⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-05-16 更新
Meta-learning Slice-to-Volume Reconstruction in Fetal Brain MRI using Implicit Neural Representations
Authors:Maik Dannecker, Thomas Sanchez, Meritxell Bach Cuadra, Özgün Turgut, Anthony N. Price, Lucilio Cordero-Grande, Vanessa Kyriakopoulou, Joseph V. Hajnal, Daniel Rueckert
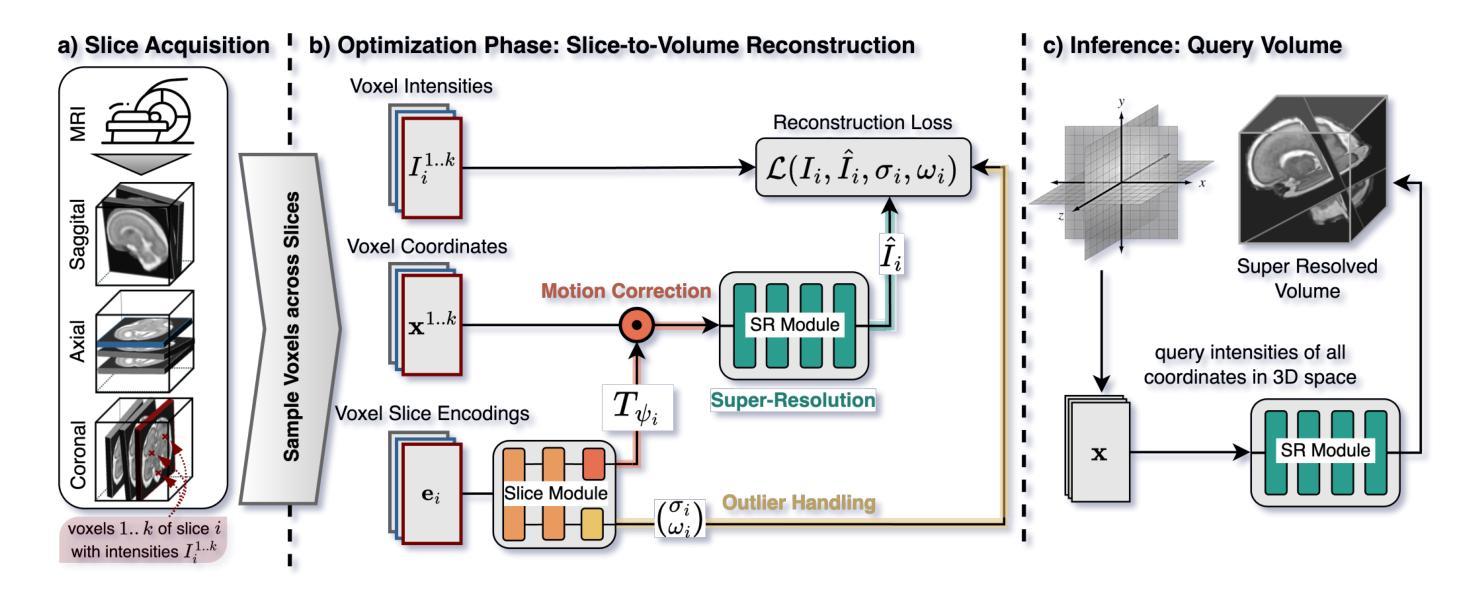
High-resolution slice-to-volume reconstruction (SVR) from multiple motion-corrupted low-resolution 2D slices constitutes a critical step in image-based diagnostics of moving subjects, such as fetal brain Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI). Existing solutions struggle with image artifacts and severe subject motion or require slice pre-alignment to achieve satisfying reconstruction performance. We propose a novel SVR method to enable fast and accurate MRI reconstruction even in cases of severe image and motion corruption. Our approach performs motion correction, outlier handling, and super-resolution reconstruction with all operations being entirely based on implicit neural representations. The model can be initialized with task-specific priors through fully self-supervised meta-learning on either simulated or real-world data. In extensive experiments including over 480 reconstructions of simulated and clinical MRI brain data from different centers, we prove the utility of our method in cases of severe subject motion and image artifacts. Our results demonstrate improvements in reconstruction quality, especially in the presence of severe motion, compared to state-of-the-art methods, and up to 50% reduction in reconstruction time.
从多个受运动影响的低分辨率2D切片进行高分辨率切片到体积重建(SVR),是在移动主体的图像诊断中,如胎儿脑部磁共振成像(MRI)的一个关键步骤。现有解决方案在图像伪影和严重主体运动方面存在困难,或者需要切片预对齐以实现令人满意的重建性能。我们提出了一种新型SVR方法,即使在图像和运动严重受损的情况下,也能实现快速、准确的MRI重建。我们的方法执行运动校正、异常值处理以及超分辨率重建,所有操作都完全基于隐式神经表示。该模型可以通过模拟或真实数据的完全自监督元学习,以特定任务的先验知识来进行初始化。在包括从不同中心获取的临床和模拟MRI脑部数据的超过480次重建的广泛实验中,我们验证了我们的方法在严重主体运动和图像伪影情况下的实用性。我们的结果表明,在存在严重运动的情况下,与最先进的方法相比,我们的重建质量有所提高,并且重建时间减少了高达50%。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 10 pages, 6 figures
Summary
针对动态主体(如胎儿脑部磁共振成像)的图像诊断中的高分辨率切片到体积重建(SVR),现有解决方案存在图像伪影和主体严重运动问题或需要切片预对齐以获得满意的重建性能。我们提出了一种新型SVR方法,可在图像和运动严重失真情况下实现快速准确的MRI重建。该方法基于隐神经表示进行运动校正、异常值处理和超分辨率重建。模型可通过模拟或真实数据的全自监督元学习进行特定任务先验初始化。实验证明,该方法在严重主体运动和图像伪影情况下具有实用性,与现有方法相比,重建质量有所提高,特别是在严重运动情况下,重建时间减少高达50%。
Key Takeaways
- 高分辨率切片到体积重建(SVR)在动态主体的图像诊断中至关重要,如胎儿脑部磁共振成像。
- 现有SVR解决方案在应对图像伪影和严重主体运动问题时表现不足,或需要切片预对齐。
- 提出了一种新型SVR方法,可处理图像和运动严重失真情况下的MRI重建。
- 该方法基于隐神经表示进行运动校正、异常值处理和超分辨率重建。
- 模型可通过模拟或真实数据的全自监督元学习进行任务特定先验初始化。
- 实验证明,该方法在严重主体运动和图像伪影情况下具有实用性。
点此查看论文截图

Conformal Bounds on Full-Reference Image Quality for Imaging Inverse Problems
Authors:Jeffrey Wen, Rizwan Ahmad, Philip Schniter
In imaging inverse problems, we would like to know how close the recovered image is to the true image in terms of full-reference image quality (FRIQ) metrics like PSNR, SSIM, LPIPS, etc. This is especially important in safety-critical applications like medical imaging, where knowing that, say, the SSIM was poor could potentially avoid a costly misdiagnosis. But since we don’t know the true image, computing FRIQ is non-trivial. In this work, we combine conformal prediction with approximate posterior sampling to construct bounds on FRIQ that are guaranteed to hold up to a user-specified error probability. We demonstrate our approach on image denoising and accelerated magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) problems. Code is available at https://github.com/jwen307/quality_uq.
在成像反问题中,我们想知道根据全参考图像质量(FRIQ)指标(如PSNR、SSIM、LPIPS等),恢复的图像与真实图像有多接近。这在医疗成像等安全关键应用中尤为重要,例如知道SSIM指标不佳可能会避免发生昂贵的误诊。但是因为我们不知道真实的图像,计算FRIQ是非常困难的。在这项工作中,我们将合规预测与近似后采样相结合,构建对FRIQ的界限,保证达到用户指定的错误概率。我们在图像去噪和加速磁共振成像(MRI)问题上展示了我们的方法。代码可通过链接访问:https://github.com/jwen307/quality_uq 。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文关注成像反问题中恢复图像与真实图像之间的全参考图像质量(FRIQ)指标接近程度的问题,特别是在医疗成像等安全关键应用中尤为重要。由于不知道真实图像,计算FRIQ具有挑战性。本研究结合conformal预测和近似后采样构建FRIQ的界限,可保证达到用户指定的错误概率。该方法在图像去噪和加速磁共振成像问题中得到了验证。
Key Takeaways
- 成像反问题中,恢复图像与真实图像之间的全参考图像质量(FRIQ)指标接近程度是关键,尤其在医疗成像等安全应用中尤为重要。
- 由于不知道真实图像,计算FRIQ具有挑战性。
- 本研究结合conformal预测和近似后采样构建FRIQ的界限。
- 方法可保证达到用户指定的错误概率。
- 该方法在图像去噪和加速磁共振成像问题中得到了验证。
- 代码已公开,便于其他研究者使用和改进。
点此查看论文截图

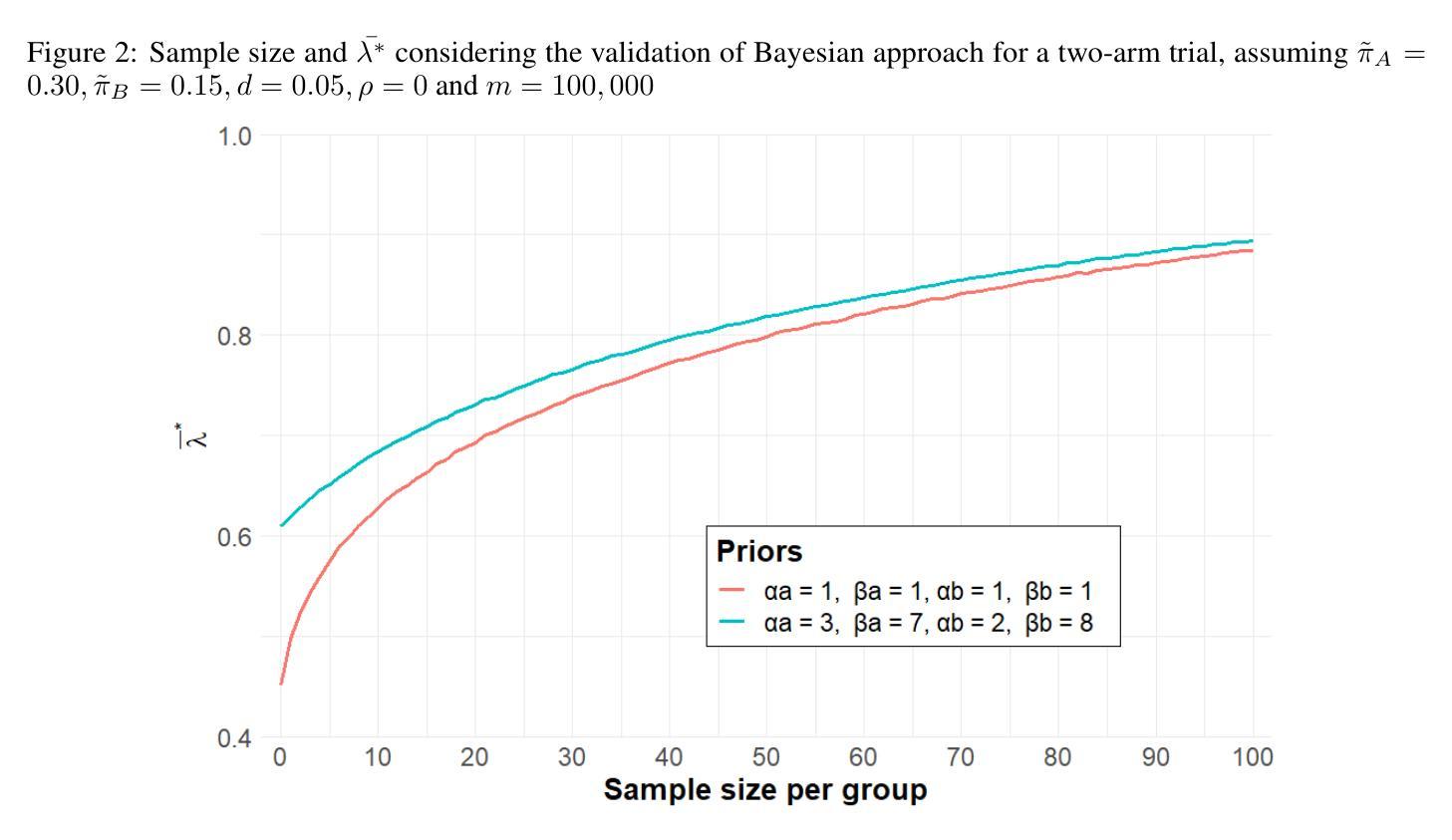
A Bayesian Treatment Selection Design for Phase II Randomised Cancer Clinical Trials
Authors:Moka Komaki, Satoru Shinoda, Haiyan Zheng, Kouji Yamamoto
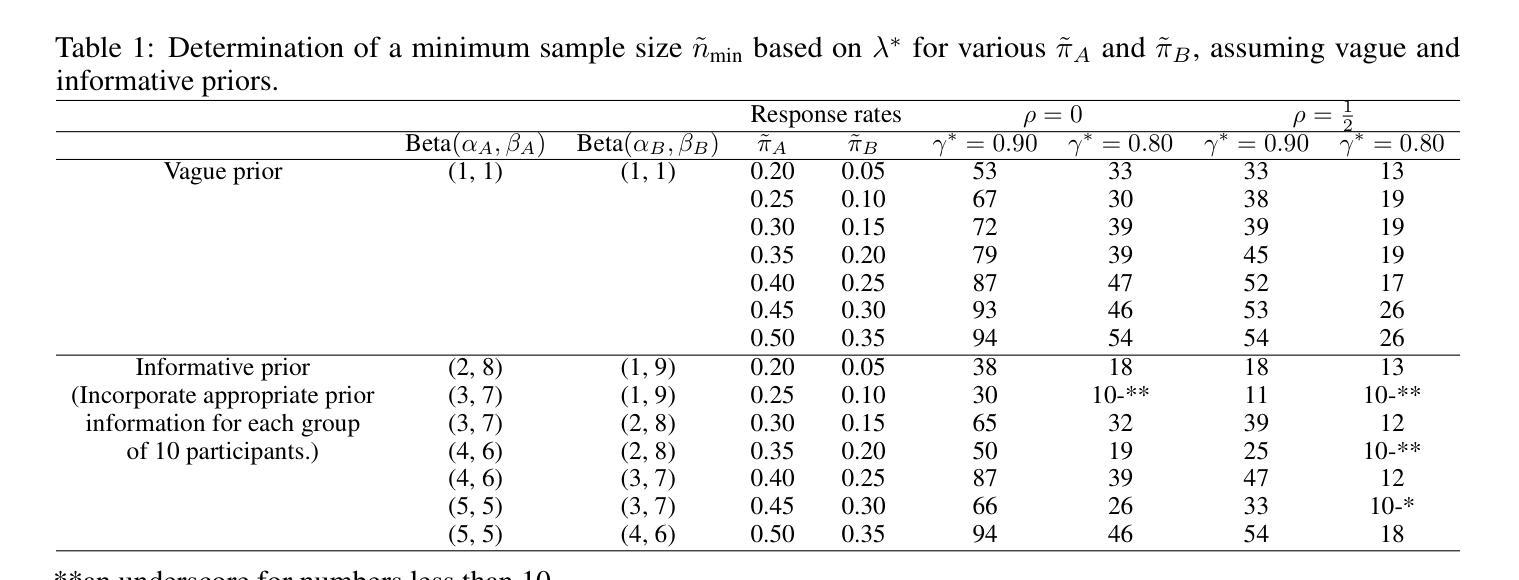
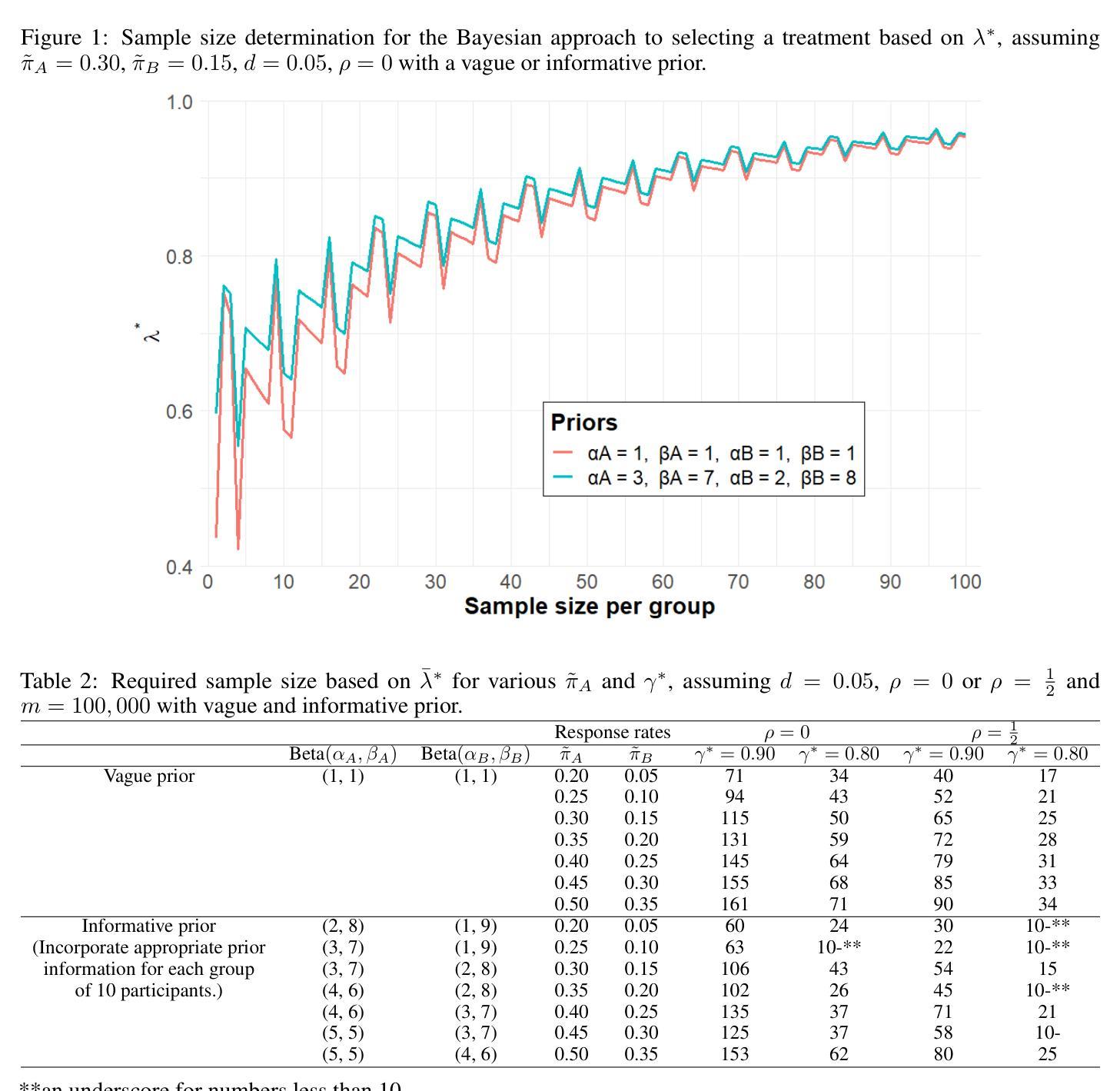
It is crucial to design Phase II cancer clinical trials that balance the efficiency of treatment selection with clinical practicality. Sargent and Goldberg proposed a frequentist design that allow decision-making even when the primary endpoint is ambiguous. However, frequentist approaches rely on fixed thresholds and long-run frequency properties, which can limit flexibility in practical applications. In contrast, the Bayesian decision rule, based on posterior probabilities, enables transparent decision-making by incorporating prior knowledge and updating beliefs with new data, addressing some of the inherent limitations of frequentist designs. In this study, we propose a novel Bayesian design, allowing selection of a best-performing treatment. Specifically, concerning phase II clinical trials with a binary outcome, our decision rule employs posterior interval probability by integrating the joint distribution over all values, for which the ‘success rate’ of the bester-performing treatment is greater than that of the other(s). This design can then determine which a treatment should proceed to the next phase, given predefined decision thresholds. Furthermore, we propose two sample size determination methods to empower such treatment selection designs implemented in a Bayesian framework. Through simulation studies and real-data applications, we demonstrate how this approach can overcome challenges related to sample size constraints in randomised trials. In addition, we present a user-friendly R Shiny application, enabling clinicians to Bayesian designs. Both our methodology and the software application can advance the design and analysis of clinical trials for evaluating cancer treatments.
在设计第二阶段癌症临床试验时,需要在治疗选择效率和临床实用性之间取得平衡。Sargent和Goldberg提出了一种基于频繁统计的决策设计,即使主要终点不明确也能做出决策。然而,频繁的方法依赖于固定的阈值和长期频率属性,这限制了在实际应用中的灵活性。相比之下,基于后验概率的贝叶斯决策规则可以通过整合先验知识和利用新数据更新信念来实现透明的决策过程,从而解决了频繁设计的一些固有局限性。在这项研究中,我们提出了一种新型的贝叶斯设计,允许选择表现最佳的治疗方案。具体来说,对于具有二元结果的第二阶段临床试验,我们的决策规则采用后验区间概率,通过整合所有值的联合分布来确定哪种治疗方案的“成功率”高于其他方案。这种设计可以根据预先设定的决策阈值来确定哪种治疗方案应进入下一阶段。此外,我们还提出了两种样本量确定方法,以支持在贝叶斯框架中实现的治疗选择设计。通过模拟研究和实际应用数据的分析,我们展示了这种方法如何克服随机试验中与样本规模有关的挑战。此外,我们还提供了一个用户友好的R Shiny应用程序,使临床医生能够使用贝叶斯设计。我们的方法和软件应用程序都能推动临床试验的设计和分析,以评估癌症治疗方法的效果。
论文及项目相关链接
摘要
针对二期癌症临床试验的设计,需要在治疗选择效率和临床实践之间取得平衡。本研究提出一种新型贝叶斯设计,采用后验区间概率决策规则,用于选择表现最佳的治疗方案。该设计通过联合分布对所有值进行积分,确定最佳治疗方案的“成功率”高于其他方案。此外,还提出两种样本量确定方法,以支持在贝叶斯框架下实施此类治疗选择设计。通过模拟研究和实际应用,证明了该方法在克服随机试验中的样本量约束挑战方面的有效性。
关键见解
- 二期癌症临床试验设计需平衡治疗选择效率和临床实践。
- Sargent和Goldberg提出的频繁主义设计在主要终点模糊时仍允许决策。
- 频繁主义方法依赖于固定的阈值和长期频率属性,这可能限制了实际应用中的灵活性。
- 贝叶斯决策规则基于后验概率,通过融入先验知识和新数据的信念更新,解决了频繁主义设计的一些固有局限性。
- 研究提出了一种新型贝叶斯设计,采用后验区间概率决策规则来选择最佳治疗方案。
- 通过模拟研究和实际应用,证明了该设计方法在克服样本量约束方面的优势。
点此查看论文截图

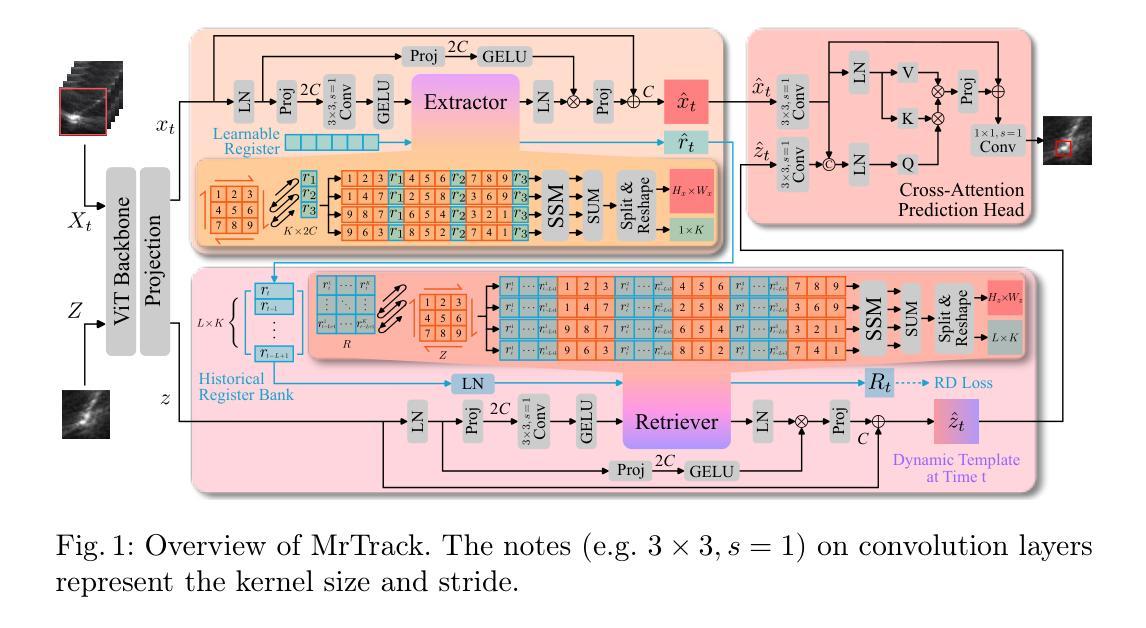
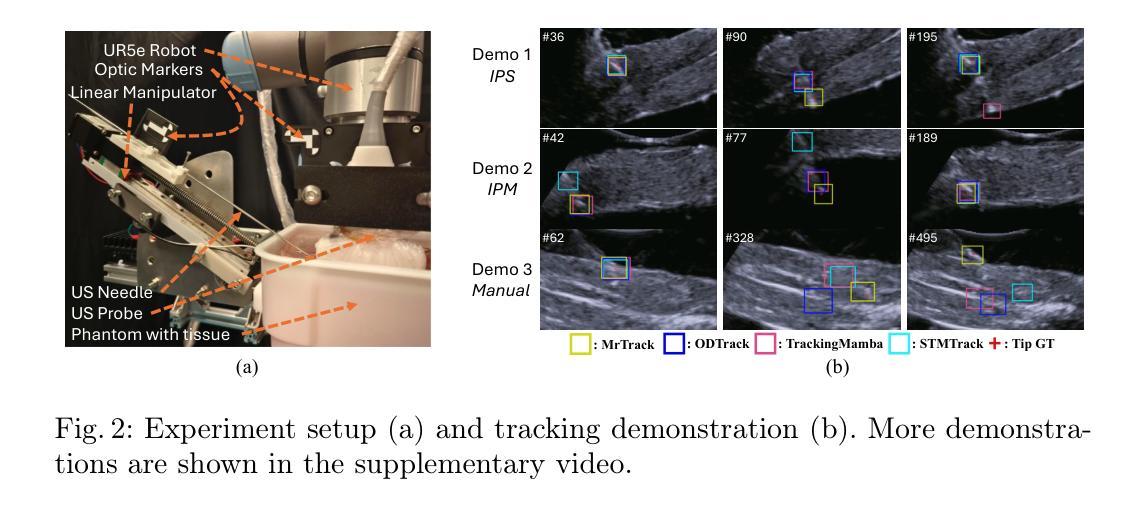
MrTrack: Register Mamba for Needle Tracking with Rapid Reciprocating Motion during Ultrasound-Guided Aspiration Biopsy
Authors:Yuelin Zhang, Qingpeng Ding, Long Lei, Yongxuan Feng, Raymond Shing-Yan Tang, Shing Shin Cheng
Ultrasound-guided fine needle aspiration (FNA) biopsy is a common minimally invasive diagnostic procedure. However, an aspiration needle tracker addressing rapid reciprocating motion is still missing. MrTrack, an aspiration needle tracker with a mamba-based register mechanism, is proposed. MrTrack leverages a Mamba-based register extractor to sequentially distill global context from each historical search map, storing these temporal cues in a register bank. The Mamba-based register retriever then retrieves temporal prompts from the register bank to provide external cues when current vision features are temporarily unusable due to rapid reciprocating motion and imaging degradation. A self-supervised register diversify loss is proposed to encourage feature diversity and dimension independence within the learned register, mitigating feature collapse. Comprehensive experiments conducted on both motorized and manual aspiration datasets demonstrate that MrTrack not only outperforms state-of-the-art trackers in accuracy and robustness but also achieves superior inference efficiency.
超声引导下细针穿刺活检(FNA)是一种常见的微创诊断程序。然而,针对快速往复运动的穿刺针跟踪器仍然缺失。本文提出了MrTrack穿刺针跟踪器,它采用基于蟒蛇的注册机制。MrTrack利用基于蟒蛇的注册提取器,从每个历史搜索图中顺序提取全局上下文,将这些时序线索存储在寄存器银行中。然后,基于蟒蛇的寄存器检索器从寄存器银行中提取时序提示,在当前视觉特征因快速往复运动和图像退化而暂时无法使用的情况下,提供外部线索。提出了一种自监督寄存器多样化损失,以促进学习寄存器内的特征多样性和维度独立性,减轻特征崩溃。在机动和手动穿刺数据集上进行的综合实验表明,MrTrack不仅在准确性和稳健性方面优于最新跟踪技术,而且实现了更高的推理效率。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Early Accepted by MICCAI 2025
Summary
超声引导下细针穿刺活检(FNA)是一种常见的微创诊断程序。为解决快速往复运动中的穿刺针跟踪问题,提出了MrTrack穿刺针跟踪器,采用基于mamba的寄存器机制。它通过全局上下文信息蒸馏和寄存器银行中的时序线索存储,为当前视觉特征因快速往复运动和图像退化而暂时无法使用的情况提供外部线索。此外,还提出了一种自监督寄存器多样化损失,以鼓励学习到的寄存器内的特征多样性和维度独立性,减轻特征崩溃。实验证明,MrTrack不仅准确度和稳健性优于现有跟踪器,而且推理效率更高。
Key Takeaways
- MrTrack是一种解决超声引导下细针穿刺活检中快速往复运动问题的穿刺针跟踪器。
- MrTrack采用基于mamba的寄存器机制,能够处理全局上下文信息和时序线索。
- 寄存器银行用于存储历史搜索图的时间线索,为当前视觉特征的缺失提供外部线索。
- 自监督寄存器多样化损失鼓励特征多样性和维度独立性,提高跟踪器的性能。
- MrTrack在电机驱动和手动穿刺数据集上的实验结果表明其准确性和稳健性优于最新跟踪技术。
- MrTrack还实现了较高的推理效率。
点此查看论文截图

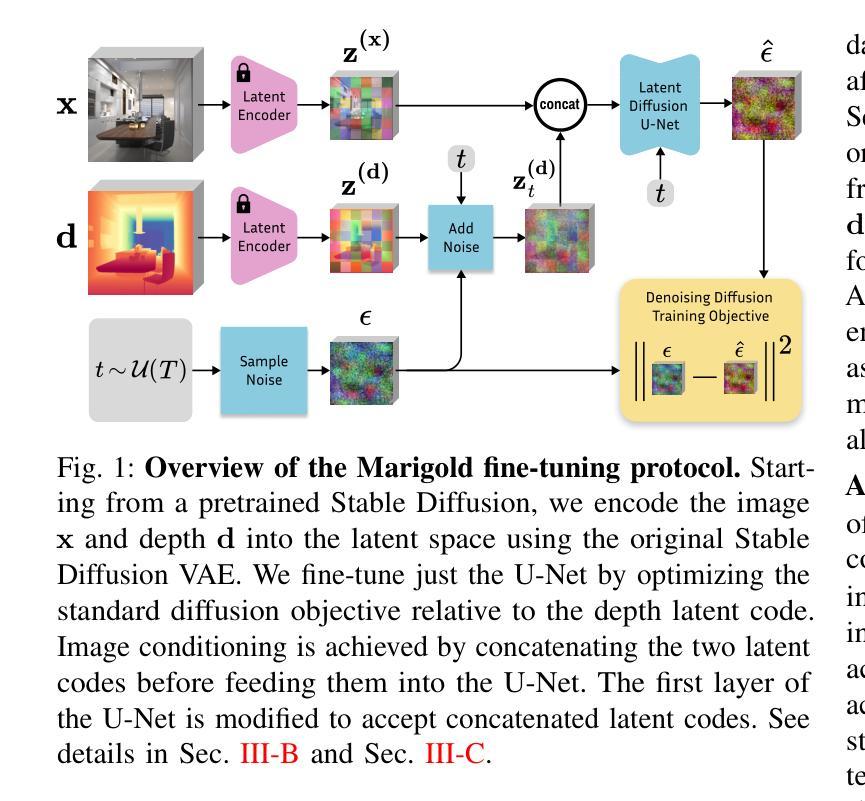
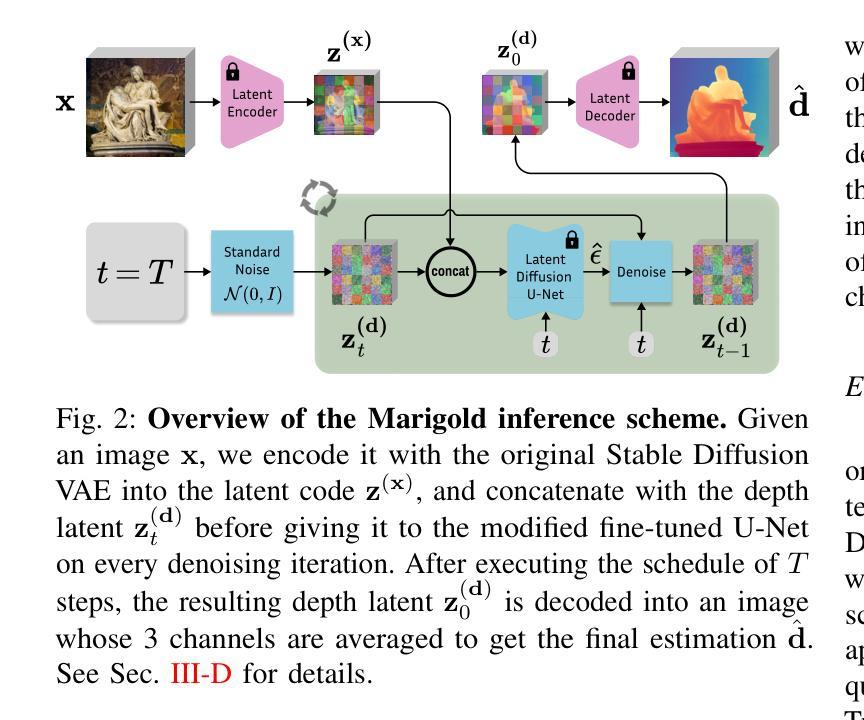
Marigold: Affordable Adaptation of Diffusion-Based Image Generators for Image Analysis
Authors:Bingxin Ke, Kevin Qu, Tianfu Wang, Nando Metzger, Shengyu Huang, Bo Li, Anton Obukhov, Konrad Schindler
The success of deep learning in computer vision over the past decade has hinged on large labeled datasets and strong pretrained models. In data-scarce settings, the quality of these pretrained models becomes crucial for effective transfer learning. Image classification and self-supervised learning have traditionally been the primary methods for pretraining CNNs and transformer-based architectures. Recently, the rise of text-to-image generative models, particularly those using denoising diffusion in a latent space, has introduced a new class of foundational models trained on massive, captioned image datasets. These models’ ability to generate realistic images of unseen content suggests they possess a deep understanding of the visual world. In this work, we present Marigold, a family of conditional generative models and a fine-tuning protocol that extracts the knowledge from pretrained latent diffusion models like Stable Diffusion and adapts them for dense image analysis tasks, including monocular depth estimation, surface normals prediction, and intrinsic decomposition. Marigold requires minimal modification of the pre-trained latent diffusion model’s architecture, trains with small synthetic datasets on a single GPU over a few days, and demonstrates state-of-the-art zero-shot generalization. Project page: https://marigoldcomputervision.github.io
过去十年,深度学习在计算机视觉领域取得的成功在很大程度上依赖于大规模有标签数据集和强大的预训练模型。在数据稀缺的环境中,这些预训练模型的质量对于有效的迁移学习至关重要。图像分类和自监督学习一直是预训练CNN和基于transformer架构的主要方法。最近,文本到图像生成模型的兴起,特别是那些在潜在空间使用去噪扩散的模型,引入了一类新的基础模型,这些模型在大型有标注图像数据集上进行训练。这些模型生成未见内容的逼真图像的能力表明它们对视觉世界有深刻的理解。在这项工作中,我们提出了Marigold,这是一系列条件生成模型和微调协议,它从预训练的潜在扩散模型(如Stable Diffusion)中提取知识,并适应密集图像分析任务,包括单目深度估计、表面法线预测和内在分解。Marigold对预训练的潜在扩散模型的架构进行了最小的修改,可以在单个GPU上使用小型合成数据集进行几天的训练,并展示了最先进的零样本泛化能力。项目页面:https://marigoldcomputervision.github.io
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Journal extension of our CVPR 2024 paper, featuring new tasks, improved efficiency, high-resolution capabilities, and enhanced accessibility
Summary
深度学习方法在计算机视觉领域的成功依赖于大规模标注数据集和强大的预训练模型。在数据稀缺的情况下,预训练模型的质量对迁移学习至关重要。传统图像分类和自监督学习是预训练CNN和基于转换器架构的主要方法。近期文本到图像生成模型的兴起,特别是潜在空间中降噪扩散模型的出现,引入了一种新型基础模型。该模型在巨大的有标题图像数据集上进行训练,能生成逼真的未见内容图像,表明其对视觉世界的深度理解。本研究提出Marigold,一系列条件生成模型和微调协议,从预训练的潜在扩散模型如Stable Diffusion中提取知识,并适应密集图像分析任务,包括单眼深度估计、表面法线预测和内在分解。Marigold对预训练的潜在扩散模型的架构进行了最小的修改,可在单个GPU上使用小型合成数据集进行几天的训练,并展示了零样本泛化的最新水平。
Key Takeaways
- 深度学习方法在计算机视觉领域的成功依赖于大规模标注数据集和强大的预训练模型。
- 在数据稀缺的情况下,预训练模型的质量对迁移学习至关重要。
- 文本到图像生成模型的兴起引入了一种新型基础模型,能生成未见内容图像。
- Marigold是一种条件生成模型和微调协议,适用于密集图像分析任务。
- Marigold能够从预训练的潜在扩散模型中提取知识并适应多种图像分析任务。
- Marigold在预训练模型架构上进行了最小修改,可在有限资源下高效训练。
- Marigold展示了零样本泛化的最新水平。
点此查看论文截图
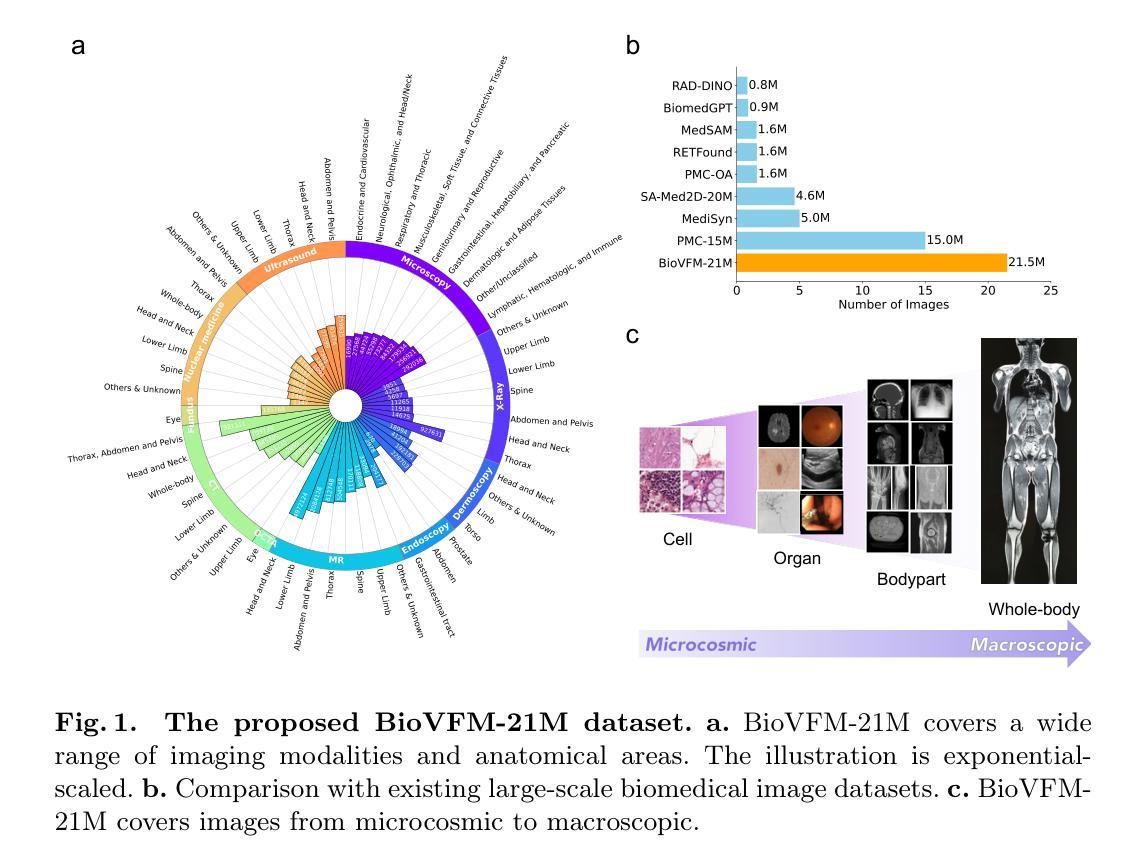
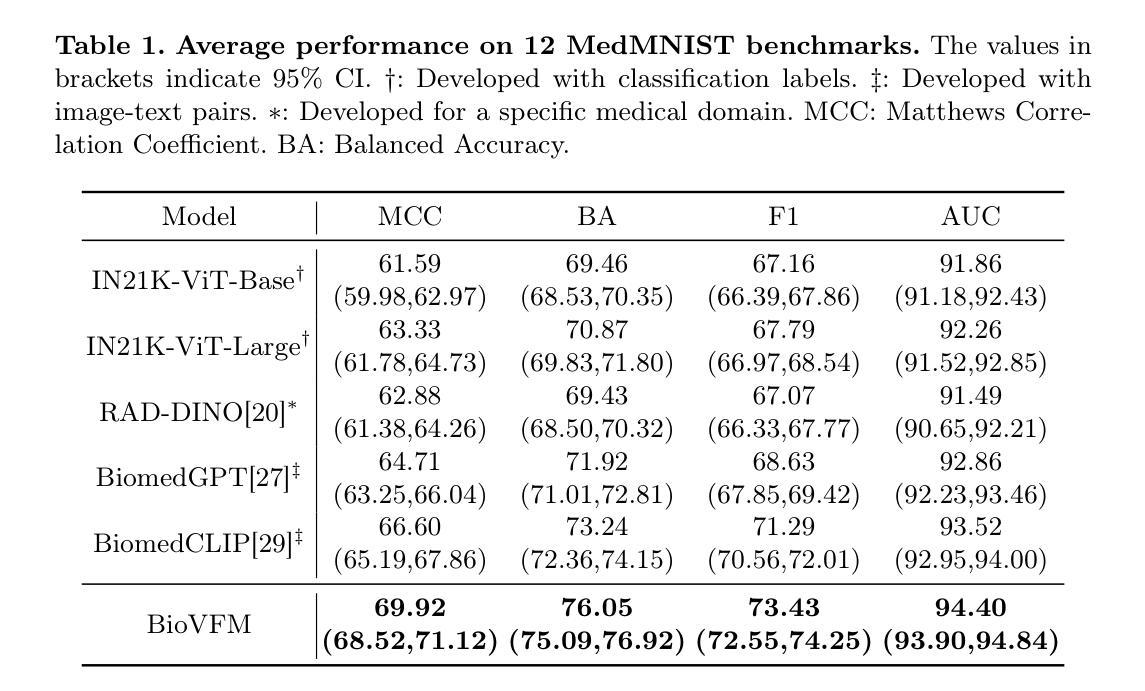
BioVFM-21M: Benchmarking and Scaling Self-Supervised Vision Foundation Models for Biomedical Image Analysis
Authors:Jiarun Liu, Hong-Yu Zhou, Weijian Huang, Hao Yang, Dongning Song, Tao Tan, Yong Liang, Shanshan Wang
Scaling up model and data size have demonstrated impressive performance improvement over a wide range of tasks. Despite extensive studies on scaling behaviors for general-purpose tasks, medical images exhibit substantial differences from natural data. It remains unclear the key factors in developing medical vision foundation models at scale due to the absence of an extensive understanding of scaling behavior in the medical domain. In this paper, we explored the scaling behavior across model sizes, training algorithms, data sizes, and imaging modalities in developing scalable medical vision foundation models by self-supervised learning. To support scalable pretraining, we introduce BioVFM-21M, a large-scale biomedical image dataset encompassing a wide range of biomedical image modalities and anatomies. We observed that scaling up does provide benefits but varies across tasks. Additional analysis reveals several factors correlated with scaling benefits. Finally, we propose BioVFM, a large-scale medical vision foundation model pretrained on 21 million biomedical images, which outperforms the previous state-of-the-art foundation models across 12 medical benchmarks. Our results highlight that while scaling up is beneficial for pursuing better performance, task characteristics, data diversity, pretraining methods, and computational efficiency remain critical considerations for developing scalable medical foundation models.
随着模型和数据规模的扩大,在各种任务上均实现了令人印象深刻的性能提升。尽管针对通用任务的扩展行为已经进行了广泛的研究,但医学图像与自然数据之间存在显著差异。由于缺乏在医学领域对扩展行为的深入了解,因此在开发大规模医学视觉基础模型时,关键因素尚不清楚。在本文中,我们通过自监督学习,探索了模型大小、训练算法、数据大小和成像方式在开发可扩展医学视觉基础模型时的扩展行为。为了支持可扩展的预训练,我们引入了BioVFM-21M,这是一个涵盖广泛生物医学图像模式和解剖结构的的大规模生物医学图像数据集。我们发现扩大规模确实有益,但不同任务间的效益有所不同。额外的分析揭示了与扩展效益相关的几个因素。最后,我们提出了BioVFM,这是一个在2100万生物医学图像上进行预训练的大规模医学视觉基础模型,在12项医学基准测试中超过了之前的先进基础模型。我们的结果强调,虽然扩大规模对追求更好性能有益,但任务特征、数据多样性、预训练方法和计算效率仍是开发可扩展医学基础模型的关键考虑因素。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 11 pages, 4 figures
Summary
本文探索了通过自监督学习在开发可扩展医疗视觉基础模型时的模型大小、训练算法、数据量以及成像模式等扩展行为。为支持大规模预训练,引入了包含广泛生物医学图像模态和解剖结构的大型生物医学图像数据集BioVFM-21M。观察到扩展规模确实有益于提升性能,但不同任务之间存在差异。综合分析揭示了一些与扩展效益相关的因素。最后,提出了在2100万生物医学图像上预训练的大型医疗视觉基础模型BioVFM,在12项医疗基准测试中表现出优于先前最先进的水平。研究结果表明,虽然扩展规模有助于提高性能,但任务特性、数据多样性、预训练方法和计算效率仍是开发可扩展医疗基础模型的关键考虑因素。
Key Takeaways
- 扩展模型和数据规模在多种任务上展现出显著性能提升。
- 医疗图像与天然数据在扩展行为上存在显著差异。
- 开发医疗视觉基础模型的大规模扩展面临关键因素的挑战,包括对医学领域扩展行为的广泛理解不足。
- 通过自监督学习,本文研究了模型大小、训练算法、数据量以及成像模式在开发可扩展医疗视觉基础模型中的扩展行为。
- 引入的大型生物医学图像数据集BioVFM-21M支持大规模预训练,包含多种生物医学图像模态和解剖结构。
- 扩展规模有益于性能提升,但不同任务之间存在差异,任务特性是关键考虑因素之一。
点此查看论文截图

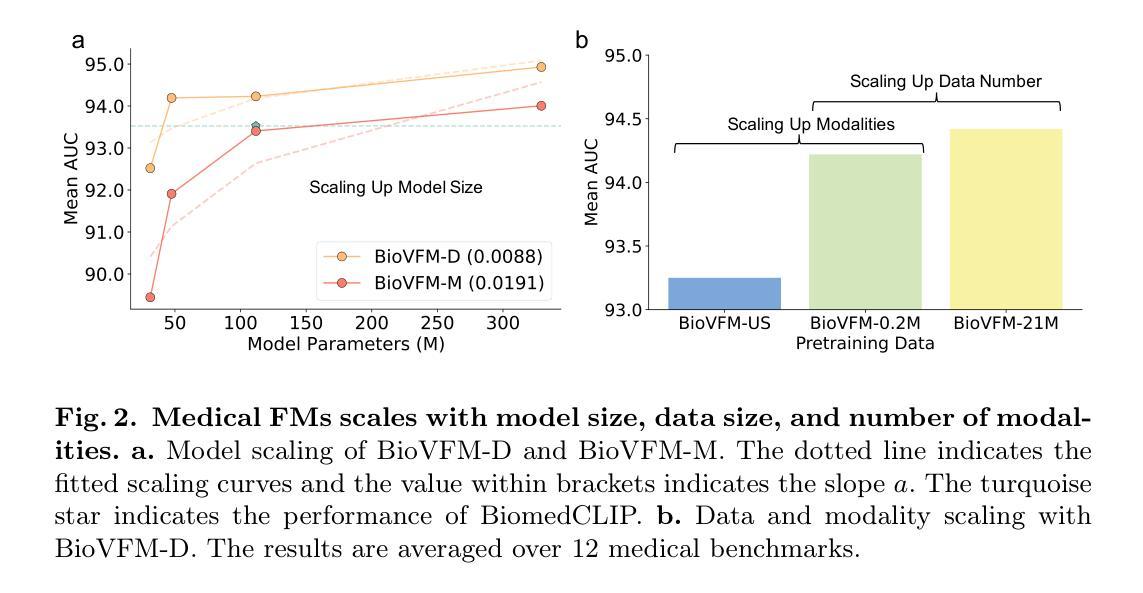
Q-space Guided Collaborative Attention Translation Network for Flexible Diffusion-Weighted Images Synthesis
Authors:Pengli Zhu, Yingji Fu, Nanguang Chen, Anqi Qiu
This study, we propose a novel Q-space Guided Collaborative Attention Translation Networks (Q-CATN) for multi-shell, high-angular resolution DWI (MS-HARDI) synthesis from flexible q-space sampling, leveraging the commonly acquired structural MRI data. Q-CATN employs a collaborative attention mechanism to effectively extract complementary information from multiple modalities and dynamically adjust its internal representations based on flexible q-space information, eliminating the need for fixed sampling schemes. Additionally, we introduce a range of task-specific constraints to preserve anatomical fidelity in DWI, enabling Q-CATN to accurately learn the intrinsic relationships between directional DWI signal distributions and q-space. Extensive experiments on the Human Connectome Project (HCP) dataset demonstrate that Q-CATN outperforms existing methods, including 1D-qDL, 2D-qDL, MESC-SD, and QGAN, in estimating parameter maps and fiber tracts both quantitatively and qualitatively, while preserving fine-grained details. Notably, its ability to accommodate flexible q-space sampling highlights its potential as a promising toolkit for clinical and research applications. Our code is available at https://github.com/Idea89560041/Q-CATN.
本研究提出了一种新型的Q空间引导协同注意力转换网络(Q-CATN),用于从灵活的q空间采样中合成多壳、高分辨率扩散加权成像(MS-HARDI),并利用常见的结构磁共振成像数据进行辅助。Q-CATN采用协同注意力机制,有效提取多模态的互补信息,并根据灵活的q空间信息动态调整其内部表示,从而无需固定的采样方案。此外,我们引入了一系列特定任务的约束以保持DWI的解剖保真度,使Q-CATN能够准确学习方向性DWI信号分布与q空间之间的内在关系。在人类连接组项目(Human Connectome Project,简称HCP)数据集上的大量实验表明,在定量和定性评估参数映射和纤维束估计方面,Q-CATN优于现有方法,包括1D-qDL、2D-qDL、MESC-SD和QGAN,同时保留了精细的细节。值得注意的是,其适应灵活q空间采样的能力凸显了其在临床和研究应用中的潜力。我们的代码可通过https://github.com/Idea89560041/Q-CATN获取。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF MICCAI 2025
Summary
该研究提出了一种新型的Q空间引导协同注意力翻译网络(Q-CATN),用于从灵活的q空间采样中合成多壳、高角分辨率DWI(MS-HARDI)。借助常见结构MRI数据,Q-CATN采用协同注意力机制有效提取多模态的互补信息,并根据灵活的q空间信息动态调整其内部表示,无需固定采样方案。此外,引入了一系列任务特定约束以保留DWI中的解剖保真度,使Q-CATN能够准确学习方向性DWI信号分布与q空间之间的内在关系。在Human Connectome Project数据集上的广泛实验表明,Q-CATN在估计参数映射和纤维束方面定量和定性上均优于现有方法,包括1D-qDL、2D-qDL、MESC-SD和QGAN,同时保留精细细节。其适应灵活q空间采样的能力凸显了其在临床和研究应用中的潜力。
Key Takeaways
- 研究提出了Q-CATN网络,旨在用于从灵活的q空间采样中合成MS-HARDI。
- Q-CATN利用协同注意力机制融合多模态信息,并基于灵活的q空间信息动态调整内部表示。
- 引入任务特定约束以维持DWI的解剖保真度。
- Q-CATN在Human Connectome Project数据集上的表现优于其他现有方法。
- Q-CATN能够准确学习DWI信号分布与q空间之间的内在关系。
- Q-CATN具有适应灵活q空间采样的能力,显示出在临床和研究应用中的潜力。
点此查看论文截图

Recent Advances in Medical Imaging Segmentation: A Survey
Authors:Fares Bougourzi, Abdenour Hadid
Medical imaging is a cornerstone of modern healthcare, driving advancements in diagnosis, treatment planning, and patient care. Among its various tasks, segmentation remains one of the most challenging problem due to factors such as data accessibility, annotation complexity, structural variability, variation in medical imaging modalities, and privacy constraints. Despite recent progress, achieving robust generalization and domain adaptation remains a significant hurdle, particularly given the resource-intensive nature of some proposed models and their reliance on domain expertise. This survey explores cutting-edge advancements in medical image segmentation, focusing on methodologies such as Generative AI, Few-Shot Learning, Foundation Models, and Universal Models. These approaches offer promising solutions to longstanding challenges. We provide a comprehensive overview of the theoretical foundations, state-of-the-art techniques, and recent applications of these methods. Finally, we discuss inherent limitations, unresolved issues, and future research directions aimed at enhancing the practicality and accessibility of segmentation models in medical imaging. We are maintaining a \href{https://github.com/faresbougourzi/Awesome-DL-for-Medical-Imaging-Segmentation}{GitHub Repository} to continue tracking and updating innovations in this field.
医学影像是现代医疗的基石,推动了诊断、治疗计划和患者护理的进步。在多种任务中,分割仍然是一个最具挑战性的难题,因为它涉及到数据可访问性、标注复杂性、结构变化性、医学影像模式的变化以及隐私限制等因素。尽管取得了最新的进展,实现稳健的泛化和域适应仍然是一个巨大的障碍,特别是考虑到某些模型的资源密集型和它们对专业知识的依赖。这篇综述探讨了医学影像分割的最新进展,重点关注人工智能生成技术、少样本学习、基础模型和通用模型等研究方法。这些方法为解决长期存在的挑战提供了很有前景的解决方案。我们全面概述了这些方法的理论基础、最新技术和最新应用。最后,我们讨论了固有的局限性、未解决的问题以及未来的研究方向,旨在提高医学影像分割模型的实用性和可访问性。我们正在维护一个GitHub仓库(https://github.com/faresbougourzi/Awesome-DL-for-Medical-Imaging-Segmentation),以继续跟踪和更新这一领域的创新。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
医学成像在现代医疗中占据重要地位,是推动诊断、治疗计划和患者护理发展的关键力量。本文综述了医学图像分割领域的最新进展,探讨了生成式人工智能、小样本学习、基础模型和通用模型等前沿方法,为解决长期存在的挑战提供了有力支持。文章全面概述了这些方法的理论基础、最新技术和实际应用,并讨论了其内在局限性和未来研究方向,旨在提高医学图像分割模型的实用性和可访问性。
Key Takeaways
- 医学成像在诊断、治疗计划和患者护理中起关键作用。
- 医学图像分割是医学成像领域最具挑战性的问题之一,涉及数据获取、标注复杂性、结构变异、成像模式变异和隐私约束等因素。
- 最新的技术进展包括生成式人工智能、小样本学习、基础模型和通用模型等。
- 这些方法为解决医学图像分割问题提供了有前途的解决方案。
- 文章全面概述了这些方法的理论基础和实际应用。
- 文章讨论了医学图像分割领域的内在局限性和未来研究方向。
点此查看论文截图

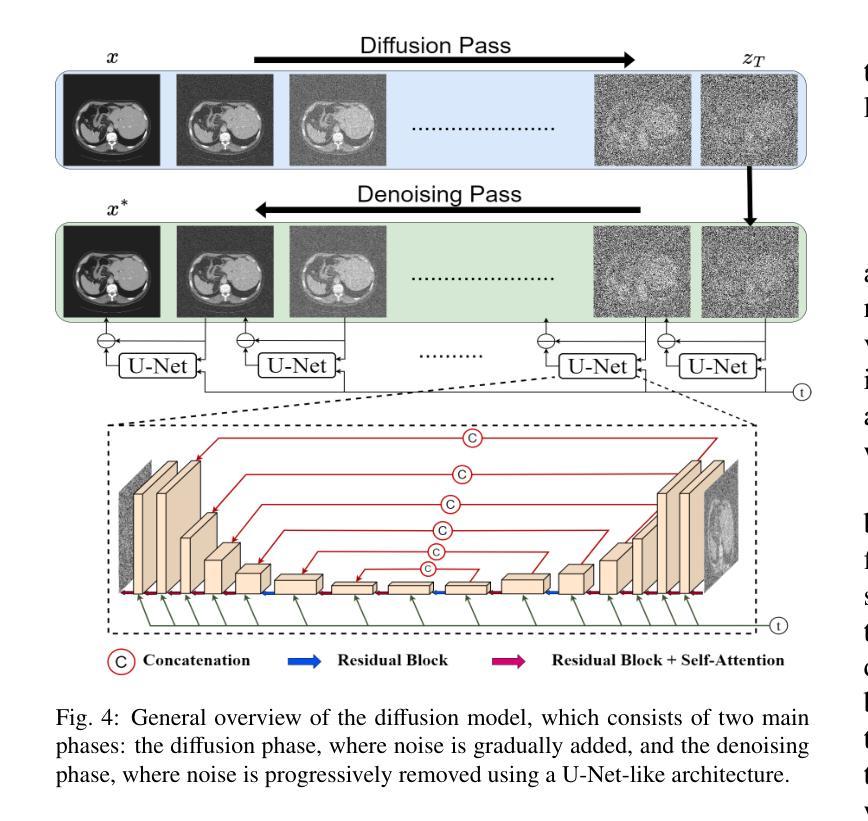
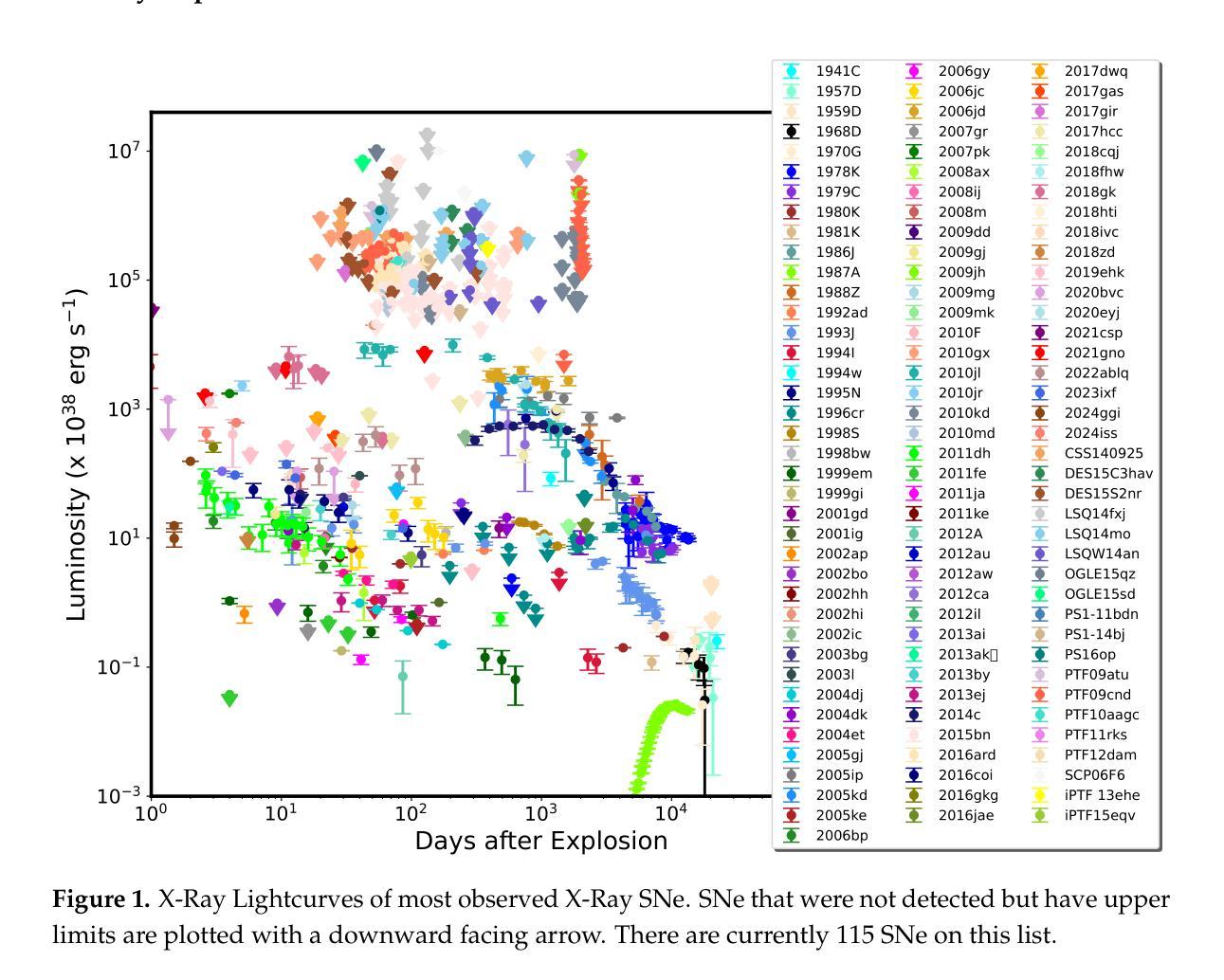
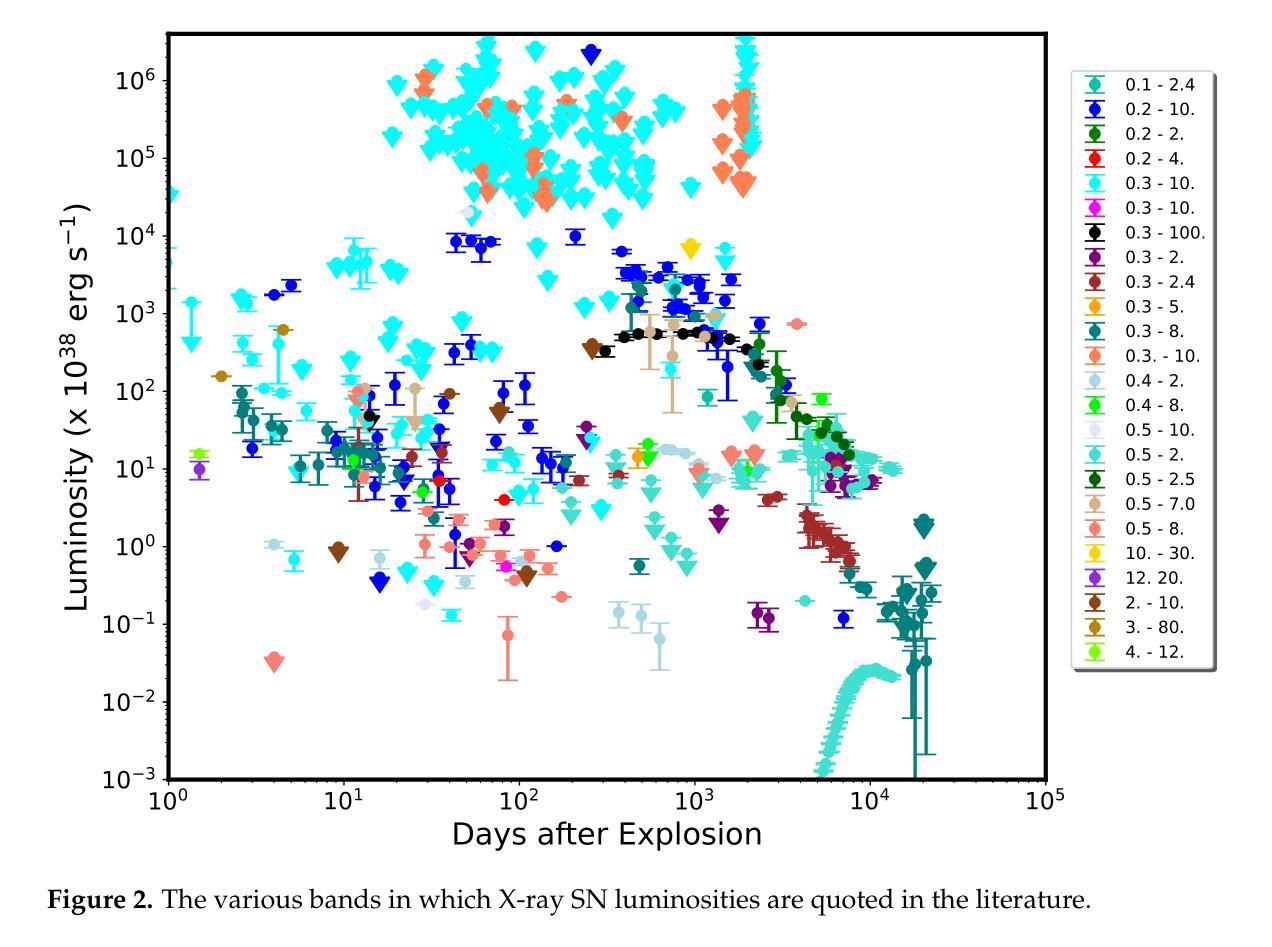
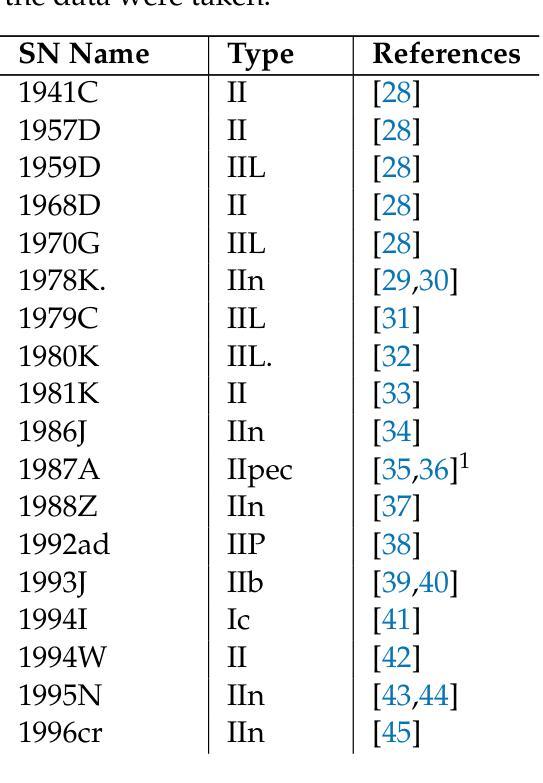
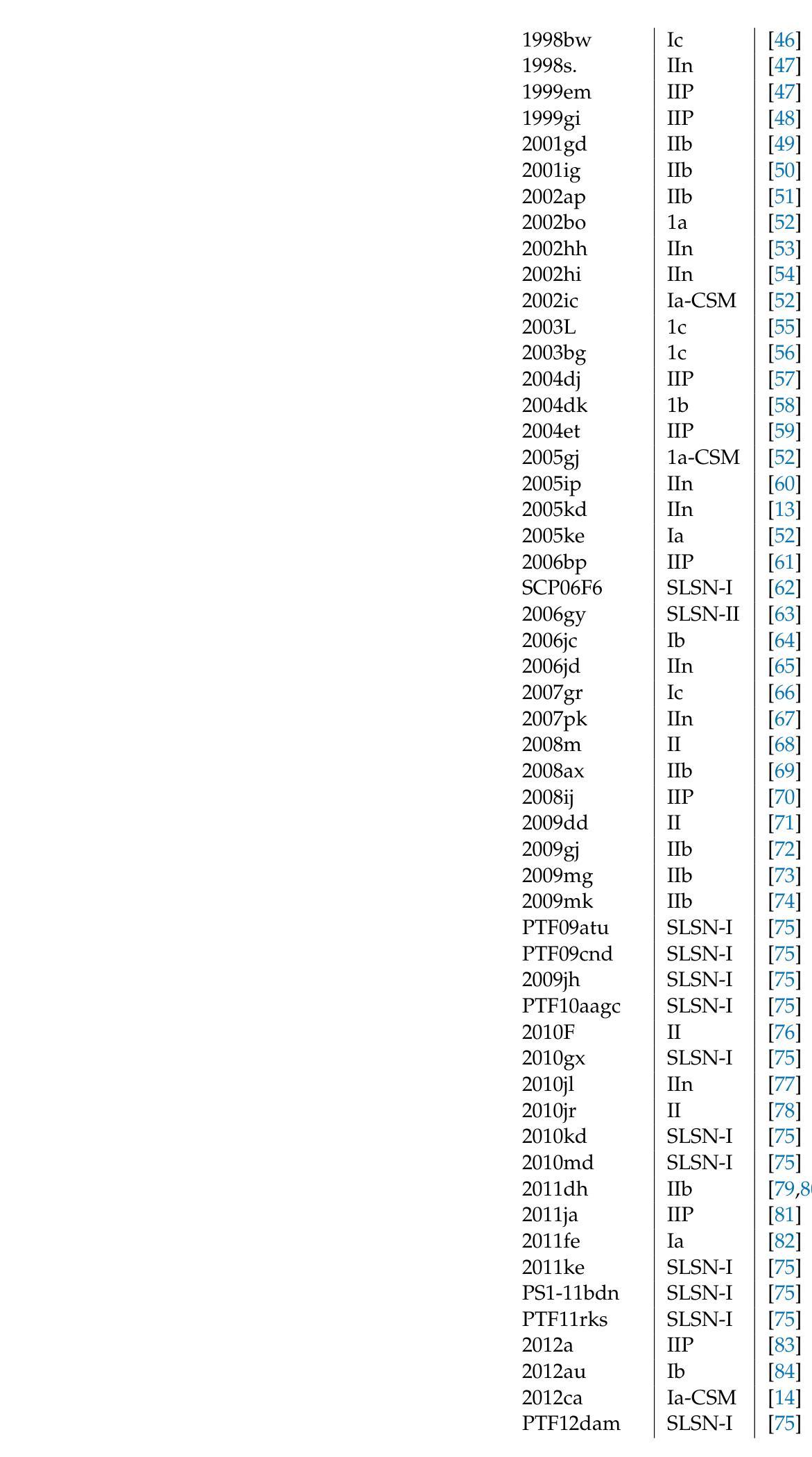
On the X-ray Emission From Supernovae, and Implications for the Mass-Loss Rates of their Progenitor Stars
Authors:Vikram V. Dwarkadas
We summarize the X-ray emission from young SNe. Having accumulated data on most observed X-ray SNe, we display the X-ray lightcurves of young SNe. We also explore the X-ray spectra of various SN types. The X-ray emission from Type Ib/c SNe is non-thermal. It is also likely that the emission from Type IIP SNe with low mass-loss rates (around 10$^{-7} , Msun ,$ yr$^{-1}$) is non-thermal. As the mass-loss rate increases, thermal emission begins to dominate. Type IIn SNe have the highest X-ray luminosities, and are clearly thermal. We do not find evidence of non-thermal emission from Type IIb SNe. The aggregated data are used to obtain approximate mass-loss rates of the progenitor stars of these SNe. Type IIP’s have progenitors with mass-loss rates $< 10^{-5}, Msun ,$ yr$^{-1}$, while Type IIn progenitors generally have mass-loss rates $> 10^{-3}, Msun $ yr$^{-1}$. However, we emphasize that the density of the ambient medium is the important parameter, and if it is due to a non-steady outflow solution, it can not be translated into a mass-loss rate.
我们总结了年轻超新星(SNe)的X射线发射。在积累了大多数观察到的X射线超新星数据后,我们展示了年轻超新星的X射线光度曲线。我们还探讨了各种SN类型的X射线光谱。Ib/c型超新星的X射线发射是非热性的。IIP型超新星在质量损失率较低(约为10$^{-7} , Msun ,$ yr$^{-1}$)的情况下,其发射也可能是非热性的。随着质量损失率的增加,热发射开始占据主导地位。IIn型超新星的X射线光度最高,显然是热性的。我们没有发现IIb型超新星存在非热发射的证据。这些数据汇总后用于获得这些超新星祖星的大致质量损失率。IIP型的祖星质量损失率小于10$^{-5}, Msun ,$ yr$^{-1}$,而IIn型的祖星质量损失率一般大于10$^{-3}, Msun , \text{yr}^{-1}$。然而,我们强调环境介质的密度是重要参数,如果它是由于非稳态流出解决方案导致的,那么不能将其转化为质量损失率。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 33 Pages, 12 Figures, 2 Tables. To be published in the journal “Universe”, in the special issue “A Multiwavelength View of Supernovae”. The figures in this paper update those in Dwarkadas & Gruszko (2012) and should be used preferably. Please let me know by email of any supernovae that I am missing, I will update in subsequent plots
Summary
年轻的超新星(SNe)的X射线发射概述。通过积累大多数观察到的X射线超新星数据,展示了年轻超新星的X射线光度曲线。还探讨了不同类型超新星的X射线光谱。发现某些类型超新星的X射线发射是非热性的,如某些低质量损失率的IIP型超新星。随着质量损失率的增加,热发射开始占据主导地位。IIn型超新星具有最高的X射线光度,并且显然是热性的。没有发现IIb型超新星存在非热性发射的证据。利用综合数据推测了这些超新星前身星的大致质量损失率。发现某些超新星可能适合转化为慢速脉动器(只有存在时才会有快速或慢速的说法)。重要的是指出周围介质的密度是关键参数,而非恒定外流的情况下不能将其转化为质量损失率。这些信息可以帮助更好地理解和预测超新星爆发的行为以及早期演化模型。这些研究对于理解超新星爆炸的物理过程以及早期宇宙演化模型具有重要的科学价值。总的来说,这是一项关于年轻超新星X射线发射特性的重要研究。
Key Takeaways
- 年轻超新星的X射线发射数据被总结并展示了其光度曲线。
- 不同类型超新星的X射线光谱被探讨。
- 一些低质量损失率的超新星X射线发射可能是非热性的。
- 随着质量损失率增加,热发射在超新星X射线发射中的地位逐渐上升。
- IIn型超新星的X射线光度最高,且其发射是热性的。
- 没有证据显示IIb型超新星存在非热性发射。
点此查看论文截图

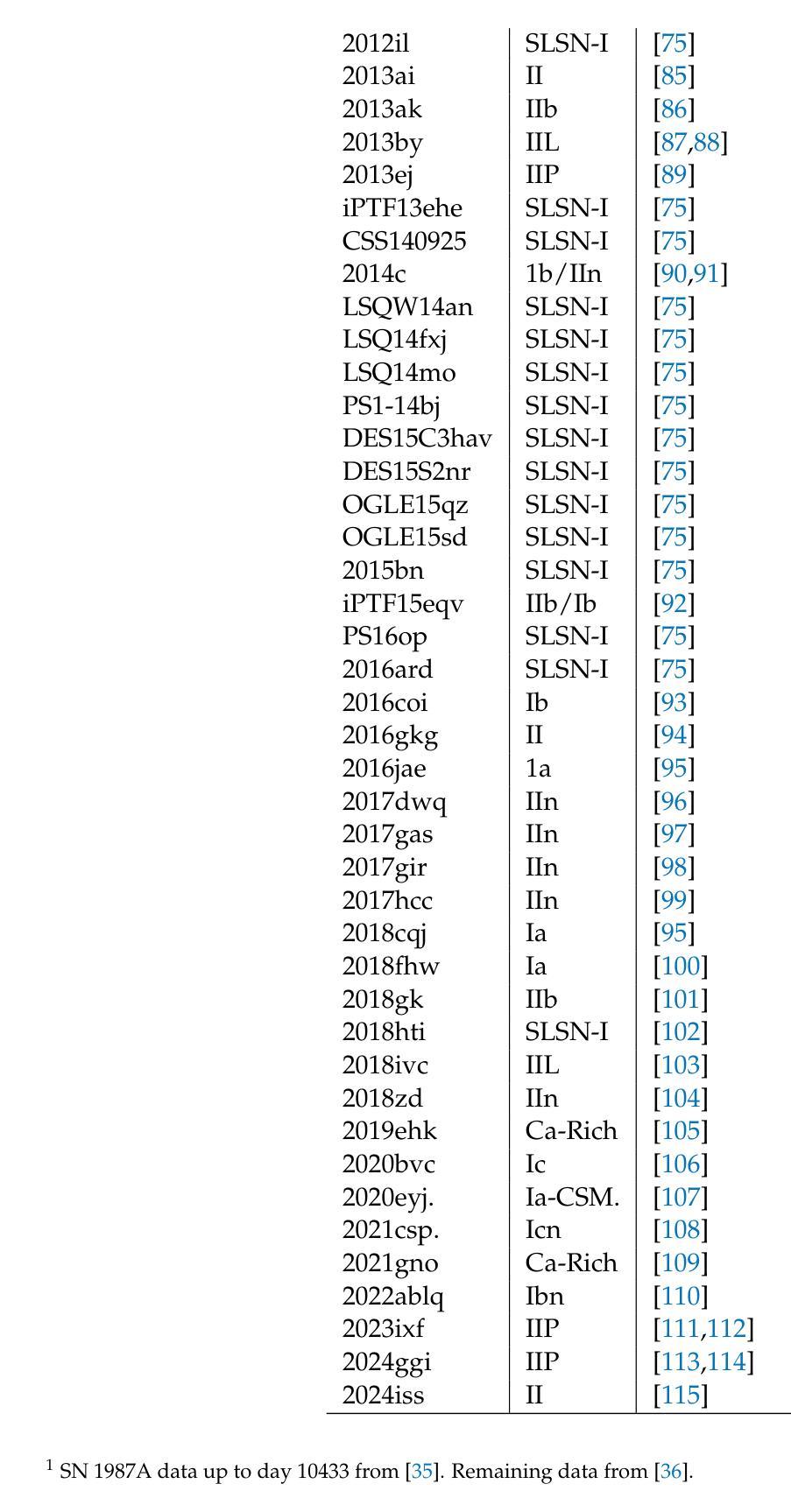
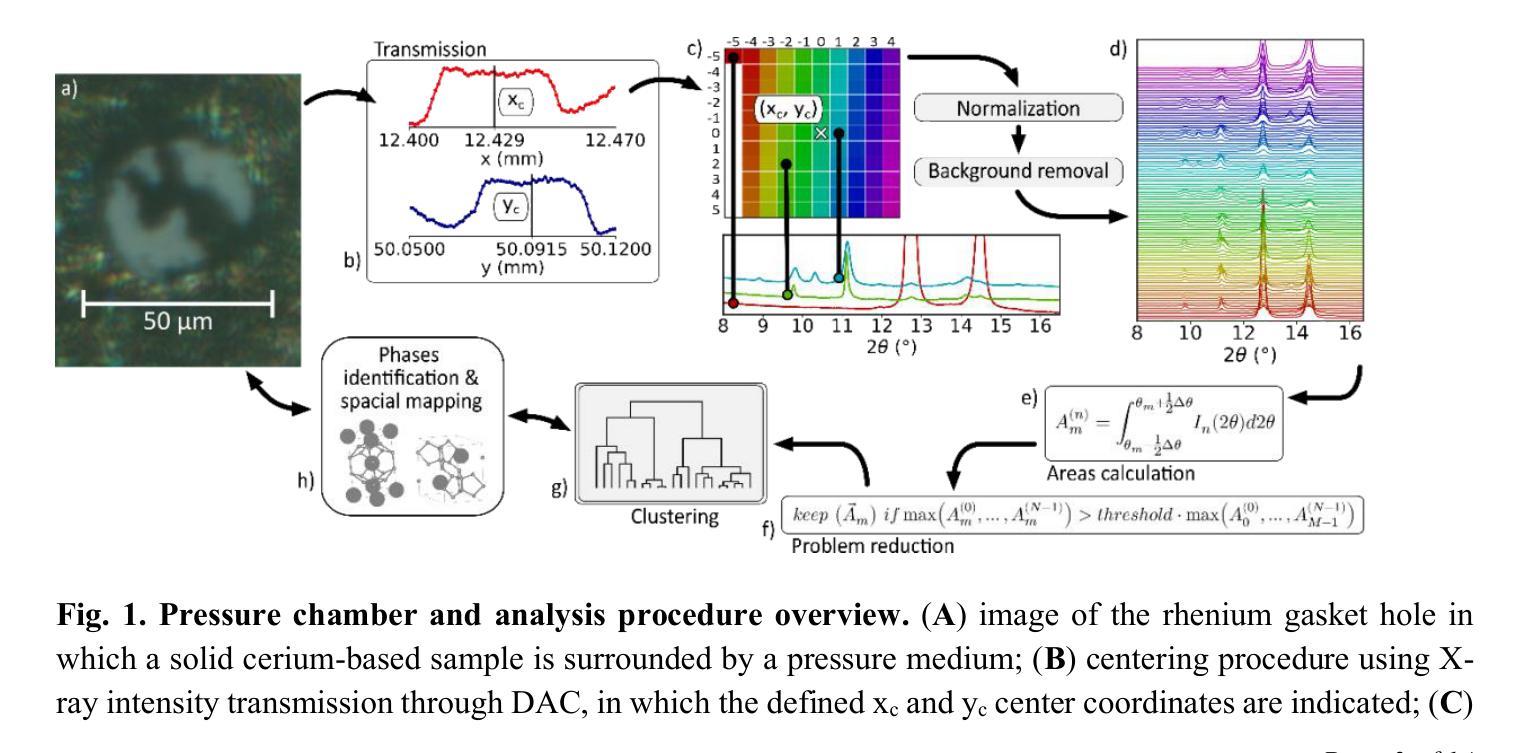
Physics-informed machine learning applied to the identification of high-pressure elusive phases from spatially resolved X-ray diffraction large datasets
Authors:Lucas H. Francisco, Camila M. Araújo, André A. M. C. Silva, Ulisses F. Kaneko, Jairo Fonseca Jr, Guilherme A. Calligaris, Audrey D. Grockowiak, Danusa do Carmo, Ricardo D. dos Reis, Narcizo M. Souza-Neto
Multi-technique high resolution X-ray mapping enhanced by the recent advent of 4th generation synchrotron facilities can produce colossal datasets, challenging traditional analysis methods. Such difficulty is clearly materialized when probing crystal structure of inhomogeneous samples, where the number of diffraction patterns quickly increases with map resolution, making the identification of crystal phases within a vast collection of reflections unfeasibly challenging by direct human inspection. Here we develop a novel analysis approach based on unsupervised clustering algorithms for identifying independent phases within a diffraction spatial map, which allowed us to identify the material distribution across a high-pressure cerium hydride. By investigating the specific compound, we also contribute to the understanding of synthesis inhomogeneities among the superhydrides, a prominent superconductor class in condensed matter physics whose characterization is highly challenging even for state-of-the-art materials techniques. The analysis framework we present may be readily extended to any correlated set of curves whose features are tied to specific entities, such as structural phases.
借助第四代同步加速器设施的最新发展,多技术高分辨率X射线映射能够产生巨大的数据集,对传统分析方法构成挑战。当探测不均匀样品的晶体结构时,这种困难变得尤为明显,随着映射分辨率的提高,衍射图谱的数量迅速增加,使得在大量反射中直接通过人工检查识别晶体相变得不切实际。在这里,我们开发了一种基于无监督聚类算法的新型分析方法,用于识别衍射空间图中的独立相,使我们能够识别高压氢化铈中的材料分布。通过对特定化合物的研究,我们还为理解合成不均匀性对超氢化物(凝聚态物理学中的一种重要超导体,其表征即使是对于最先进的材料技术也是极具挑战性的)的影响做出了贡献。我们提出的分析框架可以很容易地扩展到任何与特定实体(如结构相)相关的曲线集合。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 14 pages, 4 figures,
Summary
本文介绍了利用第四代同步加速器设施的高分辨率X射线映射技术产生的庞大数据集,对于探测非均匀样品的晶体结构带来了挑战。文章提出了一种基于无监督聚类算法的新型分析方法,用于识别衍射空间图中的独立相,通过调查特定化合物为理解合成超氢中的不均匀性做出了贡献。这种分析方法框架可轻松扩展到任何与特定实体相关的曲线集,如结构相。
Key Takeaways
- 高分辨率X射线映射技术面临处理庞大数据集的挑战。
- 无监督聚类算法可用于识别衍射空间图中的独立相。
- 通过分析特定化合物,对理解合成超氢的不均匀性有所贡献。
- 分析方法框架可应用于任何与特定实体相关的曲线集,如结构相。
- 这种新方法在识别高压力下的材料分布方面具有应用潜力。
- 该研究对凝聚态物理学中的超导材料表征提出了挑战。
点此查看论文截图

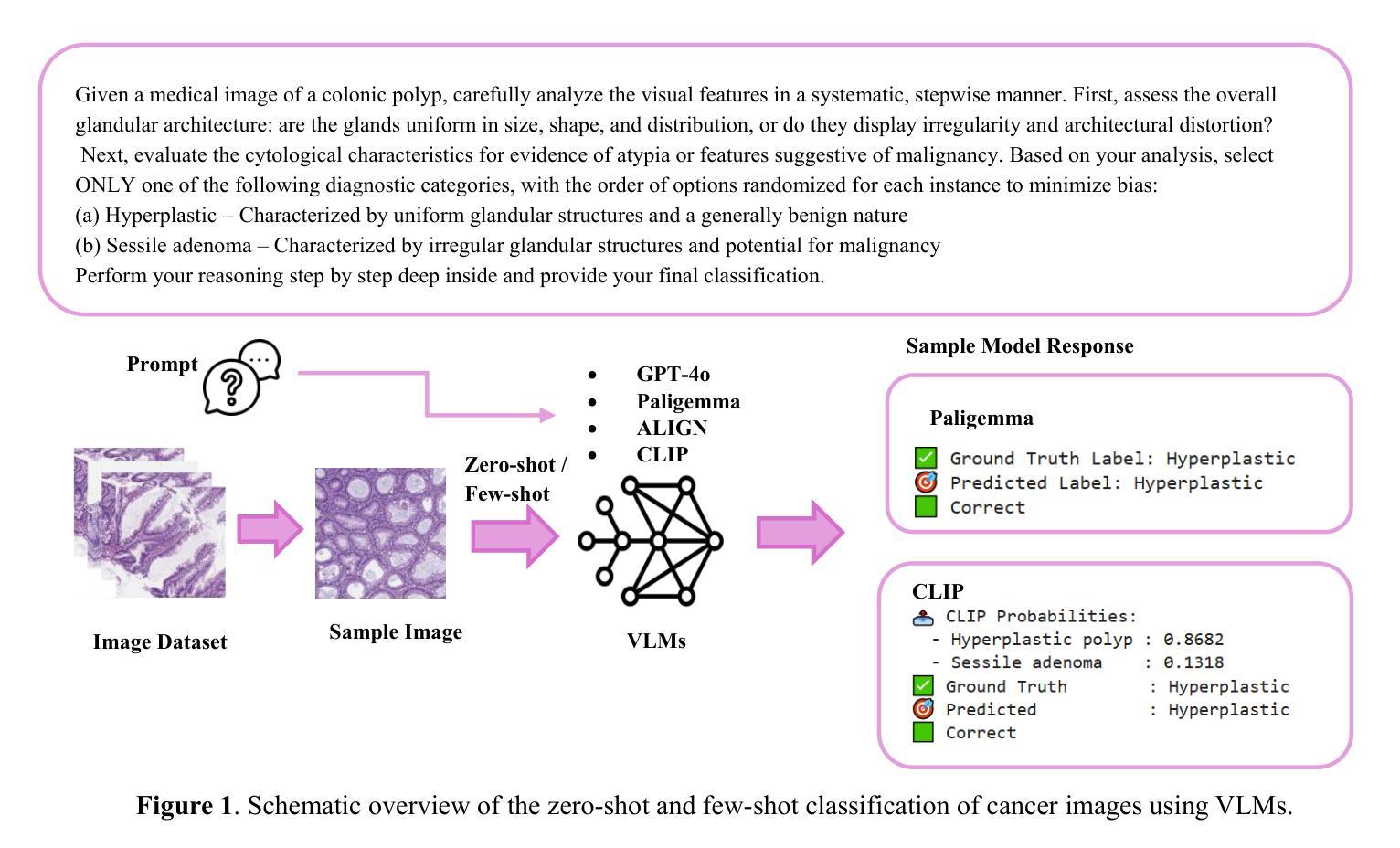
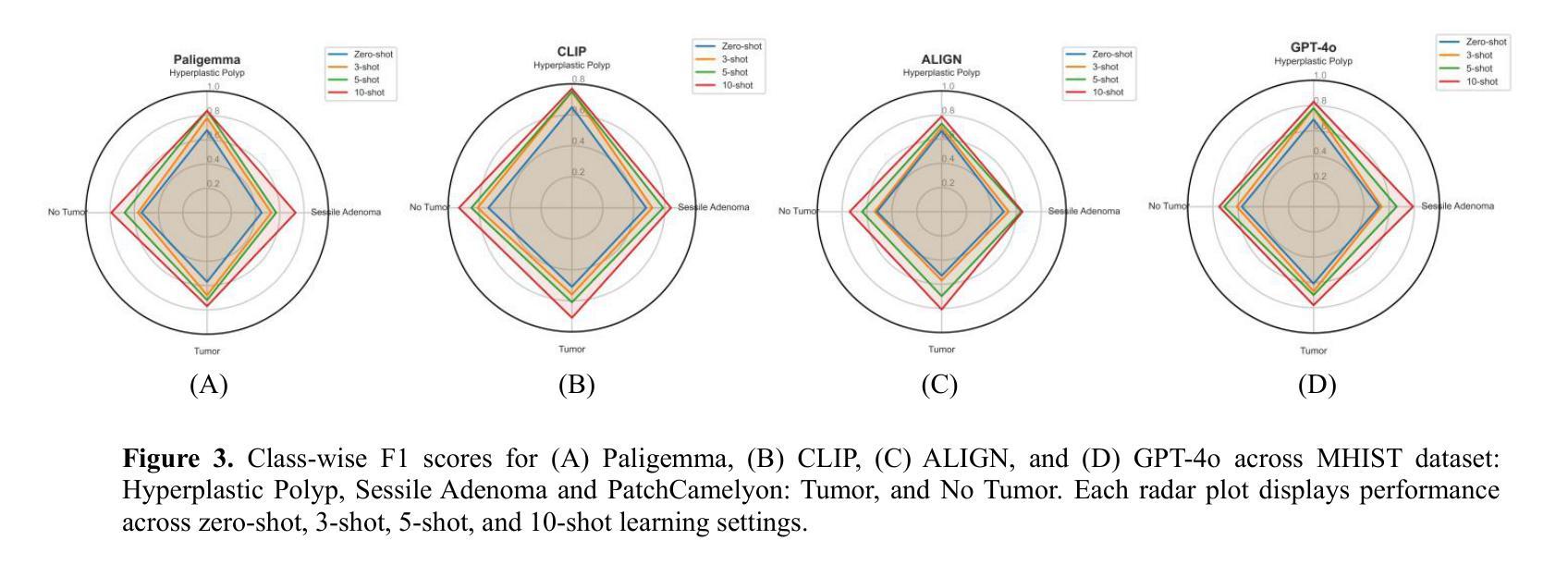
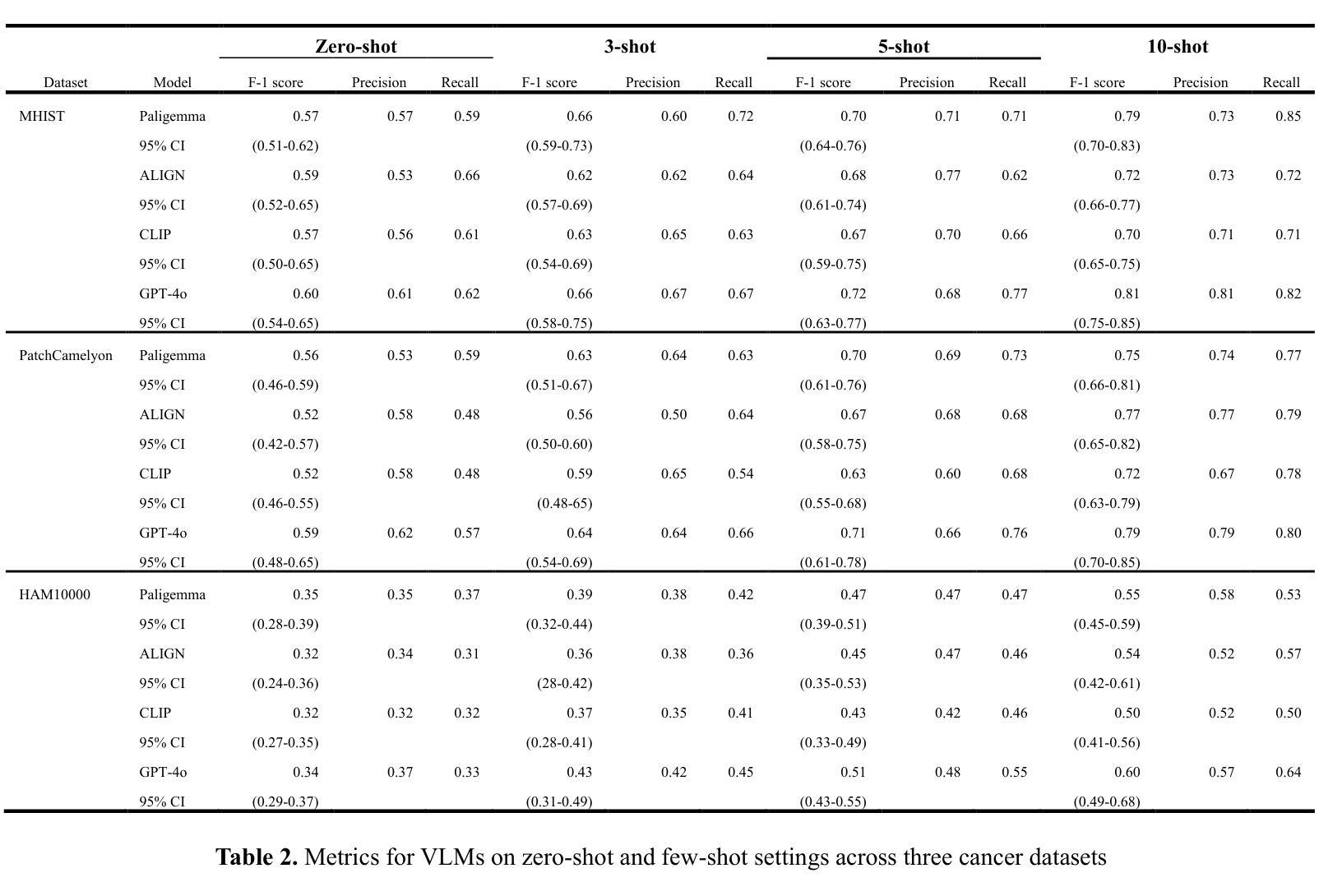
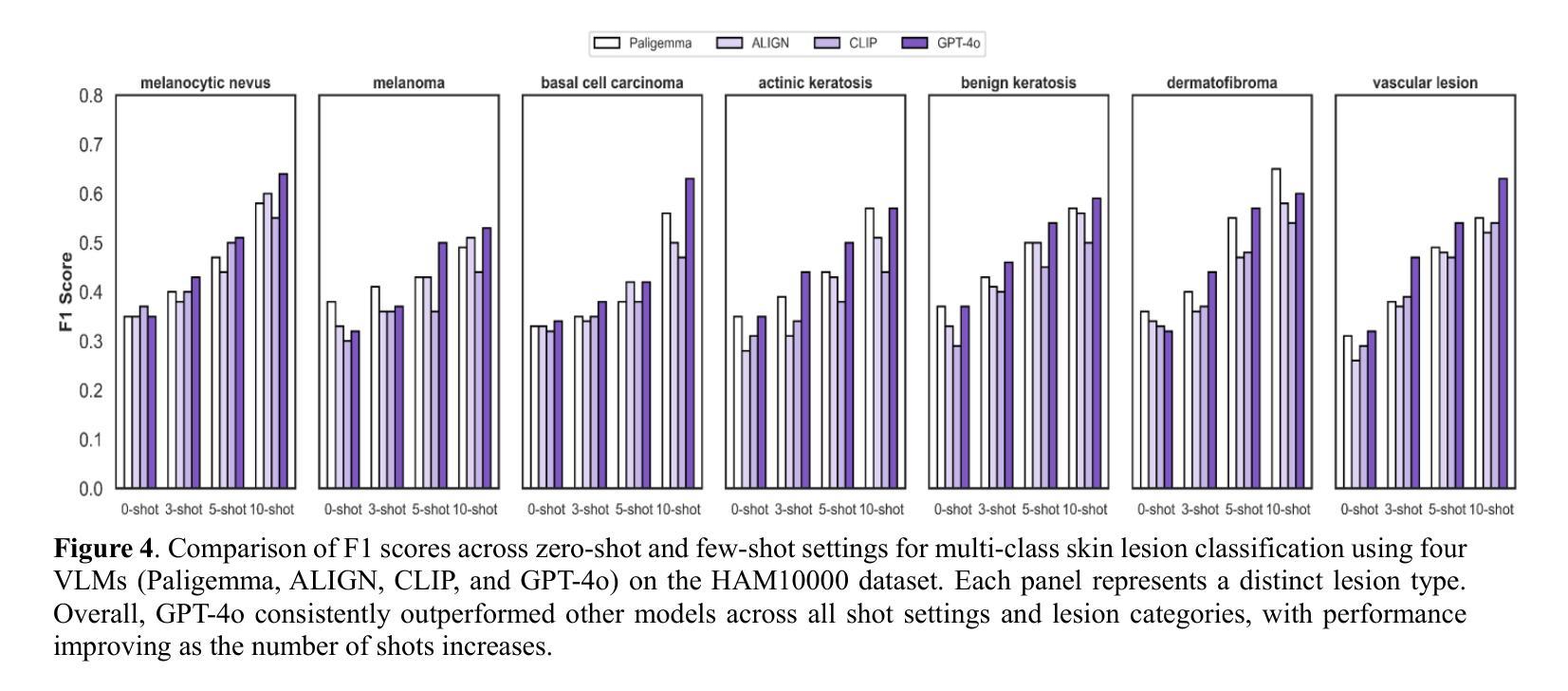
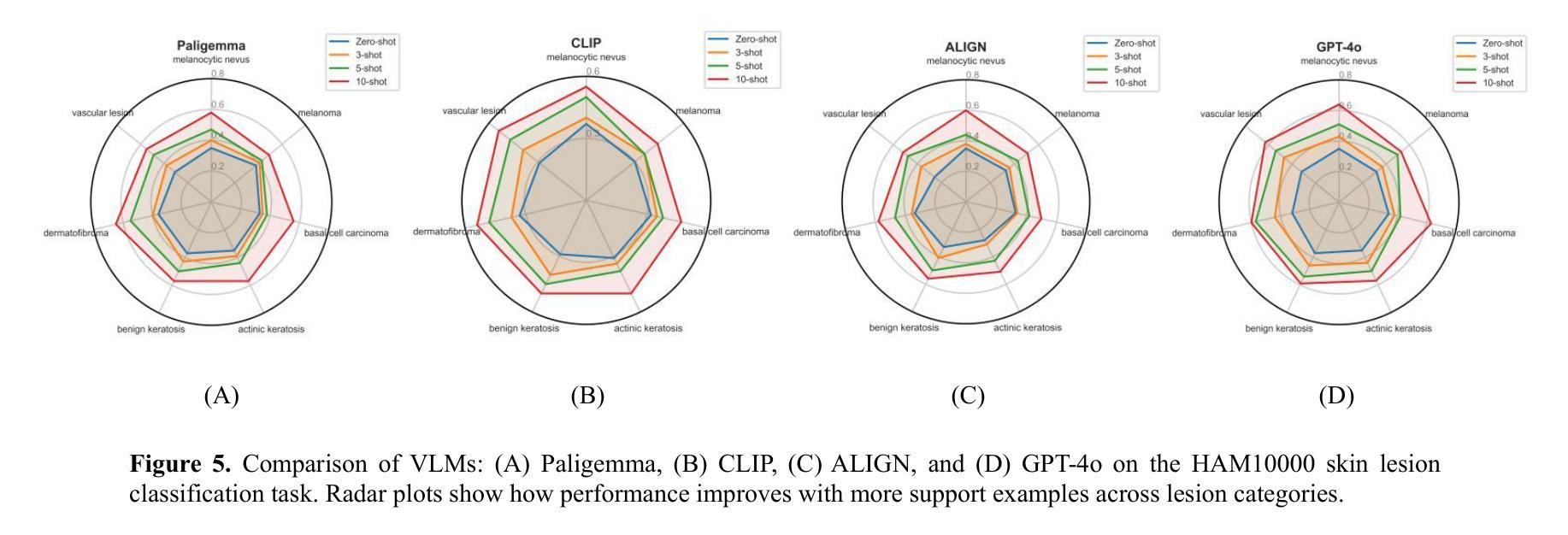
In-Context Learning for Label-Efficient Cancer Image Classification in Oncology
Authors:Mobina Shrestha, Bishwas Mandal, Vishal Mandal, Asis Shrestha
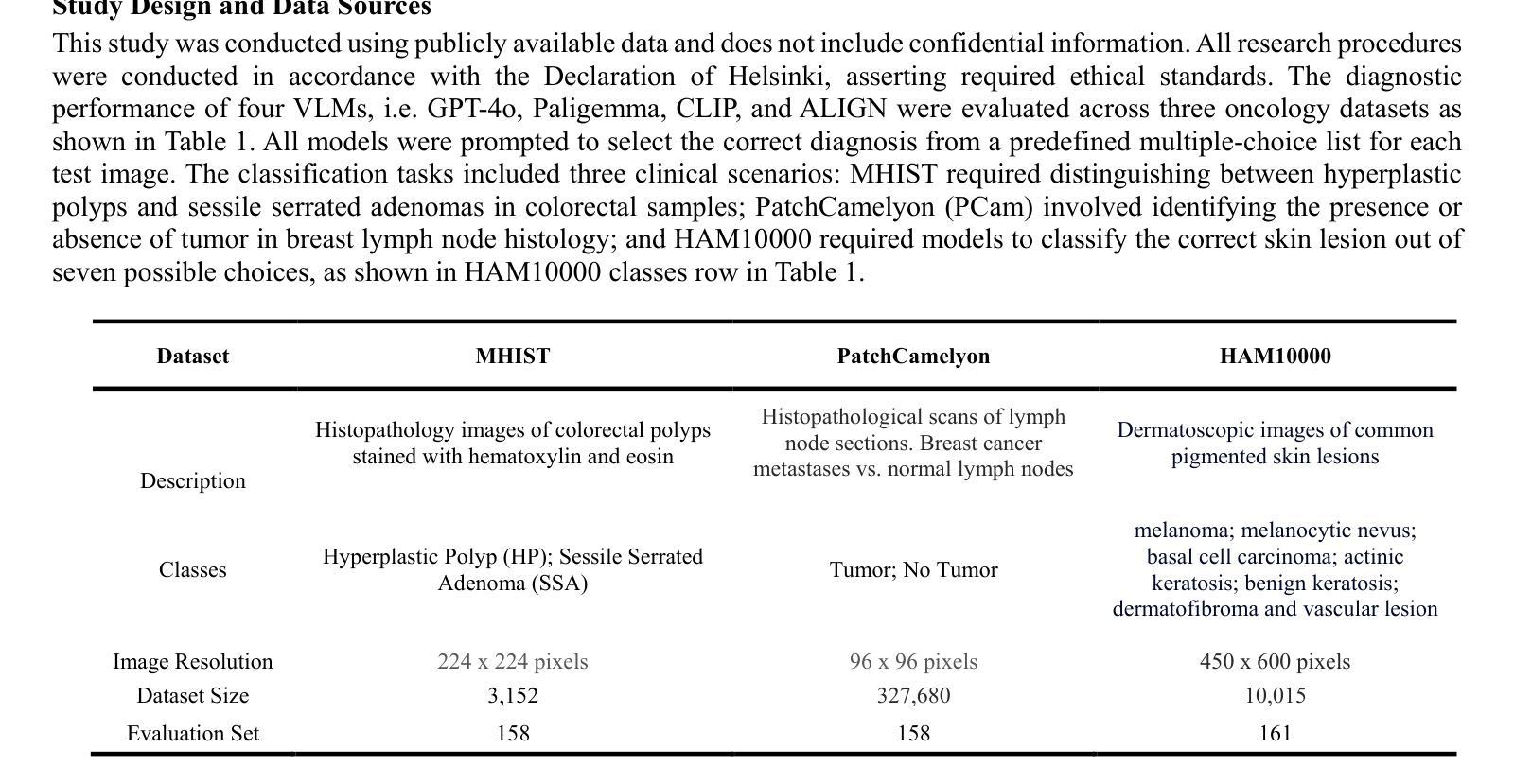
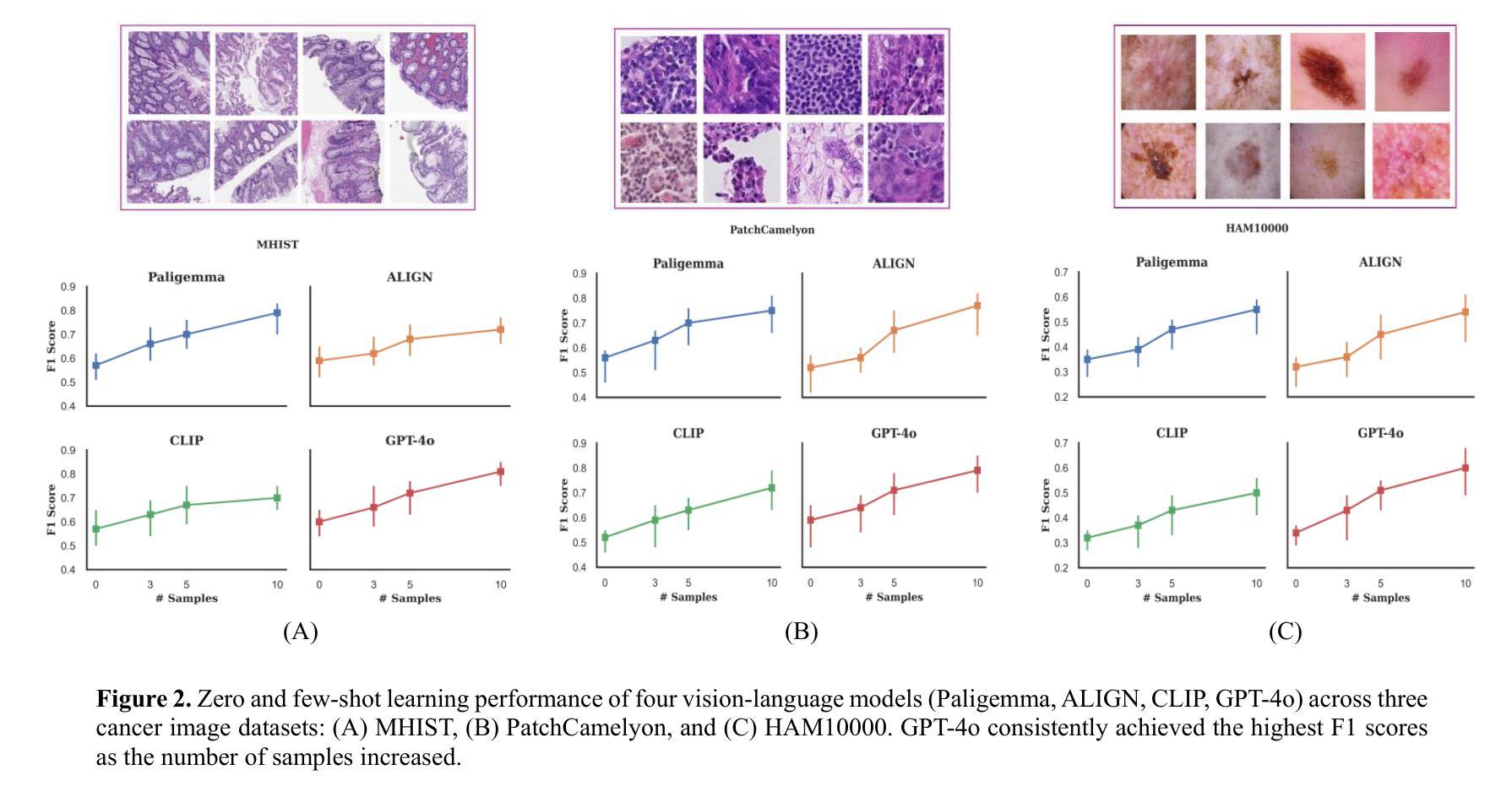
The application of AI in oncology has been limited by its reliance on large, annotated datasets and the need for retraining models for domain-specific diagnostic tasks. Taking heed of these limitations, we investigated in-context learning as a pragmatic alternative to model retraining by allowing models to adapt to new diagnostic tasks using only a few labeled examples at inference, without the need for retraining. Using four vision-language models (VLMs)-Paligemma, CLIP, ALIGN and GPT-4o, we evaluated the performance across three oncology datasets: MHIST, PatchCamelyon and HAM10000. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first study to compare the performance of multiple VLMs on different oncology classification tasks. Without any parameter updates, all models showed significant gains with few-shot prompting, with GPT-4o reaching an F1 score of 0.81 in binary classification and 0.60 in multi-class classification settings. While these results remain below the ceiling of fully fine-tuned systems, they highlight the potential of ICL to approximate task-specific behavior using only a handful of examples, reflecting how clinicians often reason from prior cases. Notably, open-source models like Paligemma and CLIP demonstrated competitive gains despite their smaller size, suggesting feasibility for deployment in computing constrained clinical environments. Overall, these findings highlight the potential of ICL as a practical solution in oncology, particularly for rare cancers and resource-limited contexts where fine-tuning is infeasible and annotated data is difficult to obtain.
人工智能在肿瘤学领域的应用受限于其对大规模标注数据集和针对特定诊断任务重新训练模型的依赖。考虑到这些限制,我们研究了上下文学习作为一种实用的替代模型再训练方法。该方法允许模型在推理过程中仅使用少量标注示例来适应新诊断任务,无需重新训练。我们使用了四种视觉语言模型(VLMs)——Paligemma、CLIP、ALIGN和GPT-4o,并在三个肿瘤学数据集(MHIST、PatchCamelyon和HAM10000)上评估了它们的性能。据我们所知,这是第一项比较多个VLM在不同肿瘤分类任务上性能的研究。在不更新任何参数的情况下,所有模型通过少样本提示都取得了显著的提升,GPT-4o在二分类和多分类设置中的F1分数分别达到了0.81和0.60。虽然这些结果仍低于完全微调系统的上限,但它们突出了上下文学习(ICL)仅使用少数几个例子就能近似特定任务行为的潜力,反映了临床医生经常根据以往病例进行推理的方式。值得注意的是,像Paligemma和CLIP这样的开源模型尽管规模较小,但也表现出了竞争力,这表明它们可以在计算资源受限的临床环境中进行部署是可行的。总体而言,这些研究结果表明,上下文学习在肿瘤学领域具有实际应用潜力,特别是在罕见癌症和资源有限的环境中,微调不可行且难以获得标注数据时。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本研究探索了在肿瘤学领域应用人工智能(AI)时面临的挑战,包括依赖大量标注数据集和需要针对特定诊断任务重新训练模型的问题。通过采用上下文学习(In-Context Learning,ICL)方法,我们评估了四种视觉语言模型(VLMs)在三个肿瘤数据集上的性能。研究结果显示,通过少样本提示,所有模型无需参数更新即可获得显著的性能提升。尽管这些结果仍低于完全微调系统的上限,但研究表明ICL具有仅使用少量示例即可近似特定任务行为的潜力,反映了临床医生常根据以往病例进行推理的方式。总体而言,该研究突显了ICL在肿瘤学中的实际应用潜力,尤其在罕见癌症和资源有限的环境中,微调不可行且获取标注数据困难时,具有实用价值。
Key Takeaways
- AI在肿瘤学中的应用受限于对大规模标注数据集和针对特定诊断任务重新训练模型的需求。
- 采用上下文学习(ICL)方法,无需参数更新即可通过少量标注示例提高模型性能。
- 在三个肿瘤数据集上评估了四种视觉语言模型(VLMs)的性能。
- GPT-4o在二分类和多分类设置下分别达到F1分数0.81和0.60。
- 尽管结果低于完全微调的系统,但ICL显示出近似任务特定行为的潜力,反映临床推理方式。
- 开源模型如Paligemma和CLIP表现出竞争力,适合在计算资源有限的临床环境中部署。
点此查看论文截图

KTaO3(001) Preparation Methods in Vacuum: Effects on Surface Stoichiometry, Crystallography, and in-gap States
Authors:Andrea M. Lucero Manzano, Esteban D. Cantero, Emanuel A. Martínez, F. Y. Bruno, Esteban A. Sánchez, Oscar Grizzi
KTaO3 single crystals with different orientations are used as substrates for the epitaxial growth of thin films and/or as hosts for two-dimensional electron gases. Due to the polar nature of the KTaO3(001) surface, one can expect difficulties and challenges to arise in its preparation. Maintaining good insulating characteristics without adding undesirable in-gap electronic states, obtaining good crystalline order up to the top surface layer, a sufficiently flat surface, and complete cleanliness of the surface (without water, C or OH contaminants), are in general difficult conditions to accomplish simultaneously. Cleaving in vacuum is likely the best option for obtaining a clean surface. However, since KTaO3 is cubic and lacks a well-defined cleavage plane, this method is notsuitable for sample growth or reproducible device fabrication. Here, we systematically evaluate the effect of typical preparation methods applied on the surfaces of KTaO3(001) single crystals. In particular, we used annealing in vacuum at different temperatures, light sputtering with Ar+ ions at low energy (500 eV) followed by annealing, heavy Ar+ ion bombardment and annealing, and grazing Ar+ ion bombardment under continuous azimuthal rotation combined with both annealing in vacuum and in O2 atmosphere. Possible side effects after each treatment are evaluated by a combination of techniques, including low-energy ion scattering at forward angles, Auger electron spectroscopy, low-energy electron energy loss, X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy, low-energy electron diffraction, and time of flightsecondary ion mass spectrometry. Advantages and shortcomings of each preparation method are discussed in detail.
KTaO3单晶具有不同的取向,可作为外延生长薄膜的衬底或二维电子气体的宿主。由于KTaO3(001)表面的极性特征,其制备过程中可能会出现一些困难和挑战。在保持良好的绝缘特性而不增加不需要的带内电子态、获得良好的晶体序达到表层、表面足够平坦以及表面完全清洁(无水分、碳或羟基污染物)的同时,一般很难同时实现这些条件。真空中的劈裂很可能是获得清洁表面的最佳方法。然而,由于KTaO3是立方的并且缺乏明确的劈裂平面,这种方法不适用于样品生长或可重复的器件制造。在这里,我们系统地评估了典型制备方法对KTaO3(001)单晶表面的影响。特别是,我们使用了在真空中的不同温度退火、低能量(500电子伏特)的氩离子轻度溅射后结合退火、重氩离子轰击和退火、以及连续方位旋转下的倾斜氩离子轰击,并结合真空和氧气氛围中的退火处理。通过一系列技术评估每种处理后的可能副作用,包括前向角度下的低能离子散射、俄歇电子光谱、低能电子能量损失、X射线光电子光谱、低能电子衍射以及飞行时间二次离子质谱仪。每种制备方法的优点和缺点都进行了详细讨论。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 30 pages, 8 figures
Summary
KTaO3单晶因其极性表面在制备过程中面临诸多挑战,如保持良好绝缘性、获得良好结晶序、平坦且无污染的表层等。不同制备方法对其表面的影响不同,通过真空退火、轻离子轰击与真空退火等处理方式后,利用多种技术评估处理效果及可能产生的副作用。本文详细讨论了各种制备方法的优缺点。
Key Takeaways
- KTaO3单晶用作外延薄膜生长或二维电子气宿主材料,但其极性表面带来制备挑战。
- 制备过程中需同步实现良好绝缘性、结晶序、平坦表面及无污染物等条件。
- 真空裂解可能是获得干净表面的最佳方法,但KTaO3无明确解理面,不适用于样品生长和可复制器件制造。
- 系统评估了不同表面处理方法对KTaO3(001)单晶表面的影响。
- 处理方法包括真空退火、低能Ar+离子溅射后退火、重离子轰击及在真空和氧气环境下的旋转式Ar+离子轰击等。
- 利用多种技术评估各种处理方法的效果及可能产生的副作用。
点此查看论文截图

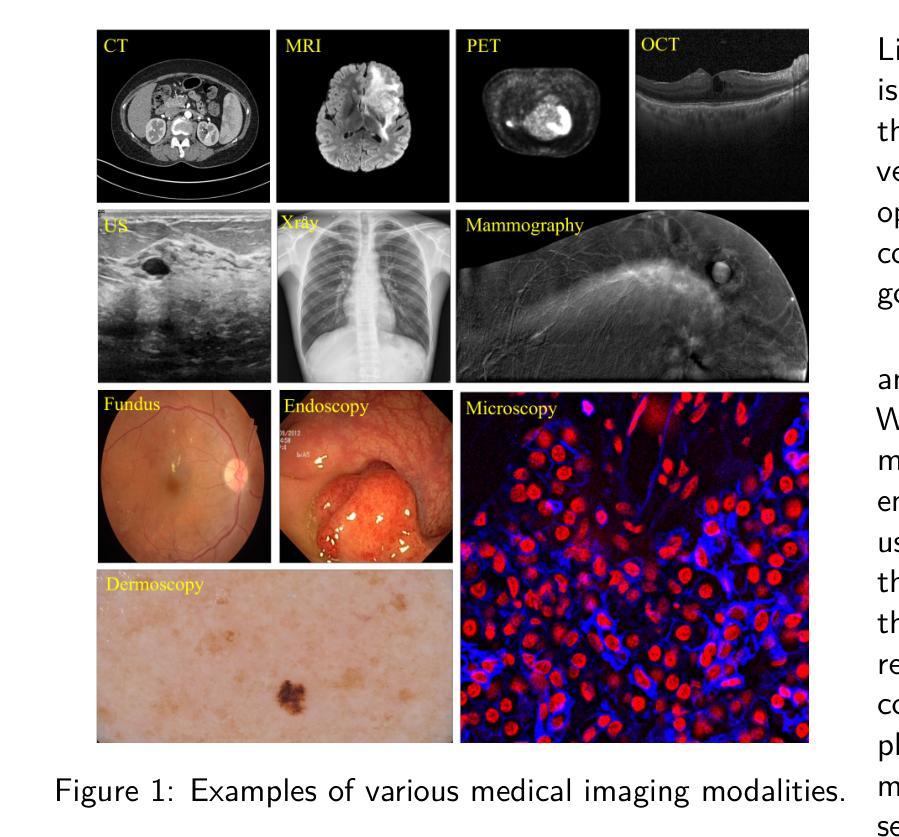
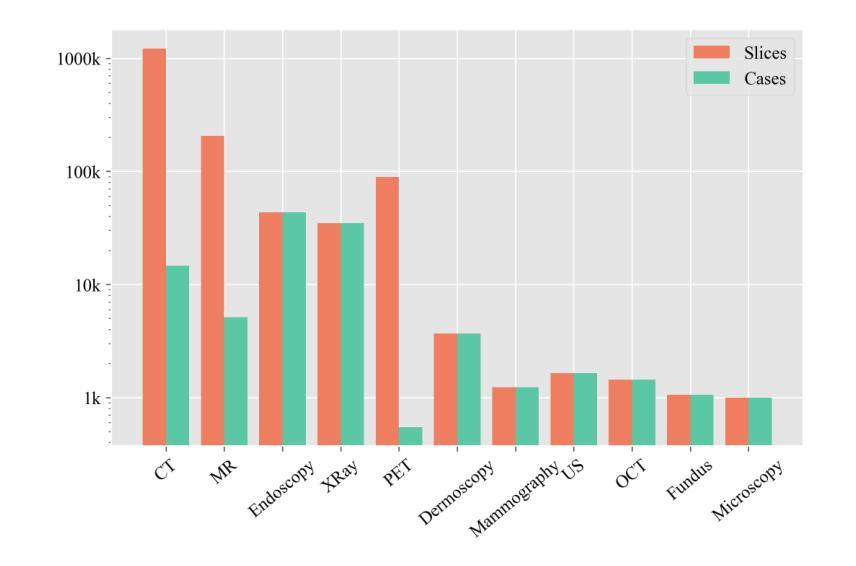
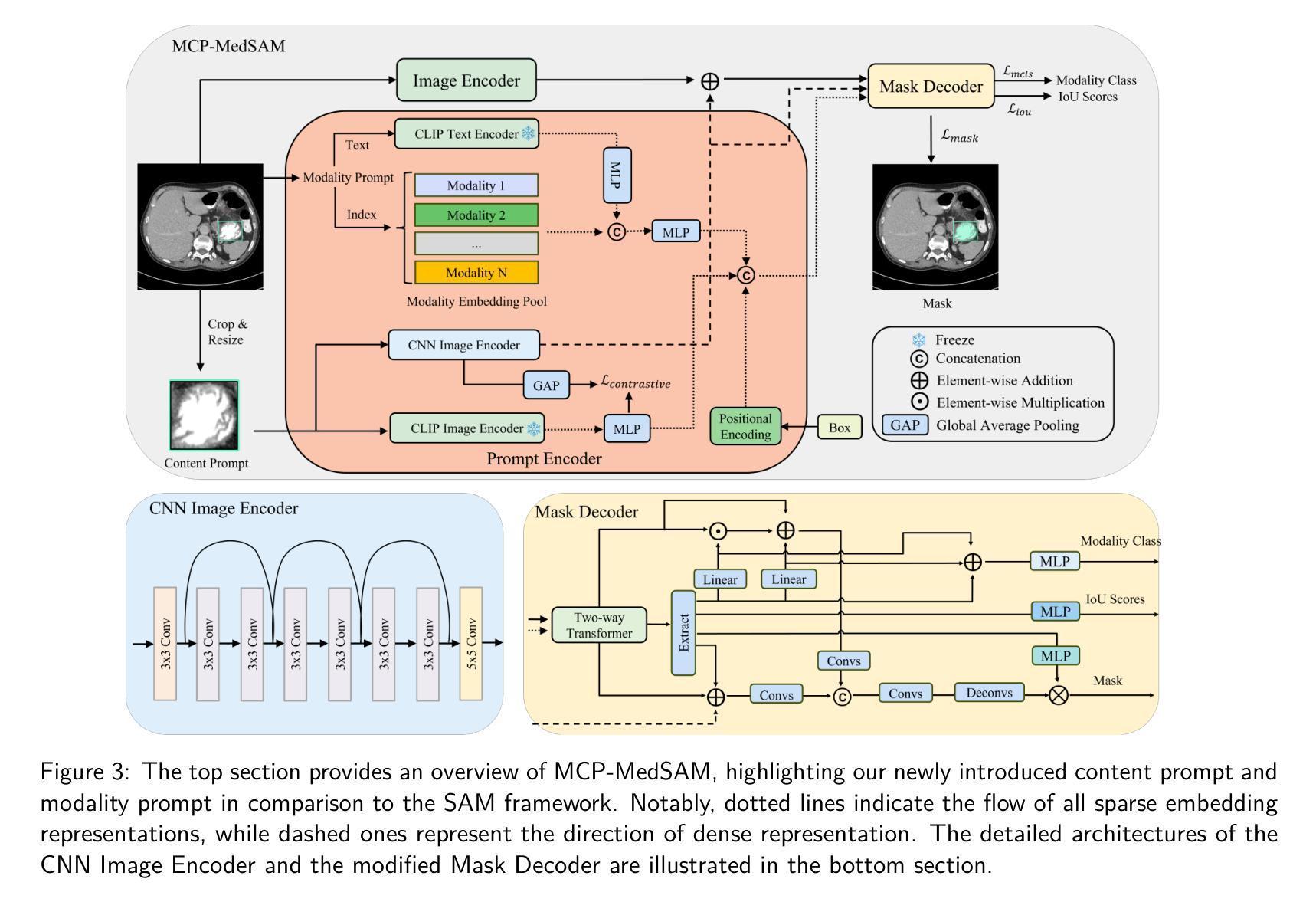
MCP-MedSAM: A Powerful Lightweight Medical Segment Anything Model Trained with a Single GPU in Just One Day
Authors:Donghang Lyu, Ruochen Gao, Marius Staring
Medical image segmentation involves partitioning medical images into meaningful regions, with a focus on identifying anatomical structures and lesions. It has broad applications in healthcare, and deep learning methods have enabled significant advancements in automating this process. Recently, the introduction of the Segmentation Anything Model (SAM), the first foundation model for segmentation task, has prompted researchers to adapt it for the medical domain to improve performance across various tasks. However, SAM’s large model size and high GPU requirements hinder its scalability and development in the medical domain. In this work, we propose MCP-MedSAM, a powerful and lightweight medical SAM model designed to be trainable on a single A100 GPU with 40GB of memory within one day while delivering superior segmentation performance. Recognizing the significant internal differences between modalities and the need for direct segmentation target information within bounding boxes, we introduce two kinds of prompts: the modality prompt and the content prompt. After passing through the prompt encoder, their embedding representations can further improve the segmentation performance by incorporating more relevant information without adding significant training overhead. Additionally, we adopt an effective modality-based data sampling strategy to address data imbalance between modalities, ensuring more balanced performance across all modalities. Our method was trained and evaluated using a large-scale challenge dataset, compared to top-ranking methods on the challenge leaderboard, MCP-MedSAM achieved superior performance while requiring only one day of training on a single GPU. The code is publicly available at \textcolor{blue}{https://github.com/dong845/MCP-MedSAM}.}
医学图像分割涉及将医学图像分割成有意义的区域,重点关注解剖结构和病变的识别。它在医疗保健领域有着广泛的应用,深度学习方法已经能够实现这个过程的自动化,并取得了显著的进展。最近,分割任务的第一基础模型——Segmentation Anything Model(SAM)的引入,促使研究者将其适应于医学领域,以提高各种任务的性能。然而,SAM的大型模型尺寸和高GPU要求限制了其在医学领域的可扩展性和发展。在这项工作中,我们提出了MCP-MedSAM,这是一个强大且轻量级的医学SAM模型,旨在能够在单个A100 GPU上进行训练,并在一天内使用40GB内存提供卓越的分割性能。考虑到不同模态之间的显著内部差异以及需要在边界框内进行直接分割目标信息的需要,我们引入了两种提示:模态提示和内容提示。经过提示编码器的处理,它们的嵌入表示可以进一步通过融入更多相关信息来提高分割性能,而不会增加显著的训练开销。此外,我们采用了一种有效的基于模态的数据采样策略,以解决不同模态之间的数据不平衡问题,确保所有模态的性能更加平衡。我们的方法使用大规模挑战数据集进行训练和评估。与排行榜上的顶尖方法相比,MCP-MedSAM在单个GPU上仅需要一天的训练时间就实现了卓越的性能。代码已公开发布在https://github.com/dong845/MCP-MedSAM。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted for publication at the Journal of Machine Learning for Biomedical Imaging (MELBA)
Summary
本文介绍了医疗图像分割的重要性和在医疗领域的应用。针对Segmentation Anything Model(SAM)在医疗领域应用时存在的模型体积大、GPU需求高等问题,提出了MCP-MedSAM这一轻量级医疗SAM模型。该模型能在单块A100 GPU上完成训练,且性能卓越。通过引入模态提示和内容提示,该模型能够更有效地处理不同模态之间的差异并直接分割目标信息。同时,采用基于模态的数据采样策略解决数据不平衡问题,确保跨所有模态的性能更平衡。实验证明,MCP-MedSAM在大型挑战数据集上的表现优于其他顶尖方法,且训练时间仅需一天。
Key Takeaways
- 医疗图像分割旨在将医学图像分割成有意义的区域,重点识别解剖结构和病变。
- Segmentation Anything Model(SAM)在医疗领域应用存在模型体积大、GPU需求高等问题。
- MCP-MedSAM是一个轻量级的医疗SAM模型,能在单块A100 GPU上完成训练,且性能卓越。
- MCP-MedSAM通过引入模态提示和内容提示,更有效地处理不同模态间的差异并直接分割目标信息。
- 采用基于模态的数据采样策略解决数据不平衡问题。
- MCP-MedSAM在大型挑战数据集上的表现优于其他顶尖方法。
点此查看论文截图