⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-05-15 更新
GNCAF: A GNN-based Neighboring Context Aggregation Framework for Tertiary Lymphoid Structures Semantic Segmentation in WSI
Authors:Lei Su
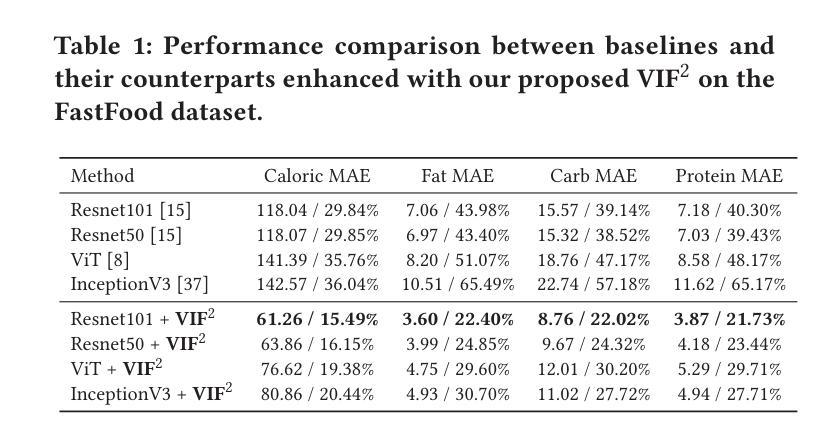
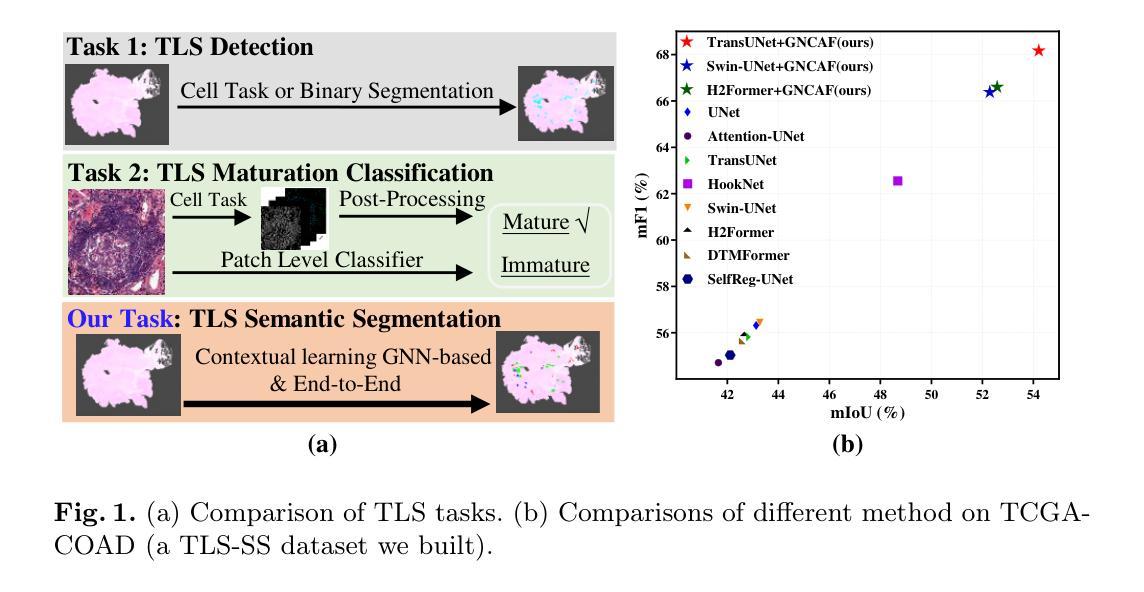
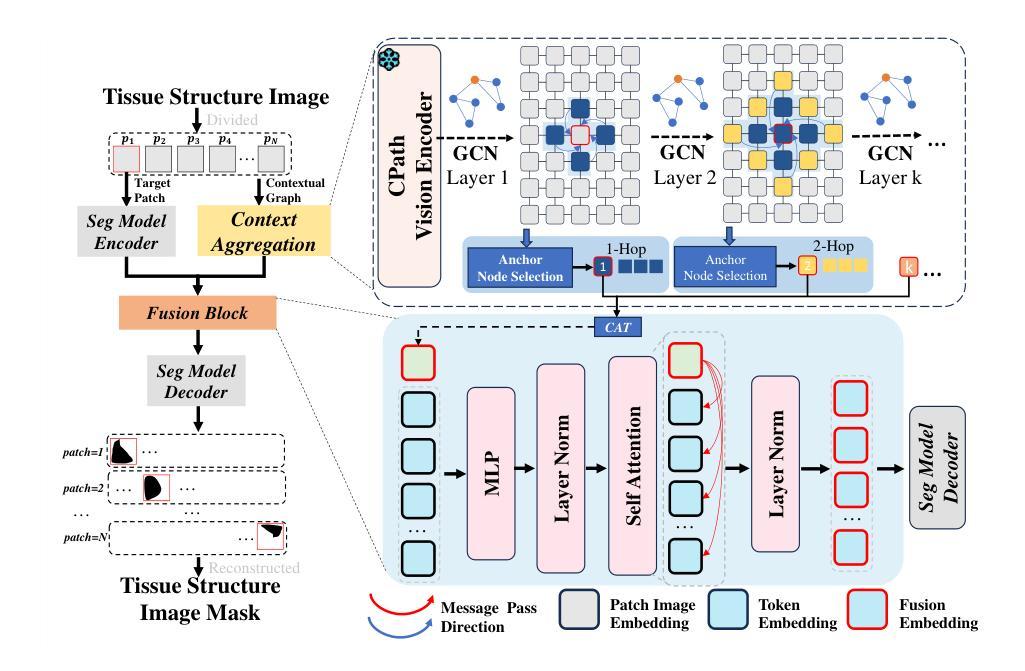
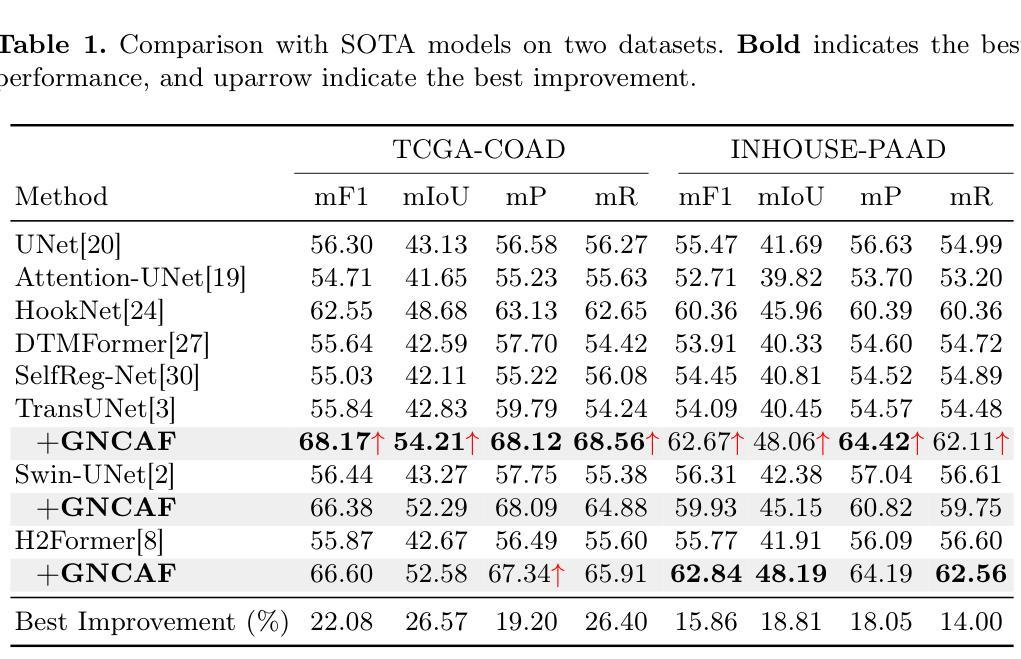
Tertiary lymphoid structures (TLS) are organized clusters of immune cells, whose maturity and area can be quantified in whole slide image (WSI) for various prognostic tasks. Existing methods for assessing these characteristics typically rely on cell proxy tasks and require additional post-processing steps. In this work, We focus on a novel task-TLS Semantic Segmentation (TLS-SS)-which segments both the regions and maturation stages of TLS in WSI in an end-to-end manner. Due to the extensive scale of WSI and patch-based segmentation strategies, TLS-SS necessitates integrating from neighboring patches to guide target patch (target) segmentation. Previous techniques often employ on multi-resolution approaches, constraining the capacity to leverage the broader neighboring context while tend to preserve coarse-grained information. To address this, we propose a GNN-based Neighboring Context Aggregation Framework (GNCAF), which progressively aggregates multi-hop neighboring context from the target and employs a self-attention mechanism to guide the segmentation of the target. GNCAF can be integrated with various segmentation models to enhance their ability to perceive contextual information outside of the patch. We build two TLS-SS datasets, called TCGA-COAD and INHOUSE-PAAD, and make the former (comprising 225 WSIs and 5041 TLSs) publicly available. Experiments on these datasets demonstrate the superiority of GNCAF, achieving a maximum of 22.08% and 26.57% improvement in mF1 and mIoU, respectively. Additionally, we also validate the task scalability of GNCAF on segmentation of lymph node metastases.
三级淋巴结构(TLS)是免疫细胞的聚集簇,其成熟度和面积可以在全切片图像(WSI)中进行量化,用于各种预后任务。现有的评估这些方法通常依赖于细胞代理任务,并且需要额外的后处理步骤。在这项工作中,我们专注于一个新的任务——TLS语义分割(TLS-SS),它以一种端到端的方式分割WSI中TLS的区域和成熟阶段。由于WSI的广泛规模和基于补丁的分割策略,TLS-SS需要从相邻的补丁中集成信息来引导目标补丁(目标)的分割。以前的技术经常采用多分辨率方法,这在利用更广泛的相邻上下文时受到限制,同时倾向于保留粗略的信息。为了解决这一问题,我们提出了基于图神经网络(GNN)的相邻上下文聚合框架(GNCAF),它逐步聚合来自目标的多跳相邻上下文,并采用自注意力机制来引导目标的分割。GNCAF可以与各种分割模型集成,以增强它们感知补丁之外上下文信息的能力。我们建立了两个TLS-SS数据集,分别是TCGA-COAD和INHOUSE-PAAD,并公开了前者(包含225个WSI和5041个TLS)。在这些数据集上的实验证明了GNCAF的优越性,在mF1和mIoU上分别实现了最高达22.08%和26.57%的改进。此外,我们还验证了GNCAF在淋巴结转移分割任务的可扩展性。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary:
本文关注三级淋巴结构(TLS)的语义分割任务,旨在实现对WSI中TLS区域和成熟阶段的端到端分割。由于WSI的大规模性和基于补丁的分割策略,TLS-SS需要从邻近补丁集成信息以指导目标补丁的分割。为此,本文提出了一种基于图神经网络(GNN)的邻近上下文聚合框架(GNCAF),它能逐步聚合多跳邻近上下文,并采用自注意力机制来指导目标分割。实验证明,GNCAF在TLS-SS任务上表现优越,且在淋巴结节转移灶的分割任务中也展现了良好的可扩展性。
Key Takeaways:
- TLS是免疫细胞的聚集簇,其成熟程度和面积可通过WSI进行量化,对预后评估有重要意义。
- 现有评估TLS特性的方法通常依赖于细胞代理任务,并需要额外的后处理步骤。
- 本文专注于一个新的任务——TLS语义分割(TLS-SS),旨在以端到端的方式分割WSI中的TLS区域和成熟阶段。
- WSI的大规模性和基于补丁的分割策略要求从邻近补丁集成信息以指导目标补丁的分割。
- 提出了一种基于图神经网络(GNN)的邻近上下文聚合框架(GNCAF),以逐步聚合多跳邻近上下文并引导目标分割。
- GNCAF可与各种分割模型集成,增强其感知补丁外部上下文信息的能力。
点此查看论文截图

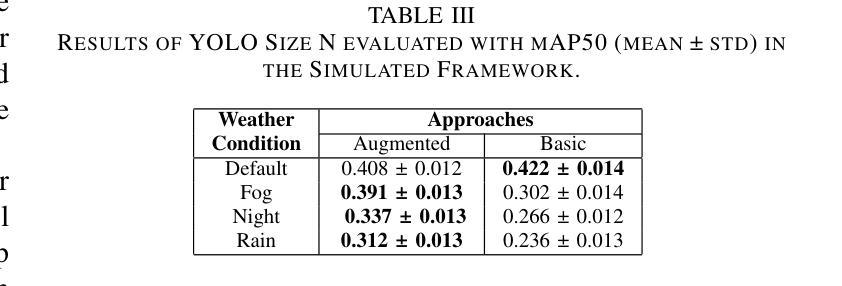
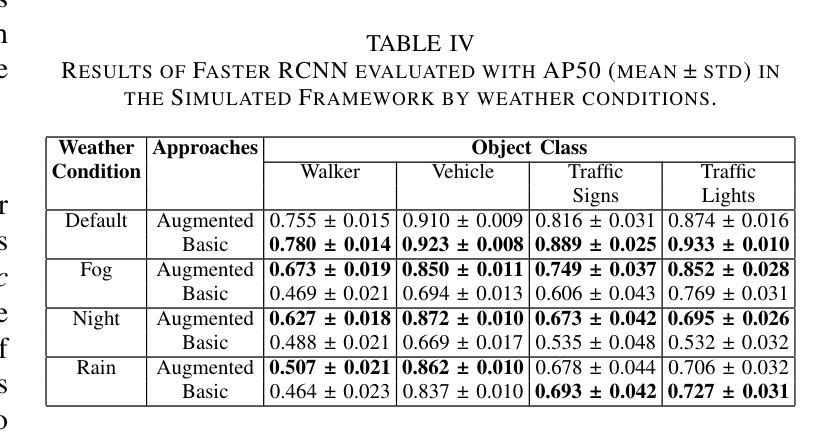
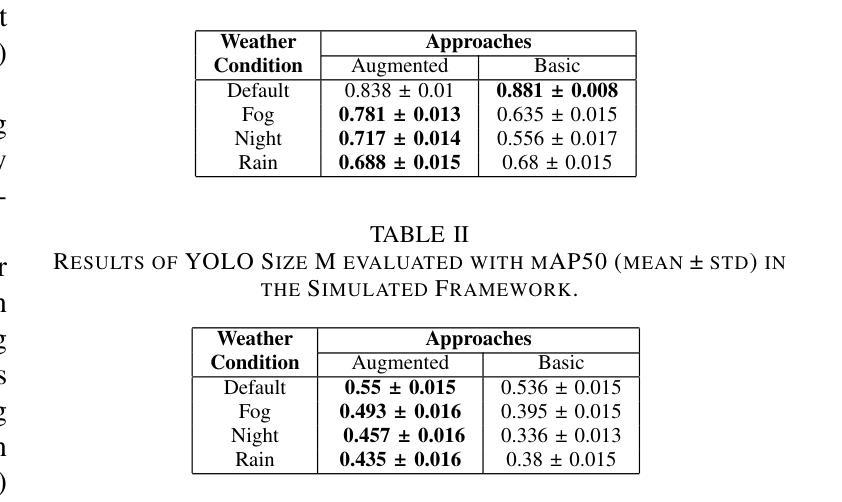
Object detection in adverse weather conditions for autonomous vehicles using Instruct Pix2Pix
Authors:Unai Gurbindo, Axel Brando, Jaume Abella, Caroline König
Enhancing the robustness of object detection systems under adverse weather conditions is crucial for the advancement of autonomous driving technology. This study presents a novel approach leveraging the diffusion model Instruct Pix2Pix to develop prompting methodologies that generate realistic datasets with weather-based augmentations aiming to mitigate the impact of adverse weather on the perception capabilities of state-of-the-art object detection models, including Faster R-CNN and YOLOv10. Experiments were conducted in two environments, in the CARLA simulator where an initial evaluation of the proposed data augmentation was provided, and then on the real-world image data sets BDD100K and ACDC demonstrating the effectiveness of the approach in real environments. The key contributions of this work are twofold: (1) identifying and quantifying the performance gap in object detection models under challenging weather conditions, and (2) demonstrating how tailored data augmentation strategies can significantly enhance the robustness of these models. This research establishes a solid foundation for improving the reliability of perception systems in demanding environmental scenarios, and provides a pathway for future advancements in autonomous driving.
提高恶劣天气条件下物体检测系统(Object Detection Systems)的稳健性对于自动驾驶技术的进步至关重要。本研究提出了一种新的方法,借助扩散模型Instruct Pix2Pix,发展出一种生成现实数据集的提示方法(prompting methodologies),这些数据集包含基于天气的增强技术(weather-based augmentations),旨在减轻恶劣天气对最先进的物体检测模型感知能力的影响,包括Faster R-CNN和YOLOv10。实验在两个环境中进行:在CARLA模拟器中进行初步评估所提出的数据增强技术,然后在真实世界图像数据集BDD100K和ACDC上展示该策略的有效性。这项工作有两个关键贡献:一是识别和量化挑战天气条件下物体检测模型的性能差距;二是展示了量身定制的数据增强策略如何显著增强这些模型的稳健性。该研究为在苛刻环境场景中提高感知系统的可靠性奠定了坚实的基础,并为自动驾驶技术的未来发展提供了路径。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 8 pages, 5 figures. Accepted at the International Joint Conference on Neural Networks (IJCNN) 2025 (to appear)
Summary
本文研究了恶劣天气条件下增强对象检测系统稳健性的重要性,对于自动驾驶技术的发展至关重要。该研究提出了一种利用扩散模型Instruct Pix2Pix开发提示方法的新方法,生成具有天气增强的现实数据集,旨在减轻恶劣天气对当前先进对象检测模型感知能力的影响,包括Faster R-CNN和YOLOv10。实验在CARLA模拟器环境和真实世界图像数据集BDD100K和ACDC中进行,验证了该方法的实际效果。该研究的关键贡献在于识别和量化挑战天气条件下对象检测模型的性能差距,并展示了针对性数据增强策略如何显著增强这些模型的稳健性。这为改善需求环境下的感知系统可靠性奠定了坚实基础,并为自动驾驶技术的未来发展提供了途径。
Key Takeaways
- 研究对象检测系统在恶劣天气下的稳健性对自动驾驶技术的发展至关重要。
- 提出一种利用扩散模型Instruct Pix2Pix开发提示方法,生成现实数据集的新方法,以增强模型在各种天气条件下的性能。
- 在CARLA模拟器环境中初步评估了所提出的数据增强方法的有效性。
- 在真实世界图像数据集BDD100K和ACDC上的实验证明了该方法在恶劣天气条件下的有效性。
- 研究识别和量化挑战天气条件下对象检测模型的性能差距是关键贡献之一。
- 研究展示了数据增强策略能显著提高对象检测模型的稳健性。
点此查看论文截图