⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-05-16 更新
Streaming Multi-agent Pathfinding
Authors:Mingkai Tang, Lu Gan, Kaichen Zhang
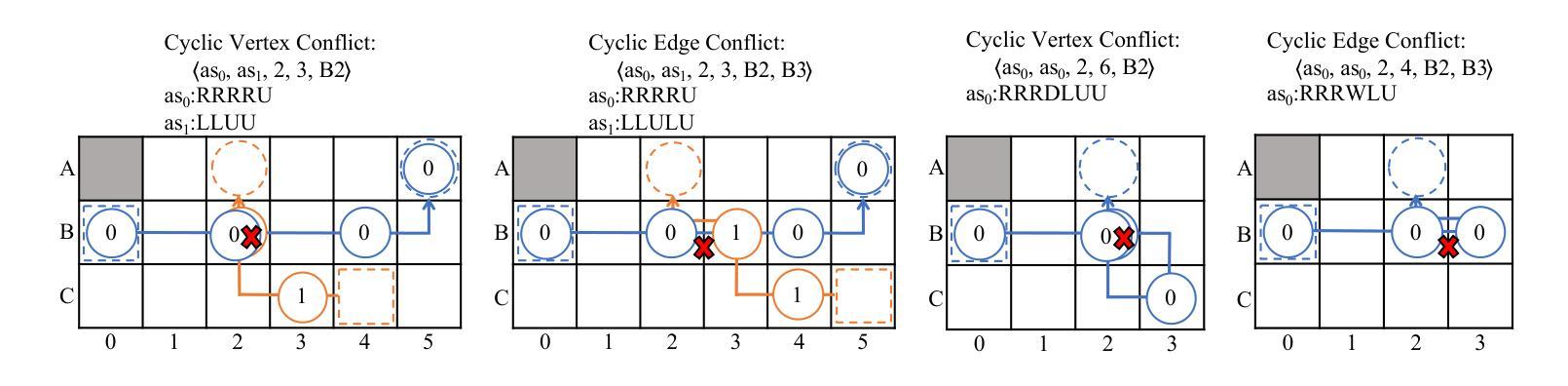
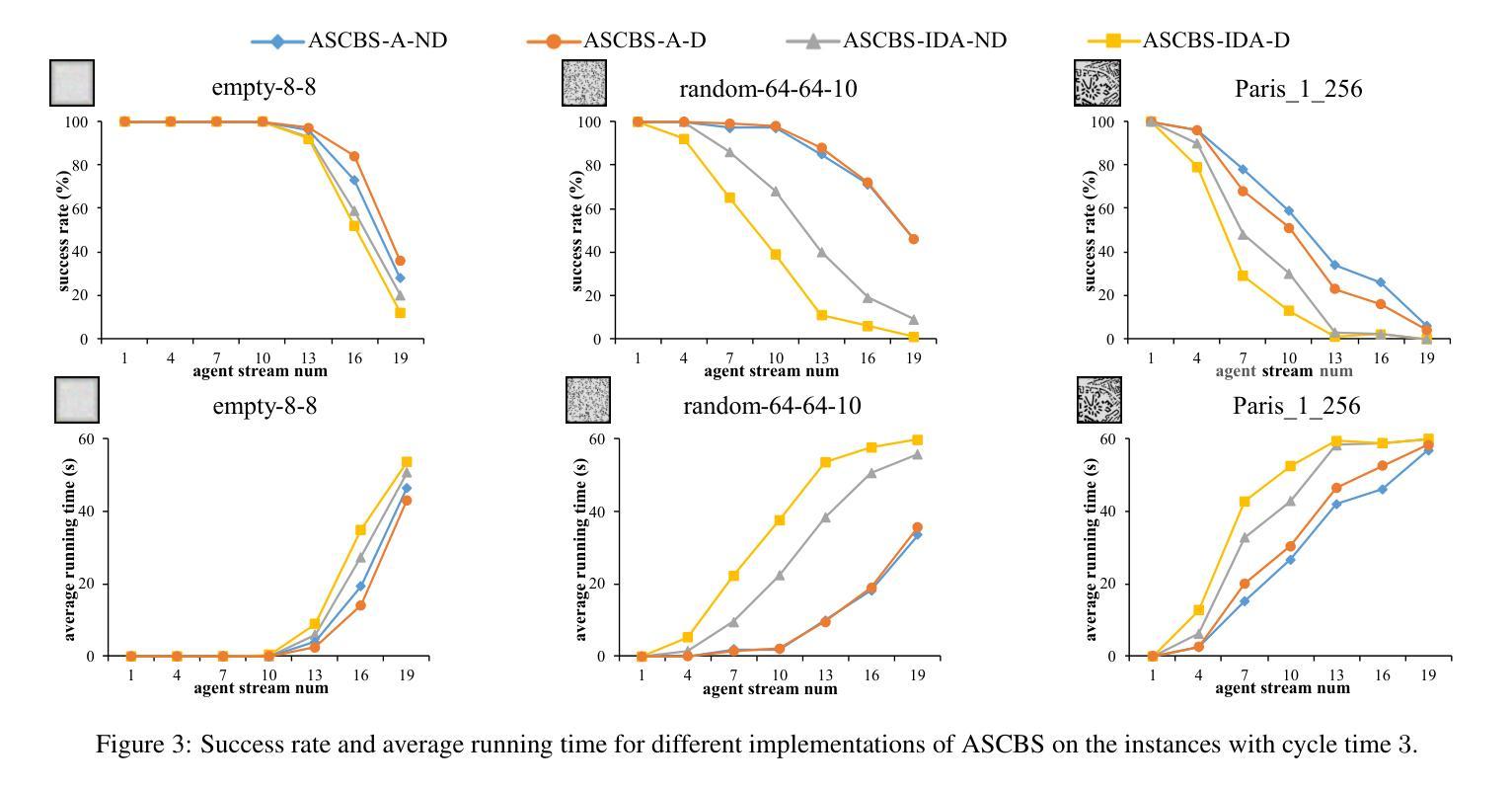
The task of the multi-agent pathfinding (MAPF) problem is to navigate a team of agents from their start point to the goal points. However, this setup is unsuitable in the assembly line scenario, which is periodic with a long working hour. To address this issue, the study formalizes the streaming MAPF (S-MAPF) problem, which assumes that the agents in the same agent stream have a periodic start time and share the same action sequence. The proposed solution, Agent Stream Conflict-Based Search (ASCBS), is designed to tackle this problem by incorporating a cyclic vertex/edge constraint to handle conflicts. Additionally, this work explores the potential usage of the disjoint splitting strategy within ASCBS. Experimental results indicate that ASCBS surpasses traditional MAPF solvers in terms of runtime for scenarios with prolonged working hours.
多智能体路径查找(MAPF)问题的任务是为一组智能体从起点导航到目标点。然而,对于具有长时间工作周期的流水线场景来说,这种设置并不合适。为了解决这一问题,该研究正式提出了流式MAPF(S-MAPF)问题,假设同一智能流中的智能体具有周期性的开始时间并共享相同的动作序列。所提出的解决方案是“基于智能流冲突的搜索”(ASCBS),它通过引入循环顶点/边约束来处理冲突来解决这个问题。此外,这项工作还探讨了ASCBS内部使用不相交分割策略的可能性。实验结果表明,ASCBS在处理长时间工作周期的场景中,在运行时超过了传统的MAPF求解器。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF to be published in IJCAI2025
Summary
在简化多代理路径查找(MAPF)问题中,任务是为团队中的代理提供从起点到目标点的导航路径。然而,对于流水线场景而言,由于其周期性长时间工作的特点,这种设置不适用。该研究解决了流多代理路径查找(S-MAPF)问题,假定代理具有周期性开始时间并共享相同的动作序列。提出的解决方案Agent Stream冲突基于搜索(ASCBS)通过引入循环顶点/边约束来解决冲突问题。实验结果表明,ASCBS在长时间工作场景下运行时超越传统MAPF求解器。
Key Takeaways
- 多代理路径查找(MAPF)旨在帮助团队代理从起点导航至目标点。
- 流水线场景具有周期性长时间工作的特点,使得传统MAPF设置不适用。
- 提出流多代理路径查找(S-MAPF)问题,考虑代理的周期性开始时间和共享动作序列。
- ASCBS算法通过引入循环顶点/边约束来解决冲突问题。
- ASCBS算法探索了不相交分割策略的应用潜力。
点此查看论文截图


Towards Autonomous UAV Visual Object Search in City Space: Benchmark and Agentic Methodology
Authors:Yatai Ji, Zhengqiu Zhu, Yong Zhao, Beidan Liu, Chen Gao, Yihao Zhao, Sihang Qiu, Yue Hu, Quanjun Yin, Yong Li
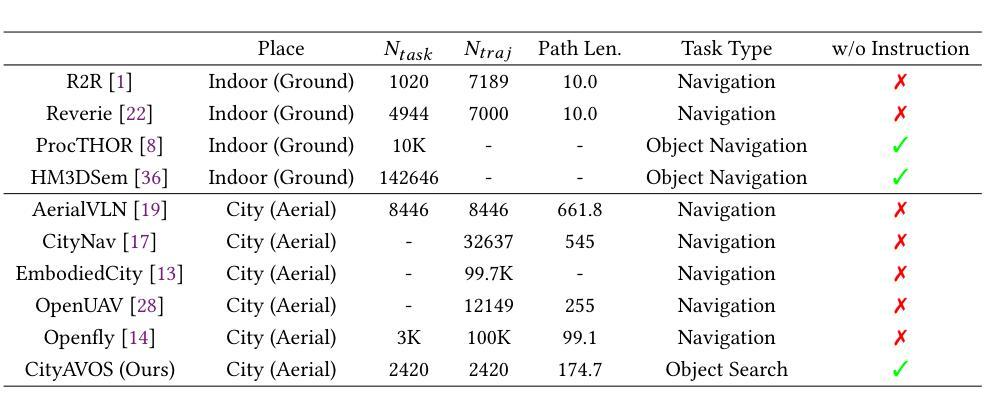
Aerial Visual Object Search (AVOS) tasks in urban environments require Unmanned Aerial Vehicles (UAVs) to autonomously search for and identify target objects using visual and textual cues without external guidance. Existing approaches struggle in complex urban environments due to redundant semantic processing, similar object distinction, and the exploration-exploitation dilemma. To bridge this gap and support the AVOS task, we introduce CityAVOS, the first benchmark dataset for autonomous search of common urban objects. This dataset comprises 2,420 tasks across six object categories with varying difficulty levels, enabling comprehensive evaluation of UAV agents’ search capabilities. To solve the AVOS tasks, we also propose PRPSearcher (Perception-Reasoning-Planning Searcher), a novel agentic method powered by multi-modal large language models (MLLMs) that mimics human three-tier cognition. Specifically, PRPSearcher constructs three specialized maps: an object-centric dynamic semantic map enhancing spatial perception, a 3D cognitive map based on semantic attraction values for target reasoning, and a 3D uncertainty map for balanced exploration-exploitation search. Also, our approach incorporates a denoising mechanism to mitigate interference from similar objects and utilizes an Inspiration Promote Thought (IPT) prompting mechanism for adaptive action planning. Experimental results on CityAVOS demonstrate that PRPSearcher surpasses existing baselines in both success rate and search efficiency (on average: +37.69% SR, +28.96% SPL, -30.69% MSS, and -46.40% NE). While promising, the performance gap compared to humans highlights the need for better semantic reasoning and spatial exploration capabilities in AVOS tasks. This work establishes a foundation for future advances in embodied target search. Dataset and source code are available at https://anonymous.4open.science/r/CityAVOS-3DF8.
无人机在城区环境中执行空中视觉目标搜索(AVOS)任务,需要自主利用视觉和文字线索进行目标对象的搜索和识别,而无需外部指导。现有的方法在处理复杂的城市环境时面临困难,如冗余语义处理、相似对象区分以及探索与开发困境等问题。为了缩小这一差距并支持AVOS任务,我们引入了CityAVOS数据集,这是针对城市常见对象自主搜索的第一个基准数据集。该数据集包含六个不同难度级别的对象类别的共2,420个任务,能够全面评估无人机搜索能力的评估。为了解决AVOS任务,我们还提出了PRPSearcher(感知推理规划搜索器),这是一种由多模态大型语言模型(MLLMs)驱动的新型智能方法,可模拟人类的三层认知。具体来说,PRPSearcher构建了三张专门的地图:一张增强空间感知的对象中心动态语义地图,一张基于目标推理的语义吸引值的3D认知地图,以及一张平衡探索与开发的3D不确定性地图。此外,我们的方法还加入了一种去噪机制以减轻来自相似对象的干扰,并使用了一种名为“灵感促进思考”(IPT)的提示机制来进行自适应行动规划。在CityAVOS上的实验结果表明,PRPSearcher在成功率和搜索效率上均超越了现有基线(平均成功率提高+37.69%,SPL提高+28.96%,MSS减少-30.69%,NE减少-46.40%)。虽然取得了不错的成果,但与人类相比还存在性能差距,这凸显了在AVOS任务中需要更好的语义推理和空间探索能力。这项工作为未来的嵌入式目标搜索研究奠定了基础。数据集和源代码可通过https://anonymous.4open.science/r/CityAVOS-3DF8获取。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
该文本介绍了在城市环境中无人机进行空中视觉目标搜索(AVOS)的任务挑战和现状。为了解决这个问题,引入了CityAVOS数据集和PRPSearcher方法。PRPSearcher利用多模态大型语言模型(MLLMs)模拟人类的三层认知结构,通过构建三种特殊地图和采用降噪机制等方法,提高了无人机在AVOS任务中的搜索能力和效率。实验结果表明,PRPSearcher在成功率和搜索效率上均超过了现有基线。然而,与人类相比仍存在性能差距,强调了语义推理和空间探索能力在AVOS任务中的重要性。
Key Takeaways
- AVOS任务要求无人机在城市环境中自主搜索和识别目标对象,但现有方法面临复杂环境的挑战。
- 引入CityAVOS数据集,包含2420个任务和六个对象类别,用于评估无人机的搜索能力。
- PRPSearcher方法模拟人类的三层认知结构,通过构建三种特殊地图提高无人机的搜索效率和成功率。
- PRPSearcher采用降噪机制和IPT提示机制来处理类似物体的干扰和适应性行动规划。
- 实验结果表明PRPSearcher在AVOS任务中超过现有基线,但在与人类性能对比中仍存在差距。
- 语义推理和空间探索能力在AVOS任务中至关重要。
点此查看论文截图


Agent RL Scaling Law: Agent RL with Spontaneous Code Execution for Mathematical Problem Solving
Authors:Xinji Mai, Haotian Xu, Xing W, Weinong Wang, Yingying Zhang, Wenqiang Zhang
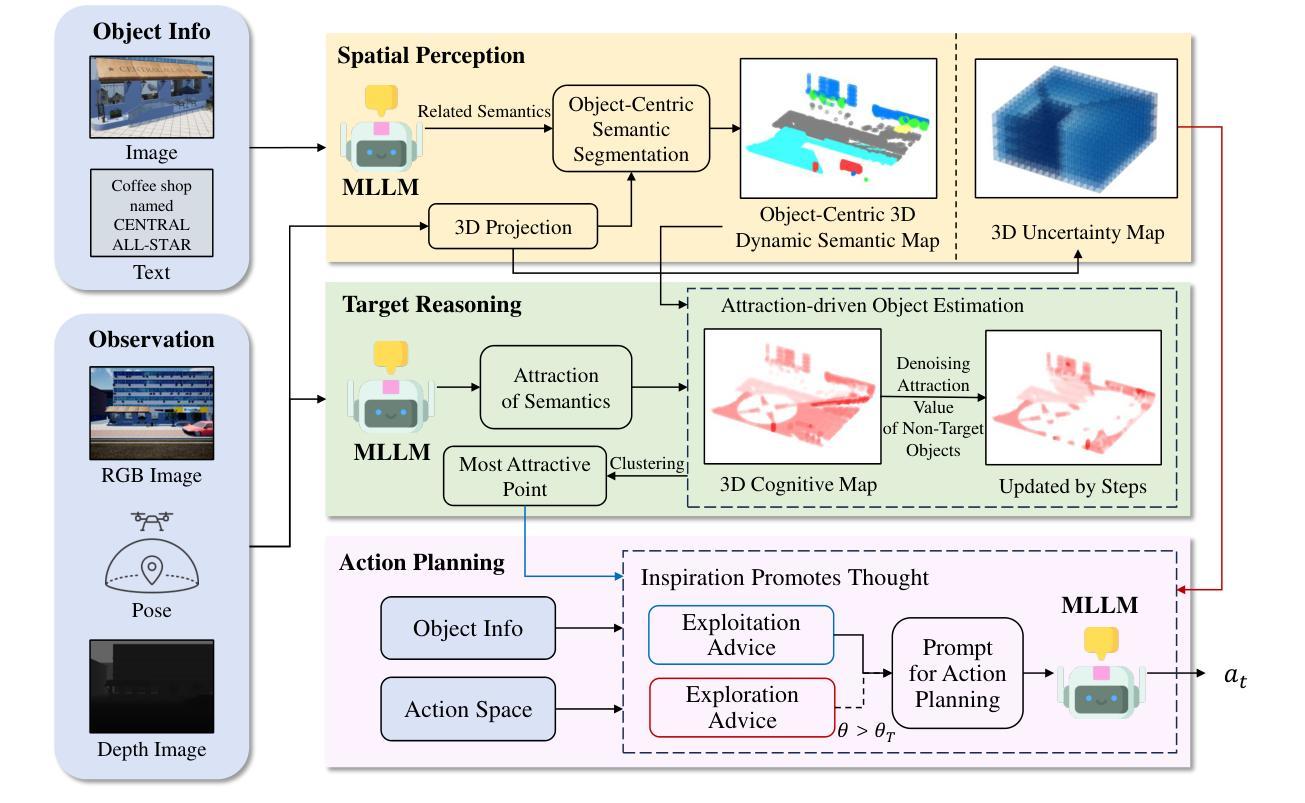
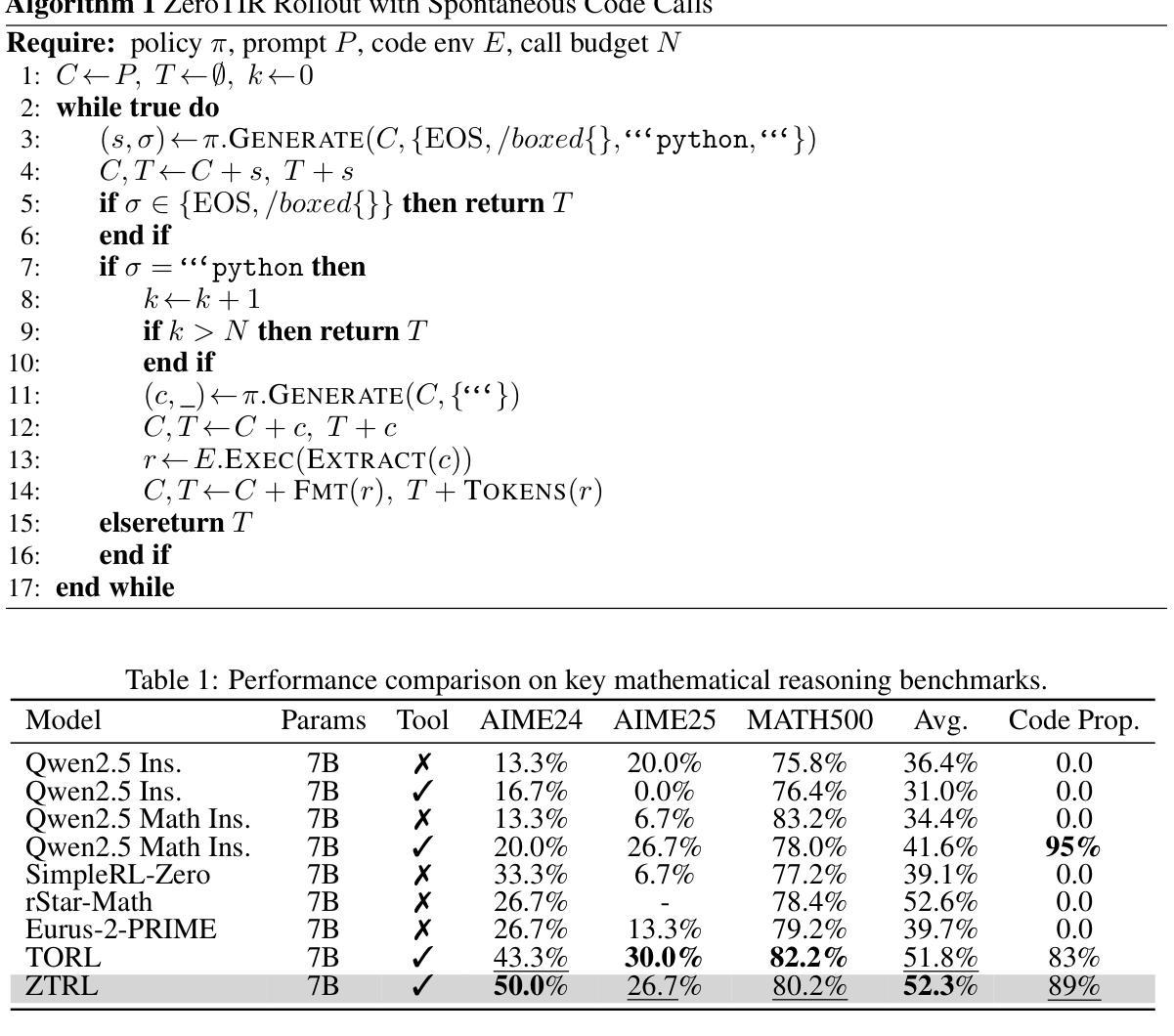
Large Language Models (LLMs) often struggle with mathematical reasoning tasks requiring precise, verifiable computation. While Reinforcement Learning (RL) from outcome-based rewards enhances text-based reasoning, understanding how agents autonomously learn to leverage external tools like code execution remains crucial. We investigate RL from outcome-based rewards for Tool-Integrated Reasoning, ZeroTIR, training base LLMs to spontaneously generate and execute Python code for mathematical problems without supervised tool-use examples. Our central contribution is we demonstrate that as RL training progresses, key metrics scale predictably. Specifically, we observe strong positive correlations where increased training steps lead to increases in the spontaneous code execution frequency, the average response length, and, critically, the final task accuracy. This suggests a quantifiable relationship between computational effort invested in training and the emergence of effective, tool-augmented reasoning strategies. We implement a robust framework featuring a decoupled code execution environment and validate our findings across standard RL algorithms and frameworks. Experiments show ZeroTIR significantly surpasses non-tool ZeroRL baselines on challenging math benchmarks. Our findings provide a foundational understanding of how autonomous tool use is acquired and scales within Agent RL, offering a reproducible benchmark for future studies. Code is released at \href{https://github.com/yyht/openrlhf_async_pipline}{https://github.com/yyht/openrlhf\_async\_pipline}.
大型语言模型(LLM)通常在需要精确、可验证计算的数学推理任务上表现挣扎。虽然基于结果奖励的强化学习(RL)增强了文本推理能力,但了解智能体如何自主学习利用如代码执行等外部工具仍然至关重要。我们研究了基于结果奖励的强化学习在工具集成推理(Tool-Integrated Reasoning)方面的应用,即ZeroTIR。我们训练基础LLM,使其能够针对数学问题自发生成并执行Python代码,而无需监督的工具使用示例。我们的主要贡献是,我们证明了随着强化学习训练的进行,关键指标的可预测性。具体来说,我们观察到强烈的正相关关系,更多的训练步骤导致自发代码执行频率、平均响应长度和最终任务准确度的提高。这表明在训练中所投入的计算努力与有效工具增强推理策略的出现之间存在可量化的关系。我们实施了一个稳健的框架,其中包括一个解耦的代码执行环境,并对标准强化学习算法和框架验证了我们的发现。实验表明,ZeroTIR在具有挑战性的数学基准测试上显著超越了非工具ZeroRL基线。我们的研究为自主工具获取如何在代理强化学习中获得并扩展提供了基础理解,并为未来的研究提供了可复制的基准。相关代码已发布在:[https://github.com/yyht/openrlhf_async_pipline。](点击链接即可访问。)
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
大型语言模型(LLM)在处理需要精确可验证计算的数学推理任务时表现欠佳。本研究通过强化学习(RL)从结果导向的奖励出发,探究工具集成推理(Tool-Integrated Reasoning)的自主学习策略。本研究通过ZeroTIR训练基础LLM,使其无需监督工具使用示例,即可为数学问题自发生成并执行Python代码。研究发现,随着RL训练的进行,关键指标呈现可预测的增长趋势。特别是观察到训练步骤的增加导致自发代码执行频率、平均响应长度和任务准确率的提高。这表明训练中的计算投入与有效工具增强推理策略的出现之间存在可量化的关系。本研究实施了一个稳健的框架,其中包括解耦的代码执行环境,并在标准RL算法和框架上验证了这些发现。实验表明,ZeroTIR在非工具ZeroRL基准测试上表现显著超越挑战数学基准测试的结果。本研究为自主工具使用在Agent RL中的获取和扩展提供了基础理解,并为未来的研究提供了可复制的标准。
Key Takeaways
- 大型语言模型在数学推理任务上的表现存在不足。
- 强化学习(RL)在工具集成推理中的应用有助于提升LLM的自发代码生成和执行能力。
- 随着训练步骤的增加,LLM的自发代码执行频率、平均响应长度和任务准确率均有显著提高。
- 训练中的计算投入与有效工具增强推理策略的出现存在可量化的关系。
- 实施了一个稳健的框架来验证这些发现,其中包括解耦的代码执行环境。
- ZeroTIR在非工具ZeroRL基准测试上的表现显著超越挑战数学基准测试的结果。
点此查看论文截图



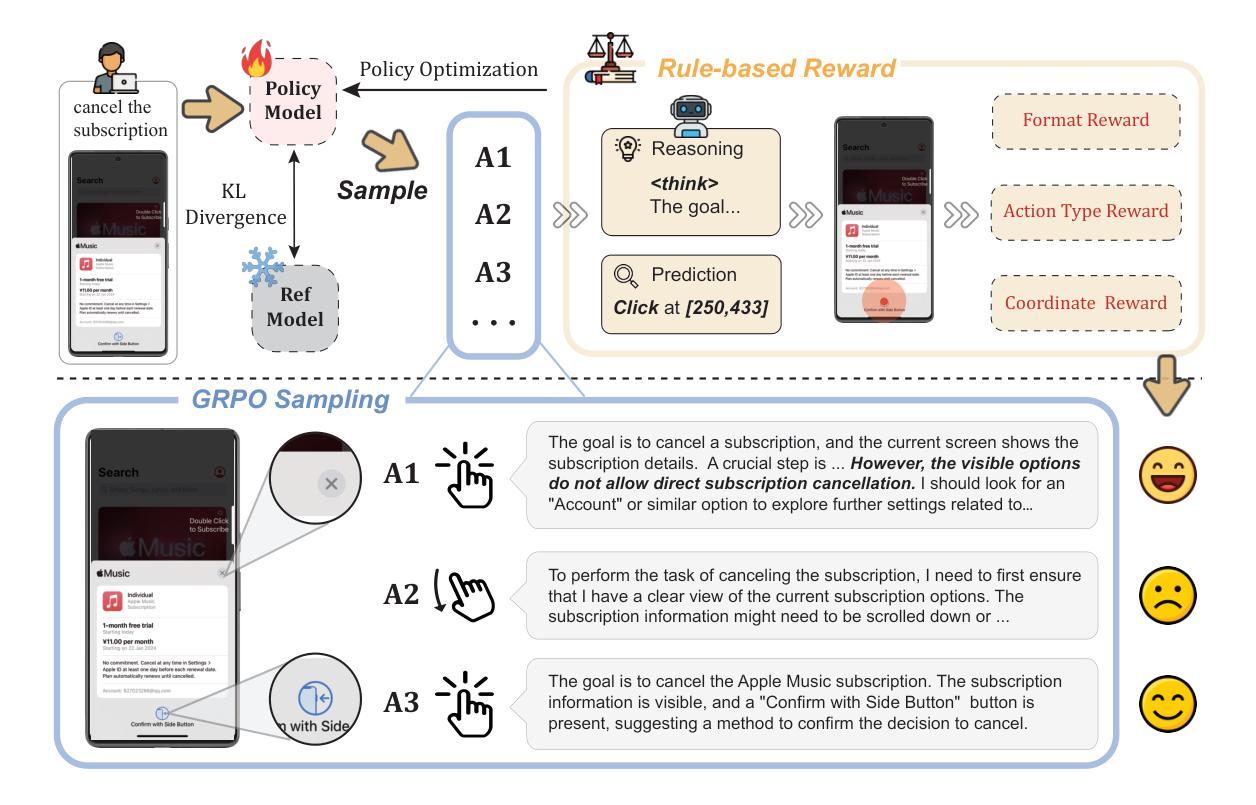
UI-R1: Enhancing Efficient Action Prediction of GUI Agents by Reinforcement Learning
Authors:Zhengxi Lu, Yuxiang Chai, Yaxuan Guo, Xi Yin, Liang Liu, Hao Wang, Han Xiao, Shuai Ren, Guanjing Xiong, Hongsheng Li
The recent DeepSeek-R1 has showcased the emergence of reasoning capabilities in LLMs through reinforcement learning (RL) with rule-based rewards. Despite its success in language models, its application in multi-modal domains, particularly in graphic user interface (GUI) agent tasks, remains under-explored. To address this issue, we propose UI-R1, the first framework to explore how rule-based RL can enhance the reasoning capabilities of multimodal large language models (MLLMs) for GUI action prediction tasks. Specifically, UI-R1 introduces a novel rule-based action reward, enabling model optimization via policy-based algorithms such as Group Relative Policy Optimization (GRPO). For efficient training, we curate a small yet high-quality dataset of 136 challenging tasks, encompassing five common action types on mobile devices. Experimental results demonstrate that our proposed UI-R1-3B achieves significant improvements over the base model (i.e. Qwen2.5-VL-3B) on both in-domain (ID) and out-of-domain (OOD) tasks, with average accuracy gains of 22.1% on ScreenSpot, 6.0% on ScreenSpot-Pro, and 12.7% on ANDROIDCONTROL. Furthermore, UI-R1-3B delivers competitive performance compared to larger models (e.g., OS-Atlas-7B) trained via supervised fine-tuning (SFT) on 76K samples. We additionally develop an optimized version, UI-R1-E-3B, which significantly improves both grounding efficiency and accuracy. These results underscore the potential of rule-based reinforcement learning to advance GUI understanding and control, paving the way for future research in this domain. Code website: https://github.com/lll6gg/UI-R1.
近期,DeepSeek-R1通过基于规则的奖励强化学习(RL)展示了大型语言模型(LLM)中的推理能力。尽管其在语言模型方面的应用取得了成功,但在多模态领域,特别是在图形用户界面(GUI)代理任务中的应用仍然缺乏探索。为了解决这个问题,我们提出了UI-R1,这是第一个探索基于规则的RL如何增强多模态大型语言模型(MLLM)的推理能力以执行GUI动作预测任务的框架。具体来说,UI-R1引入了一种新的基于动作的规则奖励,通过基于策略算法(如Group Relative Policy Optimization(GRPO))优化模型。为了进行有效的训练,我们创建了一个规模小但质量高的数据集,包含136个具有挑战性的任务,涵盖移动设备上的五种常见动作类型。实验结果表明,我们提出的UI-R1-3B模型在域内(ID)和域外(OOD)任务上都较基础模型(即Qwen2.5-VL-3B)有显著改进,在ScreenSpot上平均精度提高22.1%,在ScreenSpot-Pro上提高6.0%,在ANDROIDCONTROL上提高12.7%。此外,UI-R1-3B在7.6万个样本上进行监督微调(SFT)训练的较大模型(如OS-Atlas-7B)面前也表现出竞争力。我们还开发了一个优化版本UI-R1-E-3B,显著提高了接地效率和精度。这些结果突显了基于规则的强化学习在GUI理解和控制方面的潜力,为未来的研究铺平了道路。相关代码网站为:https://github.com/lll6gg/UI-R1。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Updated UI-R1-E-3B
Summary
在最新的DeepSeek-R1中,展示了通过基于规则的奖励强化学习(RL)在大型语言模型(LLM)中出现的推理能力。然而,它在多模态领域,特别是在图形用户界面(GUI)代理任务中的应用仍然未被充分探索。为解决此问题,我们提出了UI-R1框架,这是第一个探索基于规则的RL如何增强多模态大型语言模型(MLLM)的GUI动作预测任务的推理能力的框架。实验结果表明,与基准模型相比,UI-R1-3B在域内(ID)和域外(OOD)任务上的表现均有显著提高,在ScreenSpot、ScreenSpot-Pro和ANDROIDCONTROL上的平均准确率分别提高了22.1%、6.0%和12.7%。此外,与在7.6万样本上通过监督微调(SFT)训练的更大模型(如OS-Atlas-7B)相比,UI-R1-3B表现出具有竞争力的性能。这些结果突显了基于规则的强化学习在GUI理解和控制方面的潜力,为未来的研究提供了方向。
Key Takeaways
- DeepSeek-R1展示了大型语言模型中的推理能力通过基于规则的奖励强化学习出现。
- UI-R1框架旨在探索增强多模态大型语言模型在GUI动作预测任务中的推理能力。
- UI-R1引入了一种新的基于规则的行动奖励,通过策略优化算法如GRPO来优化模型。
- UI-R1在多种任务上表现优异,包括移动设备的五种常见动作类型。
- 与基准模型相比,UI-R1显著提高平均准确率,且性能优于更大的监督微调模型。
- 实验结果突显了基于规则的强化学习在GUI理解和控制方面的潜力。
点此查看论文截图