⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-05-17 更新
Consistent Quantity-Quality Control across Scenes for Deployment-Aware Gaussian Splatting
Authors:Fengdi Zhang, Hongkun Cao, Ruqi Huang
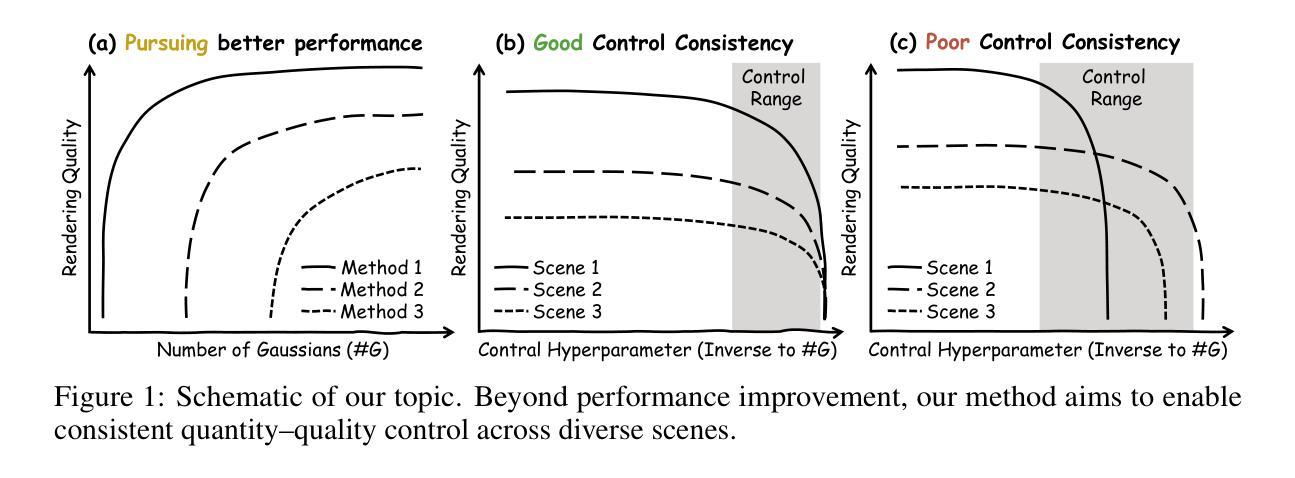
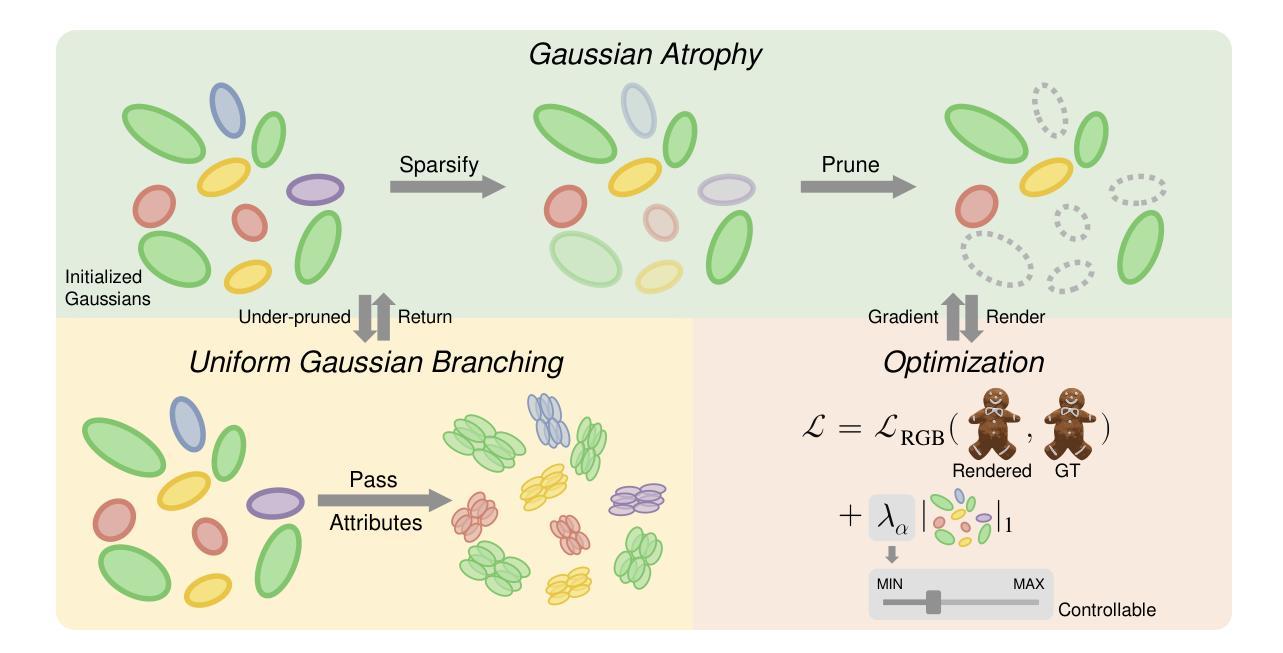
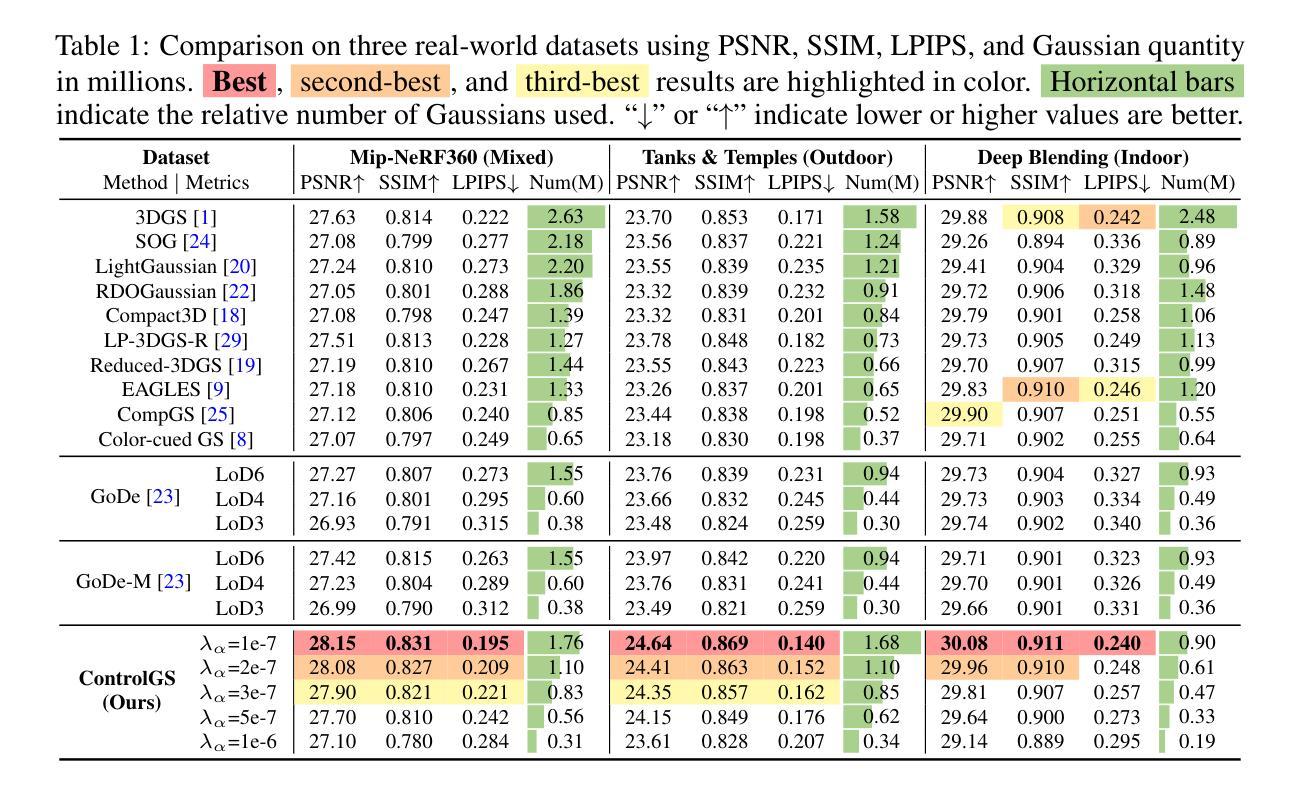
To reduce storage and computational costs, 3D Gaussian splatting (3DGS) seeks to minimize the number of Gaussians used while preserving high rendering quality, introducing an inherent trade-off between Gaussian quantity and rendering quality. Existing methods strive for better quantity-quality performance, but lack the ability for users to intuitively adjust this trade-off to suit practical needs such as model deployment under diverse hardware and communication constraints. Here, we present ControlGS, a 3DGS optimization method that achieves semantically meaningful and cross-scene consistent quantity-quality control while maintaining strong quantity-quality performance. Through a single training run using a fixed setup and a user-specified hyperparameter reflecting quantity-quality preference, ControlGS can automatically find desirable quantity-quality trade-off points across diverse scenes, from compact objects to large outdoor scenes. It also outperforms baselines by achieving higher rendering quality with fewer Gaussians, and supports a broad adjustment range with stepless control over the trade-off.
为了减少存储和计算成本,3D高斯展开(3DGS)旨在减少使用的高斯数量,同时保持高渲染质量,从而在高斯数量和渲染质量之间引入固有的权衡。现有方法努力追求数量与质量的性能,但缺乏让用户能够直观地调整这种权衡以适应实际需求的能力,例如在各种硬件和通信约束下的模型部署。在这里,我们提出了ControlGS,这是一种3DGS优化方法,它实现了语义上有意义和跨场景一致的数量与质量控制,同时保持了强大的数量-质量性能。通过一次固定的训练运行和用户指定的反映数量-质量偏好的超参数,ControlGS可以在不同的场景中自动找到理想化的数量-质量权衡点,从紧凑对象到大范围户外场景。它还通过以更少的高斯实现更高的渲染质量超过了基线,并支持广泛的调整范围和逐步控制权衡。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了ControlGS,这是一种优化的三维高斯融合技术,旨在通过用户指定的超参数调整高斯数量与渲染质量之间的权衡,以实现对不同场景下的数量质量偏好控制。ControlGS能在不同场景下自动找到理想的数量质量权衡点,并支持大范围的无级调整。
Key Takeaways
- ControlGS是一种优化的三维高斯融合技术(3DGS),旨在减少存储和计算成本。
- 现有的方法在数量与质量之间取得平衡时面临挑战,而ControlGS引入了一种直观的方法来调整这种权衡以适应不同的实际需求。
- ControlGS通过单一训练过程,实现了对各类场景的高质量渲染与高性能的均衡处理。它能根据不同的用户需求寻找合适的数量质量权衡点。
点此查看论文截图

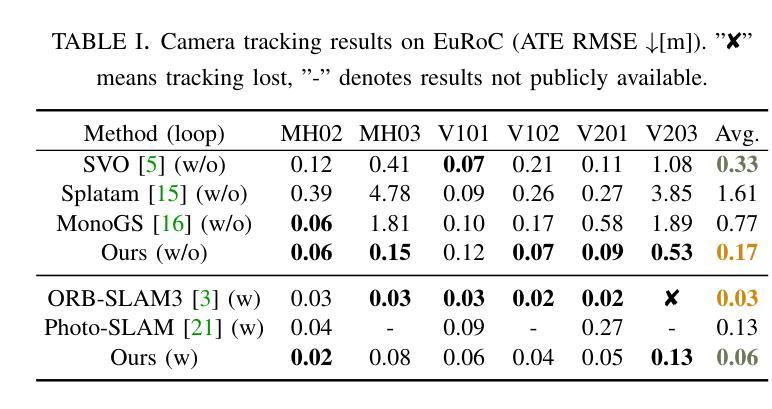
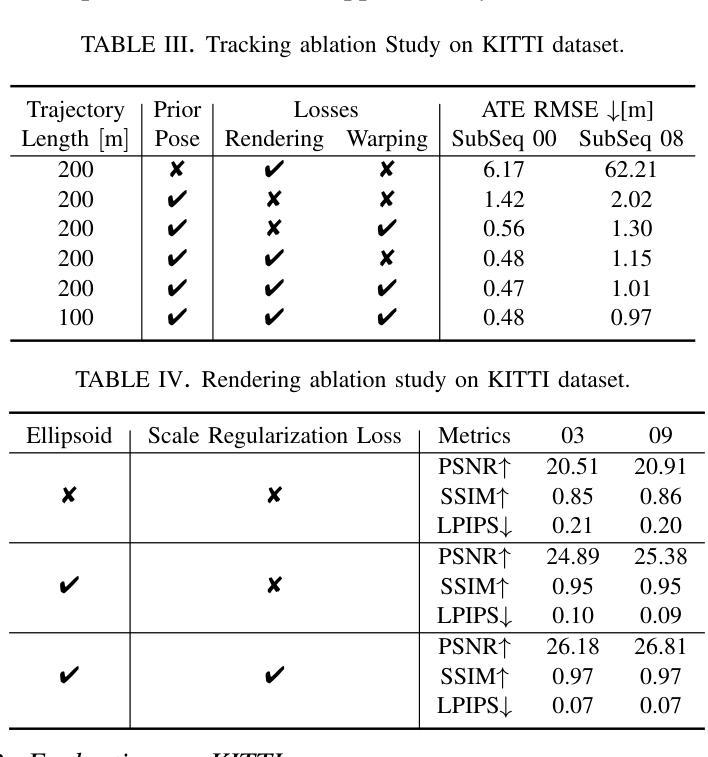
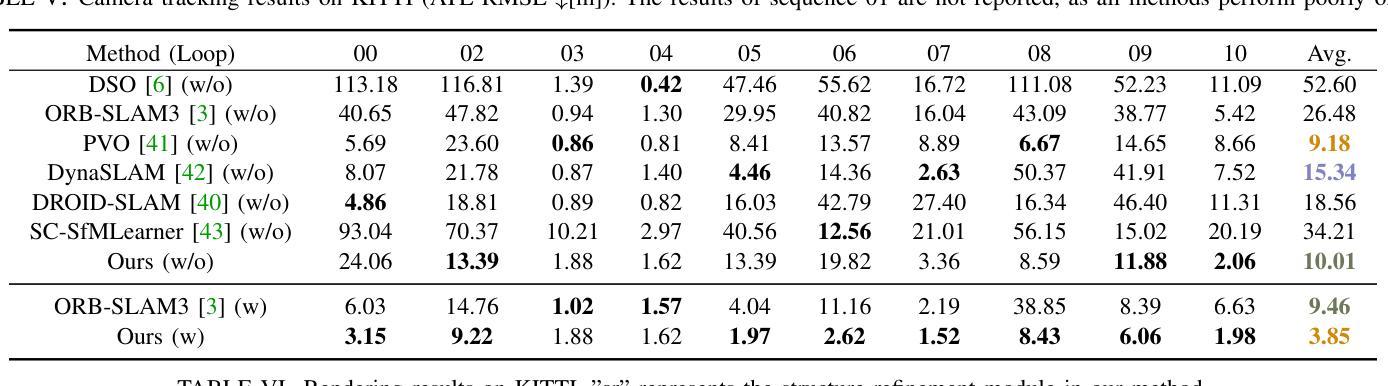
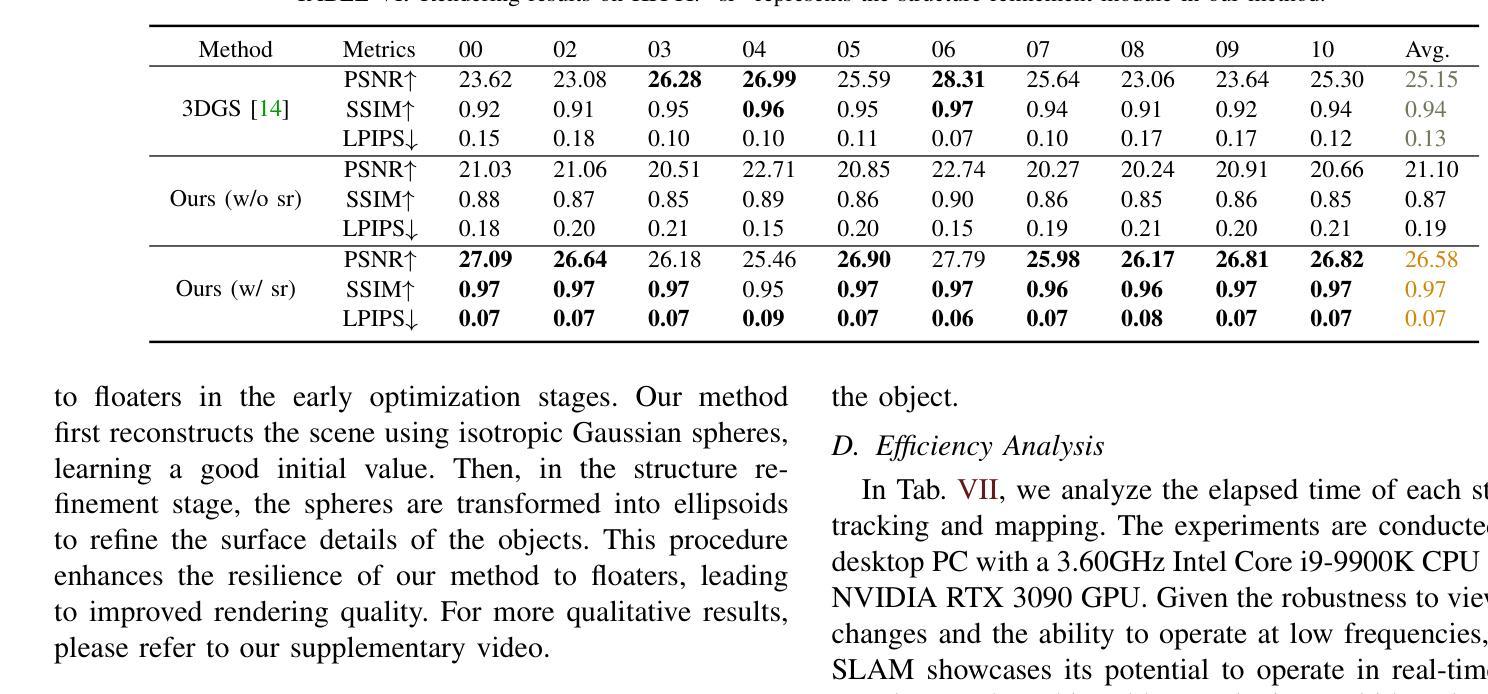
Large-Scale Gaussian Splatting SLAM
Authors:Zhe Xin, Chenyang Wu, Penghui Huang, Yanyong Zhang, Yinian Mao, Guoquan Huang
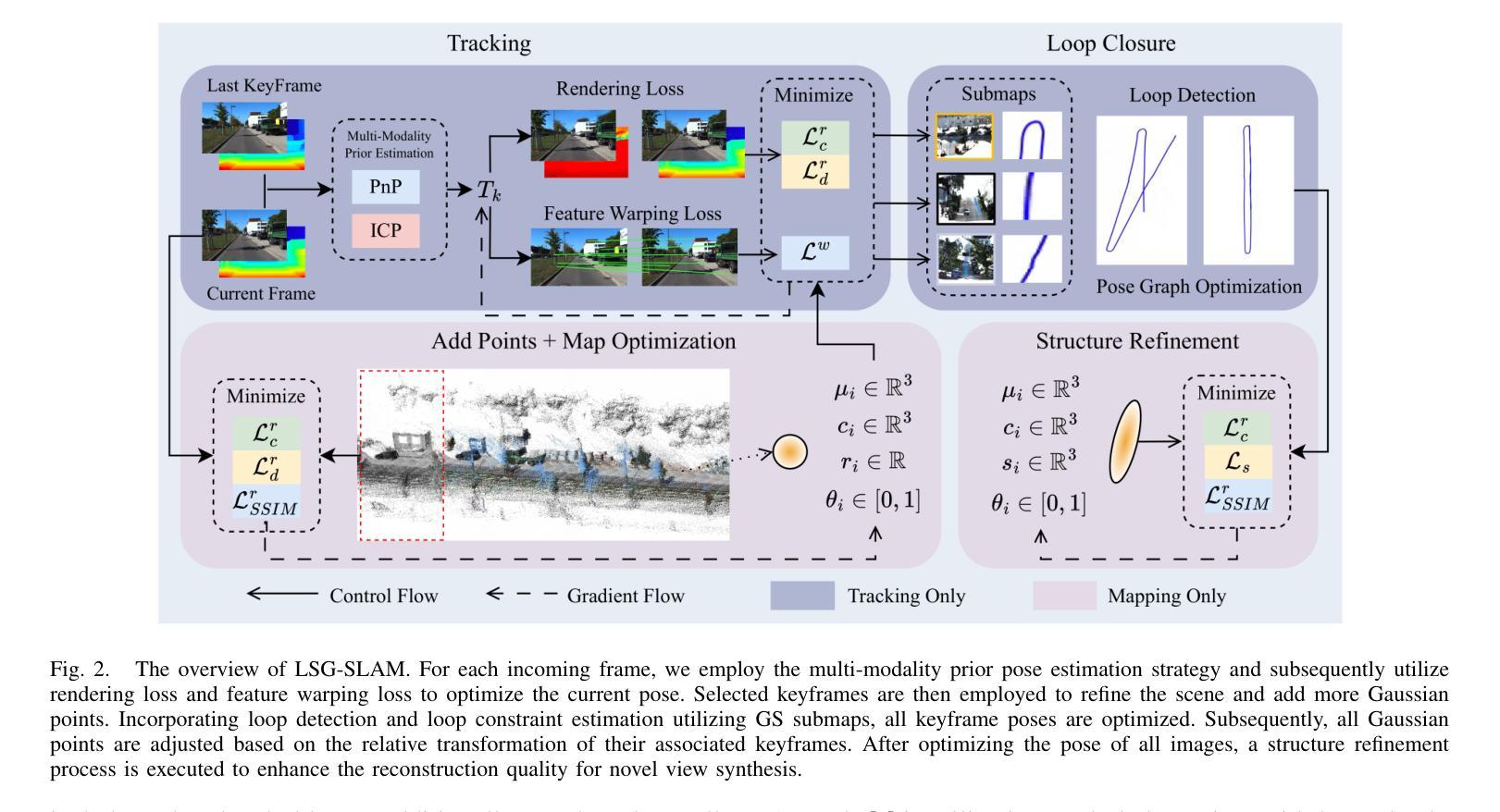
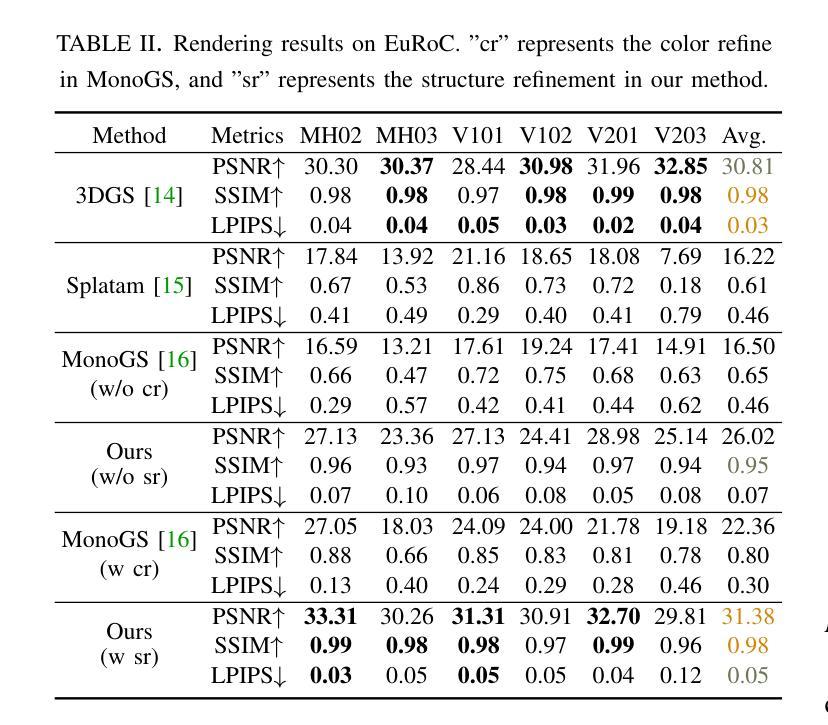
The recently developed Neural Radiance Fields (NeRF) and 3D Gaussian Splatting (3DGS) have shown encouraging and impressive results for visual SLAM. However, most representative methods require RGBD sensors and are only available for indoor environments. The robustness of reconstruction in large-scale outdoor scenarios remains unexplored. This paper introduces a large-scale 3DGS-based visual SLAM with stereo cameras, termed LSG-SLAM. The proposed LSG-SLAM employs a multi-modality strategy to estimate prior poses under large view changes. In tracking, we introduce feature-alignment warping constraints to alleviate the adverse effects of appearance similarity in rendering losses. For the scalability of large-scale scenarios, we introduce continuous Gaussian Splatting submaps to tackle unbounded scenes with limited memory. Loops are detected between GS submaps by place recognition and the relative pose between looped keyframes is optimized utilizing rendering and feature warping losses. After the global optimization of camera poses and Gaussian points, a structure refinement module enhances the reconstruction quality. With extensive evaluations on the EuRoc and KITTI datasets, LSG-SLAM achieves superior performance over existing Neural, 3DGS-based, and even traditional approaches. Project page: https://lsg-slam.github.io.
最近开发的神经辐射场(NeRF)和3D高斯涂绘(3DGS)在视觉SLAM方面显示出令人鼓舞和令人印象深刻的结果。然而,大多数代表性方法需要RGBD传感器,并且仅适用于室内环境。在大规模室外场景中的重建稳健性尚未被探索。本文介绍了一种基于大规模3DGS的视觉SLAM与立体相机,称为LSG-SLAM。所提出的LSG-SLAM采用多模态策略来估计大视角变化下的先验姿势。在跟踪过程中,我们引入了特征对齐扭曲约束,以减轻渲染损失中外观相似性带来的不利影响。为了解决大规模场景的扩展性,我们引入了连续的高斯涂绘子图,以处理有限的内存中的无界场景。通过位置识别检测GS子图之间的环路,并利用渲染和特征扭曲损失优化环路关键帧之间的相对姿态。经过全局优化的相机姿态和高斯点之后,结构细化模块提高了重建质量。在EuRoc和KITTI数据集上的广泛评估表明,LSG-SLAM的性能优于现有的神经、基于3DGS甚至传统的方法。项目页面:https://lsg-slam.github.io。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
NeRF和3DGS在视觉SLAM领域展现出良好效果,但受限于RGBD传感器和室内环境。本文提出一种基于大规模3DGS的视觉SLAM方法,称为LSG-SLAM,适用于室外场景。它采用多模态策略估计大视角变化下的先验姿态,引入特征对齐扭曲约束减轻渲染损失中的外观相似性不良影响。通过连续高斯拼贴子图处理大规模场景,采用位置识别检测GS子图之间的环路,并利用渲染和特征扭曲损失优化环路关键帧的相对姿态。经过全局优化相机姿态和高斯点后进行结构细化,提高重建质量。在EuRoc和KITTI数据集上的评估显示,LSG-SLAM性能优于现有神经网络、基于3DGS甚至传统方法。
Key Takeaways
- LSG-SLAM结合NeRF和3DGS技术,针对大规模室外场景提出一种新型的视觉SLAM方法。
- 该方法采用多模态策略应对大视角变化下的姿态估计问题。
- LSG-SLAM通过特征对齐扭曲约束减轻渲染损失中的外观相似性带来的不良影响。
- 为处理大规模场景,LSG-SLAM引入连续高斯拼贴子图技术,并实现位置识别以检测环路。
- 该方法通过优化环路关键帧的相对姿态,提高了系统的精度和稳定性。
- LSG-SLAM通过全局优化相机姿态和高斯点,进一步提升了重建质量。
- 在EuRoc和KITTI数据集上的实验表明,LSG-SLAM性能优于其他现有方法。
点此查看论文截图

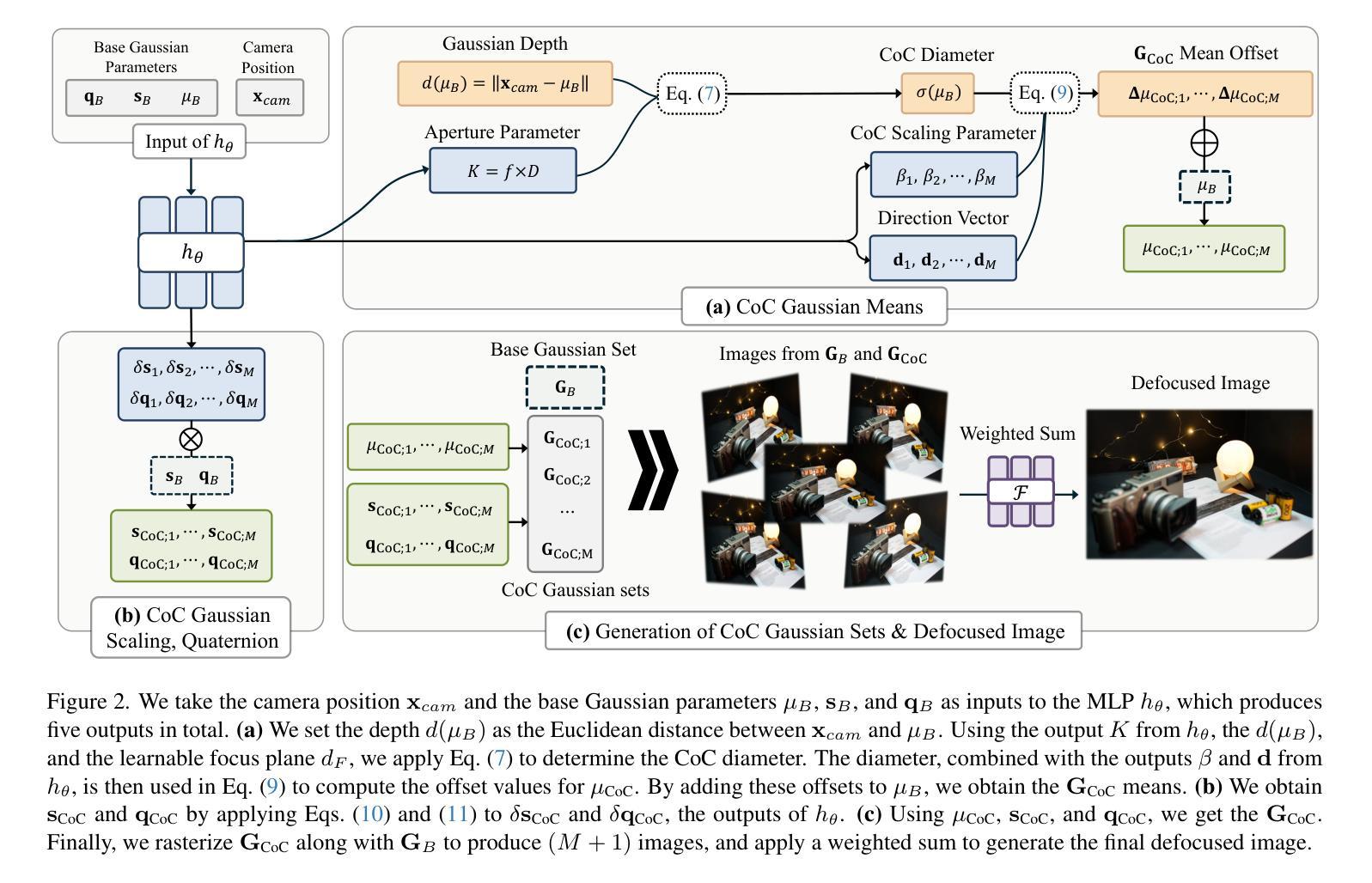
CoCoGaussian: Leveraging Circle of Confusion for Gaussian Splatting from Defocused Images
Authors:Jungho Lee, Suhwan Cho, Taeoh Kim, Ho-Deok Jang, Minhyeok Lee, Geonho Cha, Dongyoon Wee, Dogyoon Lee, Sangyoun Lee
3D Gaussian Splatting (3DGS) has attracted significant attention for its high-quality novel view rendering, inspiring research to address real-world challenges. While conventional methods depend on sharp images for accurate scene reconstruction, real-world scenarios are often affected by defocus blur due to finite depth of field, making it essential to account for realistic 3D scene representation. In this study, we propose CoCoGaussian, a Circle of Confusion-aware Gaussian Splatting that enables precise 3D scene representation using only defocused images. CoCoGaussian addresses the challenge of defocus blur by modeling the Circle of Confusion (CoC) through a physically grounded approach based on the principles of photographic defocus. Exploiting 3D Gaussians, we compute the CoC diameter from depth and learnable aperture information, generating multiple Gaussians to precisely capture the CoC shape. Furthermore, we introduce a learnable scaling factor to enhance robustness and provide more flexibility in handling unreliable depth in scenes with reflective or refractive surfaces. Experiments on both synthetic and real-world datasets demonstrate that CoCoGaussian achieves state-of-the-art performance across multiple benchmarks.
三维高斯描绘技术(3DGS)以其高质量的新视角渲染而受到广泛关注,并激发了解决现实世界挑战的研究。虽然传统方法依赖于清晰图像进行准确的场景重建,但由于有限的景深,现实世界场景往往受到失焦模糊的影响,因此需要考虑到现实的三维场景表示。在本研究中,我们提出了基于模糊圆意识的CoCoGaussian高斯描绘技术,该技术仅使用失焦图像即可实现精确的三维场景表示。CoCoGaussian通过基于摄影失焦原理的物理建模方法来解决失焦模糊的挑战。通过利用三维高斯函数,我们从深度和可学习的光圈信息计算模糊圆的直径,生成多个高斯函数来精确捕捉模糊圆的形状。此外,我们还引入了一个可学习的缩放因子,以提高稳健性,并在处理具有反射或折射表面的场景中不可靠深度时提供更多灵活性。在合成和真实数据集上的实验表明,CoCoGaussian在多个基准测试中达到了最先进的性能。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF CVPR 2025, Project Page: https://Jho-Yonsei.github.io/CoCoGaussian/
Summary
本文介绍了名为CoCoGaussian的基于圆散焦意识的高斯喷射渲染技术,该技术通过使用只有散焦图像来实现精确的3D场景表示。它通过物理基础的方法模拟圆散焦(CoC),利用深度信息和可学习的光圈信息计算CoC直径,生成多个高斯来精确捕捉CoC形状。此外,引入可学习的缩放因子以提高对不可靠深度的稳健性,并处理具有反射或折射表面的场景中的不确定深度。实验证明,CoCoGaussian在多个基准测试中达到了业界领先的表现。
Key Takeaways
- 3D Gaussian Splatting(3DGS)因其高质量的新视角渲染而备受关注。
- 传统方法依赖清晰图像进行准确的场景重建,但现实世界场景中的散焦模糊是一个挑战。
- CoCoGaussian是一种解决散焦模糊的新方法,它通过物理基础的方法模拟圆散焦(CoC)。
- CoCoGaussian使用深度信息和可学习的光圈信息计算CoC直径,生成多个高斯来精确表示散焦效果。
- 引入可学习的缩放因子以增强技术的稳健性,并处理不可靠深度信息。
- 实验证明,在合成和真实数据集上,CoCoGaussian在多个基准测试中表现优异。
点此查看论文截图

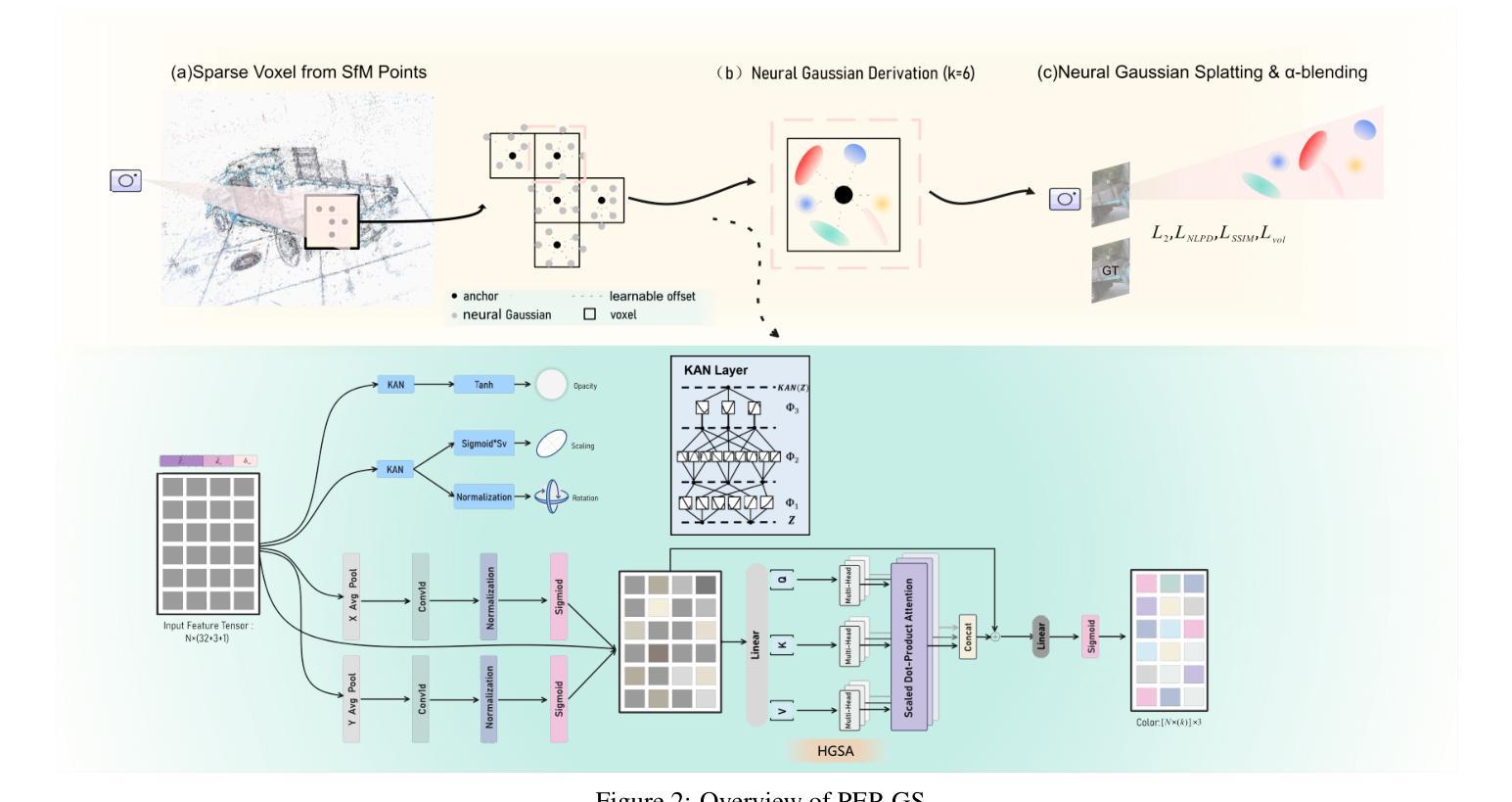
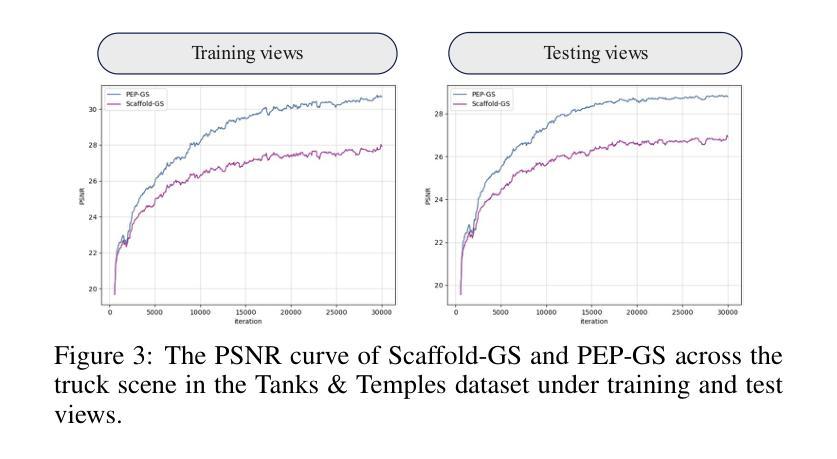
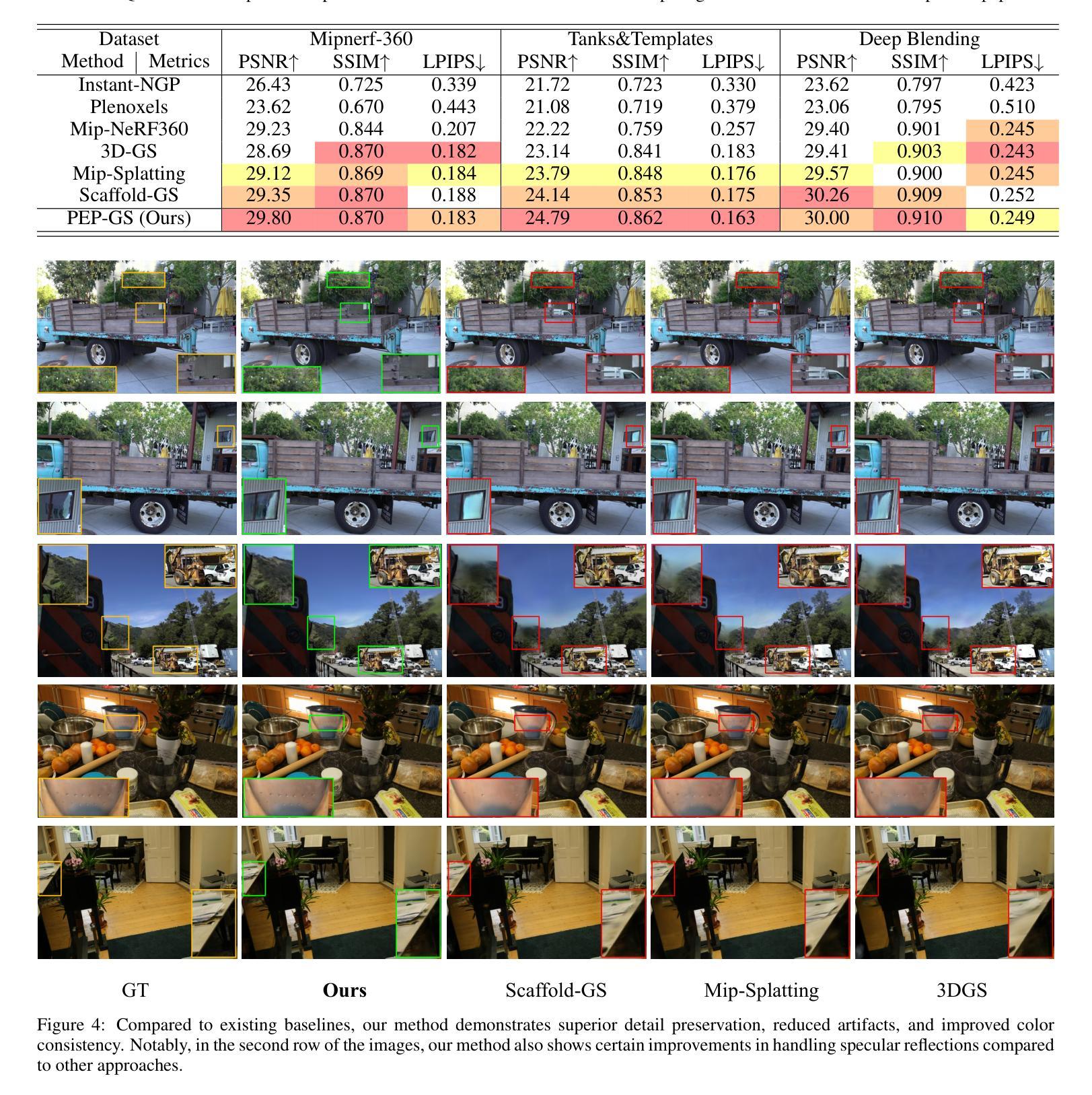
PEP-GS: Perceptually-Enhanced Precise Structured 3D Gaussians for View-Adaptive Rendering
Authors:Junxi Jin, Xiulai Li, Haiping Huang, Lianjun Liu, Yujie Sun, Logan Liu
Recently, 3D Gaussian Splatting (3D-GS) has achieved significant success in real-time, high-quality 3D scene rendering. However, it faces several challenges, including Gaussian redundancy, limited ability to capture view-dependent effects, and difficulties in handling complex lighting and specular reflections. Additionally, methods that use spherical harmonics for color representation often struggle to effectively capture anisotropic components, especially when modeling view-dependent colors under complex lighting conditions, leading to insufficient contrast and unnatural color saturation. To address these limitations, we introduce PEP-GS, a perceptually-enhanced framework that dynamically predicts Gaussian attributes, including opacity, color, and covariance. We replace traditional spherical harmonics with a Hierarchical Granular-Structural Attention mechanism, which enables more accurate modeling of complex view-dependent color effects. By employing a stable and interpretable framework for opacity and covariance estimation, PEP-GS avoids the removal of essential Gaussians prematurely, ensuring a more accurate scene representation. Furthermore, perceptual optimization is applied to the final rendered images, enhancing perceptual consistency across different views and ensuring high-quality renderings with improved texture fidelity and fine-scale detail preservation. Experimental results demonstrate that PEP-GS outperforms state-of-the-art methods, particularly in challenging scenarios involving view-dependent effects and fine-scale details.
最近,3D高斯延展(3D-GS)在实时高质量3D场景渲染中取得了显著的成功。然而,它面临几个挑战,包括高斯冗余、捕捉视角相关效应的能力有限,以及处理复杂光线和镜面反射的困难。此外,使用球面谐波进行颜色表示的方法在捕捉各向异性成分时经常遇到困难,特别是在复杂光照条件下对视角相关颜色进行建模时,这会导致对比度不足和颜色饱和度不自然。为了解决这些局限性,我们引入了PEP-GS,这是一种感知增强框架,可以动态预测高斯属性,包括不透明度、颜色和协方差。我们用分层粒状结构注意机制取代了传统的球面谐波,这可以更准确地模拟复杂的视角相关颜色效应。通过采用稳定和可解释的不透明度和协方差估计框架,PEP-GS避免了过早地去除重要的高斯成分,确保了更准确的场景表示。此外,对最终渲染的图像进行了感知优化,提高了不同视角下的感知一致性,确保了高质量渲染的图像具有改善的纹理保真度和精细细节保留。实验结果表明,PEP-GS优于最先进的方法,特别是在涉及视角相关效应和精细细节的挑战场景中。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了PEP-GS,一种针对3D高斯拼贴(3D-GS)的感知增强框架。该框架解决了传统方法在处理实时高质量3D场景渲染时面临的挑战,如高斯冗余、难以捕捉视角相关效应以及处理复杂光照和镜面反射的困难。通过引入分层粒状结构注意力机制,PEP-GS可以更准确地模拟复杂的视角相关颜色效应。同时,该框架避免了关键高斯过早去除的问题,确保了更准确的场景表示。实验结果表明,PEP-GS在视角相关效应和精细细节方面的场景中表现出优于现有方法的效果。
Key Takeaways
- PEP-GS解决了传统方法在实时高质量3D场景渲染中的挑战,如高斯冗余和捕捉视角相关效应的难度。
- 引入了分层粒状结构注意力机制,以更准确模拟复杂的视角相关颜色效应。
- 通过稳定的框架估计不透明度和协方差,避免关键高斯过早去除的问题,确保更准确的场景表示。
- 应用感知优化到最终渲染的图像上,增强了不同视图之间的感知一致性,确保了高质量渲染和纹理保真度的提高。
- PEP-GS在视角相关效应和精细细节方面比现有方法表现出优越的性能。
- 实验结果证明了PEP-GS的有效性,特别是在复杂光照条件下的视图相关颜色建模方面。
点此查看论文截图