⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-05-15 更新
NavDP: Learning Sim-to-Real Navigation Diffusion Policy with Privileged Information Guidance
Authors:Wenzhe Cai, Jiaqi Peng, Yuqiang Yang, Yujian Zhang, Meng Wei, Hanqing Wang, Yilun Chen, Tai Wang, Jiangmiao Pang
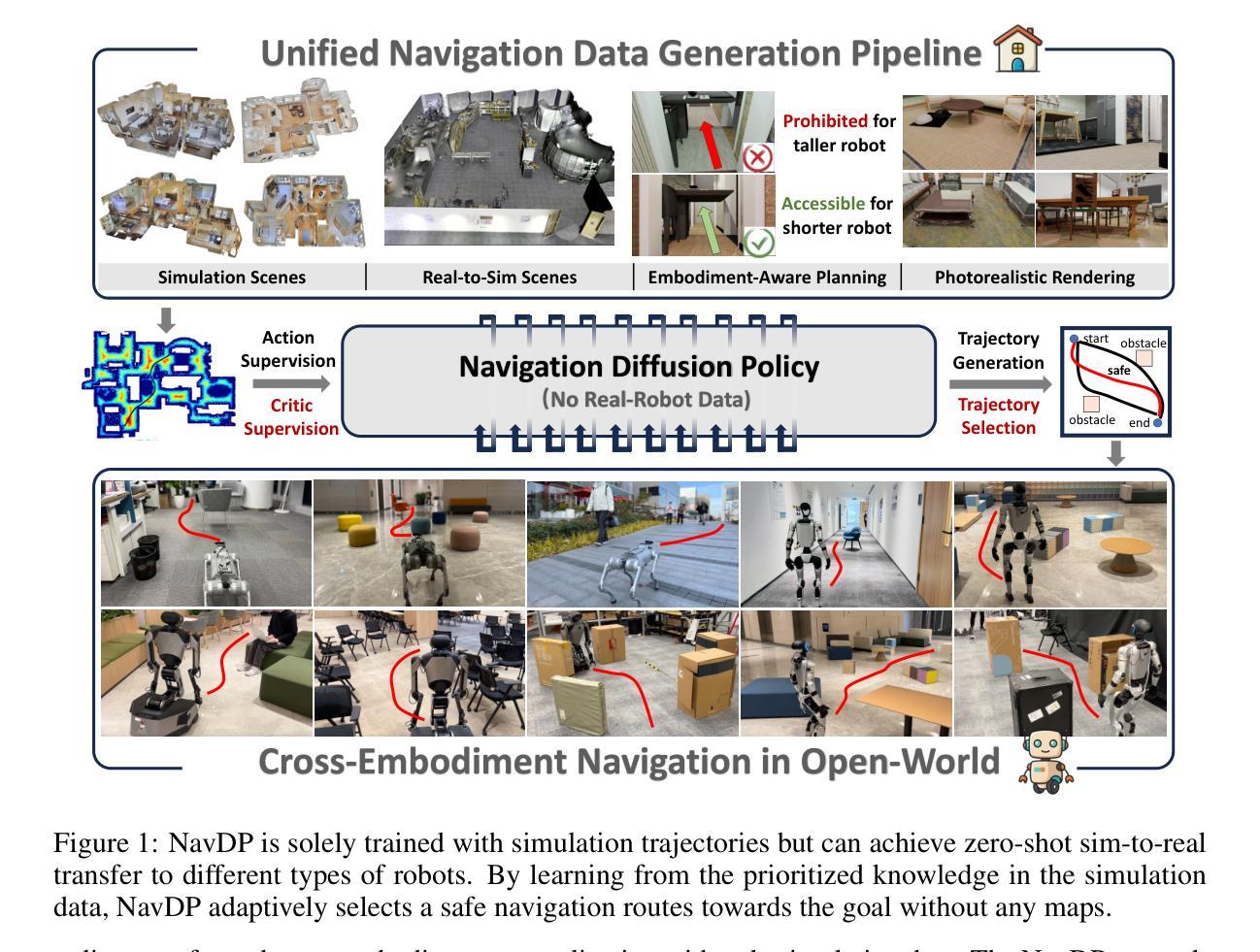
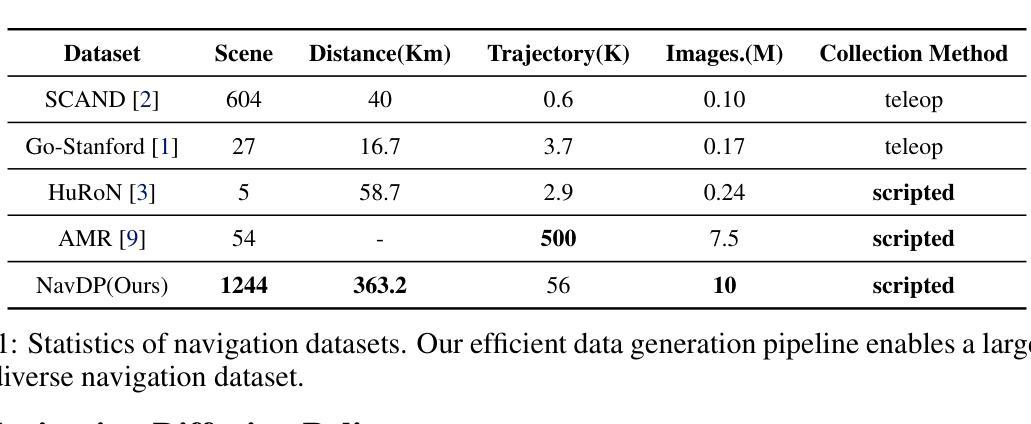
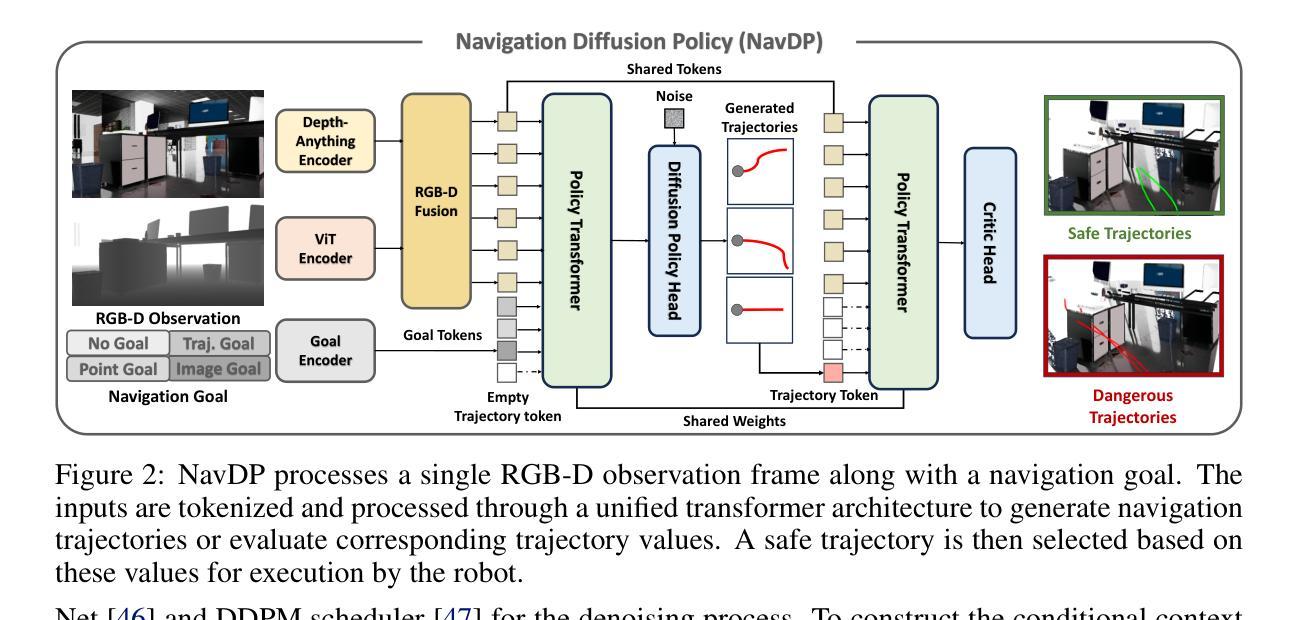
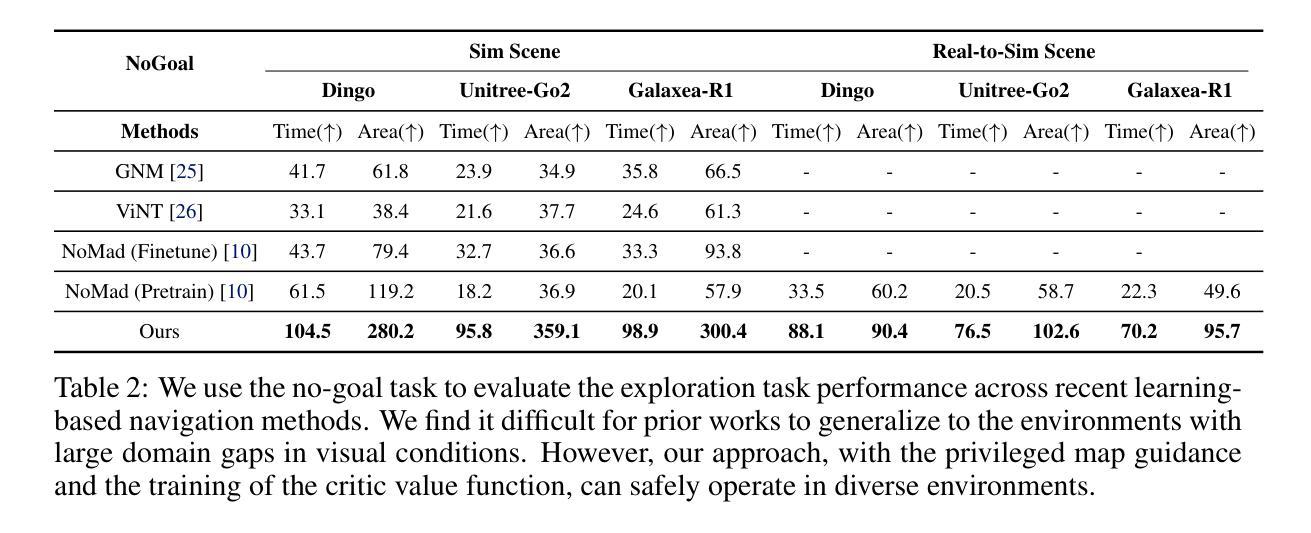
Learning navigation in dynamic open-world environments is an important yet challenging skill for robots. Most previous methods rely on precise localization and mapping or learn from expensive real-world demonstrations. In this paper, we propose the Navigation Diffusion Policy (NavDP), an end-to-end framework trained solely in simulation and can zero-shot transfer to different embodiments in diverse real-world environments. The key ingredient of NavDP’s network is the combination of diffusion-based trajectory generation and a critic function for trajectory selection, which are conditioned on only local observation tokens encoded from a shared policy transformer. Given the privileged information of the global environment in simulation, we scale up the demonstrations of good quality to train the diffusion policy and formulate the critic value function targets with contrastive negative samples. Our demonstration generation approach achieves about 2,500 trajectories/GPU per day, 20$\times$ more efficient than real-world data collection, and results in a large-scale navigation dataset with 363.2km trajectories across 1244 scenes. Trained with this simulation dataset, NavDP achieves state-of-the-art performance and consistently outstanding generalization capability on quadruped, wheeled, and humanoid robots in diverse indoor and outdoor environments. In addition, we present a preliminary attempt at using Gaussian Splatting to make in-domain real-to-sim fine-tuning to further bridge the sim-to-real gap. Experiments show that adding such real-to-sim data can improve the success rate by 30% without hurting its generalization capability.
机器人学习动态开放环境中的导航是一项重要且具有挑战性的技能。大多数之前的方法依赖于精确的定位和地图构建,或者从昂贵的真实世界演示中学习。在本文中,我们提出了导航扩散策略(NavDP),这是一种端到端的框架,仅通过模拟进行训练,并可以在不同的实体中零样本迁移到各种真实世界环境中。NavDP网络的关键成分是结合基于扩散的轨迹生成和用于轨迹选择的评论家函数,它们仅基于来自共享政策转换器的局部观察标记。利用模拟中全局环境的特权信息,我们扩大了高质量演示的规模来训练扩散策略,并用对比负样本制定评论家价值函数的目标。我们的演示生成方法每天每GPU生成约2500条轨迹,比真实世界的数据收集效率高出20倍,并形成了包含跨越1244个场景的363.2公里轨迹的大规模导航数据集。使用该模拟数据集进行训练,NavDP在多种室内和室外环境中的四足、轮式和人形机器人上达到了最新性能,并始终具有出色的泛化能力。此外,我们初步尝试使用高斯平铺(Gaussian Splatting)来进行域内真实到模拟的微调,以进一步缩小模拟到真实的差距。实验表明,添加此类真实到模拟的数据可以在不损害其泛化能力的情况下将成功率提高3%个百分点。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 14 pages, 6 figures
摘要
本文提出一种名为NavDP的端到端框架,用于在动态开放世界环境中学习机器人导航。该框架仅通过模拟进行训练,并能零样本迁移至不同实体的各种现实环境。NavDP网络的关键在于结合基于扩散的轨迹生成和用于轨迹选择的评价函数,这两个部分仅基于共享策略转换器的局部观测符号。利用模拟中的全局环境特权信息,我们扩大了优质演示数据的规模,以训练扩散策略和制定评价价值函数的目标,同时采用对比负样本。我们的演示生成方法每天每GPU可实现约2500条轨迹,比现实数据收集的效率高出20倍,并生成了一个大型导航数据集,包含1244个场景中的363.2公里轨迹。使用该模拟数据集进行训练,NavDP在多种四足、轮式和人形机器人上实现了最先进的性能,并在室内和室外环境中表现出卓越的一致泛化能力。此外,我们还初步尝试使用高斯贴图进行领域内实到模拟微调,以进一步缩小模拟到现实的差距。实验表明,添加这种实到模拟数据可以在不影响泛化能力的情况下将成功率提高30%。
关键见解
- 机器人学习在动态开放世界环境中的导航是一项重要而具有挑战性的技能。
- NavDP是一个端到端的框架,能够在模拟中训练并零样本迁移到不同的现实环境。
- NavDP结合了基于扩散的轨迹生成和轨迹选择的评价函数,仅基于局部观测符号。
- 使用模拟中的全局环境信息来训练扩散策略和制定评价价值函数的目标,采用对比负样本的方法。
- 演示生成方法高效,每天每GPU可生成大量轨迹数据。
- NavDP在多种机器人上实现先进性能,并在室内和室外环境表现出卓越的泛化能力。
点此查看论文截图

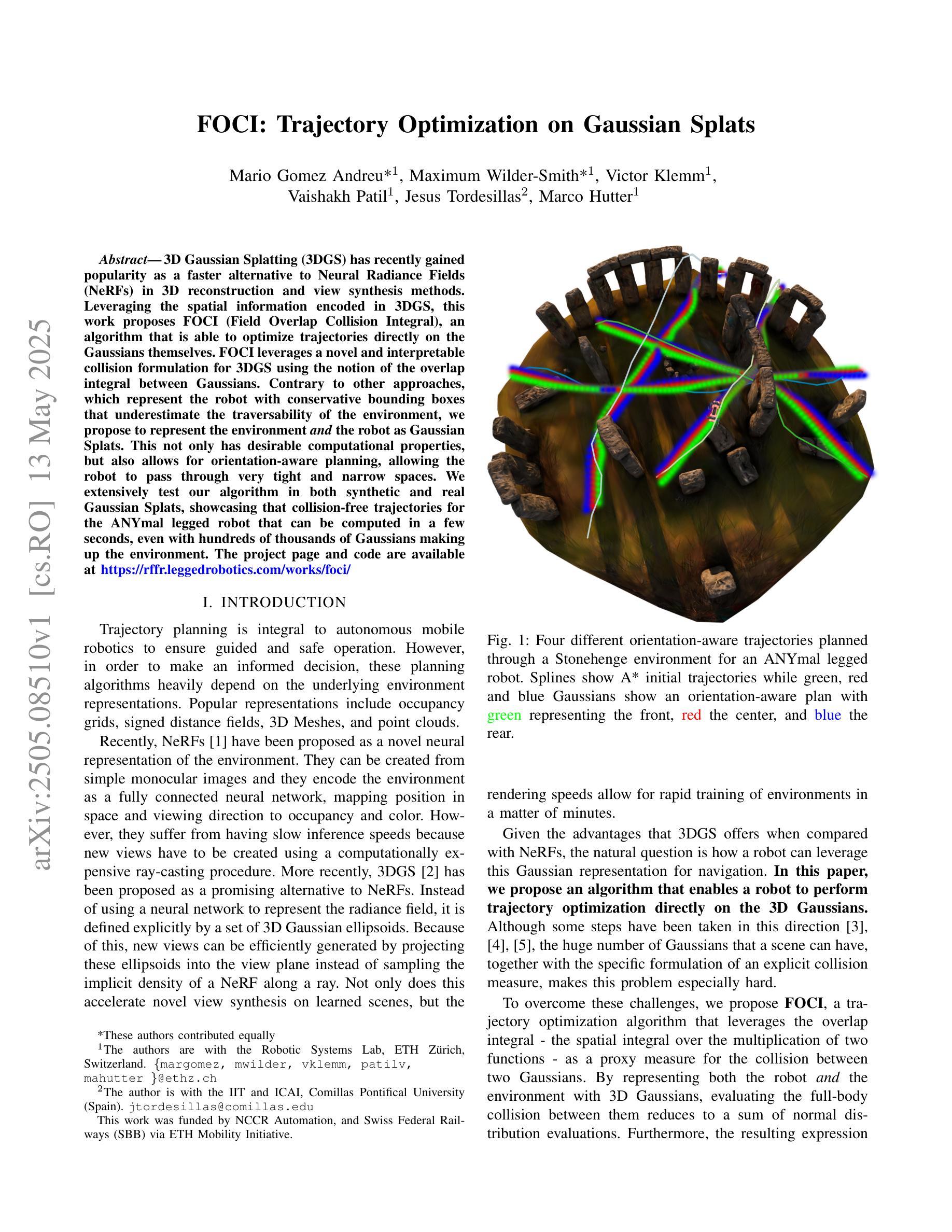
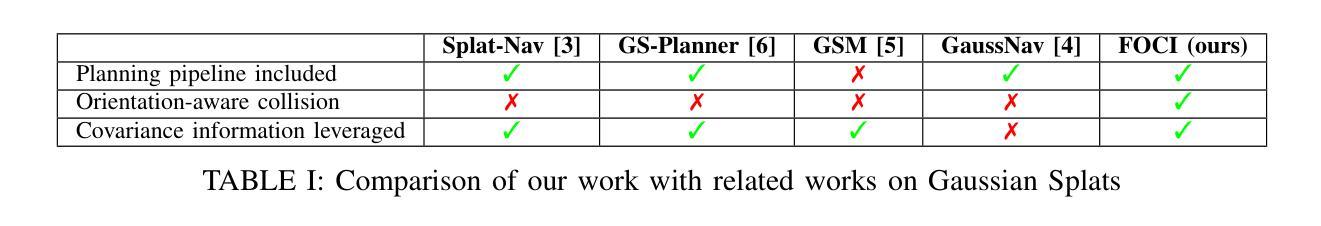
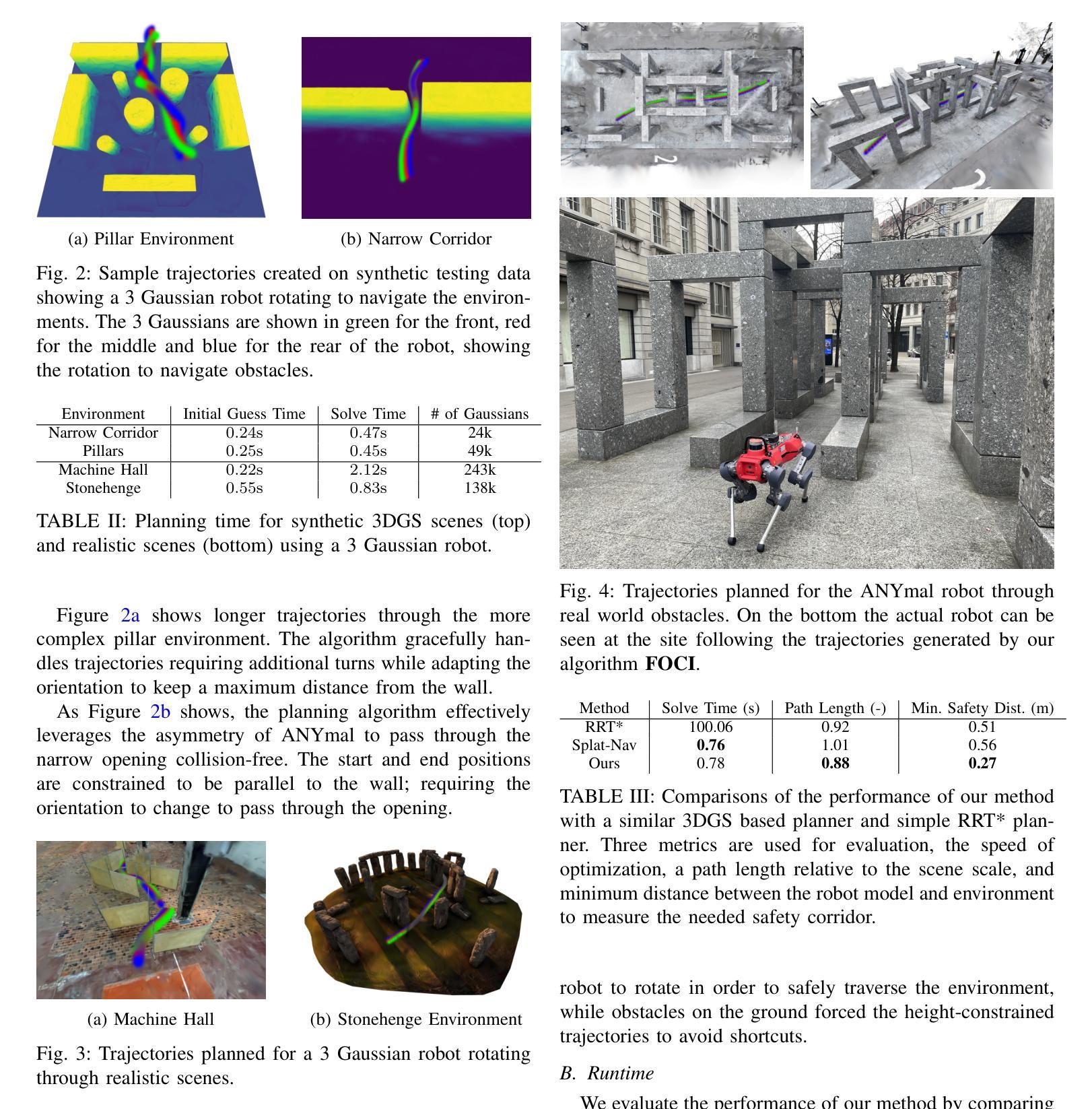
FOCI: Trajectory Optimization on Gaussian Splats
Authors:Mario Gomez Andreu, Maximum Wilder-Smith, Victor Klemm, Vaishakh Patil, Jesus Tordesillas, Marco Hutter
3D Gaussian Splatting (3DGS) has recently gained popularity as a faster alternative to Neural Radiance Fields (NeRFs) in 3D reconstruction and view synthesis methods. Leveraging the spatial information encoded in 3DGS, this work proposes FOCI (Field Overlap Collision Integral), an algorithm that is able to optimize trajectories directly on the Gaussians themselves. FOCI leverages a novel and interpretable collision formulation for 3DGS using the notion of the overlap integral between Gaussians. Contrary to other approaches, which represent the robot with conservative bounding boxes that underestimate the traversability of the environment, we propose to represent the environment and the robot as Gaussian Splats. This not only has desirable computational properties, but also allows for orientation-aware planning, allowing the robot to pass through very tight and narrow spaces. We extensively test our algorithm in both synthetic and real Gaussian Splats, showcasing that collision-free trajectories for the ANYmal legged robot that can be computed in a few seconds, even with hundreds of thousands of Gaussians making up the environment. The project page and code are available at https://rffr.leggedrobotics.com/works/foci/
3D高斯Splatting(3DGS)作为一种更快的替代方法,在三维重建和视图合成方法中受到欢迎,成为神经辐射场(NeRFs)的替代方案。利用编码在3DGS中的空间信息,这项工作提出了FOCI(场重叠碰撞积分)算法,该算法能够在高斯本身上直接优化轨迹。FOCI利用一种新颖的、可解释的碰撞公式为3DGS使用高斯之间的重叠积分的概念。与其他使用保守边界框表示机器人并低估环境可通行性的方法不同,我们提出将环境和机器人表示为高斯Splats。这不仅具有理想的计算属性,而且允许具有方向感知的规划,允许机器人在非常紧凑和狭窄的空间中通过。我们在合成和真实的高斯Splats中都测试了我们的算法,展示了即使在由数十万个高斯组成的环境中,也可以在几秒钟内计算出ANYmal腿式机器人的无碰撞轨迹。项目页面和代码可在https://rffr.leggedrobotics.com/works/foci/找到。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 7 pages, 8 figures, Mario Gomez Andreu and Maximum Wilder-Smith contributed equally
Summary
本文介绍了基于三维高斯贴片(3DGS)技术的最新研究成果,提出一种名为FOCI(基于高斯重叠积分的碰撞算法)的算法。该算法利用高斯贴片的空间信息优化轨迹,通过高斯之间的重叠积分实现碰撞检测,进而应用于环境机器人学的任务。该算法相比保守框近似方式更具有准确性,并且能够针对狭窄空间的精确操作,能够自主穿越复杂的非线性空间进行执行任务。已在仿真与实际场景中的测试和性能验证展示了FOCI的高效性。此外项目内容和代码均已在线公开可供参考和学习。
Key Takeaways
- 3DGS作为一种更快的替代方法被广泛应用于三维重建和视图合成方法中替代NeRFs技术。
- FOCI算法通过优化高斯贴片来优化轨迹,能够更准确地评估机器人的移动性能和环境情况。
- FOCI利用高斯重叠积分进行碰撞检测,提供了一种新颖且可解释的碰撞公式。
- 与保守框近似方法不同,FOCI算法将机器人和环境表示为高斯贴片,具有更好的计算性能和方向感知规划能力。
- FOCI算法能够在狭窄空间内实现精确操作,允许机器人穿越复杂的非线性空间执行任务。
- 在合成和实际高斯贴片环境中进行了广泛的测试,验证了FOCI算法的高效性。
点此查看论文截图

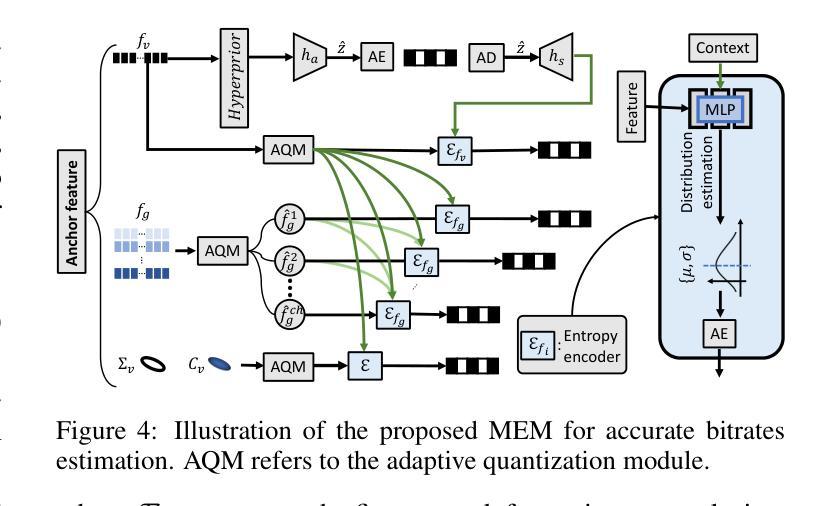
ADC-GS: Anchor-Driven Deformable and Compressed Gaussian Splatting for Dynamic Scene Reconstruction
Authors:He Huang, Qi Yang, Mufan Liu, Yiling Xu, Zhu Li
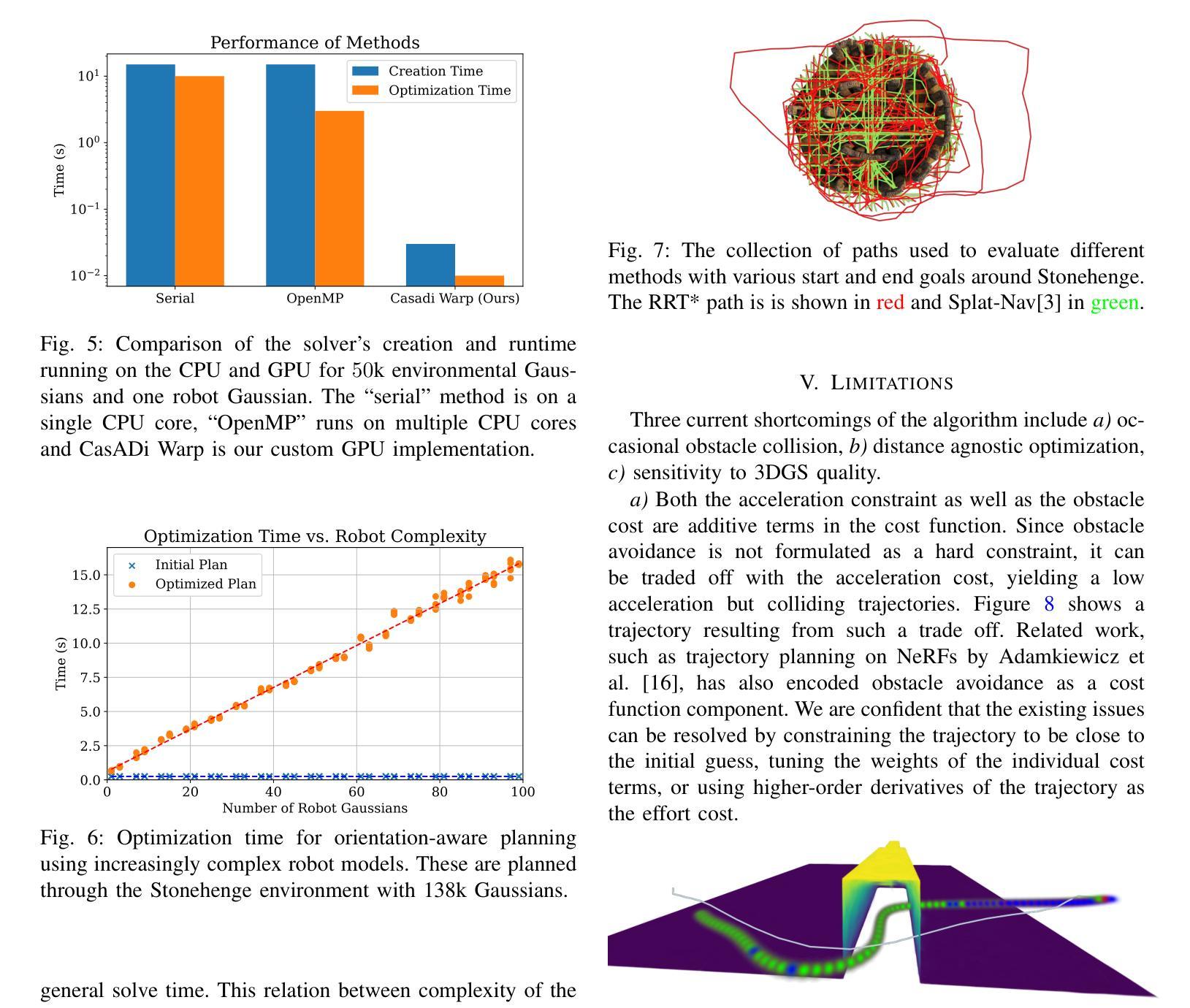
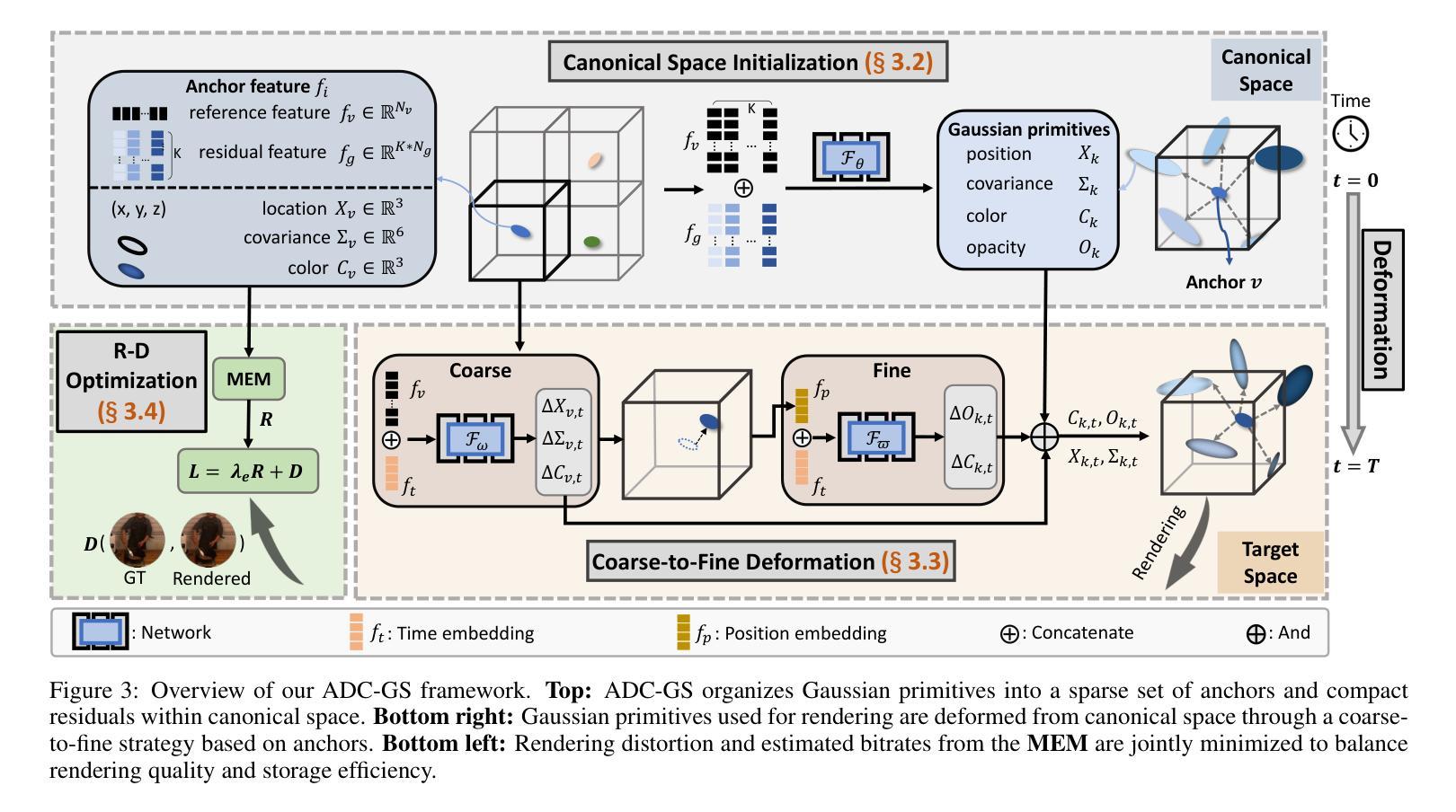
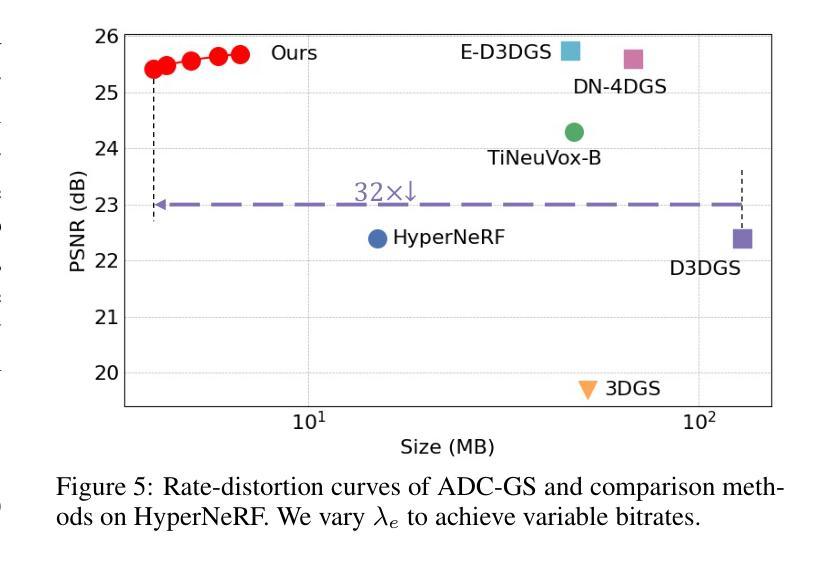
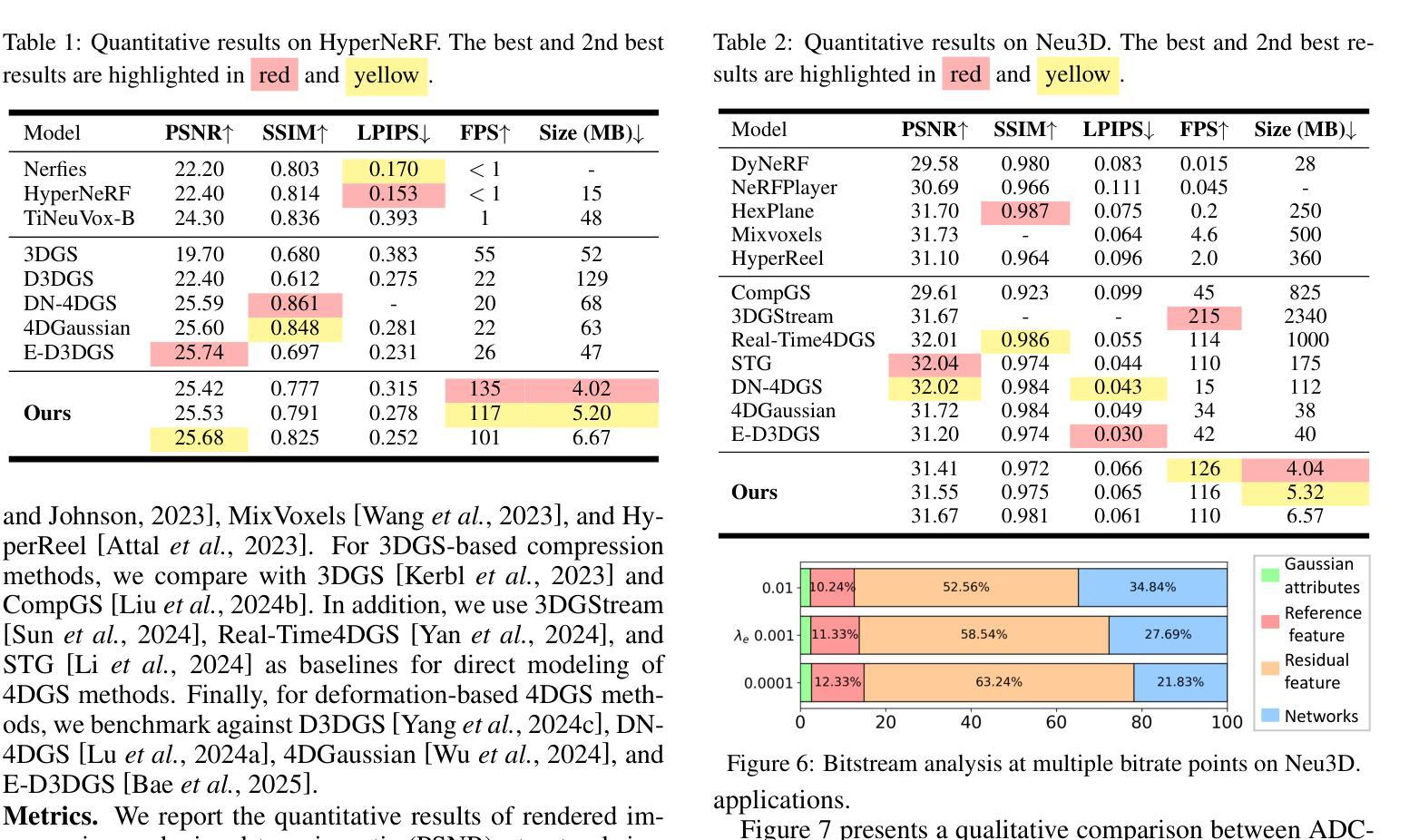
Existing 4D Gaussian Splatting methods rely on per-Gaussian deformation from a canonical space to target frames, which overlooks redundancy among adjacent Gaussian primitives and results in suboptimal performance. To address this limitation, we propose Anchor-Driven Deformable and Compressed Gaussian Splatting (ADC-GS), a compact and efficient representation for dynamic scene reconstruction. Specifically, ADC-GS organizes Gaussian primitives into an anchor-based structure within the canonical space, enhanced by a temporal significance-based anchor refinement strategy. To reduce deformation redundancy, ADC-GS introduces a hierarchical coarse-to-fine pipeline that captures motions at varying granularities. Moreover, a rate-distortion optimization is adopted to achieve an optimal balance between bitrate consumption and representation fidelity. Experimental results demonstrate that ADC-GS outperforms the per-Gaussian deformation approaches in rendering speed by 300%-800% while achieving state-of-the-art storage efficiency without compromising rendering quality. The code is released at https://github.com/H-Huang774/ADC-GS.git.
现有的4D高斯贴片方法依赖于从规范空间到目标帧的高斯变形,这忽略了相邻高斯基元之间的冗余性,导致性能不佳。为了解决这一局限性,我们提出了锚驱动可变形和压缩高斯贴片(ADC-GS),这是一种用于动态场景重建的紧凑高效表示方法。具体而言,ADC-GS在规范空间内采用基于锚点的结构来组织高斯基元,并使用基于时间重要性的锚点优化策略进行增强。为了减少变形冗余,ADC-GS引入了一个分层粗细管道,以捕获不同粒度的运动。此外,采用速率失真优化以实现比特率消耗和表示保真度之间的最佳平衡。实验结果表明,在渲染速度方面,ADC-GS较基于高斯变形的传统方法提高了300%-800%,同时实现了最先进的存储效率,而渲染质量并未受到影响。代码已发布在https://github.com/H-Huang774/ADC-GS.git上。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
该文针对现有4D高斯绘制方法在处理高斯原始数据时的冗余问题,提出了基于锚点驱动的可变形和压缩高斯绘制(ADC-GS)方法。该方法将高斯原始数据组织成基于锚点的结构,并采用基于时间重要性的锚点优化策略。通过层次化的粗到细流程来减少变形冗余,并实现了在比特率消耗和表示保真度之间的最优平衡。实验结果表明,ADC-GS在渲染速度上比基于高斯原始数据的方法提高了300%-800%,同时达到了业界领先的存储效率,且不影响渲染质量。相关代码已发布在GitHub上。
Key Takeaways
- ADC-GS解决了现有4D高斯绘制方法在处理高斯原始数据时的冗余问题。
- 方法通过基于锚点的结构组织高斯原始数据,并利用时间重要性策略进行锚点优化。
- ADC-GS引入了层次化的粗到细流程以减少变形冗余。
- 方法采用率失真优化来实现比特率消耗和表示保真度之间的平衡。
- ADC-GS提高了渲染速度,最高可达传统方法的3到8倍。此方法提供了业界领先的存储效率,且不会牺牲渲染质量。
点此查看论文截图
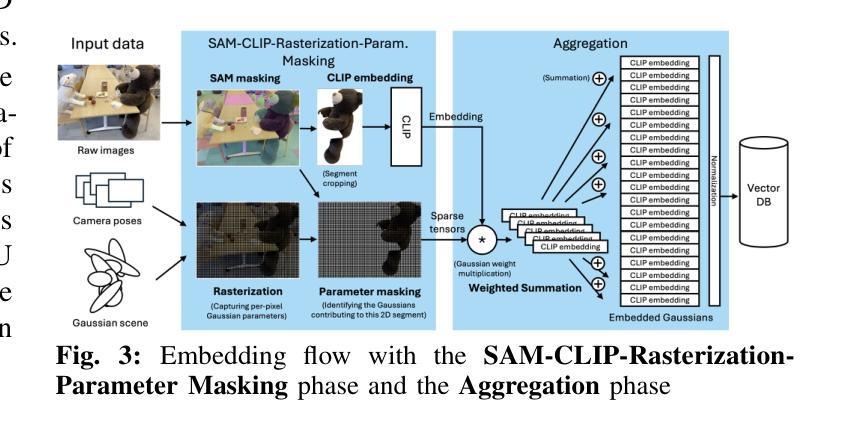
SLAG: Scalable Language-Augmented Gaussian Splatting
Authors:Laszlo Szilagyi, Francis Engelmann, Jeannette Bohg
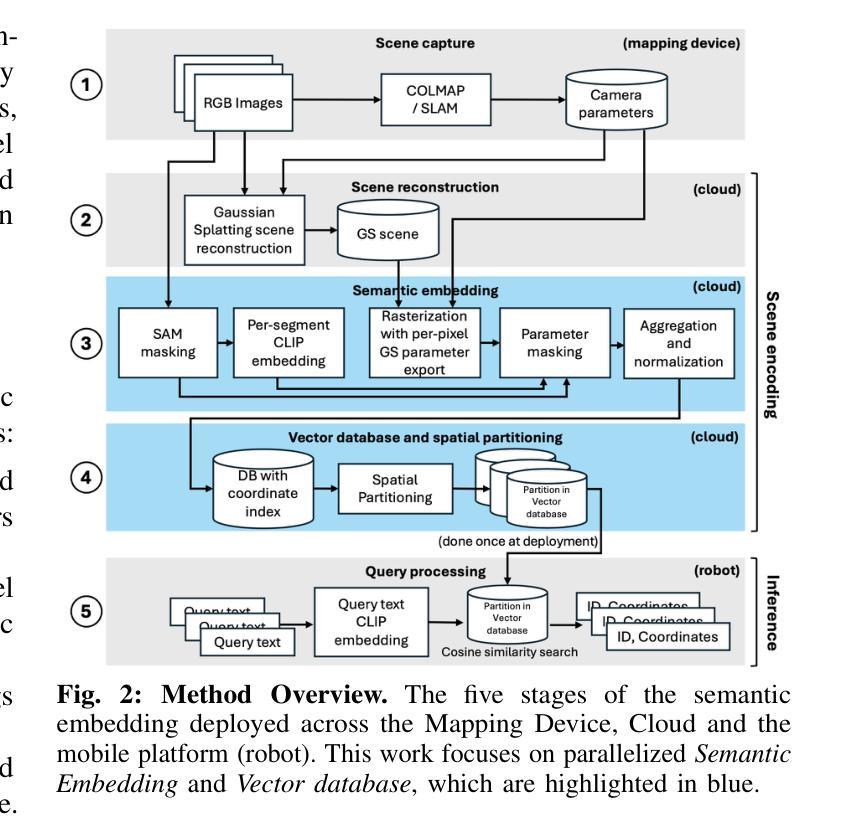
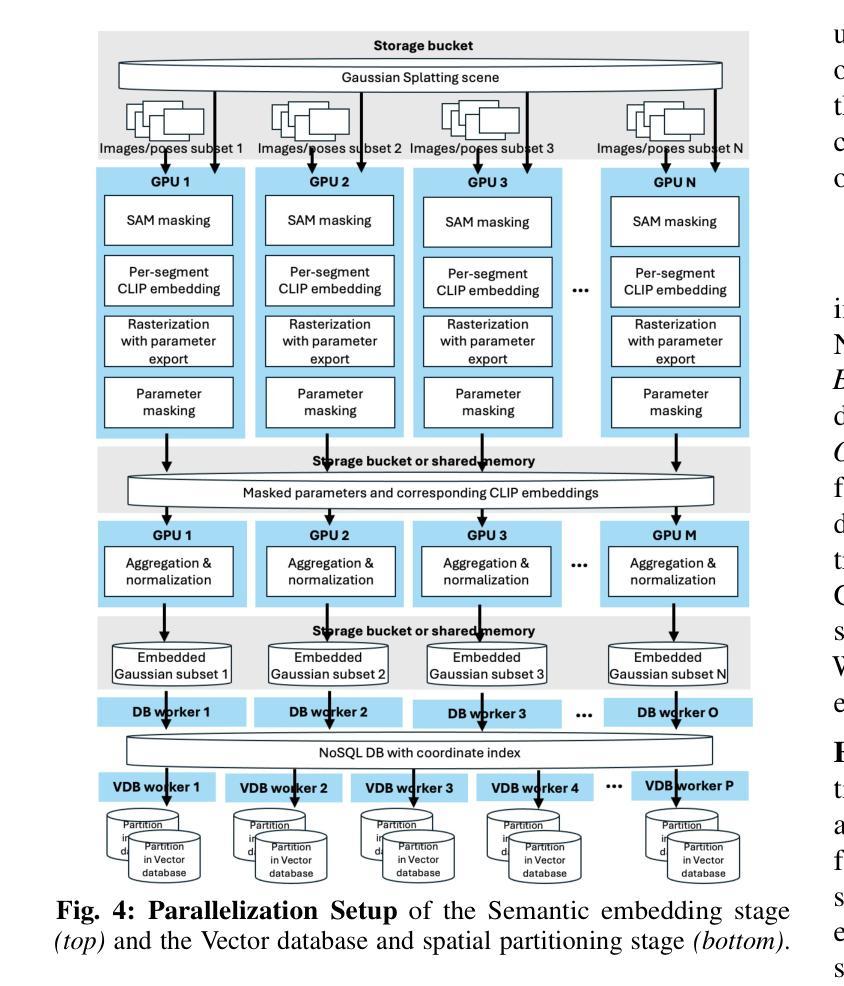
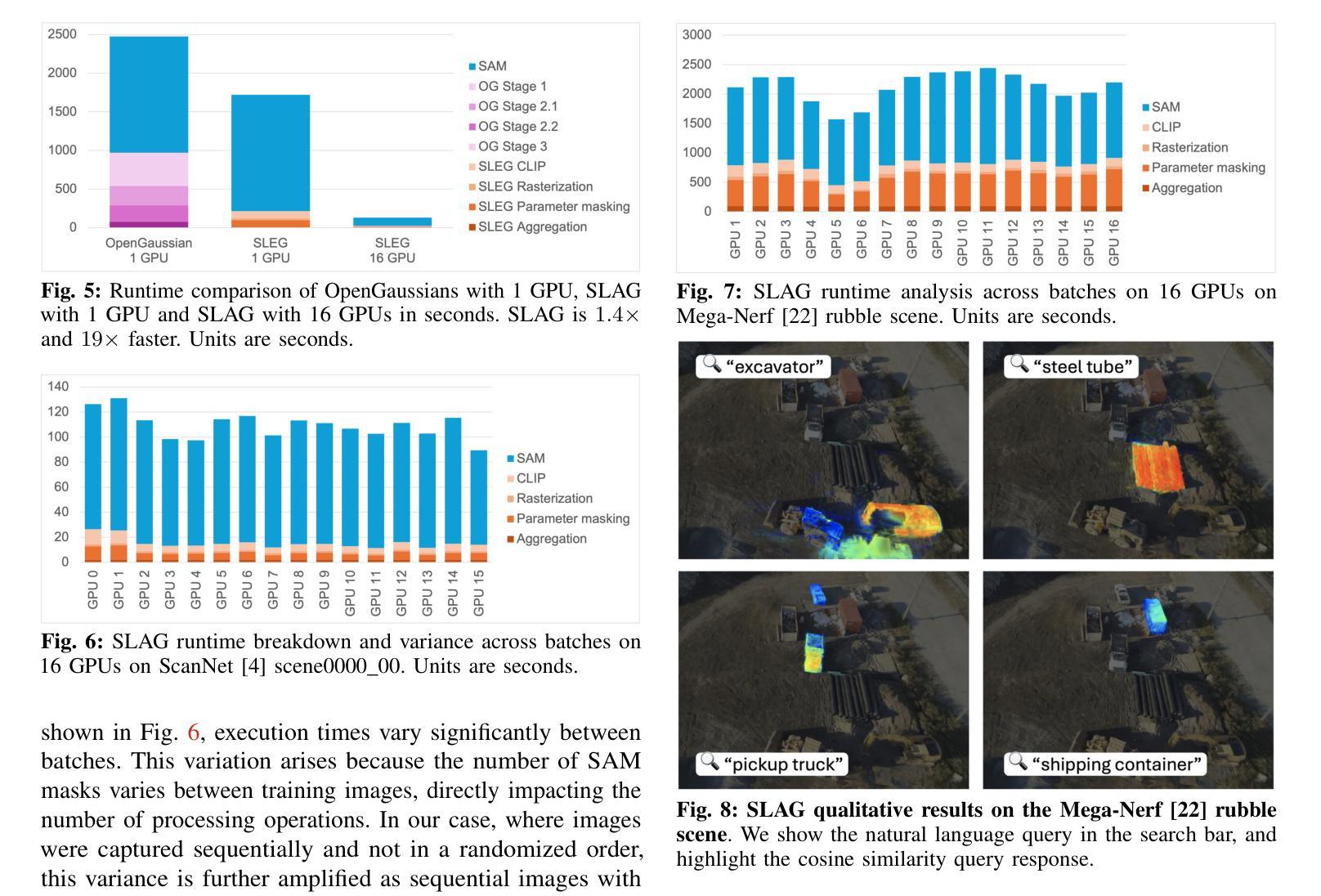
Language-augmented scene representations hold great promise for large-scale robotics applications such as search-and-rescue, smart cities, and mining. Many of these scenarios are time-sensitive, requiring rapid scene encoding while also being data-intensive, necessitating scalable solutions. Deploying these representations on robots with limited computational resources further adds to the challenge. To address this, we introduce SLAG, a multi-GPU framework for language-augmented Gaussian splatting that enhances the speed and scalability of embedding large scenes. Our method integrates 2D visual-language model features into 3D scenes using SAM and CLIP. Unlike prior approaches, SLAG eliminates the need for a loss function to compute per-Gaussian language embeddings. Instead, it derives embeddings from 3D Gaussian scene parameters via a normalized weighted average, enabling highly parallelized scene encoding. Additionally, we introduce a vector database for efficient embedding storage and retrieval. Our experiments show that SLAG achieves an 18 times speedup in embedding computation on a 16-GPU setup compared to OpenGaussian, while preserving embedding quality on the ScanNet and LERF datasets. For more details, visit our project website: https://slag-project.github.io/.
语言增强的场景表示在大型机器人应用方面,如搜索和救援、智能城市和采矿等领域具有巨大潜力。许多这些场景都是时间敏感型的,需要在快速场景编码的同时处理大量数据,需要可扩展的解决方案。在具有有限计算资源的机器人上部署这些表示形式进一步增加了挑战。为了解决这一问题,我们引入了SLAG,这是一个用于语言增强的多GPU高斯拼接框架,提高了大规模场景嵌入的速度和可扩展性。我们的方法通过将2D视觉语言模型特征集成到3D场景中,使用SAM和CLIP。不同于以前的方法,SLAG不需要使用损失函数来计算每个高斯语言嵌入。相反,它通过归一化加权平均从3D高斯场景参数中提取嵌入,实现高度并行的场景编码。此外,我们还引入了一个向量数据库,用于有效地存储和检索嵌入。我们的实验表明,与OpenGaussian相比,SLAG在16 GPU设置上实现了嵌入计算的速度提升18倍,同时在ScanNet和LERF数据集上保持了嵌入质量。如需更多详细信息,请访问我们的项目网站:https://slag-project.github.io/。%E3%80%82
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
该文本介绍了语言增强场景表示在机器人等大型应用场景中的潜力,如搜救、智能城市和采矿。针对大型场景的快速编码和数据密集需求,提出了一种基于多GPU的语言增强高斯喷绘框架SLAG。该方法通过整合二维视觉语言模型特征到三维场景,提升了场景编码的速度和可扩展性。SLAG通过归一化加权平均从三维高斯场景参数中导出嵌入,无需使用损失函数计算每个高斯语言的嵌入。此外,还引入了向量数据库,以便高效存储和检索嵌入。实验表明,SLAG在16 GPU设置上的嵌入计算速度比OpenGaussian快18倍,同时在ScanNet和LERF数据集上保持嵌入质量。
Key Takeaways
- 语言增强场景表示在大型应用场景(如搜救、智能城市和采矿)中具有巨大潜力。
- SLAG是一种多GPU框架,用于语言增强的高斯喷绘,可提高场景编码的速度和可扩展性。
- SLAG通过将2D视觉语言模型特征集成到3D场景中,改进了场景表示。
- SLAG通过归一化加权平均从3D高斯场景参数中导出嵌入,简化了计算过程。
- SLAG引入向量数据库,实现高效嵌入存储和检索。
- 实验显示,SLAG在嵌入计算速度方面比OpenGaussian快18倍,同时保持嵌入质量。
点此查看论文截图

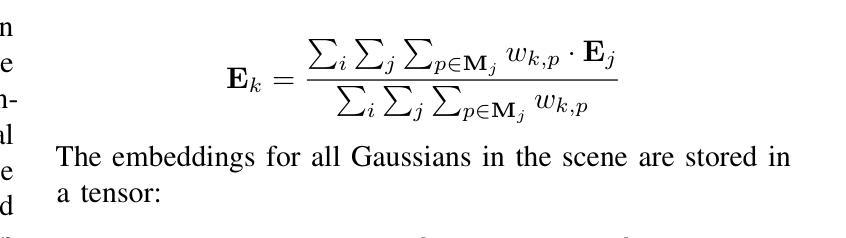
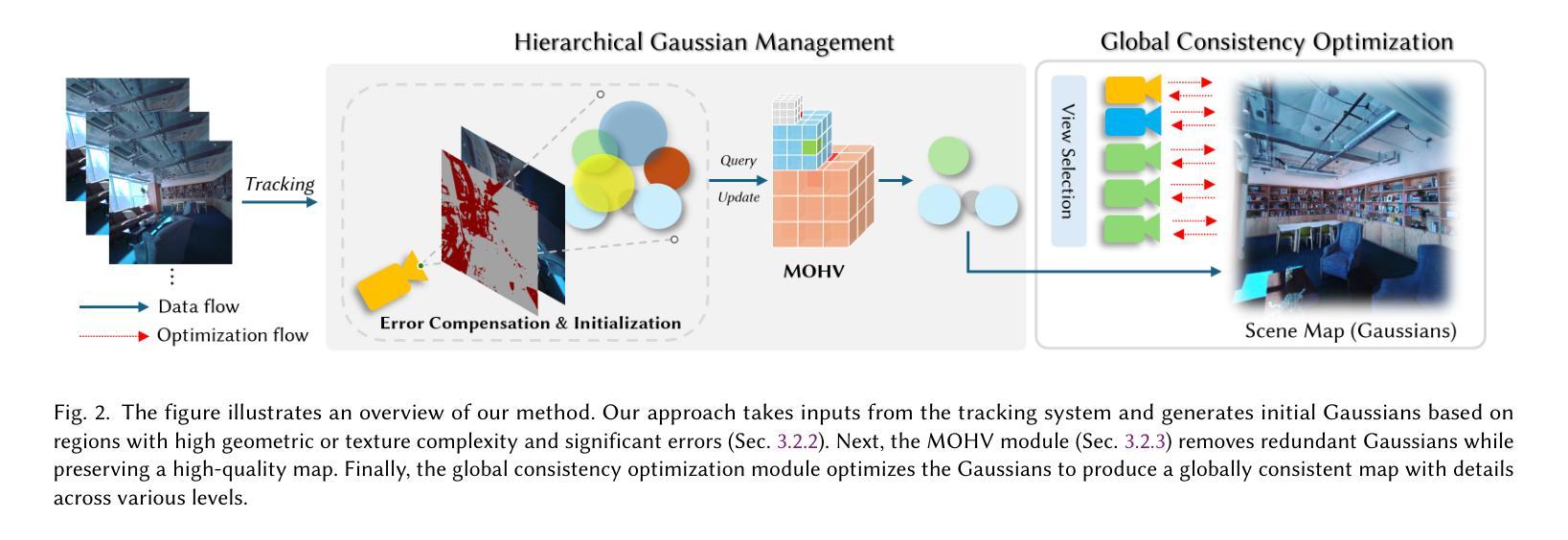
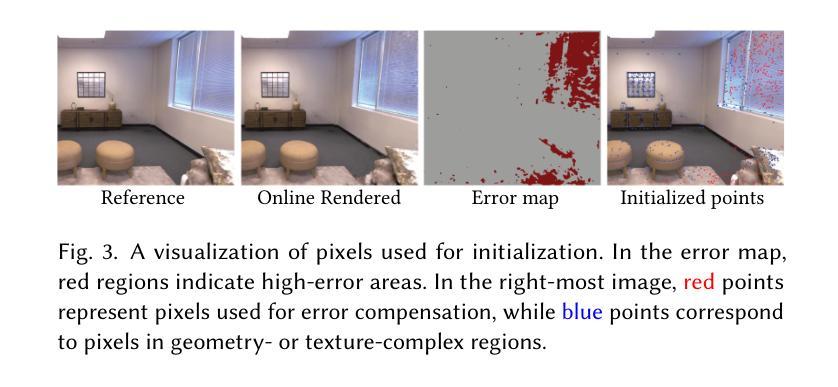
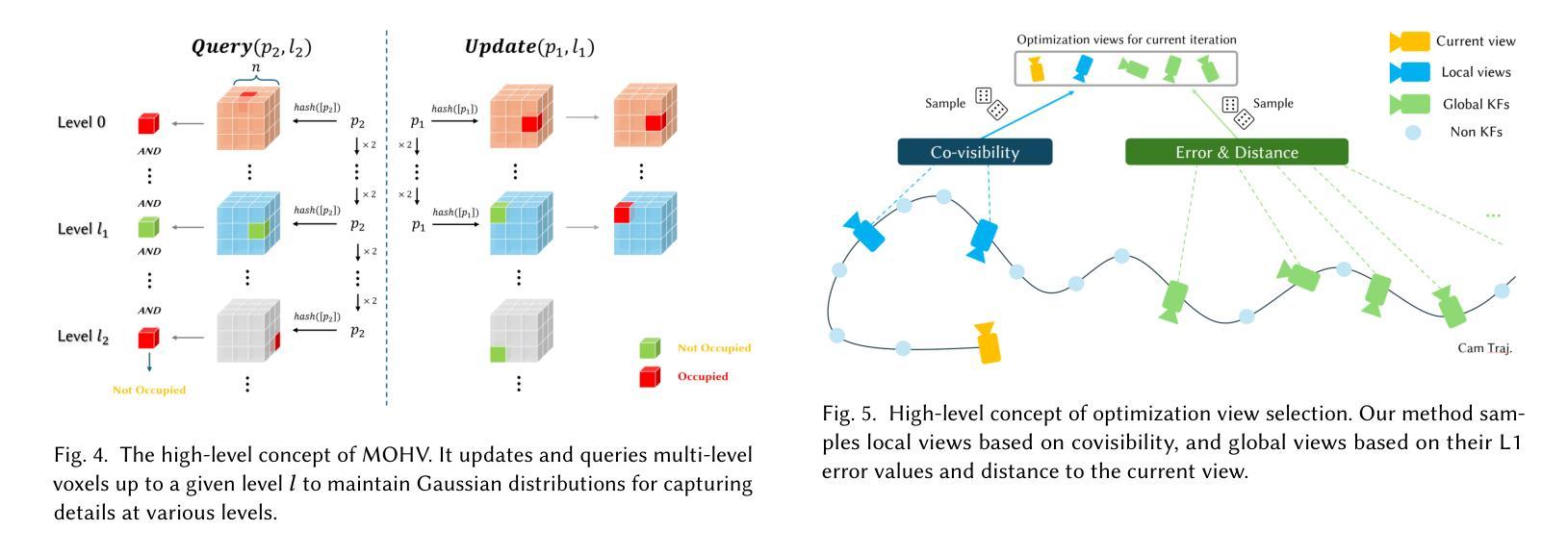
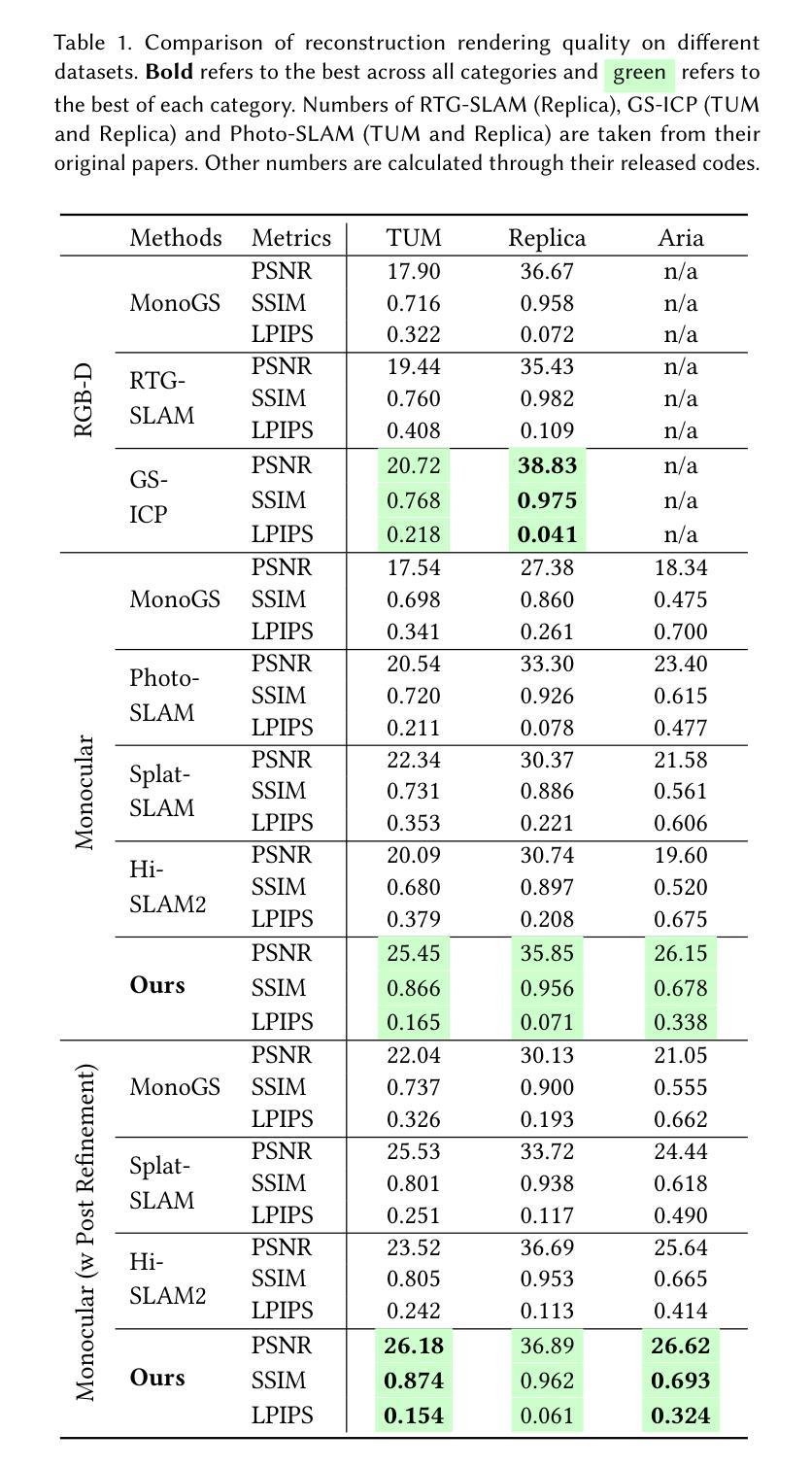
Monocular Online Reconstruction with Enhanced Detail Preservation
Authors:Songyin Wu, Zhaoyang Lv, Yufeng Zhu, Duncan Frost, Zhengqin Li, Ling-Qi Yan, Carl Ren, Richard Newcombe, Zhao Dong
We propose an online 3D Gaussian-based dense mapping framework for photorealistic details reconstruction from a monocular image stream. Our approach addresses two key challenges in monocular online reconstruction: distributing Gaussians without relying on depth maps and ensuring both local and global consistency in the reconstructed maps. To achieve this, we introduce two key modules: the Hierarchical Gaussian Management Module for effective Gaussian distribution and the Global Consistency Optimization Module for maintaining alignment and coherence at all scales. In addition, we present the Multi-level Occupancy Hash Voxels (MOHV), a structure that regularizes Gaussians for capturing details across multiple levels of granularity. MOHV ensures accurate reconstruction of both fine and coarse geometries and textures, preserving intricate details while maintaining overall structural integrity. Compared to state-of-the-art RGB-only and even RGB-D methods, our framework achieves superior reconstruction quality with high computational efficiency. Moreover, it integrates seamlessly with various tracking systems, ensuring generality and scalability.
我们提出了一种基于在线三维高斯分布的密集映射框架,用于从单目图像流中重建逼真的细节。我们的方法解决了单目在线重建中的两个关键挑战:在不依赖深度图的情况下分布高斯,以及在重建地图中确保局部和全局的一致性。为了实现这一点,我们引入了两个关键模块:分层高斯管理模块,用于有效的高斯分布;全局一致性优化模块,用于在所有尺度上保持对齐和连贯性。此外,我们提出了多级占用哈希体素(MOHV),这是一种使高斯正规化的结构,能够捕捉多粒度级别的细节。MOHV确保精细和粗糙的几何形状和纹理的准确重建,保留细节的同时保持整体结构完整性。与最先进的仅使用RGB甚至是RGB-D方法相比,我们的框架在计算效率高的情况下实现了更出色的重建质量。此外,它与各种跟踪系统无缝集成,确保了通用性和可扩展性。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
该文提出了一种在线三维高斯密集映射框架,用于从单目图像流重建逼真的细节。该方法解决了单目在线重建中的两个关键挑战:在不依赖深度图的情况下分布高斯并确保了重建地图的局部和全局一致性。为实现这一目标,引入了关键的两个模块:分层高斯管理模块用于有效的高斯分布和全局一致性优化模块,以在所有尺度上保持对齐和连贯性。此外,还提出了多级别占用哈希体素(MOHV),这种结构可以规范高斯分布以捕捉多个粒度级别的细节。MOHV确保精细和粗糙几何以及纹理的准确重建,保留细节的同时保持整体结构完整性。与最新的仅RGB甚至RGB-D方法相比,该框架具有更高的计算效率和优越的重建质量。此外,它与各种跟踪系统无缝集成,确保通用性和可扩展性。
Key Takeaways
以下是关键要点概述:
- 提出了一种在线三维高斯密集映射框架用于单目图像流的逼真细节重建。
- 解决单目在线重建中的两个关键挑战:高斯分布与深度图的无关性和局部与全局一致性的保证。
- 引入两个核心模块:分层高斯管理模块和全局一致性优化模块。
- 提出多级别占用哈希体素(MOHV)以捕捉多个粒度级别的细节并实现准确的重建细节和整体结构完整性。
- 与现有方法相比,该框架具有更高的计算效率和优越的重建质量。
点此查看论文截图

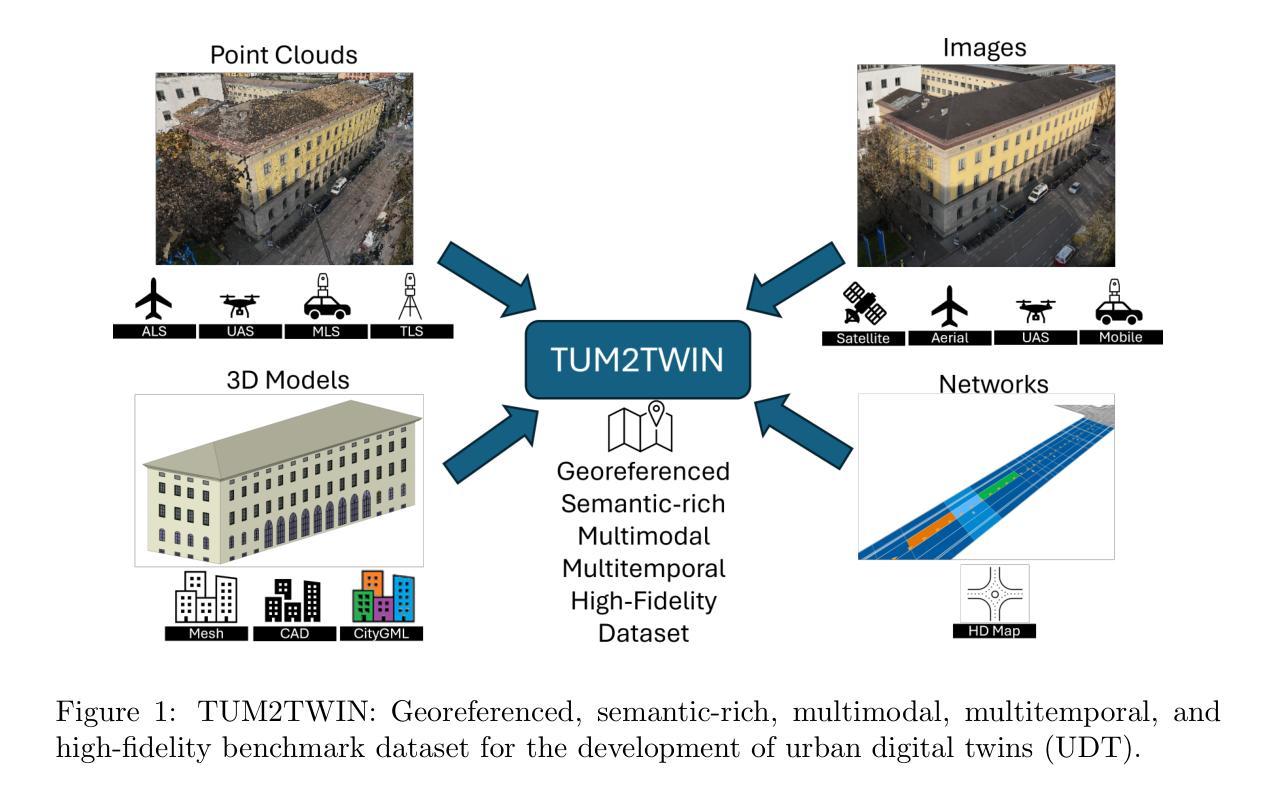
TUM2TWIN: Introducing the Large-Scale Multimodal Urban Digital Twin Benchmark Dataset
Authors:Olaf Wysocki, Benedikt Schwab, Manoj Kumar Biswanath, Michael Greza, Qilin Zhang, Jingwei Zhu, Thomas Froech, Medhini Heeramaglore, Ihab Hijazi, Khaoula Kanna, Mathias Pechinger, Zhaiyu Chen, Yao Sun, Alejandro Rueda Segura, Ziyang Xu, Omar AbdelGafar, Mansour Mehranfar, Chandan Yeshwanth, Yueh-Cheng Liu, Hadi Yazdi, Jiapan Wang, Stefan Auer, Katharina Anders, Klaus Bogenberger, Andre Borrmann, Angela Dai, Ludwig Hoegner, Christoph Holst, Thomas H. Kolbe, Ferdinand Ludwig, Matthias Nießner, Frank Petzold, Xiao Xiang Zhu, Boris Jutzi
Urban Digital Twins (UDTs) have become essential for managing cities and integrating complex, heterogeneous data from diverse sources. Creating UDTs involves challenges at multiple process stages, including acquiring accurate 3D source data, reconstructing high-fidelity 3D models, maintaining models’ updates, and ensuring seamless interoperability to downstream tasks. Current datasets are usually limited to one part of the processing chain, hampering comprehensive UDTs validation. To address these challenges, we introduce the first comprehensive multimodal Urban Digital Twin benchmark dataset: TUM2TWIN. This dataset includes georeferenced, semantically aligned 3D models and networks along with various terrestrial, mobile, aerial, and satellite observations boasting 32 data subsets over roughly 100,000 $m^2$ and currently 767 GB of data. By ensuring georeferenced indoor-outdoor acquisition, high accuracy, and multimodal data integration, the benchmark supports robust analysis of sensors and the development of advanced reconstruction methods. Additionally, we explore downstream tasks demonstrating the potential of TUM2TWIN, including novel view synthesis of NeRF and Gaussian Splatting, solar potential analysis, point cloud semantic segmentation, and LoD3 building reconstruction. We are convinced this contribution lays a foundation for overcoming current limitations in UDT creation, fostering new research directions and practical solutions for smarter, data-driven urban environments. The project is available under: https://tum2t.win
城市数字双胞胎(UDTs)对于管理城市以及整合来自不同源的复杂、异构数据已经变得至关重要。创建UDTs涉及多个流程阶段的挑战,包括获取准确的3D源数据、重建高保真3D模型、保持模型的更新以及确保无缝集成到下游任务中。当前的数据集通常仅限于处理链的一部分,阻碍了全面的UDTs验证。为了解决这些挑战,我们引入了第一个全面的多模式城市数字双胞胎基准数据集:TUM2TWIN。该数据集包括地理参考、语义对齐的3D模型和网络,以及各种地面、移动、空中和卫星观测,拥有超过约10万平方米的32个数据子集和目前767GB的数据。通过确保地理参考的室内外采集、高精度和多模式数据集成,该基准支持对传感器的稳健分析和高级重建方法的发展。此外,我们还探索了展示TUM2TWIN潜力的下游任务,包括NeRF和高斯拼贴的新视图合成、太阳能潜力分析、点云语义分割和LOD3建筑重建。我们相信这一贡献为克服UDTs创建中的当前局限性奠定了基础,促进了新的研究方向和针对数据驱动的智能城市环境的实用解决方案。项目网址为:https://tum2t.win
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Submitted to the ISPRS Journal of Photogrammetry and Remote Sensing
Summary
本文介绍了城市数字双胞胎(UDTs)在管理城市和整合复杂、异构数据方面的作用。针对创建UDTs所面临的挑战,如获取准确的3D源数据、重建高保真3D模型等,提出了一种新的综合多模态城市数字双胞胎基准数据集——TUM2TWIN。该数据集包含地理参考的语义对齐的3D模型和网络,以及各种地面、移动、空中和卫星观测数据,包含约10万平米的32个数据子集和目前共767GB的数据。该基准数据集支持传感器稳健性分析以及高级重建方法的发展。此外,还探讨了下游任务,展示了TUM2TWIN的潜力,包括新型视图合成、太阳能潜力分析、点云语义分割和LOD3建筑重建等。此贡献为克服当前UDT创建中的限制奠定了基础,为智能数据驱动的城市环境研究提供了新的研究方向和实用解决方案。
Key Takeaways
- UDTs在现代城市管理中的作用:管理复杂、异构数据,提升城市智能化水平。
- 创建UDTs的挑战包括获取准确的3D源数据、模型重建、模型更新和无缝集成等。
- TUM2TWIN是一个综合多模态城市数字双胞胎基准数据集,包含地理参考的语义对齐的3D模型和各种观测数据。
- 数据集大小为约767GB,覆盖多个领域,如地面、移动、空中和卫星观测数据。
- 基准数据集支持传感器稳健性分析以及高级重建方法的发展。
- TUM2TWIN的下游任务展示了其在新型视图合成、太阳能潜力分析等领域的潜力。
点此查看论文截图


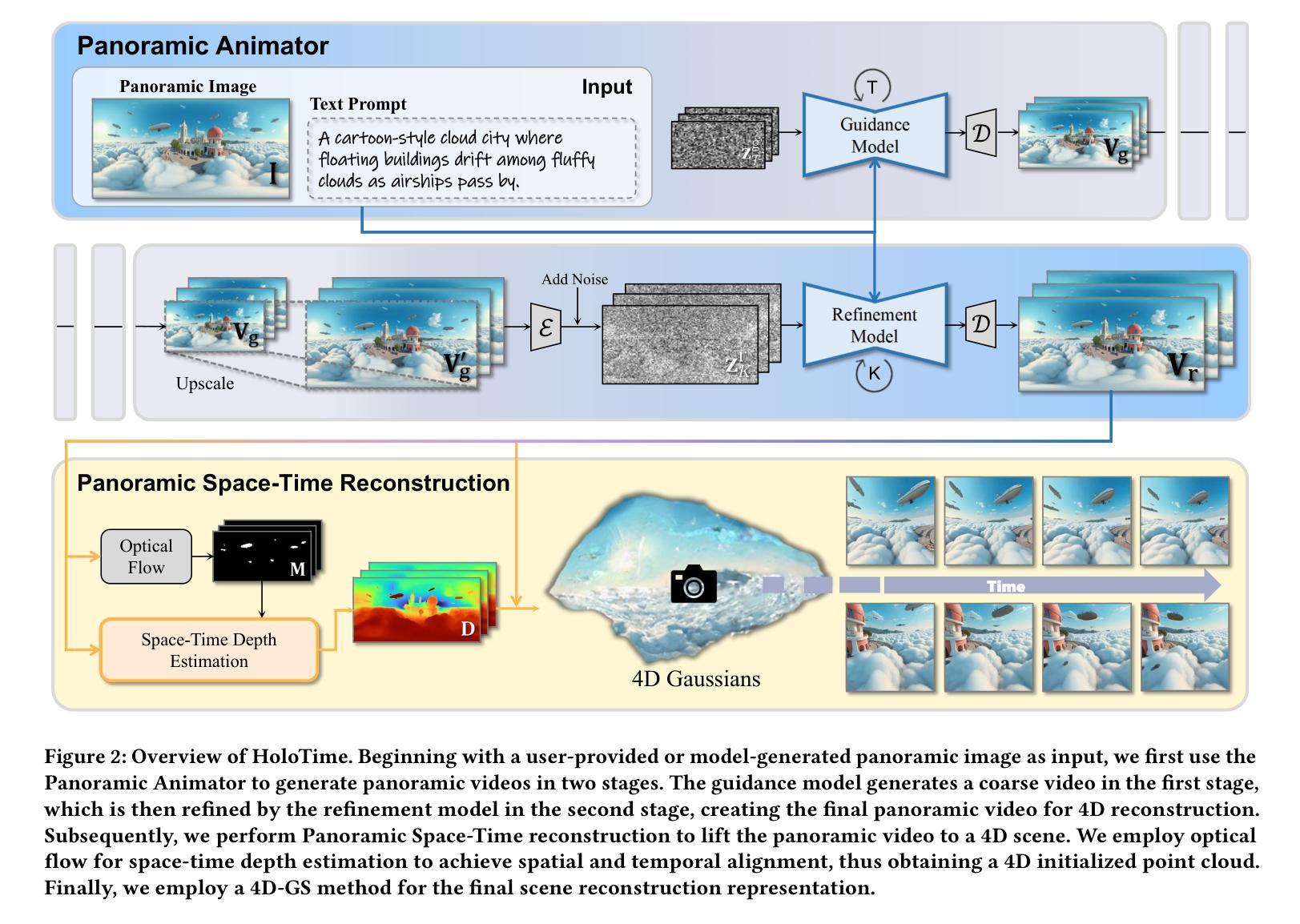
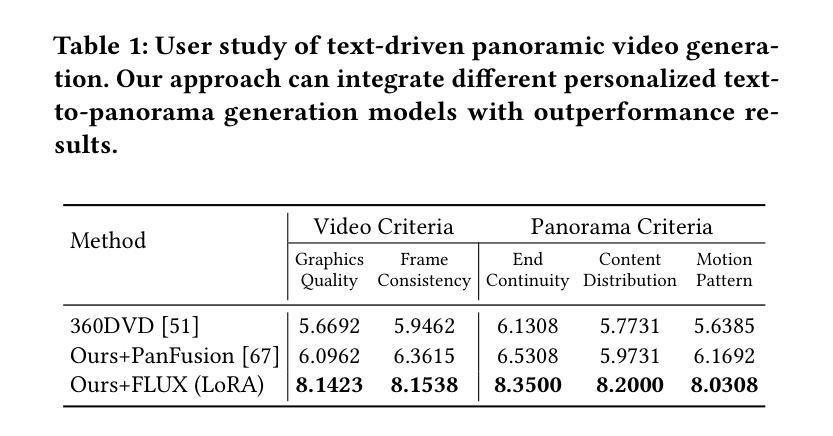
HoloTime: Taming Video Diffusion Models for Panoramic 4D Scene Generation
Authors:Haiyang Zhou, Wangbo Yu, Jiawen Guan, Xinhua Cheng, Yonghong Tian, Li Yuan
The rapid advancement of diffusion models holds the promise of revolutionizing the application of VR and AR technologies, which typically require scene-level 4D assets for user experience. Nonetheless, existing diffusion models predominantly concentrate on modeling static 3D scenes or object-level dynamics, constraining their capacity to provide truly immersive experiences. To address this issue, we propose HoloTime, a framework that integrates video diffusion models to generate panoramic videos from a single prompt or reference image, along with a 360-degree 4D scene reconstruction method that seamlessly transforms the generated panoramic video into 4D assets, enabling a fully immersive 4D experience for users. Specifically, to tame video diffusion models for generating high-fidelity panoramic videos, we introduce the 360World dataset, the first comprehensive collection of panoramic videos suitable for downstream 4D scene reconstruction tasks. With this curated dataset, we propose Panoramic Animator, a two-stage image-to-video diffusion model that can convert panoramic images into high-quality panoramic videos. Following this, we present Panoramic Space-Time Reconstruction, which leverages a space-time depth estimation method to transform the generated panoramic videos into 4D point clouds, enabling the optimization of a holistic 4D Gaussian Splatting representation to reconstruct spatially and temporally consistent 4D scenes. To validate the efficacy of our method, we conducted a comparative analysis with existing approaches, revealing its superiority in both panoramic video generation and 4D scene reconstruction. This demonstrates our method’s capability to create more engaging and realistic immersive environments, thereby enhancing user experiences in VR and AR applications.
扩散模型的快速发展有望彻底改变VR和AR技术的应用,这些技术通常需要场景级的四维资产来提升用户体验。然而,现有的扩散模型主要集中在静态三维场景的建模或对象级别的动态建模上,这限制了它们提供真正沉浸式体验的能力。为了解决这个问题,我们提出了HoloTime框架,它结合了视频扩散模型来生成全景视频,从一个单一的提示或参考图像开始,以及一种360度的四维场景重建方法,它将生成的全景视频无缝地转换为四维资产,为用户提供了完整的沉浸式四维体验。具体来说,为了驾驭视频扩散模型以生成高保真全景视频,我们引入了全景视频数据集——迄今为止最全面的全景视频集之一,这些视频适用于下游四维场景重建任务。有了这个精选的数据集,我们提出了全景动画生成器(Panoramic Animator),这是一个两阶段的图像到视频的扩散模型,可以将全景图像转换为高质量的全景视频。之后,我们提出了全景时空重建技术(Panoramic Space-Time Reconstruction),它利用时空深度估计方法将生成的全景视频转换为四维点云,从而优化整体的四维高斯映射表示法(Gaussian Splatting)来重建时间和空间一致的四维场景。为了验证我们方法的效力,我们与现有方法进行了比较分析,揭示了其在全景视频生成和四维场景重建方面的优势。这表明我们的方法能够创建更加引人入胜和现实主义的沉浸式环境,从而增强VR和AR应用中的用户体验。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Project Homepage: https://zhouhyocean.github.io/holotime/ Code: https://github.com/PKU-YuanGroup/HoloTime
摘要
扩散模型的快速发展有望彻底改变VR和AR技术的应用,这些技术通常需要场景级的4D资产来提升用户体验。然而,现有的扩散模型主要集中在静态3D场景的建模或对象级的动态建模上,这限制了它们提供真正沉浸式体验的能力。为了解决这个问题,我们提出了HoloTime框架,它集成了视频扩散模型来生成全景视频,从一个单一的提示或参考图像开始,以及一种360度的4D场景重建方法,无缝地将生成的全景视频转化为4D资产,为用户提供全方位的沉浸式体验。具体来说,为了驾驭生成高保真全景视频的视频扩散模型,我们引入了首个全景视频综合数据集——360World数据集,适用于下游的4D场景重建任务。借助这个数据集,我们提出了全景动画师(Panoramic Animator)——一个两阶段的图像到视频的扩散模型,能将全景图像转换为高质量的全景视频。之后我们推出全景时空重建技术(Panoramic Space-Time Reconstruction),它采用时空深度估计方法来生成全景视频转换为空间的点云模型为整个四维场景的构建在时间上都实现了空间和时间的连贯性一致性重建在时空上的连贯性验证。我们的比较分析揭示了其在全景视频生成和场景重建上的优势在展现全息场景中实现的虚拟现实应用大幅增强了用户体验中的吸引力和现实沉浸感证明其出色的用户互动能力和娱乐效果吸引力潜力大潜力巨大。
关键要点
一、扩散模型的快速发展对VR和AR技术革命具有巨大潜力。它们正在推动全景视频和沉浸式体验的进步。然而,现有的扩散模型主要集中在静态场景的建模上,缺乏动态场景建模的能力。
点此查看论文截图


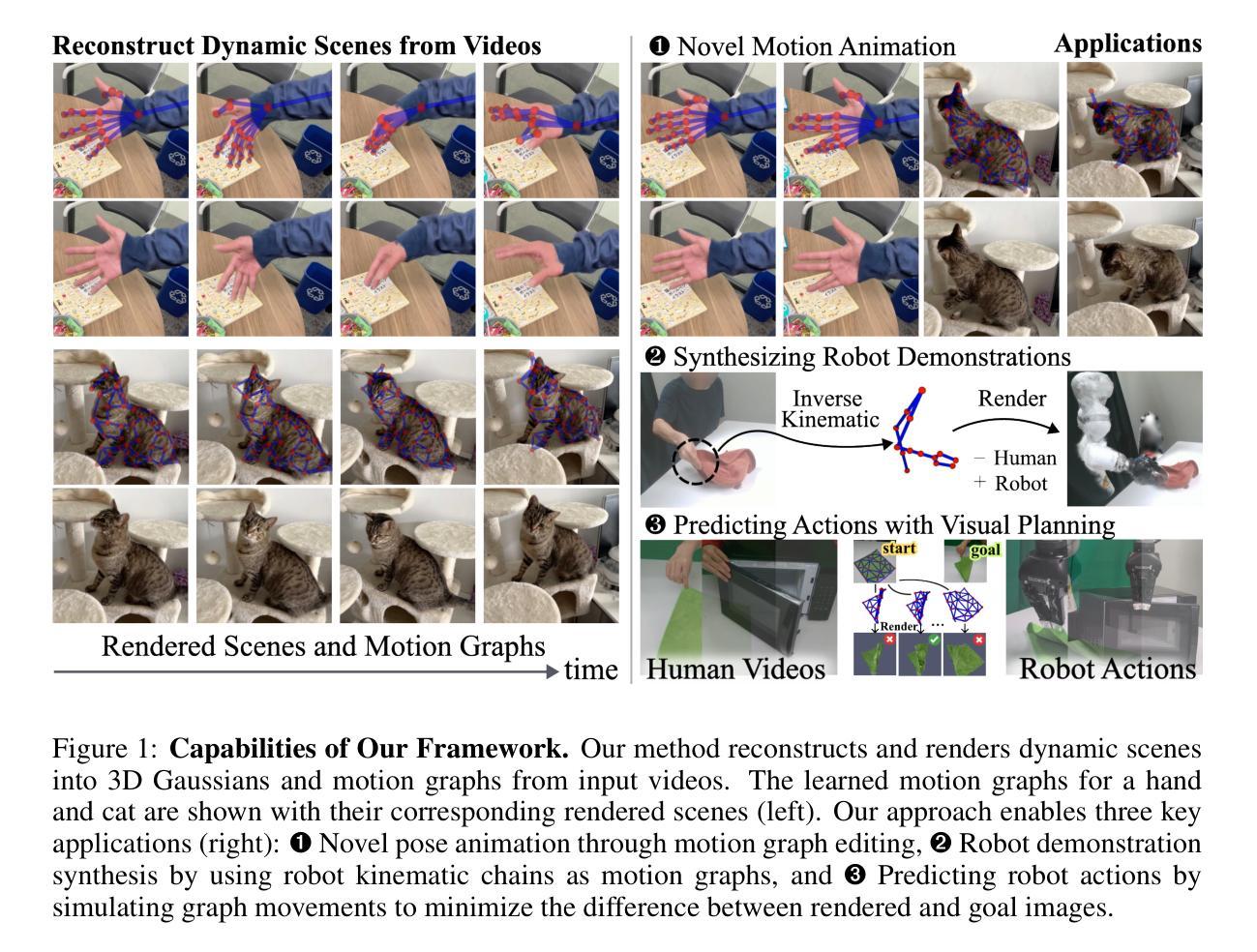
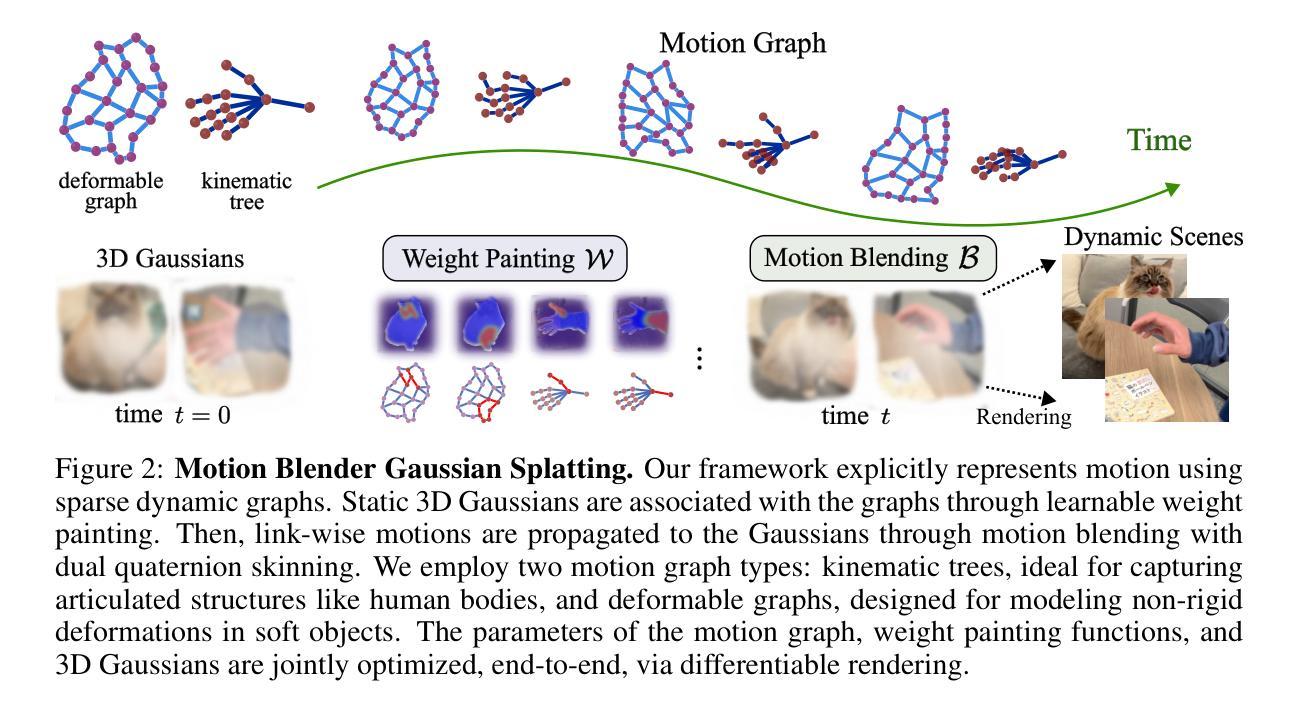
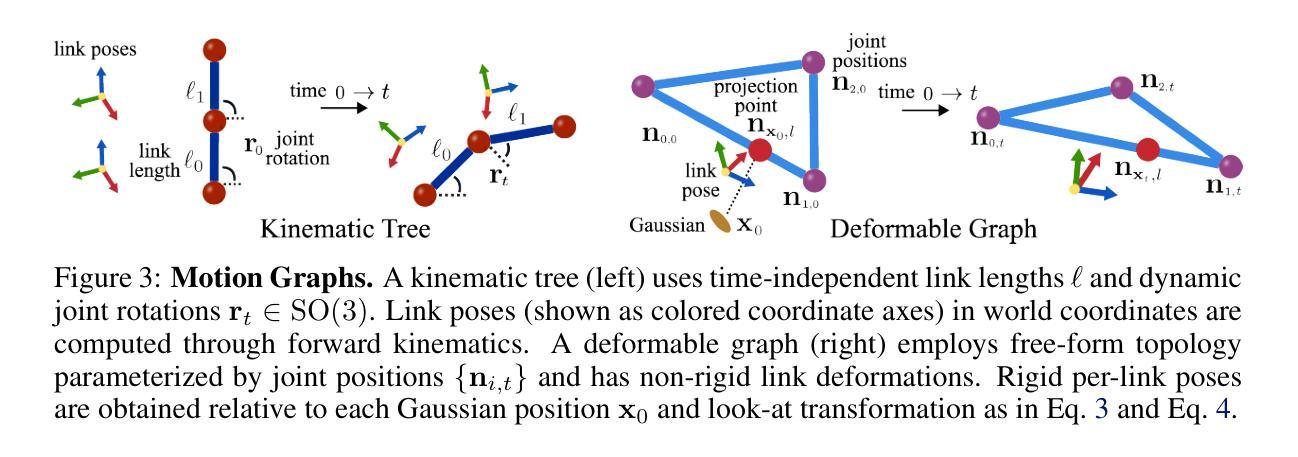
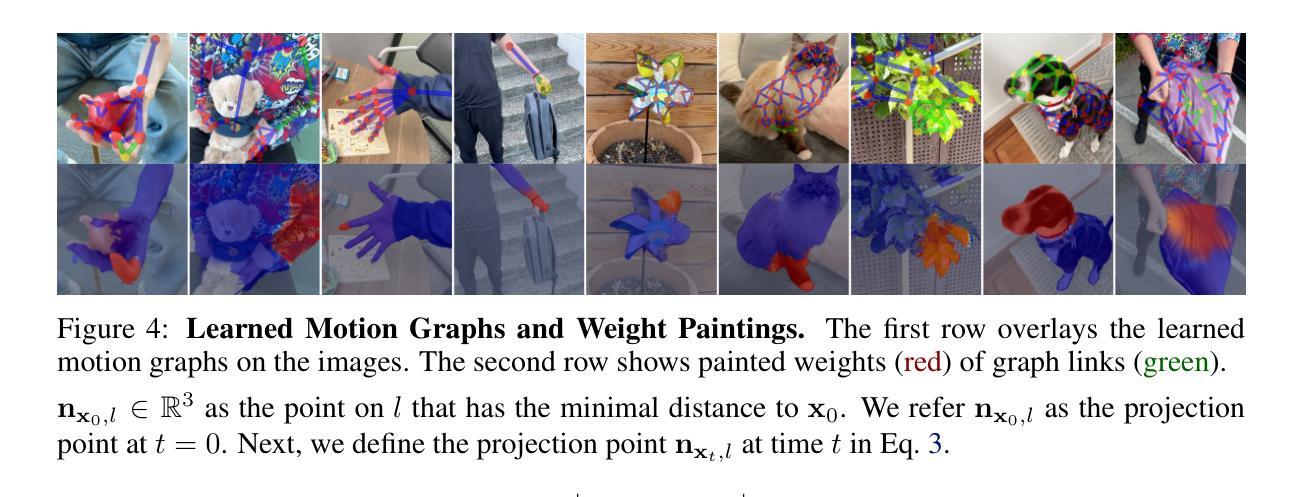
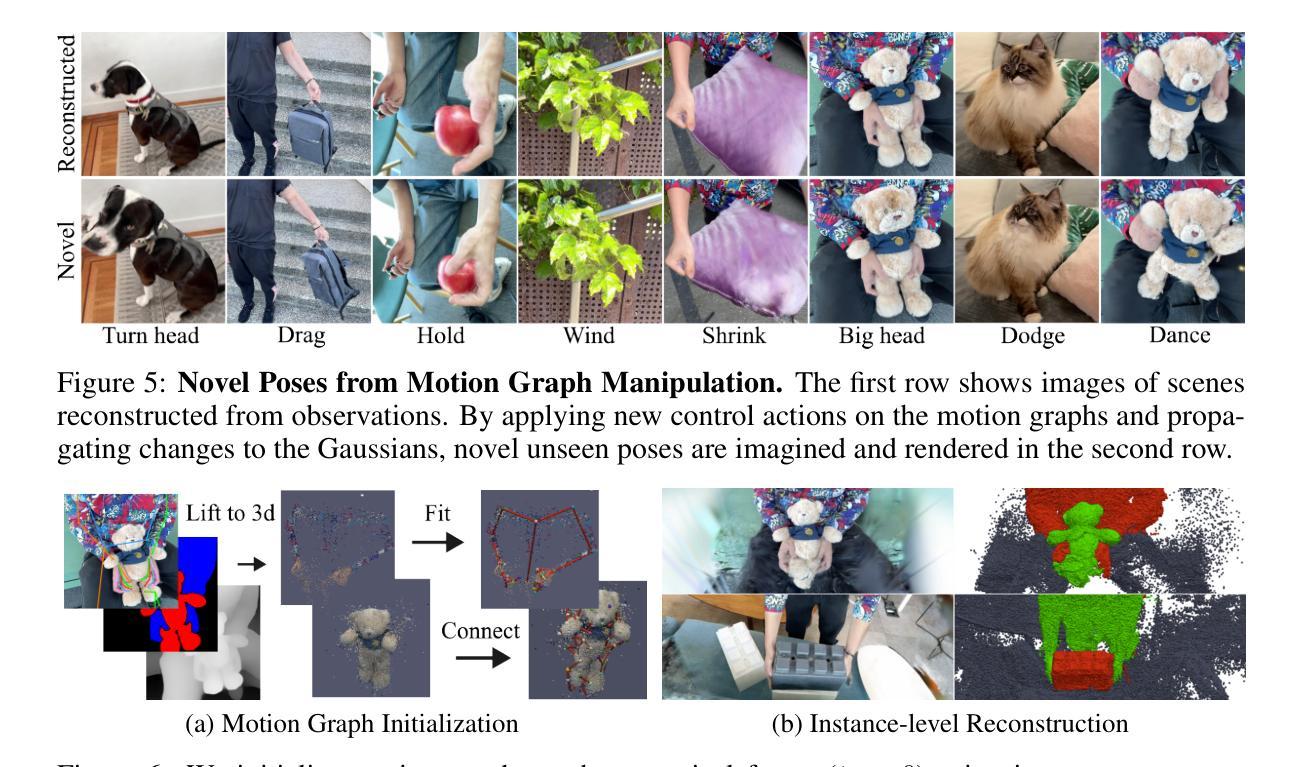
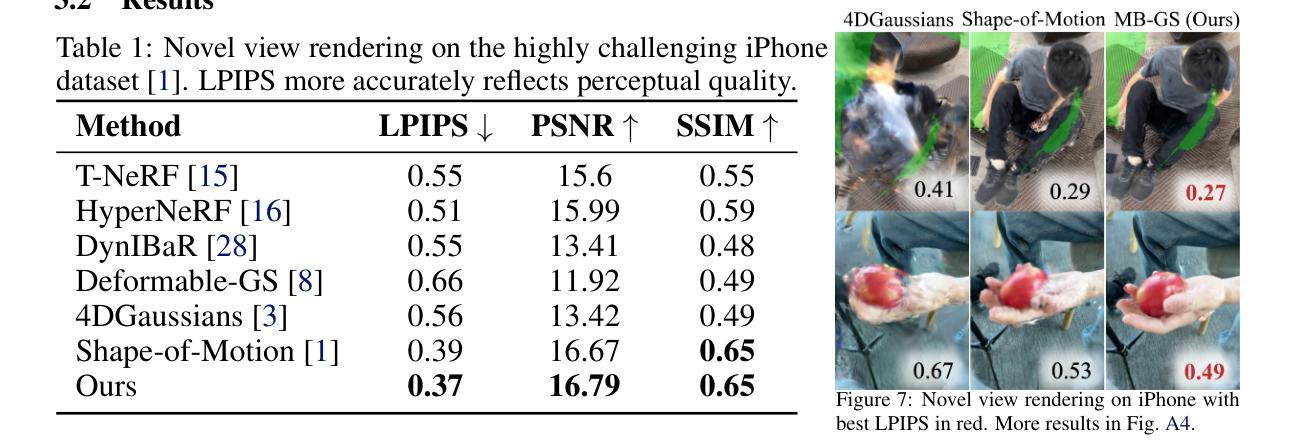
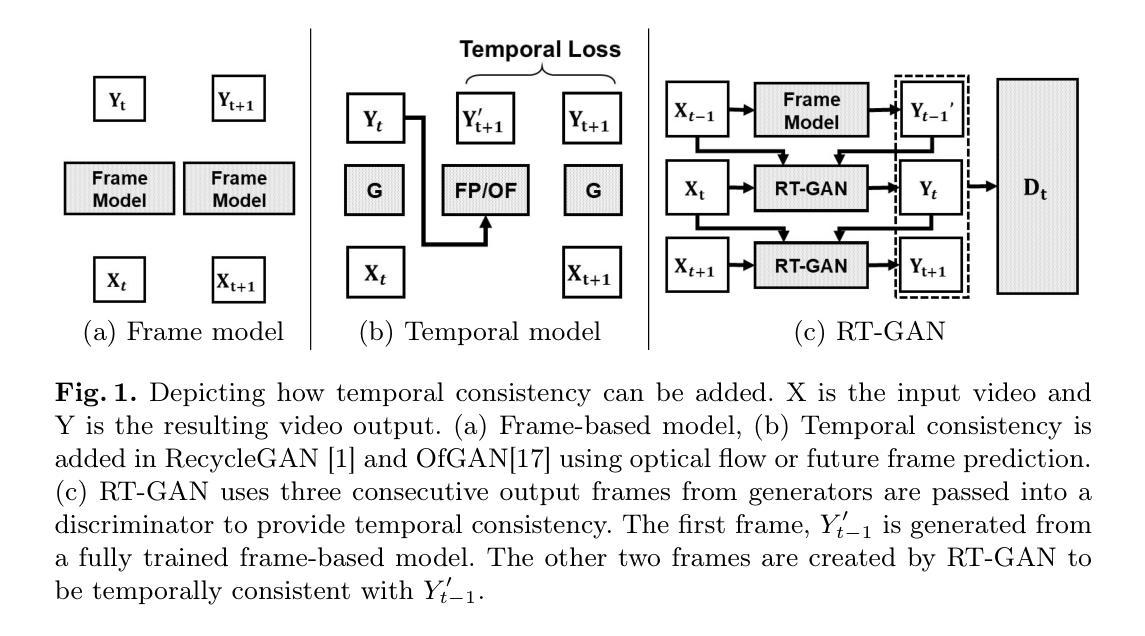
Motion Blender Gaussian Splatting for Dynamic Scene Reconstruction
Authors:Xinyu Zhang, Haonan Chang, Yuhan Liu, Abdeslam Boularias
Gaussian splatting has emerged as a powerful tool for high-fidelity reconstruction of dynamic scenes. However, existing methods primarily rely on implicit motion representations, such as encoding motions into neural networks or per-Gaussian parameters, which makes it difficult to further manipulate the reconstructed motions. This lack of explicit controllability limits existing methods to replaying recorded motions only, which hinders a wider application in robotics. To address this, we propose Motion Blender Gaussian Splatting (MBGS), a novel framework that uses motion graphs as an explicit and sparse motion representation. The motion of a graph’s links is propagated to individual Gaussians via dual quaternion skinning, with learnable weight painting functions that determine the influence of each link. The motion graphs and 3D Gaussians are jointly optimized from input videos via differentiable rendering. Experiments show that MBGS achieves state-of-the-art performance on the highly challenging iPhone dataset while being competitive on HyperNeRF. We demonstrate the application potential of our method in animating novel object poses, synthesizing real robot demonstrations, and predicting robot actions through visual planning. The source code, models, video demonstrations can be found at http://mlzxy.github.io/motion-blender-gs.
高斯混合法已经成为重建动态场景的高保真工具。然而,现有的方法主要依赖于隐式运动表示,如将运动编码到神经网络或每个高斯参数中,这使得进一步操纵重建运动变得困难。这种缺乏明确的可控性限制了现有方法只能回放记录的运动,阻碍了其在机器人技术中的更广泛应用。为解决这一问题,我们提出了运动混合高斯混合法(MBGS),这是一种使用运动图作为显式且稀疏运动表示的新型框架。图链接的运动通过双四元数蒙皮传播到单个高斯,通过可学习的权重绘制函数来确定每个链接的影响。运动图和三维高斯通过可微分渲染从输入视频联合优化。实验表明,MBGS在极具挑战性的iPhone数据集上达到了最先进的性能,同时在HyperNeRF上表现具有竞争力。我们展示了该方法在动画新物体姿态、合成真实机器人演示以及通过视觉规划预测机器人动作方面的应用潜力。源代码、模型和视频演示可在http://mlzxy.github.io/motion-blender-gs找到。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
高斯贴片技术已成为重建动态场景的高保真工具。然而,现有方法主要依赖于隐式运动表示,如将运动编码到神经网络或每个高斯参数中,这使得难以进一步操作重建的运动。缺乏明确的可控性限制了现有方法仅回放记录的运动,阻碍了其在机器人技术中的更广泛应用。为解决此问题,我们提出使用运动图作为显式且稀疏的运动表示的新框架——Motion Blender Gaussian Splatting (MBGS)。图链接的运动通过双四元数蒙皮传播到各个高斯,通过可学习的权重绘制函数来确定每个链接的影响。运动图和3D高斯通过可微分渲染从输入视频联合优化。实验表明,MBGS在极具挑战性的iPhone数据集上达到了最先进的性能,同时在HyperNeRF上具有很强的竞争力。我们在动画新颖物体姿态、合成真实机器人演示以及通过视觉规划预测机器人动作等方面展示了该方法的潜力。更多详情可访问http://mlzxy.github.io/motion-blender-gs。
Key Takeaways
- 高斯贴片技术已成为重建动态场景的重要工具。
- 现有方法主要依赖隐式运动表示,存在操作难度和可控性限制。
- MBGS框架使用运动图作为显式和稀疏的运动表示来解决这一问题。
- 运动图链接的运动通过双四元数蒙皮传播到高斯。
- MBGS通过可微分渲染联合优化运动图和3D高斯。
- MBGS在多个数据集上表现优秀,包括具有挑战性的iPhone数据集和HyperNeRF。
点此查看论文截图