⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-05-15 更新
LLM-based Prompt Ensemble for Reliable Medical Entity Recognition from EHRs
Authors:K M Sajjadul Islam, Ayesha Siddika Nipu, Jiawei Wu, Praveen Madiraju
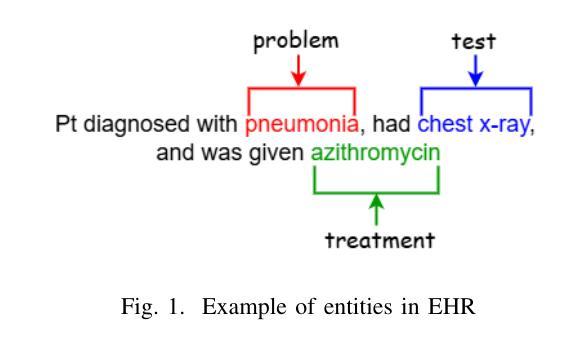
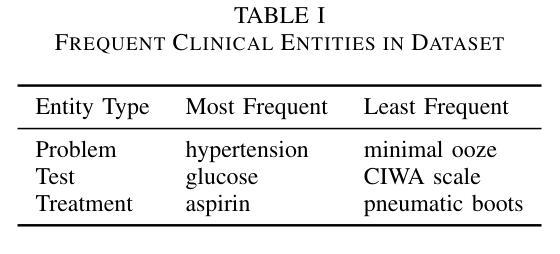
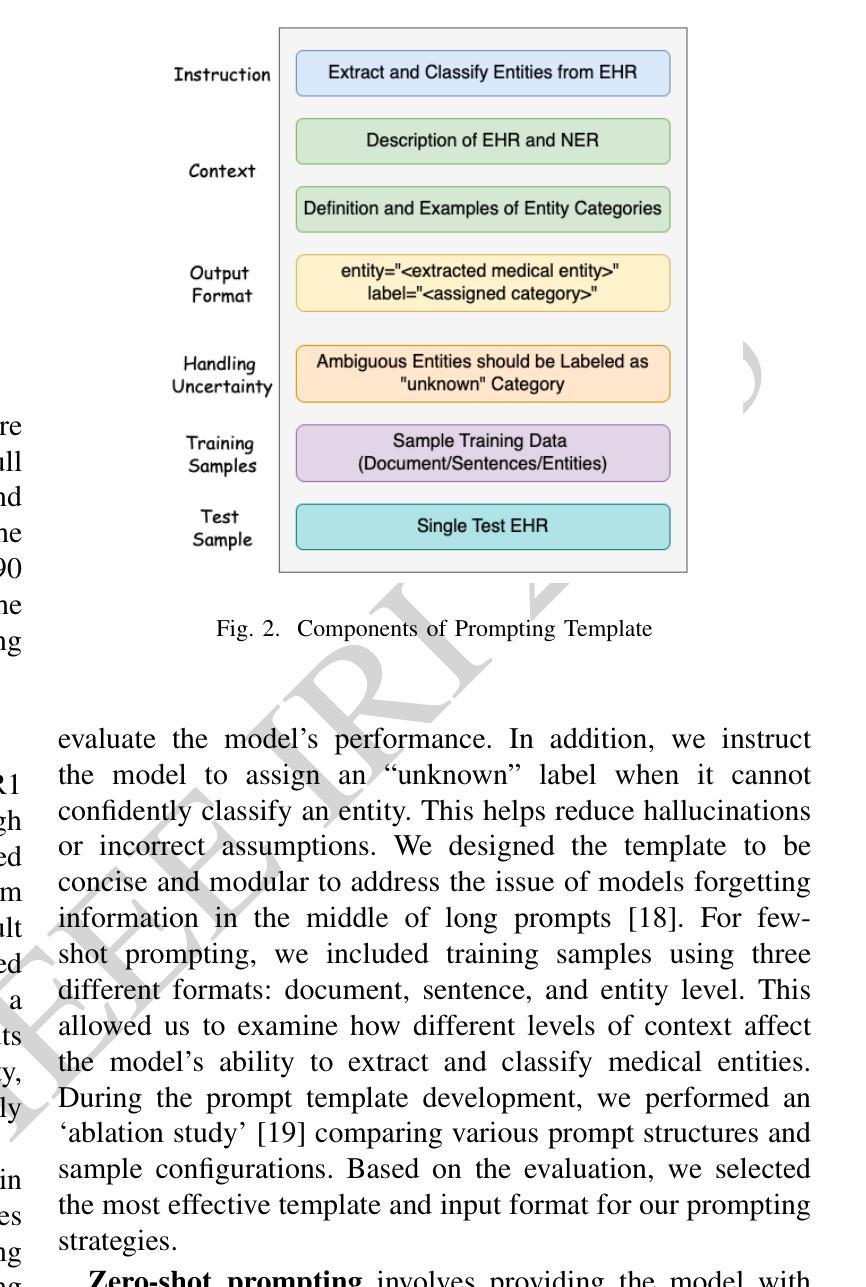
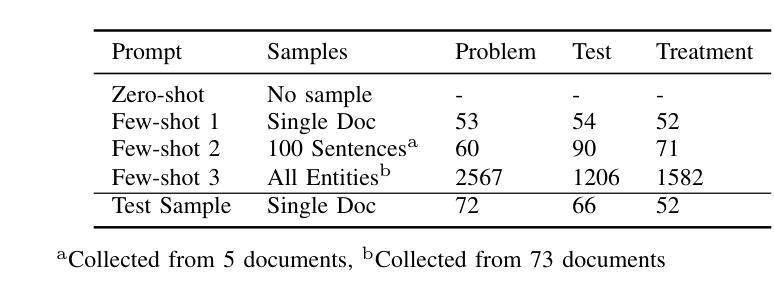
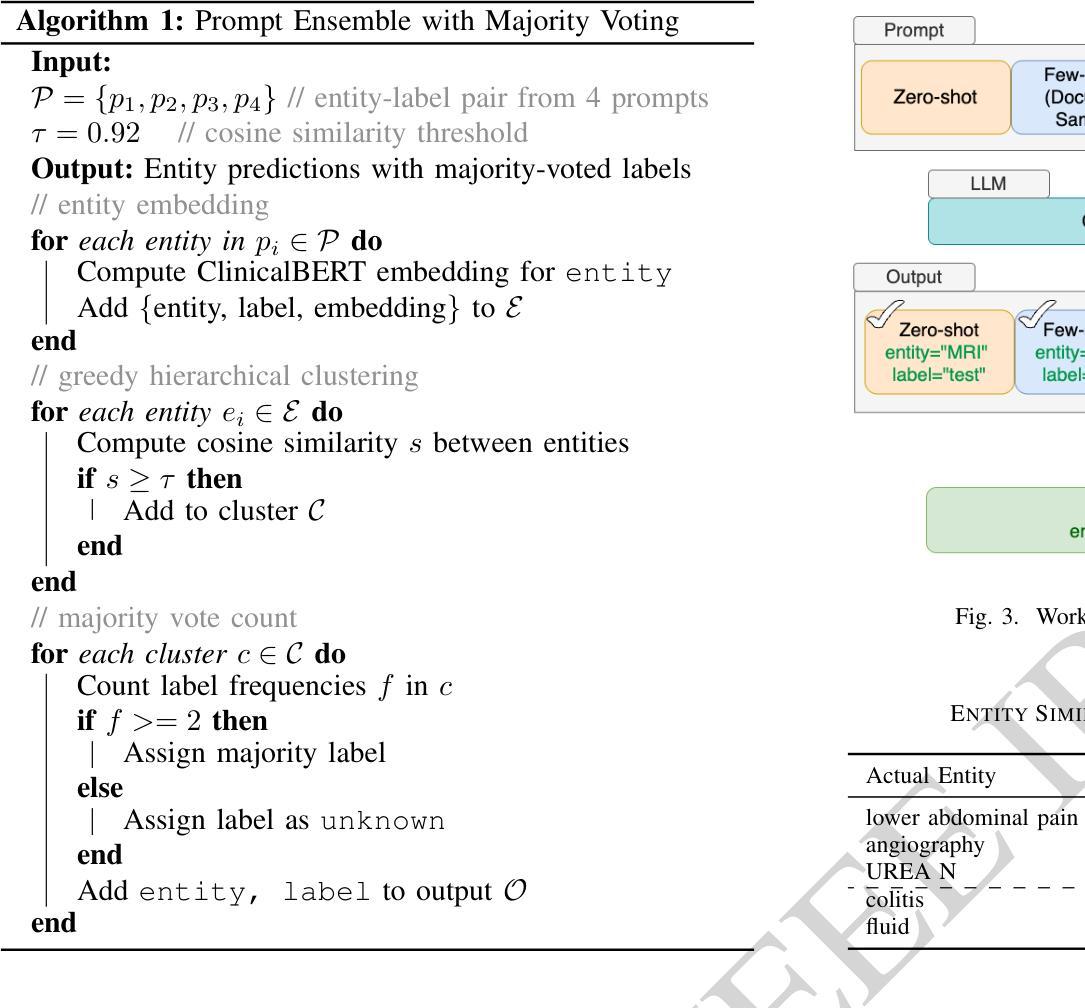
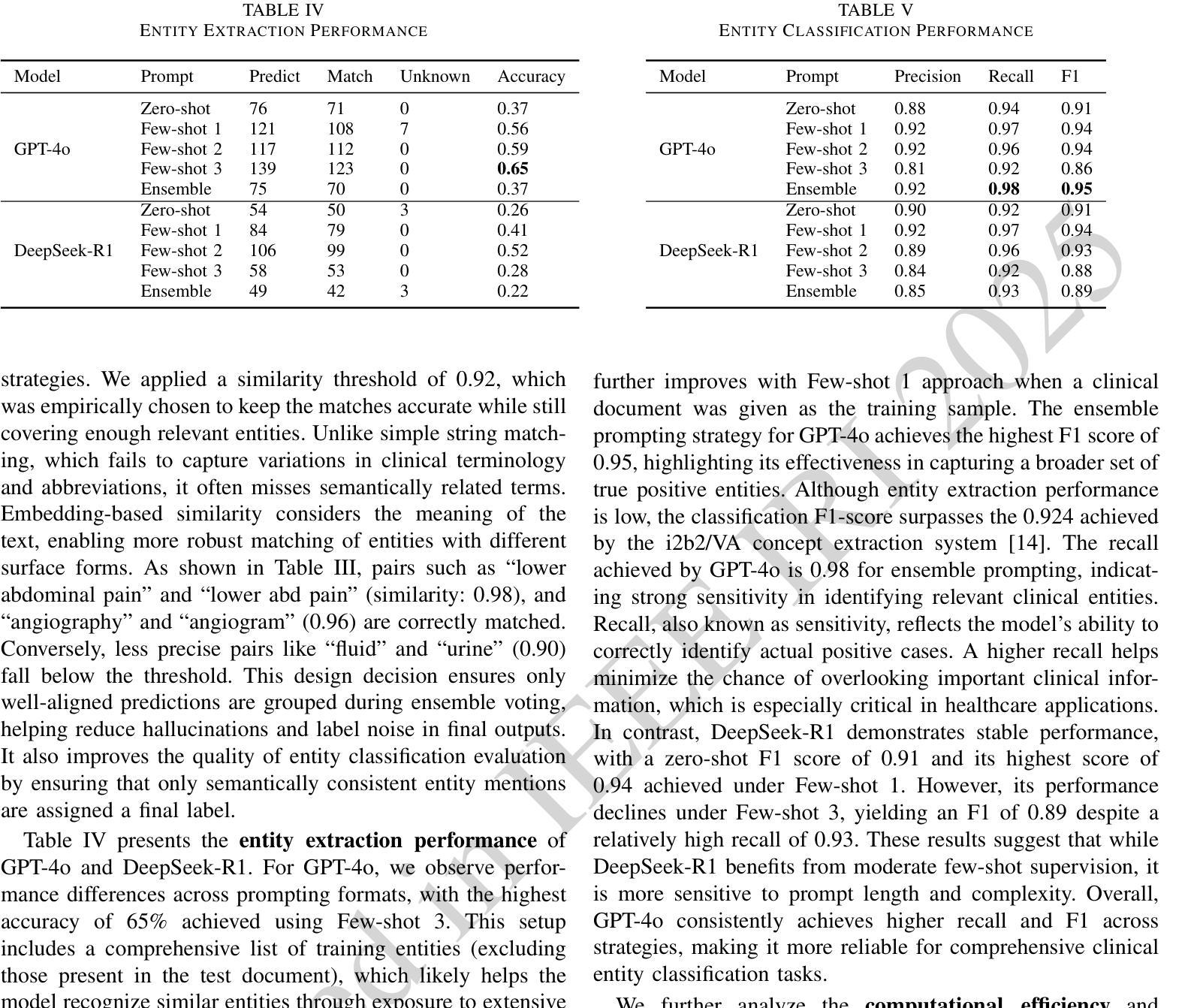
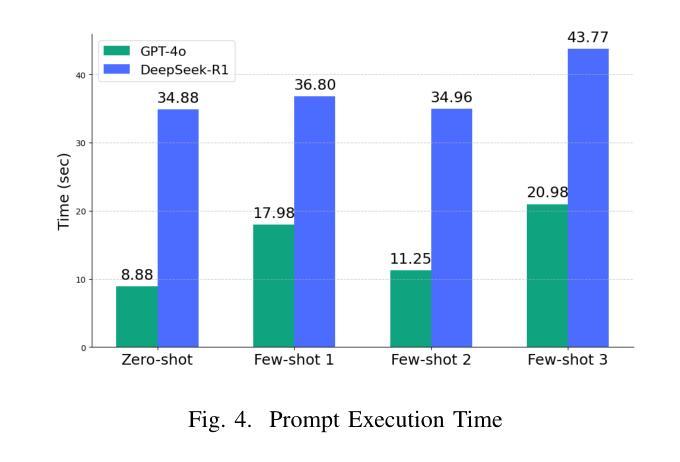
Electronic Health Records (EHRs) are digital records of patient information, often containing unstructured clinical text. Named Entity Recognition (NER) is essential in EHRs for extracting key medical entities like problems, tests, and treatments to support downstream clinical applications. This paper explores prompt-based medical entity recognition using large language models (LLMs), specifically GPT-4o and DeepSeek-R1, guided by various prompt engineering techniques, including zero-shot, few-shot, and an ensemble approach. Among all strategies, GPT-4o with prompt ensemble achieved the highest classification performance with an F1-score of 0.95 and recall of 0.98, outperforming DeepSeek-R1 on the task. The ensemble method improved reliability by aggregating outputs through embedding-based similarity and majority voting.
电子健康记录(EHRs)是患者信息的数字记录,通常包含非结构化的临床文本。在电子健康记录中,命名实体识别(NER)对于提取关键医疗实体至关重要,如问题、测试和治疗方法,以支持下游的临床应用。本文探讨了基于提示的医疗实体识别,使用大型语言模型(LLM),特别是GPT-4o和DeepSeek-R1,在各种提示工程技术指导下,包括零样本、少样本和集成方法。在所有策略中,GPT-4o通过提示集成取得了最高的分类性能,F1分数为0.95,召回率为0.98,在该任务上优于DeepSeek-R1。集成方法通过基于嵌入的相似性和多数投票来聚合输出,提高了可靠性。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF IEEE 26th International Conference on Information Reuse and Integration for Data Science (IRI 2025), San Jose, CA, USA
Summary
本文主要探讨了基于大型语言模型的命名实体识别在电子健康记录(EHRs)中的应用。通过运用多种提示工程技术,包括零样本、少样本和集成方法,使用GPT-4o和DeepSeek-R1进行医学实体识别。其中,GPT-4o与提示集成策略取得了最高的分类性能,F1分数为0.95,召回率为0.98,在该任务上优于DeepSeek-R1。集成方法通过基于嵌入的相似性和多数投票法聚合输出,提高了可靠性。
Key Takeaways
- 电子健康记录(EHRs)中的命名实体识别(NER)是关键技术,可提取问题、测试和治疗等关键医疗实体,支持下游临床应用。
- 本文探讨了基于大型语言模型(LLMs)的提示工程技术在医学实体识别中的应用。
- GPT-4o和DeepSeek-R1被用于此任务,其中GPT-4o与提示集成策略表现出最佳性能。
- 集成方法通过嵌入相似性度和多数投票法提高可靠性。
- GPT-4o在F1分数和召回率方面表现出较高的分类性能。
- 提示工程技术,如零样本和少样本方法,也被用于医学实体识别任务。
点此查看论文截图

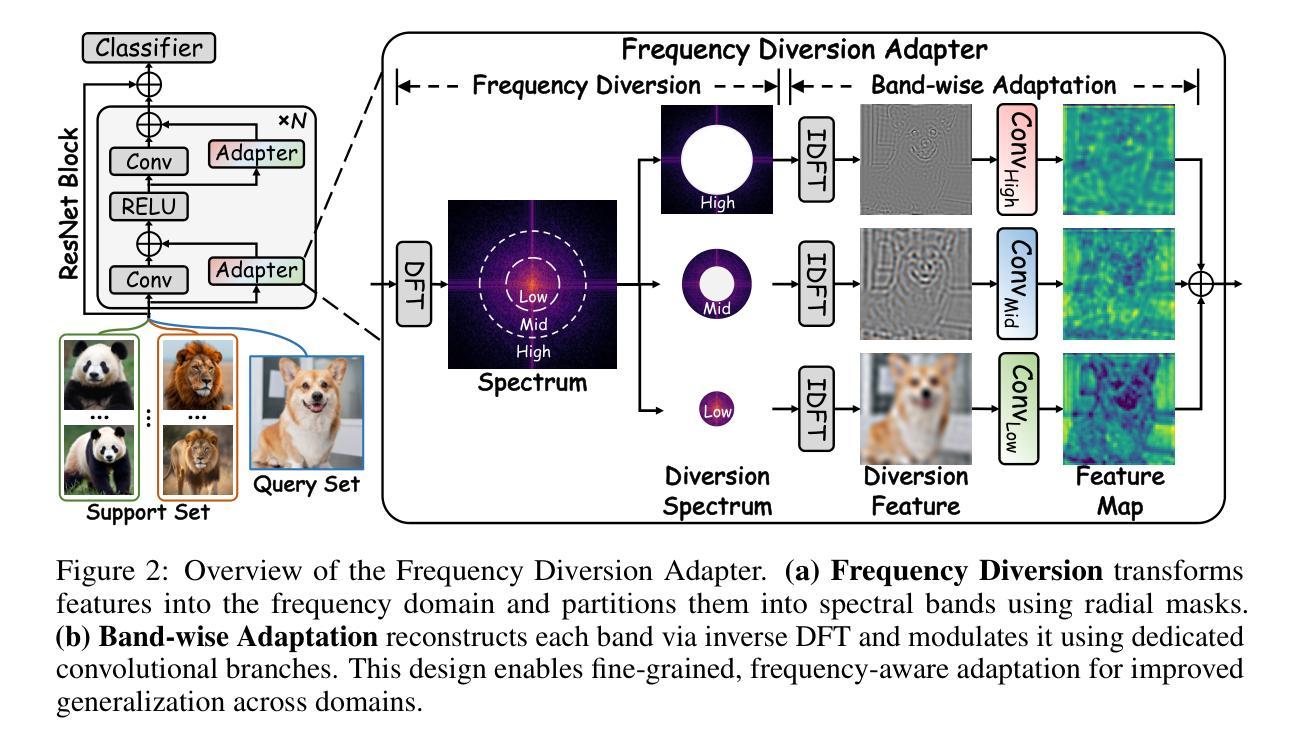
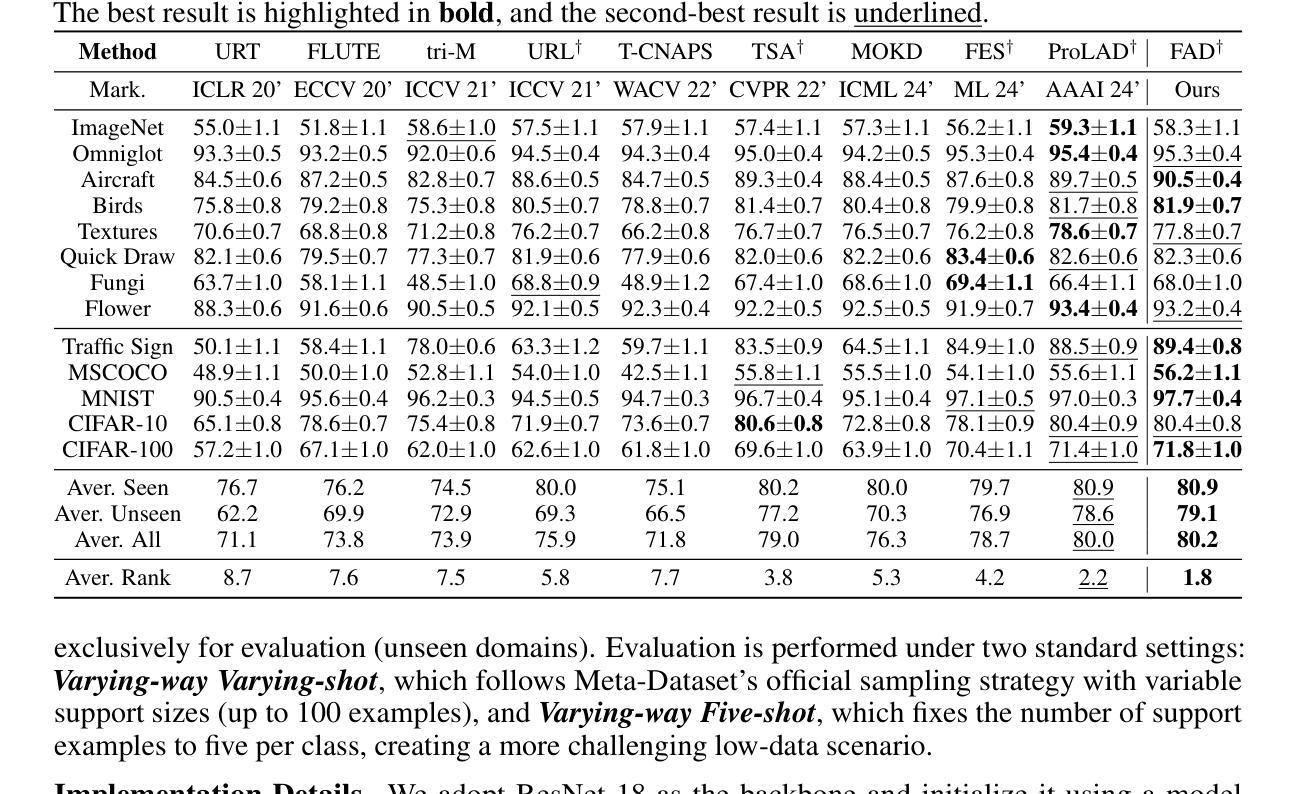
FAD: Frequency Adaptation and Diversion for Cross-domain Few-shot Learning
Authors:Ruixiao Shi, Fu Feng, Yucheng Xie, Jing Wang, Xin Geng
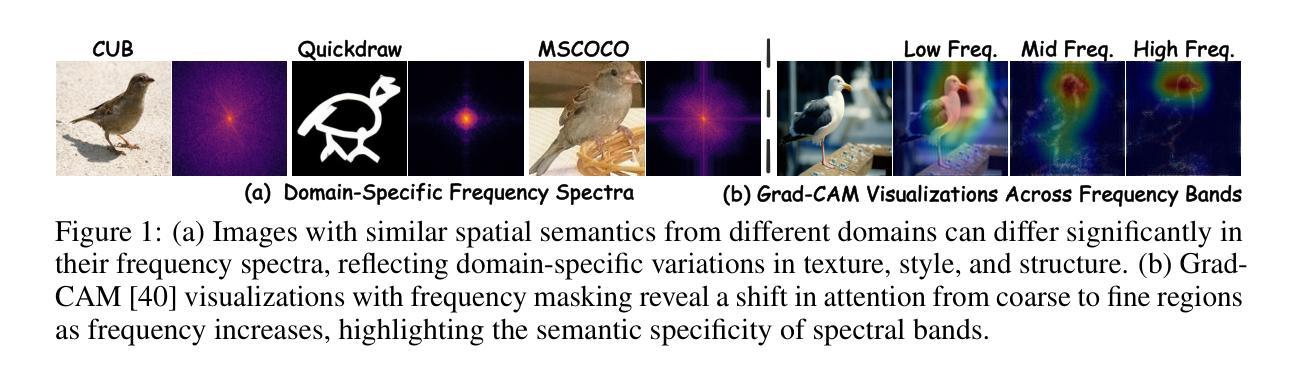
Cross-domain few-shot learning (CD-FSL) requires models to generalize from limited labeled samples under significant distribution shifts. While recent methods enhance adaptability through lightweight task-specific modules, they operate solely in the spatial domain and overlook frequency-specific variations that are often critical for robust transfer. We observe that spatially similar images across domains can differ substantially in their spectral representations, with low and high frequencies capturing complementary semantic information at coarse and fine levels. This indicates that uniform spatial adaptation may overlook these spectral distinctions, thus constraining generalization. To address this, we introduce Frequency Adaptation and Diversion (FAD), a frequency-aware framework that explicitly models and modulates spectral components. At its core is the Frequency Diversion Adapter, which transforms intermediate features into the frequency domain using the discrete Fourier transform (DFT), partitions them into low, mid, and high-frequency bands via radial masks, and reconstructs each band using inverse DFT (IDFT). Each frequency band is then adapted using a dedicated convolutional branch with a kernel size tailored to its spectral scale, enabling targeted and disentangled adaptation across frequencies. Extensive experiments on the Meta-Dataset benchmark demonstrate that FAD consistently outperforms state-of-the-art methods on both seen and unseen domains, validating the utility of frequency-domain representations and band-wise adaptation for improving generalization in CD-FSL.
跨域小样本学习(CD-FSL)需要模型在显著分布偏移的情况下从有限的标记样本中进行泛化。虽然最近的方法通过轻量级的任务特定模块增强了适应性,但它们仅在空间域中操作,并忽略了频率特定变化,这些变化对于稳健的迁移通常至关重要。我们观察到,跨域的图像在空间上可能非常相似,但在其光谱表示中可能存在显著差异,低频和高频在粗细级别上捕获互补的语义信息。这表明,统一的适应策略可能会忽略这些光谱差异,从而限制泛化能力。为了解决这个问题,我们引入了频率适应和分流(FAD),这是一个频率感知框架,可以显式地建模和调制光谱成分。其核心是频率分流适配器,它将中间特征转换为频率域使用离散傅里叶变换(DFT),通过径向掩膜将它们划分为低频、中频和高频波段,并使用逆DFT(IDFT)重建每个波段。然后,每个频率波段都使用专门的卷积分支进行适应,卷积核大小根据其光谱尺度量身定制,从而实现有针对性的解耦频率适应。在Meta-Dataset基准测试上的大量实验表明,FAD在可见和不可见域上均优于最新方法,验证了频率域表示和波段适应对于提高CD-FSL中的泛化能力的实用性。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
该研究探讨了跨域小样本学习(CD-FSL)中模型在有限标注样本下的泛化能力问题。针对现有方法忽略频率特定变化,该文提出了频率适应和偏离(FAD)框架,该框架显式地建模和调制光谱成分。通过离散傅里叶变换(DFT)将中间特征转换到频率域,并通过径向掩膜将频率分成低、中、高频带,再进行逆DFT(IDFT)重建每个频带。针对每个频带,使用专门的卷积分支进行适应,其内核大小适应于其光谱尺度,从而实现有针对性的解耦频率适应。在Meta-Dataset基准测试上的实验表明,FAD在可见和不可见域上均优于现有方法,验证了频率域表示和频带适应在提高CD-FSL泛化能力方面的实用性。
Key Takeaways
- CD-FSL面临模型在有限标注样本下的泛化难题。
- 现有方法主要关注空间域适应,忽略了频率特定变化的重要性。
- 文中提出频率适应和偏离(FAD)框架,该框架显式建模和调制光谱成分。
- FAD使用DFT转换中间特征到频率域,并分区为不同频率带。
- 每个频率带通过专门的卷积分支进行适应,实现有针对性的解耦频率适应。
- 在Meta-Dataset上的实验表明FAD在跨域小样本学习上的优越性能。
点此查看论文截图

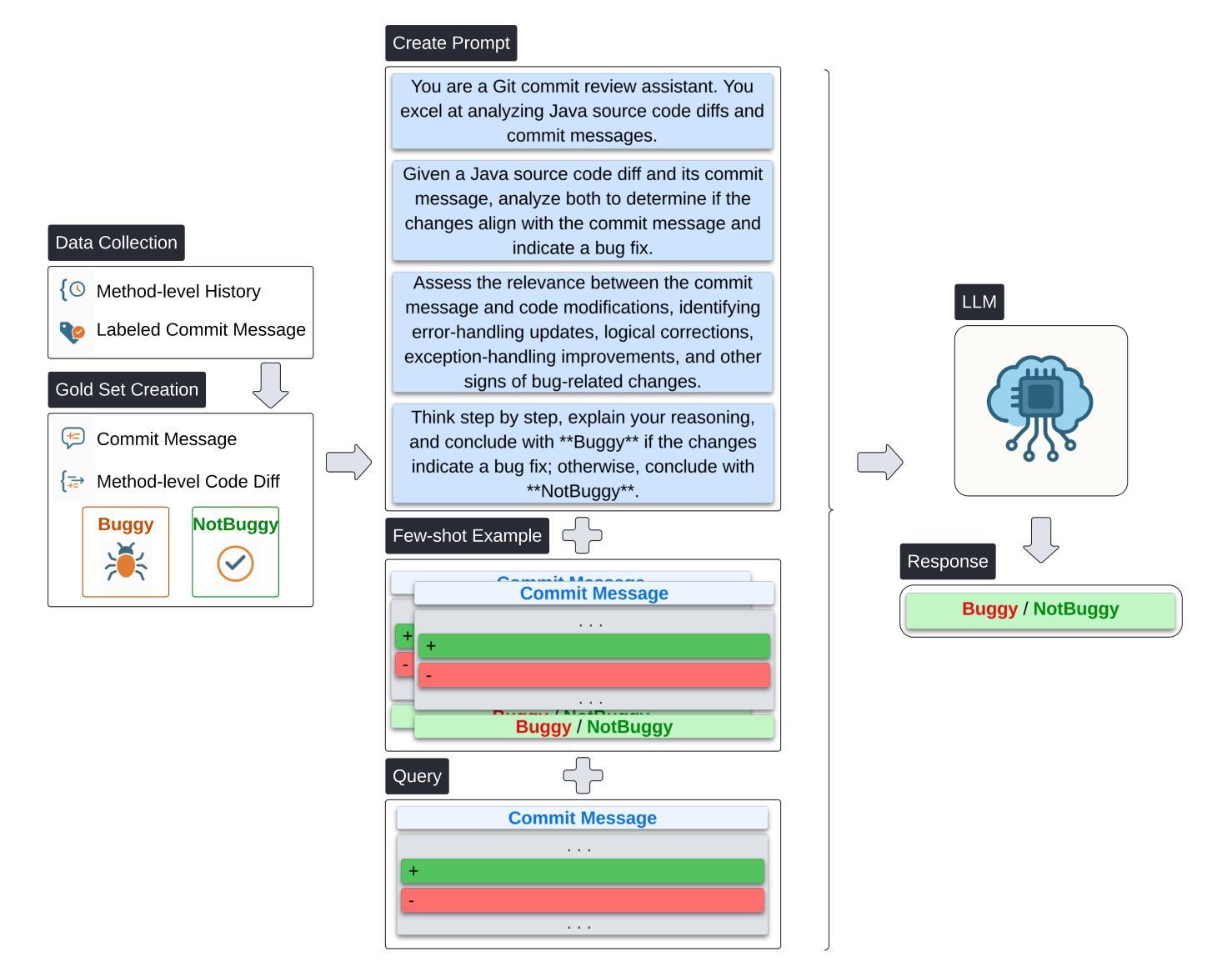
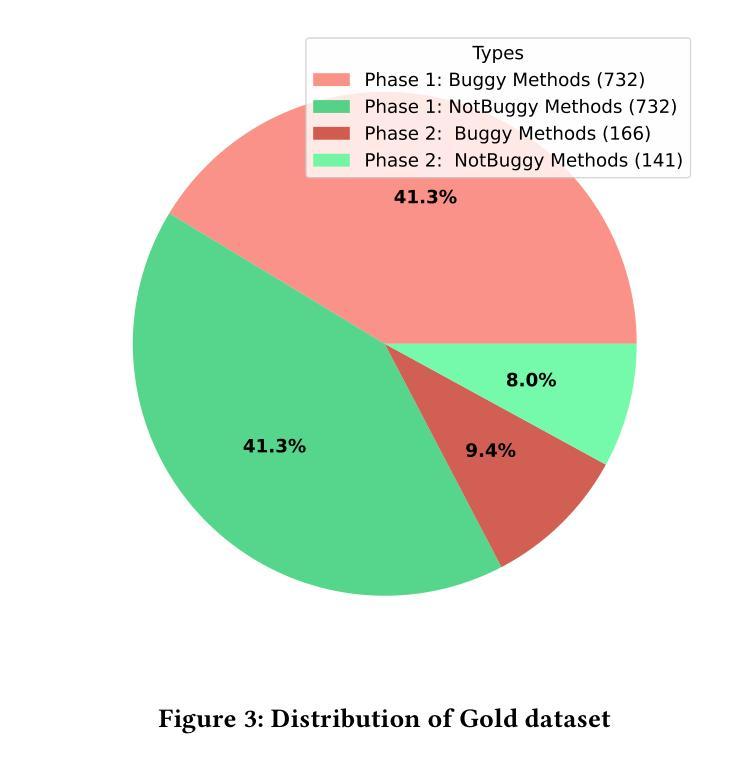
LLM-Based Detection of Tangled Code Changes for Higher-Quality Method-Level Bug Datasets
Authors:Md Nahidul Islam Opu, Shaowei Wang, Shaiful Chowdhury
Tangled code changes-commits that conflate unrelated modifications such as bug fixes, refactorings, and enhancements-introduce significant noise into bug datasets and adversely affect the performance of bug prediction models. Addressing this issue at a fine-grained, method-level granularity remains underexplored. This is critical to address, as recent bug prediction models, driven by practitioner demand, are increasingly focusing on finer granularity rather than traditional class- or file-level predictions. This study investigates the utility of Large Language Models (LLMs) for detecting tangled code changes by leveraging both commit messages and method-level code diffs. We formulate the problem as a binary classification task and evaluate multiple prompting strategies, including zero-shot, few-shot, and chain-of-thought prompting, using state-of-the-art proprietary LLMs such as GPT-4o and Gemini-2.0-Flash. Our results demonstrate that combining commit messages with code diffs significantly enhances model performance, with the combined few-shot and chain-of-thought prompting achieving an F1-score of 0.88. Additionally, we explore embedding-based machine learning models trained on LLM-generated embeddings, where a multi-layer perceptron classifier achieves superior performance (F1-score: 0.906, MCC: 0.807). These findings are encouraging for the research community, as method-level bug prediction remains an open research problem, largely due to the lack of noise-free bug datasets. This research not only contributes a novel method-level perspective to the untangling problem but also highlights practical avenues for enhancing automated software quality assessment tools.
混杂的代码更改(将无关修改混杂在一起,如错误修复、重构和增强功能)为错误数据集引入了重大噪声,并对错误预测模型的性能产生了不利影响。在精细粒度的代码级别上解决这一问题尚未得到充分的探索和研究。这是亟需解决的问题,因为由从业者需求的推动,最新的错误预测模型越来越关注更精细的粒度,而非传统的类或文件级别的预测。本研究旨在通过利用提交消息和方法级代码差异来检测混杂的代码更改,从而探究大型语言模型(LLM)的效用。我们将该问题表述为二分类任务,并评估了多种提示策略,包括零样本、小样本和思维链提示策略,使用了最先进的专有大型语言模型如GPT-4o和Gemini-2.0-Flash。结果显示,结合提交消息和代码差异可以显著提高模型性能,其中结合了小样本和思维链提示策略的模型达到了0.88的F1分数。此外,我们还探索了基于嵌入的机器学习任务学习模型,该模型使用大型语言模型生成的嵌入进行训练,其中多层感知器分类器取得了出色的性能(F1分数:0.906,马修斯相关系数:0.807)。这些发现对研究界具有鼓舞人心的意义,因为方法级错误预测仍然是一个开放的研究问题,很大程度上是由于缺乏无噪声的错误数据集。本研究不仅为解决混淆问题提供了一个新颖的方法级视角,而且也为提高自动化软件质量评估工具提供了实际的改进途径。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
该文本探讨了如何运用大型语言模型(LLMs)检测混乱的代码更改的问题。研究通过结合提交信息和代码差异,利用多种提示策略(包括零样本、小样本和思维链提示)来识别混乱的代码更改。结合使用小样本和思维链提示的方法取得了较高的F1分数。此外,该研究还探索了基于嵌入的机器学习方法,其中多层感知器分类器取得了最佳性能。该研究为方法级别的bug预测提供了新的视角,并强调了增强自动化软件质量评估工具的实际途径。
Key Takeaways
- 混乱的代码更改会对bug数据集引入大量噪声,影响bug预测模型的性能。
- 方法级别的精细粒度处理是解决此问题的关键,但当前对此的研究仍然不足。
- 大型语言模型(LLMs)可用于检测混乱的代码更改,通过结合提交信息和代码差异显著提高模型性能。
- 研究评估了多种提示策略,包括小样本和思维链提示,取得了较高的F1分数。
- 基于LLM生成的嵌入的嵌入式机器学习方法表现出最佳性能。
- 该研究为方法级别的bug预测提供了新的视角。
点此查看论文截图


Exploiting Text Semantics for Few and Zero Shot Node Classification on Text-attributed Graph
Authors:Yuxiang Wang, Xiao Yan, Shiyu Jin, Quanqing Xu, Chuang Hu, Yuanyuan Zhu, Bo Du, Jia Wu, Jiawei Jiang
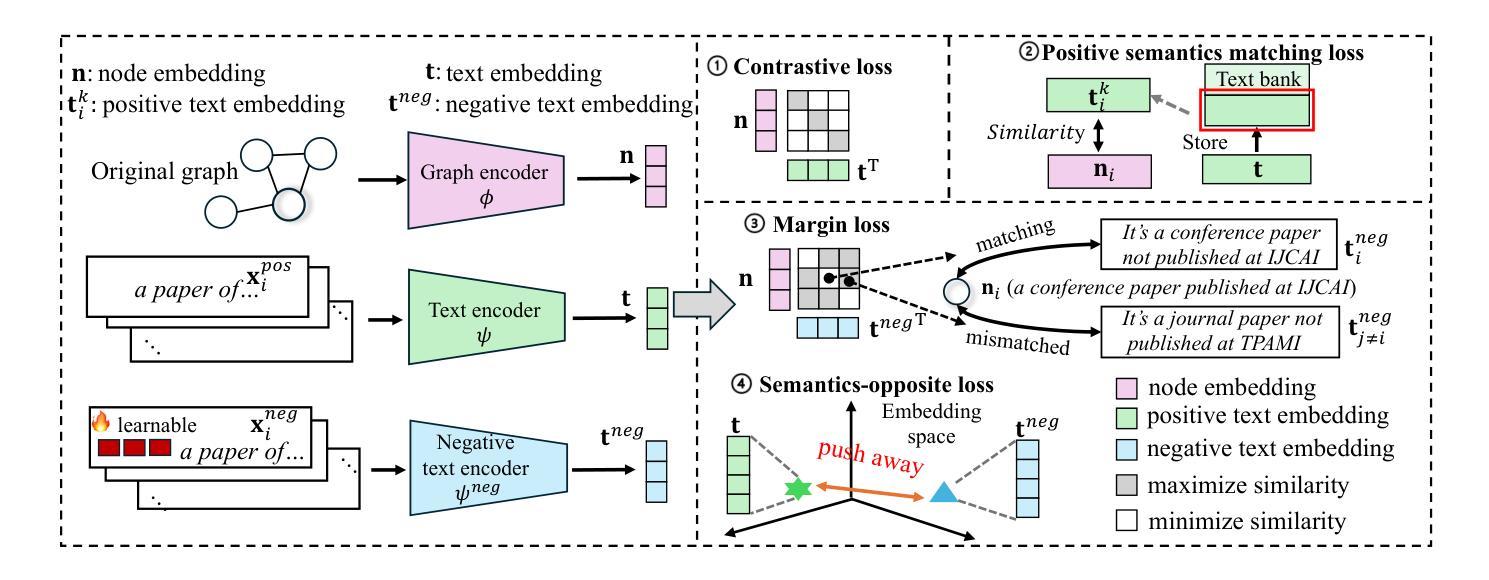
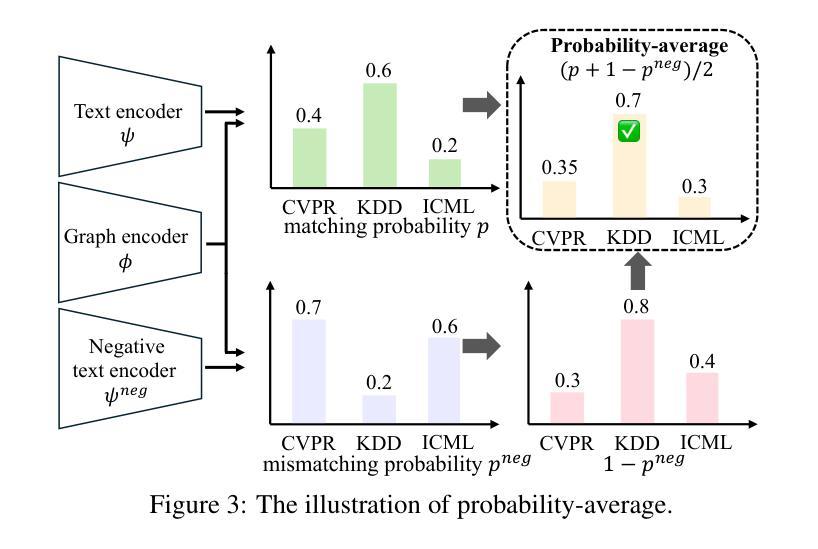
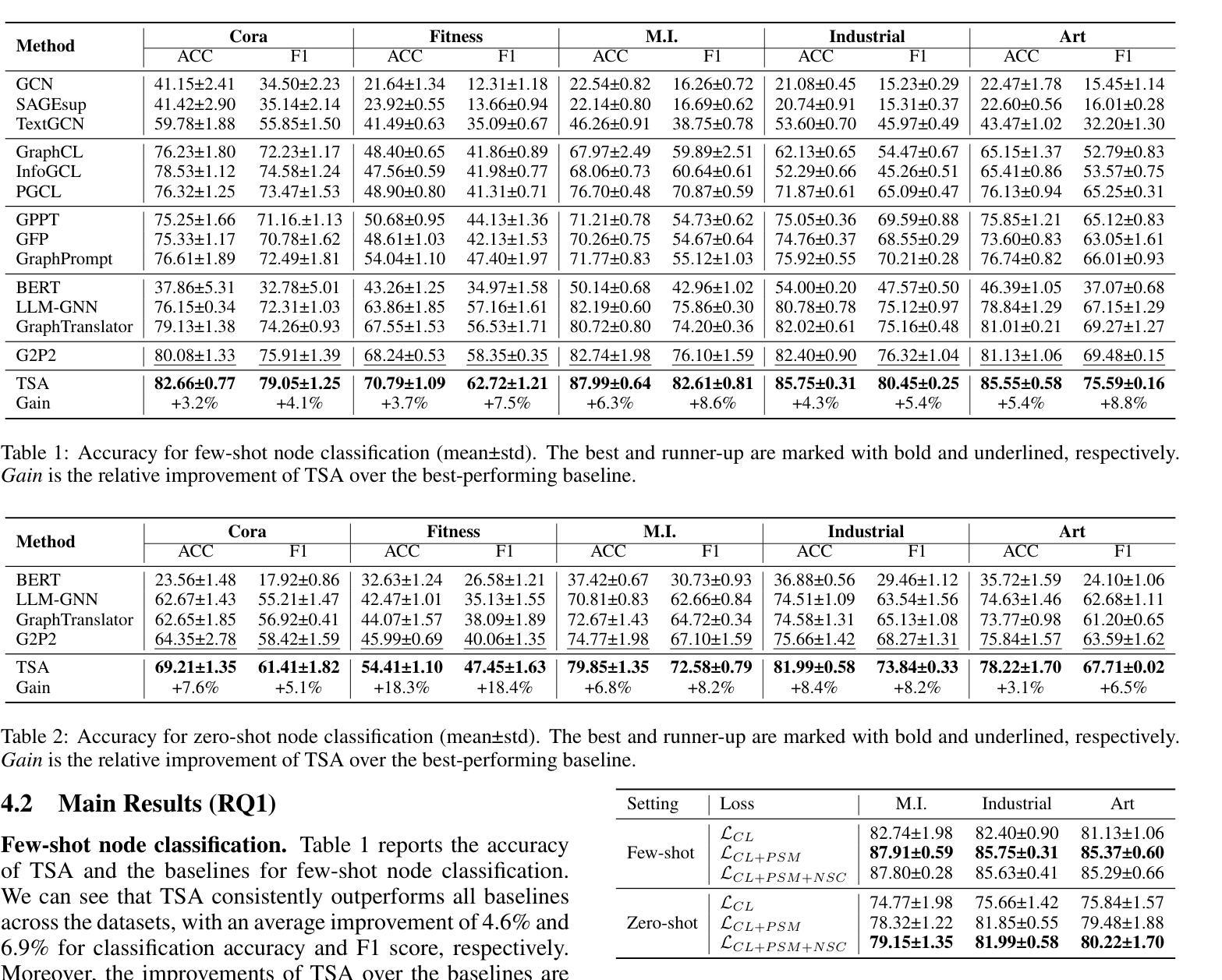
Text-attributed graph (TAG) provides a text description for each graph node, and few- and zero-shot node classification on TAGs have many applications in fields such as academia and social networks. Existing work utilizes various graph-based augmentation techniques to train the node and text embeddings, while text-based augmentations are largely unexplored. In this paper, we propose Text Semantics Augmentation (TSA) to improve accuracy by introducing more text semantic supervision signals. Specifically, we design two augmentation techniques, i.e., positive semantics matching and negative semantics contrast, to provide more reference texts for each graph node or text description. Positive semantic matching retrieves texts with similar embeddings to match with a graph node. Negative semantic contrast adds a negative prompt to construct a text description with the opposite semantics, which is contrasted with the original node and text. We evaluate TSA on 5 datasets and compare with 13 state-of-the-art baselines. The results show that TSA consistently outperforms all baselines, and its accuracy improvements over the best-performing baseline are usually over 5%.
文本属性图(TAG)为每个图节点提供了文本描述,而TAG上的小样本和零样本节点分类在学术和社会网络等领域有许多应用。现有工作利用各种基于图的增强技术来训练节点和文本嵌入,而基于文本的增强技术则很少被探索。在本文中,我们提出文本语义增强(TSA),通过引入更多的文本语义监督信号来提高准确性。具体来说,我们设计了两种增强技术,即正向语义匹配和负向语义对比,为每个图节点或文本描述提供更多的参考文本。正向语义匹配检索具有相似嵌入的文本以与图节点匹配。负向语义对比则通过添加负提示来构建一个具有相反语义的文本描述,该描述与原始节点和文本形成对比。我们在5个数据集上评估了TSA,并与1 3个最新基线进行了比较。结果表明,TSA始终优于所有基线,并且相对于表现最佳的基线,其准确率提高通常超过5%。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
文本语义增强(TSA)方法通过引入更多的文本语义监督信号,提高了文本节点分类的准确性。具体设计了两种增强技术:正向语义匹配和负向语义对比,为每个图节点或文本描述提供更多的参考文本。在五个数据集上评估TSA,与13个先进基线相比,TSA表现优越,准确率提高通常超过5%。
Key Takeaways
- Text-attributed graph (TAG) 为图节点提供文本描述,这在学术和社会网络等领域有着广泛的应用。
- 尽管现有工作使用了各种基于图的增强技术来训练节点和文本嵌入,但基于文本的增强方法仍被大量忽视。
- 文本语义增强(TSA)通过引入更多的文本语义监督信号提高了节点分类的准确性。
- TSA设计了两种增强技术:正向语义匹配和负向语义对比,为图节点或文本描述提供更多的参考文本。
- 正向语义匹配通过检索与图节点嵌入相似的文本进行匹配。
- 负向语义对比通过添加负提示构建与原始节点具有相反语义的文本描述。
点此查看论文截图

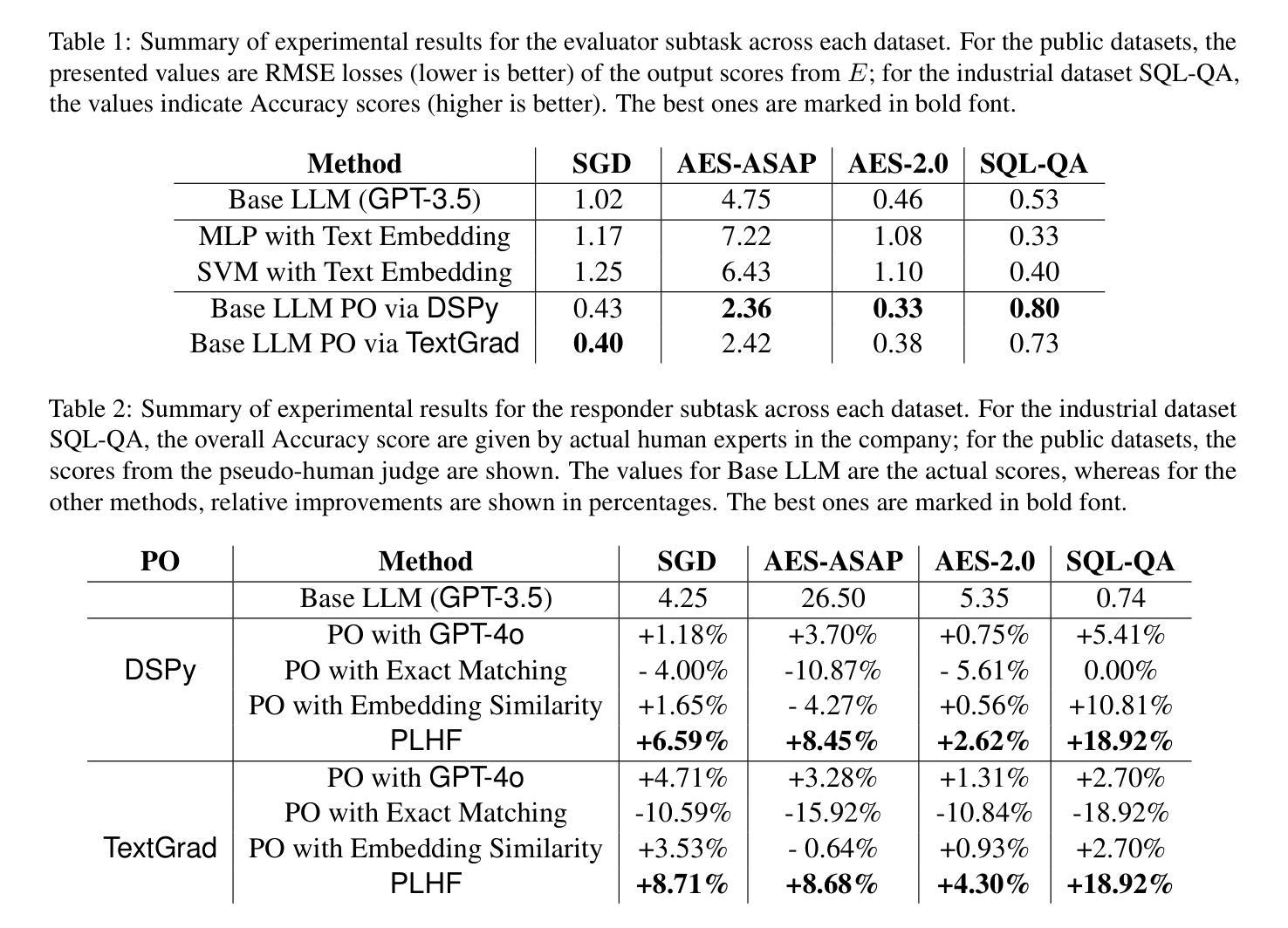
PLHF: Prompt Optimization with Few-Shot Human Feedback
Authors:Chun-Pai Yang, Kan Zheng, Shou-De Lin
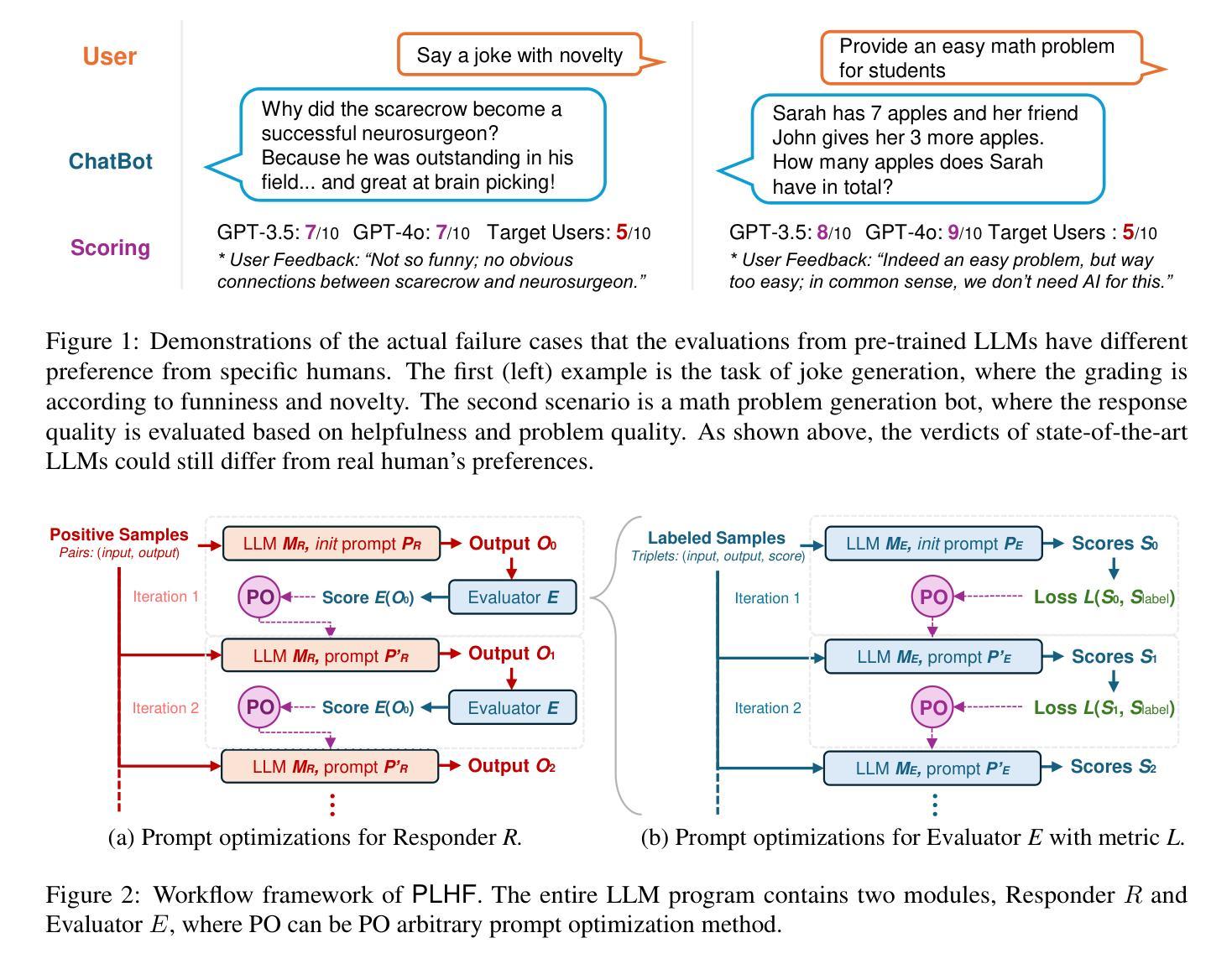
Automatic prompt optimization frameworks are developed to obtain suitable prompts for large language models (LLMs) with respect to desired output quality metrics. Although existing approaches can handle conventional tasks such as fixed-solution question answering, defining the metric becomes complicated when the output quality cannot be easily assessed by comparisons with standard golden samples. Consequently, optimizing the prompts effectively and efficiently without a clear metric becomes a critical challenge. To address the issue, we present PLHF (which stands for “P”rompt “L”earning with “H”uman “F”eedback), a few-shot prompt optimization framework inspired by the well-known RLHF technique. Different from naive strategies, PLHF employs a specific evaluator module acting as the metric to estimate the output quality. PLHF requires only a single round of human feedback to complete the entire prompt optimization process. Empirical results on both public and industrial datasets show that PLHF outperforms prior output grading strategies for LLM prompt optimizations.
自动提示优化框架是针对期望的输出质量指标为大语言模型(LLM)获得合适提示而开发的。尽管现有方法能够处理诸如固定解决方案问答之类的常规任务,但是当输出质量不能通过与标准金样样本的比较来轻松评估时,定义度量指标会变得复杂。因此,在没有明确指标的情况下有效和高效地优化提示成为一个关键挑战。为了解决这一问题,我们提出了PLHF(代表“P”rompt“L”earning with “H”uman “F”eedback),这是一个受广受欢迎的RLHF技术启发的少提示优化框架。不同于简单策略,PLHF采用特定评估模块作为度量指标来估计输出质量。PLHF仅需要一轮人类反馈即可完成整个提示优化过程。在公共和工业数据集上的经验结果表明,对于LLM提示优化,PLHF优于先前的输出评分策略。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
自动提示优化框架旨在针对大型语言模型(LLM)获得合适的提示,以达到期望的输出质量指标。当输出质量无法通过与标准金样样本的比较进行评估时,定义指标变得复杂。PLHF是一个基于RLHF技术的few-shot提示优化框架,它使用一个特定的评估器模块作为指标来估计输出质量。PLHF只需一轮人类反馈即可完成整个提示优化过程,并在公共和工业数据集上的实证结果都表明其在LLM提示优化方面优于先前的输出评分策略。
Key Takeaways
- 自动提示优化框架旨在帮助大型语言模型获得合适的提示以提高输出质量。
- 在输出质量难以通过标准金样样本评估时,定义合适的评估指标是关键挑战。
- PLHF是一个基于RLHF技术的few-shot提示优化框架,能有效解决这一挑战。
- PLHF使用一个特定的评估器模块来估计输出质量,作为优化的指标。
- PLHF只需一轮人类反馈即可完成整个提示优化过程,提高了效率。
- 实证结果表明,PLHF在LLM提示优化方面优于先前的输出评分策略。
点此查看论文截图


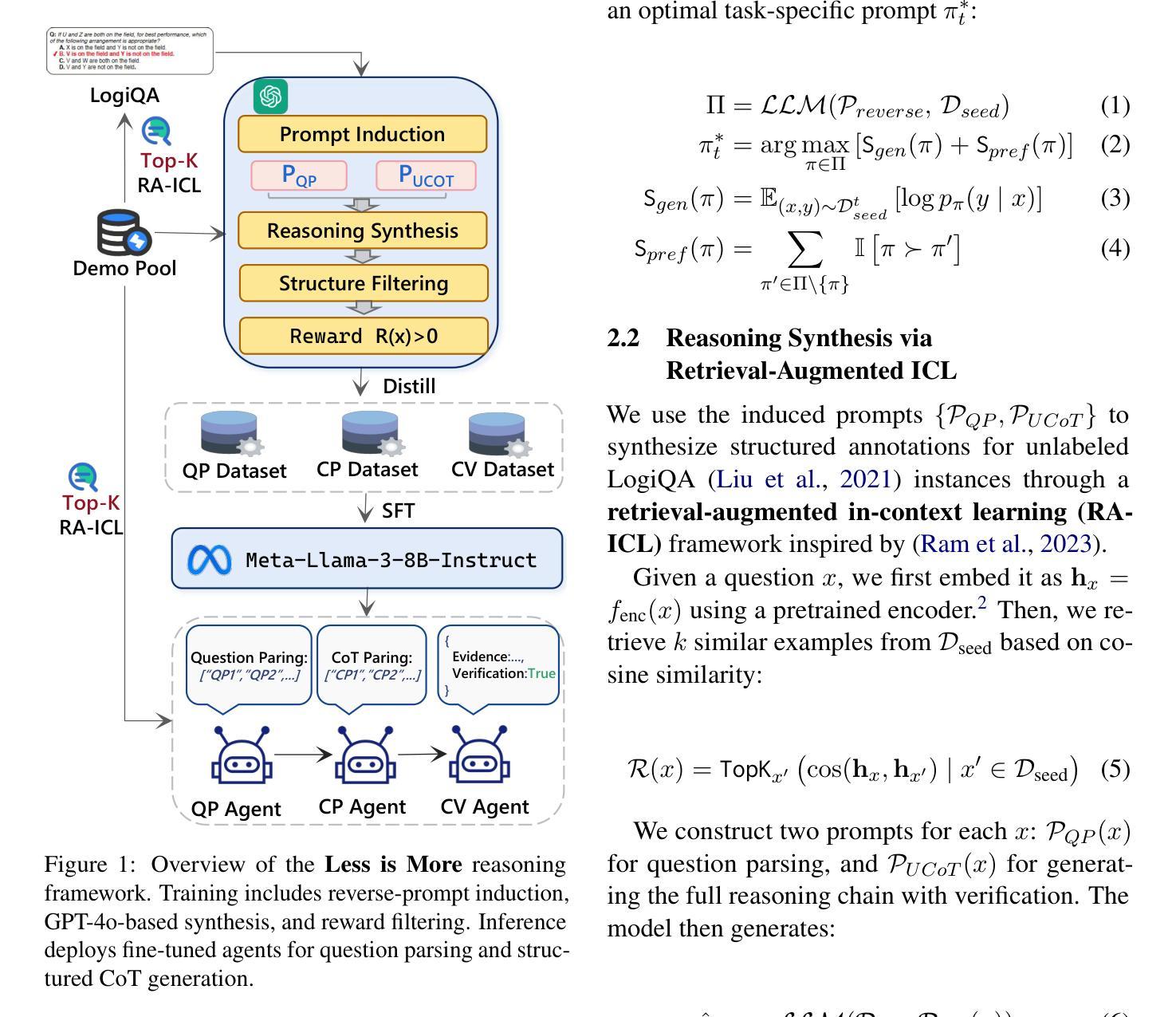
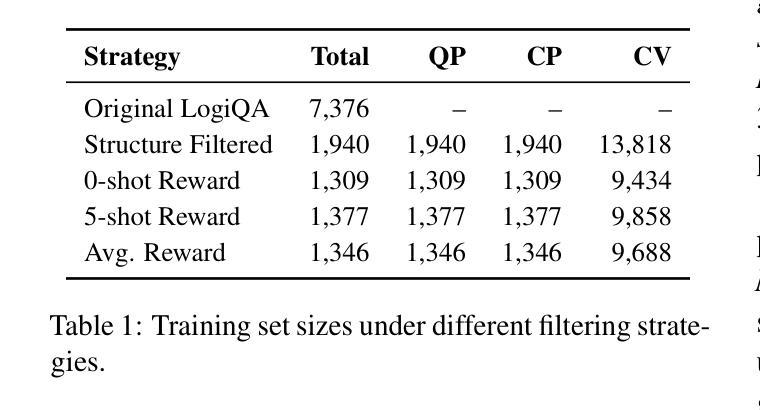
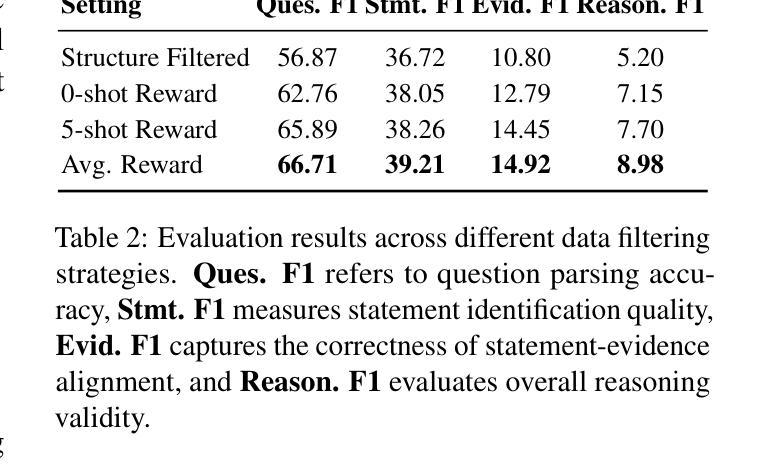
LLMSR@XLLM25: Less is More: Enhancing Structured Multi-Agent Reasoning via Quality-Guided Distillation
Authors:Jiahao Yuan, Xingzhe Sun, Xing Yu, Jingwen Wang, Dehui Du, Zhiqing Cui, Zixiang Di
The LLMSR@XLLM25 formulates a low-resource structural reasoning task that challenges LLMs to generate interpretable, step-by-step rationales with minimal labeled data. We present Less is More, the third-place winning approach in the LLMSR@XLLM25, which focuses on structured reasoning from only 24 labeled examples. Our approach leverages a multi-agent framework with reverse-prompt induction, retrieval-augmented reasoning synthesis via GPT-4o, and dual-stage reward-guided filtering to distill high-quality supervision across three subtasks: question parsing, CoT parsing, and step-level verification. All modules are fine-tuned from Meta-Llama-3-8B-Instruct under a unified LoRA+ setup. By combining structure validation with reward filtering across few-shot and zero-shot prompts, our pipeline consistently improves structure reasoning quality. These results underscore the value of controllable data distillation in enhancing structured inference under low-resource constraints. Our code is available at https://github.com/JhCircle/Less-is-More.
LLMSR@XLLM25提出了一个低资源结构推理任务,该任务挑战大型语言模型在少量标注数据的情况下生成可解释的、逐步的推理过程。我们提出了“少即是多”的方法,这是LLMSR@XLLM25竞赛中的第三名获奖方案,它专注于仅使用24个标注样本进行结构化推理。我们的方法利用多智能体框架进行逆向提示归纳,通过GPT-4o增强推理合成,以及两阶段奖励引导过滤,以提炼高质量监督信息,涵盖三个子任务:问题解析、思维链解析和步骤级验证。所有模块均采用统一的LoRA+设置,在Meta-Llama-3-8B-Instruct上进行微调。通过结合结构验证和奖励过滤在少量样本和零样本提示之间进行过滤,我们的管道不断提高了结构推理质量。这些结果强调了可控数据蒸馏在增强低资源约束下的结构化推理中的价值。我们的代码可在https://github.com/JhCircle/Less-is-More找到。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF XLLM @ ACL 2025 Shared Task-III: LLM for Structural Reasoning (LLM-SR)
Summary
少量标注数据的低资源结构化推理任务LLMSR@XLLM25提出挑战,Less is More方法凭借仅使用24个标注示例的结构化推理获得第三名。该方法采用多智能体框架结合逆向提示归纳、基于GPT-4o的检索增强推理合成以及双阶段奖励引导过滤技术,进行高质量监督学习,优化任务包括问题解析、CoT解析和步骤级别验证等模块。借助结构化验证与奖励过滤的结合,此方法能在少量甚至无示例情况下改善结构化推理质量,展示了可控数据蒸馏在增强低资源条件下的结构化推断价值。代码已公开于GitHub。
Key Takeaways
- LLMSR@XLLM25提出了一个低资源结构化推理任务,挑战LLMs在少量标注数据下生成可解释的逐步推理。
- Less is More方法在低资源条件下通过结构化推理获得优异表现,仅使用24个标注示例。
- 该方法采用多智能体框架结合逆向提示归纳技术,实现高质量监督学习。
- 方法结合了检索增强推理合成技术,通过GPT-4o支持。
- 方法包含三个子任务:问题解析、CoT解析和步骤级别验证,通过双阶段奖励引导过滤技术进行改进。
- 通过结合结构验证与奖励过滤技术,方法提高了结构化推理的质量,展现了可控数据蒸馏在低资源条件下的重要性。
点此查看论文截图


Are Transformers Able to Reason by Connecting Separated Knowledge in Training Data?
Authors:Yutong Yin, Zhaoran Wang
Humans exhibit remarkable compositional reasoning by integrating knowledge from various sources. For example, if someone learns ( B = f(A) ) from one source and ( C = g(B) ) from another, they can deduce ( C=g(B)=g(f(A)) ) even without encountering ( ABC ) together, showcasing the generalization ability of human intelligence. In this paper, we introduce a synthetic learning task, “FTCT” (Fragmented at Training, Chained at Testing), to validate the potential of Transformers in replicating this skill and interpret its inner mechanism. In the training phase, data consist of separated knowledge fragments from an overall causal graph. During testing, Transformers must infer complete causal graph traces by integrating these fragments. Our findings demonstrate that few-shot Chain-of-Thought prompting enables Transformers to perform compositional reasoning on FTCT by revealing correct combinations of fragments, even if such combinations were absent in the training data. Furthermore, the emergence of compositional reasoning ability is strongly correlated with the model complexity and training-testing data similarity. We propose, both theoretically and empirically, that Transformers learn an underlying generalizable program from training, enabling effective compositional reasoning during testing.
人类能够通过整合来自不同来源的知识展现出惊人的组合推理能力。例如,如果有人从某一来源学习到(B=f(A))并从另一来源学习到(C=g(B)),即使没有同时遇到(ABC),他们也能推断出(C=g(B)=g(f(A))),展示了人类智力的推广能力。在本文中,我们引入了一项合成学习任务——“FTCT”(训练时分散,测试时链接),以验证Transformer复制这种技能的潜力并解释其内在机制。在训练阶段,数据由来自整体因果图的分离知识片段组成。在测试期间,Transformer必须通过整合这些片段来推断完整的因果图轨迹。我们的研究发现,通过揭示正确的片段组合,即使在训练数据中不存在这样的组合,少数链式思维提示也能使Transformer在FTCT上表现出组合推理能力。此外,组合推理能力的出现与模型复杂度和训练-测试数据相似性之间存在强烈相关性。我们从理论和实践两方面提出,Transformer从训练中学习了一个通用的基础程序,从而在测试期间能够进行有效的组合推理。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by ICLR 2025
Summary
本文介绍了人类展现出的组合推理能力,通过整合不同来源的知识进行推理。为验证Transformer模型是否具有这种能力并解析其内在机制,提出了一种名为“FTCT”(训练时片段化,测试时连锁)的合成学习任务。在训练阶段,数据由来自整体因果图的知识片段组成。在测试阶段,Transformer必须通过这些片段推断完整的因果图轨迹。研究发现,少数链式思维提示(Chain-of-Thought)能够使Transformer在FTCT上执行组合推理,正确组合知识片段,即使这些组合在训练数据中不存在。此外,模型复杂性和训练测试数据相似性对组合推理能力的出现有重要影响。本文提出,Transformer从训练中学习了一个通用的底层程序,能够在测试时进行有效的组合推理。
Key Takeaways
- 人类能整合不同来源的知识进行组合推理。
- 提出一种名为“FTCT”的合成学习任务来验证Transformer模型的组合推理能力。
- 在训练阶段,数据由因果图的知识片段组成;测试时,Transformer需整合这些片段来推断完整的因果图轨迹。
- 少数链式思维提示(Chain-of-Thought)使Transformer能执行组合推理,正确组合知识片段。
- 模型复杂性和训练测试数据相似性对组合推理能力有显著影响。
- Transformer从训练中学习了一个通用的底层程序,能在测试时进行组合推理。
点此查看论文截图

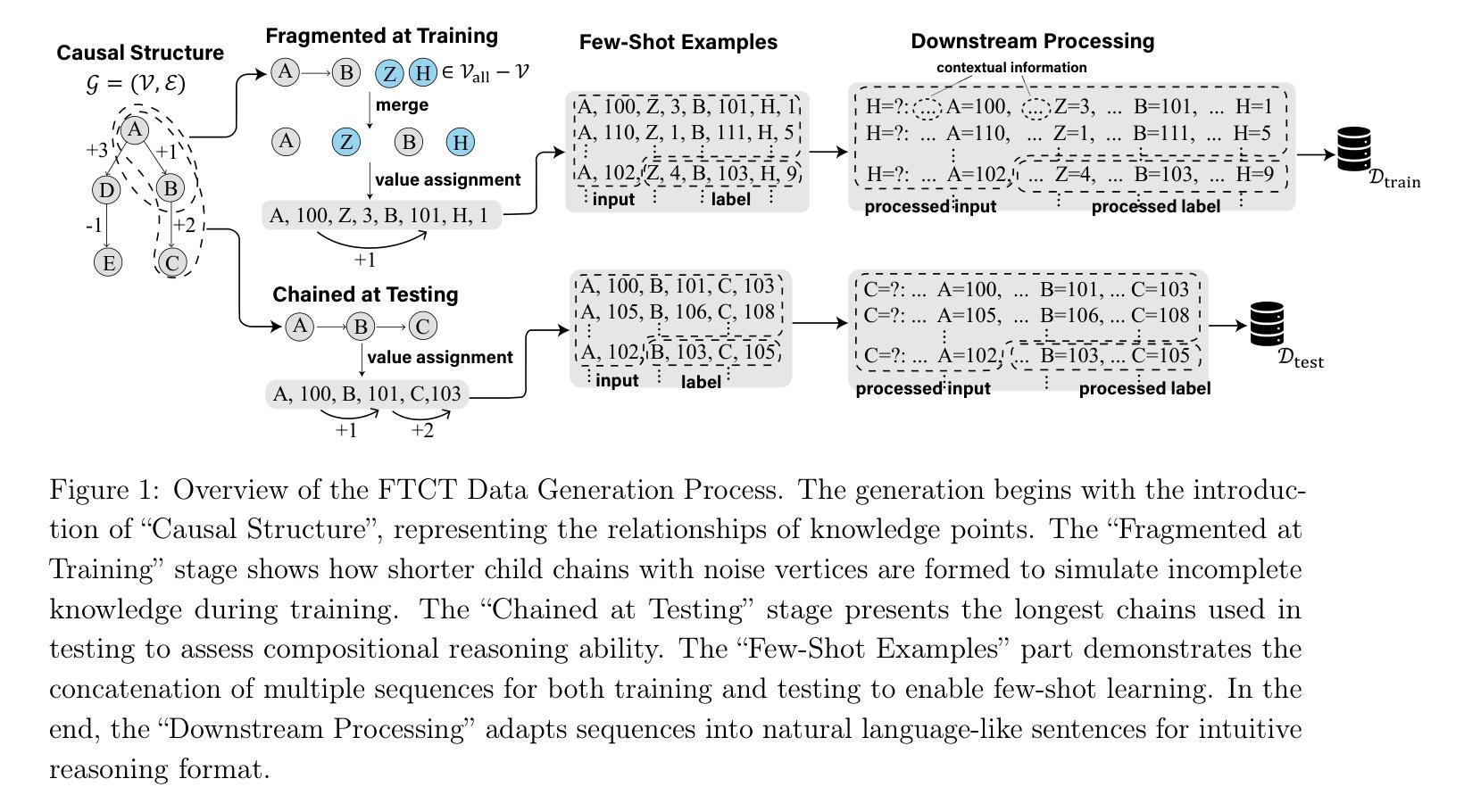
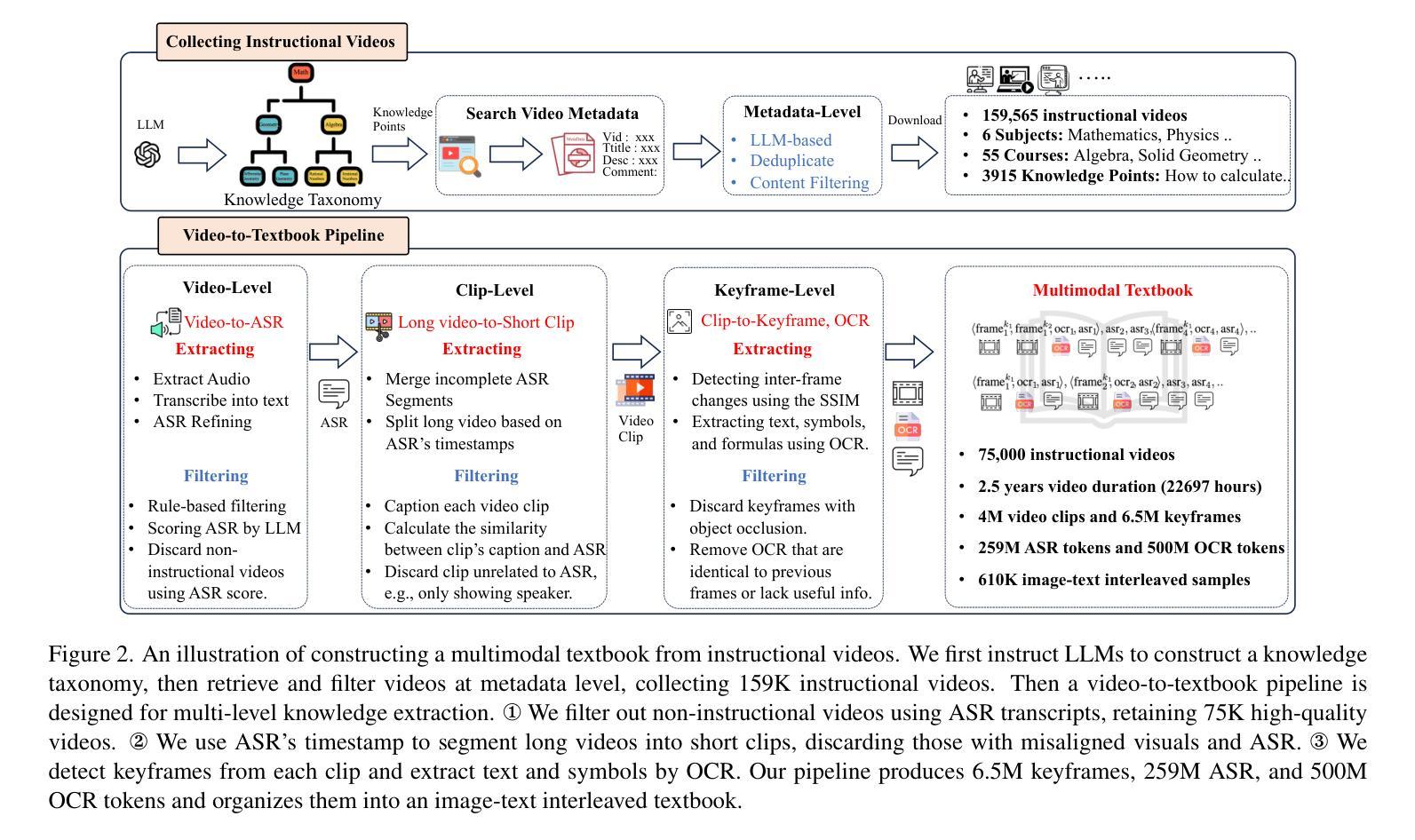
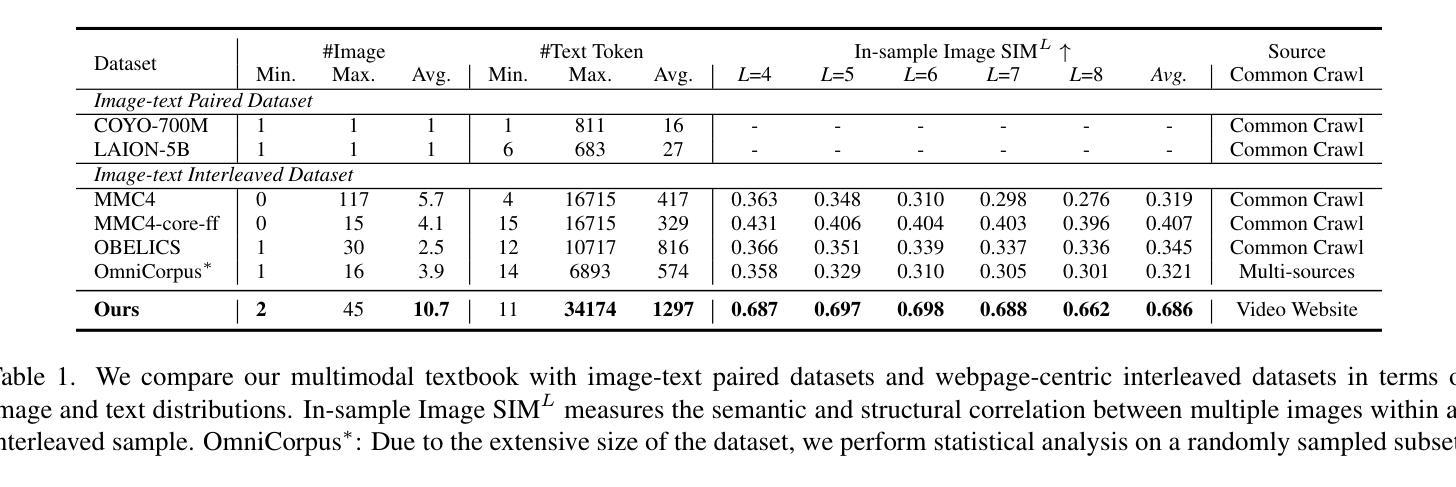
2.5 Years in Class: A Multimodal Textbook for Vision-Language Pretraining
Authors:Wenqi Zhang, Hang Zhang, Xin Li, Jiashuo Sun, Yongliang Shen, Weiming Lu, Deli Zhao, Yueting Zhuang, Lidong Bing
Compared to image-text pair data, interleaved corpora enable Vision-Language Models (VLMs) to understand the world more naturally like humans. However, such existing datasets are crawled from webpage, facing challenges like low knowledge density, loose image-text relations, and poor logical coherence between images. On the other hand, the internet hosts vast instructional videos (e.g., online geometry courses) that are widely used by humans to learn foundational subjects, yet these valuable resources remain underexplored in VLM training. In this paper, we introduce a high-quality \textbf{multimodal textbook} corpus with richer foundational knowledge for VLM pretraining. It collects over 2.5 years of instructional videos, totaling 22,000 class hours. We first use an LLM-proposed taxonomy to systematically gather instructional videos. Then we progressively extract and refine visual (keyframes), audio (ASR), and textual knowledge (OCR) from the videos, and organize as an image-text interleaved corpus based on temporal order. Compared to its counterparts, our video-centric textbook offers more coherent context, richer knowledge, and better image-text alignment. Experiments demonstrate its superb pretraining performance, particularly in knowledge- and reasoning-intensive tasks like ScienceQA and MathVista. Moreover, VLMs pre-trained on our textbook exhibit outstanding interleaved context awareness, leveraging visual and textual cues in their few-shot context for task solving. Our code are available at https://github.com/DAMO-NLP-SG/multimodal_textbook.
与图像文本配对数据相比,交错语料库使视觉语言模型(VLMs)能够像人类一样更自然地理解世界。然而,这些现有的数据集是从网页上爬取的,面临着知识密度低、图像文本关系松散、图像之间逻辑连贯性差等挑战。另一方面,互联网上有大量教学视频(如在线几何课程),人类广泛用来学习基础学科,但这些宝贵资源在VLM训练中仍被忽视。在本文中,我们引入了一种高质量的多模式教科书语料库,具有丰富的基础知识,用于VLM预训练。它收集了超过2.5年的教学视频,总计2.2万节课时。我们首先使用大型语言模型(LLM)提出的分类法来系统地收集教学视频。然后,我们从视频中逐步提取和精炼视觉(关键帧)、音频(ASR)和文本知识(OCR),并按时间顺序组织成图像文本交错语料库。与其他语料库相比,我们的以视频为中心的教学资料提供了更连贯的上下文、更丰富的知识和更好的图像文本对齐。实验证明其预训练性能卓越,特别是在知识密集和推理密集的任务(如ScienceQA和MathVista)中。此外,在我们教科书上进行预训练的VLMs表现出出色的交错上下文意识,利用视觉和文本线索解决少量上下文的任务。我们的代码可在https://github.com/DAMO-NLP-SG/multimodal_textbook中找到。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Under review
Summary
本文介绍了为视觉语言模型(VLM)预训练设计的高质量多模态教科书语料库。该语料库通过收集超过2.5年的教学视频,以图像和文本交错的方式组织,提供丰富的基础知识。实验表明,该语料库在知识密集和推理密集型任务上的预训练性能出色,如ScienceQA和MathVista。此外,在此语料库上训练的VLM具有出色的交错上下文意识,能够在少量情境下利用视觉和文本线索解决问题。
Key Takeaways
- 多模态教科书语料库结合了教学视频、图像和文本,为视觉语言模型(VLM)预训练提供了丰富资源。
- 该语料库通过收集超过2.5年的教学视频,包含总计22,000课时,具有更丰富的基础知识和连贯的上下文。
- 相比其他数据集,该语料库在知识密集和推理密集型任务上的预训练性能优越。
- 该语料库通过图像和文本的交错组织方式,提高了图像和文本的对齐性。
- 在此语料库上训练的VLM具有出色的上下文意识,能在少量情境下利用视觉和文本线索解决问题。
- 该研究提供了一个公开可用的代码库,方便其他人使用和研究。
点此查看论文截图


Clickbait Detection via Large Language Models
Authors:Han Wang, Yi Zhu, Ye Wang, Yun Li, Yunhao Yuan, Jipeng Qiang
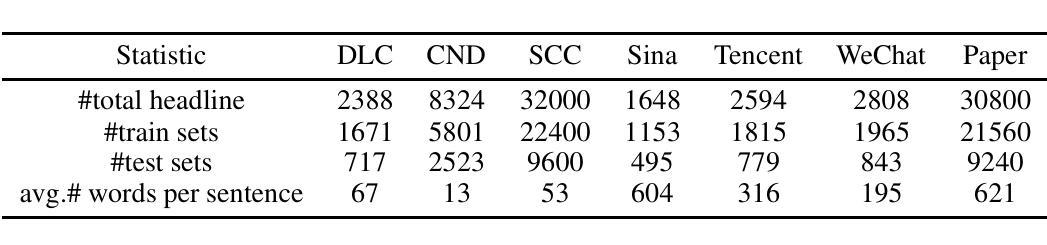
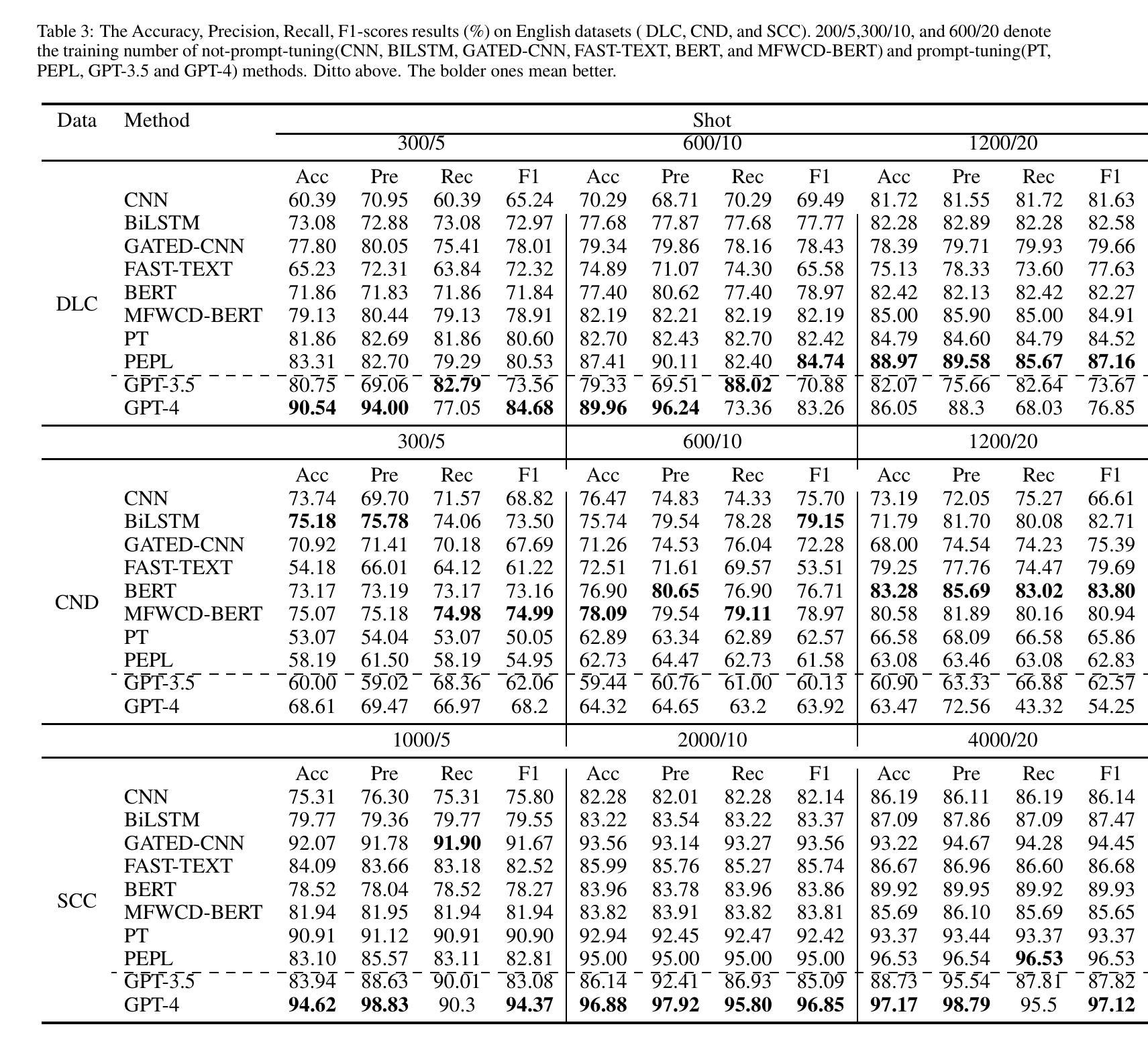
Clickbait, which aims to induce users with some surprising and even thrilling headlines for increasing click-through rates, permeates almost all online content publishers, such as news portals and social media. Recently, Large Language Models (LLMs) have emerged as a powerful instrument and achieved tremendous success in a series of NLP downstream tasks. However, it is not yet known whether LLMs can be served as a high-quality clickbait detection system. In this paper, we analyze the performance of LLMs in the few-shot and zero-shot scenarios on several English and Chinese benchmark datasets. Experimental results show that LLMs cannot achieve the best results compared to the state-of-the-art deep and fine-tuning PLMs methods. Different from human intuition, the experiments demonstrated that LLMs cannot make satisfied clickbait detection just by the headlines.
标题诱导(Clickbait)通过设计一些令人惊讶甚至兴奋的标题来增加点击率,几乎渗透到了所有的在线内容发布者,如新闻门户和社交媒体。近期,大型语言模型(LLMs)作为一种强大的工具,在一系列NLP下游任务中取得了巨大的成功。然而,尚不清楚LLMs是否可以作为高质量的标题诱导检测系统进行应用。在本文中,我们在少量样本甚至零样本场景下分析了LLMs在多个英文和中文基准数据集上的表现。实验结果表明,与目前先进的深度学习和微调预训练语言模型(PLMs)方法相比,LLMs无法取得最佳结果。不同于人类的直觉,实验证明LLMs仅通过标题无法进行有效的标题诱导检测。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 10 pages, 4 figures
Summary:
大型语言模型(LLMs)用于检测点击诱饵的效果分析。研究发现,在有限的几个场景中,LLMs相较于深度与微调的语言模型方法并未达到最佳效果。实验表明,LLMs仅依靠标题无法有效检测点击诱饵,与人类直觉不同。
Key Takeaways:
- LLMs被尝试用于点击诱饵检测,但实验结果并不理想。
- LLMs在少数场景和零场景下的表现不如深度与微调的语言模型方法。
- 仅依靠标题,LLMs无法有效检测点击诱饵。
- 实验结果与人类直觉存在差异。
- 目前尚不清楚LLMs是否能作为高质量的点击诱饵检测系统。
- 该研究涉及到自然语言处理下游任务中的大型语言模型应用。
点此查看论文截图