⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-05-14 更新
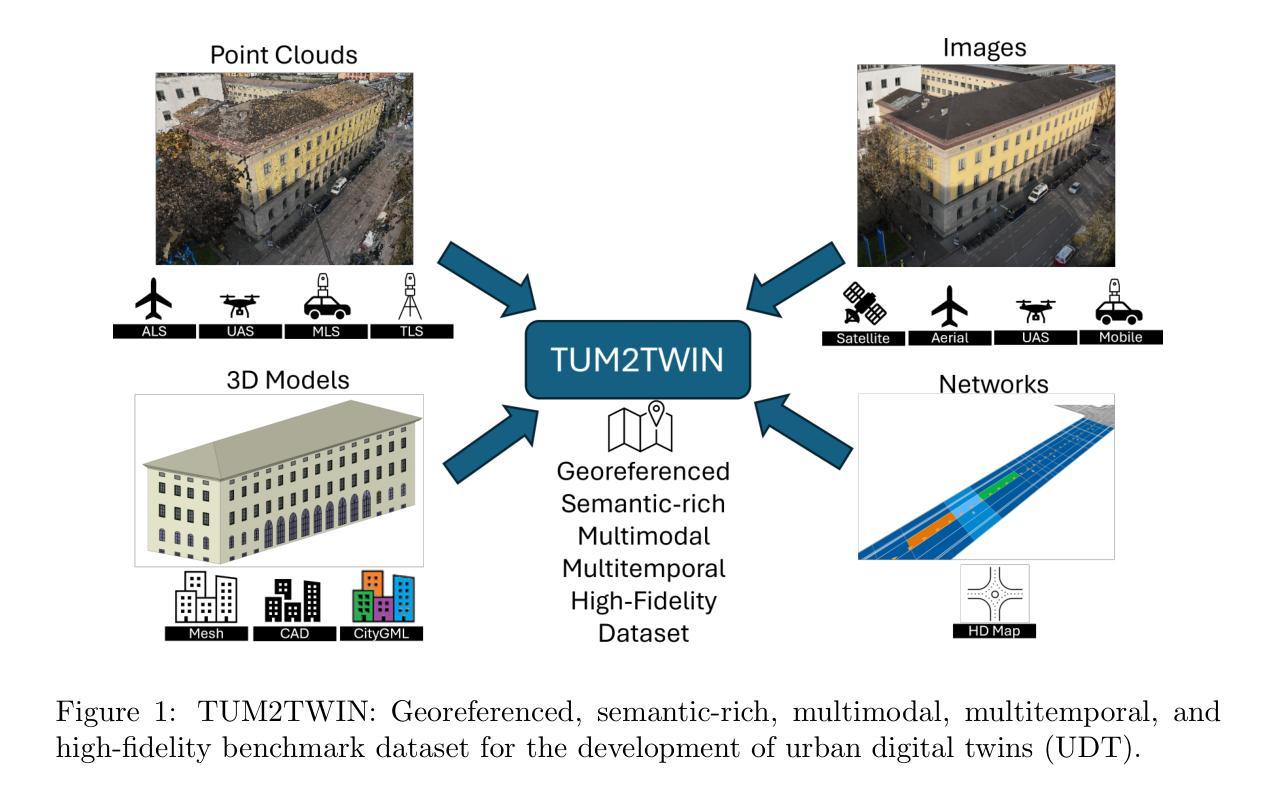
TUM2TWIN: Introducing the Large-Scale Multimodal Urban Digital Twin Benchmark Dataset
Authors:Olaf Wysocki, Benedikt Schwab, Manoj Kumar Biswanath, Qilin Zhang, Jingwei Zhu, Thomas Froech, Medhini Heeramaglore, Ihab Hijazi, Khaoula Kanna, Mathias Pechinger, Zhaiyu Chen, Yao Sun, Alejandro Rueda Segura, Ziyang Xu, Omar AbdelGafar, Mansour Mehranfar, Chandan Yeshwanth, Yueh-Cheng Liu, Hadi Yazdi, Jiapan Wang, Stefan Auer, Katharina Anders, Klaus Bogenberger, Andre Borrmann, Angela Dai, Ludwig Hoegner, Christoph Holst, Thomas H. Kolbe, Ferdinand Ludwig, Matthias Nießner, Frank Petzold, Xiao Xiang Zhu, Boris Jutzi
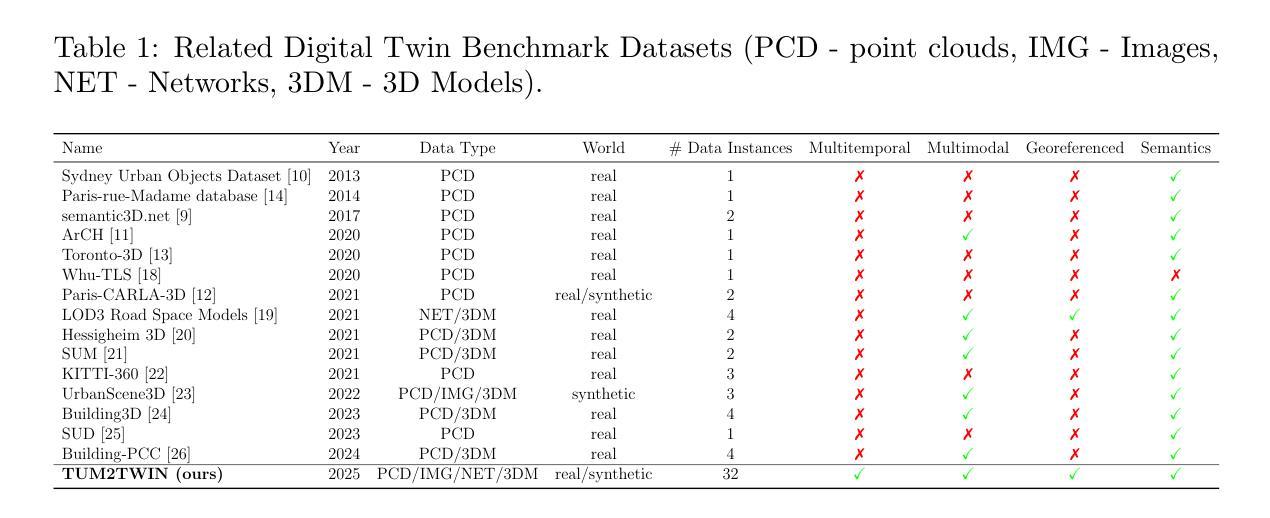
Urban Digital Twins (UDTs) have become essential for managing cities and integrating complex, heterogeneous data from diverse sources. Creating UDTs involves challenges at multiple process stages, including acquiring accurate 3D source data, reconstructing high-fidelity 3D models, maintaining models’ updates, and ensuring seamless interoperability to downstream tasks. Current datasets are usually limited to one part of the processing chain, hampering comprehensive UDTs validation. To address these challenges, we introduce the first comprehensive multimodal Urban Digital Twin benchmark dataset: TUM2TWIN. This dataset includes georeferenced, semantically aligned 3D models and networks along with various terrestrial, mobile, aerial, and satellite observations boasting 32 data subsets over roughly 100,000 $m^2$ and currently 767 GB of data. By ensuring georeferenced indoor-outdoor acquisition, high accuracy, and multimodal data integration, the benchmark supports robust analysis of sensors and the development of advanced reconstruction methods. Additionally, we explore downstream tasks demonstrating the potential of TUM2TWIN, including novel view synthesis of NeRF and Gaussian Splatting, solar potential analysis, point cloud semantic segmentation, and LoD3 building reconstruction. We are convinced this contribution lays a foundation for overcoming current limitations in UDT creation, fostering new research directions and practical solutions for smarter, data-driven urban environments. The project is available under: https://tum2t.win
城市数字双胞胎(UDTs)对于管理城市以及从各种来源整合复杂、异质的数据变得至关重要。创建UDTs面临多个阶段的挑战,包括获取准确的3D源数据、重建高保真3D模型、保持模型的更新,以及确保无缝地参与下游任务。当前的数据集通常仅限于处理链的一部分,阻碍了全面的UDTs验证。为了应对这些挑战,我们引入了第一个综合多模式城市数字双胞胎基准数据集:TUM2TWIN。该数据集包括地理参考、语义对齐的3D模型和网络,以及各种地面、移动、空中和卫星观测,拥有超过约10万$m^2$区域的32个数据子集和当前767GB的数据。通过确保地理参考的室内外采集、高精度和多模式数据集成,该基准数据集支持对传感器的稳健分析以及先进重建方法的发展。此外,我们还探索了展示TUM2TWIN潜力的下游任务,包括NeRF和高斯贴图的全新视图合成、太阳能潜力分析、点云语义分割和LoD3建筑重建。我们相信这一贡献为克服UDT创建中的当前局限性奠定了基础,为智能、数据驱动的城市环境研究提供了新的研究方向和实用解决方案。项目网址为:https://tum2t.win
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Submitted to the ISPRS Journal of Photogrammetry and Remote Sensing
Summary
基于城市数字双胞胎(UDTs)在处理城市管理和整合复杂、异构数据方面的关键作用,当前面临的多阶段挑战以及现有数据集的限制,研究者推出了首个综合多模态城市数字双胞胎基准数据集:TUM2TWIN。该数据集包含地理参考、语义对齐的3D模型和网络,以及各种地面、移动、空中和卫星观测数据,包含约10万平米的32个数据子集和当前容量为767GB的数据。通过确保室内外采集的地理参照、高精度和多模态数据集成,该基准支持传感器稳健分析和先进重建方法的发展。数据集包含多种下游任务演示的潜力。该项目的推出为克服当前城市数字双胞胎创建中的局限性奠定了基础,促进了新的研究方向和面向数据驱动的智能城市环境的实际解决方案的开发。数据集访问链接:https://tum2t.win。
Key Takeaways
- 城市数字双胞胎(UDTs)在管理和整合复杂、异构城市数据中的关键作用。
- 创建UDTs面临的多阶段挑战包括获取准确的3D源数据、重建高保真度模型等。
- 当前数据集通常仅限于处理链的一部分,阻碍了全面的UDT验证。
- 引入首个综合多模态城市数字双胞胎基准数据集TUM2TWIN,包含地理参考的室内外数据和多模态观测数据。
- TUM2TWIN支持传感器稳健分析和先进重建方法的发展。
- 数据集展示了下游任务的潜力,如NeRF和Gaussian Splatting的新视图合成等。
点此查看论文截图


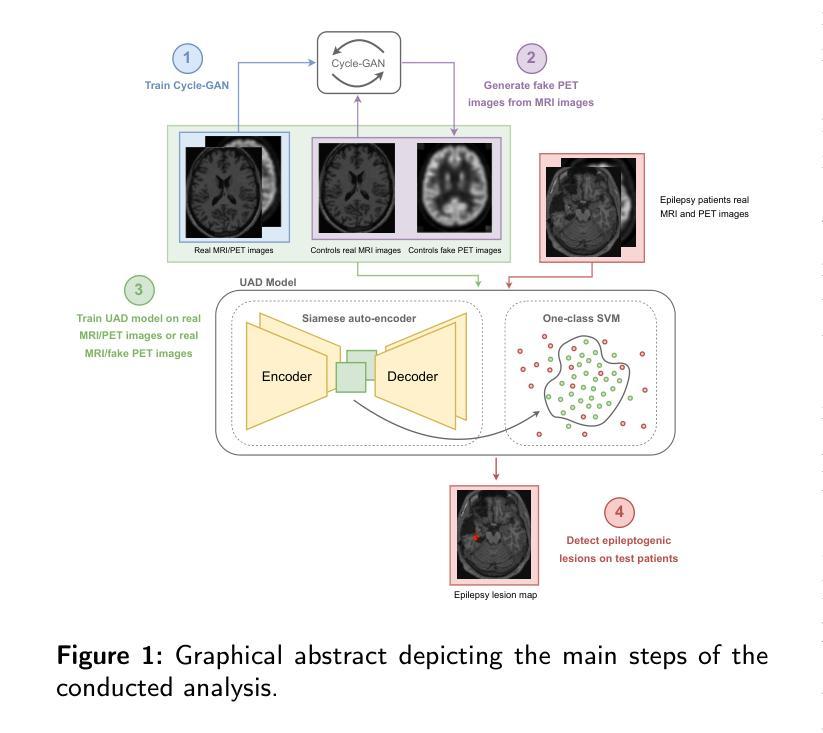
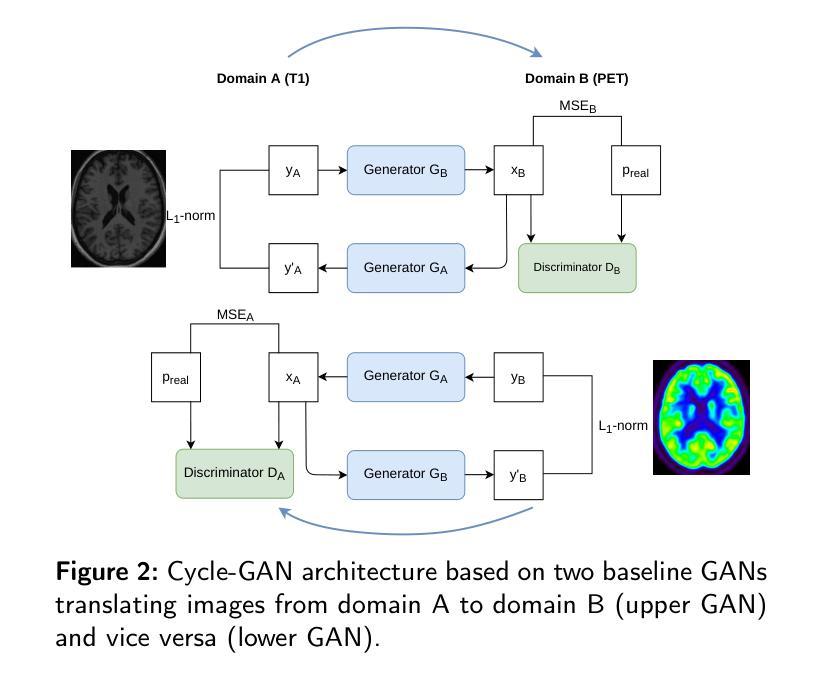
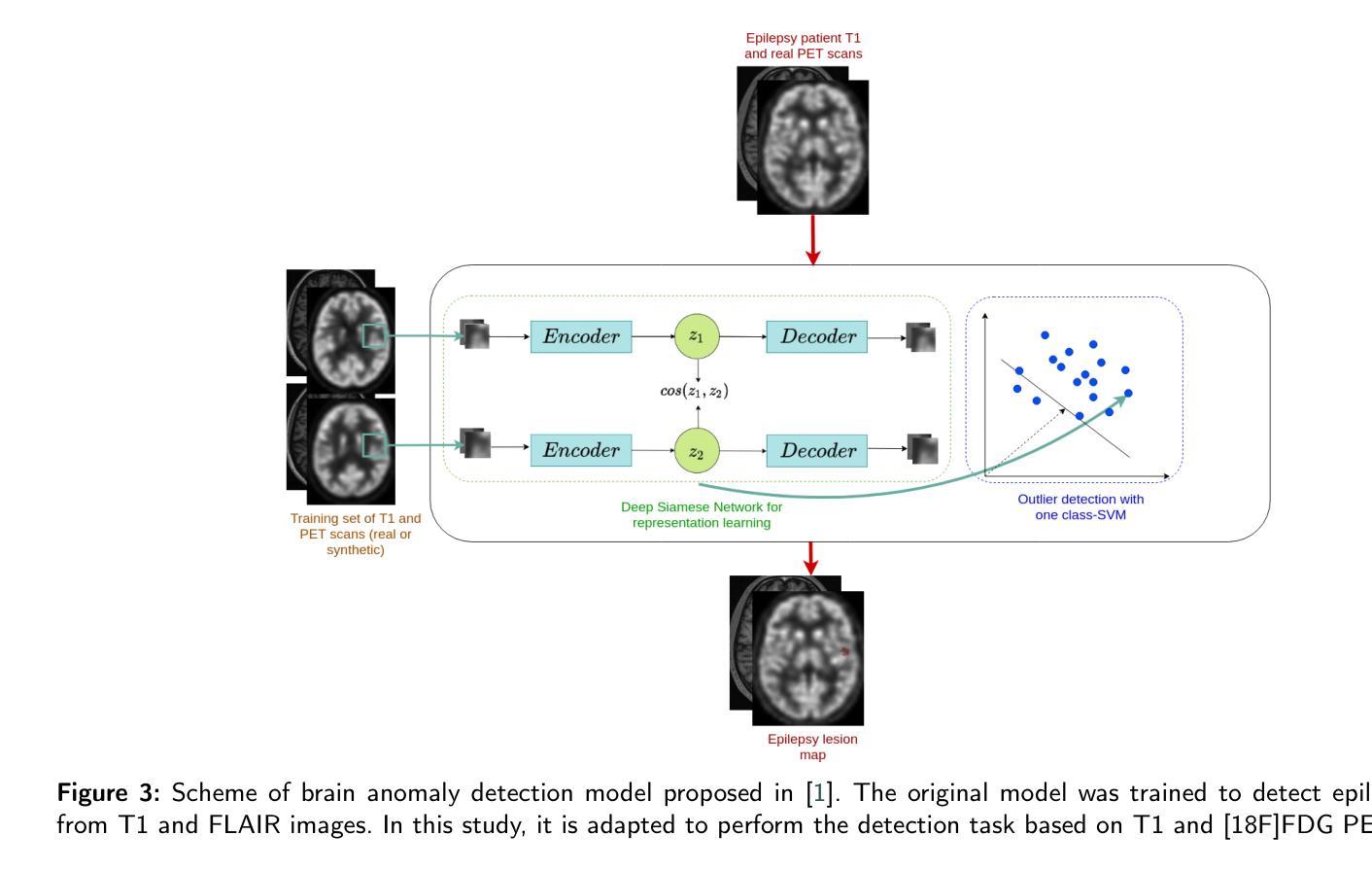
GAN-based synthetic FDG PET images from T1 brain MRI can serve to improve performance of deep unsupervised anomaly detection models
Authors:Daria Zotova, Nicolas Pinon, Robin Trombetta, Romain Bouet, Julien Jung, Carole Lartizien
Background and Objective. Research in the cross-modal medical image translation domain has been very productive over the past few years in tackling the scarce availability of large curated multimodality datasets with the promising performance of GAN-based architectures. However, only a few of these studies assessed task-based related performance of these synthetic data, especially for the training of deep models. Method. We design and compare different GAN-based frameworks for generating synthetic brain [18F]fluorodeoxyglucose (FDG) PET images from T1 weighted MRI data. We first perform standard qualitative and quantitative visual quality evaluation. Then, we explore further impact of using these fake PET data in the training of a deep unsupervised anomaly detection (UAD) model designed to detect subtle epilepsy lesions in T1 MRI and FDG PET images. We introduce novel diagnostic task-oriented quality metrics of the synthetic FDG PET data tailored to our unsupervised detection task, then use these fake data to train a use case UAD model combining a deep representation learning based on siamese autoencoders with a OC-SVM density support estimation model. This model is trained on normal subjects only and allows the detection of any variation from the pattern of the normal population. We compare the detection performance of models trained on 35 paired real MR T1 of normal subjects paired either on 35 true PET images or on 35 synthetic PET images generated from the best performing generative models. Performance analysis is conducted on 17 exams of epilepsy patients undergoing surgery. Results. The best performing GAN-based models allow generating realistic fake PET images of control subject with SSIM and PSNR values around 0.9 and 23.8, respectively and in distribution (ID) with regard to the true control dataset. The best UAD model trained on these synthetic normative PET data allows reaching 74% sensitivity. Conclusion. Our results confirm that GAN-based models are the best suited for MR T1 to FDG PET translation, outperforming transformer or diffusion models. We also demonstrate the diagnostic value of these synthetic data for the training of UAD models and evaluation on clinical exams of epilepsy patients. Our code and the normative image dataset are available.
背景与目的。过去几年,基于GAN架构在解决大型整合多模式数据集稀缺的问题上的出色表现,跨模态医学图像翻译领域的研究取得了丰硕的成果。然而,只有少数研究评估了这些合成数据在特定任务上的性能,尤其是用于训练深度学习模型方面。
方法。我们设计并比较了基于不同GAN的框架,用于从T1加权MRI数据生成合成的大脑[¹⁸F]氟脱氧葡萄糖(FDG)PET图像。我们首先进行标准的定性和定量视觉质量评估。然后,我们进一步探讨了使用这些假PET数据在训练深度无监督异常检测(UAD)模型中的影响,该模型旨在检测T1 MRI和FDG PET图像中的微妙癫痫病灶。我们引入了针对我们的无监督检测任务量身定制的合成FDG PET数据的新型诊断任务导向质量指标,然后使用这些假数据来训练一个用例UAD模型,该模型结合了基于孪生自编码器的深度表示学习和OC-SVM密度支持估计模型。该模型仅在正常受试者上进行训练,可以检测到任何与正常人群模式的偏差。我们比较了在真实MR T1图像上训练的模型的表现,这些图像配对的是真实的PET图像或由表现最佳的生成模型生成的合成PET图像。性能分析是在接受手术的癫痫患者的17次考试上进行的。
结果。表现最佳的基于GAN的模型能够生成逼真性强的假PET图像,其SSIM和PSNR值分别为约0.9和23.8,与真实对照组数据集在分布上相匹配。使用这些合成规范性PET数据训练的最好的UAD模型能够达到74%的敏感度。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
基于GAN架构的跨模态医学图像转换研究取得显著进展,但相关研究多在数据集层面,较少涉及任务性能评估。本研究通过设计不同GAN框架生成模拟大脑[¹⁸F]氟脱氧葡萄糖(FDG)PET图像,从T1加权MRI数据中评估其质量,并进一步探索这些模拟数据在训练深度无监督异常检测模型中的应用价值。采用新型诊断任务导向质量指标评估模拟数据质量,并用于训练模型,最终实现了对癫痫病变的无监督检测。结果显示,最佳GAN模型生成的模拟PET图像逼真度较高,无监督检测模型的敏感性达到74%。本研究验证了GAN模型在医学图像转换领域的优势,并证明了模拟数据在诊断中的价值。
Key Takeaways
- 研究采用GAN架构生成模拟医学图像,涉及跨模态医学图像翻译领域。
- 研究重点评估了模拟数据在训练深度模型中的任务性能,尤其是无监督异常检测模型在癫痫病变检测中的应用。
- 设计了新型诊断任务导向质量指标以评估模拟数据质量。
- 最佳GAN模型生成的模拟PET图像具有较高的逼真度,与真实图像相似度高。
- 训练的无监督检测模型在模拟数据上表现出较好的性能,敏感性达到74%。
- 结果表明GAN模型在医学图像转换领域具有优势,验证了模拟数据在诊断中的价值。
点此查看论文截图

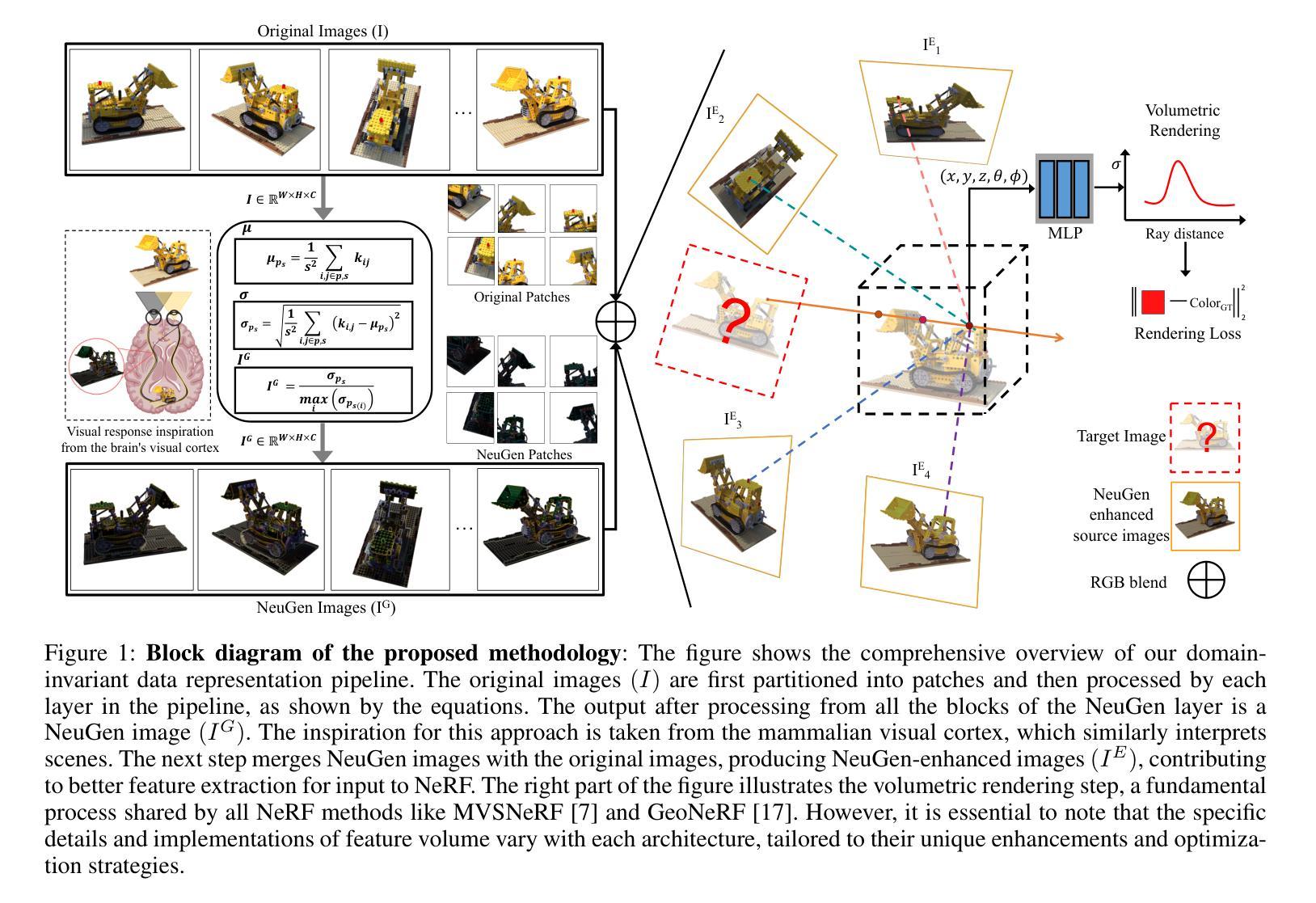
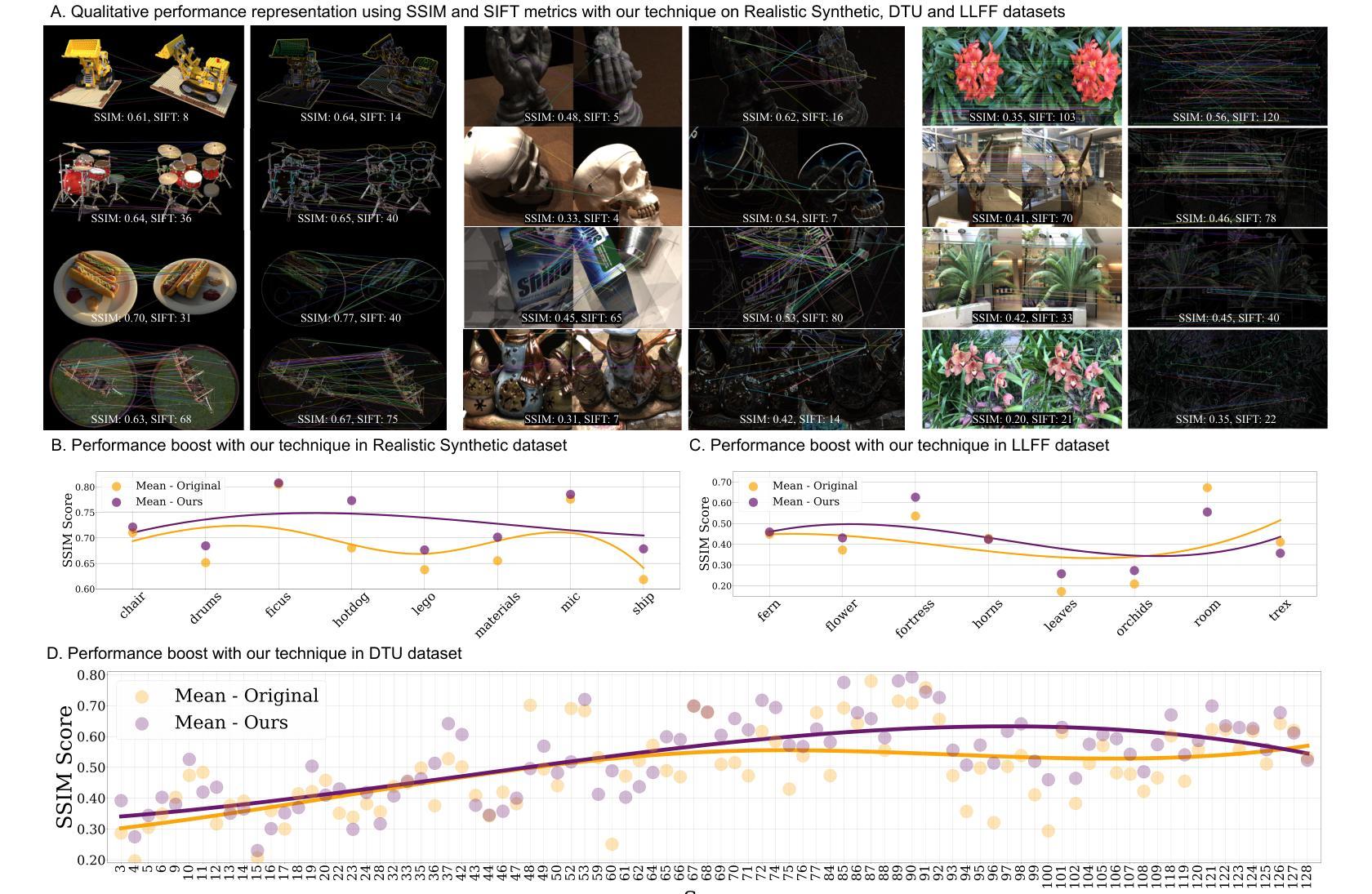
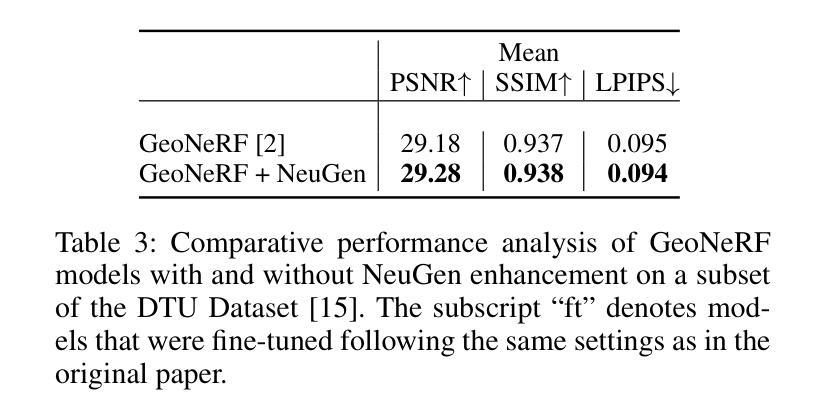
NeuGen: Amplifying the ‘Neural’ in Neural Radiance Fields for Domain Generalization
Authors:Ahmed Qazi, Abdul Basit, Asim Iqbal
Neural Radiance Fields (NeRF) have significantly advanced the field of novel view synthesis, yet their generalization across diverse scenes and conditions remains challenging. Addressing this, we propose the integration of a novel brain-inspired normalization technique Neural Generalization (NeuGen) into leading NeRF architectures which include MVSNeRF and GeoNeRF. NeuGen extracts the domain-invariant features, thereby enhancing the models’ generalization capabilities. It can be seamlessly integrated into NeRF architectures and cultivates a comprehensive feature set that significantly improves accuracy and robustness in image rendering. Through this integration, NeuGen shows improved performance on benchmarks on diverse datasets across state-of-the-art NeRF architectures, enabling them to generalize better across varied scenes. Our comprehensive evaluations, both quantitative and qualitative, confirm that our approach not only surpasses existing models in generalizability but also markedly improves rendering quality. Our work exemplifies the potential of merging neuroscientific principles with deep learning frameworks, setting a new precedent for enhanced generalizability and efficiency in novel view synthesis. A demo of our study is available at https://neugennerf.github.io.
神经辐射场(NeRF)在新型视图合成领域取得了显著进展,但在不同场景和条件下的泛化仍然具有挑战性。为解决这一问题,我们提出了一种新型的受大脑启发的归一化技术——神经泛化(NeuGen)技术,并将其集成到主流的NeRF架构中,包括MVSNeRF和GeoNeRF。NeuGen能够提取领域不变特征,从而提升模型的泛化能力。它可以无缝地集成到NeRF架构中,并培养了一套全面的特征集,在图像渲染中显著提高准确性和稳健性。通过这一集成,NeuGen在多种数据集上的基准测试表现出改进的性能,在先进的NeRF架构中,使其在多种场景中的泛化能力更强。我们的全面评估,包括定量和定性评估,证实我们的方法不仅超越了现有模型的可泛化性,还显著提高了渲染质量。我们的工作证明了将神经科学原理与深度学习框架相结合的可能性,为新型视图合成中的增强泛化能力和效率树立了新的先例。我们的研究演示网站可通过https://neugennerf.github.io访问。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 18 pages, 6 figures
Summary
神经网络辐射场(NeRF)在新型视图合成领域取得了显著进展,但在不同场景和条件下的泛化能力仍面临挑战。为解决这一问题,我们提出了将一种新型的脑启发归一化技术——神经泛化(NeuGen)集成到领先的NeRF架构中,包括MVSNeRF和GeoNeRF。NeuGen提取领域不变特征,增强了模型的泛化能力。它可以无缝地集成到NeRF架构中,并培养了一个全面的特征集,显著提高了图像渲染的准确性和鲁棒性。通过集成NeuGen,在多样化的数据集上的基准测试中,我们的方法不仅提高了模型的泛化性能,而且提高了渲染质量。我们的研究展示了将神经科学原理与深度学习框架相结合的可能性,为新型视图合成中的增强泛化和效率树立了新标准。研究演示网站为:https://neugennerf.github.io。
Key Takeaways
- NeRF在新型视图合成领域有显著的进展,但泛化能力仍面临挑战。
- 提出了一种新型的脑启发归一化技术——神经泛化(NeuGen),用于增强NeRF架构的泛化能力。
- NeuGen能够提取领域不变特征,无缝集成到NeRF架构中。
- 通过全面集成的特征集,NeuGen显著提高了图像渲染的准确性和鲁棒性。
- 在多样化的数据集上的基准测试中,NeuGen提高了模型的泛化性能和渲染质量。
- 研究展示了神经科学原理与深度学习框架相结合的可能性。
点此查看论文截图

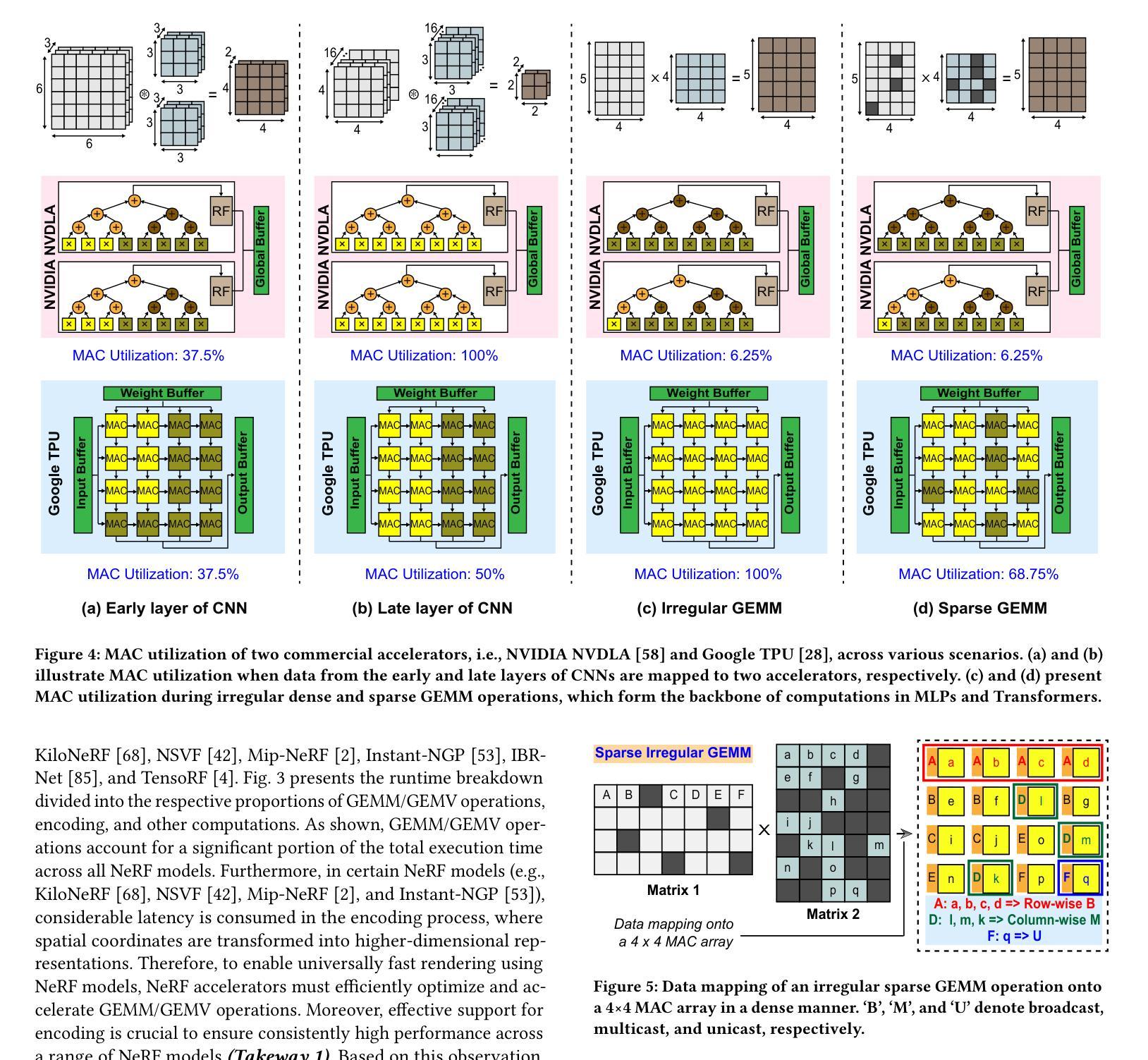
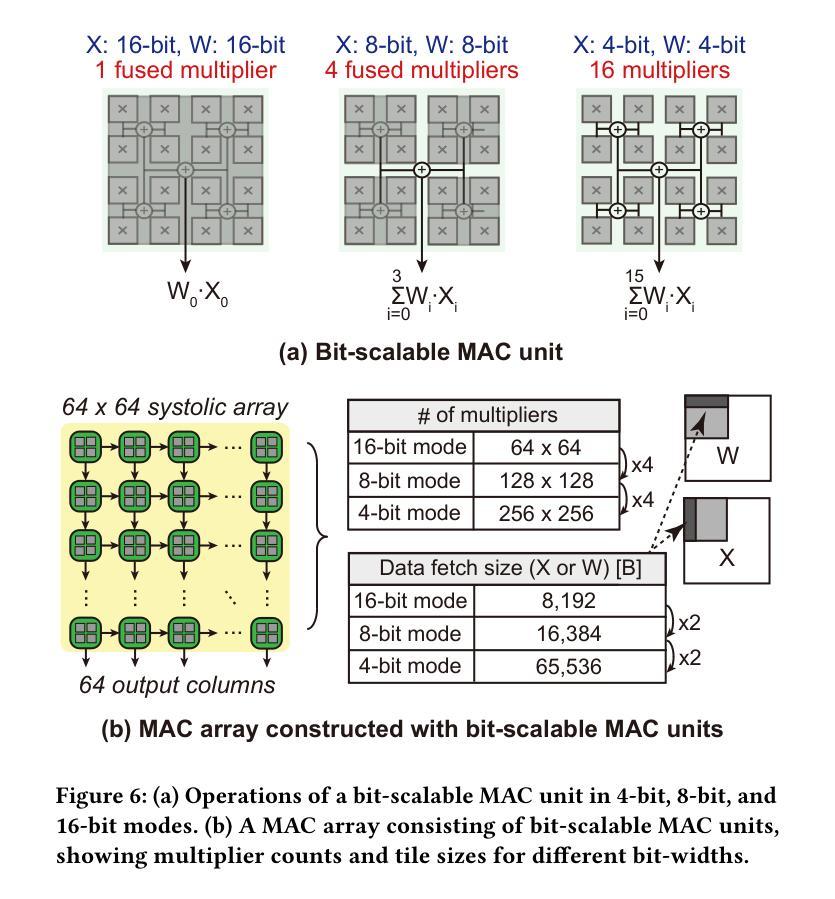
FlexNeRFer: A Multi-Dataflow, Adaptive Sparsity-Aware Accelerator for On-Device NeRF Rendering
Authors:Seock-Hwan Noh, Banseok Shin, Jeik Choi, Seungpyo Lee, Jaeha Kung, Yeseong Kim
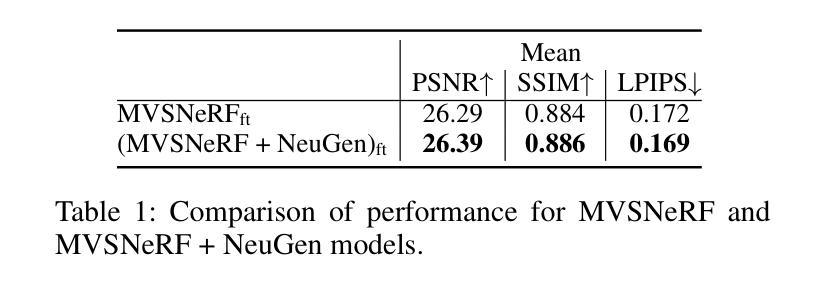
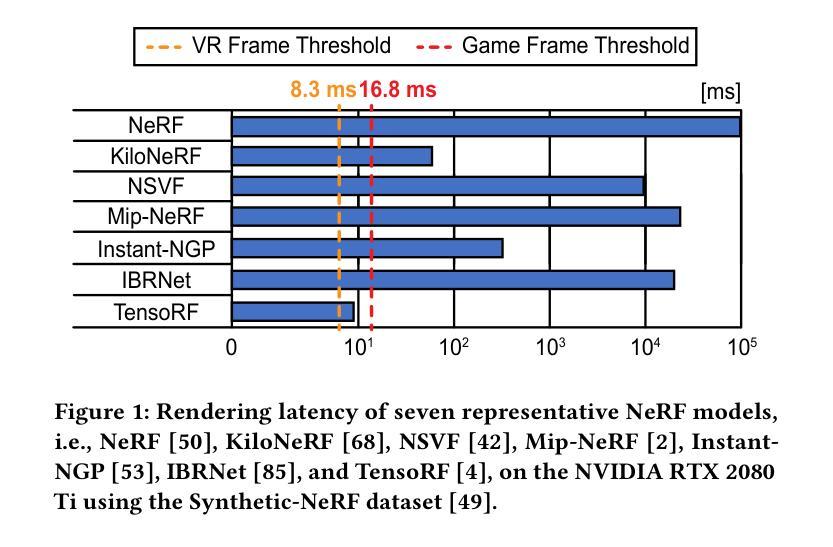
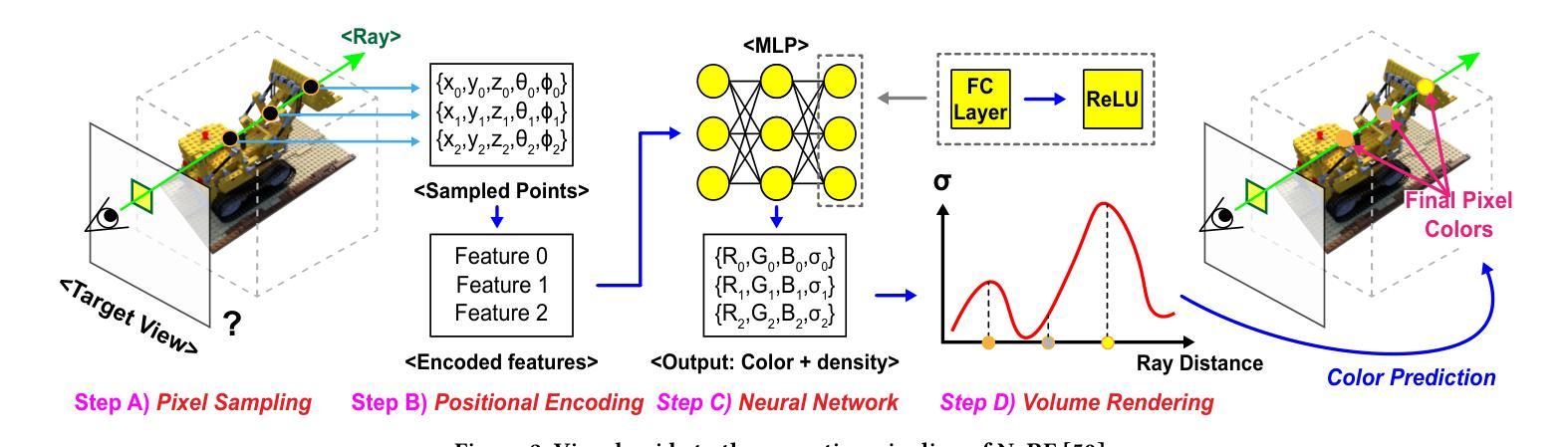
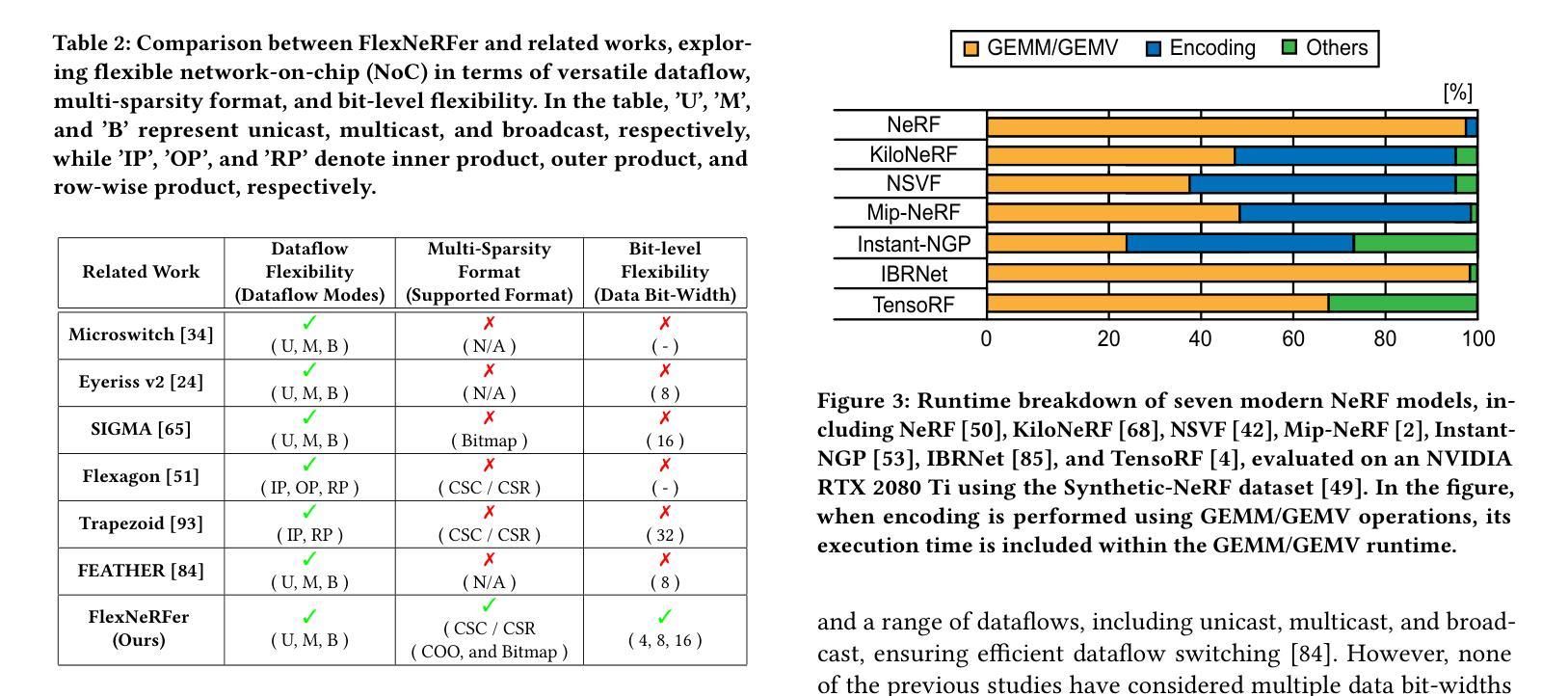
Neural Radiance Fields (NeRF), an AI-driven approach for 3D view reconstruction, has demonstrated impressive performance, sparking active research across fields. As a result, a range of advanced NeRF models has emerged, leading on-device applications to increasingly adopt NeRF for highly realistic scene reconstructions. With the advent of diverse NeRF models, NeRF-based applications leverage a variety of NeRF frameworks, creating the need for hardware capable of efficiently supporting these models. However, GPUs fail to meet the performance, power, and area (PPA) cost demanded by these on-device applications, or are specialized for specific NeRF algorithms, resulting in lower efficiency when applied to other NeRF models. To address this limitation, in this work, we introduce FlexNeRFer, an energy-efficient versatile NeRF accelerator. The key components enabling the enhancement of FlexNeRFer include: i) a flexible network-on-chip (NoC) supporting multi-dataflow and sparsity on precision-scalable MAC array, and ii) efficient data storage using an optimal sparsity format based on the sparsity ratio and precision modes. To evaluate the effectiveness of FlexNeRFer, we performed a layout implementation using 28nm CMOS technology. Our evaluation shows that FlexNeRFer achieves 8.2243.3x speedup and 24.1520.3x improvement in energy efficiency over a GPU (i.e., NVIDIA RTX 2080 Ti), while demonstrating 4.286.9x speedup and 2.347.5x improvement in energy efficiency compared to a state-of-the-art NeRF accelerator (i.e., NeuRex).
神经辐射场(NeRF)是一种用于三维视图重建的AI驱动方法,它表现出了令人印象深刻的效果,引发了各领域的积极研究。因此,出现了许多先进的NeRF模型,导致越来越多的设备应用程序采用NeRF进行高度逼真的场景重建。随着各种NeRF模型的出现,NeRF应用程序利用了各种NeRF框架,从而产生对能够高效支持这些模型的硬件的需求。然而,GPU无法满足这些应用程序所需的性能、功耗和面积(PPA)成本要求,或者针对特定的NeRF算法进行专门设计,导致在应用于其他NeRF模型时效率较低。为了解决这个问题,在这项工作中,我们引入了FlexNeRFer,这是一种节能的多功能NeRF加速器。FlexNeRFer的增强功能的关键组件包括:(i)一个灵活的片上网络(NoC),支持多数据流和在精度可扩展的MAC阵列上进行稀疏处理;(ii)使用基于稀疏比和精度模式的最佳稀疏格式进行高效数据存储。为了评估FlexNeRFer的有效性,我们使用28nm CMOS技术进行了布局实现。我们的评估表明,与GPU(即NVIDIA RTX 2080 Ti)相比,FlexNeRFer实现了8.2~243.3倍的速度提升和24.1~520.3倍的能效改进;与最新的NeRF加速器(即NeuRex)相比,实现了4.2~86.9倍的速度提升和2.3~47.5倍的能效改进。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted for publication at the 52nd IEEE/ACM International Symposium on Computer Architecture (ISCA-52), 2025
Summary
神经辐射场(NeRF)的AI驱动方法用于三维视图重建,展现出令人印象深刻的效果,引发各领域积极研究。出现多种高级NeRF模型,使得NeRF在设备上的场景重建应用越来越广泛。为满足NeRF应用的需求,需要硬件支持这些模型的高效运行。然而,GPU无法满足性能、功耗和面积的需求或专为特定NeRF算法优化,效率较低。本研究提出了灵活的NeRF加速器FlexNeRFer,关键组件包括灵活的网络芯片内通信系统以及基于稀疏比率精度模式的最优稀疏格式数据存储。评估显示,FlexNeRFer相较于GPU实现8.2至243.3倍的速度提升和24.1至520.3倍的能效改善。相较于现有的NeRF加速器,其表现更佳。
Key Takeaways
- NeRF作为一种AI驱动的三维视图重建技术,受到广泛关注并推动了各领域的研究发展。
- 当前多种先进的NeRF模型已被开发,促进了其在高度逼真的场景重建中的应用。
- 由于NeRF模型的应用需求多样化,对硬件的效率提出了较高要求,而现有GPU难以满足这些需求。
- FlexNeRFer作为一种灵活的NeRF加速器被引入,具有支持多数据流和精度可伸缩的MAC阵列的灵活网络芯片内通信系统。
- FlexNeRFer采用基于稀疏比率和精度模式的最优稀疏格式数据存储,提高了效率。
- 与GPU相比,FlexNeRFer在速度和能效方面实现了显著的提升。
点此查看论文截图

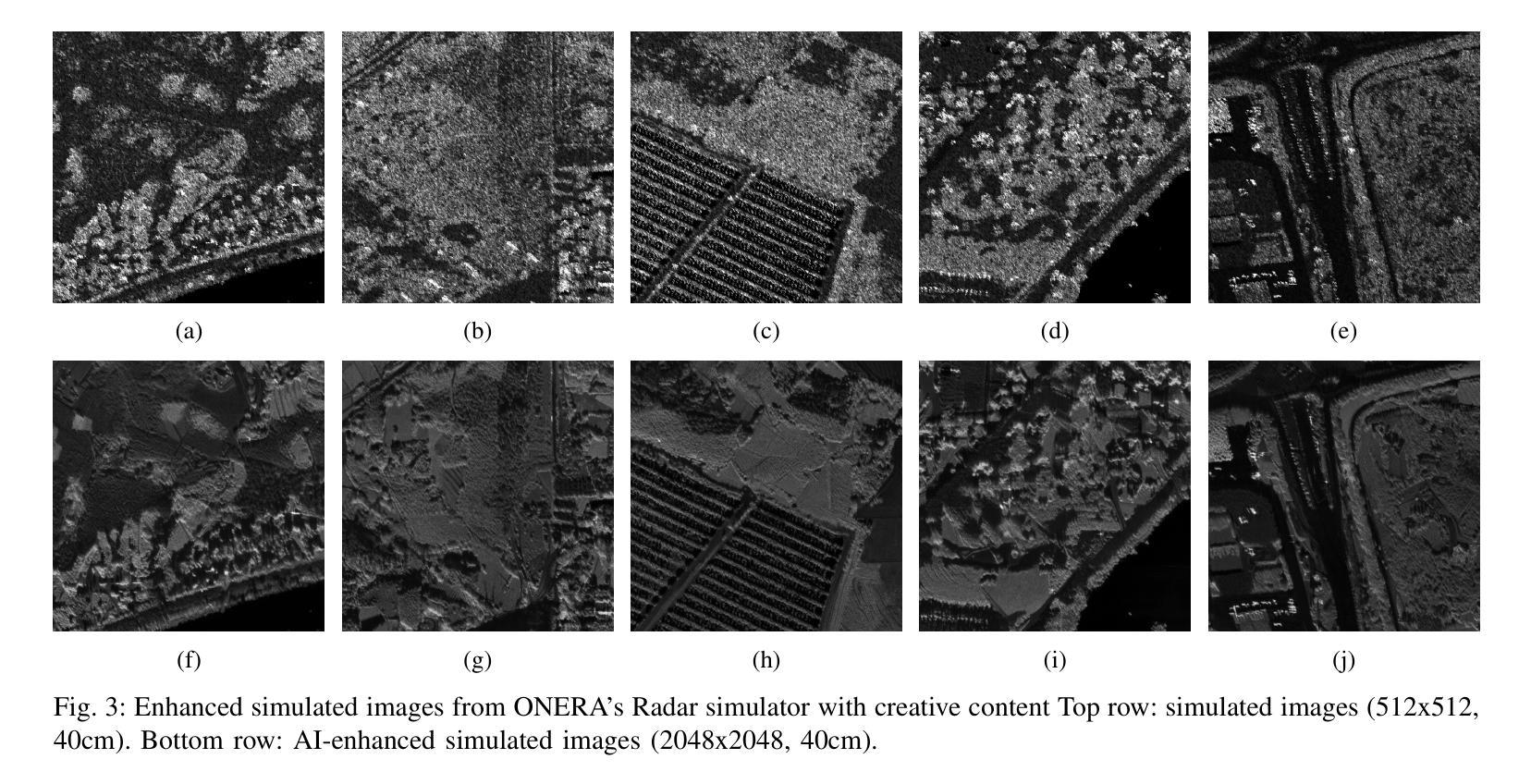
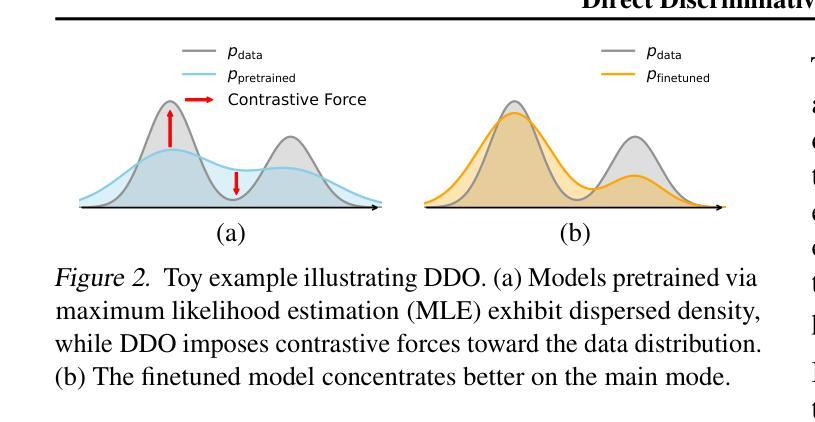
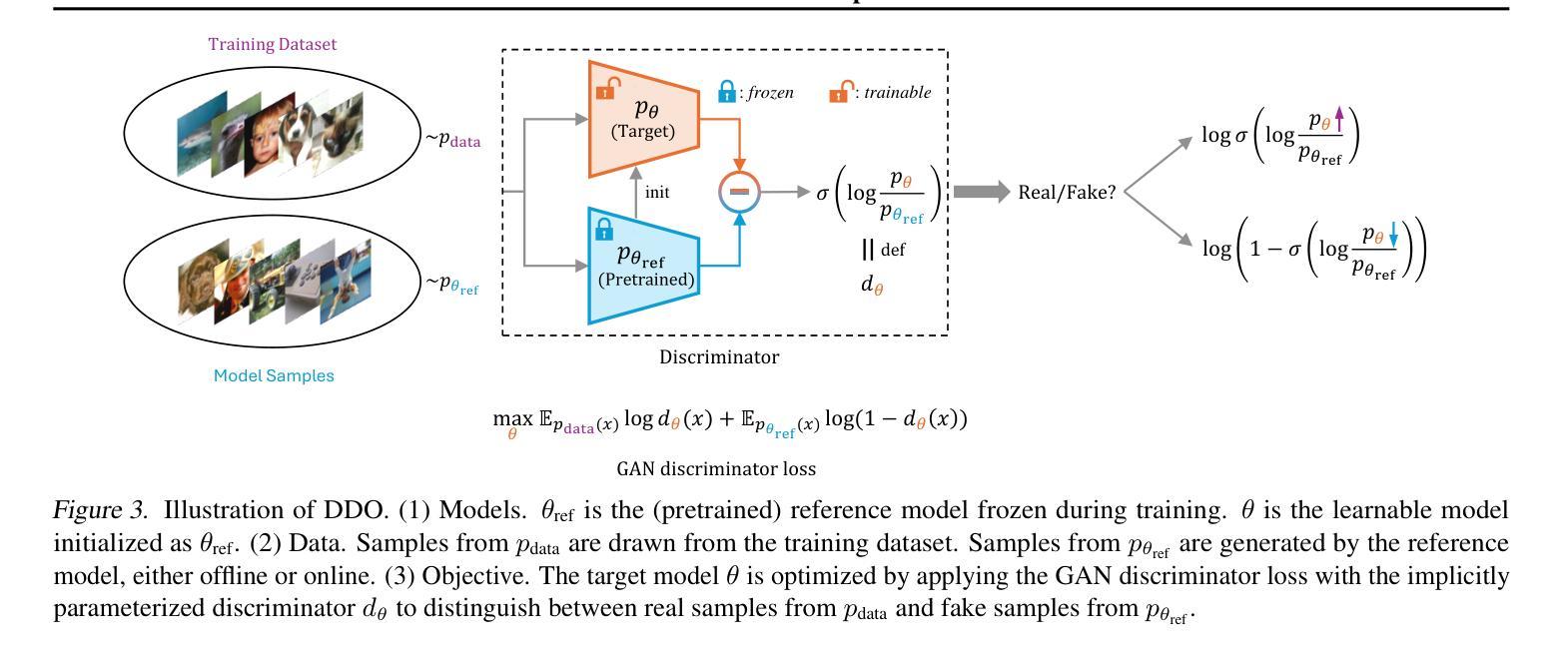
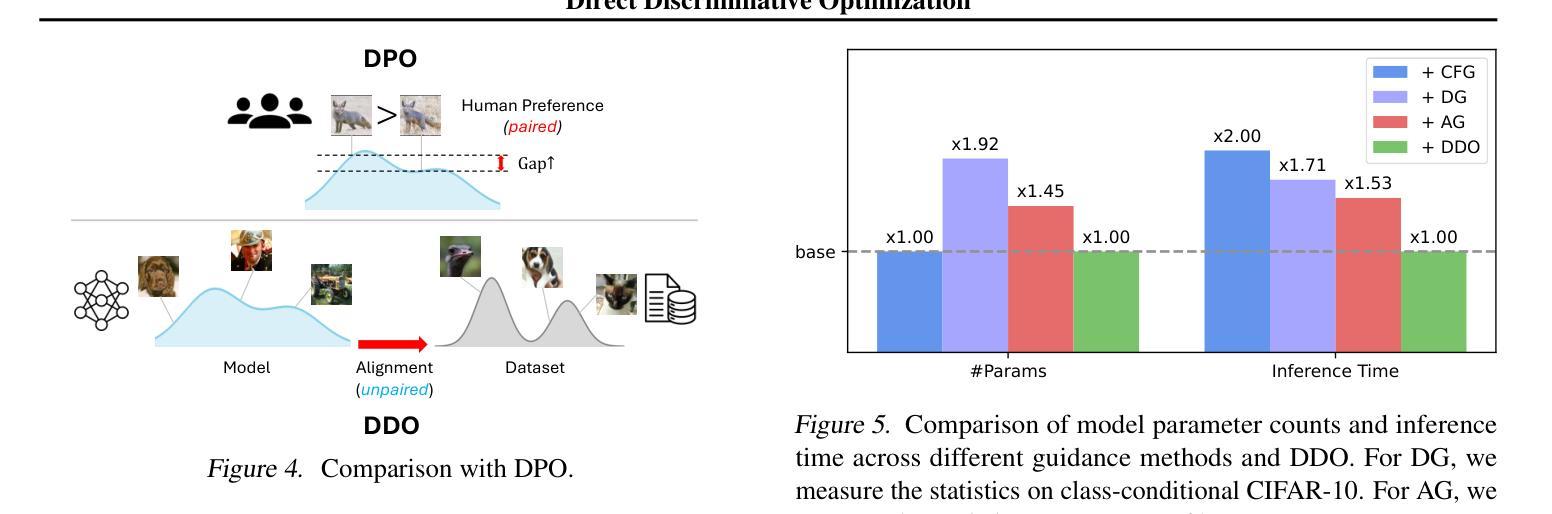
Direct Discriminative Optimization: Your Likelihood-Based Visual Generative Model is Secretly a GAN Discriminator
Authors:Kaiwen Zheng, Yongxin Chen, Huayu Chen, Guande He, Ming-Yu Liu, Jun Zhu, Qinsheng Zhang
While likelihood-based generative models, particularly diffusion and autoregressive models, have achieved remarkable fidelity in visual generation, the maximum likelihood estimation (MLE) objective, which minimizes the forward KL divergence, inherently suffers from a mode-covering tendency that limits the generation quality under limited model capacity. In this work, we propose Direct Discriminative Optimization (DDO) as a unified framework that integrates likelihood-based generative training and GAN-type discrimination to bypass this fundamental constraint by exploiting reverse KL and self-generated negative signals. Our key insight is to parameterize a discriminator implicitly using the likelihood ratio between a learnable target model and a fixed reference model, drawing parallels with the philosophy of Direct Preference Optimization (DPO). Unlike GANs, this parameterization eliminates the need for joint training of generator and discriminator networks, allowing for direct, efficient, and effective finetuning of a well-trained model to its full potential beyond the limits of MLE. DDO can be performed iteratively in a self-play manner for progressive model refinement, with each round requiring less than 1% of pretraining epochs. Our experiments demonstrate the effectiveness of DDO by significantly advancing the previous SOTA diffusion model EDM, reducing FID scores from 1.79/1.58/1.96 to new records of 1.30/0.97/1.26 on CIFAR-10/ImageNet-64/ImageNet 512x512 datasets without any guidance mechanisms, and by consistently improving both guidance-free and CFG-enhanced FIDs of visual autoregressive models on ImageNet 256x256.
基于概率的生成模型,特别是扩散和自回归模型,在视觉生成方面取得了显著的保真度。最大似然估计(MLE)目标通过最小化正向KL散度,本质上存在一种模式覆盖的趋势,这在有限的模型容量下限制了生成质量。在这项工作中,我们提出了直接判别优化(DDO)作为一个统一的框架,它将基于概率的生成训练和GAN型判别结合起来,通过利用反向KL和自我生成的负信号来绕过这个基本约束。我们的关键见解是,使用一个判别器隐式地利用可学习目标模型与固定参考模型之间的概率比作为参数,这与直接偏好优化(DPO)的理念相类似。不同于生成对抗网络(GANs),这种参数化消除了生成器和判别器网络联合训练的需要,允许对良好训练的模型进行直接、高效和有效的微调,充分发挥其潜力,超越MLE的限制。DDO可以以一种自我对抗的方式迭代进行,以实现模型的逐步改进,每一轮需要的预训练周期不到1%。我们的实验证明了DDO的有效性,它通过显著地提升先前的最佳扩散模型EDM,在无任何指导机制的情况下,将CIFAR-10/ImageNet-64/ImageNet 512x512数据集的FID得分从1.79/1.58/1.96降低到新的记录1.30/0.97/1.26,并且持续提高了无指导和CFG增强的视觉自回归模型在ImageNet 256x256上的FID得分。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF ICML 2025 Spotlight Project Page: https://research.nvidia.com/labs/dir/ddo/ Code: https://github.com/NVlabs/DDO
摘要
本文提出一种名为Direct Discriminative Optimization(DDO)的统一框架,该框架结合了基于概率生成训练和GAN型判别训练,以绕过最大似然估计(MLE)目标固有的模式覆盖倾向限制。通过利用反向KL和自我生成的负信号,DDO能直接在预训练模型的基础上进行微调,无需联合训练生成器和判别器网络。实验表明,DDO能有效提升现有扩散模型的性能,并在无指导机制的情况下降低CIFAR-10/ImageNet-64/ImageNet 512x512数据集的FID得分。此外,DDO还能在不使用指导机制和CFG增强的情冏下改进视觉自回归模型在ImageNet 256x256上的FID得分。
关键见解
- 本文提出Direct Discriminative Optimization(DDO)框架,结合了基于概率的生成训练和GAN型判别训练。
- DDO通过利用反向KL和自我生成的负信号,绕过MLE目标的模式覆盖倾向限制。
- DDO能在预训练模型的基础上进行直接、高效和有效的微调,无需联合训练生成器和判别器网络。
- 实验表明,DDO能显著提升扩散模型的性能,降低FID得分。
- DDO在无需指导机制的情况下,能改进视觉自回归模型在ImageNet 256x256上的FID得分。
- DDO可以通过自我迭代的方式进行模型逐步优化,每次迭代所需的训练时间少于预训练的1%。
- DDO的创新之处在于利用可学习目标模型和固定参考模型之间的概率比来隐式参数化判别器,这与Direct Preference Optimization(DPO)的理念相似。
点此查看论文截图