modulator in Ultrafast Transmission Electron Microscopes
Authors:Beatrice Matilde Ferrari, Cameron James Richard Duncan, Michael Yannai, Raphael Dahan, Paolo Rosi, Irene Ostroman, Maria Giulia Bravi, Arthur Niedermayr, Tom Lenkiewicz Abudi, Yuval Adiv, Tal Fishman, Sang Tae Park, Dan Masiel, Thomas Lagrange, Fabrizio Carbone, Vincenzo Grillo, F. Javier García de Abajo, Ido Kaminer, Giovanni Maria Vanacore
Spatial and temporal light modulation is a well-established technology that enables dynamic shaping of the phase and amplitude of optical fields, significantly enhancing the resolution and sensitivity of imaging methods. Translating this capability to electron beams is highly desirable within the framework of a transmission electron microscope (TEM) to benefit from the nanometer spatial resolution of these instruments. In this work, we report on the experimental realization of a photonic-based free-electron modulator integrated into the column of two ultrafast TEMs for pre-sample electron-beam shaping. Electron-photon interaction is employed to coherently modulate both the transverse and longitudinal components of the electron wave function, while leveraging dynamically controlled optical fields and tailored design of electron-laser-sample interaction geometry. Using energy- and momentum-resolved electron detection, we successfully reconstruct the shaped electron wave function at the TEM sample plane. These results demonstrate the ability to manipulate the electron wave function before probing the sample, paving the way for the future development of innovative imaging methods in ultrafast electron microscopy.
空间和时间光调制是一项成熟的技术,能够动态地改变光场的相位和振幅,从而极大地提高成像方法的分辨率和灵敏度。在透射电子显微镜(TEM)的框架下,将这一能力应用到电子束上是非常理想的,以利用这些仪器的纳米空间分辨率。在这项工作中,我们报告了将光子基自由电子调制器集成到两台超快透射电子显微镜的支柱中,用于样品前的电子束整形。利用电子-光子相互作用,相干地调制电子波函数的横向和纵向分量,同时利用动态控制的光场和定制的电子-激光-样品相互作用几何结构。通过能量和动量解析的电子检测,我们成功地在透射电子显微镜样品平面上重建了整形后的电子波函数。这些结果证明了在探测样品之前操作电子波函数的能力,为超快电子显微镜中创新成像方法的未来发展铺平了道路。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 14 pages, 5, figures, includes supplementary information, journal paper
Summary
空间和时间光调制技术已广泛应用于光学领域,实现了对光场相位和振幅的动态调控,大大提高了成像方法的分辨率和灵敏度。本文将此技术应用于透射电子显微镜(TEM)中,实现了电子束的预样本调控。该研究利用电子光子相互作用,对电子波函数的横向和纵向成分进行相干调控,同时采用动态控制的光场和定制的电子激光样品相互作用几何设计。通过能量和动量解析的电子检测,成功重建了样品平面上的电子波函数。这一成果展示了在探测样品之前操控电子波函数的能力,为超快电子显微镜中创新成像方法的发展铺平了道路。
Key Takeaways
- 空间和时间光调制技术已广泛应用于光学领域,实现对光场相位和振幅的动态调控。
- 技术被成功应用于透射电子显微镜(TEM)中,实现了电子束的预样本调控。
- 通过电子光子相互作用对电子波函数的横向和纵向成分进行相干调控。
- 利用动态控制的光场和定制的几何设计实现电子激光样品相互作用。
- 通过能量和动量解析的电子检测成功重建了样品平面上的电子波函数。
- 该技术展示了在探测样品前操控电子波函数的能力。
点此查看论文截图