⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-05-16 更新
LightLab: Controlling Light Sources in Images with Diffusion Models
Authors:Nadav Magar, Amir Hertz, Eric Tabellion, Yael Pritch, Alex Rav-Acha, Ariel Shamir, Yedid Hoshen
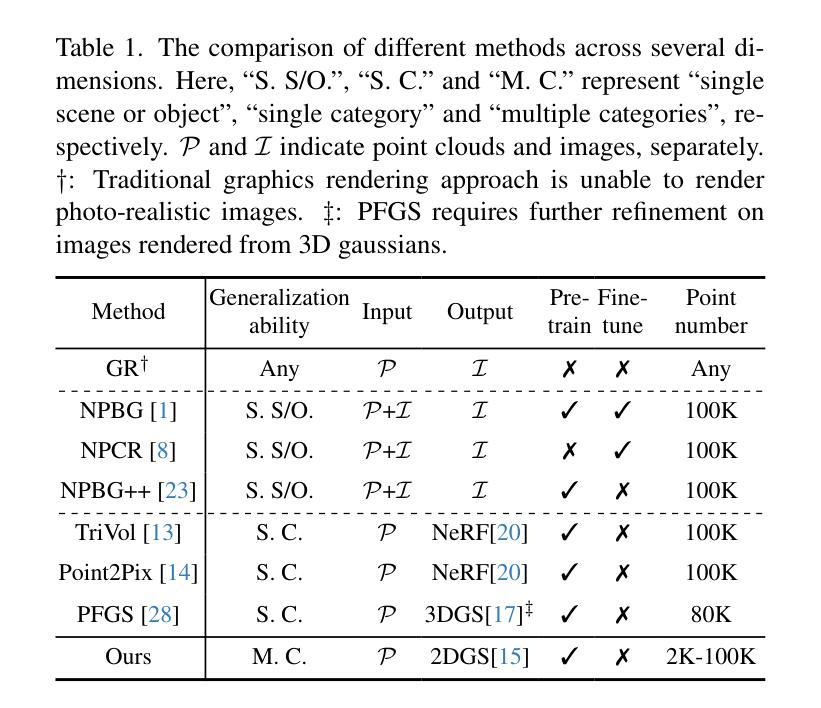
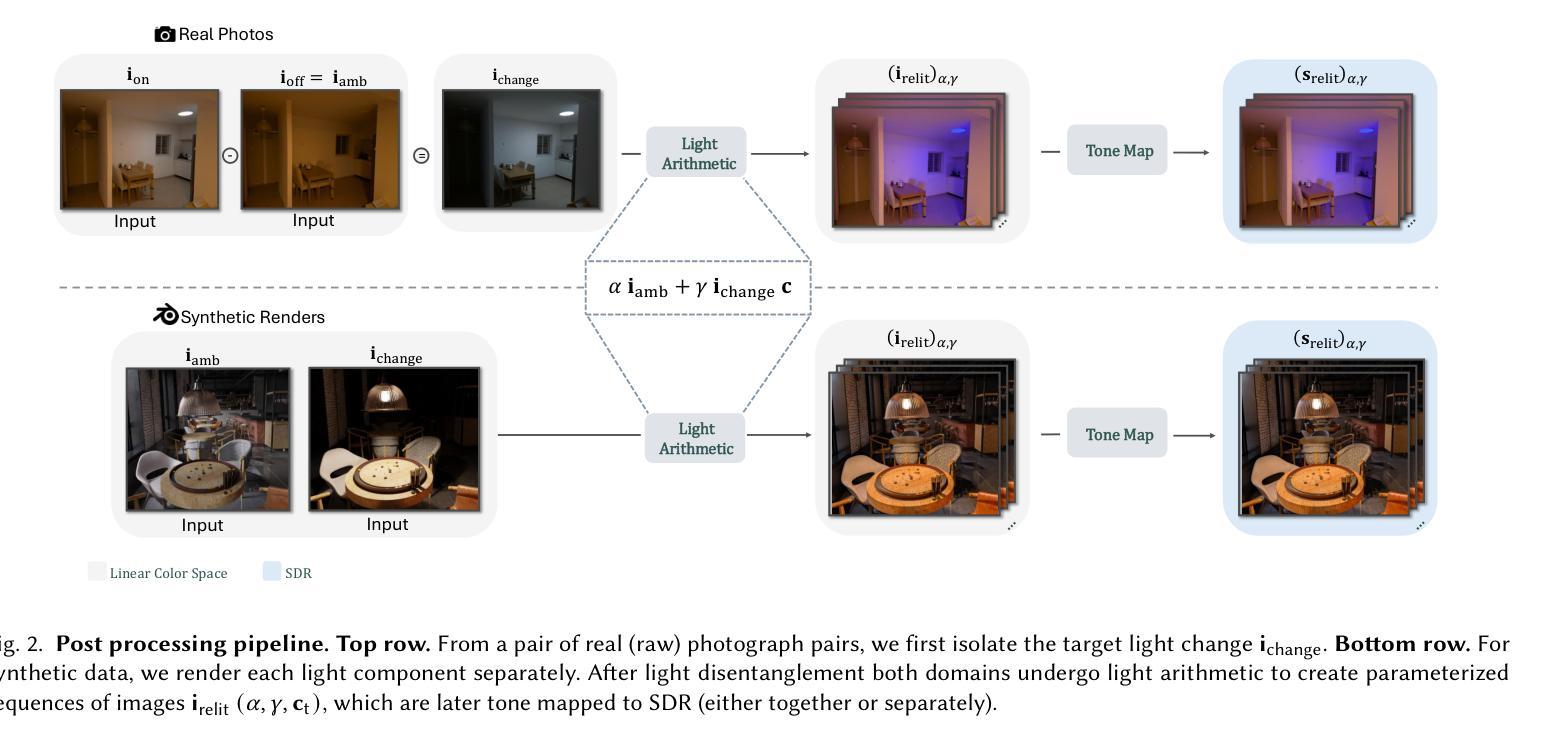
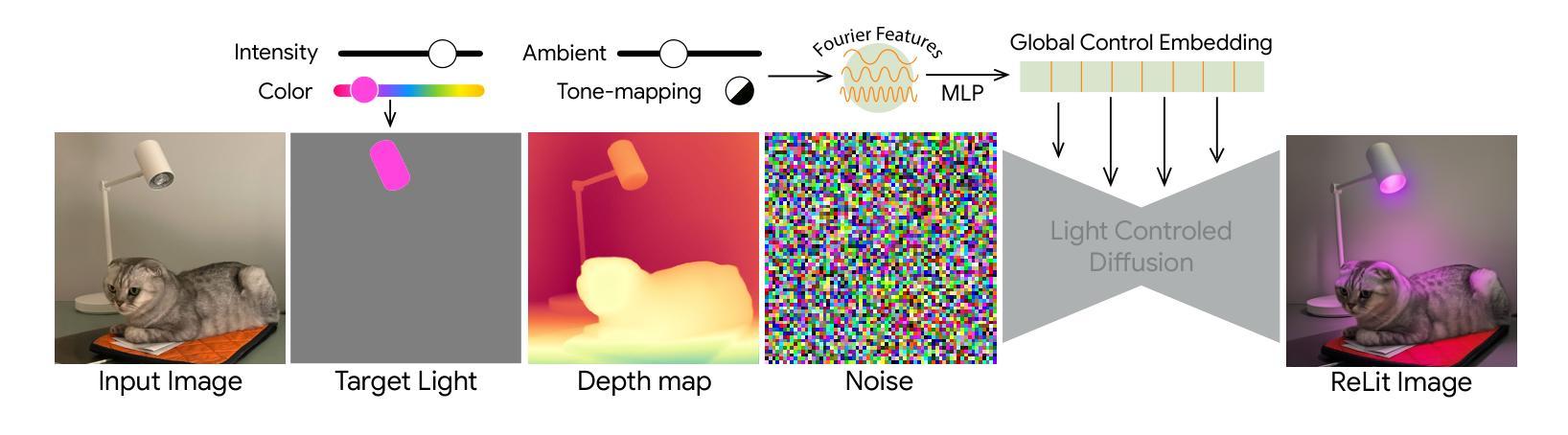
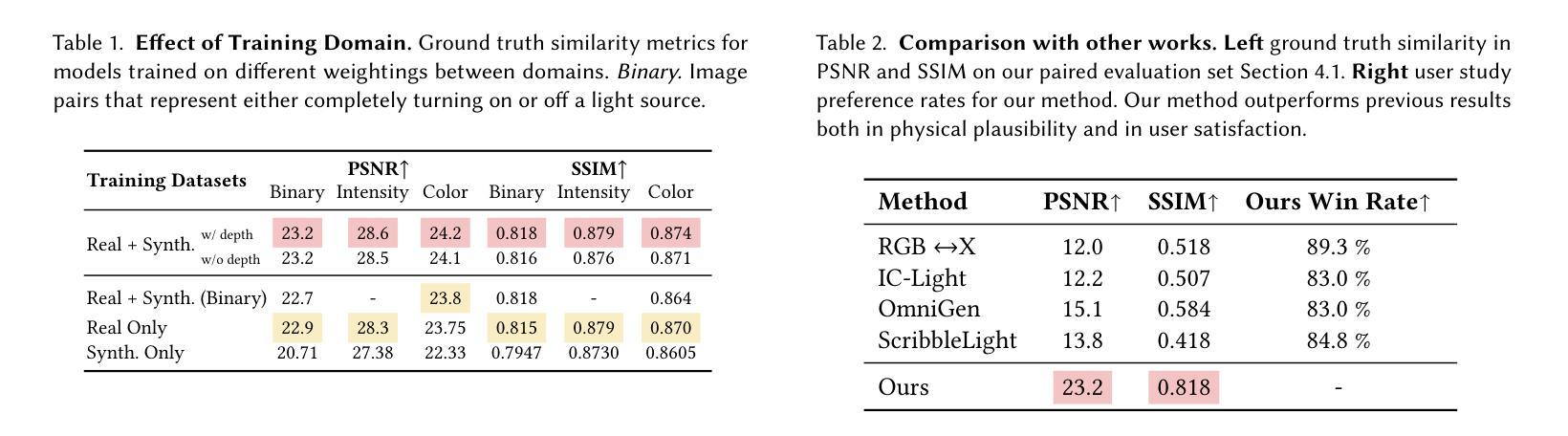
We present a simple, yet effective diffusion-based method for fine-grained, parametric control over light sources in an image. Existing relighting methods either rely on multiple input views to perform inverse rendering at inference time, or fail to provide explicit control over light changes. Our method fine-tunes a diffusion model on a small set of real raw photograph pairs, supplemented by synthetically rendered images at scale, to elicit its photorealistic prior for relighting. We leverage the linearity of light to synthesize image pairs depicting controlled light changes of either a target light source or ambient illumination. Using this data and an appropriate fine-tuning scheme, we train a model for precise illumination changes with explicit control over light intensity and color. Lastly, we show how our method can achieve compelling light editing results, and outperforms existing methods based on user preference.
我们提出了一种简单而有效的基于扩散的方法,用于对图像中的光源进行精细的、参数化的控制。现有的重照明方法要么依赖于多个输入视图在推理时进行逆向渲染,要么无法提供对光线变化的明确控制。我们的方法通过微调一组真实的原始照片对扩散模型,辅以大规模合成渲染的图像,以激发其用于重照明的逼真度先验。我们利用光线的线性合成图像对,展示目标光源或环境照明的受控光线变化。使用此数据和适当的微调方案,我们训练了一个模型,可以对光照强度进行精确控制,并实现明确的色彩控制。最后,我们展示了我们的方法如何实现引人注目的光线编辑结果,并基于用户偏好优于现有方法。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Project Page: https://nadmag.github.io/LightLab/
Summary
本文介绍了一种基于扩散的简单而有效的方法,用于对图像中的光源进行精细控制。现有重照明方法要么依赖于多个输入视图进行逆向渲染,要么无法提供对光照变化的明确控制。本文通过微调扩散模型,实现了对光源的精细控制,并展示了令人信服的光编辑结果。
Key Takeaways
- 提出了一种基于扩散的方法,用于图像中的精细光源控制。
- 现有重照明方法存在逆向渲染和缺乏明确光照控制的问题。
- 通过微调扩散模型,结合真实照片和合成渲染图像数据,训练模型以实现精确照明变化。
- 该方法可控制光源的光强度和颜色。
- 实现了令人信服的光编辑结果。
- 该方法在用户偏好评估中优于现有方法。
点此查看论文截图



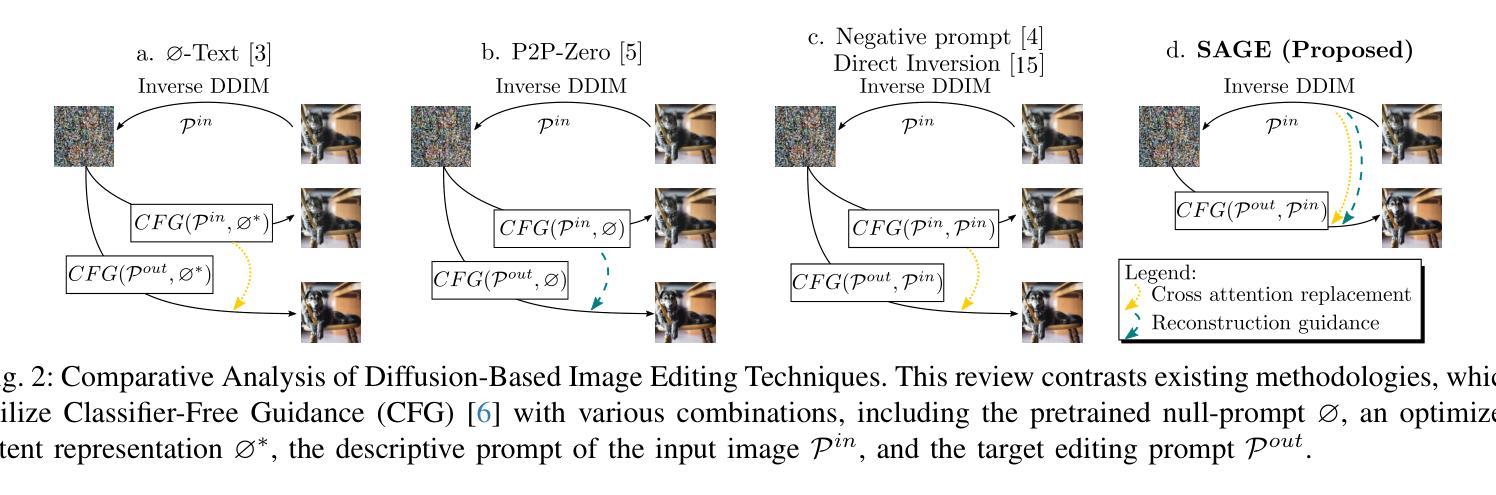
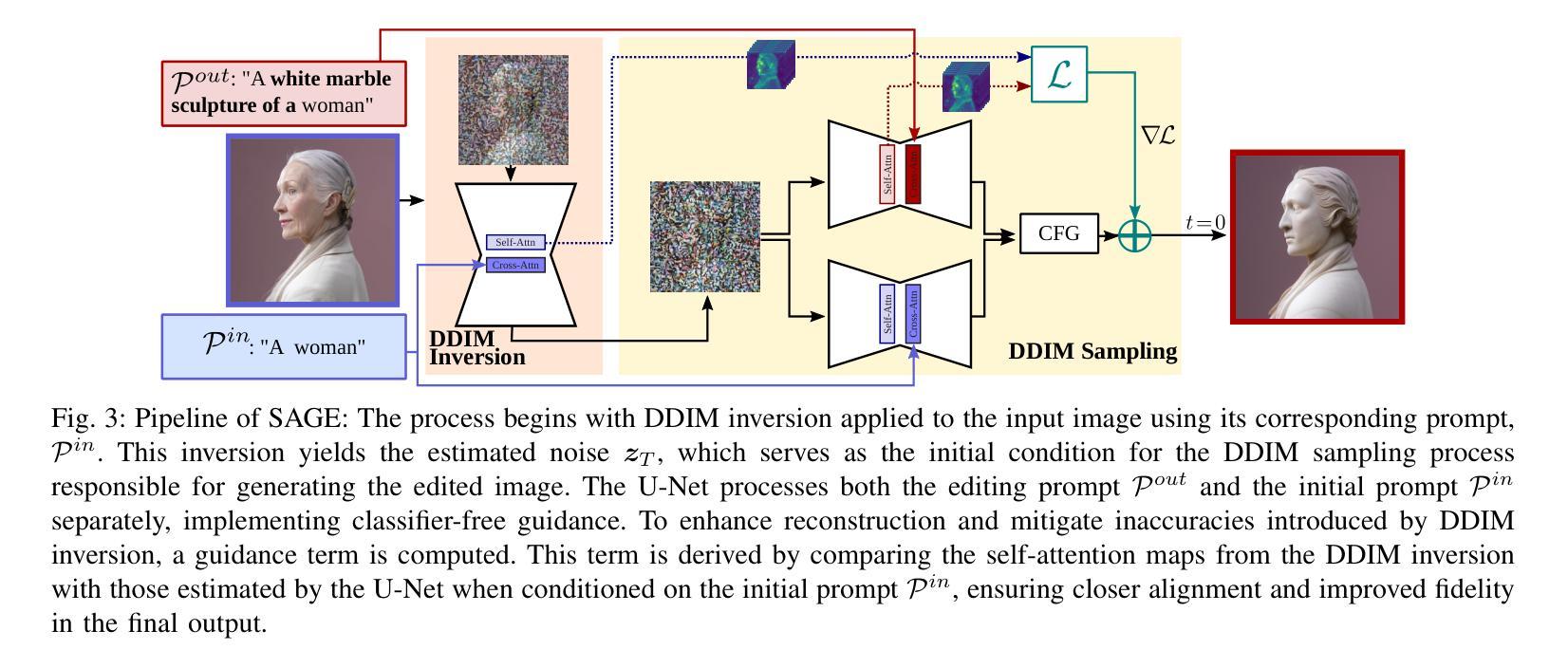
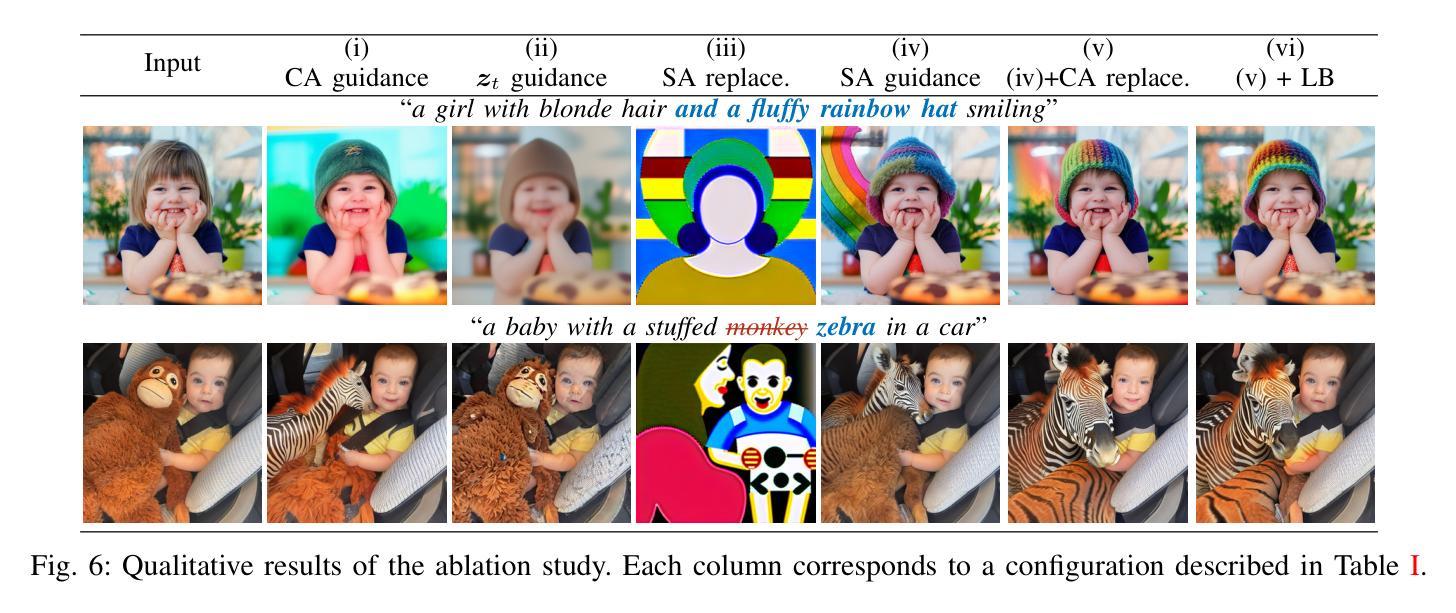
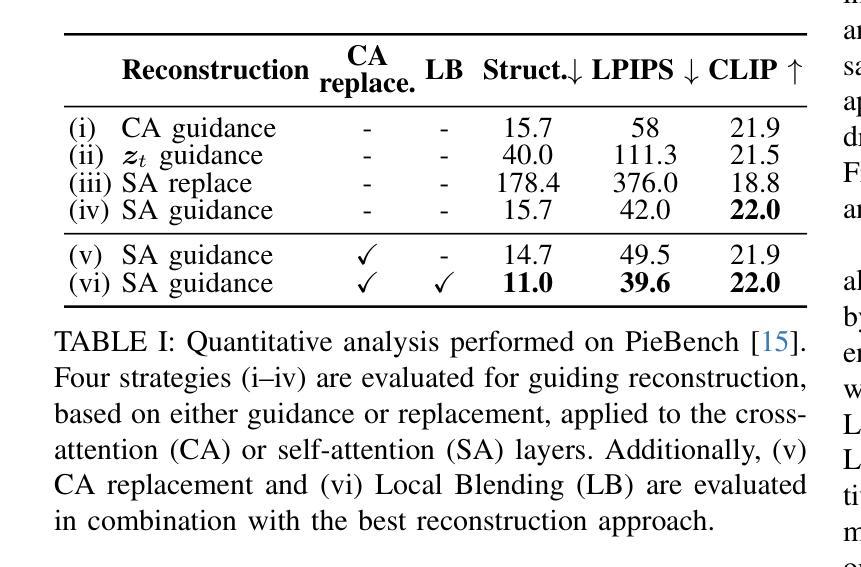
Don’t Forget your Inverse DDIM for Image Editing
Authors:Guillermo Gomez-Trenado, Pablo Mesejo, Oscar Cordón, Stéphane Lathuilière
The field of text-to-image generation has undergone significant advancements with the introduction of diffusion models. Nevertheless, the challenge of editing real images persists, as most methods are either computationally intensive or produce poor reconstructions. This paper introduces SAGE (Self-Attention Guidance for image Editing) - a novel technique leveraging pre-trained diffusion models for image editing. SAGE builds upon the DDIM algorithm and incorporates a novel guidance mechanism utilizing the self-attention layers of the diffusion U-Net. This mechanism computes a reconstruction objective based on attention maps generated during the inverse DDIM process, enabling efficient reconstruction of unedited regions without the need to precisely reconstruct the entire input image. Thus, SAGE directly addresses the key challenges in image editing. The superiority of SAGE over other methods is demonstrated through quantitative and qualitative evaluations and confirmed by a statistically validated comprehensive user study, in which all 47 surveyed users preferred SAGE over competing methods. Additionally, SAGE ranks as the top-performing method in seven out of 10 quantitative analyses and secures second and third places in the remaining three.
随着扩散模型(diffusion models)的引入,文本到图像生成领域已经取得了重大进展。然而,编辑真实图像的挑战仍然存在,因为大多数方法要么计算量大,要么产生的重建效果差。本文介绍了一种利用预训练的扩散模型进行图像编辑的新型技术——SAGE(Self-Attention Guidance for image Editing)。SAGE基于DDIM算法构建,并融入了一种新型指导机制,该机制利用扩散U-Net的自注意力层。这种机制基于反向DDIM过程中生成的注意力图计算重建目标,无需精确重建整个输入图像,即可有效地重建未编辑区域。因此,SAGE直接解决了图像编辑中的关键挑战。SAGE的优越性通过定量和定性评估以及经过统计验证的综合用户研究得到了证明,在调查的47名用户中,所有用户都认为SAGE优于其他方法。此外,在10项定量分析中有7项排名第一,其余三项分别获得第二和第三名。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 12 pages, 12 figures, code available at https://guillermogotre.github.io/sage/
Summary
文本到图像生成领域在扩散模型的引入下取得了显著进展。然而,编辑真实图像的挑战仍然存在,因为大多数方法要么计算量大,要么产生的重建效果差。本文介绍了SAGE(用于图像编辑的自我注意引导),这是一种利用预训练的扩散模型的新技术。SAGE建立在DDIM算法的基础上,并引入了一种新的引导机制,利用扩散U-Net的自注意层。该机制基于反向DDIM过程中生成的注意力图计算重建目标,能够高效重建未编辑区域,无需精确重建整个输入图像。因此,SAGE直接解决了图像编辑中的关键挑战。SAGE的优越性通过定量和定性评估以及经过统计验证的综合用户研究得到了证明,47名受访用户都更倾向于使用SAGE而非其他方法。此外,在10项定量分析中,SAGE在7项中排名第一,在其余三项中分别获得第二和第三名。
Key Takeaways
- 扩散模型在文本到图像生成领域取得了显著进展。
- 现有图像编辑方法面临计算量大或重建效果差的挑战。
- SAGE技术利用预训练的扩散模型进行图像编辑。
- SAGE建立在DDIM算法之上,并引入自我注意引导机制。
- SAGE通过注意力图计算重建目标,实现高效区域重建。
- SAGE在多项定量分析和用户研究中表现出优越性。
点此查看论文截图




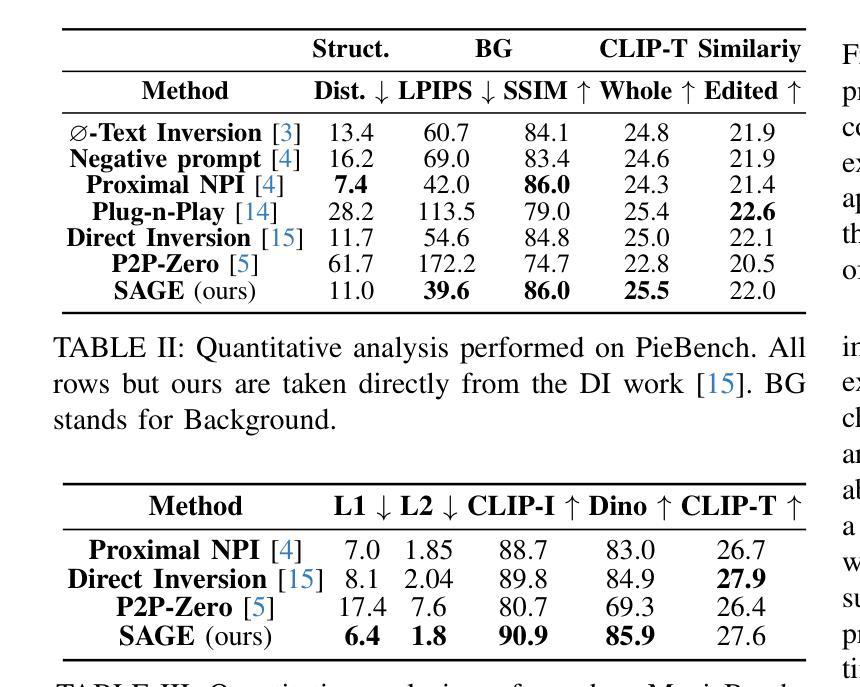
BLIP3-o: A Family of Fully Open Unified Multimodal Models-Architecture, Training and Dataset
Authors:Jiuhai Chen, Zhiyang Xu, Xichen Pan, Yushi Hu, Can Qin, Tom Goldstein, Lifu Huang, Tianyi Zhou, Saining Xie, Silvio Savarese, Le Xue, Caiming Xiong, Ran Xu
Unifying image understanding and generation has gained growing attention in recent research on multimodal models. Although design choices for image understanding have been extensively studied, the optimal model architecture and training recipe for a unified framework with image generation remain underexplored. Motivated by the strong potential of autoregressive and diffusion models for high-quality generation and scalability, we conduct a comprehensive study of their use in unified multimodal settings, with emphasis on image representations, modeling objectives, and training strategies. Grounded in these investigations, we introduce a novel approach that employs a diffusion transformer to generate semantically rich CLIP image features, in contrast to conventional VAE-based representations. This design yields both higher training efficiency and improved generative quality. Furthermore, we demonstrate that a sequential pretraining strategy for unified models-first training on image understanding and subsequently on image generation-offers practical advantages by preserving image understanding capability while developing strong image generation ability. Finally, we carefully curate a high-quality instruction-tuning dataset BLIP3o-60k for image generation by prompting GPT-4o with a diverse set of captions covering various scenes, objects, human gestures, and more. Building on our innovative model design, training recipe, and datasets, we develop BLIP3-o, a suite of state-of-the-art unified multimodal models. BLIP3-o achieves superior performance across most of the popular benchmarks spanning both image understanding and generation tasks. To facilitate future research, we fully open-source our models, including code, model weights, training scripts, and pretraining and instruction tuning datasets.
在多模态模型领域的最新研究中,统一图像理解和生成已经引起了越来越多的关注。虽然图像理解的设计选择已经得到了广泛的研究,但在统一框架中进行图像生成的模型架构和训练策略仍然鲜有研究。受自回归和扩散模型在高质量和可扩展性生成方面的强大潜力的驱动,我们对它们在统一多模态设置中的使用进行了全面研究,重点研究图像表示、建模目标和训练策略。基于这些研究,我们介绍了一种新方法,该方法采用扩散变压器生成语义丰富的CLIP图像特征,这与传统的基于VAE的表示形成对比。这种设计不仅提高了训练效率,还提高了生成质量。此外,我们证明了统一模型的顺序预训练策略(首先在图像理解上进行训练,随后在图像生成上进行训练)具有实用价值,能够在保持图像理解能力的同时,发展强大的图像生成能力。最后,我们通过使用涵盖各种场景、物体、人类动作等的多样化描述来精心创建高质量指令调整数据集BLIP3o-60k,为GPT-4o提供提示来进行图像生成的训练。基于我们创新的模型设计、训练配方和数据集,我们开发了一系列最先进的统一多模态模型BLIP3-o。BLIP3-o在涵盖图像理解和生成任务的大多数流行基准测试中实现了卓越的性能。为了促进未来的研究,我们全面开源我们的模型,包括代码、模型权重、训练脚本以及预训练和指令调整数据集。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文探讨了多模态模型中的图像理解和生成技术,对采用扩散模型和自回归模型的统一框架进行了深入研究,并介绍了新的图像特征生成方法。通过采用扩散变压器生成语义丰富的CLIP图像特征,提高了训练效率和生成质量。此外,文章还提出了一种序贯预训练策略,并开发了一系列最先进的统一多模态模型BLIP3-o,该模型在图像理解和生成任务上的表现均达到或超越了现有水平。
Key Takeaways
- 研究关注多模态模型中图像理解和生成的结合。
- 探讨了采用扩散模型和自回归模型的统一框架。
- 引入了一种新的图像特征生成方法,使用扩散变压器生成语义丰富的CLIP图像特征。
- 提出了序贯预训练策略,先训练图像理解,再训练图像生成,以提高模型的实用性能。
- 开发了一系列先进的统一多模态模型BLIP3-o。
- BLIP3-o模型在图像理解和生成任务上的表现均达到或超越了现有水平。
点此查看论文截图

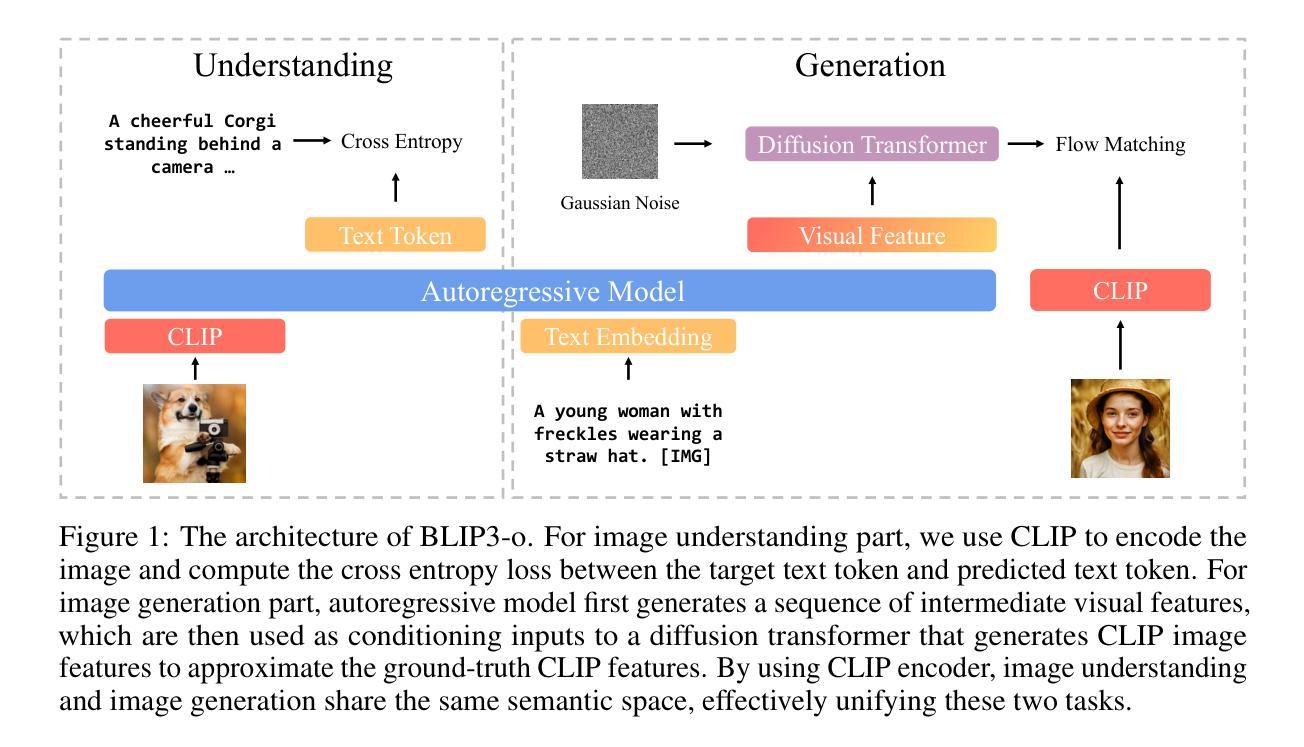

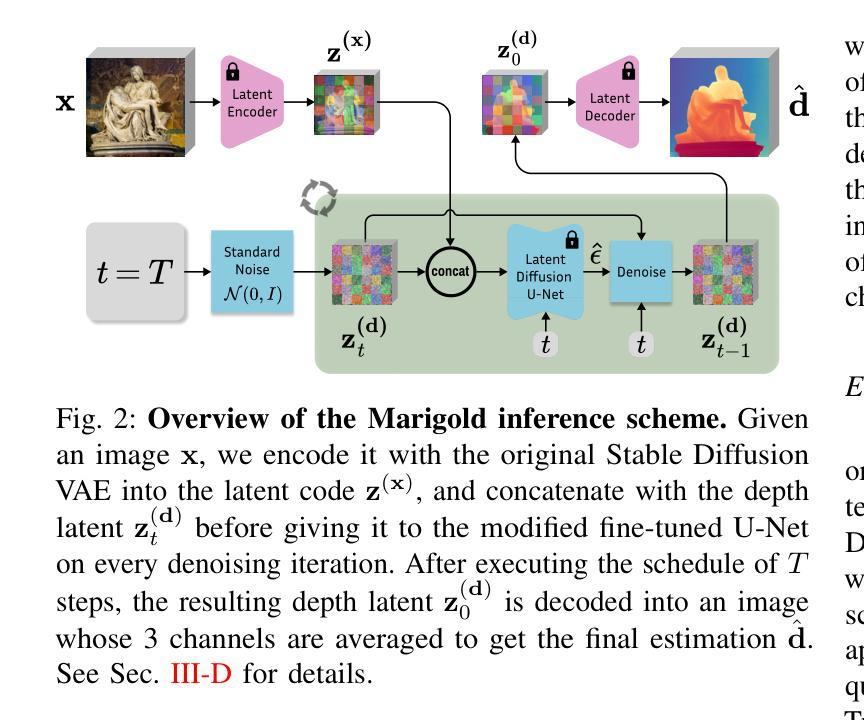
Marigold: Affordable Adaptation of Diffusion-Based Image Generators for Image Analysis
Authors:Bingxin Ke, Kevin Qu, Tianfu Wang, Nando Metzger, Shengyu Huang, Bo Li, Anton Obukhov, Konrad Schindler
The success of deep learning in computer vision over the past decade has hinged on large labeled datasets and strong pretrained models. In data-scarce settings, the quality of these pretrained models becomes crucial for effective transfer learning. Image classification and self-supervised learning have traditionally been the primary methods for pretraining CNNs and transformer-based architectures. Recently, the rise of text-to-image generative models, particularly those using denoising diffusion in a latent space, has introduced a new class of foundational models trained on massive, captioned image datasets. These models’ ability to generate realistic images of unseen content suggests they possess a deep understanding of the visual world. In this work, we present Marigold, a family of conditional generative models and a fine-tuning protocol that extracts the knowledge from pretrained latent diffusion models like Stable Diffusion and adapts them for dense image analysis tasks, including monocular depth estimation, surface normals prediction, and intrinsic decomposition. Marigold requires minimal modification of the pre-trained latent diffusion model’s architecture, trains with small synthetic datasets on a single GPU over a few days, and demonstrates state-of-the-art zero-shot generalization. Project page: https://marigoldcomputervision.github.io
过去十年,深度学习在计算机视觉领域的成功主要依赖于大规模有标注数据集和强大的预训练模型。在数据稀缺的情况下,这些预训练模型的质量对于有效的迁移学习至关重要。图像分类和自监督学习一直是预训练CNN和基于transformer架构的传统主要方法。最近,文本到图像生成模型的兴起,特别是那些在潜在空间使用去噪扩散的模型,引入了一类新的基础模型,这些模型在大型有字幕图像数据集上进行训练。这些模型生成未见内容的现实图像的能力表明它们对视觉世界有深入理解。在这项工作中,我们提出了Marigold,这是一系列条件生成模型和微调协议,它从预训练的潜在扩散模型(如Stable Diffusion)中提取知识,并适应密集图像分析任务,包括单眼深度估计、表面法线预测和内在分解。Marigold只需对预训练的潜在扩散模型的架构进行最小修改,使用小型合成数据集在单个GPU上进行几天的训练,并展示了零样本迁移的卓越泛化能力。项目页面:https://marigoldcomputervision.github.io
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Journal extension of our CVPR 2024 paper, featuring new tasks, improved efficiency, high-resolution capabilities, and enhanced accessibility
Summary
深度学习在计算机视觉领域的成功,得益于大规模标注数据集和强大的预训练模型。在数据稀缺的情况下,预训练模型的质量对迁移学习至关重要。近期文本到图像生成模型,特别是潜在空间去噪扩散模型的兴起,引入了一种新的基础模型,该模型在大型带字幕的图像数据集上进行训练。本文介绍Marigold,这是一系列条件生成模型和微调协议,它从预训练的潜在扩散模型如Stable Diffusion中提取知识,并适应密集图像分析任务,包括单眼深度估计、表面法线预测和内在分解。Marigold对预训练的潜在扩散模型的架构进行了最小的修改,使用小型合成数据集在单个GPU上进行几天的训练,并展示了零样本迁移学习的最新水平。
Key Takeaways
- 深度学习在计算机视觉领域的成功依赖于大规模标注数据集和强大的预训练模型。
- 在数据稀缺的环境中,预训练模型的质量对迁移学习至关重要。
- 文本到图像生成模型的兴起,特别是潜在空间去噪扩散模型,为计算机视觉领域引入了新的基础模型。
- Marigold是一种条件生成模型和微调协议,能够从预训练的潜在扩散模型中提取知识并适应密集图像分析任务。
- Marigold具有最小的架构修改需求,使用小型合成数据集在单个GPU上进行训练。
- Marigold展示了零样本迁移学习的最新水平。
点此查看论文截图
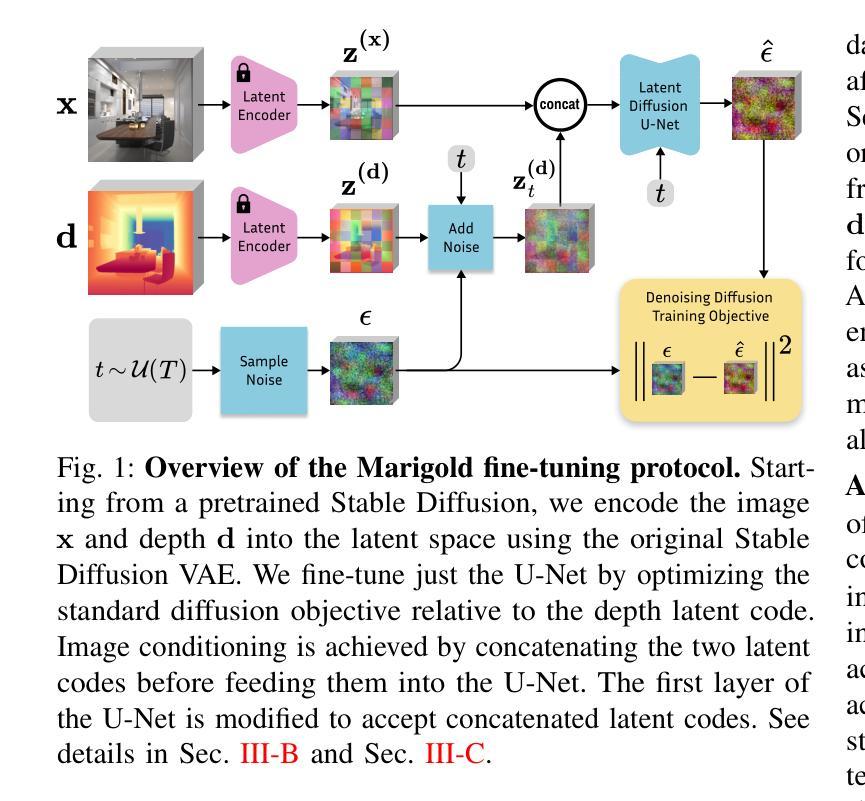
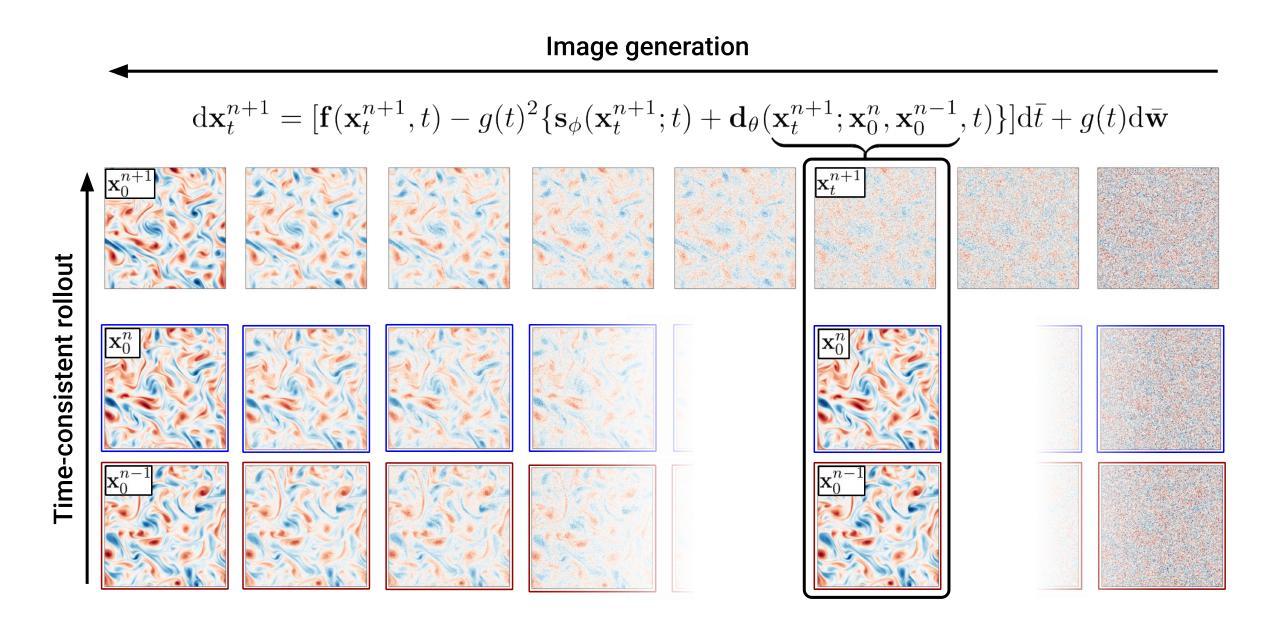
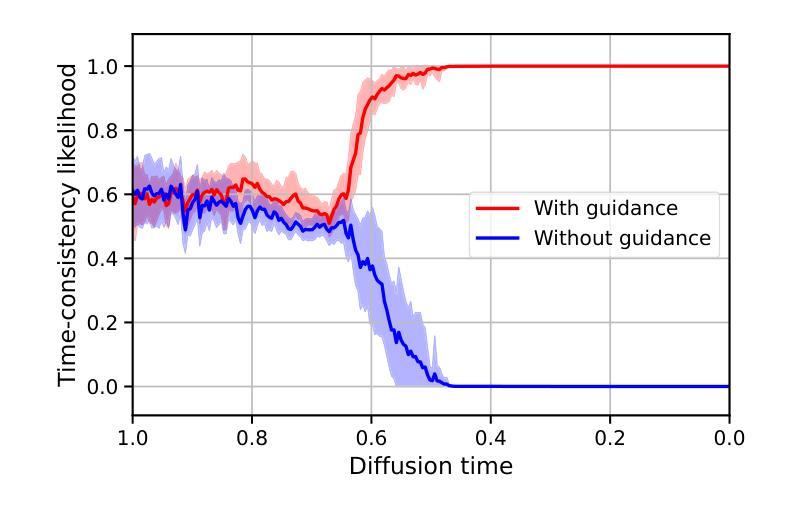
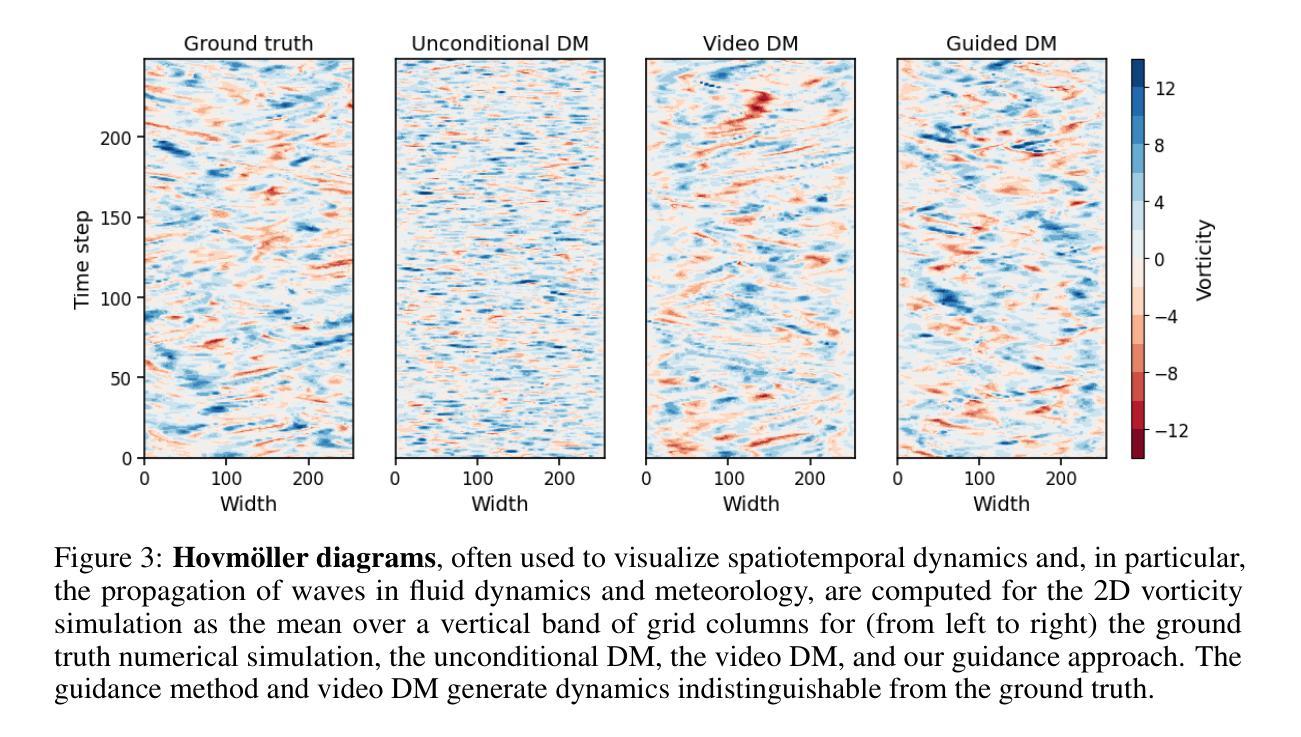
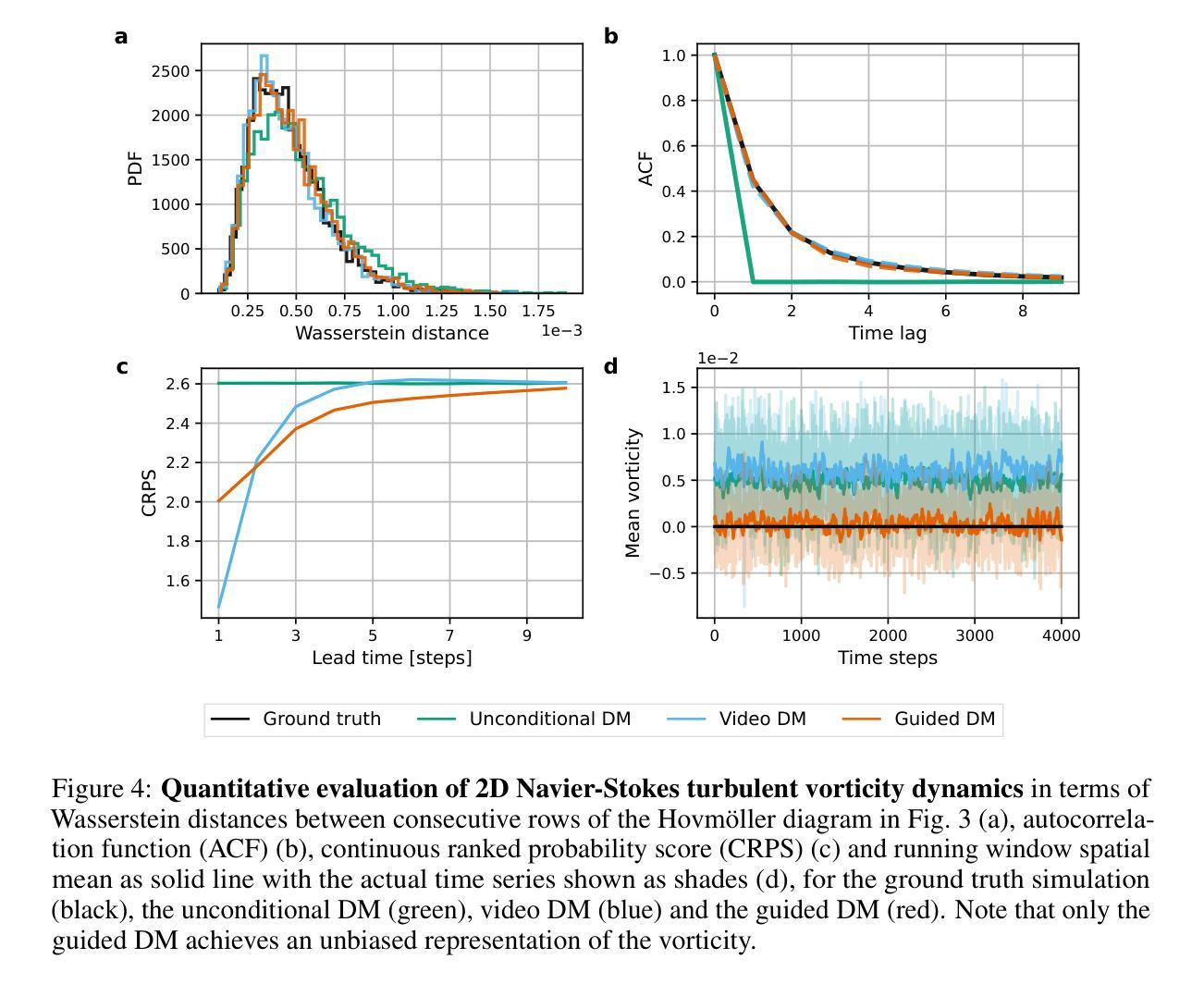
Generating time-consistent dynamics with discriminator-guided image diffusion models
Authors:Philipp Hess, Maximilian Gelbrecht, Christof Schötz, Michael Aich, Yu Huang, Shangshang Yang, Niklas Boers
Realistic temporal dynamics are crucial for many video generation, processing and modelling applications, e.g. in computational fluid dynamics, weather prediction, or long-term climate simulations. Video diffusion models (VDMs) are the current state-of-the-art method for generating highly realistic dynamics. However, training VDMs from scratch can be challenging and requires large computational resources, limiting their wider application. Here, we propose a time-consistency discriminator that enables pretrained image diffusion models to generate realistic spatiotemporal dynamics. The discriminator guides the sampling inference process and does not require extensions or finetuning of the image diffusion model. We compare our approach against a VDM trained from scratch on an idealized turbulence simulation and a real-world global precipitation dataset. Our approach performs equally well in terms of temporal consistency, shows improved uncertainty calibration and lower biases compared to the VDM, and achieves stable centennial-scale climate simulations at daily time steps.
现实的时间动态对于许多视频生成、处理和建模应用至关重要,例如在计算流体动力学、天气预报或长期气候模拟中。视频扩散模型(VDM)是目前生成高度真实动态的最先进方法。然而,从头训练VDM可能具有挑战性,并需要巨大的计算资源,这限制了其更广泛的应用。在这里,我们提出了一种时间一致性鉴别器,它可以让预训练的图像扩散模型生成逼真的时空动态。鉴别器引导采样推理过程,并不需要对图像扩散模型进行扩展或微调。我们将我们的方法与在理想化的湍流模拟和真实世界全球降水数据集上从头训练的VDM进行比较。我们的方法在时间一致性方面表现同样出色,与VDM相比,显示出改进的不确定性校准和更低的偏差,并在每日时间步长下实现稳定世纪尺度的气候模拟。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了视频扩散模型(VDMs)在生成高度逼真的动态视频中的重要性及其面临的挑战。为应对这些挑战,本文提出了一种时间一致性鉴别器,该鉴别器可使预训练的图像扩散模型生成逼真的时空动态。该鉴别器能够引导采样推理过程,且无需扩展或微调图像扩散模型。通过对比实验,本文方法在时间一致性方面表现优异,不确定性校准和偏差改进明显,相较于VDM更加稳定地实现了按日常时间步长进行世纪规模的气候模拟。
Key Takeaways
- 视频扩散模型(VDMs)是生成高度逼真的动态视频的最新技术。
- 训练VDMs存在挑战,需要大量的计算资源。
- 提出了一种时间一致性鉴别器,使预训练的图像扩散模型能够生成逼真的时空动态。
- 时间一致性鉴别器能引导采样推理过程,无需扩展或微调图像扩散模型。
- 对比实验表明,该方法在时间一致性方面表现优秀。
- 与VDM相比,该方法在不确定性校准和偏差改进方面有明显优势。
点此查看论文截图

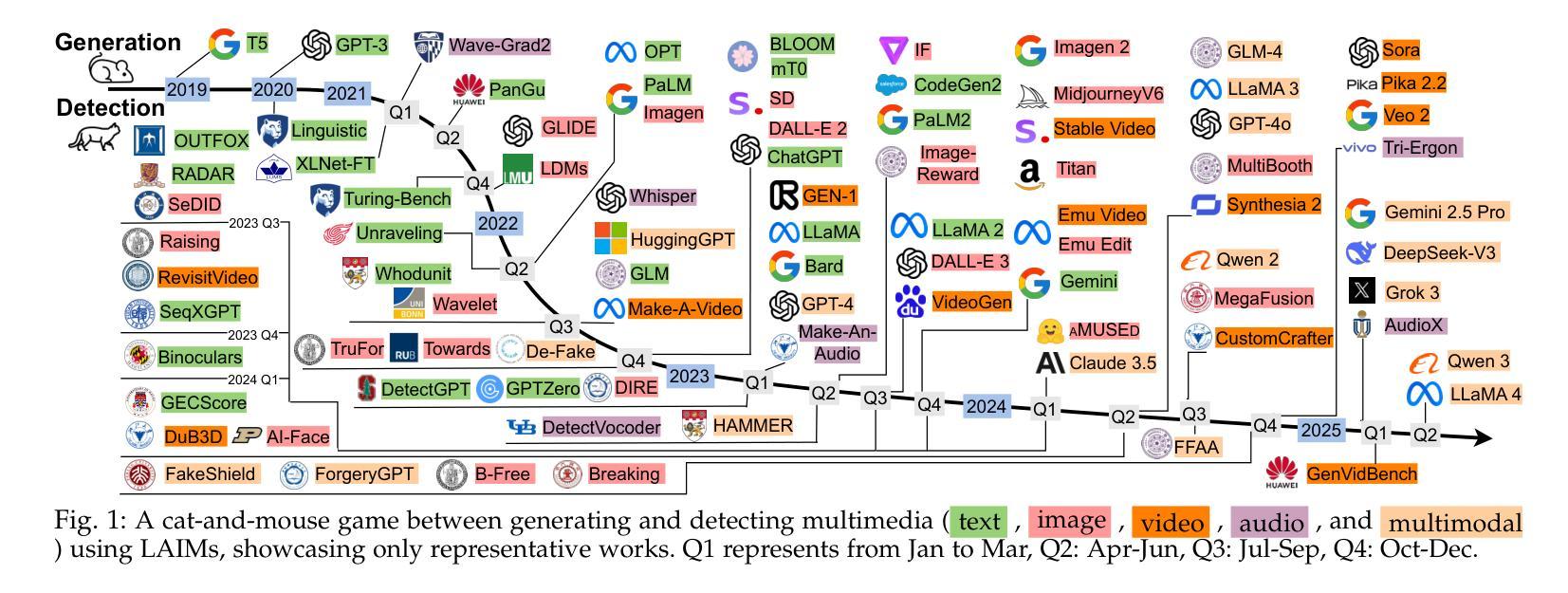
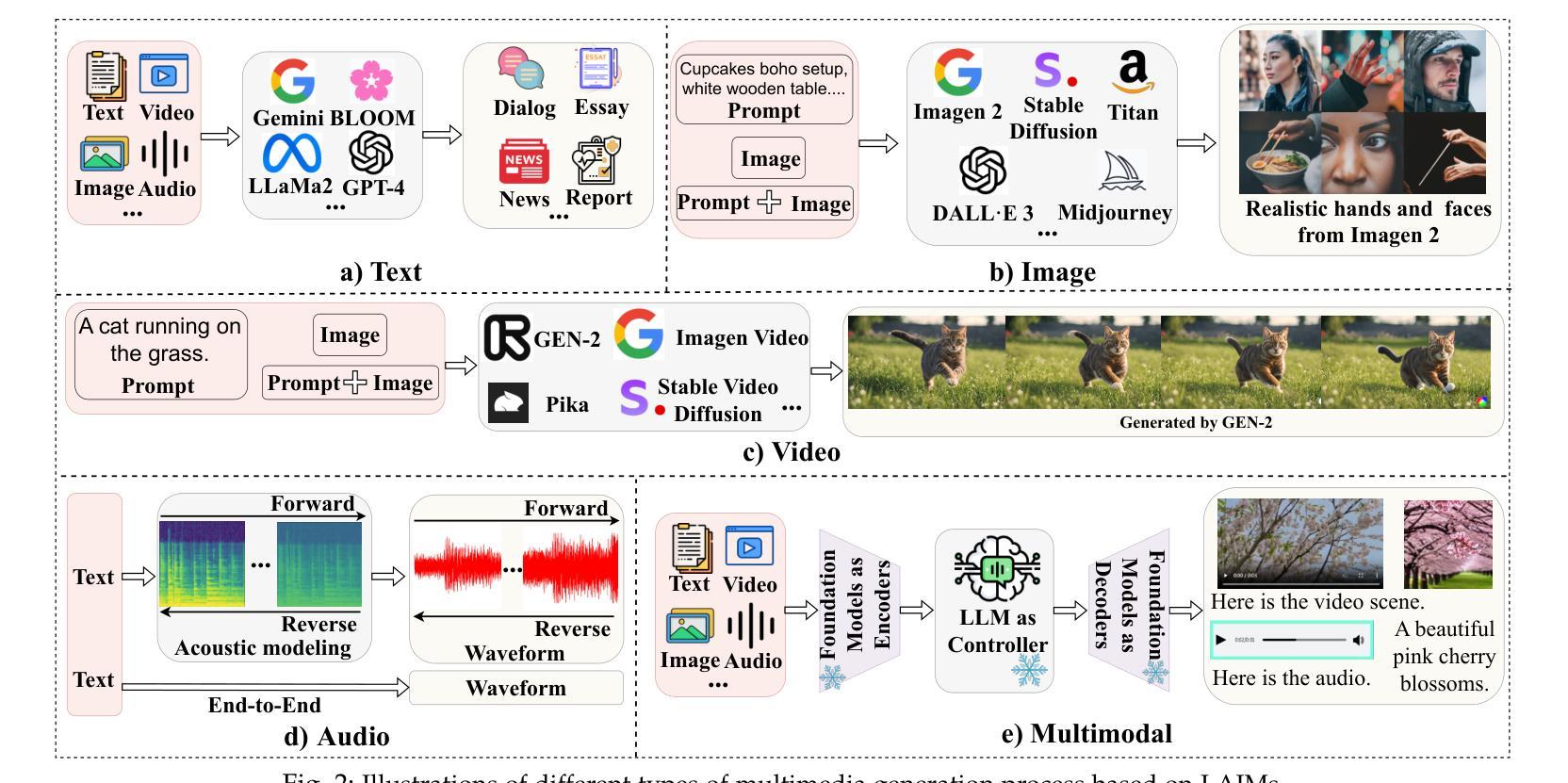
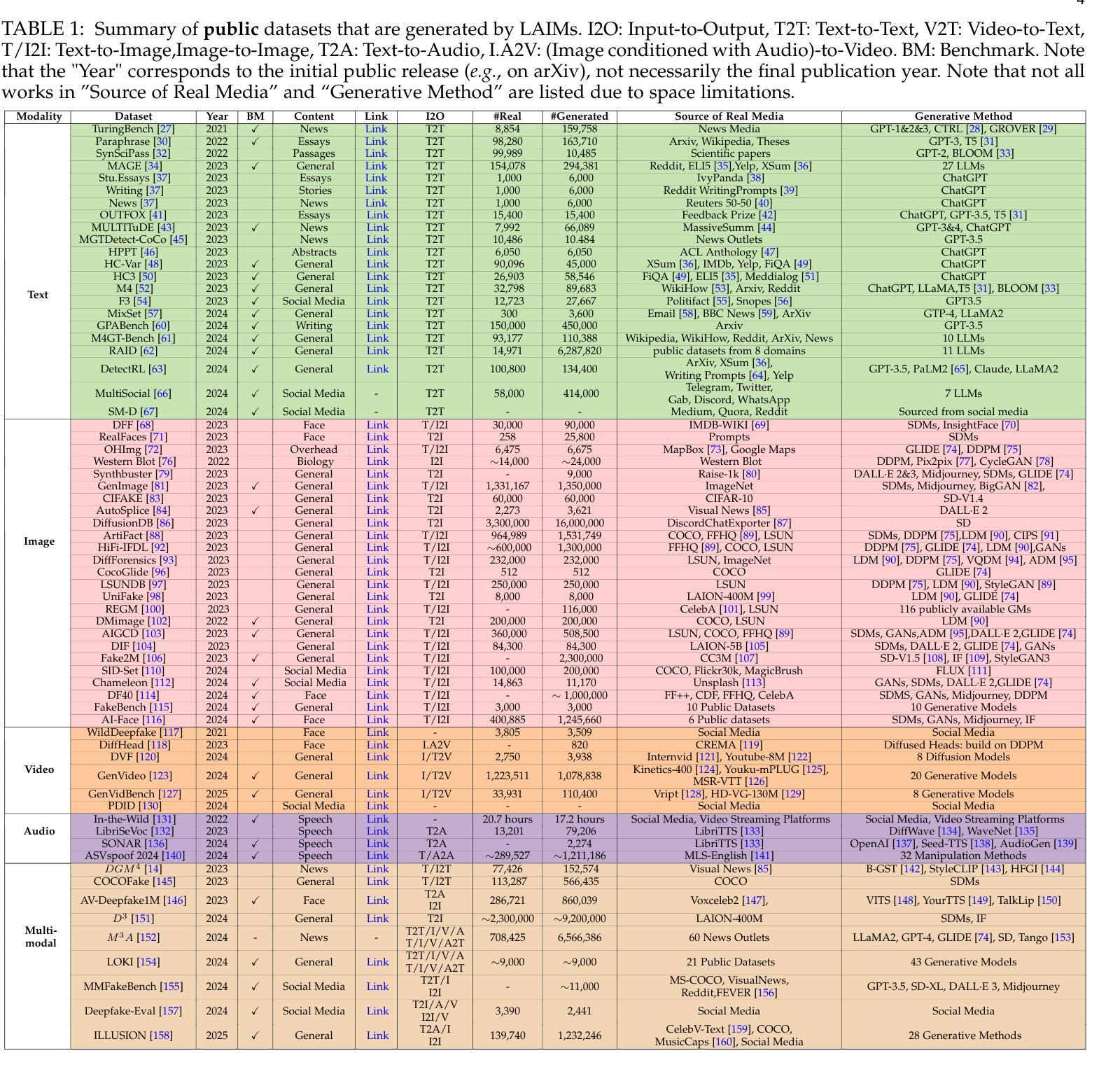
Detecting Multimedia Generated by Large AI Models: A Survey
Authors:Li Lin, Neeraj Gupta, Yue Zhang, Hainan Ren, Chun-Hao Liu, Feng Ding, Xin Wang, Xin Li, Luisa Verdoliva, Shu Hu
The rapid advancement of Large AI Models (LAIMs), particularly diffusion models and large language models, has marked a new era where AI-generated multimedia is increasingly integrated into various aspects of daily life. Although beneficial in numerous fields, this content presents significant risks, including potential misuse, societal disruptions, and ethical concerns. Consequently, detecting multimedia generated by LAIMs has become crucial, with a marked rise in related research. Despite this, there remains a notable gap in systematic surveys that focus specifically on detecting LAIM-generated multimedia. Addressing this, we provide the first survey to comprehensively cover existing research on detecting multimedia (such as text, images, videos, audio, and multimodal content) created by LAIMs. Specifically, we introduce a novel taxonomy for detection methods, categorized by media modality, and aligned with two perspectives: pure detection (aiming to enhance detection performance) and beyond detection (adding attributes like generalizability, robustness, and interpretability to detectors). Additionally, we have presented a brief overview of generation mechanisms, public datasets, online detection tools, and evaluation metrics to provide a valuable resource for researchers and practitioners in this field. Most importantly, we offer a focused analysis from a social media perspective to highlight their broader societal impact. Furthermore, we identify current challenges in detection and propose directions for future research that address unexplored, ongoing, and emerging issues in detecting multimedia generated by LAIMs. Our aim for this survey is to fill an academic gap and contribute to global AI security efforts, helping to ensure the integrity of information in the digital realm. The project link is https://github.com/Purdue-M2/Detect-LAIM-generated-Multimedia-Survey.
大型人工智能模型(LAIMs)的快速发展,尤其是扩散模型和大语言模型,标志着一个人工智能生成多媒体越来越融入日常生活的时代来临。尽管这些技术在许多领域都带来了好处,但它们也带来了显著的风险,包括潜在误用、社会混乱和伦理问题。因此,检测由LAIM生成的多媒体已经成为至关重要的事情,相关的研究也出现了显著增长。尽管如此,专门针对检测LAIM生成的多媒体的系统性综述仍存在明显差距。为了解决这个问题,我们提供了第一篇全面涵盖现有检测LAIM生成多媒体(如文本、图像、视频、音频和多模态内容)的研究综述。具体来说,我们引入了一种新的检测方法的分类法,按媒体模态分类,并从两个角度进行对齐:纯检测(旨在提高检测性能)和超越检测(向检测器添加通用性、鲁棒性和可解释性等属性)。此外,我们还简要概述了生成机制、公共数据集、在线检测工具和评估指标,为这一领域的研究人员和实践者提供了有价值的资源。最重要的是,我们从社交媒体的角度进行了重点分析,以强调它们对社会的更广泛影响。此外,我们还确定了当前检测面临的挑战,并提出了未来研究的方向,解决在检测由LAIM生成的多媒体方面尚未探索、正在出现和新兴的问题。我们撰写此综述的目的是填补学术空白,为全球人工智能安全努力做出贡献,帮助确保数字领域的信息完整性。项目链接是https://github.com/Purdue-M2/Detect-LAIM-generated-Multimedia-Survey。
论文及项目相关链接
摘要
扩散模型等大型AI模型(LAIMs)的快速发展为日常生活带来机遇和挑战,这些AI生成的多媒体内容在许多领域有着广泛应用。因此,检测和识别LAIM生成的多媒体内容变得至关重要。本文首次全面综述了关于检测LAIM生成的多媒体内容的研究,包括文本、图像、视频、音频和多模态内容等。文章提出了检测方法的全新分类法,按媒体类型分类,并从纯粹检测(旨在提高检测性能)和超越检测(增加通用性、鲁棒性和可解释性)两个角度进行阐述。此外,文章还概述了生成机制、公开数据集、在线检测工具和评估指标等。更重要的是,文章从社交媒体的角度分析了LAIM的广泛社会影响,并指出了当前面临的挑战和未来研究方向。本文旨在填补学术空白,为AI安全做出贡献,确保数字领域的信息完整性。
关键见解
- 大型AI模型(LAIMs)尤其是扩散模型的快速发展推动了AI生成多媒体内容的普及,广泛应用于日常各方面。
- AI生成的多媒体内容面临着潜在的误用、社会混乱和伦理问题等重大风险。
- 检测LAIM生成的多媒体内容至关重要,但现有的系统综述存在显著缺口。
- 本文首次全面综述了检测LAIM生成的多媒体内容的研究,涵盖了各种媒体类型。
- 提出了检测方法的全新分类法,从纯粹检测和超越检测两个角度阐述。
- 文章还分析了LAIM的社会影响,并指出了当前面临的挑战和未来研究方向。
点此查看论文截图