⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-05-15 更新
A Survey of Deep Learning for Complex Speech Spectrograms
Authors:Yuying Xie, Zheng-Hua Tan
Recent advancements in deep learning have significantly impacted the field of speech signal processing, particularly in the analysis and manipulation of complex spectrograms. This survey provides a comprehensive overview of the state-of-the-art techniques leveraging deep neural networks for processing complex spectrograms, which encapsulate both magnitude and phase information. We begin by introducing complex spectrograms and their associated features for various speech processing tasks. Next, we explore the key components and architectures of complex-valued neural networks, which are specifically designed to handle complex-valued data and have been applied for complex spectrogram processing. We then discuss various training strategies and loss functions tailored for training neural networks to process and model complex spectrograms. The survey further examines key applications, including phase retrieval, speech enhancement, and speech separation, where deep learning has achieved significant progress by leveraging complex spectrograms or their derived feature representations. Additionally, we examine the intersection of complex spectrograms with generative models. This survey aims to serve as a valuable resource for researchers and practitioners in the field of speech signal processing and complex-valued neural networks.
最近深度学习领域的进展对语音信号处理领域产生了重大影响,特别是在分析和处理复杂频谱图方面。这篇综述全面概述了利用深度神经网络处理包含幅度和相位信息的复杂频谱图的最新技术。我们首先介绍复杂频谱图及其用于各种语音处理任务的相关特征。接下来,我们探索专为处理复数数据而设计的复数神经网络的关键组件和架构,这些网络已应用于复杂频谱图处理。然后,我们讨论了为训练用于处理和建模复杂频谱图的神经网络而量身定制的各种训练策略和损失函数。这篇综述还进一步研究了关键应用,包括相位恢复、语音增强和语音分离,其中深度学习通过利用复杂频谱图或其衍生的特征表示取得了重大进展。此外,我们还检查了复杂频谱图与生成模型的交集。这篇综述旨在为语音信号处理领域和复数神经网络的研究人员和实践者提供有价值的资源。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
深度学习技术的最新进展对语音信号处理领域产生了重大影响,特别是在处理和操作复杂频谱图方面。本综述全面概述了利用深度神经网络处理复杂频谱图的最新技术,这些技术结合了幅度和相位信息。文章介绍了复杂频谱图及其在各种语音处理任务中的相关特征,探讨了专为处理复杂值数据而设计的复杂值神经网络的关键组件和架构,并讨论了针对复杂频谱图处理和建模的神经网络的训练策略和损失函数。此外,文章还介绍了深度学习在相位恢复、语音增强和语音分离等关键应用方面取得的进展。
Key Takeaways
- 深度学习在语音信号处理领域具有显著影响,特别是在处理和操作复杂频谱图方面。
- 复杂频谱图结合了幅度和相位信息,成为语音处理的重要工具。
- 复杂值神经网络专门处理复杂值数据,并已应用于复杂频谱图处理。
- 针对复杂频谱图处理和建模的神经网络的训练策略和损失函数是关键。
- 深度学习在相位恢复、语音增强和语音分离等应用方面取得了重要进展。
- 复杂频谱图与生成模型之间的交集是研究的热点。
点此查看论文截图

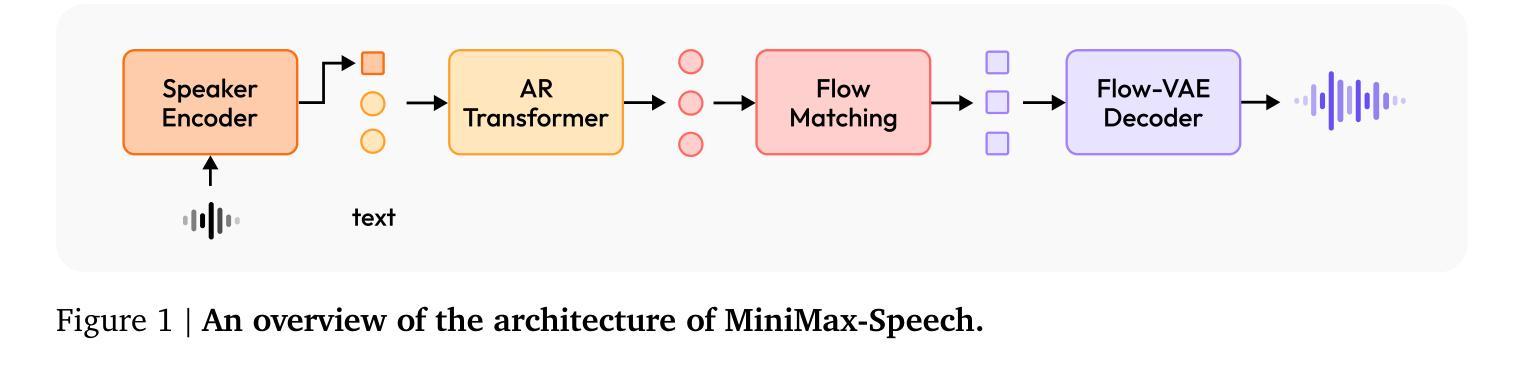
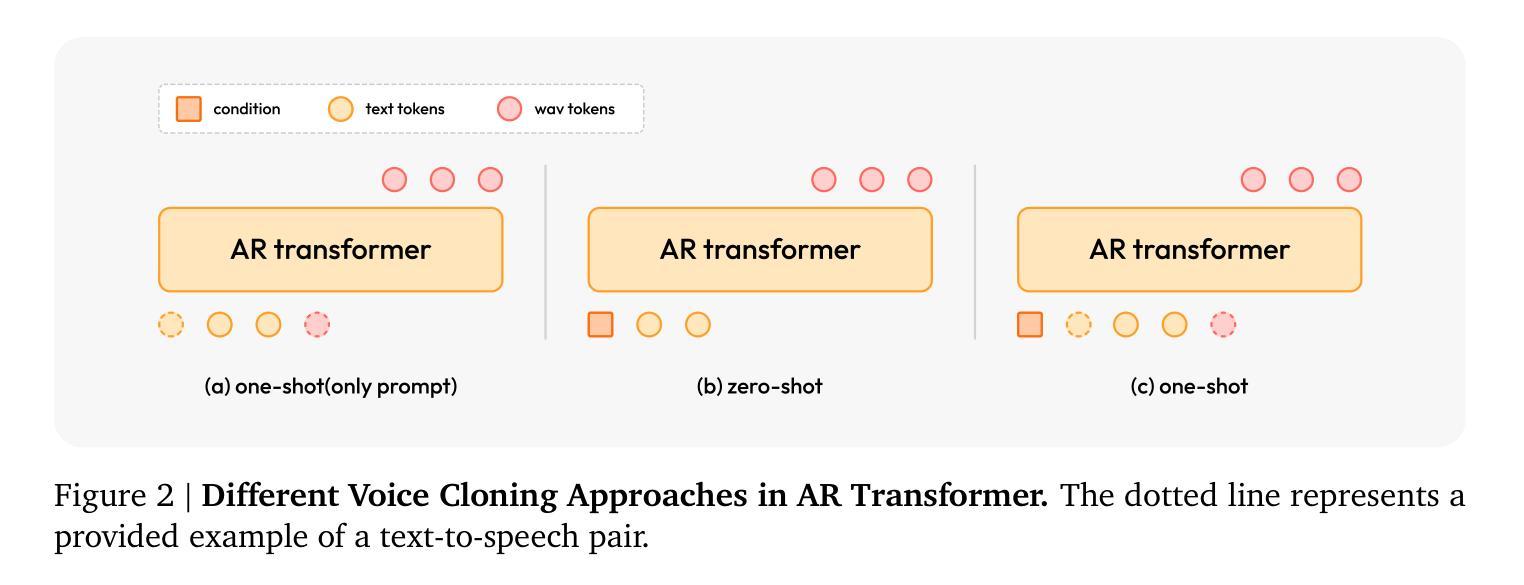
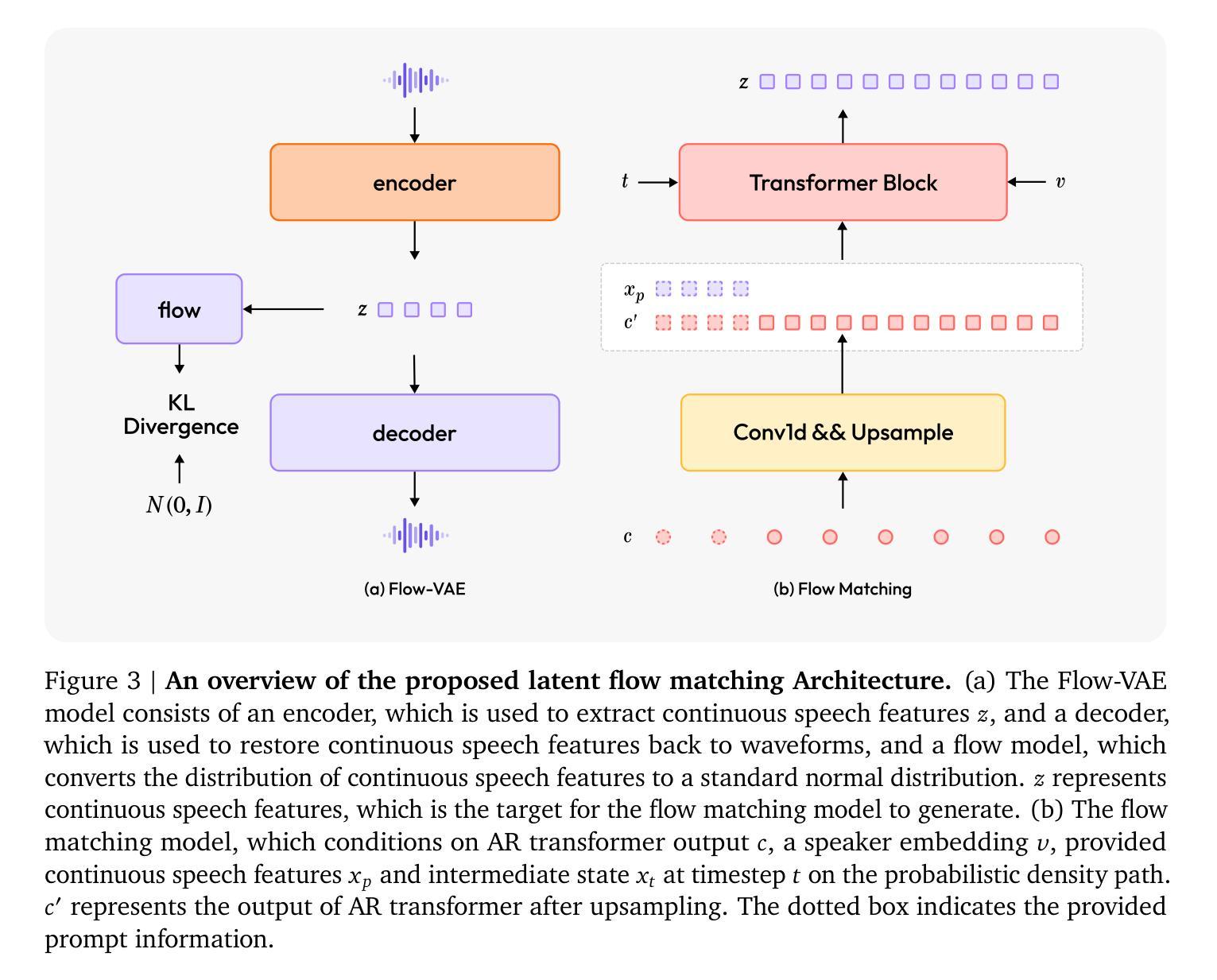
MiniMax-Speech: Intrinsic Zero-Shot Text-to-Speech with a Learnable Speaker Encoder
Authors:Bowen Zhang, Congchao Guo, Geng Yang, Hang Yu, Haozhe Zhang, Heidi Lei, Jialong Mai, Junjie Yan, Kaiyue Yang, Mingqi Yang, Peikai Huang, Ruiyang Jin, Sitan Jiang, Weihua Cheng, Yawei Li, Yichen Xiao, Yiying Zhou, Yongmao Zhang, Yuan Lu, Yucen He
We introduce MiniMax-Speech, an autoregressive Transformer-based Text-to-Speech (TTS) model that generates high-quality speech. A key innovation is our learnable speaker encoder, which extracts timbre features from a reference audio without requiring its transcription. This enables MiniMax-Speech to produce highly expressive speech with timbre consistent with the reference in a zero-shot manner, while also supporting one-shot voice cloning with exceptionally high similarity to the reference voice. In addition, the overall quality of the synthesized audio is enhanced through the proposed Flow-VAE. Our model supports 32 languages and demonstrates excellent performance across multiple objective and subjective evaluations metrics. Notably, it achieves state-of-the-art (SOTA) results on objective voice cloning metrics (Word Error Rate and Speaker Similarity) and has secured the top position on the public TTS Arena leaderboard. Another key strength of MiniMax-Speech, granted by the robust and disentangled representations from the speaker encoder, is its extensibility without modifying the base model, enabling various applications such as: arbitrary voice emotion control via LoRA; text to voice (T2V) by synthesizing timbre features directly from text description; and professional voice cloning (PVC) by fine-tuning timbre features with additional data. We encourage readers to visit https://minimax-ai.github.io/tts_tech_report for more examples.
我们介绍了MiniMax-Speech,这是一款基于自回归Transformer的文本到语音(TTS)模型,能够生成高质量语音。我们的主要创新之处在于可学习的说话人编码器,它可以从参考音频中提取音色特征,而无需其转录。这使得MiniMax-Speech能够以零样本的方式产生与参考音色一致的富有表现力的语音,同时支持一次性的声音克隆,与参考声音的相似度极高。此外,通过提出的Flow-VAE,合成音频的整体质量得到了提高。我们的模型支持32种语言,并在多个客观和主观评估指标上表现出卓越的性能。值得注意的是,它在客观声音克隆指标(词错误率和说话人相似性)上达到了最新水平,并在公共TTS Arena排行榜上获得了第一名。MiniMax-Speech的另一大优点是由说话人编码器的稳健和分离表示所赋予的扩展性,无需修改基础模型即可支持各种应用,例如通过LoRA实现任意语音情感控制;通过文本描述直接合成音色特征实现文本到语音(T2V);以及通过微调音色特征使用额外数据进行专业语音克隆(PVC)。更多示例请访问:https://minimax-ai.github.io/tts_tech_report。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了基于Transformer的文本转语音(TTS)模型MiniMax-Speech。该模型具有可学习的说话人编码器,可从参考音频中提取音色特征而无需其转录信息。MiniMax-Speech能够实现零样本的表达性语音生成并保持音色的一致性,并支持一键式语音克隆。通过Flow-VAE技术的加持,生成的音频质量得到提升。模型支持多种语言,客观与主观评价效果均卓越,且在公开TTS Arena排行榜上占据榜首。MiniMax-Speech的另一优势在于其通过强大的音色编码器实现了强大的可扩展性,可以在不修改基础模型的情况下应用于各种应用场景,如通过LoRA实现任意语音情感控制等。
Key Takeaways
- MiniMax-Speech是一个基于Transformer的文本转语音(TTS)模型,用于生成高质量语音。
- 该模型引入了可学习的说话人编码器,可以从参考音频中提取音色特征,无需转录信息。
- MiniMax-Speech支持零样本表达性语音生成和一键式语音克隆,且音色与参考一致。
- 通过Flow-VAE技术,提升了合成音频的整体质量。
- 模型支持多种语言,并在客观和主观评估中表现出卓越性能。
- MiniMax-Speech在公开TTS Arena排行榜上获得榜首,并在客观语音克隆指标上达到业界最佳。
点此查看论文截图