⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-05-16 更新
Endo-CLIP: Progressive Self-Supervised Pre-training on Raw Colonoscopy Records
Authors:Yili He, Yan Zhu, Peiyao Fu, Ruijie Yang, Tianyi Chen, Zhihua Wang, Quanlin Li, Pinghong Zhou, Xian Yang, Shuo Wang
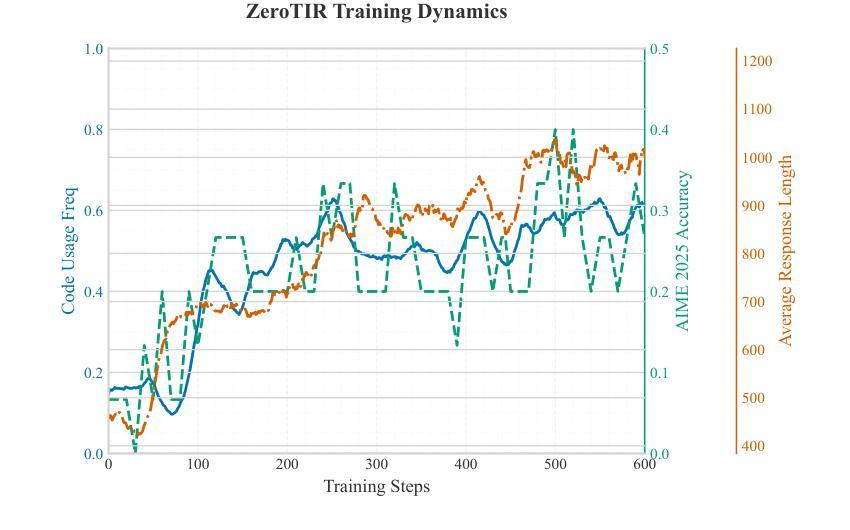
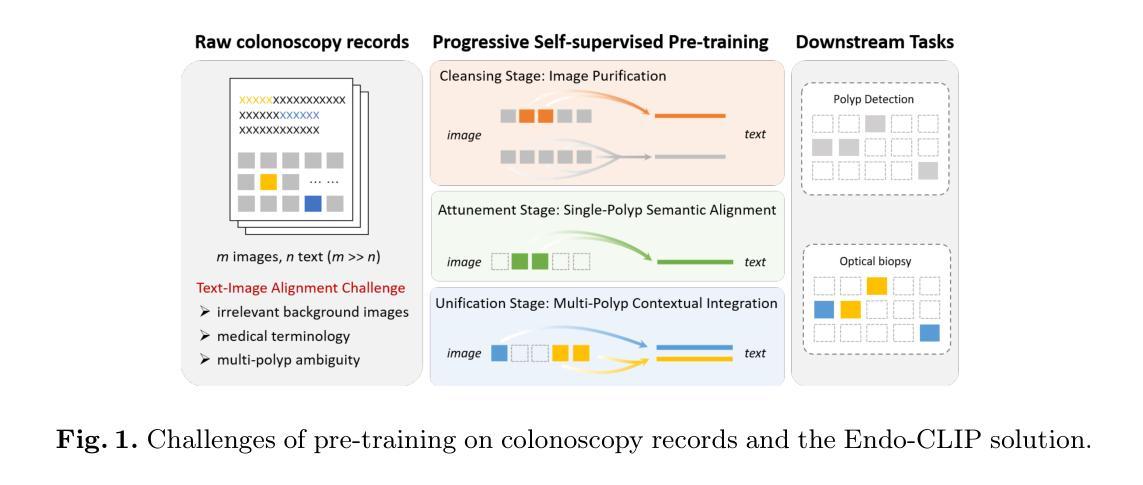
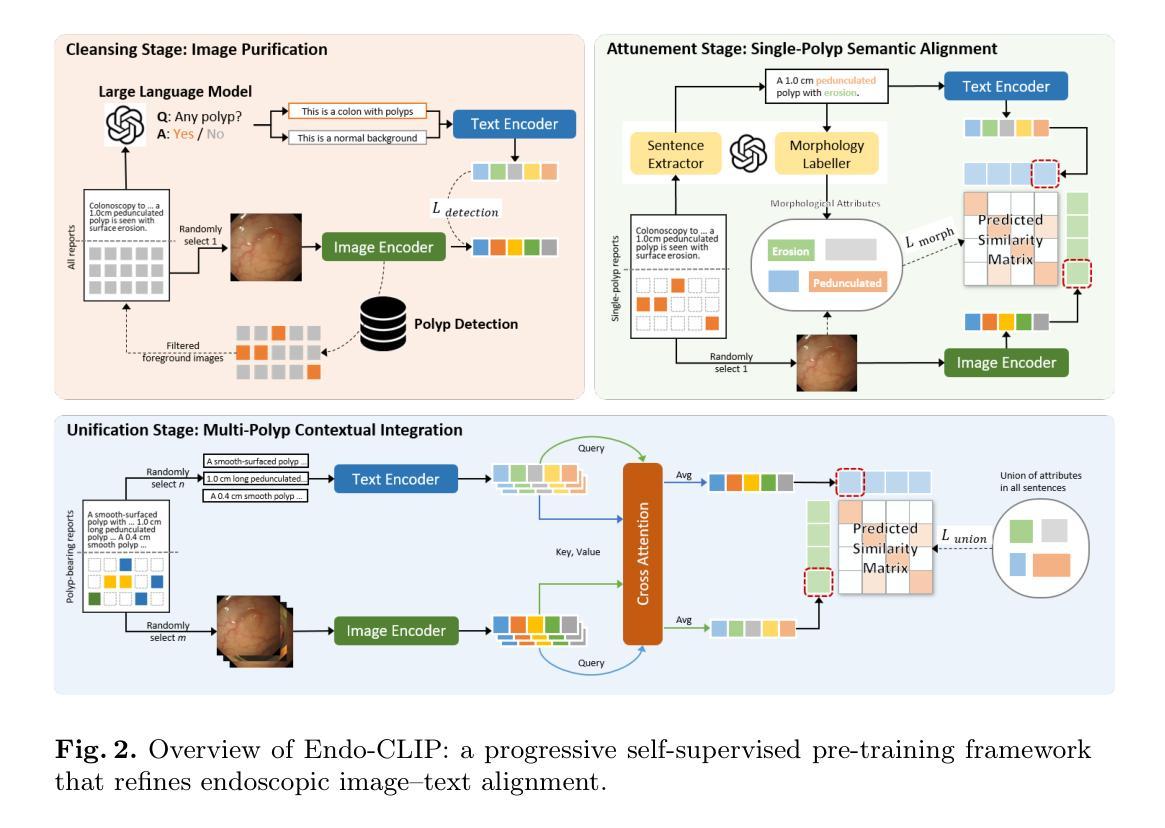
Pre-training on image-text colonoscopy records offers substantial potential for improving endoscopic image analysis, but faces challenges including non-informative background images, complex medical terminology, and ambiguous multi-lesion descriptions. We introduce Endo-CLIP, a novel self-supervised framework that enhances Contrastive Language-Image Pre-training (CLIP) for this domain. Endo-CLIP’s three-stage framework–cleansing, attunement, and unification–addresses these challenges by (1) removing background frames, (2) leveraging large language models to extract clinical attributes for fine-grained contrastive learning, and (3) employing patient-level cross-attention to resolve multi-polyp ambiguities. Extensive experiments demonstrate that Endo-CLIP significantly outperforms state-of-the-art pre-training methods in zero-shot and few-shot polyp detection and classification, paving the way for more accurate and clinically relevant endoscopic analysis.
对图像文本结肠镜检查记录进行预训练,在提高内镜图像分析方面存在巨大潜力,但也面临着非信息背景图像、复杂医学术语和模糊多病灶描述等挑战。我们引入了Endo-CLIP,这是一种新型自监督框架,能够增强此领域的对比语言图像预训练(CLIP)。Endo-CLIP的三阶段框架——清洁、调整和统一,通过(1)去除背景帧,(2)利用大型语言模型提取用于精细对比学习的临床属性,(3)采用患者级交叉注意力来解决多息肉模糊问题。大量实验表明,Endo-CLIP在零样本和少样本息肉检测和分类方面显著优于最新的预训练模型,为更准确和临床相关的内镜分析铺平了道路。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Early accepted to MICCAI 2025
Summary:预训练图像文本结肠镜检查记录对于改进内窥镜图像分析具有巨大潜力,但面临非信息背景图像、复杂医学术语和模糊多病灶描述等挑战。我们引入了Endo-CLIP,这是一种新型自监督框架,可增强此领域的对比语言图像预训练(CLIP)。Endo-CLIP的三阶段框架——净化、调整和统一,通过(1)去除背景帧,(2)利用大型语言模型提取临床特征进行精细对比学习,(3)采用患者级交叉注意力来解决多息肉模糊问题。实验表明,Endo-CLIP在零样本和少样本息肉检测和分类方面显著优于最新预训练方法,为更准确和临床相关的内窥镜分析铺平了道路。
Key Takeaways:
- 预训练图像文本结肠镜检查记录有助于改进内窥镜图像分析。
- Endo-CLIP是一个针对此领域的自监督框架,增强了对比语言图像预训练(CLIP)。
- Endo-CLIP通过去除背景帧、利用大型语言模型提取临床特征来解决挑战。
- Endo-CLIP采用患者级交叉注意力来解决多息肉模糊问题。
- 实验表明,Endo-CLIP在零样本和少样本息肉检测和分类方面表现优异。
- Endo-CLIP的方法为更准确和临床相关的内窥镜分析提供了可能。
- Endo-CLIP框架包括净化、调整和统一三个阶段。
点此查看论文截图

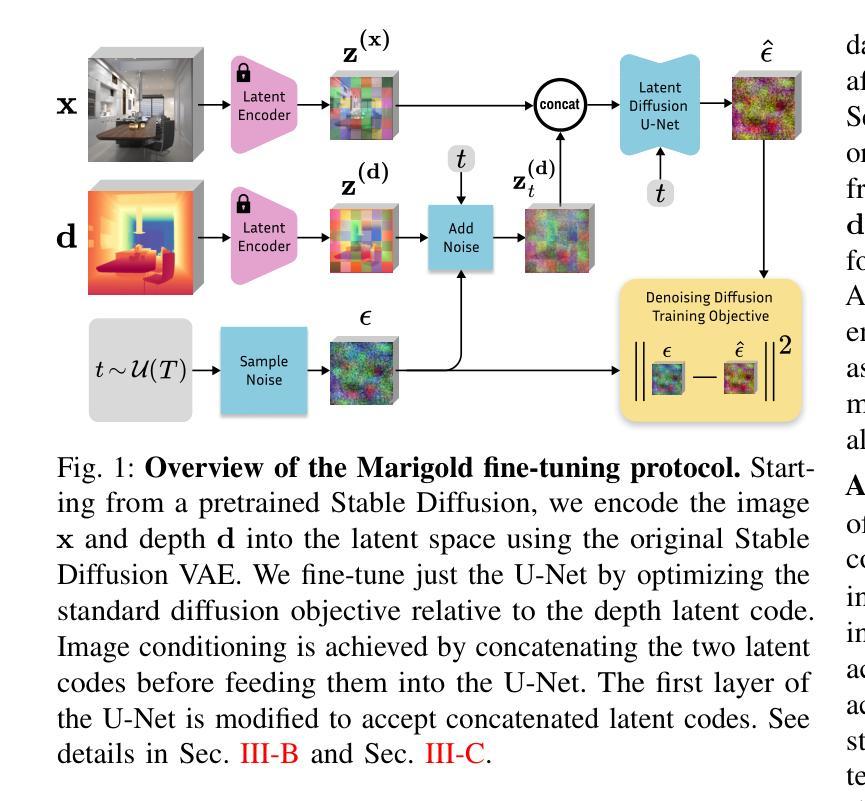
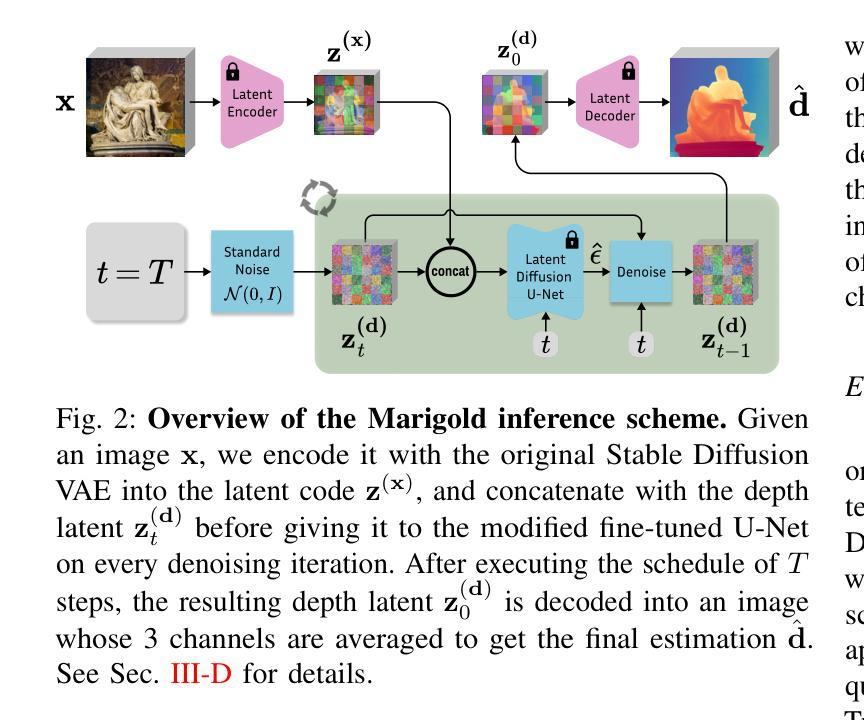
Marigold: Affordable Adaptation of Diffusion-Based Image Generators for Image Analysis
Authors:Bingxin Ke, Kevin Qu, Tianfu Wang, Nando Metzger, Shengyu Huang, Bo Li, Anton Obukhov, Konrad Schindler
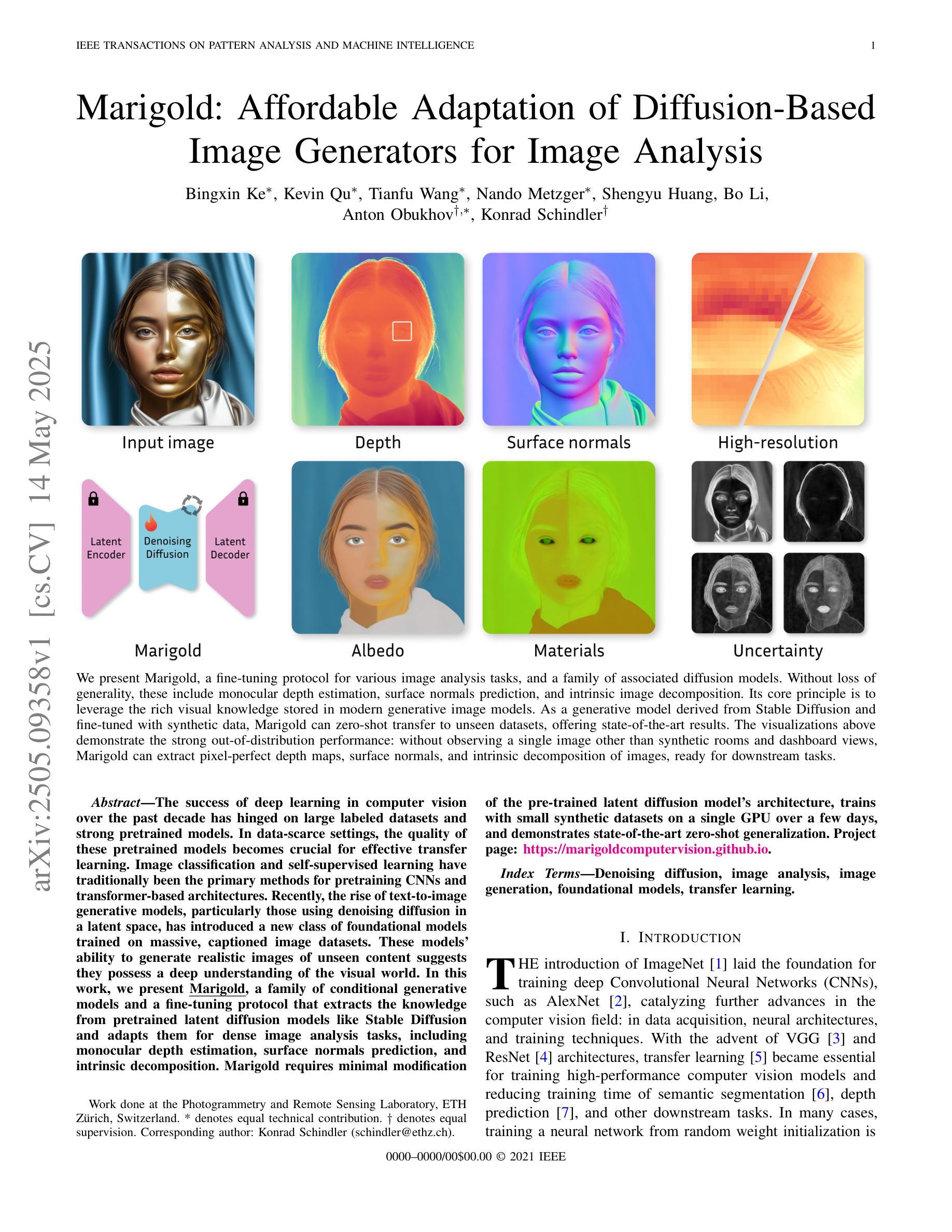
The success of deep learning in computer vision over the past decade has hinged on large labeled datasets and strong pretrained models. In data-scarce settings, the quality of these pretrained models becomes crucial for effective transfer learning. Image classification and self-supervised learning have traditionally been the primary methods for pretraining CNNs and transformer-based architectures. Recently, the rise of text-to-image generative models, particularly those using denoising diffusion in a latent space, has introduced a new class of foundational models trained on massive, captioned image datasets. These models’ ability to generate realistic images of unseen content suggests they possess a deep understanding of the visual world. In this work, we present Marigold, a family of conditional generative models and a fine-tuning protocol that extracts the knowledge from pretrained latent diffusion models like Stable Diffusion and adapts them for dense image analysis tasks, including monocular depth estimation, surface normals prediction, and intrinsic decomposition. Marigold requires minimal modification of the pre-trained latent diffusion model’s architecture, trains with small synthetic datasets on a single GPU over a few days, and demonstrates state-of-the-art zero-shot generalization. Project page: https://marigoldcomputervision.github.io
过去十年,深度学习在计算机视觉领域取得的成功主要依赖于大量标注数据集和强大的预训练模型。在数据稀缺的环境中,这些预训练模型的质量对于有效的迁移学习至关重要。图像分类和自监督学习一直是预训练CNN和基于Transformer架构的传统主要方法。最近,文本到图像的生成模型兴起,特别是在潜在空间使用去噪扩散的模型,引入了一类新的基础模型,这些模型在大量的带字幕图像数据集上进行训练。这些模型生成未见内容的现实图像的能力表明它们对视觉世界有深刻的理解。在这项工作中,我们提出了Marigold,这是一系列条件生成模型和微调协议,它从预训练的潜在扩散模型(如Stable Diffusion)中提取知识,并适应密集图像分析任务,包括单目深度估计、表面法线预测和内在分解。Marigold对预训练的潜在扩散模型的架构进行了最小的修改,使用小型合成数据集在单个GPU上进行几天的训练,并展示了最先进的零样本泛化能力。项目页面:https://marigoldcomputervision.github.io
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Journal extension of our CVPR 2024 paper, featuring new tasks, improved efficiency, high-resolution capabilities, and enhanced accessibility
Summary
深度学习在过去十年在计算机视觉领域的成功,依赖于大规模标注数据集和强大的预训练模型。在数据稀缺的情况下,预训练模型的质量对于有效的迁移学习至关重要。传统的图像分类和自监督学习是预训练CNN和基于transformer架构的主要方法。最近,文本到图像生成模型的兴起,特别是在潜在空间中使用去噪扩散的模型,引入了一类新的基础模型,这些模型在大型带字幕的图像数据集上进行训练。这类模型能够生成未见内容的真实图像,表明它们对视觉世界有深刻的理解。在这项工作中,我们提出了Marigold,一系列条件生成模型和微调协议,从预训练的潜在扩散模型如Stable Diffusion中提取知识,并适应密集图像分析任务,包括单目深度估计、表面法线预测和内在分解。Marigold对预训练的潜在扩散模型的架构进行了最小的修改,可在单个GPU上使用小型合成数据集进行几天的训练,并展示了零样本泛化的最新水平。
Key Takeaways
- 深度学习在计算机视觉领域的成功依赖于大规模标注数据集和强大的预训练模型。
- 在数据稀缺的情况下,预训练模型的质量对迁移学习至关重要。
- 文本到图像生成模型的兴起引入了一类新的基础模型,能生成未见内容的真实图像。
- Marigold是一种条件生成模型和微调协议,可从预训练的潜在扩散模型中提取知识。
- Marigold适应密集图像分析任务,包括单目深度估计、表面法线预测和内在分解。
- Marigold对预训练模型的架构进行了最小修改,可在单个GPU上几天内完成训练。
点此查看论文截图
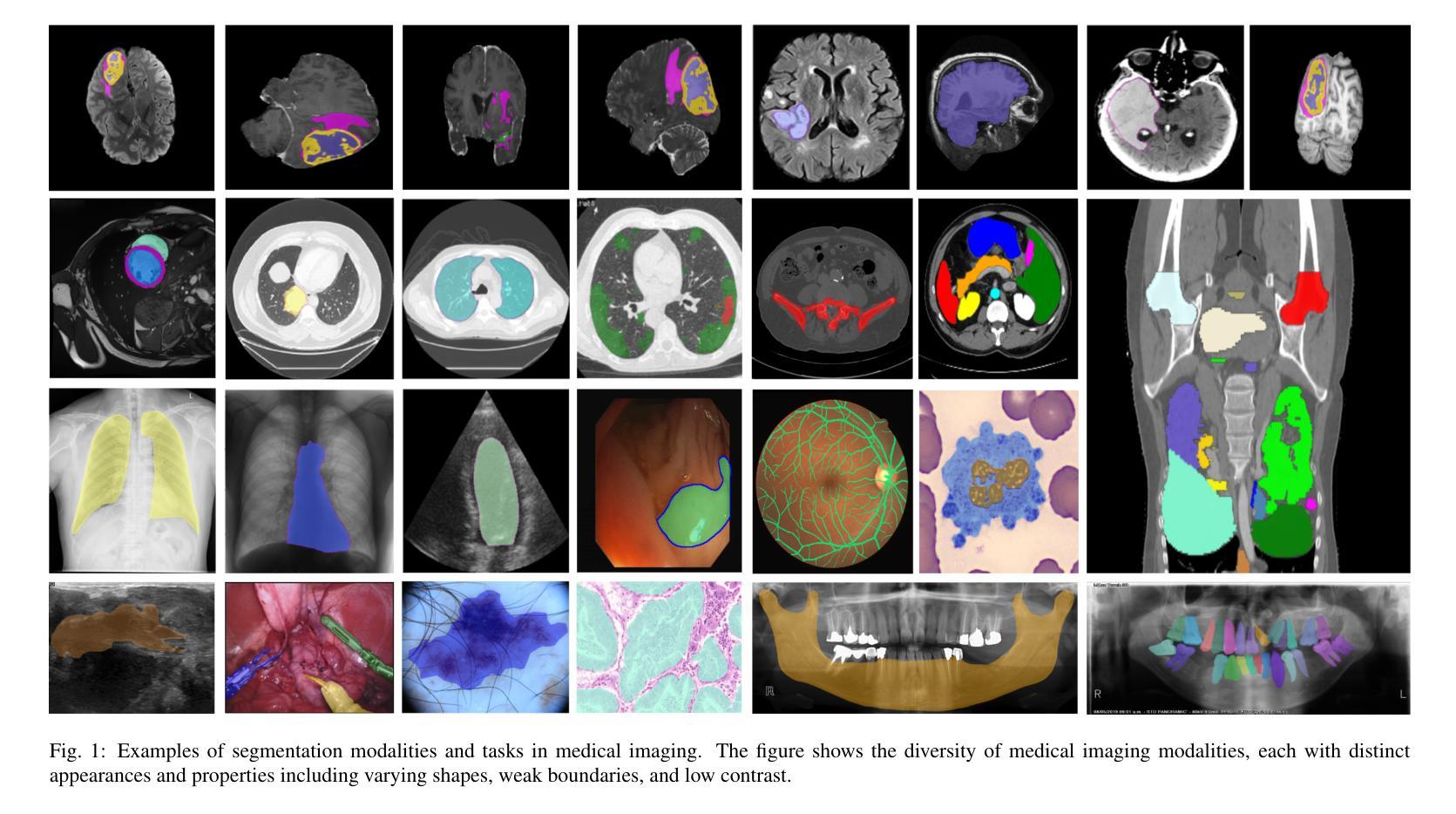
Recent Advances in Medical Imaging Segmentation: A Survey
Authors:Fares Bougourzi, Abdenour Hadid
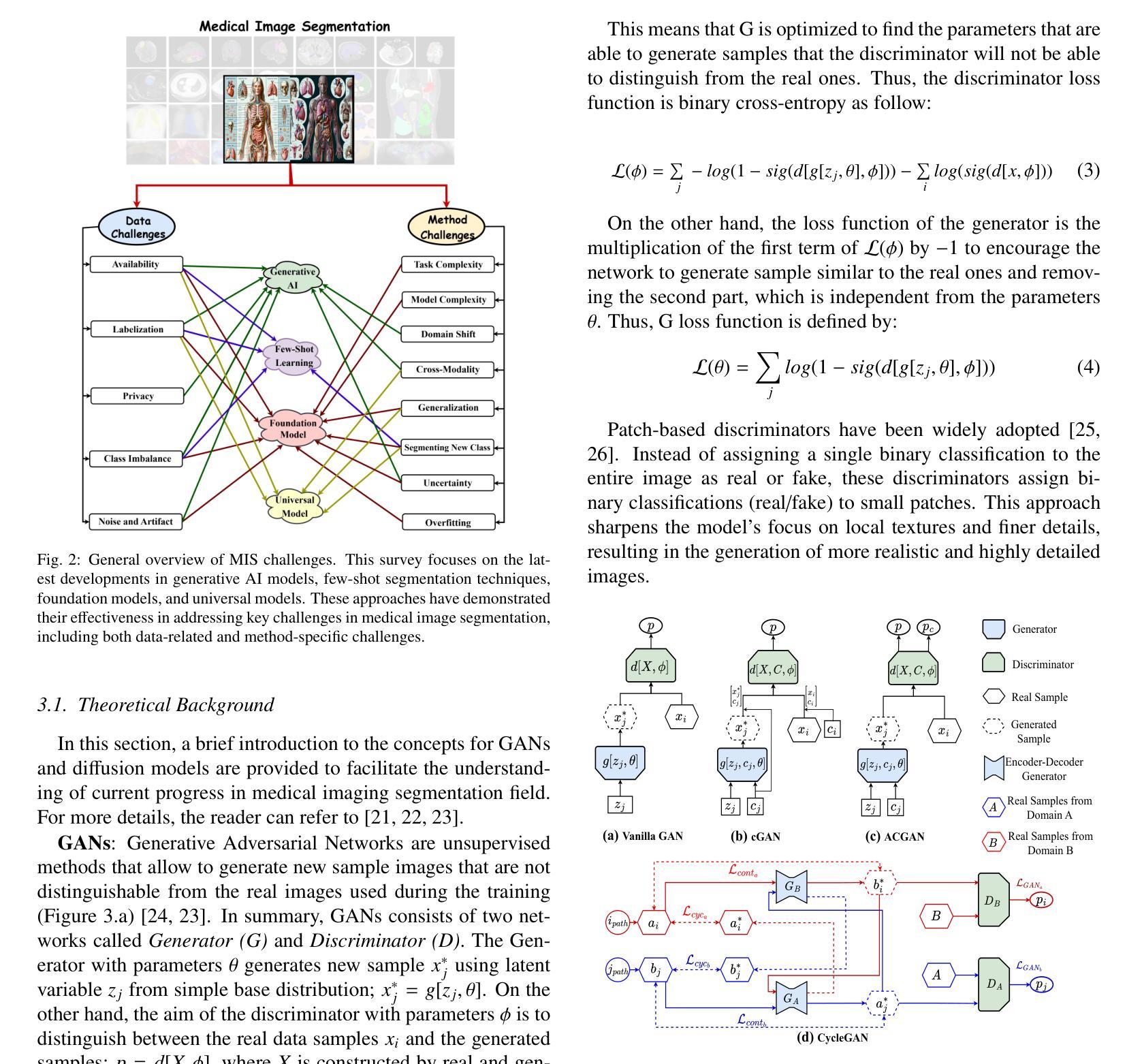
Medical imaging is a cornerstone of modern healthcare, driving advancements in diagnosis, treatment planning, and patient care. Among its various tasks, segmentation remains one of the most challenging problem due to factors such as data accessibility, annotation complexity, structural variability, variation in medical imaging modalities, and privacy constraints. Despite recent progress, achieving robust generalization and domain adaptation remains a significant hurdle, particularly given the resource-intensive nature of some proposed models and their reliance on domain expertise. This survey explores cutting-edge advancements in medical image segmentation, focusing on methodologies such as Generative AI, Few-Shot Learning, Foundation Models, and Universal Models. These approaches offer promising solutions to longstanding challenges. We provide a comprehensive overview of the theoretical foundations, state-of-the-art techniques, and recent applications of these methods. Finally, we discuss inherent limitations, unresolved issues, and future research directions aimed at enhancing the practicality and accessibility of segmentation models in medical imaging. We are maintaining a \href{https://github.com/faresbougourzi/Awesome-DL-for-Medical-Imaging-Segmentation}{GitHub Repository} to continue tracking and updating innovations in this field.
医学影像是现代医疗的基石,推动着诊断、治疗计划和患者护理的进步。在其众多任务中,由于数据可访问性、注释复杂性、结构变化性、医学影像模式的变化以及隐私约束等因素,分割仍然是最具挑战性的问题之一。尽管最近有所进展,但实现稳健的泛化和域适应仍然是一个重大障碍,尤其是一些提出的模型资源密集且依赖于专业领域知识。这篇综述探讨了医学影像分割的最新进展,重点关注生成人工智能、小样本学习、基础模型和通用模型等方法。这些方法为解决长期存在的挑战提供了有希望的解决方案。我们全面概述了这些方法的理论基础、最新技术和最新应用。最后,我们讨论了固有的局限性、未解决的问题以及未来的研究方向,旨在提高医学影像分割模型的实用性和可访问性。我们正在维护一个GitHub仓库(https://github.com/faresbougourzi/Awesome-DL-for-Medical-Imaging-Segmentation),以继续跟踪和更新该领域的创新。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
医学成像是现代医疗的核心,驱动诊断、治疗计划和患者护理的进步。分割是医学成像中最具挑战性的任务之一,面临数据获取、标注复杂性、结构变化、医学成像模式变化及隐私约束等问题。虽然最近的进步显著,但在实现稳健的泛化和域适应方面仍存在重大障碍,尤其是一些提出的模型资源密集且依赖领域专业知识。这篇综述探讨了医疗图像分割的最新进展,重点关注生成人工智能、小样本学习、基础模型和通用模型等方法。这些方法为解决长期存在的挑战提供了有前景的解决方案。我们全面概述了这些方法的理论基础、最新技术和近期应用。最后,我们讨论了固有的局限性、未解决的问题以及未来的研究方向,旨在提高医学成像分割模型的实用性和可访问性。
Key Takeaways
- 医学成像是现代医疗的重要支柱,推动诊断、治疗计划和患者护理的进步。
- 分割是医学成像中的一项具有挑战性的任务,受到多种因素的影响,如数据获取难度、标注复杂性等。
- 尽管已有显著进展,但实现模型的稳健泛化和域适应仍是医学图像分割中的一大挑战。
- 综述探讨了医疗图像分割的最新进展,重点关注生成人工智能等方法。
- 这些方法为解决长期存在的挑战提供了前景,包括最新的理论、技术和应用。
- 存在固有的局限性和未解决的问题需要解决,以提高模型的实用性和可访问性。
点此查看论文截图

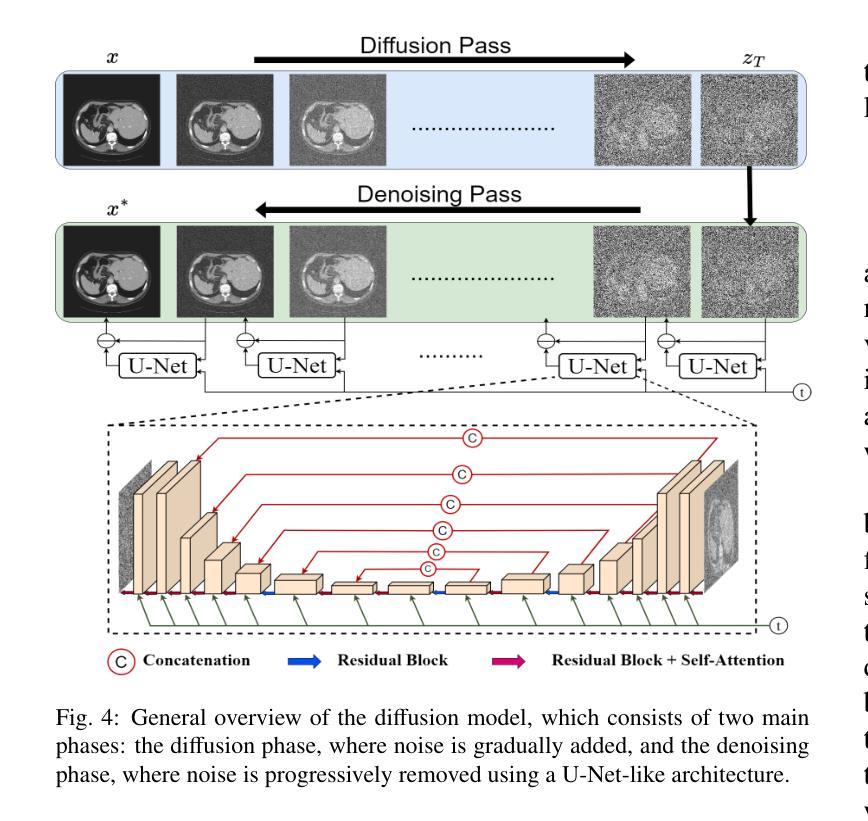
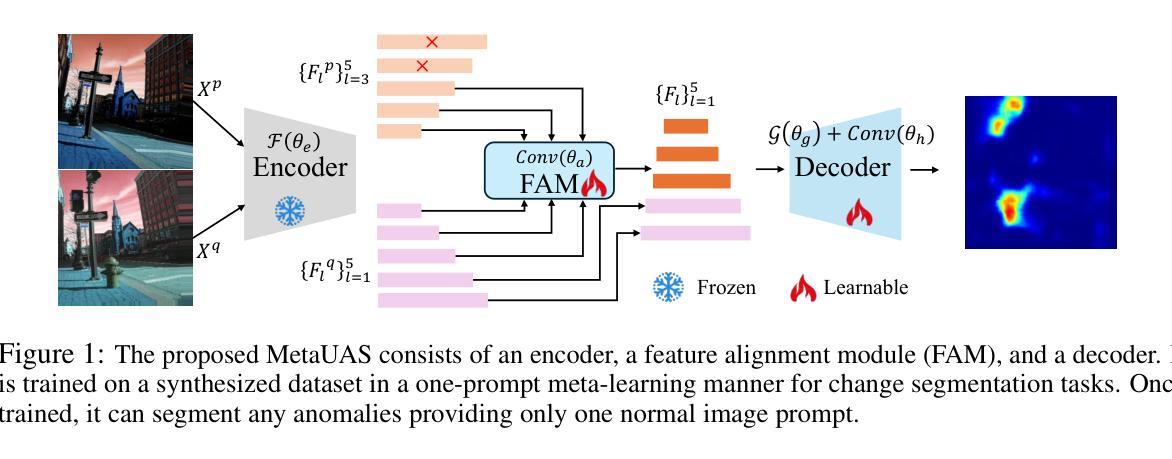
MetaUAS: Universal Anomaly Segmentation with One-Prompt Meta-Learning
Authors:Bin-Bin Gao
Zero- and few-shot visual anomaly segmentation relies on powerful vision-language models that detect unseen anomalies using manually designed textual prompts. However, visual representations are inherently independent of language. In this paper, we explore the potential of a pure visual foundation model as an alternative to widely used vision-language models for universal visual anomaly segmentation. We present a novel paradigm that unifies anomaly segmentation into change segmentation. This paradigm enables us to leverage large-scale synthetic image pairs, featuring object-level and local region changes, derived from existing image datasets, which are independent of target anomaly datasets. We propose a one-prompt Meta-learning framework for Universal Anomaly Segmentation (MetaUAS) that is trained on this synthetic dataset and then generalizes well to segment any novel or unseen visual anomalies in the real world. To handle geometrical variations between prompt and query images, we propose a soft feature alignment module that bridges paired-image change perception and single-image semantic segmentation. This is the first work to achieve universal anomaly segmentation using a pure vision model without relying on special anomaly detection datasets and pre-trained visual-language models. Our method effectively and efficiently segments any anomalies with only one normal image prompt and enjoys training-free without guidance from language. Our MetaUAS significantly outperforms previous zero-shot, few-shot, and even full-shot anomaly segmentation methods. The code and pre-trained models are available at https://github.com/gaobb/MetaUAS.
零样本和少样本视觉异常分割依赖于强大的视觉语言模型,这些模型使用手动设计的文本提示来检测未见过的异常。然而,视觉表示本质上独立于语言。本文中,我们探索了纯视觉基础模型作为广泛使用的视觉语言模型的替代方案,用于通用视觉异常分割的潜力。我们提出了一种将异常分割统一为变化分割的新范式。这种范式使我们能够利用从现有图像数据集派生的对象级别和局部区域变化的大规模合成图像对。这些图像对独立于目标异常数据集。我们提出了一种用于通用异常分割的一提示元学习框架(MetaUAS),该框架在这个合成数据集上进行训练,然后很好地推广到现实世界中任何新型或未见过的视觉异常的分割。为了处理提示图像和查询图像之间的几何变化,我们提出了一个软特征对齐模块,该模块桥梁了配对图像变化感知和单图像语义分割。这是第一项工作,使用纯视觉模型实现通用异常分割,而无需依赖特定的异常检测数据集和预训练的视觉语言模型。我们的方法只需一个正常图像提示,就能有效且高效地分割任何异常,并且无需语言的指导即可实现无训练。我们的MetaUAS显著优于之前的零样本、少样本甚至全样本异常分割方法。代码和预训练模型可在[https://github.com/gaobb/MetaUAS找到。]
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by NeurIPS 2024
Summary
本文探索了纯视觉基础模型在通用视觉异常分割中的潜力,提出了一种将异常分割整合为变化分割的新范式。该研究利用从现有图像数据集派生的大规模合成图像对,独立于目标异常数据集,实现任何新型或未见过的视觉异常的分割。研究还提出了一种基于元学习的一提示框架MetaUAS,该框架在此合成数据集上进行训练,并能很好地推广到现实世界中的异常分割。此外,该研究还提出了一种软特征对齐模块,以解决提示图像和查询图像之间的几何变化问题。这是第一项仅使用纯视觉模型实现通用异常分割的工作,不依赖于特殊异常检测数据集和预训练的语言模型。
Key Takeaways
- 研究探索了纯视觉基础模型在视觉异常分割中的潜力,提出了一种新的变化分割范式。
- 利用大规模合成图像对进行训练,这些图像对独立于目标异常数据集。
- 提出了一提示框架MetaUAS,能在现实世界中很好地推广异常分割。
- 引入软特征对齐模块以解决提示图像和查询图像之间的几何变化问题。
- 该方法是首个使用纯视觉模型实现通用异常分割的工作,无需特殊异常检测数据集和预训练的语言模型。
- MetaUAS显著优于先前的零样本、少样本甚至全样本异常分割方法。
点此查看论文截图


Few-Shot Anomaly-Driven Generation for Anomaly Classification and Segmentation
Authors:Guan Gui, Bin-Bin Gao, Jun Liu, Chengjie Wang, Yunsheng Wu
Anomaly detection is a practical and challenging task due to the scarcity of anomaly samples in industrial inspection. Some existing anomaly detection methods address this issue by synthesizing anomalies with noise or external data. However, there is always a large semantic gap between synthetic and real-world anomalies, resulting in weak performance in anomaly detection. To solve the problem, we propose a few-shot Anomaly-driven Generation (AnoGen) method, which guides the diffusion model to generate realistic and diverse anomalies with only a few real anomalies, thereby benefiting training anomaly detection models. Specifically, our work is divided into three stages. In the first stage, we learn the anomaly distribution based on a few given real anomalies and inject the learned knowledge into an embedding. In the second stage, we use the embedding and given bounding boxes to guide the diffusion model to generate realistic and diverse anomalies on specific objects (or textures). In the final stage, we propose a weakly-supervised anomaly detection method to train a more powerful model with generated anomalies. Our method builds upon DRAEM and DesTSeg as the foundation model and conducts experiments on the commonly used industrial anomaly detection dataset, MVTec. The experiments demonstrate that our generated anomalies effectively improve the model performance of both anomaly classification and segmentation tasks simultaneously, \eg, DRAEM and DseTSeg achieved a 5.8% and 1.5% improvement in AU-PR metric on segmentation task, respectively. The code and generated anomalous data are available at https://github.com/gaobb/AnoGen.
异常检测是一项实用且具有挑战性的任务,因为在工业检测中异常样本非常稀缺。一些现有的异常检测方法通过合成异常和噪声或外部数据来解决这个问题。然而,合成异常和真实世界异常之间始终存在较大的语义差距,导致异常检测性能较弱。为了解决这个问题,我们提出了一种小样本的Anomaly驱动生成(AnoGen)方法,该方法仅使用少量真实异常来指导扩散模型生成现实且多样的异常,从而有益于训练异常检测模型。具体来说,我们的工作分为三个阶段。在第一阶段,我们基于给定的少量真实异常学习异常分布,并将学到的知识注入嵌入中。在第二阶段,我们使用嵌入和给定的边界框来指导扩散模型在特定对象(或纹理)上生成现实且多样的异常。在第三阶段,我们提出了一种弱监督的异常检测方法,利用生成的异常来训练更强大的模型。我们的方法以DRAEM和DesTSeg作为基础模型,并在常用的工业异常检测数据集MVTec上进行实验。实验表明,我们生成的异常有效地提高了异常分类和分割任务的模型性能,例如,DRAEM和DseTSeg在分割任务的AU-PR指标上分别提高了5.8%和1.5%。代码和生成的异常数据可在https://github.com/gaobb/AnoGen找到。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by ECCV 2024
Summary
本文提出一种基于少量真实异常样本驱动的生成方法(AnoGen),用于解决工业检测中的异常检测问题。该方法通过三个阶段实现:学习异常分布并注入知识到嵌入中,使用嵌入和边界框指导扩散模型生成特定对象(或纹理)上的真实和多样化的异常,以及使用弱监督方法训练更强大的异常检测模型。实验证明,该方法能有效提高异常分类和分割任务的模型性能。
Key Takeaways
- 异常检测是工业检测中的实际挑战,因缺乏异常样本。
- 现有方法通过合成异常和噪声或外部数据来解决此问题,但存在语义鸿沟。
- 提出了一种基于少量真实异常样本驱动的生成方法(AnoGen)。
4.AnoGen分为三个阶段:学习异常分布,指导扩散模型生成真实和多样化的异常,以及训练弱监督异常检测模型。 - 方法建立在DRAEM和DesTSeg模型之上,并在MVTec工业异常检测数据集上进行实验验证。
- 实验证明,该方法能有效提高异常分类和分割任务的模型性能。
点此查看论文截图