⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-05-17 更新
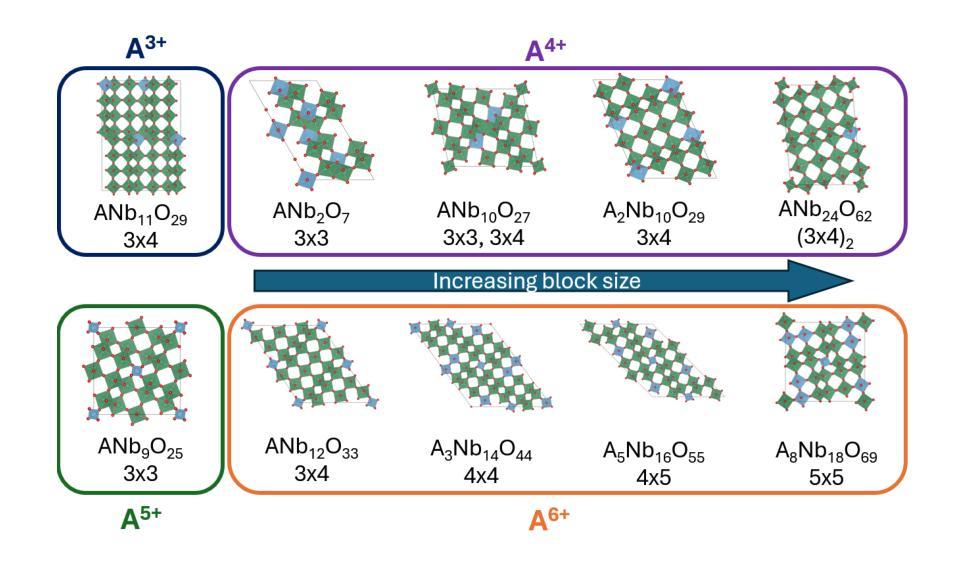
Computational screening and experimental validation of promising Wadsley-Roth Niobates
Authors:Zachary J. L. Bare, CJ Sturgill, Manish Kumar, Iva Milisavljevic, Hans-Conrad zur Loye, Scott Misture, Morgan Stefik, Christopher Sutton
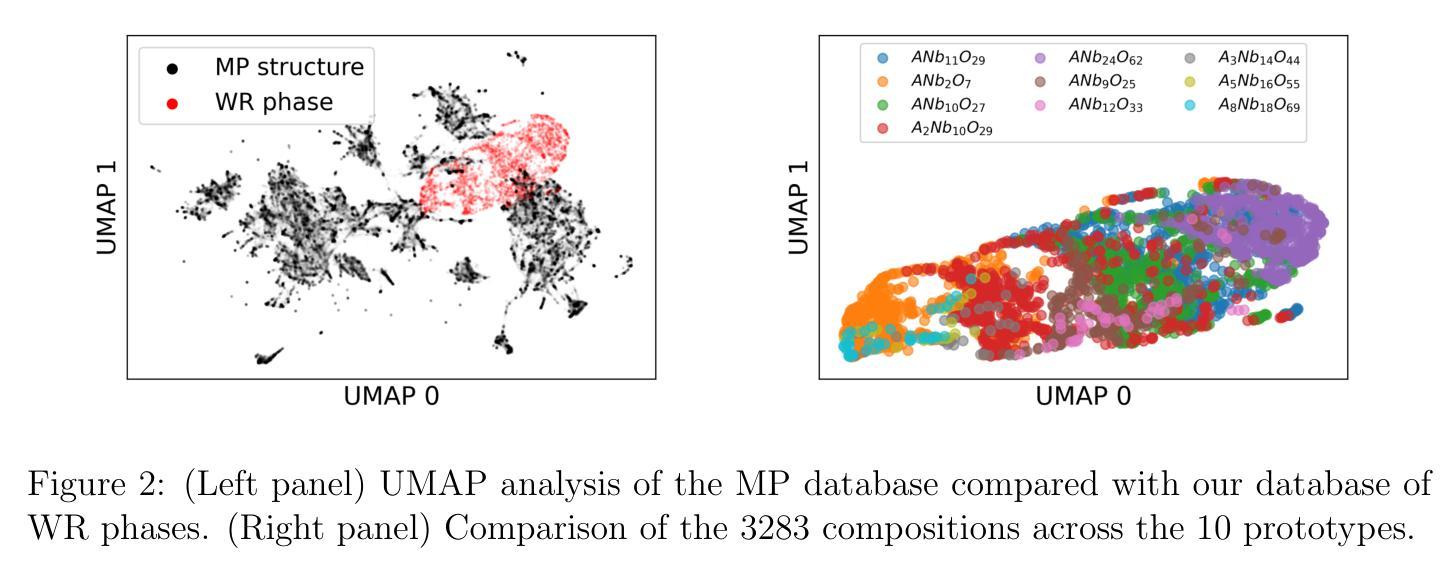
The growing demand for efficient, high-capacity energy storage systems has driven extensive research into advanced materials for lithium-ion batteries. Among the various candidates, Wadsley-Roth (WR) niobates have emerged as a promising class of materials for fast Li+ storage due to rapid ion diffusion within their ReO3-like blocks in combination with good electronic conductivity along the shear planes. Despite the remarkable features of WR phases, there are presently less than 30 known structures which limits identification of structure-property relationships for improved performance as well as the identification of phases with more earth-abundant elements. In this work, we have dramatically expanded the set of potentially (meta)stable compositions (with $\Delta$ Hd < 22 meV/atom) to 1301 (out of 3283) through high-throughput screening with density functional theory (DFT). This large space of compound was generated through single- and double-site substitution into 10 known WR-niobate prototypes using 48 elements across the periodic table. To confirm the structure predictions, we successfully synthesized and validated with X-ray diffraction a new material, MoWNb24O66. The measured lithium diffusivity in MoWNb24O66 has a peak value of 1.0x10-16 m2/s at 1.45 V vs. Li/Li+ and achieved 225 mAh/g at 5C. Thus a computationally predicted phase was realized experimentally with performance exceeding Nb16W5O55, a recent WR benchmark. Overall, the computational dataset of potentially stable novel compounds and with one realized that has competitive performance provide a valuable guide for experimentalists in discovering new durable battery materials.
随着对高效、大容量能源存储系统需求的不断增长,针对锂离子电池先进材料的研究已经广泛开展。在各种候选材料中,Wadsley-Roth(WR)铌酸盐因其ReO3型块内的快速离子扩散以及剪切平面上的良好电子导电性,成为快速Li+存储的有前途的材料。尽管WR相具有引人注目的特征,但目前仅已知不到30种结构,这限制了识别改善性能的结构-属性关系以及具有更丰富地球元素的阶段的识别。在这项工作中,我们通过高通量筛选密度泛函理论(DFT),将可能(元)稳定的组合物(ΔHd <22 meV/atom)从3283个显著扩展至1301个。这个巨大的化合物空间是通过对10种已知的WR-铌酸原型进行单点和双点取代,使用周期表中的48个元素而生成的。为了验证结构预测,我们成功合成并通过X射线衍射验证了一种新材料MoWNb24O66。在MoWNb24O66中测量的锂扩散率在1.45V(相对于Li/Li+)时达到峰值1.0x10-16 m2/s,并在5C时达到225 mAh/g。因此,实验上实现了一种计算预测的阶段,其性能超过了最近的WR基准Nb16W5O55。总体而言,具有竞争力性能的潜在稳定新型化合物的计算数据集以及一种已实现的材料,为实验者发现新的持久电池材料提供了宝贵的指南。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
WR型铌酸盐材料在锂离子电池的快速发展中展现出巨大的潜力,其快速的离子扩散和良好的电子导电性使其成为快速存储Li+的理想选择。然而,已知的结构数量有限(不到30种),限制了性能与结构关系的研究以及更丰富元素相的发现。本研究通过高通量筛选和密度泛函理论(DFT)计算,大幅扩展了潜在稳定化合物范围,从已知的WR型铌酸原型中通过单双位点取代得到1301种化合物(共3283种)。合成并验证了一种新材料MoWNb24O66,其锂离子扩散速率峰值达到1.0x10-16 m2/s,放电电压为1.45 V,容量达到225 mAh/g,性能超越现有WR型基准材料Nb16W5O55。该计算数据集为实验发现新型持久电池材料提供了宝贵指南。
Key Takeaways
- Wadsley-Roth(WR)型铌酸盐材料在锂离子电池领域具有快速离子扩散和电子导电性的潜力。
- 目前已知WR型结构数量有限(少于30种),限制了性能提升和新材料发现的潜力。
- 通过高通量筛选和密度泛函理论(DFT)计算,大幅扩展了潜在稳定化合物的范围。
- 成功合成并验证了新材料MoWNb24O66,具有出色的锂离子扩散性能和电池容量。
- MoWNb24O66的锂离子扩散速率峰值高,且放电电压和容量表现优秀,性能超越现有基准材料。
- 计算数据集为实验发现新型持久电池材料提供了有价值的指导。
点此查看论文截图

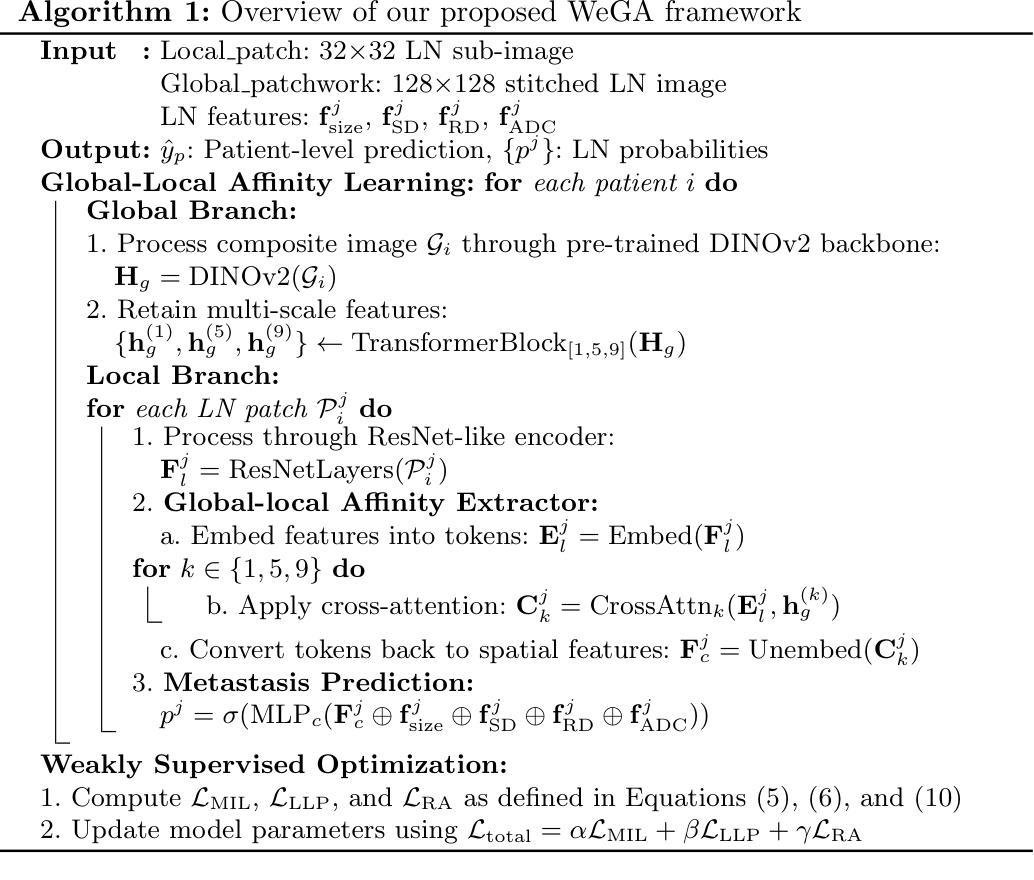
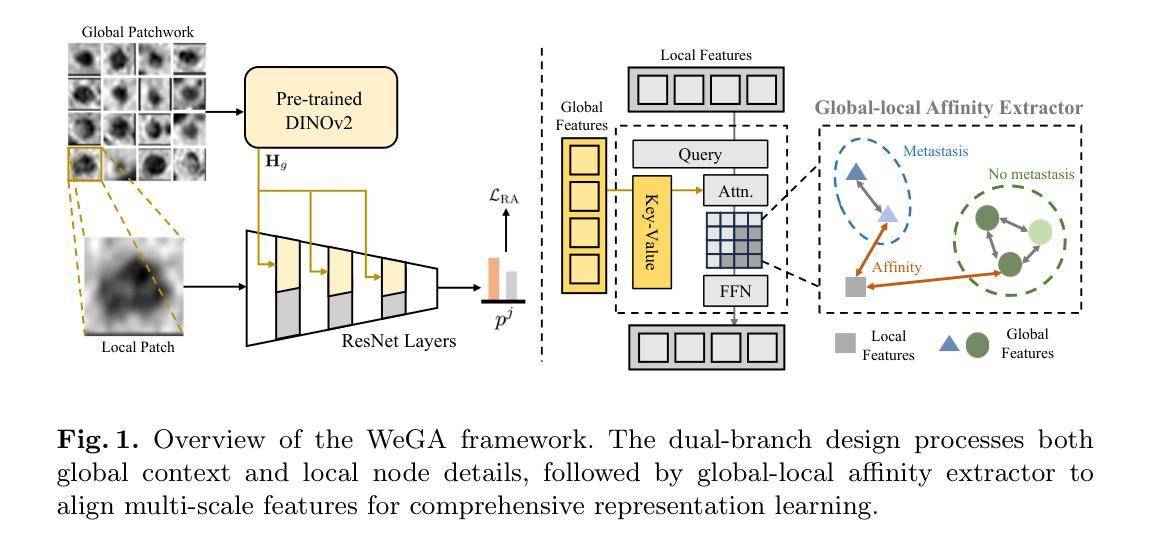
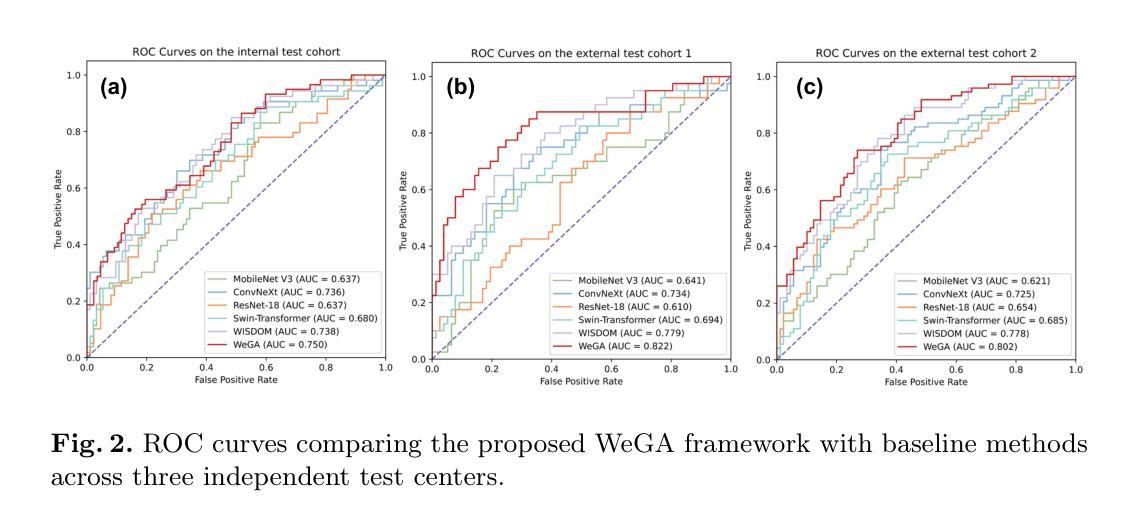
WeGA: Weakly-Supervised Global-Local Affinity Learning Framework for Lymph Node Metastasis Prediction in Rectal Cancer
Authors:Yifan Gao, Yaoxian Dong, Wenbin Wu, Chaoyang Ge, Feng Yuan, Jiaxi Sheng, Haoyue Li, Xin Gao
Accurate lymph node metastasis (LNM) assessment in rectal cancer is essential for treatment planning, yet current MRI-based evaluation shows unsatisfactory accuracy, leading to suboptimal clinical decisions. Developing automated systems also faces significant obstacles, primarily the lack of node-level annotations. Previous methods treat lymph nodes as isolated entities rather than as an interconnected system, overlooking valuable spatial and contextual information. To solve this problem, we present WeGA, a novel weakly-supervised global-local affinity learning framework that addresses these challenges through three key innovations: 1) a dual-branch architecture with DINOv2 backbone for global context and residual encoder for local node details; 2) a global-local affinity extractor that aligns features across scales through cross-attention fusion; and 3) a regional affinity loss that enforces structural coherence between classification maps and anatomical regions. Experiments across one internal and two external test centers demonstrate that WeGA outperforms existing methods, achieving AUCs of 0.750, 0.822, and 0.802 respectively. By effectively modeling the relationships between individual lymph nodes and their collective context, WeGA provides a more accurate and generalizable approach for lymph node metastasis prediction, potentially enhancing diagnostic precision and treatment selection for rectal cancer patients.
对直肠癌淋巴结转移(LNM)的准确评估是治疗计划的关键,但目前的MRI评估准确性不佳,可能导致临床决策失误。自动系统的开发也面临重大障碍,主要是缺乏节点级别的注释。以往的方法将淋巴结视为孤立的实体,而非互联系统,从而忽略了宝贵的空间和上下文信息。为了解决这一问题,我们提出了WeGA,这是一种新型的弱监督全局-局部亲和力学习框架,通过三项关键创新解决这些挑战:1)具有DINOv2主干和残差编码器分支的 Dual-Branch 架构,用于全局上下文和局部节点细节;2)全局-局部亲和力提取器,通过跨注意力融合来跨尺度对齐特征;3)区域亲和力损失,在分类图和解剖区域之间强制执行结构一致性。在一个内部和两个外部测试中心的实验表明,WeGA优于现有方法,分别实现了AUC值为0.750、0.822和0.802。通过有效地建模单个淋巴结之间的关系及其集体上下文,WeGA为淋巴结转移预测提供了更准确和可推广的方法,可能提高直肠癌患者的诊断精度和治疗选择。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文提出一种新型的弱监督全局局部亲和力学习框架WeGA,用于准确评估直肠癌淋巴节点转移情况。该方法通过采用双分支架构、全局局部亲和力提取器和区域亲和力损失,有效解决了当前MRI评估及自动化系统中的问题。实验证明,WeGA在淋巴节点转移预测方面的性能优于现有方法,为直肠癌患者的诊断和治疗的精确性提供了提高的可能。
Key Takeaways
- WeGA是一个新型的弱监督全局局部亲和力学习框架,旨在提高直肠癌淋巴节点转移的评估准确性。
- 该方法通过采用双分支架构,结合全局上下文和局部节点细节信息。
- WeGA利用全局局部亲和力提取器,通过跨尺度注意力融合,对齐特征。
- 区域亲和力损失模型的引入,增强了分类图与解剖区域之间的结构一致性。
- 实验结果表明,WeGA在内部和外部测试中心均表现出优异的性能,实现了较高的AUC值。
- WeGA通过建模单个淋巴节点与其集体上下文之间的关系,提供了一种更准确、更通用的淋巴节点转移预测方法。
点此查看论文截图

HWA-UNETR: Hierarchical Window Aggregate UNETR for 3D Multimodal Gastric Lesion Segmentation
Authors:Jiaming Liang, Lihuan Dai, Xiaoqi Sheng, Xiangguang Chen, Chun Yao, Guihua Tao, Qibin Leng, Honming Cai, Xi Zhong
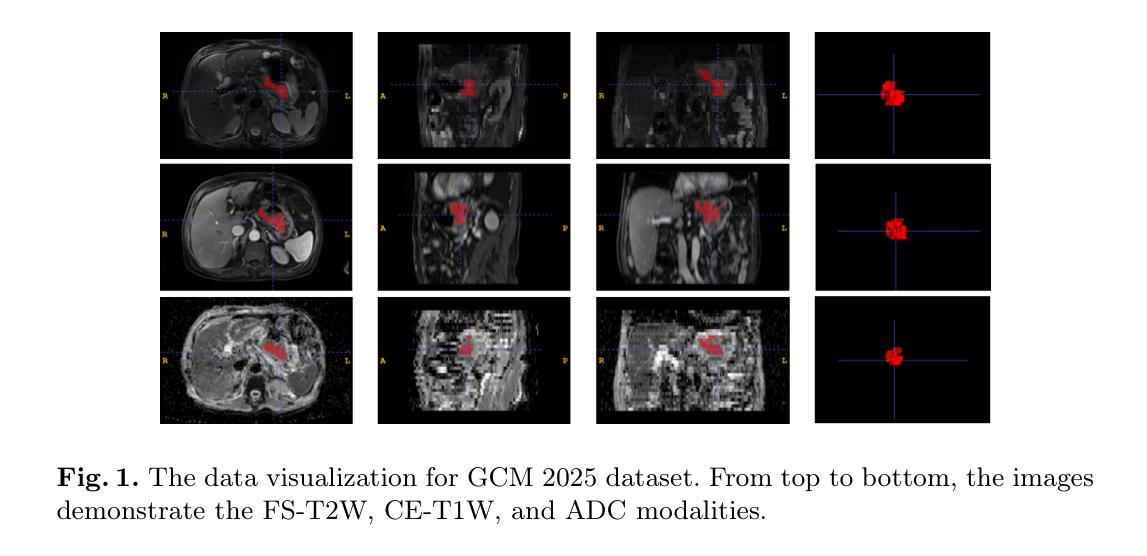
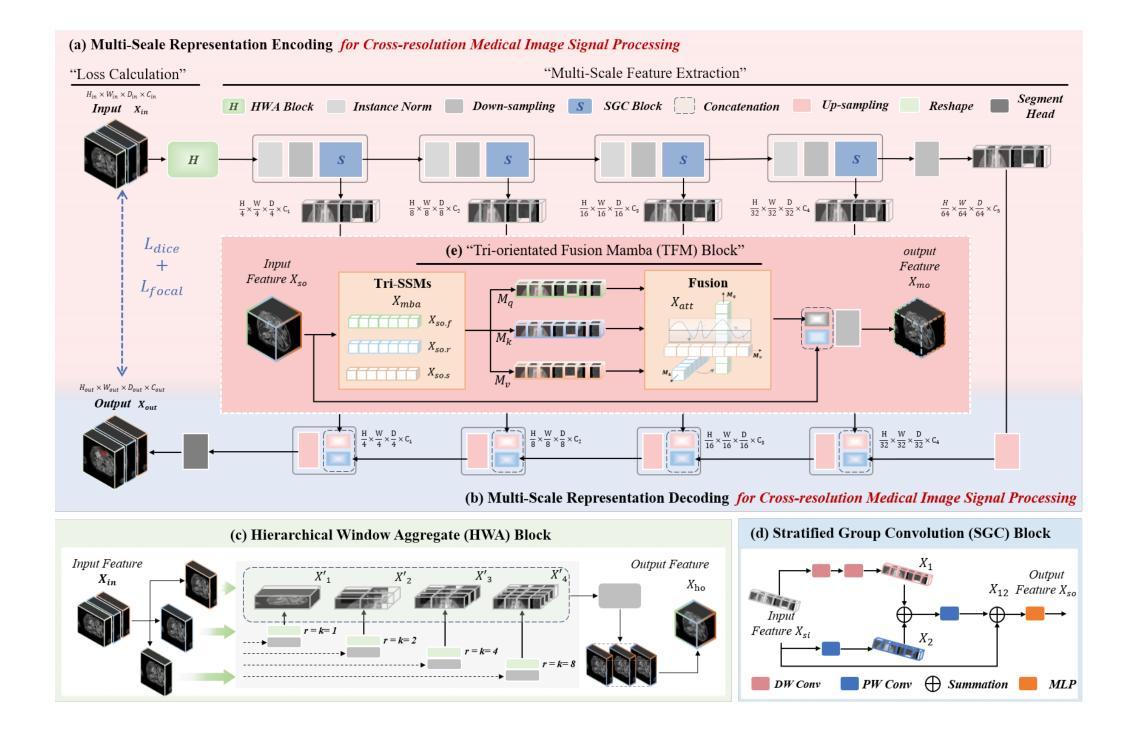
Multimodal medical image segmentation faces significant challenges in the context of gastric cancer lesion analysis. This clinical context is defined by the scarcity of independent multimodal datasets and the imperative to amalgamate inherently misaligned modalities. As a result, algorithms are constrained to train on approximate data and depend on application migration, leading to substantial resource expenditure and a potential decline in analysis accuracy. To address those challenges, we have made two major contributions: First, we publicly disseminate the GCM 2025 dataset, which serves as the first large-scale, open-source collection of gastric cancer multimodal MRI scans, featuring professionally annotated FS-T2W, CE-T1W, and ADC images from 500 patients. Second, we introduce HWA-UNETR, a novel 3D segmentation framework that employs an original HWA block with learnable window aggregation layers to establish dynamic feature correspondences between different modalities’ anatomical structures, and leverages the innovative tri-orientated fusion mamba mechanism for context modeling and capturing long-range spatial dependencies. Extensive experiments on our GCM 2025 dataset and the publicly BraTS 2021 dataset validate the performance of our framework, demonstrating that the new approach surpasses existing methods by up to 1.68% in the Dice score while maintaining solid robustness. The dataset and code are public via https://github.com/JeMing-creater/HWA-UNETR.
在多模态医学图像分割中,胃癌病灶分析面临重大挑战。这一临床环境的特点是缺乏独立的多模态数据集,并且需要将本质上不对齐的模式融合在一起。因此,算法受限于在近似数据上进行训练,并依赖于应用迁移,导致资源消耗巨大,分析精度可能下降。为了应对这些挑战,我们做出了两大贡献:首先,我们公开传播了GCM 2025数据集,这是首个大规模的、开源的胃癌多模态MRI扫描集合,包含来自500名患者的专业注释FS-T2W、CE-T1W和ADC图像。其次,我们引入了HWA-UNETR,这是一种新型的3D分割框架,采用原始HWA块和可学习的窗口聚合层来建立不同模态解剖结构之间的动态特征对应关系,并利用创新的Tri-oriented融合Mamba机制进行上下文建模和捕捉长距离空间依赖性。在我们的GCM 2025数据集和公开的BraTS 2021数据集上的大量实验验证了我们的框架性能,证明新方法在Dice得分上超越了现有方法,最高提高了1.68%,同时保持了稳健性。数据集和代码可通过https://github.com/JeMing-creater/HWA-UNETR公开访问。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF This work has been provisionally accepted for MICCAI 2025
摘要
胃癌病灶分析的多模态医学图像分割面临重大挑战。由于缺少独立多模态数据集和必须融合固有错位模态的必要性,算法受到训练数据近似性的限制,并依赖于应用迁移,导致资源消耗大且分析精度可能下降。为应对这些挑战,我们做出了两项重大贡献:首先,我们公开发布了GCM 2025数据集,这是首个大规模的公开胃癌多模态MRI扫描数据集,包含来自500名患者的专业注释FS-T2W、CE-T1W和ADC图像;其次,我们引入了HWA-UNETR,这是一种新的3D分割框架,采用可学习的窗口聚合层建立不同模态解剖结构之间的动态特征对应关系,并利用创新的三向融合mamba机制进行上下文建模和捕获远程空间依赖性。在我们的GCM 2025数据集和公开的BraTS 2021数据集上的广泛实验验证了该框架的性能,证明新方法在Dice得分上最多提高了1.68%,同时保持了稳健性。数据集和代码可通过https://github.com/JeMing-creater/HWA-UNETR公开访问。
关键见解
- 多模态医学图像分割在胃癌病灶分析中面临挑战,主要由于缺少独立多模态数据集和模态对齐的难度。
- 提出了GCM 2025数据集,为胃癌多模态MRI扫描提供了首个大规模、公开的数据集。
- 介绍了HWA-UNETR框架,该框架能够在不同模态的解剖结构之间建立动态特征对应关系。
- HWA-UNETR利用可学习的窗口聚合层和创新的tri-orientated融合mamba机制进行上下文建模和空间依赖性捕获。
- 在GCM 2025和BraTS 2021数据集上的实验表明,HWA-UNETR框架的性能优于现有方法,Dice得分有所提高。
- 该框架的稳健性得到了验证。
点此查看论文截图

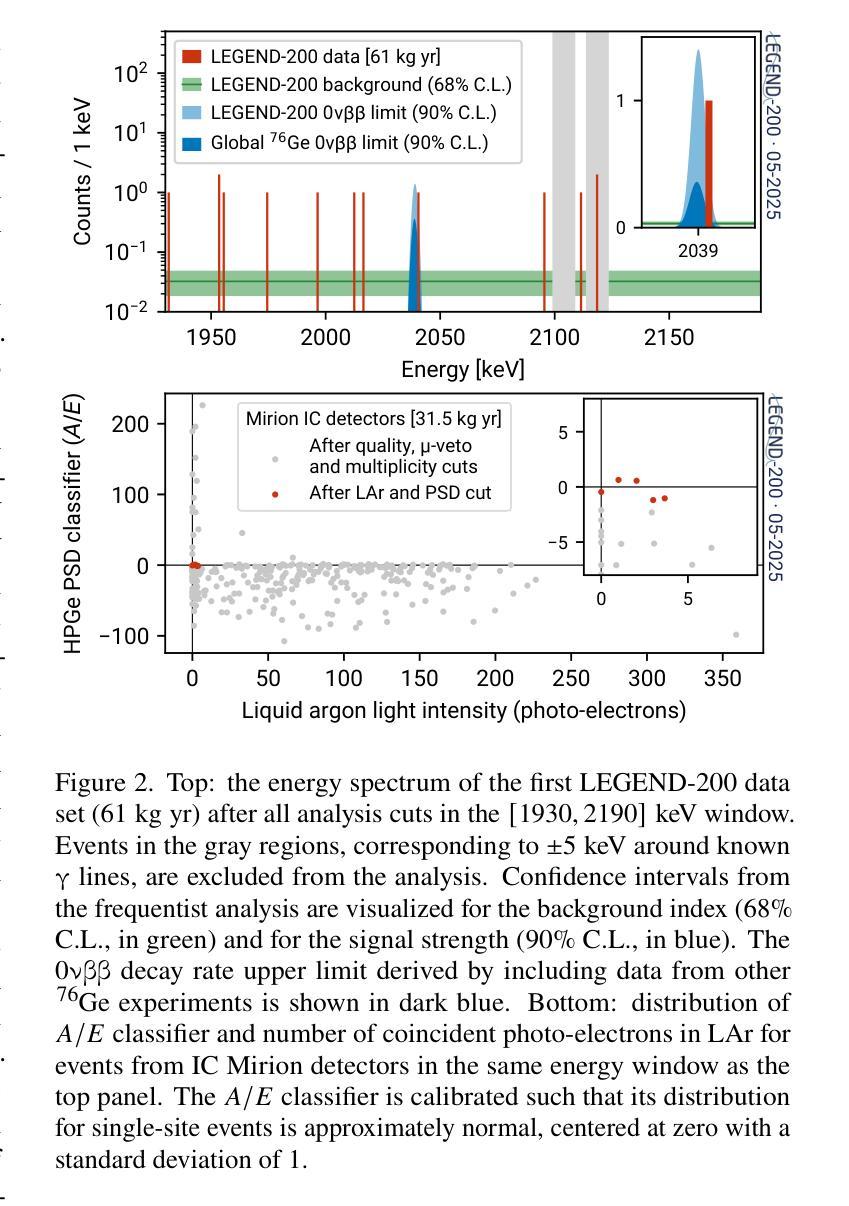
First Results on the Search for Lepton Number Violating Neutrinoless Double Beta Decay with the LEGEND-200 Experiment
Authors:H. Acharya, N. Ackermann, M. Agostini, A. Alexander, C. Andreoiu, G. R. Araujo, F. T. Avignone III, M. Babicz, W. Bae, A. Bakalyarov, M. Balata, A. S. Barabash, P. S. Barbeau, C. J. Barton, L. Baudis, C. Bauer, E. Bernieri, L. Bezrukov, K. H. Bhimani, V. Biancacci, E. Blalock, S. J. Borden, G. Borghi, F. Borra, B. Bos, A. Boston, V. Bothe, R. Bouabid, R. Brugnera, N. Burlac, M. Busch, S. Calgaro, L. Canonica, S. Capra, M. Carminati, R. M. D. Carney, C. Cattadori, R. Cesarano, Y. -D. Chan, J. R. Chapman, A. Chernogorov, P. -J. Chiu, C. D. Christofferson, M. L. Clark, A. I. Colon-Rivera, T. Comellato, V. D’Andrea, R. Deckert, J. A. Detwiler, A. Di Giacinto, N. Di Marco, T. Dixon, K. -M. Dong, A. Drobizhev, G. Duran, Yu. Efremenko, S. R. Elliott, C. H. J. Emmanuel, E. Engelhardt, E. Esch, M. T. Febbraro, F. Ferella, D. E. Fields, C. Fiorini, M. Fomina, N. Fuad, R. Gala, A. Galindo-Uribarri, A. Gangapshev, A. Garfagnini, S. Gazzana, A. Geraci, L. Gessler, C. Ghiano, A. Gieb, S. Giri, M. Gold, C. Gooch, G. Grünauer, M. P. Green, J. Gruszko, I. Guinn, V. E. Guiseppe, V. Gurentsov, Y. Gurov, K. Gusev, B. Hackett, F. Hagemann, M. Haranczyk, F. Henkes, R. Henning, J. Herrera, D. Hervas Aguilar, J. Hinton, R. Hodák, H. F. R. Hoffmann, M. A. Howe, M. Huber, M. Hult, A. Ianni, K. Jędrzejczak, J. Jochum, R. W. L. Jones, D. S. Judson, M. Junker, J. Kaizer, V. Kazalov, M. F. Kidd, T. Kihm, K. Kilgus, A. Klimenko, K. T. Knöpfle, I. Kochanek, O. Kochetov, I. Kontul, L. L. Kormos, V. N. Kornoukhov, P. Krause, H. Krishnamoorthy, V. V. Kuzminov, K. Lang, M. Laubenstein, N. N. P. N. Lay, E. León, A. Leder, B. Lehnert, A. Leonhardt, N. Levashko, L. Y. Li, A. Li, Y. -R. Lin, M. Lindner, I. Lippi, A. Love, A. Lubashevskiy, B. Lubsandorzhiev, N. Lusardi, C. Macolino, B. Majorovits, F. Mamedov, L. Manzanillas, G. G. Marshall, R. D. Martin, E. L. Martin, R. Massarczyk, A. Mazumdar, G. McDowell, D. -M. Mei, S. P. Meireles, M. Menzel, S. Mertens, E. Miller, I. Mirza, M. Misiaszek, M. Morella, B. Morgan, T. Mroz, D. Muenstermann, C. J. Nave, I. Nemchenok, M. Neuberger, N. O’Briant, F. Paissan, L. Papp, L. S. Paudel, K. Pelczar, L. Pertoldi, W. Pettus, F. Piastra, M. Pichotta, P. Piseri, A. W. P. Poon, P. P. Povinec, M. Pruckner, A. Pullia, W. S. Quinn, D. C. Radford, Y. A. Ramachers, A. Razeto, M. Redchuk, A. L. Reine, S. Riboldi, K. Rielage, C. Romo-Luque, N. Rossi, S. Rozov, T. J. Ruland, N. Rumyantseva, J. Runge, R. Saakyan, S. Sailer, G. Salamanna, F. Salamida, G. Saleh, V. Sandukovsky, C. Savarese, S. Schönert, A. -K. Schütz, D. C. Schaper, L. Schlüter, S. J. Schleich, O. Schulz, M. Schwarz, B. Schwingenheuer, C. Seibt, O. Selivanenko, G. Senatore, A. Serafini, K. Shakhov, E. Shevchik, M. Shirchenko, Y. Shitov, H. Simgen, F. Šimkovic, S. Simonaitis-Boyd, M. Skorokhvatov, M. Slavíčková, A. Smolnikov, J. A. Solomon, G. Song, A. C. Sousa, A. R. Sreekala, L. Steinhart, I. Štekl, T. Sterr, M. Stommel, S. A. Sullivan, R. R. Sumathi, K. Szczepaniec, L. Taffarello, D. Tagnani, D. J. Tedeschi, T. N. Thorpe, V. Tretyak, M. Turqueti, E. E. Van Nieuwenhuizen, L. J. Varriano, S. Vasilyev, A. Veresnikova, C. Vignoli, C. Vogl, K. von Sturm, A. Warren, D. Waters, S. L. Watkins, C. Wiesinger, J. F. Wilkerson, M. Willers, C. Wiseman, M. Wojcik, D. Xu, W. Xu, E. Yakushev, T. Ye, C. -H. Yu, V. Yumatov, D. Zinatulina, K. Zuber, G. Zuzel
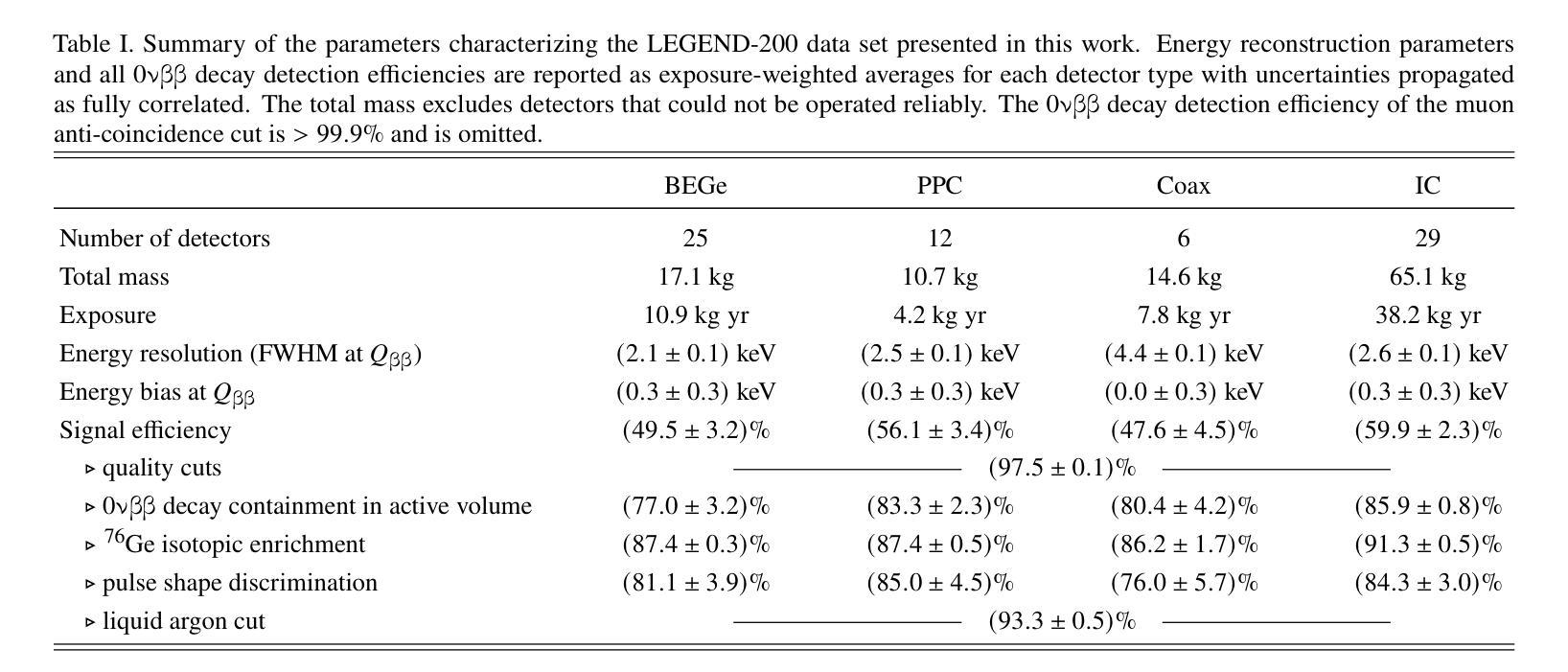
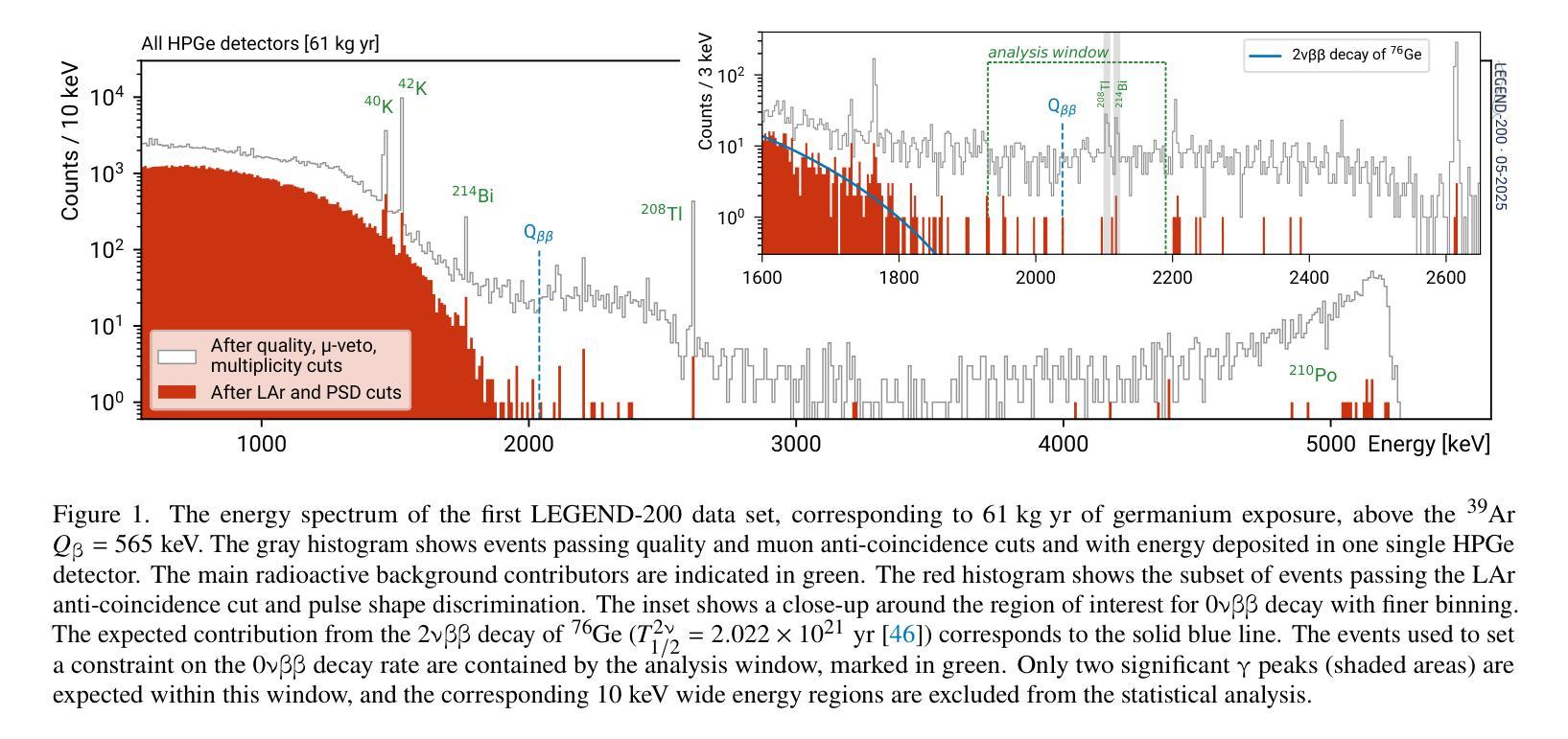
The LEGEND collaboration is searching for neutrinoless double beta ($0\nu\beta\beta$) decay by operating high-purity germanium detectors enriched in $^{76}$Ge in a low-background liquid argon environment. Building on key technological innovations from GERDA and the MAJORANA DEMONSTRATOR, LEGEND-200 has performed a first $0\nu\beta\beta$ decay search based on 61 kg yr of data. Over half of this exposure comes from our highest performing detectors, including newly developed inverted-coaxial detectors, and is characterized by an estimated background level of $0.5^{+0.3}{-0.2}$ cts/(keV kg yr) in the $0\nu\beta\beta$ decay signal region. A combined analysis of data from GERDA, the MAJORANA DEMONSTRATOR, and LEGEND-200, characterized by a 90% confidence level exclusion sensitivity of $2.8 \times 10^{26}$ yr on the half-life of $0\nu\beta\beta$ decay, reveals no evidence for a signal and sets a new observed lower limit at $T^{0\nu}{1/2} > 1.9 \times 10^{26}$ yr (90% confidence level). Assuming the decay is mediated by Majorana neutrinos, this corresponds to an upper limit on the effective Majorana mass in the range $m_{\beta\beta} < 70-200$ meV, depending on the adopted nuclear matrix element.
传奇(LEGEND)合作组正在低背景液氩环境中运行高度富集的^{76}Ge高纯度锗探测器,以寻找无中微子双β(0νββ)衰变。传奇-200基于GERDA和MAJORANA演示者(DEMONSTRATOR)的关键技术创新,使用我们的高性能探测器(包括新开发的倒置同轴探测器)进行了首次基于61公斤年数据的无中微子双β衰变搜索。该曝光量的一半以上来自我们的高性能探测器,在估计的背景水平为$ 0νββ衰变信号区域的每千克年数据量0.5_{- 0.2}^{+ 0.3}$cts/(kev kg·年)时。通过对GERDA、MAJORANA演示器和传奇-200的数据进行综合分析,显示出没有证据表明存在信号,并且在无中微子双β衰变的半衰期设定了新的观察到的下限为T^{0ν}{半衰期} > 假设衰变是由大质量马约拉纳中微子介导的,这对应于有效的马约拉纳中微子在应用中原子核矩阵元素的有效范围质量限制在<上限范围内在环境有效性以内时为㎊范围为范围为m{ββ}< 70-200 meV。这取决于所采用的核矩阵元素。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Prepared for submission to Physical Review Letters
Summary
LEGEND合作利用高纯度锗探测器搜索无中微子双β衰变($0νββ$),探测器以$^{76}$Ge浓缩物为工作介质,在低本底液氩环境中操作。基于GERDA和MAJORANA DEMONSTRATOR的关键技术创新,LEGEND-200利用采集的为期一年的61公斤数据进行了首次$0νββ$衰变搜索。研究采用了新型倒置同轴探测器等高性能探测器,并估计背景水平为$0νββ$衰变信号区域的$0.5^{+0.3}{-0.2}$ cts/(kg年)。综合分析GERDA、MAJORANA DEMONSTRATOR和LEGEND-200的数据,没有发现衰变信号,设定了新的观测下限$T^{0ν}{1/2} > 1.9 × 10^{26}$ 年。在假设衰变由Majorana中微子介导的前提下,对应的有效Majorana质量上限取决于所采用的核矩阵元素,范围为$m_{ββ} < 70-200$ meV。
Key Takeaways
- LEGEND合作使用高纯度锗探测器搜索无中微子双β衰变。
- 操作环境为低本底液氩,并采用了创新技术。
- 基于61公斤年的数据进行了首次搜索。
- 高性能探测器如新型倒置同轴探测器被应用。
- 背景水平估计在$0νββ$衰变信号区域为$0.5^{+0.3}_{-0.2}$ cts/(kg年)。
- 综合分析三个实验数据,未发现衰变信号,设定了新的观测下限。
点此查看论文截图

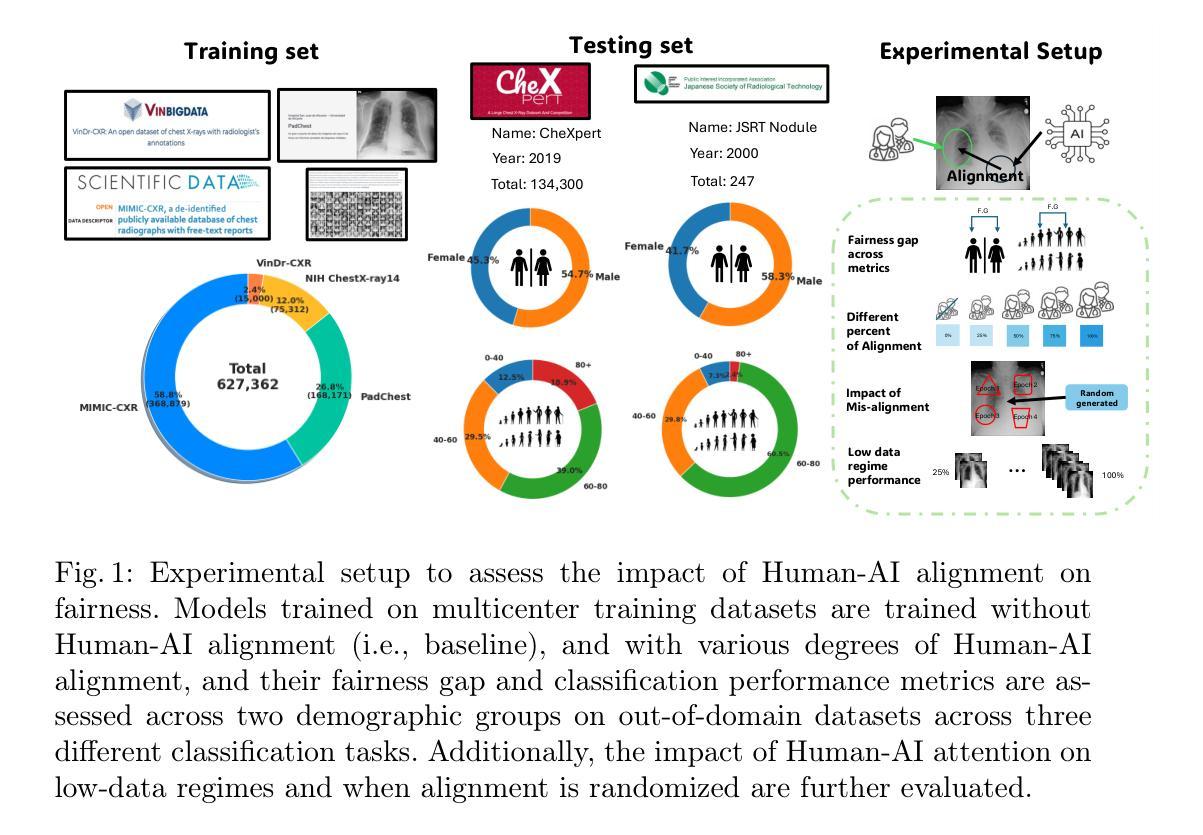
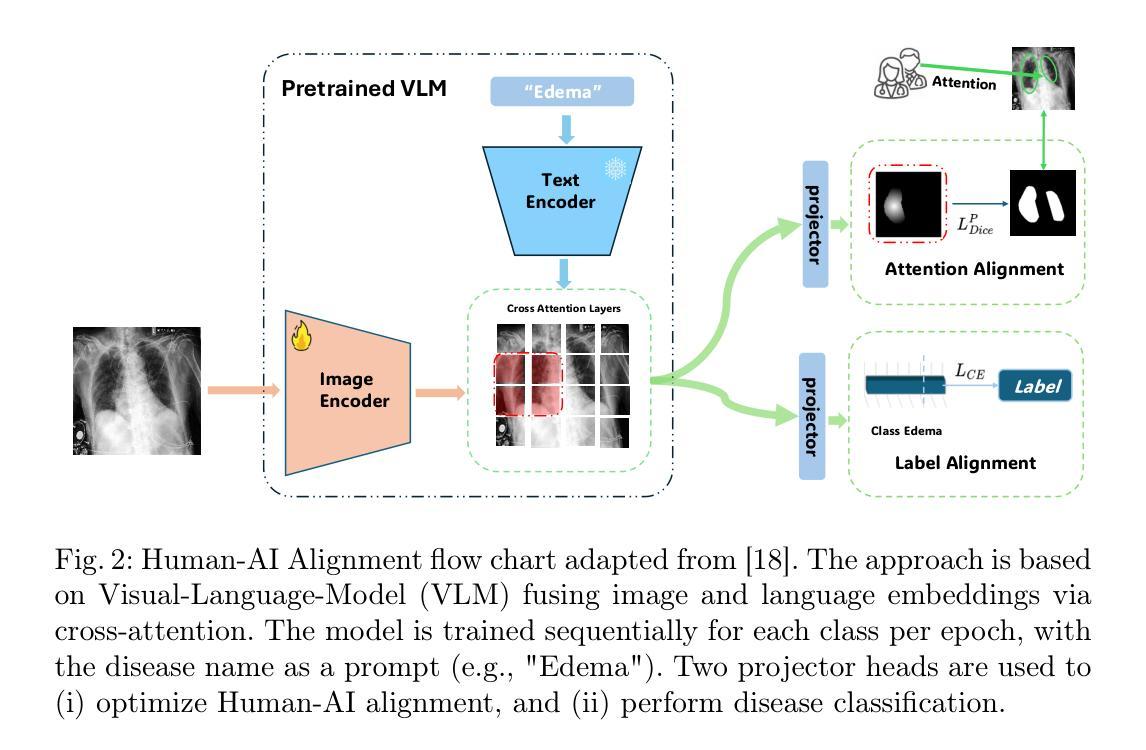
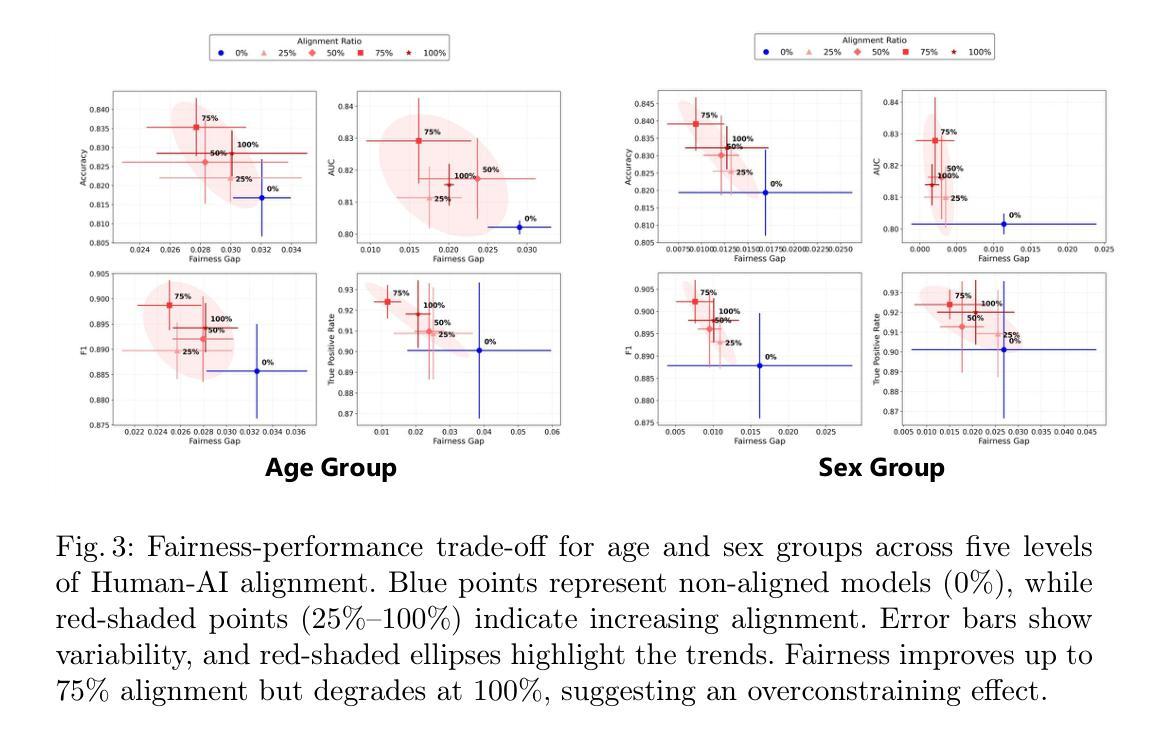
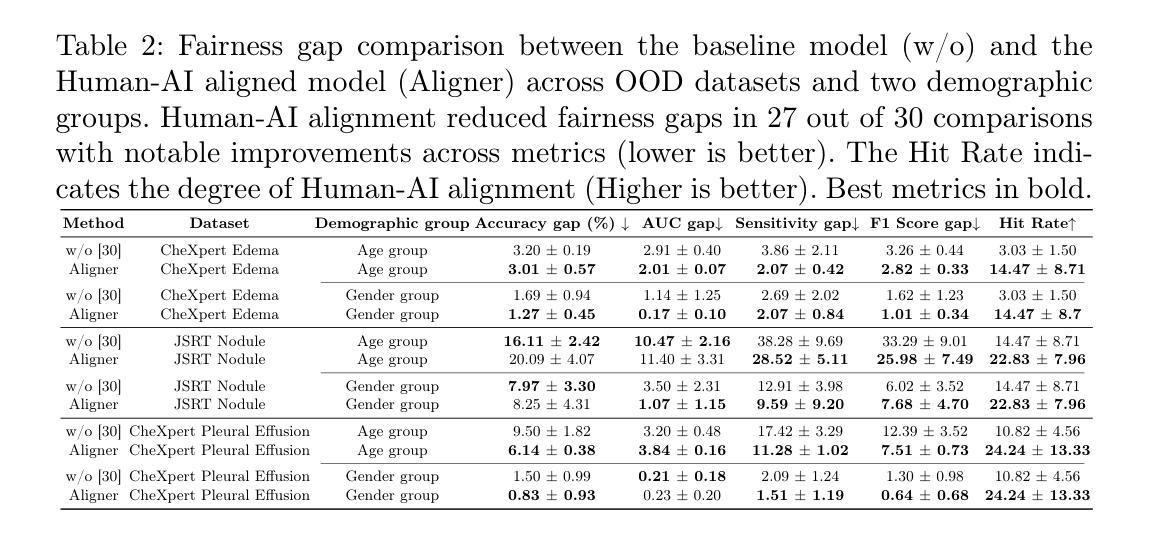
On the Interplay of Human-AI Alignment,Fairness, and Performance Trade-offs in Medical Imaging
Authors:Haozhe Luo, Ziyu Zhou, Zixin Shu, Aurélie Pahud de Mortanges, Robert Berke, Mauricio Reyes
Deep neural networks excel in medical imaging but remain prone to biases, leading to fairness gaps across demographic groups. We provide the first systematic exploration of Human-AI alignment and fairness in this domain. Our results show that incorporating human insights consistently reduces fairness gaps and enhances out-of-domain generalization, though excessive alignment can introduce performance trade-offs, emphasizing the need for calibrated strategies. These findings highlight Human-AI alignment as a promising approach for developing fair, robust, and generalizable medical AI systems, striking a balance between expert guidance and automated efficiency. Our code is available at https://github.com/Roypic/Aligner.
深度神经网络在医学成像方面表现出色,但仍易受到偏见的影响,从而在不同人群之间产生公平性问题。我们首次系统地探索了人类与人工智能在该领域的对齐与公平性。我们的结果表明,融入人类见解可以持续减少公平差距并增强跨域泛化能力,但过度对齐可能会引入性能权衡,强调校准策略的必要性。这些发现突显了人类与人工智能的对齐作为一个有前景的方法,用于开发公平、稳健和可泛化的医学人工智能系统,在专家指导和自动化效率之间取得平衡。我们的代码可在Roypic/Aligner上获取。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
医学领域中,深度神经网络在医学影像上表现优异,但仍存在偏见问题,造成不同人群间的公平性问题。本研究首次系统性探索了人工智能与人类对齐及该领域的公平性。结果显示,融入人类见解有助于缩小公平差距并提升跨域泛化能力,但过度对齐可能引发性能权衡,需采用校准策略。研究强调,人类与人工智能的对齐是开发公平、稳健、泛化的医疗人工智能系统的有效途径,实现了专家指导与自动化效率之间的平衡。
Key Takeaways
- 深度神经网络在医学成像上表现出卓越性能,但存在偏见问题,影响不同人群间的公平性。
- 人类与人工智能的对齐有助于缩小公平差距,提高模型的泛化能力。
- 融入人类见解可以改进模型的性能,使其更加稳健和可靠。
- 过度的人类与人工智能对齐可能导致性能上的权衡,需要采取校准策略来平衡效率和性能。
- Human-AI对齐是开发公平、稳健和泛化的医疗人工智能系统的有前途的方法。
- 通过专家指导与自动化效率之间的平衡,可以提高医疗AI系统的性能和可靠性。
点此查看论文截图

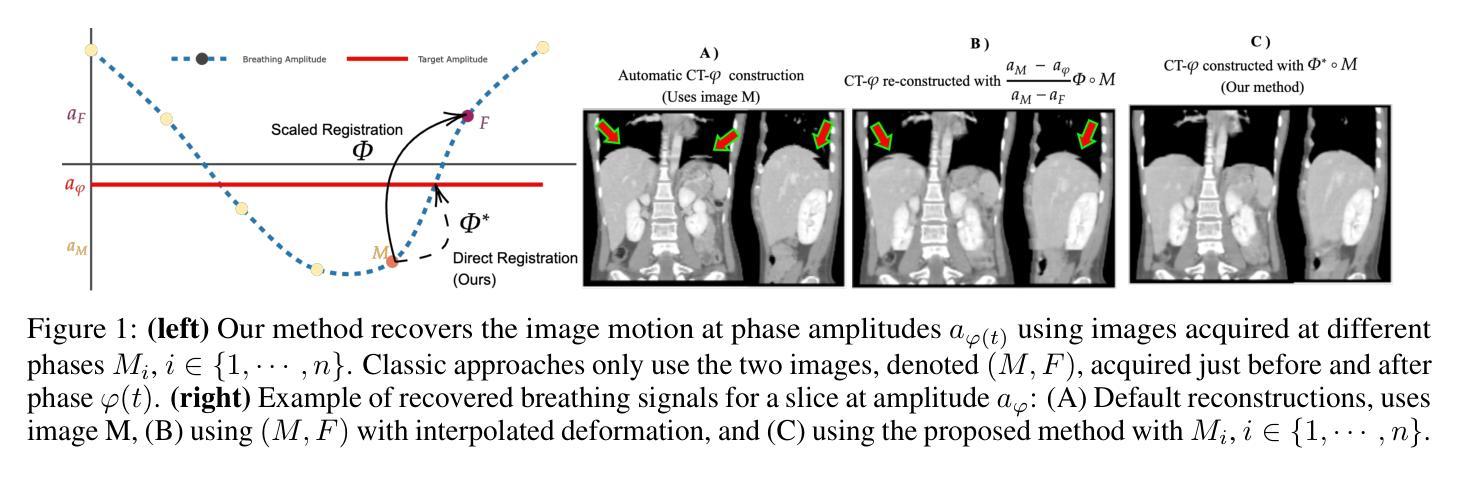
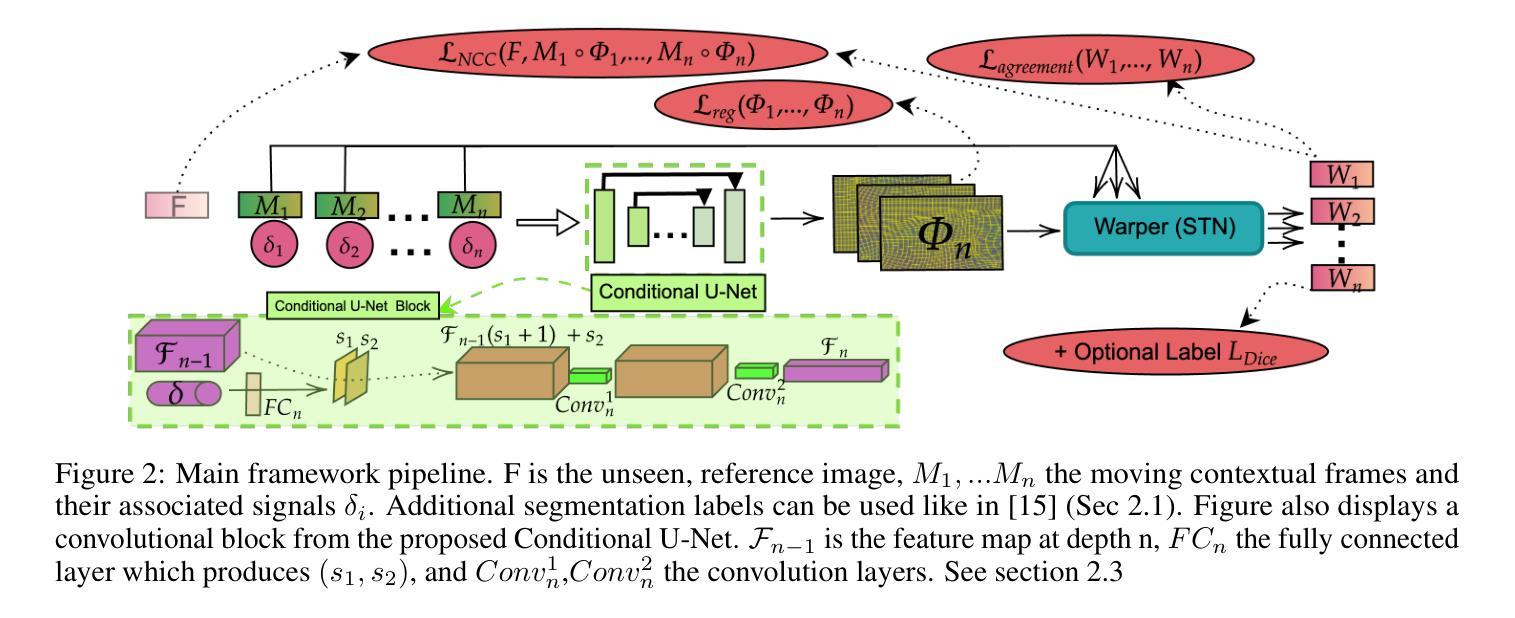
IMITATE: Image Registration with Context for unknown time frame recovery
Authors:Ziad Kheil, Lucas Robinet, Laurent Risser, Soleakhena Ken
In this paper, we formulate a novel image registration formalism dedicated to the estimation of unknown condition-related images, based on two or more known images and their associated conditions. We show how to practically model this formalism by using a new conditional U-Net architecture, which fully takes into account the conditional information and does not need any fixed image. Our formalism is then applied to image moving tumors for radiotherapy treatment at different breathing amplitude using 4D-CT (3D+t) scans in thoracoabdominal regions. This driving application is particularly complex as it requires to stitch a collection of sequential 2D slices into several 3D volumes at different organ positions. Movement interpolation with standard methods then generates well known reconstruction artefacts in the assembled volumes due to irregular patient breathing, hysteresis and poor correlation of breathing signal to internal motion. Results obtained on 4D-CT clinical data showcase artefact-free volumes achieved through real-time latencies. The code is publicly available at https://github.com/Kheil-Z/IMITATE .
本文提出了一种新型图像配准方法,专门用于估计与条件相关的未知图像,该方法基于两个或多个已知图像及其相关条件。我们展示了如何使用新的条件U-Net架构来实际建模这种方法,该架构充分考虑了条件信息,并且不需要任何固定图像。然后,我们将该方法应用于在放射治疗中使用不同呼吸幅度的图像移动肿瘤研究。由于需要对多个不同器官位置的序列2D切片进行拼合成多个3D体积,因此这项应用特别复杂。使用标准方法进行运动插值会在组合体积中产生众所周知的重建伪影,这是由于患者呼吸不规则、滞后以及呼吸信号与内部运动之间的相关性较差所导致的。在四维CT临床数据上获得的结果展示了通过实时延迟实现的伪影自由体积。代码公开在https://github.com/Kheil-Z/IMITATE上可供使用。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF IEEE ISBI 2025
Summary
医学图像配准研究,提出一种新型图像配准形式,利用已知图像估计未知条件图像。利用条件U-Net架构建模实际应用,不需固定图像即可充分考虑条件信息。该方法应用于不同呼吸幅度下的放射治疗肿瘤图像配准,采用4D-CT扫描处理胸腹区域。成功将一系列连续2D切片缝合成多个三维体积,解决患者不规则呼吸等问题导致的重建伪影。代码公开于GitHub上。
Key Takeaways
- 提出了一种基于已知图像估计未知条件图像的全新医学图像配准形式。
- 采用条件U-Net架构进行实际应用建模,充分考虑条件信息。
- 方法应用于不同呼吸幅度下的肿瘤放射治疗图像配准。
- 利用4D-CT扫描处理胸腹区域图像,将连续2D切片缝合成三维体积。
- 成功解决患者不规则呼吸等问题导致的重建伪影问题。
- 该研究提供的代码已公开于GitHub上。
点此查看论文截图

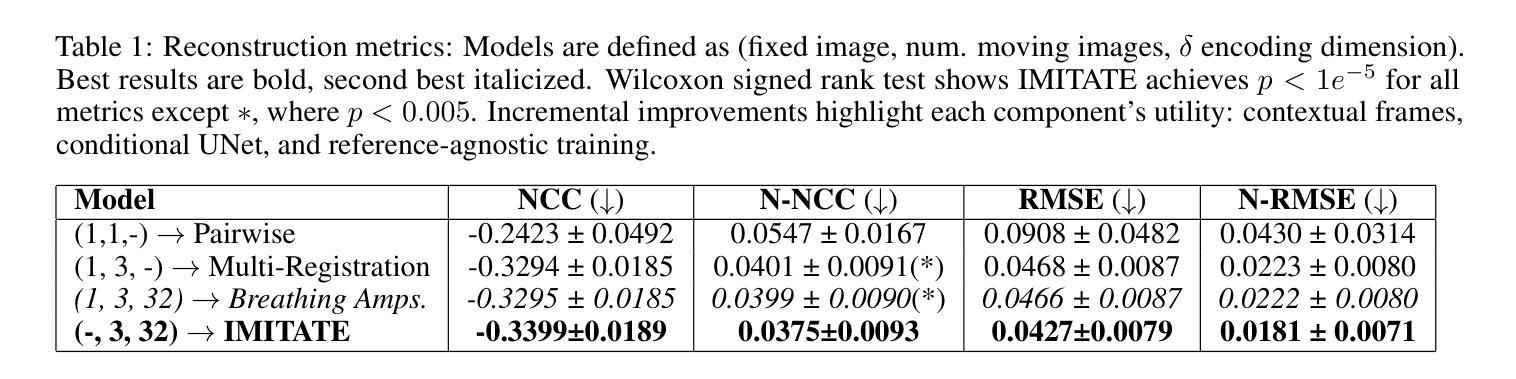
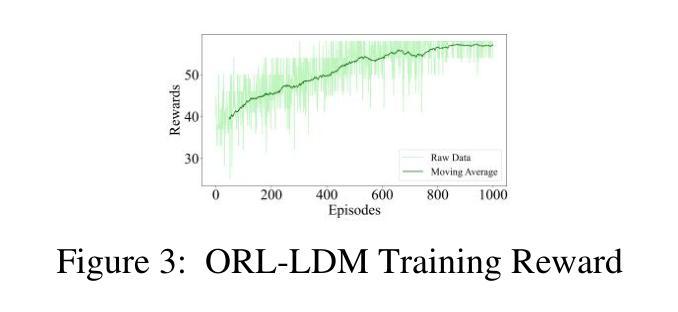
ORL-LDM: Offline Reinforcement Learning Guided Latent Diffusion Model Super-Resolution Reconstruction
Authors:Shijie Lyu
With the rapid advancement of remote sensing technology, super-resolution image reconstruction is of great research and practical significance. Existing deep learning methods have made progress but still face limitations in handling complex scenes and preserving image details. This paper proposes a reinforcement learning-based latent diffusion model (LDM) fine-tuning method for remote sensing image super-resolution. The method constructs a reinforcement learning environment with states, actions, and rewards, optimizing decision objectives through proximal policy optimization (PPO) during the reverse denoising process of the LDM model. Experiments on the RESISC45 dataset show significant improvements over the baseline model in PSNR, SSIM, and LPIPS, with PSNR increasing by 3-4dB, SSIM improving by 0.08-0.11, and LPIPS reducing by 0.06-0.10, particularly in structured and complex natural scenes. The results demonstrate the method’s effectiveness in enhancing super-resolution quality and adaptability across scenes.
随着遥感技术的快速发展,超分辨率图像重建在研究和实践中具有重要意义。现有的深度学习方法已经取得了一些进展,但在处理复杂场景和保留图像细节方面仍存在局限性。本文提出了一种基于强化学习的潜在扩散模型(LDM)微调方法,用于遥感图像超分辨率。该方法构建了一个具有状态、动作和奖励的强化学习环境,通过潜在扩散模型的逆向去噪过程中的近端策略优化(PPO)来优化决策目标。在RESISC45数据集上的实验表明,该方法在峰值信噪比(PSNR)、结构相似性(SSIM)和局部感知图像相似性(LPIPS)等指标上较基线模型有显著改善,其中PSNR提高3-4dB,SSIM提高0.08-0.11,LPIPS降低0.06-0.10。特别是在结构和复杂自然场景方面,该方法在提升超分辨率质量和场景适应性方面表现出良好的效果。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by the 4th International Conference on Computing Innovation and Applied Physics (CONF-CIAP 2025), and will be published in EAI Community Research Series-CORE or Theoretical and Natural Science (TNS)
Summary
随着遥感技术的快速发展,超分辨率图像重建具有重大的研究和实践意义。本文提出一种基于强化学习的潜在扩散模型(LDM)微调方法,用于遥感图像超分辨率。该方法构建强化学习环境,通过近端策略优化(PPO)在LDM模型的反向去噪过程中优化决策目标。在RESISC45数据集上的实验表明,该方法在PSNR、SSIM和LPIPS指标上较基线模型有显著改善,特别是结构和复杂自然场景。
Key Takeaways
- 遥感图像超分辨率重建具有重大研究和实践价值。
- 现有深度学习方法在处理复杂场景和保留图像细节方面存在局限性。
- 本文提出一种基于强化学习的潜在扩散模型(LDM)微调方法。
- 该方法通过构建强化学习环境,优化决策目标。
- 实验在RESISC45数据集上进行,结果显示该方法在PSNR、SSIM和LPIPS指标上较基线模型有显著改善。
- 该方法在提高超分辨率质量和场景适应性方面有效。
点此查看论文截图

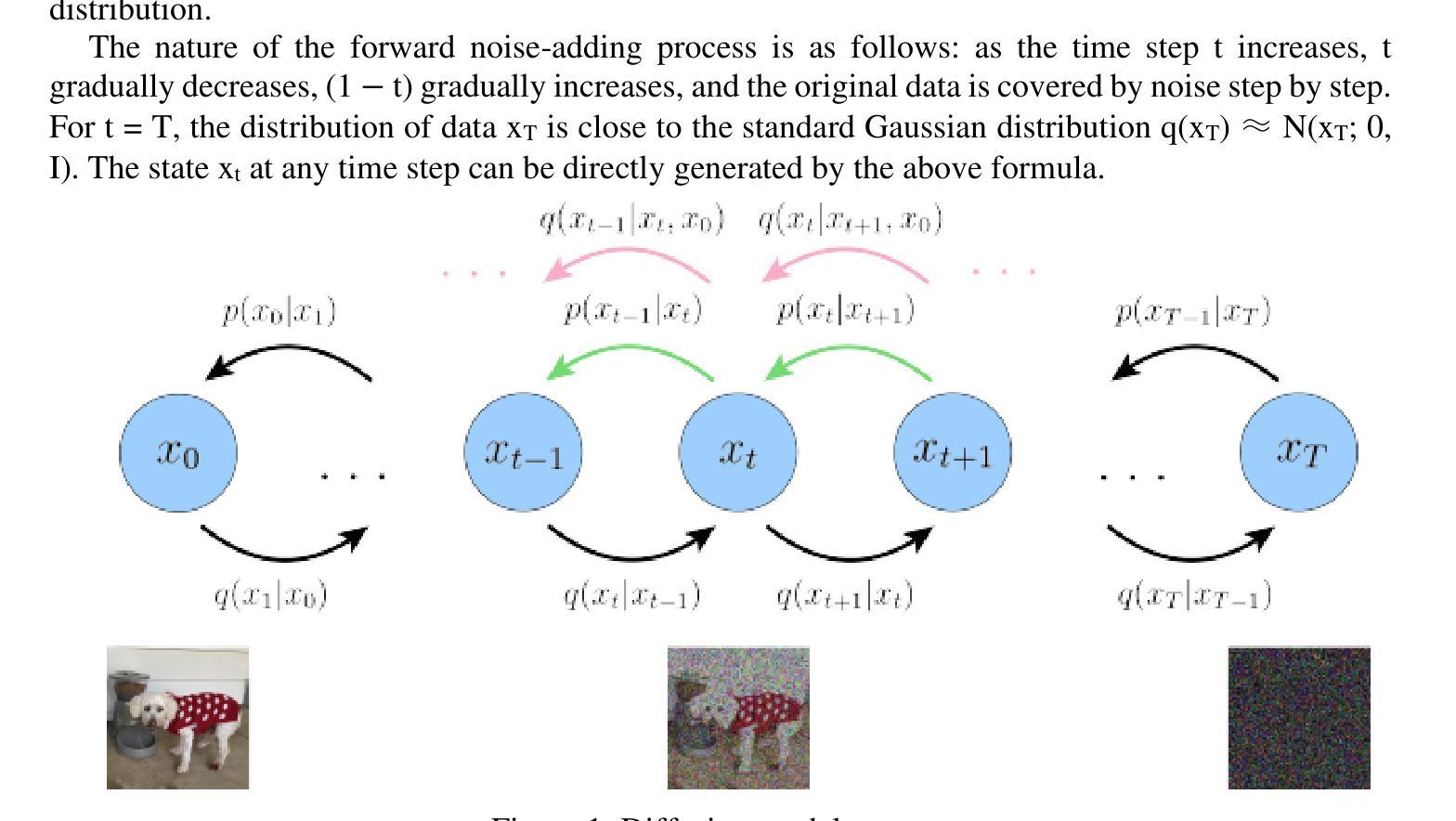
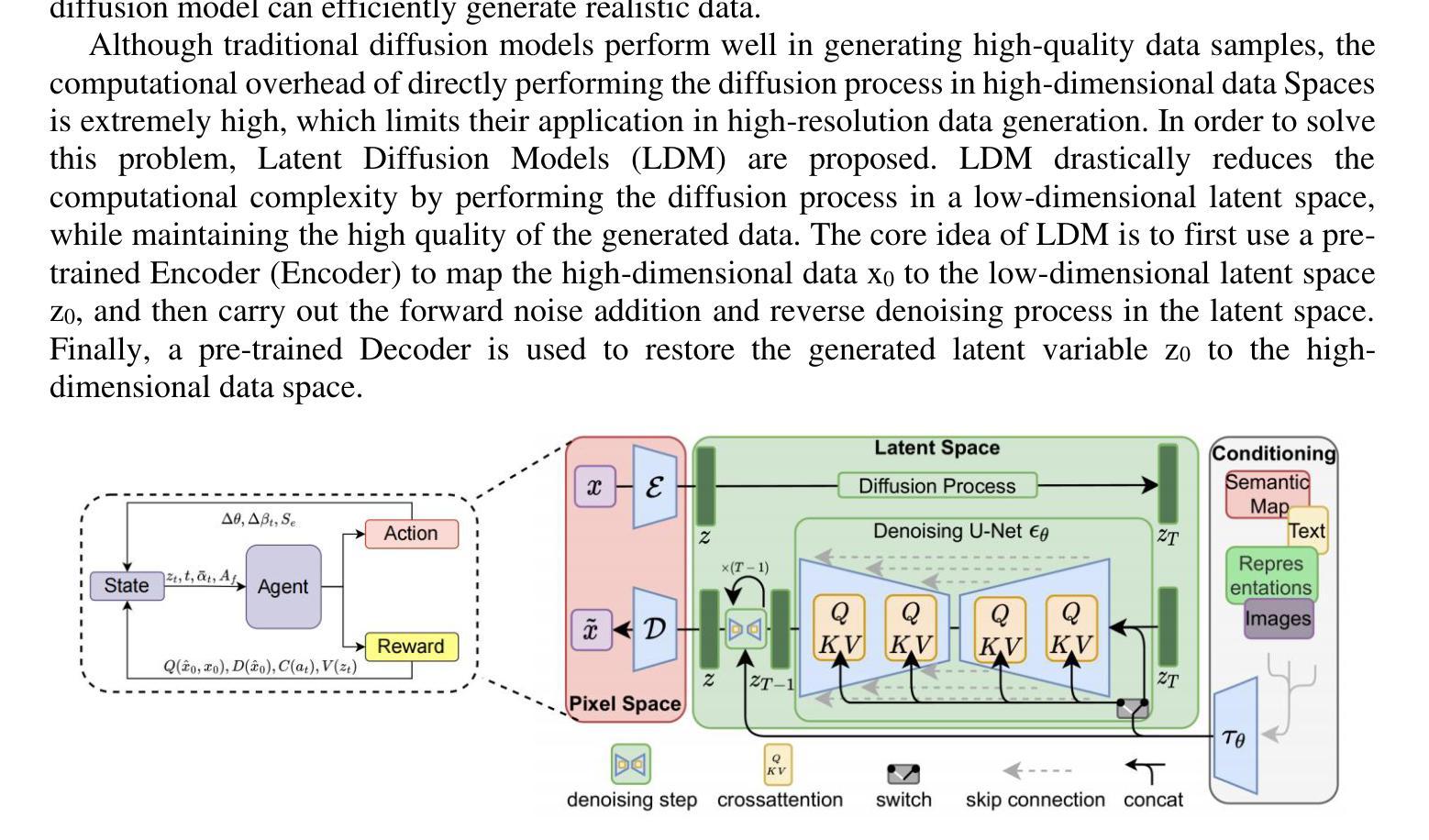
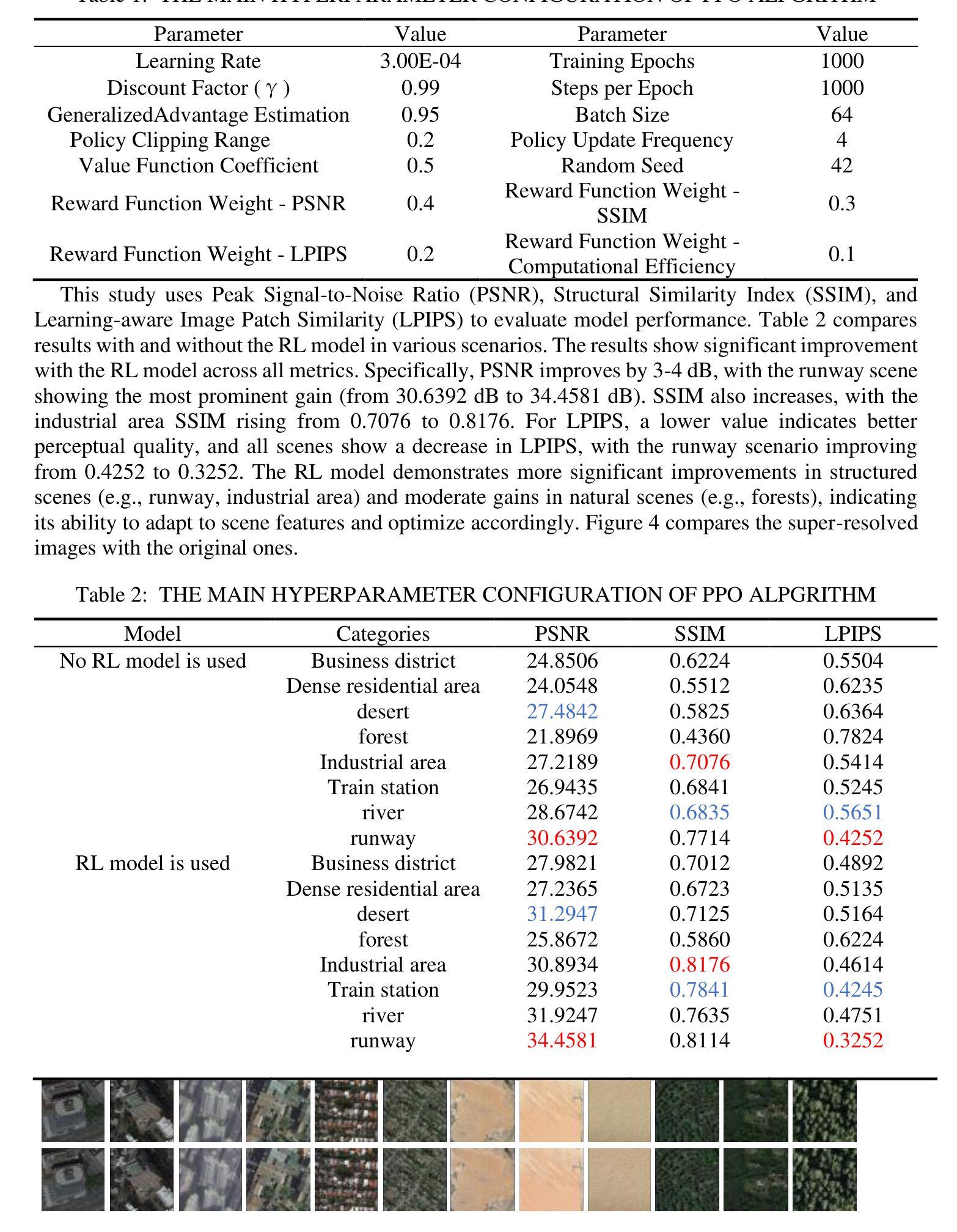
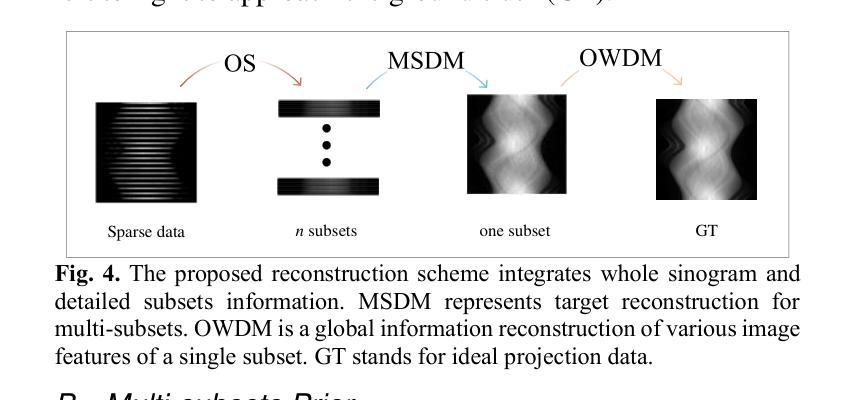
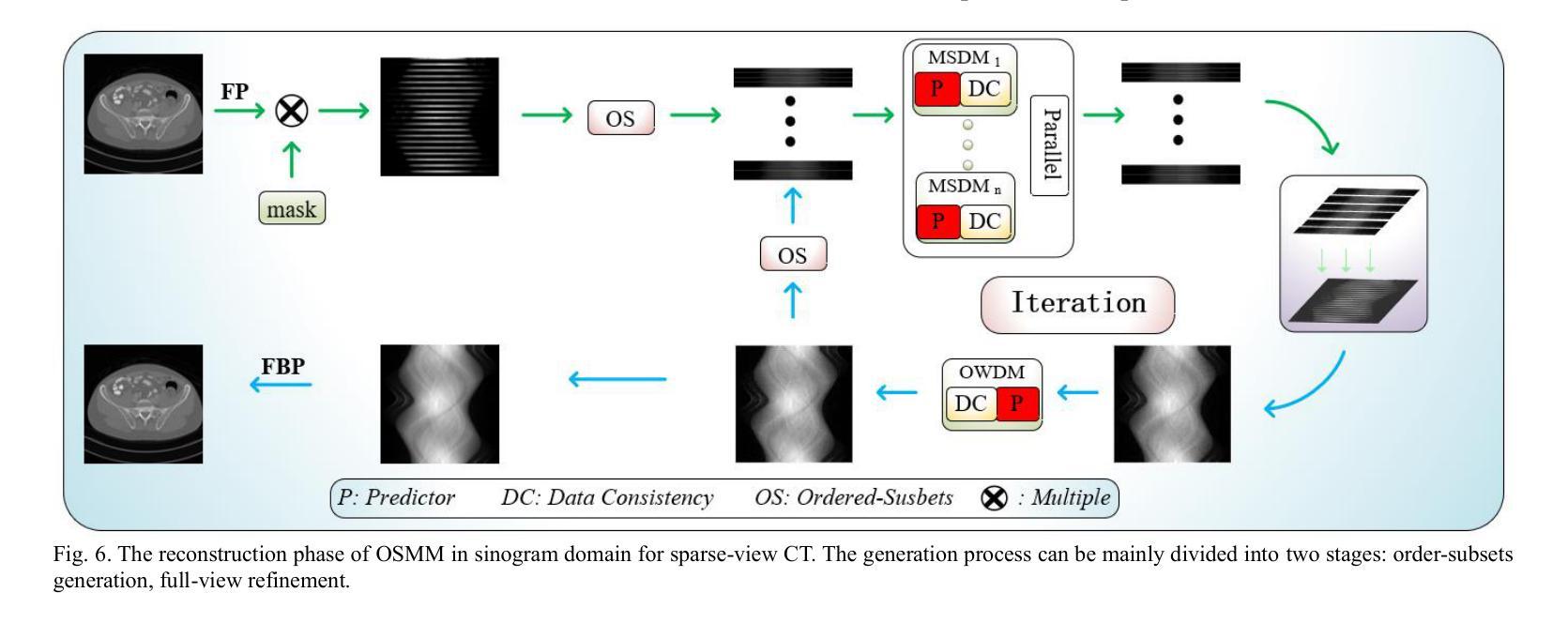
Ordered-subsets Multi-diffusion Model for Sparse-view CT Reconstruction
Authors:Pengfei Yu, Bin Huang, Minghui Zhang, Weiwen Wu, Shaoyu Wang, Qiegen Liu
Score-based diffusion models have shown significant promise in the field of sparse-view CT reconstruction. However, the projection dataset is large and riddled with redundancy. Consequently, applying the diffusion model to unprocessed data results in lower learning effectiveness and higher learning difficulty, frequently leading to reconstructed images that lack fine details. To address these issues, we propose the ordered-subsets multi-diffusion model (OSMM) for sparse-view CT reconstruction. The OSMM innovatively divides the CT projection data into equal subsets and employs multi-subsets diffusion model (MSDM) to learn from each subset independently. This targeted learning approach reduces complexity and enhances the reconstruction of fine details. Furthermore, the integration of one-whole diffusion model (OWDM) with complete sinogram data acts as a global information constraint, which can reduce the possibility of generating erroneous or inconsistent sinogram information. Moreover, the OSMM’s unsupervised learning framework provides strong robustness and generalizability, adapting seamlessly to varying sparsity levels of CT sinograms. This ensures consistent and reliable performance across different clinical scenarios. Experimental results demonstrate that OSMM outperforms traditional diffusion models in terms of image quality and noise resilience, offering a powerful and versatile solution for advanced CT imaging in sparse-view scenarios.
基于得分的扩散模型在稀疏视图CT重建领域显示出巨大的潜力。然而,投影数据集庞大且存在冗余。因此,将扩散模型应用于未处理的数据会导致学习效率低下和学习难度增加,经常导致重建的图像缺乏细节。为了解决这些问题,我们提出了有序子集多扩散模型(OSMM)用于稀疏视图CT重建。OSMM创新地将CT投影数据分成相等的子集,并采用多子集扩散模型(MSDM)从每个子集中独立学习。这种有针对性的学习方法降低了复杂性,提高了细节重建能力。此外,将整体扩散模型(OWDM)与完整辛恩图数据相结合,作为全局信息约束,降低了产生错误或不一致辛恩图信息的可能性。而且,OSMM的无监督学习框架具有很强的鲁棒性和通用性,能够无缝适应CT辛恩图的不同稀疏级别。这确保了在不同临床场景中的一致和可靠性能。实验结果表明,OSMM在图像质量和噪声韧性方面优于传统扩散模型,为稀疏视图场景中的高级CT成像提供了强大且通用的解决方案。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了针对稀疏视图CT重建的有序子集多扩散模型(OSMM)。OSMM通过将CT投影数据分成多个子集,并采用多子集扩散模型(MSDM)进行独立学习,以提高学习效率和重建图像的质量。结合完整辛氏图数据的一体式扩散模型(OWDM)作为全局信息约束,减少了错误或不一致辛氏图信息的可能性。OSMM的无监督学习框架具有强大的鲁棒性和通用性,能够适应不同CT辛氏图稀疏度水平的变化,为稀疏视图场景下的高级CT成像提供了强大而通用的解决方案。
Key Takeaways
- 稀疏视图CT重建中,投影数据集庞大且存在冗余,直接应用扩散模型会导致学习效率低下,影响图像重建质量。
- 有序子集多扩散模型(OSMM)将CT投影数据分成多个子集进行学习,提高学习效率和精细细节重建能力。
- OSMM采用多子集扩散模型(MSDM)进行独立学习,降低复杂度。
- 结合完整辛氏图数据的一体式扩散模型(OWDM)作为全局信息约束,减少错误或不一致辛氏图信息的可能性。
- OSMM的无监督学习框架具有强大的鲁棒性和通用性,能适应不同稀疏度水平的CT辛氏图。
- OSMM在图像质量和噪声韧性方面优于传统扩散模型。
点此查看论文截图

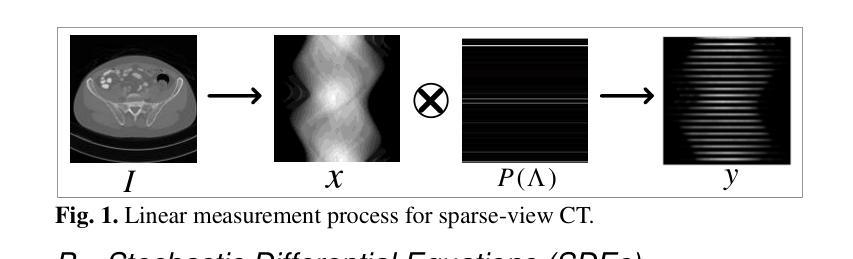
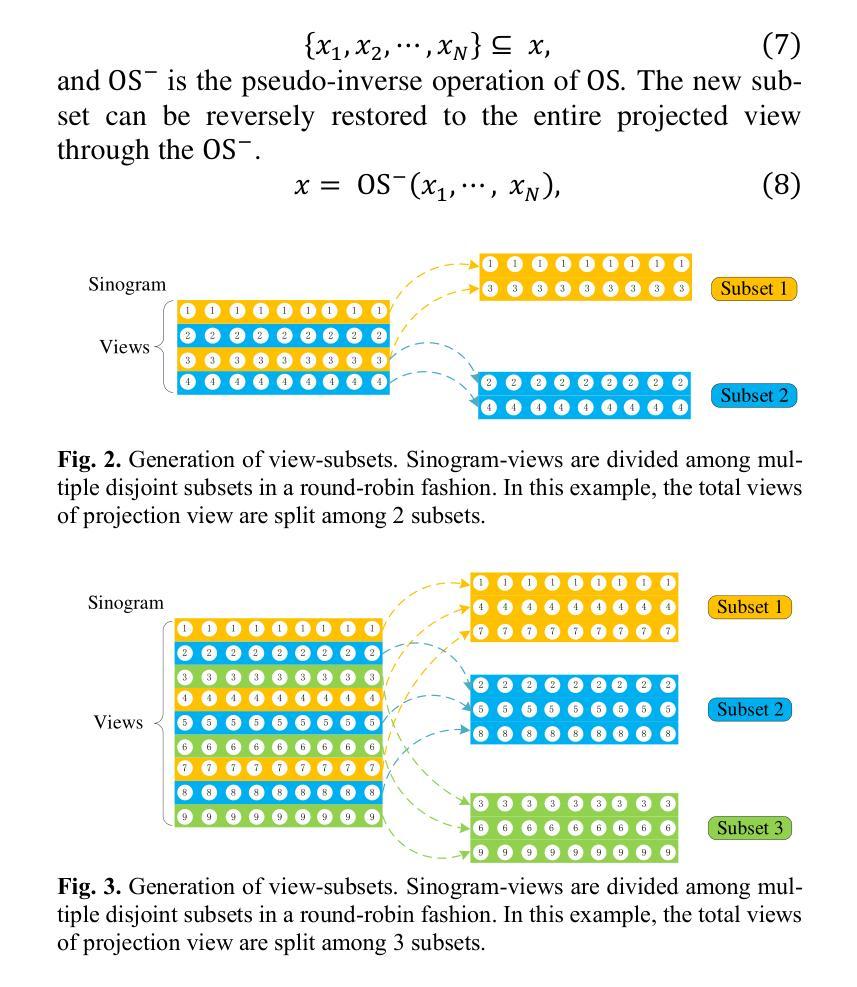
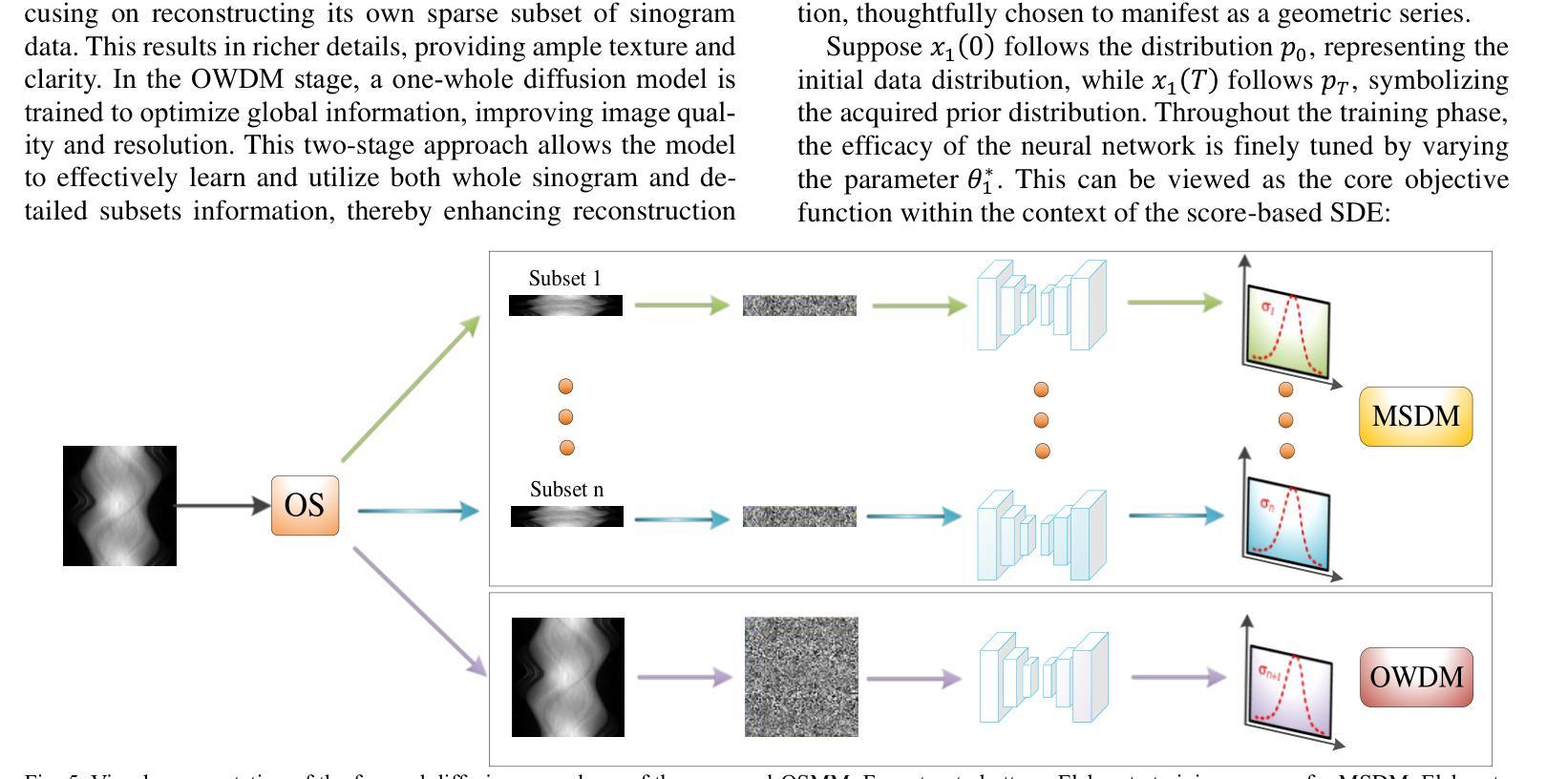
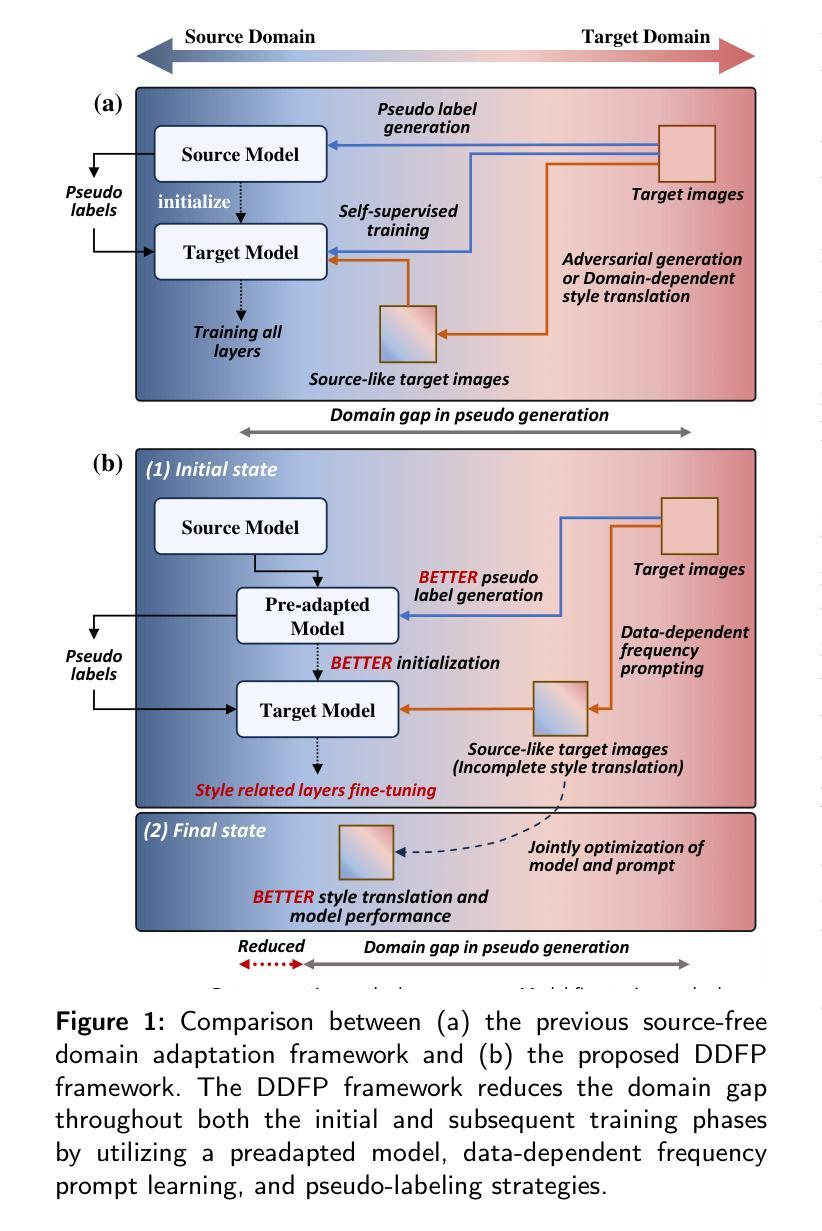
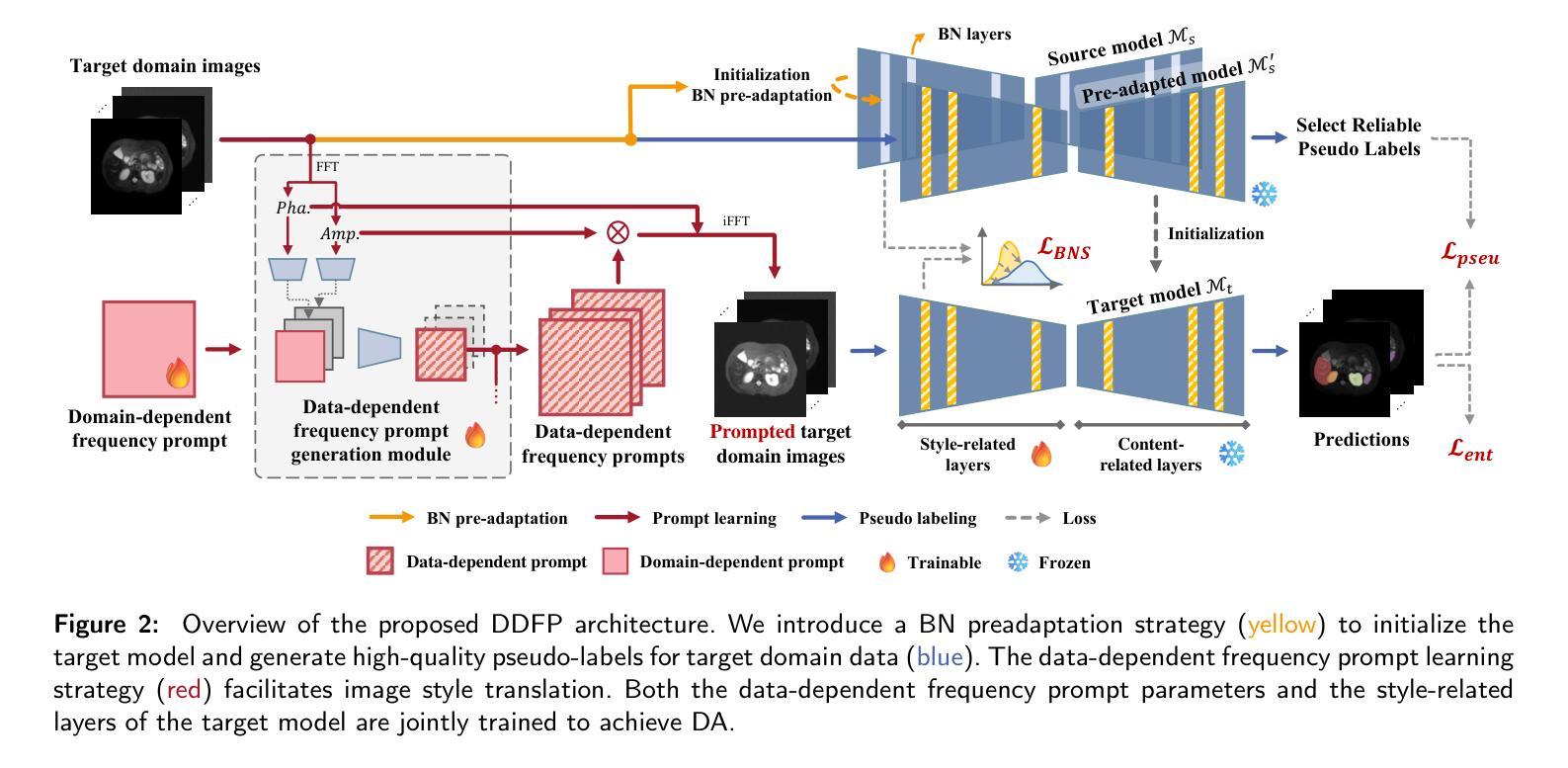
DDFP: Data-dependent Frequency Prompt for Source Free Domain Adaptation of Medical Image Segmentation
Authors:Siqi Yin, Shaolei Liu, Manning Wang
Domain adaptation addresses the challenge of model performance degradation caused by domain gaps. In the typical setup for unsupervised domain adaptation, labeled data from a source domain and unlabeled data from a target domain are used to train a target model. However, access to labeled source domain data, particularly in medical datasets, can be restricted due to privacy policies. As a result, research has increasingly shifted to source-free domain adaptation (SFDA), which requires only a pretrained model from the source domain and unlabeled data from the target domain data for adaptation. Existing SFDA methods often rely on domain-specific image style translation and self-supervision techniques to bridge the domain gap and train the target domain model. However, the quality of domain-specific style-translated images and pseudo-labels produced by these methods still leaves room for improvement. Moreover, training the entire model during adaptation can be inefficient under limited supervision. In this paper, we propose a novel SFDA framework to address these challenges. Specifically, to effectively mitigate the impact of domain gap in the initial training phase, we introduce preadaptation to generate a preadapted model, which serves as an initialization of target model and allows for the generation of high-quality enhanced pseudo-labels without introducing extra parameters. Additionally, we propose a data-dependent frequency prompt to more effectively translate target domain images into a source-like style. To further enhance adaptation, we employ a style-related layer fine-tuning strategy, specifically designed for SFDA, to train the target model using the prompted target domain images and pseudo-labels. Extensive experiments on cross-modality abdominal and cardiac SFDA segmentation tasks demonstrate that our proposed method outperforms existing state-of-the-art methods.
领域适应(Domain Adaptation)旨在解决因领域差异导致的模型性能下降的挑战。在典型的无监督领域适应设置中,使用来自源域的带标签数据以及来自目标域的无标签数据来训练目标模型。然而,由于隐私政策限制,特别是在医学数据集中,访问源域的带标签数据可能会受到限制。因此,研究越来越转向无源领域适应(SFDA),它只需要源域的预训练模型以及来自目标域的无标签数据进行适应。现有的SFDA方法通常依赖于特定领域的图像风格转换和自监督技术来弥合领域差距并训练目标域模型。然而,这些方法产生的特定领域风格转换图像和伪标签的质量仍有提升空间。此外,在有限的监督下,在适应过程中训练整个模型可能效率低下。在本文中,我们提出了一种新颖的SFDA框架来解决这些挑战。具体来说,为了有效减轻初始训练阶段中的领域差距影响,我们引入预适应(preadaptation)来生成预适应模型,作为目标模型的初始化,并允许生成高质量的增强伪标签,而不会引入额外的参数。此外,我们提出了一种数据依赖的频率提示(frequency prompt),以更有效地将目标域图像转换为类似源域的样式。为了进一步增强适应性,我们采用了一种针对SFDA设计的样式相关层微调策略,使用提示的目标域图像和伪标签训练目标模型。在跨模态腹部和心脏SFDA分割任务上的大量实验表明,我们提出的方法优于现有的最先进方法。
论文及项目相关链接
摘要
本文提出一种无源域适应(SFDA)框架,解决模型性能因领域差异而下降的问题。该框架仅需要源域的预训练模型和来自目标域的无标签数据进行适应。为有效缓解初始训练阶段的领域差异影响,引入预适应生成预适应模型,作为目标模型的初始化,并生成高质量增强伪标签。同时,提出数据相关频率提示,更有效地将目标域图像翻译成类似源的风格。最后,采用针对SFDA设计的风格相关层微调策略,使用提示的目标域图像和伪标签训练目标模型。在跨模态腹部和心脏SFDA分割任务上的实验表明,该方法优于现有先进方法。
关键见解
- 领域适应是解决模型性能因领域差异而下降的有效方法。
- 无源域适应(SFDA)框架仅需要源域的预训练模型和来自目标域的无标签数据。
- 引入预适应生成预适应模型,作为目标模型的初始化,缓解领域差异的影响。
- 提出数据相关频率提示,提高目标域图像的风格翻译质量。
- 采用针对SFDA设计的风格相关层微调策略,提高目标模型的训练效果。
- 在跨模态腹部和心脏SFDA分割任务上,该方法表现优于现有先进方法。
- 该方法为解决医学图像领域中的模型性能下降问题提供了新的思路。
点此查看论文截图

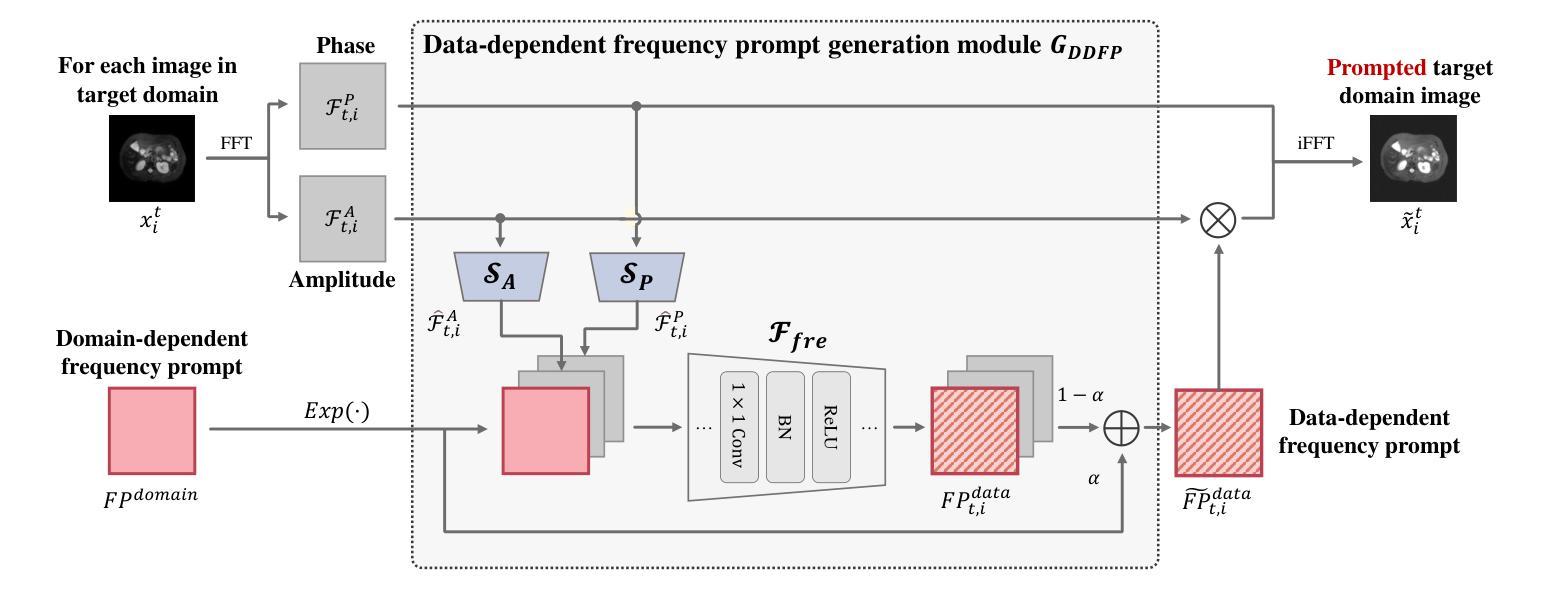
ImplicitStainer: Data-Efficient Medical Image Translation for Virtual Antibody-based Tissue Staining Using Local Implicit Functions
Authors:Tushar Kataria, Beatrice Knudsen, Shireen Y. Elhabian
Hematoxylin and eosin (H&E) staining is a gold standard for microscopic diagnosis in pathology. However, H&E staining does not capture all the diagnostic information that may be needed. To obtain additional molecular information, immunohistochemical (IHC) stains highlight proteins that mark specific cell types, such as CD3 for T-cells or CK8/18 for epithelial cells. While IHC stains are vital for prognosis and treatment guidance, they are typically only available at specialized centers and time consuming to acquire, leading to treatment delays for patients. Virtual staining, enabled by deep learning-based image translation models, provides a promising alternative by computationally generating IHC stains from H&E stained images. Although many GAN and diffusion based image to image (I2I) translation methods have been used for virtual staining, these models treat image patches as independent data points, which results in increased and more diverse data requirements for effective generation. We present ImplicitStainer, a novel approach that leverages local implicit functions to improve image translation, specifically virtual staining performance, by focusing on pixel-level predictions. This method enhances robustness to variations in dataset sizes, delivering high-quality results even with limited data. We validate our approach on two datasets using a comprehensive set of metrics and benchmark it against over fifteen state-of-the-art GAN- and diffusion based models. Full Code and models trained will be released publicly via Github upon acceptance.
苏木精和伊红染色(H&E染色)是病理学显微诊断的金标准。然而,H&E染色并不能捕获所有所需的诊断信息。为了获取额外的分子信息,免疫组织化学染色(IHC染色)会突出显示标记特定细胞类型的蛋白质,如T细胞的CD3或上皮细胞的CK8/18。虽然IHC染色对于预后和治疗指导至关重要,但它们通常仅在专业中心可用,并且获取时间较长,导致患者治疗延迟。深度学习图像翻译模型实现的虚拟染色提供了一种有前景的替代方案,可从H&E染色图像中计算生成IHC染色。尽管许多生成对抗网络(GAN)和基于扩散的图像到图像(I2I)翻译方法已被用于虚拟染色,但这些模型将图像补丁视为独立的数据点,导致需要更多和更多样化的数据来进行有效的生成。我们提出了ImplicitStainer这一新方法,它通过利用局部隐函数来提高图像翻译,特别是虚拟染色性能,重点关注像素级预测。此方法提高了对数据集大小变化的稳健性,即使在有限数据的情况下也能产生高质量的结果。我们在两个数据集上验证了我们的方法,使用了一套综合指标,并将其与超过十五种最先进的GAN和基于扩散的模型进行了基准测试。一旦接受,我们将通过GitHub公开发布完整的代码和训练好的模型。
论文及项目相关链接
摘要
H&E染色是病理学显微诊断的金标准,但其诊断信息并不全面。为了获取额外的分子信息,免疫组织化学染色(IHC)能够突出特定细胞类型的蛋白质标记,如T细胞的CD3或上皮细胞的CK8/18。虽然IHC染色对于预后和治疗指导至关重要,但它通常在专业中心才可用,且获取时间较长,导致患者治疗延迟。深度学习图像翻译模型启用的虚拟染色提供了一个有前景的替代方案,能够从H&E染色图像中计算生成IHC染色。虽然已有许多用于虚拟染色的生成对抗网络(GAN)和扩散图像到图像(I2I)翻译方法,但这些方法将图像块视为独立的数据点,导致有效生成所需的数据要求增加且更加多样化。本文提出了ImplicitStainer这一新方法,利用局部隐函数改进图像翻译,特别是虚拟染色性能,专注于像素级预测。该方法提高了对数据集大小变化的稳健性,即使在有限数据的情况下也能产生高质量的结果。我们在两个数据集上验证了该方法,使用了一套综合指标对其进行了评估,并与十五种以上的最先进GAN和扩散模型进行了比较。一旦接受,我们将通过Github公开发布完整的代码和训练好的模型。
关键见解
- H&E染色是病理学显微诊断的金标准,但缺乏全面的诊断信息。
- 免疫组织化学染色(IHC)对于获取特定细胞类型标记的分子信息至关重要。
- 虚拟染色通过深度学习图像翻译模型提供了一种有前途的替代方案来生成IHC染色。
- 现有方法(如GAN和扩散模型)在处理图像数据时存在局限性,需要更多和更多样化的数据。
- ImplicitStainer方法利用局部隐函数改进图像翻译,专注于像素级预测,提高稳健性和生成质量。
- ImplicitStainer在有限数据的情况下也能产生高质量的结果。
- 该方法在多个数据集上进行了验证,并与其他先进模型进行了比较。
点此查看论文截图

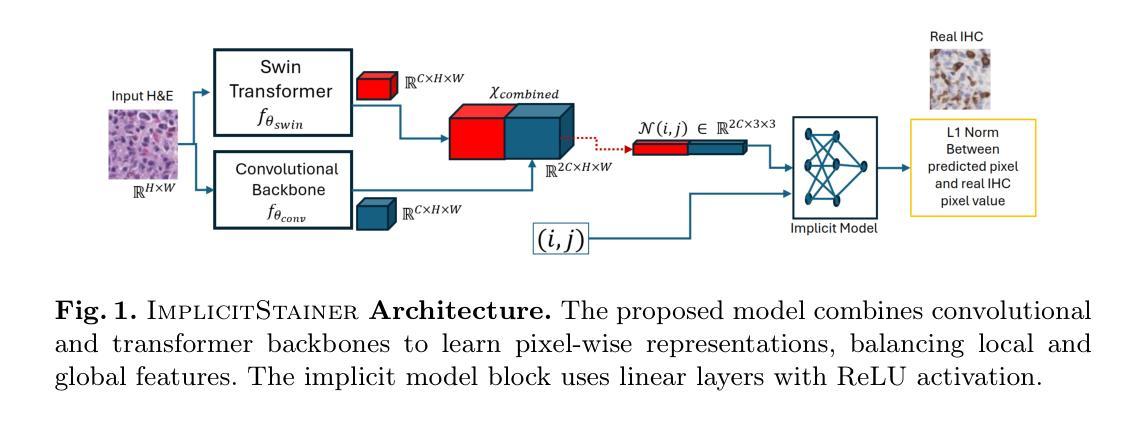
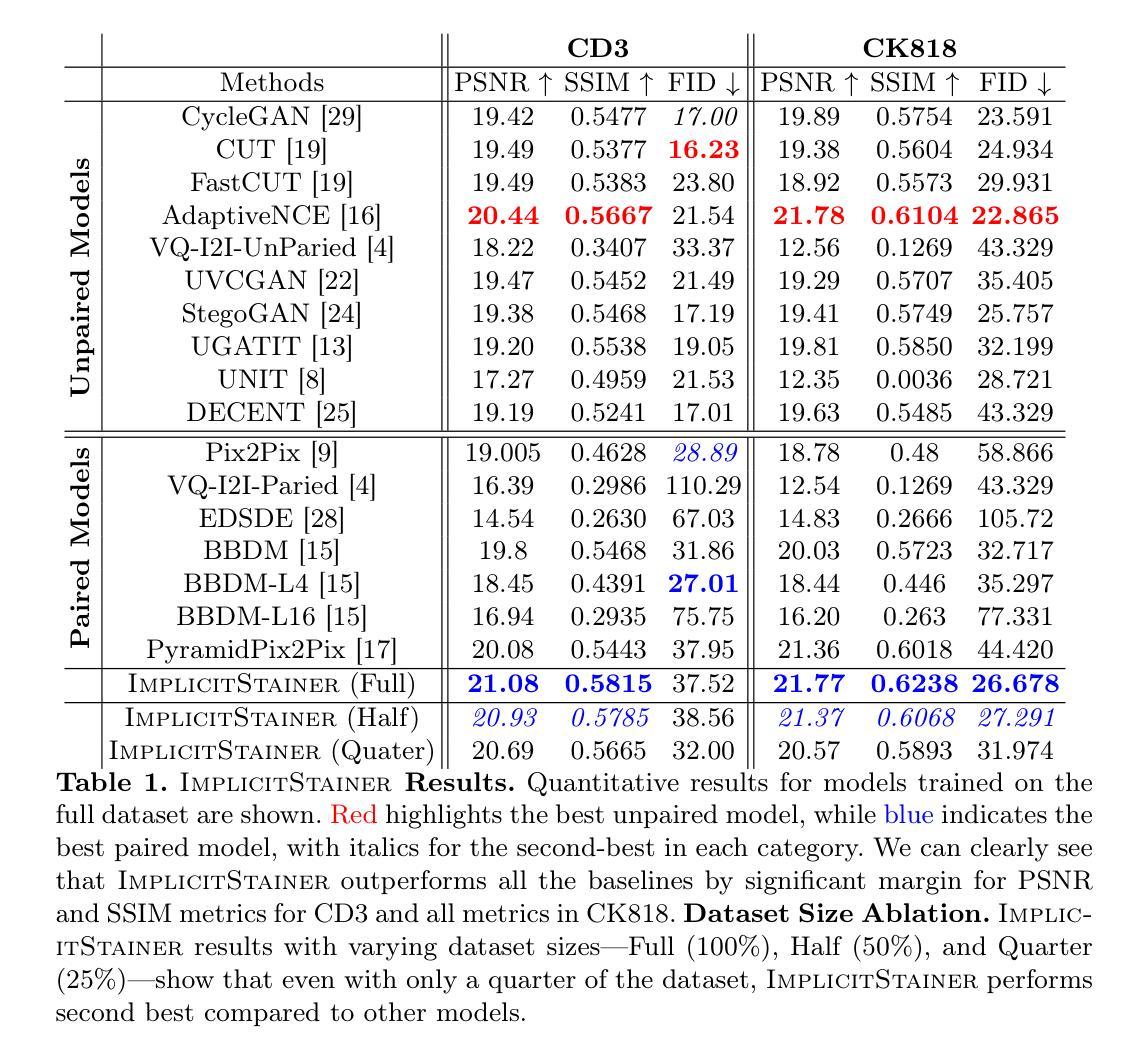
BoundarySeg:An Embarrassingly Simple Method To Boost Medical Image Segmentation Performance for Low Data Regimes
Authors:Tushar Kataria, Shireen Y. Elhabian
Obtaining large-scale medical data, annotated or unannotated, is challenging due to stringent privacy regulations and data protection policies. In addition, annotating medical images requires that domain experts manually delineate anatomical structures, making the process both time-consuming and costly. As a result, semi-supervised methods have gained popularity for reducing annotation costs. However, the performance of semi-supervised methods is heavily dependent on the availability of unannotated data, and their effectiveness declines when such data are scarce or absent. To overcome this limitation, we propose a simple, yet effective and computationally efficient approach for medical image segmentation that leverages only existing annotations. We propose BoundarySeg , a multi-task framework that incorporates organ boundary prediction as an auxiliary task to full organ segmentation, leveraging consistency between the two task predictions to provide additional supervision. This strategy improves segmentation accuracy, especially in low data regimes, allowing our method to achieve performance comparable to or exceeding state-of-the-art semi supervised approaches all without relying on unannotated data or increasing computational demands. Code will be released upon acceptance.
获取大规模医学数据,无论是有标注的还是无标注的,都因为严格的隐私法规和数据处理政策而面临挑战。此外,标注医学图像需要领域专家手动描绘解剖结构,使得这一过程既耗时又成本高昂。因此,半监督方法已经流行起来,用于降低标注成本。然而,半监督方法的性能严重依赖于无标注数据的可用性,当这类数据稀缺或不存在时,其有效性会降低。为了克服这一局限性,我们提出了一种简单、有效且计算效率高的医学图像分割方法,仅利用现有标注。我们提出了BoundarySeg,这是一个多任务框架,它将器官边界预测作为辅助任务融入到全器官分割中,利用两个任务预测之间的一致性提供额外的监督。这一策略提高了分割精度,特别是在数据较少的情况下,使我们的方法在不依赖无标注数据或增加计算需求的情况下,实现了与或超过最新半监督方法的性能。论文接受后将发布代码。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
医学图像标注数据获取困难,因隐私法规和保政策严苛。半监督方法可减少标注成本,但依赖未标注数据,当其稀缺时效果下降。本文提出一种仅利用现有标注数据的医学图像分割方法,采用多任务框架BoundarySeg,以器官边界预测为辅助任务,通过两个任务预测的一致性提供额外监督,提高分割精度,尤其在小数据集下表现优异。
Key Takeaways
- 医学图像数据获取面临挑战,因隐私法规和保政策严格,标注数据尤其困难。
- 半监督方法可减少标注成本,但依赖未标注数据,数据稀缺时效果下降。
- 本文提出一种仅利用现有标注数据的医学图像分割方法,名为BoundarySeg。
- BoundarySeg采用多任务框架,结合器官边界预测作为辅助任务。
- 通过两个任务预测的一致性,BoundarySeg提供额外监督,提高分割精度。
- BoundarySeg尤其在小数据集下表现优异,性能可与最先进的半监督方法相媲美或超过。
点此查看论文截图

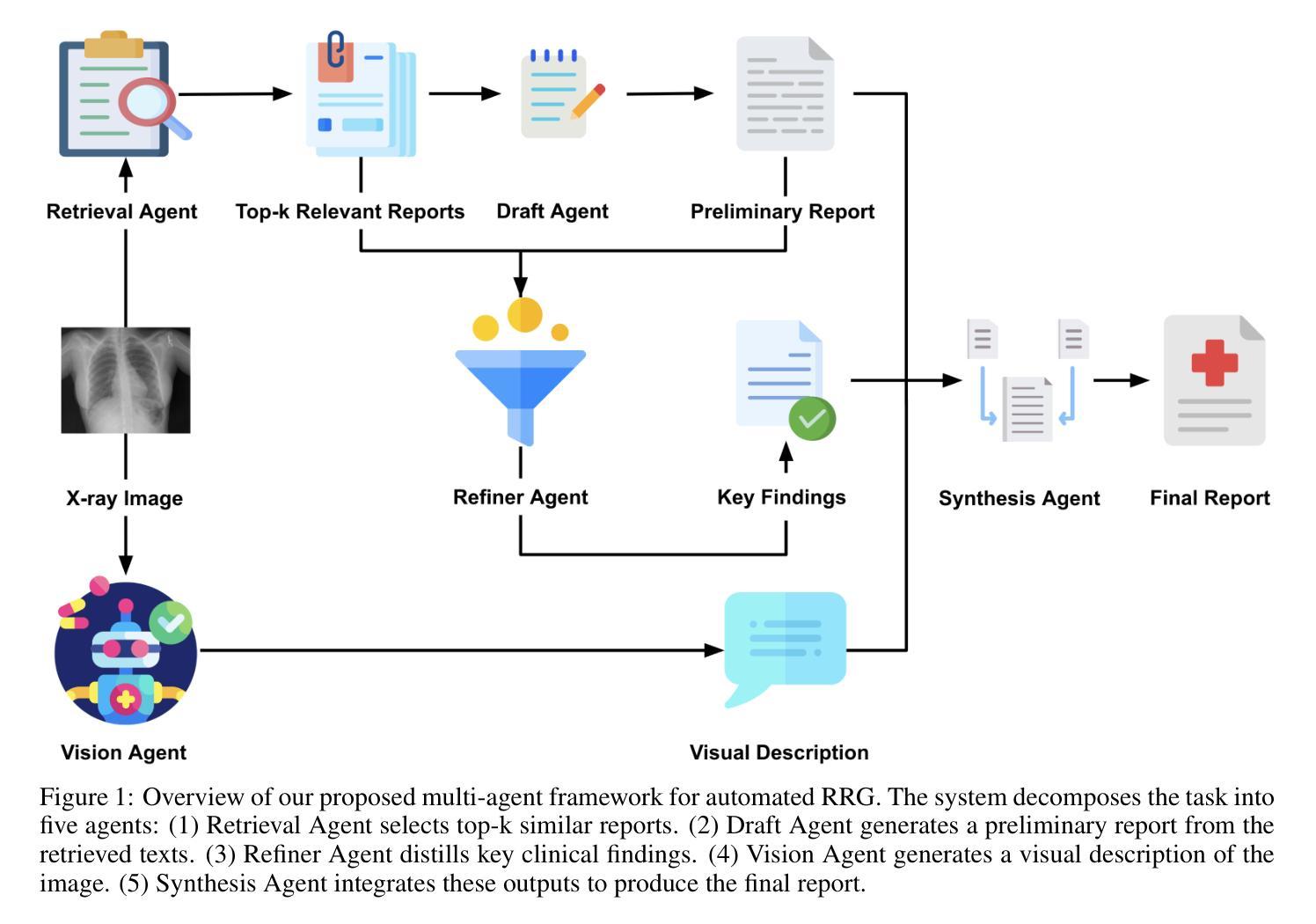
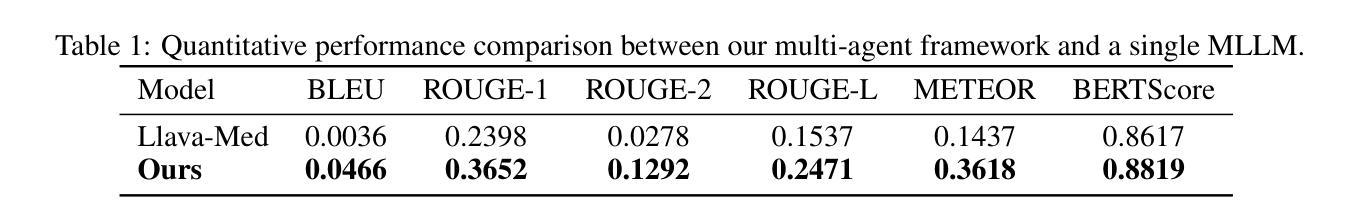
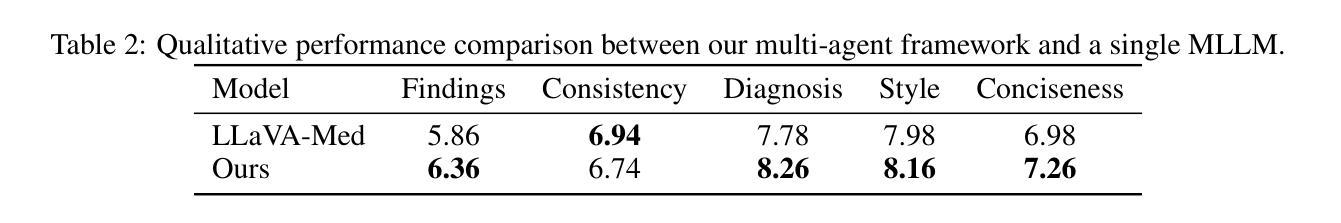
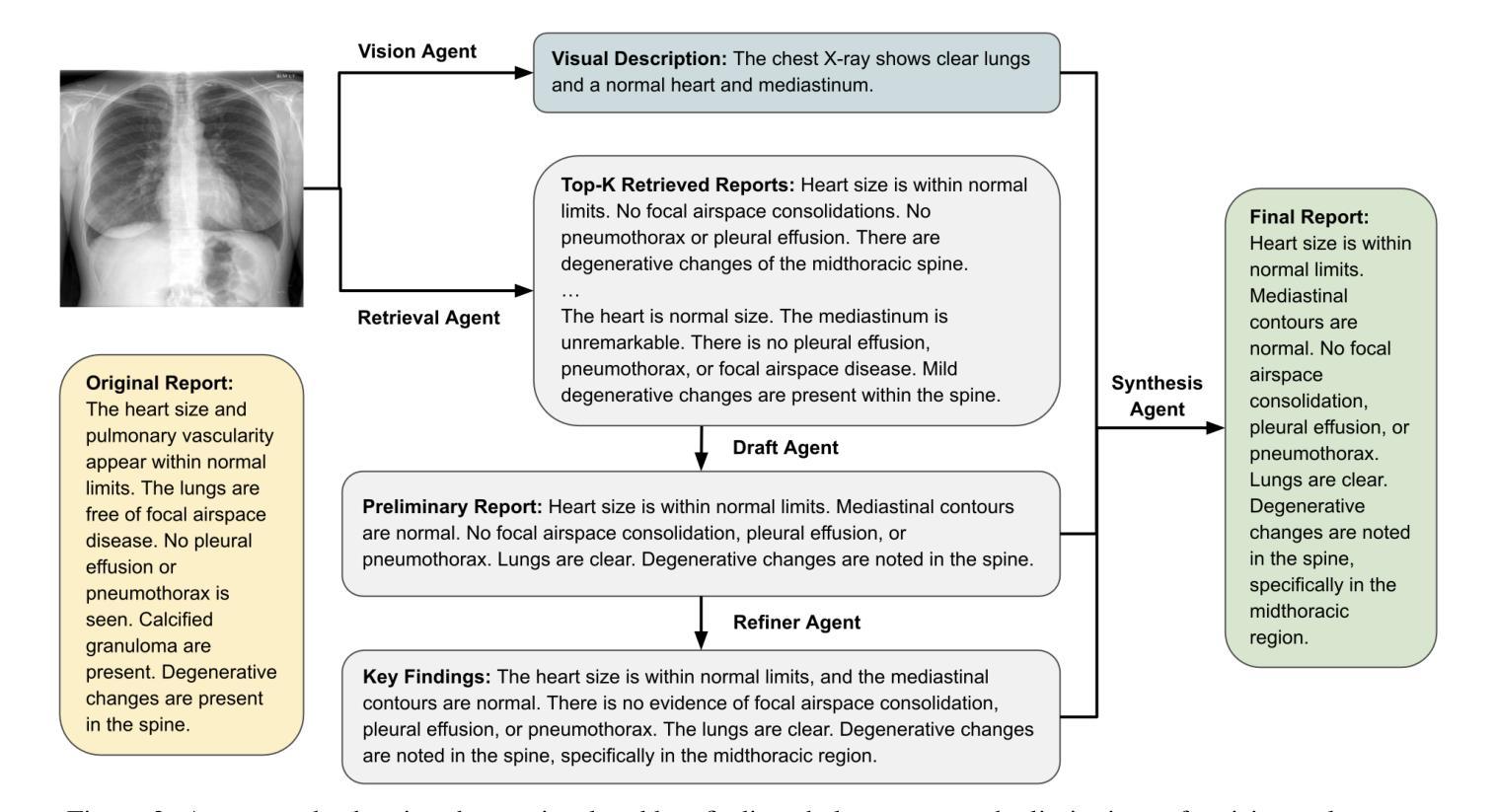
A Multimodal Multi-Agent Framework for Radiology Report Generation
Authors:Ziruo Yi, Ting Xiao, Mark V. Albert
Radiology report generation (RRG) aims to automatically produce diagnostic reports from medical images, with the potential to enhance clinical workflows and reduce radiologists’ workload. While recent approaches leveraging multimodal large language models (MLLMs) and retrieval-augmented generation (RAG) have achieved strong results, they continue to face challenges such as factual inconsistency, hallucination, and cross-modal misalignment. We propose a multimodal multi-agent framework for RRG that aligns with the stepwise clinical reasoning workflow, where task-specific agents handle retrieval, draft generation, visual analysis, refinement, and synthesis. Experimental results demonstrate that our approach outperforms a strong baseline in both automatic metrics and LLM-based evaluations, producing more accurate, structured, and interpretable reports. This work highlights the potential of clinically aligned multi-agent frameworks to support explainable and trustworthy clinical AI applications.
医学影像报告生成(RRG)旨在从医学图像中自动生成诊断报告,具有提高临床工作效率和减轻放射科医生工作负担的潜力。虽然最近采用多模态大型语言模型(MLLMs)和检索增强生成(RAG)的方法取得了很好的效果,但它们仍面临事实不一致、幻想和跨模态不对齐等挑战。我们提出了一种用于RRG的多模态多智能体框架,该框架与分阶段的临床推理工作流程相一致,其中任务特定的智能体负责检索、初稿生成、视觉分析、精化和综合。实验结果表明,我们的方法在自动指标和基于LLM的评估中都优于强大的基线方法,能够生成更准确、结构化、可解释的报告。这项工作突出了临床对齐的多智能体框架在支持可解释和可信赖的临床人工智能应用方面的潜力。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了一种用于放射报告生成的跨模态多智能体框架。该框架通过特定任务智能体实现检索、草稿生成、视觉分析、改进和合成等功能,与临床推理流程相一致。实验结果证明该框架优于现有基线模型,提高了报告的准确性、结构化和可解释性,并支持可解释和可信的临床人工智能应用。
Key Takeaways
- 放射报告生成(RRG)的目标是自动从医学图像生成诊断报告,以提高临床工作效率并减轻放射科医生的工作量。
- 尽管已有利用多模态大型语言模型(MLLMs)和检索增强生成(RAG)的方法取得了显著成果,但它们仍面临事实不一致、幻觉和跨模态不匹配等挑战。
- 提出了一种跨模态多智能体框架,用于RRG,与临床推理流程相一致。
- 该框架包括特定任务的智能体,用于处理检索、草稿生成、视觉分析、改进和合成等功能。
- 实验结果表明,该框架在自动指标和LLM评估中均优于强大的基线模型。
- 该框架生成的报告更准确、结构化且可解释。
点此查看论文截图

Explainability Through Human-Centric Design for XAI in Lung Cancer Detection
Authors:Amy Rafferty, Rishi Ramaesh, Ajitha Rajan
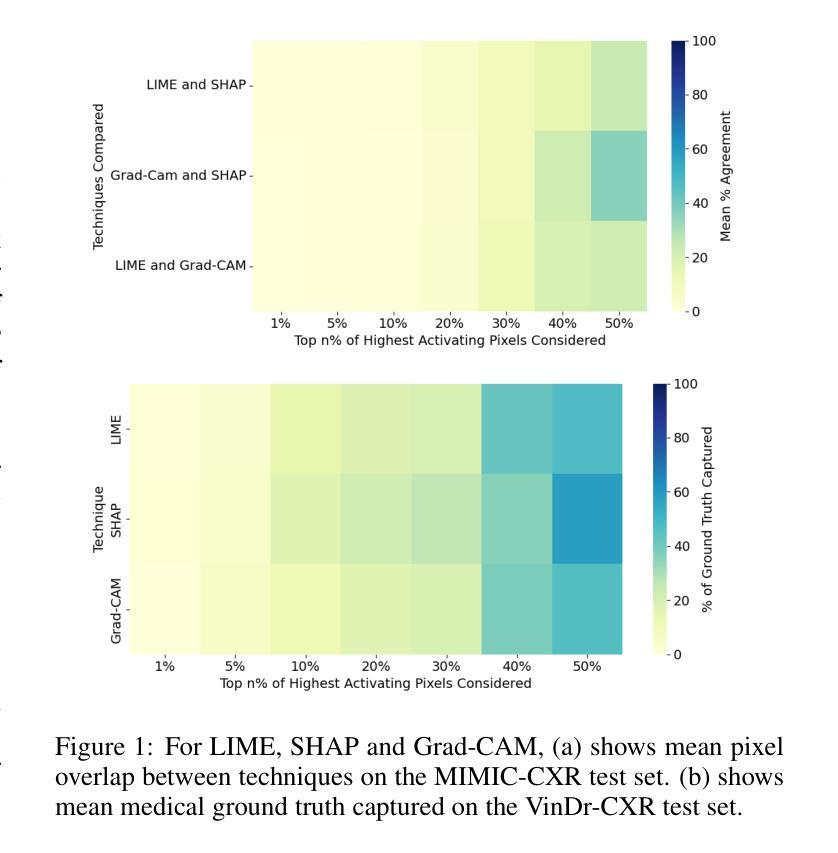
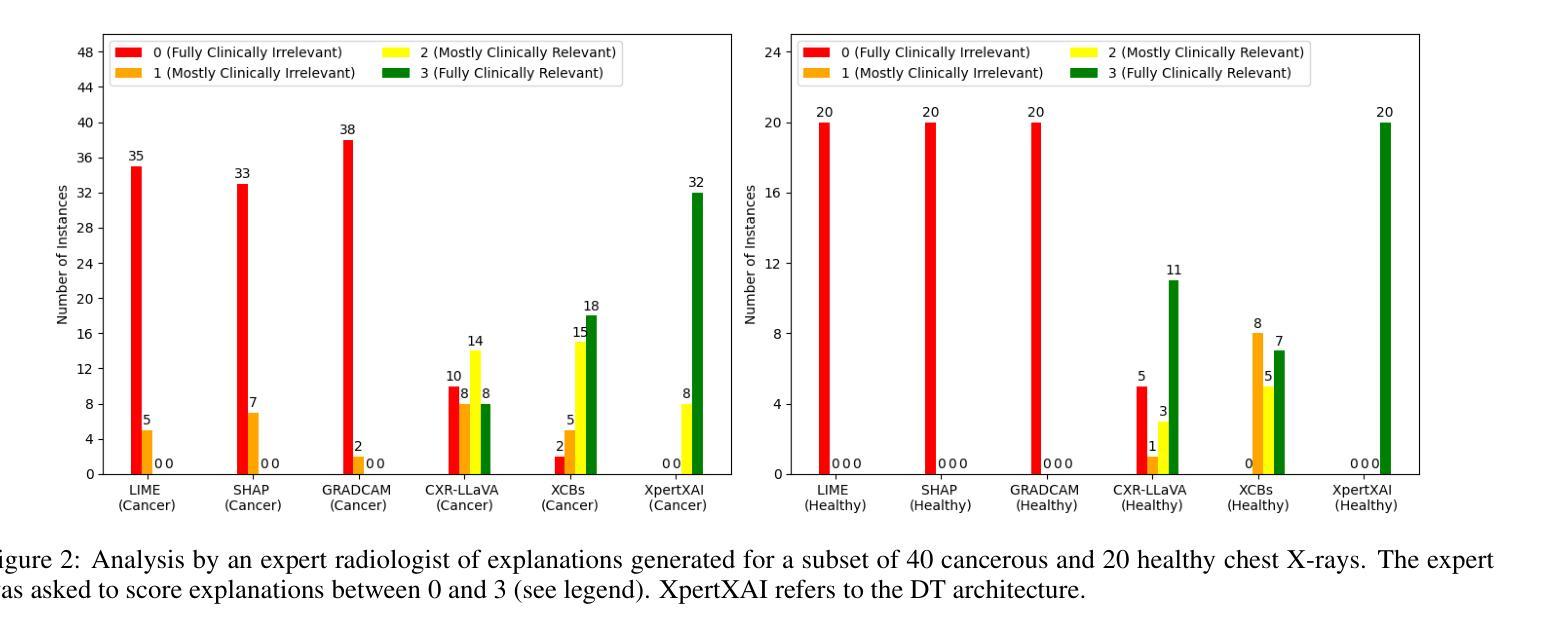
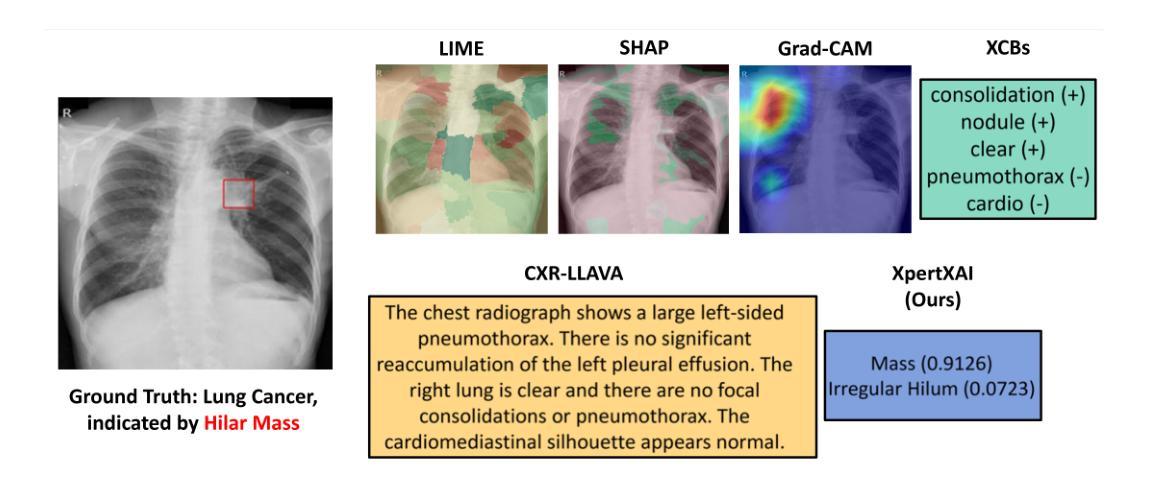
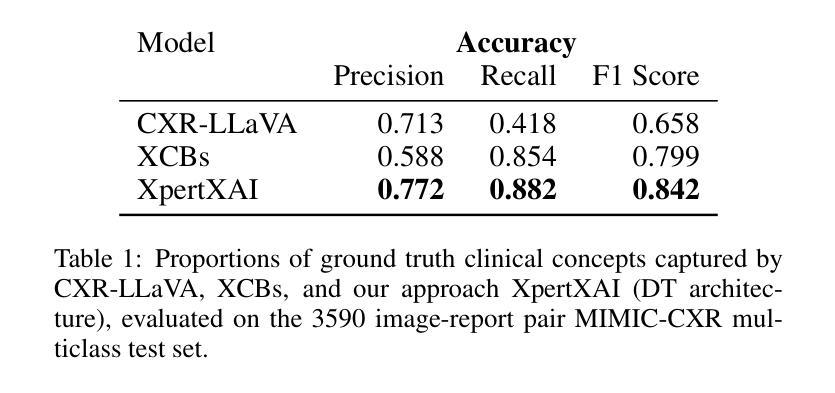
Deep learning models have shown promise in lung pathology detection from chest X-rays, but widespread clinical adoption remains limited due to opaque model decision-making. In prior work, we introduced ClinicXAI, a human-centric, expert-guided concept bottleneck model (CBM) designed for interpretable lung cancer diagnosis. We now extend that approach and present XpertXAI, a generalizable expert-driven model that preserves human-interpretable clinical concepts while scaling to detect multiple lung pathologies. Using a high-performing InceptionV3-based classifier and a public dataset of chest X-rays with radiology reports, we compare XpertXAI against leading post-hoc explainability methods and an unsupervised CBM, XCBs. We assess explanations through comparison with expert radiologist annotations and medical ground truth. Although XpertXAI is trained for multiple pathologies, our expert validation focuses on lung cancer. We find that existing techniques frequently fail to produce clinically meaningful explanations, omitting key diagnostic features and disagreeing with radiologist judgments. XpertXAI not only outperforms these baselines in predictive accuracy but also delivers concept-level explanations that better align with expert reasoning. While our focus remains on explainability in lung cancer detection, this work illustrates how human-centric model design can be effectively extended to broader diagnostic contexts - offering a scalable path toward clinically meaningful explainable AI in medical diagnostics.
深度学习模型在胸部X光片中检测肺部病变方面显示出巨大潜力,但由于模型决策不透明,其在临床上的广泛应用仍然有限。先前,我们引入了ClinicXAI,一种以人为中心、专家指导的概念瓶颈模型(CBM),旨在实现可解释的肺癌诊断。现在我们扩展了该方法,并推出了XpertXAI,这是一种通用专家驱动模型,在保持人类可解释的临床概念的同时,能够扩展以检测多种肺部病变。我们采用高性能的基于InceptionV3的分类器以及带有放射学报告的公共胸部X光数据集,将XpertXAI与领先的事后解释方法以及无监督CBM(XCBs)进行比较。我们通过专家放射科医生注释和医学真相来评估解释。尽管XpertXAI是为多种病变而训练的,但我们的专家验证主要集中在肺癌上。我们发现现有技术往往无法产生具有临床意义的解释,它们会遗漏关键诊断特征并与放射科医生判断相悖。XpertXAI不仅在预测准确性方面超越这些基线,而且提供与专家推理更相符的概念层面解释。虽然我们的重点仍然是肺癌检测中的可解释性,但这项工作说明了以人为中心的设计模型如何有效地扩展到更广泛的诊断背景,为临床上有意义的可解释人工智能在医学诊断中提供了一条可扩展的道路。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
引入ClinicXAI模型进行肺癌诊断后,现在扩展该方案,提出XpertXAI模型,该模型采用可推广的专家驱动方式,既保留了解释性临床概念,又能扩展到检测多种肺部病变。与顶尖事后解释方法和无监督CBM相比,XpertXAI使用高性能的InceptionV3分类器与公共胸部X射线数据集和放射学报告进行比较评估。尽管XpertXAI经过多种病理训练,但专家验证主要集中在肺癌上。现有技术往往无法产生具有临床意义的解释,遗漏关键诊断特征并与放射科医生判断相悖。XpertXAI不仅预测精度超过基线水平,而且提供与专家推理更相符的概念层面解释。虽然重点仍然是肺癌检测中的解释性,但这项工作展示了以人为中心的设计方案如何有效地扩展到更广泛的诊断环境,为临床上有意义的可解释人工智能在医学诊断中的发展提供了可扩展路径。
Key Takeaways
- XpertXAI模型是一个新的、基于专家驱动的模型,旨在解释肺部疾病的诊断过程。它基于先前ClinicXAI模型的基础上进行扩展。
- XpertXAI在预测精度上超过了现有技术。它通过引入高性能的InceptionV3分类器实现对胸部X射线图像的精准分类和诊断。
- XpertXAI提供了一个概念层面的解释框架,使得诊断过程更符合专家推理模式。该模型通过结合医学知识和人工智能技术,生成了具有临床意义的解释。
- 与其他解释方法相比,现有的技术往往无法产生与专家判断一致的解释结果。它们可能遗漏关键的诊断特征或与放射科医生的判断相悖。而XpertXAI能够更好地捕捉这些关键特征并给出准确的解释。
- 虽然本研究的重点在于肺癌检测中的解释性,但所展示的以人为中心的设计思路可应用于更广泛的医学诊断领域。这表明该模型具有广泛的应用前景和可扩展性。
- XpertXAI模型使用公共数据集进行训练,这些数据集包含胸部X射线图像和相关的放射学报告。这为模型的训练和验证提供了真实世界的数据支持。通过与这些数据集进行交互训练,模型的诊断准确性得以进一步提高。同时增强了模型的临床意义及其解释的准确性。
点此查看论文截图

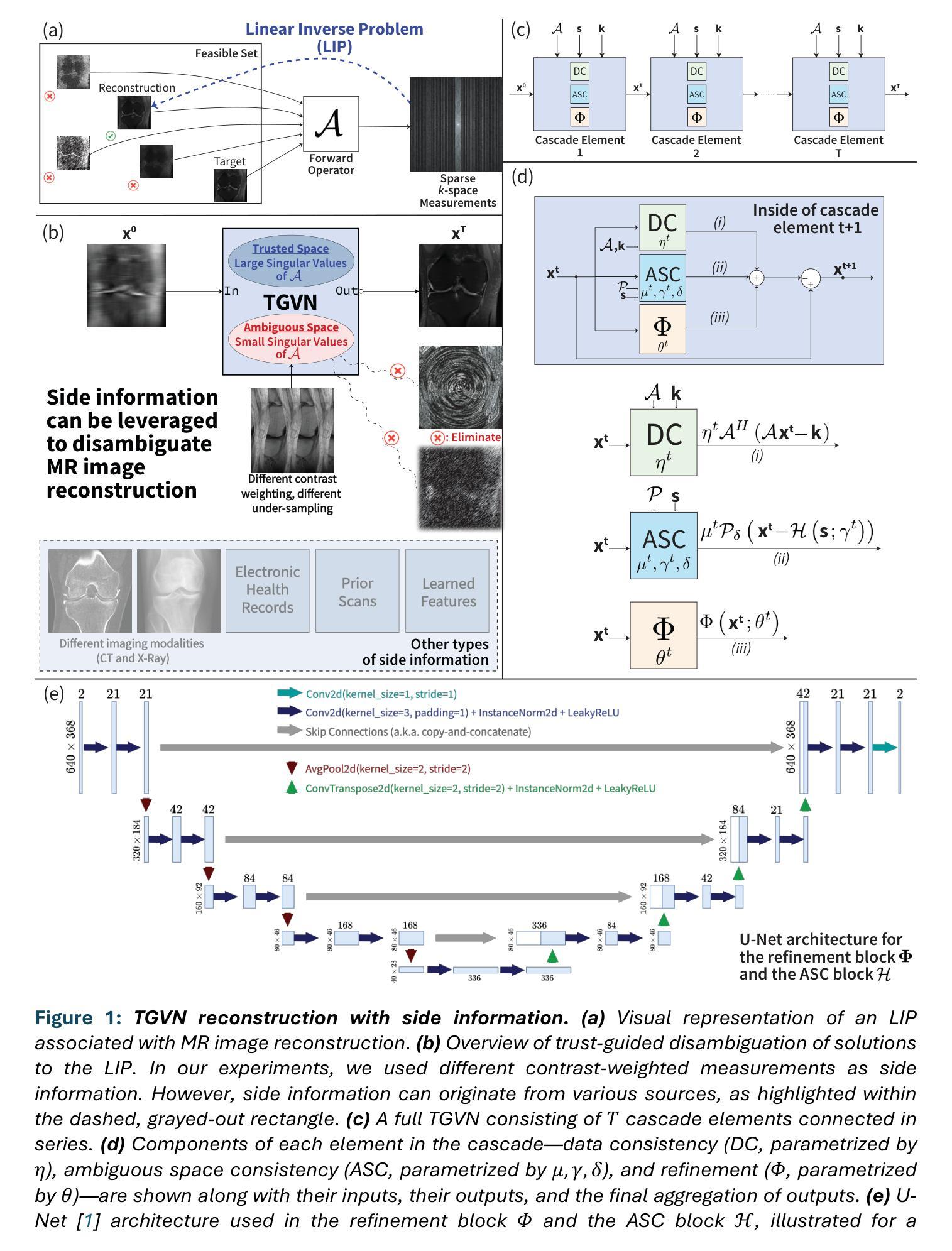
A Trust-Guided Approach to MR Image Reconstruction with Side Information
Authors:Arda Atalık, Sumit Chopra, Daniel K. Sodickson
Reducing MRI scan times can improve patient care and lower healthcare costs. Many acceleration methods are designed to reconstruct diagnostic-quality images from sparse k-space data, via an ill-posed or ill-conditioned linear inverse problem (LIP). To address the resulting ambiguities, it is crucial to incorporate prior knowledge into the optimization problem, e.g., in the form of regularization. Another form of prior knowledge less commonly used in medical imaging is the readily available auxiliary data (a.k.a. side information) obtained from sources other than the current acquisition. In this paper, we present the Trust- Guided Variational Network (TGVN), an end-to-end deep learning framework that effectively and reliably integrates side information into LIPs. We demonstrate its effectiveness in multi-coil, multi-contrast MRI reconstruction, where incomplete or low-SNR measurements from one contrast are used as side information to reconstruct high-quality images of another contrast from heavily under-sampled data. TGVN is robust across different contrasts, anatomies, and field strengths. Compared to baselines utilizing side information, TGVN achieves superior image quality while preserving subtle pathological features even at challenging acceleration levels, drastically speeding up acquisition while minimizing hallucinations. Source code and dataset splits are available on github.com/sodicksonlab/TGVN.
减少MRI扫描时间可以改善患者护理并降低医疗成本。许多加速方法旨在通过不适定或病态的线性逆问题(LIP)从稀疏的k空间数据中重建诊断质量的图像。为了解决由此产生的模糊性,将先验知识融入优化问题至关重要,例如以正则化的形式。另一种在医学成像中较少使用的先验知识是易于获得的辅助数据(也称为侧信息),这些辅助数据来源于当前采集之外的其他来源。在本文中,我们提出了Trust-Guided Variational Network(TGVN),这是一个端到端的深度学习框架,能够有效且可靠地将侧信息集成到LIPs中。我们在多线圈、多对比度MRI重建中展示了其有效性,其中来自一种对比度的不完整或低SNR测量值被用作侧信息,以从高度欠采样的数据中重建另一种对比度的高质量图像。TGVN在不同的对比度、解剖结构和磁场强度之间表现出稳健性。与利用侧信息的基线相比,TGVN在具有挑战性的加速级别下实现了更高的图像质量,即使在细微的病理性特征下也能保持其清晰度,极大地加快了采集速度并减少了幻觉。源代码和数据集分割可在github.com/sodicksonlab/TGVN找到。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 27 pages, 9 figures
Summary
本文介绍了一种名为Trust-Guided Variational Network(TGVN)的深度学习框架,它能有效地将辅助信息融入线性逆问题中,用于MRI扫描时间的减少和图像重建。该框架在多线圈、多对比度的MRI重建中表现出色,能够利用一种对比度的低质量测量数据作为辅助信息,重建另一种对比度的高质量图像。TGVN在不同的对比度、解剖结构和磁场强度下具有稳健性,相较于其他使用辅助信息的基线方法,能够在挑战性的加速级别下实现更优质的图像质量,同时保留微妙的病理特征。
Key Takeaways
- TGVN框架能有效减少MRI扫描时间,提高患者护理和降低医疗保健成本。
- TGVN通过将辅助信息融入线性逆问题中,提高了图像重建的质量。
- 该框架在多对比度的MRI重建中有出色表现,特别是利用一种对比度的数据作为辅助信息来重建另一种对比度的数据。
- TGVN具有在不同对比度、解剖结构和磁场强度下的稳健性。
- TGVN相比其他方法能够实现更优质的图像质量,尤其在具有挑战性的加速级别下。
- TGVN框架能保留微妙的病理特征,这是其他方法可能忽略的细节。
点此查看论文截图