⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-05-17 更新
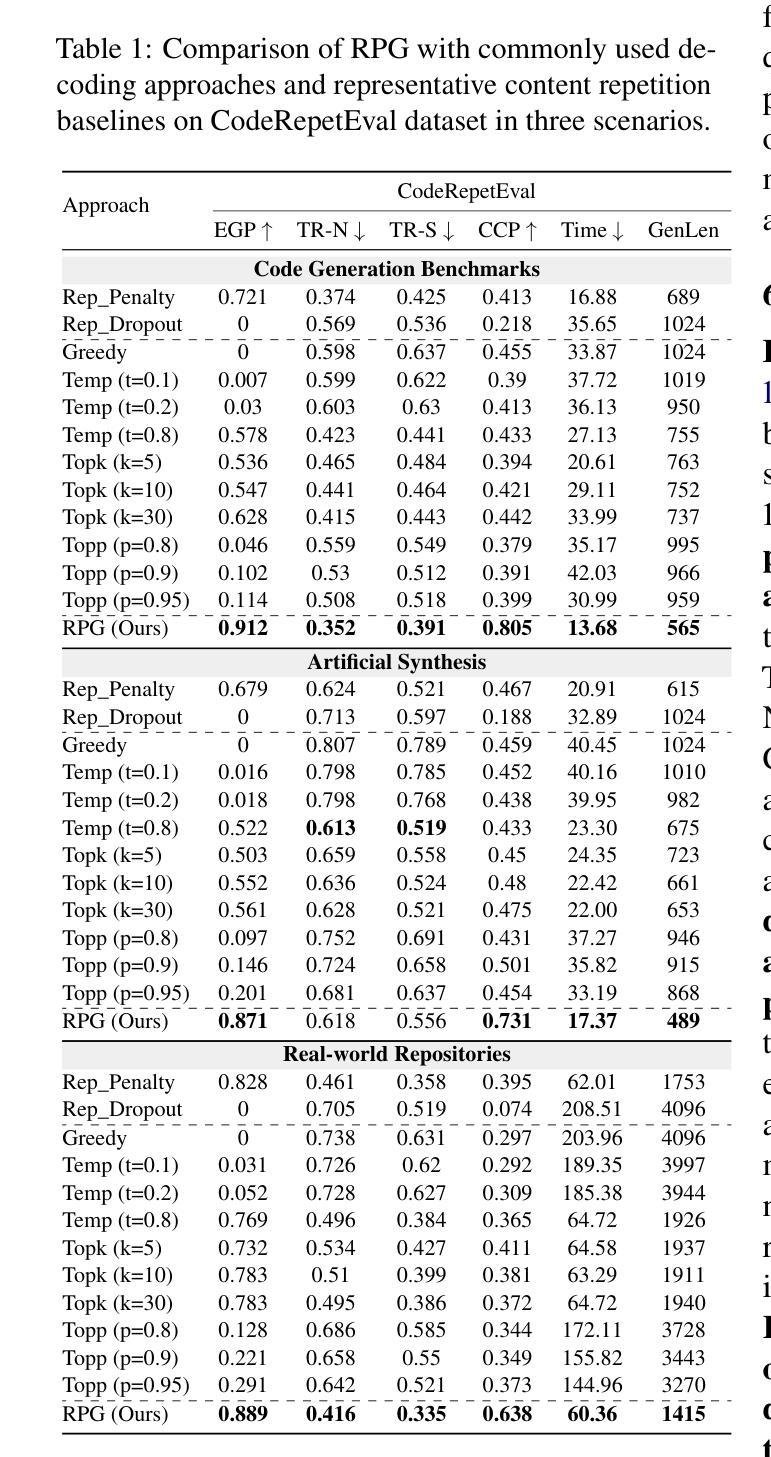
AutoPentest: Enhancing Vulnerability Management With Autonomous LLM Agents
Authors:Julius Henke
A recent area of increasing research is the use of Large Language Models (LLMs) in penetration testing, which promises to reduce costs and thus allow for higher frequency. We conduct a review of related work, identifying best practices and common evaluation issues. We then present AutoPentest, an application for performing black-box penetration tests with a high degree of autonomy. AutoPentest is based on the LLM GPT-4o from OpenAI and the LLM agent framework LangChain. It can perform complex multi-step tasks, augmented by external tools and knowledge bases. We conduct a study on three capture-the-flag style Hack The Box (HTB) machines, comparing our implementation AutoPentest with the baseline approach of manually using the ChatGPT-4o user interface. Both approaches are able to complete 15-25 % of the subtasks on the HTB machines, with AutoPentest slightly outperforming ChatGPT. We measure a total cost of $96.20 US when using AutoPentest across all experiments, while a one-month subscription to ChatGPT Plus costs $20. The results show that further implementation efforts and the use of more powerful LLMs released in the future are likely to make this a viable part of vulnerability management.
近期研究越来越多的一个领域是利用大型语言模型(LLMs)进行渗透测试,这有望降低成本,从而提高测试频率。我们对相关工作进行了回顾,识别了最佳实践和常见的评估问题。然后,我们展示了AutoPentest,这是一个用于执行高度自治的黑盒渗透测试的应用程序。AutoPentest基于OpenAI的LLM GPT-4o和LLM代理框架LangChain。它可以执行复杂的多步骤任务,辅以外部工具和知识库。我们在三场捕获标志风格的Hack The Box(HTB)机器上进行了研究,将我们的AutoPentest实现与手动使用ChatGPT-4o用户界面的基准方法进行了比较。两种方法都能够在HTB机器上完成15-25%的子任务,AutoPentest略微优于ChatGPT。在使用AutoPentest进行所有实验时,总成本为96.20美元,而ChatGPT Plus的一个月订阅费用为20美元。结果表明,未来的进一步实施努力和使用更强大的LLMs很可能使这一技术成为漏洞管理的一个可行部分。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 24 pages, 1 figure, for implementation, see https://github.com/JuliusHenke/autopentest
Summary
大型语言模型(LLM)在渗透测试中的应用日益受到研究关注,能够降低成本并允许更高频率的测试。本文回顾了相关工作,提出了自动渗透测试应用程序AutoPentest,基于OpenAI的GPT-4o和LangChain的LLM代理框架,能够执行复杂的多步骤任务,辅以外部工具和知识库。在Hack The Box(HTB)机器上的研究表明,AutoPentest略优于ChatGPT。
Key Takeaways
- 大型语言模型(LLM)在渗透测试中的应用是最新研究热点。
- LLMs可以降低渗透测试的成本,并提高测试频率。
- AutoPentest是一个基于LLM的应用程序,用于执行黑盒渗透测试,具有高度自主性。
- AutoPentest使用GPT-4o和LangChain框架,能执行复杂的多步骤任务。
- 在Hack The Box(HTB)机器上的研究表明,AutoPentest与ChatGPT相比略占优势。
- 使用AutoPentest的总成本为96.20美元,而ChatGPT Plus一个月订阅费用为20美元。
点此查看论文截图

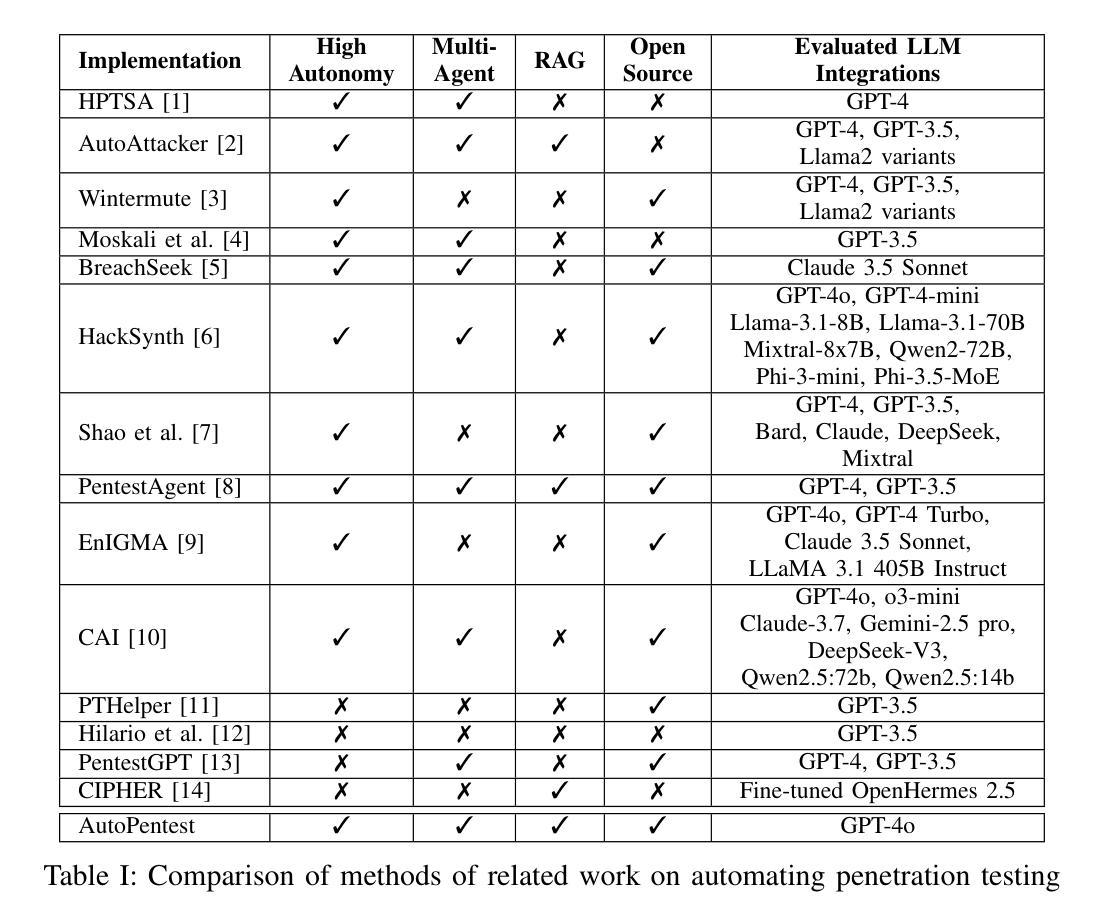
MASS: Multi-Agent Simulation Scaling for Portfolio Construction
Authors:Taian Guo, Haiyang Shen, Jinsheng Huang, Zhengyang Mao, Junyu Luo, Zhuoru Chen, Xuhui Liu, Bingyu Xia, Luchen Liu, Yun Ma, Ming Zhang
LLM-based multi-agent has gained significant attention for their potential in simulation and enhancing performance. However, existing works are limited to pure simulations or are constrained by predefined workflows, restricting their applicability and effectiveness. In this paper, we introduce the Multi-Agent Scaling Simulation (MASS) for portfolio construction. MASS achieves stable and continuous excess returns by progressively increasing the number of agents for large-scale simulations to gain a superior understanding of the market and optimizing agent distribution end-to-end through a reverse optimization process, rather than relying on a fixed workflow. We demonstrate its superiority through performance experiments, ablation studies, backtesting experiments, experiments on updated data and stock pools, scaling experiments, parameter sensitivity experiments, and visualization experiments, conducted in comparison with 6 state-of-the-art baselines on 3 challenging A-share stock pools. We expect the paradigm established by MASS to expand to other tasks with similar characteristics. The implementation of MASS has been open-sourced at https://github.com/gta0804/MASS.
基于LLM的多智能体因其模拟和增强性能方面的潜力而受到广泛关注。然而,现有工作仅限于纯模拟或受预设工作流程的限制,这限制了其应用效果和效率。在本文中,我们介绍了用于投资组合构建的多智能体扩展模拟(MASS)。MASS通过逐步增加智能体的数量进行大规模模拟,实现对市场的深入理解,并通过反向优化过程端到端优化智能体的分布,而不是依赖于固定的流程,从而实现稳定且持续的超额回报。我们通过性能实验、消融研究、回测实验、更新数据和股票池的实验、规模扩展实验、参数敏感性实验和可视化实验,与6个最先进的基线在3个具有挑战性的A股股票池上进行了比较,证明了其优越性。我们希望MASS所建立的模式能够扩展到具有类似特征的其他任务中。MASS的实现已经开源,地址为https://github.com/gta0804/MASS。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
大规模基于LLM的多智能体仿真技术在投资组合构建领域受到广泛关注,具有模拟和优化性能潜力。然而,现有研究局限于纯仿真或受限于预设工作流程,限制了其应用性和效果。本文介绍了一种用于投资组合构建的多智能体扩展仿真(MASS)。MASS通过逐步增加智能体数量进行大规模仿真,实现对市场的深刻理解并优化反向优化过程实现端到端的智能体分布优化,从而带来稳定且持续的超额回报。其在A股股票池上的表现优于其他六种前沿基线模型,具有广泛的应用前景。具体实现已开源。
Key Takeaways
- LLM-based multi-agent仿真技术在投资组合构建中得到应用。
- 目前方法学受限于纯仿真或预设工作流程。
- 多智能体扩展仿真(MASS)通过大规模仿真实现对市场的深入理解。
- MASS通过逐步增加智能体数量和优化智能体分布来优化性能。
- MASS在A股股票池上的表现优于其他前沿模型。
- MASS实现了稳定且持续的超额回报。
点此查看论文截图
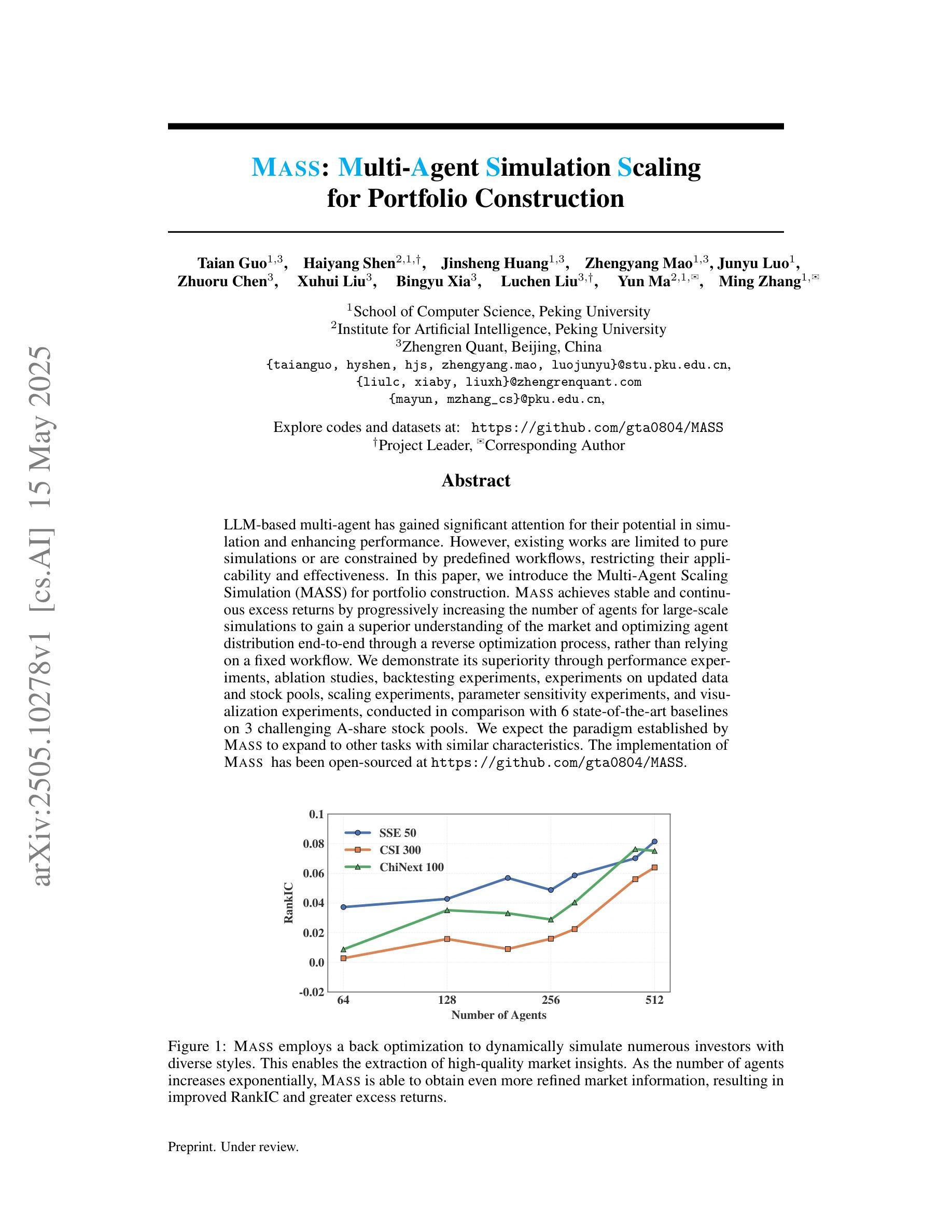
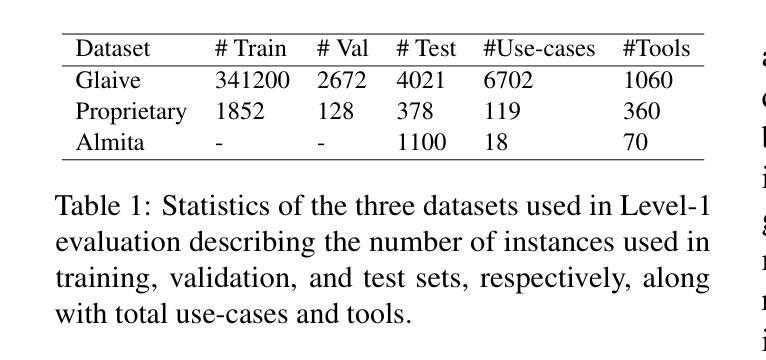
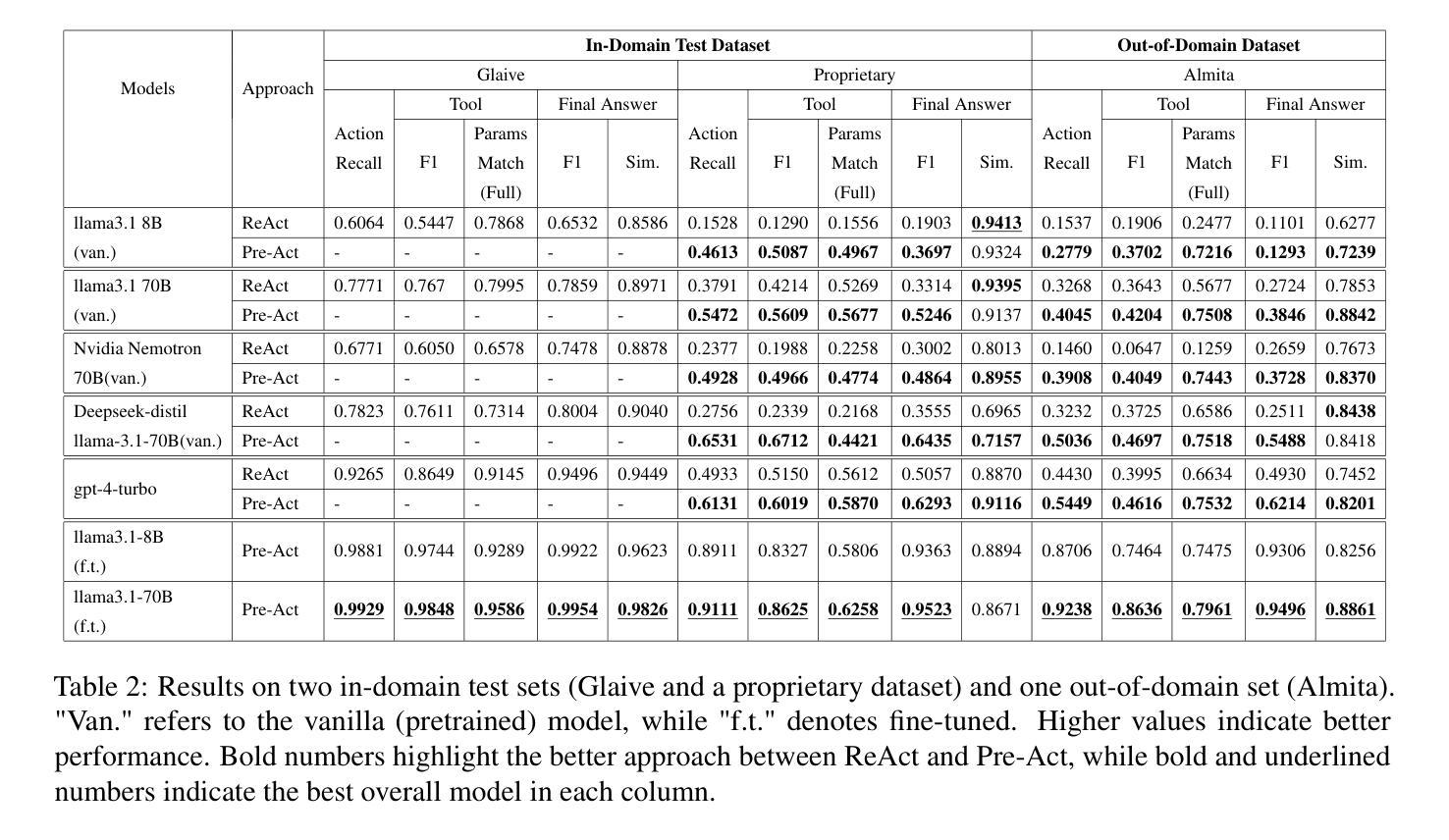
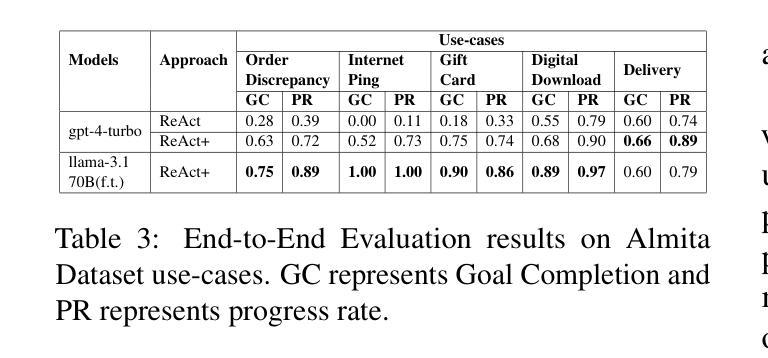
Pre-Act: Multi-Step Planning and Reasoning Improves Acting in LLM Agents
Authors:Mrinal Rawat, Ambuje Gupta, Rushil Goomer, Alessandro Di Bari, Neha Gupta, Roberto Pieraccini
The ReAct (Reasoning + Action) capability in large language models (LLMs) has become the foundation of modern agentic systems. Recent LLMs, such as DeepSeek-R1 and OpenAI o1/o3, exemplify this by emphasizing reasoning through the generation of ample intermediate tokens, which help build a strong premise before producing the final output tokens. In this paper, we introduce Pre-Act, a novel approach that enhances the agent’s performance by creating a multi-step execution plan along with the detailed reasoning for the given user input. This plan incrementally incorporates previous steps and tool outputs, refining itself after each step execution until the final response is obtained. Our approach is applicable to both conversational and non-conversational agents. To measure the performance of task-oriented agents comprehensively, we propose a two-level evaluation framework: (1) turn level and (2) end-to-end. Our turn-level evaluation, averaged across five models, shows that our approach, Pre-Act, outperforms ReAct by 70% in Action Recall on the Almita dataset. While this approach is effective for larger models, smaller models crucial for practical applications, where latency and cost are key constraints, often struggle with complex reasoning tasks required for agentic systems. To address this limitation, we fine-tune relatively small models such as Llama 3.1 (8B & 70B) using the proposed Pre-Act approach. Our experiments show that the fine-tuned 70B model outperforms GPT-4, achieving a 69.5% improvement in action accuracy (turn-level) and a 28% improvement in goal completion rate (end-to-end) on the Almita (out-of-domain) dataset.
大型语言模型(LLM)中的ReAct(推理+行动)能力已成为现代智能系统的基础。最近的LLM,如DeepSeek-R1和OpenAI o1/o3,通过强调生成大量中间令牌进行推理,帮助构建强有力前提后再产生最终输出令牌,以此为例。在本文中,我们介绍了Pre-Act,这是一种通过创建多步执行计划与给定用户输入的详细推理来增强智能体性能的新型方法。此计划会逐步融入先前的步骤和工具输出,并在每一步执行后进行自我完善,直到获得最终响应。我们的方法适用于对话式和非对话式智能体。为了全面衡量面向任务的智能体的性能,我们提出了两级评估框架:(1)回合级和(2)端到端。我们的回合级评估,在五个模型上的平均结果显示,我们的Pre-Act方法在Almita数据集上的行动回忆率比ReAct高出70%。虽然此方法对于大型模型有效,但对于实际应用中至关重要的小型模型,在延迟和成本是主要约束的情况下,往往难以应对智能系统所需的复杂推理任务。为了解决这个问题,我们使用提出的Pre-Act方法对相对较小的模型(如Llama 3.1(8B和70B))进行微调。实验表明,经过调教的70B模型在Almita(离域)数据集上的行动准确性(回合级)提高了69.5%,目标完成率(端到端)提高了28%,表现优于GPT-4。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了Pre-Act方法,它提高了大型语言模型中智能主体的性能。该方法通过建立多步执行计划,并利用详细推理对用户输入进行回应,增强智能主体的任务执行能力。研究结果表明,Pre-Act方法在Almita数据集上的表现优于ReAct方法,特别是在动作记忆方面。此外,研究还解决了小型模型在处理复杂推理任务时的局限性,通过微调小型模型以适应Pre-Act方法,使其在Almita数据集上的表现优于GPT-4。
Key Takeaways
- 大型语言模型的ReAct能力已逐渐成为现代智能主体的基础。
- Pre-Act方法通过建立多步执行计划来提高智能主体的性能。
- Pre-Act方法对用户的输入进行回应并详细推理。
- Pre-Act方法在Almita数据集上的表现优于ReAct方法。
- 小型模型在处理复杂推理任务时面临局限性。
- 通过微调小型模型以适应Pre-Act方法,可以提高其在复杂任务上的表现。
点此查看论文截图


Design and Evaluation of Generative Agent-based Platform for Human-Assistant Interaction Research: A Tale of 10 User Studies
Authors:Ziyi Xuan, Yiwen Wu, Xuhai Xu, Vinod Namboodiri, Mooi Choo Chuah, Yu Yang
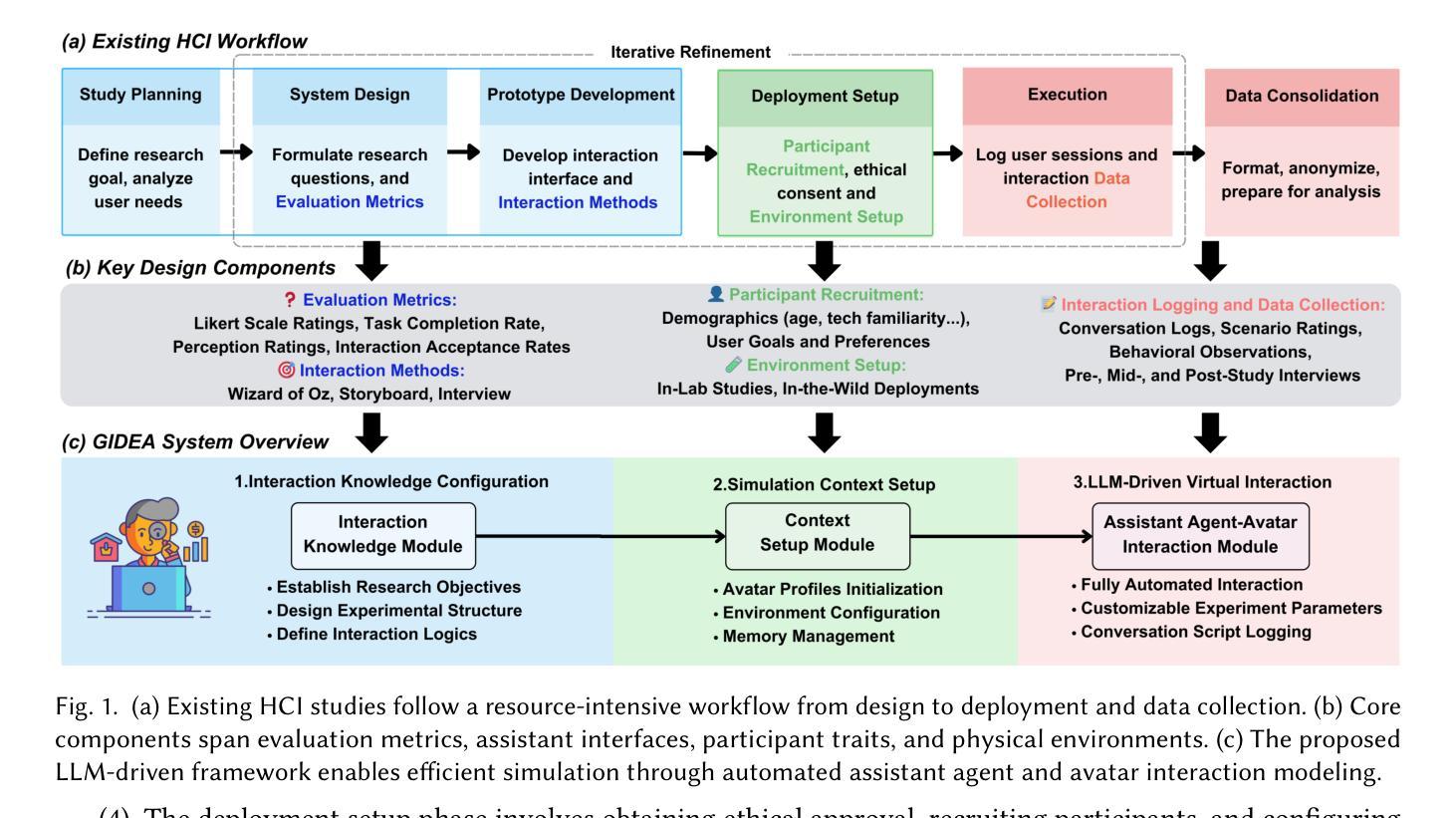
Designing and evaluating personalized and proactive assistant agents remains challenging due to the time, cost, and ethical concerns associated with human-in-the-loop experimentation. Existing Human-Computer Interaction (HCI) methods often require extensive physical setup and human participation, which introduces privacy concerns and limits scalability. Simulated environments offer a partial solution but are typically constrained by rule-based scenarios and still depend heavily on human input to guide interactions and interpret results. Recent advances in large language models (LLMs) have introduced the possibility of generative agents that can simulate realistic human behavior, reasoning, and social dynamics. However, their effectiveness in modeling human-assistant interactions remains largely unexplored. To address this gap, we present a generative agent-based simulation platform designed to simulate human-assistant interactions. We identify ten prior studies on assistant agents that span different aspects of interaction design and replicate these studies using our simulation platform. Our results show that fully simulated experiments using generative agents can approximate key aspects of human-assistant interactions. Based on these simulations, we are able to replicate the core conclusions of the original studies. Our work provides a scalable and cost-effective approach for studying assistant agent design without requiring live human subjects. We will open source both the platform and collected results from the experiments on our website: https://dash-gidea.github.io/.
设计并评估个性化和主动性的助理代理仍然充满挑战,这主要是因为涉及人类参与的实验存在时间、成本和道德上的担忧。现有的人机交互(HCI)方法通常需要大量的物理设置和人类参与,这引发了隐私担忧并限制了可扩展性。模拟环境提供了部分解决方案,但通常受限于基于规则的场景,并且仍然严重依赖于人类输入来指导交互和解释结果。最近大型语言模型(LLM)的进步为能够模拟真实人类行为、推理和社会动态的生成代理的可能性打开了大门。然而,它们在模拟人类助理交互方面的有效性在很大程度上尚未被探索。为了弥补这一差距,我们推出了一个基于生成代理的模拟平台,旨在模拟人类与助理的交互。我们确定了关于助理代理的十个早期研究,这些研究涵盖了不同方面的交互设计,并使用我们的模拟平台进行复制。结果表明,使用生成代理进行的完全模拟实验可以近似模拟人类与助理之间的关键交互方面。基于这些模拟,我们能够复制原始研究的核心结论。我们的工作提供了一种可扩展且经济实惠的研究助理代理设计的方法,而无需真实的受试者参与。我们将在我们的网站上开源平台和实验收集的结果:网站链接。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
模拟平台实现人机互动新突破
该模拟平台使用生成性代理人实现了对人机交互的全面仿真,使助理型智能体研究能够高效、低成本进行。成功还原十大现有互动设计研究的关键点,并通过仿真实验有效模拟真实的人机互动。未来该平台将开源并公开实验结果,推动助理型智能体设计的深入研究。
Key Takeaways
- 设计并评估个性化、主动性助理代理是一项挑战,由于实验中存在时间成本以及伦理问题。传统的HCI方法需要复杂的物理设置和人类参与,引发隐私担忧并限制了可扩展性。
- 大型语言模型(LLMs)的发展为模拟真实人类行为、推理和社会动态提供了可能。然而,它们在模拟人机互动方面的效果尚未得到充分探索。
- 提出一种基于生成代理的模拟平台来模拟人机互动,成功复制了十个关于助理代理的研究案例。该平台可实现人机交互的全面仿真。
点此查看论文截图

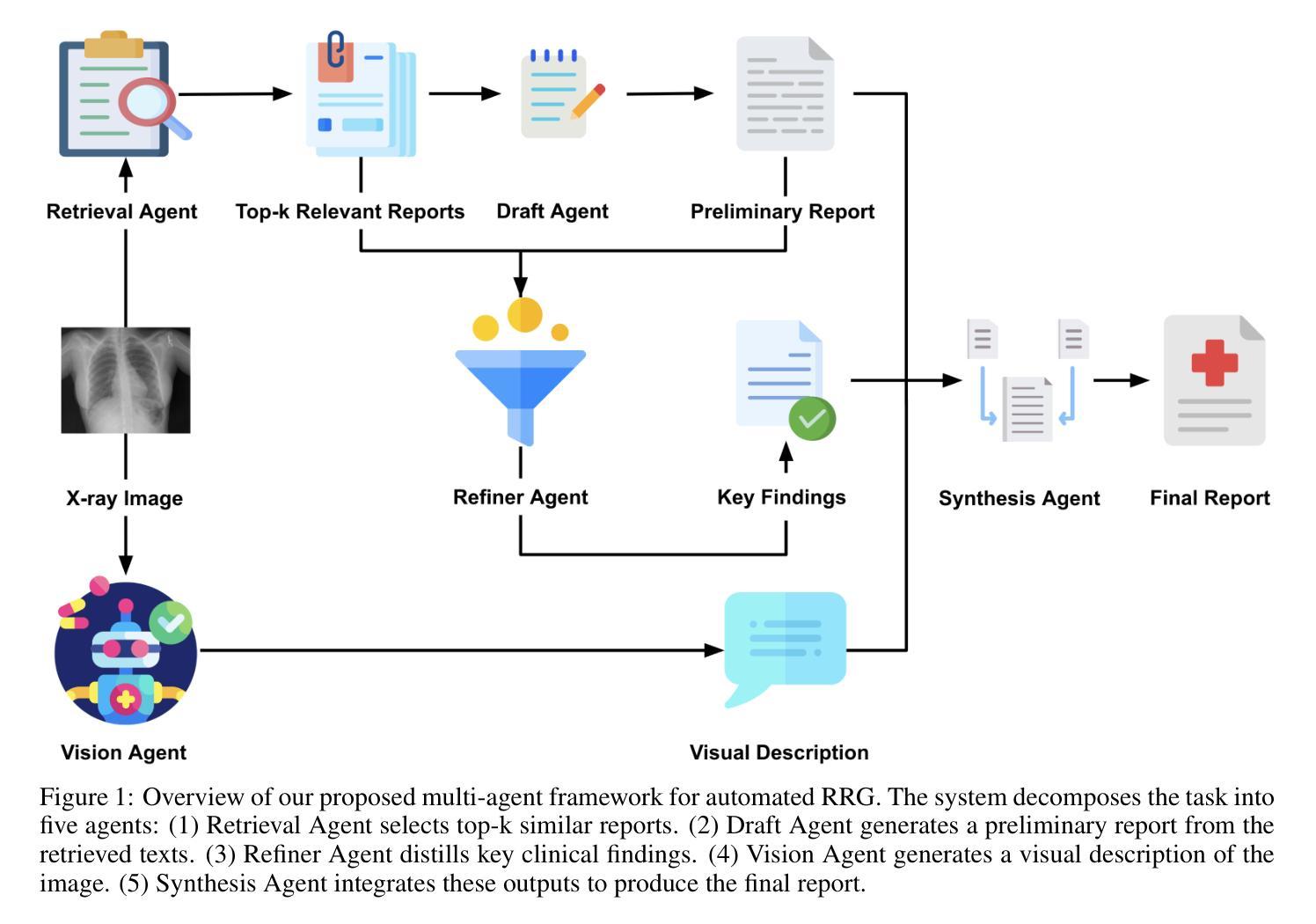
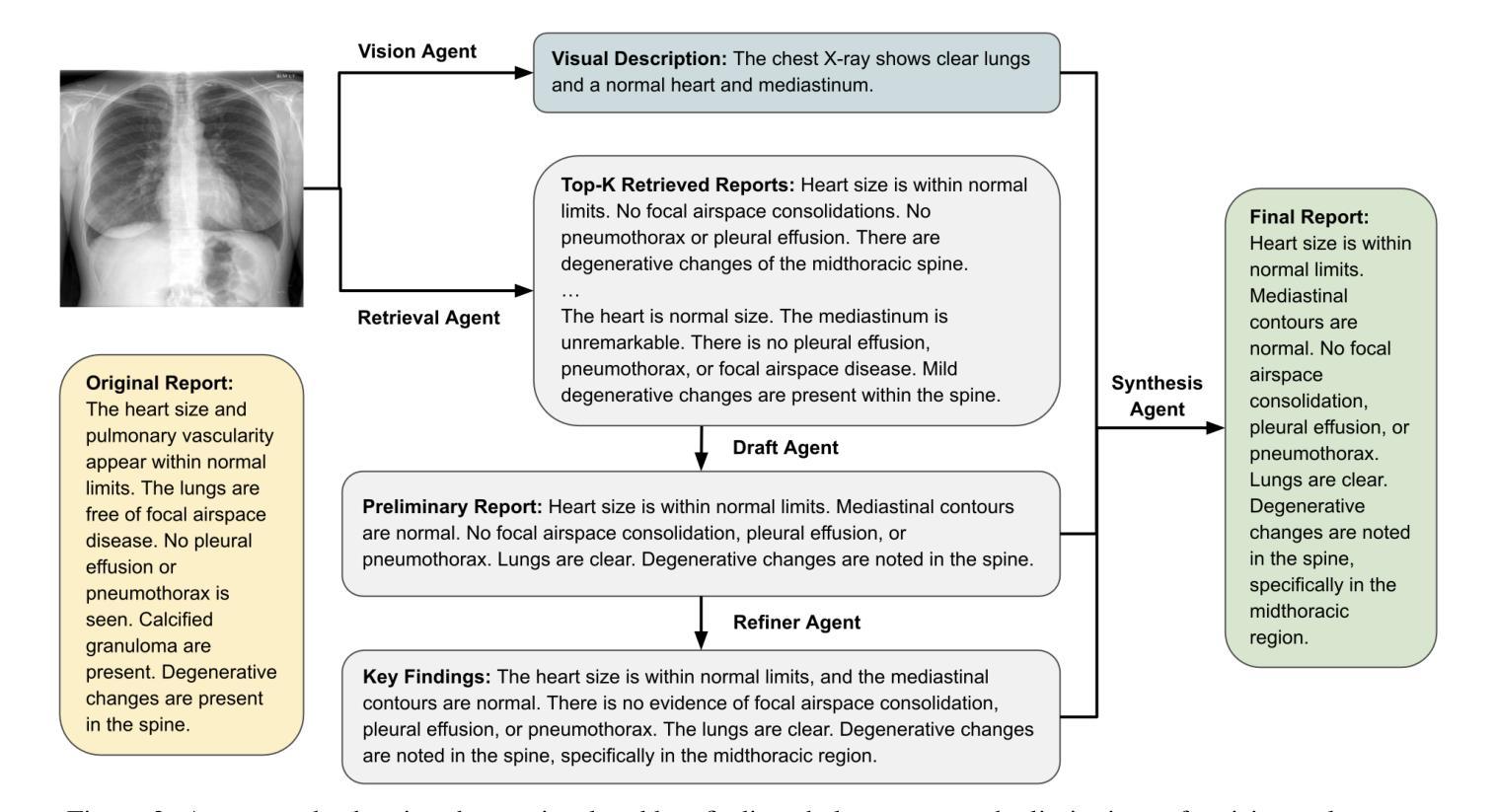
A Multimodal Multi-Agent Framework for Radiology Report Generation
Authors:Ziruo Yi, Ting Xiao, Mark V. Albert
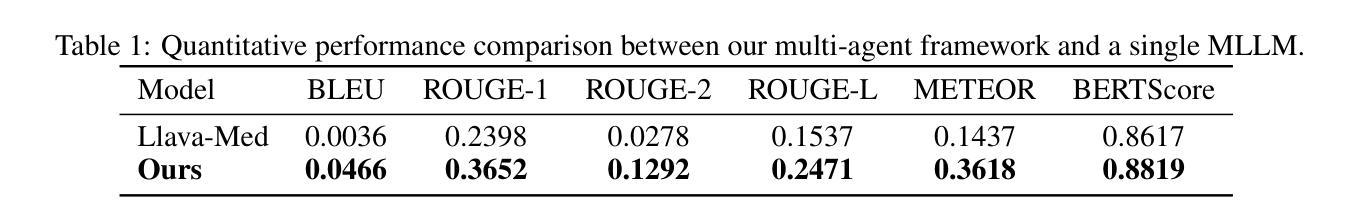
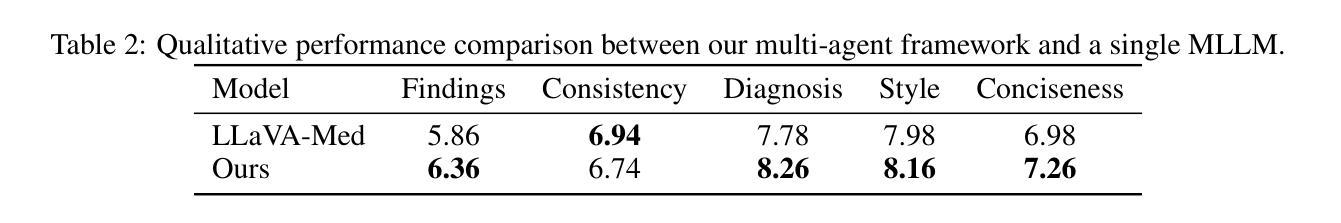
Radiology report generation (RRG) aims to automatically produce diagnostic reports from medical images, with the potential to enhance clinical workflows and reduce radiologists’ workload. While recent approaches leveraging multimodal large language models (MLLMs) and retrieval-augmented generation (RAG) have achieved strong results, they continue to face challenges such as factual inconsistency, hallucination, and cross-modal misalignment. We propose a multimodal multi-agent framework for RRG that aligns with the stepwise clinical reasoning workflow, where task-specific agents handle retrieval, draft generation, visual analysis, refinement, and synthesis. Experimental results demonstrate that our approach outperforms a strong baseline in both automatic metrics and LLM-based evaluations, producing more accurate, structured, and interpretable reports. This work highlights the potential of clinically aligned multi-agent frameworks to support explainable and trustworthy clinical AI applications.
放射学报告生成(RRG)旨在自动根据医学图像生成诊断报告,这有望改进临床工作流程并减少放射科医师的工作量。尽管最近采用多模态大型语言模型(MLLMs)和增强检索生成(RAG)的方法取得了显著成果,但它们仍然面临事实不一致、幻觉和跨模态不匹配等挑战。我们提出了一种用于RRG的多模态多智能体框架,该框架与分阶段的临床推理工作流程相一致,其中特定任务的智能体负责检索、初稿生成、视觉分析、改进和综合。实验结果表明,我们的方法在自动指标和基于LLM的评估中都优于强大的基线方法,能够生成更准确、结构化、可解释的报告。这项工作突出了临床对齐的多智能体框架在支持可解释和可信赖的临床人工智能应用方面的潜力。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了放射学报告生成(RRG)的目标,即通过自动产生医学图像诊断报告来优化临床工作流程并减轻放射科医生的工作量。尽管现有的利用多模态大型语言模型(MLLMs)和检索增强生成(RAG)的方法已经取得了显著成果,但它们仍然面临事实不一致、幻觉和跨模态不匹配等挑战。本研究提出了一种多模态多智能体框架,该框架与临床推理的逐步工作流程相一致,其中特定任务的智能体负责检索、初稿生成、视觉分析、细化和综合。实验结果表明,该方法在自动指标和基于LLM的评估上均优于强大基线,产生的报告更准确、结构化和可解释。这项工作突出了与临床相一致的多智能体框架在支持可解释和可信赖的临床人工智能应用方面的潜力。
Key Takeaways
- 放射学报告生成(RRG)旨在自动产生医学图像诊断报告,优化临床流程,减轻医生工作量。
- 现有方法虽然利用多模态大型语言模型(MLLMs)和检索增强生成(RAG)取得显著成果,但仍存在挑战,如事实不一致、幻觉和跨模态不匹配。
- 提出了一种多模态多智能体框架,模拟临床推理的逐步流程,包含多个任务特定智能体。
- 智能体负责不同的任务,如检索、初稿生成、视觉分析、细化和综合。
- 实验表明,该方法在自动指标和基于LLM的评估上表现优越,生成的报告更准确、结构化、可解释。
- 该方法提高了报告的准确性,有助于临床决策的可解释性和信赖性。
点此查看论文截图

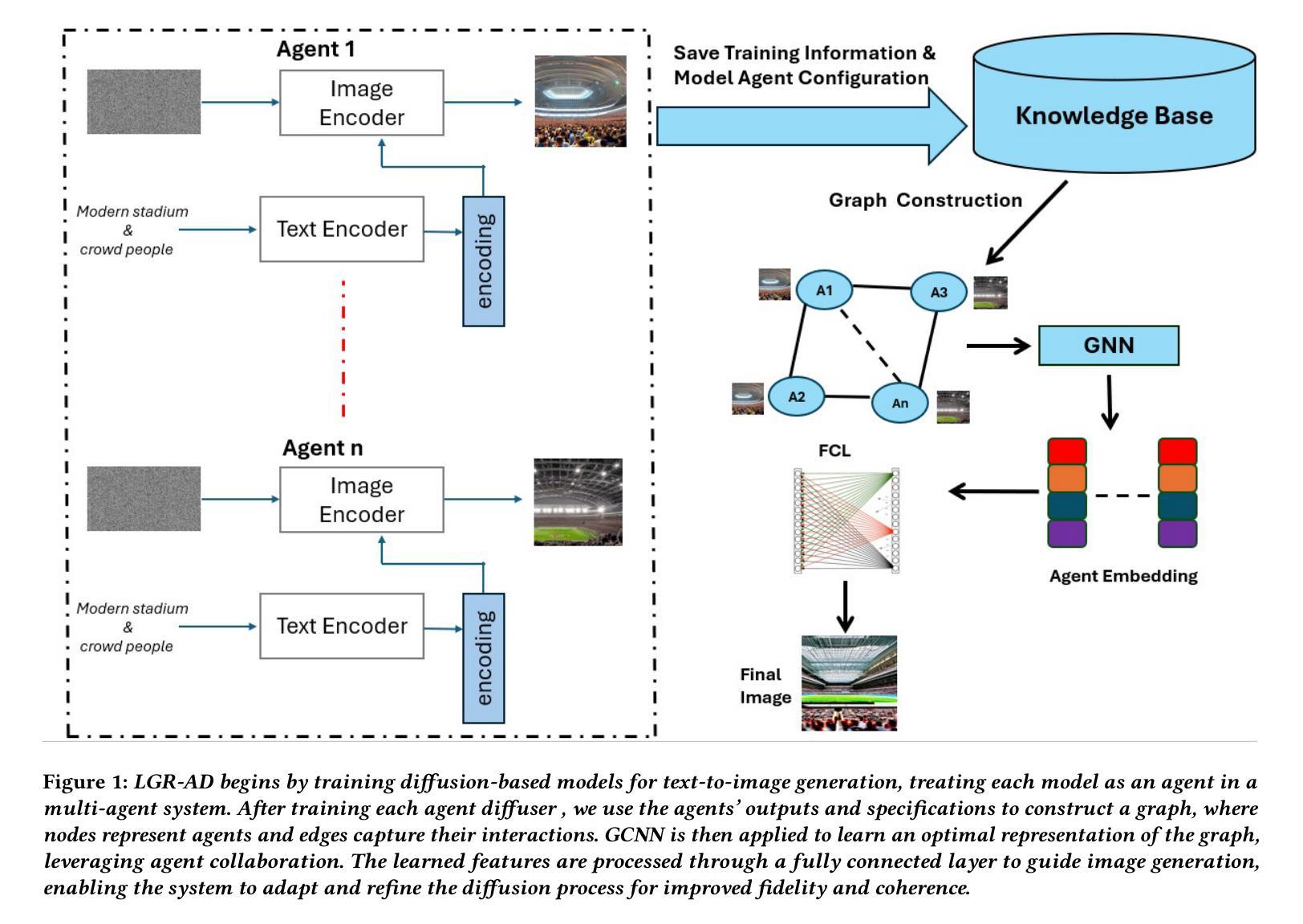
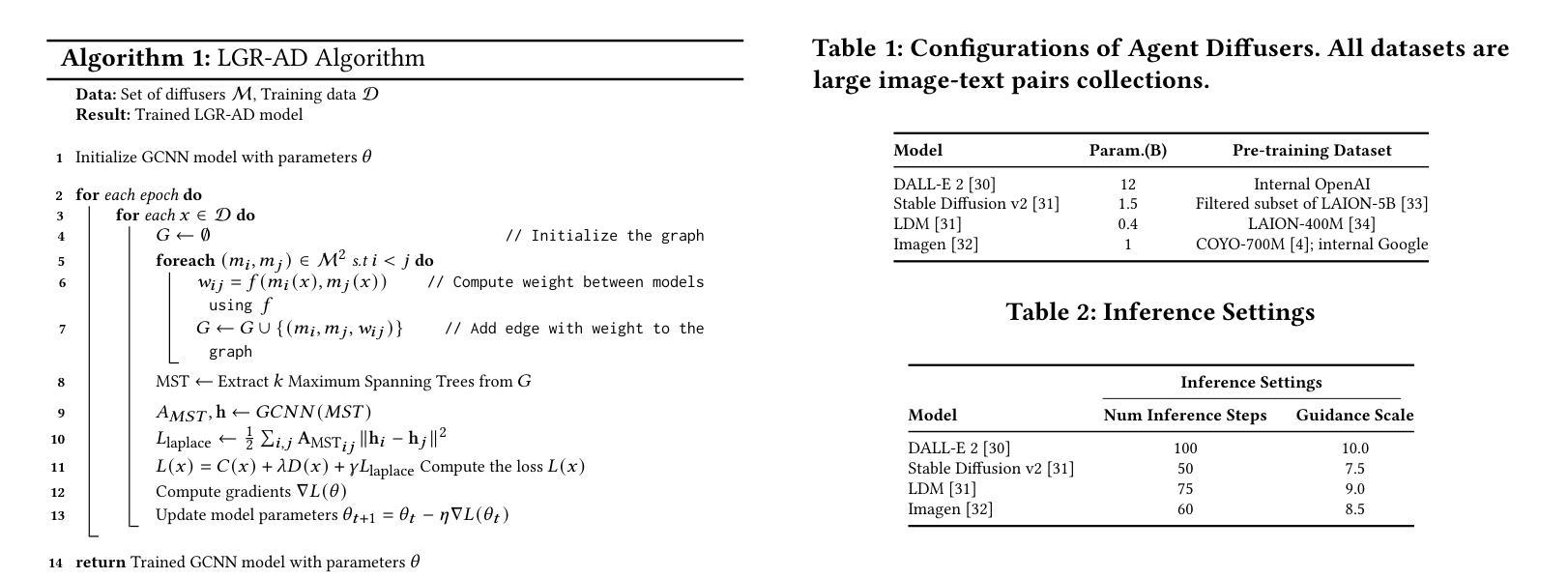
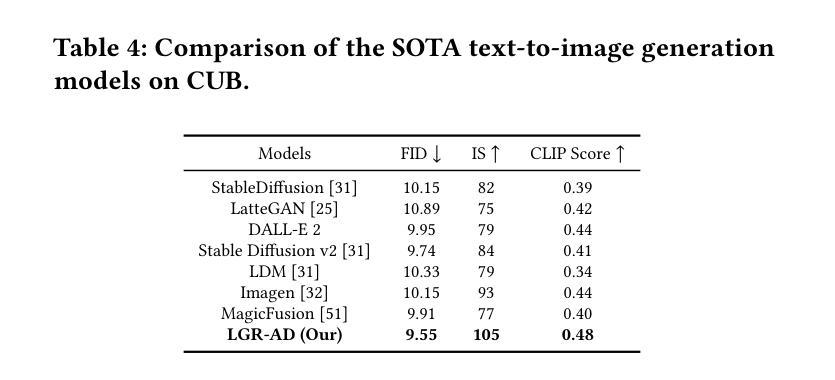
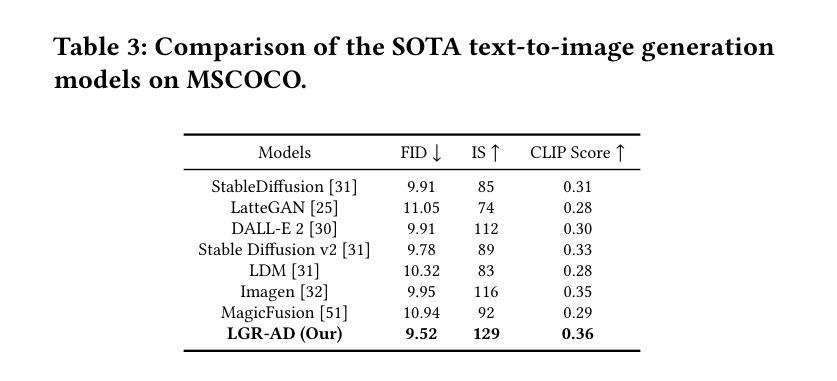
Learning Graph Representation of Agent Diffusers
Authors:Youcef Djenouri, Nassim Belmecheri, Tomasz Michalak, Jan Dubiński, Ahmed Nabil Belbachir, Anis Yazidi
Diffusion-based generative models have significantly advanced text-to-image synthesis, demonstrating impressive text comprehension and zero-shot generalization. These models refine images from random noise based on textual prompts, with initial reliance on text input shifting towards enhanced visual fidelity over time. This transition suggests that static model parameters might not optimally address the distinct phases of generation. We introduce LGR-AD (Learning Graph Representation of Agent Diffusers), a novel multi-agent system designed to improve adaptability in dynamic computer vision tasks. LGR-AD models the generation process as a distributed system of interacting agents, each representing an expert sub-model. These agents dynamically adapt to varying conditions and collaborate through a graph neural network that encodes their relationships and performance metrics. Our approach employs a coordination mechanism based on top-$k$ maximum spanning trees, optimizing the generation process. Each agent’s decision-making is guided by a meta-model that minimizes a novel loss function, balancing accuracy and diversity. Theoretical analysis and extensive empirical evaluations show that LGR-AD outperforms traditional diffusion models across various benchmarks, highlighting its potential for scalable and flexible solutions in complex image generation tasks. Code is available at: https://github.com/YousIA/LGR_AD
基于扩散的生成模型在文本到图像合成方面取得了重大进展,展示了令人印象深刻的文本理解和零样本泛化能力。这些模型根据文本提示从随机噪声中细化图像,最初依赖文本输入,随着时间的推移转向增强视觉保真度。这种转变表明,静态模型参数可能无法最佳地应对生成的不同阶段。我们引入了LGR-AD(学习代理扩散图表示),这是一个新型多代理系统,旨在提高动态计算机视觉任务的适应性。LGR-AD将生成过程建模为交互代理的分布式系统,每个代理代表一个专家子模型。这些代理动态适应各种条件,并通过编码其关系和性能指标的图神经网络进行协作。我们的方法采用基于top-k最大生成树的协调机制,优化生成过程。每个代理的决策制定由元模型引导,该模型最小化新型损失函数,平衡准确性和多样性。理论分析和广泛的实证评估表明,LGR-AD在各种基准测试中超越了传统扩散模型,突显其在复杂图像生成任务中可扩展和灵活解决方案的潜力。代码可在https://github.com/YousIA/LGR_AD找到。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted at AAMAS2025 International Conference on Autonomous Agents and Multiagent Systems
Summary
文本描述了基于扩散的生成模型在文本到图像合成方面的显著进展,并展示了其对文本理解和零样本泛化的能力。文章提出了一种新型多智能体系统LGR-AD,用于改进动态计算机视觉任务中的适应性。LGR-AD将生成过程建模为交互智能体的分布式系统,通过图神经网络进行协作和适应。理论分析和广泛的实证评估表明,LGR-AD在多个基准测试中优于传统扩散模型,在复杂图像生成任务中具有可扩展和灵活解决方案的潜力。
Key Takeaways
- 扩散生成模型在文本到图像合成中取得显著进展,展现出强大的文本理解和零样本泛化能力。
- LGR-AD是一个新型多智能体系统,旨在提高动态计算机视觉任务的适应性。
- LGR-AD将生成过程建模为交互智能体的分布式系统,智能体通过图神经网络进行协作和适应。
- LGR-AD采用基于top-k最大生成树的协调机制来优化生成过程。
- 每个智能体的决策制定由一个元模型引导,该模型通过最小化新型损失函数来平衡准确性和多样性。
- 理论分析和广泛的实证评估表明,LGR-AD在多个基准测试中优于传统扩散模型。
点此查看论文截图

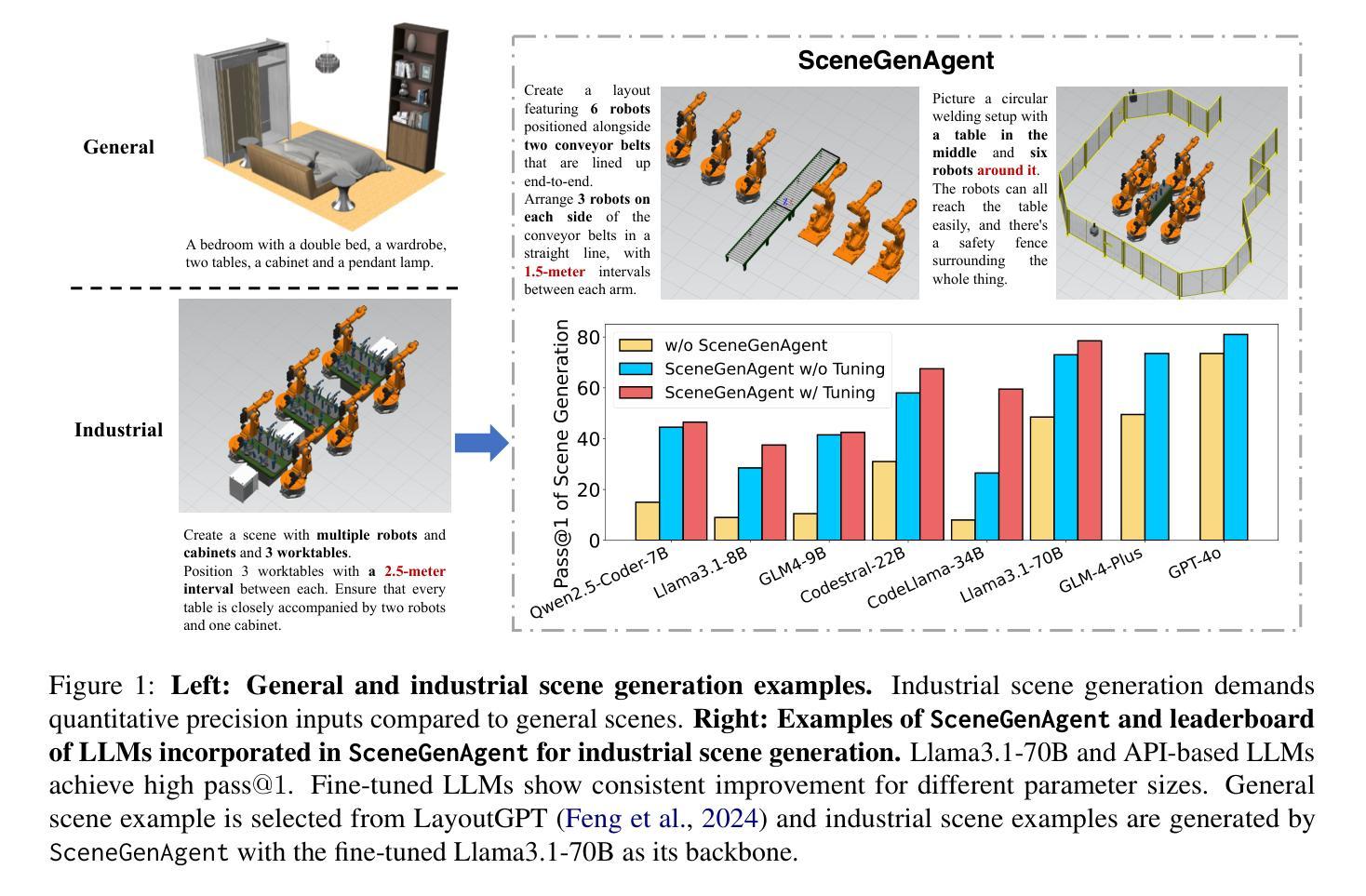
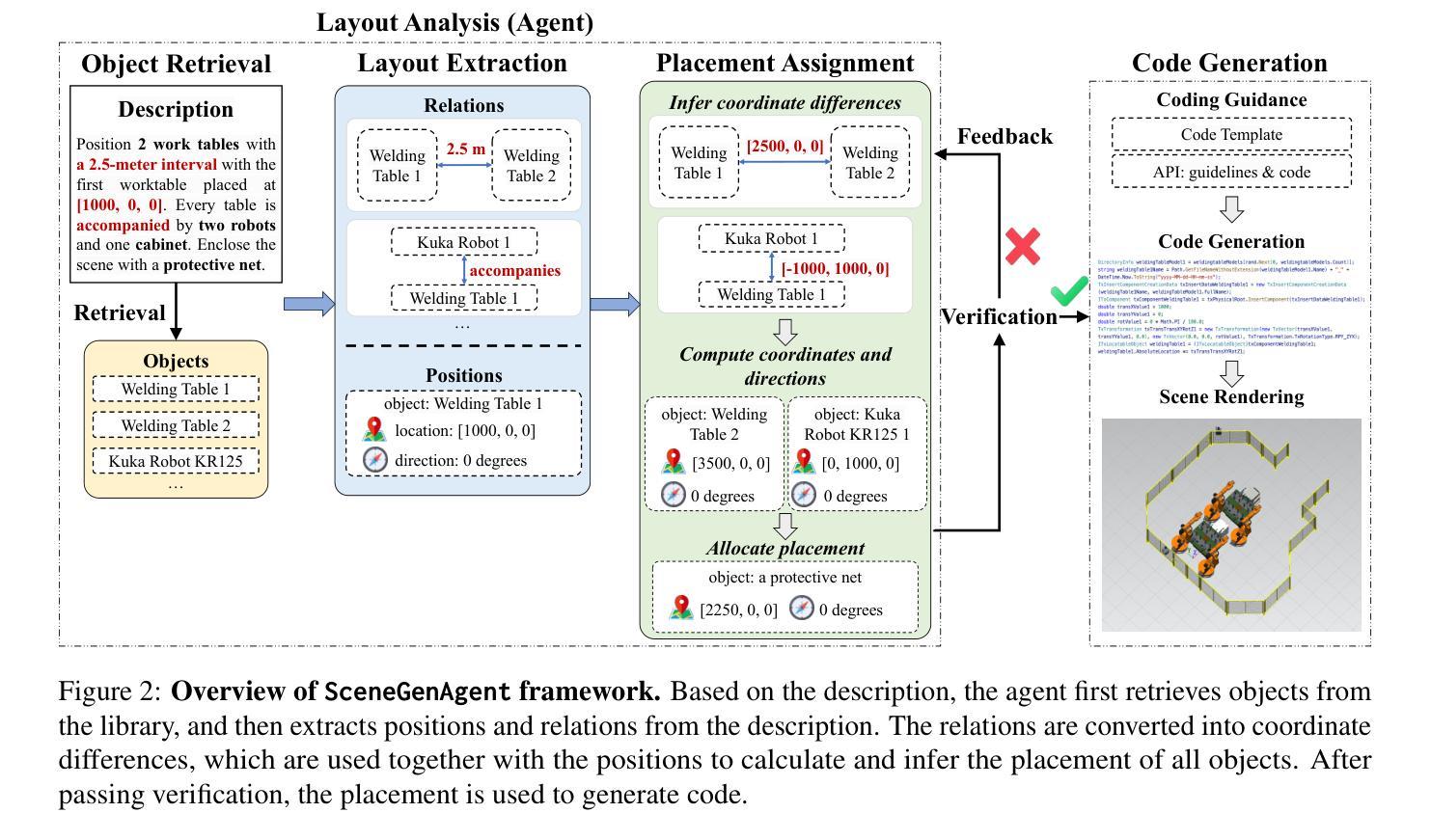
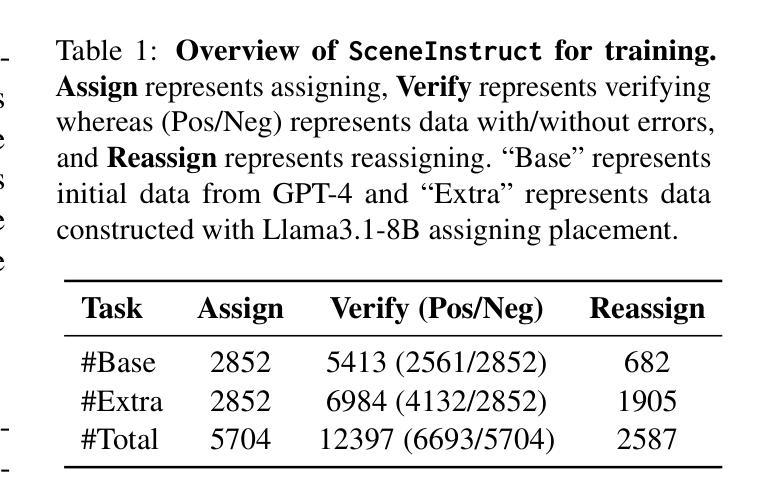
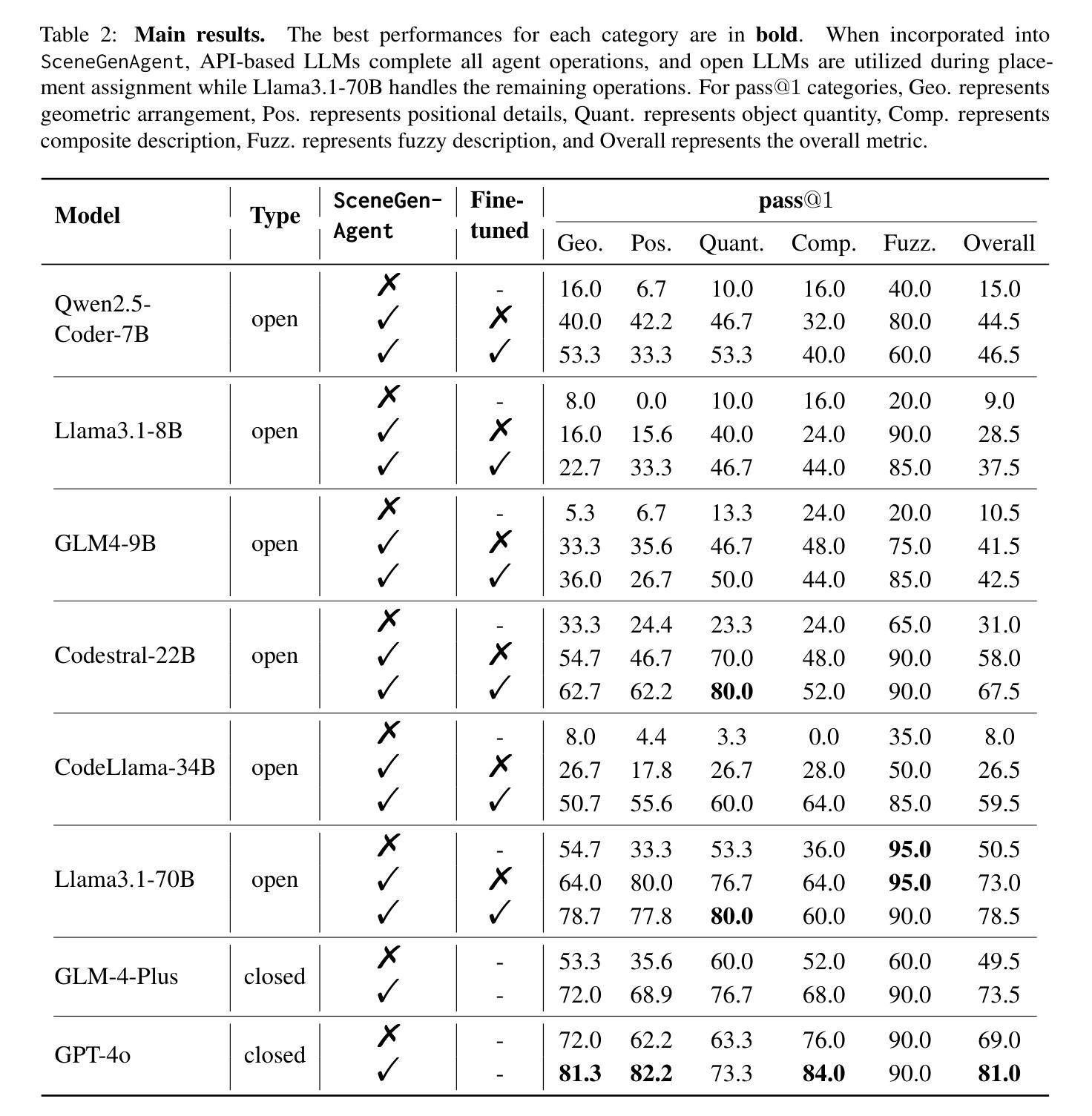
SceneGenAgent: Precise Industrial Scene Generation with Coding Agent
Authors:Xiao Xia, Dan Zhang, Zibo Liao, Zhenyu Hou, Tianrui Sun, Jing Li, Ling Fu, Yuxiao Dong
The modeling of industrial scenes is essential for simulations in industrial manufacturing. While large language models (LLMs) have shown significant progress in generating general 3D scenes from textual descriptions, generating industrial scenes with LLMs poses a unique challenge due to their demand for precise measurements and positioning, requiring complex planning over spatial arrangement. To address this challenge, we introduce SceneGenAgent, an LLM-based agent for generating industrial scenes through C# code. SceneGenAgent ensures precise layout planning through a structured and calculable format, layout verification, and iterative refinement to meet the quantitative requirements of industrial scenarios. Experiment results demonstrate that LLMs powered by SceneGenAgent exceed their original performance, reaching up to 81.0% success rate in real-world industrial scene generation tasks and effectively meeting most scene generation requirements. To further enhance accessibility, we construct SceneInstruct, a dataset designed for fine-tuning open-source LLMs to integrate into SceneGenAgent. Experiments show that fine-tuning open-source LLMs on SceneInstruct yields significant performance improvements, with Llama3.1-70B approaching the capabilities of GPT-4o. Our code and data are available at https://github.com/THUDM/SceneGenAgent .
工业场景的建模对于工业制造中的模拟至关重要。虽然大型语言模型(LLM)在根据文本描述生成一般的3D场景方面取得了显著进展,但使用LLM生成工业场景却构成了一项独特挑战,因为这需要精确的测量和定位,并要求对空间布局进行复杂规划。为了应对这一挑战,我们推出了SceneGenAgent,这是一个基于LLM的通过C#代码生成工业场景的代理。SceneGenAgent通过结构化和可计算格式、布局验证以及迭代优化,确保精确布局规划,以满足工业场景的定量要求。实验结果表明,由SceneGenAgent驱动的大型语言模型超出了其原始性能,在现实世界的工业场景生成任务中成功率高达8 结弦 绍儿你啥玩意% 并有效地满足大多数场景生成要求。为了进一步提高可及性,我们构建了SceneInstruct数据集,用于微调开源LLM以集成到SceneGenAgent中。实验表明,在SceneInstruct上微调开源LLM会带来显著的性能改进,Llama3.1-70B接近GPT-4o的能力。我们的代码和数据集可在https://github.com/THUDM/SceneGenAgent找到。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
基于文本描述,工业场景的建模对于工业制造中的模拟至关重要。大型语言模型(LLMs)在生成通用3D场景方面已取得了显著进展,但在生成工业场景时面临精确测量和定位的需求,需要复杂的空间布局规划,构成了一大挑战。为应对这一挑战,我们推出了SceneGenAgent,这是一个基于LLM的代理,可通过C#代码生成工业场景。SceneGenAgent通过结构化、可计算格式、布局验证和迭代完善来确保精确布局规划,以满足工业场景的定量要求。实验结果证明,SceneGenAgent加持下的LLM性能超越原有水平,在现实工业场景生成任务中的成功率高达81.0%,并能有效满足大多数场景生成要求。为进一步提高可访问性,我们构建了SceneInstruct数据集,用于微调开源LLM以融入SceneGenAgent。实验表明,在SceneInstruct上微调开源LLM能带来显著的性能改进。
Key Takeaways
- 工业场景的建模对模拟至关重要,需要精确测量和定位以及复杂的空间布局规划。
- SceneGenAgent是一个基于LLM的代理,能够通过C#代码生成工业场景,确保精确布局规划。
- SceneGenAgent结合了结构化格式、布局验证和迭代完善来满足工业场景的定量要求。
- 在现实工业场景生成任务中,SceneGenAgent加持下的LLM成功率高达81.0%。
- SceneInstruct数据集用于微调开源LLM,以提高其在工业场景生成任务中的性能。
- 在SceneInstruct上微调的Llama3.1-70B模型接近GPT-4o的能力。
点此查看论文截图

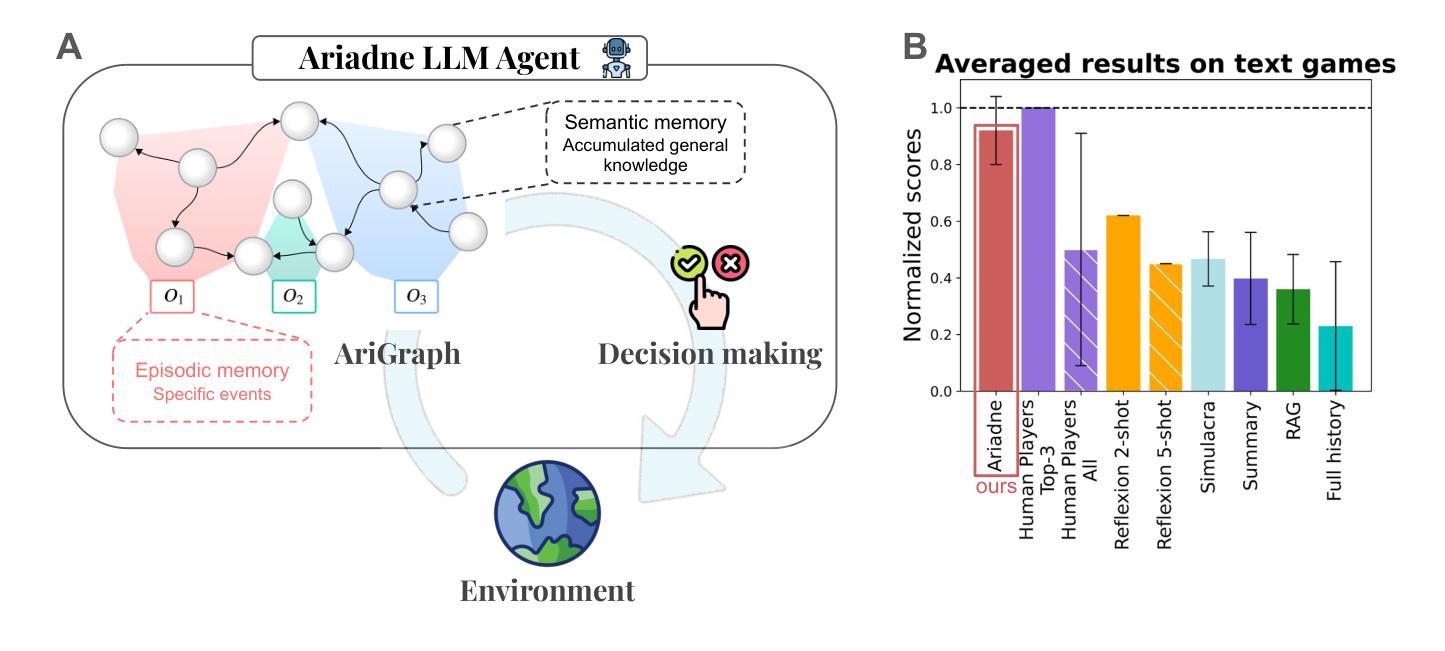
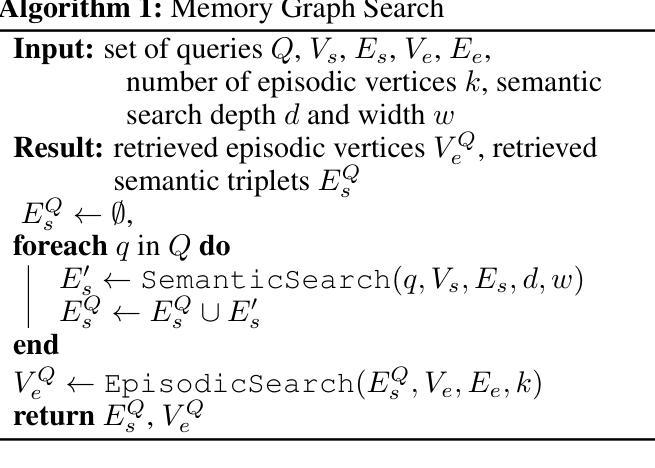
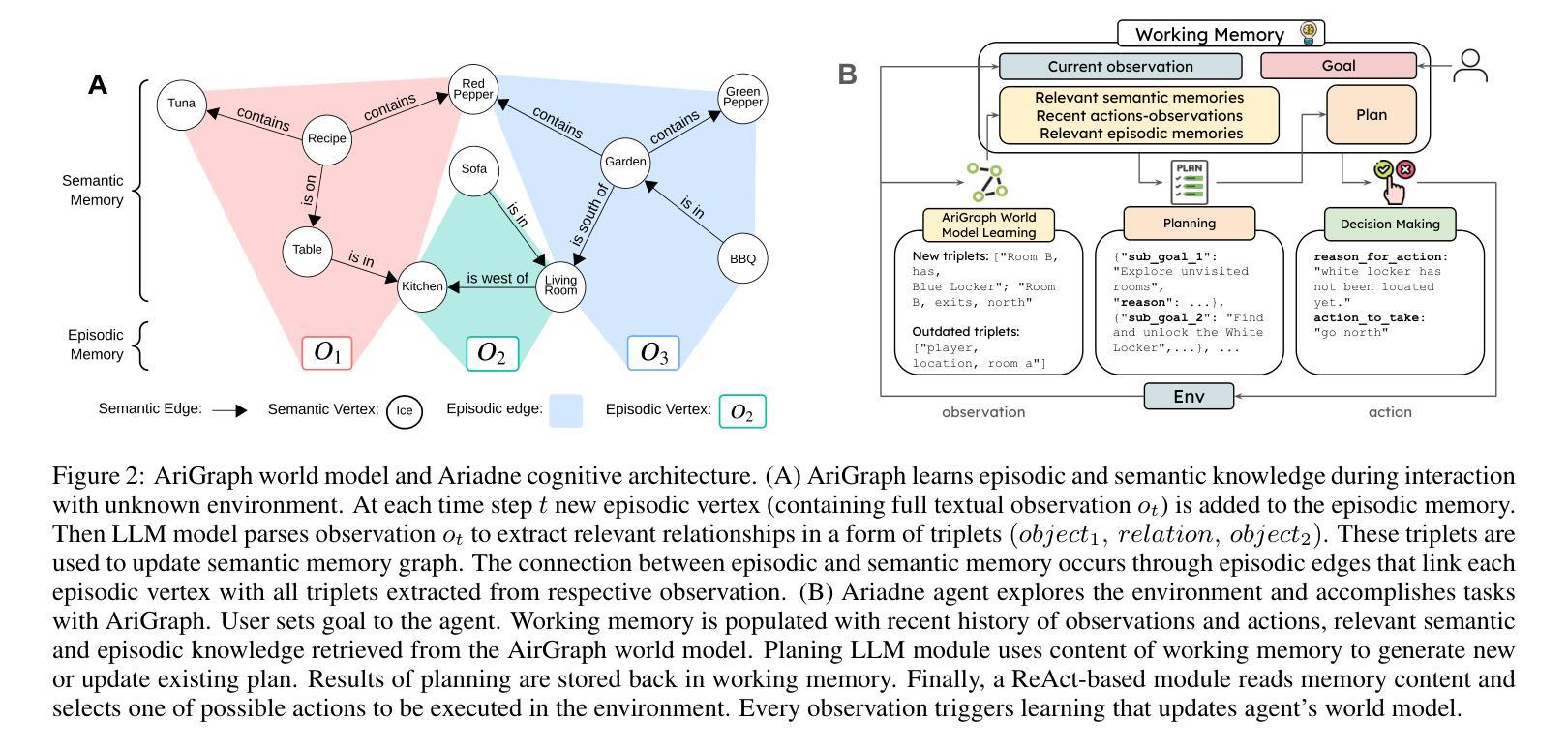
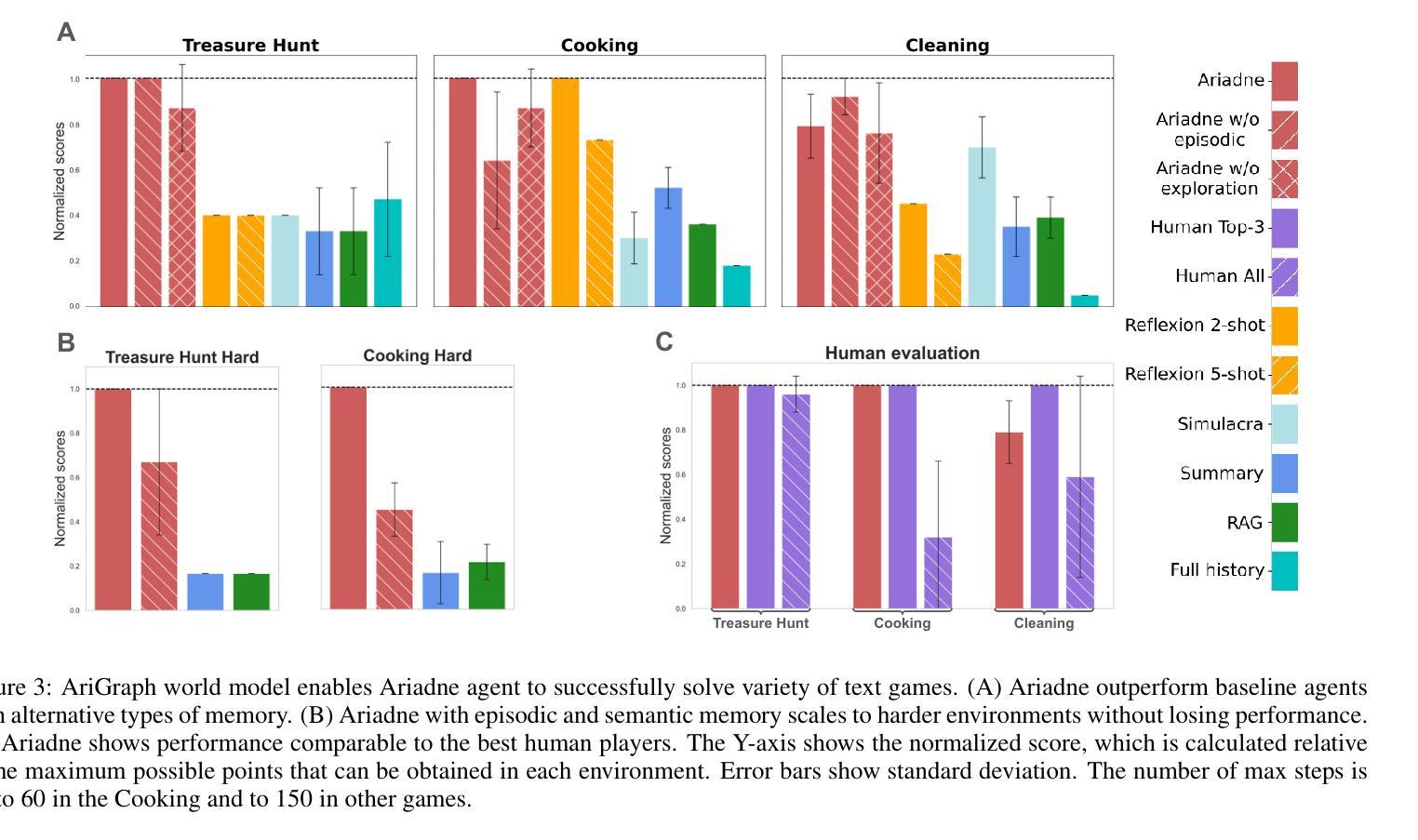
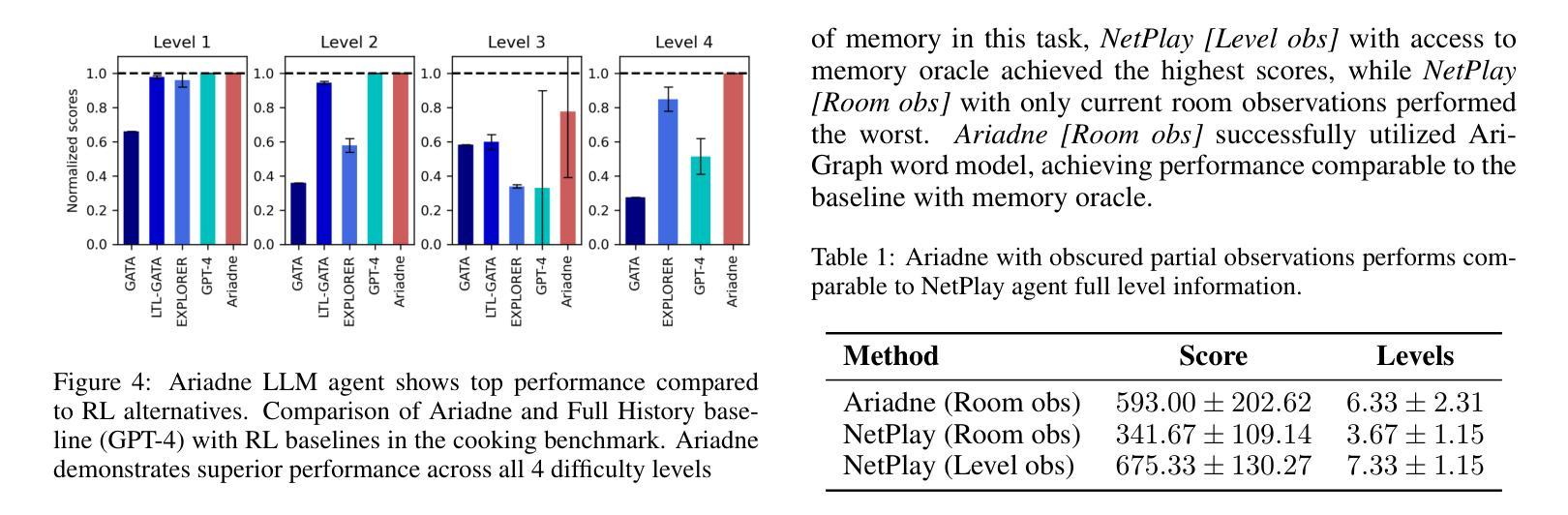
AriGraph: Learning Knowledge Graph World Models with Episodic Memory for LLM Agents
Authors:Petr Anokhin, Nikita Semenov, Artyom Sorokin, Dmitry Evseev, Andrey Kravchenko, Mikhail Burtsev, Evgeny Burnaev
Advancements in the capabilities of Large Language Models (LLMs) have created a promising foundation for developing autonomous agents. With the right tools, these agents could learn to solve tasks in new environments by accumulating and updating their knowledge. Current LLM-based agents process past experiences using a full history of observations, summarization, retrieval augmentation. However, these unstructured memory representations do not facilitate the reasoning and planning essential for complex decision-making. In our study, we introduce AriGraph, a novel method wherein the agent constructs and updates a memory graph that integrates semantic and episodic memories while exploring the environment. We demonstrate that our Ariadne LLM agent, consisting of the proposed memory architecture augmented with planning and decision-making, effectively handles complex tasks within interactive text game environments difficult even for human players. Results show that our approach markedly outperforms other established memory methods and strong RL baselines in a range of problems of varying complexity. Additionally, AriGraph demonstrates competitive performance compared to dedicated knowledge graph-based methods in static multi-hop question-answering.
随着大型语言模型(LLM)的能力不断提升,为开发自主智能体奠定了坚实的基础。使用合适的工具,这些智能体可以通过积累和更新知识来学习解决新环境中的任务。当前基于LLM的智能体利用观察的全历史记录、摘要、检索增强等方法来处理过去的经历。然而,这些非结构化的记忆表示不利于复杂的决策所需的推理和规划。在我们的研究中,我们引入了AriGraph,这是一种新方法,智能体在其中构建并更新一个记忆图,该图在探索环境时整合语义和情景记忆。我们证明,我们的Ariadne LLM智能体由提议的记忆架构辅以规划和决策构成,可以有效地处理交互式文本游戏环境中的复杂任务,这些任务甚至对人类玩家来说也是困难的。结果表明,我们的方法在各种不同复杂度的任务中显著优于其他现有的记忆方法和强大的强化学习基线。此外,AriGraph在静态多跳问答方面表现出与专用知识图谱方法相当的性能。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Code for this work is avaliable at https://github.com/AIRI-Institute/AriGraph
Summary
大型语言模型(LLM)的进展为开发自主智能体提供了有前景的基础。借助适当工具,这些智能体能够通过积累并更新知识学习在新环境中完成任务。本研究引入了一种名为AriGraph的新方法,其中智能体在探索环境时构建并更新一个融合语义和情景记忆的记忆图。实验证明,配备规划决策功能的Ariadne LLM智能体在交互式文本游戏环境中成功完成复杂任务,即使对人类玩家来说也非常困难。相较于其他记忆方法和强化学习基线,该方法在多种不同复杂度的任务中表现优异。此外,在静态多跳问答场景中,AriGraph与专用知识图谱方法相比表现良好。
Key Takeaways
- 大型语言模型(LLM)为开发自主智能体提供了坚实的基础。
- LLM智能体通过积累并更新知识,能在各种环境中学习完成任务。
- AriGraph是一种新引入的方法,智能体在探索环境时构建和更新融合语义和情景记忆的记忆图。
- Ariadne LLM智能体在交互式文本游戏环境中成功完成复杂任务,表现超越其他记忆方法和强化学习基线。
- 与其他记忆方法相比,AriGraph在多种任务中展现出显著优势。
- AriGraph在静态多跳问答场景中的表现具有竞争力。
点此查看论文截图

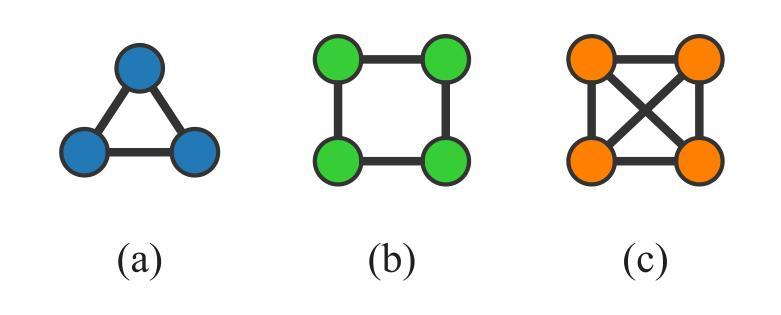
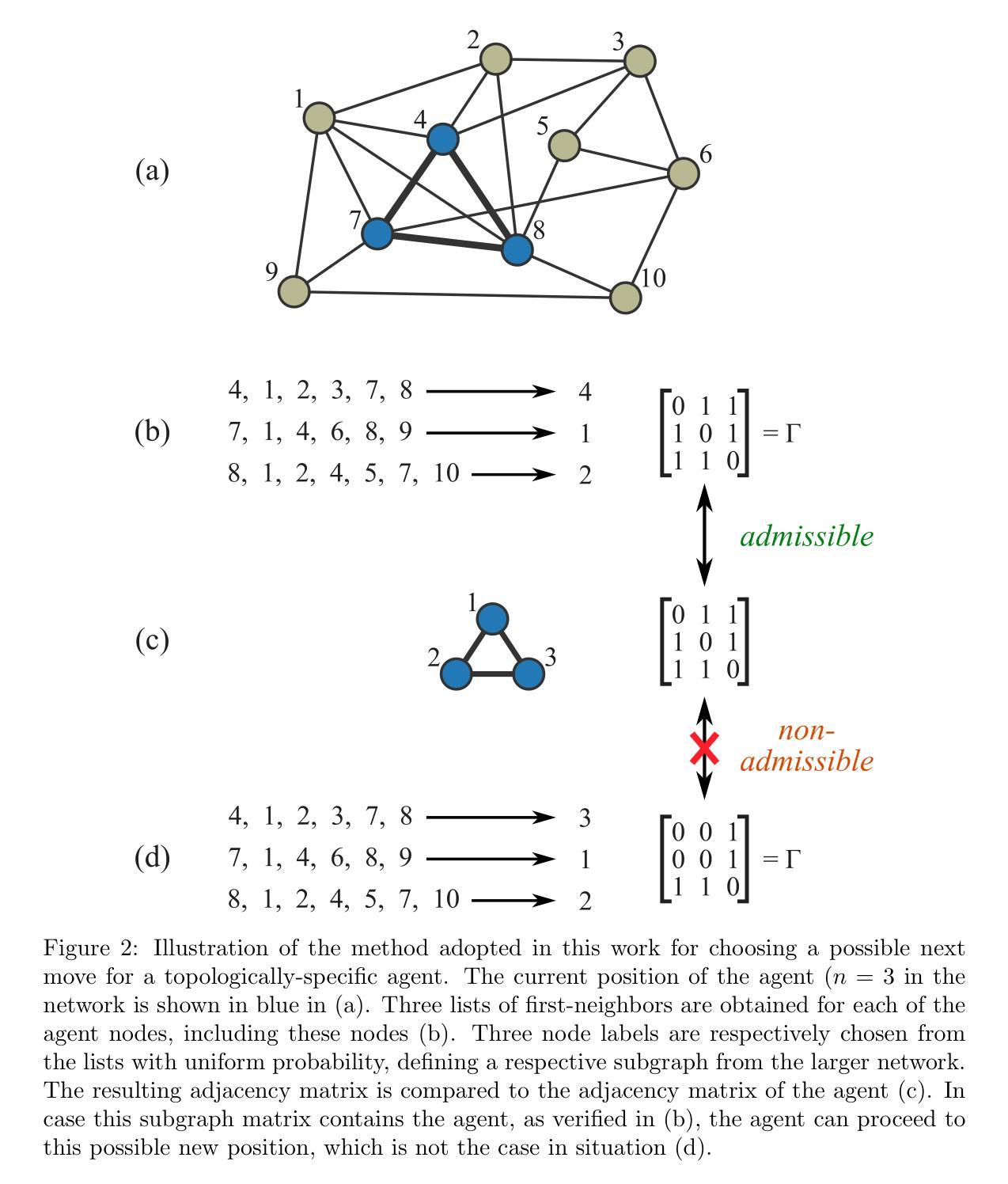
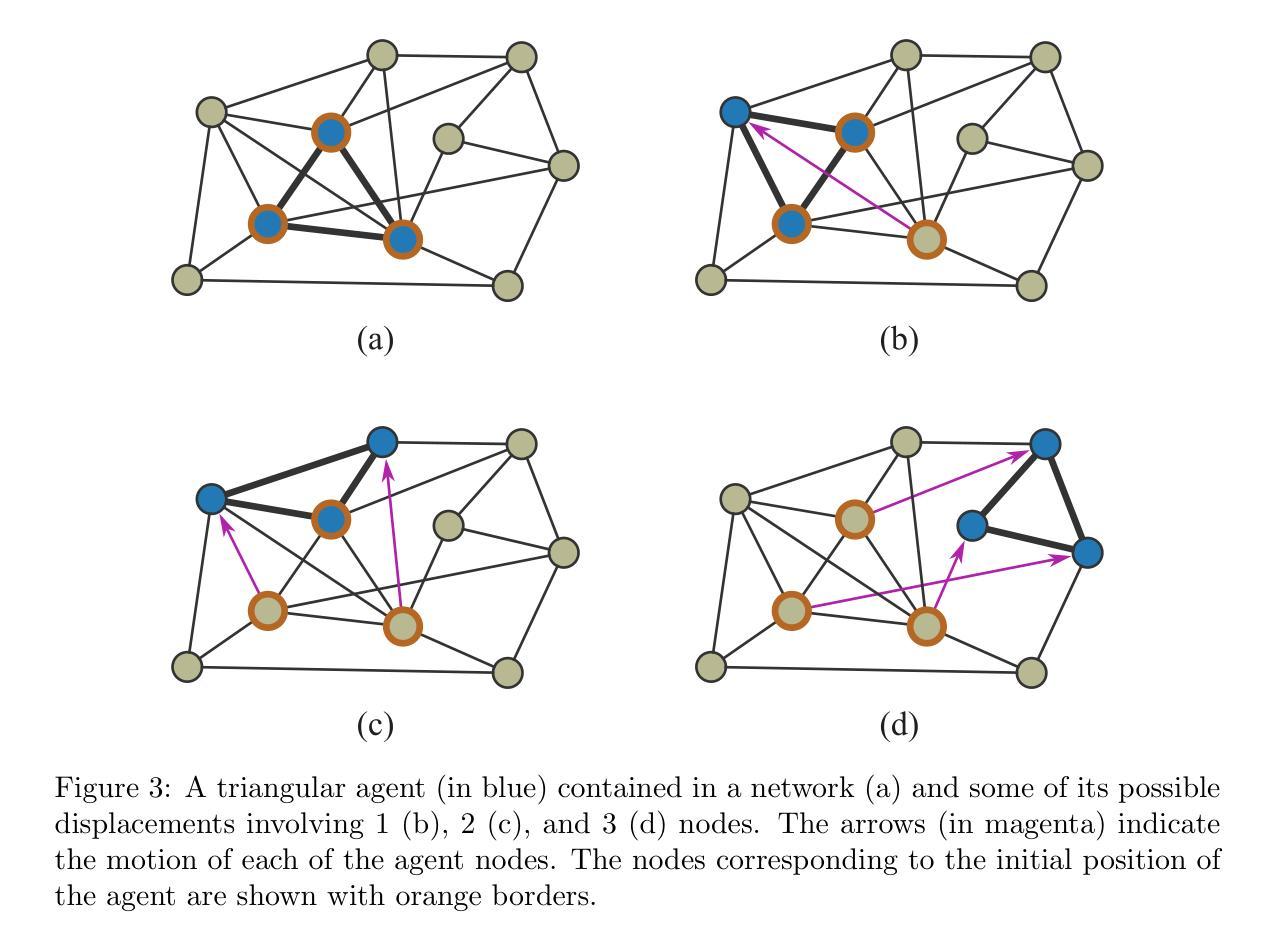
Random Walks Performed by Topologically-Specific Agents on Complex Networks
Authors:Alexandre Benatti, Luciano da F. Costa
Random walks by single-node agents have been systematically conducted on various types of complex networks in order to investigate how their topologies can affect the dynamics of the agents. However, by fitting any network node, these agents do not engage in topological interactions with the network. In the present work, we describe random walks on complex networks performed by agents that are actually small graphs. These agents can only occupy admissible portions of the network onto which they fit topologically, hence their name being taken as topologically-specific agents. These agents are also allowed to move to adjacent subgraphs in the network, which have each node adjacent to a distinct original respective node of the agent. Given a network and a specific agent, it is possible to obtain a respective associated network, in which each node corresponds to a possible instance of the agent and the edges indicate adjacent positions. Associated networks are obtained and studied respectively to three types of topologically-specific agents (triangle, square, and slashed square) considering three types of complex networks (geometrical, Erd\H{o}s-R'enyi, and Barab'asi-Albert). Uniform random walks are also performed on these structures, as well as networks respectively obtained by removing the five nodes with the highest degree, and studied in terms of the number of covered nodes along the walks. Several results are reported and discussed, including the fact that substantially distinct associated networks can be obtained for each of the three considered agents and for varying average node degrees. Respectively to the coverage of the networks by uniform random walks, the square agent led to the most effective coverage of the nodes, followed by the triangle and slashed square agents. In addition, the geometric network turned out to be less effectively covered.
针对各种类型的复杂网络,对单节点代理进行了系统的随机游走研究,以调查其拓扑结构如何影响代理的动力学。然而,通过匹配任何网络节点,这些代理并没有与网络进行拓扑交互。当前工作中,我们描述了由实际上是小型图的代理在复杂网络上进行的随机游走。这些代理只能占据与网络拓扑结构相匹配的可行部分,因此被命名为拓扑特定代理。这些代理也被允许移动到网络中的相邻子图,其中每个节点都与代理的原始不同节点相邻。给定一个网络和特定的代理,我们可以获得一个相关的网络,其中每个节点对应于代理的一个可能实例,边表示相邻位置。对于三种拓扑特定代理(三角形、正方形和斜线正方形)和三种复杂网络(几何网络、Erd\H{o}s-Rényi网络和Barab\Ási-Albert网络),分别获得了相关的网络并进行了研究。这些结构上以及通过移除五个度数最高的节点后得到的网络上执行了统一的随机游走,并根据游走过程中覆盖的节点数量进行了研究。报告并讨论了一些结果,包括对于每种考虑的代理和不同的平均节点度数,可以获得截然不同的相关网络。在统一随机游走对网络覆盖方面,正方形代理导致节点覆盖最有效,其次是三角形和斜线正方形代理。此外,几何网络的覆盖效果较差。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 21 pages, 15 figures
Summary
拓扑特定型智能体在复杂网络上的随机游走研究。这些智能体能贴合网络拓扑结构,在非相邻子图中游走。三种类型的智能体(三角形、正方形、斜线型)在三种不同的复杂网络结构(几何型、Erd\H{o}s-Rényi型和Barabasi-Albert型)上的随机游走行为被研究,同时还研究了移除度数最高的五个节点后的网络中的随机游走情况。研究发现在不同的智能体和不同的平均节点度条件下,会得到非常不同的关联网络。在均匀随机游走中,正方形智能体的节点覆盖效果最佳,其次是三角形和斜线型智能体。几何网络的覆盖效果较差。
Key Takeaways
- 拓扑特定型智能体可以在复杂网络的非相邻子图中进行随机游走,能贴合网络拓扑结构。
- 三种类型的智能体(三角形、正方形、斜线型)在三种不同的复杂网络结构上的随机游走行为被研究。
- 在移除度数最高的节点后的网络中,也进行了随机游走研究。
- 智能体和平均节点度的不同会导致得到的关联网络显著不同。
- 在均匀随机游走中,正方形智能体的节点覆盖效果最佳。
- 几何网络的节点覆盖效果较差。
- 智能体的拓扑结构对随机游走的动力学有显著影响。
点此查看论文截图