⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-05-15 更新
FOCI: Trajectory Optimization on Gaussian Splats
Authors:Mario Gomez Andreu, Maximum Wilder-Smith, Victor Klemm, Vaishakh Patil, Jesus Tordesillas, Marco Hutter
3D Gaussian Splatting (3DGS) has recently gained popularity as a faster alternative to Neural Radiance Fields (NeRFs) in 3D reconstruction and view synthesis methods. Leveraging the spatial information encoded in 3DGS, this work proposes FOCI (Field Overlap Collision Integral), an algorithm that is able to optimize trajectories directly on the Gaussians themselves. FOCI leverages a novel and interpretable collision formulation for 3DGS using the notion of the overlap integral between Gaussians. Contrary to other approaches, which represent the robot with conservative bounding boxes that underestimate the traversability of the environment, we propose to represent the environment and the robot as Gaussian Splats. This not only has desirable computational properties, but also allows for orientation-aware planning, allowing the robot to pass through very tight and narrow spaces. We extensively test our algorithm in both synthetic and real Gaussian Splats, showcasing that collision-free trajectories for the ANYmal legged robot that can be computed in a few seconds, even with hundreds of thousands of Gaussians making up the environment. The project page and code are available at https://rffr.leggedrobotics.com/works/foci/
三维高斯展平技术(3DGS)作为神经辐射场(NeRF)在三维重建和视图合成方法中的更快替代方案,近期受到广泛关注。利用编码在三维高斯展平中的空间信息,这项工作提出了FOCI(场重叠碰撞积分)算法,它能够直接在高斯本身上优化轨迹。FOCI利用一个新颖且可解释的碰撞公式用于三维高斯展平,采用高斯之间的重叠积分的概念。与其他方法不同,后者使用保守的边界框来表示机器人,从而低估环境的可通行性,我们提出将环境和机器人表示为高斯展平。这不仅具有理想的计算属性,而且允许进行方向感知规划,允许机器人在非常紧凑和狭窄的空间中通过。我们在合成和真实的高斯展平中对我们的算法进行了广泛测试,展示了即使在由数十万高斯组成的环境中,也可以为ANYmal腿式机器人计算数秒内无碰撞轨迹。项目页面和代码可通过https://rffr.leggedrobotics.com/works/foci/查看。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 7 pages, 8 figures, Mario Gomez Andreu and Maximum Wilder-Smith contributed equally
Summary
3D高斯融合技术(3DGS)在三维重建和视图合成方法中作为神经网络辐射场(NeRFs)的更快替代方案而受到关注。本研究提出FOCI算法,利用3DGS中的空间信息直接在高斯上优化轨迹。FOCI使用可解释性强的高斯重叠积分法构建全新的碰撞模型。相较于使用保守边界框表示机器人以低估环境可通行性的传统方法,该研究采用高斯融合来表示环境和机器人,这不仅有利于计算,而且实现方向感知规划,允许机器人在极狭窄的空间中通过。实验证明,该算法能在几秒内计算出ANYmal四足机器人在由数十万高斯组成的环境中无碰撞轨迹。具体内容和代码参见项目网站:[https://rffr.leggedrobotics.com/works/foci/] 。
Key Takeaways
- 3DGS技术作为一种更快的替代方案在三维重建和视图合成方法中获得关注。
- FOCI算法利用空间信息优化轨迹。
- 提出高斯重叠积分法来构建新的碰撞模型。
- 采用高斯融合表示环境和机器人以提高计算效率。
- 实现方向感知规划,允许机器人在狭窄空间中通过。
- 实验证明算法能迅速计算出机器人在复杂环境中的无碰撞轨迹。
点此查看论文截图

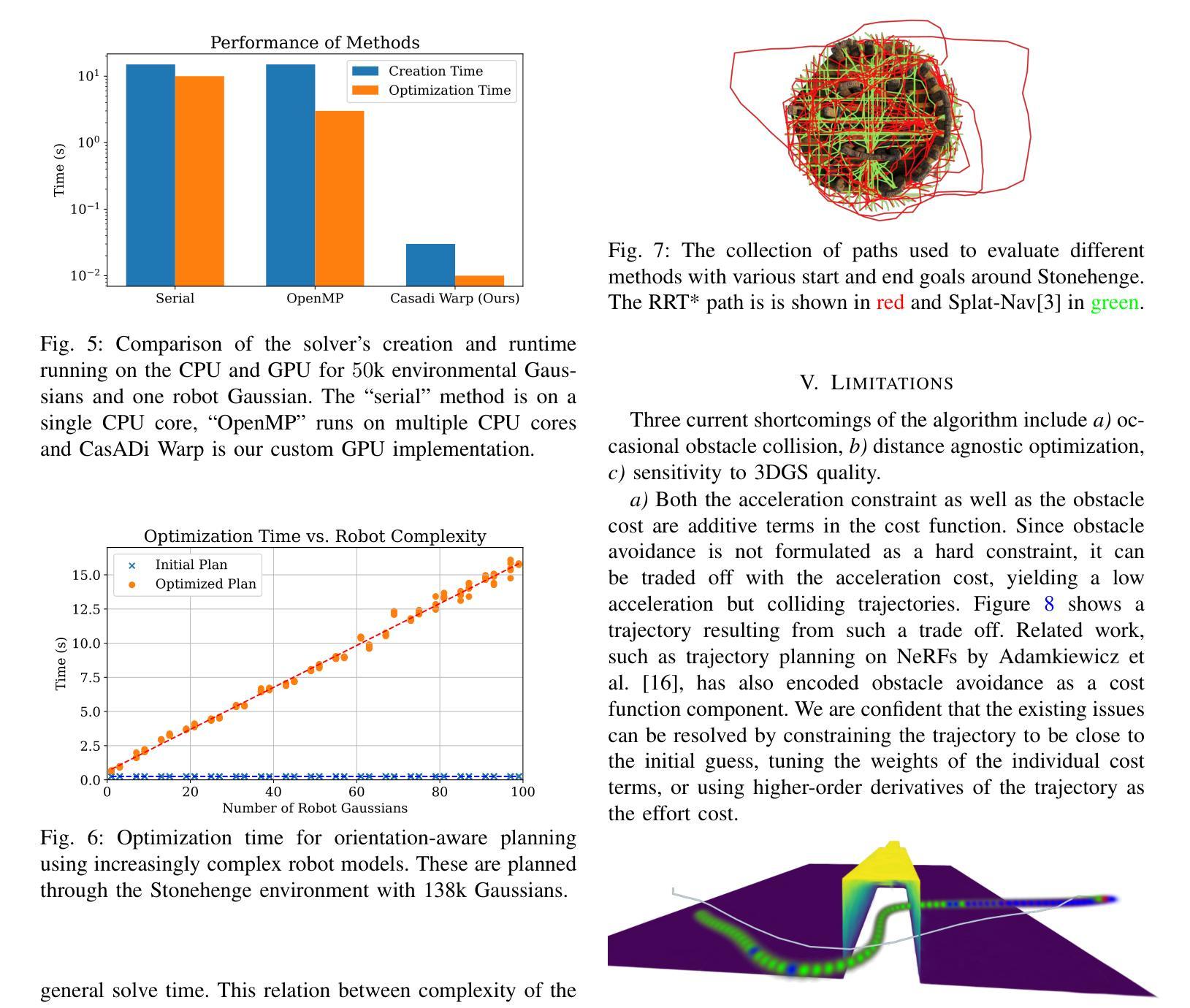
TUM2TWIN: Introducing the Large-Scale Multimodal Urban Digital Twin Benchmark Dataset
Authors:Olaf Wysocki, Benedikt Schwab, Manoj Kumar Biswanath, Michael Greza, Qilin Zhang, Jingwei Zhu, Thomas Froech, Medhini Heeramaglore, Ihab Hijazi, Khaoula Kanna, Mathias Pechinger, Zhaiyu Chen, Yao Sun, Alejandro Rueda Segura, Ziyang Xu, Omar AbdelGafar, Mansour Mehranfar, Chandan Yeshwanth, Yueh-Cheng Liu, Hadi Yazdi, Jiapan Wang, Stefan Auer, Katharina Anders, Klaus Bogenberger, Andre Borrmann, Angela Dai, Ludwig Hoegner, Christoph Holst, Thomas H. Kolbe, Ferdinand Ludwig, Matthias Nießner, Frank Petzold, Xiao Xiang Zhu, Boris Jutzi
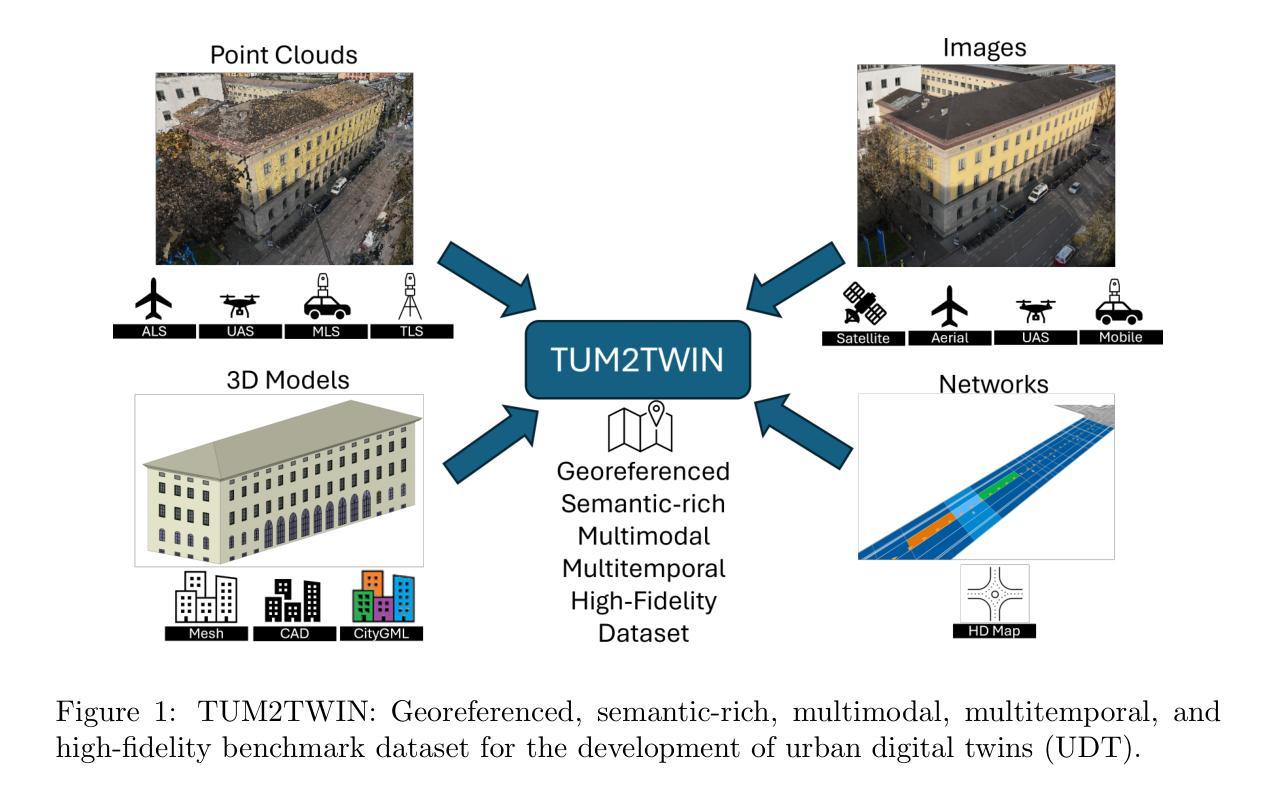
Urban Digital Twins (UDTs) have become essential for managing cities and integrating complex, heterogeneous data from diverse sources. Creating UDTs involves challenges at multiple process stages, including acquiring accurate 3D source data, reconstructing high-fidelity 3D models, maintaining models’ updates, and ensuring seamless interoperability to downstream tasks. Current datasets are usually limited to one part of the processing chain, hampering comprehensive UDTs validation. To address these challenges, we introduce the first comprehensive multimodal Urban Digital Twin benchmark dataset: TUM2TWIN. This dataset includes georeferenced, semantically aligned 3D models and networks along with various terrestrial, mobile, aerial, and satellite observations boasting 32 data subsets over roughly 100,000 $m^2$ and currently 767 GB of data. By ensuring georeferenced indoor-outdoor acquisition, high accuracy, and multimodal data integration, the benchmark supports robust analysis of sensors and the development of advanced reconstruction methods. Additionally, we explore downstream tasks demonstrating the potential of TUM2TWIN, including novel view synthesis of NeRF and Gaussian Splatting, solar potential analysis, point cloud semantic segmentation, and LoD3 building reconstruction. We are convinced this contribution lays a foundation for overcoming current limitations in UDT creation, fostering new research directions and practical solutions for smarter, data-driven urban environments. The project is available under: https://tum2t.win
城市数字双胞胎(UDTs)对于管理城市和整合来自不同源的复杂、异构数据变得至关重要。创建UDTs涉及多个流程阶段的挑战,包括获取准确的3D源数据、重建高保真3D模型、保持模型的更新,以及确保无缝衔接下游任务。当前的数据集通常仅限于处理链的一部分,阻碍了全面的UDTs验证。为了应对这些挑战,我们引入了第一个综合多模式城市数字双胞胎基准数据集:TUM2TWIN。该数据集包括地理参考、语义对齐的3D模型和网络,以及各种地面、移动、空中和卫星观测,拥有超过约100,000平方米的32个数据子集和当前767GB的数据。通过确保地理参考的室内外采集、高精度和多模式数据集成,该基准数据集支持对传感器的稳健分析和先进重建方法的发展。此外,我们探索了展示TUM2TWIN潜力的下游任务,包括NeRF和高斯拼贴的新视角合成、太阳能潜力分析、点云语义分割和LoD3建筑重建。我们相信这一贡献为克服UDTs创建中的当前局限性奠定了基础,促进了新的研究方向和面向数据驱动的智能城市环境的实用解决方案。项目网址为:https://tum2t.win
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Submitted to the ISPRS Journal of Photogrammetry and Remote Sensing
Summary
基于数字双胞胎技术的城市数字化在城市管理和复杂、异质数据源集成中变得至关重要。为了解决现有数据集在处理链条中的局限性,推出了首个综合多模态城市数字双胞胎基准数据集:TUM2TWIN。此数据集包含了地理参考的、语义对齐的3D模型和网络,以及各种陆地、移动、空中和卫星观测,提供了约达十万平方米的32个数据子集和目前总计达767GB的数据。该基准数据集支持传感器稳健分析和高级重建方法的发展,并展示了其潜力,包括NeRF和Gaussian Splatting合成新视角、太阳能潜力分析、点云语义分割和LOD3建筑重建等任务。该贡献为克服当前数字双胞胎创建的局限性奠定了基石,并推动智慧型城市的新研究方向和实践解决方案的发展。数据集详情可访问:https://tum2t.win了解。
Key Takeaways
- 城市数字双胞胎(UDTs)对于城市管理和复杂数据源集成至关重要。
- 当前数据集在处理链条中存在局限性,缺乏全面验证UDTs的工具。
- TUM2TWIN是首个综合多模态城市数字双胞胎基准数据集,包含丰富的地理参考和语义对齐的3D数据。
- 数据集集成了各种陆地、移动、空中和卫星观测数据,覆盖面广,数据量大。
- 该数据集支持传感器稳健分析和高级重建方法的发展。
- TUM2TWIN在多种下游任务中展现出潜力,包括新视角合成、太阳能潜力分析、点云语义分割和建筑重建等。
点此查看论文截图


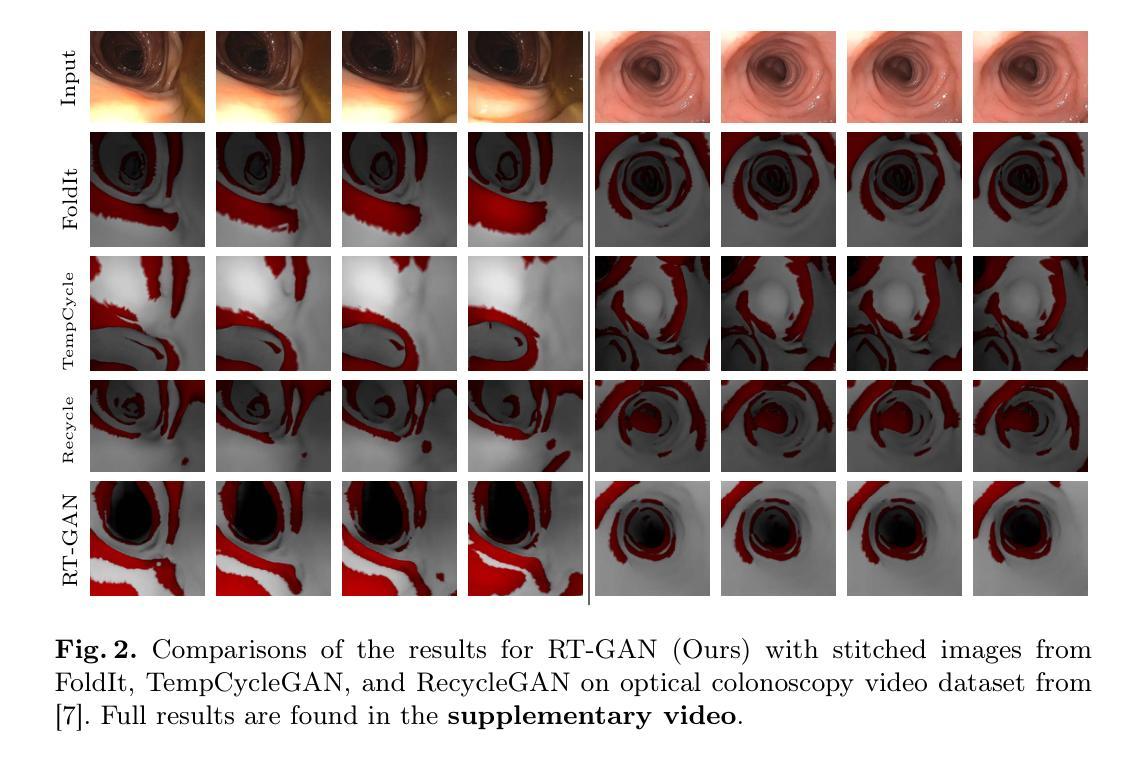
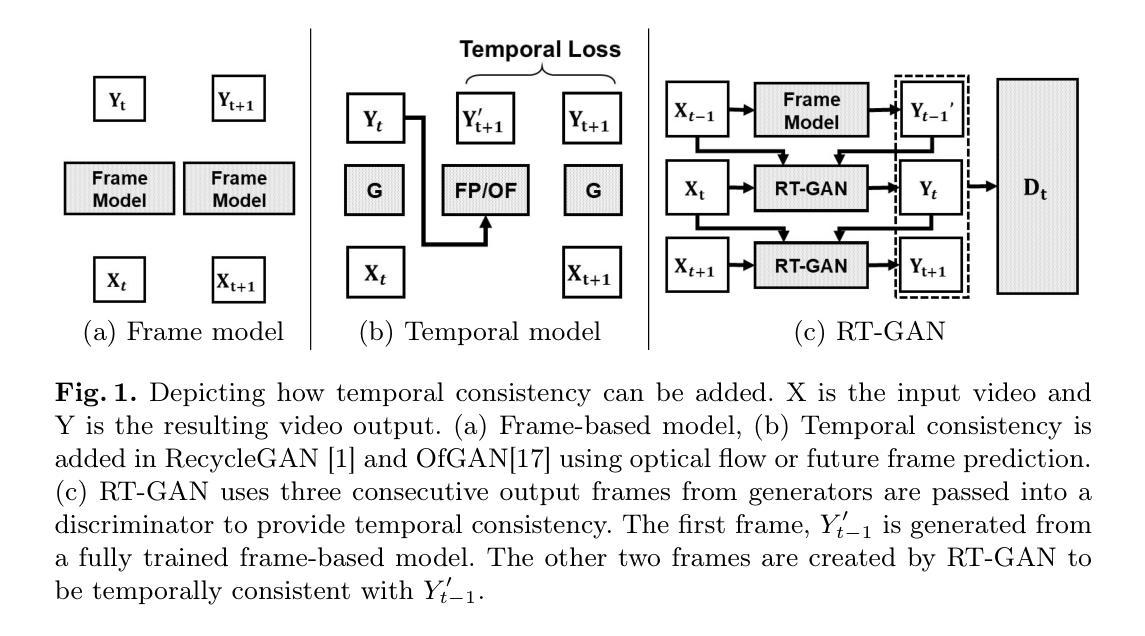
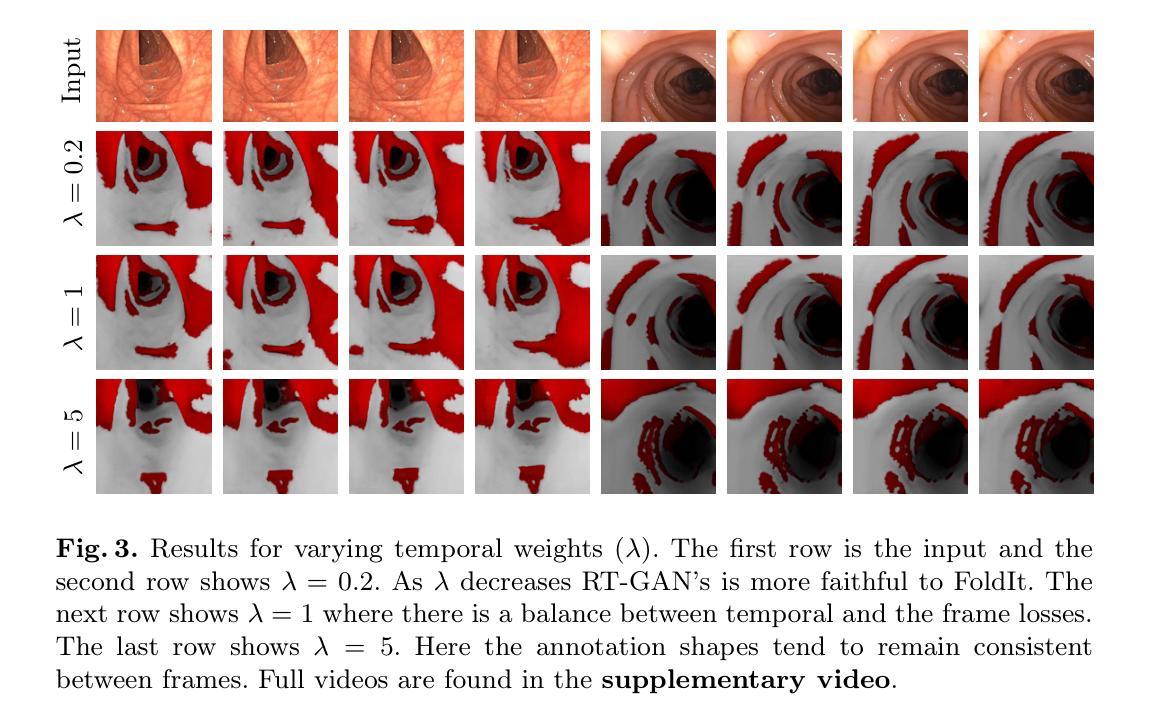
RT-GAN: Recurrent Temporal GAN for Adding Lightweight Temporal Consistency to Frame-Based Domain Translation Approaches
Authors:Shawn Mathew, Saad Nadeem, Alvin C. Goh, Arie Kaufman
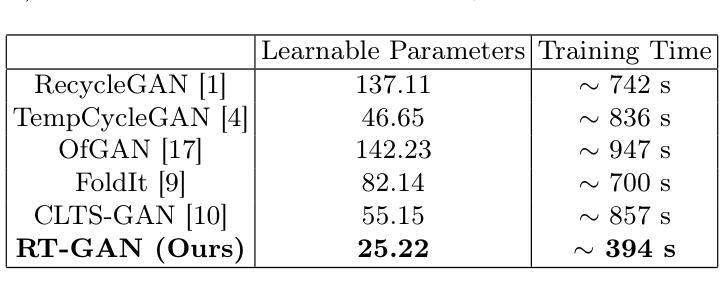
Fourteen million colonoscopies are performed annually just in the U.S. However, the videos from these colonoscopies are not saved due to storage constraints (each video from a high-definition colonoscope camera can be in tens of gigabytes). Instead, a few relevant individual frames are saved for documentation/reporting purposes and these are the frames on which most current colonoscopy AI models are trained on. While developing new unsupervised domain translation methods for colonoscopy (e.g. to translate between real optical and virtual/CT colonoscopy), it is thus typical to start with approaches that initially work for individual frames without temporal consistency. Once an individual-frame model has been finalized, additional contiguous frames are added with a modified deep learning architecture to train a new model from scratch for temporal consistency. This transition to temporally-consistent deep learning models, however, requires significantly more computational and memory resources for training. In this paper, we present a lightweight solution with a tunable temporal parameter, RT-GAN (Recurrent Temporal GAN), for adding temporal consistency to individual frame-based approaches that reduces training requirements by a factor of 5. We demonstrate the effectiveness of our approach on two challenging use cases in colonoscopy: haustral fold segmentation (indicative of missed surface) and realistic colonoscopy simulator video generation. We also release a first-of-its kind temporal dataset for colonoscopy for the above use cases. The datasets, accompanying code, and pretrained models will be made available on our Computational Endoscopy Platform GitHub (https://github.com/nadeemlab/CEP). The supplementary video is available at https://youtu.be/UMVP-uIXwWk.
每年仅在美围就有超过一千万次结肠镜检查得以实施。然而,由于存储限制,这些结肠镜检查的视频并未保存(每个高清结肠镜摄像机拍摄的视频可能达到几十千兆字节)。相反,一些相关的个别帧被保存用于文档记录或报告目的,这也是当前大多数结肠镜检查人工智能模型训练的依托。在开发结肠镜检查的新型无监督域转换方法(例如,用于真实光学与虚拟或计算机断层扫描结肠镜之间的转换)时,通常最初采用不随时间变化的单个帧的初步解决方案。在单个帧模型完成后,再通过增加额外的连续帧以及修改深度学习架构,来从头开始训练一个新模型以实现时间一致性。然而,这种向时间一致的深度学习模型的过渡需要更多的计算和内存资源来进行训练。在本文中,我们提出了一种带有可调整时间参数的轻型解决方案——循环时序生成对抗网络(RT-GAN),该方案可以在基于单个帧的方法上增加时间一致性,并将训练需求降低至原先的十分之一。我们在结肠镜检查的两个挑战性应用场景中验证了该方法的有效性:结肠黏膜折叠分割(表明有未观察到的表面)和现实结肠镜检查模拟器视频生成。我们还发布了第一个用于上述用例的结肠镜检查时序数据集。数据集、相关代码和预训练模型将在我们的计算内窥镜平台GitHub上提供(https://github.com/nadeemlab/CEP)。补充视频可在https://youtu.be/UMVP-uIXwWk观看。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF MICCAI 2025 Early Accept. First two authors contributed equally
Summary
本文介绍了在结肠镜检查中使用人工智能模型的情况。由于存储限制,结肠镜检查的视频不会被保存,只有少数关键帧被用于存档和报告。当前大多数结肠镜检查的AI模型都是在这些关键帧上训练的。本文提出了一种轻量级解决方案RT-GAN,它可以通过添加时间参数来增强基于单帧的方法的时间一致性,减少五倍的培训需求。本文在两个有挑战性的结肠镜检查用例中验证了该方法的有效性:结肠黏膜皱襞分割和真实结肠镜检查模拟器视频生成。相关数据集、代码和预训练模型可在我们的计算内窥镜平台GitHub上获取。
Key Takeaways
- 结肠镜检查中每年进行超过十四万次操作,但视频由于存储限制未被保存。
- 当前AI模型主要在结肠镜检查的关键帧上进行训练。
- RT-GAN是一种轻量级解决方案,可以增强基于单帧的方法的时间一致性。
- RT-GAN通过添加可调的时间参数,可以减少五倍的培训需求。
- 本文在结肠黏膜皱襞分割和真实结肠镜检查模拟器视频生成两个用例中验证了RT-GAN的有效性。
- 本文发布了首个针对结肠镜检查的时空数据集。
点此查看论文截图