⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-05-14 更新
DialogueReason: Rule-Based RL Sparks Dialogue Reasoning in LLMs
Authors:Yubo Shu, Zhewei Huang, Xin Wu, Chen Hu, Shuchang Zhou, Daxin Jiang
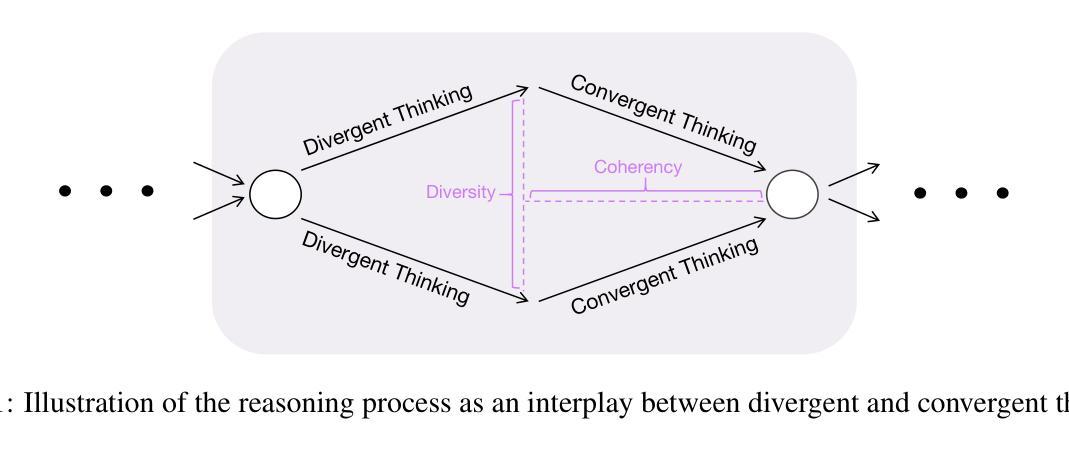
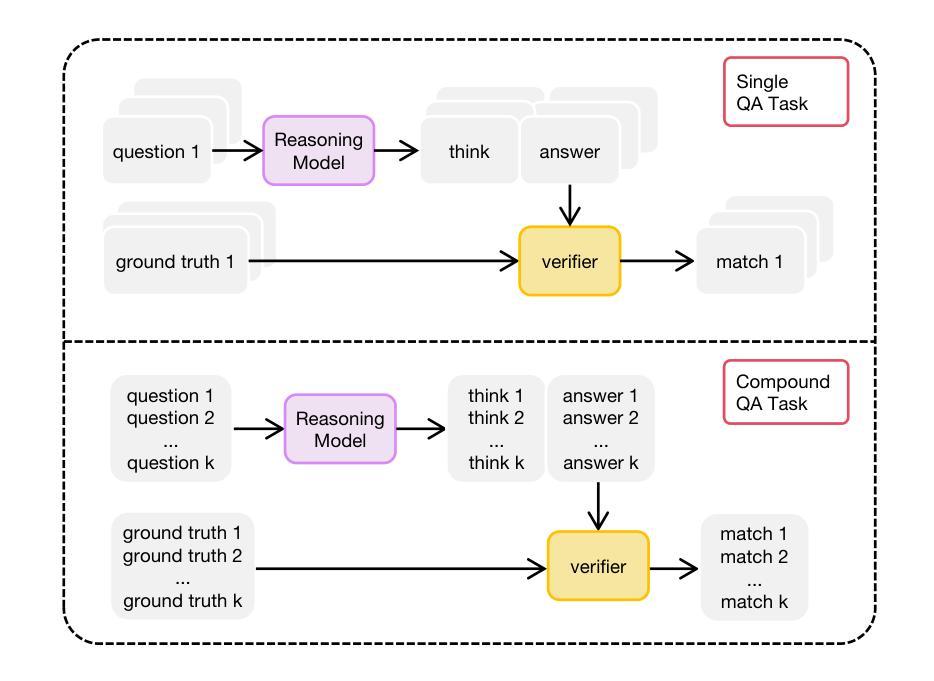
We propose DialogueReason, a reasoning paradigm that uncovers the lost roles in monologue-style reasoning models, aiming to boost diversity and coherency of the reasoning process. Recent advances in RL-based large reasoning models have led to impressive long CoT capabilities and high performance on math and science benchmarks. However, these reasoning models rely mainly on monologue-style reasoning, which often limits reasoning diversity and coherency, frequently recycling fixed strategies or exhibiting unnecessary shifts in attention. Our work consists of an analysis of monologue reasoning patterns and the development of a dialogue-based reasoning approach. We first introduce the Compound-QA task, which concatenates multiple problems into a single prompt to assess both diversity and coherency of reasoning. Our analysis shows that Compound-QA exposes weaknesses in monologue reasoning, evidenced by both quantitative metrics and qualitative reasoning traces. Building on the analysis, we propose a dialogue-based reasoning, named DialogueReason, structured around agents, environment, and interactions. Using PPO with rule-based rewards, we train open-source LLMs (Qwen-QWQ and Qwen-Base) to adopt dialogue reasoning. We evaluate trained models on MATH, AIME, and GPQA datasets, showing that the dialogue reasoning model outperforms monologue models under more complex compound questions. Additionally, we discuss how dialogue-based reasoning helps enhance interpretability, facilitate more intuitive human interaction, and inspire advances in multi-agent system design.
我们提出一种名为DialogueReason的推理范式,旨在揭示独白式推理模型中的缺失角色,以提升推理过程的多样性和连贯性。最近基于RL的大型推理模型的进步展现了令人印象深刻的长期CoT能力,并在数学和科学基准测试中取得了高性能。然而,这些推理模型主要依赖于独白式推理,这常常限制了推理的多样性和连贯性,经常重复使用固定策略或表现出不必要的注意力转移。我们的工作包括对独白推理模式的分析和基于对话的推理方法的开发。我们首先引入Compound-QA任务,它将多个问题合并到一个提示中来评估推理的多样性和连贯性。我们的分析表明,Compound-QA暴露了独白推理的弱点,这由定量指标和定性推理轨迹证明。在分析的基础上,我们提出了基于对话的推理方式,名为DialogueReason,其结构围绕代理、环境和交互。我们使用带有基于规则的奖励的PPO来训练开源LLM(Qwen-QWQ和Qwen-Base)以采用对话推理。我们在MATH、AIME和GPQA数据集上评估训练模型,结果表明对话推理模型在更复杂的问题组合中表现优于独白模型。此外,我们还讨论了基于对话的推理如何帮助增强可解释性、促进更直观的人类互动,并激发多代理系统设计的进步。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文提出一种名为DialogueReason的对话式推理范式,旨在解决单口式推理模型中丢失的角色问题,以提升推理过程的多样性和连贯性。通过分析单口推理模式并发展基于对话的推理方法,我们引入了Compound-QA任务,该任务将多个问题串联成一个提示,以评估推理的多样性和连贯性。基于分析,我们提出一种对话式推理,名为DialogueReason,以代理、环境和交互为中心。使用带有规则奖励的PPO进行训练,我们在MATH、AIME和GPQA数据集上评估了训练模型,结果表明对话式推理模型在复杂复合问题上的表现优于单口模型。
Key Takeaways
- DialogueReason是一种对话式推理范式,旨在解决单口式推理模型的多样性和连贯性问题。
- Compound-QA任务被用来评估推理的多样性和连贯性,通过串联多个问题来创建一个提示。
- 单口推理模型在Compound-QA中表现出弱点,需要通过对话式推理模型来改善。
- DialogueReason模型采用代理、环境和交互的结构,使用PPO和规则奖励进行训练。
- 对话式推理模型在复杂复合问题上的表现优于单口模型。
- 对话式推理有助于提高模型的解释性,促进更直观的人机交互。
点此查看论文截图


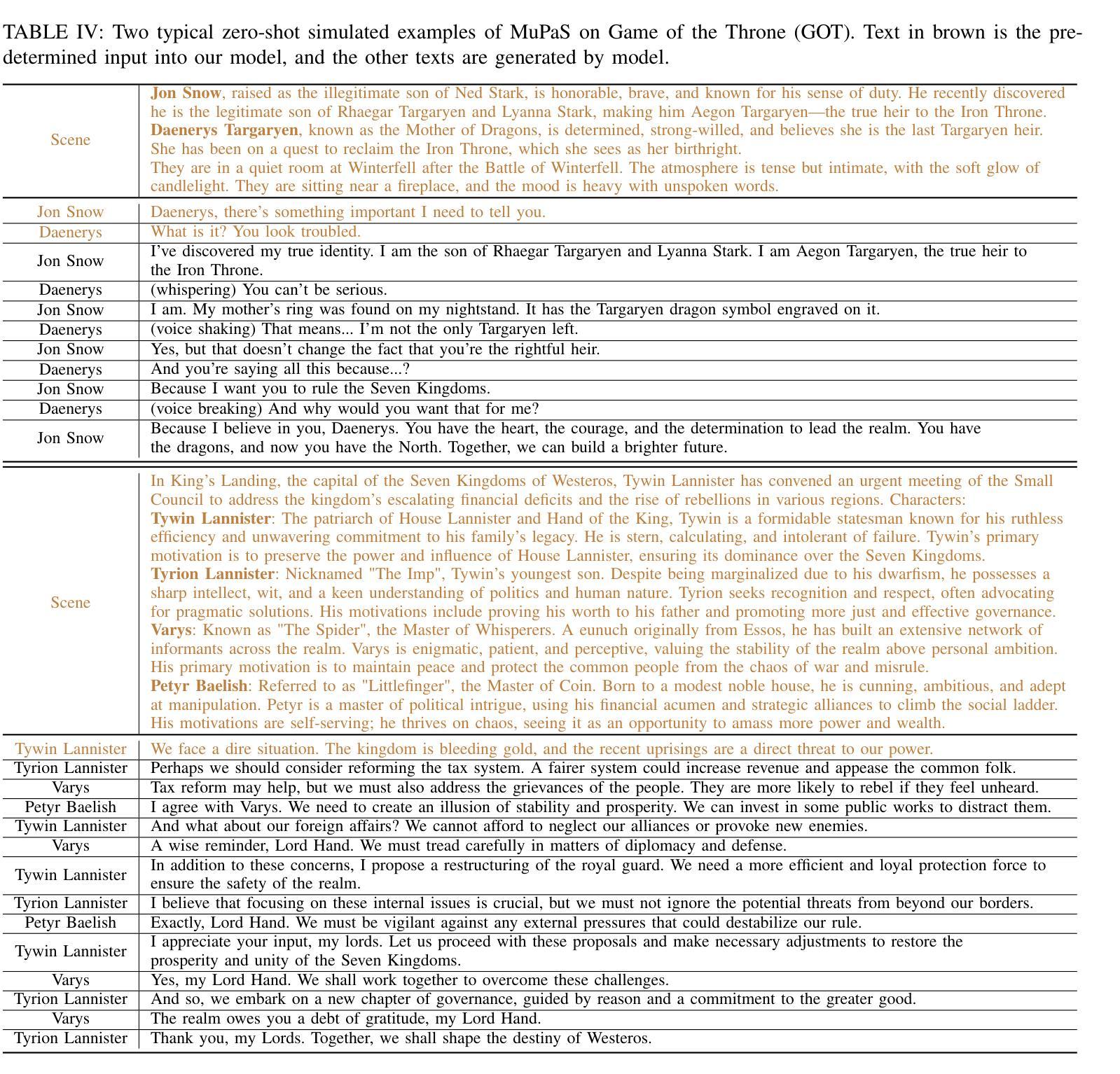
Multi-Party Supervised Fine-tuning of Language Models for Multi-Party Dialogue Generation
Authors:Xiaoyu Wang, Ningyuan Xi, Teng Chen, Qingqing Gu, Yue Zhao, Xiaokai Chen, Zhonglin Jiang, Yong Chen, Luo Ji
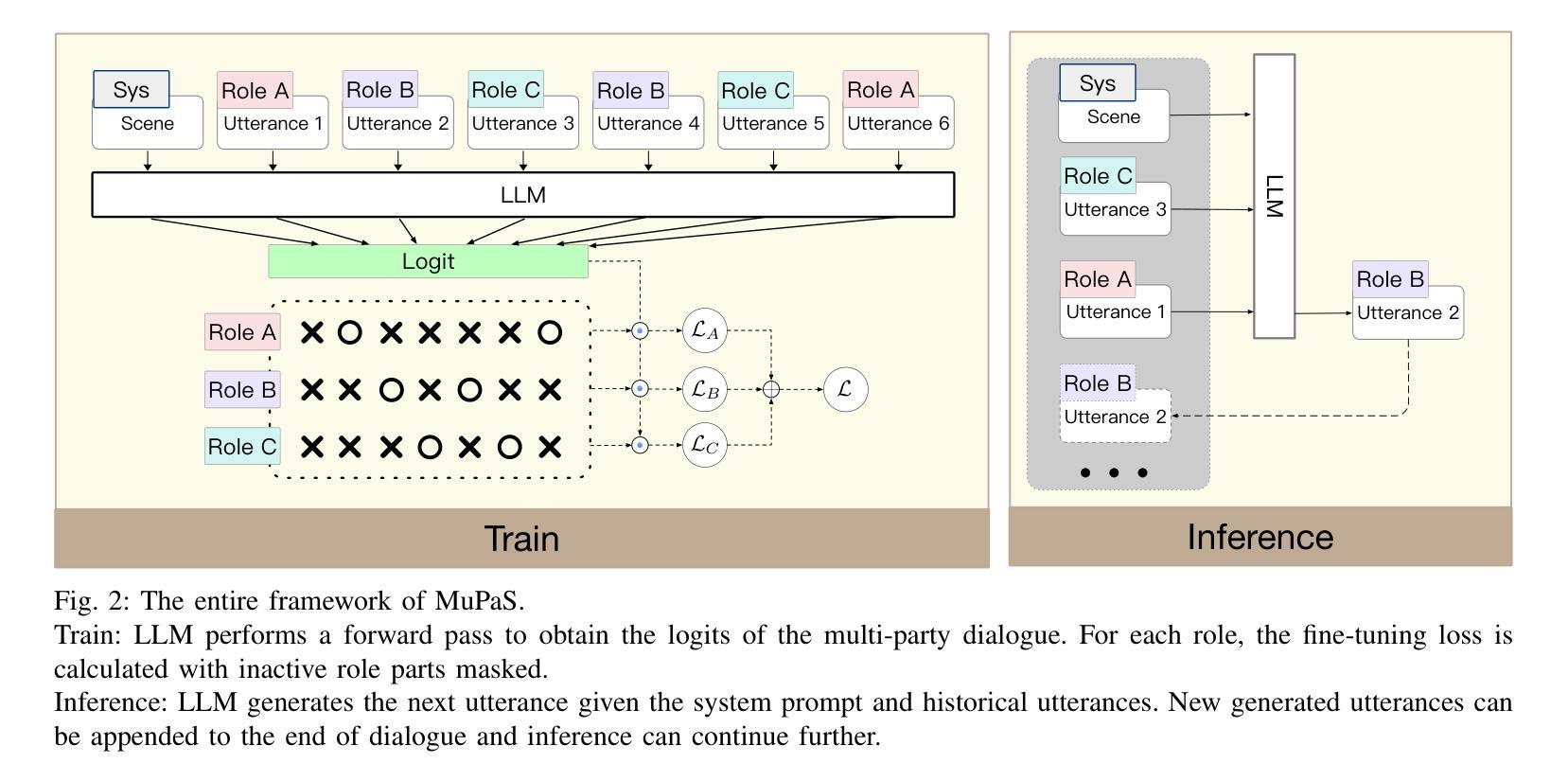
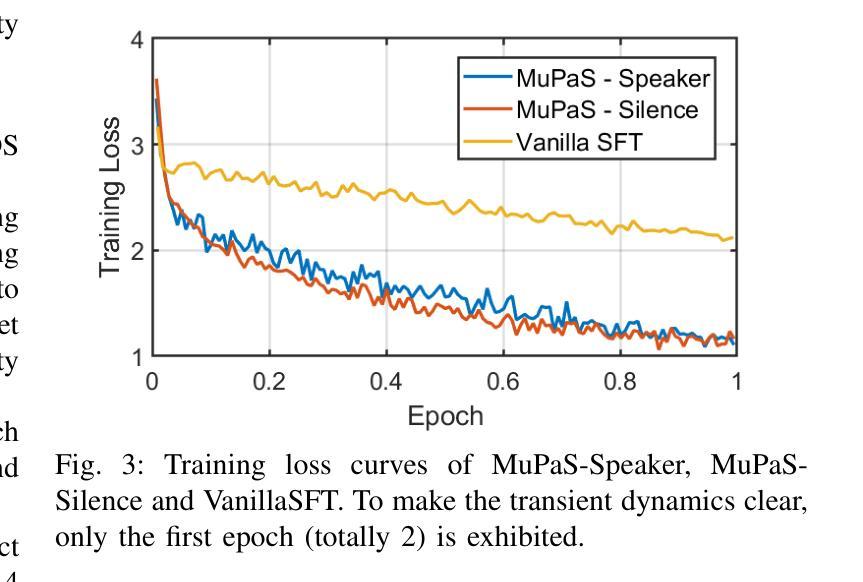
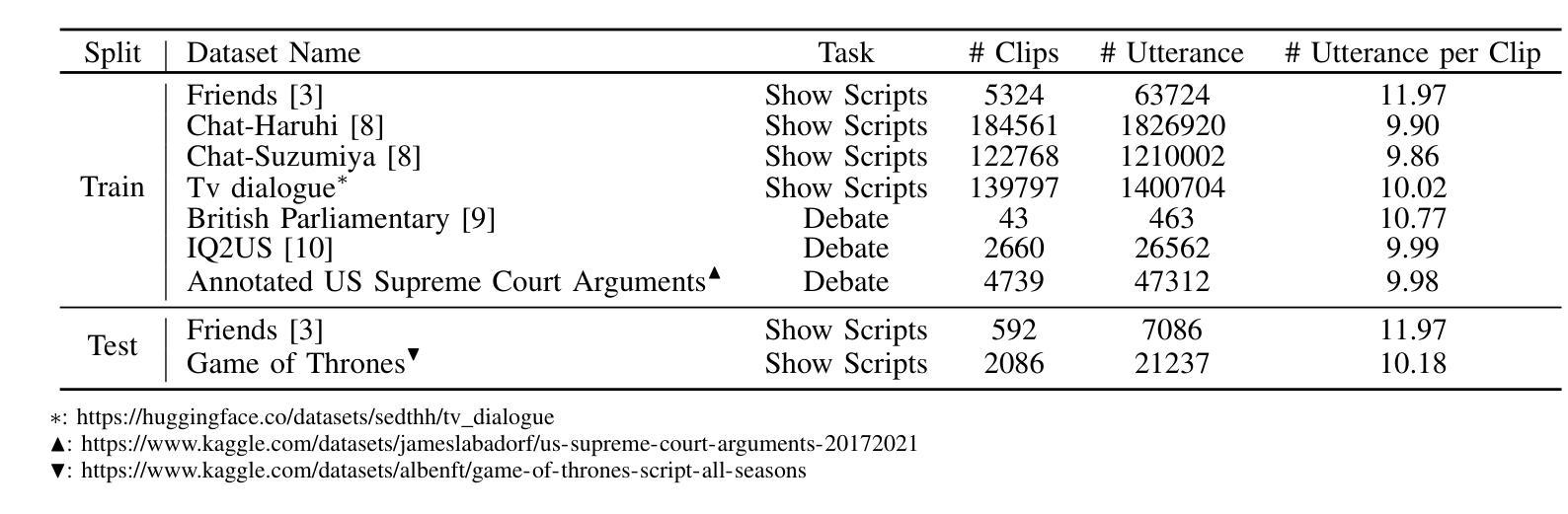
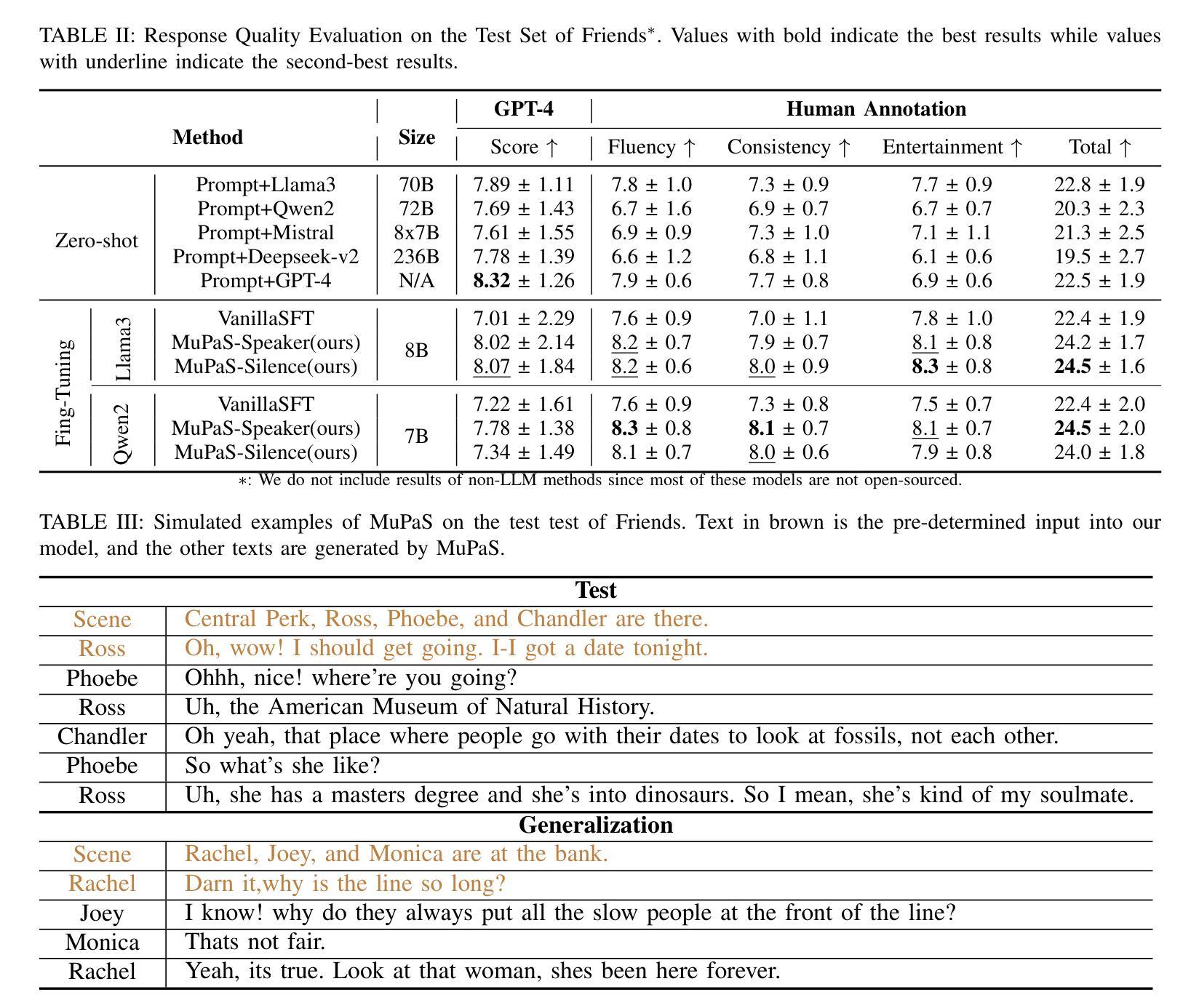
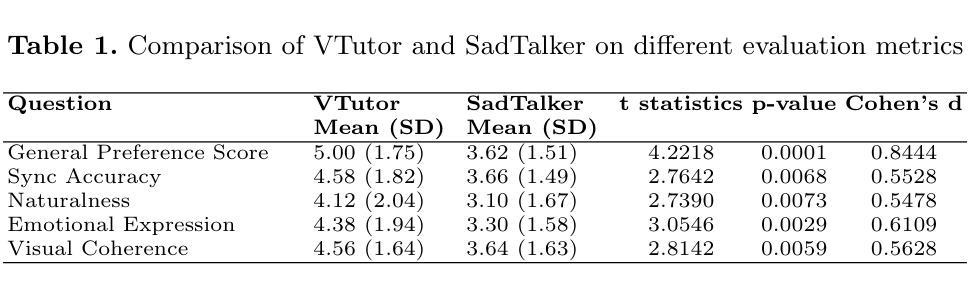
Large Language Models (LLM) are usually fine-tuned to participate in dyadic or two-party dialogues, which can not adapt well to multi-party dialogues (MPD), which hinders their applications in such scenarios including multi-personal meetings, discussions and daily communication. Previous LLM-based researches mainly focus on the multi-agent framework, while their base LLMs are still pairwisely fine-tuned. In this work, we design a multi-party fine-tuning framework (MuPaS) for LLMs on the multi-party dialogue datasets, and prove such a straightforward framework can let the LLM align with the multi-party conversation style efficiently and effectively. We also design two training strategies which can convert MuPaS into the MPD simulator. Substantial experiments show that MuPaS can achieve state-of-the-art multi-party response, higher accuracy of the-next-speaker prediction, higher human and automatic evaluated utterance qualities, and can even generate reasonably with out-of-distribution scene, topic and role descriptions. The MuPaS framework bridges the LLM training with more complicated multi-party applications, such as conversation generation, virtual rehearsal or meta-universe.
大型语言模型(LLM)通常经过微调以参与二元或两方对话,但它们无法很好地适应多方对话(MPD),这阻碍了它们在包括多人会议、讨论和日常交流等场景中的应用。之前基于LLM的研究主要集中在多代理框架上,而它们的基础LLM仍然是对两两对话进行微调。在这项工作中,我们为LLM设计了多方微调框架(MuPaS),该框架适用于多方对话数据集。我们证明这种简单的框架可以让LLM高效且有效地适应多方对话风格。我们还设计了两种训练策略,可以将MuPaS转化为MPD模拟器。大量实验表明,MuPaS可以实现最新的多方响应、更高的下一位发言者预测准确率、更高的人类和自动评估的话语质量,并且可以在离分布场景、主题和角色描述中生成合理的响应。MuPaS框架将LLM训练与更复杂的多方应用(如对话生成、虚拟排练或元宇宙)联系起来。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by IJCNN 2025
Summary
大型语言模型(LLM)在应对多方对话(MPD)时存在局限性,主要应用于双人对话场景。针对这一问题,本研究设计了多党微调框架(MuPaS),在多方对话数据集上对LLM进行训练,以高效适应多方对话场景。实验表明,MuPaS可实现前沿的多方响应能力,提高预测下一位发言者的准确性,提高人机评估的话语质量,并可在场景、话题和角色描述超出分布的情况下生成合理的响应。MuPaS框架为大型语言模型与更复杂的多方对话应用之间的桥梁。
Key Takeaways
- 大型语言模型(LLM)在多方对话(MPD)场景中表现不佳,主要局限于双人对话场景。
- 提出了一种多党微调框架(MuPaS),用于训练大型语言模型以更好地适应多方对话场景。
- MuPaS通过设计两种训练策略来模拟实际的多方对话环境。
- 实验表明,MuPaS在多方响应能力、预测下一位发言者的准确性以及话语质量方面达到了最新水平。
- MuPaS框架能够生成合理的响应,即使在场景、话题和角色描述超出分布的情况下也能保持表现。
- MuPaS填补了大型语言模型与更复杂的多方对话应用之间的鸿沟。
点此查看论文截图