⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-05-15 更新
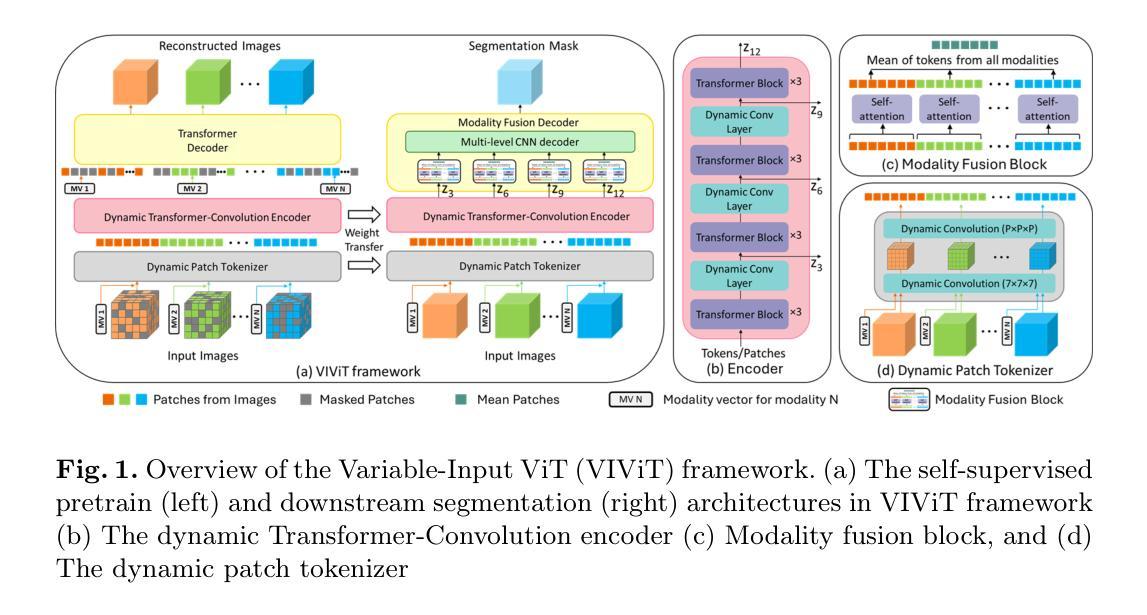
VIViT: Variable-Input Vision Transformer Framework for 3D MR Image Segmentation
Authors:Badhan Kumar Das, Ajay Singh, Gengyan Zhao, Han Liu, Thomas J. Re, Dorin Comaniciu, Eli Gibson, Andreas Maier
Self-supervised pretrain techniques have been widely used to improve the downstream tasks’ performance. However, real-world magnetic resonance (MR) studies usually consist of different sets of contrasts due to different acquisition protocols, which poses challenges for the current deep learning methods on large-scale pretrain and different downstream tasks with different input requirements, since these methods typically require a fixed set of input modalities or, contrasts. To address this challenge, we propose variable-input ViT (VIViT), a transformer-based framework designed for self-supervised pretraining and segmentation finetuning for variable contrasts in each study. With this ability, our approach can maximize the data availability in pretrain, and can transfer the learned knowledge from pretrain to downstream tasks despite variations in input requirements. We validate our method on brain infarct and brain tumor segmentation, where our method outperforms current CNN and ViT-based models with a mean Dice score of 0.624 and 0.883 respectively. These results highlight the efficacy of our design for better adaptability and performance on tasks with real-world heterogeneous MR data.
自监督预训练技术在提高下游任务性能方面得到了广泛应用。然而,由于不同的采集协议,现实世界中的磁共振(MR)研究通常由不同的对比组合构成,这给当前深度学习方法在大型预训练和不同下游任务上带来了挑战,这些下游任务有不同的输入要求,因为这些方法通常需要一组固定的输入模式或对比组合。为了应对这一挑战,我们提出了可变输入ViT(VIViT),这是一个基于transformer的框架,用于针对每项研究中的可变对比进行自监督预训练和分割微调。通过这种方式,我们的方法可以在预训练期间最大化数据可用性,并且即使输入要求发生变化,也能将从预训练中学习的知识转移到下游任务。我们在脑梗死和脑肿瘤分割任务上验证了我们的方法,我们的方法在平均Dice得分上超过了当前的CNN和ViT模型,分别达到了0.624和0.883。这些结果凸显了我们的设计在适应和解决具有现实世界中异质MR数据任务时的有效性。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 9 pages
Summary
本文提出一种基于变压器的可变输入自监督预训练与分割微调框架(VIViT),旨在解决磁共振成像研究中不同对比度数据带来的挑战。该框架可适应不同输入要求,提高数据利用率,并将预训练中的知识转移到下游任务。在脑梗死和脑肿瘤分割验证中,该方法优于现有CNN和ViT模型,显示出更好的适应性和性能。
Key Takeaways
- VIViT框架是基于变压器的可变输入自监督预训练设计,适用于磁共振成像研究中的不同对比度数据。
- 该框架能够最大化预训练中的数据可用性,并适应不同的下游任务输入要求。
- VIViT框架通过自监督预训练与分割微调,提高了模型对真实世界异质磁共振数据的适应性和性能。
- 在脑梗死和脑肿瘤分割验证中,VIViT方法表现出优于现有CNN和ViT模型的性能,平均Dice得分分别为0.624和0.883。
- VIViT框架解决了当前深度学习方法在处理大规模预训练和不同下游任务时面临的挑战,这些任务具有不同的输入要求。
- VIViT框架的设计提高了模型的效能,使其更适用于处理真实世界的异质数据。
点此查看论文截图

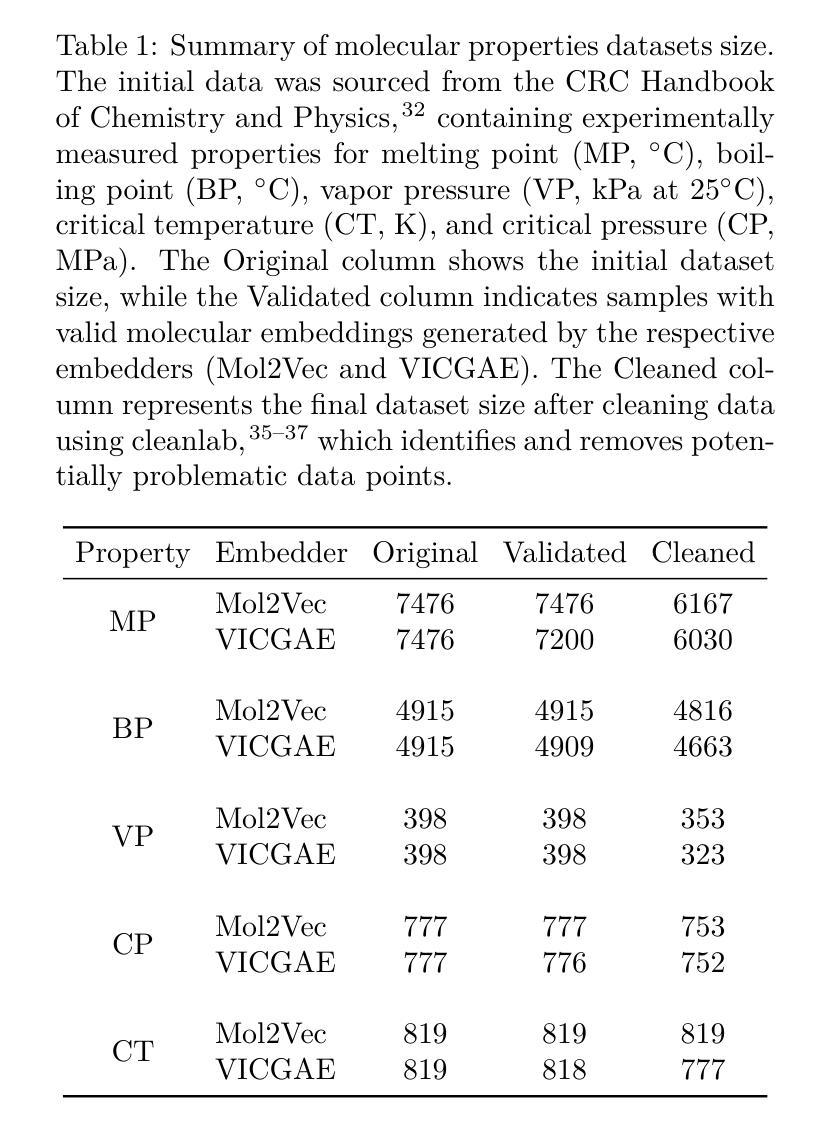
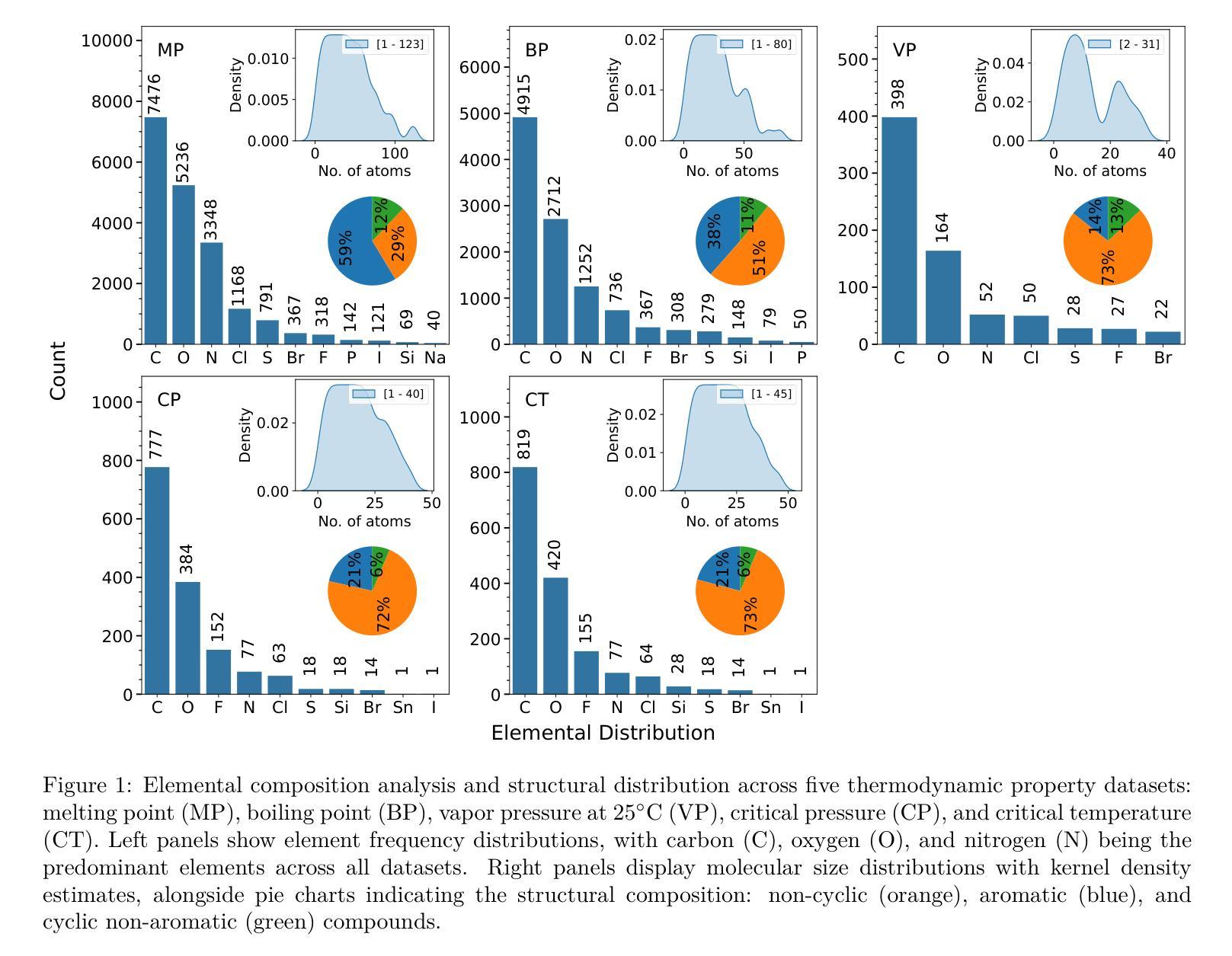
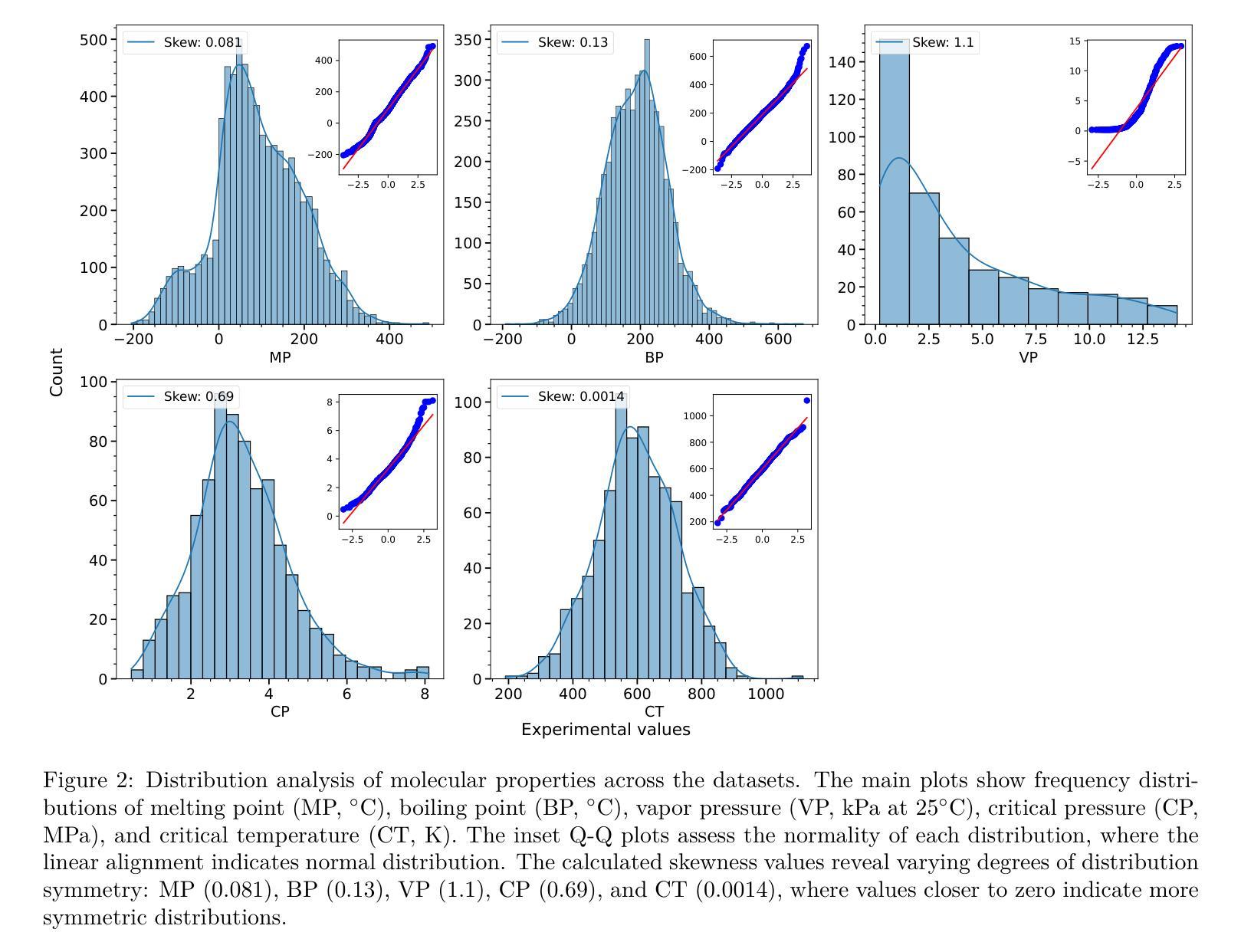
A Machine Learning Pipeline for Molecular Property Prediction using ChemXploreML
Authors:Aravindh Nivas Marimuthu, Brett A. McGuire
We present ChemXploreML, a modular desktop application designed for machine learning-based molecular property prediction. The framework’s flexible architecture allows integration of any molecular embedding technique with modern machine learning algorithms, enabling researchers to customize their prediction pipelines without extensive programming expertise. To demonstrate the framework’s capabilities, we implement and evaluate two molecular embedding approaches - Mol2Vec and VICGAE (Variance-Invariance-Covariance regularized GRU Auto-Encoder) - combined with state-of-the-art tree-based ensemble methods (Gradient Boosting Regression, XGBoost, CatBoost, and LightGBM). Using five fundamental molecular properties as test cases - melting point (MP), boiling point (BP), vapor pressure (VP), critical temperature (CT), and critical pressure (CP) - we validate our framework on a dataset from the CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics. The models achieve excellent performance for well-distributed properties, with R$^2$ values up to 0.93 for critical temperature predictions. Notably, while Mol2Vec embeddings (300 dimensions) delivered slightly higher accuracy, VICGAE embeddings (32 dimensions) exhibited comparable performance yet offered significantly improved computational efficiency. ChemXploreML’s modular design facilitates easy integration of new embedding techniques and machine learning algorithms, providing a flexible platform for customized property prediction tasks. The application automates chemical data preprocessing (including UMAP-based exploration of molecular space), model optimization, and performance analysis through an intuitive interface, making sophisticated machine learning techniques accessible while maintaining extensibility for advanced cheminformatics users.
我们推出ChemXploreML,这是一款基于机器学习的模块化桌面应用程序,用于分子属性预测。该框架灵活的架构允许将任何分子嵌入技术与现代机器学习算法相结合,使研究人员能够根据自己的预测管道定制无需深厚的编程技能。为了展示框架的功能,我们实现了两种分子嵌入方法并进行评估,分别是Mol2Vec和VICGAE(方差-协方差正则化GRU自编码器)。我们将这些方法与现代树形集成方法(梯度增强回归、XGBoost、CatBoost和LightGBM)相结合。以五种基本分子属性作为测试案例:熔点(MP)、沸点(BP)、蒸汽压(VP)、临界温度(CT)和临界压力(CP)。我们在CRC化学物理手册的数据集上验证了我们的框架。对于分布良好的属性,模型取得了出色的性能表现,临界温度预测的R²值高达0.93。值得注意的是,虽然Mol2Vec嵌入(300维)略微提高了准确性,但VICGAE嵌入(32维)表现出相当的性能并大大提高了计算效率。ChemXploreML的模块化设计促进了新嵌入技术和机器学习算法的轻松集成,为定制属性预测任务提供了灵活的平台。该应用程序通过直观界面自动执行化学数据预处理(包括基于UMAP的分子空间探索)、模型优化和性能分析,使得复杂的机器学习技术变得易于访问,同时保持了高级化学信息学用户的可扩展性。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 17 pages, 7 figures, accepted in Journal of Chemical Information and Modeling
Summary
ChemXploreML是一个模块化桌面应用程序,用于基于机器学习的分子属性预测。该程序架构灵活,可集成任何分子嵌入技术和现代机器学习算法,无需深厚编程经验即可定制预测流程。通过对Mol2Vec和VICGAE两种分子嵌入方法与最新的树集成方法进行结合应用,对熔点、沸点、蒸汽压、临界温度和临界压力等五种基本分子属性进行预测验证,取得了良好效果。其中,Mol2Vec嵌入虽精度稍高,但VICGAE嵌入在计算效率上表现更优秀。ChemXploreML的模块化设计便于集成新的嵌入技术和机器学习算法,为定制属性预测任务提供了灵活平台,同时自动化化学数据预处理、模型优化和性能分析,通过直观界面使高级化学信息学用户更易访问和使用。
Key Takeaways
- ChemXploreML是一个模块化桌面应用程序,用于基于机器学习的分子属性预测。
- 框架允许灵活集成不同的分子嵌入技术和机器学习算法。
- 展示了使用Mol2Vec和VICGAE嵌入与树集成方法结合预测分子属性的能力。
- 框架在CRC化学物理手册数据集上验证,对分布良好的属性表现优异,R²值高达0.93。
- Mol2Vec嵌入精度高但维度较大,而VICGAE嵌入在计算效率上有优势。
- ChemXploreML自动化数据预处理、模型优化和性能分析,并通过直观界面提供用户友好体验。
点此查看论文截图

Calibration and Uncertainty for multiRater Volume Assessment in multiorgan Segmentation (CURVAS) challenge results
Authors:Meritxell Riera-Marin, Sikha O K, Julia Rodriguez-Comas, Matthias Stefan May, Zhaohong Pan, Xiang Zhou, Xiaokun Liang, Franciskus Xaverius Erick, Andrea Prenner, Cedric Hemon, Valentin Boussot, Jean-Louis Dillenseger, Jean-Claude Nunes, Abdul Qayyum, Moona Mazher, Steven A Niederer, Kaisar Kushibar, Carlos Martin-Isla, Petia Radeva, Karim Lekadir, Theodore Barfoot, Luis C. Garcia Peraza Herrera, Ben Glocker, Tom Vercauteren, Lucas Gago, Justin Englemann, Joy-Marie Kleiss, Anton Aubanell, Andreu Antolin, Javier Garcia-Lopez, Miguel A. Gonzalez Ballester, Adrian Galdran
Deep learning (DL) has become the dominant approach for medical image segmentation, yet ensuring the reliability and clinical applicability of these models requires addressing key challenges such as annotation variability, calibration, and uncertainty estimation. This is why we created the Calibration and Uncertainty for multiRater Volume Assessment in multiorgan Segmentation (CURVAS), which highlights the critical role of multiple annotators in establishing a more comprehensive ground truth, emphasizing that segmentation is inherently subjective and that leveraging inter-annotator variability is essential for robust model evaluation. Seven teams participated in the challenge, submitting a variety of DL models evaluated using metrics such as Dice Similarity Coefficient (DSC), Expected Calibration Error (ECE), and Continuous Ranked Probability Score (CRPS). By incorporating consensus and dissensus ground truth, we assess how DL models handle uncertainty and whether their confidence estimates align with true segmentation performance. Our findings reinforce the importance of well-calibrated models, as better calibration is strongly correlated with the quality of the results. Furthermore, we demonstrate that segmentation models trained on diverse datasets and enriched with pre-trained knowledge exhibit greater robustness, particularly in cases deviating from standard anatomical structures. Notably, the best-performing models achieved high DSC and well-calibrated uncertainty estimates. This work underscores the need for multi-annotator ground truth, thorough calibration assessments, and uncertainty-aware evaluations to develop trustworthy and clinically reliable DL-based medical image segmentation models.
深度学习(DL)已成为医学图像分割的主流方法,但要确保这些模型可靠性和临床适用性,需要解决标注变异性、校准和不确定性估计等关键挑战。因此,我们创建了多评估者体积评估中的校准和不确定性(CURVAS),它强调了多个标注者在建立更全面真实情况中的关键作用,并强调分割本质上是主观的,利用标注者之间的变异性对于稳健的模型评估至关重要。七个团队参与了此次挑战,提交了多种深度学习模型,采用狄克相似系数(DSC)、期望校准误差(ECE)和连续排名概率分数(CRPS)等指标进行评估。通过纳入共识和非共识真实情况,我们评估深度学习模型如何处理不确定性,以及它们的置信度估计是否与真正的分割性能相符。我们的研究结果再次强调了良好校准模型的重要性,因为更好的校准与结果质量密切相关。此外,我们证明在多样化数据集上训练并丰富预训练知识的分割模型表现出更大的稳健性,特别是在偏离标准解剖结构的情况下。值得注意的是,表现最佳的模型实现了高DSC和良好的校准不确定性估计。这项工作强调了多评估者真实情况、全面的校准评估和不确定性感知评估的需求,以开发可信和临床可靠的基于深度学习的医学图像分割模型。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF This challenge was hosted in MICCAI 2024
Summary
深度学习在医学图像分割中占据主导地位,但确保模型的可靠性和临床适用性需要解决标注变异性、校准和不确定性估计等关键挑战。CURVAS研究强调多标注者在建立更全面真实标签中的关键作用,指出分割本质上是主观的,利用标注者间变异性对于稳健模型评估至关重要。研究通过融入共识和分歧真实标签,评估深度学习模型如何处理不确定性和其置信度估计是否与真实分割性能相符。研究表明,良好校准的模型非常重要,且在多样化数据集上训练的、用预训练知识丰富的分割模型更稳健。最佳模型实现高DSC和良好校准的不确定性估计。强调需要多标注者真实标签、全面的校准评估和不确定性感知评估,以开发可信且临床可靠的基于深度学习的医学图像分割模型。
Key Takeaways
- 深度学习是医学图像分割的主导方法,但确保模型的可靠性和临床适用性面临挑战。
- CURVAS研究强调多标注者在建立更全面真实标签中的关键作用。
- 分割本质上是主观的,利用标注者间变异性对稳健模型评估至关重要。
- 研究通过融入共识和分歧真实标签,评估深度学习模型的不确定性处理。
- 良好校准的模型非常重要,且与分割质量强相关。
- 在多样化数据集上训练的、用预训练知识丰富的分割模型更稳健。
点此查看论文截图

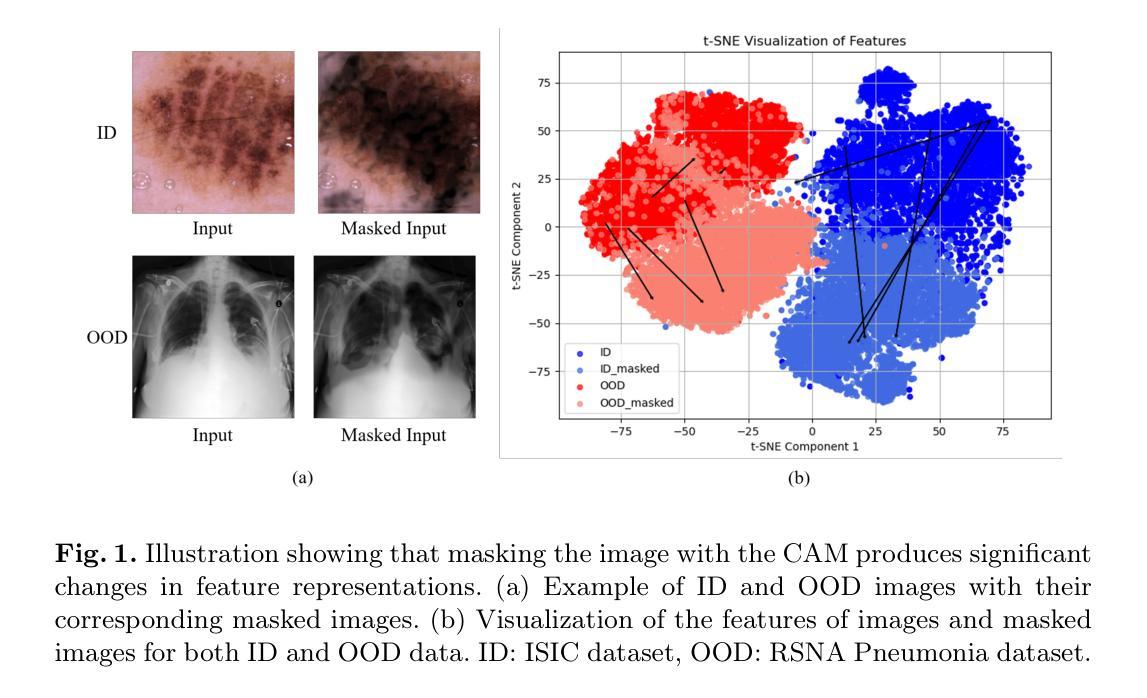
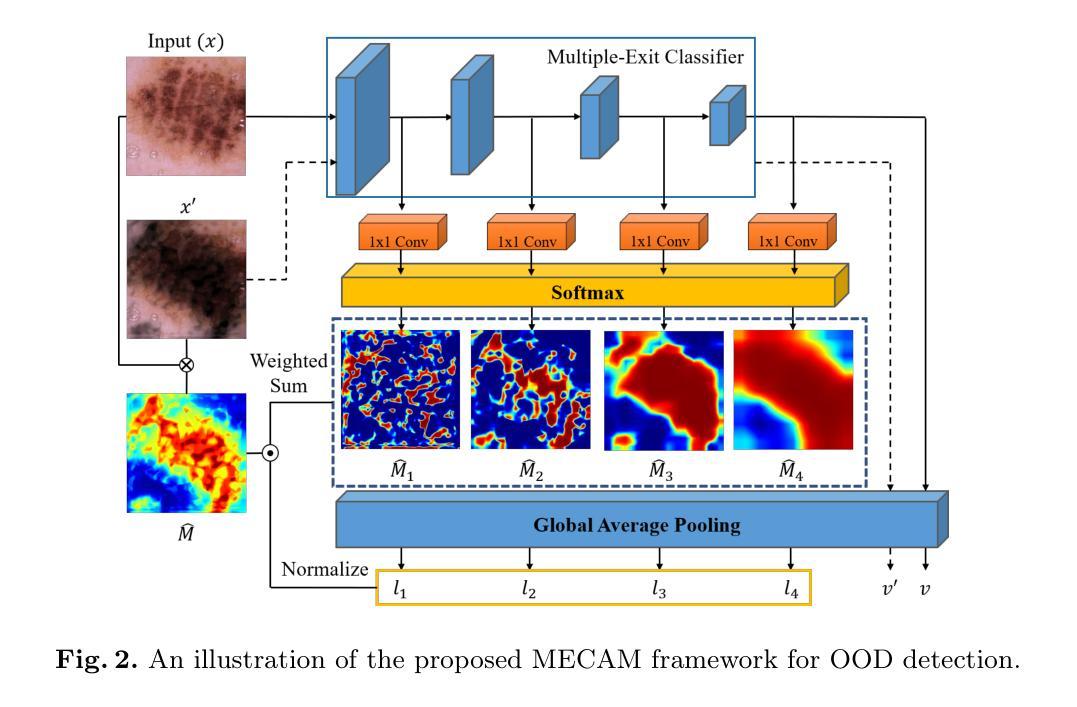
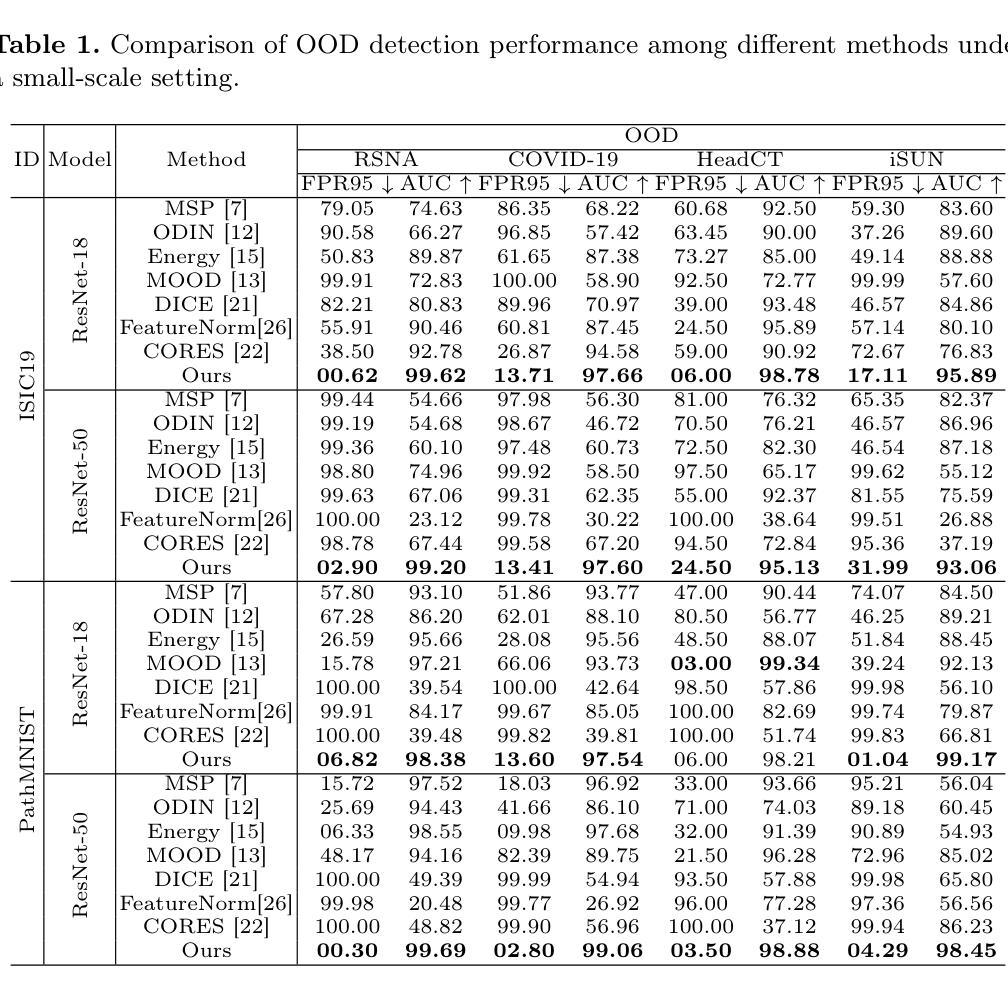
Unsupervised Out-of-Distribution Detection in Medical Imaging Using Multi-Exit Class Activation Maps and Feature Masking
Authors:Yu-Jen Chen, Xueyang Li, Yiyu Shi, Tsung-Yi Ho
Out-of-distribution (OOD) detection is essential for ensuring the reliability of deep learning models in medical imaging applications. This work is motivated by the observation that class activation maps (CAMs) for in-distribution (ID) data typically emphasize regions that are highly relevant to the model’s predictions, whereas OOD data often lacks such focused activations. By masking input images with inverted CAMs, the feature representations of ID data undergo more substantial changes compared to those of OOD data, offering a robust criterion for differentiation. In this paper, we introduce a novel unsupervised OOD detection framework, Multi-Exit Class Activation Map (MECAM), which leverages multi-exit CAMs and feature masking. By utilizing mult-exit networks that combine CAMs from varying resolutions and depths, our method captures both global and local feature representations, thereby enhancing the robustness of OOD detection. We evaluate MECAM on multiple ID datasets, including ISIC19 and PathMNIST, and test its performance against three medical OOD datasets, RSNA Pneumonia, COVID-19, and HeadCT, and one natural image OOD dataset, iSUN. Comprehensive comparisons with state-of-the-art OOD detection methods validate the effectiveness of our approach. Our findings emphasize the potential of multi-exit networks and feature masking for advancing unsupervised OOD detection in medical imaging, paving the way for more reliable and interpretable models in clinical practice.
分布外(OOD)检测对于确保医疗成像应用中深度学习模型的可靠性至关重要。本研究工作受到以下观察结果的启发:对于内部分布(ID)数据的类别激活图(CAMs)通常强调与模型预测高度相关的区域,而OOD数据通常缺乏这种有针对性的激活。通过用反向CAMs遮挡输入图像,ID数据的特征表示经历了比OOD数据更大的变化,为差异化提供了稳健的标准。在本文中,我们引入了一种新型的无监督OOD检测框架——多出口类别激活图(MECAM),它利用多出口CAMs和特征遮蔽技术。通过利用结合不同分辨率和深度CAMs的多出口网络,我们的方法能够捕捉全局和局部特征表示,从而提高了OOD检测的稳健性。我们在多个ID数据集上评估了MECAM,包括ISIC19和PathMNIST,并在三个医学OOD数据集(RSNA肺炎、COVID-19和HeadCT)和一个自然图像OOD数据集(iSUN)上测试了其性能。与最先进的OOD检测方法的全面比较验证了我们方法的有效性。我们的研究结果表明了多出口网络和特征遮蔽在推进医学成像中的无监督OOD检测方面的潜力,为临床实践中的更可靠和可解释的模型铺平了道路。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 10 pages, 2 figures
Summary
本文提出了一种基于多出口类激活映射(MECAM)的无监督异常检测框架,用于医学图像中的离群值检测。通过利用多出口网络结合不同分辨率和深度的CAMs,结合特征遮蔽技术,MECAM能有效捕捉图像的全局和局部特征表示,提高离群值检测的稳健性。在多个数据集上的实验验证了MECAM的有效性。
Key Takeaways
- OOD检测在医学成像应用中对于确保深度学习模型的可靠性至关重要。
- 类激活映射(CAMs)对于区分ID数据和OOD数据非常有用,ID数据的CAMs通常强调与模型预测高度相关的区域,而OOD数据则缺乏这种聚焦的激活。
- 通过使用多出口网络结合不同分辨率和深度的CAMs,可以提高OOD检测的稳健性。
- MECAM框架利用特征遮蔽技术,通过掩蔽输入图像来区分ID数据和OOD数据的特征表示。
- 在多个数据集上的实验验证了MECAM的有效性,包括ISIC19、PathMNIST、RSNA Pneumonia、COVID-19、HeadCT以及自然图像OOD数据集iSUN。
- 与最新的OOD检测方法相比,MECAM具有优越的性能。
点此查看论文截图

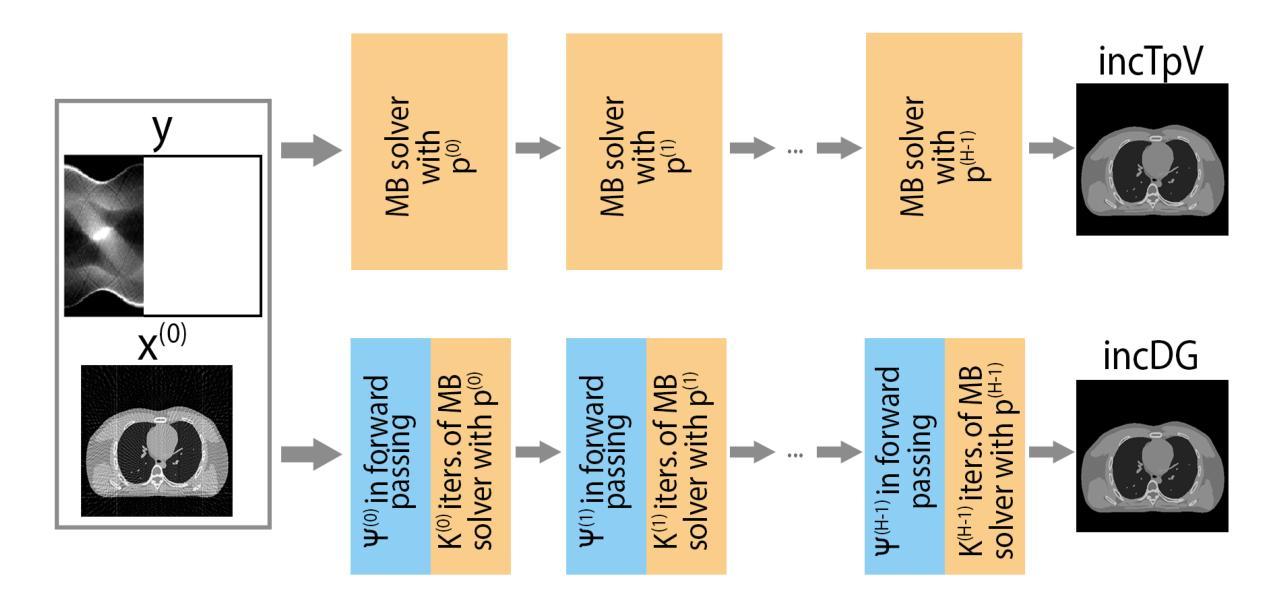
An incremental algorithm for non-convex AI-enhanced medical image processing
Authors:Elena Morotti
Solving non-convex regularized inverse problems is challenging due to their complex optimization landscapes and multiple local minima. However, these models remain widely studied as they often yield high-quality, task-oriented solutions, particularly in medical imaging, where the goal is to enhance clinically relevant features rather than merely minimizing global error. We propose incDG, a hybrid framework that integrates deep learning with incremental model-based optimization to efficiently approximate the $\ell_0$-optimal solution of imaging inverse problems. Built on the Deep Guess strategy, incDG exploits a deep neural network to generate effective initializations for a non-convex variational solver, which refines the reconstruction through regularized incremental iterations. This design combines the efficiency of Artificial Intelligence (AI) tools with the theoretical guarantees of model-based optimization, ensuring robustness and stability. We validate incDG on TpV-regularized optimization tasks, demonstrating its effectiveness in medical image deblurring and tomographic reconstruction across diverse datasets, including synthetic images, brain CT slices, and chest-abdomen scans. Results show that incDG outperforms both conventional iterative solvers and deep learning-based methods, achieving superior accuracy and stability. Moreover, we confirm that training incDG without ground truth does not significantly degrade performance, making it a practical and powerful tool for solving non-convex inverse problems in imaging and beyond.
解决非凸正则化反问题具有挑战性,因为它们具有复杂的优化景观和多个局部最小值。然而,这些模型仍被广泛研究,因为它们通常会产生高质量的任务导向解决方案,特别是在医学成像中,目标是增强与临床相关的特征,而不仅仅是减少全局错误。我们提出了incDG,这是一个混合框架,它将深度学习与增量模型优化相结合,以有效地逼近成像反问题的l_0最优解。incDG建立在Deep Guess策略之上,利用深度神经网络为非线性变分求解器生成有效的初始化,通过正则化的增量迭代来完善重建。这种设计结合了人工智能工具的效率和模型优化的理论保证,确保了稳健性和稳定性。我们在TpV正则化优化任务上验证了incDG的有效性,它在医学图像去模糊和断层重建方面表现出色,涉及多种数据集,包括合成图像、脑部CT切片和腹部扫描。结果表明,incDG在准确性和稳定性方面优于传统的迭代求解器和基于深度学习的方法。此外,我们确认在没有真实值的情况下训练incDG不会显著降低其性能,使其成为解决成像和非凸反问题领域的实用且强大的工具。
论文及项目相关链接
摘要
针对非凸正则化反问题的求解,由于其复杂的优化景观和多个局部最小值,带来很大挑战。然而,这些模型因常常能针对特定任务提供高质量解决方案,特别是在医疗成像领域,其目标在于增强临床相关特征,而非仅仅减少全局错误,因此仍受到广泛研究。本文提出incDG这一混合框架,它整合深度学习及增量模型优化,以高效近似成像反问题的l_0最优解。incDG基于深度猜测策略,利用深度神经网络为非线性变分求解器生成有效初始化,通过正则化增量迭代优化重建。此设计结合人工智能工具的高效性与模型基础优化的理论保障,确保了稳健性和稳定性。本文在TpV正则优化任务上验证了incDG的有效性,展示其在医疗图像去模糊和层析重建中的优势,涉及合成图像、脑部CT切片和腹部扫描等多种数据集。结果显示,incDG相较于传统迭代求解器和深度学习方法表现出更高的准确性和稳定性。此外,无需真实值训练incDG并不会显著影响性能,使其成为解决成像和非凸反问题实用且强大的工具。
关键见解
- 非凸正则化反问题由于复杂的优化景观和多个局部最小值而具有挑战性。
- incDG框架结合了深度学习与增量模型优化,以高效求解成像反问题的l_0最优解。
- incDG基于深度猜测策略,利用深度神经网络初始化非线性变分求解器。
- incDG在医疗图像去模糊和层析重建任务上展现出优越性能。
- incDG在多种数据集上的性能优于传统迭代求解器和深度学习方法。
- incDG的设计结合了人工智能工具的高效性和模型基础优化的理论保障。
点此查看论文截图

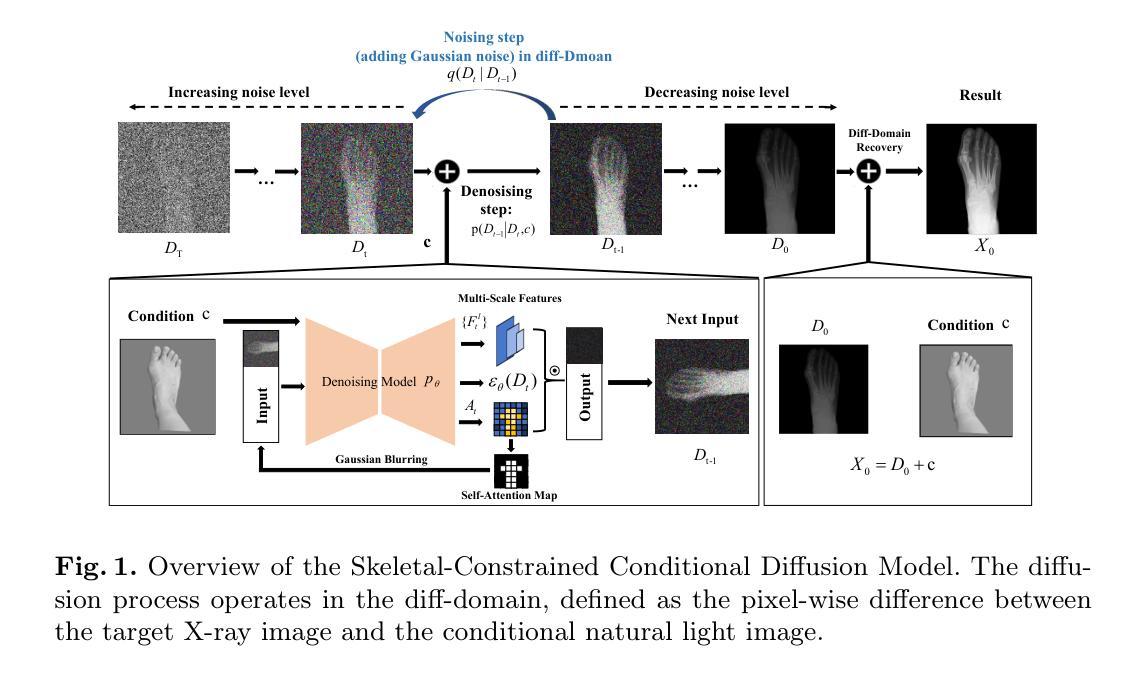
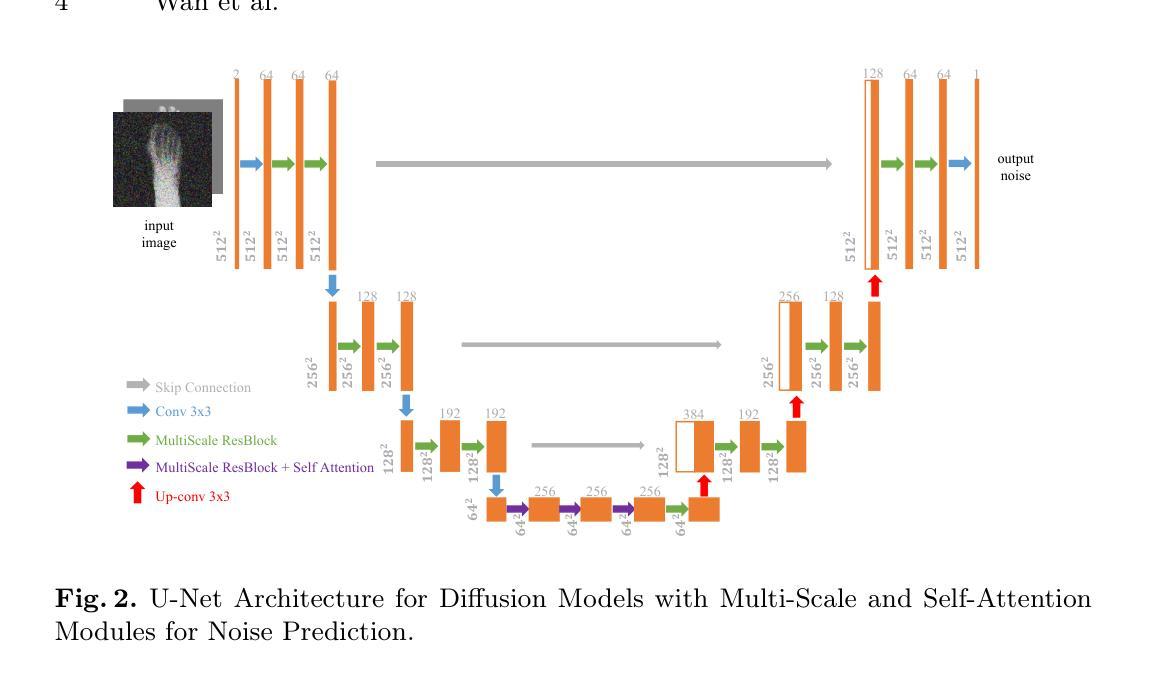
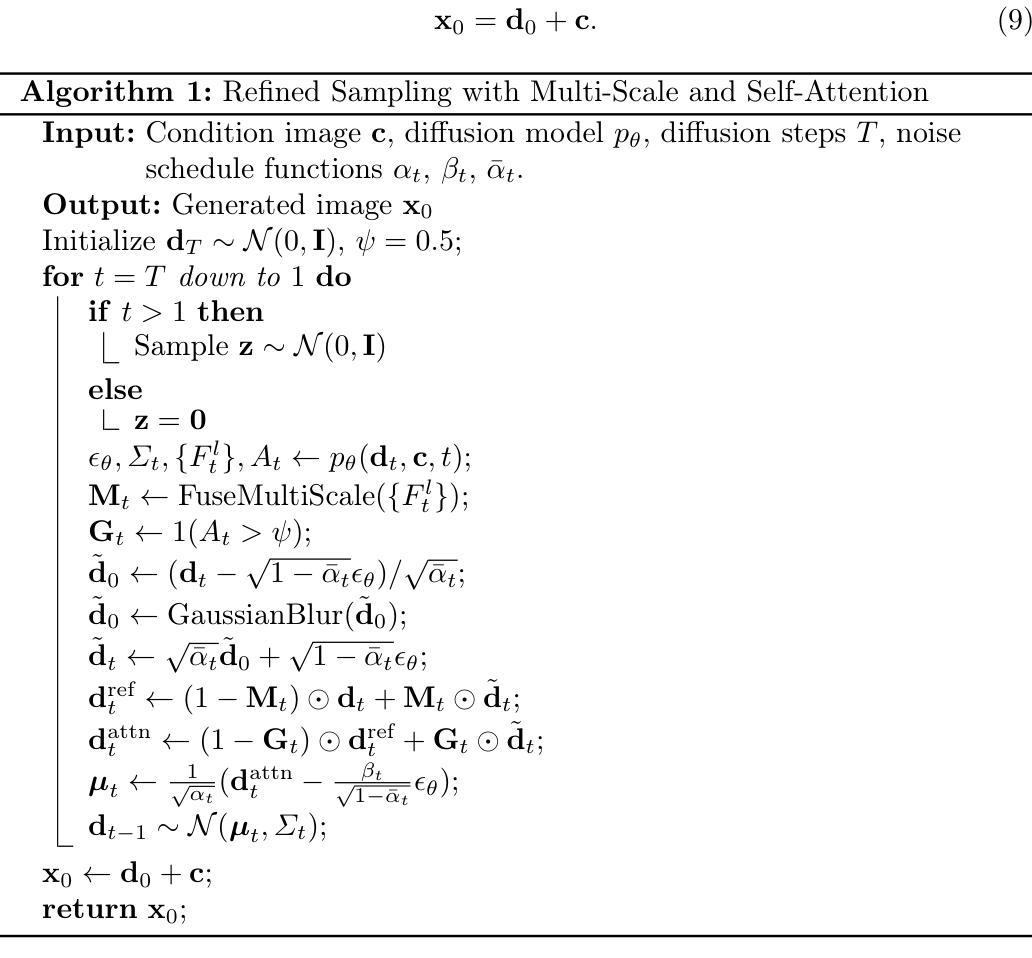
Skeleton-Guided Diffusion Model for Accurate Foot X-ray Synthesis in Hallux Valgus Diagnosis
Authors:Midi Wan, Pengfei Li, Yizhuo Liang, Di Wu, Yushan Pan, Guangzhen Zhu, Hao Wang
Medical image synthesis plays a crucial role in providing anatomically accurate images for diagnosis and treatment. Hallux valgus, which affects approximately 19% of the global population, requires frequent weight-bearing X-rays for assessment, placing additional strain on both patients and healthcare providers. Existing X-ray models often struggle to balance image fidelity, skeletal consistency, and physical constraints, particularly in diffusion-based methods that lack skeletal guidance. We propose the Skeletal-Constrained Conditional Diffusion Model (SCCDM) and introduce KCC, a foot evaluation method utilizing skeletal landmarks. SCCDM incorporates multi-scale feature extraction and attention mechanisms, improving the Structural Similarity Index (SSIM) by 5.72% (0.794) and Peak Signal-to-Noise Ratio (PSNR) by 18.34% (21.40 dB). When combined with KCC, the model achieves an average score of 0.85, demonstrating strong clinical applicability. The code is available at https://github.com/midisec/SCCDM.
医学图像合成在提供用于诊断和治疗解剖准确的图像方面起着至关重要的作用。大约19%的全球人口受到拇趾外翻的影响,这需要经常进行负重X射线检查进行评估,给患者和医疗服务提供者带来额外的压力。现有的X射线模型往往难以平衡图像保真度、骨骼一致性和物理约束,特别是在缺乏骨骼指导的基于扩散的方法中更是如此。我们提出了骨骼约束条件扩散模型(SCCDM),并引入了利用骨骼标志的足部评估方法KCC。SCCDM结合了多尺度特征提取和注意力机制,提高了结构相似性指数(SSIM)5.72%(得分为0.794),峰值信噪比(PSNR)提高了18.34%(得分为21.40分贝)。与KCC相结合后,模型得分平均为0.85,显示出很强的临床适用性。代码可在https://github.com/midisec/SCCDM获取。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
医学图像合成在诊断和治疗中提供解剖准确的图像,起到关键作用。针对足拇趾外翻(影响全球约19%人口)的评估,现有X射线模型在图像保真度、骨骼一致性和物理约束之间难以平衡。我们提出了骨骼约束条件扩散模型(SCCDM),并结合足部评估方法KCC,利用骨骼地标实现多尺度特征提取和注意力机制,提高了结构相似性指数(SSIM)和峰值信噪比(PSNR),展现出强大的临床适用性。
Key Takeaways
- 医学图像合成在诊断和治疗中至关重要,能够提供解剖准确的图像。
- 足拇趾外翻是一种常见的病症,需要频繁进行负重X射线检查,对病人和医疗提供者都增加了负担。
- 现有X射线模型在平衡图像质量方面存在挑战,特别是在扩散模型中缺乏骨骼指导。
- 提出的骨骼约束条件扩散模型(SCCDM)结合了多尺度特征提取和注意力机制。
- SCCDM通过结合KCC方法,提高了结构相似性指数(SSIM)和峰值信噪比(PSNR),展现出良好的性能。
- SCCDM模型的临床适用性得到了验证,平均得分为0.85。
点此查看论文截图

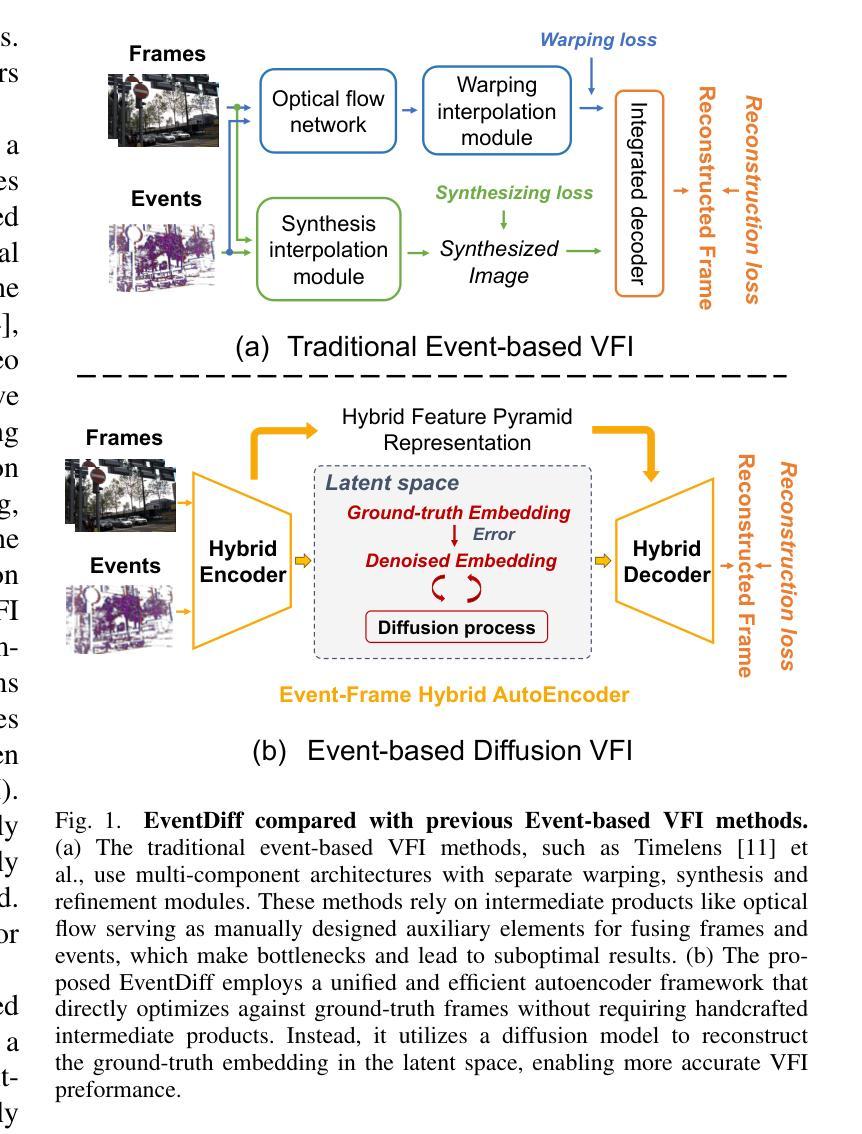
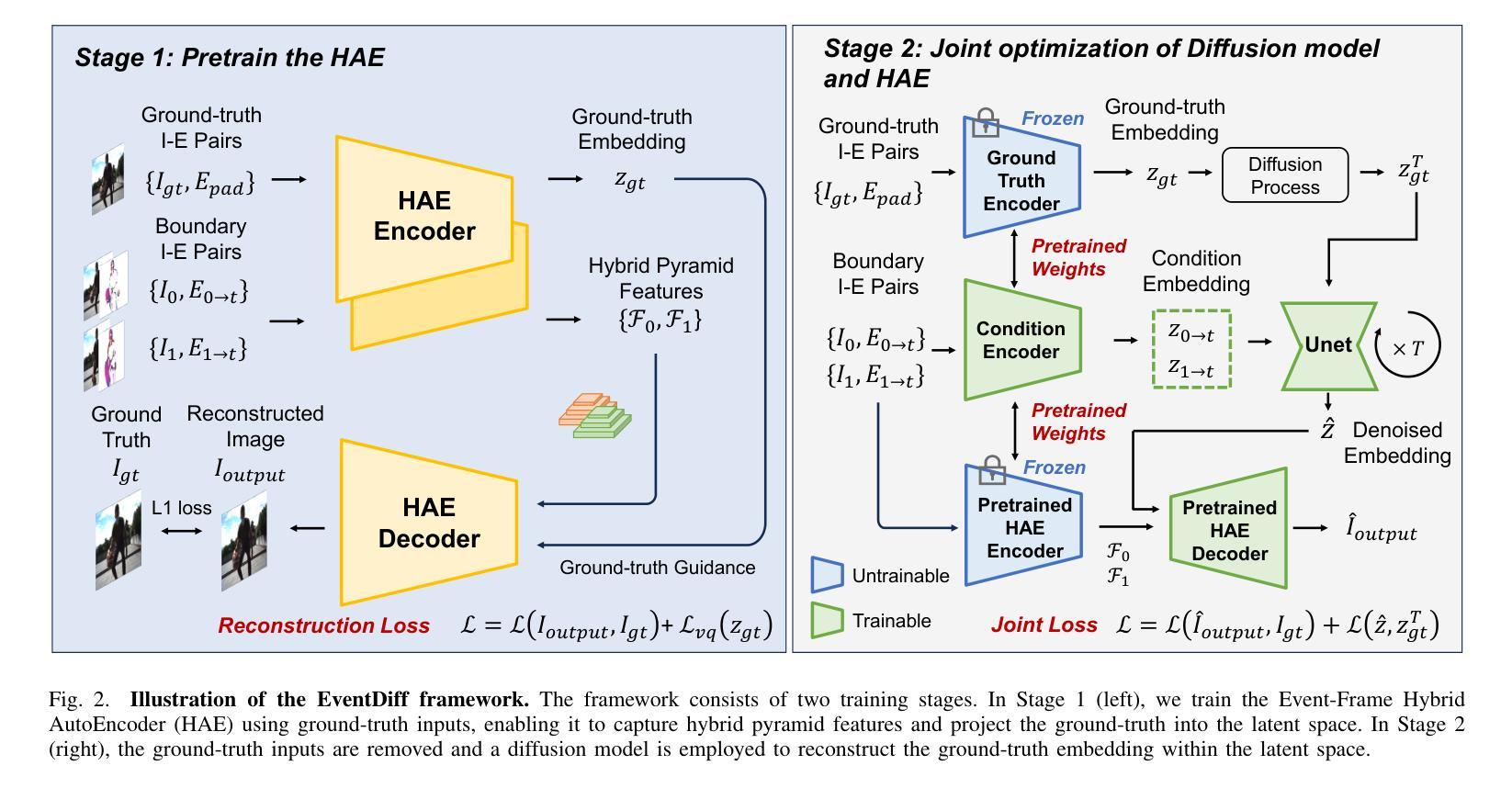
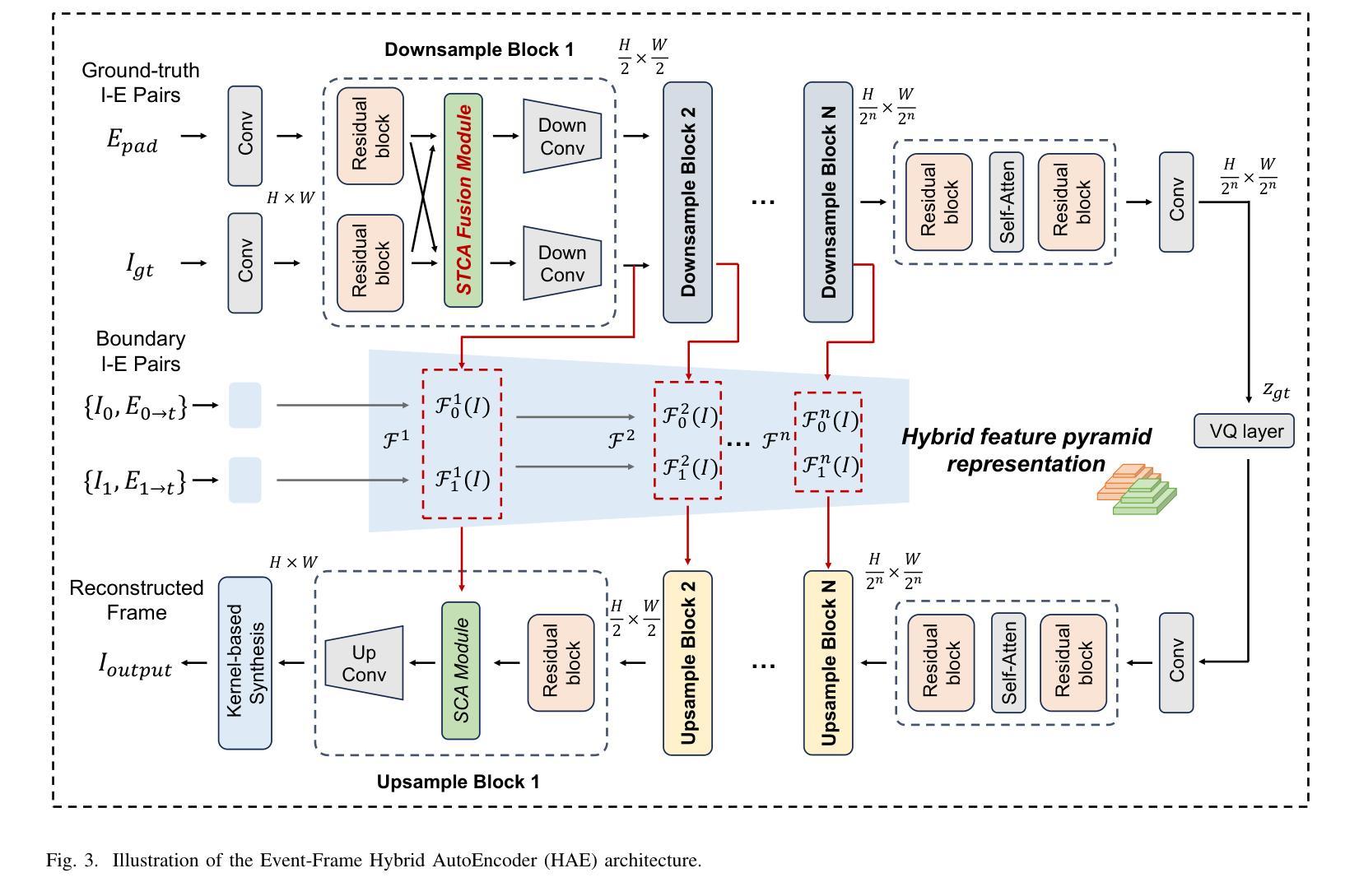
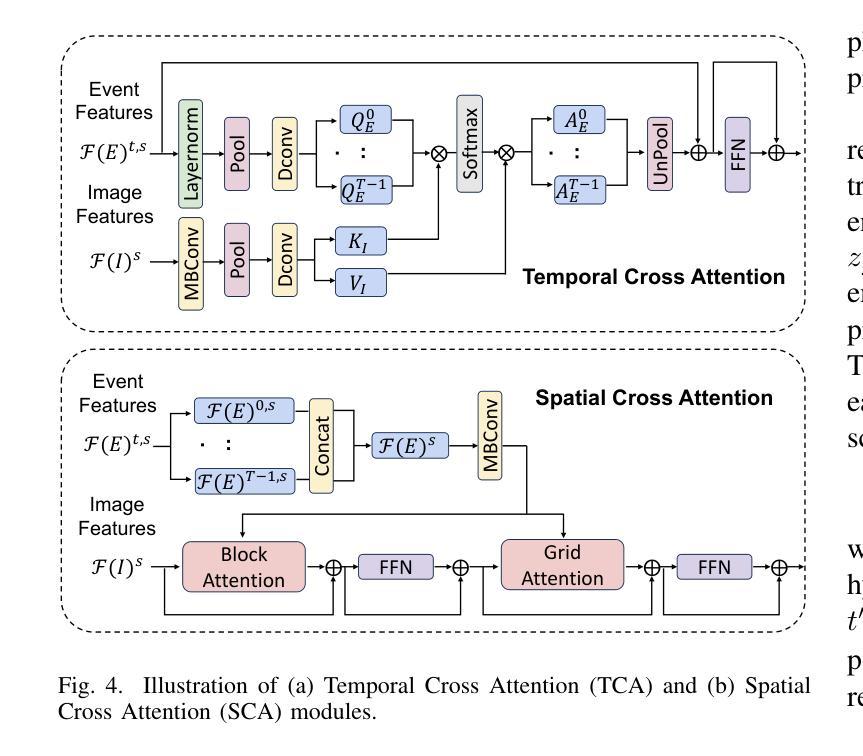
EventDiff: A Unified and Efficient Diffusion Model Framework for Event-based Video Frame Interpolation
Authors:Hanle Zheng, Xujie Han, Zegang Peng, Shangbin Zhang, Guangxun Du, Zhuo Zou, Xilin Wang, Jibin Wu, Hao Guo, Lei Deng
Video Frame Interpolation (VFI) is a fundamental yet challenging task in computer vision, particularly under conditions involving large motion, occlusion, and lighting variation. Recent advancements in event cameras have opened up new opportunities for addressing these challenges. While existing event-based VFI methods have succeeded in recovering large and complex motions by leveraging handcrafted intermediate representations such as optical flow, these designs often compromise high-fidelity image reconstruction under subtle motion scenarios due to their reliance on explicit motion modeling. Meanwhile, diffusion models provide a promising alternative for VFI by reconstructing frames through a denoising process, eliminating the need for explicit motion estimation or warping operations. In this work, we propose EventDiff, a unified and efficient event-based diffusion model framework for VFI. EventDiff features a novel Event-Frame Hybrid AutoEncoder (HAE) equipped with a lightweight Spatial-Temporal Cross Attention (STCA) module that effectively fuses dynamic event streams with static frames. Unlike previous event-based VFI methods, EventDiff performs interpolation directly in the latent space via a denoising diffusion process, making it more robust across diverse and challenging VFI scenarios. Through a two-stage training strategy that first pretrains the HAE and then jointly optimizes it with the diffusion model, our method achieves state-of-the-art performance across multiple synthetic and real-world event VFI datasets. The proposed method outperforms existing state-of-the-art event-based VFI methods by up to 1.98dB in PSNR on Vimeo90K-Triplet and shows superior performance in SNU-FILM tasks with multiple difficulty levels. Compared to the emerging diffusion-based VFI approach, our method achieves up to 5.72dB PSNR gain on Vimeo90K-Triplet and 4.24X faster inference.
视频帧插值(VFI)是计算机视觉的一项基本且具有挑战性的任务,特别是在涉及大运动、遮挡和光照变化的情况下。事件相机的最新进展为应对这些挑战提供了新的机遇。虽然现有的基于事件驱动的VFI方法已经能够通过利用手工制作的中间表示(如光流)来恢复复杂的大运动,但这些设计在细微运动场景下往往牺牲了高保真图像重建,因为它们依赖于显式运动建模。与此同时,扩散模型通过去噪过程重建帧,无需显式运动估计或扭曲操作,为VFI提供了有前景的替代方案。在这项工作中,我们提出了基于事件的扩散模型框架EventDiff,用于VFI。EventDiff的特点是一种新型的事件帧混合自动编码器(HAE),配备了一个轻量级的时空交叉注意力(STCA)模块,可以有效地融合动态事件流和静态帧。与以前的基于事件的VFI方法不同,EventDiff通过在潜在空间中进行去噪扩散过程直接执行插值,使其在多样且具有挑战性的VFI场景中更加稳健。通过首先预训练HAE,然后与其扩散模型联合优化的两阶段训练策略,我们的方法在多个合成和现实世界的事件VFI数据集上实现了卓越的性能。所提出的方法在Vimeo90K-Triplet上的峰值信噪比(PSNR)比现有的基于事件的VFI方法高出1.98dB,在具有多个难度级别的SNU-FILM任务上表现出卓越的性能。与新兴的基于扩散的VFI方法相比,我们的方法在Vimeo90K-Triplet上实现了高达5.72dB的PSNR增益,推理速度提高了4.24倍。
论文及项目相关链接
摘要
本文提出了一个基于事件扩散模型的视频帧插值(VFI)框架,名为EventDiff。它通过结合事件流与静态帧,利用事件帧混合自动编码器(HAE)和时空交叉注意力(STCA)模块,实现了在潜在空间中的直接插值。与传统的基于事件的VFI方法相比,EventDiff更加稳健,适用于各种挑战性的VFI场景。通过两阶段训练策略,该方法在多个合成和真实世界事件VFI数据集上实现了最先进的性能。在Vimeo90K-Triplet上,该方法较现有技术提高了1.98dB的峰值信噪比(PSNR),在SNU-FILM任务中也表现出卓越性能,且推理速度比新兴的扩散VFI方法快4.24倍。
关键见解
- 视频帧插值(VFI)是计算机视觉领域的一项基本而具有挑战的任务,尤其在涉及大运动、遮挡和光照变化的情况下。
- 事件相机的发展为解决这些挑战提供了新的机会。
- 现有的基于事件的方法虽然能够通过利用光学流等中间表示来恢复大运动,但在细微运动场景下难以实现高保真图像重建。
- 扩散模型通过去噪过程重建帧,无需显式运动估计或扭曲操作,为VFI提供了有前景的替代方案。
- EventDiff是一个基于事件的扩散模型框架,通过事件帧混合自动编码器和时空交叉注意力模块,实现了在潜在空间中的直接插值。
- EventDiff采用两阶段训练策略,先在静态数据集上训练自动编码器,然后将其与优化扩散模型相结合,达到最优性能。
点此查看论文截图

JSover: Joint Spectrum Estimation and Multi-Material Decomposition from Single-Energy CT Projections
Authors:Qing Wu, Hongjiang Wei, Jingyi Yu, S. Kevin Zhou, Yuyao Zhang
Multi-material decomposition (MMD) enables quantitative reconstruction of tissue compositions in the human body, supporting a wide range of clinical applications. However, traditional MMD typically requires spectral CT scanners and pre-measured X-ray energy spectra, significantly limiting clinical applicability. To this end, various methods have been developed to perform MMD using conventional (i.e., single-energy, SE) CT systems, commonly referred to as SEMMD. Despite promising progress, most SEMMD methods follow a two-step image decomposition pipeline, which first reconstructs monochromatic CT images using algorithms such as FBP, and then performs decomposition on these images. The initial reconstruction step, however, neglects the energy-dependent attenuation of human tissues, introducing severe nonlinear beam hardening artifacts and noise into the subsequent decomposition. This paper proposes JSover, a fundamentally reformulated one-step SEMMD framework that jointly reconstructs multi-material compositions and estimates the energy spectrum directly from SECT projections. By explicitly incorporating physics-informed spectral priors into the SEMMD process, JSover accurately simulates a virtual spectral CT system from SE acquisitions, thereby improving the reliability and accuracy of decomposition. Furthermore, we introduce implicit neural representation (INR) as an unsupervised deep learning solver for representing the underlying material maps. The inductive bias of INR toward continuous image patterns constrains the solution space and further enhances estimation quality. Extensive experiments on both simulated and real CT datasets show that JSover outperforms state-of-the-art SEMMD methods in accuracy and computational efficiency.
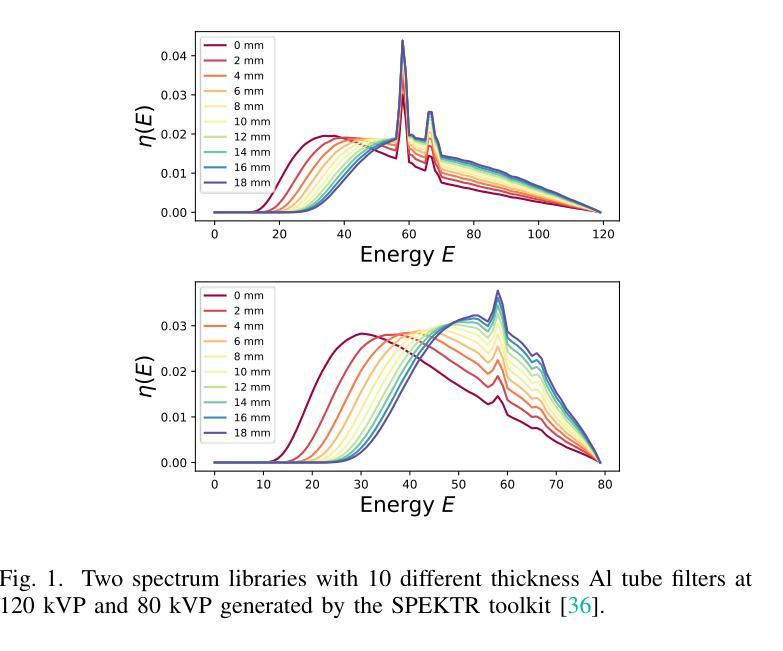
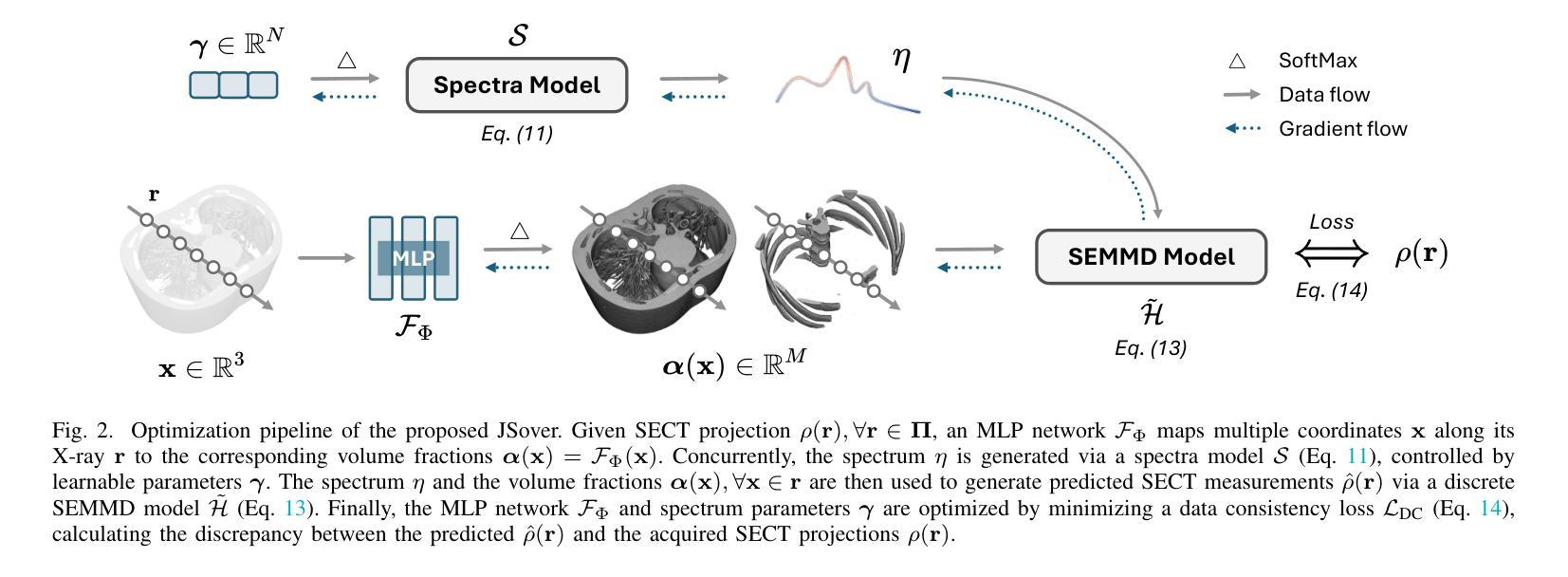
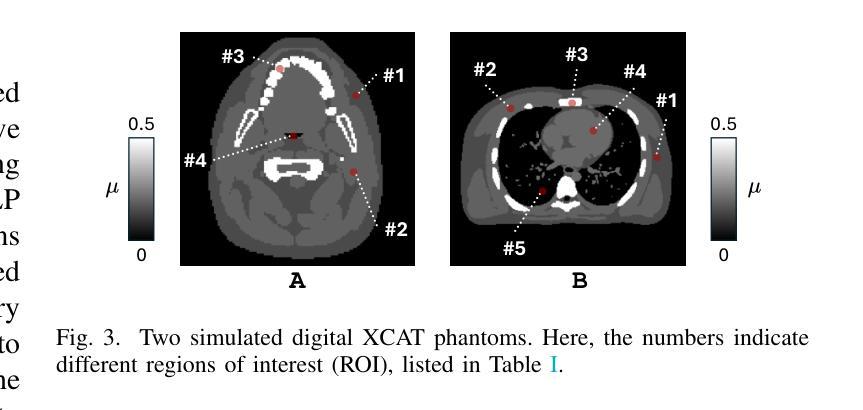
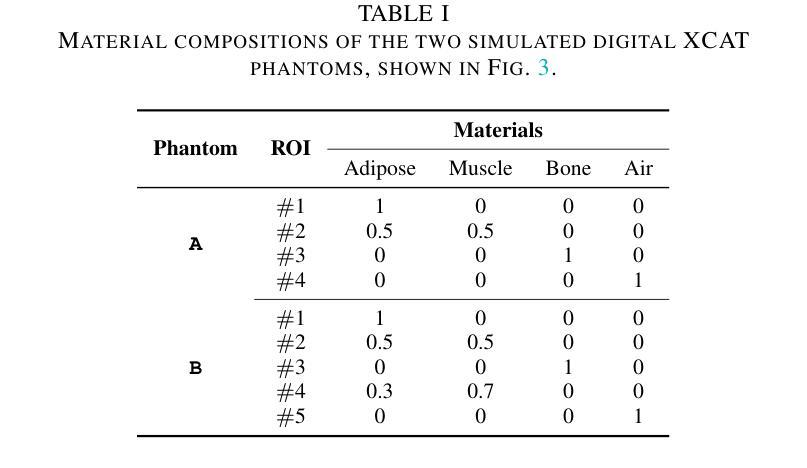
多材料分解(MMD)技术能够定量重建人体组织成分,支持广泛的应用于临床。然而,传统的MMD通常需要光谱CT扫描仪和预测量的X射线能量光谱,这极大地限制了其在临床上的适用性。为此,已经开发了各种使用常规(即单能量,SE)CT系统的MMD方法,通常被称为SEMMD。尽管前景充满希望,但大多数SEMMD方法遵循两步图像分解流程,首先使用FBP等算法重建单色CT图像,然后对这些图像进行分解。然而,最初的重建步骤忽视了人体组织的能量依赖衰减,引入了严重的非线性束硬化伪影和噪声,影响后续的分解。本文提出了JSover,这是一个从根本上重新制定的一步式SEMMD框架,它联合重建多材料成分并直接从SECT投影估计能量光谱。通过显式地将物理信息光谱先验知识纳入SEMMD过程,JSover能够模拟从SE采集中的虚拟光谱CT系统,从而提高分解的可靠性和准确性。此外,我们引入了隐式神经表示(INR)作为一种无监督深度学习求解器,用于表示底层材料图。INR对连续图像模式的归纳偏见约束了解空间,进一步提高了估计质量。在模拟和真实CT数据集上的大量实验表明,JSover在准确性和计算效率上优于最先进的SEMMD方法。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 11 pages
Summary
本文介绍了多材料分解(MMD)在人体组织成分定量重建中的应用,并支持广泛的应用于临床。传统MMD需要光谱CT扫描仪和预测X射线能量光谱,限制了其在临床的适用性。为解决这个问题,研究者开发了一种使用常规CT系统的SEMMD方法。本文提出了一种名为JSover的一站式SEMMD框架,能够直接从SECT投影联合重建多材料成分并估计能量光谱。该框架通过融入物理光谱先验信息,模拟出虚拟光谱CT系统,提高了分解的可靠性和准确性。此外,引入隐式神经表示(INR)作为无监督深度学习求解器,用于表示基础材料图。实验证明,JSover在准确性和计算效率上优于现有SEMMD方法。
Key Takeaways
- MMD技术用于人体组织成分的定量重建,具有广泛的应用于临床的潜力。
- 传统MMD方法需要光谱CT扫描仪和预测X射线能量光谱,限制了其在临床的适用性。
- JSover是一种新型的SEMMD框架,能在一步内直接从SECT投影进行多材料成分的重建和能量光谱的估计。
- JSover通过融入物理光谱先验信息,有效地模拟出虚拟光谱CT系统。
- 隐式神经表示(INR)被引入作为无监督深度学习求解器,用于表示基础材料图,提高了估计质量。
- JSover在准确性和计算效率上超越了现有的SEMMD方法。
点此查看论文截图

Probabilistic approach to longitudinal response prediction: application to radiomics from brain cancer imaging
Authors:Isabella Cama, Michele Piana, Cristina Campi, Sara Garbarino
Longitudinal imaging analysis tracks disease progression and treatment response over time, providing dynamic insights into treatment efficacy and disease evolution. Radiomic features extracted from medical imaging can support the study of disease progression and facilitate longitudinal prediction of clinical outcomes. This study presents a probabilistic model for longitudinal response prediction, integrating baseline features with intermediate follow-ups. The probabilistic nature of the model naturally allows to handle the instrinsic uncertainty of the longitudinal prediction of disease progression. We evaluate the proposed model against state-of-the-art disease progression models in both a synthetic scenario and using a brain cancer dataset. Results demonstrate that the approach is competitive against existing methods while uniquely accounting for uncertainty and controlling the growth of problem dimensionality, eliminating the need for data from intermediate follow-ups.
纵向成像分析可以追踪疾病的进展和治疗效果随时间的变化,为治疗效果和疾病演变提供动态见解。从医学图像中提取的放射学特征可以支持对疾病进展的研究,并促进对临床结果的纵向预测。本研究提出了一种基于概率的纵向反应预测模型,该模型将基线特征与中间随访结果相结合。该模型的概率性质自然地处理了疾病进展纵向预测的内在不确定性。我们在合成场景和脑癌数据集上对所提出的模型进行了评估,结果表明该方法与现有方法相比具有竞争力,同时独特地考虑了不确定性并控制了问题维度的增长,从而无需中间随访数据。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 21 pages, 5 figures
Summary
纵向成像分析能随时间追踪疾病进展和治疗效果,为治疗效果和疾病演变提供动态见解。从医学影像中提取的放射组学特征有助于研究疾病进展,并促进对临床结果的纵向预测。本研究提出了一种基于概率的纵向反应预测模型,该模型将基线特征与中间随访相结合。该模型的概率性自然地处理了疾病进展纵向预测的内在不确定性。我们在合成场景和脑癌数据集中评估了所提出的模型。结果表明,该方法在应对不确定性及控制问题维度增长方面具有竞争力,且无需中间随访数据。
Key Takeaways
- 纵向成像分析能追踪疾病进展和治疗效果。
- 医学影像中的放射组学特征有助于研究疾病进展。
- 提出的基于概率的纵向反应预测模型结合了基线特征与中间随访。
- 该模型能处理疾病进展预测中的内在不确定性。
- 评估显示,该模型在竞争性与处理不确定性方面表现优秀。
- 模型能有效控制问题维度的增长。
点此查看论文截图

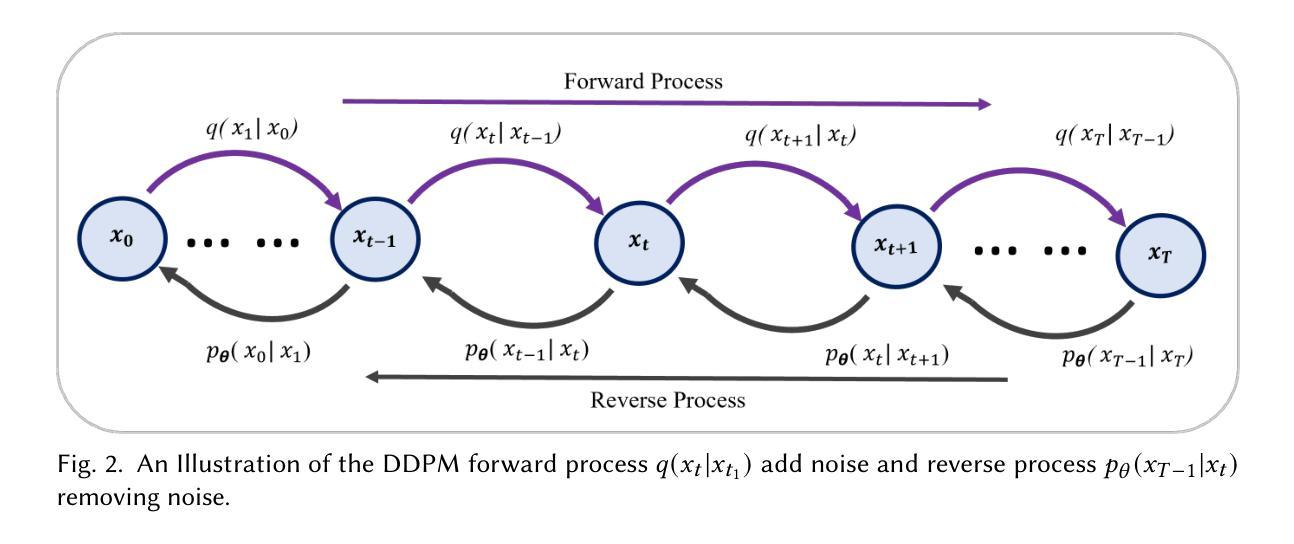
Computationally Efficient Diffusion Models in Medical Imaging: A Comprehensive Review
Authors: Abdullah, Tao Huang, Ickjai Lee, Euijoon Ahn
The diffusion model has recently emerged as a potent approach in computer vision, demonstrating remarkable performances in the field of generative artificial intelligence. Capable of producing high-quality synthetic images, diffusion models have been successfully applied across a range of applications. However, a significant challenge remains with the high computational cost associated with training and generating these models. This study focuses on the efficiency and inference time of diffusion-based generative models, highlighting their applications in both natural and medical imaging. We present the most recent advances in diffusion models by categorizing them into three key models: the Denoising Diffusion Probabilistic Model (DDPM), the Latent Diffusion Model (LDM), and the Wavelet Diffusion Model (WDM). These models play a crucial role in medical imaging, where producing fast, reliable, and high-quality medical images is essential for accurate analysis of abnormalities and disease diagnosis. We first investigate the general framework of DDPM, LDM, and WDM and discuss the computational complexity gap filled by these models in natural and medical imaging. We then discuss the current limitations of these models as well as the opportunities and future research directions in medical imaging.
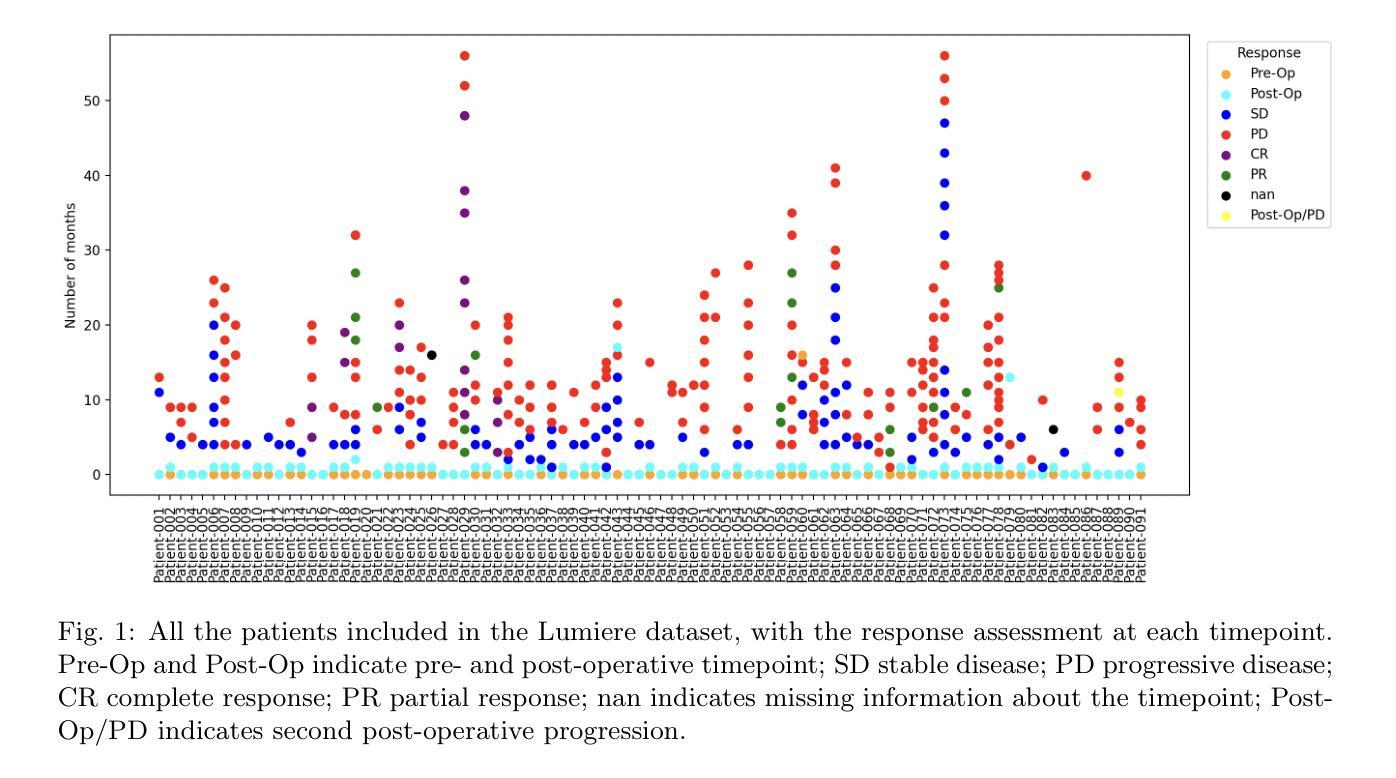
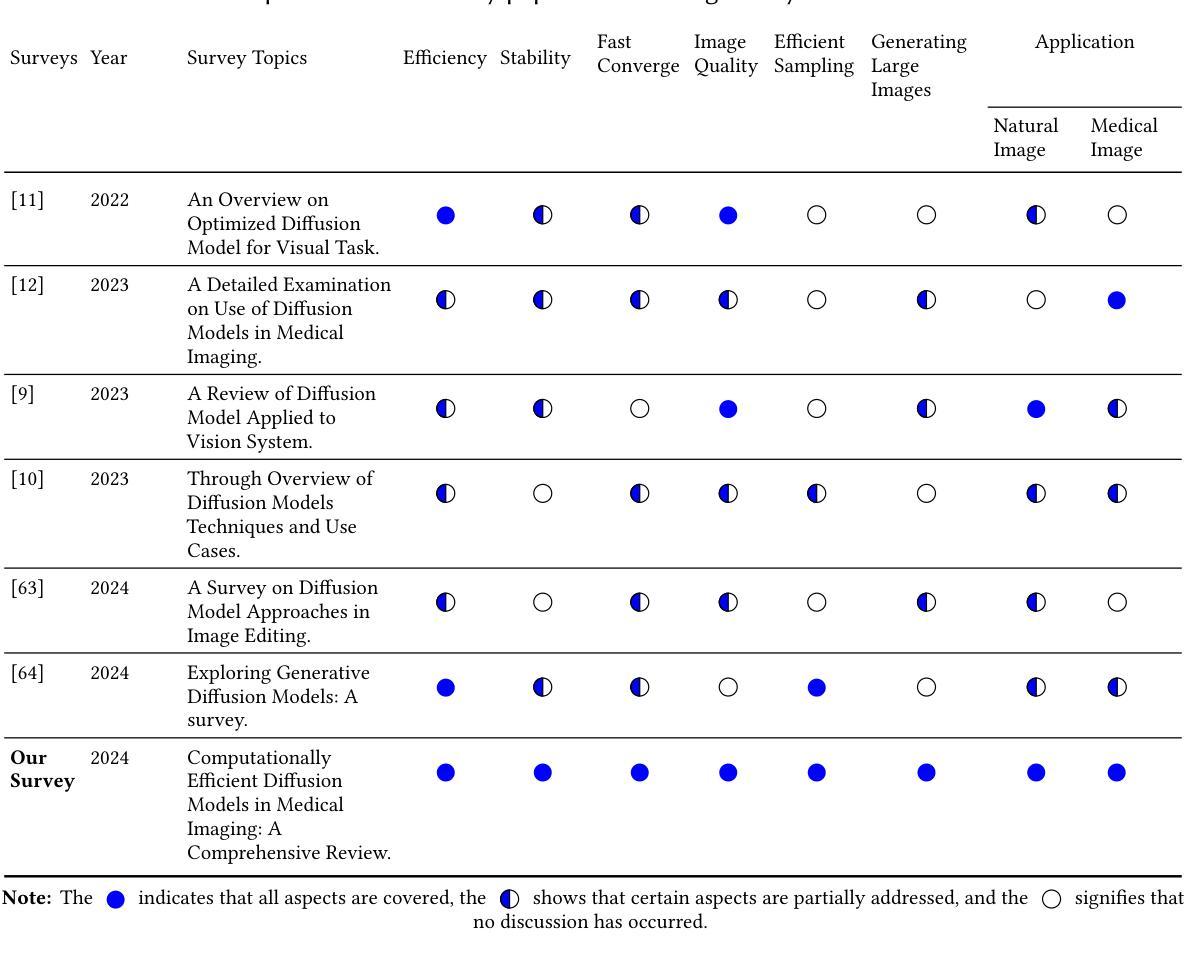
扩散模型最近作为计算机视觉中的一种强大方法而出现,在生成式人工智能领域表现出了显著的性能。扩散模型能够产生高质量的合成图像,并已成功应用于多种应用程序。然而,与训练和生成这些模型相关的高计算成本仍然是一个重大挑战。本研究重点关注基于扩散的生成模型的效率和推理时间,强调它们在自然和医学影像中的应用。我们通过将扩散模型分类为三个关键模型:去噪扩散概率模型(DDPM)、潜在扩散模型(LDM)和小波扩散模型(WDM),来介绍其最新进展。这些模型在医学影像中发挥着关键作用,其中快速、可靠、高质量的医学影像对于异常分析和疾病诊断至关重要。我们首先研究DDPM、LDM和WDM的一般框架,并讨论这些模型在自然和医学影像中填补的计算复杂性差距。然后,我们讨论了这些模型的当前局限性以及未来在医学影像中的机遇和研究方向。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF pages 36, 6 figures
Summary
扩散模型在计算机视觉领域崭露头角,尤其在生成式人工智能领域表现突出。其能生成高质量合成图像,并成功应用于多个领域。然而,训练与生成模型的计算成本高昂仍是重大挑战。本研究关注扩散式生成模型的效率与推理时间,并强调其在自然与医学影像中的应用。将扩散模型分为三大关键模型:去噪扩散概率模型(DDPM)、潜在扩散模型(LDM)和小波扩散模型(WDM)。这些模型在医学影像中扮演关键角色,能快速、可靠、高质量生成医疗图像,对异常分析与疾病诊断至关重要。研究首先探讨DDPM、LDM和WDM的一般框架及其在影像领域的计算复杂度差距,接着讨论当前模型的局限以及未来医学影像的研究机遇和方向。
Key Takeaways
- 扩散模型在计算机视觉领域表现突出,尤其在生成式人工智能方面。
- 扩散模型能生成高质量合成图像,并成功应用于多个领域,包括医学影像。
- 扩散模型面临计算成本高昂的挑战。
- 研究关注扩散模型的效率与推理时间。
- 扩散模型分为三大关键模型:DDPM、LDM和WDM。
- 这些模型在医学影像中具有重要应用,能快速生成高质量图像,有助于异常分析和疾病诊断。
点此查看论文截图

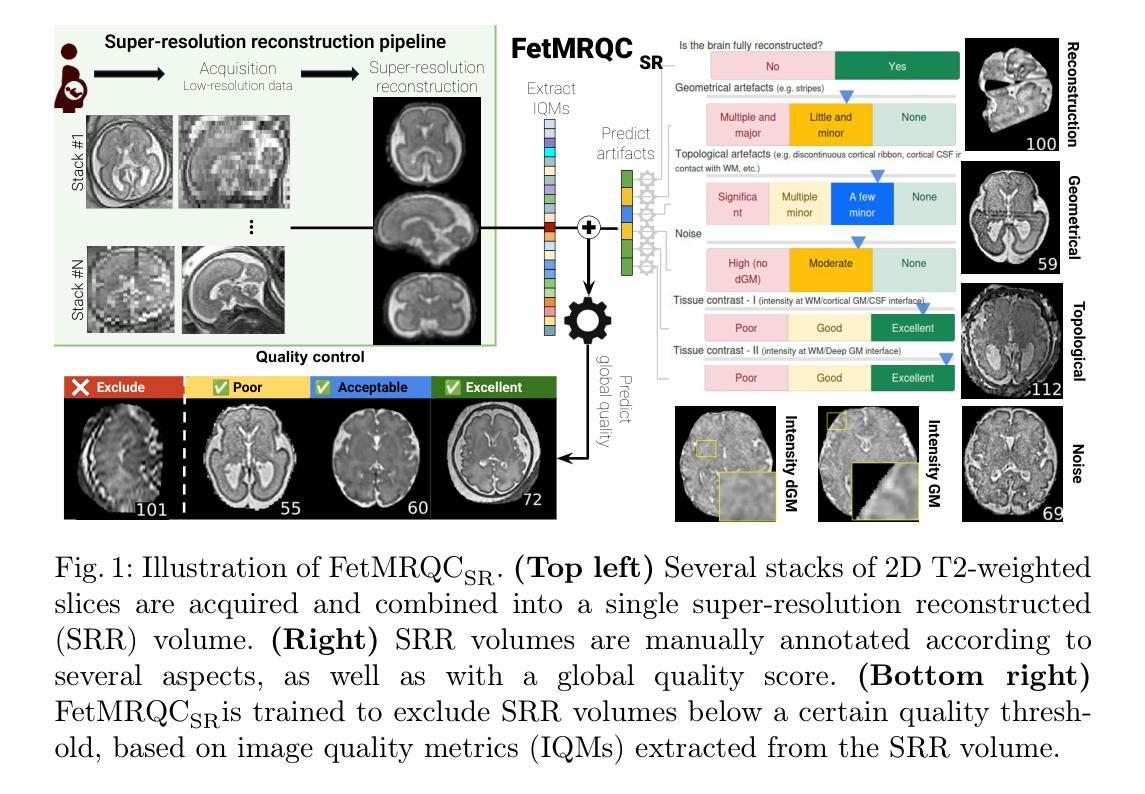
Automatic quality control in multi-centric fetal brain MRI super-resolution reconstruction
Authors:Thomas Sanchez, Vladyslav Zalevskyi, Angeline Mihailov, Gerard Martí-Juan, Elisenda Eixarch, Andras Jakab, Vincent Dunet, Mériam Koob, Guillaume Auzias, Meritxell Bach Cuadra
Quality control (QC) has long been considered essential to guarantee the reliability of neuroimaging studies. It is particularly important for fetal brain MRI, where acquisitions and image processing techniques are less standardized than in adult imaging. In this work, we focus on automated quality control of super-resolution reconstruction (SRR) volumes of fetal brain MRI, an important processing step where multiple stacks of thick 2D slices are registered together and combined to build a single, isotropic and artifact-free T2 weighted volume. We propose FetMRQC${SR}$, a machine-learning method that extracts more than 100 image quality metrics to predict image quality scores using a random forest model. This approach is well suited to a problem that is high dimensional, with highly heterogeneous data and small datasets. We validate FetMRQC${SR}$ in an out-of-domain (OOD) setting and report high performance (ROC AUC = 0.89), even when faced with data from an unknown site or SRR method. We also investigate failure cases and show that they occur in $45%$ of the images due to ambiguous configurations for which the rating from the expert is arguable. These results are encouraging and illustrate how a non deep learning-based method like FetMRQC$_{SR}$ is well suited to this multifaceted problem. Our tool, along with all the code used to generate, train and evaluate the model are available at https://github.com/Medical-Image-Analysis-Laboratory/fetmrqc_sr/ .
质量控制(QC)对于神经影像学研究的可靠性至关重要,这一点长期以来备受关注。对于胎儿脑部MRI(磁共振成像)而言尤其如此,因为与成人成像相比,胎儿脑部MRI的采集和图像处理技术标准化程度较低。在这项工作中,我们专注于胎儿脑部MRI的超分辨率重建(SRR)体积的自动质量控制。这是一个重要的处理步骤,需要将多个厚的二维切片堆叠起来,并组合成一个单一的、各向同性的、无伪影的T2加权体积。我们提出了一种名为FetMRQC_{SR}的机器学习方法,该方法提取了超过100项图像质量指标,并使用随机森林模型预测图像质量评分。这种方法非常适合高维、数据高度异质且数据集较小的问题。我们在域外(OOD)环境中验证了FetMRQC_{SR},并报告了出色的性能(ROC AUC = 0.89),即使在面对来自未知站点或SRR方法的数据时也是如此。我们还调查了失败的情况,并表明这些失败发生在45%的图像中,是由于模糊配置导致的,专家对此的评分具有争议。这些结果令人鼓舞,并说明了像FetMRQC_{SR}这样的非深度学习方法如何适应这种多面问题。我们的工具以及用于生成、训练和评估模型的所有代码均可在https://github.com/Medical-Image-Analysis-Laboratory/fetmrqc_sr/找到。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 11 pages, 3 figures
摘要
本文关注胎儿脑部MRI的超分辨率重建(SRR)体积的自动化质量控制。提出一种名为FetMRQC_{SR}的机器学习方法,通过提取超过100个图像质量指标,使用随机森林模型预测图像质量分数。该方法适用于高维、数据高度异质且数据集较小的问题。在领域外(OOD)环境下验证了FetMRQC_{SR}的性能,即使面对来自未知站点或SRR方法的数据,也表现出高性能(ROC AUC = 0.89)。调查失败案例发现,45%的图像由于模糊配置导致专家评分有争议。结果鼓励人心,说明非深度学习方法如FetMRQC_{SR}适合这种多面问题。相关工具和代码可在https://github.com/Medical-Image-Analysis-Laboratory/fetmrqc_sr/获取。
要点
- 本研究关注胎儿脑部MRI的超分辨率重建(SRR)的质量控制。
- 提出一种机器学习方法FetMRQC_{SR},通过提取超过100个图像质量指标预测图像质量分数。
- 该方法适应于高维、数据高度异质且数据集小的场景。
- 在领域外环境下验证了FetMRQC_{SR}的高性能。
- 45%的图像质量评分存在争议,主要由于图像模糊配置导致。
- 非深度学习方法如FetMRQC_{SR}适合解决此类多面问题。
点此查看论文截图

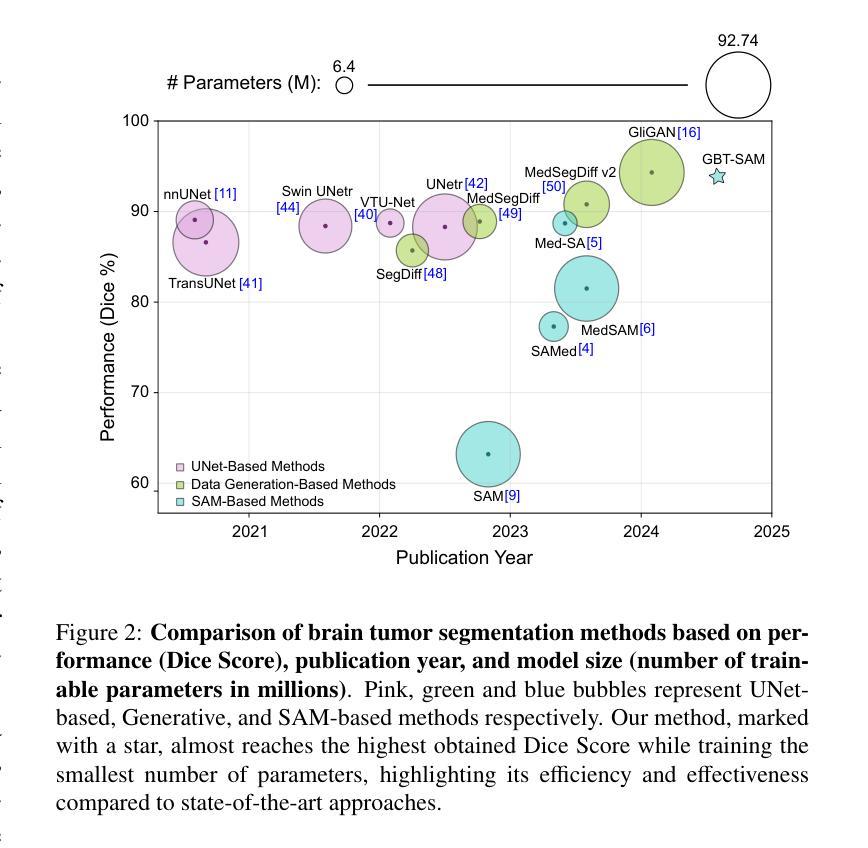
GBT-SAM: Adapting a Foundational Deep Learning Model for Generalizable Brain Tumor Segmentation via Efficient Integration of Multi-Parametric MRI Data
Authors:Cecilia Diana-Albelda, Roberto Alcover-Couso, Álvaro García-Martín, Jesus Bescos, Marcos Escudero-Viñolo
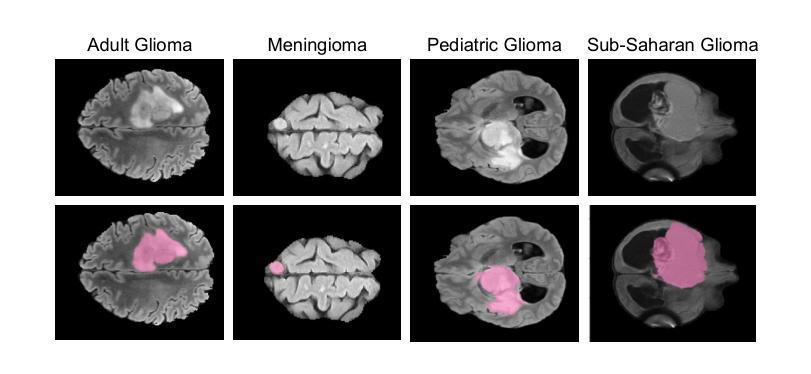
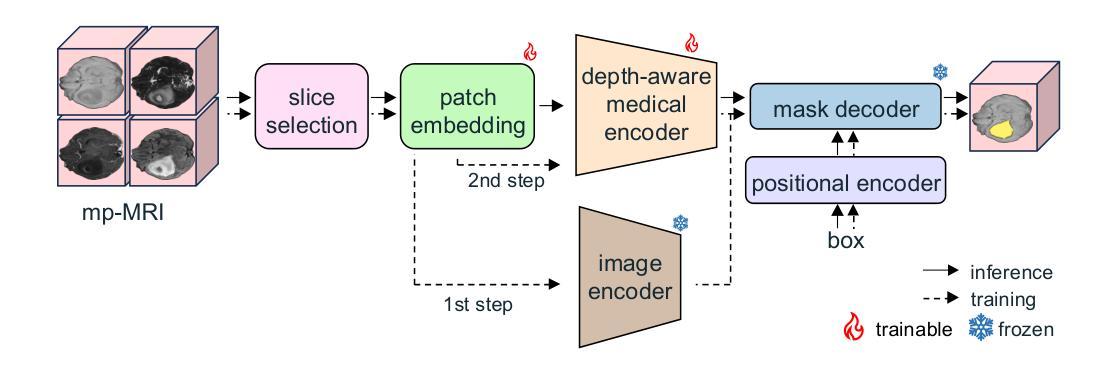
Gliomas are aggressive brain tumors that require accurate imaging-based diagnosis, with segmentation playing a critical role in evaluating morphology and treatment decisions. Manual delineation of gliomas is time-consuming and prone to variability, motivating the use of deep learning to improve consistency and alleviate clinical workload. However, existing methods often fail to fully exploit the information available in multi-parametric MRI (mp-MRI), particularly inter-slice contextual features, and typically require considerable computational resources while lacking robustness across tumor type variations. We present GBT-SAM, a parameter-efficient deep learning framework that adapts the Segment Anything Model (SAM), a large-scale vision model, to volumetric mp-MRI data. GBT-SAM reduces input complexity by selecting fewer than 2.6% of slices per scan while incorporating all four MRI modalities, preserving essential tumor-related information with minimal cost. Furthermore, our model is trained by a two-step fine-tuning strategy that incorporates a depth-aware module to capture inter-slice correlations and lightweight adaptation layers, resulting in just 6.5M trainable parameters, which is the lowest among SAM-based approaches. GBT-SAM achieves a Dice Score of 93.54 on the BraTS Adult Glioma dataset and demonstrates robust performance on Meningioma, Pediatric Glioma, and Sub-Saharan Glioma datasets. These results highlight GBT-SAM’s potential as a computationally efficient and domain-robust framework for brain tumor segmentation using mp-MRI. Our code and models are available at https://github.com/vpulab/med-sam-brain .
胶质瘤是侵袭性的脑肿瘤,需要基于准确的成像进行诊断,其中分割在评估形态和治治疗决策中发挥着关键作用。手动描绘胶质瘤既耗时又容易产生偏差,因此促使使用深度学习来提高一致性并减轻临床工作量。然而,现有方法往往未能充分利用多参数MRI(mp-MRI)中的可用信息,尤其是切片间的上下文特征,并且通常需要大量的计算资源,而且在肿瘤类型变化方面缺乏稳健性。我们提出了GBT-SAM,这是一个高效的深度学习框架,它适应了大规模视觉模型的Segment Anything Model(SAM)到体积mp-MRI数据。GBT-SAM通过选择每扫描少于2.6%的切片来降低输入复杂性,同时结合所有四种MRI模式,以最低的成本保留与肿瘤相关的基本信息。此外,我们的模型通过两步微调策略进行训练,该策略结合了深度感知模块来捕获切片间的相关性以及轻量级适应层,使得可训练的参数仅为650万,是SAM方法中参数最少的一种。GBT-SAM在BraTS成人胶质瘤数据集上取得了93.54的Dice得分,并在脑膜瘤、儿童胶质瘤和撒哈拉以南胶质瘤数据集上表现出稳健的性能。这些结果突出了GBT-SAM作为使用mp-MRI进行脑肿瘤分割的计算高效且稳健的框架的潜力。我们的代码和模型可在https://github.com/vpulab/med-sam-brain上找到。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
该研究提出一种参数效率高的深度学习框架GBT-SAM,基于Segment Anything Model(SAM),应用于体积型多参数MRI(mp-MRI)数据。GBT-SAM减少扫描切片数量至每扫描少于2.6%,同时结合所有四种MRI模式,以最小的成本保留关键的肿瘤相关信息。通过两步微调策略和深度感知模块,GBT-SAM实现了在BraTS成人胶质瘤数据集上的Dice Score为93.54%,并在脑膜瘤、儿童胶质瘤和撒哈拉以南胶质瘤数据集上表现出稳健的性能。
Key Takeaways
1.Gliomas需要基于成像的精确诊断,分割在评估形态和治疗决策中起关键作用。
2.手动勾勒胶质瘤耗时且易出错,深度学习可改善一致性和减轻临床工作量。
3.现有方法未能充分利用多参数MRI(mp-MRI)的信息,特别是在切片间的上下文特征方面。
4.GBT-SAM是一个参数高效的深度学习框架,基于SAM模型应用于体积型mp-MRI数据。
5.GBT-SAM减少扫描切片数量,同时结合所有MRI模式以保留关键肿瘤信息。
6.GBT-SAM通过两步微调策略和深度感知模块实现高性能,在BraTS成人胶质瘤数据集上的Dice Score为93.54%。
点此查看论文截图

Ptychographic Image Reconstruction from Limited Data via Score-Based Diffusion Models with Physics-Guidance
Authors:Refik Mert Cam, Junjing Deng, Rajkumar Kettimuthu, Mathew J. Cherukara, Tekin Bicer
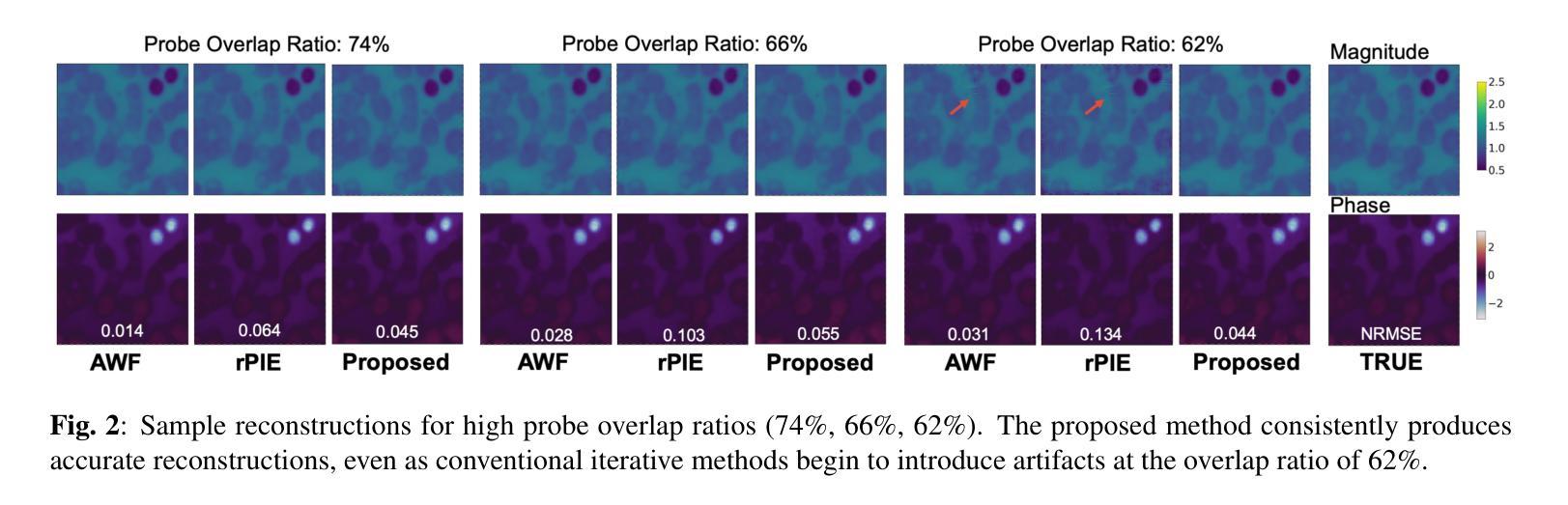
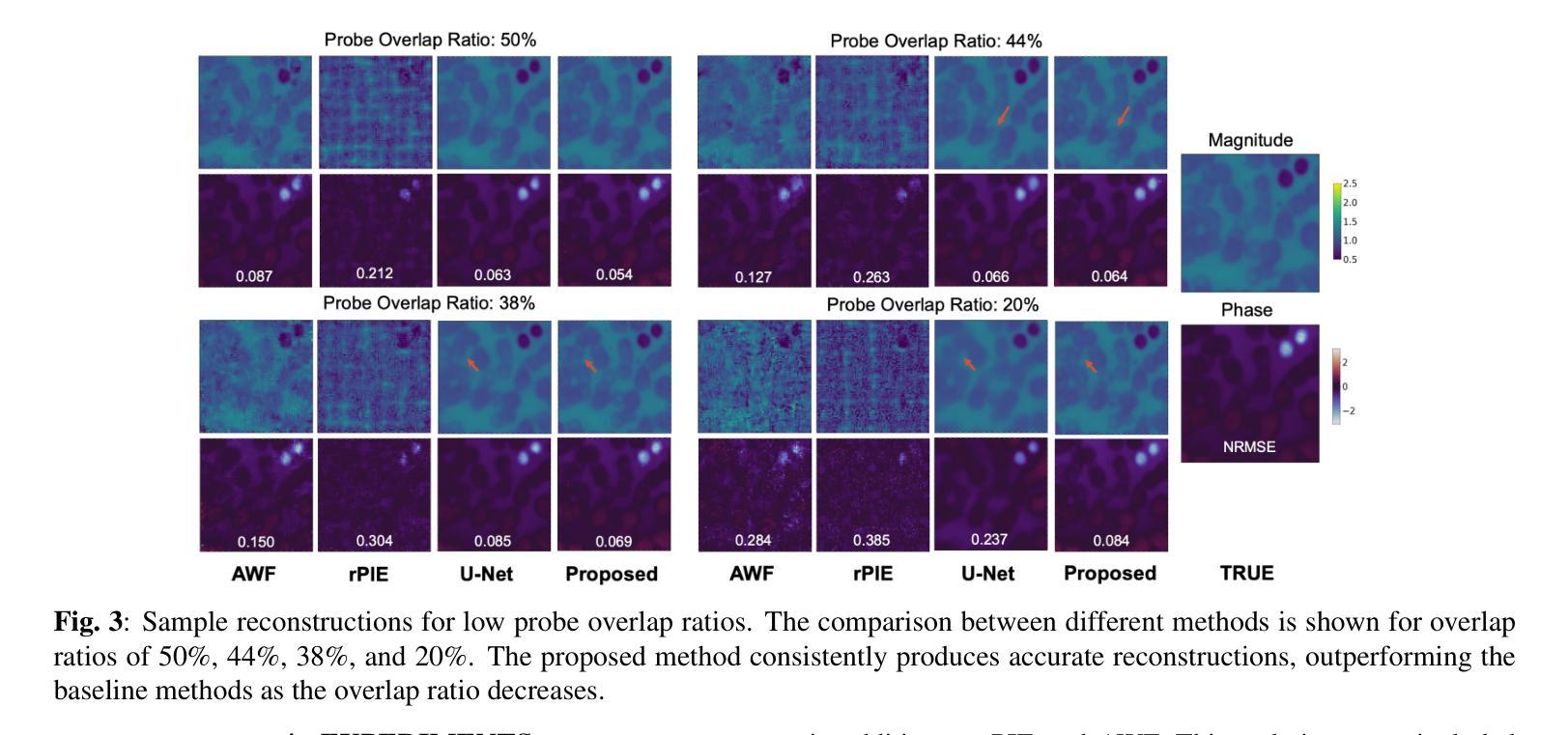
Ptychography is a data-intensive computational imaging technique that achieves high spatial resolution over large fields of view. The technique involves scanning a coherent beam across overlapping regions and recording diffraction patterns. Conventional reconstruction algorithms require substantial overlap, increasing data volume and experimental time, reaching PiB-scale experimental data and weeks to month-long data acquisition times. To address this, we propose a reconstruction method employing a physics-guided score-based diffusion model. Our approach trains a diffusion model on representative object images to learn an object distribution prior. During reconstruction, we modify the reverse diffusion process to enforce data consistency, guiding reverse diffusion toward a physically plausible solution. This method requires a single pretraining phase, allowing it to generalize across varying scan overlap ratios and positions. Our results demonstrate that the proposed method achieves high-fidelity reconstructions with only a 20% overlap, while the widely employed rPIE method requires a 62% overlap to achieve similar accuracy. This represents a significant reduction in data requirements, offering an alternative to conventional techniques.
Ptychography是一种数据密集型的计算成像技术,可以在大视野范围内实现高空间分辨率。该技术涉及在重叠区域扫描相干光束并记录衍射图案。传统的重建算法需要大量的重叠,这增加了数据量和实验时间,达到PiB规模的实验数据和长达数周至数月的数据采集时间。针对这一问题,我们提出了一种采用物理引导评分扩散模型的重建方法。我们的方法通过在具有代表性的对象图像上训练扩散模型来学习对象分布先验。在重建过程中,我们修改反向扩散过程以强制执行数据一致性,引导反向扩散朝着物理可行解进行。该方法仅需一个预训练阶段,可针对各种扫描重叠率和位置进行推广。我们的结果表明,所提出的方法在仅20%的重叠情况下实现了高保真度的重建,而广泛使用的rPIE方法则需要62%的重叠才能达到类似的准确性。这代表了数据需求的显著减少,为传统技术提供了替代方案。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Preprint submitted to IEEE MLSP 2025
Summary
基于物理模型的扩散模型在减少扫描重叠度的要求下实现了高效的Ptychography成像重建。通过训练扩散模型学习物体分布先验,利用反向扩散过程达到高保真重建的效果。与需要更高重叠度的传统技术相比,本文方法更加高效,大幅降低实验时间和数据量需求。
Key Takeaways
- Ptychography是一种计算成像技术,具有高空间分辨率和大视野的特点。
- 传统重建算法需要大量重叠区域,增加了实验时间和数据量需求。
- 基于物理模型的扩散模型被应用于Ptychography成像重建中。
- 训练扩散模型学习物体分布先验信息以优化重建过程。
- 修改反向扩散过程以实现数据一致性,向物理上合理的结果引导。
- 所提出的方法仅需要较低的重叠度(20%)即可实现高保真重建。
点此查看论文截图

Can open source large language models be used for tumor documentation in Germany? – An evaluation on urological doctors’ notes
Authors:Stefan Lenz, Arsenij Ustjanzew, Marco Jeray, Meike Ressing, Torsten Panholzer
Tumor documentation in Germany is largely done manually, requiring reading patient records and entering data into structured databases. Large language models (LLMs) could potentially enhance this process by improving efficiency and reliability. This evaluation tests eleven different open source LLMs with sizes ranging from 1-70 billion model parameters on three basic tasks of the tumor documentation process: identifying tumor diagnoses, assigning ICD-10 codes, and extracting the date of first diagnosis. For evaluating the LLMs on these tasks, a dataset of annotated text snippets based on anonymized doctors’ notes from urology was prepared. Different prompting strategies were used to investigate the effect of the number of examples in few-shot prompting and to explore the capabilities of the LLMs in general. The models Llama 3.1 8B, Mistral 7B, and Mistral NeMo 12 B performed comparably well in the tasks. Models with less extensive training data or having fewer than 7 billion parameters showed notably lower performance, while larger models did not display performance gains. Examples from a different medical domain than urology could also improve the outcome in few-shot prompting, which demonstrates the ability of LLMs to handle tasks needed for tumor documentation. Open source LLMs show a strong potential for automating tumor documentation. Models from 7-12 billion parameters could offer an optimal balance between performance and resource efficiency. With tailored fine-tuning and well-designed prompting, these models might become important tools for clinical documentation in the future. The code for the evaluation is available from https://github.com/stefan-m-lenz/UroLlmEval. We also release the dataset as a new valuable resource that addresses the shortage of authentic and easily accessible benchmarks in German-language medical NLP.
在德国,肿瘤记录工作大多以手动方式进行,需要阅读患者病历并将数据输入结构化数据库。大型语言模型(LLMs)有望通过提高效率可靠性增强这一过程。本次评估对三种肿瘤记录基本任务(识别肿瘤诊断、分配ICD-10代码和提取首次诊断日期)上,测试了规模在1亿至70亿模型参数之间的11种不同开源LLMs。为了评估这些LLMs在这些任务上的表现,我们准备了一份基于泌尿科匿名医生笔记的标注文本片段数据集。使用了不同的提示策略来探究少量提示中示例数量对LLMs能力的影响,并探索LLMs的一般能力。Llama 3.1 8B、Mistral 7B和Mistral NeMo 12B等模型在这些任务中表现良好。具有较少训练数据或参数少于7亿的模型表现明显较差,而大型模型并未显示出性能提升。来自不同于泌尿科的医学领域的例子也能在少量提示中改善结果,这证明了LLMs处理肿瘤记录所需任务的能力。开源LLMs在自动肿瘤记录方面显示出巨大潜力。具有7-12亿参数的模型可能在性能和资源效率之间提供最佳平衡。通过有针对性的微调和良好的提示设计,这些模型可能成为未来临床记录的重要工具。评估的代码可从https://github.com/stefan-m-lenz/UroLlmEval获取。我们还公开了数据集,作为解决德国医学NLP领域中真实、易于访问的基准测试资源短缺的新有价值资源。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 53 pages, 5 figures
Summary
本文本介绍了德国肿瘤记录的现状,以及大型语言模型(LLMs)在自动化肿瘤记录过程中的潜力。通过对11种不同规模(从1亿到70亿参数)的开源LLMs进行评价,发现它们在肿瘤诊断识别、ICD-10代码分配和首次诊断日期提取等任务中表现出良好的性能。模型参数在7-12亿之间的模型在性能和资源效率之间达到了平衡。通过精细调整和精心设计提示,这些模型有望在未来成为临床文档管理的重要工具。
Key Takeaways
- 肿瘤记录在德国主要依赖手动处理,需要阅读患者记录和将数据输入结构化数据库。
- 大型语言模型(LLMs)有潜力提高肿瘤记录的效率和可靠性。
- 在三项基本任务(识别肿瘤诊断、分配ICD-10代码和提取首次诊断日期)中评估了11种不同规模和类型的开源LLMs。
- Llama 3.1 8B、Mistral 7B和Mistral NeMo 12B等模型在这些任务中表现良好。
- 模型参数在7-12亿之间的模型在性能和资源效率之间达到平衡。
- 通过精细调整和精心设计提示,这些模型可以在未来的临床文档管理中发挥重要作用。
点此查看论文截图

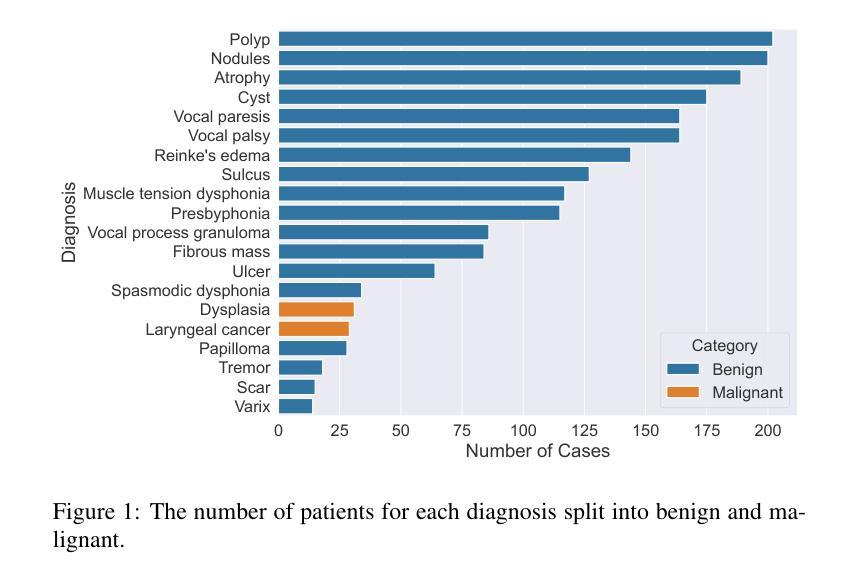
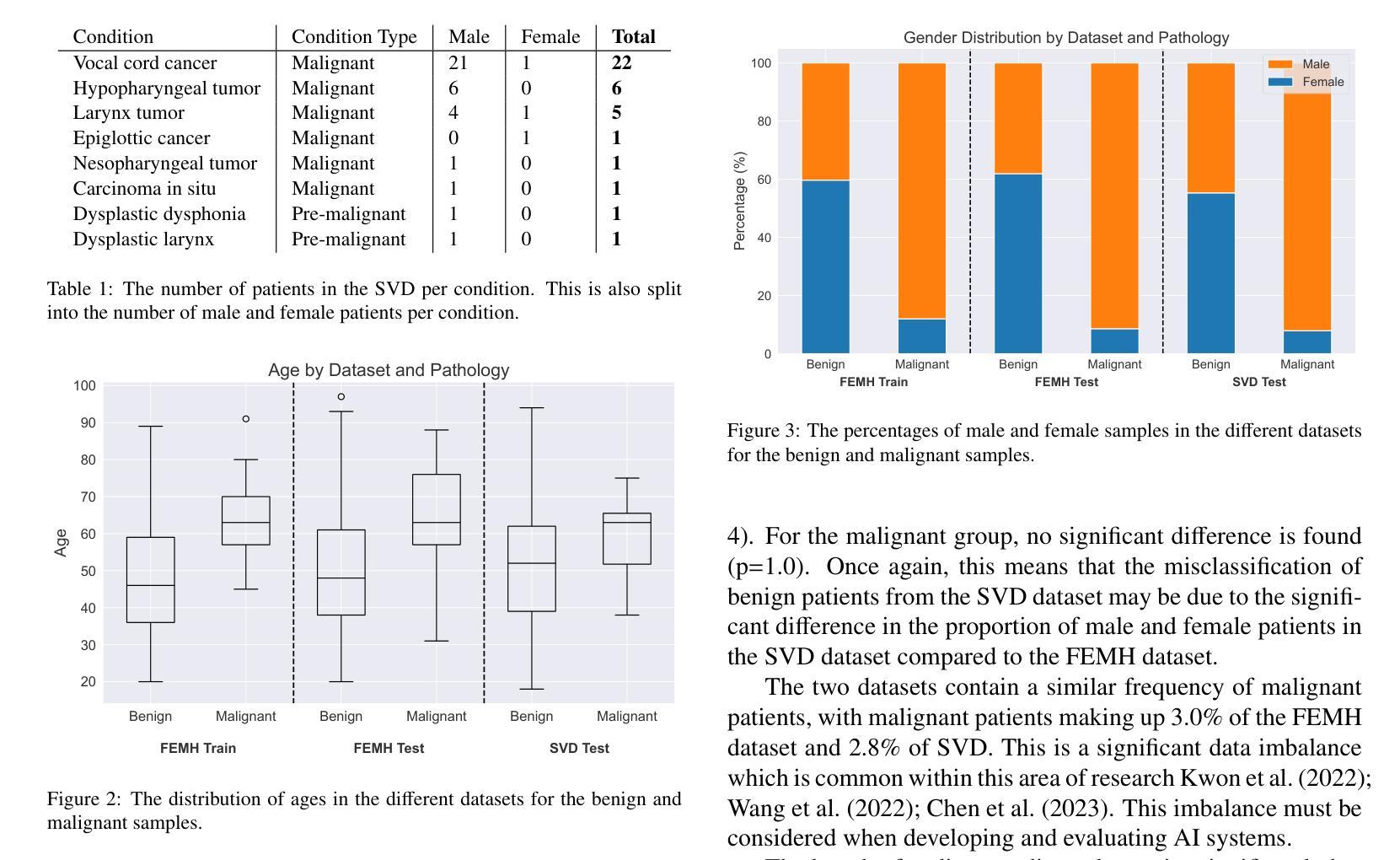
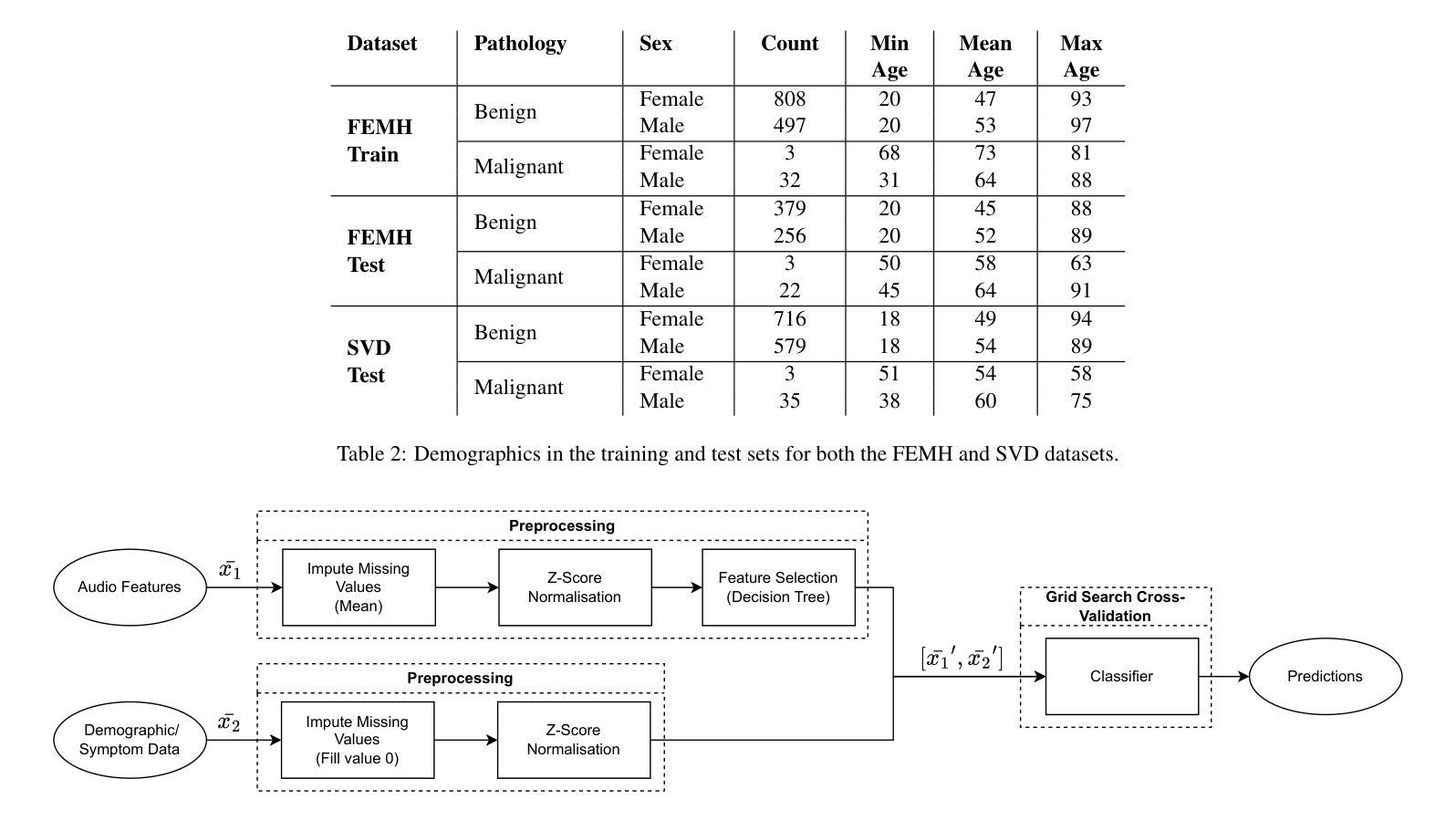
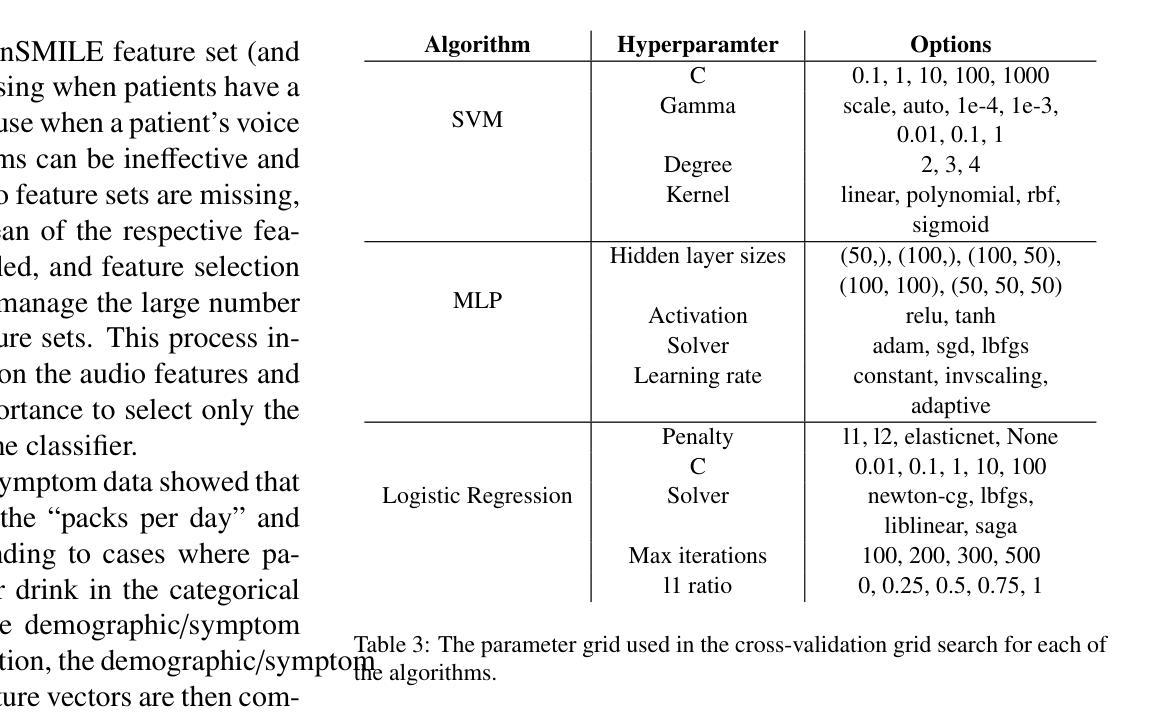
A Classification Benchmark for Artificial Intelligence Detection of Laryngeal Cancer from Patient Voice
Authors:Mary Paterson, James Moor, Luisa Cutillo
Cases of laryngeal cancer are predicted to rise significantly in the coming years. Current diagnostic pathways are inefficient, putting undue stress on both patients and the medical system. Artificial intelligence offers a promising solution by enabling non-invasive detection of laryngeal cancer from patient voice, which could help prioritise referrals more effectively. A major barrier in this field is the lack of reproducible methods. Our work addresses this challenge by introducing a benchmark suite comprising 36 models trained and evaluated on open-source datasets. These models classify patients with benign and malignant voice pathologies. All models are accessible in a public repository, providing a foundation for future research. We evaluate three algorithms and three audio feature sets, including both audio-only inputs and multimodal inputs incorporating demographic and symptom data. Our best model achieves a balanced accuracy of 83.7%, sensitivity of 84.0%, specificity of 83.3%, and AUROC of 91.8%.
喉癌病例预计将在未来几年显著增加。当前的诊断途径效率低下,给患者和医疗系统带来了不必要的压力。人工智能通过实现通过患者声音进行喉癌无创检测,为解决这一问题提供了有前景的解决方案,这有助于更有效地优先处理转诊事宜。该领域的一个主要障碍是缺乏可重复的方法。我们的工作通过引入一个包含36个模型的基准测试套件来解决这一挑战,这些模型在开源数据集上进行训练和评估。这些模型对良性或恶性语音病理患者进行分类。所有模型都可在公共存储库中访问,为未来研究提供了基础。我们评估了三种算法和三种音频特征集,包括仅使用音频输入和结合人口统计数据和症状数据的多媒体输入。我们的最佳模型实现了83.7%的平衡准确率、84.0%的灵敏度、83.3%的特异性和91.8%的AUROC值。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 16 pages, 6 figures, 10 tables
Summary
未来喉癌病例预计显著上升,当前诊断流程低效,给患者和医疗系统带来压力。人工智能可通过患者声音非侵入性检测喉癌,有效优化转诊优先级。本研究解决了领域内的重大挑战,即缺乏可重复的方法。我们推出了一套基准测试套件,包含36个在开源数据集上训练和评估的模型,用于分类良性和恶性语音病理患者。所有模型均可在公共仓库中访问,为未来的研究打下基础。我们评估了三种算法和三种音频特征集,包括仅音频输入和结合人口统计学和症状数据的多模式输入。最佳模型达到83.7%的平衡准确率,敏感度为84.0%,特异度为83.3%,AUROC为91.8%。
Key Takeaways
- 喉癌病例预计在未来几年显著上升。
- 当前诊断喉癌的方法存在效率问题。
- 人工智能为喉癌的非侵入性检测提供了解决方案。
- 公共仓库中提供了一套包含36个模型的基准测试套件。
- 这些模型用于分类良性和恶性语音病理患者。
- 最佳模型的准确率、敏感度和特异度表现良好。
点此查看论文截图

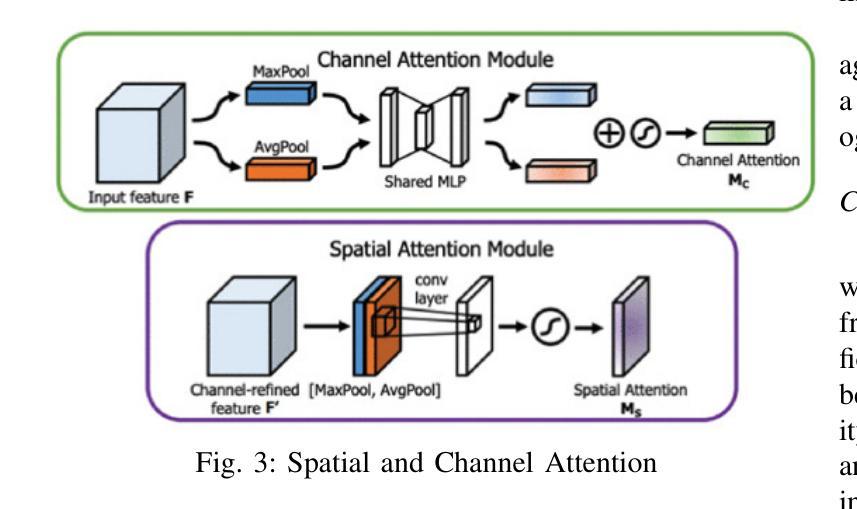
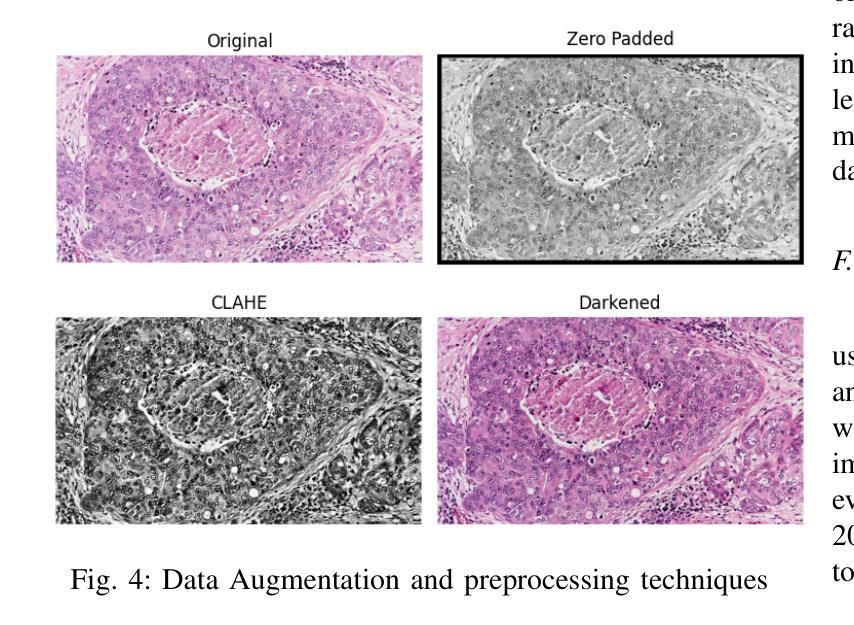
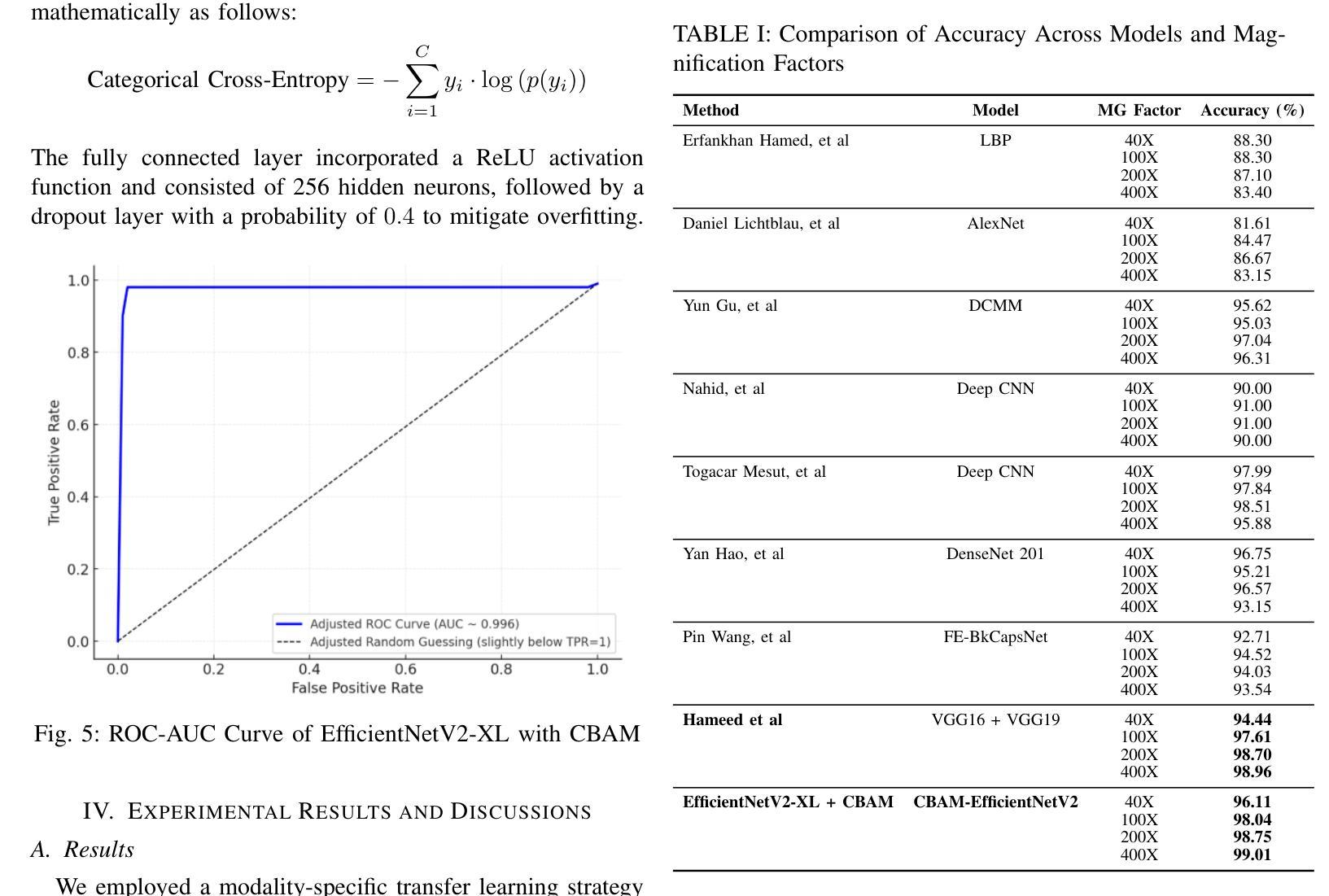
Breast Cancer Histopathology Classification using CBAM-EfficientNetV2 with Transfer Learning
Authors:Naren Sengodan
Breast cancer histopathology image classification is critical for early detection and improved patient outcomes. 1 This study introduces a novel approach leveraging EfficientNetV2 models, to improve feature extraction and focus on relevant tissue regions. The proposed models were evaluated on the BreakHis dataset across multiple magnification scales (40X, 100X, 200X, and 400X). 2 Among them, the EfficientNetV2-XL with CBAM achieved outstanding performance, reaching a peak accuracy of 99.01 percent and an F1-score of 98.31 percent at 400X magnification, outperforming state-of-the-art methods. 3 By integrating Contrast Limited Adaptive Histogram Equalization (CLAHE) for preprocessing and optimizing computational efficiency, this method demonstrates its suitability for real-time clinical deployment. 3 The results underscore the potential of attention-enhanced scalable architectures in advancing diagnostic precision for breast cancer detection.
乳腺癌组织病理学图像分类对早期检测和改善患者预后至关重要。本研究介绍了一种利用EfficientNetV2模型的新方法,以提高特征提取并关注相关组织区域。所提出的模型在BreakHis数据集上的多个放大倍数(40X、100X、200X和400X)上进行了评估。其中,带有CBAM的EfficientNetV2-XL表现突出,在400X放大倍数下达到了99.01%的峰值准确率和98.31%的F1分数,超过了最先进的方法。通过集成对比度受限自适应直方图均衡化(CLAHE)进行预处理并优化计算效率,该方法显示出适用于实时临床部署的适用性。结果强调了注意力增强可扩展架构在提高乳腺癌检测诊断精度方面的潜力。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了一种利用EfficientNetV2模型进行乳腺癌组织病理学图像分类的新方法,该方法在BreakHis数据集上进行了多尺度评估,表现出优异的性能。通过结合CLAHE预处理技术和优化计算效率,该方法适合实时临床部署,有望提高乳腺癌诊断的精确度。
Key Takeaways
- EfficientNetV2模型被用于乳腺癌组织病理学图像分类,以提高特征提取和关注相关组织区域。
- 在BreakHis数据集上,EfficientNetV2-XL与CBAM结合的方法表现出最佳性能。
- 该方法在400X放大率下达到99.01%的准确率和98.31%的F1分数,优于现有先进方法。
- 通过结合CLAHE进行预处理和优化计算效率,该方法适合实时临床部署。
- 该研究强调了注意增强型可扩展架构在改进乳腺癌检测诊断精度方面的潜力。
- 该方法有助于提高乳腺癌的早期检测率,进而改善患者的预后。
点此查看论文截图

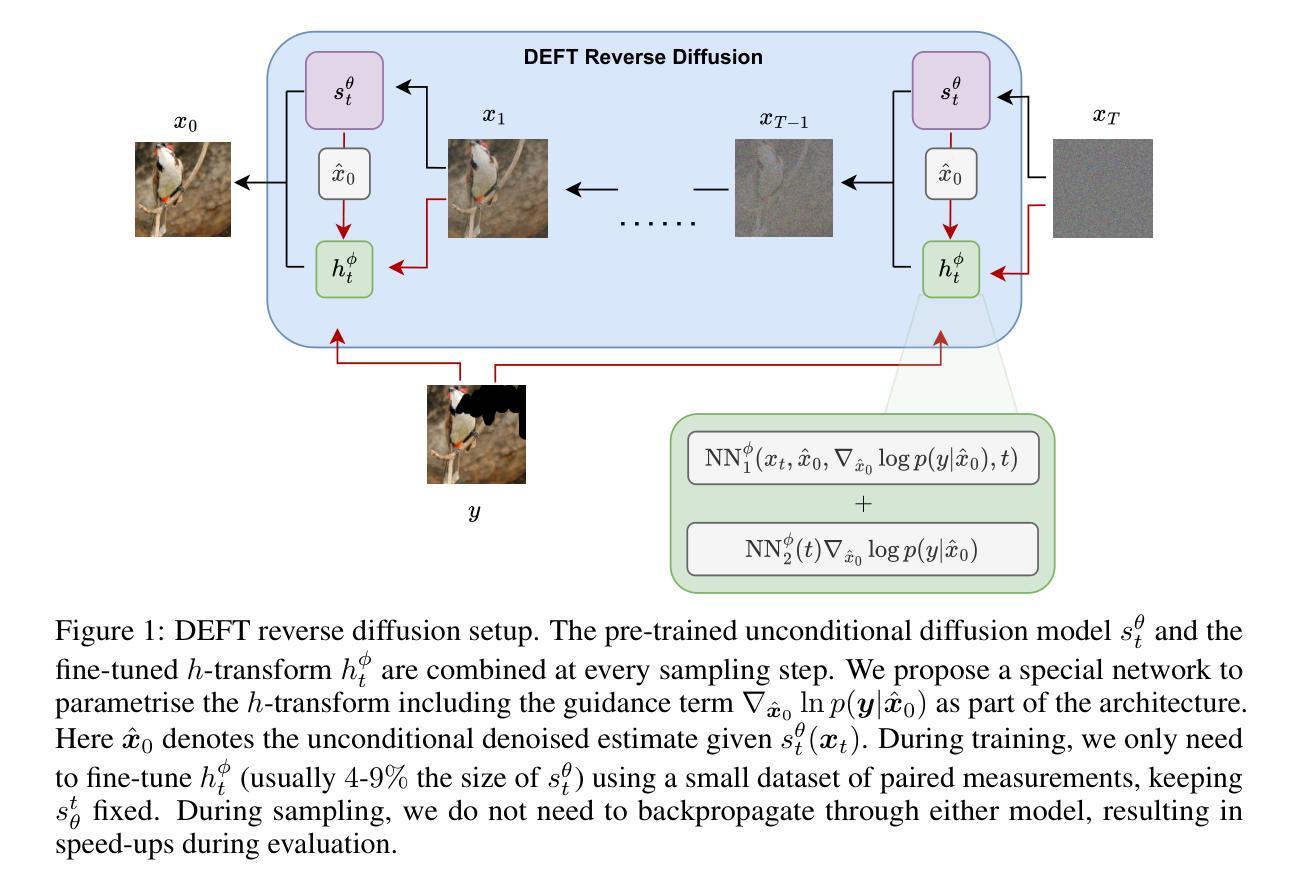
DEFT: Efficient Fine-Tuning of Diffusion Models by Learning the Generalised $h$-transform
Authors:Alexander Denker, Francisco Vargas, Shreyas Padhy, Kieran Didi, Simon Mathis, Vincent Dutordoir, Riccardo Barbano, Emile Mathieu, Urszula Julia Komorowska, Pietro Lio
Generative modelling paradigms based on denoising diffusion processes have emerged as a leading candidate for conditional sampling in inverse problems. In many real-world applications, we often have access to large, expensively trained unconditional diffusion models, which we aim to exploit for improving conditional sampling. Most recent approaches are motivated heuristically and lack a unifying framework, obscuring connections between them. Further, they often suffer from issues such as being very sensitive to hyperparameters, being expensive to train or needing access to weights hidden behind a closed API. In this work, we unify conditional training and sampling using the mathematically well-understood Doob’s h-transform. This new perspective allows us to unify many existing methods under a common umbrella. Under this framework, we propose DEFT (Doob’s h-transform Efficient FineTuning), a new approach for conditional generation that simply fine-tunes a very small network to quickly learn the conditional $h$-transform, while keeping the larger unconditional network unchanged. DEFT is much faster than existing baselines while achieving state-of-the-art performance across a variety of linear and non-linear benchmarks. On image reconstruction tasks, we achieve speedups of up to 1.6$\times$, while having the best perceptual quality on natural images and reconstruction performance on medical images. Further, we also provide initial experiments on protein motif scaffolding and outperform reconstruction guidance methods.
基于去噪扩散过程的生成建模范式已成为逆问题中条件采样的领先候选方法。在许多实际应用中,我们常常能够访问大型且训练成本高昂的无条件扩散模型,我们旨在利用这些模型来改善条件采样。虽然最近的方法大多受到启发并缺乏统一框架的推动,导致它们之间的联系变得模糊。此外,它们经常面临诸如对超参数非常敏感、训练成本高昂或需要访问隐藏在封闭API之后的权重等问题。在这项工作中,我们使用数学上理解良好的Doob的h变换来统一条件训练和采样。这个新视角允许我们在一个通用框架下统一许多现有方法。在该框架下,我们提出了DEFT(Doob的h变换高效微调),这是一种新的条件生成方法,它只需微调一个非常小的网络来快速学习条件h变换,同时保持较大的无条件网络不变。DEFT相较于现有基准测试速度更快,同时在各种线性和非线性基准测试中实现了卓越的性能。在图像重建任务上,我们实现了高达1.6倍的速度提升,同时在自然图像上具有最佳的感知质量和在医学图像上的重建性能。此外,我们还对蛋白质动机脚手架进行了初步实验并超越了重建指导方法。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF arXiv admin note: text overlap with arXiv:2312.09236
Summary
基于去噪扩散过程的生成建模范式已成为解决反问题中条件采样的领先候选方法。本文利用数学上理解良好的Doob的h-变换统一了条件训练和采样。在此框架下,提出了一种新的条件生成方法DEFT(Doob的h-变换高效微调),它只需微调一个非常小的网络即可快速学习条件h-变换,同时保持较大的无条件网络不变。DEFT在多种线性和非线性基准测试上实现了最先进的性能,并在图像重建任务上实现了最高达1.6倍的加速,同时在自然图像上具有最佳的感知质量和医学图像的重建性能。
Key Takeaways
- 生成建模范式在解决反问题的条件采样方面表现出色。
- 基于去噪扩散过程的模型在许多真实世界应用中用于改善条件采样。
- 现有方法缺乏统一框架,且经常面临超参数敏感、训练成本高或依赖封闭API等问题。
- Doob的h-变换提供了一个新的视角来统一条件训练和采样。
- DEFT(Doob的h-变换高效微调)是一种新的条件生成方法,它通过微调小网络快速学习条件h-变换,同时保持大网络不变。
- DEFT在图像重建任务上实现了显著的速度提升和先进的性能。
点此查看论文截图

How to build the best medical image segmentation algorithm using foundation models: a comprehensive empirical study with Segment Anything Model
Authors:Hanxue Gu, Haoyu Dong, Jichen Yang, Maciej A. Mazurowski
Automated segmentation is a fundamental medical image analysis task, which enjoys significant advances due to the advent of deep learning. While foundation models have been useful in natural language processing and some vision tasks for some time, the foundation model developed with image segmentation in mind - Segment Anything Model (SAM) - has been developed only recently and has shown similar promise. However, there are still no systematic analyses or “best-practice” guidelines for optimal fine-tuning of SAM for medical image segmentation. This work summarizes existing fine-tuning strategies with various backbone architectures, model components, and fine-tuning algorithms across 18 combinations, and evaluates them on 17 datasets covering all common radiology modalities. Our study reveals that (1) fine-tuning SAM leads to slightly better performance than previous segmentation methods, (2) fine-tuning strategies that use parameter-efficient learning in both the encoder and decoder are superior to other strategies, (3) network architecture has a small impact on final performance, (4) further training SAM with self-supervised learning can improve final model performance. We also demonstrate the ineffectiveness of some methods popular in the literature and further expand our experiments into few-shot and prompt-based settings. Lastly, we released our code and MRI-specific fine-tuned weights, which consistently obtained superior performance over the original SAM, at https://github.com/mazurowski-lab/finetune-SAM.
自动分割是医学图像分析中的一项基本任务,随着深度学习的出现,它取得了显著的进展。虽然基础模型在自然语言处理和某些视觉任务中已有一段时间的应用,但以图像分割为中心开发的基础模型——任意分割模型(SAM)的开发却是在最近才完成,并显示出巨大的潜力。然而,对于SAM在医学图像分割中的最佳微调,仍然没有系统的分析或“最佳实践”指南。这项工作总结了使用各种主干架构、模型组件和微调算法的现有微调策略,共涉及18种组合,并在涵盖所有常见放射学模态的17个数据集上进行了评估。我们的研究表明:(1)对SAM进行微调略优于以前的分割方法;(2)在编码器和解码器中都使用参数有效学习的微调策略优于其他策略;(3)网络架构对最终性能的影响很小;(4)使用自监督学习进一步训练SAM可以提高最终模型性能。我们还证明了文献中一些流行方法的无效性,并将我们的实验进一步扩展到小样本文本和基于提示的设置中。最后,我们在https://github.com/mazurowski-lab/finetune-SAM上发布了我们的代码和针对MRI的特定微调权重,这些权重在原始SAM上始终获得了优越的性能。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted for publication at the Journal of Machine Learning for Biomedical Imaging (MELBA)
Summary
基于深度学习的自动化分割是医学图像分析的基本任务之一。新开发的针对图像分割的foundation模型Segment Anything Model(SAM)显示出巨大的潜力,但目前仍缺乏针对SAM优化微调的系统分析和最佳实践指南。本研究总结了使用不同骨干架构、模型组件和微调算法的现有微调策略,并在涵盖所有常见放射学模态的17个数据集上进行了评估。研究发现,微调SAM略优于以前的方法,使用参数有效学习的微调策略优于其他策略,网络架构对最终性能的影响较小,而使用自监督学习进一步训练SAM可以提高最终模型性能。
Key Takeaways
- 微调SAM在医学图像分割上的性能略优于前期方法。
- 使用参数有效学习的微调策略,在编码器和解码器中都表现出优越性。
- 网络架构对最终性能的影响较小。
- 通过自监督学习进一步训练SAM,可以提高最终模型性能。
- 研究证实了部分文献中流行的方法并不有效。
- 实验进一步扩展到了小样本和基于提示的设置。
点此查看论文截图

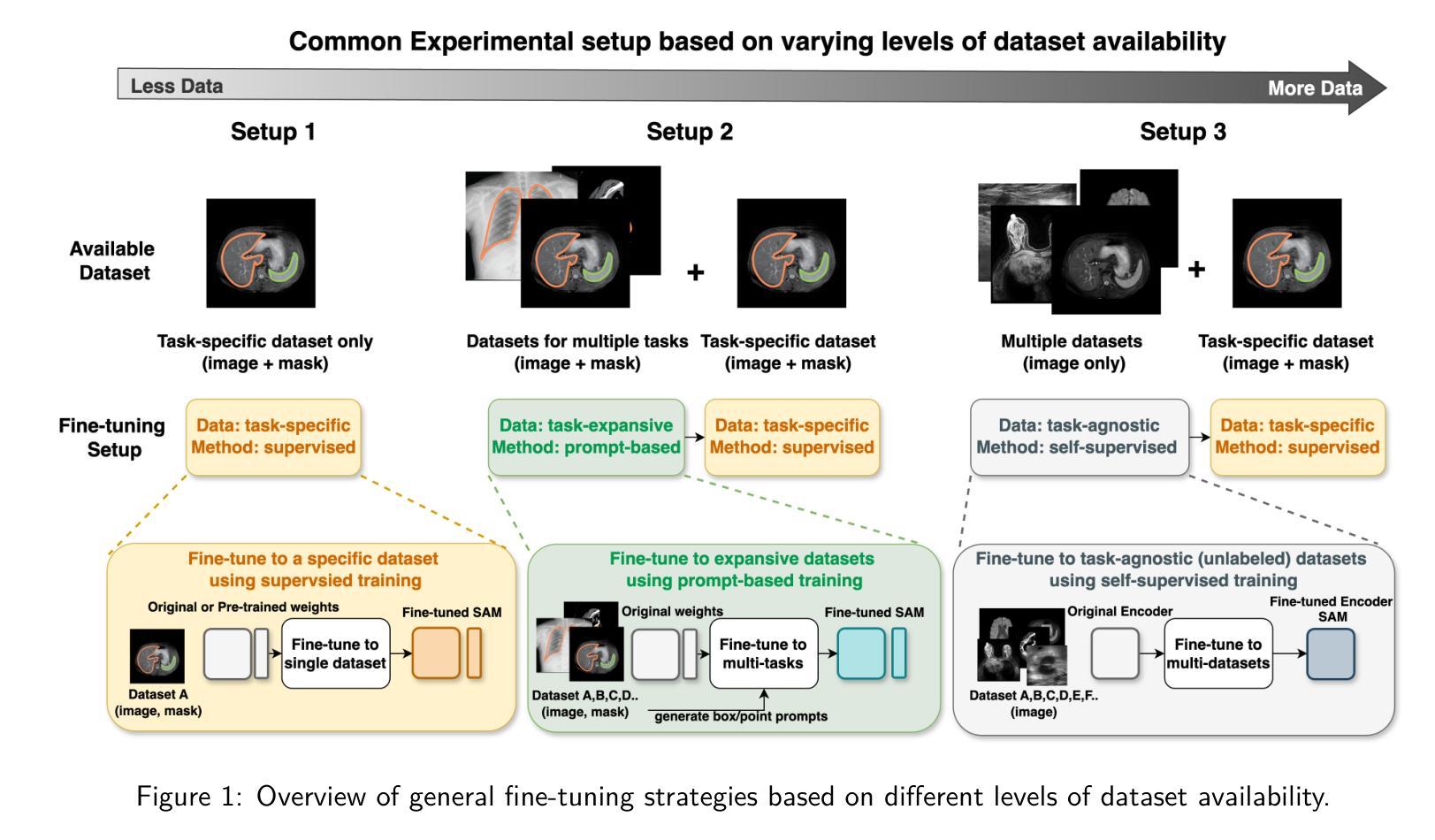
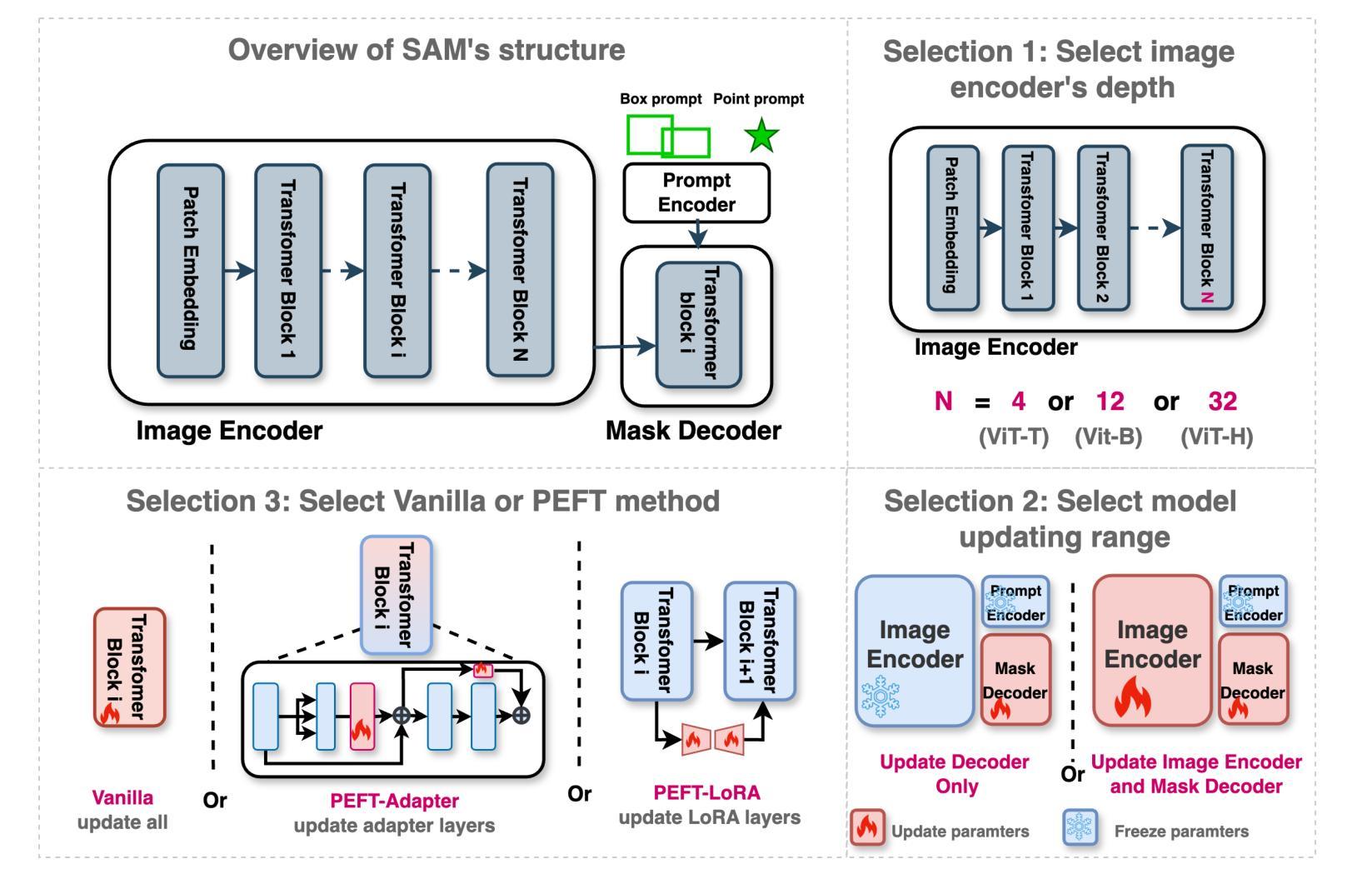
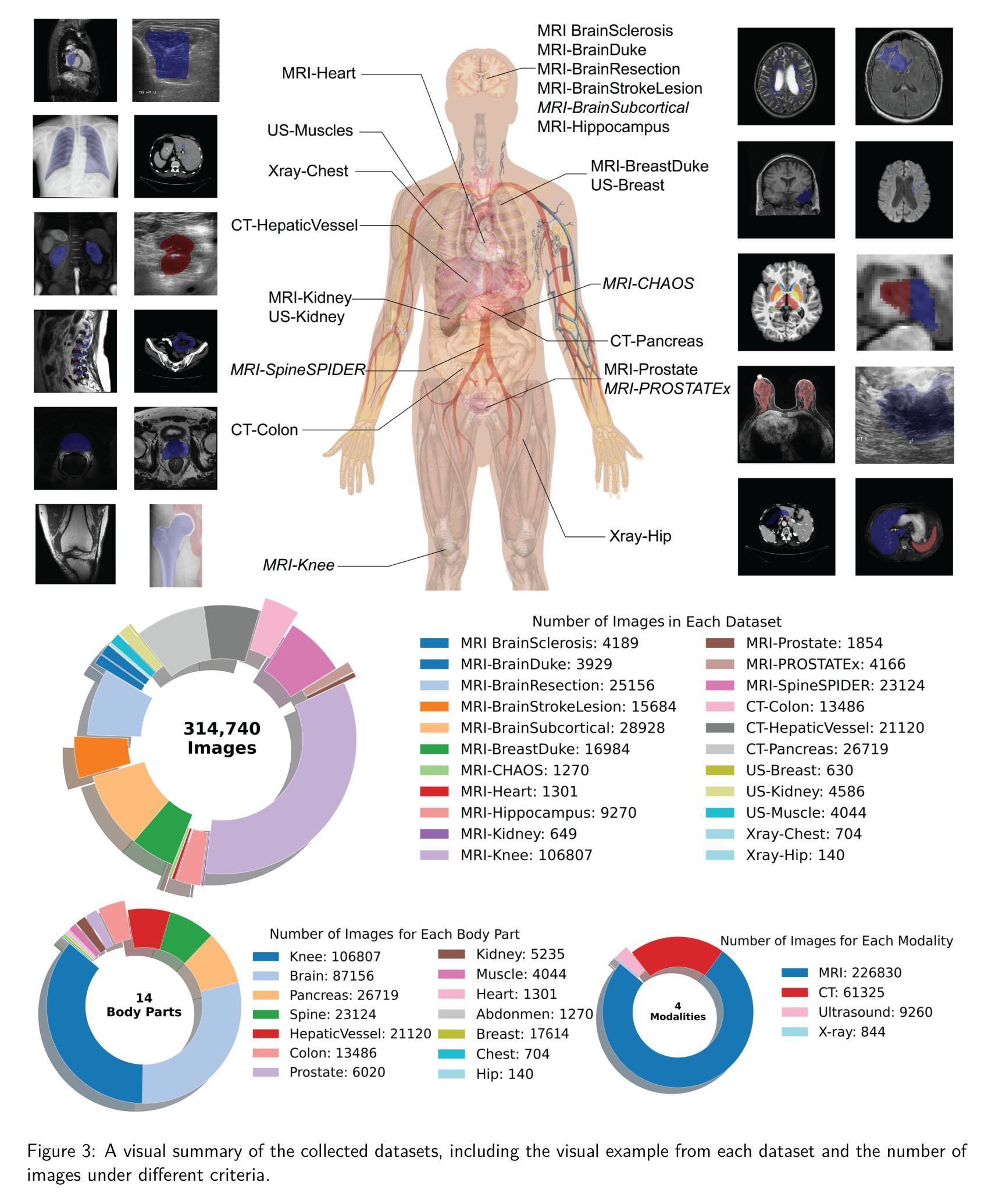
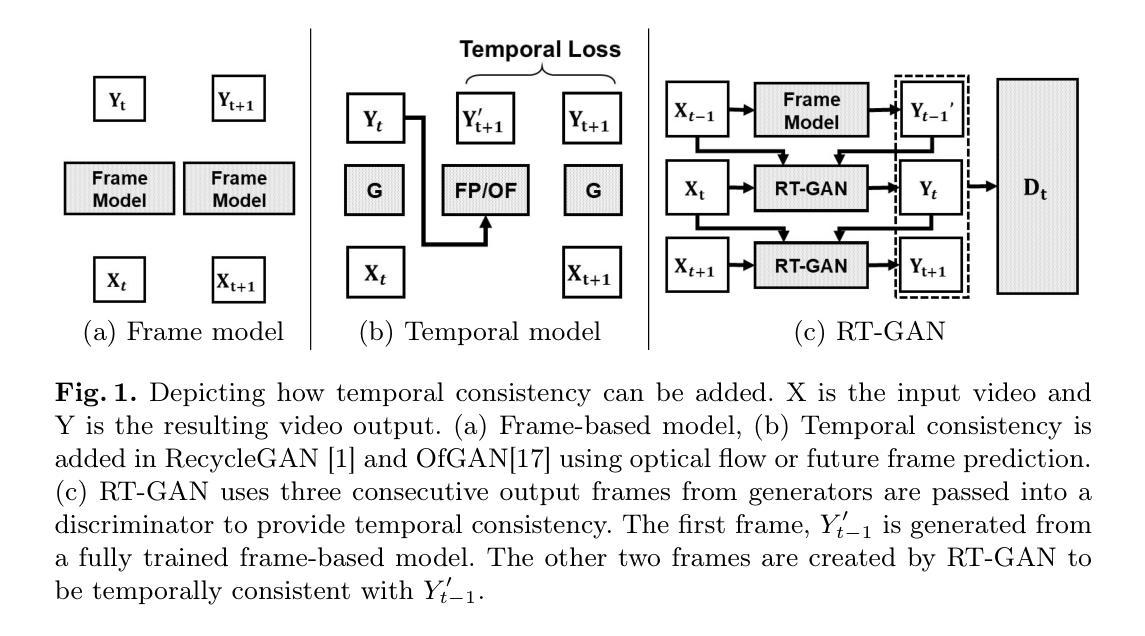
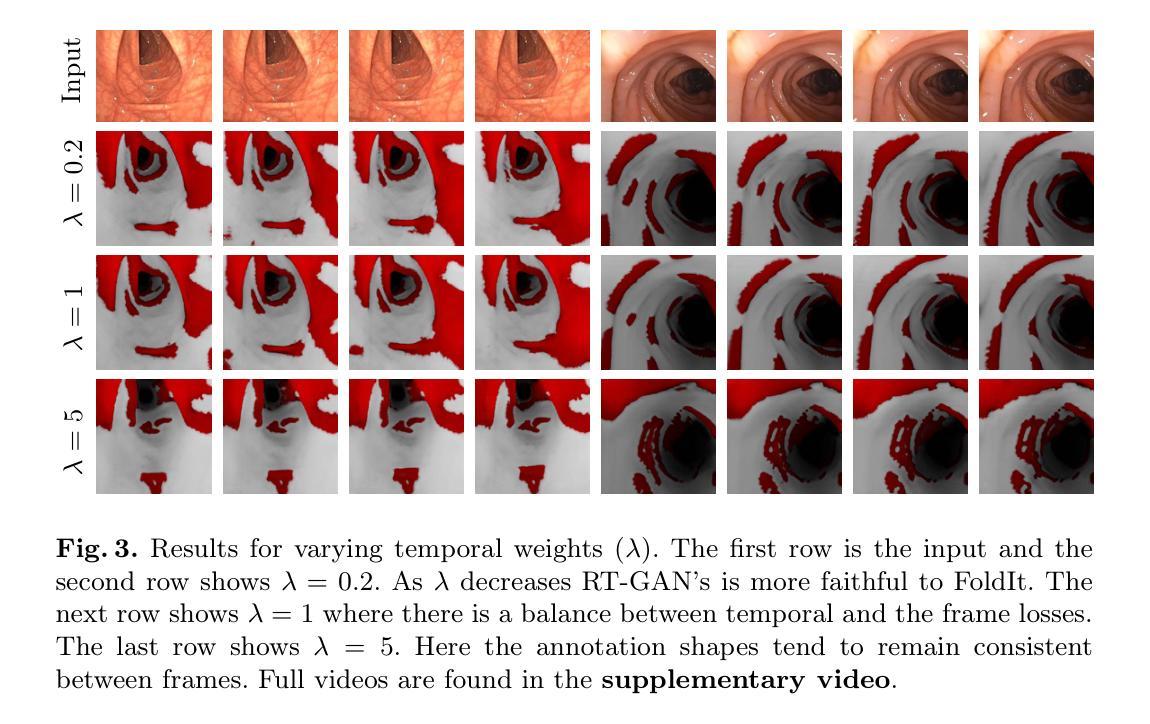
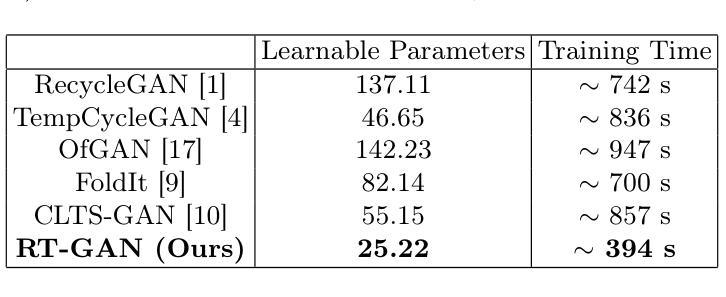
RT-GAN: Recurrent Temporal GAN for Adding Lightweight Temporal Consistency to Frame-Based Domain Translation Approaches
Authors:Shawn Mathew, Saad Nadeem, Alvin C. Goh, Arie Kaufman
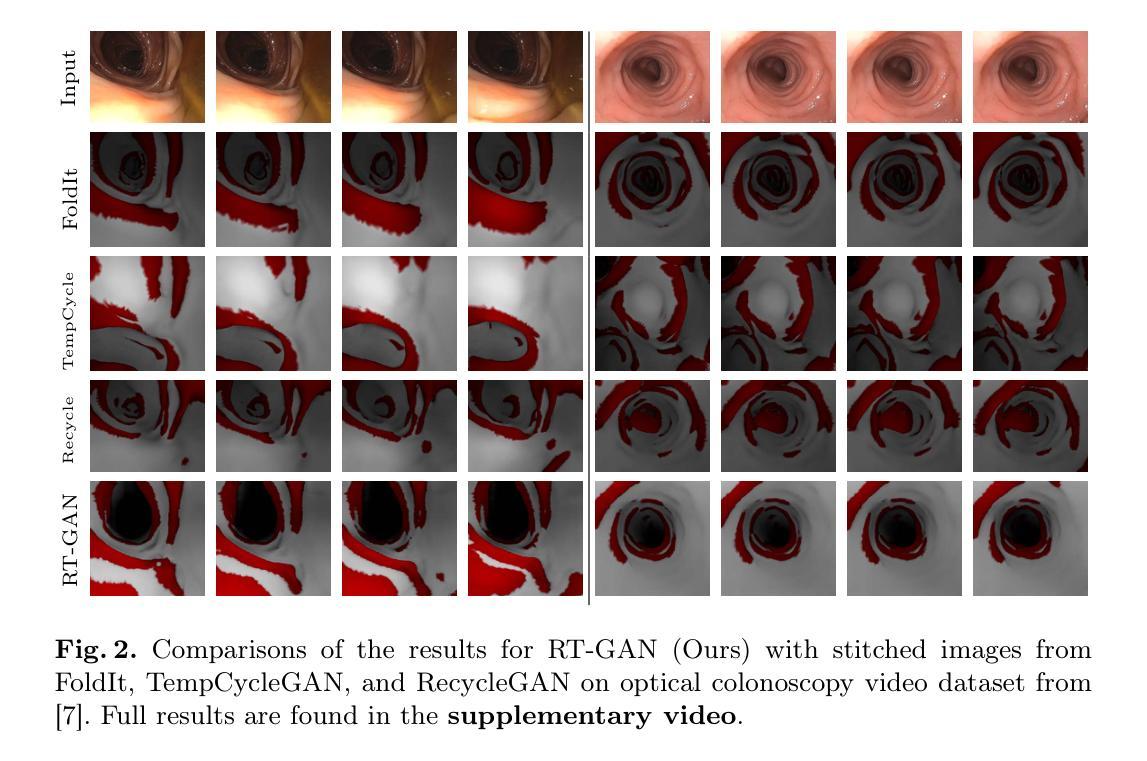
Fourteen million colonoscopies are performed annually just in the U.S. However, the videos from these colonoscopies are not saved due to storage constraints (each video from a high-definition colonoscope camera can be in tens of gigabytes). Instead, a few relevant individual frames are saved for documentation/reporting purposes and these are the frames on which most current colonoscopy AI models are trained on. While developing new unsupervised domain translation methods for colonoscopy (e.g. to translate between real optical and virtual/CT colonoscopy), it is thus typical to start with approaches that initially work for individual frames without temporal consistency. Once an individual-frame model has been finalized, additional contiguous frames are added with a modified deep learning architecture to train a new model from scratch for temporal consistency. This transition to temporally-consistent deep learning models, however, requires significantly more computational and memory resources for training. In this paper, we present a lightweight solution with a tunable temporal parameter, RT-GAN (Recurrent Temporal GAN), for adding temporal consistency to individual frame-based approaches that reduces training requirements by a factor of 5. We demonstrate the effectiveness of our approach on two challenging use cases in colonoscopy: haustral fold segmentation (indicative of missed surface) and realistic colonoscopy simulator video generation. We also release a first-of-its kind temporal dataset for colonoscopy for the above use cases. The datasets, accompanying code, and pretrained models will be made available on our Computational Endoscopy Platform GitHub (https://github.com/nadeemlab/CEP). The supplementary video is available at https://youtu.be/UMVP-uIXwWk.
每年仅在美囘国就有多达一千四百万次结肠镜检查。然而,由于存储限制(每个高清结肠镜摄像机拍摄的视频可能达到数十千兆),这些结肠镜检查的视频并未保存。相反,为了记录或报告目的,仅保存了一些相关的单独帧,而这些帧也是当前大多数结肠镜检查AI模型的训练基础。在开发用于结肠镜检查的新型无监督域转换方法(例如,用于真实光学结肠镜和虚拟/CT结肠镜之间的转换)时,因此通常会采用首先针对单独帧进行工作的方法,而无需考虑时间一致性。一旦完成单个帧模型的最终确定,将使用经过修改的深度学习架构添加连续的相邻帧,然后从头开始训练一个新模型以实现时间一致性。然而,这种向时间一致的深度学习模型的过渡需要更多的计算和内存资源进行训练。在本文中,我们提出了一种具有可调时间参数的轻量级解决方案RT-GAN(递归时间GAN),该方案可为基于单个帧的方法提供时间一致性,通过将训练要求降低五分之一来减少训练需求。我们通过在结肠镜检查中的两个具有挑战性的用例来证明我们方法的有效性:结肠袋分割(指示丢失的表面)和逼真的结肠镜检查模拟器视频生成。我们还针对上述用例发布了首个结肠镜检查时间序列数据集。数据集、配套代码和预训练模型将发布在我们的计算内窥镜平台GitHub上(https://github.com/nadeemlab/CEP)。补充视频可通过以下链接查看:[视频链接](https://youtu.be/UMVP-uIXwWk)。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF MICCAI 2025 Early Accept. First two authors contributed equally
Summary
本文介绍了一种基于可调整时间参数的轻量级解决方案RT-GAN,用于为单帧方法增加时间一致性,减少培训要求,并在结肠镜检查的两个用例上验证其有效性:结肠皱襞分割和逼真的结肠镜检查模拟器视频生成。
Key Takeaways
- 每年在美国进行14万次结肠镜检查,但由于存储限制,这些检查的视频并未保存。
- 当前结肠镜检查AI模型主要在保存的个别帧上进行训练。
- 在开发结肠镜检查的跨域翻译方法时,通常首先关注单帧方法,然后逐步引入时间一致性。
- 实现时间一致性的深度学习模型需要更多的计算和内存资源进行训练。
- 本文提出了一种基于可调整时间参数的轻量级解决方案RT-GAN,为单帧方法增加时间一致性,降低训练要求。
- RT-GAN在结肠皱襞分割和逼真的结肠镜检查模拟器视频生成两个用例上进行了验证。
点此查看论文截图