⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-05-15 更新
Towards Autonomous UAV Visual Object Search in City Space: Benchmark and Agentic Methodology
Authors:Yatai Ji, Zhengqiu Zhu, Yong Zhao, Beidan Liu, Chen Gao, Yihao Zhao, Sihang Qiu, Yue Hu, Quanjun Yin, Yong Li
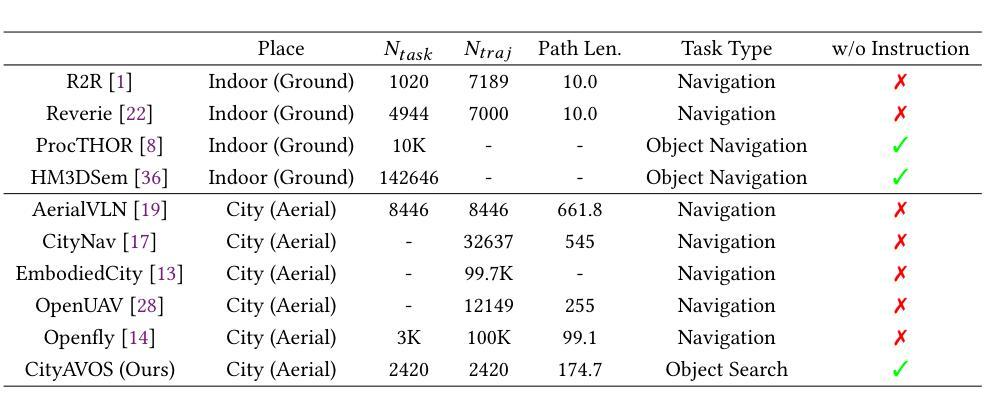
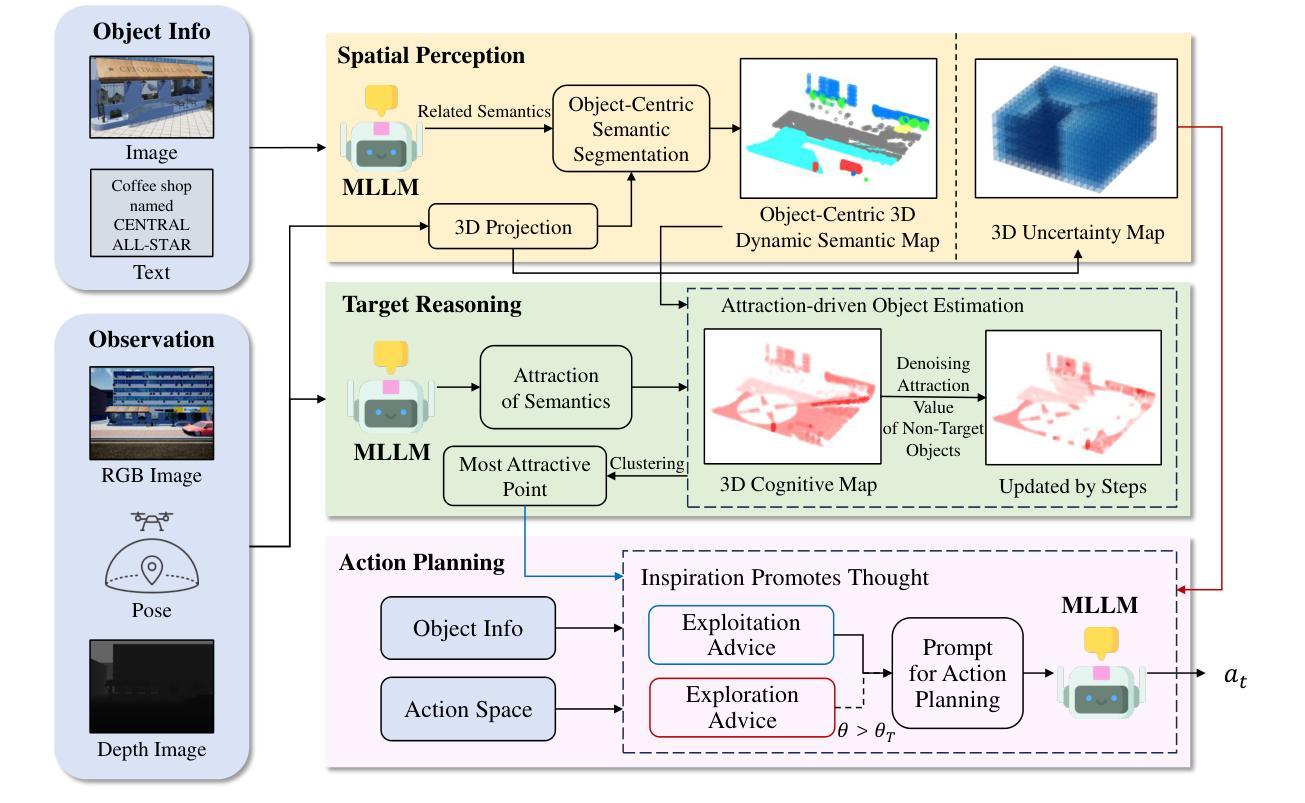
Aerial Visual Object Search (AVOS) tasks in urban environments require Unmanned Aerial Vehicles (UAVs) to autonomously search for and identify target objects using visual and textual cues without external guidance. Existing approaches struggle in complex urban environments due to redundant semantic processing, similar object distinction, and the exploration-exploitation dilemma. To bridge this gap and support the AVOS task, we introduce CityAVOS, the first benchmark dataset for autonomous search of common urban objects. This dataset comprises 2,420 tasks across six object categories with varying difficulty levels, enabling comprehensive evaluation of UAV agents’ search capabilities. To solve the AVOS tasks, we also propose PRPSearcher (Perception-Reasoning-Planning Searcher), a novel agentic method powered by multi-modal large language models (MLLMs) that mimics human three-tier cognition. Specifically, PRPSearcher constructs three specialized maps: an object-centric dynamic semantic map enhancing spatial perception, a 3D cognitive map based on semantic attraction values for target reasoning, and a 3D uncertainty map for balanced exploration-exploitation search. Also, our approach incorporates a denoising mechanism to mitigate interference from similar objects and utilizes an Inspiration Promote Thought (IPT) prompting mechanism for adaptive action planning. Experimental results on CityAVOS demonstrate that PRPSearcher surpasses existing baselines in both success rate and search efficiency (on average: +37.69% SR, +28.96% SPL, -30.69% MSS, and -46.40% NE). While promising, the performance gap compared to humans highlights the need for better semantic reasoning and spatial exploration capabilities in AVOS tasks. This work establishes a foundation for future advances in embodied target search. Dataset and source code are available at https://anonymous.4open.science/r/CityAVOS-3DF8.
无人机在城区环境中执行空中视觉目标搜索(AVOS)任务,需要自主利用视觉和文字线索进行目标对象的搜索和识别,而无需外部指导。现有的方法在处理复杂的城市环境时面临困难,例如冗余语义处理、相似对象区分以及探索与利用之间的困境。为了弥补这一差距并支持AVOS任务,我们引入了CityAVOS,这是首个用于城市常见目标自主搜索的基准数据集。该数据集包含六个对象类别的2420个任务,难度级别各异,能够全面评估无人机代理的搜索能力。为了解决AVOS任务,我们还提出了PRPSearcher(感知-推理-规划搜索器),这是一种新型代理方法,借助多模态大型语言模型(MLLMs)的力量,模拟人类的三层认知。具体来说,PRPSearcher构建了三张专业地图:一张增强空间感知的对象中心动态语义地图,一张基于目标推理的语义吸引值3D认知地图,以及一张平衡探索与利用的3D不确定性地图。此外,我们的方法还融入了一种降噪机制,以减轻相似对象的干扰,并采用了灵感促进思考(IPT)的提示机制,用于自适应行动规划。在CityAVOS上的实验结果表明,PRPSearcher在成功率和搜索效率上均超越了现有基线(平均成功率+37.69%,SPL+28.96%,MSS-30.69%,NE-46.40%)。尽管表现具有潜力,但与人类性能之间的差距仍然很大,这突显出在AVOS任务中需要更好的语义推理和空间探索能力。这项工作为未来的实体目标搜索进步奠定了基础。数据集和源代码可通过https://anonymous.4open.science/r/CityAVOS-3DF8获取。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
在复杂城市环境中,无人飞行器(UAVs)执行空中视觉目标搜索(AVOS)任务时面临诸多挑战。为解决这一问题并支持AVOS任务,本研究推出了CityAVOS数据集,这是首个针对城市常见目标自主搜索的基准数据集。本研究还提出了一种新型方法PRPSearcher,通过构建三类专门地图模仿人类认知层次结构,提高了UAV的智能搜索能力。实验结果显示,PRPSearcher在成功率和搜索效率上均超越了现有基线方法。然而,与人类性能相比仍存在差距,强调了语义推理和空间探索能力在AVOS任务中的重要性。
Key Takeaways
- 城市环境中的空中视觉目标搜索(AVOS)要求无人机使用视觉和文本线索自主寻找并识别目标物体。现有的方法在复杂城市环境中表现不佳。
- CityAVOS数据集是首个针对城市常见目标自主搜索的基准数据集,包含不同难度级别的任务。它支持对无人机搜索能力的全面评估。
点此查看论文截图


TRAIL: Trace Reasoning and Agentic Issue Localization
Authors:Darshan Deshpande, Varun Gangal, Hersh Mehta, Jitin Krishnan, Anand Kannappan, Rebecca Qian
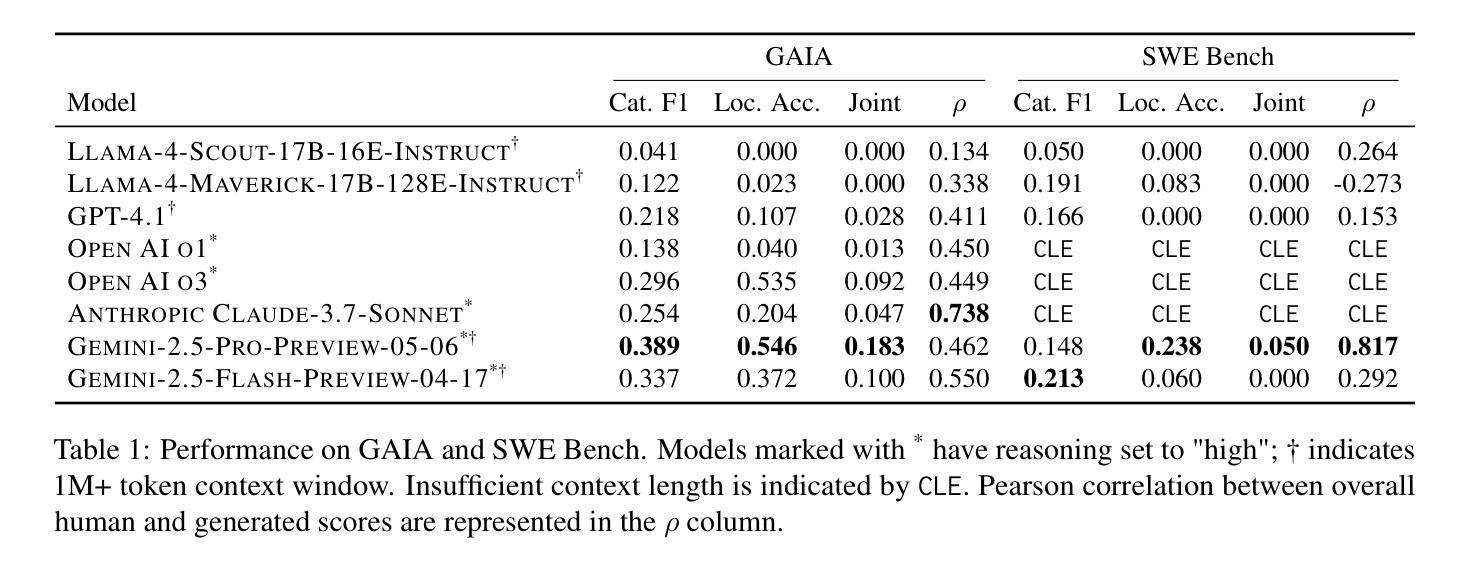
The increasing adoption of agentic workflows across diverse domains brings a critical need to scalably and systematically evaluate the complex traces these systems generate. Current evaluation methods depend on manual, domain-specific human analysis of lengthy workflow traces - an approach that does not scale with the growing complexity and volume of agentic outputs. Error analysis in these settings is further complicated by the interplay of external tool outputs and language model reasoning, making it more challenging than traditional software debugging. In this work, we (1) articulate the need for robust and dynamic evaluation methods for agentic workflow traces, (2) introduce a formal taxonomy of error types encountered in agentic systems, and (3) present a set of 148 large human-annotated traces (TRAIL) constructed using this taxonomy and grounded in established agentic benchmarks. To ensure ecological validity, we curate traces from both single and multi-agent systems, focusing on real-world applications such as software engineering and open-world information retrieval. Our evaluations reveal that modern long context LLMs perform poorly at trace debugging, with the best Gemini-2.5-pro model scoring a mere 11% on TRAIL. Our dataset and code are made publicly available to support and accelerate future research in scalable evaluation for agentic workflows.
随着代理工作流在各个领域中的日益普及,对可扩展且系统地评估这些系统产生的复杂轨迹的需求变得至关重要。当前的评估方法依赖于对冗长工作流轨迹进行手动、特定领域的人类分析——这种方法无法随着代理输出的不断增长的复杂性和数量而扩展。这些环境中的错误分析进一步受到外部工具输出和语言模型推理之间相互作用的影响,使其比传统软件调试更具挑战性。在这项工作中,我们(1)阐述了为代理工作流轨迹制定稳健和动态评估方法的必要性,(2)介绍了在代理系统中遇到的错误类型的正式分类,(3)基于该分类构建了一组包含 148 条由人类大规模标注的轨迹(TRAIL),这些轨迹建立在了公认的代理基准测试之上。为了确保生态有效性,我们从单代理系统和多代理系统中筛选轨迹,重点关注现实世界的应用,如软件工程和开放世界信息检索。我们的评估显示,现代大型语境语言模型(LLM)在轨迹调试方面表现不佳,最佳Gemini-2.5专业模型在TRAIL上的得分仅为11%。为了支持和加速对未来可扩展代理工作流评估的研究,我们的数据集和代码均已公开发布。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Dataset link: https://huggingface.co/datasets/PatronusAI/TRAIL
Summary
本文讨论了随着agentic工作流在多个领域的广泛应用,对其生成的复杂轨迹进行可伸缩和系统评价的重要性。现有的评估方法依赖于对冗长工作流轨迹进行手动、特定领域的分析,无法适应agentic输出不断增长和复杂性。本文提出了对agentic工作流轨迹的评估需求、错误类型的正式分类以及使用此分类和基于既定的agentic基准测试构建的大型人为注释轨迹集(TRAIL)。这些轨迹涵盖了单智能体和多智能体系统,并专注于软件工程和开放世界信息检索等实际应用。评估显示现代大型语言模型在轨迹调试方面表现不佳,最佳模型在TRAIL上的得分仅为11%。公开提供数据集和代码以支持并加速对未来agentic工作流评估的研究。
Key Takeaways
- Agentic工作流的广泛应用需要可伸缩和系统评价其复杂轨迹的方法。
- 当前评估方法主要依赖手动、特定领域的分析,难以应对增长和复杂性。
- 提出了对agentic工作流轨迹的评估需求以及错误类型的正式分类。
- 构建了基于这些分类的大型人为注释轨迹集(TRAIL)。
- TRAIL涵盖了单智能体和多智能体系统,并专注于实际应用如软件工程和信息检索。
- 评估显示现代大型语言模型在轨迹调试方面表现不佳。
点此查看论文截图

Credit Assignment and Efficient Exploration based on Influence Scope in Multi-agent Reinforcement Learning
Authors:Shuai Han, Mehdi Dastani, Shihan Wang
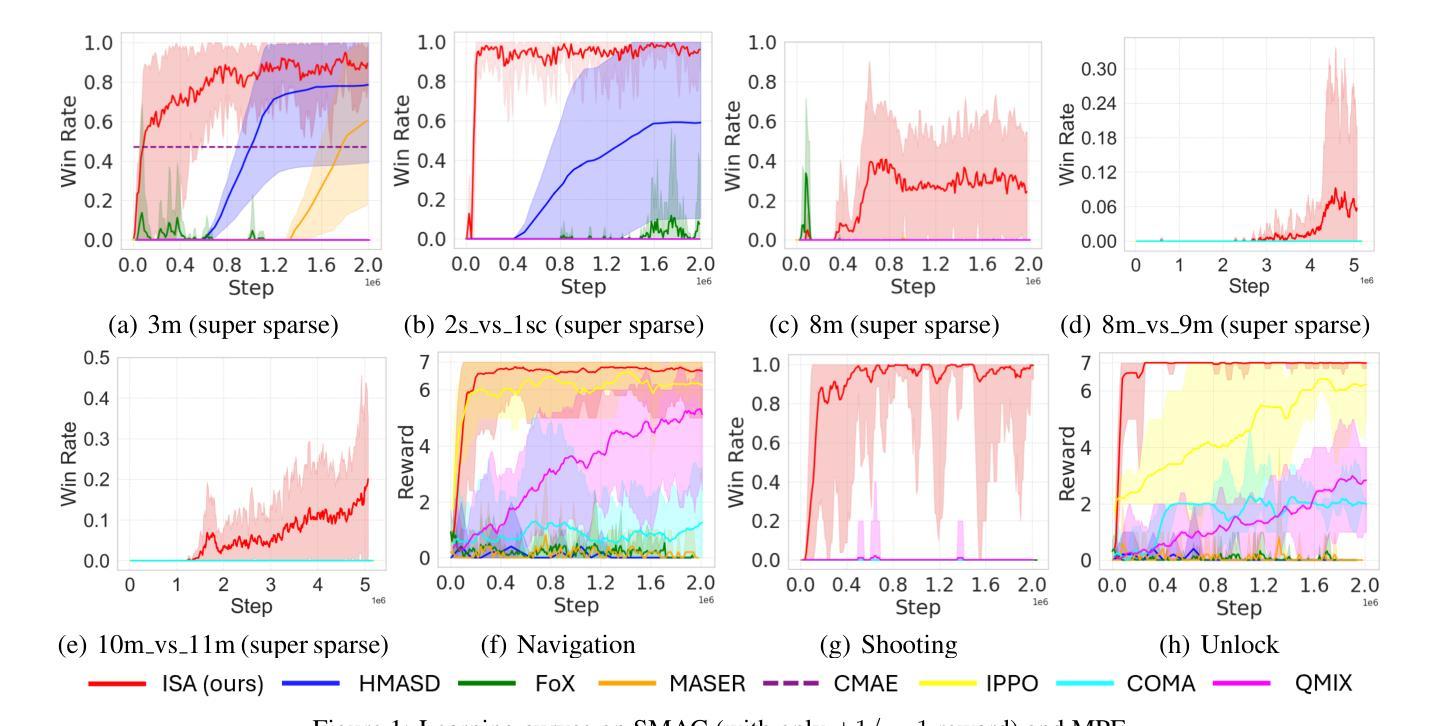
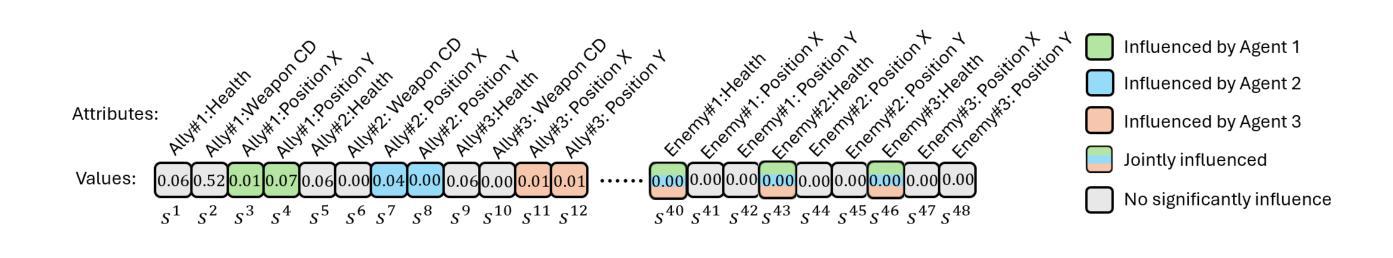
Training cooperative agents in sparse-reward scenarios poses significant challenges for multi-agent reinforcement learning (MARL). Without clear feedback on actions at each step in sparse-reward setting, previous methods struggle with precise credit assignment among agents and effective exploration. In this paper, we introduce a novel method to deal with both credit assignment and exploration problems in reward-sparse domains. Accordingly, we propose an algorithm that calculates the Influence Scope of Agents (ISA) on states by taking specific value of the dimensions/attributes of states that can be influenced by individual agents. The mutual dependence between agents’ actions and state attributes are then used to calculate the credit assignment and to delimit the exploration space for each individual agent. We then evaluate ISA in a variety of sparse-reward multi-agent scenarios. The results show that our method significantly outperforms the state-of-art baselines.
在多智能体强化学习(MARL)中,训练稀疏奖励场景下的合作智能体面临着重大挑战。在稀疏奖励设置中,由于没有关于每个步骤行动的明确反馈,以前的方法在智能体之间的精确信用分配和有效探索方面遇到了困难。在本文中,我们介绍了一种解决稀疏奖励领域中的信用分配和探索问题的新方法。因此,我们提出了一种算法,通过计算智能体对状态的影响范围(ISA)来解决这一问题,具体方法是考虑智能体可以影响的状态的维度/属性的特定值。然后利用智能体行动和状态属性之间的相互依赖关系来计算信用分配并为每个个体智能体划定探索空间。我们在各种稀疏奖励的多智能体场景中评估ISA。结果表明,我们的方法显著优于最新基线。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
训练多智能体在稀疏奖励场景中的合作智能体对多智能体强化学习(MARL)提出了重大挑战。在稀疏奖励环境中,由于缺乏每个步骤对动作的明确反馈,之前的方法在智能体之间的精确信用分配和有效探索方面遇到了困难。本文介绍了一种应对稀疏奖励域中信用分配和探索问题的方法。据此,我们提出了一种算法,通过计算状态中被单个智能体可以影响的特定维度/属性的值来计算智能体的影响范围(ISA)。然后利用智能体行动与状态属性之间的相互作用来计算信用分配并为每个智能体界定探索空间。我们在各种稀疏奖励的多智能体场景中评估了ISA,结果表明该方法显著优于现有技术基线。
Key Takeaways
- 训练多智能体在稀疏奖励场景中的合作面临挑战。
- 稀疏奖励环境中缺乏明确反馈导致精确信用分配和探索困难。
- 引入了一种新的方法来解决稀疏奖励域中的信用分配和探索问题。
- 通过计算智能体的影响范围(ISA)来评估单个智能体对状态的影响。
- 利用智能体行动与状态属性间的相互作用进行信用分配和探索空间的界定。
- 在多种稀疏奖励的多智能体场景中评估了ISA方法,表现优异。
点此查看论文截图


Scalable UAV Multi-Hop Networking via Multi-Agent Reinforcement Learning with Large Language Models
Authors:Yanggang Xu, Weijie Hong, Jirong Zha, Geng Chen, Jianfeng Zheng, Chen-Chun Hsia, Xinlei Chen
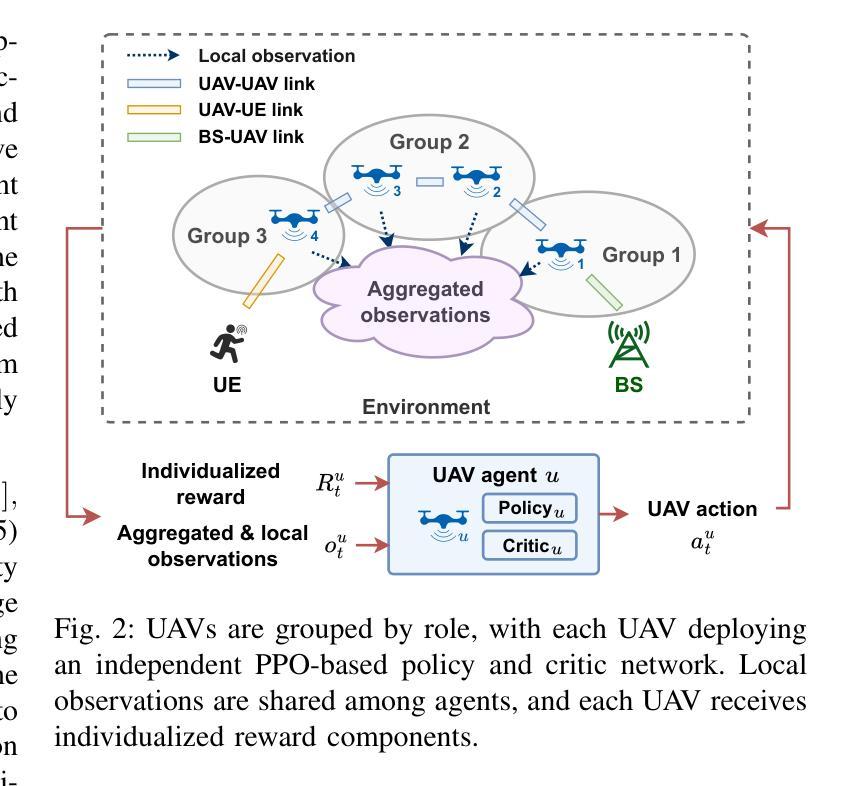
In disaster scenarios, establishing robust emergency communication networks is critical, and unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs) offer a promising solution to rapidly restore connectivity. However, organizing UAVs to form multi-hop networks in large-scale dynamic environments presents significant challenges, including limitations in algorithmic scalability and the vast exploration space required for coordinated decision-making. To address these issues, we propose MRLMN, a novel framework that integrates multi-agent reinforcement learning (MARL) and large language models (LLMs) to jointly optimize UAV agents toward achieving optimal networking performance. The framework incorporates a grouping strategy with reward decomposition to enhance algorithmic scalability and balance decision-making across UAVs. In addition, behavioral constraints are applied to selected key UAVs to improve the robustness of the network. Furthermore, the framework integrates LLM agents, leveraging knowledge distillation to transfer their high-level decision-making capabilities to MARL agents. This enhances both the efficiency of exploration and the overall training process. In the distillation module, a Hungarian algorithm-based matching scheme is applied to align the decision outputs of the LLM and MARL agents and define the distillation loss. Extensive simulation results validate the effectiveness of our approach, demonstrating significant improvements in network performance, including enhanced coverage and communication quality.
在灾难场景中,建立稳固的紧急通信网络至关重要,无人机(UAVs)为解决通信快速恢复提供了富有前景的解决方案。然而,在大规模动态环境中组织无人机形成多跳网络面临着重大挑战,包括算法可扩展性的限制和协同决策所需的大量探索空间。为了解决这些问题,我们提出了MRLMN这一新型框架,它融合了多智能体强化学习(MARL)和大型语言模型(LLM),共同优化无人机代理以实现最佳的网络性能。该框架采用分组策略和奖励分解,以提高算法的可扩展性并平衡各无人机之间的决策。此外,对选定关键无人机的行为施加约束以提高网络的稳健性。而且,该框架整合了LLM代理,利用知识蒸馏技术转移其高级决策能力给MARL代理。这提高了探索效率和整体训练过程。在蒸馏模块中,采用基于匈牙利算法的匹配方案来对齐LLM和MARL代理的决策输出并定义蒸馏损失。广泛的仿真结果验证了我们的方法的有效性,显示出网络性能的显著提高,包括覆盖范围和通信质量的增强。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
无人机(UAV)在大规模动态环境中构建多跳通信网络具有重要的现实意义。本文提出一种新型框架MRLMN,结合多智能体强化学习(MARL)与大型语言模型(LLM),优化无人机代理以实现最佳网络性能。框架采用分组策略与奖励分解,提高算法可扩展性并平衡无人机决策。此外,对关键无人机应用行为约束提高网络稳健性。集成LLM代理,利用知识蒸馏提升探索效率和整体训练过程。仿真结果验证了方法的有效性,显著提高网络性能,包括覆盖率和通信质量。
Key Takeaways
- 无人机在大规模动态环境中建立多跳通信网络的重要性。
- 提出新型框架MRLMN,结合MARL和LLM技术优化无人机代理网络性能。
- 框架采用分组策略与奖励分解,提高算法可扩展性,平衡无人机决策。
- 对关键无人机应用行为约束以增强网络稳健性。
- 集成LLM代理,利用知识蒸馏技术提升探索效率和整体训练过程。
- 仿真结果验证了框架的有效性,显著改进网络性能,如覆盖率和通信质量。
点此查看论文截图
Agent-as-a-Service based on Agent Network
Authors:Yuhan Zhu, Haojie Liu, Jian Wang, Bing Li, Zikang Yin, Yefei Liao
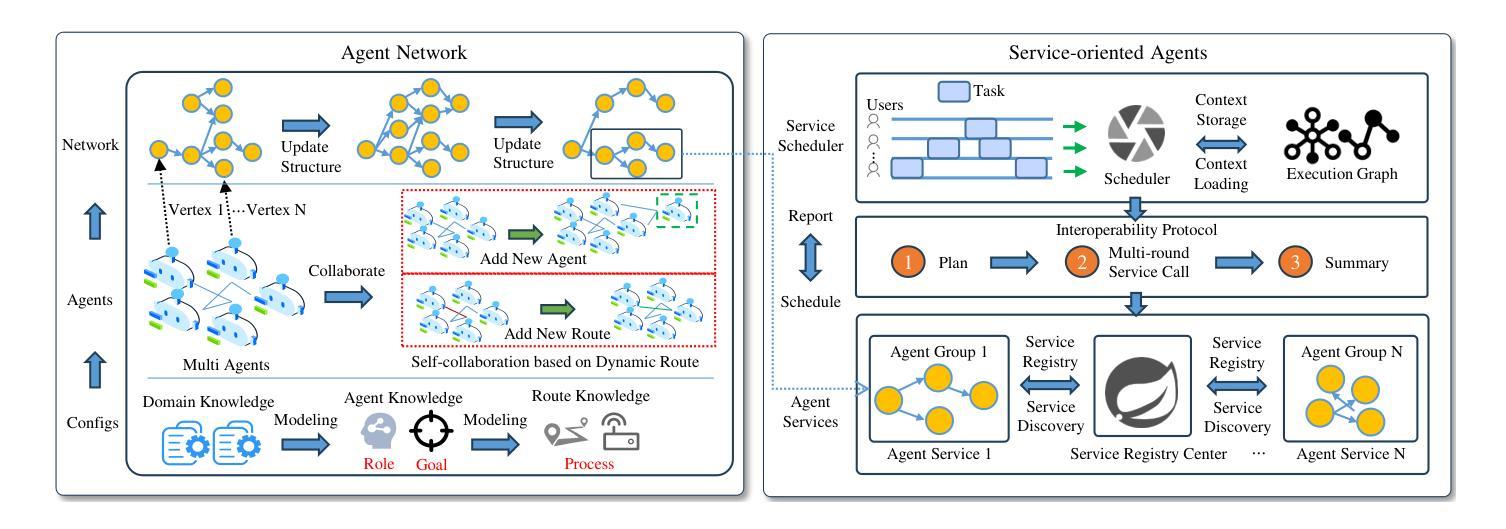
The rise of large model-based AI agents has spurred interest in Multi-Agent Systems (MAS) for their capabilities in decision-making, collaboration, and adaptability. While the Model Context Protocol (MCP) addresses tool invocation and data exchange challenges via a unified protocol, it lacks support for organizing agent-level collaboration. To bridge this gap, we propose Agent-as-a-Service based on Agent Network (AaaS-AN), a service-oriented paradigm grounded in the Role-Goal-Process-Service (RGPS) standard. AaaS-AN unifies the entire agent lifecycle, including construction, integration, interoperability, and networked collaboration, through two core components: (1) a dynamic Agent Network, which models agents and agent groups as vertexes that self-organize within the network based on task and role dependencies; (2) service-oriented agents, incorporating service discovery, registration, and interoperability protocols. These are orchestrated by a Service Scheduler, which leverages an Execution Graph to enable distributed coordination, context tracking, and runtime task management. We validate AaaS-AN on mathematical reasoning and application-level code generation tasks, which outperforms state-of-the-art baselines. Notably, we constructed a MAS based on AaaS-AN containing agent groups, Robotic Process Automation (RPA) workflows, and MCP servers over 100 agent services. We also release a dataset containing 10,000 long-horizon multi-agent workflows to facilitate future research on long-chain collaboration in MAS.
基于大型模型的人工智能代理的崛起激发了人们对多智能体系统(MAS)在决策、协作和适应性方面的能力。虽然模型上下文协议(MCP)通过统一协议解决了工具调用和数据交换挑战,但它缺乏组织智能体级别协作的支持。为了弥补这一差距,我们提出了基于智能体网络的服务化智能体(AaaS-AN),这是一种以角色目标过程服务(RGPS)标准为基础的面向服务的范式。AaaS-AN通过两个核心组件统一了整个智能体的生命周期,包括构建、集成、互操作性和网络化协作。核心组件包括:(1)动态智能体网络,它将智能体和智能体组建模为基于任务和角色依赖关系的顶点;(2)面向服务的智能体,集成了服务发现、注册和互操作性协议。这些由服务调度器编排,利用执行图实现分布式协调、上下文跟踪和运行时任务管理。我们在数学推理和应用程序级代码生成任务上验证了AaaS-AN的有效性,其性能优于现有技术基线。值得注意的是,我们基于AaaS-AN构建了一个包含智能体组、机器人流程自动化(RPA)工作流和MCP服务器的超过100个智能体服务的多智能体系统。我们还发布了一个包含1万条长周期多智能体工作流的数据库,以促进未来对多智能体系统中长链协作的研究。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF work in progress
Summary
大型基于模型的AI代理的崛起激发了人们对多智能体系统(MAS)在决策制定、协作和适应性方面的能力的研究兴趣。针对模型上下文协议(MCP)在智能体级别协作方面的不足,我们提出了基于智能体网络的代理服务(AaaS-AN)的概念。AaaS-AN采用面向服务的范式,围绕角色目标过程服务(RGPS)标准构建整个智能体生命周期的统一框架,包括构建、集成、互操作和协作网络。通过动态智能体网络和面向服务的智能体两大核心组件,AaaS-AN实现任务协作。我们对AaaS-AN进行了数学推理和应用程序级别的代码生成任务验证,表现优于当前其他主流技术方法。此外,我们建立了基于AaaS-AN的多智能体系统,包含智能体组、机器人流程自动化(RPA)工作流和MCP服务器超过一百个智能体服务,并发布包含一万个长周期多智能体工作流的数据库。旨在推动未来多智能体系统长周期协作的研究。
Key Takeaways
- 大型基于模型的AI代理的崛起引发了对多智能体系统(MAS)的决策制定、协作和适应能力的关注。
- 模型上下文协议(MCP)通过统一协议解决工具调用和数据交换挑战,但在组织智能体级别的协作方面存在不足。
- Agent-as-a-Service基于Agent网络(AaaS-AN)作为一种面向服务的范式被提出,以弥补这一不足,它统一了整个智能体的生命周期。
- AaaS-AN的核心组件包括动态智能体网络和面向服务的智能体,它们通过服务调度器实现分布式协调、上下文跟踪和运行时任务管理。
- AaaS-AN在数学推理和应用程序级别的代码生成任务验证中表现出卓越性能。
- 研究人员建立了基于AaaS-AN的多智能体系统实例,包含智能体组、机器人流程自动化(RPA)工作流和超过一百个智能体服务的MCP服务器。
点此查看论文截图

LLMSR@XLLM25: Less is More: Enhancing Structured Multi-Agent Reasoning via Quality-Guided Distillation
Authors:Jiahao Yuan, Xingzhe Sun, Xing Yu, Jingwen Wang, Dehui Du, Zhiqing Cui, Zixiang Di
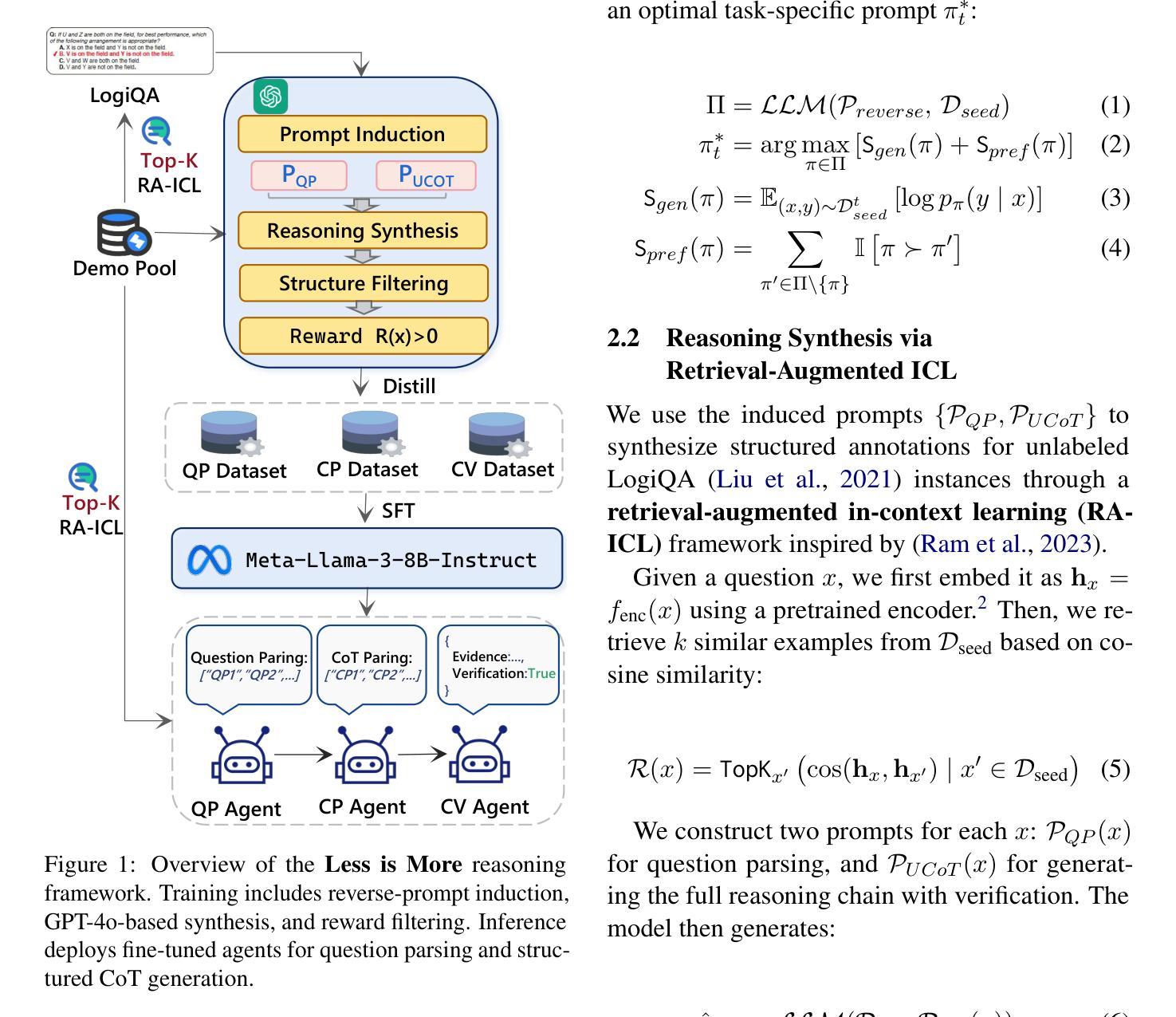
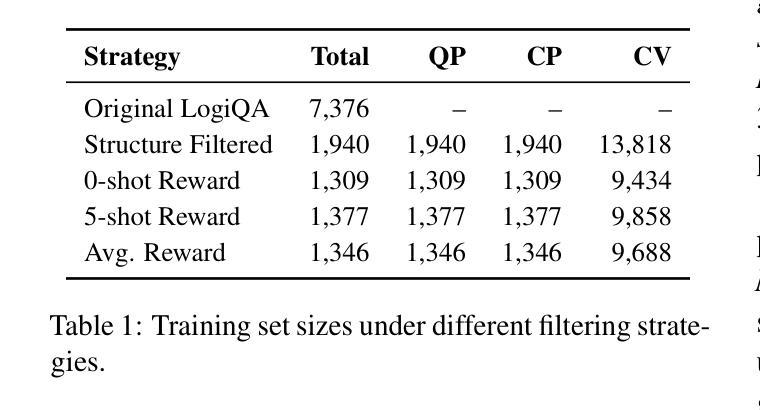
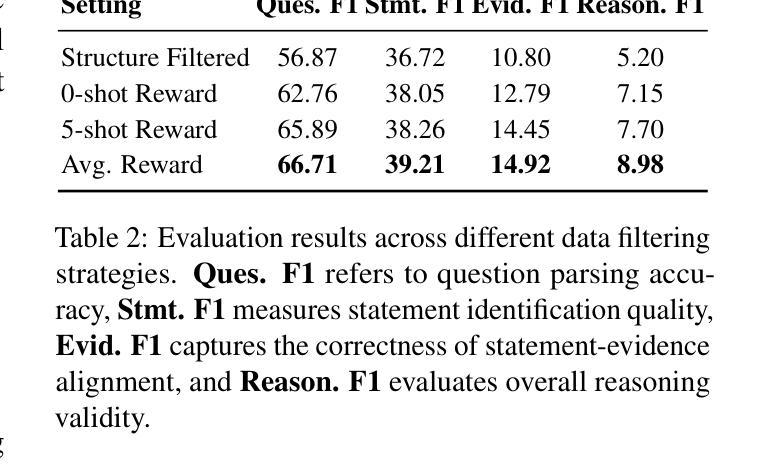
The LLMSR@XLLM25 formulates a low-resource structural reasoning task that challenges LLMs to generate interpretable, step-by-step rationales with minimal labeled data. We present Less is More, the third-place winning approach in the LLMSR@XLLM25, which focuses on structured reasoning from only 24 labeled examples. Our approach leverages a multi-agent framework with reverse-prompt induction, retrieval-augmented reasoning synthesis via GPT-4o, and dual-stage reward-guided filtering to distill high-quality supervision across three subtasks: question parsing, CoT parsing, and step-level verification. All modules are fine-tuned from Meta-Llama-3-8B-Instruct under a unified LoRA+ setup. By combining structure validation with reward filtering across few-shot and zero-shot prompts, our pipeline consistently improves structure reasoning quality. These results underscore the value of controllable data distillation in enhancing structured inference under low-resource constraints. Our code is available at https://github.com/JhCircle/Less-is-More.
LLMSR@XLLM25构建了一个低资源结构推理任务,该任务挑战了大型语言模型在少量标注数据的情况下生成可解释的、逐步的理性依据。我们提出了”少即是多”的方法,这是LLMSR@XLLM25中的第三名获奖方案,它专注于仅使用24个标注样本进行结构化推理。我们的方法利用了一种多智能体框架,通过反向提示归纳、增强推理合成的GPT-4o和双阶段奖励引导过滤来提炼三个子任务的高质量监督:问题解析、CoT解析和步骤级验证。所有模块都在统一的LoRA+设置下使用Meta-Llama-3-8B-Instruct进行微调。通过结合结构验证和奖励过滤进行跨少样本和零样本提示,我们的管道始终提高了结构推理质量。这些结果强调了可控数据蒸馏在增强低资源约束下的结构化推理中的价值。我们的代码可在https://github.com/JhCircle/Less-is-More找到。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF XLLM @ ACL 2025 Shared Task-III: LLM for Structural Reasoning (LLM-SR)
Summary
该文本介绍了LLMSR@XLLM25中提出的低资源结构推理任务,以及在该任务中获得第三名的Less is More方法。该方法仅使用24个带标签的示例进行结构化推理,采用多代理框架、反向提示归纳、通过GPT-4o增强推理合成和两阶段奖励引导过滤等技术,提高在问题解析、推理过程解析和步骤级别验证三个子任务中的监督质量。所有模块都在统一的LoRA+设置下,基于Meta-Llama-3-8B-Instruct进行微调。通过结合结构验证和奖励过滤在少量样本和零样本提示下,该管道不断提高了结构推理的质量。
Key Takeaways
- LLMSR@XLLM25 提出了一项低资源结构推理任务,挑战了大语言模型在最小标签数据下生成可解释的、逐步的推理过程。
- Less is More 方法在该任务中获得第三名,仅使用24个带标签的示例进行结构化推理。
- Less is More 方法采用多代理框架,结合反向提示归纳、检索增强推理合成和两阶段奖励引导过滤等技术。
- 该方法提高了在问题解析、推理过程解析和步骤级别验证三个子任务中的监督质量。
- 所有模块都在统一的LoRA+设置下基于Meta-Llama-3-8B-Instruct微调,确保模型性能的优化。
- 通过结合结构验证和奖励过滤,该管道在少量样本和零样本提示下都能提高结构推理的质量。
点此查看论文截图


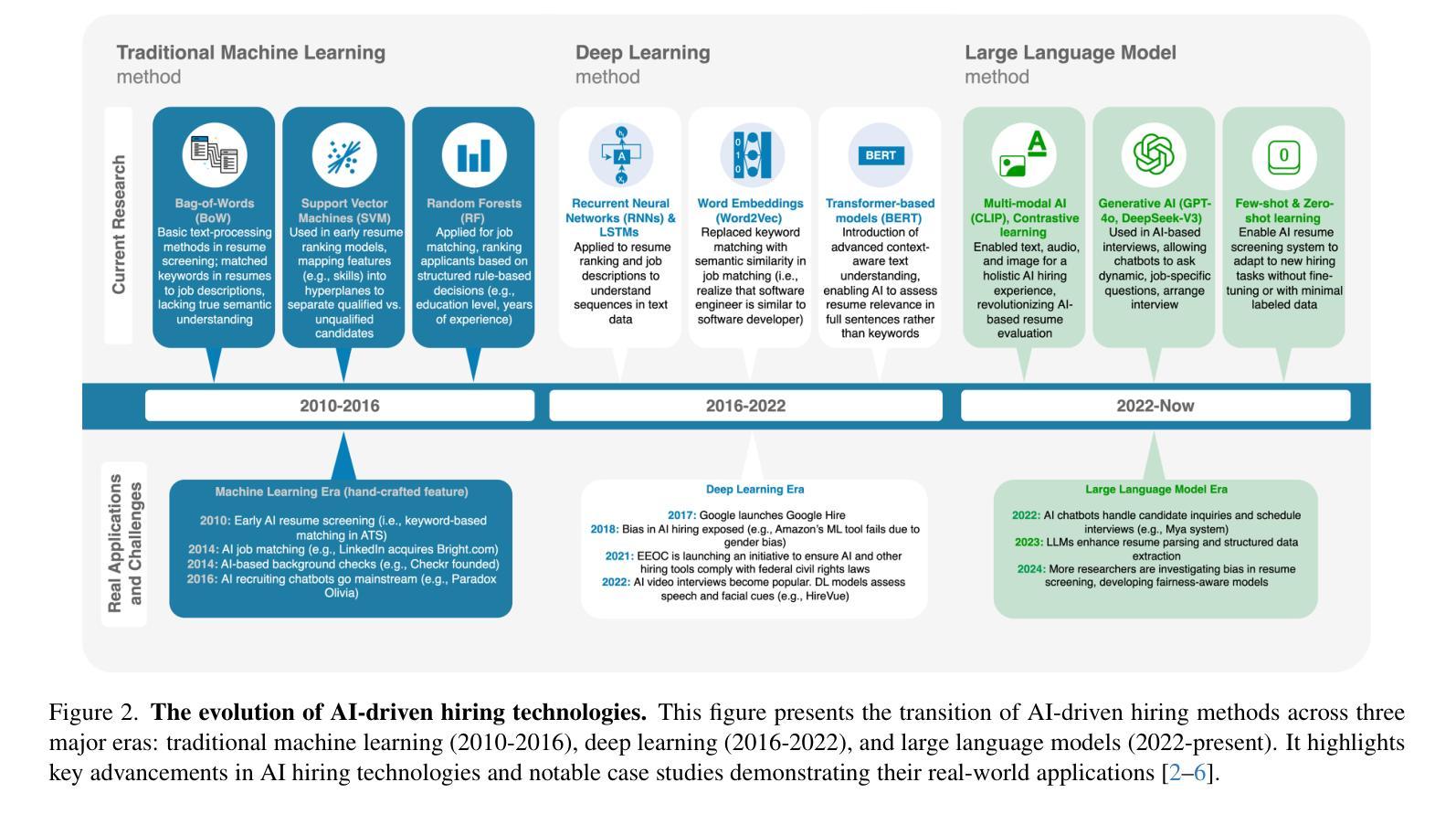
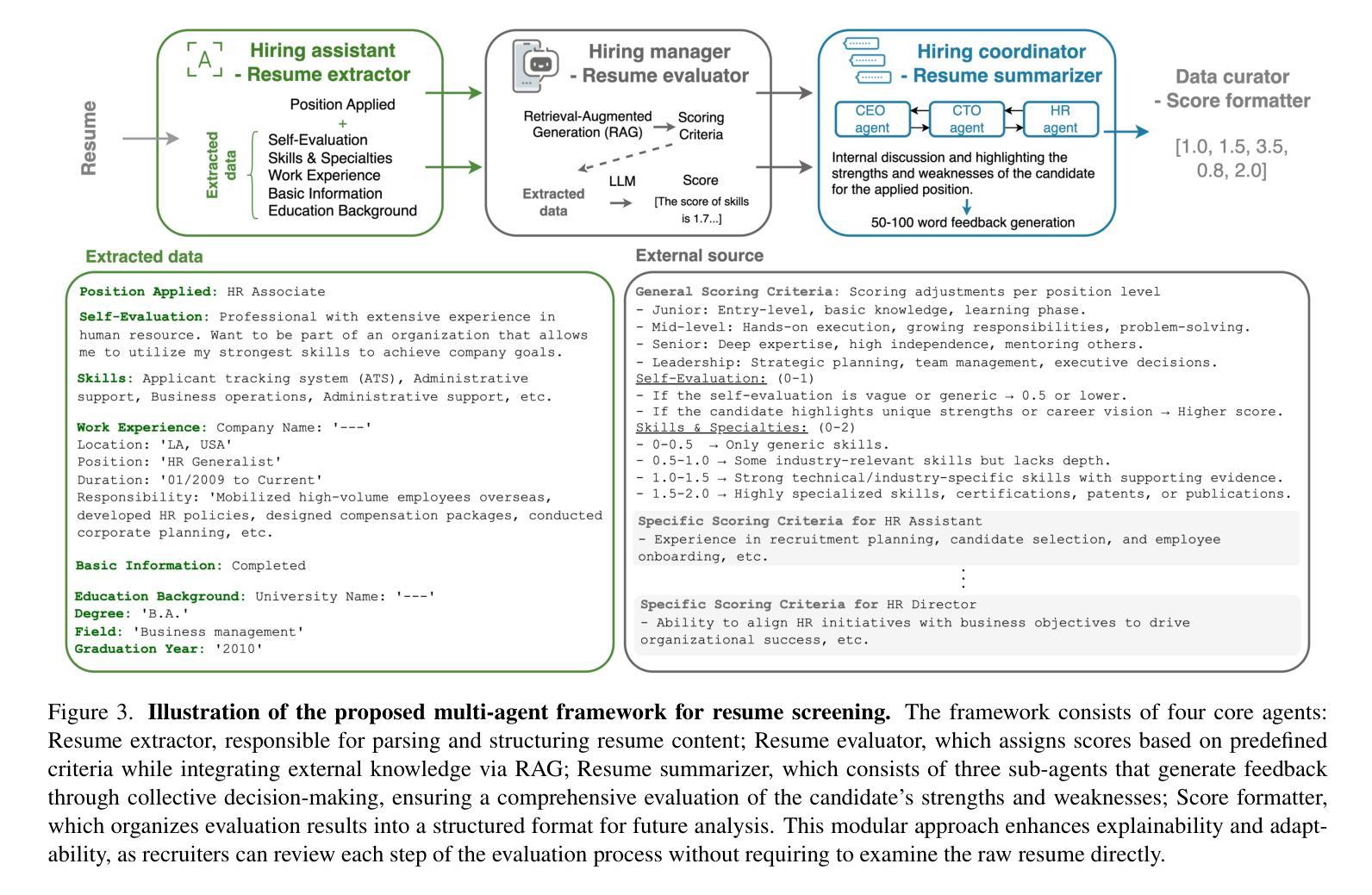
AI Hiring with LLMs: A Context-Aware and Explainable Multi-Agent Framework for Resume Screening
Authors:Frank P. -W. Lo, Jianing Qiu, Zeyu Wang, Haibao Yu, Yeming Chen, Gao Zhang, Benny Lo
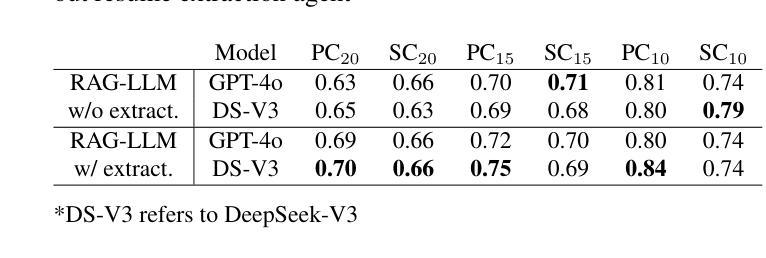
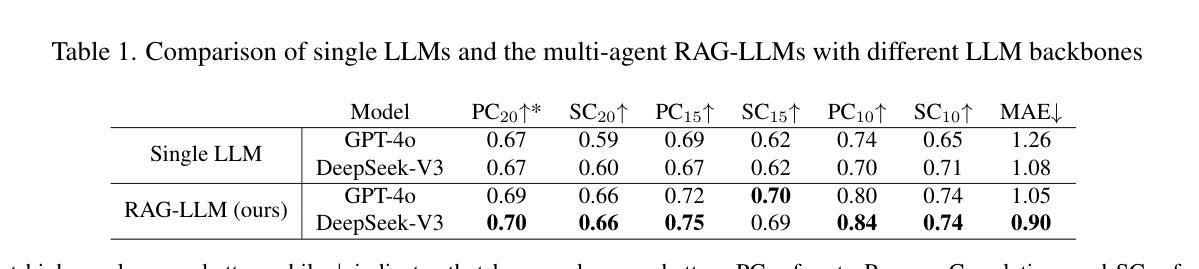
Resume screening is a critical yet time-intensive process in talent acquisition, requiring recruiters to analyze vast volume of job applications while remaining objective, accurate, and fair. With the advancements in Large Language Models (LLMs), their reasoning capabilities and extensive knowledge bases demonstrate new opportunities to streamline and automate recruitment workflows. In this work, we propose a multi-agent framework for resume screening using LLMs to systematically process and evaluate resumes. The framework consists of four core agents, including a resume extractor, an evaluator, a summarizer, and a score formatter. To enhance the contextual relevance of candidate assessments, we integrate Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) within the resume evaluator, allowing incorporation of external knowledge sources, such as industry-specific expertise, professional certifications, university rankings, and company-specific hiring criteria. This dynamic adaptation enables personalized recruitment, bridging the gap between AI automation and talent acquisition. We assess the effectiveness of our approach by comparing AI-generated scores with ratings provided by HR professionals on a dataset of anonymized online resumes. The findings highlight the potential of multi-agent RAG-LLM systems in automating resume screening, enabling more efficient and scalable hiring workflows.
简历筛选是人才招聘中一个至关重要但又耗费时间的环节,招聘人员需要分析大量的求职申请,同时保持客观、准确和公正。随着大型语言模型(LLM)的进步,其推理能力和广泛的知识库为招聘流程的简化和自动化提供了新的机会。在这项工作中,我们提出了一种使用LLM进行简历筛选的多代理框架,以系统地处理和评估简历。该框架包括四个核心代理,包括简历提取器、评估器、摘要器和计分格式化器。为了提高候选人评估的上下文相关性,我们在简历评估器中集成了检索增强生成(RAG),允许融入外部知识源,如行业专业知识、专业认证、大学排名和公司特定的招聘标准。这种动态适应使个性化招聘成为可能,缩小了人工智能自动化和人才招聘之间的差距。我们通过将人工智能生成的分数与人力资源专业人士在匿名在线简历数据集上提供的评分进行比较,来评估我们方法的有效性。研究结果突出了多代理RAG-LLM系统在自动化简历筛选方面的潜力,能够实现更高效、可扩展的招聘流程。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by CVPR 2025 Workshop
Summary
大規模招聘中,简历筛选是重要而耗时的环节。本研究提出了一种利用大型语言模型(LLM)的多智能体框架,系统地处理和评估简历。通过引入检索增强生成(RAG)技术,增强了评估的上下文相关性,并允许整合外部知识源,以实现个性化招聘。评估结果表明,该技术在自动化简历筛选方面具有较高的潜力,有助于实现更高效、可扩展的招聘流程。
Key Takeaways
- 简历筛选在招聘中至关重要,但过程耗时。
- 大型语言模型(LLM)为招聘流程自动化提供了新的机会。
- 提出了一种多智能体框架,包括简历提取器、评估器、摘要编写器和评分格式化器。
- 通过整合检索增强生成(RAG)技术,增强了评估的上下文相关性。
- 能够整合外部知识源,如行业专业知识、专业认证、大学排名和公司招聘标准。
- 该技术实现了个性化招聘,缩小了人工智能自动化与人才招聘之间的差距。
点此查看论文截图