⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-05-14 更新
Breast Cancer Classification in Deep Ultraviolet Fluorescence Images Using a Patch-Level Vision Transformer Framework
Authors:Pouya Afshin, David Helminiak, Tongtong Lu, Tina Yen, Julie M. Jorns, Mollie Patton, Bing Yu, Dong Hye Ye
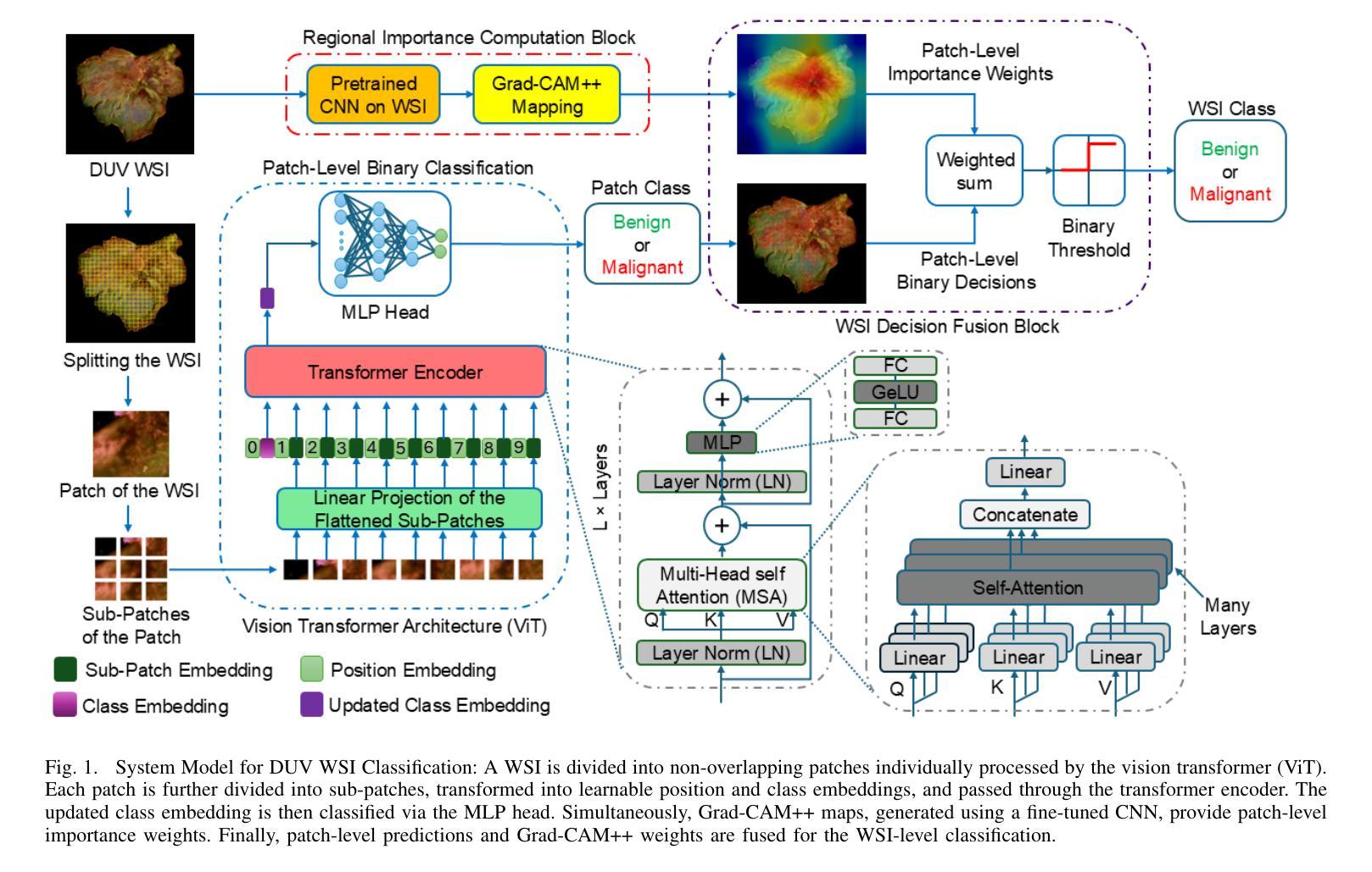
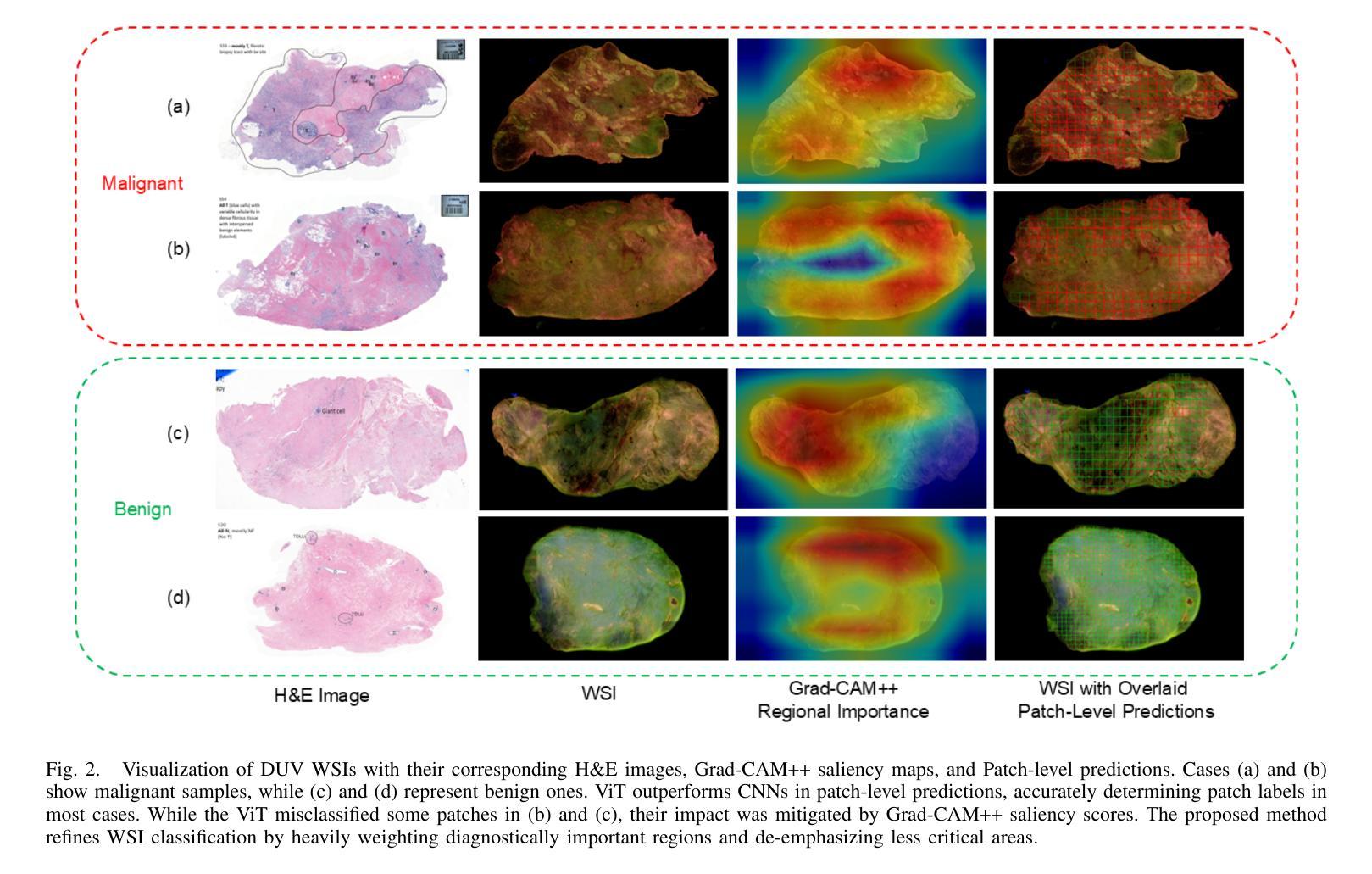
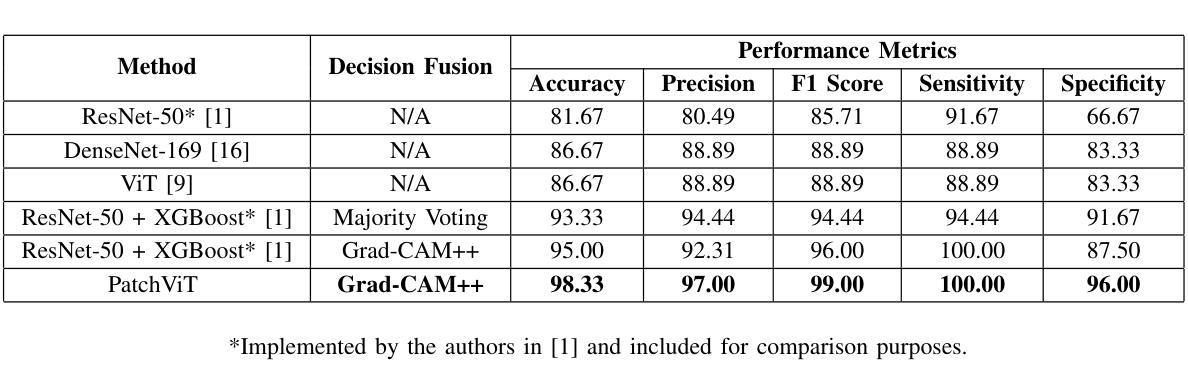
Breast-conserving surgery (BCS) aims to completely remove malignant lesions while maximizing healthy tissue preservation. Intraoperative margin assessment is essential to achieve a balance between thorough cancer resection and tissue conservation. A deep ultraviolet fluorescence scanning microscope (DUV-FSM) enables rapid acquisition of whole surface images (WSIs) for excised tissue, providing contrast between malignant and normal tissues. However, breast cancer classification with DUV WSIs is challenged by high resolutions and complex histopathological features. This study introduces a DUV WSI classification framework using a patch-level vision transformer (ViT) model, capturing local and global features. Grad-CAM++ saliency weighting highlights relevant spatial regions, enhances result interpretability, and improves diagnostic accuracy for benign and malignant tissue classification. A comprehensive 5-fold cross-validation demonstrates the proposed approach significantly outperforms conventional deep learning methods, achieving a classification accuracy of 98.33%.
乳腺保乳手术(BCS)旨在彻底切除恶性病变,同时最大限度地保留健康组织。术中边缘评估对于在彻底切除癌症和保留组织之间取得平衡至关重要。深紫外荧光扫描显微镜(DUV-FSM)可以快速获取切除组织的全表面图像(WSI),为恶性组织和正常组织提供对比。然而,由于高解析度和复杂的组织病理学特征,使用DUV WSI进行乳腺癌分类面临挑战。本研究引入了一种基于区域级别的视觉转换器(ViT)模型的DUV WSI分类框架,能够捕捉局部和全局特征。Grad-CAM++显著性权重能够突出相关的空间区域,提高结果的可解释性,并改善良性和恶性组织分类的诊断准确性。通过全面的五折交叉验证显示,该方法显著优于传统的深度学习技术,达到了98.33%的分类准确率。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
高分辨率与复杂的组织病理学特征为使用深紫外线荧光扫描显微镜(DUV-FSM)在切除组织中进行乳腺癌分类带来挑战。本研究引入了一种基于补丁级别的视觉转换器(ViT)模型的DUV宽视野图像(WSI)分类框架,捕捉局部和全局特征。Grad-CAM++显著加权方法凸显关键的空间区域,提高了结果的可解释性和对良恶性组织分类的诊断准确性。经过全面的五折交叉验证,该方法显著优于传统的深度学习模型,分类准确率达到了98.33%。
Key Takeaways
- 乳腺癌保乳手术旨在彻底切除恶性病变并最大程度地保留健康组织。
- 术中边界评估是彻底切除肿瘤和保留组织之间的平衡的关键。
- 深紫外线荧光扫描显微镜(DUV-FSM)能够迅速获取切除组织的全表面图像(WSI),区分恶性与正常组织。
- DUV WSI分类面临高分辨和复杂组织病理学特征的挑战。
- 补丁级别的视觉转换器(ViT)模型用于捕捉局部和全局特征进行分类。
- Grad-CAM++显著加权提高了分类结果的诊断准确性和可解释性。
点此查看论文截图

MAIS: Memory-Attention for Interactive Segmentation
Authors:Mauricio Orbes-Arteaga, Oeslle Lucena, Sabastien Ourselin, M. Jorge Cardoso
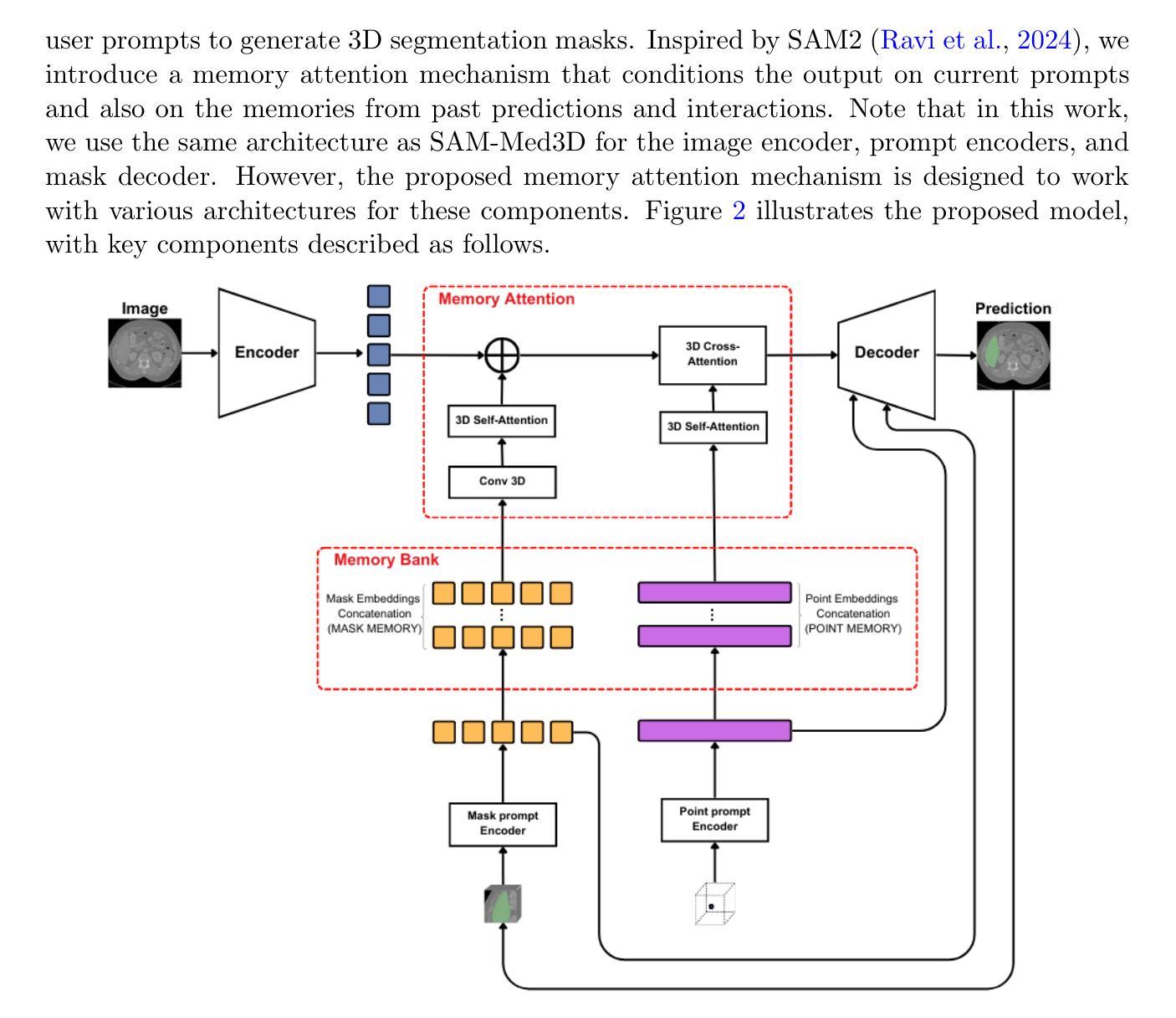
Interactive medical segmentation reduces annotation effort by refining predictions through user feedback. Vision Transformer (ViT)-based models, such as the Segment Anything Model (SAM), achieve state-of-the-art performance using user clicks and prior masks as prompts. However, existing methods treat interactions as independent events, leading to redundant corrections and limited refinement gains. We address this by introducing MAIS, a Memory-Attention mechanism for Interactive Segmentation that stores past user inputs and segmentation states, enabling temporal context integration. Our approach enhances ViT-based segmentation across diverse imaging modalities, achieving more efficient and accurate refinements.
交互式医学分割通过用户反馈来优化预测,减少了标注工作量。例如,基于Vision Transformer(ViT)的模型,如Segment Anything Model(SAM),通过使用用户点击和先验掩膜作为提示来实现最先进的性能。然而,现有方法将交互视为独立事件,导致冗余校正和有限的优化收益。我们通过引入MAIS来解决这个问题,这是一种用于交互式分割的记忆注意力机制,可以存储过去的用户输入和分割状态,实现时间上下文的整合。我们的方法在多种成像模式下增强了基于ViT的分割,实现了更高效和准确的优化。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
医学互动分割通过用户反馈优化预测,减少了标注工作量。采用Vision Transformer(ViT)模型的Segment Anything Model(SAM)利用用户点击和先验掩膜作为提示,达到最先进的性能。然而,现有方法将互动视为独立事件,导致冗余修正和有限的优化收益。我们提出通过引入MAIS(一种用于交互式分割的记忆注意力机制)来解决这一问题,它存储过去用户输入和分割状态,实现时间上下文的整合。我们的方法提高了基于ViT的跨多种成像模态的分割效率与准确性。
Key Takeaways
- 互动医学分割通过用户反馈减少标注工作量。
- Vision Transformer(ViT)模型,如Segment Anything Model(SAM),利用用户点击和先验掩膜达到顶尖性能。
- 现有方法将互动视为独立事件,造成冗余修正和有限的优化收益。
- 引入MAIS(记忆注意力机制用于交互式分割)来解决这一问题。
- MAIS能存储过去用户输入和分割状态,实现时间上下文的整合。
- 方法提高了基于ViT的跨多种成像模态的分割效率。
点此查看论文截图

Learning Graph Representation of Agent Diffuser
Authors:Youcef Djenouri, Nassim Belmecheri, Tomasz Michalak, Jan Dubiński, Ahmed Nabil Belbachir, Anis Yazidi
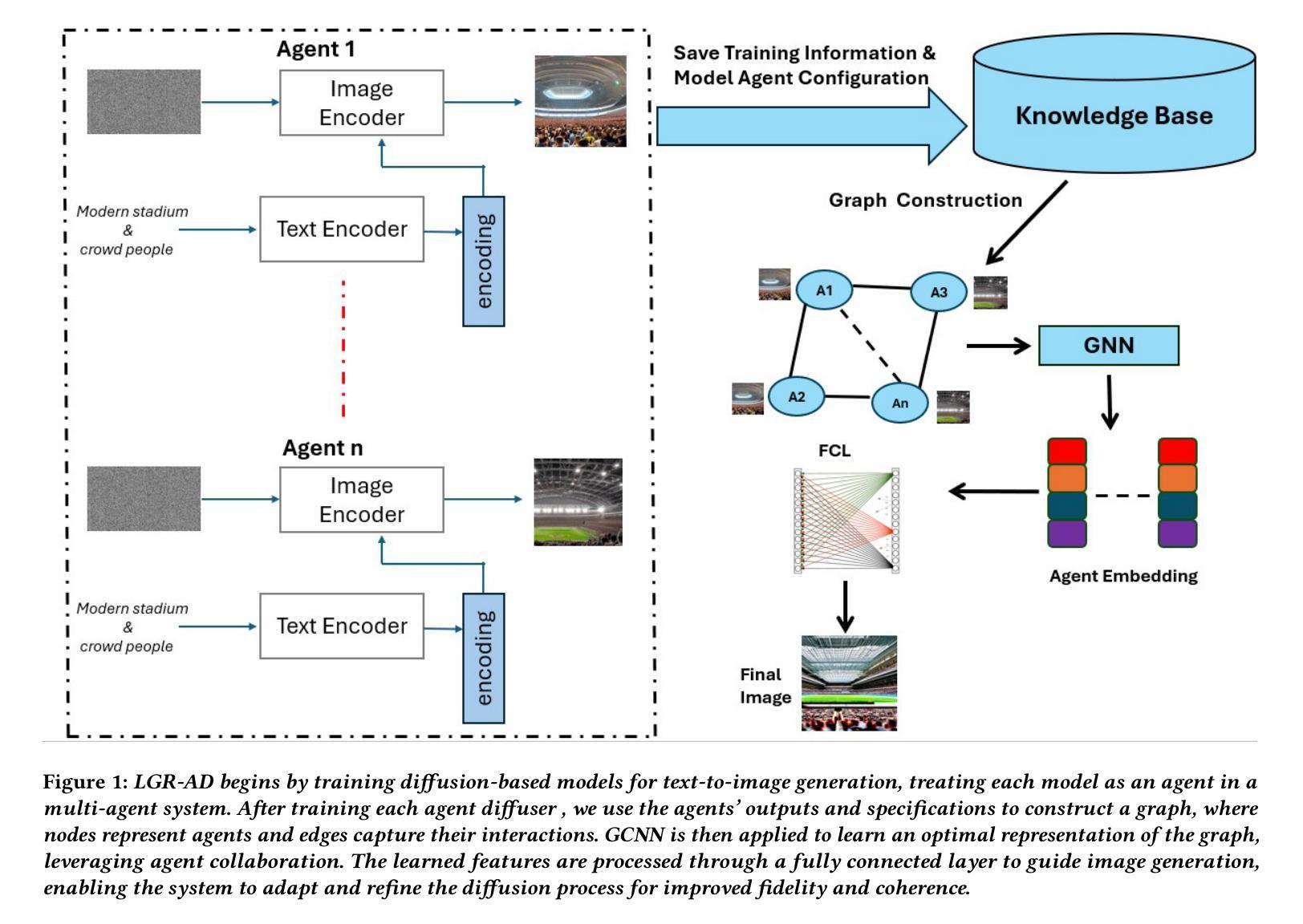
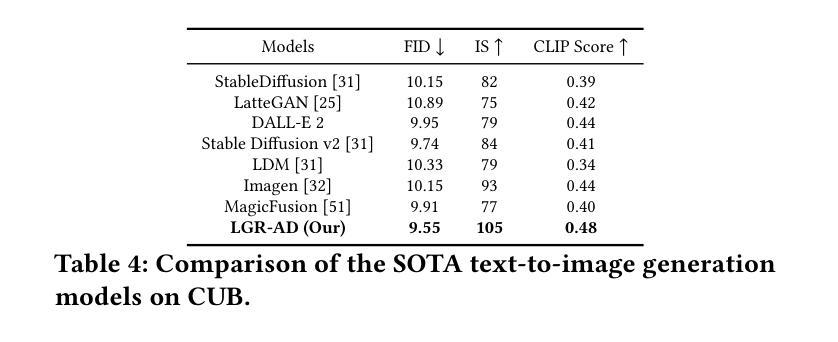
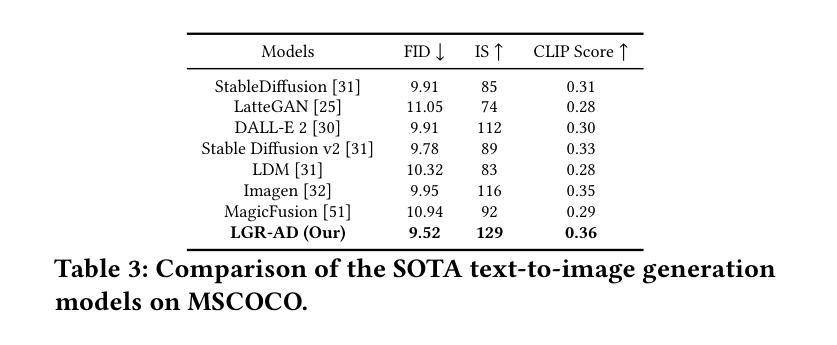
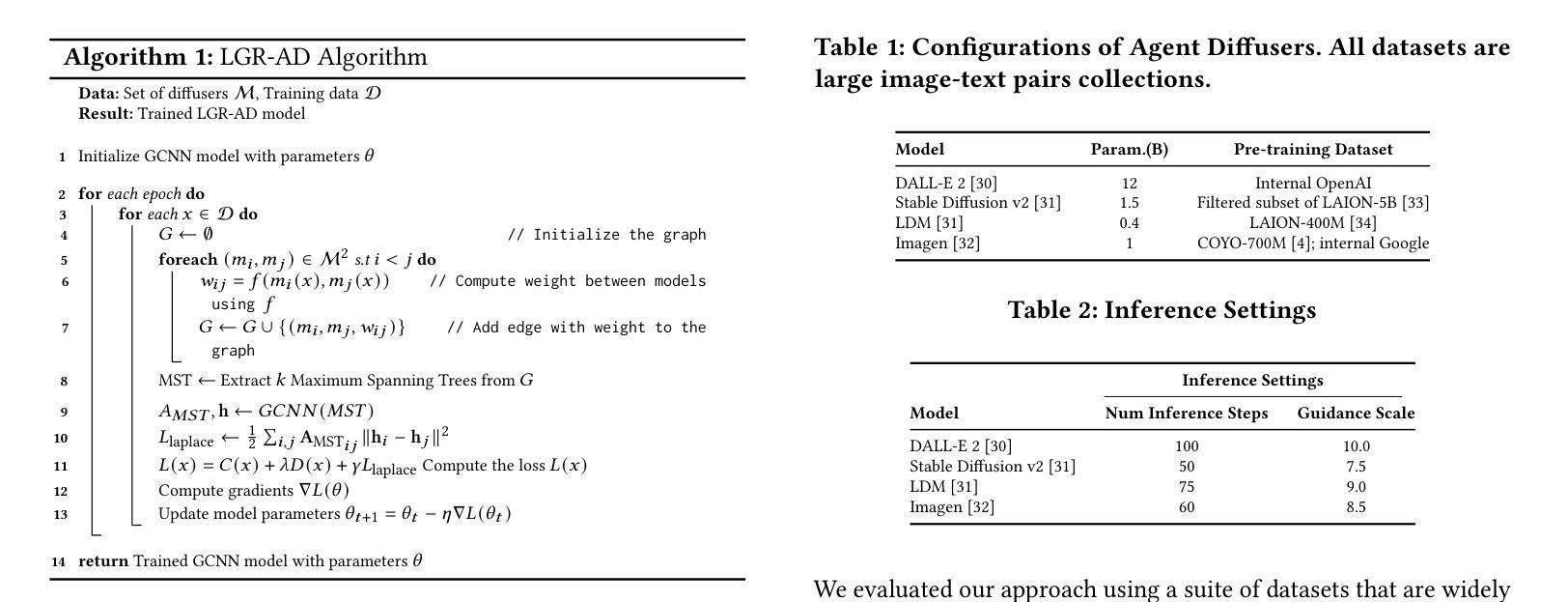
Diffusion-based generative models have significantly advanced text-to-image synthesis, demonstrating impressive text comprehension and zero-shot generalization. These models refine images from random noise based on textual prompts, with initial reliance on text input shifting towards enhanced visual fidelity over time. This transition suggests that static model parameters might not optimally address the distinct phases of generation. We introduce LGR-AD (Learning Graph Representation of Agent Diffusers), a novel multi-agent system designed to improve adaptability in dynamic computer vision tasks. LGR-AD models the generation process as a distributed system of interacting agents, each representing an expert sub-model. These agents dynamically adapt to varying conditions and collaborate through a graph neural network that encodes their relationships and performance metrics. Our approach employs a coordination mechanism based on top-$k$ maximum spanning trees, optimizing the generation process. Each agent’s decision-making is guided by a meta-model that minimizes a novel loss function, balancing accuracy and diversity. Theoretical analysis and extensive empirical evaluations show that LGR-AD outperforms traditional diffusion models across various benchmarks, highlighting its potential for scalable and flexible solutions in complex image generation tasks. Code is available at: https://github.com/YousIA/LGR_AD
基于扩散的生成模型在文本到图像合成方面取得了显著的进展,展示了令人印象深刻的文本理解和零样本泛化能力。这些模型根据文本提示从随机噪声中细化图像,最初依赖文本输入,随着时间的推移,对视觉保真度的关注逐渐增强。这种转变表明,静态模型参数可能无法最佳地应对生成的不同阶段。我们引入了LGR-AD(学习Agent扩散的图表示),这是一个新型的多Agent系统,旨在提高动态计算机视觉任务的适应性。LGR-AD将生成过程建模为交互Agent的分布式系统,每个Agent代表一个专家子模型。这些Agent可以动态适应各种条件,并通过编码其关系和性能指标的图神经网络进行协作。我们的方法采用基于top-k最大生成树的协调机制,优化生成过程。每个Agent的决策由元模型引导,该模型最小化新型损失函数,以平衡精度和多样性。理论分析和广泛的实证研究结果表明,在各种基准测试中,LGR-AD的性能优于传统扩散模型,突显其在复杂图像生成任务中可扩展和灵活解决方案的潜力。代码可用在:https://github.com/YousIA/LGR_AD。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted at AAMAS2025 International Conference on Autonomous Agents and Multiagent Systems
Summary
基于扩散模型的生成式模型在文本驱动图像合成方面取得了重大进展,这些模型展现出令人印象深刻的文本理解能力和零样本泛化能力。提出一种新型多代理系统LGR-AD,通过图神经网络动态适应不同条件并协作完成计算机视觉任务。每个代理代表一个专家子模型,通过基于top-k最大生成树的协调机制优化生成过程。理论分析和大量实证评估表明,LGR-AD在多种基准测试中优于传统扩散模型,在复杂图像生成任务中具有可扩展和灵活解决方案的潜力。
Key Takeaways
- 扩散模型在文本驱动图像合成方面取得显著进展,展现文本理解和零样本泛化能力。
- LGR-AD是一种新型多代理系统,用于改进动态计算机视觉任务的适应性。
- LGR-AD模型采用图神经网络编码代理间关系和性能度量。
- LGR-AD通过基于top-k最大生成树的协调机制优化生成过程。
- 每个代理的决策制定由元模型引导,采用新型损失函数平衡准确性和多样性。
- 理论分析和大量实证评估表明LGR-AD在多种基准测试中表现优异。
- LGR-AD具有可扩展和灵活解决方案的潜力,尤其在复杂图像生成任务中。
点此查看论文截图

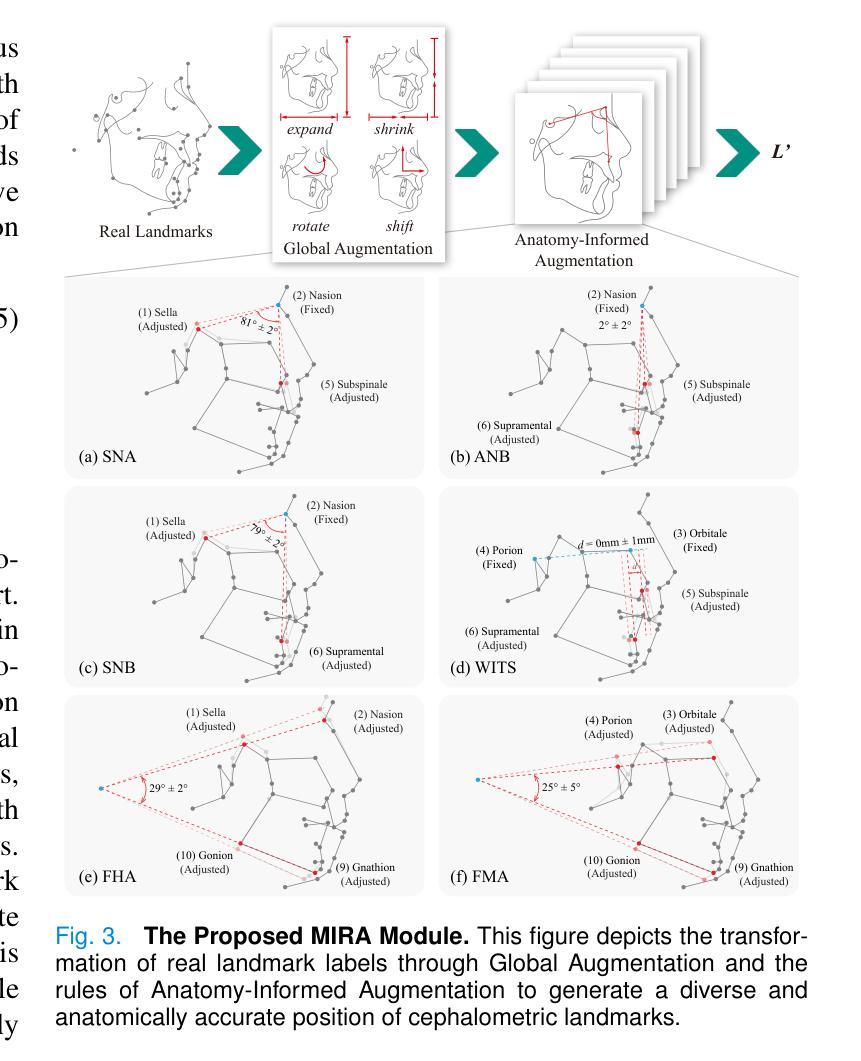
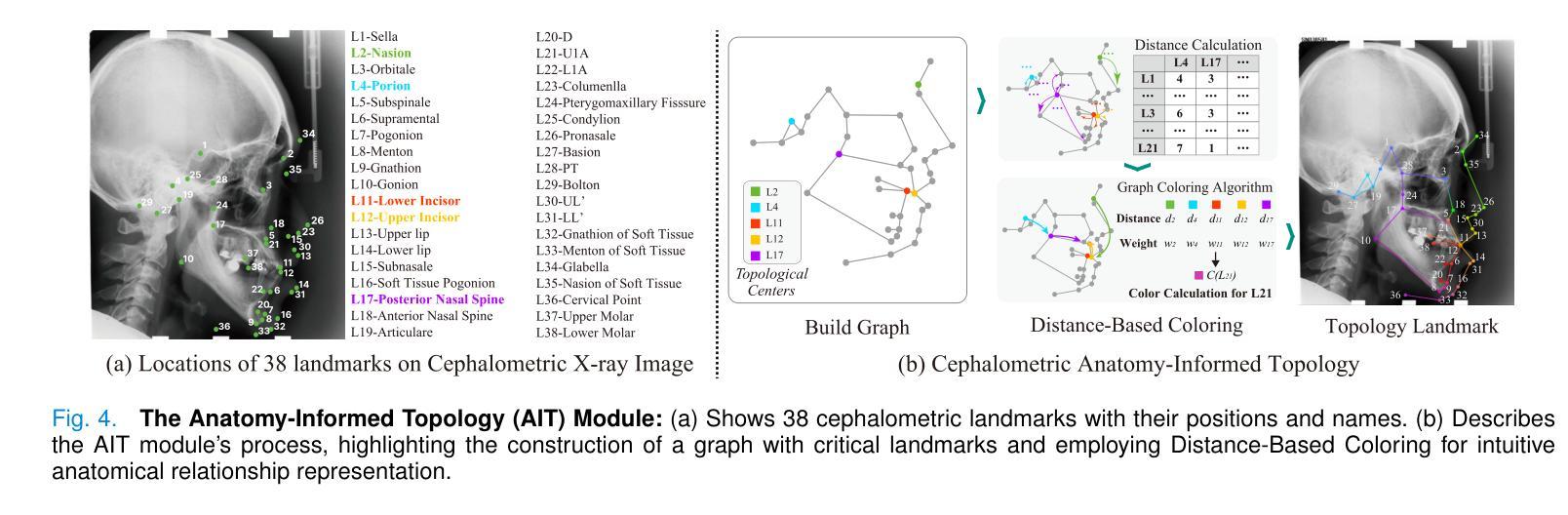
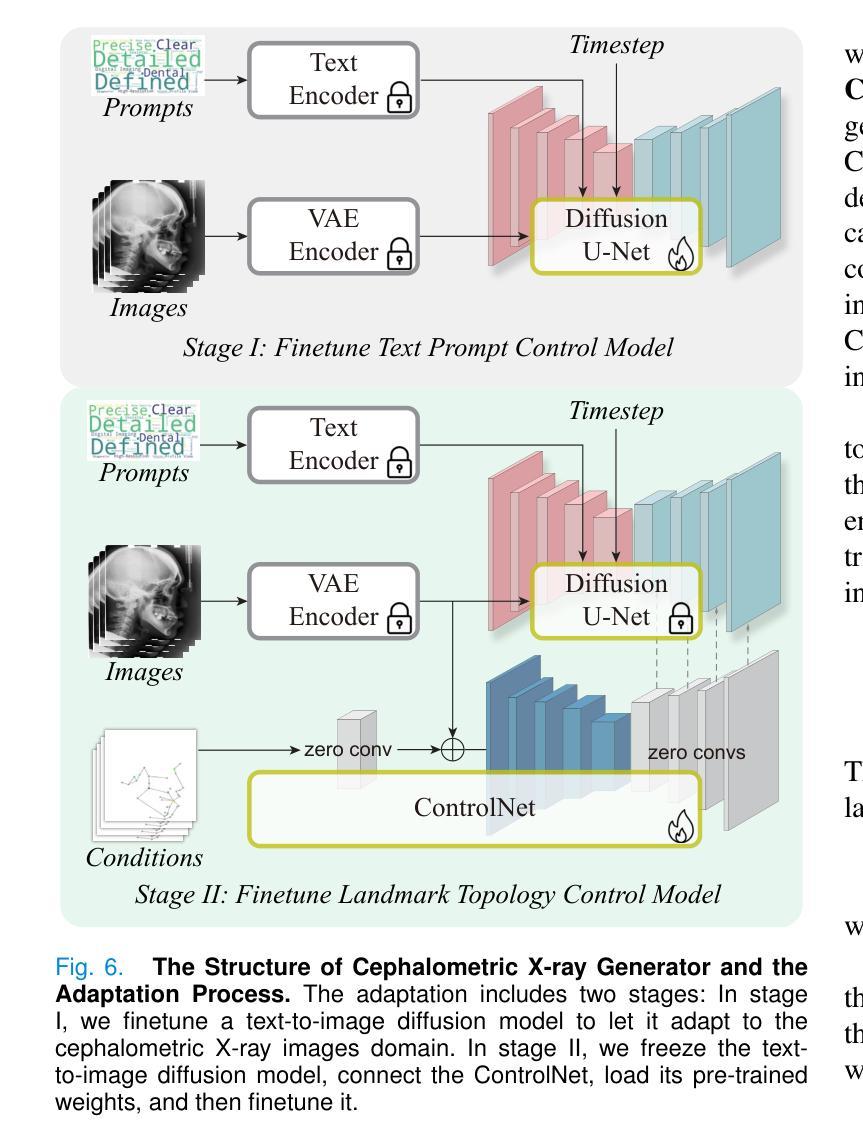
Towards Better Cephalometric Landmark Detection with Diffusion Data Generation
Authors:Dongqian Guo, Wencheng Han, Pang Lyu, Yuxi Zhou, Jianbing Shen
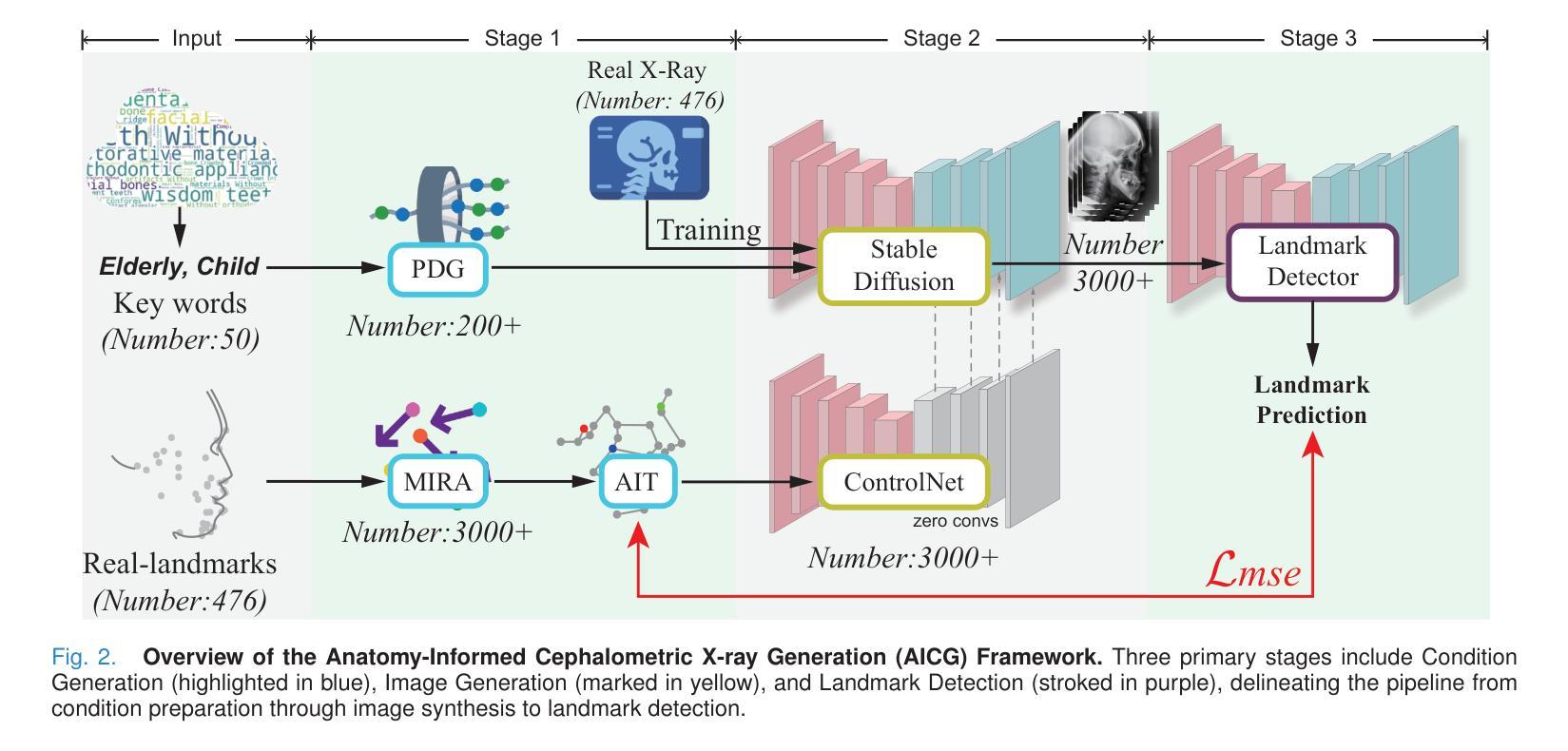
Cephalometric landmark detection is essential for orthodontic diagnostics and treatment planning. Nevertheless, the scarcity of samples in data collection and the extensive effort required for manual annotation have significantly impeded the availability of diverse datasets. This limitation has restricted the effectiveness of deep learning-based detection methods, particularly those based on large-scale vision models. To address these challenges, we have developed an innovative data generation method capable of producing diverse cephalometric X-ray images along with corresponding annotations without human intervention. To achieve this, our approach initiates by constructing new cephalometric landmark annotations using anatomical priors. Then, we employ a diffusion-based generator to create realistic X-ray images that correspond closely with these annotations. To achieve precise control in producing samples with different attributes, we introduce a novel prompt cephalometric X-ray image dataset. This dataset includes real cephalometric X-ray images and detailed medical text prompts describing the images. By leveraging these detailed prompts, our method improves the generation process to control different styles and attributes. Facilitated by the large, diverse generated data, we introduce large-scale vision detection models into the cephalometric landmark detection task to improve accuracy. Experimental results demonstrate that training with the generated data substantially enhances the performance. Compared to methods without using the generated data, our approach improves the Success Detection Rate (SDR) by 6.5%, attaining a notable 82.2%. All code and data are available at: https://um-lab.github.io/cepha-generation
头影测量标志检测在正畸诊断和治疗计划中至关重要。然而,数据采集中的样本稀缺以及手动标注所需的大量努力极大地阻碍了多样化数据集的可用性。这一局限性限制了基于深度学习检测方法的有效性,特别是基于大规模视觉模型的方法。为了应对这些挑战,我们开发了一种创新的数据生成方法,能够无需人工干预地生成多样化的头影测量X射线图像以及相应的标注。为了实现这一点,我们的方法首先利用解剖先验构建新的头影测量标志标注。然后,我们采用基于扩散的生成器来创建与这些标注紧密对应的逼真的X射线图像。为了实现具有不同属性的样本生成的精确控制,我们引入了一个新的提示头影测量X射线图像数据集。该数据集包含真实的头影测量X射线图像和详细的医学文本提示,描述这些图像。通过利用这些详细的提示,我们的方法改进了生成过程,以控制不同的风格和属性。通过大规模、多样化的生成数据,我们将大规模视觉检测模型引入到头影测量标志检测任务中,以提高准确性。实验结果表明,使用生成数据进行训练能显著提高性能。与不使用生成数据的方法相比,我们的方法成功检测率(SDR)提高了6.5%,达到了82.2%,这一成果值得注意。所有代码和数据都可在:https://um-lab.github.io/cepha-generation上找到。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了一种创新的数据生成方法,用于解决在正畸诊断与治疗计划中头影测量标志检测样本稀缺的问题。该方法通过结合解剖学先验知识构建新的头影测量标志注释,并采用基于扩散的生成器创建与这些注释相对应的逼真的X射线图像,实现了无需人工干预的多样化数据生成。通过引入带有详细描述医疗文本提示的提示头影X射线图像数据集,该方法能够控制不同样式和属性,提高生成过程的精度。利用大规模生成的多样数据,将大型视觉检测模型引入头影测量标志检测任务,提高了检测的准确性。实验结果表明,使用生成数据进行训练可以显著提高性能,与不使用生成数据的方法相比,成功率检测率(SDR)提高了6.5%,达到了82.2%。
Key Takeaways
- 解决样本稀缺和手动标注费力的问题,提出一种创新的数据生成方法。
- 利用解剖学先验知识构建新的头影测量标志注释。
- 采用基于扩散的生成器创建与注释相对应的逼真的X射线图像。
- 引入带有医疗文本提示的提示头影X射线图像数据集,控制不同样式和属性。
- 利用大规模生成的多样数据,引入大型视觉检测模型。
- 使用生成数据进行训练可以显著提高头影测量标志检测的准确性。
点此查看论文截图

Towards Facial Image Compression with Consistency Preserving Diffusion Prior
Authors:Yimin Zhou, Yichong Xia, Bin Chen, Baoyi An, Haoqian Wang, Zhi Wang, Yaowei Wang, Zikun Zhou
With the widespread application of facial image data across various domains, the efficient storage and transmission of facial images has garnered significant attention. However, the existing learned face image compression methods often produce unsatisfactory reconstructed image quality at low bit rates. Simply adapting diffusion-based compression methods to facial compression tasks results in reconstructed images that perform poorly in downstream applications due to insufficient preservation of high-frequency information. To further explore the diffusion prior in facial image compression, we propose Facial Image Compression with a Stable Diffusion Prior (FaSDiff), a method that preserves consistency through frequency enhancement. FaSDiff employs a high-frequency-sensitive compressor in an end-to-end framework to capture fine image details and produce robust visual prompts. Additionally, we introduce a hybrid low-frequency enhancement module that disentangles low-frequency facial semantics and stably modulates the diffusion prior alongside visual prompts. The proposed modules allow FaSDiff to leverage diffusion priors for superior human visual perception while minimizing performance loss in machine vision due to semantic inconsistency. Extensive experiments show that FaSDiff outperforms state-of-the-art methods in balancing human visual quality and machine vision accuracy. The code will be released after the paper is accepted.
随着面部图像数据在各个领域应用的普及,面部图像的存储和传输效率问题备受关注。然而,现有的学习面部图像压缩方法在低比特率下产生的重建图像质量往往不尽人意。简单地将基于扩散的压缩方法应用于面部压缩任务会导致重建图像在下游应用中表现不佳,因为高频信息的保留不足。为了进一步研究面部图像压缩中的扩散先验知识,我们提出了带有稳定扩散先验的面部图像压缩(FaSDiff)方法,该方法通过频率增强保持一致性。FaSDiff采用一种高频敏感压缩机,在端到端框架中捕捉图像细节,生成稳健的视觉提示。此外,我们引入了一种混合低频增强模块,该模块能够分离低频面部语义,并稳定地调节扩散先验与视觉提示。所提出的模块使FaSDiff能够利用扩散先验来提高人类视觉感知,同时最小化由于语义不一致而导致的机器视觉性能损失。大量实验表明,FaSDiff在平衡人类视觉质量和机器视觉准确性方面优于最先进的方法。论文被接受后,代码将发布。
论文及项目相关链接
摘要
针对面部图像数据在各个领域广泛应用的需求,提出一种带有稳定扩散先验的面部图像压缩方法(FaSDiff)。该方法通过频率增强保持一致性,采用端对端框架中的高频敏感压缩机来捕捉图像细节并产生稳健的视觉提示。引入混合低频增强模块,分离低频面部语义,稳定调节扩散先验与视觉提示。实验表明,FaSDiff在平衡人类视觉质量和机器视觉准确性方面优于现有方法。
关键见解
- 面部图像数据的广泛应用促使了对其高效存储和传输的需求。
- 现有学习面部图像压缩方法在低位率下重建图像质量不佳。
- 扩散先验在面部图像压缩中的应用可以提高重建图像的质量。
- FaSDiff方法通过频率增强保持一致性,采用高频敏感压缩机捕捉图像细节。
- 混合低频增强模块用于分离低频面部语义,并与扩散先验和视觉提示相结合。
- FaSDiff在平衡人类视觉质量和机器视觉准确性方面表现出优越性。
- 代码将在论文被接受后发布。
点此查看论文截图
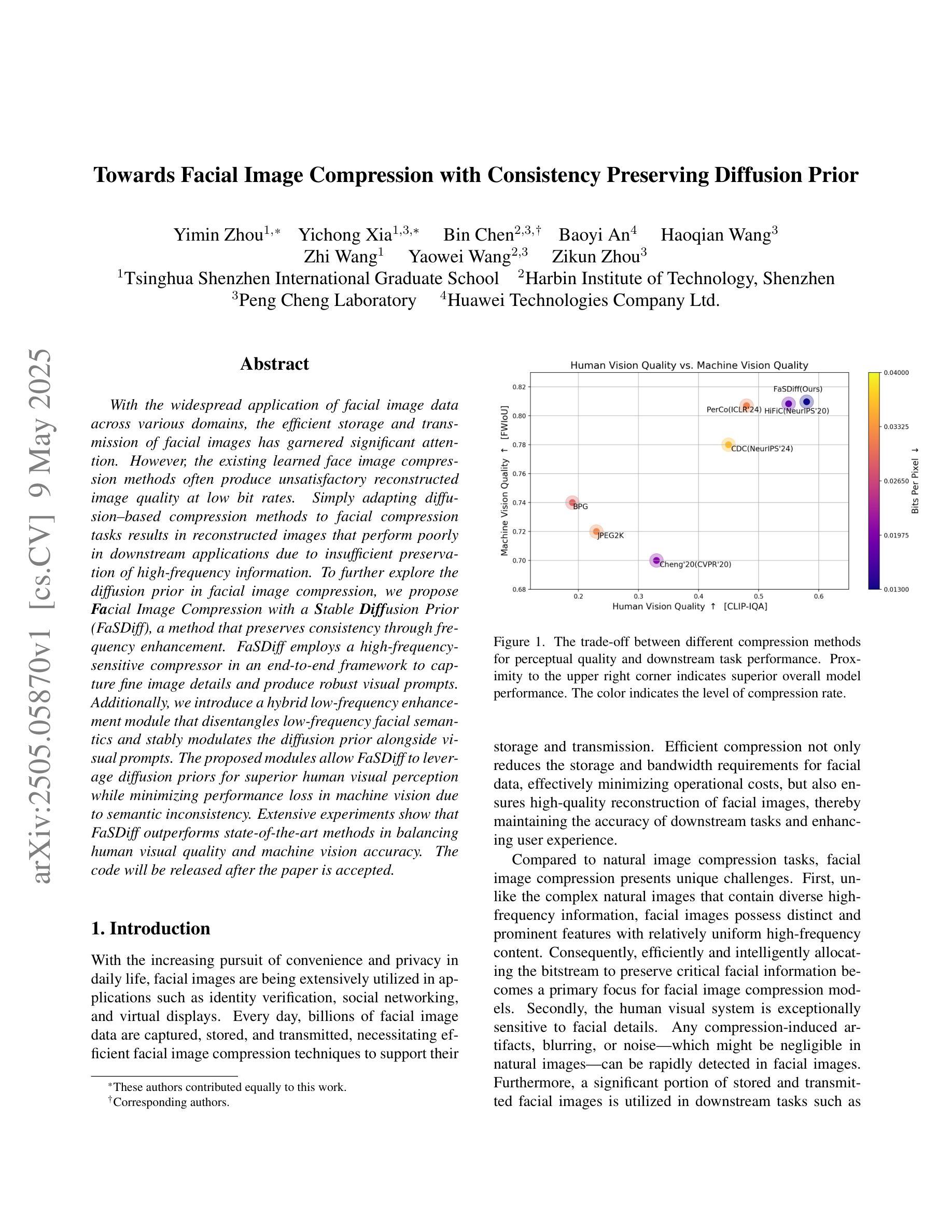
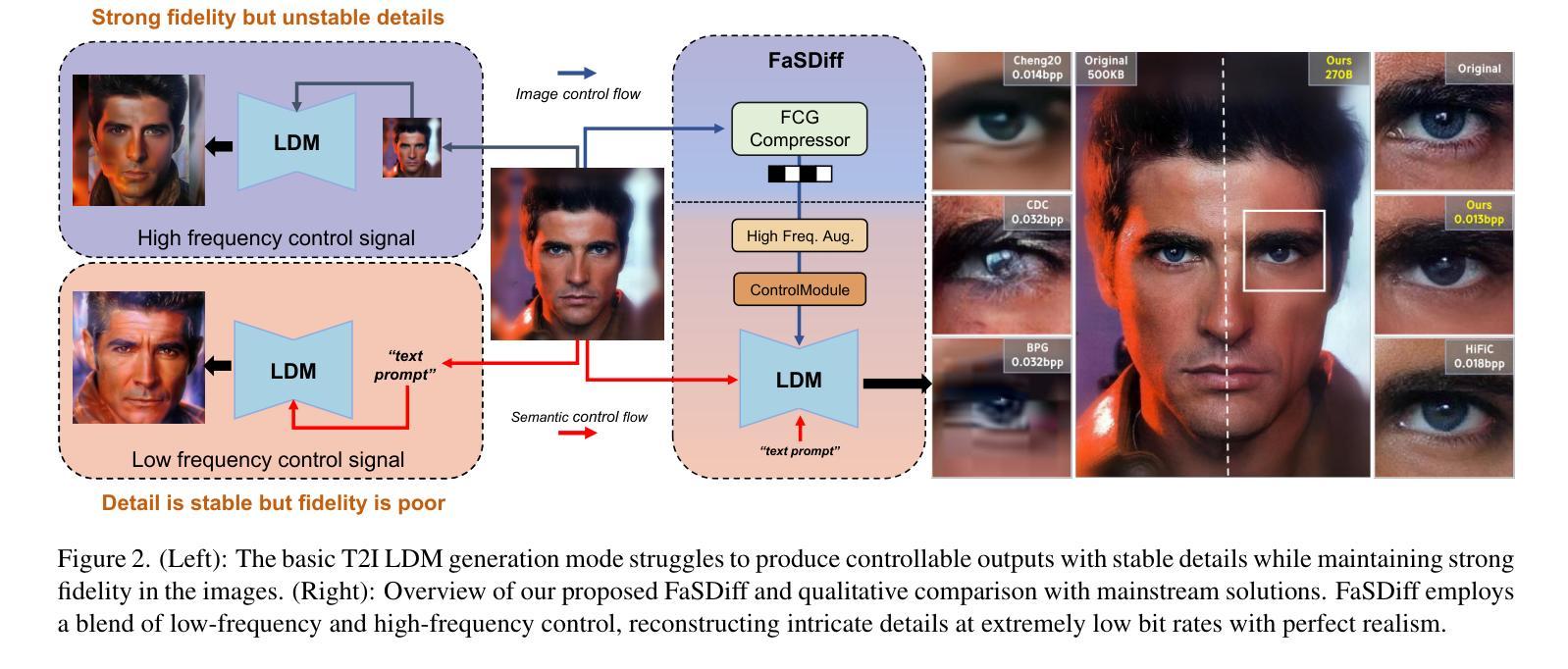
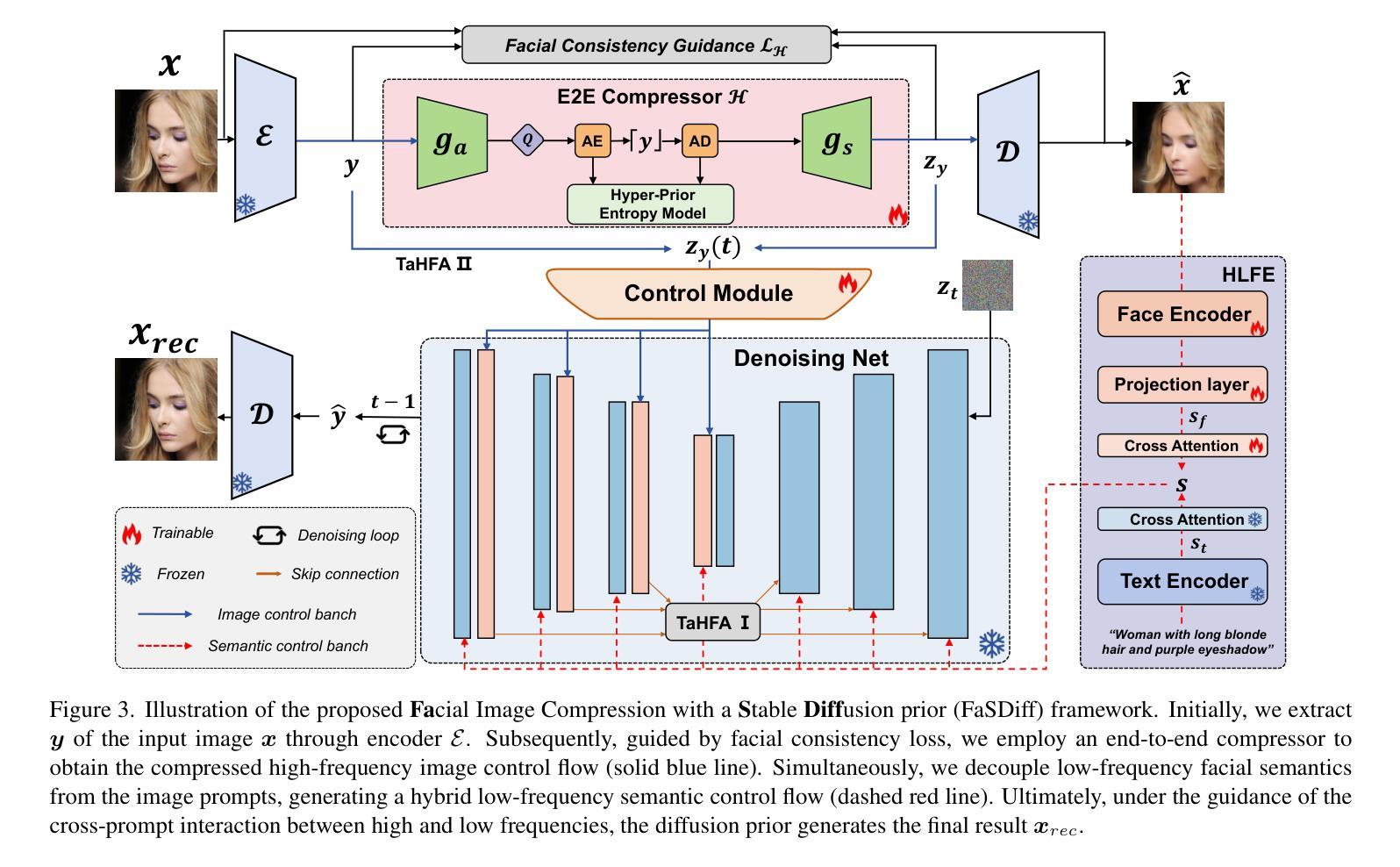
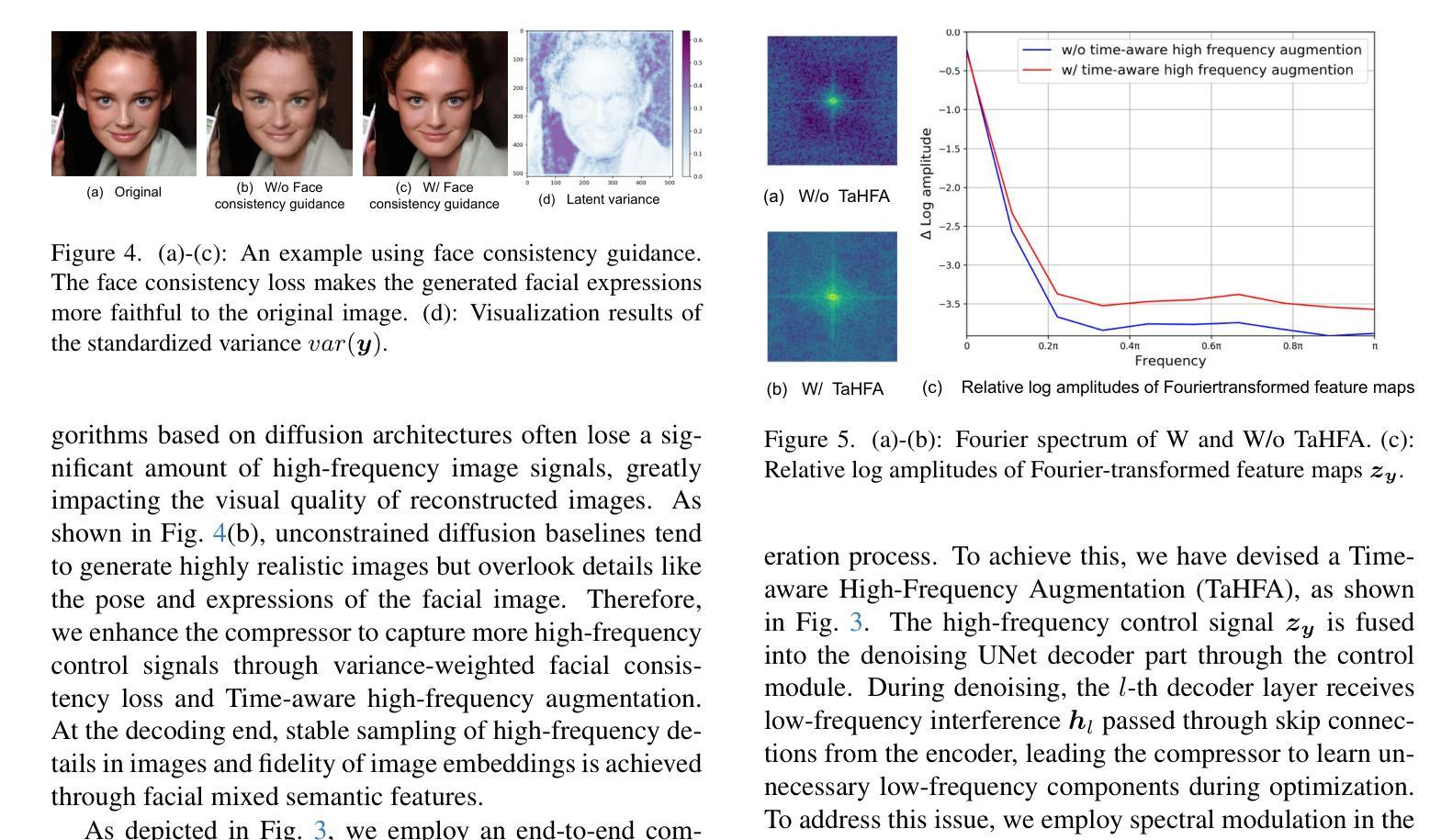
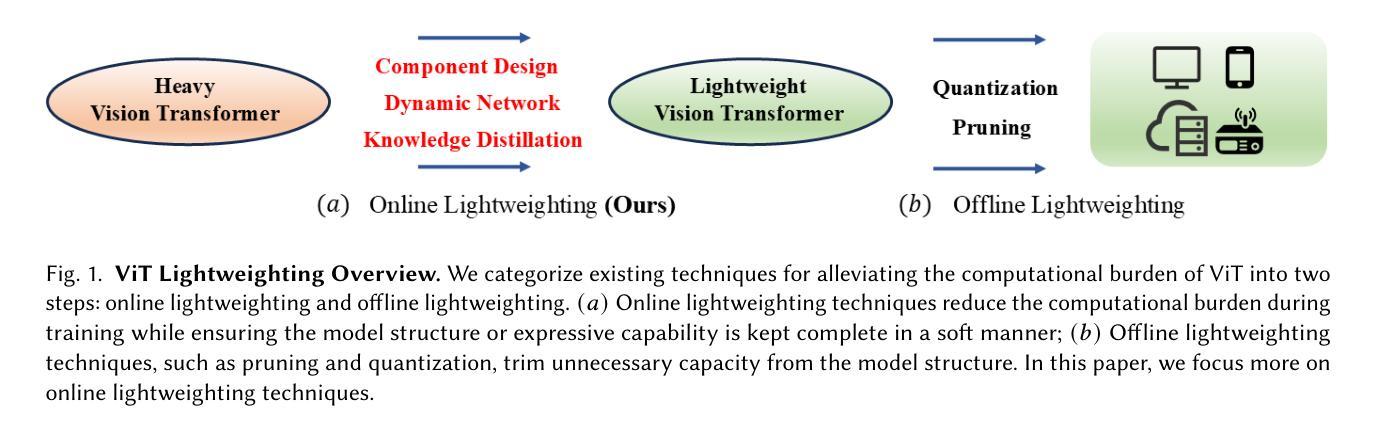
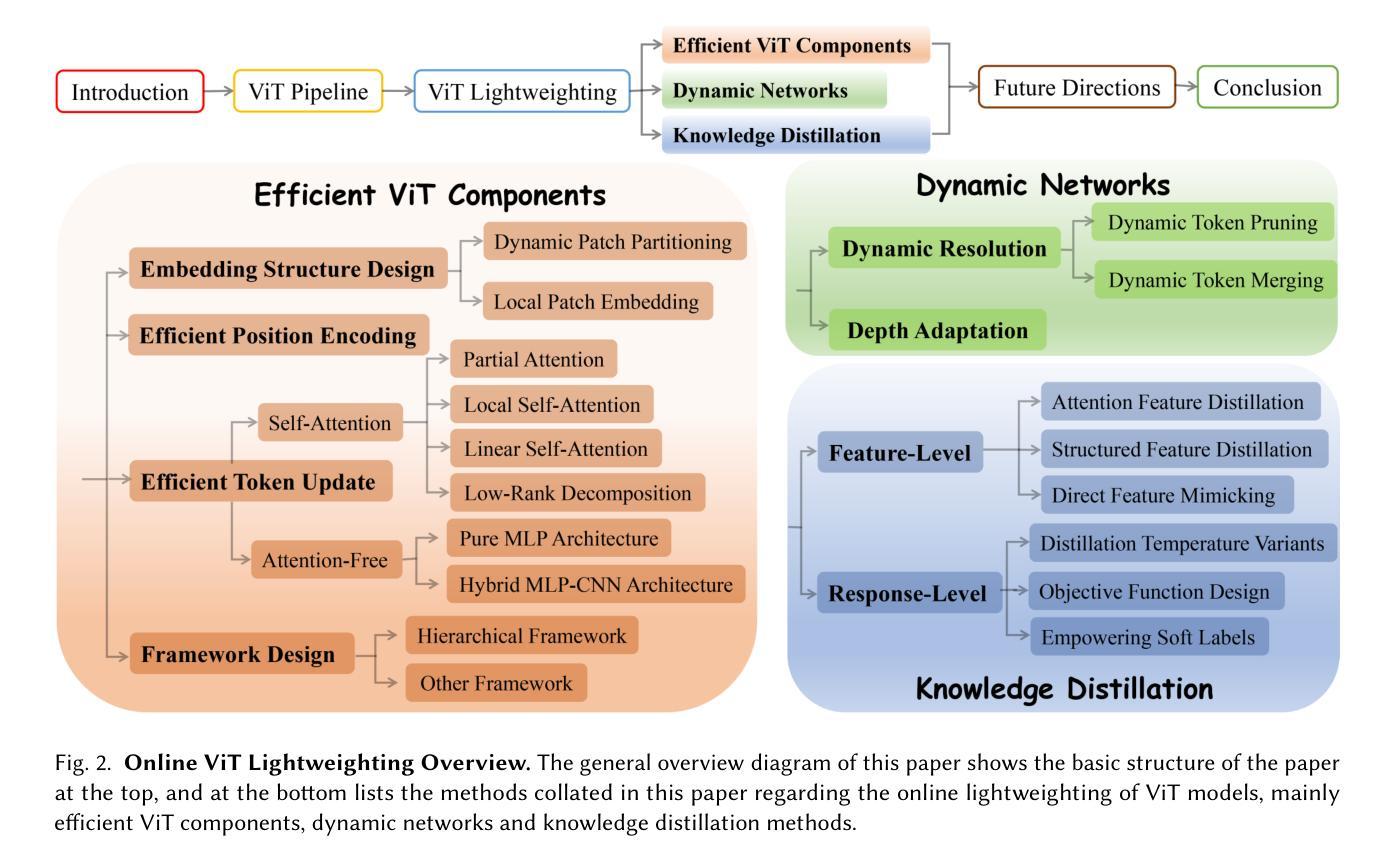
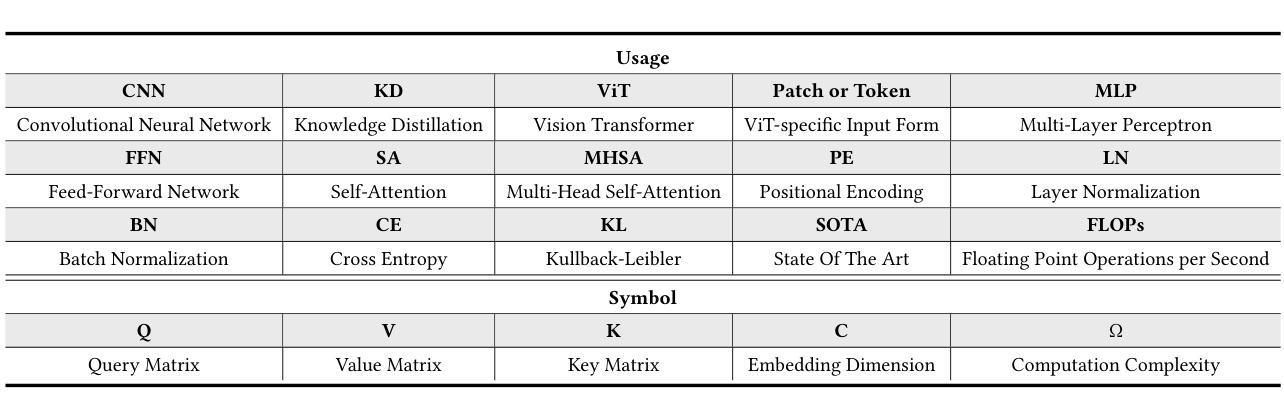
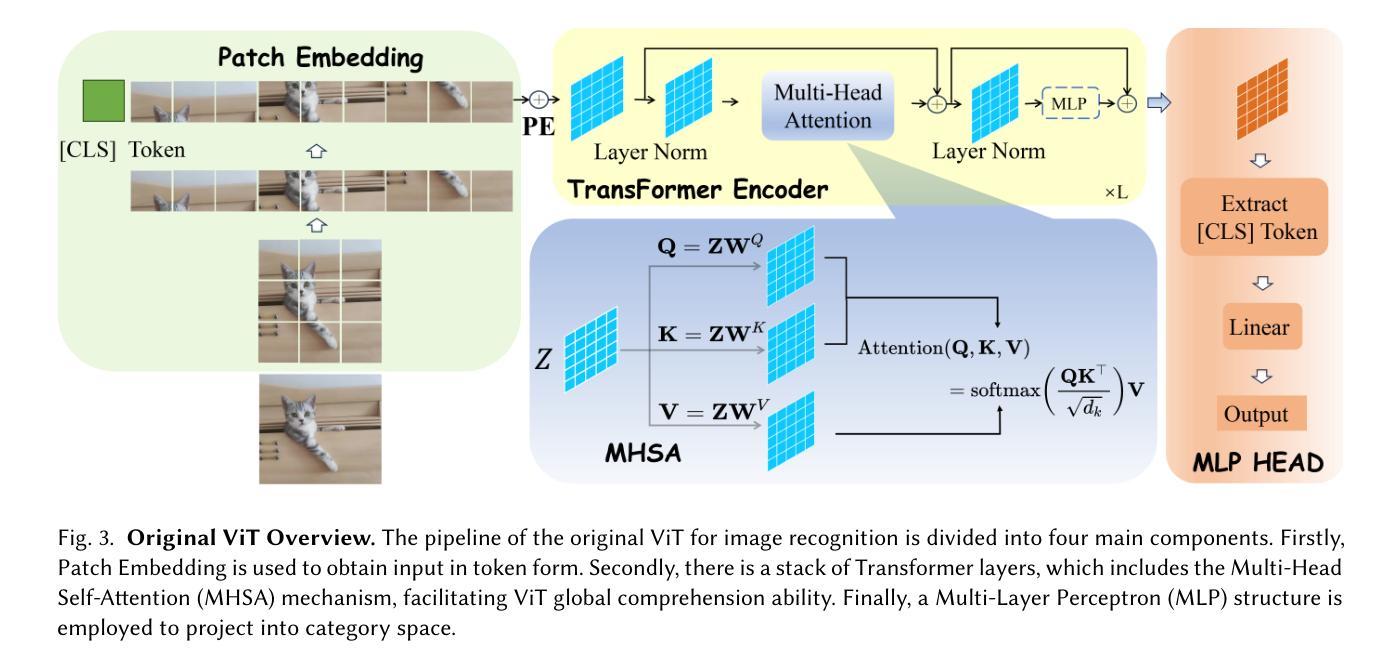
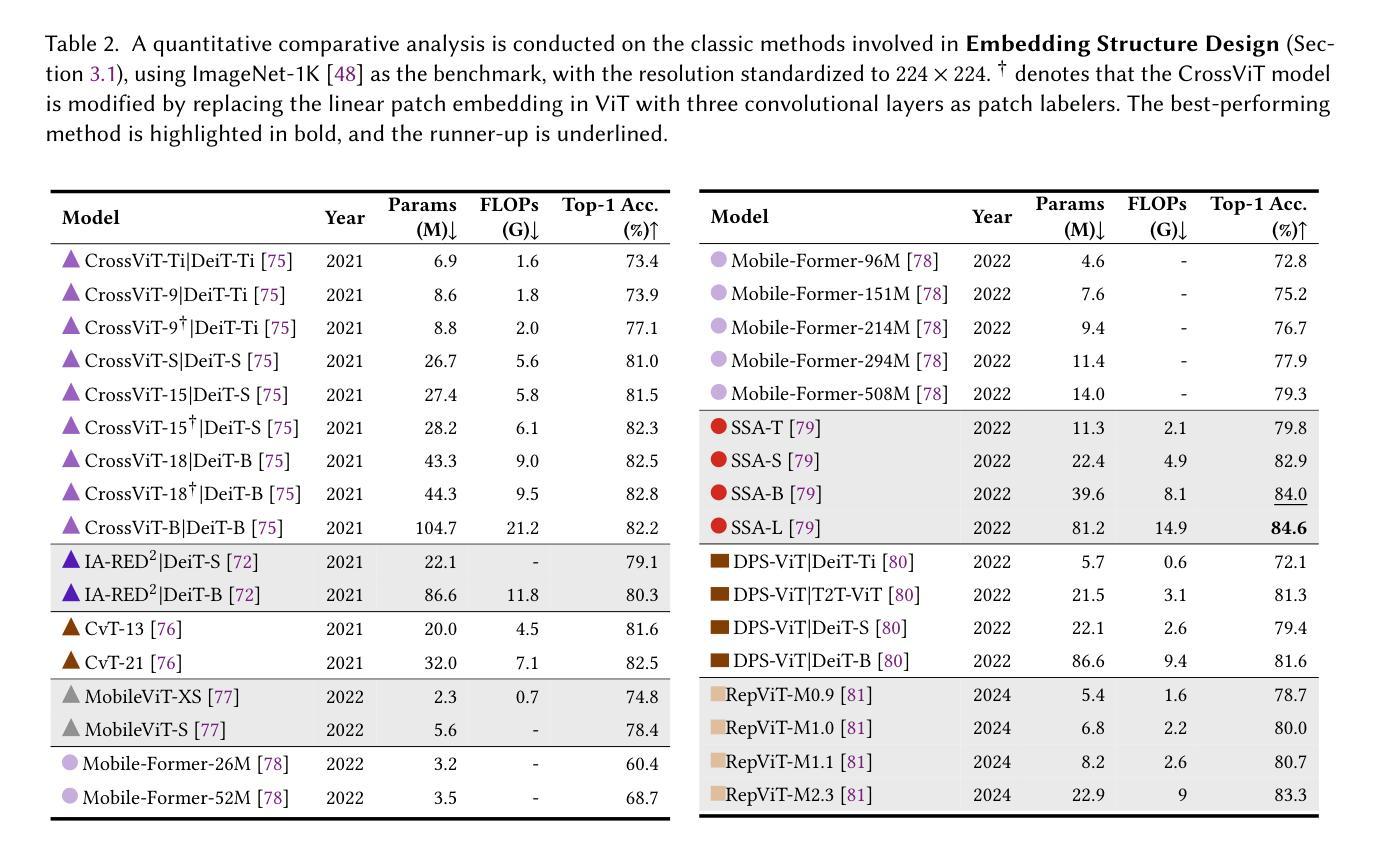
Image Recognition with Online Lightweight Vision Transformer: A Survey
Authors:Zherui Zhang, Rongtao Xu, Jie Zhou, Changwei Wang, Xingtian Pei, Wenhao Xu, Jiguang Zhang, Li Guo, Longxiang Gao, Wenbo Xu, Shibiao Xu
The Transformer architecture has achieved significant success in natural language processing, motivating its adaptation to computer vision tasks. Unlike convolutional neural networks, vision transformers inherently capture long-range dependencies and enable parallel processing, yet lack inductive biases and efficiency benefits, facing significant computational and memory challenges that limit its real-world applicability. This paper surveys various online strategies for generating lightweight vision transformers for image recognition, focusing on three key areas: Efficient Component Design, Dynamic Network, and Knowledge Distillation. We evaluate the relevant exploration for each topic on the ImageNet-1K benchmark, analyzing trade-offs among precision, parameters, throughput, and more to highlight their respective advantages, disadvantages, and flexibility. Finally, we propose future research directions and potential challenges in the lightweighting of vision transformers with the aim of inspiring further exploration and providing practical guidance for the community. Project Page: https://github.com/ajxklo/Lightweight-VIT
Transformer架构在自然语言处理领域取得了巨大成功,这促使其适应计算机视觉任务。与卷积神经网络不同,视觉Transformer天生就能捕捉长距离依赖关系并实现并行处理,然而由于缺乏归纳偏见和效率优势,它们面临着计算和内存方面的挑战,这些挑战限制了其在现实世界中的应用。本文综述了为图像识别生成轻量化视觉Transformer的各种在线策略,重点关注三个关键领域:高效组件设计、动态网络和知识蒸馏。我们在ImageNet-1K基准测试上评估了每个话题的相关探索,分析了精度、参数、吞吐量等之间的权衡,以突出各自的优势、劣势和灵活性。最后,我们提出了视觉Transformer轻量化的未来研究方向和潜在挑战,旨在激发进一步探索,为社区提供实用指导。项目页面:https://github.com/ajxklo/Lightweight-VIT
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文探讨了将Transformer架构应用于计算机视觉任务的策略,特别是在图像识别方面的应用。本文重点关注了三个关键领域:高效组件设计、动态网络和知识蒸馏。文章评价了这三个主题在ImageNet-1K基准测试上的相关研究,分析了精确度、参数、吞吐量和灵活性之间的权衡,并指出了各自的优缺点。最后,本文提出了轻量级视觉变压器的未来研究方向和潜在挑战,旨在为社区提供实际指导和激励进一步的探索。
Key Takeaways
- Transformer架构在计算机视觉任务中的成功应用引人注目。
- 视觉变压器能够捕获长距离依赖性和支持并行处理。
- 视觉变压器面临计算资源和内存的挑战,限制了其实际应用。
- 文章探讨了生成轻量级视觉变压器的在线策略,主要集中在高效组件设计、动态网络和知识蒸馏方面。
- 在ImageNet-1K基准测试上评估了相关研究的性能,包括精确度、参数、吞吐量和灵活性。
- 文章指出了每个领域的优缺点,并为未来的研究提供了方向。
点此查看论文截图

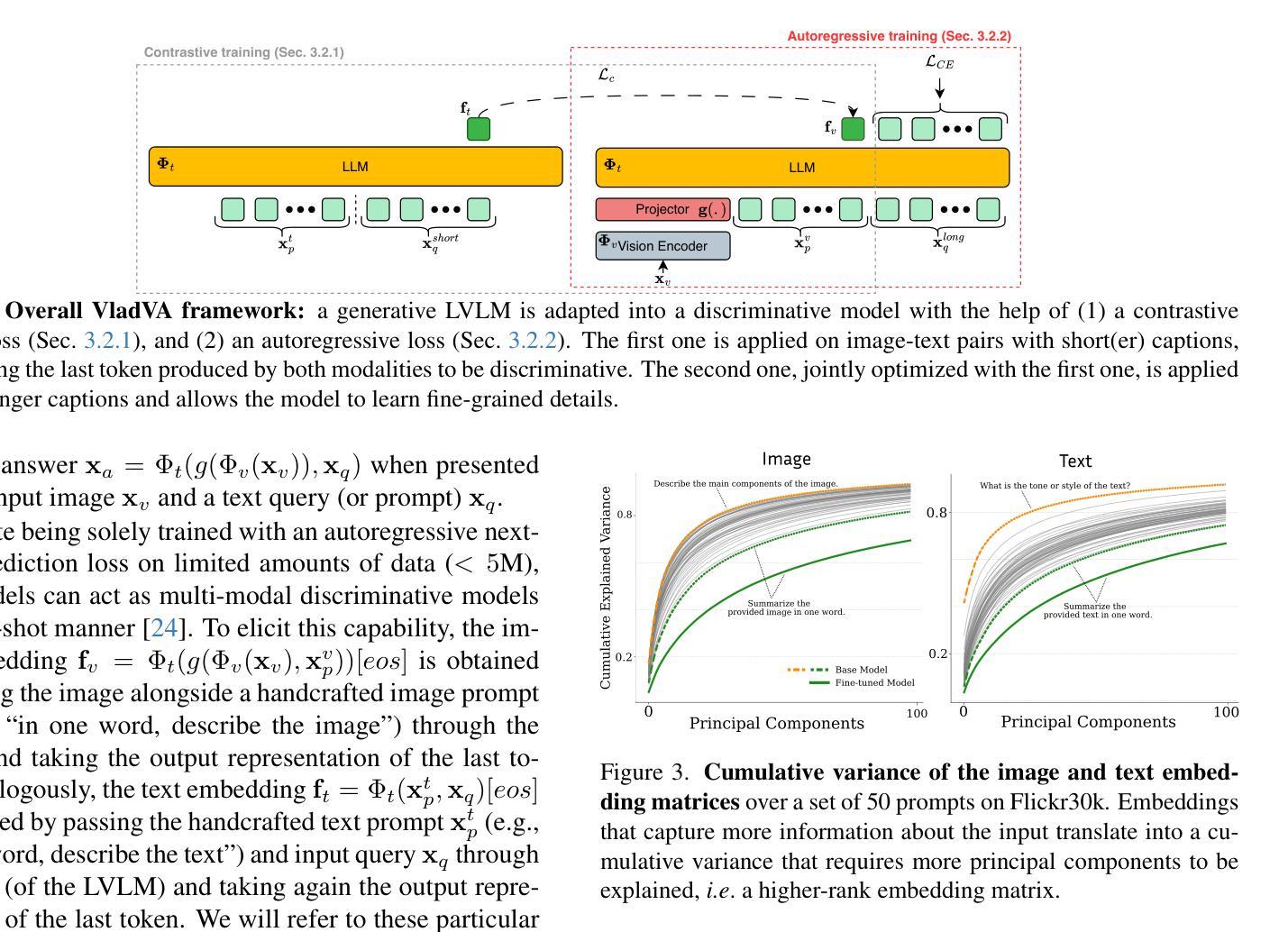
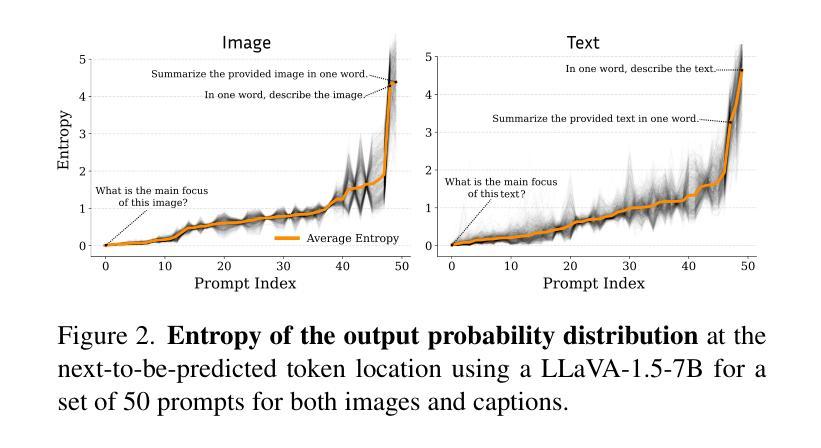
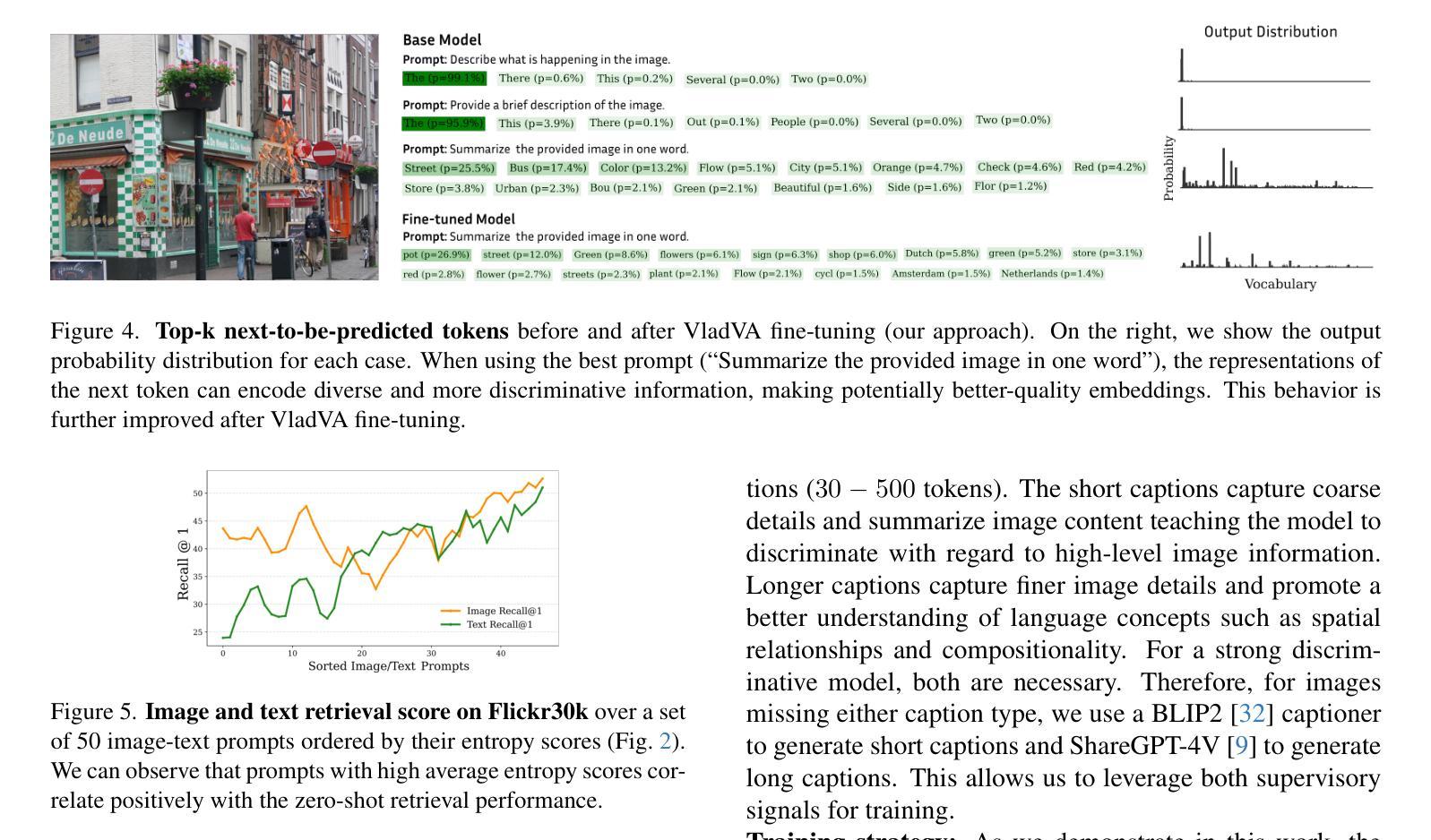
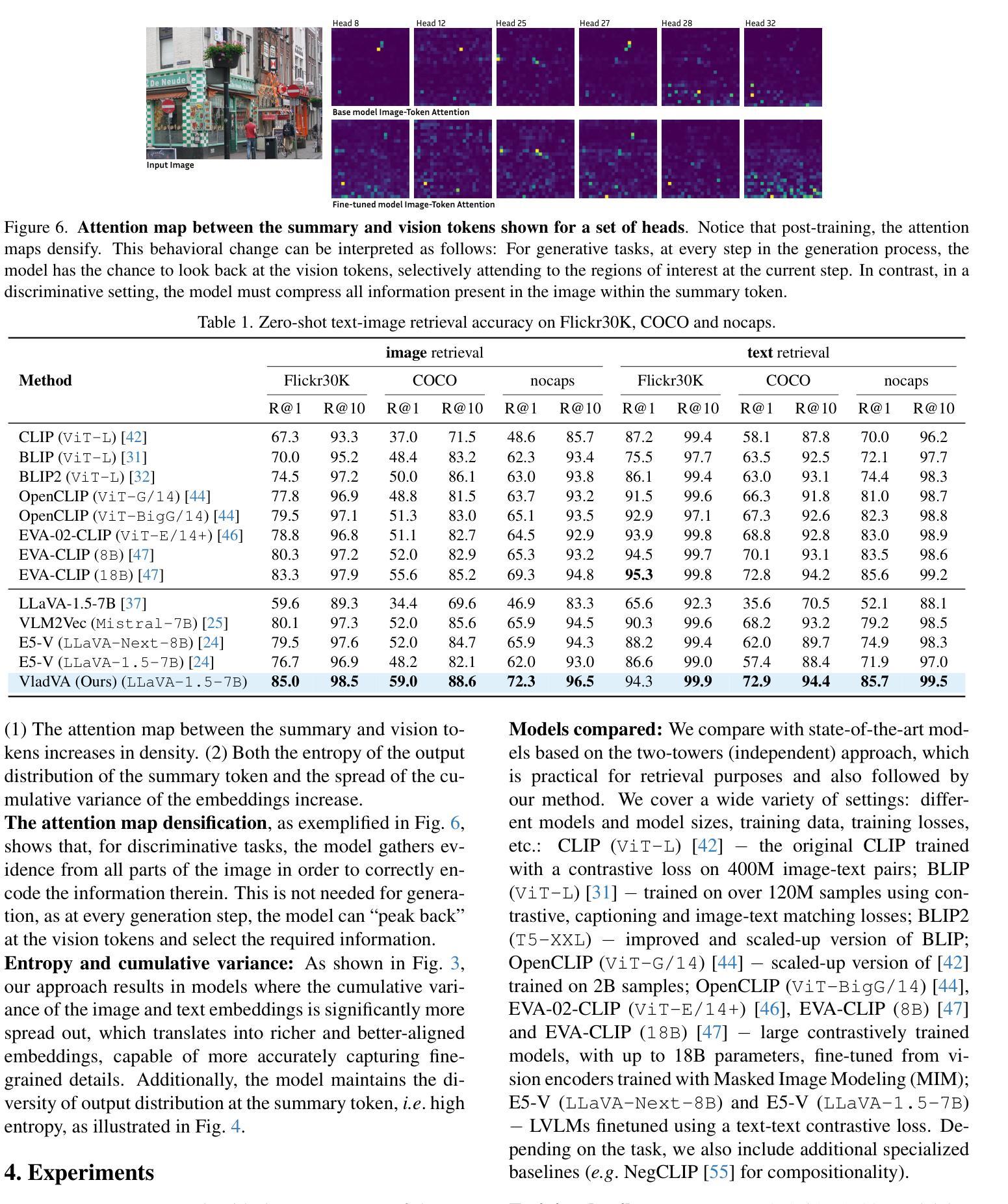
VladVA: Discriminative Fine-tuning of LVLMs
Authors:Yassine Ouali, Adrian Bulat, Alexandros Xenos, Anestis Zaganidis, Ioannis Maniadis Metaxas, Brais Martinez, Georgios Tzimiropoulos
Contrastively-trained Vision-Language Models (VLMs) like CLIP have become the de facto approach for discriminative vision-language representation learning. However, these models have limited language understanding, often exhibiting a “bag of words” behavior. At the same time, Large Vision-Language Models (LVLMs), which combine vision encoders with LLMs, have been shown to be capable of detailed vision-language reasoning, yet their autoregressive nature renders them less suitable for discriminative tasks. In this work, we propose to combine “the best of both worlds”: a new training approach for discriminative fine-tuning of LVLMs that results in strong discriminative and compositional capabilities. Essentially, our approach converts a generative LVLM into a discriminative one, unlocking its capability for powerful image-text discrimination combined with enhanced language understanding. Our contributions include (1) a carefully designed training/optimization framework that utilizes image-text pairs of variable length and granularity for training the model with both contrastive and next-token prediction losses. This is accompanied by ablation studies that justify the necessity of our framework’s components; (2) a parameter-efficient adaptation method using a combination of soft prompting and LoRA adapters; (3) significant improvements over state-of-the-art CLIP-like models of similar size, including standard image-text retrieval benchmarks and notable gains in compositionality.
对比训练的视觉语言模型(如CLIP)已成为判别式视觉语言表示学习的实际方法。然而,这些模型的语言理解能力有限,通常表现出“词袋”行为。同时,结合了视觉编码器和大型语言模型(LLM)的大型视觉语言模型(LVLM)已显示出详细的视觉语言推理能力,但其自回归性质使得它们不太适合判别任务。在这项工作中,我们提出了结合两者优点的方案:一种用于LVLM判别微调的新训练方法,具有很强的判别和组合能力。本质上,我们的方法将生成式LVLM转换为判别式,解锁其强大的图像文本判别能力,同时增强语言理解。我们的贡献包括:(1)一个精心设计的训练/优化框架,该框架利用可变长度和粒度的图像文本对进行训练,使用对比和下一个令牌预测损失来训练模型。这伴随一些消融研究,以证明我们框架组件的必要性;(2)使用软提示和LoRA适配器相结合的方法实现参数高效适应;(3)在类似规模的先进CLIP模型上实现了显著改进,包括标准图像文本检索基准测试和组合性的显著收益。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Published at CVPR 2025
Summary
基于CLIP等对比训练的多模态视觉语言模型在判别式视觉语言表征学习上表现突出,但存在语言理解有限的问题。大型视觉语言模型(LVLMs)结合了视觉编码器和大型语言模型,展现出详细的视觉语言推理能力,但其自回归特性使得它们在判别任务上表现不佳。本研究旨在结合两者的优点,提出一种针对大型视觉语言模型的判别微调新训练策略,该策略使模型兼具强大的判别能力和组合能力。研究贡献包括:(1)利用可变长度和粒度的图像文本对进行训练/优化的框架,结合对比和下一个令牌预测损失;(2)采用结合软提示和LoRA适配器的参数高效适配方法;(3)显著改进了类似规模的CLIP模型,包括图像文本检索基准测试成绩和组合性的明显提升。
Key Takeaways
- 对比训练的多模态视觉语言模型(如CLIP)在判别式视觉语言表征学习上具有优势,但存在语言理解局限。
- 大型视觉语言模型(LVLMs)具备详细的视觉语言推理能力,但自回归特性使其不适用于判别任务。
- 本研究旨在结合两者的优点,提出了一种针对LVLMs的判别微调新训练策略。
- 训练/优化框架利用可变长度和粒度的图像文本对,结合对比和下一个令牌预测损失。
- 采用结合软提示和LoRA适配器的参数高效适配方法。
- 与类似规模的CLIP模型相比,该策略在图像文本检索等方面取得了显著改进。
点此查看论文截图

MambaNUT: Nighttime UAV Tracking via Mamba-based Adaptive Curriculum Learning
Authors:You Wu, Xiangyang Yang, Xucheng Wang, Hengzhou Ye, Dan Zeng, Shuiwang Li
Harnessing low-light enhancement and domain adaptation, nighttime UAV tracking has made substantial strides. However, over-reliance on image enhancement, limited high-quality nighttime data, and a lack of integration between daytime and nighttime trackers hinder the development of an end-to-end trainable framework. Additionally, current ViT-based trackers demand heavy computational resources due to their reliance on the self-attention mechanism. In this paper, we propose a novel pure Mamba-based tracking framework (MambaNUT) that employs a state space model with linear complexity as its backbone, incorporating a single-stream architecture that integrates feature learning and template-search coupling within Vision Mamba. We introduce an adaptive curriculum learning (ACL) approach that dynamically adjusts sampling strategies and loss weights, thereby improving the model’s ability of generalization. Our ACL is composed of two levels of curriculum schedulers: (1) sampling scheduler that transforms the data distribution from imbalanced to balanced, as well as from easier (daytime) to harder (nighttime) samples; (2) loss scheduler that dynamically assigns weights based on the size of the training set and IoU of individual instances. Exhaustive experiments on multiple nighttime UAV tracking benchmarks demonstrate that the proposed MambaNUT achieves state-of-the-art performance while requiring lower computational costs. The code will be available at https://github.com/wuyou3474/MambaNUT.
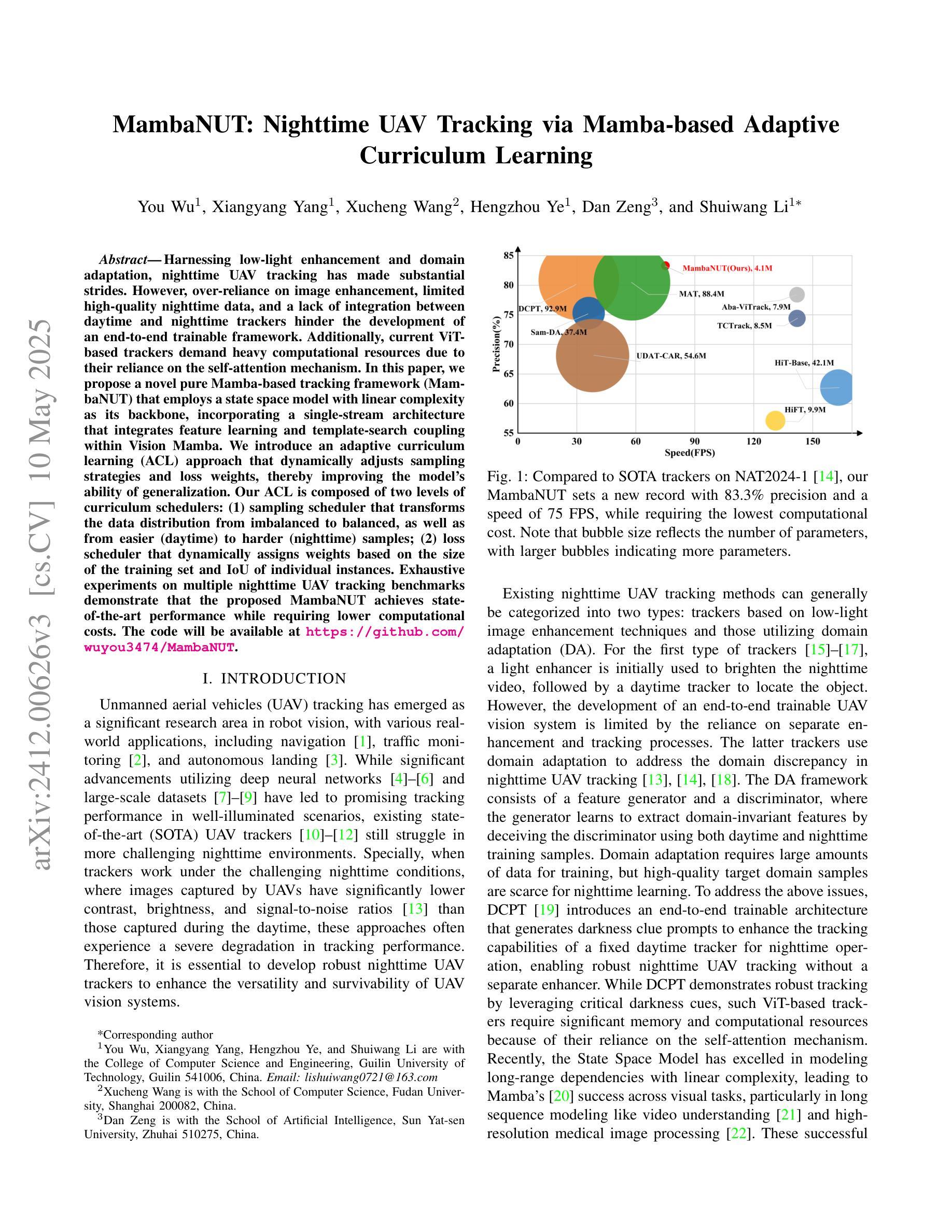
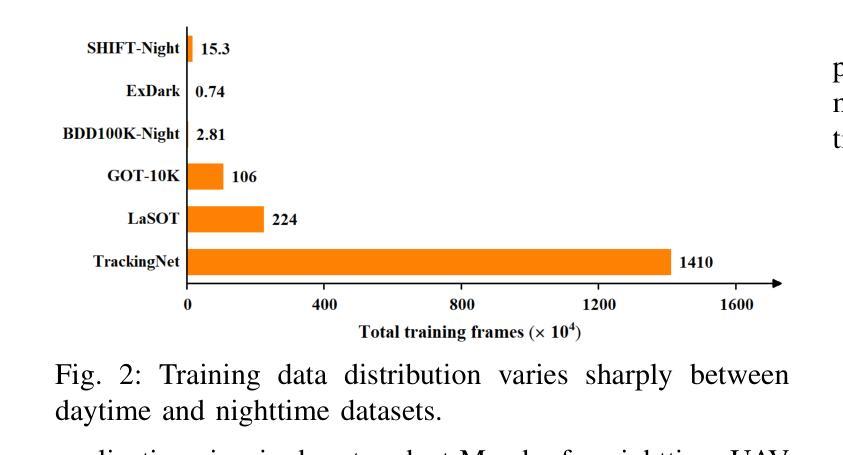
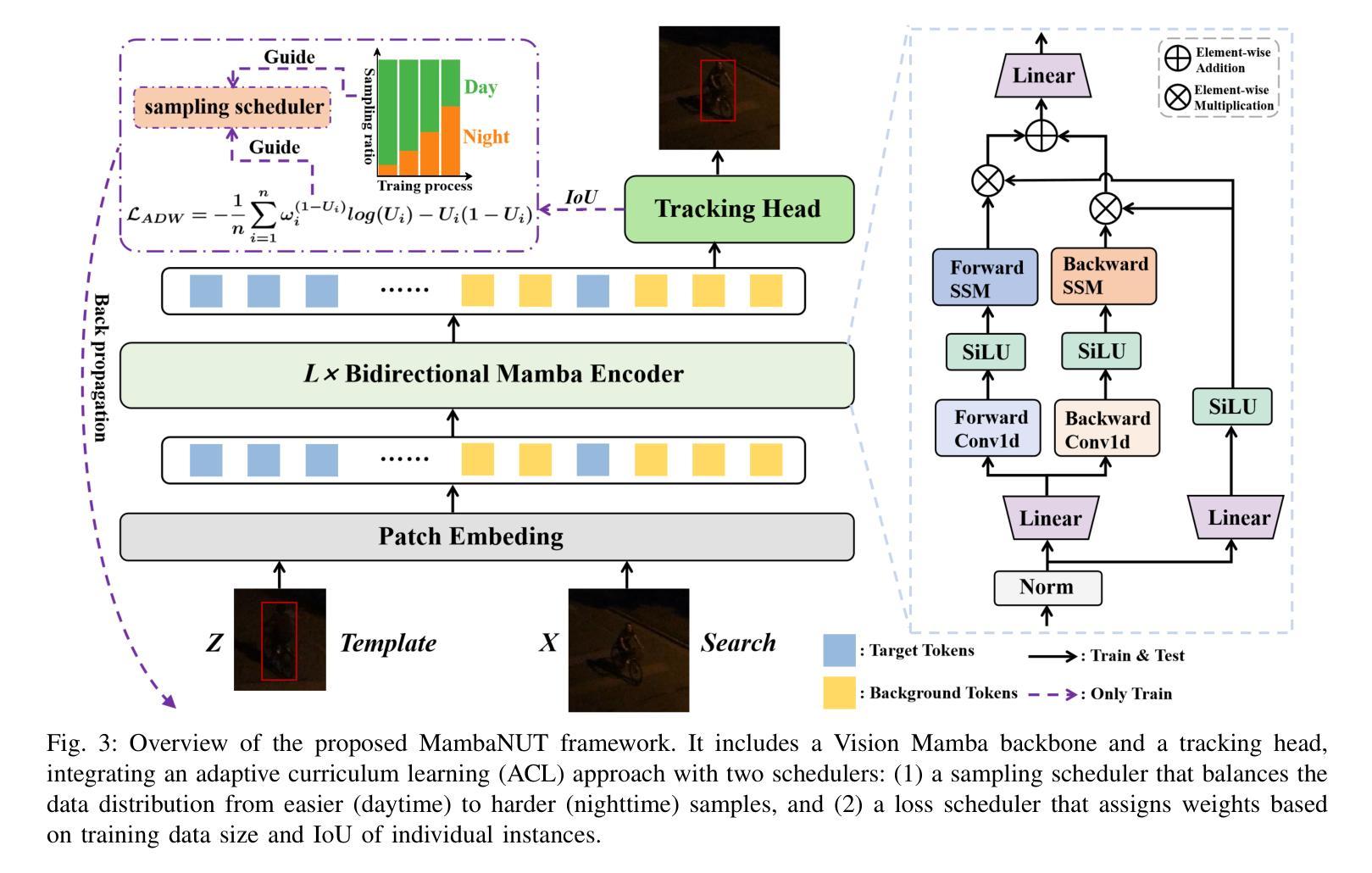
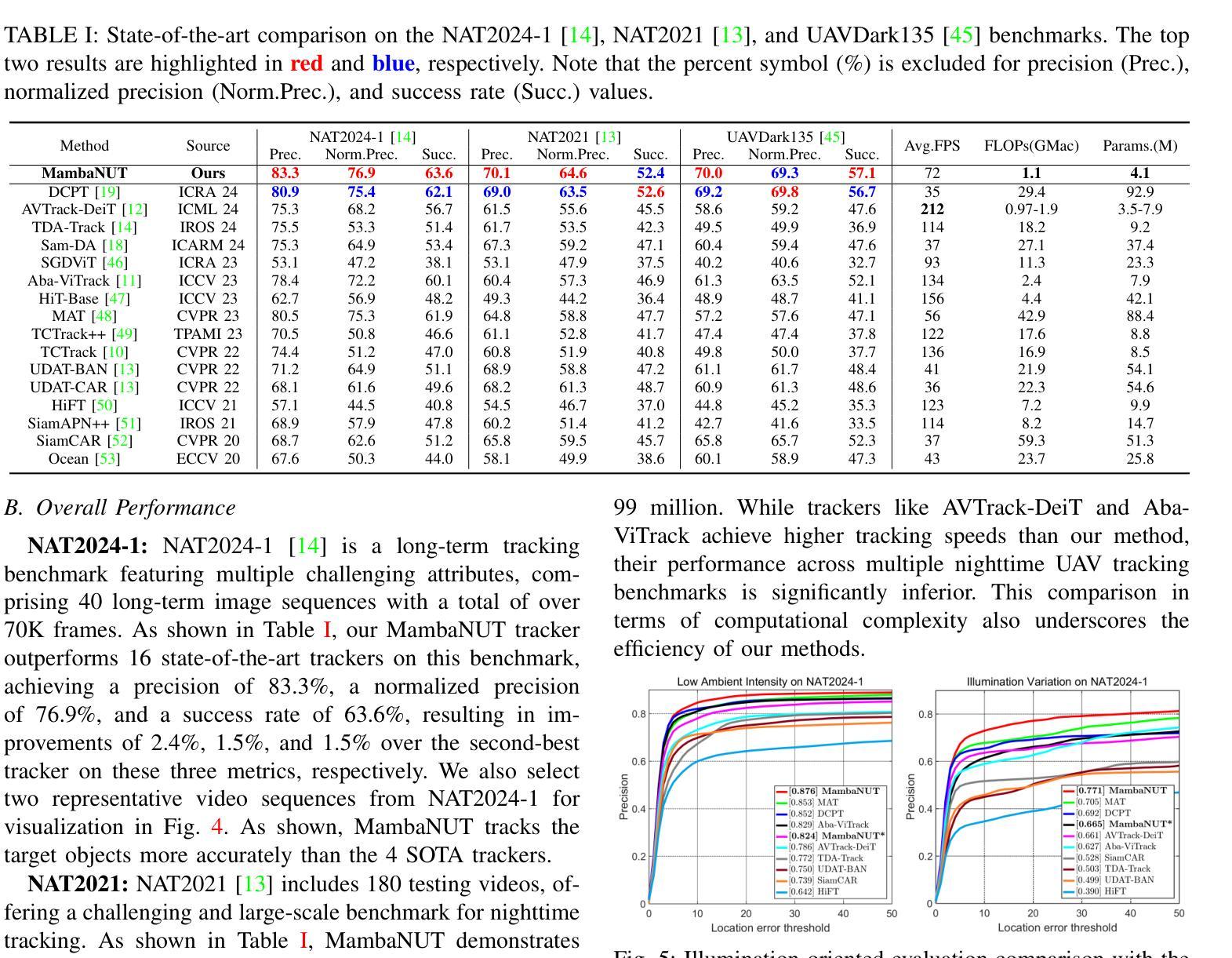
利用低光增强和领域自适应技术,夜间无人机跟踪已经取得了重大进展。然而,过于依赖图像增强、高质量夜间数据的有限性以及白天和夜间跟踪器之间缺乏整合,阻碍了端到端可训练框架的发展。此外,当前的基于ViT的跟踪器由于依赖于自注意力机制,需要大量的计算资源。在本文中,我们提出了一种基于纯Mamba的跟踪框架(MambaNUT),该框架使用线性复杂度的状态空间模型作为骨干,采用单流架构,在Vision Mamba内整合特征学习和模板搜索耦合。我们引入了一种自适应课程学习(ACL)方法,该方法可以动态调整采样策略和损失权重,从而提高模型的泛化能力。我们的ACL由两个层次的课程调度器组成:(1)采样调度器,它将数据分布从不平衡转变为平衡,同时将样本从较简单的(白天)转变为较难的(夜间);(2)损失调度器根据训练集的大小和个体的IoU动态分配权重。在多个夜间无人机跟踪基准测试上的大量实验表明,所提出的MambaNUT达到了最先进的性能,同时计算成本较低。代码将在https://github.com/wuyou3474/MambaNUT上提供。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
无人机夜间追踪技术取得显著进展,结合低光增强和领域自适应,但存在过度依赖图像增强、高质量夜间数据有限及昼夜追踪器未整合等问题。本文提出基于纯Mamba的跟踪框架MambaNUT,采用线性复杂度状态空间模型作为主干,引入自适应课程学习策略,动态调整采样策略和损失权重,提高模型泛化能力。实验证明,MambaNUT在夜间无人机追踪方面达到领先水平,同时计算成本低。
Key Takeaways
- 无人机夜间追踪技术已有多项进展,整合低光增强和领域自适应等技术来提升性能。
- 当前技术面临过度依赖图像增强、高质量夜间数据有限及昼夜追踪器整合问题。
- 提出的MambaNUT框架基于纯Mamba跟踪技术,采用线性复杂度状态空间模型。
- MambaNUT引入单流架构,集成特征学习和模板搜索耦合。
- 自适应课程学习策略动态调整采样策略和损失权重,提高模型泛化能力。
- MambaNUT在夜间无人机追踪方面表现优异,达到领先水平。
点此查看论文截图

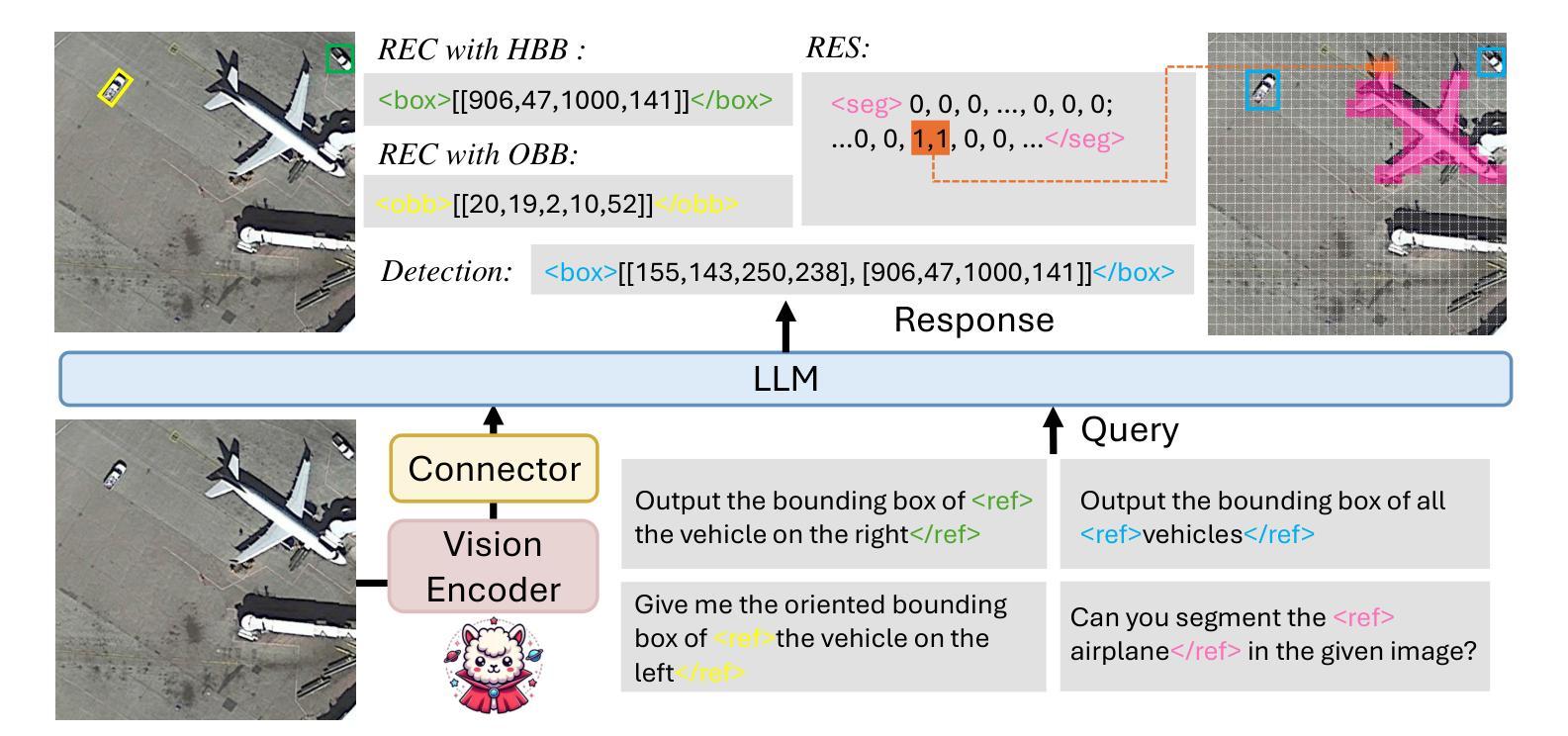
GeoGround: A Unified Large Vision-Language Model for Remote Sensing Visual Grounding
Authors:Yue Zhou, Mengcheng Lan, Xiang Li, Litong Feng, Yiping Ke, Xue Jiang, Qingyun Li, Xue Yang, Wayne Zhang
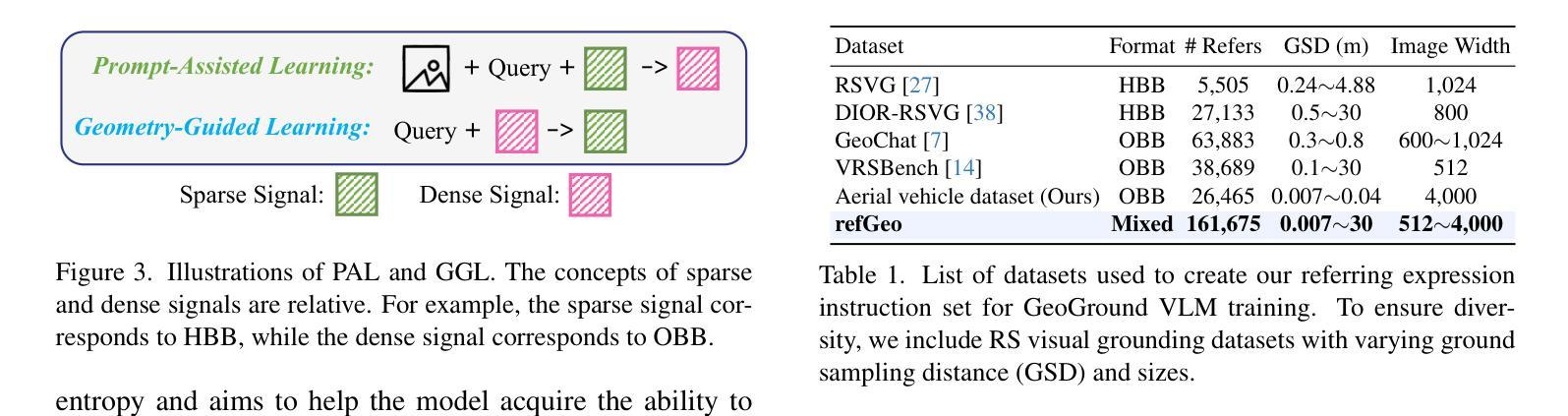
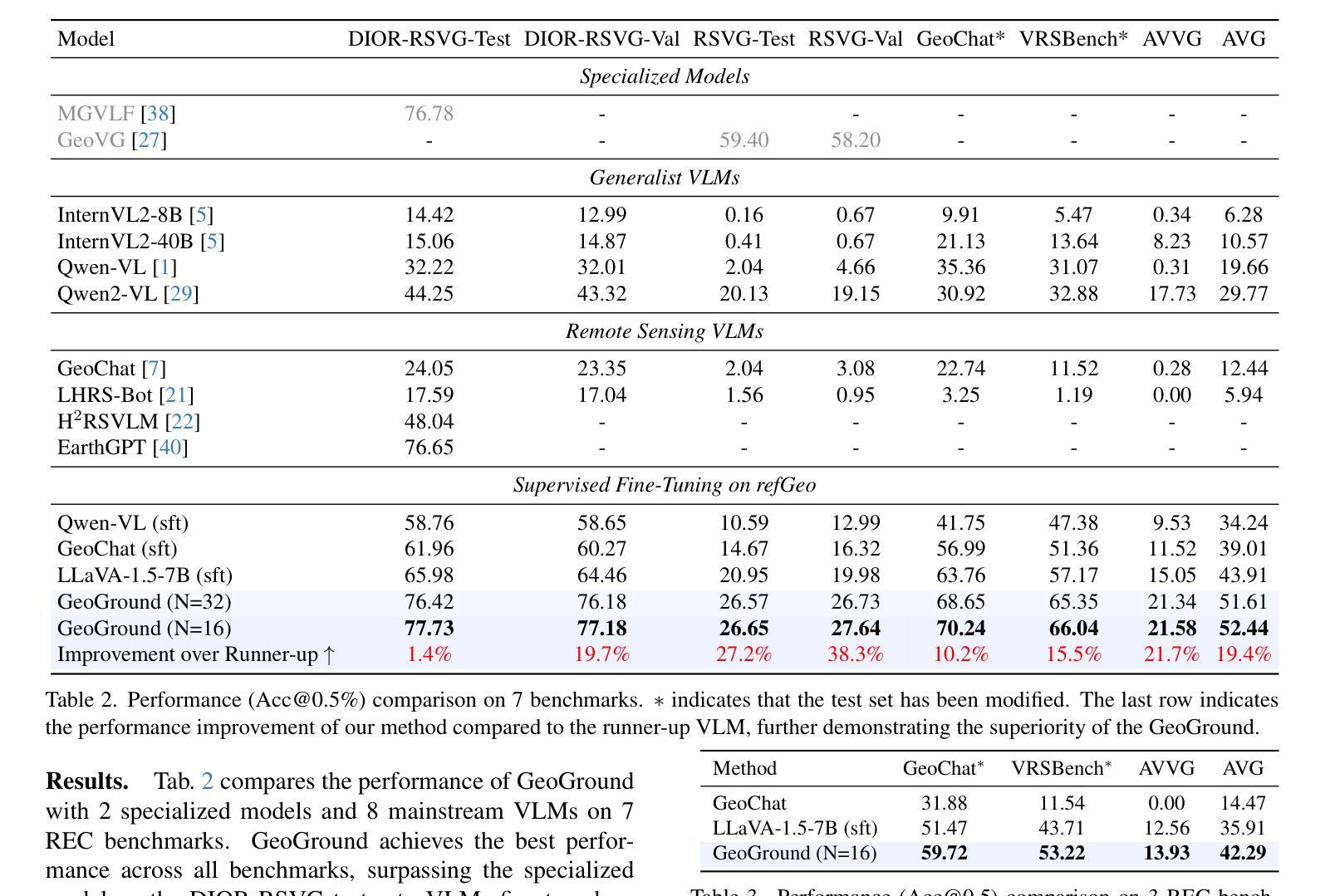
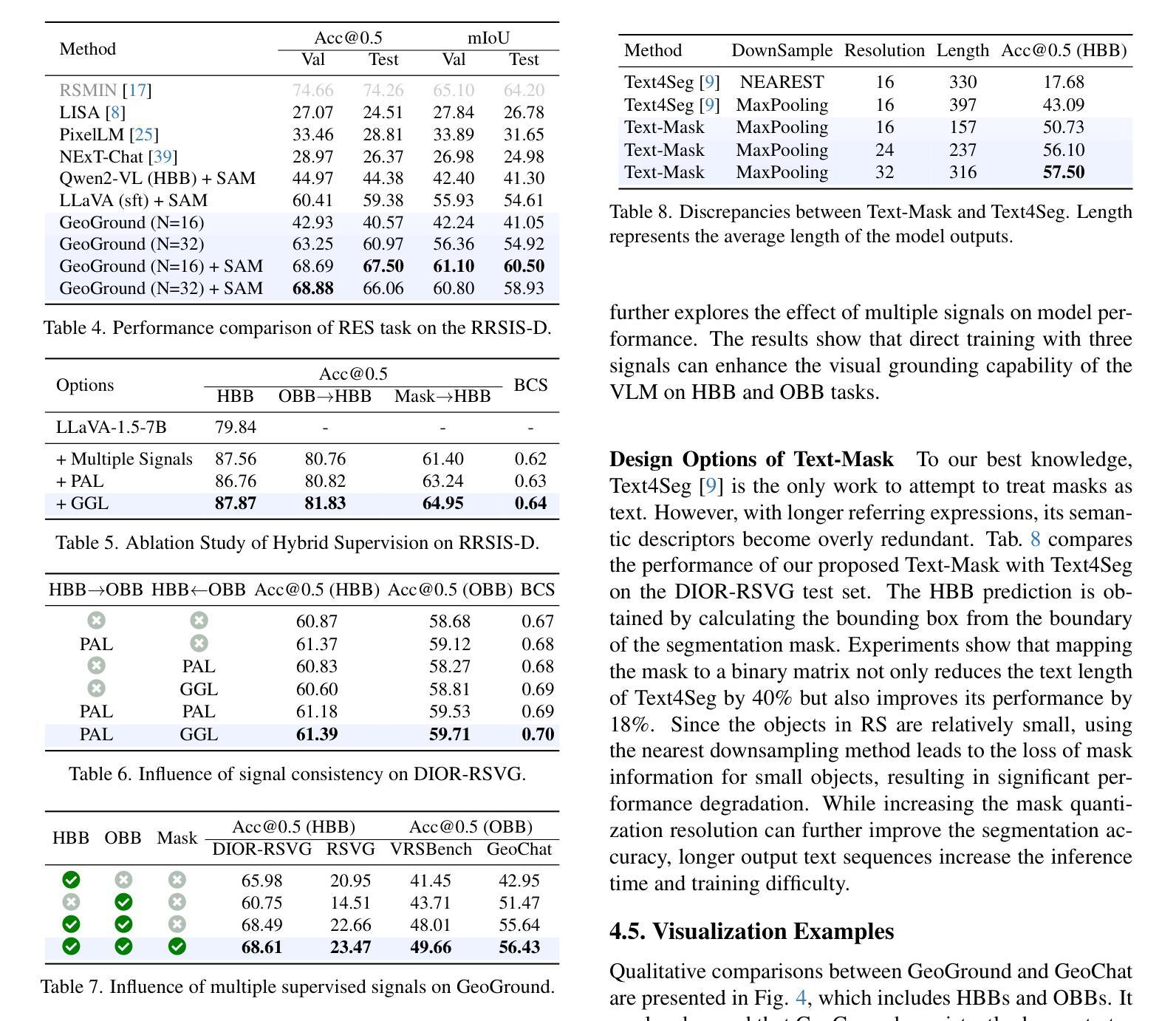
Remote sensing (RS) visual grounding aims to use natural language expression to locate specific objects (in the form of the bounding box or segmentation mask) in RS images, enhancing human interaction with intelligent RS interpretation systems. Early research in this area was primarily based on horizontal bounding boxes (HBBs), but as more diverse RS datasets have become available, tasks involving oriented bounding boxes (OBBs) and segmentation masks have emerged. In practical applications, different targets require different grounding types: HBB can localize an object’s position, OBB provides its orientation, and mask depicts its shape. However, existing specialized methods are typically tailored to a single type of RS visual grounding task and are hard to generalize across tasks. In contrast, large vision-language models (VLMs) exhibit powerful multi-task learning capabilities but struggle to handle dense prediction tasks like segmentation. This paper proposes GeoGround, a novel framework that unifies support for HBB, OBB, and mask RS visual grounding tasks, allowing flexible output selection. Rather than customizing the architecture of VLM, our work aims to elegantly support pixel-level visual grounding output through the Text-Mask technique. We define prompt-assisted and geometry-guided learning to enhance consistency across different signals. Experimental results show that GeoGround demonstrates strong performance across four RS visual grounding tasks, matching the performance of specialized methods on multiple benchmarks. Code available at https://github.com/zytx121/GeoGround
遥感(RS)视觉定位旨在利用自然语言表达式在遥感图像中定位特定对象(以边界框或分割掩码的形式),增强人类与智能遥感解释系统的交互。早期的研究主要基于水平边界框(HBB),但随着更多遥感数据集的可用,涉及定向边界框(OBB)和分割掩码的任务已经出现。在实际应用中,不同的目标需要不同的定位类型:HBB可以定位对象的位置,OBB提供其方向,而掩码描绘其形状。然而,现有的专业方法通常针对单一的遥感视觉定位任务,难以跨任务推广。相比之下,大型视觉语言模型(VLM)展现出强大的多任务学习能力,但在处理诸如分割之类的密集预测任务时却表现挣扎。本文提出了GeoGround,这是一个新颖的统一框架,支持HBB、OBB和掩码遥感视觉定位任务,允许灵活输出选择。我们的工作旨在通过文本掩码技术巧妙地支持像素级视觉定位输出,而不是自定义VLM架构。我们定义了提示辅助和几何引导学习以增强不同信号之间的一致性。实验结果表明,GeoGround在四个遥感视觉定位任务上表现出强大的性能,在多个基准测试中与专用方法的性能相匹配。代码可用https://github.com/zytx121/GeoGround。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 9 pages, 5 figures
Summary
本文介绍了遥感视觉定位技术中的新框架GeoGround。该框架旨在统一支持水平边界框(HBB)、定向边界框(OBB)和掩膜三种遥感视觉定位任务,实现灵活的输出选择。GeoGround通过文本掩膜技术优雅地支持像素级视觉定位输出,并通过提示辅助和几何引导学习增强不同信号之间的一致性。实验结果表明,GeoGround在四项遥感视觉定位任务上表现出强大的性能,并在多个基准测试中与专业方法的性能相匹配。
Key Takeaways
- 遥感视觉定位技术使用自然语言表达式在遥感图像中定位特定对象。
- 早期研究主要基于水平边界框(HBB),现在出现了定向边界框(OBB)和掩膜任务。
- 不同目标需要不同类型的定位:HBB可定位对象位置,OBB提供方向信息,掩膜描绘对象形状。
- 现有方法通常针对单一遥感视觉定位任务,难以跨任务推广。
- GeoGround框架统一支持HBB、OBB和掩膜遥感视觉定位任务,实现灵活输出选择。
- GeoGround通过文本掩膜技术实现像素级视觉定位输出。
点此查看论文截图

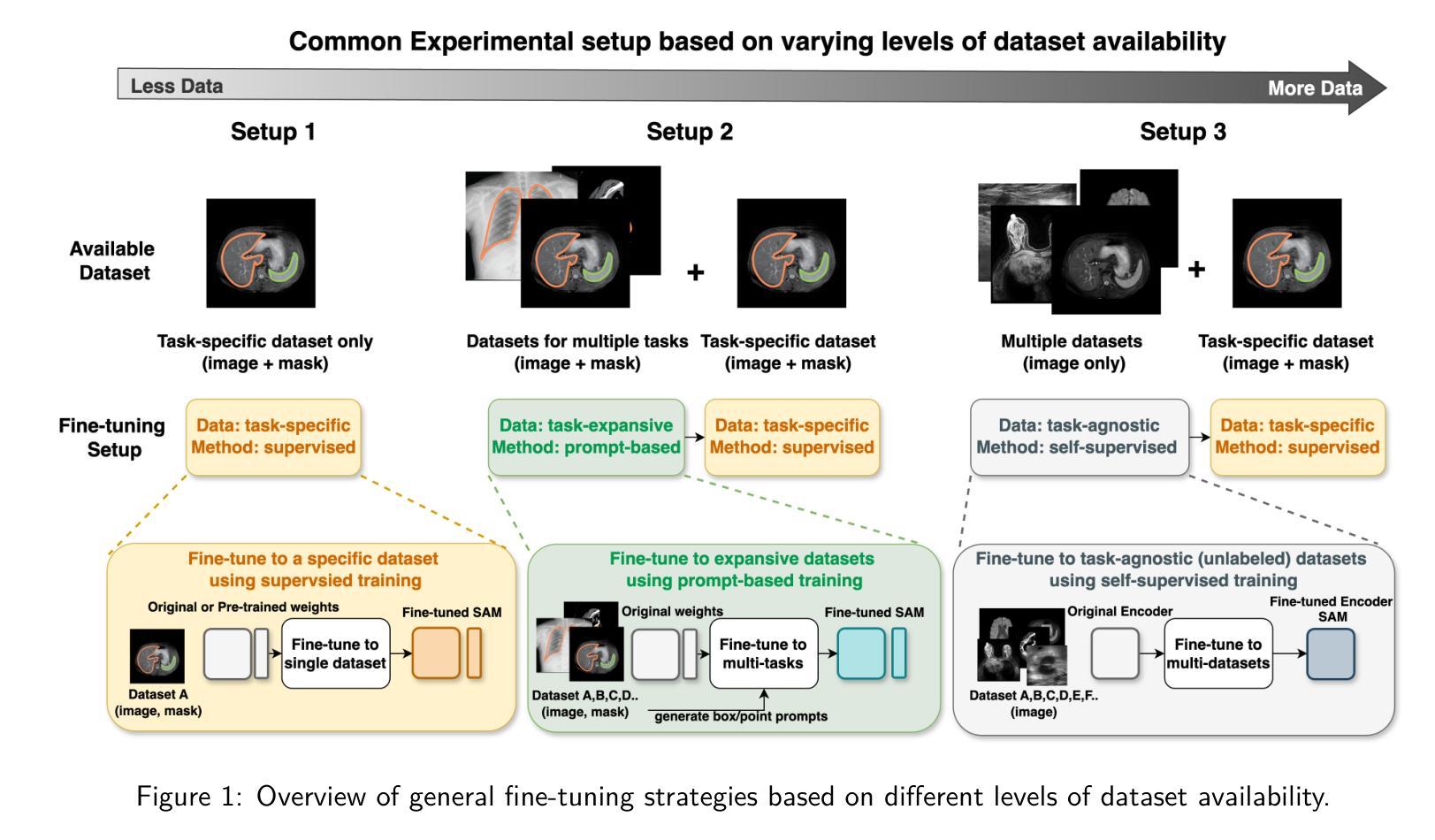
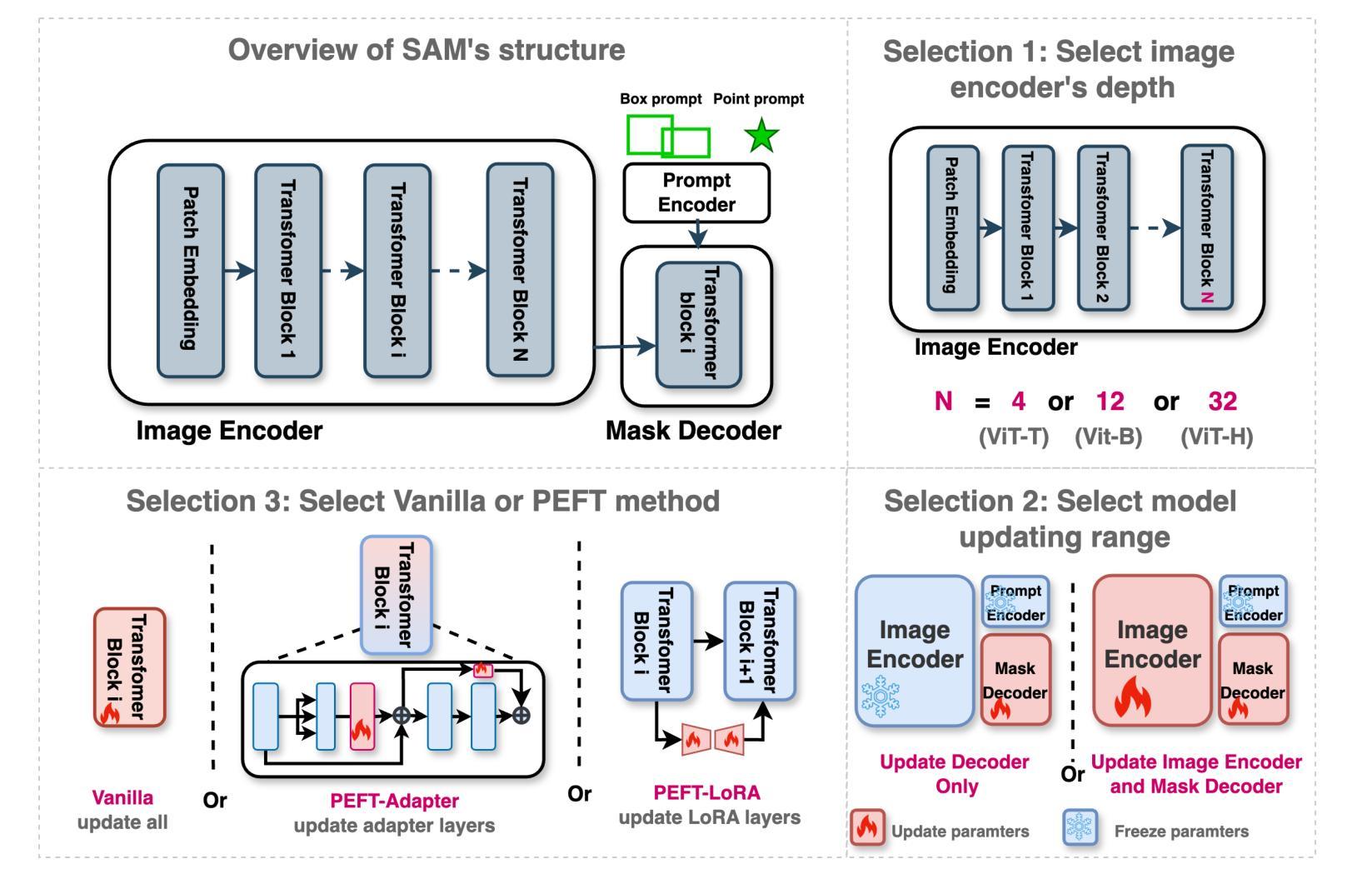
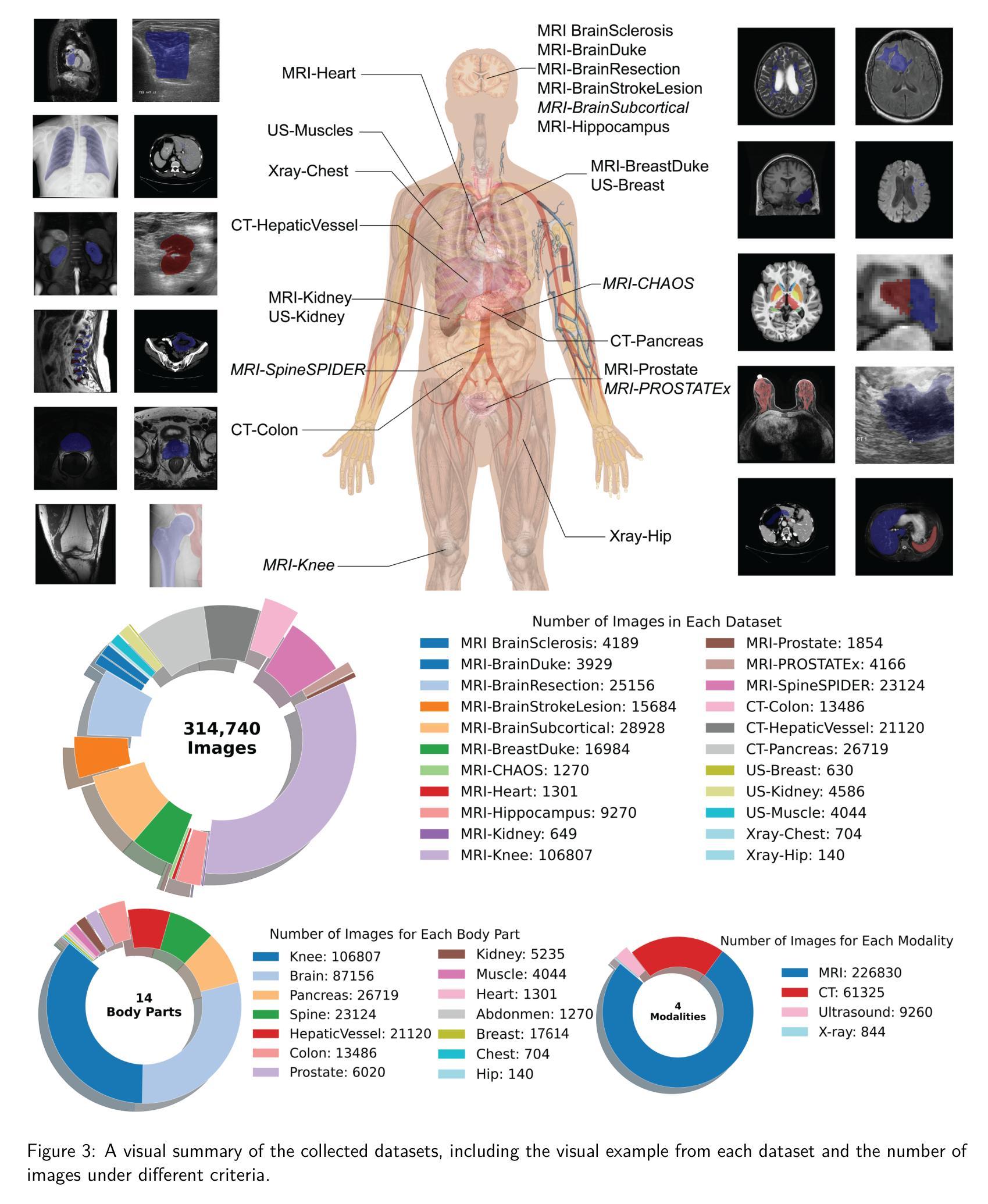
How to build the best medical image segmentation algorithm using foundation models: a comprehensive empirical study with Segment Anything Model
Authors:Hanxue Gu, Haoyu Dong, Jichen Yang, Maciej A. Mazurowski
Automated segmentation is a fundamental medical image analysis task, which enjoys significant advances due to the advent of deep learning. While foundation models have been useful in natural language processing and some vision tasks for some time, the foundation model developed with image segmentation in mind - Segment Anything Model (SAM) - has been developed only recently and has shown similar promise. However, there are still no systematic analyses or “best-practice” guidelines for optimal fine-tuning of SAM for medical image segmentation. This work summarizes existing fine-tuning strategies with various backbone architectures, model components, and fine-tuning algorithms across 18 combinations, and evaluates them on 17 datasets covering all common radiology modalities. Our study reveals that (1) fine-tuning SAM leads to slightly better performance than previous segmentation methods, (2) fine-tuning strategies that use parameter-efficient learning in both the encoder and decoder are superior to other strategies, (3) network architecture has a small impact on final performance, (4) further training SAM with self-supervised learning can improve final model performance. We also demonstrate the ineffectiveness of some methods popular in the literature and further expand our experiments into few-shot and prompt-based settings. Lastly, we released our code and MRI-specific fine-tuned weights, which consistently obtained superior performance over the original SAM, at https://github.com/mazurowski-lab/finetune-SAM.
自动化分割是医学图像分析中的一项基本任务,随着深度学习的出现,该任务取得了重大进展。虽然基础模型在自然语言处理和某些视觉任务中已有一段时间的应用,但针对图像分割而开发的基础模型——任意分割模型(SAM)是最近才开发的,并显示出同样的潜力。然而,目前尚无针对SAM在医学图像分割中的最优微调的系统性分析或“最佳实践”指南。这项工作总结了使用不同主干架构、模型组件和微调算法的现有微调策略,并在涵盖所有常见放射学模态的17个数据集上进行了评估。我们的研究表明:(1)微调SAM的性能略优于以前的分割方法;(2)在编码器和解码器中都使用参数有效学习的微调策略优于其他策略;(3)网络架构对最终性能的影响较小;(4)使用自监督学习进一步训练SAM可以提高最终模型性能。我们还证明了文献中一些流行方法的有效性不足,并将我们的实验进一步扩展到小样本和基于提示的设置中。最后,我们在https://github.com/mazurowski-lab/finetune-SAM发布了我们的代码和针对MRI的特定微调权重,这些权重在原始SAM上始终获得更好的性能。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted for publication at the Journal of Machine Learning for Biomedical Imaging (MELBA)
Summary
近期发展的用于图像分割的foundation模型Segment Anything Model(SAM)在医学图像分析领域显示出巨大的潜力。然而,针对SAM在医学图像分割任务的最优微调尚未有系统性分析或“最佳实践”指南。本研究总结了现有的使用不同骨干架构、模型组件和微调算法的微调策略,并在涵盖所有常见放射学模态的17个数据集上进行了评估。研究发现,微调SAM略优于之前的方法,参数高效学习在编码器和解码器中的使用策略优于其他策略,网络架构对最终性能影响较小,使用自监督学习进一步训练SAM可提高模型性能。同时,本研究还展示了文献中一些流行方法的有效性不足,并扩展了实验到小样本和基于提示的设置。最后,我们公开了代码和针对MRI的特定微调权重。
Key Takeaways
- Segment Anything Model (SAM)是一个专为图像分割设计的foundation模型,它在医学图像分析领域显示出巨大潜力。
- 现有研究尚未对SAM进行针对医学图像分割任务的最优微调进行系统性的分析或提供“最佳实践”指南。
- 研究总结出多种微调策略并使用多种骨干架构、模型组件和微调算法进行了评估。
- 通过对多种数据集的研究发现,微调SAM的性能略优于之前的方法。
- 参数高效学习在编码器和解码器中的使用策略表现最佳,网络架构对最终性能影响较小。
- 使用自监督学习进一步训练SAM可以提高模型性能。
点此查看论文截图

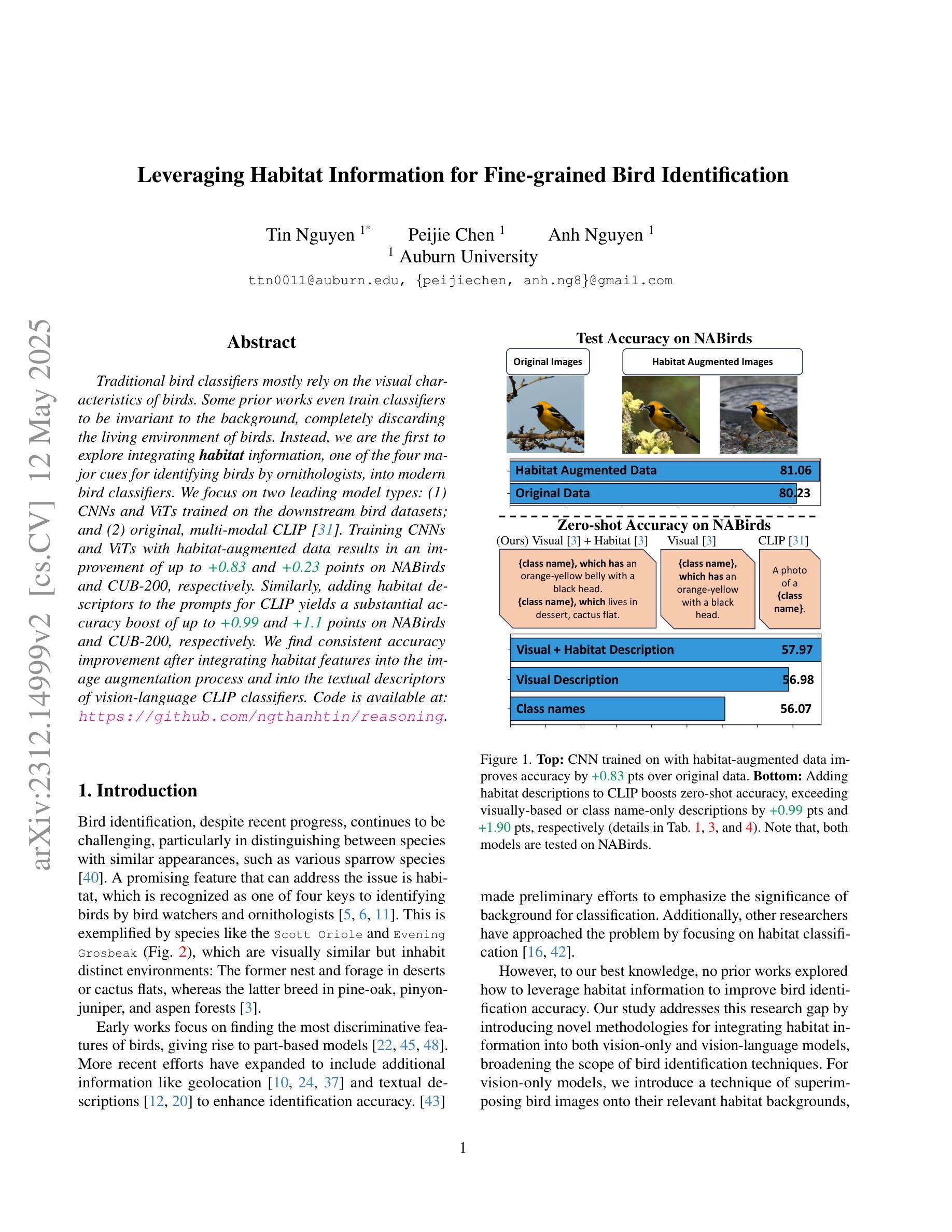
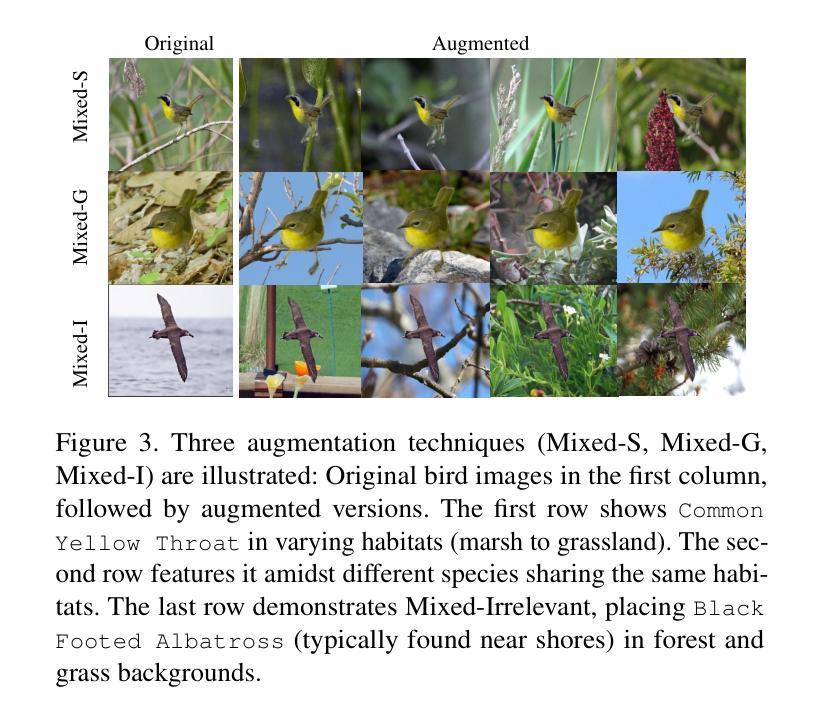
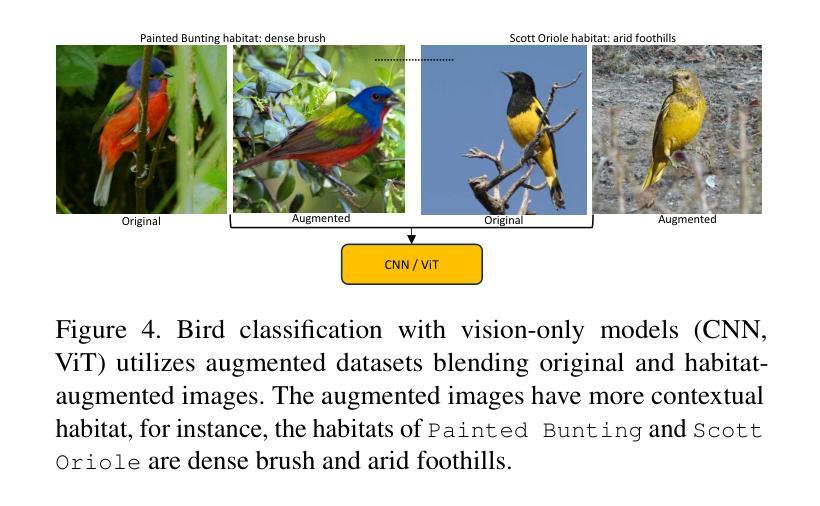
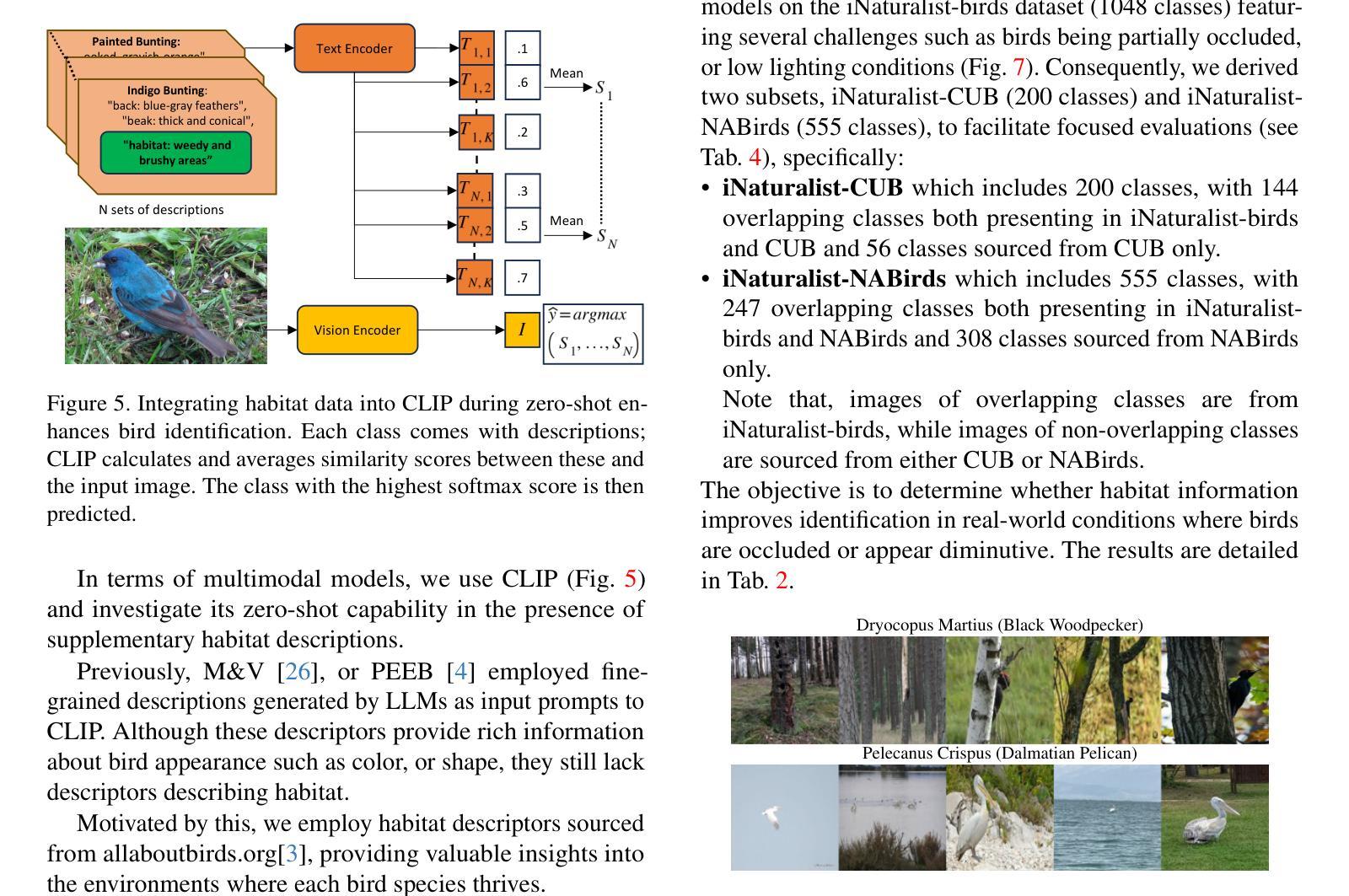
Leveraging Habitat Information for Fine-grained Bird Identification
Authors:Tin Nguyen, Peijie Chen, Anh Totti Nguyen
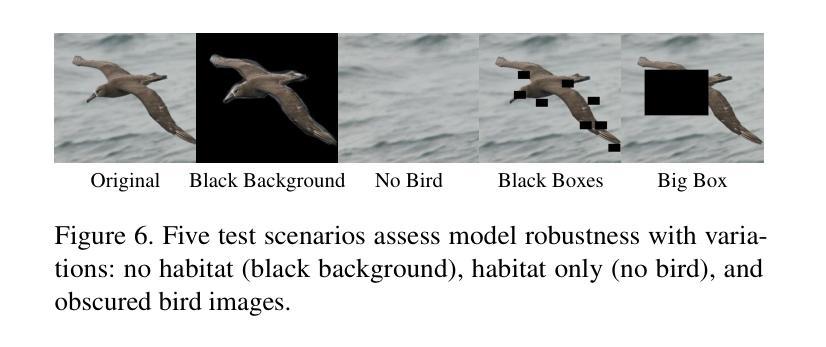
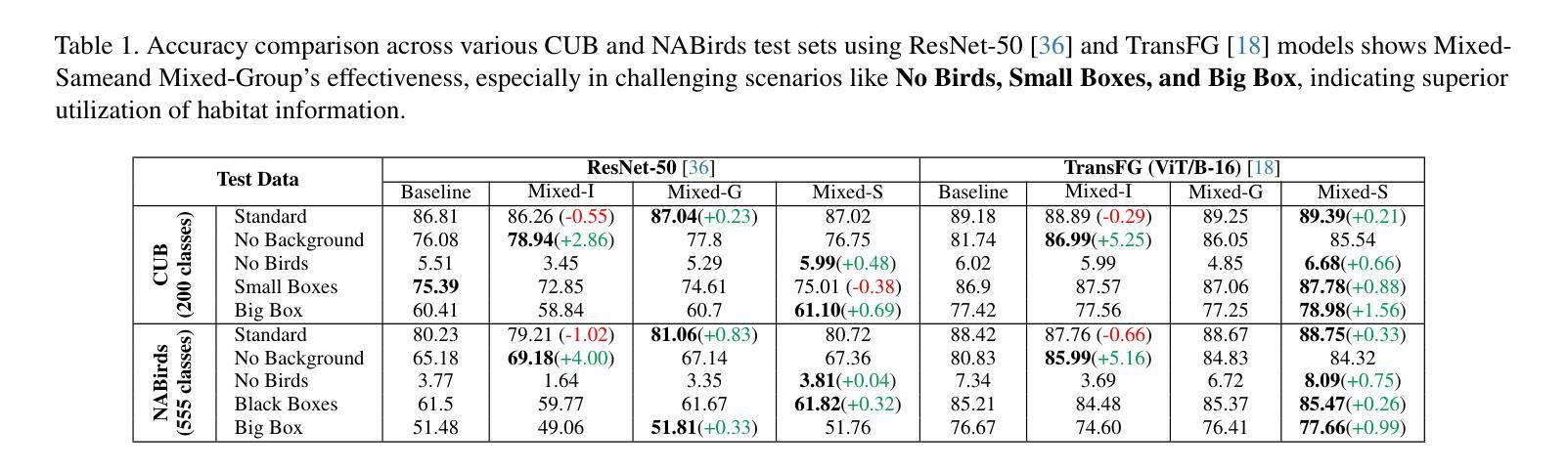
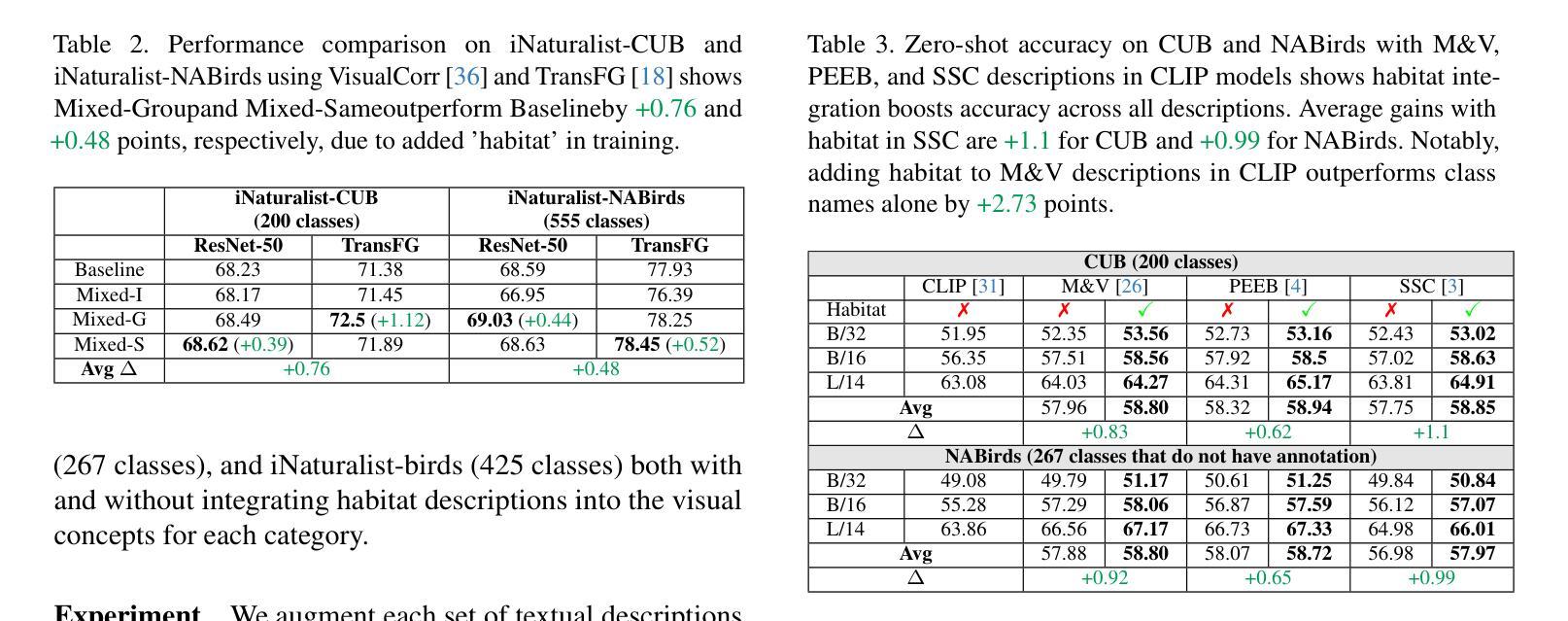
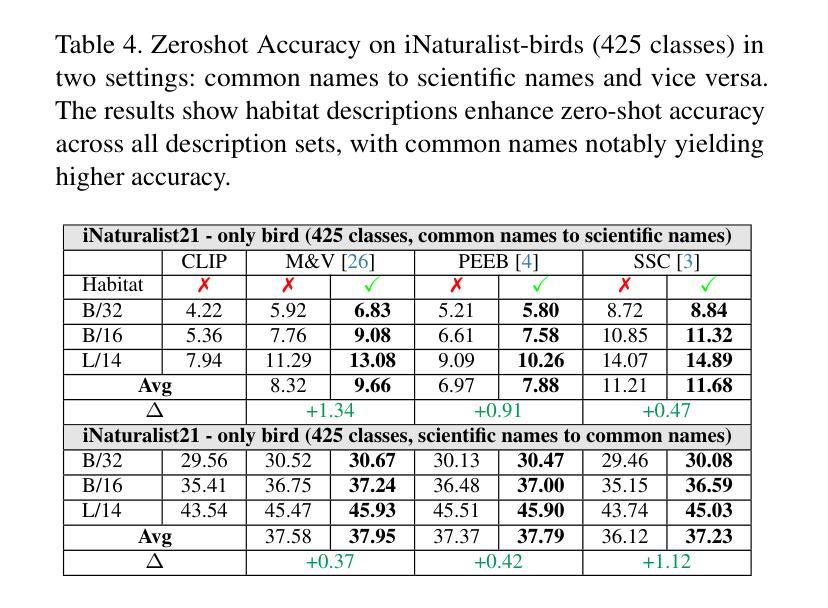
Traditional bird classifiers mostly rely on the visual characteristics of birds. Some prior works even train classifiers to be invariant to the background, completely discarding the living environment of birds. Instead, we are the first to explore integrating habitat information, one of the four major cues for identifying birds by ornithologists, into modern bird classifiers. We focus on two leading model types: (1) CNNs and ViTs trained on the downstream bird datasets; and (2) original, multi-modal CLIP. Training CNNs and ViTs with habitat-augmented data results in an improvement of up to +0.83 and +0.23 points on NABirds and CUB-200, respectively. Similarly, adding habitat descriptors to the prompts for CLIP yields a substantial accuracy boost of up to +0.99 and +1.1 points on NABirds and CUB-200, respectively. We find consistent accuracy improvement after integrating habitat features into the image augmentation process and into the textual descriptors of vision-language CLIP classifiers. Code is available at: https://anonymous.4open.science/r/reasoning-8B7E/.
传统的鸟类分类器大多依赖于鸟类的视觉特征。一些早期作品甚至训练分类器对背景保持不变,完全忽略鸟类的生活环境。相反,我们是首批探索将栖息地信息(鸟类学家识别鸟类的四大线索之一)融入现代鸟类分类器的团队。我们关注的模型类型主要有两种:(1)在下游鸟类数据集上训练的CNN和ViT;(2)原始的跨模态CLIP模型。使用栖息地增强的数据训练CNN和ViT,在NABirds和CUB-200上的准确率分别提高了+0.83点和+0.23点。同样地,将栖息地描述符添加到CLIP的提示中,在NABirds和CUB-200上的准确率分别大幅提高至+0.99点和+1.1点。我们发现,在图像增强过程和视觉语言CLIP分类器的文本描述符中集成栖息地特征后,准确率得到了一致性的提高。代码可在:匿名链接中找到。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
该文本介绍了传统鸟类分类器主要依赖鸟类的视觉特征,而忽视鸟类的生活环境信息。该研究首次探索将栖息地信息这一鸟类识别的四大线索之一融入现代鸟类分类器。该研究关注了两种领先的模型类型,并通过添加栖息地数据进行训练,发现在NABirds和CUB-200数据集上的准确率分别提高了+0.83和+0.23个点。此外,将栖息地描述符添加到CLIP的提示中也显著提高了准确率,在NABirds和CUB-200上分别提高了+0.99和+1.1个点。研究发现,将栖息地特征整合到图像增强过程和视觉语言CLIP分类器的文本描述符中,可以持续提高准确率。
Key Takeaways
- 传统鸟类分类器主要依赖鸟类的视觉特征,忽略生活环境信息。
- 首次尝试将栖息地信息融入现代鸟类分类器。
- 在NABirds和CUB-200数据集上,通过添加栖息地数据训练模型,准确率有显著提高。
- CLIP模型结合栖息地描述符的提示也显著提高了准确率。
- 整合栖息地特征到图像增强过程和文本描述符中,可进一步提高准确率。
- 该研究关注两种领先的模型类型,包括CNN和ViT。
点此查看论文截图