⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-05-14 更新
Learning Dynamics in Continual Pre-Training for Large Language Models
Authors:Xingjin Wang, Howe Tissue, Lu Wang, Linjing Li, Daniel Dajun Zeng
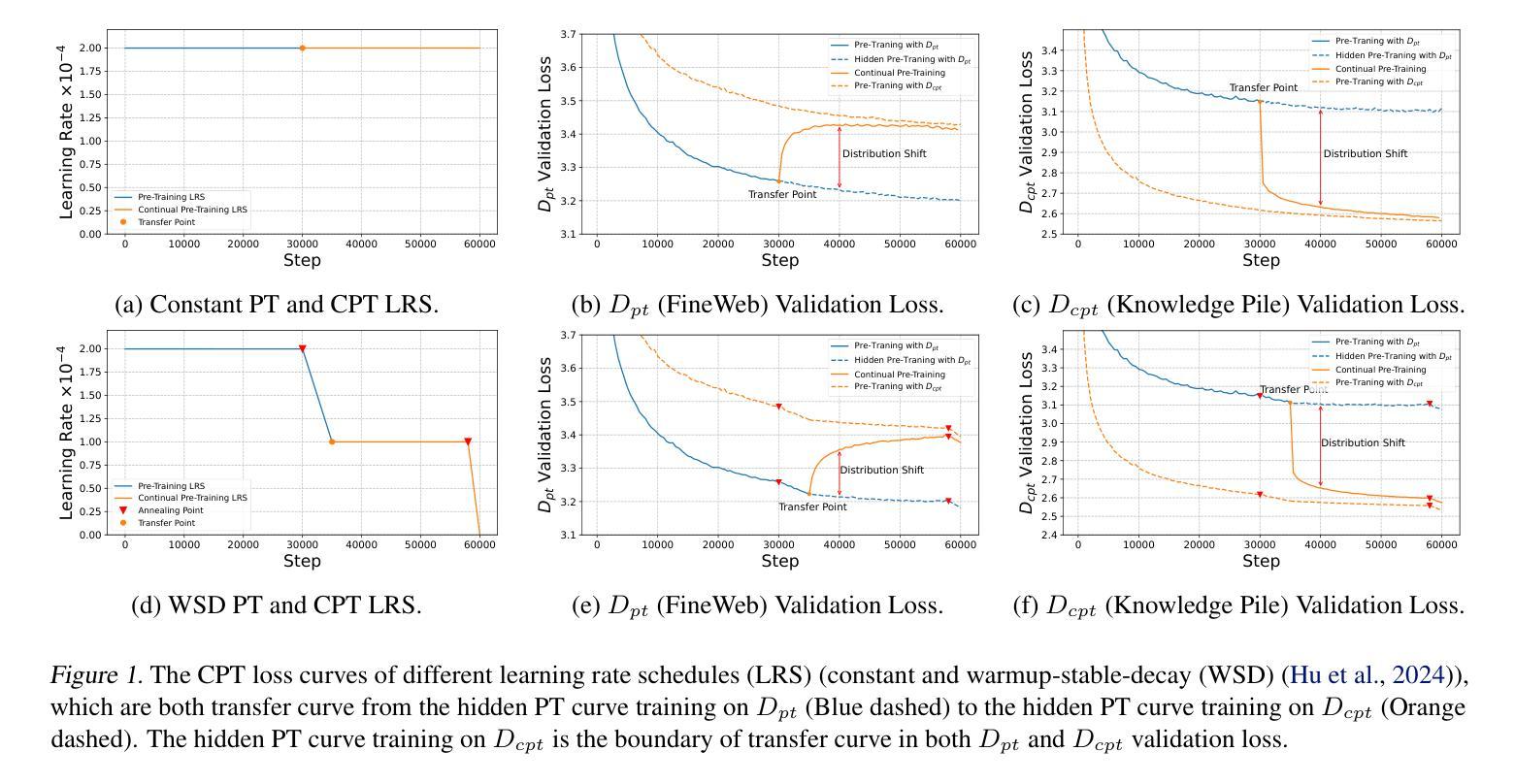
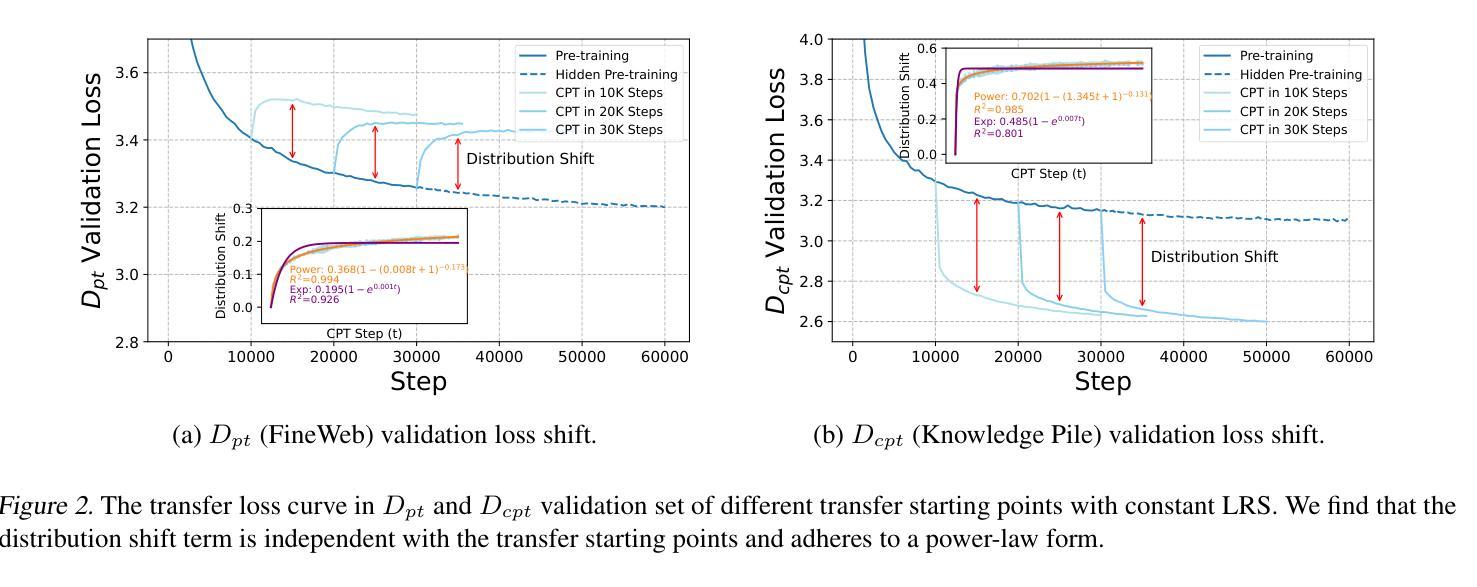
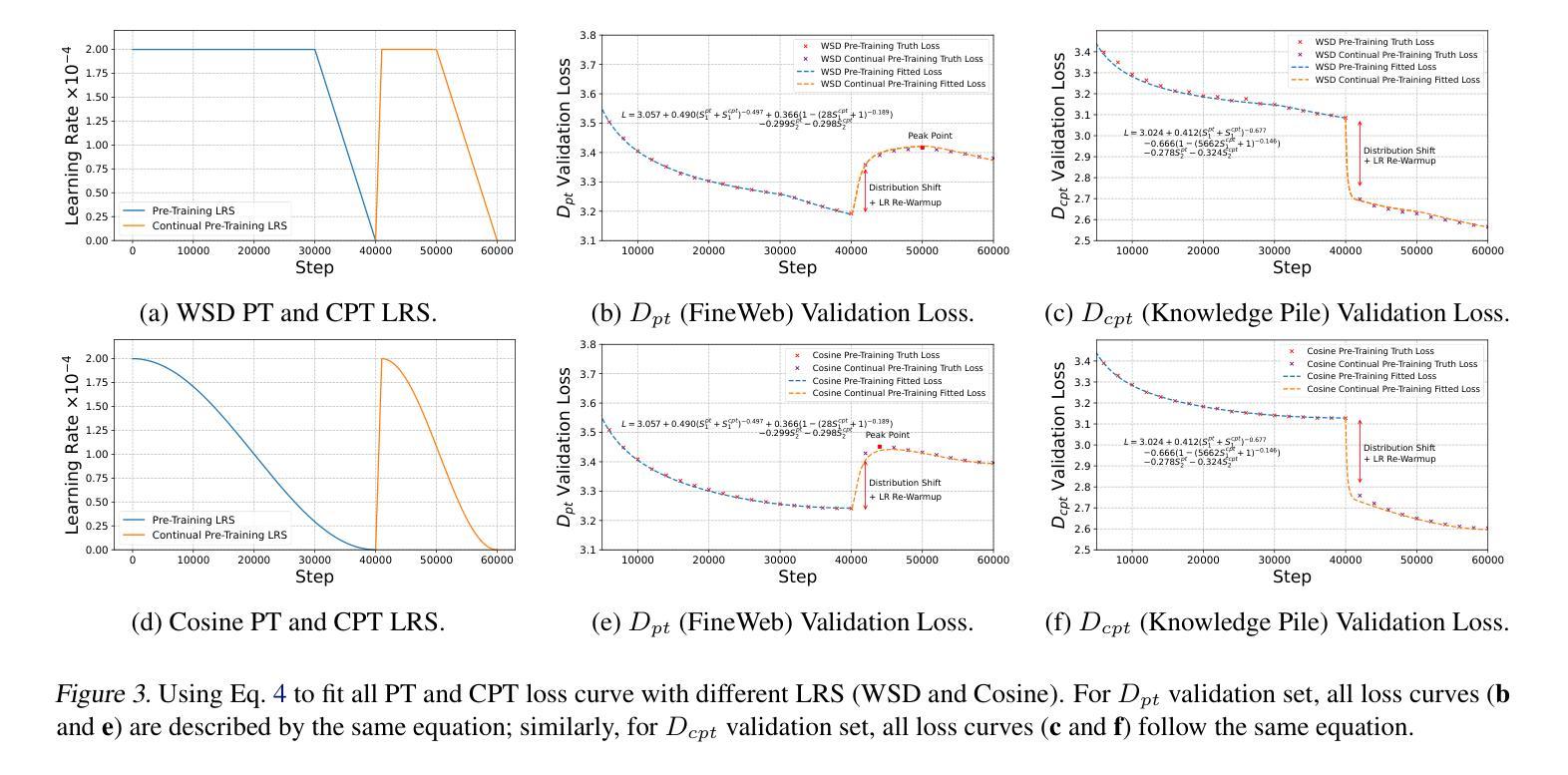
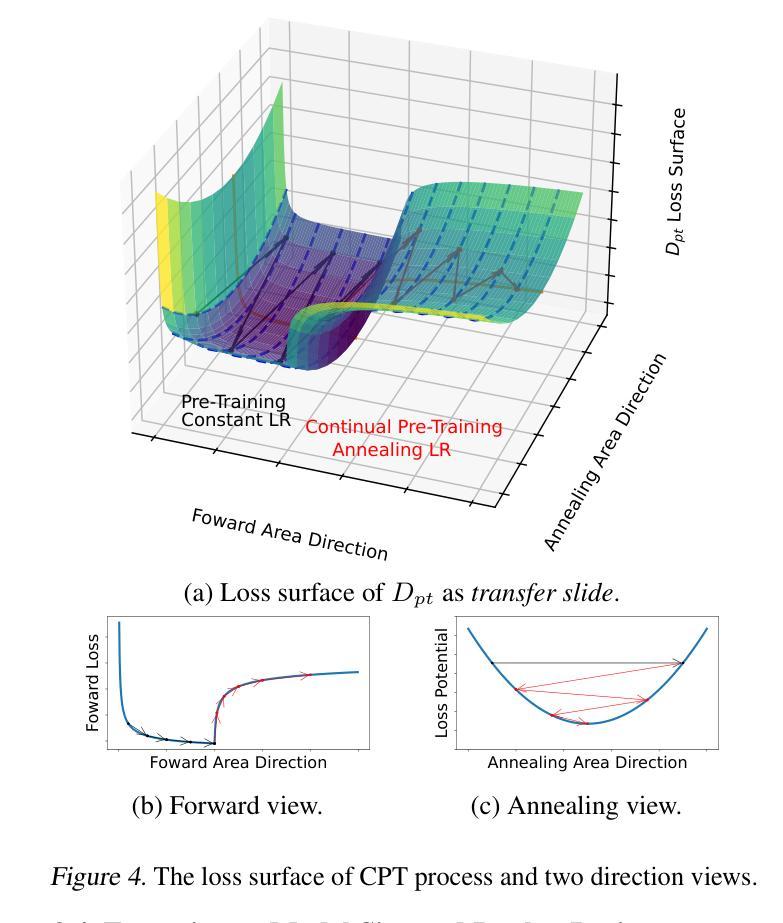
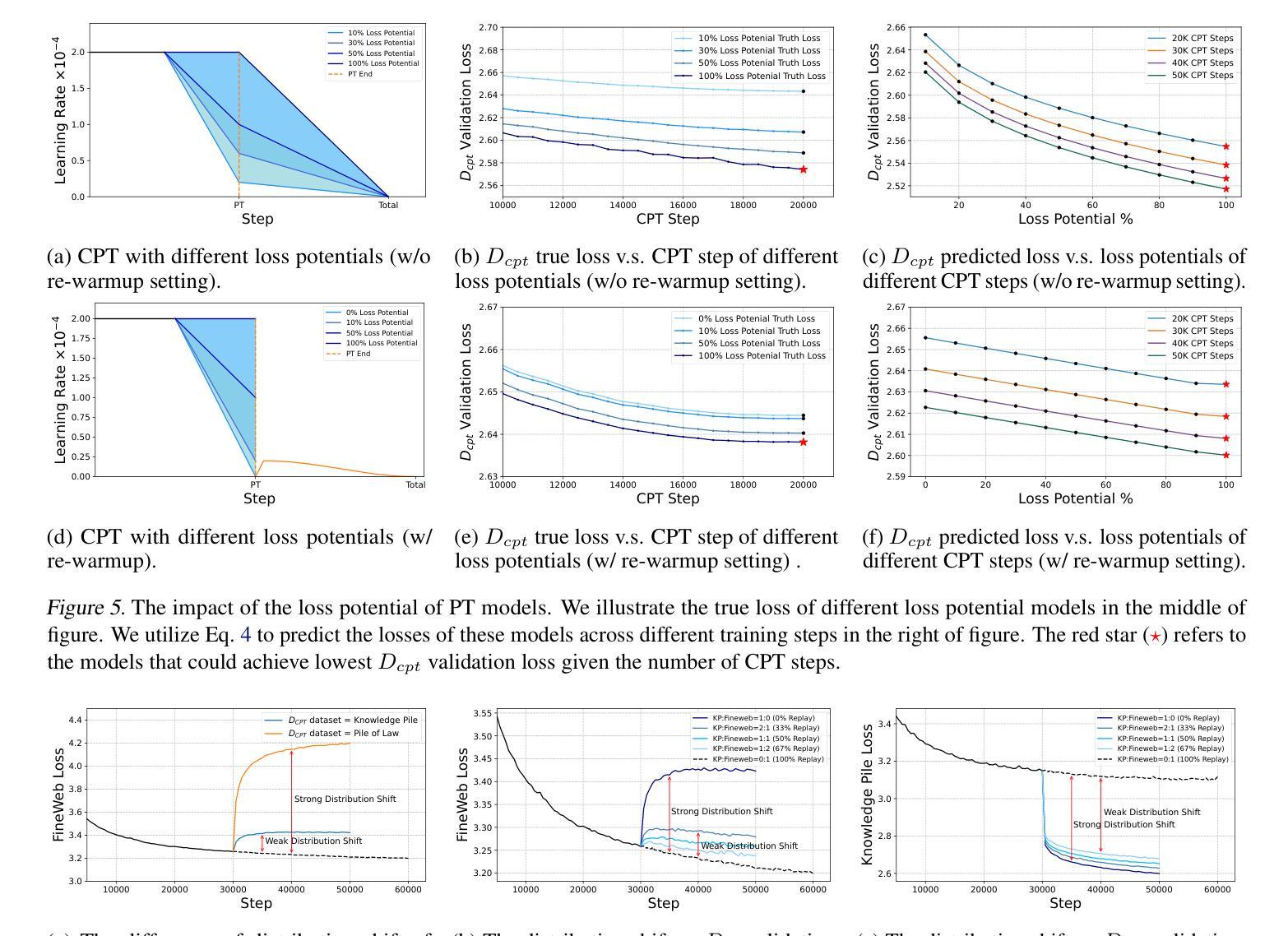
Continual Pre-Training (CPT) has become a popular and effective method to apply strong foundation models to specific downstream tasks. In this work, we explore the learning dynamics throughout the CPT process for large language models. We specifically focus on how general and downstream domain performance evolves at each training step, with domain performance measured via validation losses. We have observed that the CPT loss curve fundamentally characterizes the transition from one curve to another hidden curve, and could be described by decoupling the effects of distribution shift and learning rate annealing. We derive a CPT scaling law that combines the two factors, enabling the prediction of loss at any (continual) training steps and across learning rate schedules (LRS) in CPT. Our formulation presents a comprehensive understanding of several critical factors in CPT, including loss potential, peak learning rate, training steps, replay ratio, etc. Moreover, our approach can be adapted to customize training hyper-parameters to different CPT goals such as balancing general and domain-specific performance. Extensive experiments demonstrate that our scaling law holds across various CPT datasets and training hyper-parameters.
持续预训练(CPT)已成为将强大的基础模型应用于特定下游任务的一种流行且有效的方法。在这项工作中,我们探索了大型语言模型的CPT过程中的学习动态。我们特别关注每个训练步骤中通用领域和下游领域的性能如何发展,并通过验证损失来衡量领域性能。我们发现CPT损失曲线根本上是描述从一个曲线到另一个隐藏曲线的转变,可以通过解耦分布移位和学习率退火的影响来描述。我们推导出了一个结合这两个因素的CPT定标律,能够预测任何(持续)训练步骤的损失以及在CPT中的学习率计划(LRS)。我们的公式全面地理解了几种CPT中的关键因素,包括潜在损失、峰值学习率、训练步骤、回放比率等。此外,我们的方法可以根据不同的CPT目标调整训练超参数,如平衡通用和特定领域的性能。大量实验表明,我们的定标律适用于各种CPT数据集和培训超参数。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted to ICML2025 (spotlight)
Summary
大型语言模型的持续预训练(CPT)方法日益受到关注,本研究探索了CPT过程中的学习动态。研究重点在于通用和下游领域的性能如何随训练步骤而演变,通过验证损失来衡量领域性能。观察到CPT损失曲线本质上反映了一种曲线到另一种隐藏曲线的转变,可通过分离分布变化和衰减学习速率的影响来描述。本研究推导出结合这两个因素的CPT缩放定律,可预测任何连续训练步骤和CPT中的学习速率计划(LRS)的损失。该公式全面理解了CPT中的几个关键因素,包括潜在损失、峰值学习率、训练步骤、回放比率等。此外,该方法可适应不同的CPT目标,调整训练超参数以平衡通用和领域特定性能。大量实验表明,该缩放定律在多种CPT数据集和培训超参数中均有效。
Key Takeaways
- 持续预训练(CPT)是应用于特定下游任务的有效方法。
- 研究重点包括CPT过程中的学习动态,特别是通用和下游领域性能的演变。
- CPT损失曲线反映了从一种曲线到另一种隐藏曲线的转变。
- 通过分离分布变化和衰减学习速率的影响来描述这一转变。
- 推导出的CPT缩放定律可预测任何训练步骤和CPT中的学习速率计划的损失。
- 该公式提供了对CPT中关键因素的全面理解,包括潜在损失、峰值学习率等。
点此查看论文截图

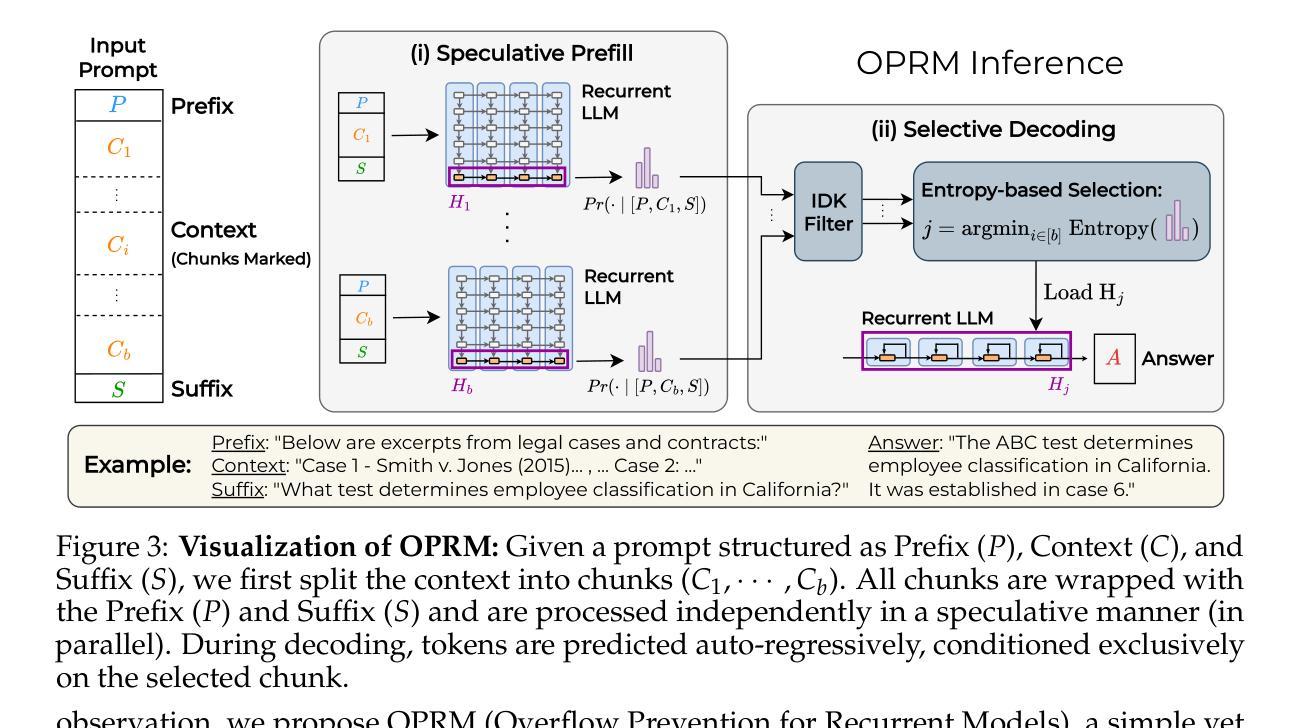
Overflow Prevention Enhances Long-Context Recurrent LLMs
Authors:Assaf Ben-Kish, Itamar Zimerman, M. Jehanzeb Mirza, James Glass, Leonid Karlinsky, Raja Giryes
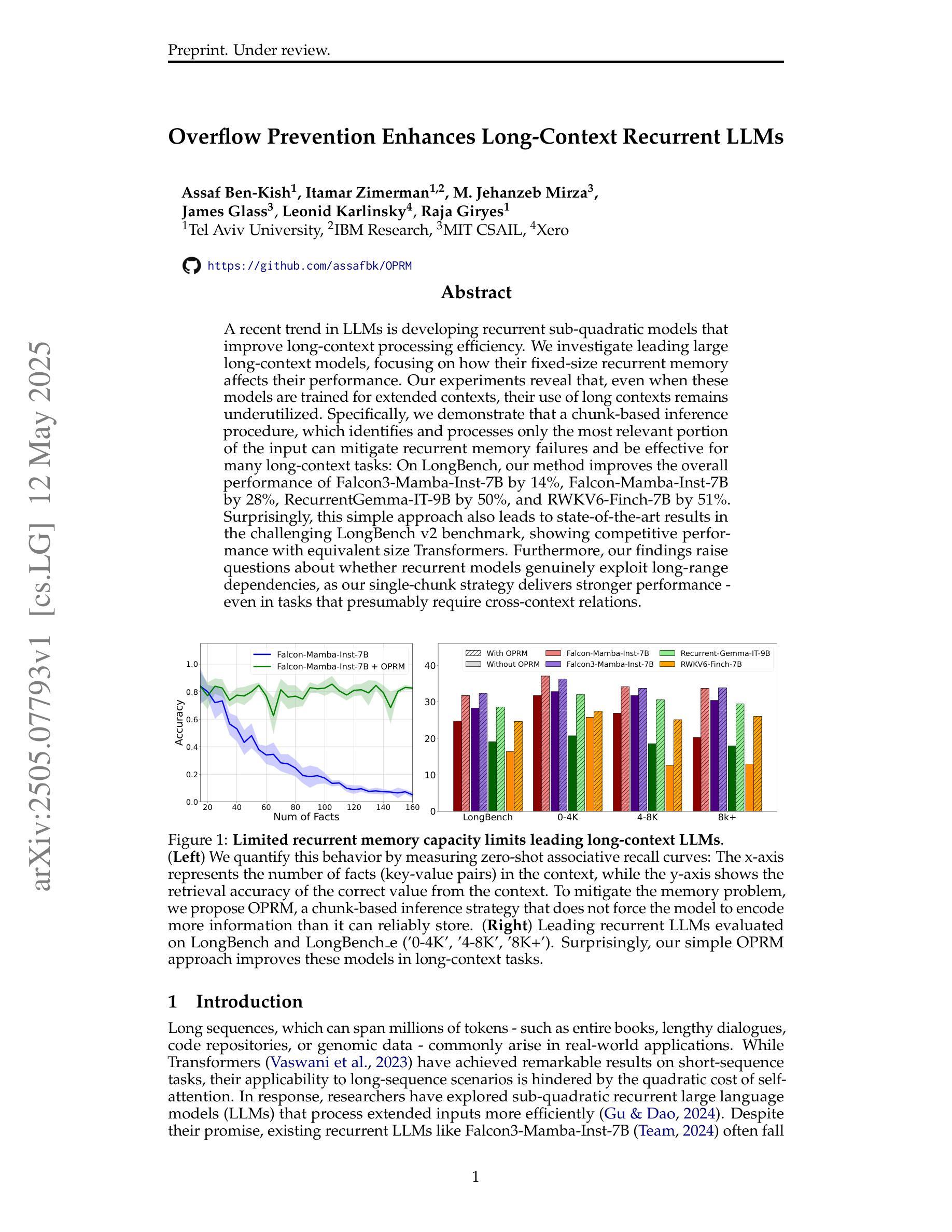
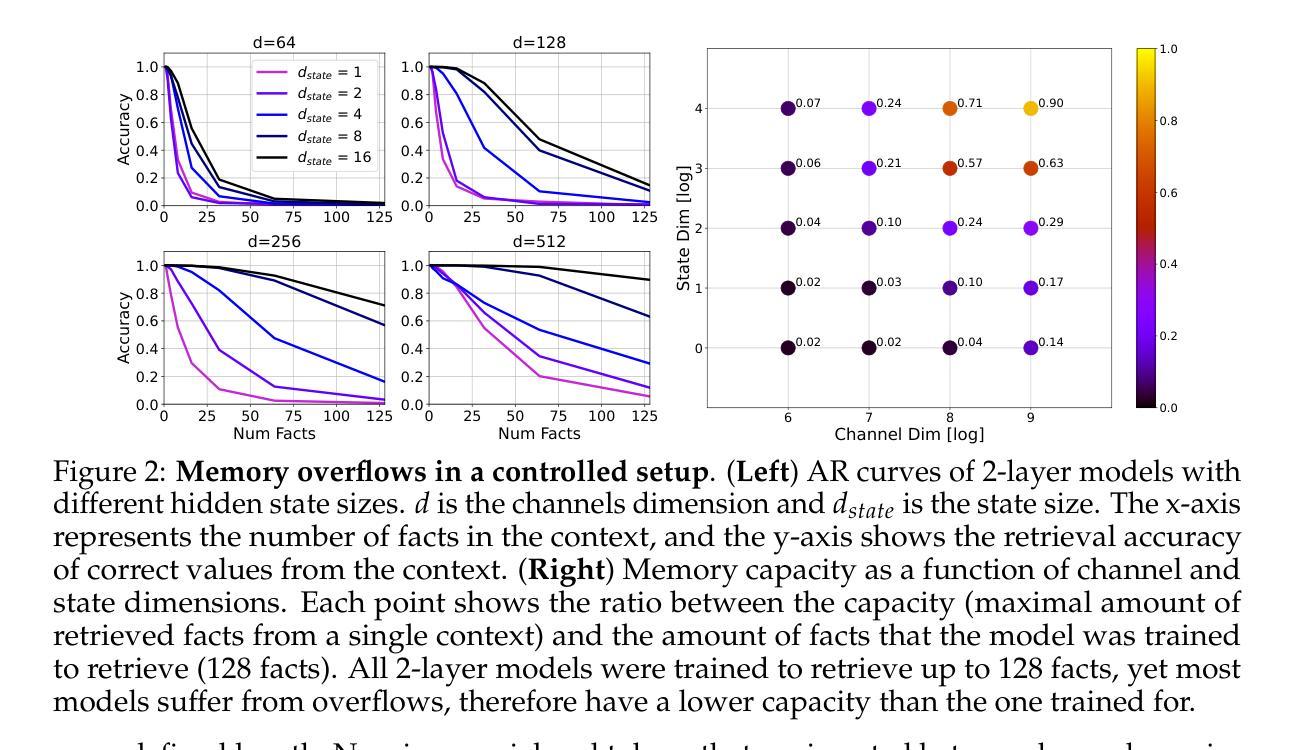
A recent trend in LLMs is developing recurrent sub-quadratic models that improve long-context processing efficiency. We investigate leading large long-context models, focusing on how their fixed-size recurrent memory affects their performance. Our experiments reveal that, even when these models are trained for extended contexts, their use of long contexts remains underutilized. Specifically, we demonstrate that a chunk-based inference procedure, which identifies and processes only the most relevant portion of the input can mitigate recurrent memory failures and be effective for many long-context tasks: On LongBench, our method improves the overall performance of Falcon3-Mamba-Inst-7B by 14%, Falcon-Mamba-Inst-7B by 28%, RecurrentGemma-IT-9B by 50%, and RWKV6-Finch-7B by 51%. Surprisingly, this simple approach also leads to state-of-the-art results in the challenging LongBench v2 benchmark, showing competitive performance with equivalent size Transformers. Furthermore, our findings raise questions about whether recurrent models genuinely exploit long-range dependencies, as our single-chunk strategy delivers stronger performance - even in tasks that presumably require cross-context relations.
在大型语言模型(LLM)领域的一个最新趋势是开发递归子二次模型,以提高长上下文处理效率。我们研究了领先的大型长上下文模型,重点研究了它们的固定大小递归内存对性能的影响。我们的实验表明,即使这些模型经过针对扩展上下文的训练,它们对长上下文的利用仍然不足。具体来说,我们证明了基于分块的推理过程(仅识别和处理输入中最相关的部分)可以缓解递归内存故障,并有效适用于许多长上下文任务:在LongBench上,我们的方法将Falcon3-Mamba-Inst-7B的总体性能提高了1 4%,将Falcon-Mamba-Inst-7B提高了2 8%,将RecurrentGemma-IT-9B提高了5 0%,将RWKV6-Finch-7B提高了5 1%。令人惊讶的是,这种简单的方法还在具有挑战性的LongBench v2基准测试中达到了最先进的水平,显示出与同等规模的Transformer相当的竞争力。此外,我们的研究结果引发了一个问题,即递归模型是否真的利用长距离依赖关系,因为我们的单块策略即使在理论上需要跨上下文关系的任务中也表现出更强的性能。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
长文本模型(LLM)领域的新趋势是开发具有亚二次方特性的递归模型,以提高处理长文本的效率。本文研究了主流的长文本模型,并重点关注其固定大小的递归内存对性能的影响。实验表明,即使这些模型经过长文本训练,但在实际应用中仍未能充分利用长文本的特性。具体来说,通过基于块的推理过程(仅识别和处理输入中最相关的部分),可以有效缓解递归内存失效问题,并对许多长文本任务产生积极影响。此方法在不同模型上的性能提升显著,并在LongBench上达到了最前沿水平。研究还发现,递归模型是否真正利用长距离依赖关系值得进一步探讨,因为单块策略在某些任务中表现出更强的性能。
Key Takeaways
- 长文本模型(LLM)正发展出具有亚二次方特性的递归模型,以提高处理长文本的效率。
- 主流长文本模型的固定大小递归内存影响其性能,未能充分利用长文本特性。
- 基于块的推理过程能缓解递归内存失效问题,对长文本任务产生积极影响。
- 方法在不同模型上的性能提升显著,并在LongBench上达到最前沿水平。
- 该方法提升性能的同时简化了操作,表现出竞争性的结果。
- 递归模型是否真正利用长距离依赖关系值得进一步探讨。
点此查看论文截图
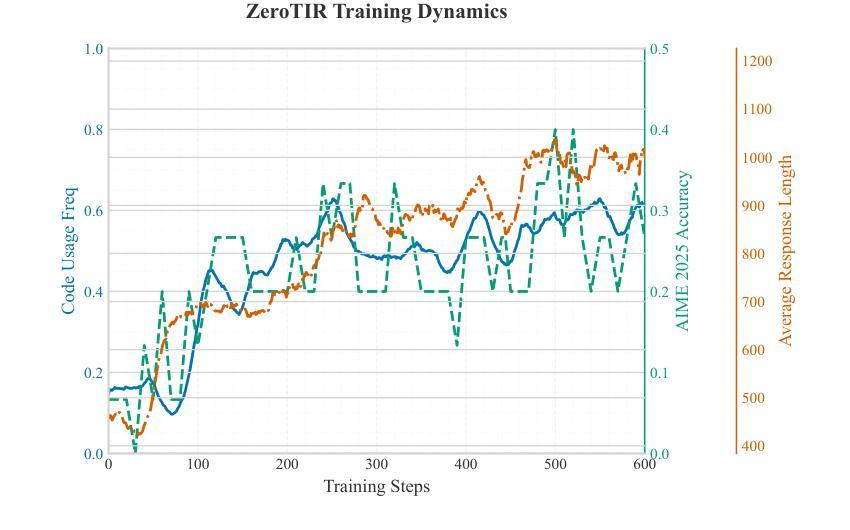
Agent RL Scaling Law: Agent RL with Spontaneous Code Execution for Mathematical Problem Solving
Authors:Xinji Mai, Haotian Xu, Xing W, Weinong Wang, Yingying Zhang, Wenqiang Zhang
Large Language Models (LLMs) often struggle with mathematical reasoning tasks requiring precise, verifiable computation. While Reinforcement Learning (RL) from outcome-based rewards enhances text-based reasoning, understanding how agents autonomously learn to leverage external tools like code execution remains crucial. We investigate RL from outcome-based rewards for Tool-Integrated Reasoning, ZeroTIR, training base LLMs to spontaneously generate and execute Python code for mathematical problems without supervised tool-use examples. Our central contribution is we demonstrate that as RL training progresses, key metrics scale predictably. Specifically, we observe strong positive correlations where increased training steps lead to increases in the spontaneous code execution frequency, the average response length, and, critically, the final task accuracy. This suggests a quantifiable relationship between computational effort invested in training and the emergence of effective, tool-augmented reasoning strategies. We implement a robust framework featuring a decoupled code execution environment and validate our findings across standard RL algorithms and frameworks. Experiments show ZeroTIR significantly surpasses non-tool ZeroRL baselines on challenging math benchmarks. Our findings provide a foundational understanding of how autonomous tool use is acquired and scales within Agent RL, offering a reproducible benchmark for future studies. Code is released at \href{https://github.com/Anonymize-Author/AgentRL}{https://github.com/Anonymize-Author/AgentRL}.
大型语言模型(LLM)在处理需要进行精确、可验证计算的数学推理任务时常常遇到困难。虽然基于结果奖励的强化学习(RL)提高了文本推理能力,但了解智能体如何自主学习利用代码执行等外部工具仍然至关重要。我们研究了基于结果奖励的强化学习在工具集成推理(Tool-Integrated Reasoning)中的应用,即ZeroTIR。我们训练基础LLM,使其能够针对数学问题自发生成并执行Python代码,而无需监督的工具使用示例。我们的主要贡献是,我们证明了随着强化学习训练的进行,关键指标的可预测性。具体来说,我们观察到强烈的正相关关系,即训练步骤的增加导致自发代码执行频率、平均响应长度和最终任务准确度的提高。这表明在训练中所投入的计算努力与有效工具增强推理策略的出现之间存在可量化的关系。我们实现了一个稳健的框架,其中包括一个解耦的代码执行环境,并对标准强化学习算法和框架验证了我们的发现。实验表明,ZeroTIR在具有挑战性的数学基准测试上显著超越了非工具ZeroRL的基准线。我们的研究为自主工具获取和智能体强化学习内的扩展提供了基本理解,并为未来的研究提供了一个可复制的基准。代码已发布在https://github.com/Anonymize-Author/AgentRL。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
大型语言模型(LLM)在处理需要精确可验证计算的数学推理任务时表现欠佳。本研究通过强化学习(RL)从结果导向的奖励出发,探索工具集成推理(Tool-Integrated Reasoning)中的ZeroTIR方法。该方法训练基础LLM,使其能够自发为数学问题生成并执行Python代码,无需监督工具使用示例。研究发现,随着RL训练的进行,关键指标呈现可预测的规模化增长。具体来说,我们观察到积极的正相关关系:训练步骤的增加导致自发代码执行频率、平均响应长度和任务准确度的提升。这表明训练中的计算投入与有效工具辅助推理策略的出现之间存在可量化的关系。实验表明,ZeroTIR在非工具ZeroRL基准线上显著超越了具有挑战性的数学基准测试。本研究为自主工具获取和Agent RL内的扩展提供了基础理解,并为未来的研究提供了可复制的标准。
Key Takeaways
- LLM在处理需要精确计算的数学推理任务时存在挑战。
- 强化学习(RL)从结果导向的奖励出发,有助于提升文本推理能力。
- ZeroTIR方法使LLM能够自发为数学问题生成并执行Python代码。
- 随着RL训练的进行,关键指标如自发代码执行频率、平均响应长度和任务准确度呈现可预测的增长。
- 训练中的计算投入与有效工具辅助推理策略的出现存在可量化的关系。
- ZeroTIR在基准测试中显著超越了非工具ZeroRL方法。
点此查看论文截图




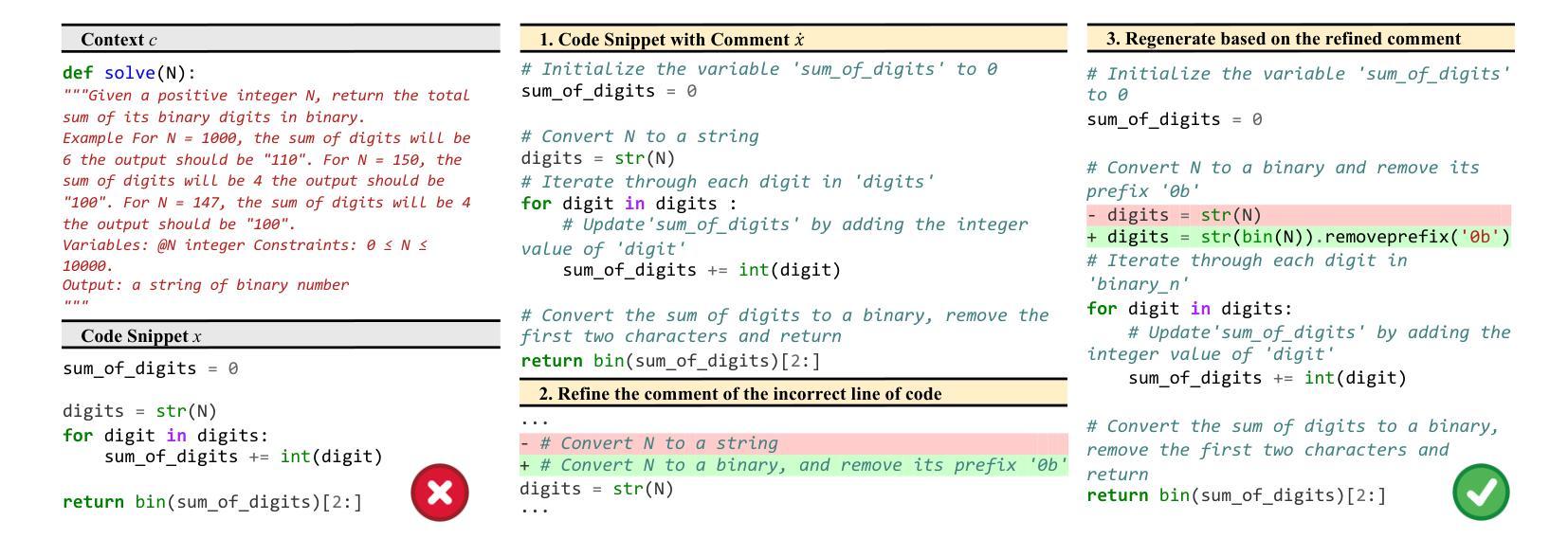
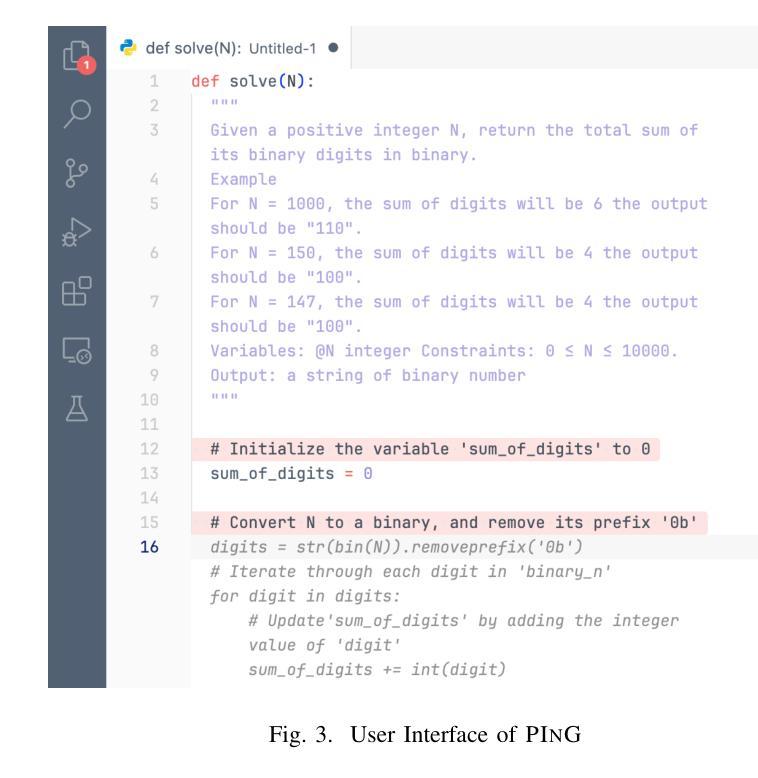
Enhancing Code Generation via Bidirectional Comment-Level Mutual Grounding
Authors:Yifeng Di, Tianyi Zhang
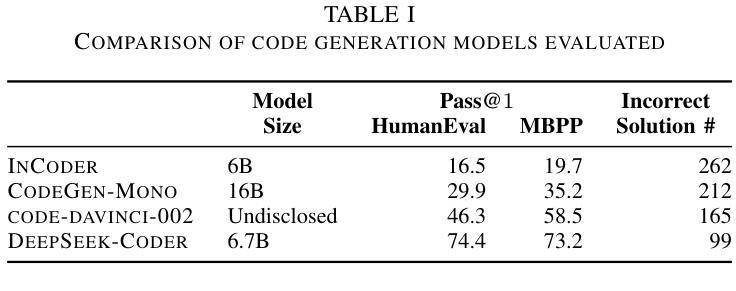
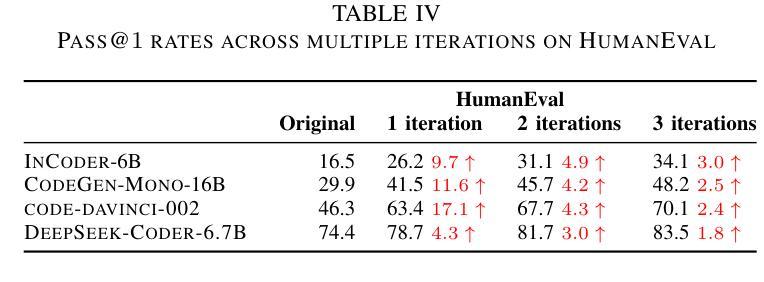
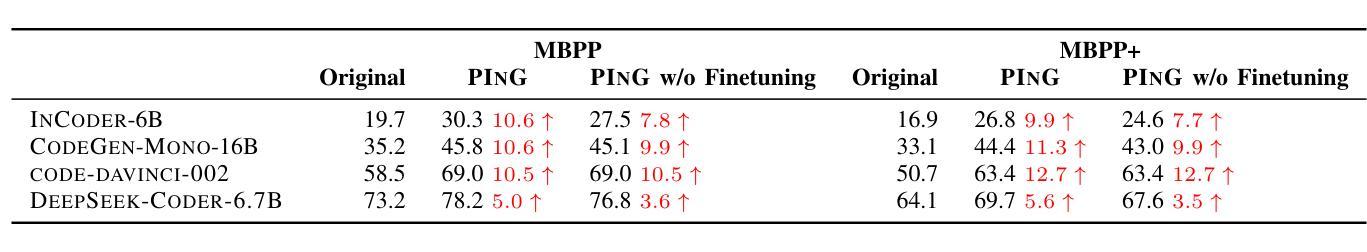
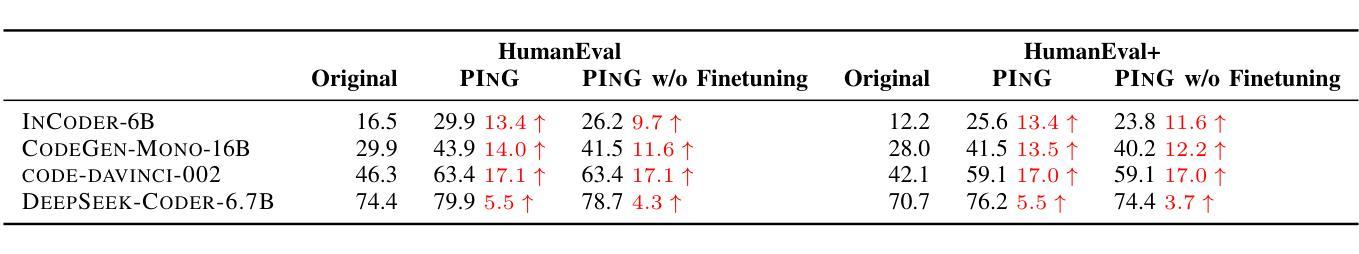
Large Language Models (LLMs) have demonstrated unprecedented capability in code generation. However, LLM-generated code is still plagued with a wide range of functional errors, especially for complex programming tasks that LLMs have not seen before. Recent studies have shown that developers often struggle with inspecting and fixing incorrect code generated by LLMs, diminishing their productivity and trust in LLM-based code generation. Inspired by the mutual grounding theory in communication, we propose an interactive approach that leverages code comments as a medium for developers and LLMs to establish a shared understanding. Our approach facilitates iterative grounding by interleaving code generation, inline comment generation, and contextualized user feedback through editable comments to align generated code with developer intent. We evaluated our approach on two popular benchmarks and demonstrated that our approach significantly improved multiple state-of-the-art LLMs, e.g., 17.1% pass@1 improvement for code-davinci-002 on HumanEval. Furthermore, we conducted a user study with 12 participants in comparison to two baselines: (1) interacting with GitHub Copilot, and (2) interacting with a multi-step code generation paradigm called Multi-Turn Program Synthesis. Participants completed the given programming tasks 16.7% faster and with 10.5% improvement in task success rate when using our approach. Both results show that interactively refining code comments enables the collaborative establishment of mutual grounding, leading to more accurate code generation and higher developer confidence.
大型语言模型(LLM)在代码生成方面表现出了前所未有的能力。然而,LLM生成的代码仍然存在着广泛的功能错误,尤其是在处理LLM未曾遇到过的复杂编程任务时。最近的研究表明,开发者在检查和修复LLM生成的错误代码时经常遇到困难,这降低了他们的生产力和对LLM代码生成的可信度。受通信中的相互基础理论的启发,我们提出了一种交互方法,该方法利用代码注释作为开发者和LLM之间的媒介,以建立共享理解。我们的方法通过交替进行代码生成、内联注释生成和通过可编辑注释的上下文用户反馈,来促进生成的代码与开发者意图的一致性。我们在两个流行的基准测试上评估了我们的方法,并证明我们的方法显著改进了多个最先进的大型语言模型,例如在人类评估(HumanEval)上,对code-davinci-002的pass@1提升了17.1%。此外,我们还与两个基准进行了用户研究:一是与GitHub Copilot互动,二是与多步代码生成模式——多轮程序合成互动。在使用我们的方法时,参与者完成给定编程任务的速度提高了16.7%,任务成功率提高了10.5%。这两个结果都表明,交互地修改代码注释有助于建立相互的基础,从而导致更准确的代码生成和更高的开发者信心。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted to ICSE 2025
摘要
大型语言模型(LLM)在代码生成方面展现出前所未有的能力。然而,LLM生成的代码仍存在广泛的功能错误,特别是在处理复杂且前所未有的编程任务时。研究表明,开发者在检查与修复LLM生成的错误代码时,往往面临挑战,进而影响其生产效率和对于LLM代码生成功能的信任度。本研究受沟通中的相互定位理论启发,提出一种交互方法,利用代码注释作为开发者和LLM建立共享理解的媒介。该方法通过交替进行代码生成、内联注释生成和基于上下文的可编辑用户反馈,使生成的代码符合开发者的意图。我们在两个流行基准测试上对该方法进行了评估,并证明其显著改进了多项最前沿的LLM性能,例如在HumanEval上,我们的方法使code-davinci-002的pass@1提升了17.1%。此外,相较于基线方法——与GitHub Copilot互动及多回合代码生成模式(Multi-Turn Program Synthesis)——我们开展了包含12名参与者的用户研究。使用我们的方法,参与者在给定的编程任务上完成速度提高了16.7%,任务成功率提高了10.5%。两项结果均表明,通过交互方式修正代码注释有助于共同建立相互定位,从而生成更准确的代码并提升开发者的信心。
关键见解
- LLM在代码生成方面存在功能错误,特别是在处理复杂且前所未有的编程任务时。
- 开发者在检查与修复LLM生成的错误代码时面临挑战,影响生产效率与对LLM的信任。
- 提出一种交互方法,利用代码注释作为媒介,促进开发者和LLM建立共享理解。
- 通过交替进行代码生成、内联注释生成和基于上下文的用户反馈,使生成的代码符合开发者意图。
- 在两个流行基准测试上的评估显示,该方法显著提升了LLM的性能。
- 与基线方法相比,使用此方法的参与者在编程任务上的完成速度和提高任务成功率方面表现出色。
- 交互方式修正代码注释有助于共同建立相互定位,提升代码生成的准确性和开发者的信心。
点此查看论文截图

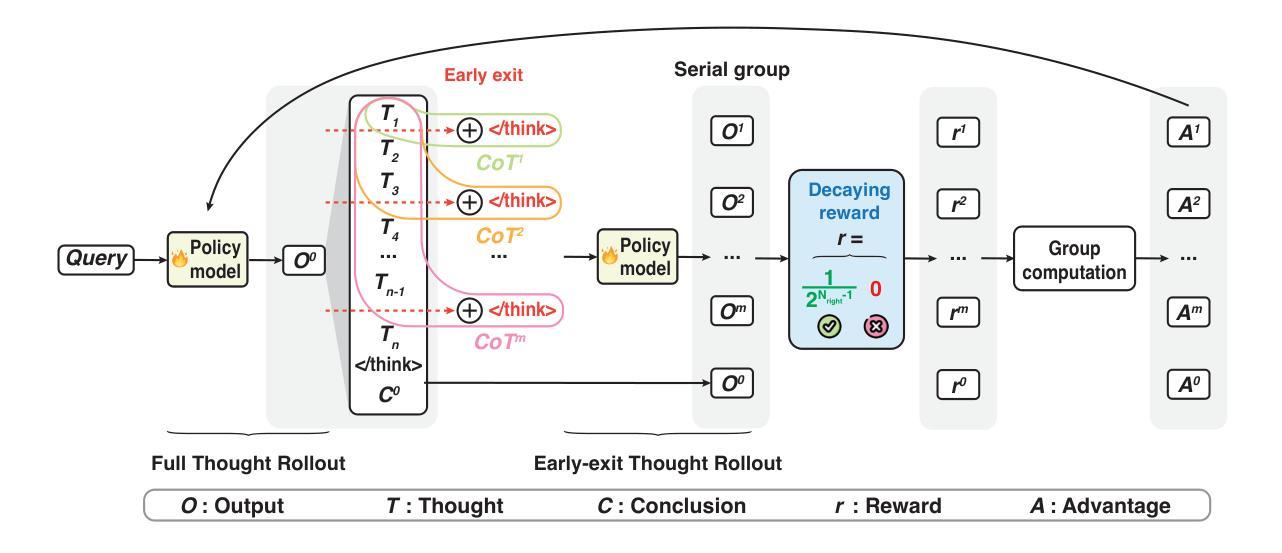
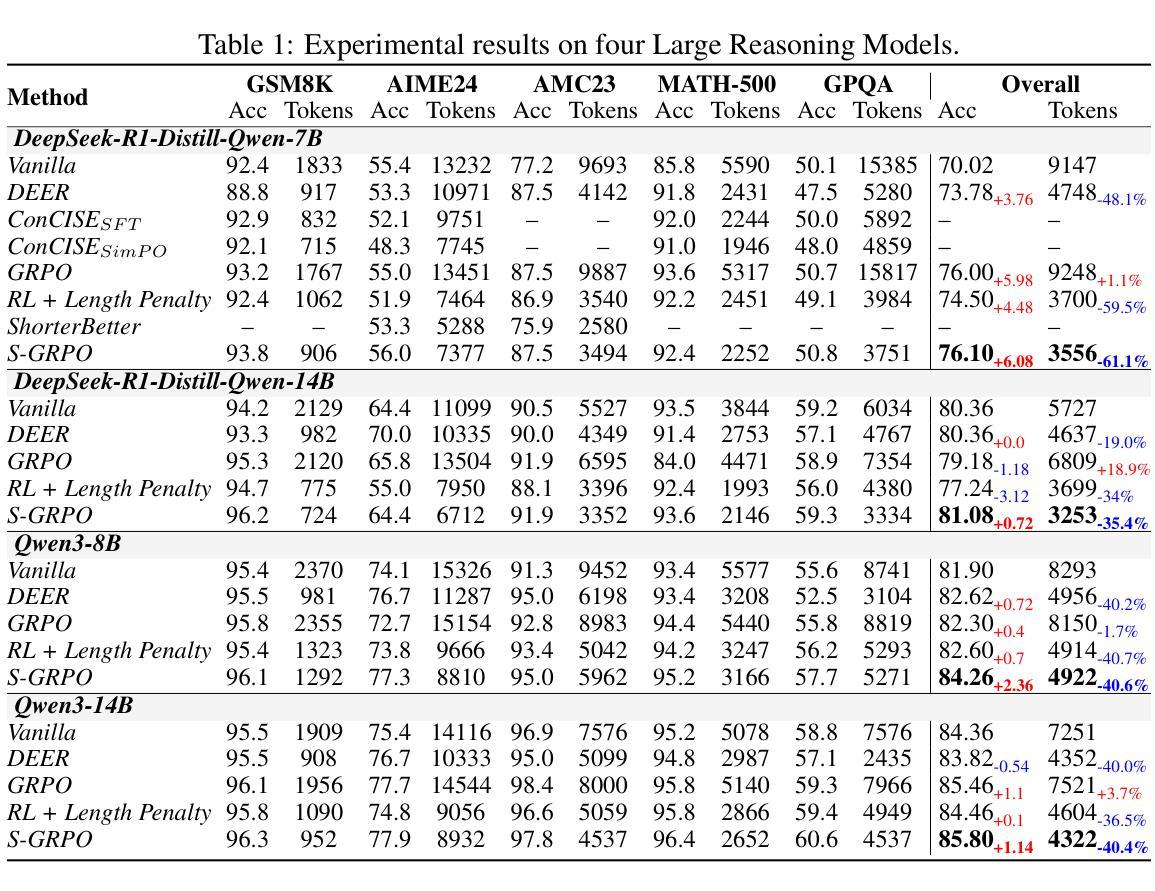
S-GRPO: Early Exit via Reinforcement Learning in Reasoning Models
Authors:Muzhi Dai, Chenxu Yang, Qingyi Si
As Test-Time Scaling emerges as an active research focus in the large language model community, advanced post-training methods increasingly emphasize extending chain-of-thought (CoT) generation length, thereby enhancing reasoning capabilities to approach Deepseek R1-like reasoning models. However, recent studies reveal that reasoning models (even Qwen3) consistently exhibit excessive thought redundancy in CoT generation. This overthinking problem stems from conventional outcome-reward reinforcement learning’s systematic neglect in regulating intermediate reasoning steps. This paper proposes Serial-Group Decaying-Reward Policy Optimization (namely S-GRPO), a novel reinforcement learning method that empowers models with the capability to determine the sufficiency of reasoning steps, subsequently triggering early exit of CoT generation. Specifically, unlike GRPO, which samples multiple possible completions (parallel group) in parallel, we select multiple temporal positions in the generation of one CoT to allow the model to exit thinking and instead generate answers (serial group), respectively. For the correct answers in a serial group, we assign rewards that decay according to positions, with lower rewards towards the later ones, thereby reinforcing the model’s behavior to generate higher-quality answers at earlier phases with earlier exits of thinking. Empirical evaluations demonstrate compatibility with state-of-the-art reasoning models, including Qwen3 and Deepseek-distill models, achieving 35.4% ~ 61.1% sequence length reduction with 0.72% ~ 6.08% accuracy improvements across GSM8K, AIME 2024, AMC 2023, MATH-500, and GPQA Diamond benchmarks.
随着测试时间缩放作为大型语言模型社区中的活跃研究焦点,先进的后训练方法越来越强调延长思维链(CoT)生成长度,从而提高推理能力,以接近Deepseek R1等推理模型。然而,最近的研究表明,推理模型(即使是Qwen3)在思维链生成中始终表现出过多的思维冗余。这种过度思考的问题源于传统结果奖励强化学习在调节中间推理步骤中的系统性忽视。本文提出了串行组衰减奖励策略优化(简称S-GRPO),这是一种新型强化学习方法,使模型具备判断推理步骤是否充足的能力,从而触发思维链生成的早期退出。具体来说,与GRPO不同,GRPO会并行采样多个可能的完成(并行组),而我们选择在一条思维链的生成过程中选择多个时间位置,让模型停止思考并开始生成答案(串行组)。对于串行组中的正确答案,我们根据位置衰减分配奖励,后期答案的奖励较低,从而强化模型在较早阶段生成高质量答案的行为,并尽早退出思考。经验评估表明,该方法与包括Qwen3和Deepseek蒸馏模型在内的最新推理模型兼容,在GSM8K、AIME 2024、AMC 2023、MATH-500和GPQA Diamond等多个基准测试上实现了35.4%~61.1%的序列长度缩减,同时准确率提高了0.72%~6.08%。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
该文探讨了在大型语言模型领域中新兴的测试时间缩放技术,强调在训练后扩展思维链生成长度的重要性,以提高模型的推理能力,接近Deepseek R1级别的推理模型。然而,研究发现推理模型(如Qwen3)在思维链生成中存在过度冗余的问题。针对这一问题,本文提出了一种名为S-GRPO的新型强化学习政策优化方法,即串行群组衰减奖励策略优化,该方法使模型具备判断推理步骤是否充足的能力,并据此提前终止思维链的生成。经验评估表明,S-GRPO与最新推理模型兼容,包括Qwen3和Deepseek蒸馏模型,在GSM8K、AIME 2024、AMC 2023、MATH-500和GPQA Diamond等多个基准测试中,实现了序列长度减少35.4%~61.1%,同时精度提高0.72%~6.08%。
Key Takeaways
- 测试时间缩放技术在大型语言模型领域是一个活跃的研究焦点。
- 先进的训练后方法强调扩展思维链生成长度以提高模型的推理能力。
- 现有推理模型存在过度冗余的问题。
- S-GRPO是一种新型强化学习政策优化方法,解决了过度冗余的问题。
- S-GRPO通过在思维链生成过程中选择多个时间位置来实现早期退出。
- S-GRPO对正确答案采用衰减奖励策略,鼓励模型在较早阶段生成高质量答案。
点此查看论文截图


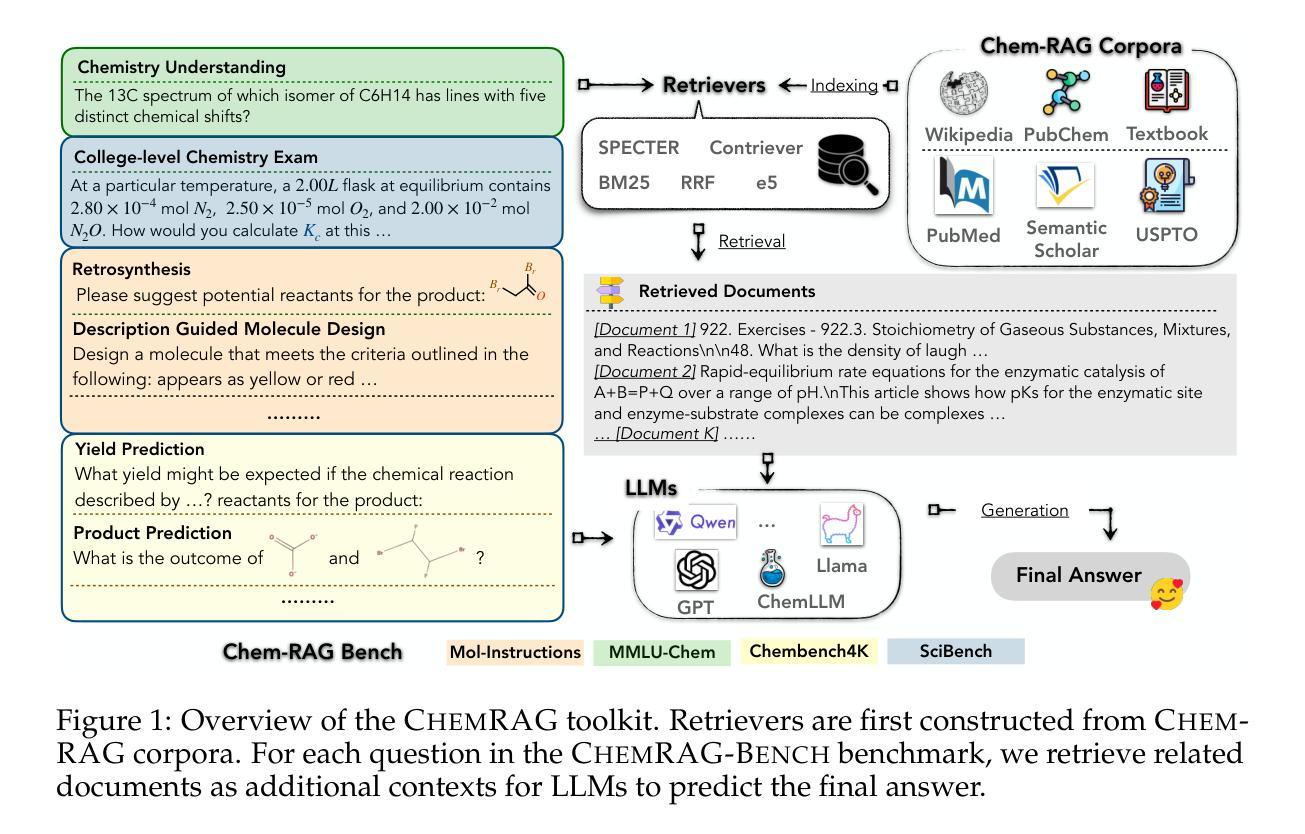
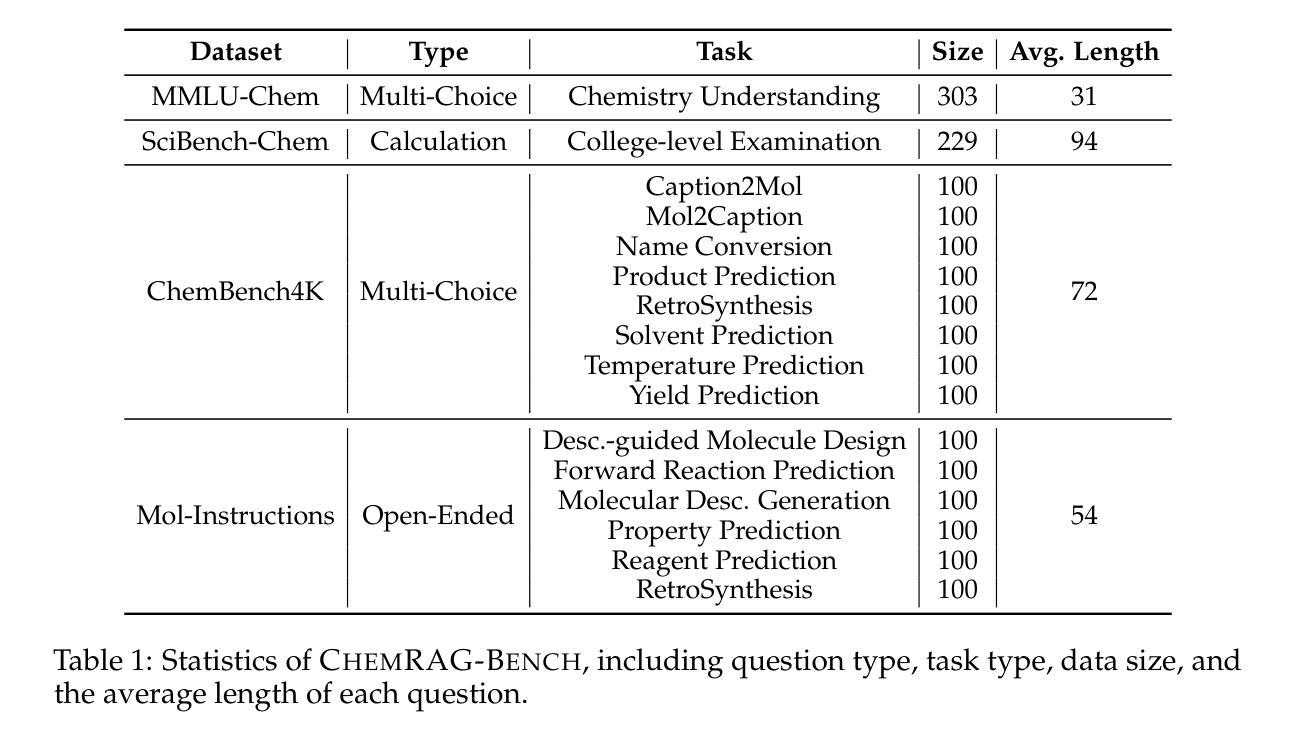
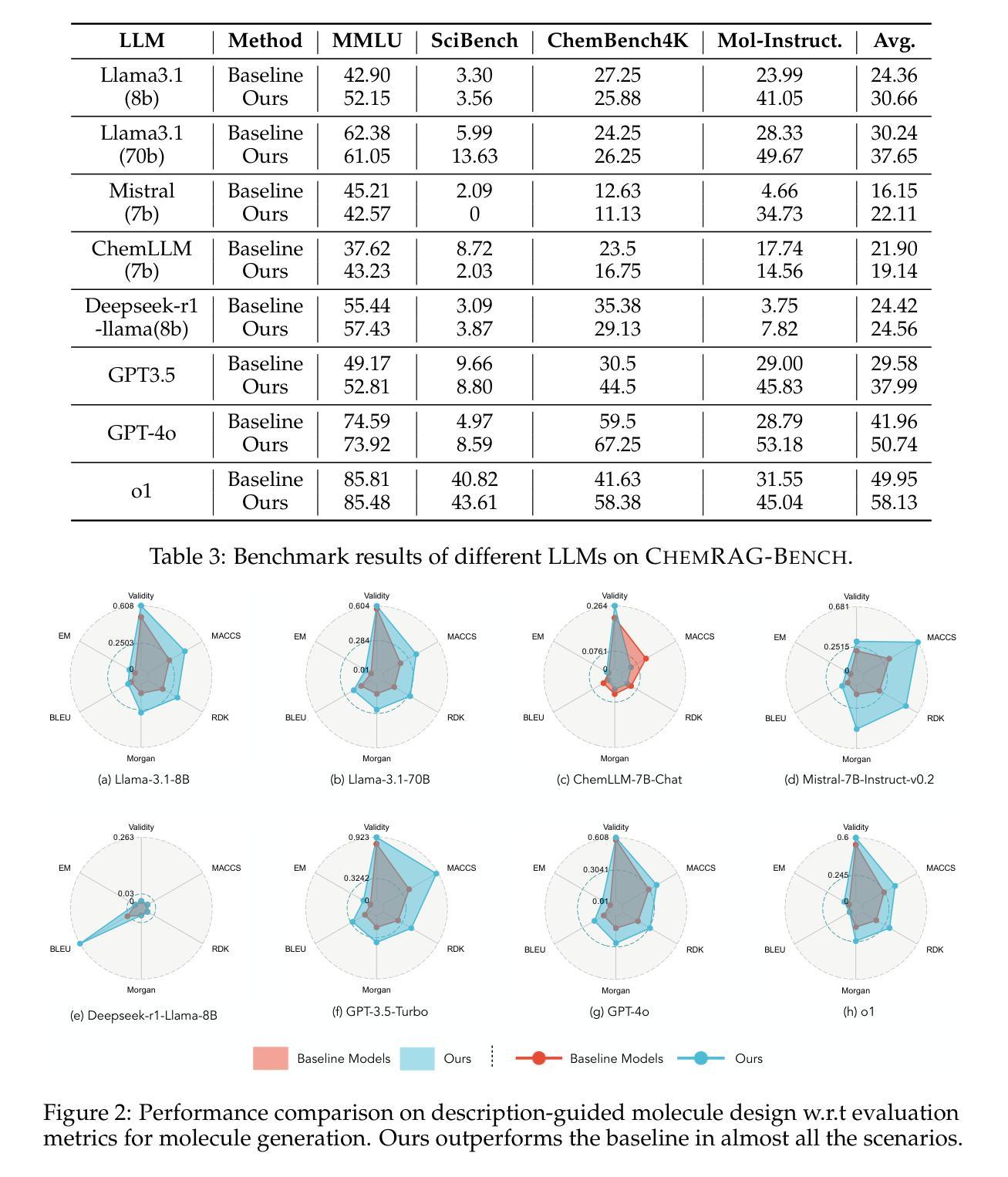
Benchmarking Retrieval-Augmented Generation for Chemistry
Authors:Xianrui Zhong, Bowen Jin, Siru Ouyang, Yanzhen Shen, Qiao Jin, Yin Fang, Zhiyong Lu, Jiawei Han
Retrieval-augmented generation (RAG) has emerged as a powerful framework for enhancing large language models (LLMs) with external knowledge, particularly in scientific domains that demand specialized and dynamic information. Despite its promise, the application of RAG in the chemistry domain remains underexplored, primarily due to the lack of high-quality, domain-specific corpora and well-curated evaluation benchmarks. In this work, we introduce ChemRAG-Bench, a comprehensive benchmark designed to systematically assess the effectiveness of RAG across a diverse set of chemistry-related tasks. The accompanying chemistry corpus integrates heterogeneous knowledge sources, including scientific literature, the PubChem database, PubMed abstracts, textbooks, and Wikipedia entries. In addition, we present ChemRAG-Toolkit, a modular and extensible RAG toolkit that supports five retrieval algorithms and eight LLMs. Using ChemRAG-Toolkit, we demonstrate that RAG yields a substantial performance gain – achieving an average relative improvement of 17.4% over direct inference methods. We further conduct in-depth analyses on retriever architectures, corpus selection, and the number of retrieved passages, culminating in practical recommendations to guide future research and deployment of RAG systems in the chemistry domain. The code and data is available at https://chemrag.github.io.
检索增强生成(RAG)作为一个强大的框架,能够通过外部知识增强大型语言模型(LLM)的功能,特别是在需要专业化和动态信息的科学领域表现出其潜力。尽管前景广阔,但RAG在化学领域的应用仍然被探索得不够深入,这主要是由于缺乏高质量、特定领域的语料库和精心策划的评估基准。在这项工作中,我们介绍了ChemRAG-Bench,这是一个全面的基准测试,旨在系统地评估RAG在多种化学相关任务中的有效性。伴随的化学语料库融合了各种异质知识来源,包括科学文献、PubChem数据库、PubMed摘要、教科书和Wikipedia条目。此外,我们还推出了ChemRAG-Toolkit,这是一个模块化且可扩展的RAG工具包,支持五种检索算法和八种LLM。使用ChemRAG-Toolkit,我们证明了RAG产生了显著的性能提升——相对于直接推理方法,平均相对提高了17.4%。我们还对检索器架构、语料库选择和检索段落数量进行了深入分析,并据此提出了实用建议,以指导未来RAG系统在化学领域的研究和部署。代码和数据可在https://chemrag.github.io获取。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
增强型检索生成框架(RAG)通过引入外部知识增强了大型语言模型(LLM)的性能,特别是在需要专业化和动态信息的科学领域。针对化学领域的RAG应用仍然缺乏探索,主要由于缺乏高质量、特定领域的语料库和评估基准。本研究引入了ChemRAG-Bench基准,旨在全面评估化学相关任务中RAG的有效性,同时提供化学语料库支持多来源知识整合。此外,ChemRAG-Toolkit作为模块化可扩展的RAG工具包,支持五种检索算法和八种LLM。通过ChemRAG-Toolkit验证,RAG相比直接推理方法显著提高性能,平均相对提高率为17.4%。我们对检索器架构、语料库选择和检索篇章数量进行了深入分析,为未来研究和部署RAG系统在化学领域提供了实践建议。相关代码和数据可通过https://chemrag.github.io获取。
Key Takeaways
- RAG框架增强了LLM在化学领域的性能表现。
- ChemRAG-Bench提供了全面的基准以评估化学相关任务中RAG的有效性。
- 提供的化学语料库融合了多源知识,包括科学文献、PubChem数据库等。
- ChemRAG-Toolkit支持多种检索算法和LLM,模块化设计便于扩展。
- RAG相比直接推理方法平均性能提升17.4%。
- 研究深入分析了检索器架构、语料库选择和检索篇章数量对性能的影响。
点此查看论文截图

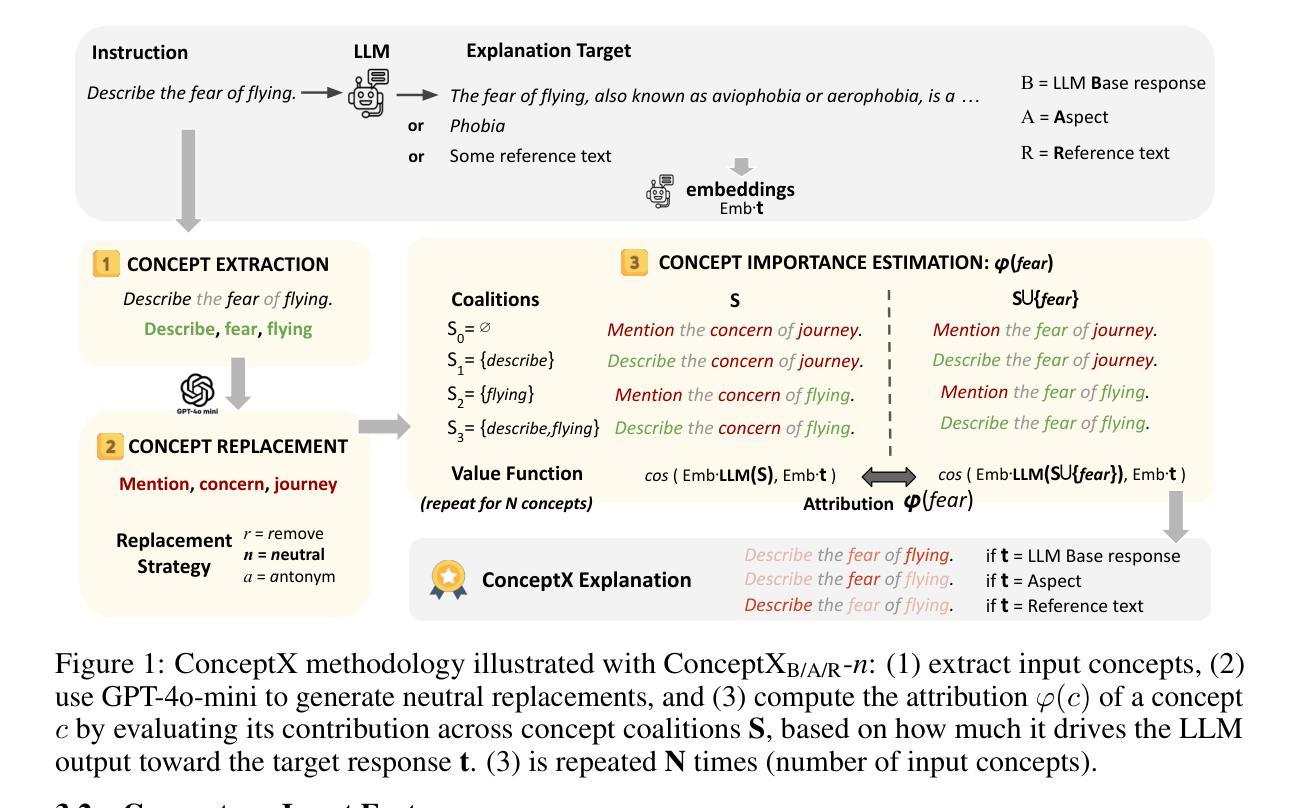
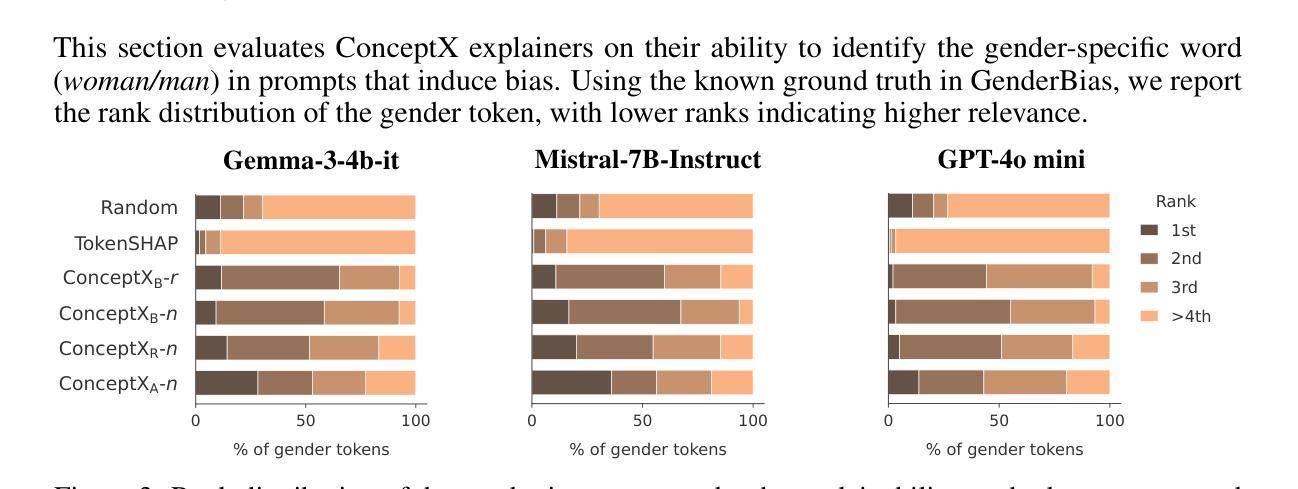
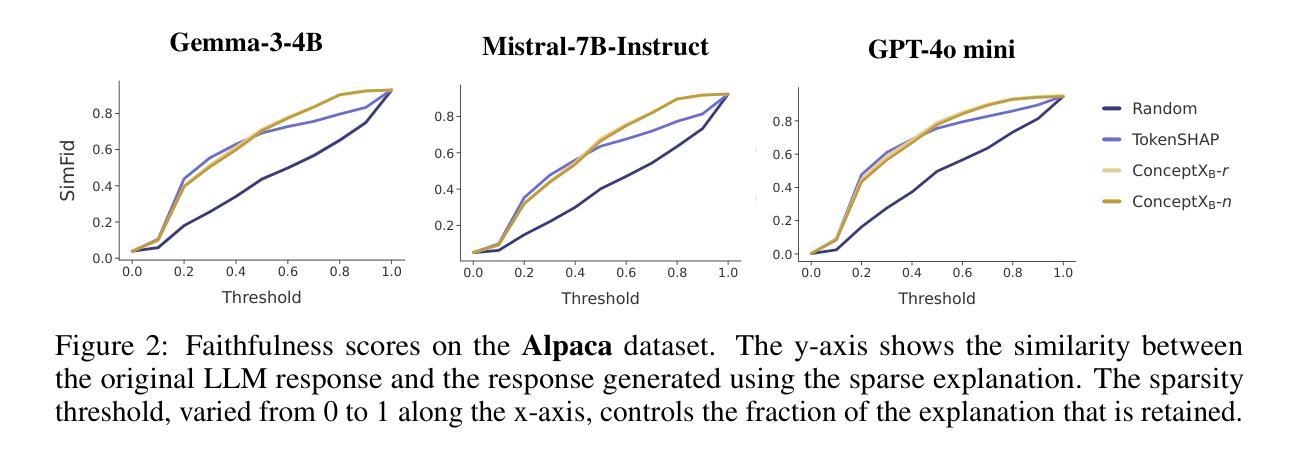
Concept-Level Explainability for Auditing & Steering LLM Responses
Authors:Kenza Amara, Rita Sevastjanova, Mennatallah El-Assady
As large language models (LLMs) become widely deployed, concerns about their safety and alignment grow. An approach to steer LLM behavior, such as mitigating biases or defending against jailbreaks, is to identify which parts of a prompt influence specific aspects of the model’s output. Token-level attribution methods offer a promising solution, but still struggle in text generation, explaining the presence of each token in the output separately, rather than the underlying semantics of the entire LLM response. We introduce ConceptX, a model-agnostic, concept-level explainability method that identifies the concepts, i.e., semantically rich tokens in the prompt, and assigns them importance based on the outputs’ semantic similarity. Unlike current token-level methods, ConceptX also offers to preserve context integrity through in-place token replacements and supports flexible explanation goals, e.g., gender bias. ConceptX enables both auditing, by uncovering sources of bias, and steering, by modifying prompts to shift the sentiment or reduce the harmfulness of LLM responses, without requiring retraining. Across three LLMs, ConceptX outperforms token-level methods like TokenSHAP in both faithfulness and human alignment. Steering tasks boost sentiment shift by 0.252 versus 0.131 for random edits and lower attack success rates from 0.463 to 0.242, outperforming attribution and paraphrasing baselines. While prompt engineering and self-explaining methods sometimes yield safer responses, ConceptX offers a transparent and faithful alternative for improving LLM safety and alignment, demonstrating the practical value of attribution-based explainability in guiding LLM behavior.
随着大型语言模型(LLM)的广泛应用,对其安全性和对齐性的担忧也在增长。引导LLM行为的方法,例如缓解偏见或防范越狱,是确定哪些提示部分影响模型输出的特定方面。令牌级归因方法提供了很有前景的解决方案,但在文本生成中仍然面临挑战,需要解释输出中每个令牌的存在,而不是整个LLM响应的潜在语义。我们推出了ConceptX,这是一种模型无关的概念级解释方法,可以识别提示中的概念,即语义丰富的令牌,并根据输出语义相似性分配它们的重要性。与当前的令牌级方法不同,ConceptX还通过就地令牌替换保留了上下文完整性,并支持灵活的解释目标,例如性别偏见。ConceptX能够通过揭示偏见的来源来进行审计,并通过修改提示来改变情绪或减少LLM响应的有害性,而无需重新训练。在三个LLM中,ConceptX在忠诚度和人类对齐方面都优于TokenSHAP等令牌级方法。与随机编辑相比,驾驶任务将情绪转移提高了0.252至0.131,攻击成功率从0.463降至0.242,超过了归属和改述基线。虽然提示工程和自解释方法有时会生成更安全的响应,但ConceptX提供了一种透明和忠诚的替代方案,用于提高LLM的安全性和对齐性,证明了基于归属的解释在实际指导LLM行为中的实用价值。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 9 pages, 7 figures, Submission to Neurips 2025
Summary
大型语言模型(LLM)的广泛应用引发了关于其安全性和对齐性的担忧。ConceptX是一种模型无关的概念级解释性方法,它能识别提示中的概念,并根据输出语义相似性为它们分配重要性。与现有的令牌级方法相比,ConceptX通过原地令牌替换保留了上下文完整性,并支持灵活的解释目标,如性别偏见。ConceptX既可用于通过揭露偏见来源进行审计,又可通过修改提示来改变情绪或减少LLM响应的危害性,而无需重新训练。ConceptX在信仰性和人类一致性方面均优于TokenSHAP等令牌级方法。引导任务使情绪转移提升了0.252,相对于随机编辑的0.131,攻击成功率从0.463降至0.242。虽然提示工程和自解释方法有时会生成更安全的响应,但ConceptX提供了一个透明和忠诚的替代方案,以改善LLM的安全性和对齐性,展示了基于归因解释的实用性。
Key Takeaways
- 大型语言模型(LLM)的安全性和对齐性问题引发关注。
- ConceptX是一种概念级的解释方法,能识别提示中的关键概念并根据输出语义相似性分配重要性。
- ConceptX通过保留上下文完整性和支持灵活的解释目标,如性别偏见等,优于现有的令牌级方法。
- ConceptX既可用于审计(揭露偏见来源),也可用于引导LLM行为,改变情绪或减少响应的危害性,无需重新训练模型。
- 在信仰性和人类一致性方面,ConceptX优于其他方法。
- 引导任务显示ConceptX在情绪转移和降低攻击成功率方面的优势。
点此查看论文截图

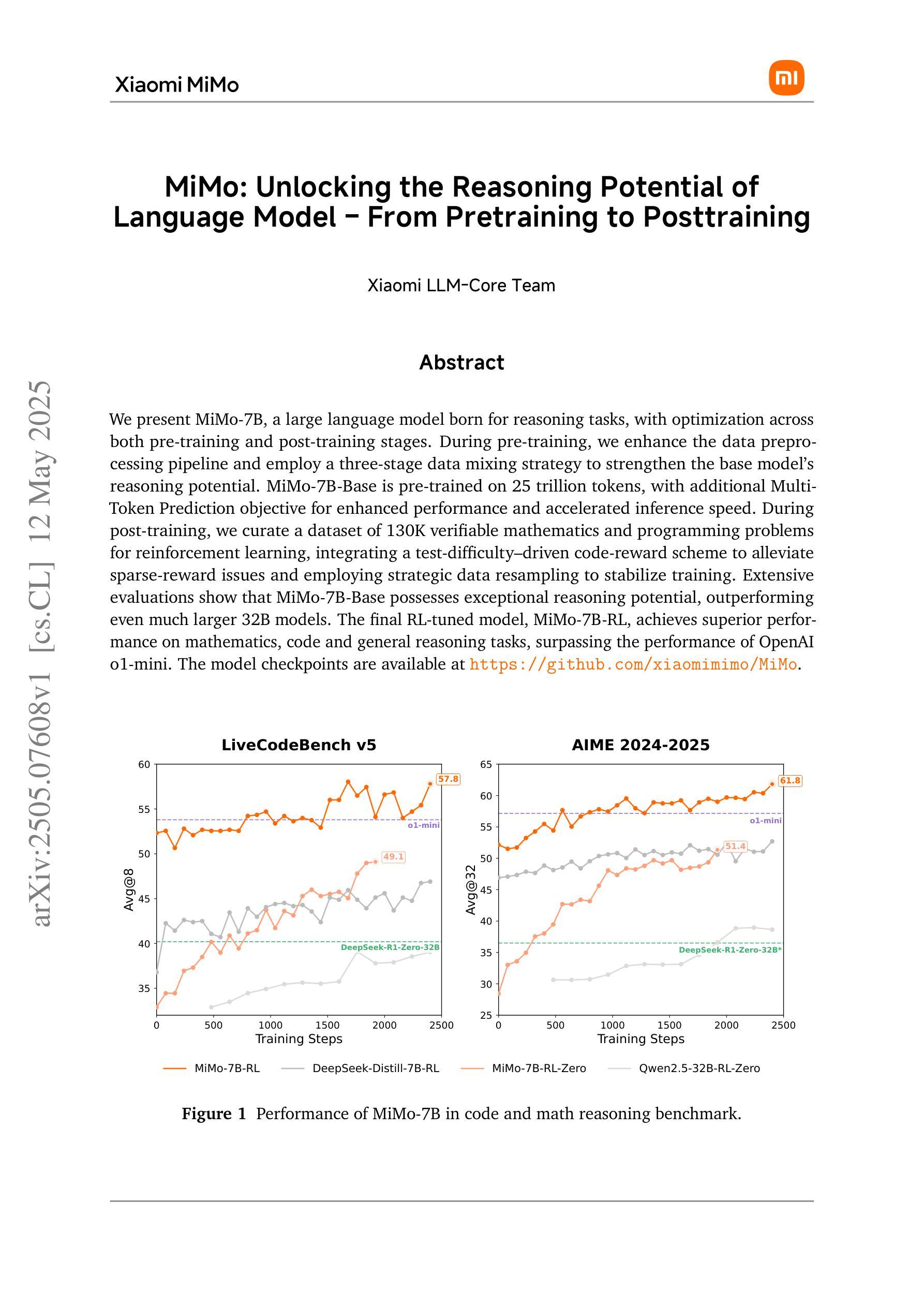
MiMo: Unlocking the Reasoning Potential of Language Model – From Pretraining to Posttraining
Authors:Xiaomi LLM-Core Team, :, Bingquan Xia, Bowen Shen, Cici, Dawei Zhu, Di Zhang, Gang Wang, Hailin Zhang, Huaqiu Liu, Jiebao Xiao, Jinhao Dong, Liang Zhao, Peidian Li, Peng Wang, Shihua Yu, Shimao Chen, Weikun Wang, Wenhan Ma, Xiangwei Deng, Yi Huang, Yifan Song, Zihan Jiang, Bowen Ye, Can Cai, Chenhong He, Dong Zhang, Duo Zhang, Guoan Wang, Hao Tian, Haochen Zhao, Heng Qu, Hongshen Xu, Jun Shi, Kainan Bao, QingKai Fang, Kang Zhou, Kangyang Zhou, Lei Li, Menghang Zhu, Nuo Chen, Qiantong Wang, Shaohui Liu, Shicheng Li, Shuhao Gu, Shuhuai Ren, Shuo Liu, Sirui Deng, Weiji Zhuang, Weiwei Lv, Wenyu Yang, Xin Zhang, Xing Yong, Xing Zhang, Xingchen Song, Xinzhe Xu, Xu Wang, Yihan Yan, Yu Tu, Yuanyuan Tian, Yudong Wang, Yue Yu, Zhenru Lin, Zhichao Song, Zihao Yue
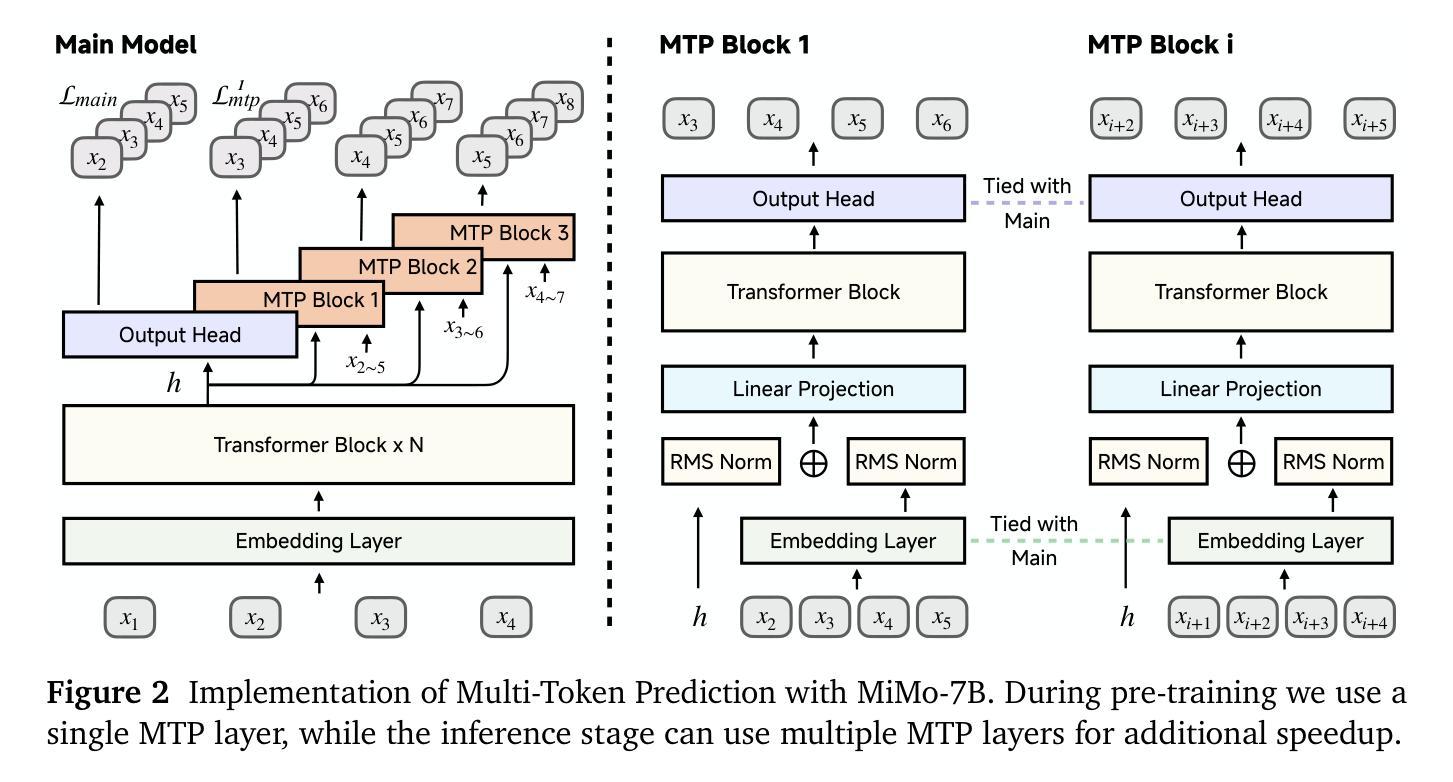
We present MiMo-7B, a large language model born for reasoning tasks, with optimization across both pre-training and post-training stages. During pre-training, we enhance the data preprocessing pipeline and employ a three-stage data mixing strategy to strengthen the base model’s reasoning potential. MiMo-7B-Base is pre-trained on 25 trillion tokens, with additional Multi-Token Prediction objective for enhanced performance and accelerated inference speed. During post-training, we curate a dataset of 130K verifiable mathematics and programming problems for reinforcement learning, integrating a test-difficulty-driven code-reward scheme to alleviate sparse-reward issues and employing strategic data resampling to stabilize training. Extensive evaluations show that MiMo-7B-Base possesses exceptional reasoning potential, outperforming even much larger 32B models. The final RL-tuned model, MiMo-7B-RL, achieves superior performance on mathematics, code and general reasoning tasks, surpassing the performance of OpenAI o1-mini. The model checkpoints are available at https://github.com/xiaomimimo/MiMo.
我们推出了MiMo-7B,这是一款专为推理任务设计的大型语言模型,在预训练和微调阶段都进行了优化。在预训练阶段,我们增强了数据预处理管道,采用了三阶段数据混合策略,以提高基础模型的推理潜力。MiMo-7B基础版在25万亿个令牌上进行预训练,并增加了多令牌预测目标,以提高性能和加速推理速度。在微调阶段,我们整理了一个包含13万个可验证的数学和编程问题的数据集,用于强化学习,采用测试难度驱动的代码奖励方案来缓解稀疏奖励问题,并采用战略数据重采样来稳定训练。广泛评估表明,MiMo-7B基础版具有出色的推理潜力,甚至超过了许多更大的32B模型。最终的强化学习调优模型MiMo-7B-RL在数学、代码和通用推理任务上实现了卓越的性能,超越了OpenAI o1-mini的性能。该模型的检查点位于https://github.com/xiaomimimo/MiMo。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
MiMo-7B是一款针对推理任务的大型语言模型,通过优化预训练和微调阶段增强其性能。它采用三阶段数据混合策略进行预训练,增加Multi-Token Prediction目标提升性能及推理速度。同时,对可验证的数学与编程问题集进行微调训练,并采用测试难度驱动的代码奖励方案及战略数据重采样技术解决训练问题。MiMo-7B模型表现卓越,超越许多更大的模型。模型检查点可在GitHub上找到。
Key Takeaways
- MiMo-7B是一个用于推理任务的大型语言模型。
- 预训练阶段通过增强数据预处理管道和三阶段数据混合策略优化模型性能。
- MiMo-7B在预训练中加入Multi-Token Prediction目标以提升性能和推理速度。
- 在微调阶段,使用数学和编程问题的数据集进行强化学习训练。
- 采用测试难度驱动的代码奖励方案以及战略数据重采样技术以解决训练过程中的稀疏奖励问题。
- MiMo-7B模型展现出卓越推理能力,超越许多更大的模型。
点此查看论文截图
Ophora: A Large-Scale Data-Driven Text-Guided Ophthalmic Surgical Video Generation Model
Authors:Wei Li, Ming Hu, Guoan Wang, Lihao Liu, Kaijin Zhou, Junzhi Ning, Xin Guo, Zongyuan Ge, Lixu Gu, Junjun He
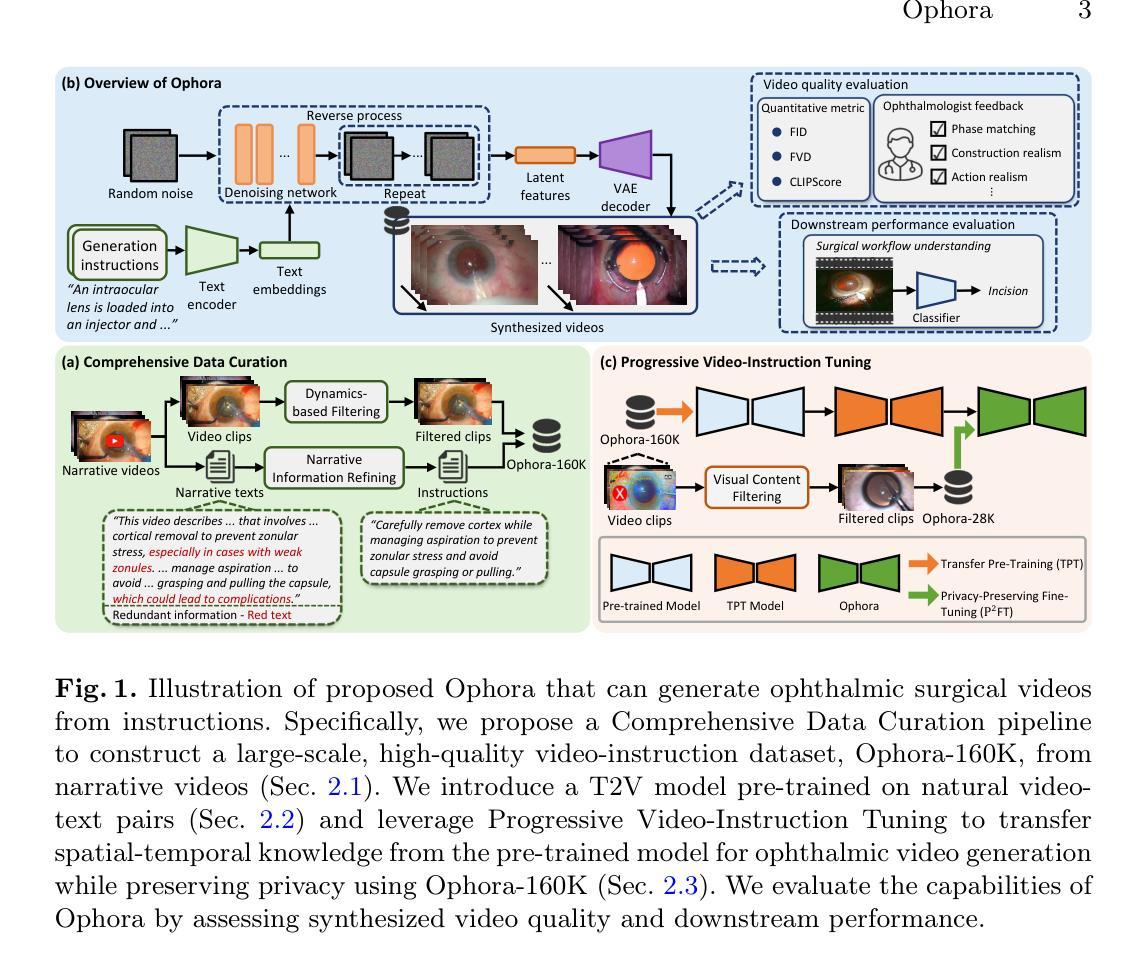
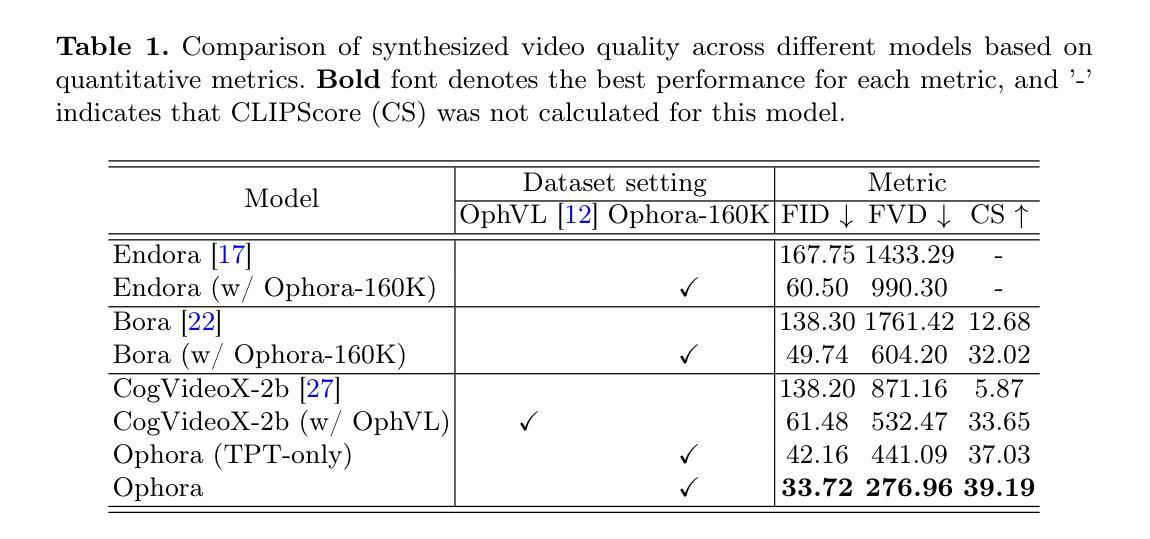
In ophthalmic surgery, developing an AI system capable of interpreting surgical videos and predicting subsequent operations requires numerous ophthalmic surgical videos with high-quality annotations, which are difficult to collect due to privacy concerns and labor consumption. Text-guided video generation (T2V) emerges as a promising solution to overcome this issue by generating ophthalmic surgical videos based on surgeon instructions. In this paper, we present Ophora, a pioneering model that can generate ophthalmic surgical videos following natural language instructions. To construct Ophora, we first propose a Comprehensive Data Curation pipeline to convert narrative ophthalmic surgical videos into a large-scale, high-quality dataset comprising over 160K video-instruction pairs, Ophora-160K. Then, we propose a Progressive Video-Instruction Tuning scheme to transfer rich spatial-temporal knowledge from a T2V model pre-trained on natural video-text datasets for privacy-preserved ophthalmic surgical video generation based on Ophora-160K. Experiments on video quality evaluation via quantitative analysis and ophthalmologist feedback demonstrate that Ophora can generate realistic and reliable ophthalmic surgical videos based on surgeon instructions. We also validate the capability of Ophora for empowering downstream tasks of ophthalmic surgical workflow understanding. Code is available at https://github.com/mar-cry/Ophora.
在眼科手术中,开发一个能够解读手术视频并预测后续操作的AI系统,需要大量的带有高质量注释的眼科手术视频。由于隐私问题和劳动消耗,这些视频的收集非常困难。文本引导的视频生成(T2V)作为一种有前途的解决方案应运而生,它可以根据外科医生的指令生成眼科手术视频。在本文中,我们介绍了Ophora,一个可以根据自然语言指令生成眼科手术视频的开创性模型。为了构建Ophora,我们首先提出了一个全面的数据整理管道,将叙述性眼科手术视频转化为大规模高质量数据集,包含超过16万对视频指令对,命名为Ophora-160K。然后,我们提出了渐进式视频指令调整方案,以从T2V模型预训练的自然视频文本数据集中转移丰富的时空知识,基于Ophora-160K进行隐私保护的眼科手术视频生成。通过对视频质量的定量分析和眼科医生的反馈进行的实验表明,Ophora可以根据外科医生的指令生成现实和可靠的眼科手术视频。我们还验证了Ophora在执行眼科手术工作流程理解等下游任务方面的能力。代码可访问https://github.com/mar-cry/Ophora获取。
论文及项目相关链接
摘要
本文提出了一种名为Ophora的模型,该模型能够根据自然语言指令生成眼科手术视频。为解决高质量眼科手术视频数据难以收集的问题,研究团队构建了大规模数据集Ophora-160K,并提出了一种全面的数据整理流程。此外,团队还提出了一种渐进的视频指令微调方案,将丰富的时空知识从预训练于自然视频文本数据集的T2V模型迁移到Ophora中。实验表明,Ophora可以根据医师指令生成真实可靠的眼科手术视频,并能赋能眼科手术工作流程理解等下游任务。相关代码已公开。
关键见解
- Ophora模型能够根据自然语言指令生成眼科手术视频,解决了高质量眼科手术视频数据难以收集的问题。
- 构建了一个大规模数据集Ophora-160K,用于训练和验证Ophora模型。
- 提出了一种全面的数据整理流程,用于从叙事眼科手术视频中生成高质量的数据集。
- 采用渐进的视频指令微调方案,将预训练的T2V模型知识迁移到Ophora模型中。
- 实验证明了Ophora在生成真实可靠的眼科手术视频方面的能力。
- Ophora有能力赋能眼科手术工作流程理解等下游任务。
点此查看论文截图

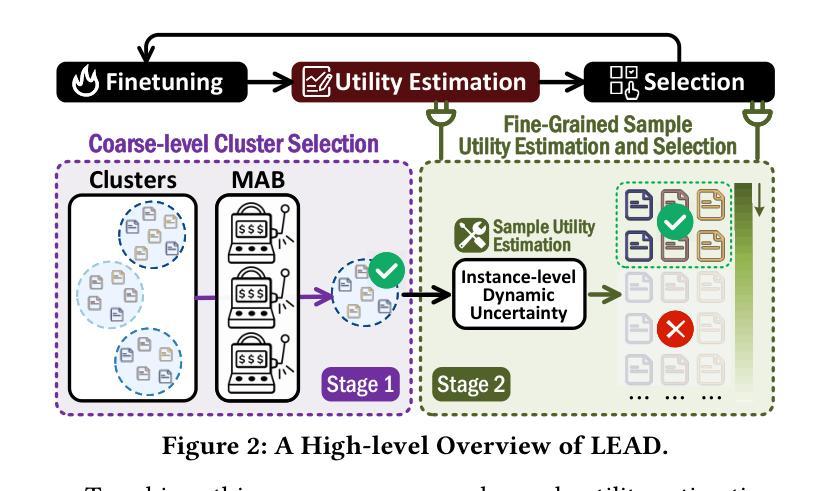
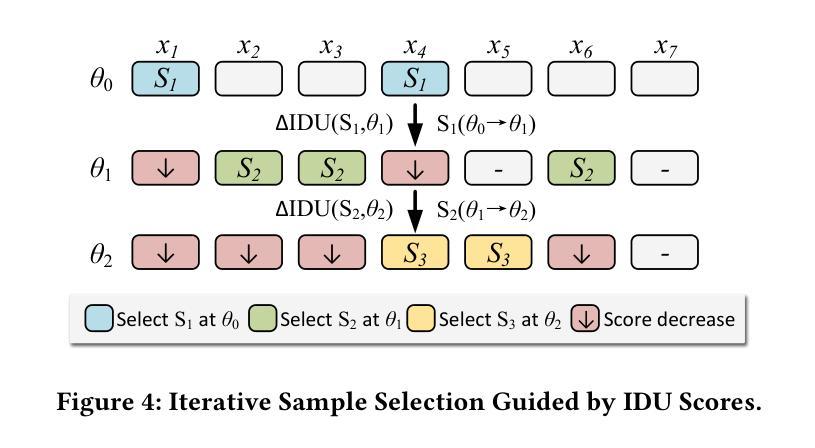
LEAD: Iterative Data Selection for Efficient LLM Instruction Tuning
Authors:Xiaotian Lin, Yanlin Qi, Yizhang Zhu, Themis Palpanas, Chengliang Chai, Nan Tang, Yuyu Luo
Instruction tuning has emerged as a critical paradigm for improving the capabilities and alignment of large language models (LLMs). However, existing iterative model-aware data selection methods incur significant computational overhead, as they rely on repeatedly performing full-dataset model inference to estimate sample utility for subsequent training iterations, creating a fundamental efficiency bottleneck. In this paper, we propose LEAD, an efficient iterative data selection framework that accurately estimates sample utility entirely within the standard training loop, eliminating the need for costly additional model inference. At its core, LEAD introduces Instance-Level Dynamic Uncertainty (IDU), a theoretically grounded utility function combining instantaneous training loss, gradient-based approximation of loss changes, and exponential smoothing of historical loss signals. To further scale efficiently to large datasets, LEAD employs a two-stage, coarse-to-fine selection strategy, adaptively prioritizing informative clusters through a multi-armed bandit mechanism, followed by precise fine-grained selection of high-utility samples using IDU. Extensive experiments across four diverse benchmarks show that LEAD significantly outperforms state-of-the-art methods, improving average model performance by 6.1%-10.8% while using only 2.5% of the training data and reducing overall training time by 5-10x.
指令调整已成为一个提高大型语言模型(LLM)能力和对齐的关键范式。然而,现有的迭代模型感知数据选择方法会产生巨大的计算开销,因为它们依赖于反复执行全数据集模型推理来估计样本效用,以供后续训练迭代使用,这创建了一个基本的效率瓶颈。在本文中,我们提出了LEAD,这是一个高效迭代数据选择框架,它能够在标准训练循环内准确估计样本效用,无需进行昂贵的额外模型推理。LEAD的核心是引入实例级动态不确定性(IDU),这是一个结合即时训练损失、损失变化的梯度近似和历史损失信号的指数平滑的理论基础效用函数。为了进一步有效地扩展到大型数据集,LEAD采用从粗到细的两阶段选择策略,通过多臂老虎机机制自适应地优先处理信息丰富的集群,然后使用IDU进行精确的高效用样本的精细粒度选择。在四个不同基准测试上的广泛实验表明,LEAD显著优于最新方法,在仅使用2.5%的训练数据的情况下,平均模型性能提高6.1%-10.8%,同时总体训练时间减少5-10倍。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary:针对大型语言模型(LLM)的能力和对齐问题,指令微调已成为一种关键范式。然而,现有的迭代模型感知数据选择方法产生了显著的计算开销,因为它们依赖于进行全数据集模型推理来估计样本效用,从而为后续的迭代训练创建效率瓶颈。本文提出了LEAD,一种高效迭代数据选择框架,它能够在标准训练循环内准确估计样本效用,无需昂贵的额外模型推理。其核心在于引入基于实例的动态不确定性(IDU),一个结合即时训练损失、基于梯度的损失变化近似和历史损失信号的指数平滑的理论基础效用函数。为了进一步提高在大规模数据集上的效率,LEAD采用从粗到细的二级选择策略,通过多臂老虎机机制自适应地优先考虑信息丰富的聚类,然后使用IDU进行高效用样本的精细粒度选择。实验证明,LEAD显著优于现有先进技术,平均模型性能提升6.1%-10.8%,同时使用的数据量仅占2.5%,整体训练时间减少5-10倍。
Key Takeaways:
- 指令微调已成为改进大型语言模型能力和对齐的关键范式。
- 现有数据选择方法存在计算开销大,因为需要反复进行全数据集模型推理。
- LEAD框架提出一种高效迭代数据选择方法,可在标准训练循环内准确估计样本效用。
- LEAD引入基于实例的动态不确定性(IDU)作为效用函数,结合即时训练损失、梯度变化和损失信号平滑。
- LEAD采用从粗到细的二级选择策略,先考虑信息丰富的聚类,再精细选择高效用样本。
- 实验显示LEAD显著优于现有技术,提高模型性能并大幅减少数据和时间成本。
点此查看论文截图


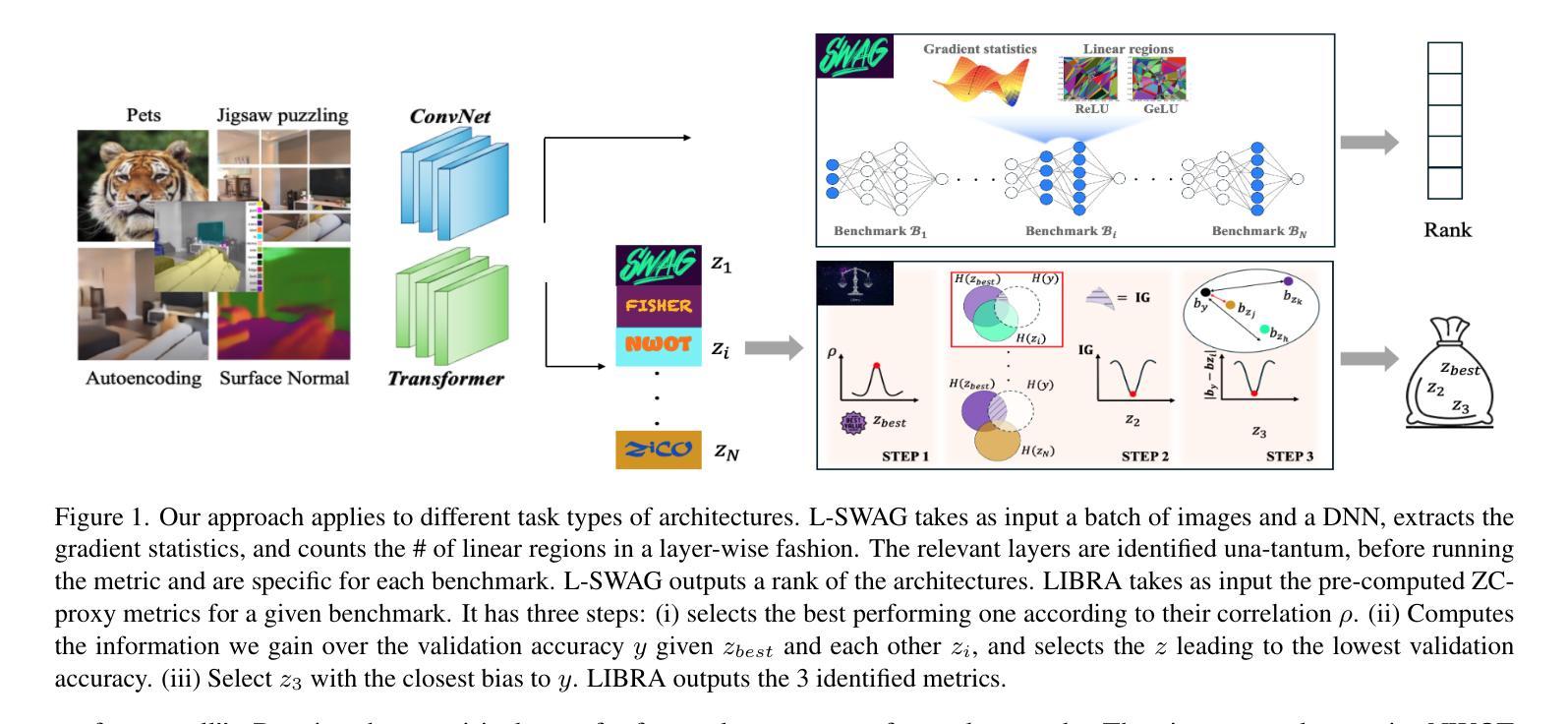
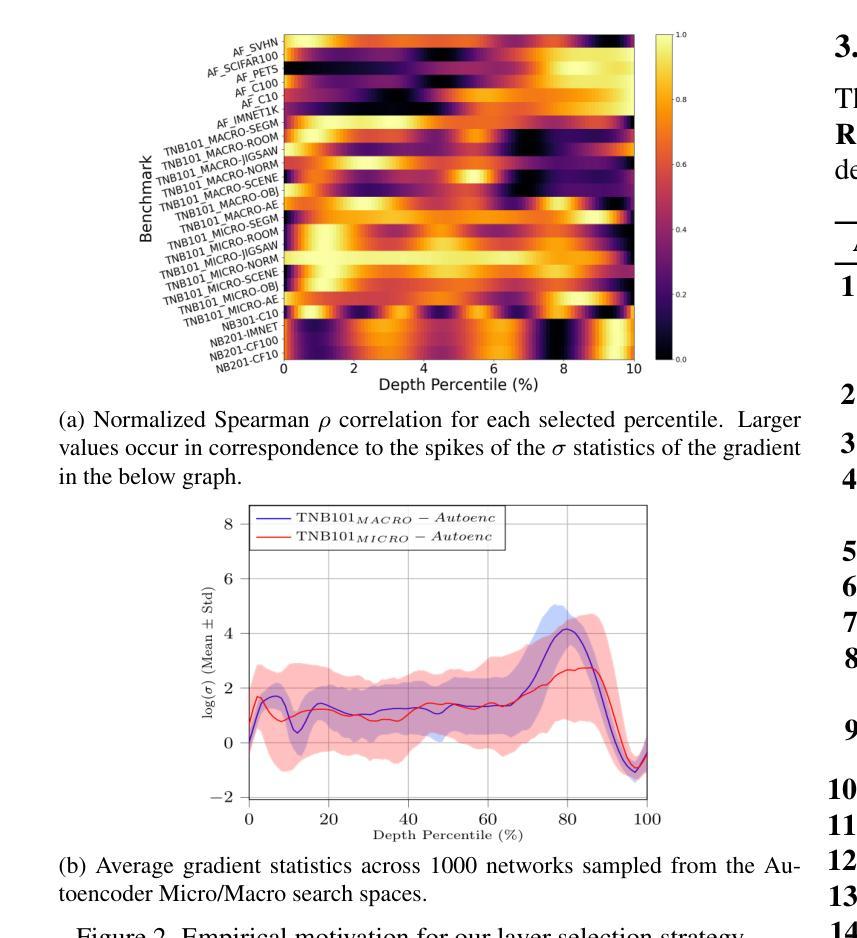
L-SWAG: Layer-Sample Wise Activation with Gradients information for Zero-Shot NAS on Vision Transformers
Authors:Sofia Casarin, Sergio Escalera, Oswald Lanz
Training-free Neural Architecture Search (NAS) efficiently identifies high-performing neural networks using zero-cost (ZC) proxies. Unlike multi-shot and one-shot NAS approaches, ZC-NAS is both (i) time-efficient, eliminating the need for model training, and (ii) interpretable, with proxy designs often theoretically grounded. Despite rapid developments in the field, current SOTA ZC proxies are typically constrained to well-established convolutional search spaces. With the rise of Large Language Models shaping the future of deep learning, this work extends ZC proxy applicability to Vision Transformers (ViTs). We present a new benchmark using the Autoformer search space evaluated on 6 distinct tasks and propose Layer-Sample Wise Activation with Gradients information (L-SWAG), a novel, generalizable metric that characterizes both convolutional and transformer architectures across 14 tasks. Additionally, previous works highlighted how different proxies contain complementary information, motivating the need for a ML model to identify useful combinations. To further enhance ZC-NAS, we therefore introduce LIBRA-NAS (Low Information gain and Bias Re-Alignment), a method that strategically combines proxies to best represent a specific benchmark. Integrated into the NAS search, LIBRA-NAS outperforms evolution and gradient-based NAS techniques by identifying an architecture with a 17.0% test error on ImageNet1k in just 0.1 GPU days.
无训练神经网络架构搜索(NAS)利用零成本(ZC)代理有效地识别高性能神经网络。与多镜头和单镜头NAS方法不同,ZC-NAS既(i)省时,无需模型训练,又(ii)具有可解释性,代理设计通常理论扎实。尽管该领域发展迅速,但当前的SOTA ZC代理通常仅限于成熟的卷积搜索空间。随着大型语言模型塑造深度学习未来,这项工作将ZC代理的应用扩展到视觉转换器(ViTs)。我们利用Autoformer搜索空间在6个不同任务上建立了一个新的基准测试,并提出了带有梯度信息的层采样激活(L-SWAG),这是一个新的、可推广的指标,可以表征14个任务的卷积和转换器架构。此外,先前的研究强调了不同代理包含互补信息,这突出了需要使用机器学习模型来识别有用组合的需要。为了进一步改进ZC-NAS,我们因此引入了LIBRA-NAS(低信息增益和偏差重新对齐),这是一种策略性地结合代理以最好地代表特定基准测试的方法。集成到NAS搜索中,LIBRA-NAS在ImageNet1k上的测试错误率为17.0%,在仅0.1个GPU天数的搜索中超过了进化策略和基于梯度的NAS技术。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF accepted at CVPR 2025
Summary
高效、无需训练的神经网络架构搜索(NAS)方法通过零成本(ZC)代理有效地识别高性能神经网络。本文将ZC-NAS扩展到用于识别未来深度学习中大型语言模型所广泛使用的视觉转换器(ViT)。本文提出一个新的基准测试方法Autoformer搜索空间,并在六个不同任务上评估。此外,提出了一种新的通用度量方法Layer-Sample Wise Activation with Gradients(L-SWAG),用于刻画卷积层和Transformer架构。为进一步提升ZC-NAS性能,引入了一种名为LIBRA-NAS的新方法,通过策略性结合代理以最佳方式代表特定基准测试。该方法在NAS搜索中集成了LIBRA-NAS,在ImageNet1k上的测试误差达到17%,仅使用0.1 GPU天的时间。
Key Takeaways
- ZC-NAS通过零成本代理高效识别高性能神经网络,无需训练模型,提高了时间效率。
- ZC代理可以扩展到视觉转换器(ViT),以适应大型语言模型在深度学习中的应用。
- 提出新的基准测试方法和Autoformer搜索空间,用于评估不同任务上的视觉转换器性能。
- 引入Layer-Sample Wise Activation with Gradients(L-SWAG)作为新的通用度量标准,可以刻画卷积和Transformer架构的特性。
- LIBRA-NAS是一种新的结合代理的方法,能够最佳地代表特定基准测试。
- LIBRA-NAS在NAS搜索中集成了进化算法和基于梯度的技术,在ImageNet1k上的测试错误率为仅使用很少计算资源的条件下的最佳表现之一。这表明其在提升神经网络架构搜索效率方面具有巨大潜力。
点此查看论文截图

EmoVLM-KD: Fusing Distilled Expertise with Vision-Language Models for Visual Emotion Analysis
Authors:SangEun Lee, Yubeen Lee, Eunil Park
Visual emotion analysis, which has gained considerable attention in the field of affective computing, aims to predict the dominant emotions conveyed by an image. Despite advancements in visual emotion analysis with the emergence of vision-language models, we observed that instruction-tuned vision-language models and conventional vision models exhibit complementary strengths in visual emotion analysis, as vision-language models excel in certain cases, whereas vision models perform better in others. This finding highlights the need to integrate these capabilities to enhance the performance of visual emotion analysis. To bridge this gap, we propose EmoVLM-KD, an instruction-tuned vision-language model augmented with a lightweight module distilled from conventional vision models. Instead of deploying both models simultaneously, which incurs high computational costs, we transfer the predictive patterns of a conventional vision model into the vision-language model using a knowledge distillation framework. Our approach first fine-tunes a vision-language model on emotion-specific instruction data and then attaches a distilled module to its visual encoder while keeping the vision-language model frozen. Predictions from the vision language model and the distillation module are effectively balanced by a gate module, which subsequently generates the final outcome. Extensive experiments show that EmoVLM-KD achieves state-of-the-art performance on multiple visual emotion analysis benchmark datasets, outperforming the existing methods while maintaining computational efficiency. The code is available in https://github.com/sange1104/EmoVLM-KD.
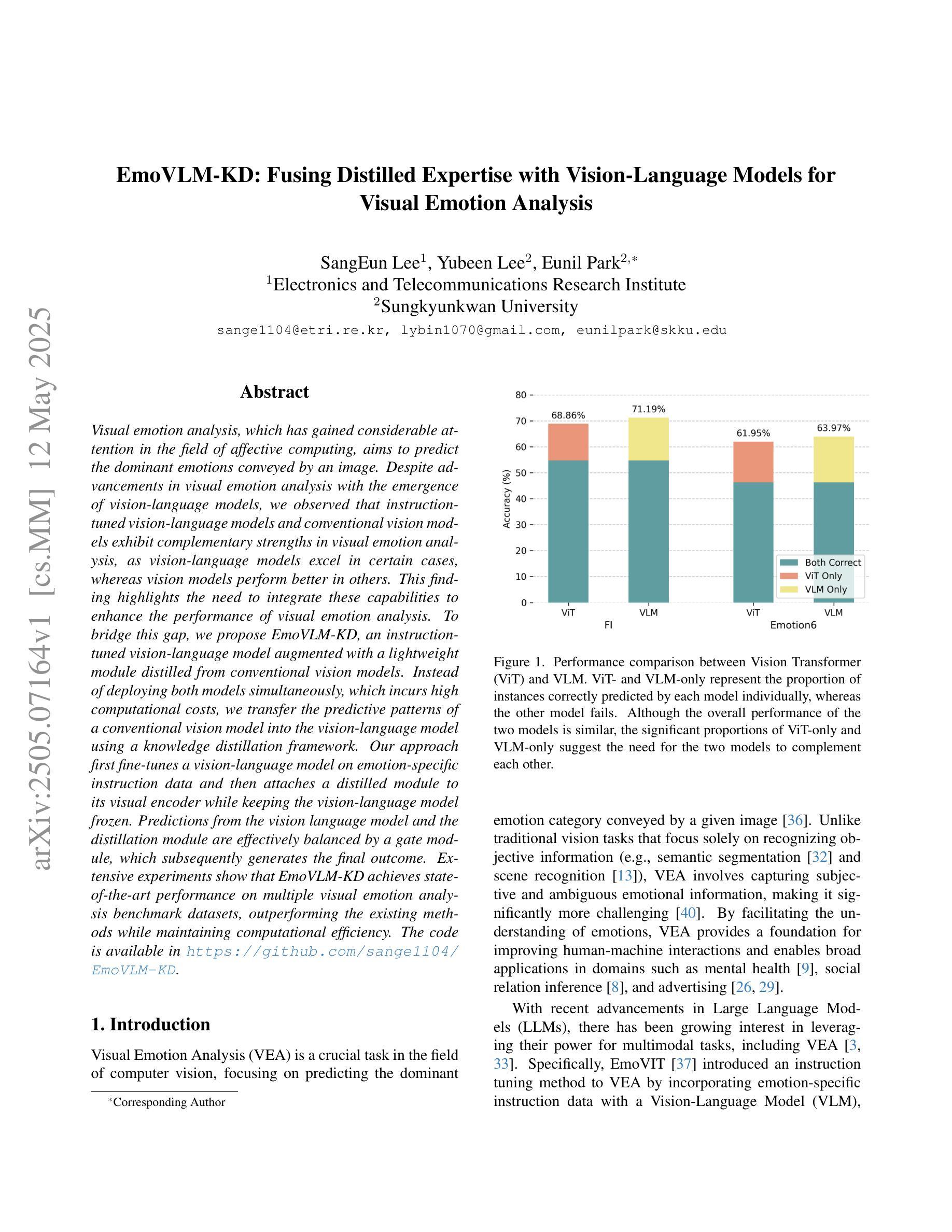
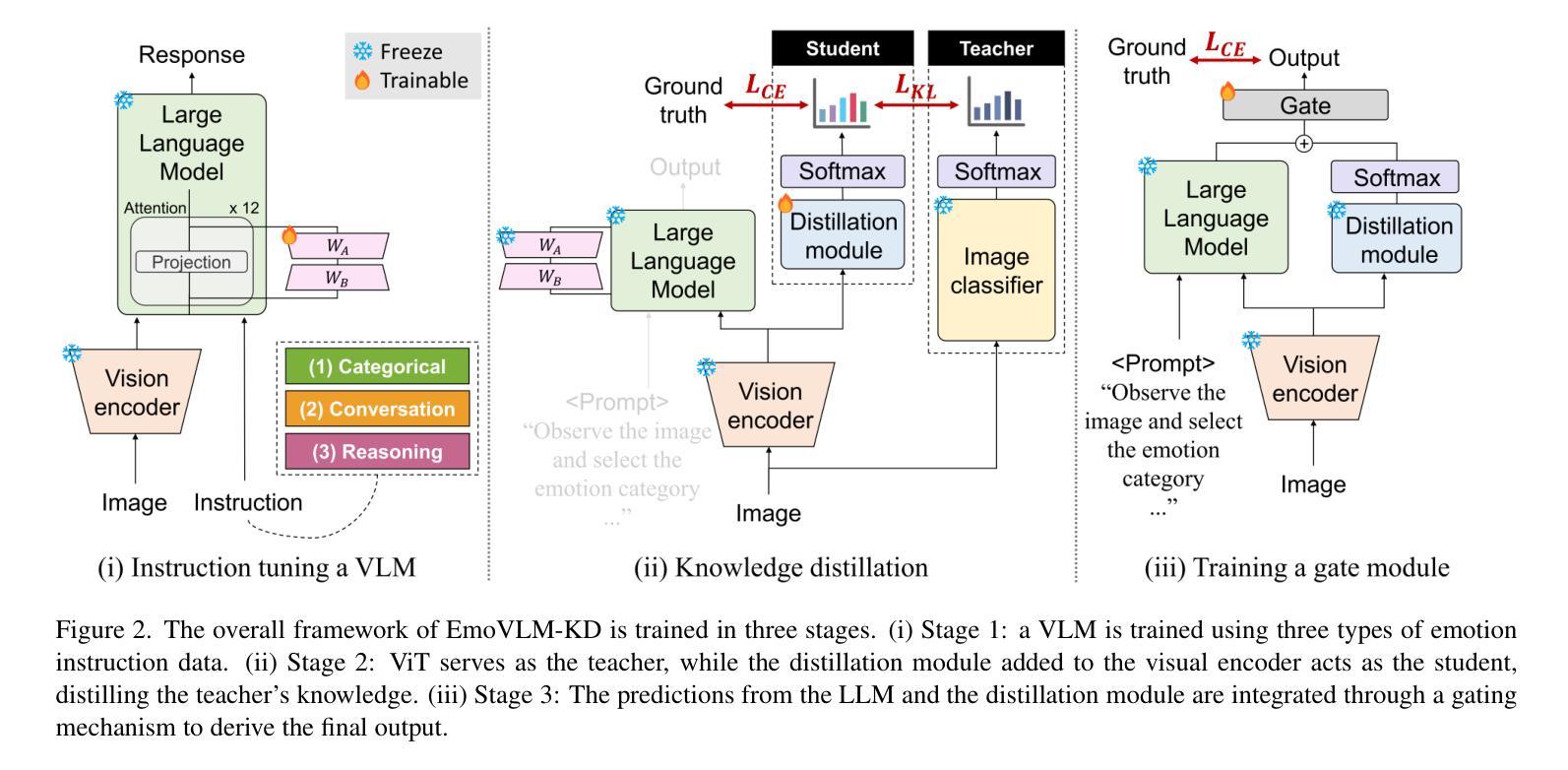
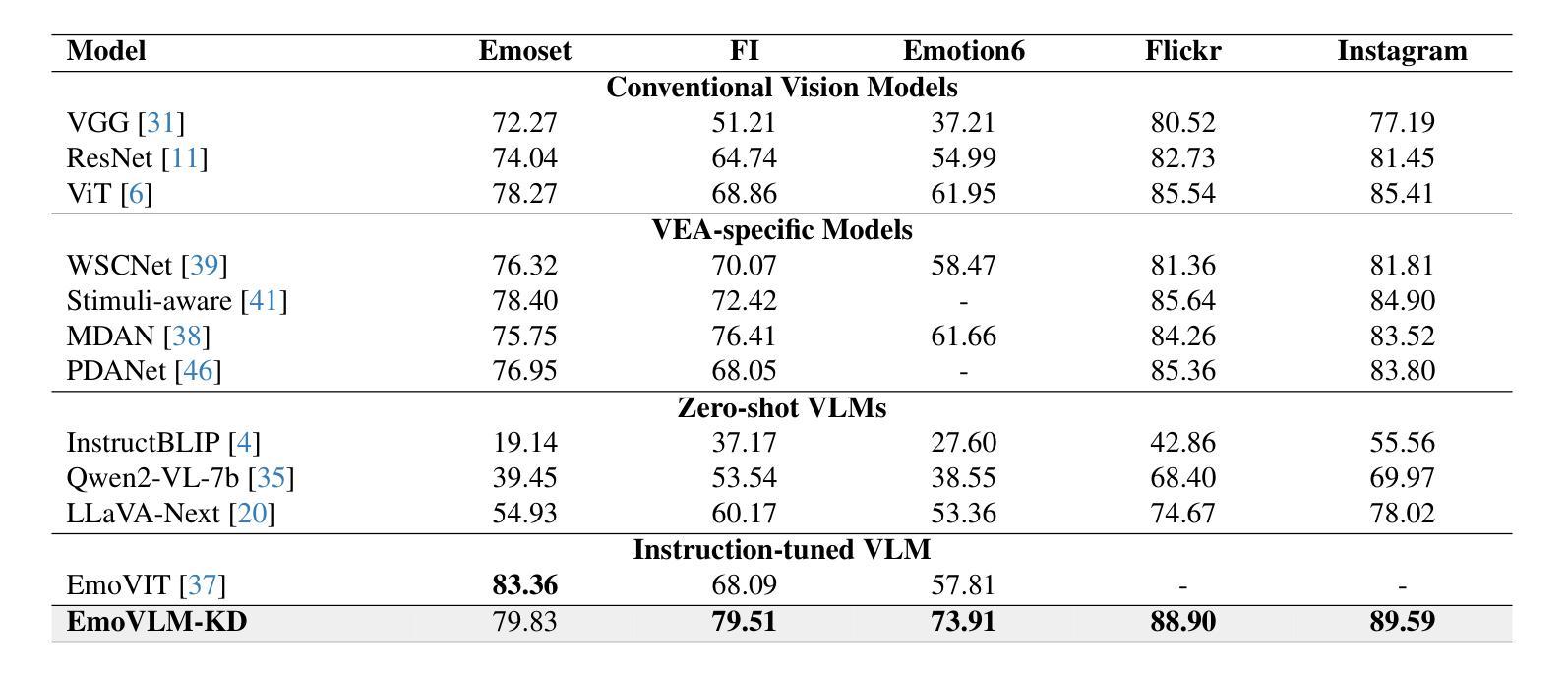
视觉情感分析是情感计算领域备受关注的研究方向,旨在预测图像所传达的主导情感。随着视觉语言模型的兴起,视觉情感分析领域取得了进展。我们观察到,指令调整型视觉语言模型和传统视觉模型在视觉情感分析中表现出互补的优势,视觉语言模型在某些情况下表现优异,而视觉模型在另一些情况下表现更好。这一发现强调了整合这些能力以提高视觉情感分析性能的重要性。为了弥补这一差距,我们提出了EmoVLM-KD,这是一个结合了传统视觉模型蒸馏出的轻量化模块的指令调整型视觉语言模型。与传统的同时部署两种模型的方法相比,我们采用知识蒸馏框架将传统视觉模型的预测模式转移到视觉语言模型中,这样可以避免高昂的计算成本。我们的方法首先通过情感特定指令数据对视觉语言模型进行微调,然后在保持视觉语言模型不变的同时,将其与蒸馏模块附加到视觉编码器上。来自视觉语言模型和蒸馏模块的预测通过一个门模块进行有效的平衡,从而生成最终的结果。大量实验表明,EmoVLM-KD在多个视觉情感分析基准数据集上实现了最先进的性能表现,不仅在性能上超越了现有方法,同时也保持了计算效率。代码可通过https://github.com/sange1104/EmoVLM-KD获取。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted at Workshop and Competition on Affective & Behavior Analysis in-the-wild (ABAW), CVPR 2025, 10 pages, 4 figures, 4 tables
Summary
视觉情感分析旨在预测图像所传达的主导情感,在情感计算领域受到广泛关注。研究发现,指令调整型视觉语言模型和传统视觉模型在视觉情感分析中具有互补优势。为此,提出EmoVLM-KD模型,该模型在指令调整型视觉语言模型的基础上,通过知识蒸馏框架融入传统视觉模型的预测模式。EmoVLM-KD通过精细化调整情感特定指令数据对视觉语言模型进行训练,并添加一个蒸馏模块到其视觉编码器上。该模型的预测结果由门模块有效平衡,生成最终输出。实验表明,EmoVLM-KD在多个视觉情感分析基准数据集上取得了最先进的性能,同时在计算效率上保持优势。
Key Takeaways
- 视觉情感分析是情感计算领域的一个重要方向,旨在预测图像中的主导情感。
- 指令调整型视觉语言模型和传统视觉模型在视觉情感分析中具有各自的优势,需要整合以提升性能。
- EmoVLM-KD模型结合了指令调整型视觉语言模型和传统视觉模型的优点,通过知识蒸馏实现高效的性能提升。
- EmoVLM-KD模型包含情感特定指令数据的精细化调整、蒸馏模块和门模块三个关键部分。
- EmoVLM-KD在多个视觉情感分析基准数据集上取得了最先进的性能。
- EmoVLM-KD模型的代码已公开可访问。
点此查看论文截图
Visual Instruction Tuning with Chain of Region-of-Interest
Authors:Yixin Chen, Shuai Zhang, Boran Han, Bernie Wang
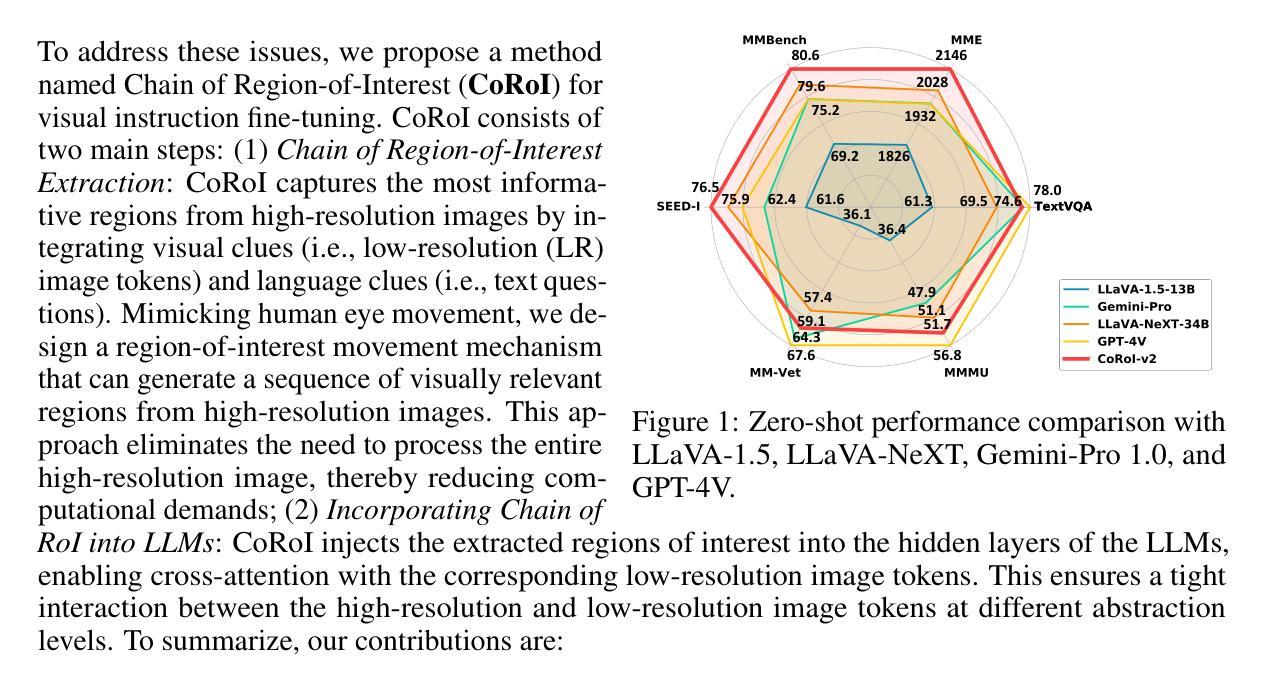
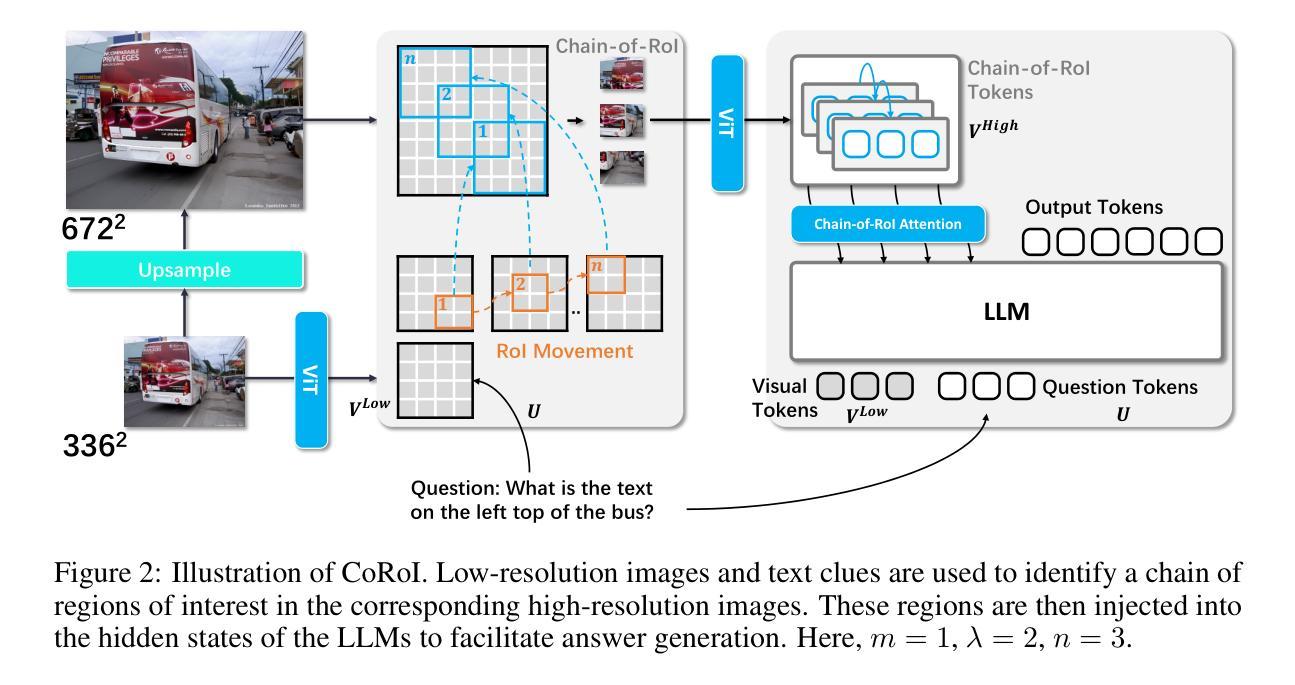
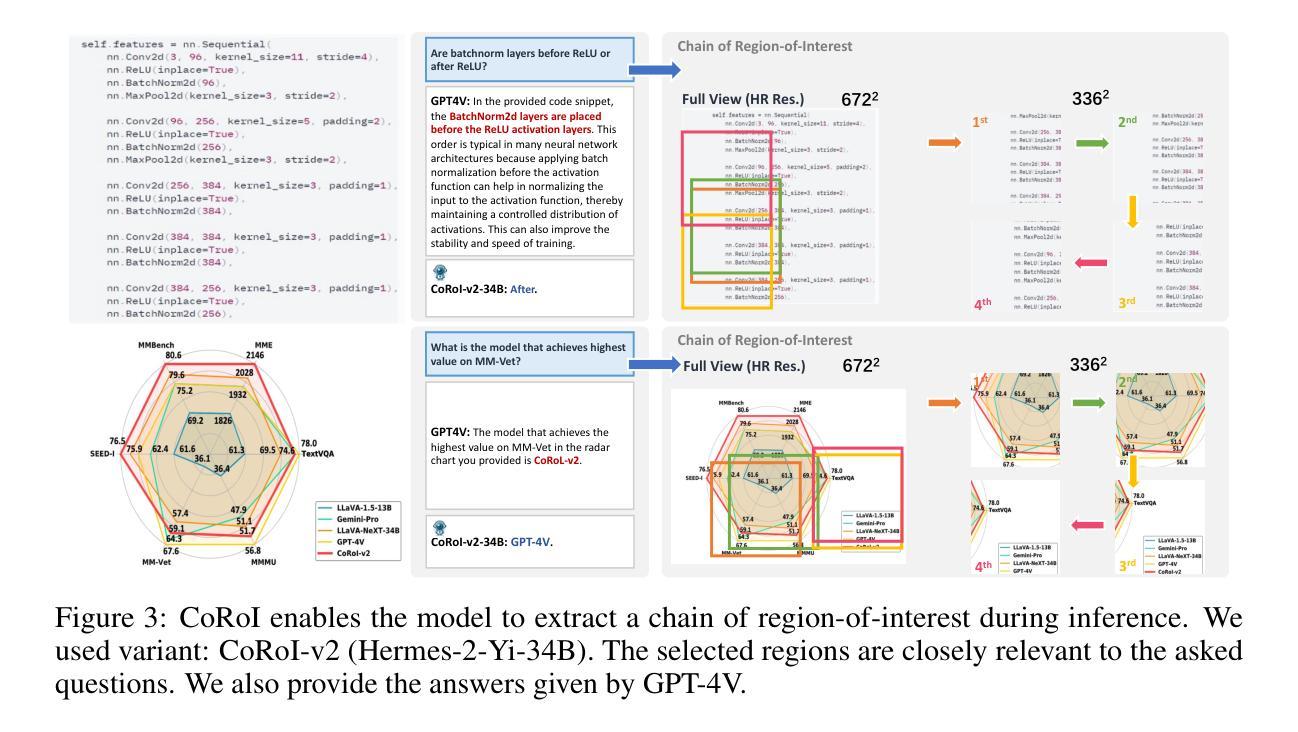
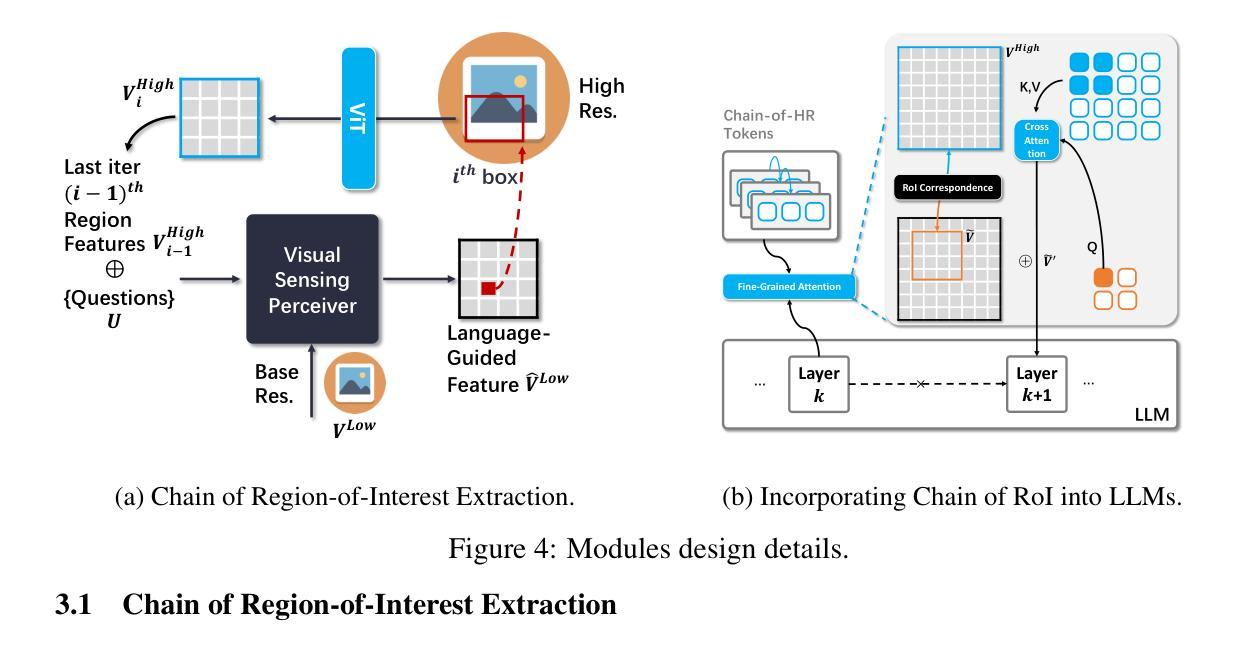
High-resolution (HR) images are pivotal for enhancing the recognition and understanding capabilities of multimodal large language models (MLLMs). However, directly increasing image resolution can significantly escalate computational demands. In this study, we propose a method called Chain of Region-of-Interest (CoRoI) for Visual Instruction Tuning, aimed at alleviating the computational burden associated with high-resolution images for MLLMs. Drawing inspiration from the selective nature of the human visual system, we recognize that not all regions within high-resolution images carry equal importance. CoRoI seeks to identify and prioritize the most informative regions, thereby enhancing multimodal visual comprehension and recognition while circumventing the need for processing lengthy HR image tokens. Through extensive experiments on 11 benchmarks, we validate the efficacy of CoRoI across varying sizes, ranging from 7B to 34B in parameters. Our models consistently demonstrate superior performance across diverse multimodal benchmarks and tasks. Notably, our method outperforms LLaVA-NeXT on almost all benchmarks and our finetuned 34B model surpasses proprietary methods like Gemini Pro 1.0 on six benchmarks, as well as outperforming GPT-4V on MMB, SEED-I, and MME.
高分辨率(HR)图像对于提高多模态大型语言模型(MLLMs)的识别和理解能力至关重要。然而,直接增加图像分辨率会大幅增加计算需求。本研究提出了一种名为“基于感兴趣区域的链”(CoRoI)的视觉指令微调方法,旨在缓解多模态语言模型处理高分辨率图像的计算负担。我们从人类视觉系统的选择性特点中汲取灵感,认识到高分辨率图像中的各个区域并非同等重要。CoRoI旨在识别并优先处理最具信息量的区域,从而提高多模态视觉的理解和识别能力,同时避免处理冗长的HR图像标记的需要。在涵盖多种规模和任务的共十一项基准测试中,我们验证了CoRoI的有效性,模型参数从数十亿到数十亿不等。我们的模型在各种多模态基准测试和任务中始终表现出卓越的性能。值得注意的是,我们的方法几乎在所有基准测试中都优于LLaVA-NeXT,我们的微调模型在六个基准测试中超过了Gemini Pro 1.0等专有方法,并在MMB、SEED-I和MME上超过了GPT-4V。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF N/A
Summary
本研究提出了一种名为CoRoI的视觉指令微调方法,旨在解决多模态大型语言模型在处理高分辨率图像时面临的计算负担问题。该方法通过识别并优先处理高分辨图像中最具信息量的区域,增强多模态视觉理解和识别能力,而无需处理冗长的图像标记。在多个基准测试中,该方法展现出优越的性能。特别是在多模态视觉领域的任务上,该方法的效率得到了有效验证,大幅提高了图像识别的准确性和效率。此外,相较于其他顶尖模型如LLaVA-NeXT和GPT-4V等,该方法的优势在于提升了在多模态任务的泛化性能,在不同规模的模型中都有稳定的表现。随着模型的规模增大,这种优势会更加明显。该研究的发现有望推动多模态视觉理解技术的进一步应用和发展。
Key Takeaways
- CoRoI方法旨在解决多模态大型语言模型在处理高分辨率图像时的计算负担问题。
- 该方法识别并优先处理最具信息量的图像区域,以实现对图像的理解和识别的高效过程。在多个基准测试中表现出了出色的性能。
点此查看论文截图
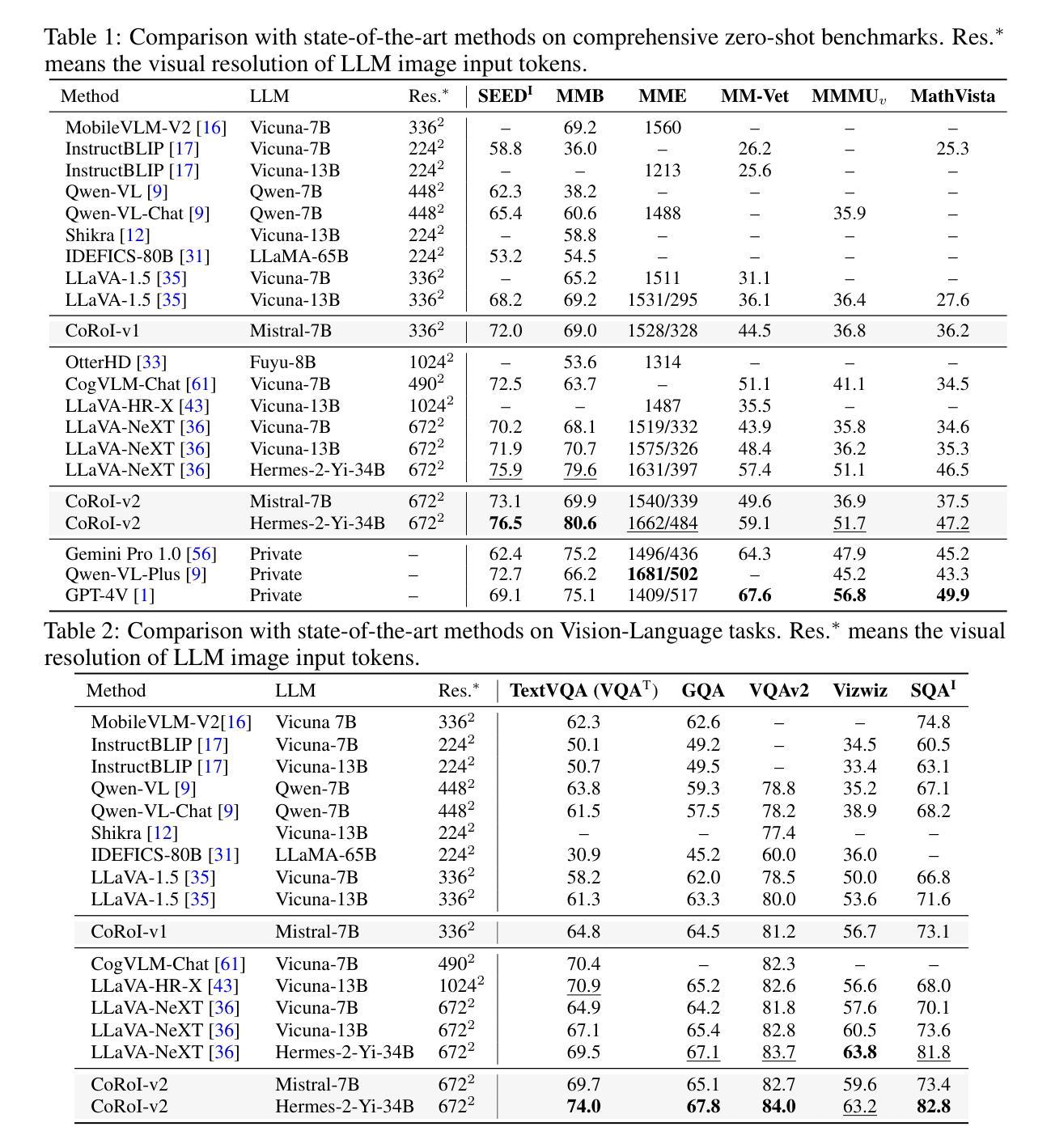
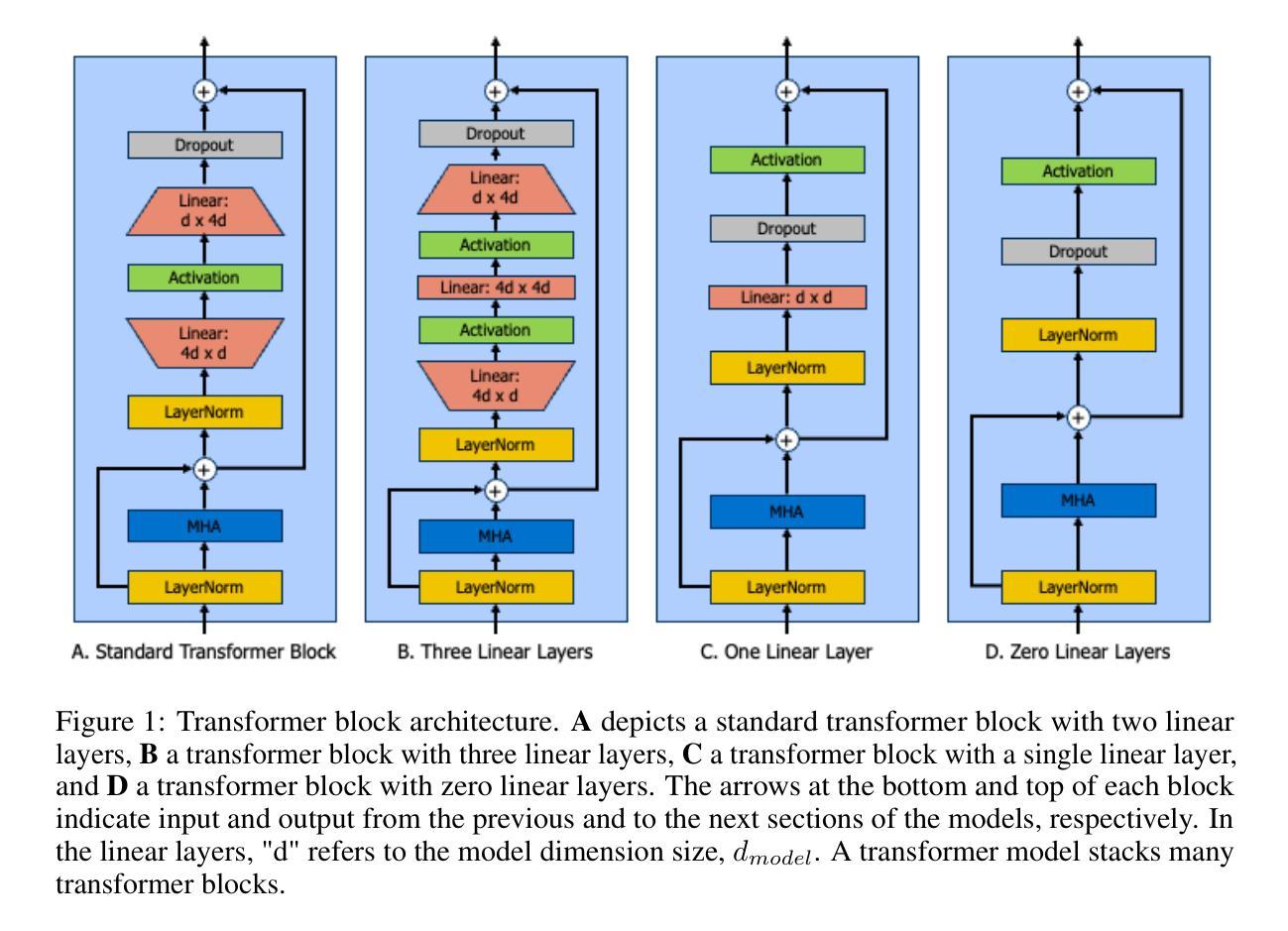
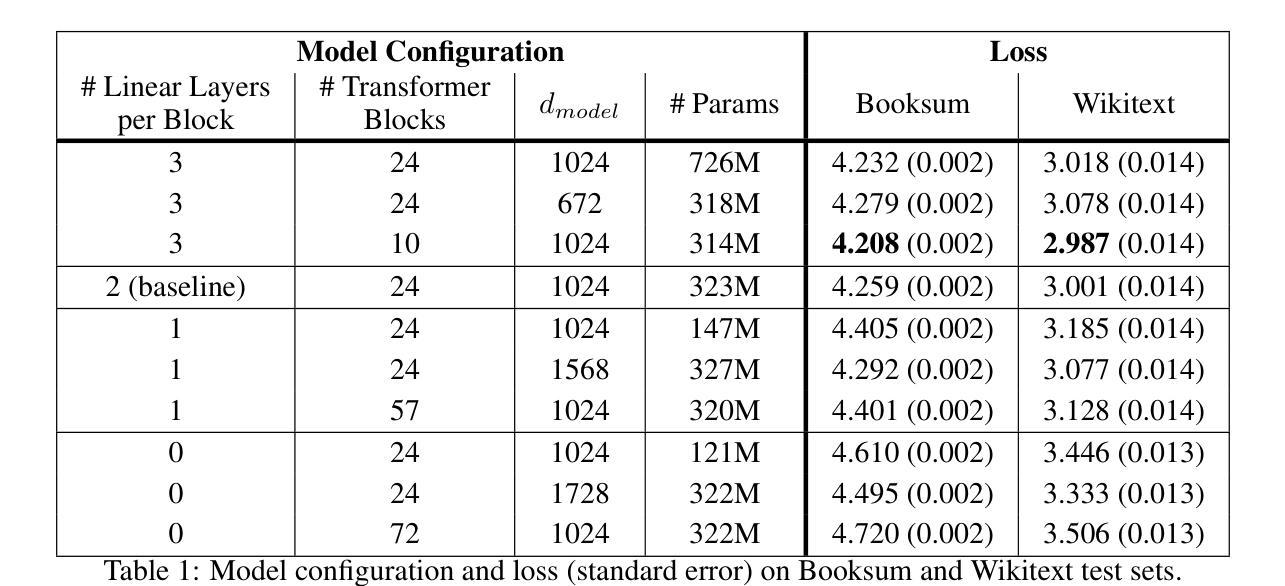
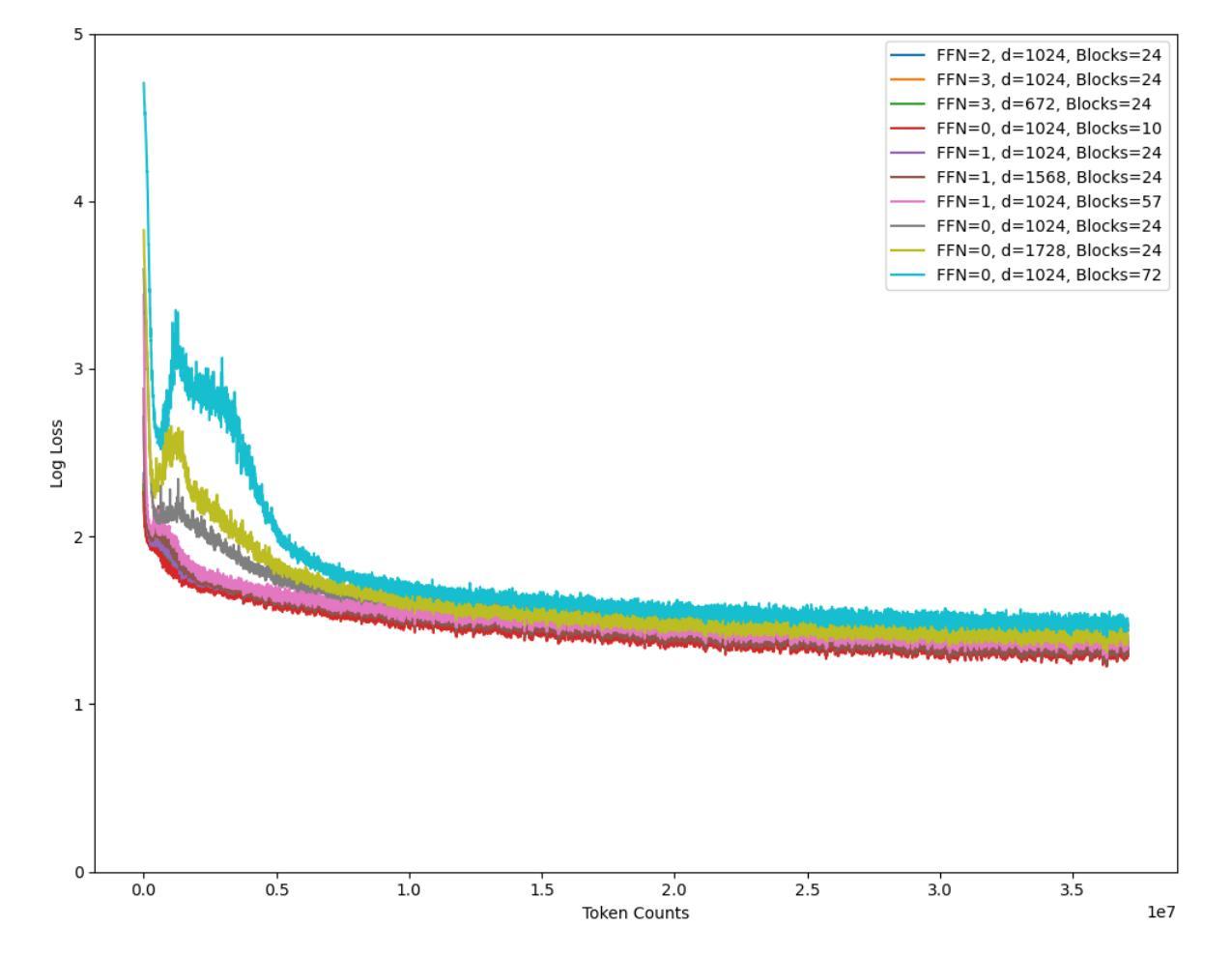
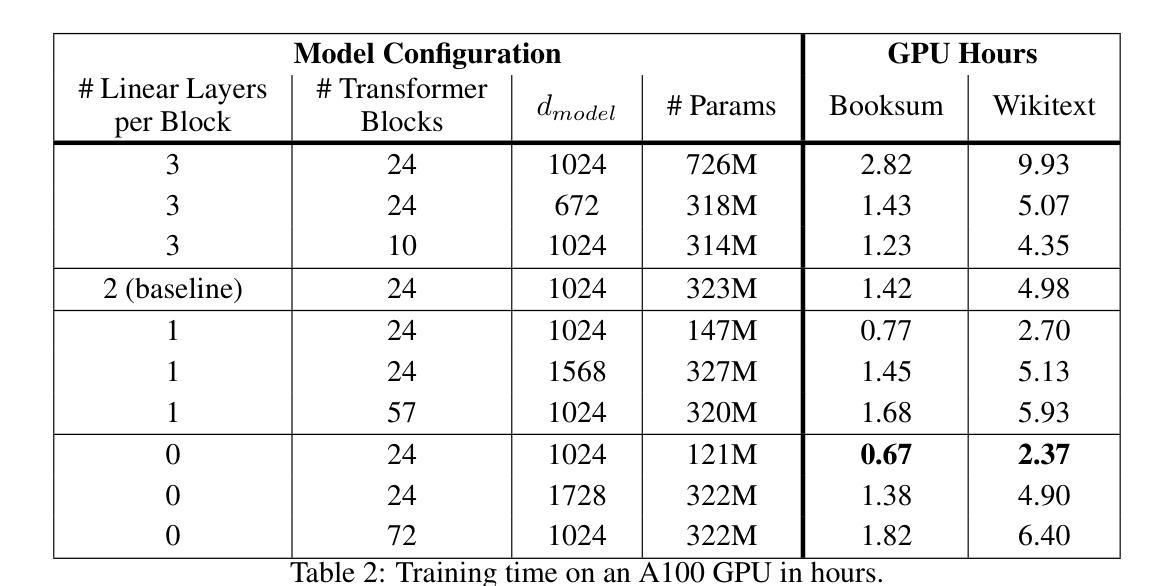
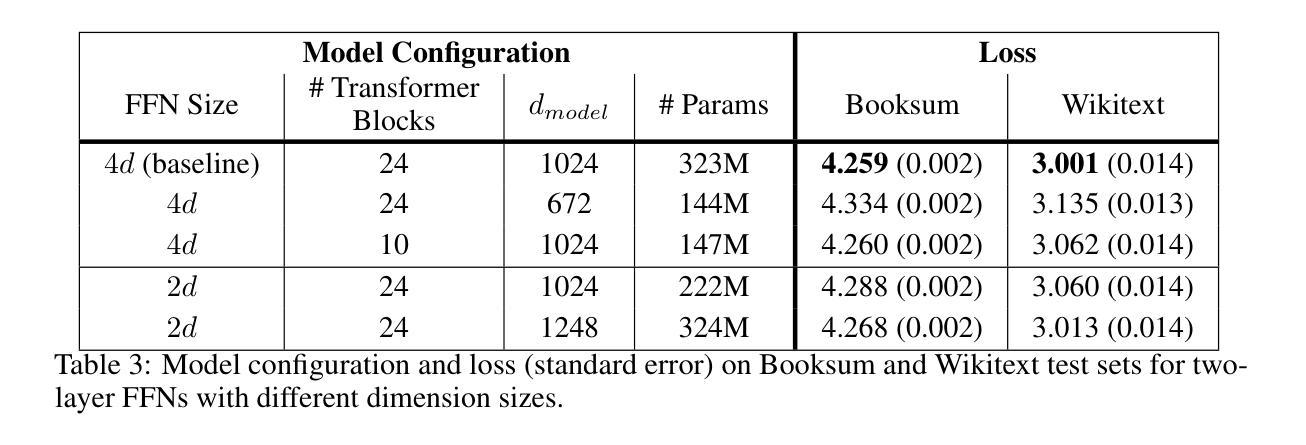
Attention Is Not All You Need: The Importance of Feedforward Networks in Transformer Models
Authors:Isaac Gerber
Decoder-only transformer networks have become incredibly popular for language modeling tasks. State-of-the-art models can have over a hundred transformer blocks, containing billions of trainable parameters, and are trained on trillions of tokens of text. Each transformer block typically consists of a multi-head attention (MHA) mechanism and a two-layer fully connected feedforward network (FFN). In this paper, we examine the importance of the FFN during the model pre-training process through a series of experiments, confirming that the FFN is important to model performance. Furthermore, we show that models using a transformer block configuration with three-layer FFNs with fewer such blocks outperform the standard two-layer configuration delivering lower training loss with fewer total parameters in less time.
解码器仅的转换器网络在建模任务中变得非常受欢迎。最先进的模型可以拥有超过一百个转换器块,包含数十亿的可训练参数,并在万亿个文本标记上进行训练。每个转换器块通常包含一个多头注意力(MHA)机制和两层全连接的前馈网络(FFN)。在这篇论文中,我们通过一系列实验来检验前馈网络在模型预训练过程中的重要性,证实了前馈网络对模型性能至关重要。此外,我们还表明,使用三层前馈网络的转换器块配置比标准的两层配置更优秀,它能在更短的时间内以更少的总参数实现更低的训练损失。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary:解码器仅的转换器网络已成为语言建模任务的热门选择。最先进的模型可能包含超过一百个转换器块,数十亿的可训练参数,并在万亿级别的文本标记上进行训练。本文通过一系列实验验证了全连接前馈网络(FFN)在模型预训练过程中的重要性,并表明采用三层FFN的转换器块配置能够在更少的时间内实现更低训练损失和更少总参数的性能超越标准两层配置。
Key Takeaways:
- 解码器仅的转换器网络已成为流行的语言建模工具。
- 最先进的模型包含众多转换器块和数十亿可训练参数。
- 模型在大量文本标记上进行训练。
- 实验验证了全连接前馈网络(FFN)在模型预训练中的重要性。
- 三层FFN的转换器块配置可以超越标准两层配置的性能。
- 优化配置能在更少的时间内实现更低训练损失。
点此查看论文截图

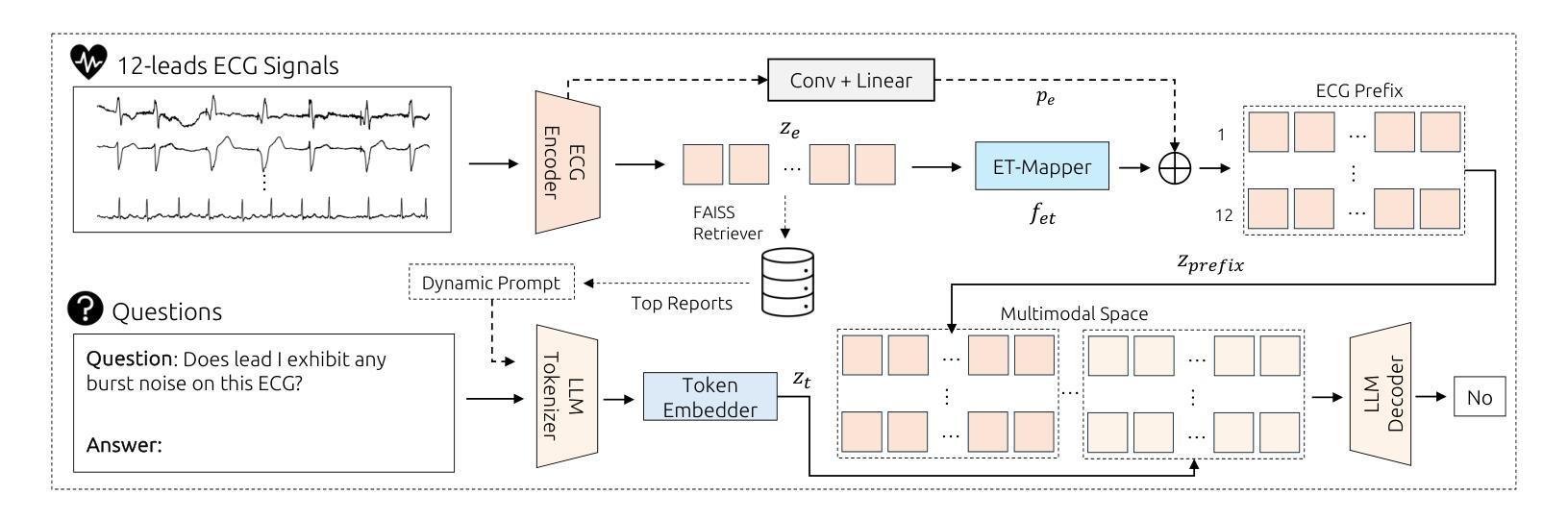
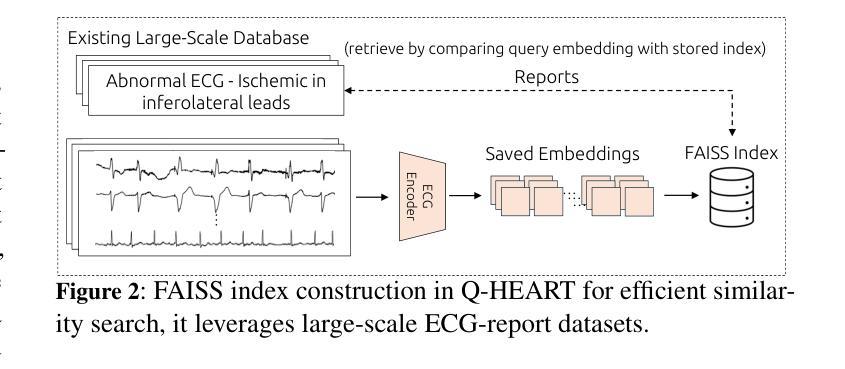
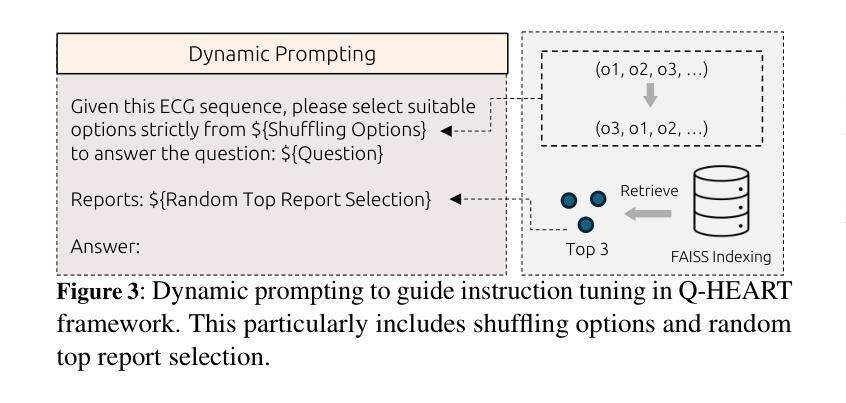
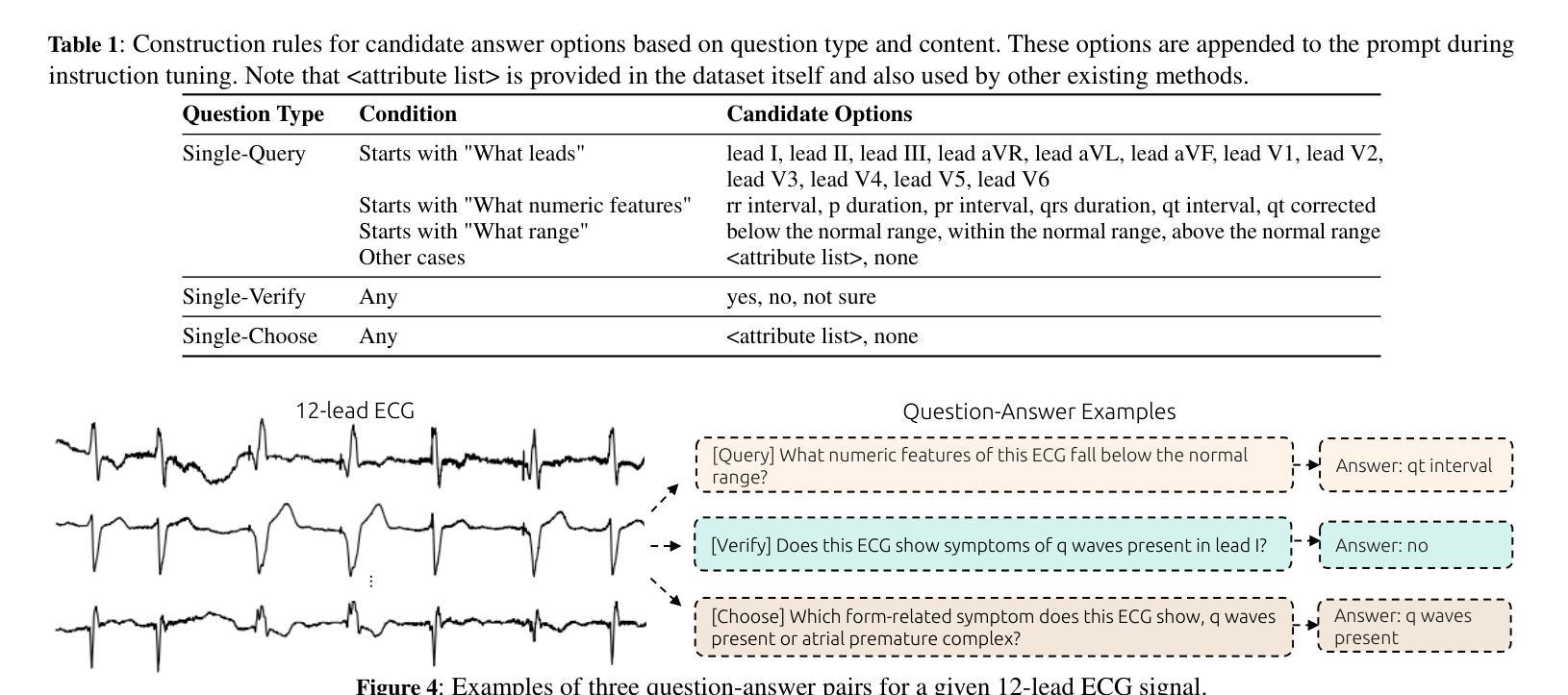
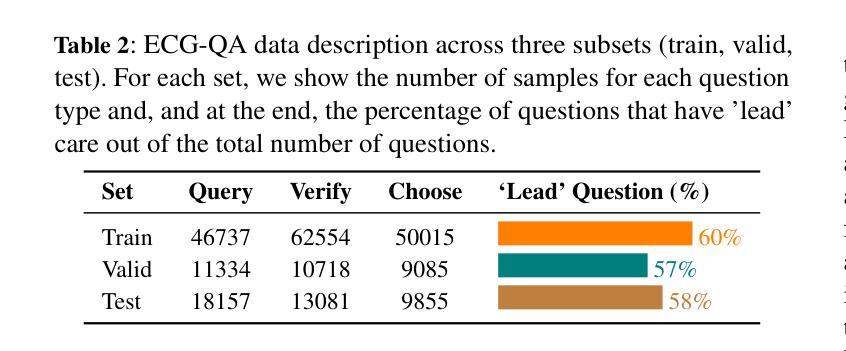
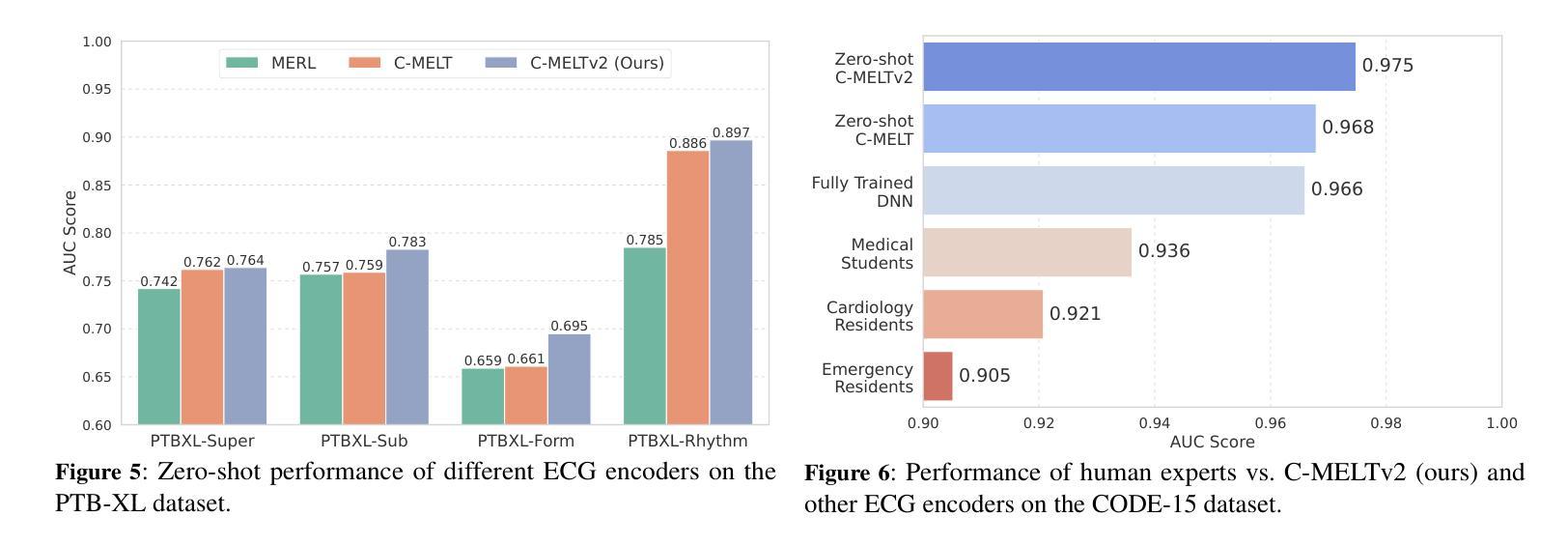
Q-Heart: ECG Question Answering via Knowledge-Informed Multimodal LLMs
Authors:Hung Manh Pham, Jialu Tang, Aaqib Saeed, Dong Ma
Electrocardiography (ECG) offers critical cardiovascular insights, such as identifying arrhythmias and myocardial ischemia, but enabling automated systems to answer complex clinical questions directly from ECG signals (ECG-QA) remains a significant challenge. Current approaches often lack robust multimodal reasoning capabilities or rely on generic architectures ill-suited for the nuances of physiological signals. We introduce Q-Heart, a novel multimodal framework designed to bridge this gap. Q-Heart leverages a powerful, adapted ECG encoder and integrates its representations with textual information via a specialized ECG-aware transformer-based mapping layer. Furthermore, Q-Heart leverages dynamic prompting and retrieval of relevant historical clinical reports to guide tuning the language model toward knowledge-aware ECG reasoning. Extensive evaluations on the benchmark ECG-QA dataset show Q-Heart achieves state-of-the-art performance, outperforming existing methods by a 4% improvement in exact match accuracy. Our work demonstrates the effectiveness of combining domain-specific architectural adaptations with knowledge-augmented LLM instruction tuning for complex physiological ECG analysis, paving the way for more capable and potentially interpretable clinical patient care systems.
心电图(ECG)提供了关于心血管的关键洞察,如识别心律失常和心肌缺血,但是使自动化系统直接从心电图信号(ECG-QA)回答复杂的临床问题仍然是一个重大挑战。当前的方法通常缺乏稳健的多模式推理能力,或者依赖于对生理信号细微差别适应能力较差的通用架构。我们引入了Q-Heart,这是一个新型的多模式框架,旨在弥合这一鸿沟。Q-Heart利用强大的自适应心电图编码器和通过基于变压器的特殊心电图感知映射层将文本信息与心电图表示相结合。此外,Q-Heart利用动态提示和检索相关的历史临床报告来指导语言模型朝向知识感知的心电图推理调整。在ECG-QA数据集上的广泛评估显示,Q-Heart达到了最先进的性能水平,在精确匹配准确性方面比现有方法提高了4%。我们的工作证明了结合特定领域的架构适应性与知识增强的大型语言模型指令调整对于复杂生理心电图分析的有效性,为更强大和潜在可解释的临床患者护理系统铺平了道路。
论文及项目相关链接
摘要
心电图(ECG)为心血管健康提供了关键的见解,如识别心律失常和心肌缺血等。然而,如何让自动化系统直接从心电图信号中回答复杂的临床问题(ECG-QA)仍然是一个巨大的挑战。当前的方法要么缺乏稳健的多模式推理能力,要么依赖于不适合生理信号细微差别的通用架构。我们引入了Q-Heart,一个旨在弥合这一鸿沟的新型多模式框架。Q-Heart利用强大的心电图编码器,并通过专业的基于变压器的心电图感知映射层将心电图表示与文本信息集成在一起。此外,Q-Heart利用动态提示和检索相关的历史临床报告来引导语言模型朝着知识感知的心电图推理方向调整。在心电图问答数据集上的广泛评估表明,Q-Heart达到了最先进的性能水平,在精确匹配准确率方面比现有方法提高了4%。我们的工作证明了将领域特定的架构适应与知识增强的大型语言模型指令调整相结合,对于复杂生理心电图分析的有效性,为更强大和可解释的临床患者护理系统铺平了道路。
关键见解
- ECG在诊断心血管疾病如心律失常和心肌缺血方面具有重要意义。
- 自动化的ECG问答系统(ECG-QA)仍存在显著挑战,尤其是在多模式推理和生理信号细微差别处理方面。
- Q-Heart是一个新型多模式框架,通过结合心电图编码器和基于变压器的映射层解决了上述问题。
- Q-Heart利用动态提示和历史临床报告的检索,增强了语言模型的知识感知能力。
- 在基准ECG-QA数据集上的评估显示,Q-Heart在精确匹配准确率方面实现了显著的提升。
- 研究证明了结合特定领域架构调整和知识增强的大型语言模型对于复杂生理心电图分析的重要性。
点此查看论文截图

Tell Me Who Your Students Are: GPT Can Generate Valid Multiple-Choice Questions When Students’ (Mis)Understanding Is Hinted
Authors:Machi Shimmei, Masaki Uto, Yuichiroh Matsubayashi, Kentaro Inui, Aditi Mallavarapu, Noboru Matsuda
The primary goal of this study is to develop and evaluate an innovative prompting technique, AnaQuest, for generating multiple-choice questions (MCQs) using a pre-trained large language model. In AnaQuest, the choice items are sentence-level assertions about complex concepts. The technique integrates formative and summative assessments. In the formative phase, students answer open-ended questions for target concepts in free text. For summative assessment, AnaQuest analyzes these responses to generate both correct and incorrect assertions. To evaluate the validity of the generated MCQs, Item Response Theory (IRT) was applied to compare item characteristics between MCQs generated by AnaQuest, a baseline ChatGPT prompt, and human-crafted items. An empirical study found that expert instructors rated MCQs generated by both AI models to be as valid as those created by human instructors. However, IRT-based analysis revealed that AnaQuest-generated questions - particularly those with incorrect assertions (foils) - more closely resembled human-crafted items in terms of difficulty and discrimination than those produced by ChatGPT.
本研究的主要目标是开发并评估一种创新性的提示技术——AnaQuest,该技术使用预训练的大型语言模型来生成多项选择题(MCQs)。在AnaQuest中,选择项是关于复杂概念的句子级断言。该技术结合了形成性评估和终结性评估。在形成性阶段,学生以自由文本的形式回答关于目标概念的问题。在终结性评估中,AnaQuest分析这些回应来生成正确的和错误的断言。为了评估生成的MCQs的有效性,应用项目反应理论(IRT)来比较AnaQuest生成的多项选择题、基线ChatGPT提示和人类制作的项目之间的项目特征。实证研究发现在专家评估中,人工智能模型生成的MCQs与人类教师创建的题目一样有效。然而,基于IRT的分析显示,AnaQuest生成的问题——特别是那些带有错误断言(伪装)的问题——在难度和区分度方面更接近于人类制作的题目,而不是ChatGPT生成的题目。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF This is a pre-print version of a paper to appear in AIED2025
Summary
AnaQuest是一项基于预训练的大型语言模型的创新技术,用于生成多重选择题(MCQs)。它通过学生在文本中回答问题并自动分析学生的回答来生成正确和错误的断言。研究表明,人工智能生成的MCQs与专家教师生成的题目在有效性上相当。然而,基于Item Response Theory(IRT)的分析显示,AnaQuest生成的题目在难度和区分度上更接近人类创作的题目。特别是有错误断言的题目更是如此。总体而言,AnaQuest是一种高效的生成有效多重选择题的技术。
Key Takeaways
- AnaQuest是一种利用大型语言模型生成多重选择题的创新技术。
- 该技术结合了形成性和总结性评估,通过学生回答开放性问题并自动分析生成正确和错误的断言来工作。
- AnaQuest生成的题目包括关于复杂概念的句子级断言。
- 实证研究表明,AI生成的MCQs与专家教师生成的题目在有效性上相当。
- Item Response Theory(IRT)分析显示,AnaQuest生成的题目在难度和区分度上更接近人类创作的题目。特别是包含错误断言的题目更是如此。
点此查看论文截图

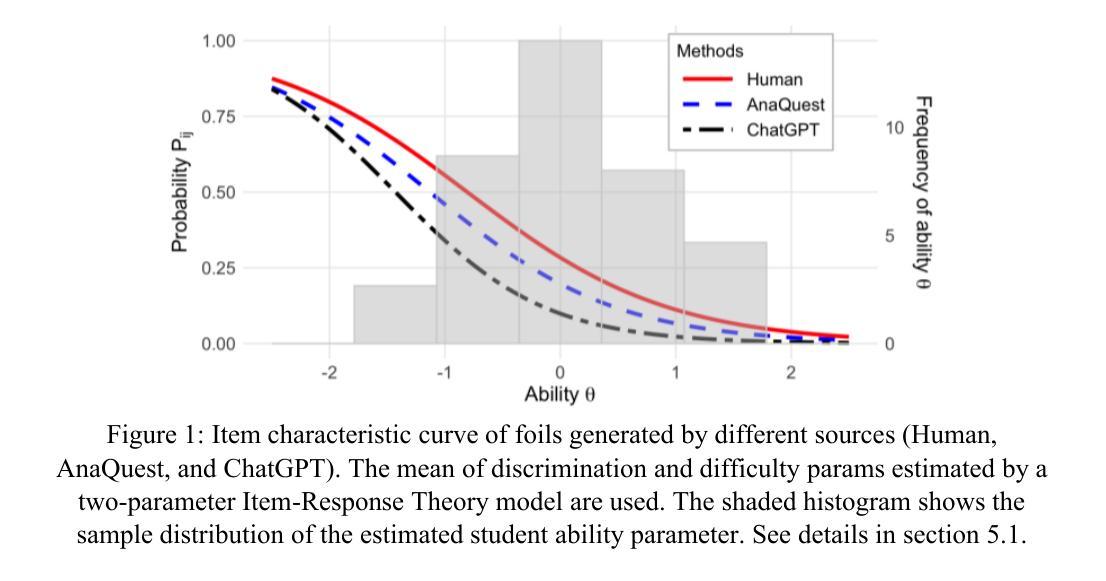

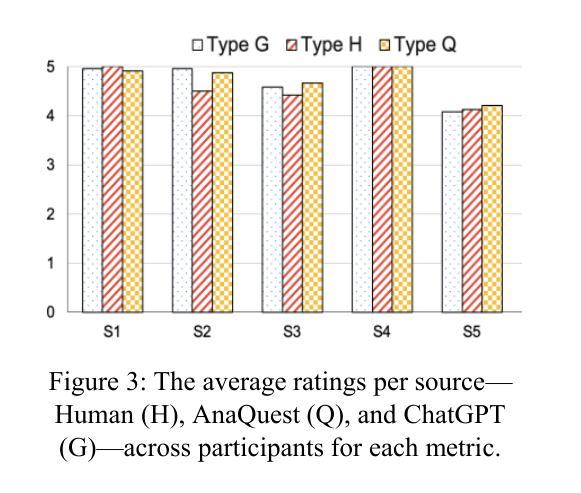
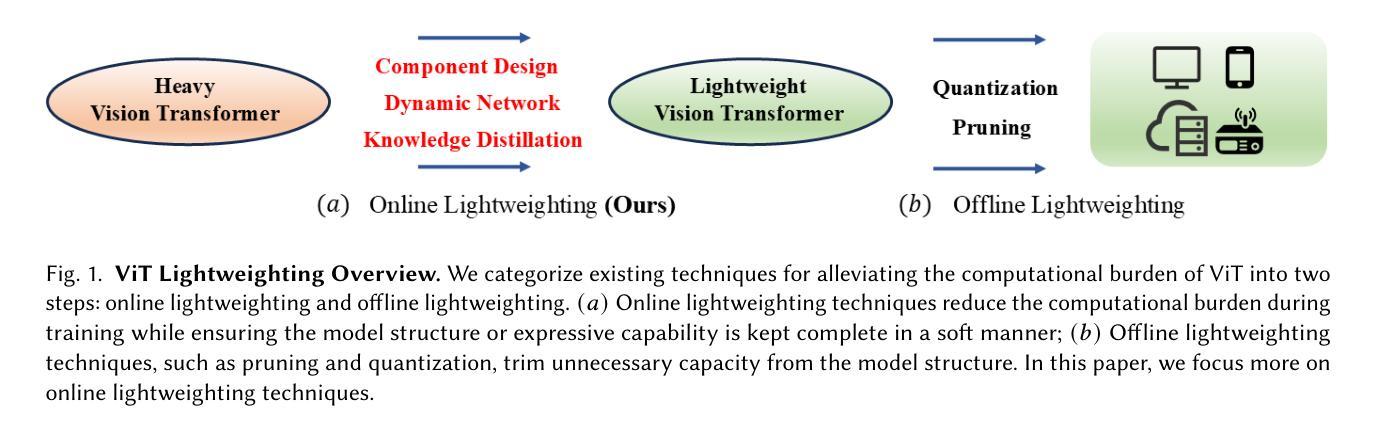
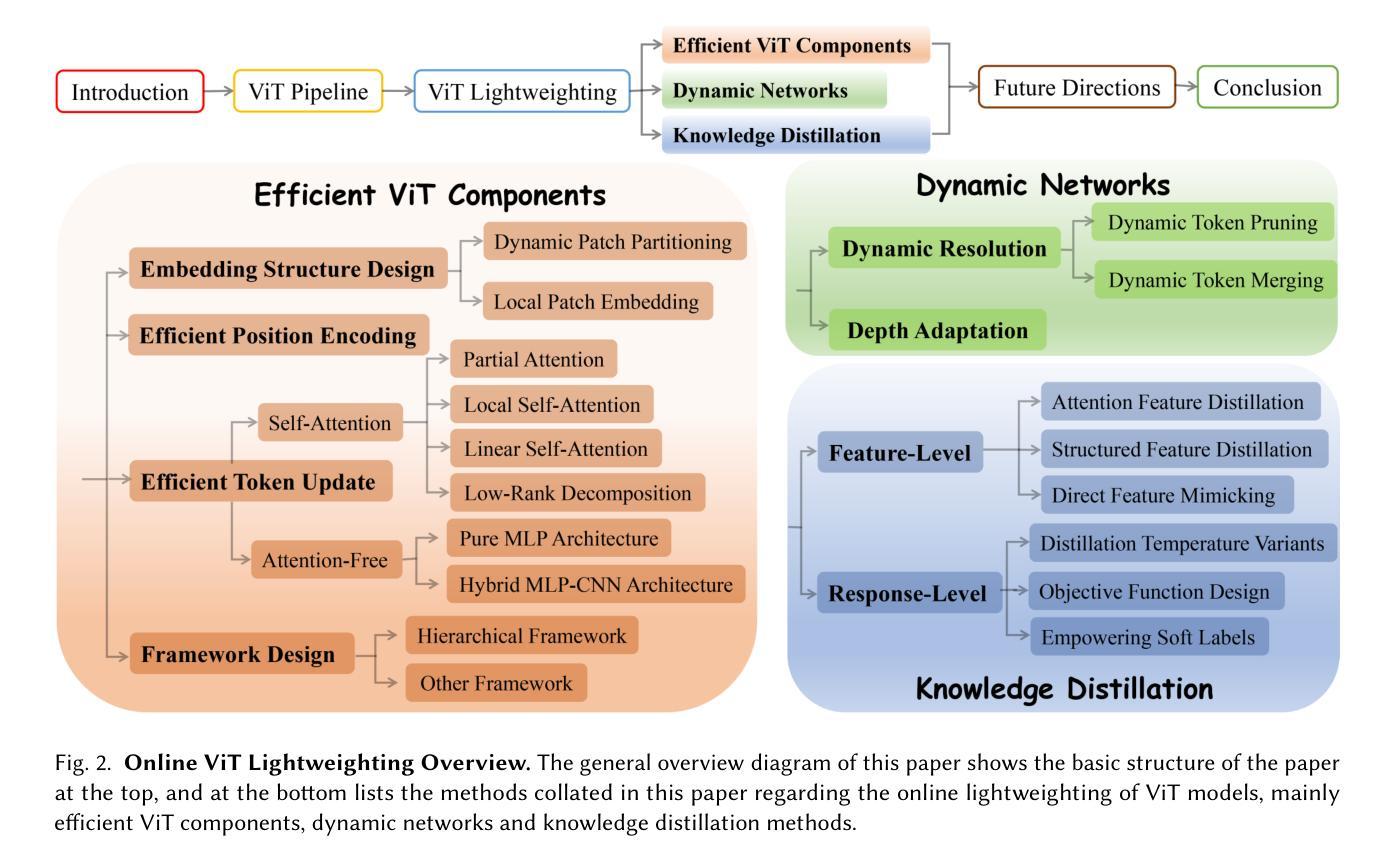
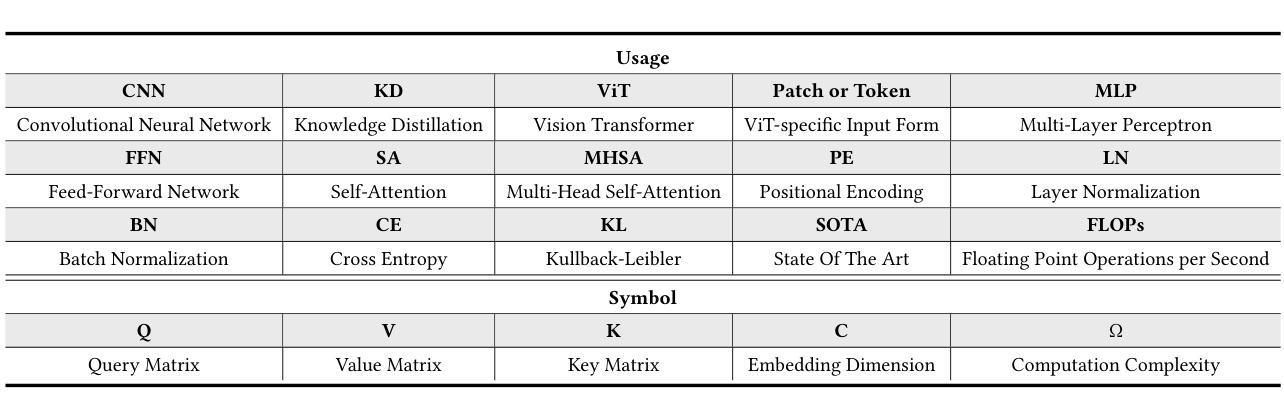
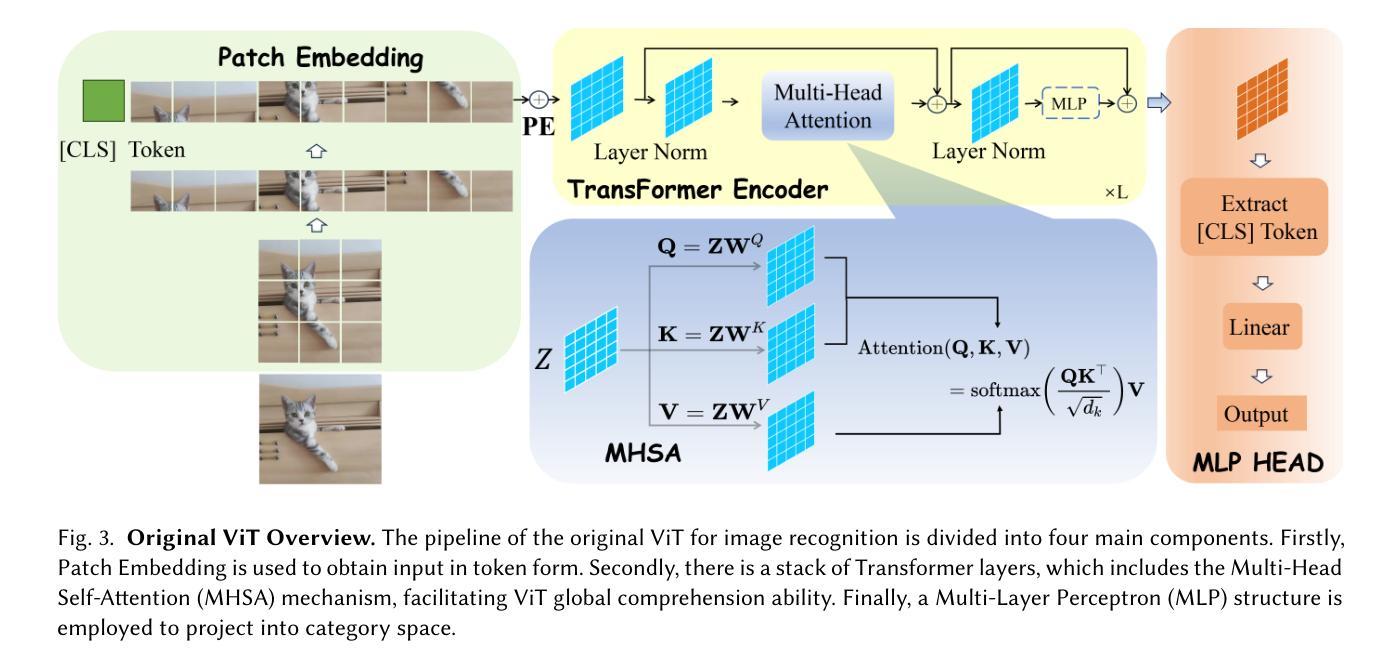
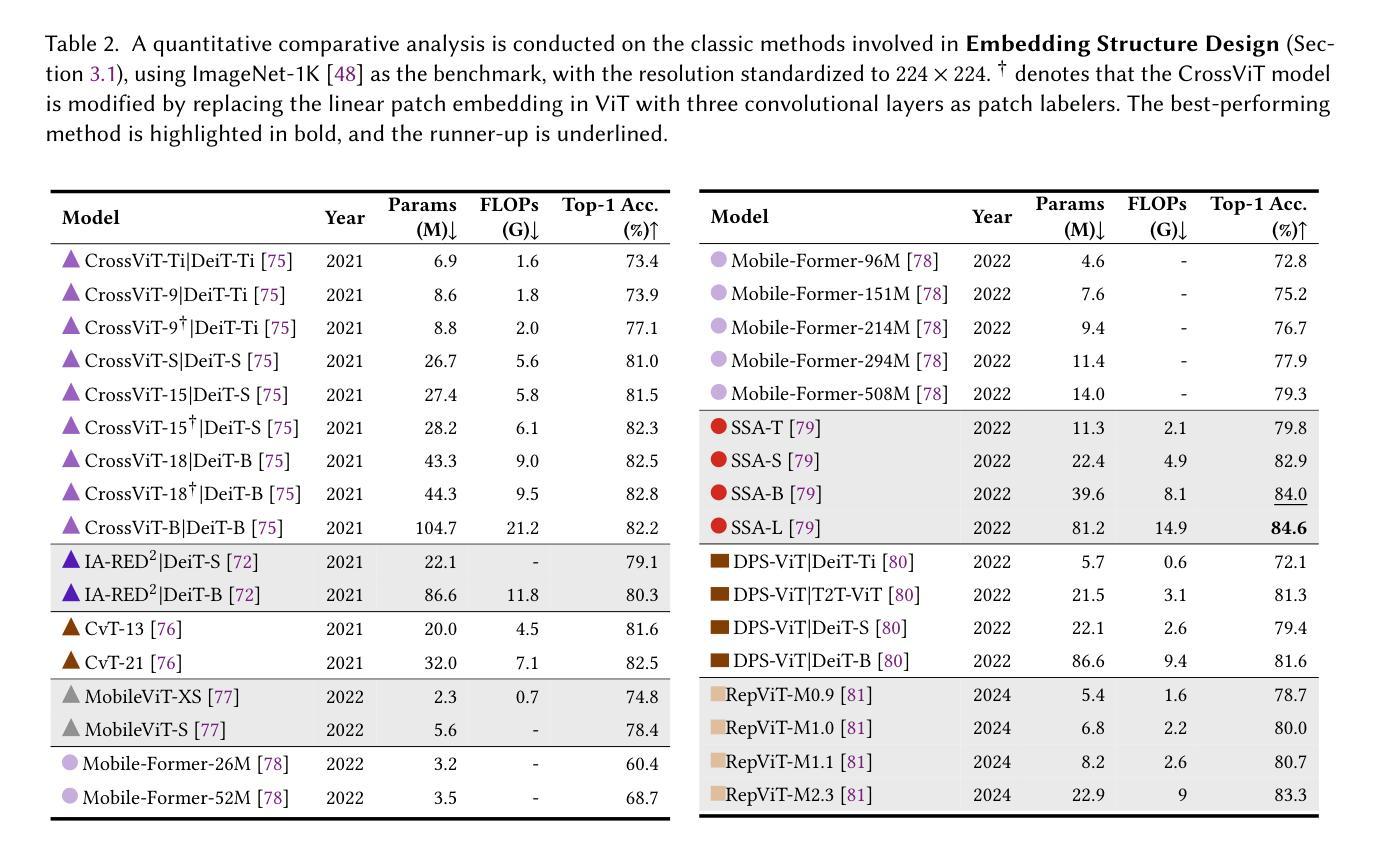
Image Recognition with Online Lightweight Vision Transformer: A Survey
Authors:Zherui Zhang, Rongtao Xu, Jie Zhou, Changwei Wang, Xingtian Pei, Wenhao Xu, Jiguang Zhang, Li Guo, Longxiang Gao, Wenbo Xu, Shibiao Xu
The Transformer architecture has achieved significant success in natural language processing, motivating its adaptation to computer vision tasks. Unlike convolutional neural networks, vision transformers inherently capture long-range dependencies and enable parallel processing, yet lack inductive biases and efficiency benefits, facing significant computational and memory challenges that limit its real-world applicability. This paper surveys various online strategies for generating lightweight vision transformers for image recognition, focusing on three key areas: Efficient Component Design, Dynamic Network, and Knowledge Distillation. We evaluate the relevant exploration for each topic on the ImageNet-1K benchmark, analyzing trade-offs among precision, parameters, throughput, and more to highlight their respective advantages, disadvantages, and flexibility. Finally, we propose future research directions and potential challenges in the lightweighting of vision transformers with the aim of inspiring further exploration and providing practical guidance for the community. Project Page: https://github.com/ajxklo/Lightweight-VIT
Transformer架构在自然语言处理领域取得了巨大成功,这促使人们将其适应于计算机视觉任务。与卷积神经网络不同,视觉Transformer本质上捕捉长程依赖关系并允许并行处理,但缺乏归纳偏见和效率优势,面临计算量和内存方面的挑战,这些挑战限制了其在现实世界中的应用性。本文综述了在线生成轻量级视觉Transformer用于图像识别的各种策略,重点关注三个关键领域:高效组件设计、动态网络和知识蒸馏。我们在ImageNet-1K基准测试上评估了每个话题的相关探索,分析了精确度、参数、吞吐量等方面的权衡,以突出各自的优势、劣势和灵活性。最后,我们提出了轻量级视觉Transformer的未来研究方向和潜在挑战,旨在激发进一步的探索,为社区提供实际指导。项目页面:https://github.com/ajxklo/Lightweight-VIT
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文探讨了将Transformer架构应用于计算机视觉任务的策略,并概述了在线策略来生成轻量级视觉Transformer用于图像识别。文章重点关注了Efficient Component Design、Dynamic Network和Knowledge Distillation三个关键领域,并在ImageNet-1K基准测试上评估了相关探索。文章分析了精确度、参数、吞吐量和灵活性之间的权衡,并指出了各自的优缺点。最后,本文提出了轻量级视觉Transformer的未来研究方向和潜在挑战,旨在为社区提供实际指导和进一步探索的灵感。
Key Takeaways
- Transformer架构在计算机视觉任务中的成功应用。
- 轻量级视觉Transformer的生成策略。
- Efficient Component Design、Dynamic Network和Knowledge Distillation三个关键领域的重点研究。
- 在ImageNet-1K基准测试上对相关探索的评估。
- 精确度、参数、吞吐量和灵活性之间的权衡分析。
- 各领域探索的优缺点分析。
点此查看论文截图

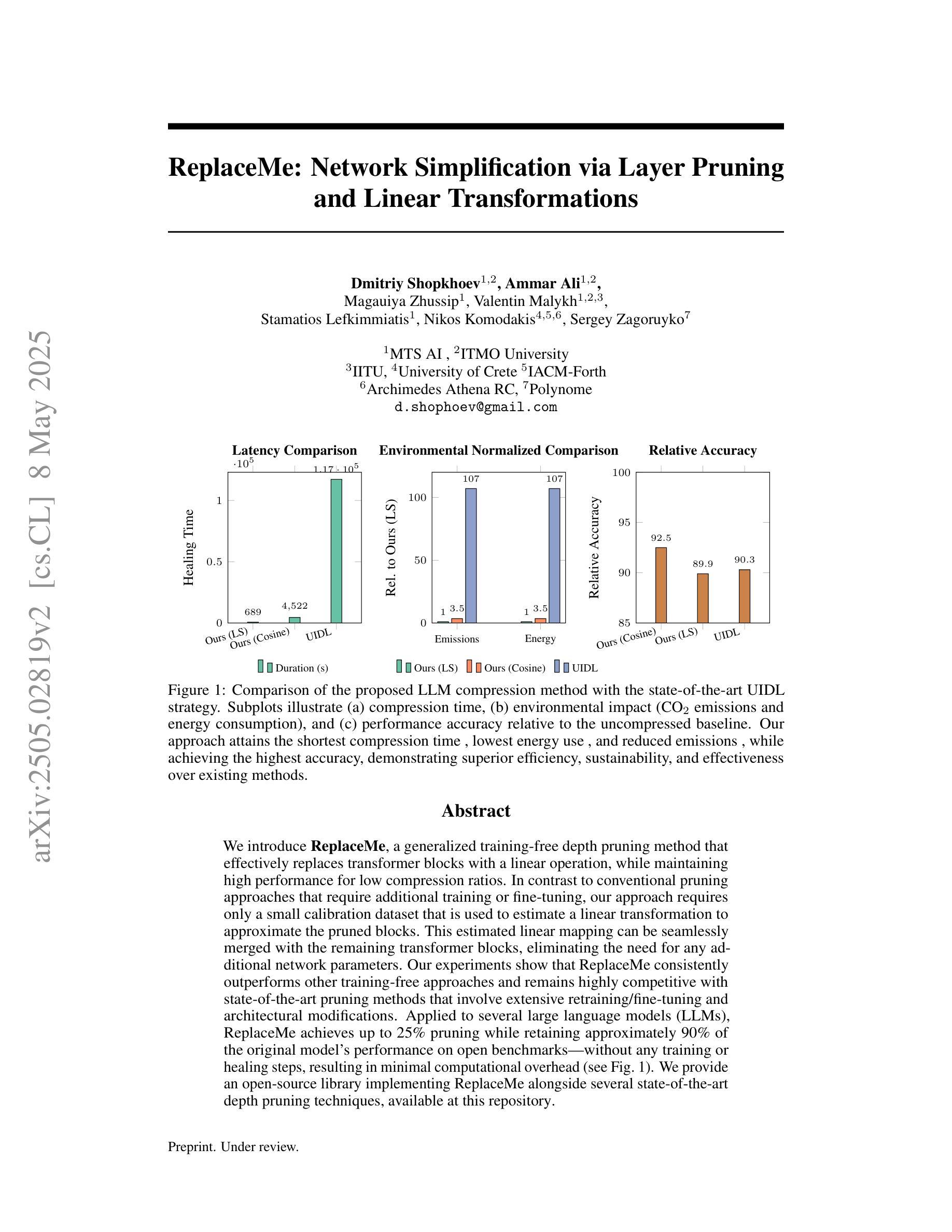
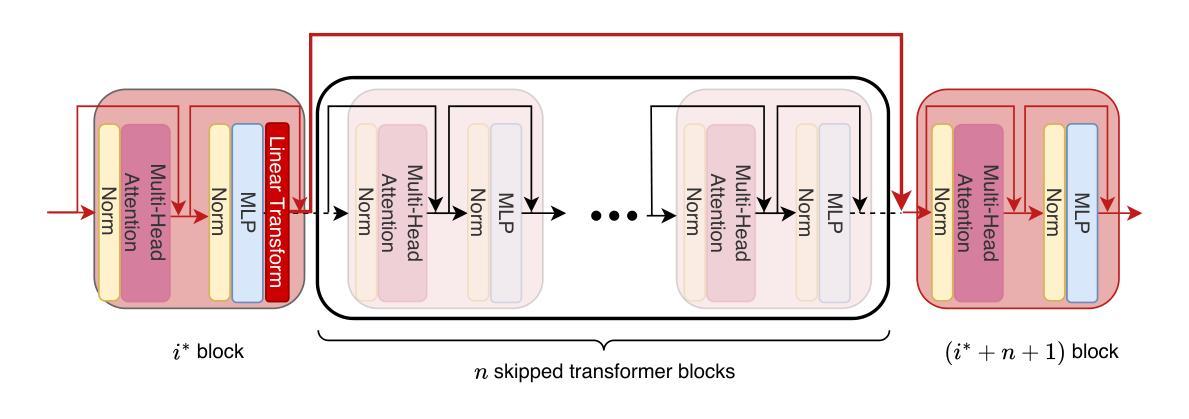
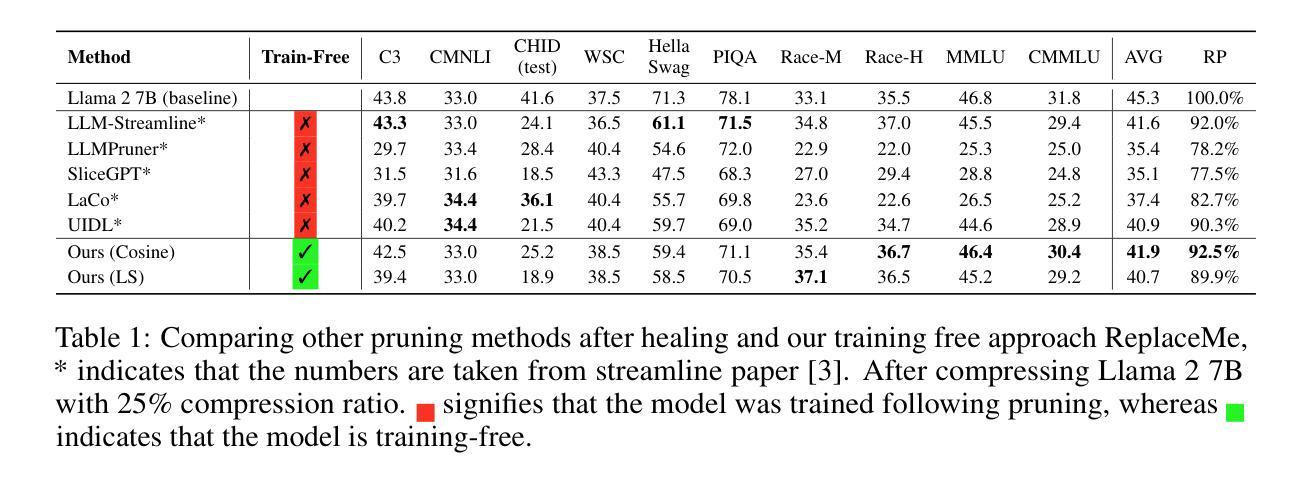
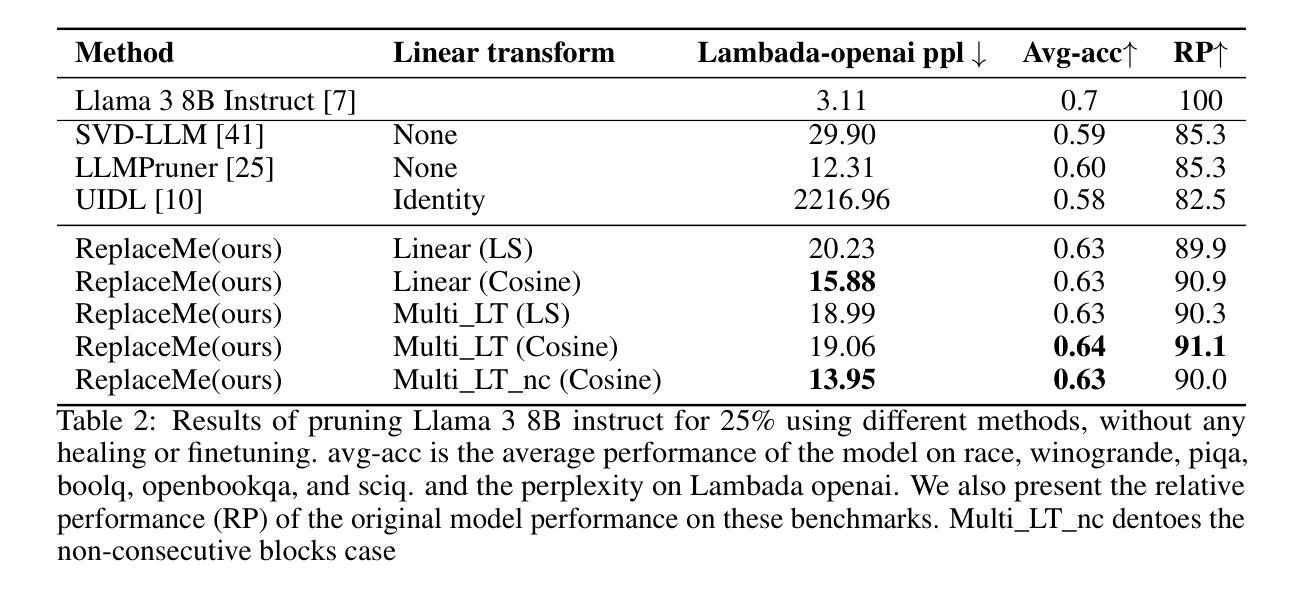
ReplaceMe: Network Simplification via Layer Pruning and Linear Transformations
Authors:Dmitriy Shopkhoev, Ammar Ali, Magauiya Zhussip, Valentin Malykh, Stamatios Lefkimmiatis, Nikos Komodakis, Sergey Zagoruyko
We introduce ReplaceMe, a generalized training-free depth pruning method that effectively replaces transformer blocks with a linear operation, while maintaining high performance for low compression ratios. In contrast to conventional pruning approaches that require additional training or fine-tuning, our approach requires only a small calibration dataset that is used to estimate a linear transformation to approximate the pruned blocks. This estimated linear mapping can be seamlessly merged with the remaining transformer blocks, eliminating the need for any additional network parameters. Our experiments show that ReplaceMe consistently outperforms other training-free approaches and remains highly competitive with state-of-the-art pruning methods that involve extensive retraining/fine-tuning and architectural modifications. Applied to several large language models (LLMs), ReplaceMe achieves up to 25% pruning while retaining approximately 90% of the original model’s performance on open benchmarks - without any training or healing steps, resulting in minimal computational overhead (see Fig.1). We provide an open-source library implementing ReplaceMe alongside several state-of-the-art depth pruning techniques, available at this repository.
我们介绍了ReplaceMe,这是一种通用的无训练深度剪枝方法,它可以通过线性运算有效地替换transformer块,同时在低压缩比的情况下保持高性能。与传统的需要额外训练或微调的剪枝方法不同,我们的方法只需要一个小型校准数据集,用于估计线性变换以近似剪枝块。估计的线性映射可以无缝地与其他transformer块合并,无需任何额外的网络参数。我们的实验表明,ReplaceMe始终优于其他无训练方法,并且在涉及大量重新训练/微调和结构修改的先进剪枝方法中表现出高度竞争力。应用于多个大型语言模型(LLM)时,ReplaceMe可实现高达25%的剪枝率,同时在开放基准测试中保留原始模型约90%的性能——无需任何训练或修复步骤,导致计算开销最小(见图1)。我们提供了一个开源库来实现ReplaceMe以及几种先进的深度剪枝技术,可在本仓库中找到。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
提出一种名为ReplaceMe的通用训练无关深度剪枝方法,通过线性操作有效替换transformer块,在低压缩比下保持高性能。与其他需要额外训练或微调的传统剪枝方法不同,该方法仅需要一个小的校准数据集来估计线性变换以近似剪枝块。估计的线性映射可以无缝地融入到剩余的transformer块中,无需添加任何网络参数。实验表明,ReplaceMe持续超越其他训练无关的方法,并且在涉及大量重新训练或精细调整的顶尖剪枝方法中表现极具竞争力。在大型语言模型(LLM)上应用时,可在无需任何训练或修复步骤的情况下实现高达25%的剪枝,同时保留原始模型在公开基准测试上约90%的性能,并且计算开销最小。
Key Takeaways
- ReplaceMe是一种训练无关的通用深度剪枝方法,旨在通过线性操作替换transformer块以实现高性能和低压缩比。
- 与传统方法不同,该方法仅需要一个小的校准数据集来估计线性映射,无需额外的训练或微调。
- 估计的线性映射可以与现有的transformer块无缝集成,无需添加任何新的网络参数。
- ReplaceMe的实验表现优于其他训练无关的方法,同时在与顶尖剪枝方法的对比中也表现不俗。
- 在大型语言模型上应用时,ReplaceMe可以实现高达25%的剪枝,同时保留原始模型约90%的性能。
- 该方法无需任何训练或修复步骤,并且计算开销较小。
点此查看论文截图
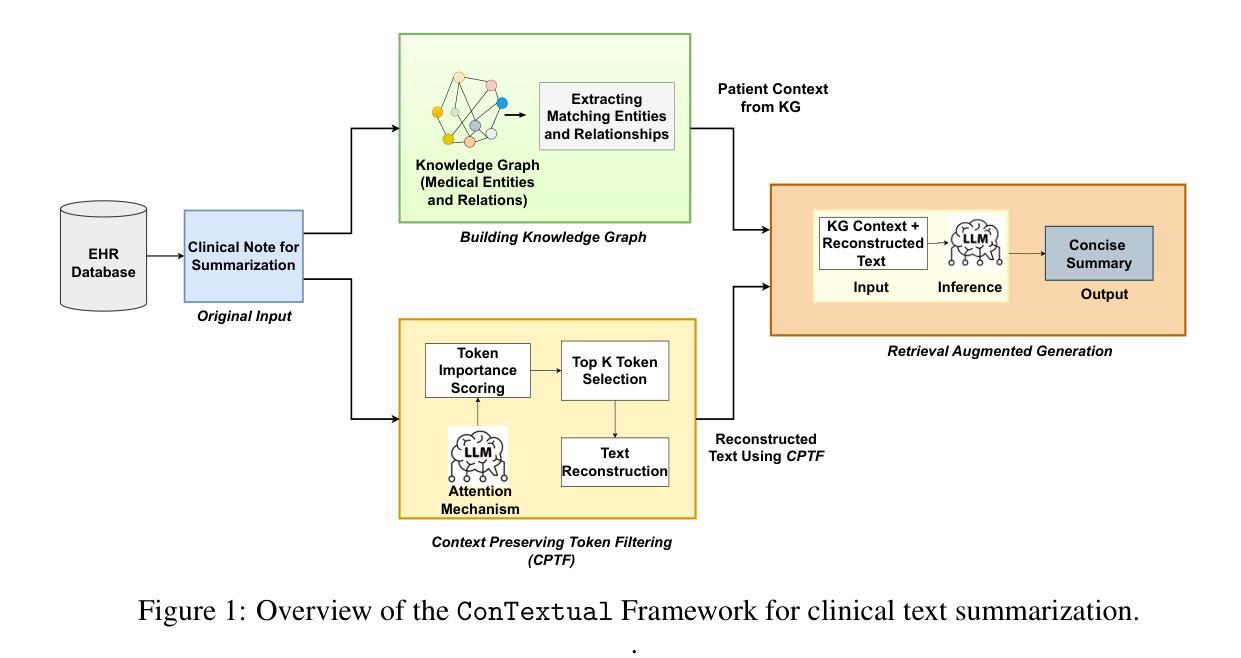
ConTextual: Improving Clinical Text Summarization in LLMs with Context-preserving Token Filtering and Knowledge Graphs
Authors:Fahmida Liza Piya, Rahmatollah Beheshti
Unstructured clinical data can serve as a unique and rich source of information that can meaningfully inform clinical practice. Extracting the most pertinent context from such data is critical for exploiting its true potential toward optimal and timely decision-making in patient care. While prior research has explored various methods for clinical text summarization, most prior studies either process all input tokens uniformly or rely on heuristic-based filters, which can overlook nuanced clinical cues and fail to prioritize information critical for decision-making. In this study, we propose Contextual, a novel framework that integrates a Context-Preserving Token Filtering method with a Domain-Specific Knowledge Graph (KG) for contextual augmentation. By preserving context-specific important tokens and enriching them with structured knowledge, ConTextual improves both linguistic coherence and clinical fidelity. Our extensive empirical evaluations on two public benchmark datasets demonstrate that ConTextual consistently outperforms other baselines. Our proposed approach highlights the complementary role of token-level filtering and structured retrieval in enhancing both linguistic and clinical integrity, as well as offering a scalable solution for improving precision in clinical text generation.
非结构化临床数据可以作为独特且丰富的信息来源,对临床实践产生有意义的影响。从这类数据中提取最关键上下文对于实现其在患者护理中的最佳和及时决策的真正潜力至关重要。虽然先前的研究已经探索了各种临床文本摘要方法,但大多数早期研究要么对所有输入标记进行统一处理,要么依赖于基于启发式过滤器,这可能会忽略微妙的临床线索并且无法优先处理对决策至关重要的信息。在这项研究中,我们提出了一个名为Contextual的框架,该框架结合了上下文保留标记过滤方法与特定领域的知识图谱(KG)进行上下文扩充。通过保留特定上下文的标记并用结构化知识丰富它们,Contextual提高了语言连贯性和临床真实性。我们在两个公共基准数据集上的广泛经验评估表明,Contextual始终优于其他基线。我们提出的方法突出了标记级过滤和结构化检索在增强语言和临床完整性方面的互补作用,并提供了提高临床文本生成精度的可扩展解决方案。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
临床非结构化数据是独特且丰富的信息来源,对临床实践具有指导意义。从这些数据中提取最关键的内容对于充分利用其潜力以做出最佳且及时的医疗决策至关重要。本研究提出了一种新的框架“Contextual”,它结合了“Context-Preserving Token Filtering”方法与领域特定的知识图谱(KG)进行上下文扩充。通过保留重要的上下文特定标记并用结构化的知识丰富它们,Contextual提高了语言连贯性和临床准确性。在公共基准数据集上的广泛实证评估表明,Contextual持续优于其他基线方法。本研究的方法突显了标记级过滤和结构化检索在增强语言和临床完整性方面的互补作用,并为提高临床文本生成的精度提供了可扩展的解决方案。
Key Takeaways
- 临床非结构化数据是独特且丰富的信息来源,对临床实践具有指导意义。
- 提取临床文本中的关键上下文信息对于做出最佳医疗决策至关重要。
- 现有研究在处理方法上有所不足,要么对所有输入标记进行统一处理,要么依赖基于启发式的过滤器,可能会忽略微妙的临床线索和关键决策信息。
- 本研究提出了一种新的框架“Contextual”,结合了上下文保留标记过滤方法和领域特定的知识图谱进行上下文扩充。
- Contextual通过保留重要的上下文特定标记并用结构化的知识丰富它们,提高了语言连贯性和临床准确性。
- 在公共基准数据集上的评估表明,Contextual优于其他基线方法。
点此查看论文截图

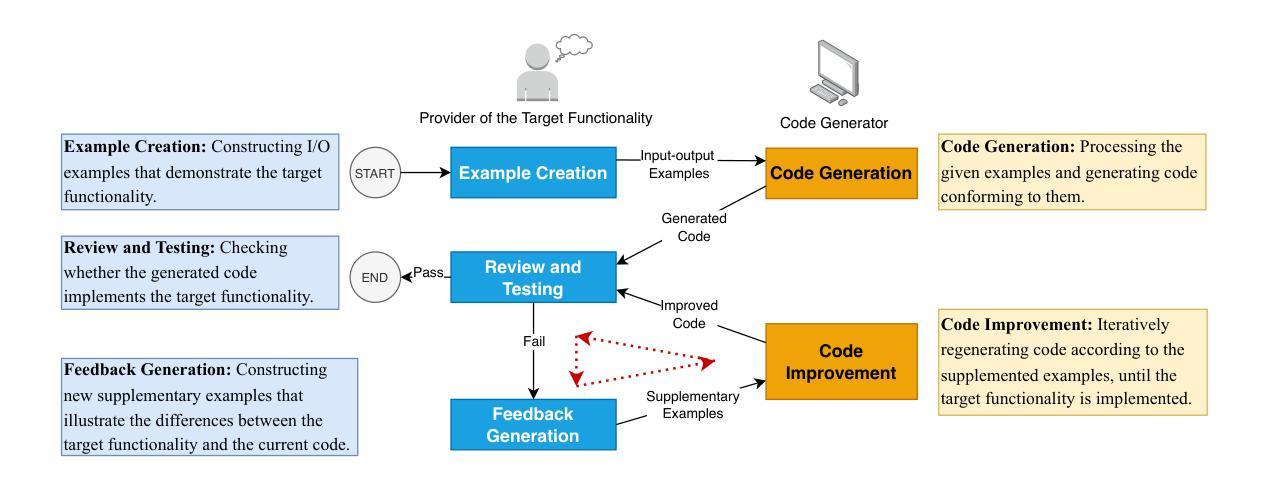
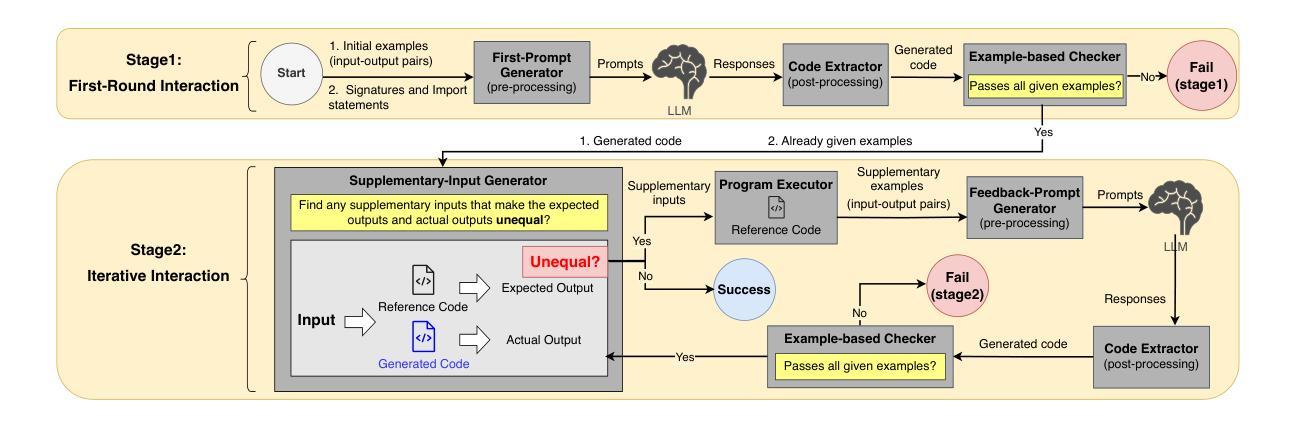
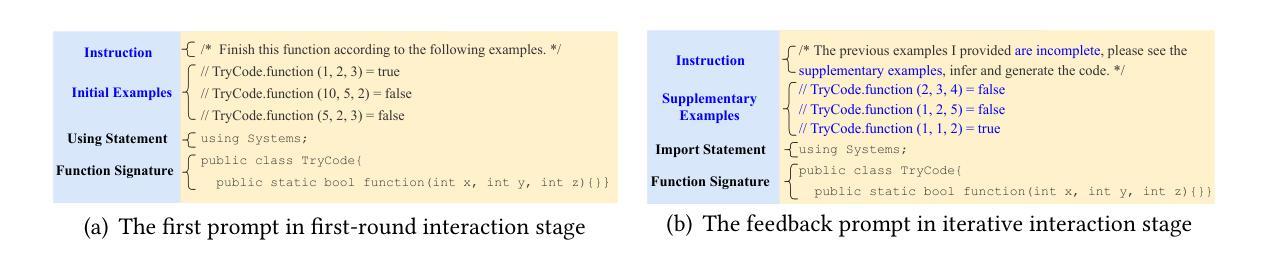
The First Prompt Counts the Most! An Evaluation of Large Language Models on Iterative Example-Based Code Generation
Authors:Yingjie Fu, Bozhou Li, Linyi Li, Wentao Zhang, Tao Xie
The capabilities of Large Language Models (LLMs) in code generation have been extensively studied, particularly for implementing target functionalities from natural-language descriptions. Alternatively, input-output (I/O) examples provide an accessible, unambiguous, and flexible way to describe functionalities. However, their inherent diversity, opaqueness, and incompleteness impose greater challenges for understanding and implementing the target requirements. Therefore, generating code from I/O examples (i.e., example-based code generation) provides a new perspective, allowing us to additionally evaluate LLMs’ capability to infer target functionalities from limited information and to process new-form requirements. However, related research about LLMs in example-based code generation remains largely unexplored. To fill this gap, this paper presents the first comprehensive study on example-based code generation using LLMs. We adopt an iterative evaluation framework and formalize the objective of example-based code generation as two sequential sub-objectives: generating code conforming to the given examples and generating code that successfully implements the target functionalities from (iteratively) given examples. We assess six state-of-the-art LLMs using a new benchmark of 172 diverse target functionalities. The results demonstrate that when requirements are described using iterative I/O examples rather than natural language, the LLMs’ score decreases by over 60%, and the vast majority (even over 95%) of successfully implemented functionalities are achieved in the first round of the iterations. Furthermore, we also find that combining I/O examples with even imprecise and fragmental natural language descriptions greatly improves LLM performance, and the selection of initial I/O examples can also influence the score, suggesting opportunities for prompt optimization.
大型语言模型(LLM)在代码生成方面的能力已经得到了广泛的研究,特别是在根据自然语言描述实现目标功能方面。另外,输入/输出(I/O)示例提供了一种易于访问、明确和灵活的方式来描述功能。然而,它们的内在多样性、模糊性和不完全性给理解和实现目标要求带来了更大的挑战。因此,从I/O示例生成代码(即基于示例的代码生成)提供了新的视角,使我们能够额外评估LLM从有限信息中推断目标功能的能力,以及处理新形式要求的能力。然而,关于LLM在基于示例的代码生成方面的相关研究仍然很少。为了填补这一空白,本文首次对基于LLM的示例代码生成进行了全面研究。我们采用迭代评估框架,将基于示例的代码生成的目标正式定义为两个顺序的子目标:生成符合给定示例的代码,以及生成能够成功实现目标功能的代码(通过迭代给出的示例)。我们使用包含172个不同目标功能的新基准测试评估了六种最新LLM。结果表明,当要求使用迭代I/O示例而不是自然语言描述时,LLM的得分下降了60%以上,绝大多数(超过95%)成功实现的功能都是在第一轮迭代中实现的。此外,我们还发现,将I/O示例与即使是不精确和片段化的自然语言描述相结合,可以大大提高LLM的性能,初始I/O示例的选择也会影响得分,这提示我们有机会进行提示优化。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by ISSTA 2025
Summary
基于迭代输入/输出(I/O)例子的代码生成是大型语言模型(LLM)的一个新视角。本文首次对此进行了全面研究,发现使用迭代I/O例子描述目标功能时,LLM的性能下降超过60%,但结合不精确和片段化的自然语言描述可以显著提高LLM性能。初始I/O例子的选择也会影响得分,提示有优化提示的机会。
Key Takeaways
- 大型语言模型(LLM)在基于输入/输出(I/O)例子的代码生成方面提供了新的视角。
- 使用迭代I/O例子描述目标功能时,LLM性能下降超过60%。
- 结合不精确和片段化的自然语言描述可以显著提高LLM在基于I/O例子的代码生成中的性能。
- 初始I/O例子的选择影响LLM的性能得分。
- 研究采用迭代评估框架,将基于I/O例子的代码生成分为两个连续的子目标:生成符合例子的代码和成功实现目标功能的代码。
- 在第一轮迭代中,成功实现的功能超过95%。
点此查看论文截图