⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-05-15 更新
Boosting Zero-shot Stereo Matching using Large-scale Mixed Images Sources in the Real World
Authors:Yuran Wang, Yingping Liang, Ying Fu
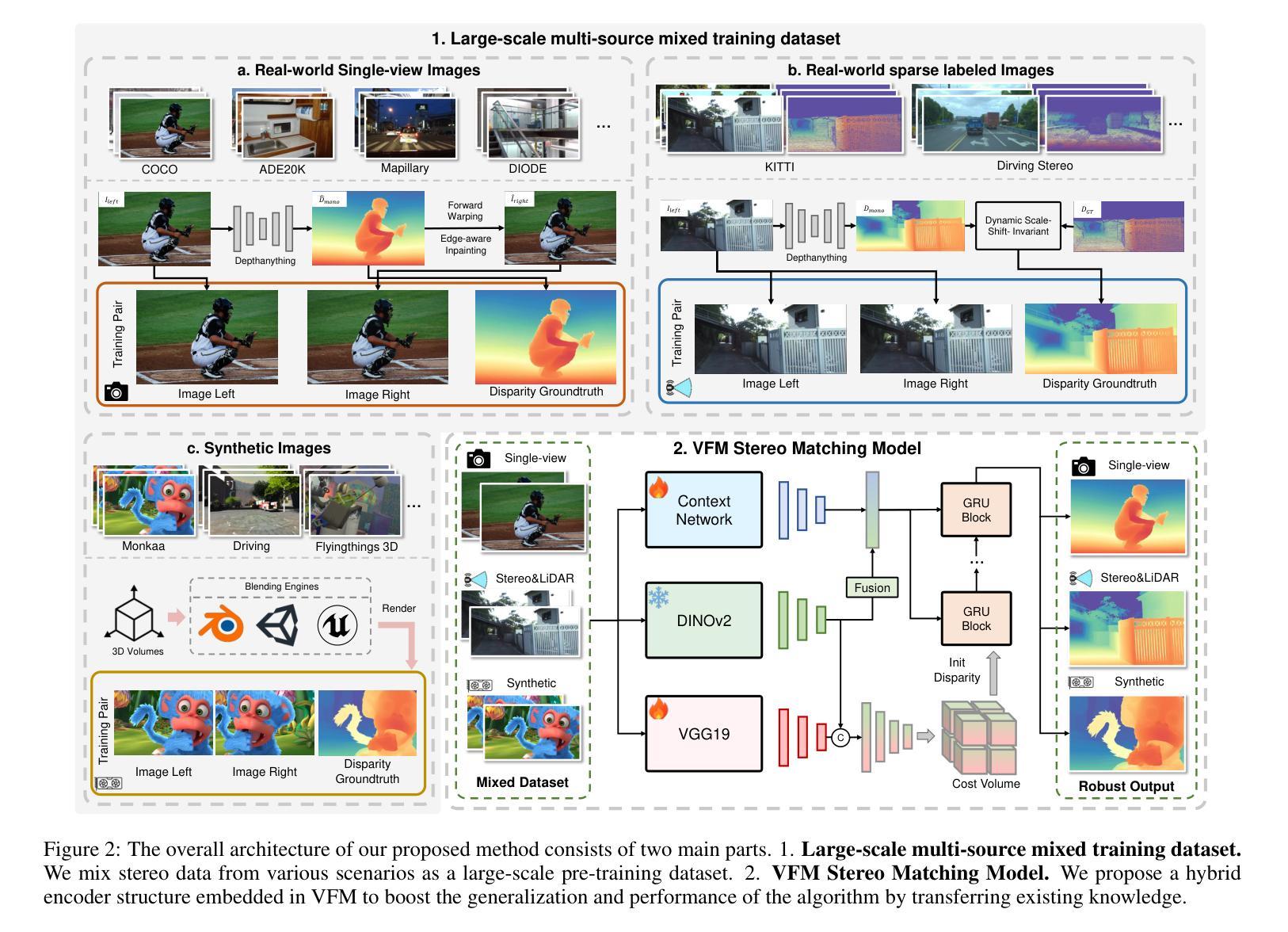
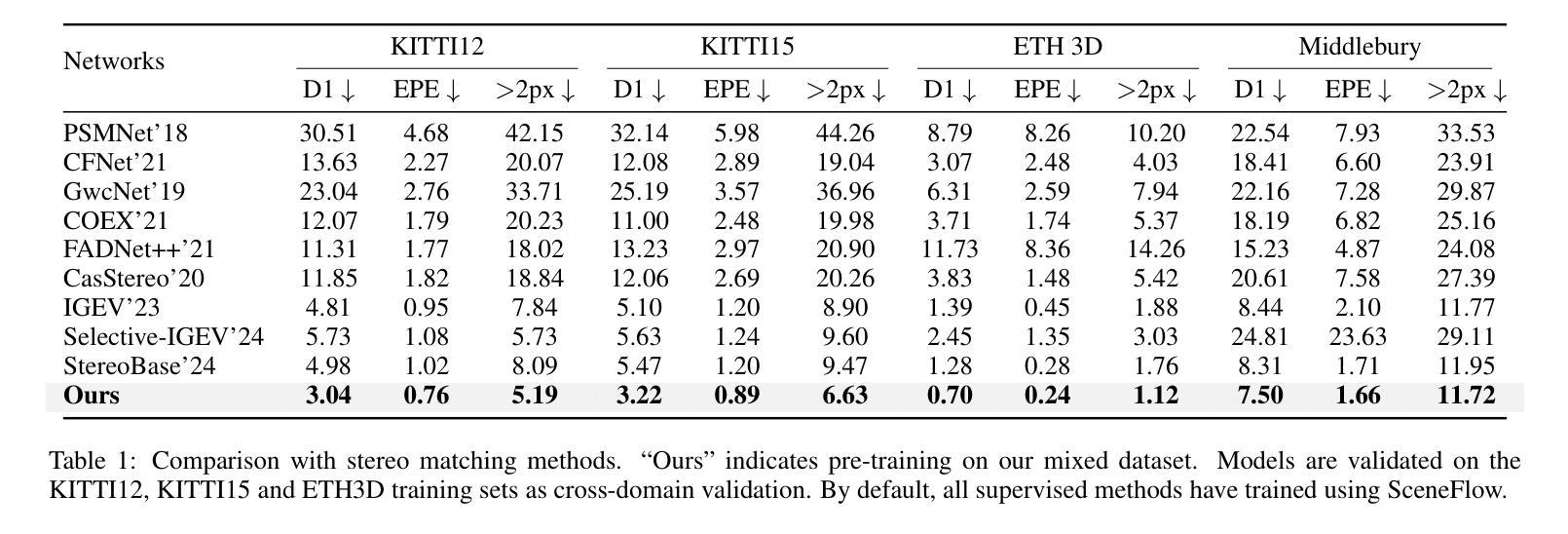
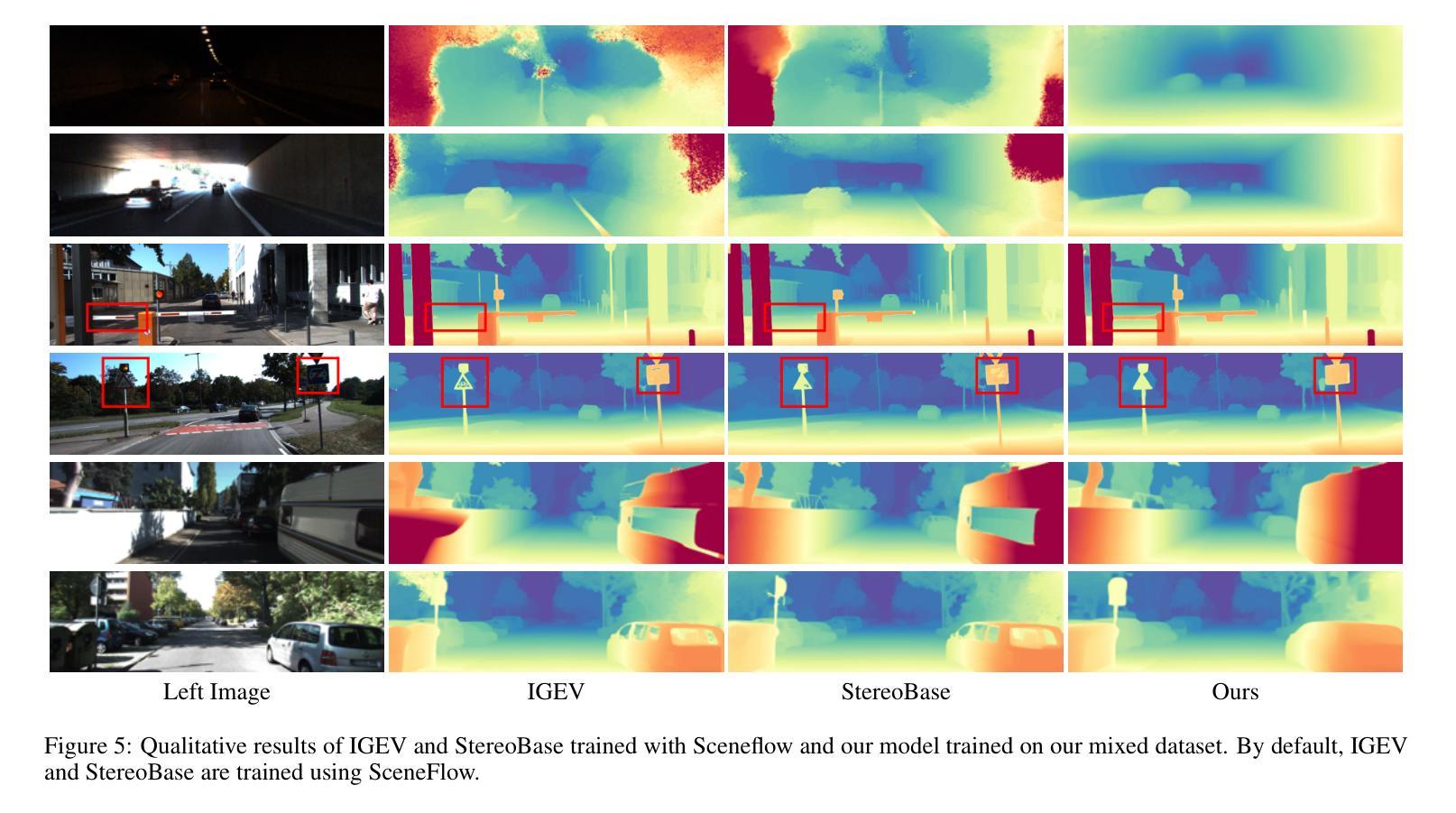
Stereo matching methods rely on dense pixel-wise ground truth labels, which are laborious to obtain, especially for real-world datasets. The scarcity of labeled data and domain gaps between synthetic and real-world images also pose notable challenges. In this paper, we propose a novel framework, \textbf{BooSTer}, that leverages both vision foundation models and large-scale mixed image sources, including synthetic, real, and single-view images. First, to fully unleash the potential of large-scale single-view images, we design a data generation strategy combining monocular depth estimation and diffusion models to generate dense stereo matching data from single-view images. Second, to tackle sparse labels in real-world datasets, we transfer knowledge from monocular depth estimation models, using pseudo-mono depth labels and a dynamic scale- and shift-invariant loss for additional supervision. Furthermore, we incorporate vision foundation model as an encoder to extract robust and transferable features, boosting accuracy and generalization. Extensive experiments on benchmark datasets demonstrate the effectiveness of our approach, achieving significant improvements in accuracy over existing methods, particularly in scenarios with limited labeled data and domain shifts.
立体匹配方法依赖于密集像素级的真实标签,而这些标签的获取非常耗时,尤其是对于真实世界的数据集。标记数据的稀缺以及合成图像和真实图像之间的领域差距也构成了显著的挑战。在本文中,我们提出了一种新的框架,名为“BooSTer”,它利用视觉基础模型和大规模混合图像源,包括合成图像、真实图像和单视图图像。首先,为了充分发挥大规模单视图图像的优势,我们设计了一种数据生成策略,结合单目深度估计和扩散模型,从单视图图像生成密集的立体匹配数据。其次,为了解决真实世界数据集中的稀疏标签问题,我们从单目深度估计模型中转移知识,使用伪单目深度标签和动态尺度及平移不变损失进行额外监督。此外,我们还将视觉基础模型作为编码器,提取稳健和可迁移的特征,提高准确性和泛化能力。在基准数据集上的广泛实验证明了我们的方法的有效性,在准确率上实现了对现有方法的显著改进,特别是在标记数据有限和领域偏移的场景下。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文提出了一种新的框架BooSTer,它利用视觉基础模型和大规模混合图像源,包括合成图像、真实图像和单视图图像。通过结合单目深度估计和扩散模型,从单视图图像生成密集立体匹配数据,解决现实世界数据集标签稀少和合成图像与真实图像领域差距的问题。同时,利用单目深度估计模型的伪单目深度标签和动态尺度与平移不变损失进行额外监督。大量实验表明,该方法在基准数据集上实现了显著的性能提升,特别是在标签数据有限和领域偏移的场景下。
Key Takeaways
- 提出了一种新的立体匹配框架BooSTer,结合了视觉基础模型与大规模混合图像源。
- 利用单目深度估计和扩散模型从单视图图像生成密集立体匹配数据。
- 解决现实世界数据集标签稀少和合成图像与真实图像领域差距的问题。
- 通过伪单目深度标签和动态尺度与平移不变损失进行额外监督。
- 融合视觉基础模型作为编码器,提取稳健且可迁移的特征。
- 在基准数据集上实现了显著的性能提升。
点此查看论文截图


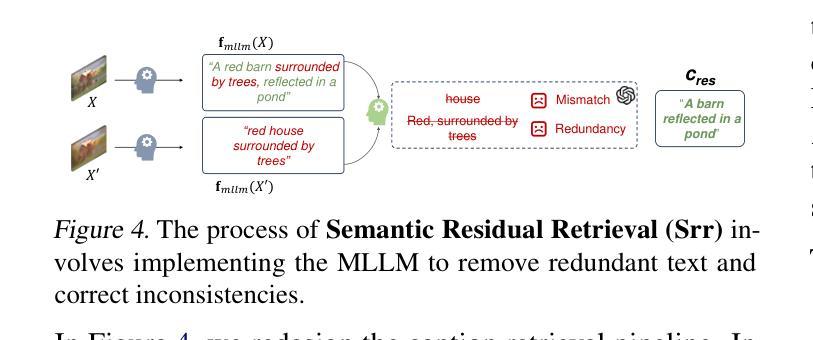
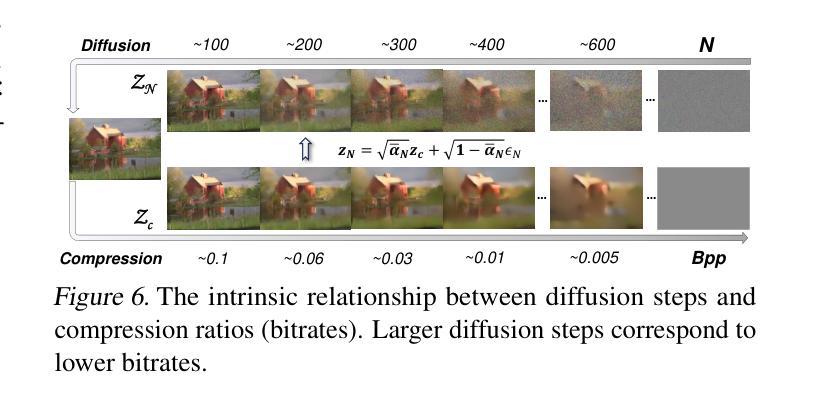
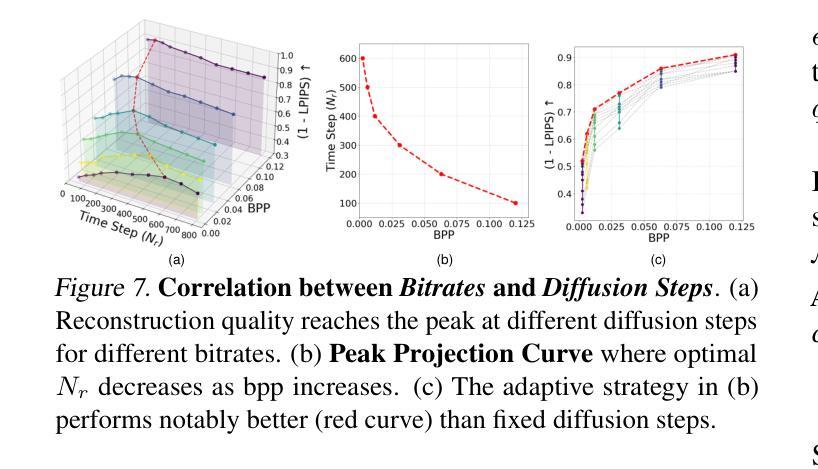
Ultra Lowrate Image Compression with Semantic Residual Coding and Compression-aware Diffusion
Authors:Anle Ke, Xu Zhang, Tong Chen, Ming Lu, Chao Zhou, Jiawen Gu, Zhan Ma
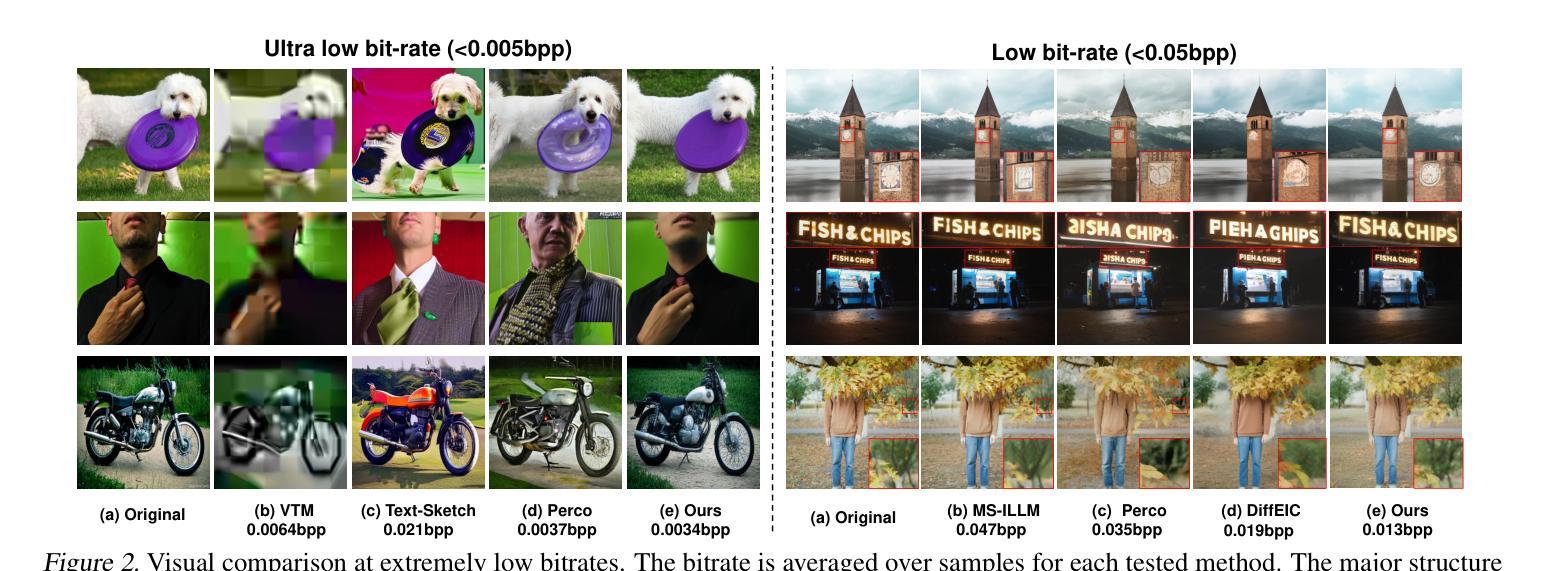
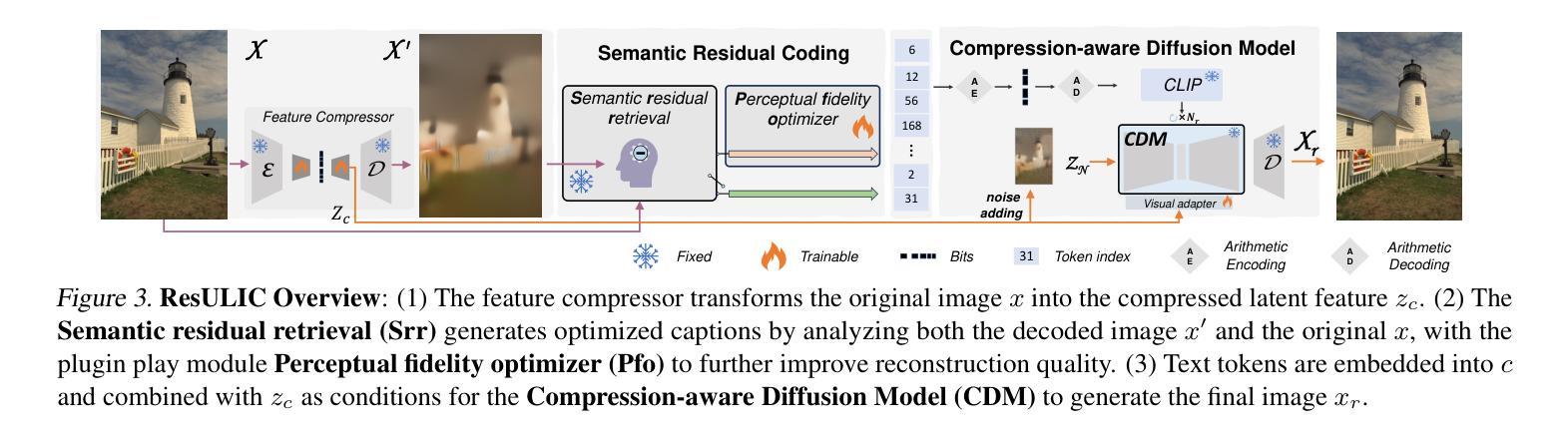
Existing multimodal large model-based image compression frameworks often rely on a fragmented integration of semantic retrieval, latent compression, and generative models, resulting in suboptimal performance in both reconstruction fidelity and coding efficiency. To address these challenges, we propose a residual-guided ultra lowrate image compression named ResULIC, which incorporates residual signals into both semantic retrieval and the diffusion-based generation process. Specifically, we introduce Semantic Residual Coding (SRC) to capture the semantic disparity between the original image and its compressed latent representation. A perceptual fidelity optimizer is further applied for superior reconstruction quality. Additionally, we present the Compression-aware Diffusion Model (CDM), which establishes an optimal alignment between bitrates and diffusion time steps, improving compression-reconstruction synergy. Extensive experiments demonstrate the effectiveness of ResULIC, achieving superior objective and subjective performance compared to state-of-the-art diffusion-based methods with - 80.7%, -66.3% BD-rate saving in terms of LPIPS and FID. Project page is available at https: //njuvision.github.io/ResULIC/.
现有的多模态大型模型图像压缩框架通常依赖于语义检索、潜在压缩和生成模型的片段化集成,导致在重建保真度和编码效率方面的性能不佳。为了解决这些挑战,我们提出了一种名为ResULIC的残差引导超低频图像压缩方法,它将残差信号融入语义检索和基于扩散的生成过程。具体来说,我们引入了语义残差编码(SRC),以捕获原始图像与其压缩潜在表示之间的语义差异。进一步应用了感知保真度优化器,以获得更优的重建质量。此外,我们提出了感知压缩扩散模型(CDM),建立了比特率与扩散时间步骤之间的最佳对齐,提高了压缩与重建的协同作用。大量实验表明,ResULIC的有效性,与最先进的扩散方法相比,其在LPIPS和FID方面实现了-80.7%、-66.3%的BD-rate节省。项目页面可在https://njuvision.github.io/ResULIC/找到。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
针对现有多模态大型模型图像压缩框架在重建保真度和编码效率方面的不足,提出了基于残差引导的超低码率图像压缩方法ResULIC。该方法结合语义检索和扩散生成过程,引入语义残差编码(SRC)捕捉原始图像与其压缩潜在表示之间的语义差异,并应用感知保真度优化器以提高重建质量。同时,提出了面向压缩的扩散模型(CDM),优化了比特率和扩散时间步之间的对齐,提高了压缩与重建的协同作用。实验证明,ResULIC在客观和主观性能上均优于最先进的方法,在LPIPS和FID指标上分别节省了-80.7%和-66.3%的比特率。项目页面可通过链接访问:https://njuvision.github.io/ResULIC/。
Key Takeaways
- 现有图像压缩框架存在重建保真度和编码效率方面的挑战。
- ResULIC方法结合了语义检索和扩散生成过程,提高了图像压缩性能。
- 语义残差编码(SRC)用于捕捉原始图像与压缩潜在表示之间的语义差异。
- 感知保真度优化器用于提高重建质量。
- 面向压缩的扩散模型(CDM)优化了比特率和扩散时间步之间的对齐。
- ResULIC在LPIPS和FID指标上实现了显著的性能提升,相比先进方法分别节省了-80.7%和-66.3%的比特率。
点此查看论文截图


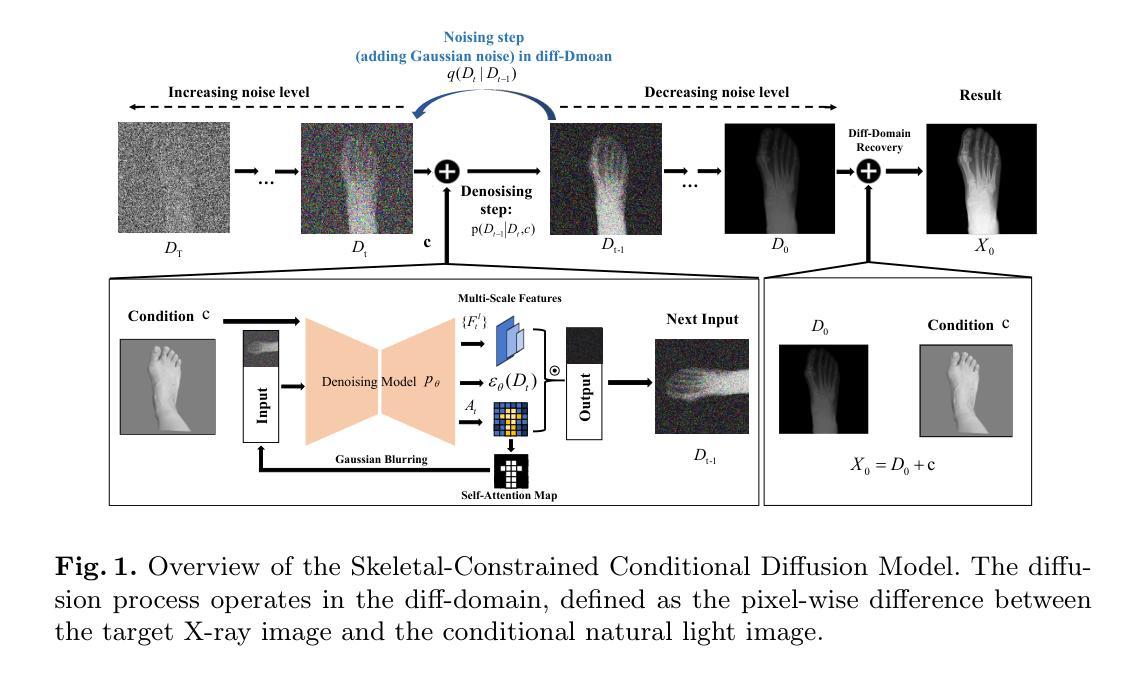
Skeleton-Guided Diffusion Model for Accurate Foot X-ray Synthesis in Hallux Valgus Diagnosis
Authors:Midi Wan, Pengfei Li, Yizhuo Liang, Di Wu, Yushan Pan, Guangzhen Zhu, Hao Wang
Medical image synthesis plays a crucial role in providing anatomically accurate images for diagnosis and treatment. Hallux valgus, which affects approximately 19% of the global population, requires frequent weight-bearing X-rays for assessment, placing additional strain on both patients and healthcare providers. Existing X-ray models often struggle to balance image fidelity, skeletal consistency, and physical constraints, particularly in diffusion-based methods that lack skeletal guidance. We propose the Skeletal-Constrained Conditional Diffusion Model (SCCDM) and introduce KCC, a foot evaluation method utilizing skeletal landmarks. SCCDM incorporates multi-scale feature extraction and attention mechanisms, improving the Structural Similarity Index (SSIM) by 5.72% (0.794) and Peak Signal-to-Noise Ratio (PSNR) by 18.34% (21.40 dB). When combined with KCC, the model achieves an average score of 0.85, demonstrating strong clinical applicability. The code is available at https://github.com/midisec/SCCDM.
医学影像合成在提供用于诊断和治疗解剖准确的图像方面发挥着至关重要的作用。拇趾外翻影响全球约19%的人口,需要进行频繁的负重X射线检查进行评估,这给病人和医疗服务提供者都带来了额外的压力。现有的X射线模型往往难以在图像保真度、骨骼一致性和物理约束之间取得平衡,特别是在缺乏骨骼指导的基于扩散的方法中更是如此。我们提出了骨骼约束条件扩散模型(SCCDM),并引入了KCC,一种利用骨骼地标进行足部评估的方法。SCCDM结合了多尺度特征提取和注意力机制,提高了结构相似性指数(SSIM)5.72%(0.794),峰值信噪比(PSNR)提高18.34%(21.40分贝)。与KCC结合使用时,该模型的平均得分为0.85,显示出强大的临床适用性。代码可在https://github.com/midisec/SCCDM找到。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了医学图像合成在诊断与治疗中的重要性,特别是在生成解剖结构准确的图像方面的应用。针对足骨病变如拇外翻,研究团队提出了骨骼约束条件扩散模型(SCCDM),并引入了利用骨骼地标的足部评估方法KCC。SCCDM通过多尺度特征提取和注意力机制改善了图像的结构相似性指数(SSIM)和峰值信噪比(PSNR),提高了医学图像的生成质量。结合KCC方法,模型的临床适用性得到显著增强,平均得分达到0.85。相关代码已公开于GitHub上。
Key Takeaways
- 医学图像合成在诊断与治疗中具有重要作用,需生成解剖结构准确的图像。
- 拇外翻是一种常见的足骨病变,需要频繁进行负重X射线检查,对病人和医疗提供者造成额外负担。
- 现有X射线模型在平衡图像保真度、骨骼一致性和物理约束方面存在挑战,特别是在基于扩散的方法中缺乏骨骼指导。
- 研究团队提出了骨骼约束条件扩散模型(SCCDM),该模型通过多尺度特征提取和注意力机制提高了结构相似性指数(SSIM)和峰值信噪比(PSNR)。
- SCCDM与足部评估方法KCC结合使用,显著增强了模型的临床适用性。
- 模型平均得分达到0.85,表明其强大的临床实用性。
点此查看论文截图

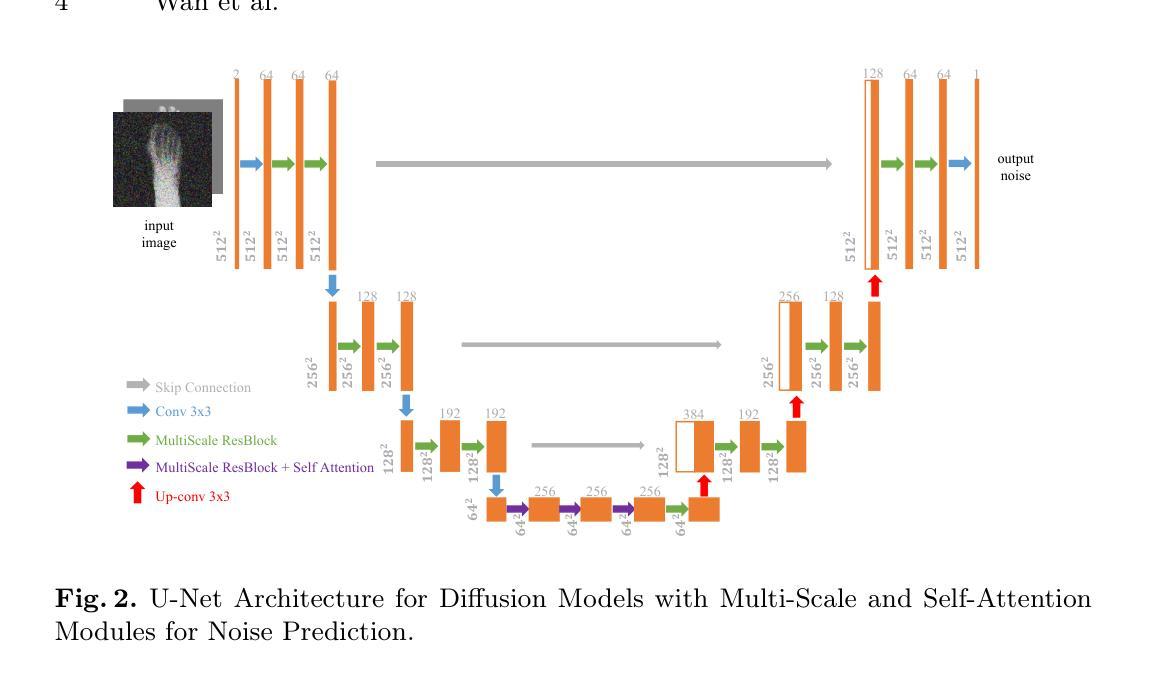
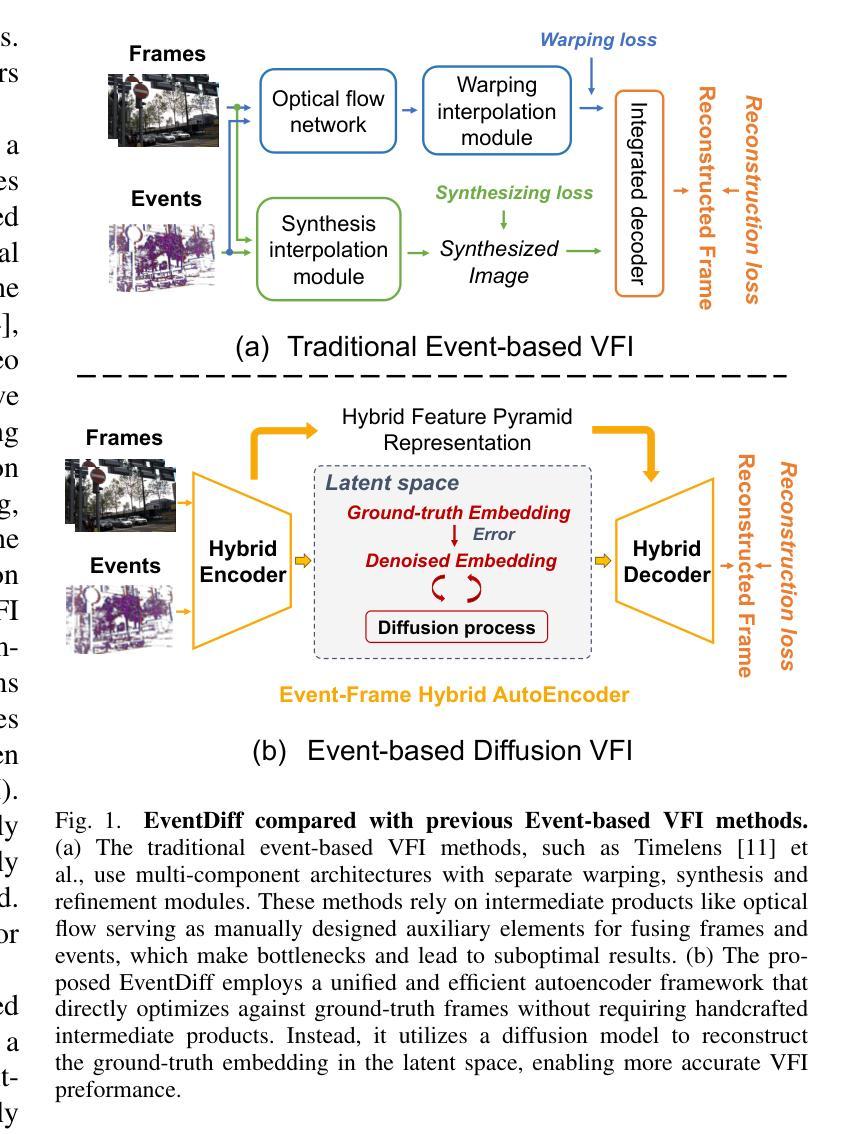
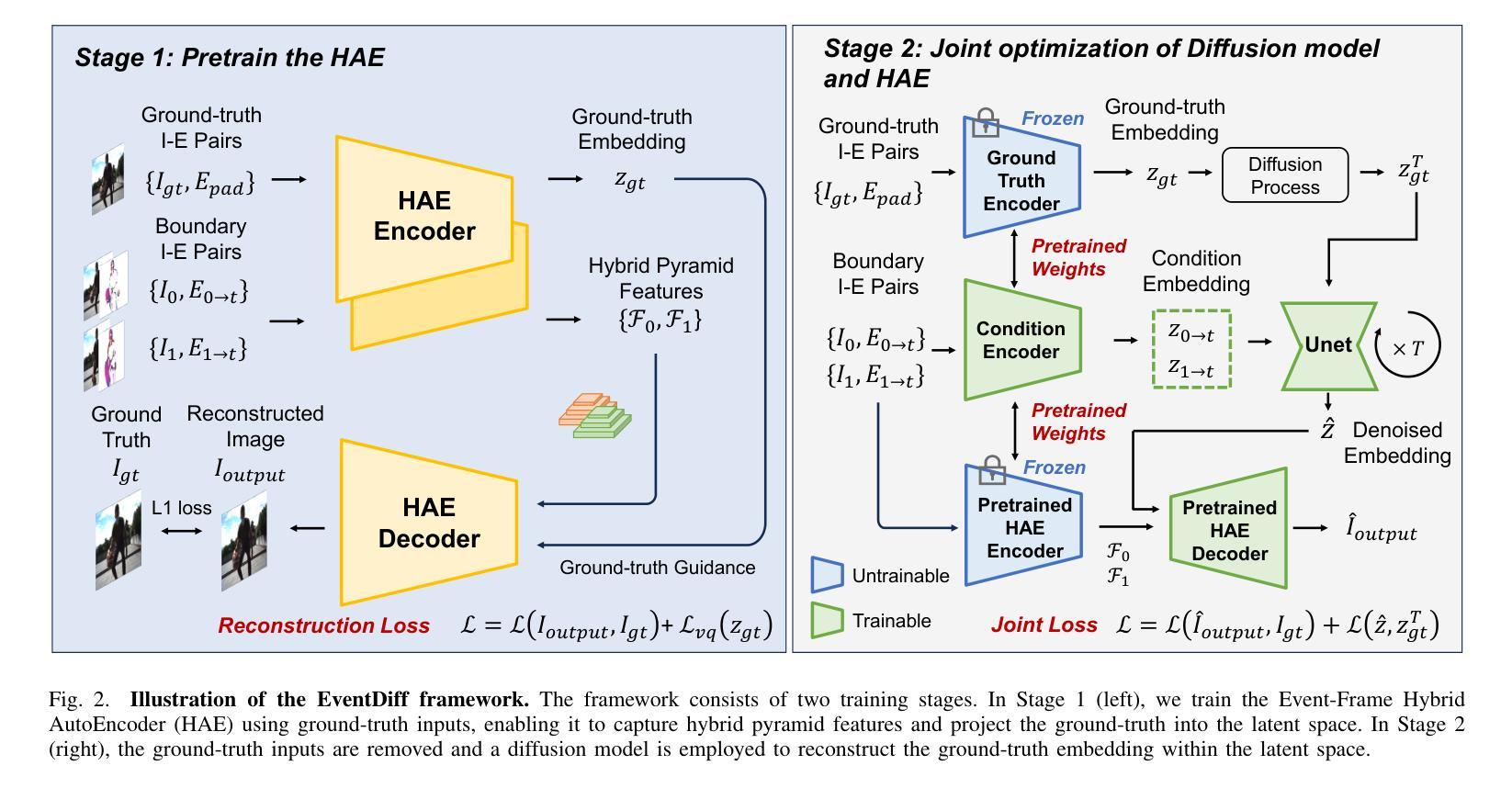
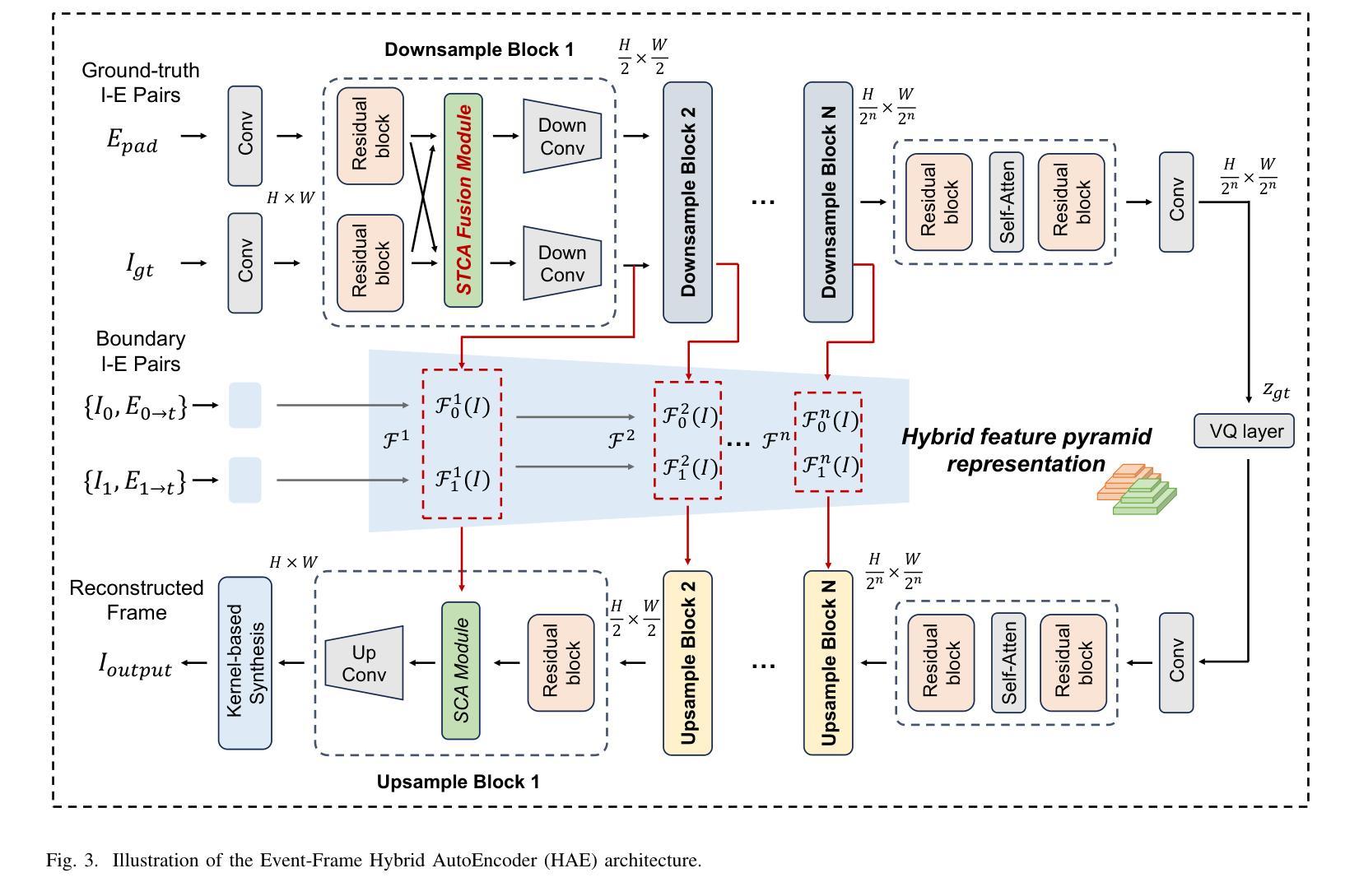
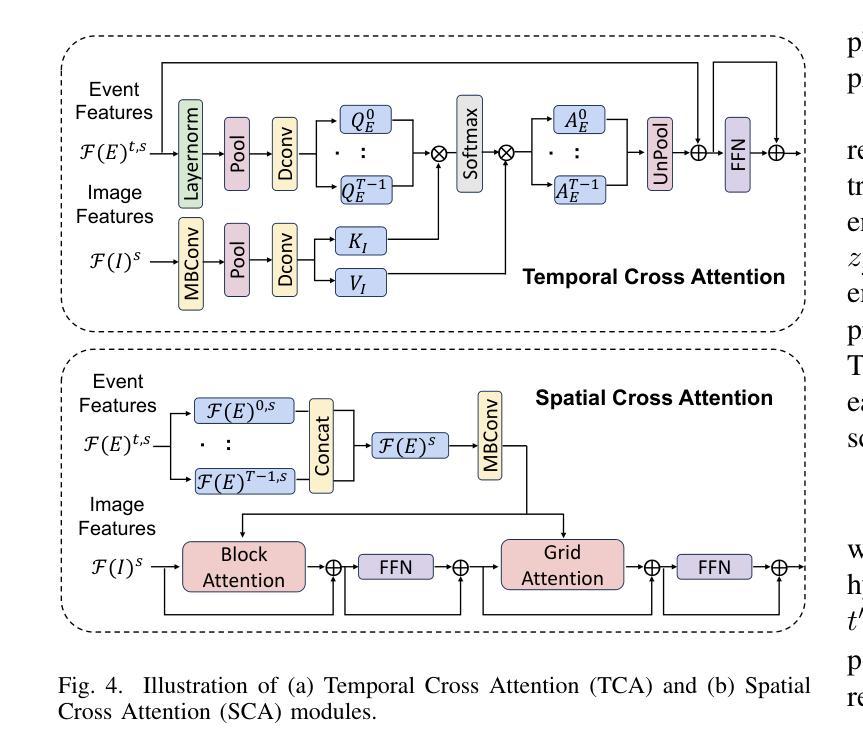
EventDiff: A Unified and Efficient Diffusion Model Framework for Event-based Video Frame Interpolation
Authors:Hanle Zheng, Xujie Han, Zegang Peng, Shangbin Zhang, Guangxun Du, Zhuo Zou, Xilin Wang, Jibin Wu, Hao Guo, Lei Deng
Video Frame Interpolation (VFI) is a fundamental yet challenging task in computer vision, particularly under conditions involving large motion, occlusion, and lighting variation. Recent advancements in event cameras have opened up new opportunities for addressing these challenges. While existing event-based VFI methods have succeeded in recovering large and complex motions by leveraging handcrafted intermediate representations such as optical flow, these designs often compromise high-fidelity image reconstruction under subtle motion scenarios due to their reliance on explicit motion modeling. Meanwhile, diffusion models provide a promising alternative for VFI by reconstructing frames through a denoising process, eliminating the need for explicit motion estimation or warping operations. In this work, we propose EventDiff, a unified and efficient event-based diffusion model framework for VFI. EventDiff features a novel Event-Frame Hybrid AutoEncoder (HAE) equipped with a lightweight Spatial-Temporal Cross Attention (STCA) module that effectively fuses dynamic event streams with static frames. Unlike previous event-based VFI methods, EventDiff performs interpolation directly in the latent space via a denoising diffusion process, making it more robust across diverse and challenging VFI scenarios. Through a two-stage training strategy that first pretrains the HAE and then jointly optimizes it with the diffusion model, our method achieves state-of-the-art performance across multiple synthetic and real-world event VFI datasets. The proposed method outperforms existing state-of-the-art event-based VFI methods by up to 1.98dB in PSNR on Vimeo90K-Triplet and shows superior performance in SNU-FILM tasks with multiple difficulty levels. Compared to the emerging diffusion-based VFI approach, our method achieves up to 5.72dB PSNR gain on Vimeo90K-Triplet and 4.24X faster inference.
视频帧插值(VFI)是计算机视觉领域的一项基本且具有挑战性的任务,特别是在涉及大运动、遮挡和光照变化的情况下。事件相机的最新进展为应对这些挑战提供了新的机会。虽然现有的基于事件驱动的VFI方法已经成功利用手工设计的中间表示(如光流)恢复了复杂的大运动,但这些设计在细微运动场景下往往牺牲了高保真图像重建,因为它们依赖于显式运动建模。同时,扩散模型通过去噪过程重建帧为VFI提供了有前景的替代方案,无需显式运动估计或扭曲操作。在这项工作中,我们提出了基于事件的扩散模型框架EventDiff,用于VFI。EventDiff具有新颖的事件帧混合自动编码器(HAE),配备轻量级时空交叉注意力(STCA)模块,可有效融合动态事件流和静态帧。与以前的基于事件的VFI方法不同,EventDiff通过在潜在空间中进行去噪扩散过程直接执行插值,使其在多样且具有挑战性的VFI场景中更加稳健。通过首先预训练HAE,然后与其扩散模型联合优化的两阶段训练策略,我们的方法在多个合成和现实世界的事件VFI数据集上实现了卓越的性能。所提出的方法在Vimeo90K-Triplet上的峰值信噪比(PSNR)比现有的基于事件的VFI方法高出1.98dB,并且在具有不同难度的SNU-FILM任务中表现出卓越的性能。与新兴的基于扩散的VFI方法相比,我们的方法在Vimeo90K-Triplet上实现了高达5.72dB的PSNR增益,推理速度提高了4.24倍。
论文及项目相关链接
摘要
视频帧插值(VFI)是计算机视觉领域的一项基本且具有挑战性的任务,特别是在涉及大动作、遮挡和光照变化的条件下。基于事件相机的最新进展为应对这些挑战提供了新的机遇。现有的基于事件VFI方法通过利用手工制作的中介表示(如光流)来恢复大型复杂运动取得了成功,但由于对显式运动建模的依赖,这些方法在轻微运动场景下往往难以实现高保真图像重建。扩散模型为VFI提供了一个有前途的替代方案,通过去噪过程重建框架,无需显式运动估计或弯曲操作。在这项工作中,我们提出了基于事件的扩散模型框架EventDiff,用于VFI。EventDiff具有配备轻量级时空交叉注意(STCA)模块的事件框架混合自动编码器(HAE),能够有效地融合动态事件流和静态框架。不同于以前的基于事件的VFI方法,EventDiff通过在潜在空间中进行去噪扩散过程直接执行插值,使其在不同多样化和具有挑战性的VFI场景中更加稳健。通过首先预训练HAE,然后与其扩散模型联合优化的两阶段训练策略,我们的方法在多个合成和真实世界事件VFI数据集上实现了最先进的性能。与现有的基于事件的VFI方法相比,我们的方法在Vimeo90K-Triplet上的峰值信噪比(PSNR)提高了高达1.98dB,并且在具有多个难度级别的SNU-FILM任务中表现出卓越的性能。与新兴的基于扩散的VFI方法相比,我们的方法在Vimeo90K-Triplet上的PSNR提高了高达5.72dB,推理速度提高了4.24倍。
要点
- 视频帧插值(VFI)是计算机视觉中的一项具有挑战性的任务,尤其在处理大动作、遮挡和光照变化时。
- 基于事件相机的新技术为VFI带来了新机遇。
- 现有基于事件的VFI方法虽然能成功恢复大型复杂运动,但在轻微运动场景下图像重建的保真度受限。
- 扩散模型提供了一种替代方法,通过去噪过程重建框架,无需显式运动估计。
- 本文提出的EventDiff框架结合了事件和框架信息,通过扩散模型实现VFI。
- EventDiff采用两阶段训练策略,在多个数据集上实现先进性能。
点此查看论文截图

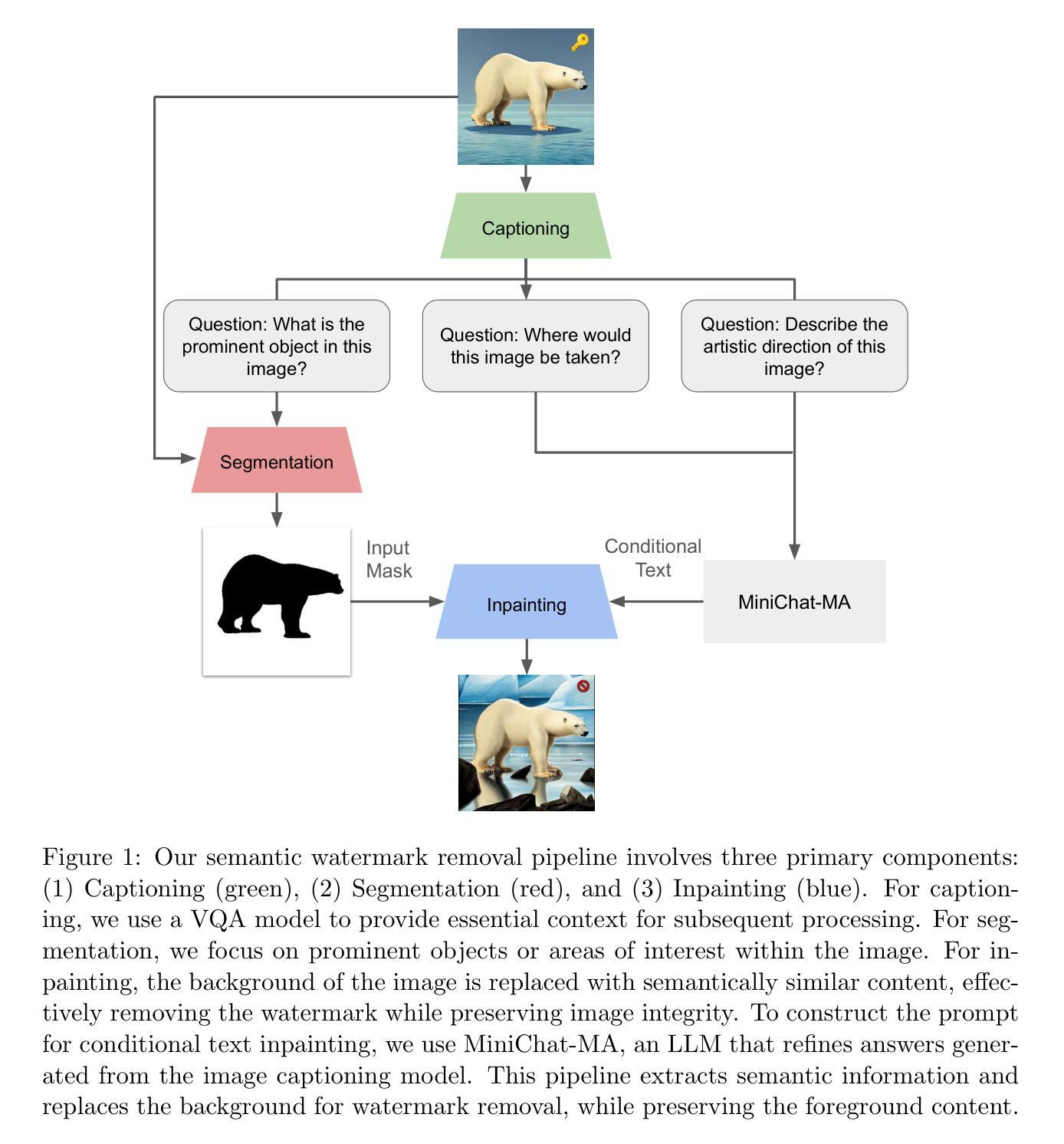
Removing Watermarks with Partial Regeneration using Semantic Information
Authors:Krti Tallam, John Kevin Cava, Caleb Geniesse, N. Benjamin Erichson, Michael W. Mahoney
As AI-generated imagery becomes ubiquitous, invisible watermarks have emerged as a primary line of defense for copyright and provenance. The newest watermarking schemes embed semantic signals - content-aware patterns that are designed to survive common image manipulations - yet their true robustness against adaptive adversaries remains under-explored. We expose a previously unreported vulnerability and introduce SemanticRegen, a three-stage, label-free attack that erases state-of-the-art semantic and invisible watermarks while leaving an image’s apparent meaning intact. Our pipeline (i) uses a vision-language model to obtain fine-grained captions, (ii) extracts foreground masks with zero-shot segmentation, and (iii) inpaints only the background via an LLM-guided diffusion model, thereby preserving salient objects and style cues. Evaluated on 1,000 prompts across four watermarking systems - TreeRing, StegaStamp, StableSig, and DWT/DCT - SemanticRegen is the only method to defeat the semantic TreeRing watermark (p = 0.10 > 0.05) and reduces bit-accuracy below 0.75 for the remaining schemes, all while maintaining high perceptual quality (masked SSIM = 0.94 +/- 0.01). We further introduce masked SSIM (mSSIM) to quantify fidelity within foreground regions, showing that our attack achieves up to 12 percent higher mSSIM than prior diffusion-based attackers. These results highlight an urgent gap between current watermark defenses and the capabilities of adaptive, semantics-aware adversaries, underscoring the need for watermarking algorithms that are resilient to content-preserving regenerative attacks.
随着人工智能生成的图像越来越普遍,隐形水印作为版权和来源的主要防线已经出现。最新的水印技术嵌入语义信号——内容感知模式,这些模式被设计成能够抵御常见的图像操作——然而,它们对自适应对手的真正稳健性仍然尚未得到充分研究。我们揭露了一个以前未报道的漏洞,并介绍了SemanticRegen,这是一种三阶段的无标签攻击,可以消除最先进语义和隐形水印,同时保持图像的表面意义完整。我们的管道(i)使用视觉语言模型来获得精细的标题,(ii)使用零样本分割提取前景掩码,(iii)仅通过LLM引导扩散模型进行背景填充,从而保留显著物体和风格线索。在针对四种水印系统的1000个提示下进行评估——TreeRing、StegaStamp、StableSig和DWT/DCT——SemanticRegen是唯一一种能够击败语义TreeRing水印的方法(p=0.10>0.05),并且对其他方案的比特准确度降至低于0.75,同时保持高感知质量(masked SSIM=0.94+/-0.01)。我们进一步引入了masked SSIM(mSSIM)来量化前景区域的保真度,显示我们的攻击在mSSIM方面比先前的基于扩散的攻击高出高达12%。这些结果突显了当前水印防御与自适应、语义感知对手的能力之间存在的紧迫差距,强调了需要能够抵御内容保留再生攻击的水印算法。
论文及项目相关链接
摘要
随着AI生成的图像越来越普遍,隐形水印作为版权和来源证明的主要防线已经出现。最新的水印技术嵌入语义信号,这些信号设计的目的是能够在常见的图像操作下存活下来,但它们对抗适应性对手的真实稳健性仍待探索。本研究揭示了一个以前未报道的漏洞,并介绍了SemanticRegen,这是一种无需标签的三阶段攻击方法,可以抹去最先进的语义和隐形水印,同时保持图像的表面意义完整。我们的管道通过(i)使用视觉语言模型获取精细的标题,(ii)使用零射击分割提取前景掩膜,(iii)通过LLM引导的扩散模型仅修复背景,从而保留了显著物体和风格线索。在TreeRing、StegaStamp、StableSig和DWT/DCT四种水印系统的1000个提示下进行评估,SemanticRegen是唯一能够击败语义TreeRing水印的方法(p=0.10>0.05),并且其余方案的位精度均低于0.75,同时保持高感知质量(掩蔽SSIM=0.94±0.01)。我们还引入了掩蔽SSIM(mSSIM)来衡量前景区域内的保真度,显示我们的攻击方法的mSSIM高于先前的扩散攻击方法高达12%。这些结果突显了当前水印防御与适应性语义感知对手的能力之间的紧迫差距,强调了需要能够抵御内容保存再生攻击的水印算法。
关键发现
- 隐形水印成为AI生成图像版权保护的主要手段。
- 最新的水印技术嵌入语义信号以提高稳健性。
- 揭示了一种新的针对水印的攻击方法——SemanticRegen,能够抹去水印同时保持图像意义完整。
- SemanticRegen通过精细的标题、前景掩膜提取和背景修复来实施攻击。
- SemanticRegen在多种水印系统上的表现优于其他方法,尤其是针对TreeRing水印。
- 引入新的评估指标mSSIM来衡量攻击中的图像保真度。
点此查看论文截图

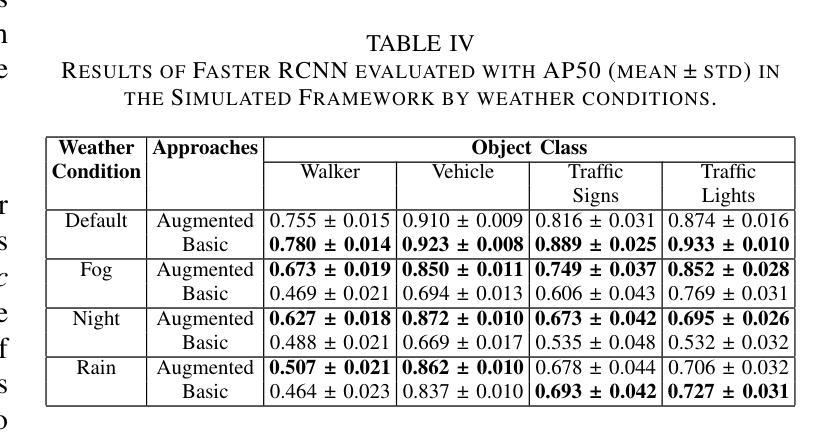
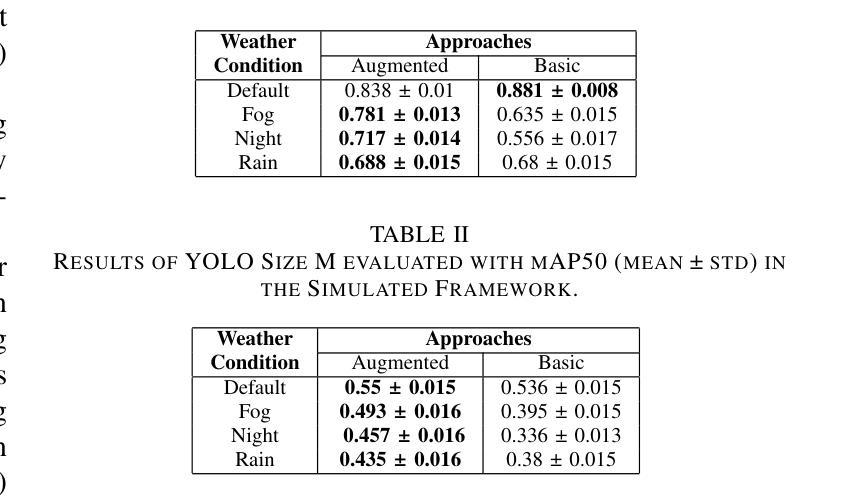
Object detection in adverse weather conditions for autonomous vehicles using Instruct Pix2Pix
Authors:Unai Gurbindo, Axel Brando, Jaume Abella, Caroline König
Enhancing the robustness of object detection systems under adverse weather conditions is crucial for the advancement of autonomous driving technology. This study presents a novel approach leveraging the diffusion model Instruct Pix2Pix to develop prompting methodologies that generate realistic datasets with weather-based augmentations aiming to mitigate the impact of adverse weather on the perception capabilities of state-of-the-art object detection models, including Faster R-CNN and YOLOv10. Experiments were conducted in two environments, in the CARLA simulator where an initial evaluation of the proposed data augmentation was provided, and then on the real-world image data sets BDD100K and ACDC demonstrating the effectiveness of the approach in real environments. The key contributions of this work are twofold: (1) identifying and quantifying the performance gap in object detection models under challenging weather conditions, and (2) demonstrating how tailored data augmentation strategies can significantly enhance the robustness of these models. This research establishes a solid foundation for improving the reliability of perception systems in demanding environmental scenarios, and provides a pathway for future advancements in autonomous driving.
增强恶劣天气条件下物体检测系统稳健性对于自动驾驶技术发展至关重要。本研究提出了一种新型方法,利用扩散模型Instruct Pix2Pix来开发提示方法,生成具有天气增强的现实数据集,旨在减轻恶劣天气对最新物体检测模型感知能力的影响,包括Faster R-CNN和YOLOv10。实验在两个环境中进行,包括CARLA模拟器,初步评估了所提出的数据增强方法,以及在BDD100K和ACDC真实世界图像数据集上展示了该方法在真实环境中的有效性。这项工作的关键贡献有两方面:(1)识别和量化物体检测模型在恶劣条件下的性能差距;(2)展示针对性数据增强策略如何显著增强这些模型的稳健性。本研究为提高需求环境场景中感知系统的可靠性奠定了坚实基础,并为自动驾驶技术的未来发展提供了途径。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 8 pages, 5 figures. Accepted at the International Joint Conference on Neural Networks (IJCNN) 2025 (to appear)
Summary
本文利用扩散模型Instruct Pix2Pix开发了一种新的提示方法,生成具有天气增强的现实数据集,旨在减轻恶劣天气对最先进的目标检测模型的影响。该研究在CARLA模拟器以及真实世界数据集BDD100K和ACDC上进行了实验验证,证明了该方法的有效性。本文的关键贡献在于识别和量化目标检测模型在恶劣天气条件下的性能差距,并展示了定制数据增强策略如何显著增强这些模型的稳健性。这为改善环境恶劣场景中的感知系统可靠性奠定了基础。
Key Takeaways
- 利用扩散模型Instruct Pix2Pix开发新的提示方法,生成具有天气增强的现实数据集。
- 旨在提高目标检测模型在恶劣天气条件下的稳健性。
- 在CARLA模拟器上进行初步评估,验证数据增强的效果。
- 在真实世界数据集BDD100K和ACDC上进行实验,证明方法的有效性。
- 识别和量化目标检测模型在恶劣天气条件下的性能差距。
- 展示定制数据增强策略如何显著增强目标检测模型的稳健性。
点此查看论文截图




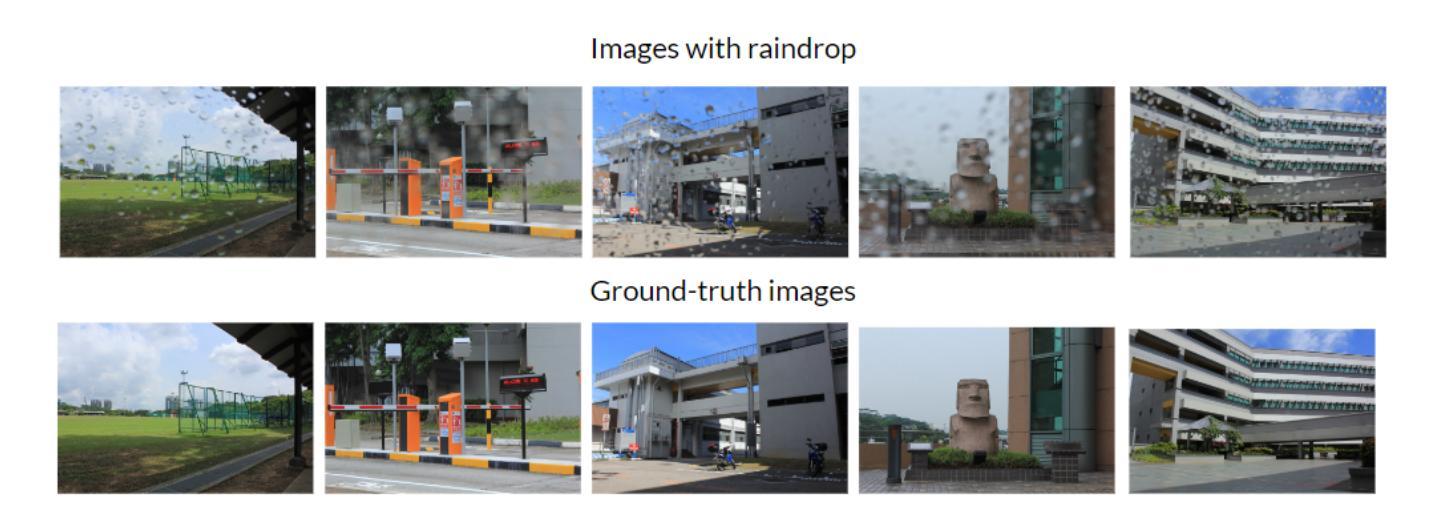
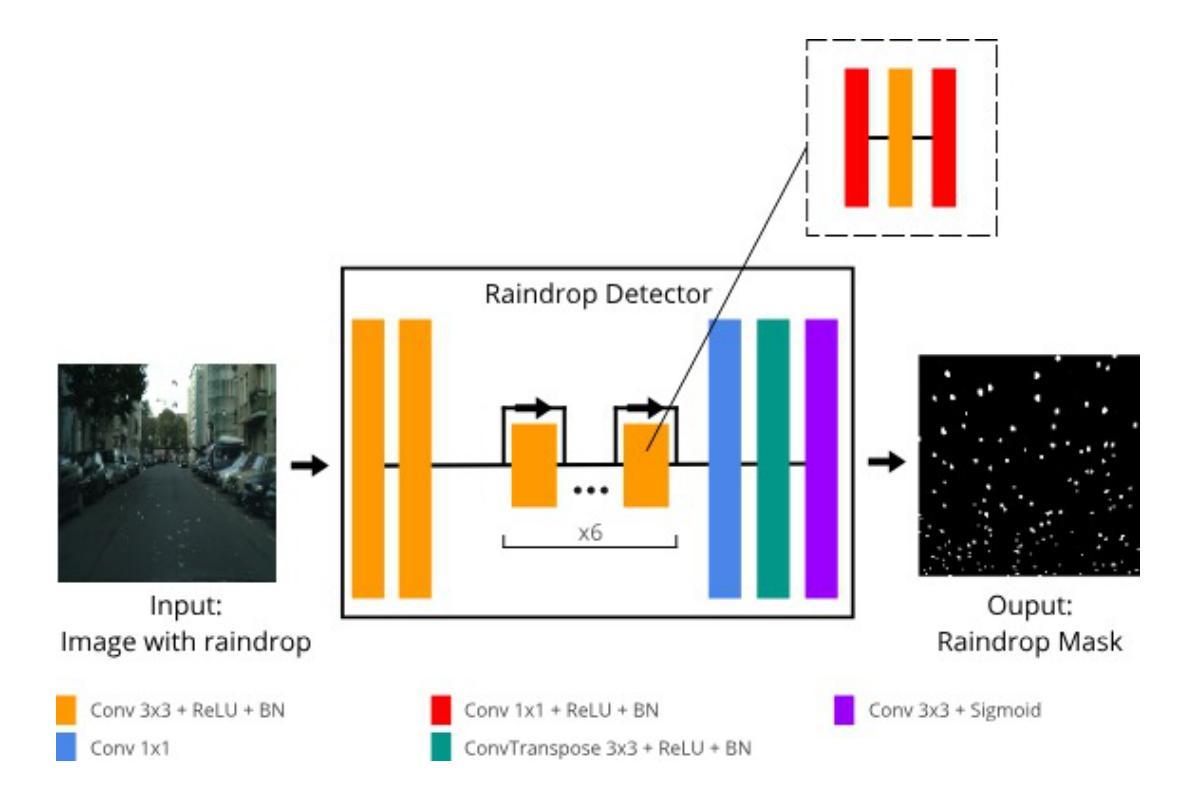
Unsupervised Raindrop Removal from a Single Image using Conditional Diffusion Models
Authors:Lhuqita Fazry, Valentino Vito
Raindrop removal is a challenging task in image processing. Removing raindrops while relying solely on a single image further increases the difficulty of the task. Common approaches include the detection of raindrop regions in the image, followed by performing a background restoration process conditioned on those regions. While various methods can be applied for the detection step, the most common architecture used for background restoration is the Generative Adversarial Network (GAN). Recent advances in the use of diffusion models have led to state-of-the-art image inpainting techniques. In this paper, we introduce a novel technique for raindrop removal from a single image using diffusion-based image inpainting.
雨滴去除是图像处理中的一项具有挑战性的任务。仅依赖单张图像进行雨滴去除进一步增加了任务的难度。常见的方法包括检测图像中的雨滴区域,然后对这些区域执行背景恢复过程。虽然检测步骤可以应用各种方法,但用于背景恢复的最常用架构是生成对抗网络(GAN)。扩散模型的使用方面的最新进展导致了最先进的图像修复技术。在本文中,我们介绍了一种使用基于扩散的图像修复从单张图像中去除雨滴的新技术。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了一种基于扩散模型的新型图像去雨技术。该技术侧重于对图像中的雨滴区域进行检测,随后利用生成对抗网络(GAN)进行背景修复。最近扩散模型的进步使得图像修复技术达到最新水平,本文利用这种技术实现单图像去雨。
Key Takeaways
- 雨滴去除是图像处理中的一项挑战,尤其是在仅使用单图像的情况下难度更高。
- 常见的去雨方法包括检测图像中的雨滴区域,然后对这些区域进行背景恢复。
- 生成对抗网络(GAN)是背景恢复最常用的架构。
- 扩散模型在去雨方面的应用是近年来的一个研究热点。
- 扩散模型在图像修复技术方面达到了最新水平。
- 本文提出了一种基于扩散模型的单图像去雨新技术。
点此查看论文截图

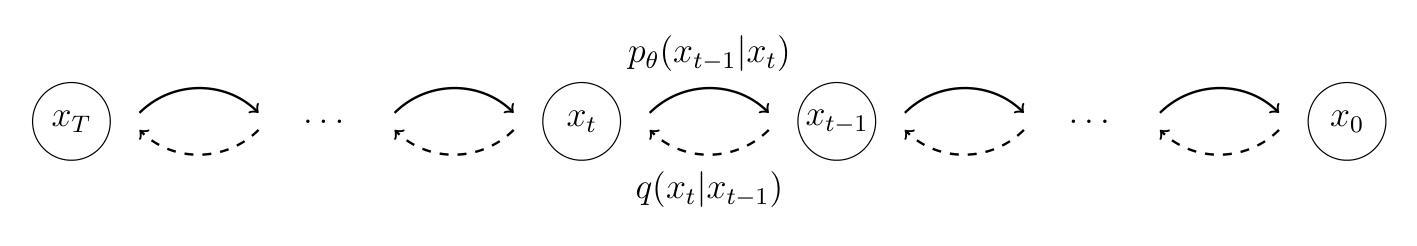
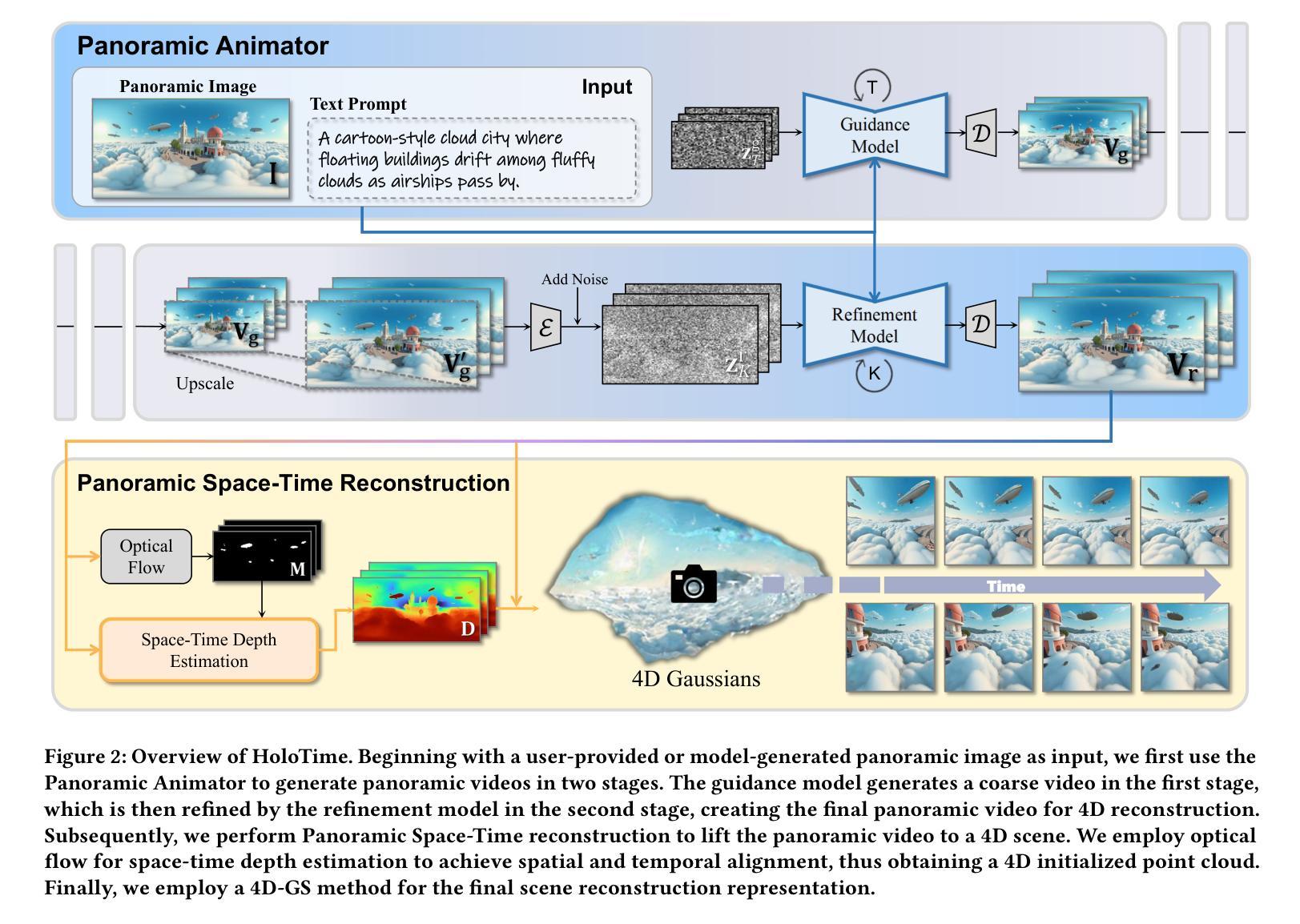
HoloTime: Taming Video Diffusion Models for Panoramic 4D Scene Generation
Authors:Haiyang Zhou, Wangbo Yu, Jiawen Guan, Xinhua Cheng, Yonghong Tian, Li Yuan
The rapid advancement of diffusion models holds the promise of revolutionizing the application of VR and AR technologies, which typically require scene-level 4D assets for user experience. Nonetheless, existing diffusion models predominantly concentrate on modeling static 3D scenes or object-level dynamics, constraining their capacity to provide truly immersive experiences. To address this issue, we propose HoloTime, a framework that integrates video diffusion models to generate panoramic videos from a single prompt or reference image, along with a 360-degree 4D scene reconstruction method that seamlessly transforms the generated panoramic video into 4D assets, enabling a fully immersive 4D experience for users. Specifically, to tame video diffusion models for generating high-fidelity panoramic videos, we introduce the 360World dataset, the first comprehensive collection of panoramic videos suitable for downstream 4D scene reconstruction tasks. With this curated dataset, we propose Panoramic Animator, a two-stage image-to-video diffusion model that can convert panoramic images into high-quality panoramic videos. Following this, we present Panoramic Space-Time Reconstruction, which leverages a space-time depth estimation method to transform the generated panoramic videos into 4D point clouds, enabling the optimization of a holistic 4D Gaussian Splatting representation to reconstruct spatially and temporally consistent 4D scenes. To validate the efficacy of our method, we conducted a comparative analysis with existing approaches, revealing its superiority in both panoramic video generation and 4D scene reconstruction. This demonstrates our method’s capability to create more engaging and realistic immersive environments, thereby enhancing user experiences in VR and AR applications.
扩散模型的快速发展有望彻底改变VR和AR技术的应用前景,这些技术通常需要场景级的四维资产来提升用户体验。然而,现有的扩散模型主要集中在静态三维场景的建模或对象级别的动态建模上,限制了它们提供真正沉浸式体验的能力。为了解决这个问题,我们提出了HoloTime框架,该框架结合了视频扩散模型来生成全景视频,通过一个提示或参考图像以及一种无缝将生成的全景视频转换为四维资产的全景四维场景重建方法,为用户提供全方位的沉浸式四维体验。具体来说,为了控制视频扩散模型生成高保真全景视频,我们引入了全景世界数据集,这是全景视频的第一个综合集合,适用于下游四维场景重建任务。有了这个精选的数据集,我们提出了全景动画师这一图像到视频的扩散模型两阶段模型,能够将全景图像转换为高质量全景视频。随后,我们展示了全景时空重建技术,该技术利用时空深度估计方法将生成的全景视频转化为四维点云数据集为优化全息四维高斯采样图提供依据最终重构空间和时间一致的四维场景为了验证我们的方法的有效性我们进行了与现有方法的比较分析发现在全景视频生成和四维场景重建方面均表现出优越性这证明了我们的方法在创建更具吸引力和更逼真的沉浸式环境方面的能力从而增强VR和AR应用程序中的用户体验。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Project Homepage: https://zhouhyocean.github.io/holotime/ Code: https://github.com/PKU-YuanGroup/HoloTime
Summary
本文提出一种名为HoloTime的框架,整合视频扩散模型生成全景视频,并利用360度4D场景重建方法将生成的全景视频转化为4D资产,为用户带来沉浸式4D体验。为解决生成高质量全景视频的问题,引入360World数据集,并提出全景动画师(Panoramic Animator)的两阶段图像到视频扩散模型。随后,采用空间时间深度估计方法将全景视频转化为4D点云,优化整体4D高斯拼贴表示,实现空间和时间上一致的4D场景重建。实验验证该方法在全景视频生成和4D场景重建方面的优越性,能创建更引人入胜、更逼真的沉浸式环境,提升VR和AR应用中的用户体验。
Key Takeaways
- 扩散模型的快速发展有望革命性应用于VR和AR技术。
- 当前扩散模型主要集中在静态场景的建模或物体级别的动态,难以提供真正的沉浸式体验。
- 提出HoloTime框架整合视频扩散模型生成全景视频。
- 引入360World数据集,为全景视频生成提供适用数据。
- 提出全景动画师(Panoramic Animator)的两阶段图像到视频扩散模型。
- 利用空间时间深度估计方法将全景视频转化为4D点云。
点此查看论文截图


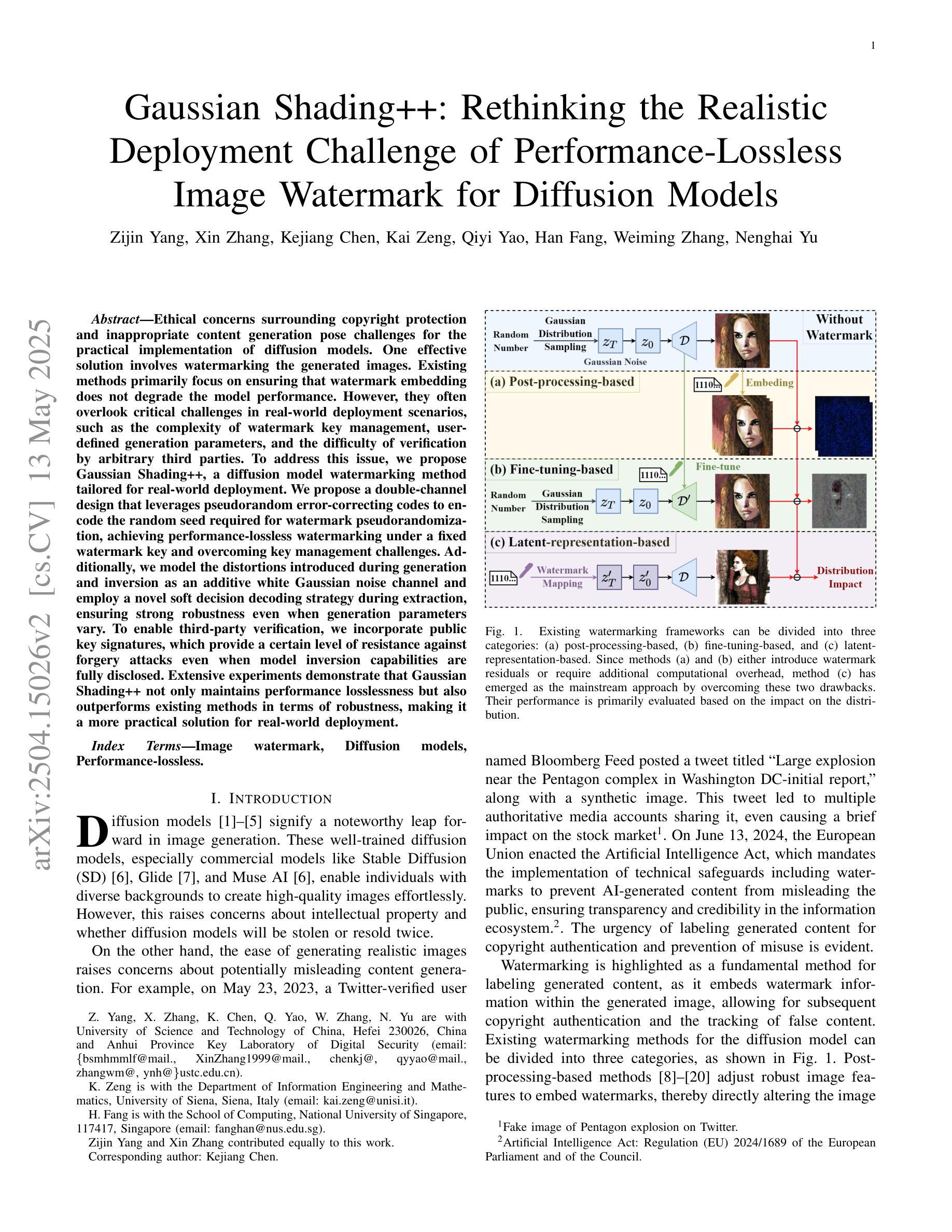
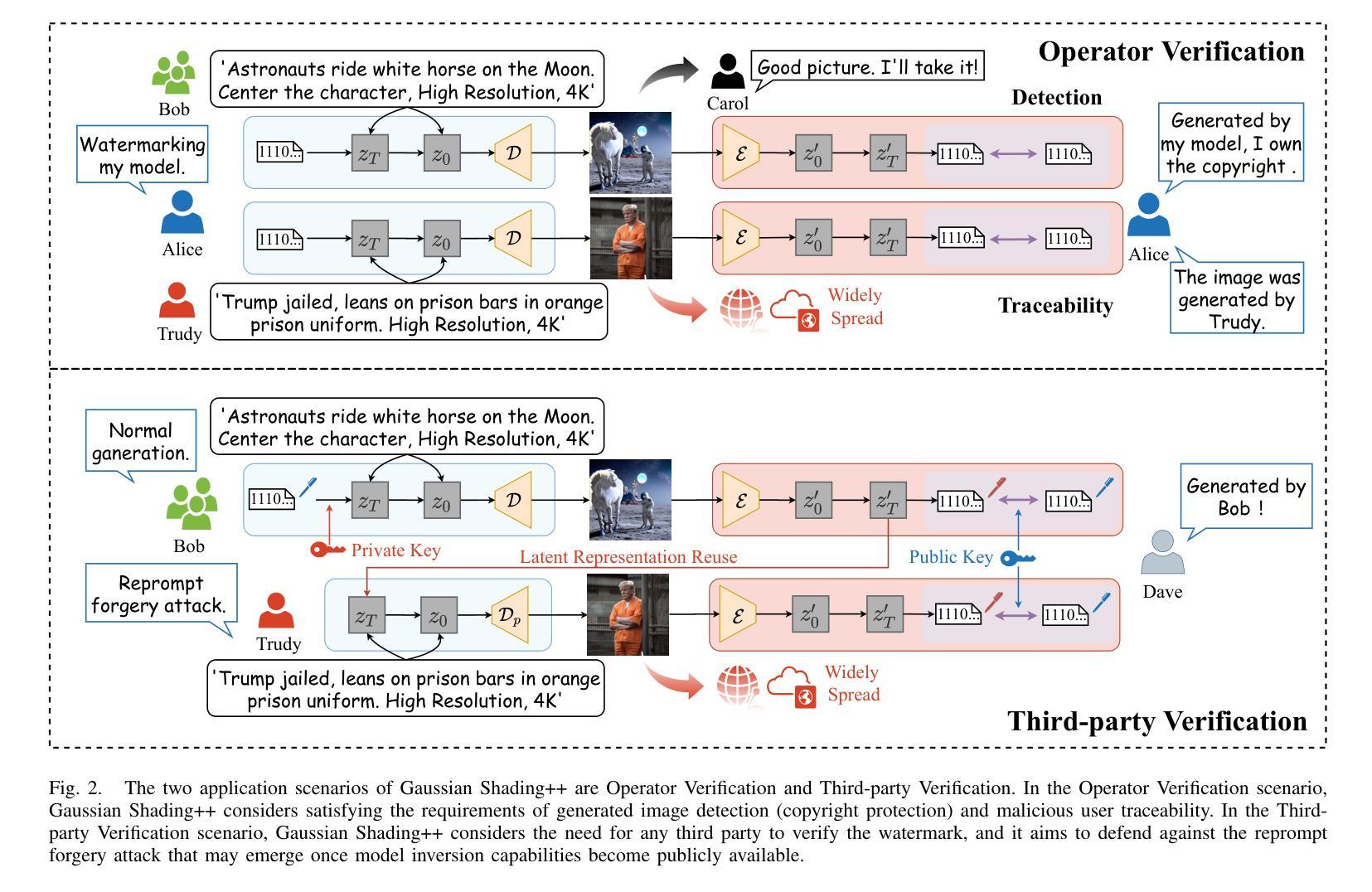
Gaussian Shading++: Rethinking the Realistic Deployment Challenge of Performance-Lossless Image Watermark for Diffusion Models
Authors:Zijin Yang, Xin Zhang, Kejiang Chen, Kai Zeng, Qiyi Yao, Han Fang, Weiming Zhang, Nenghai Yu
Ethical concerns surrounding copyright protection and inappropriate content generation pose challenges for the practical implementation of diffusion models. One effective solution involves watermarking the generated images. Existing methods primarily focus on ensuring that watermark embedding does not degrade the model performance. However, they often overlook critical challenges in real-world deployment scenarios, such as the complexity of watermark key management, user-defined generation parameters, and the difficulty of verification by arbitrary third parties. To address this issue, we propose Gaussian Shading++, a diffusion model watermarking method tailored for real-world deployment. We propose a double-channel design that leverages pseudorandom error-correcting codes to encode the random seed required for watermark pseudorandomization, achieving performance-lossless watermarking under a fixed watermark key and overcoming key management challenges. Additionally, we model the distortions introduced during generation and inversion as an additive white Gaussian noise channel and employ a novel soft decision decoding strategy during extraction, ensuring strong robustness even when generation parameters vary. To enable third-party verification, we incorporate public key signatures, which provide a certain level of resistance against forgery attacks even when model inversion capabilities are fully disclosed. Extensive experiments demonstrate that Gaussian Shading++ not only maintains performance losslessness but also outperforms existing methods in terms of robustness, making it a more practical solution for real-world deployment.
关于扩散模型的实用化实施,围绕版权保护和不当内容生成所产生的道德问题是一大挑战。一种有效的解决方案是在生成的图像上添加水印。现有方法主要集中在确保水印嵌入不会降低模型性能。然而,他们往往忽视了真实部署场景中的关键挑战,如水印密钥管理的复杂性、用户定义的生成参数以及第三方验证的困难。为了解决这一问题,我们提出了高斯阴影++(Gaussian Shading++),这是一种针对真实世界部署量身定制的扩散模型水印方法。我们提出了一种双通道设计,利用伪随机纠错编码对水印伪随机化所需的随机种子进行编码,实现在固定水印密钥下的性能无损水印,并克服密钥管理挑战。此外,我们将生成和反转过程中引入的失真建模为加性白高斯噪声通道,并在提取过程中采用新型软决策解码策略,确保即使在生成参数变化时也能保持强大的稳健性。为了实现第三方验证,我们引入了公钥签名,即使在模型反转能力完全公开的情况下,也能提供一定的抗伪造攻击能力。大量实验表明,高斯阴影++不仅保持了性能无损,而且在稳健性方面超越了现有方法,使其成为更实用的真实世界部署解决方案。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 18 pages, 8 figures
Summary
针对扩散模型实际应用中的版权保护与不当内容生成等伦理问题,提出一种名为Gaussian Shading++的模型水印方法。该方法采用双通道设计,利用伪随机纠错码对随机种子进行编码,实现性能无损的水印嵌入和固定水印密钥管理,同时建模生成和反转过程中的失真为加性白高斯噪声通道,并采用软决策解码策略确保稳健性。为第三方验证,引入了公钥签名,对抗伪造攻击。实验证明,Gaussian Shading++在保持性能无损的同时,稳健性优于现有方法,更适合实际部署。
Key Takeaways
- 扩散模型实际应用中面临版权保护和不当内容生成等伦理挑战。
- Gaussian Shading++是一种针对扩散模型的水印方法,旨在解决现实问题。
- 该方法采用双通道设计和伪随机纠错码,实现性能无损的水印嵌入。
- Gaussian Shading++解决了水印密钥管理复杂度高的挑战。
- 方法将生成和反转过程中的失真建模为加性白高斯噪声通道,采用软决策解码策略确保稳健性。
- 为实现第三方验证,引入了公钥签名,增强对抗伪造攻击的能力。
点此查看论文截图
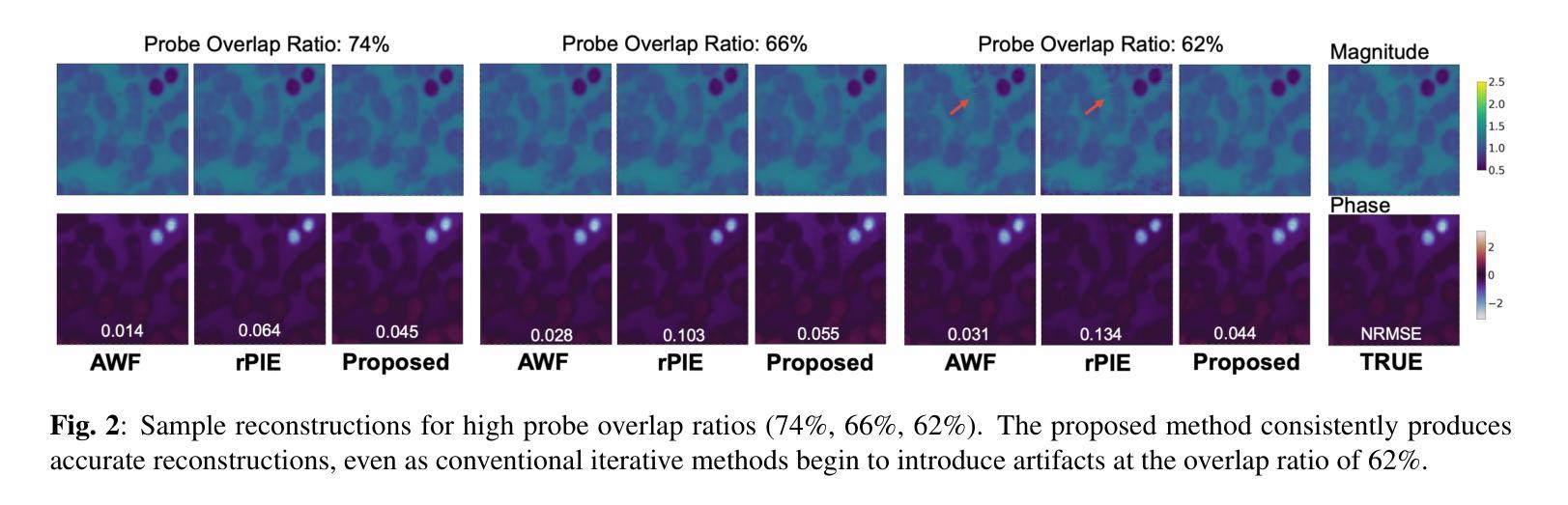
Ptychographic Image Reconstruction from Limited Data via Score-Based Diffusion Models with Physics-Guidance
Authors:Refik Mert Cam, Junjing Deng, Rajkumar Kettimuthu, Mathew J. Cherukara, Tekin Bicer
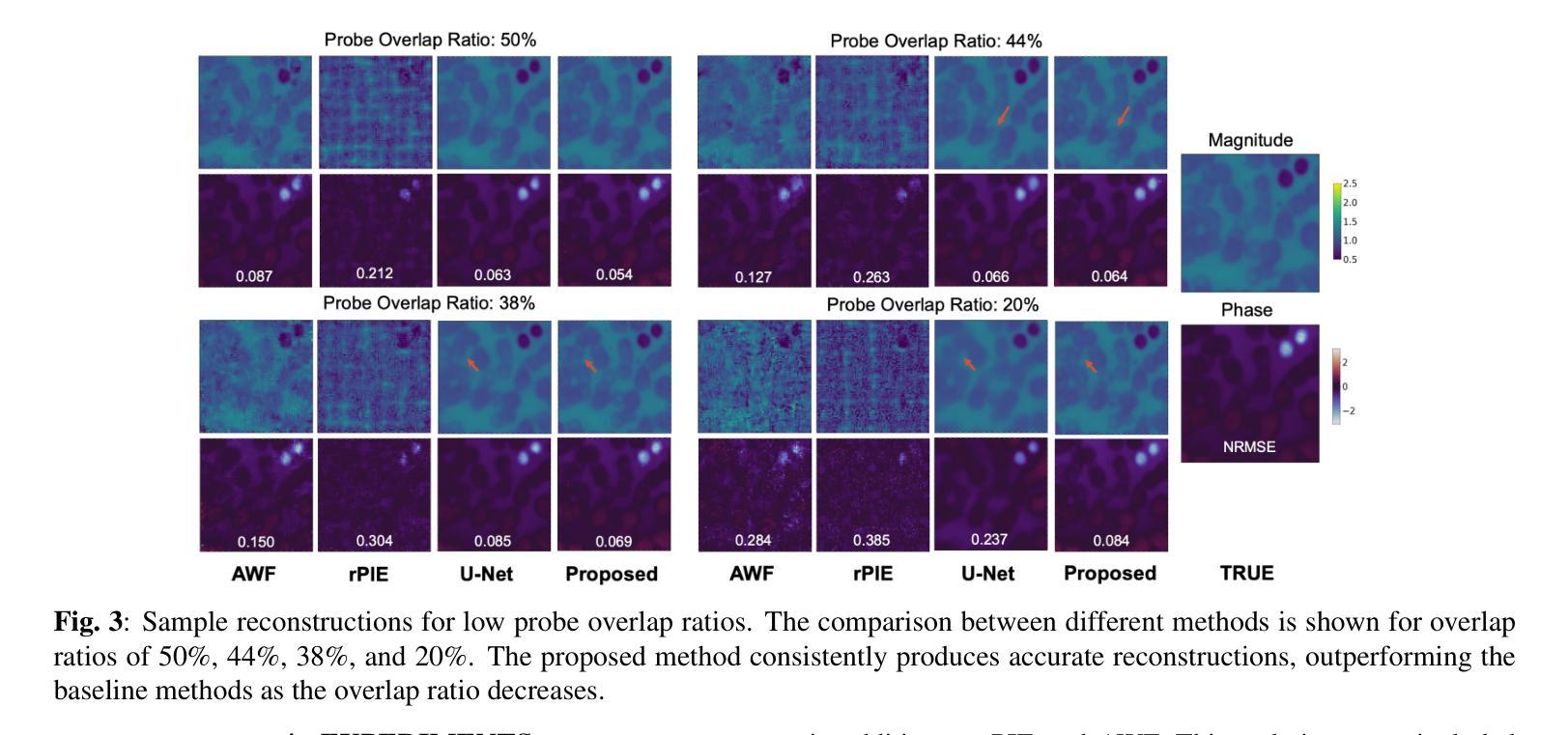
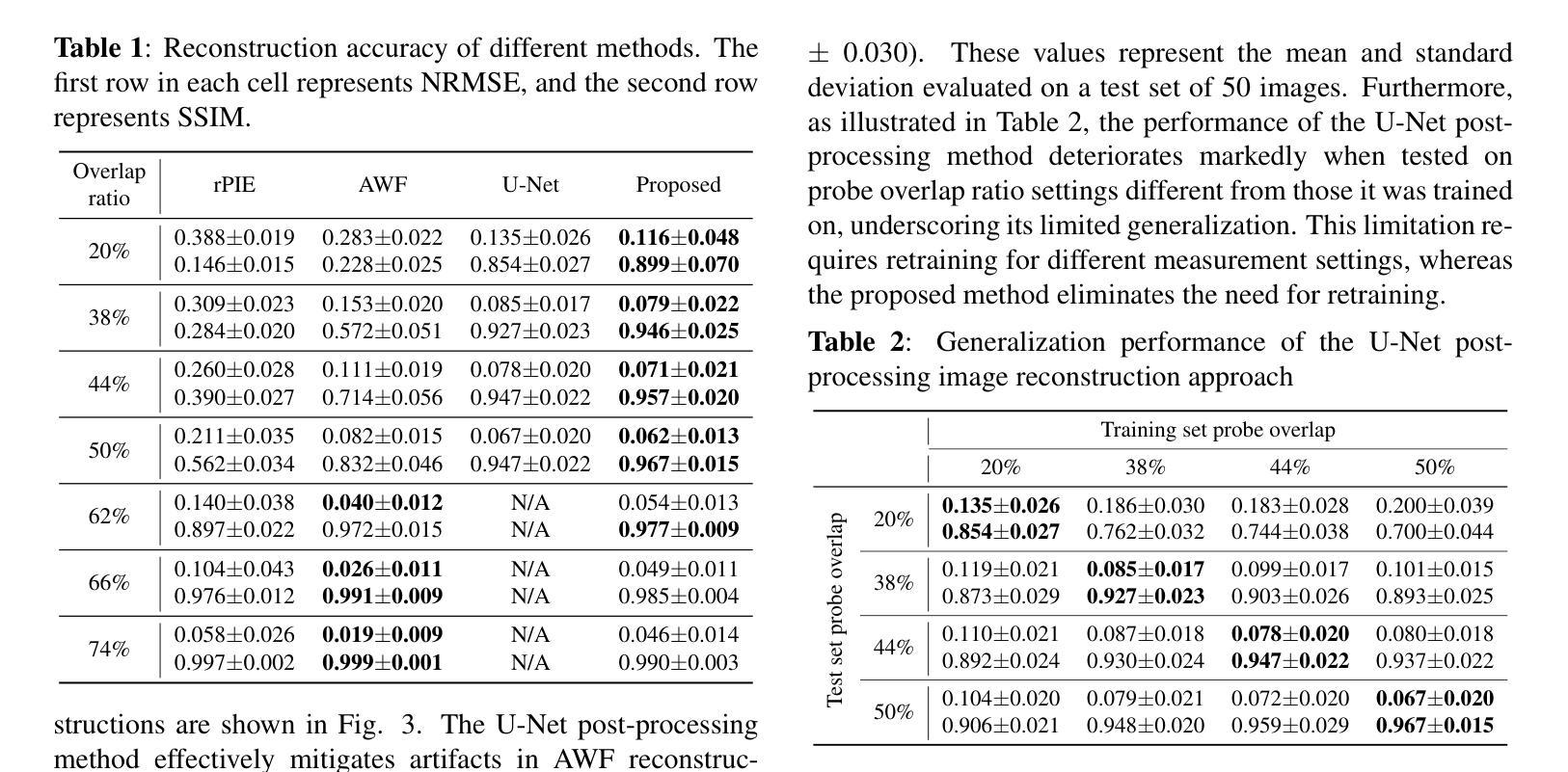
Ptychography is a data-intensive computational imaging technique that achieves high spatial resolution over large fields of view. The technique involves scanning a coherent beam across overlapping regions and recording diffraction patterns. Conventional reconstruction algorithms require substantial overlap, increasing data volume and experimental time, reaching PiB-scale experimental data and weeks to month-long data acquisition times. To address this, we propose a reconstruction method employing a physics-guided score-based diffusion model. Our approach trains a diffusion model on representative object images to learn an object distribution prior. During reconstruction, we modify the reverse diffusion process to enforce data consistency, guiding reverse diffusion toward a physically plausible solution. This method requires a single pretraining phase, allowing it to generalize across varying scan overlap ratios and positions. Our results demonstrate that the proposed method achieves high-fidelity reconstructions with only a 20% overlap, while the widely employed rPIE method requires a 62% overlap to achieve similar accuracy. This represents a significant reduction in data requirements, offering an alternative to conventional techniques.
Ptychography是一种数据密集型的计算成像技术,可以在大视野范围内实现高空间分辨率。该技术涉及扫描相干光束穿过重叠区域并记录衍射图案。传统的重建算法需要大量的重叠,这增加了数据量和实验时间,达到PiB规模的实验数据和长达数周的数据采集时间。针对这一问题,我们提出了一种采用物理引导评分扩散模型的重建方法。我们的方法通过在具有代表性的目标图像上训练扩散模型来学习目标分布先验。在重建过程中,我们修改反向扩散过程以强制执行数据一致性,引导反向扩散朝着物理可行解进行。该方法仅需一个预训练阶段,可以跨不同的扫描重叠率和位置进行推广。我们的结果表明,所提出的方法在仅23%的重叠情况下实现了高保真重建,而广泛使用的rPIE方法需要达到类似精度则需要高达62%的重叠率。这代表了数据需求的显著减少,为传统技术提供了替代方案。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Preprint submitted to IEEE MLSP 2025
Summary
该文介绍了用于实现大面积高空间分辨率成像的定量成像技术——斑点扫描成像。文中指出传统重建算法需要大量重叠区域,导致数据量和实验时间增加。为改善这一问题,提出了一种基于物理引导和扩散模型的重建方法。该方法通过在代表性目标图像上训练扩散模型来学习目标分布先验。在重建过程中,修改反向扩散过程以强制数据一致性,从而引导其向物理可行解方向进行。该方法仅需一次预训练阶段,可泛化于不同扫描重叠率和位置。实验结果显示,所提方法仅需要20%重叠率即可实现高保真重建,而广泛使用的rPIE方法需要62%重叠率才能达到相似精度。这显著降低了数据要求,为传统技术提供了替代方案。
Key Takeaways
- 斑点扫描成像是一种数据密集型计算成像技术,可在大视野上实现高空间分辨率。
- 传统重建算法需要大量重叠区域,增加了数据量和实验时间。
- 提出了一种基于物理引导和扩散模型的重建方法,通过训练扩散模型来学习目标分布先验。
- 修改了反向扩散过程以强制数据一致性,引导解决方案向物理可行方向进行。
- 该方法仅需要一次预训练阶段,并可以泛化到不同的扫描重叠率和位置。
- 实验结果显示,所提方法只需20%重叠即可实现高保真重建。
点此查看论文截图

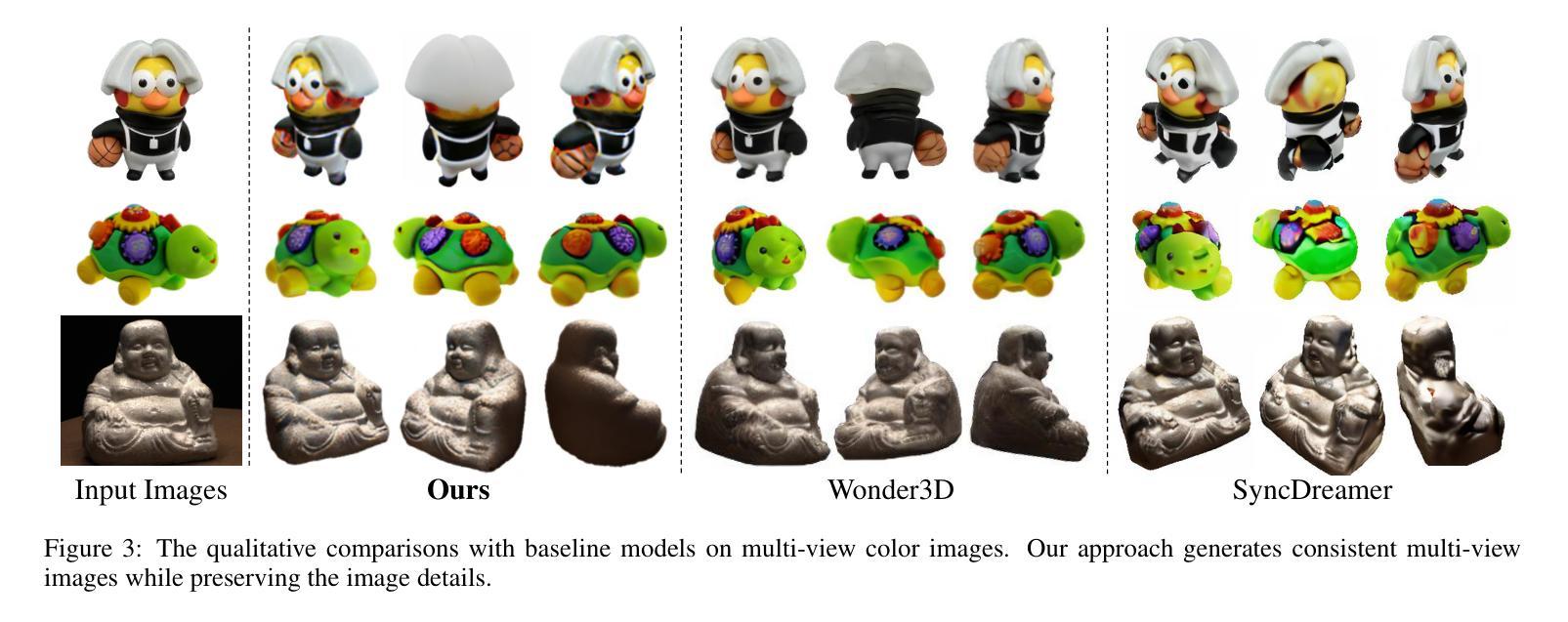
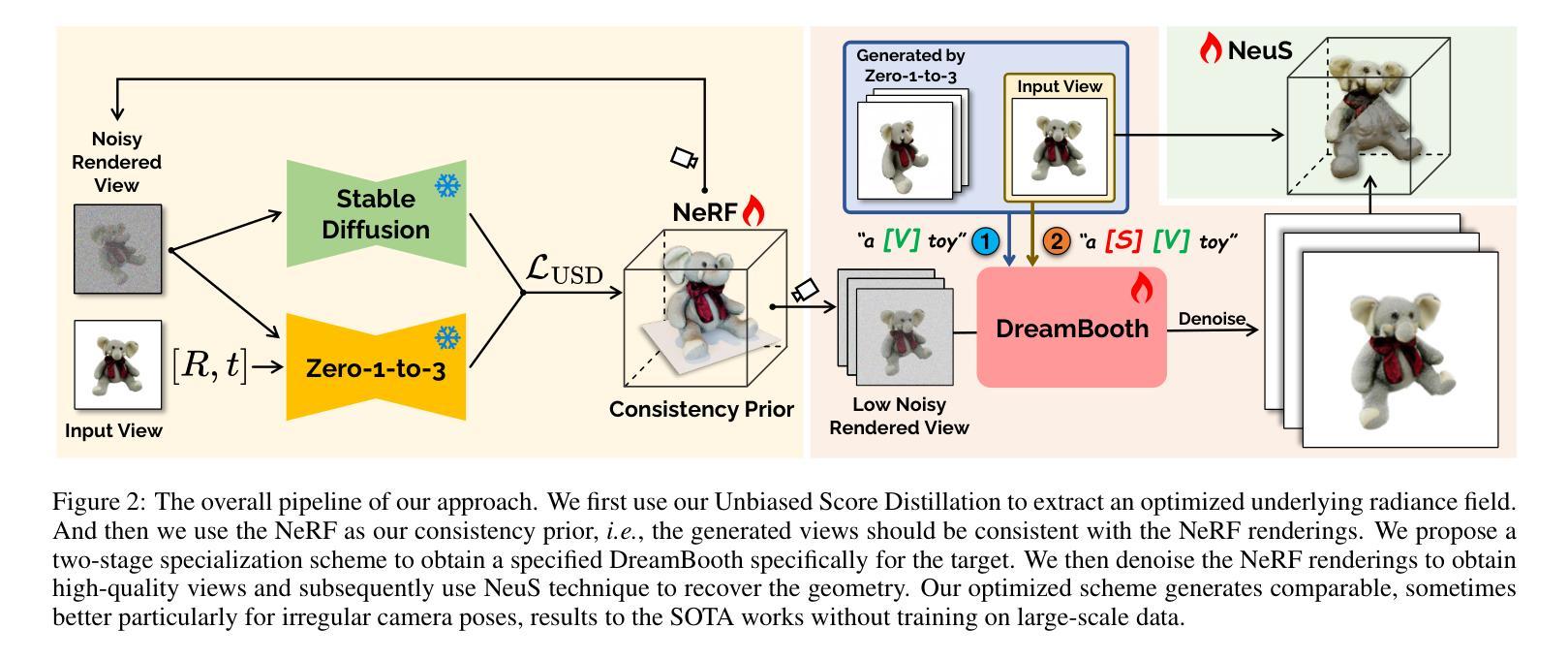
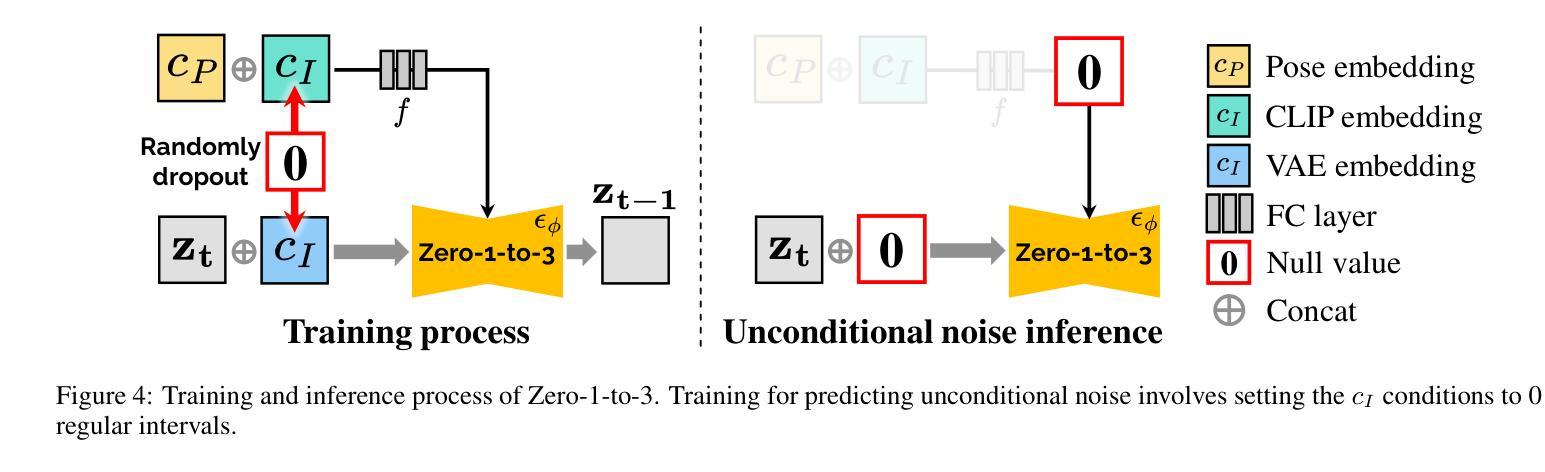
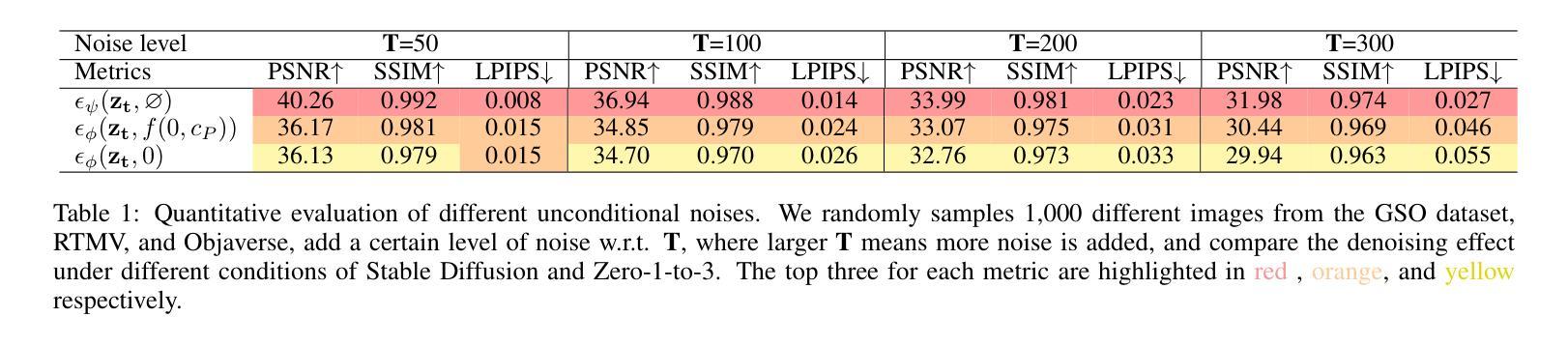
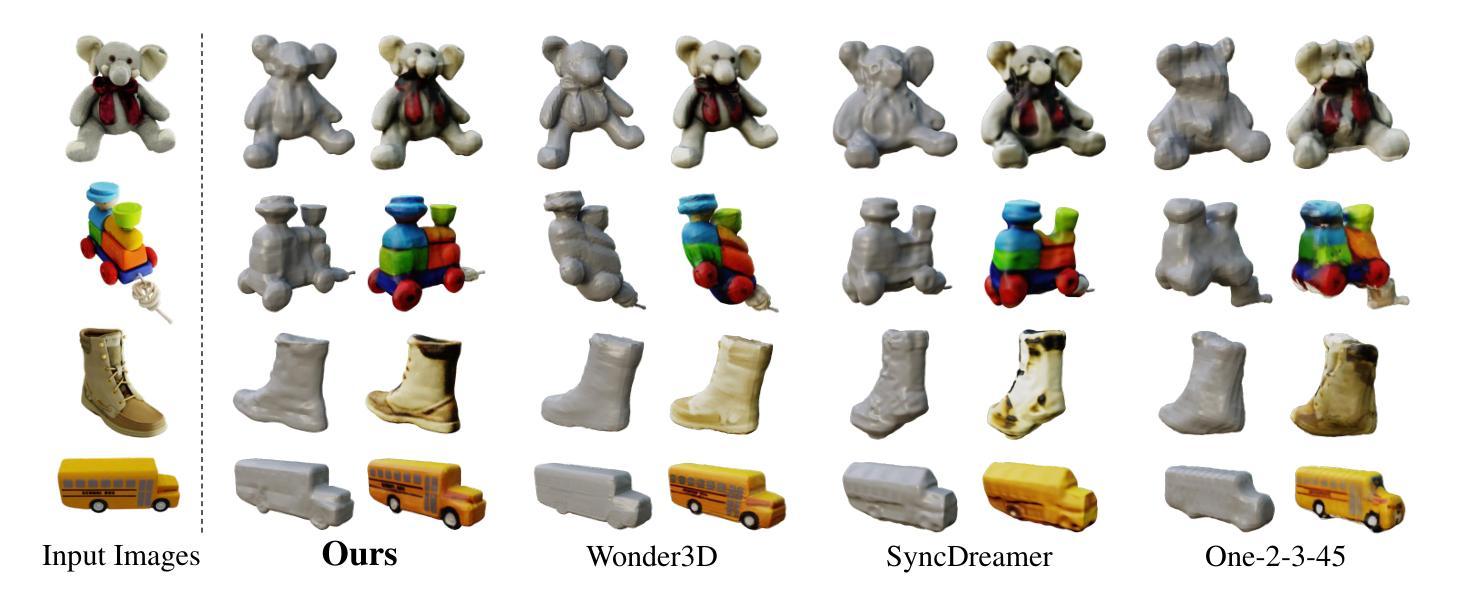
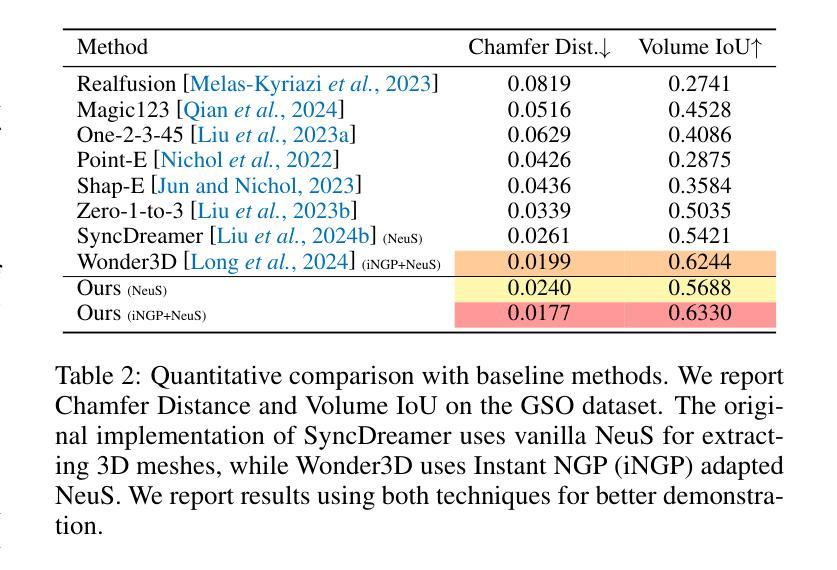
Optimized View and Geometry Distillation from Multi-view Diffuser
Authors:Youjia Zhang, Zikai Song, Junqing Yu, Yawei Luo, Wei Yang
Generating multi-view images from a single input view using image-conditioned diffusion models is a recent advancement and has shown considerable potential. However, issues such as the lack of consistency in synthesized views and over-smoothing in extracted geometry persist. Previous methods integrate multi-view consistency modules or impose additional supervisory to enhance view consistency while compromising on the flexibility of camera positioning and limiting the versatility of view synthesis. In this study, we consider the radiance field optimized during geometry extraction as a more rigid consistency prior, compared to volume and ray aggregation used in previous works. We further identify and rectify a critical bias in the traditional radiance field optimization process through score distillation from a multi-view diffuser. We introduce an Unbiased Score Distillation (USD) that utilizes unconditioned noises from a 2D diffusion model, greatly refining the radiance field fidelity. We leverage the rendered views from the optimized radiance field as the basis and develop a two-step specialization process of a 2D diffusion model, which is adept at conducting object-specific denoising and generating high-quality multi-view images. Finally, we recover faithful geometry and texture directly from the refined multi-view images. Empirical evaluations demonstrate that our optimized geometry and view distillation technique generates comparable results to the state-of-the-art models trained on extensive datasets, all while maintaining freedom in camera positioning. Please see our project page at https://youjiazhang.github.io/USD/.
使用图像条件扩散模型从单一输入视图生成多视图图像是最近的一项进展,并显示出巨大的潜力。然而,合成视图的不一致性以及提取几何图形时的过度平滑等问题仍然存在。之前的方法是通过集成多视图一致性模块或施加额外的监督来增强视图一致性,但这会损害相机定位的自由度并限制视图合成的灵活性。在这项研究中,我们认为在几何提取过程中优化的辐射场是一个更严格的一致性先验,与之前使用的体积和射线聚合相比。我们进一步通过来自多视图扩散器的分数蒸馏来识别和纠正传统辐射场优化过程中的关键偏见。我们引入了一种无偏分数蒸馏(USD),它利用来自二维扩散模型的无条件噪声,大大提高了辐射场的保真度。我们利用优化后的辐射场所呈现的视图作为基础,开发了一个两步特化过程的二维扩散模型,该模型擅长进行对象特定的去噪和生成高质量的多视图图像。最后,我们从精致的多视图图像中直接恢复几何形状和纹理。经验评估表明,我们优化的几何和视图蒸馏技术生成的结果与在大型数据集上训练的最新模型相当,同时保持了相机定位的自由度。请访问我们的项目页面https://youjiazhang.github.io/USD/了解详情。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF IJCAI 2025. Project page: https://youjiazhang.github.io/USD/
Summary
基于图像条件的扩散模型在多视角图像生成领域展现出巨大潜力,但仍存在视图不一致和几何提取过度平滑等问题。本研究通过优化几何提取过程中的辐射场,引入无偏评分蒸馏(USD)技术,并发展了一个基于优化辐射场的两步专业化过程,旨在生成高质量的多视角图像。同时,该研究能够从优化后的多视角图像中恢复真实的几何和纹理信息。
Key Takeaways
- 扩散模型在多视角图像生成中具有显著潜力。
- 存在视图不一致性和几何提取过度平滑的问题。
- 优化几何提取过程中的辐射场以提高视图一致性。
- 引入无偏评分蒸馏(USD)技术,利用无条件噪声提高辐射场的保真度。
- 发展基于优化辐射场的两步专业化过程,擅长进行对象特定的去噪和高质量多视角图像生成。
- 从优化后的多视角图像中恢复真实的几何和纹理信息。
- 实证评估表明,优化后的几何和视图蒸馏技术产生的结果与在大型数据集上训练的最新模型相当,同时保持相机定位的自由度。
点此查看论文截图