⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-05-17 更新
3D-Fixup: Advancing Photo Editing with 3D Priors
Authors:Yen-Chi Cheng, Krishna Kumar Singh, Jae Shin Yoon, Alex Schwing, Liangyan Gui, Matheus Gadelha, Paul Guerrero, Nanxuan Zhao
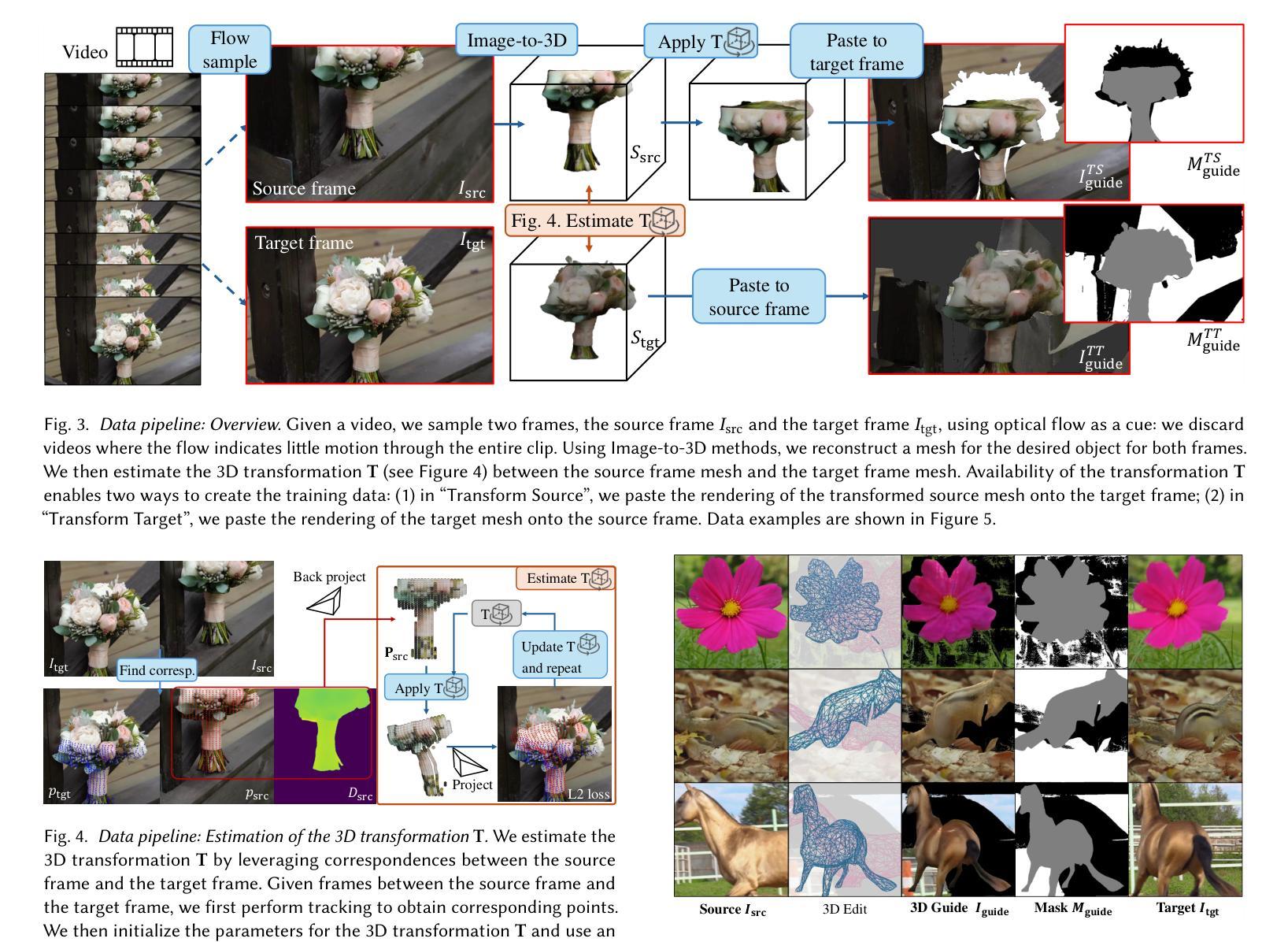
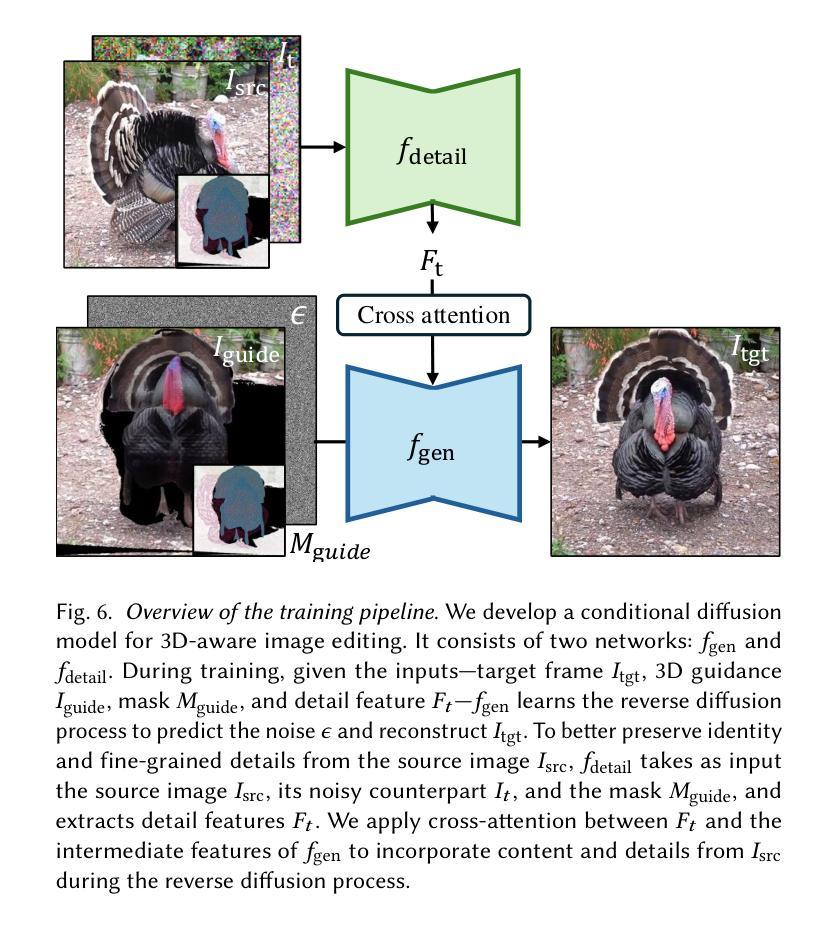
Despite significant advances in modeling image priors via diffusion models, 3D-aware image editing remains challenging, in part because the object is only specified via a single image. To tackle this challenge, we propose 3D-Fixup, a new framework for editing 2D images guided by learned 3D priors. The framework supports difficult editing situations such as object translation and 3D rotation. To achieve this, we leverage a training-based approach that harnesses the generative power of diffusion models. As video data naturally encodes real-world physical dynamics, we turn to video data for generating training data pairs, i.e., a source and a target frame. Rather than relying solely on a single trained model to infer transformations between source and target frames, we incorporate 3D guidance from an Image-to-3D model, which bridges this challenging task by explicitly projecting 2D information into 3D space. We design a data generation pipeline to ensure high-quality 3D guidance throughout training. Results show that by integrating these 3D priors, 3D-Fixup effectively supports complex, identity coherent 3D-aware edits, achieving high-quality results and advancing the application of diffusion models in realistic image manipulation. The code is provided at https://3dfixup.github.io/
尽管通过扩散模型对图像先验建模取得了重大进展,但由于对象仅通过单张图像指定,3D感知图像编辑仍然具有挑战性。为了应对这一挑战,我们提出了3D-Fixup,这是一个由学习到的3D先验引导的新框架,用于编辑2D图像。该框架支持对象平移和3D旋转等困难编辑情况。为了实现这一点,我们采用了一种基于训练的方法,利用扩散模型的生成能力。由于视频数据天然地编码了现实世界的物理动态,我们转向视频数据来生成训练数据对,即源帧和目标帧。我们不仅仅依赖单一的训练模型来推断源帧和目标帧之间的转换,还结合了来自图像到3D模型的3D指导,通过将2D信息显式投影到3D空间来应对这一具有挑战性的任务。我们设计了一个数据生成管道,以确保在整个训练过程中提供高质量的3D指导。结果表明,通过整合这些3D先验知识,3D-Fixup有效地支持了复杂、身份一致的3D感知编辑,取得了高质量的结果,并推动了扩散模型在真实图像操作中的应用。相关代码已发布在:[https://3dfixup.github.io/]上。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF SIGGRAPH 2025. Project page: https://3dfixup.github.io/
Summary:
提出一种名为3D-Fixup的新框架,利用学习到的3D先验知识对二维图像进行编辑。该框架支持物体平移和三维旋转等复杂编辑情况。通过利用扩散模型的生成能力,结合视频数据生成训练数据对,将源帧和目标帧之间的转换进行推断。同时融入Image-to-3D模型的3D指导,将二维信息显式投影到三维空间,实现高质量的三维指导。该框架能有效支持复杂、连贯的三维感知编辑,提高扩散模型在真实图像操作中的应用质量。
Key Takeaways:
- 3D-Fixup是一个利用学习的3D先验知识指导二维图像编辑的新框架。
- 该框架解决了通过单个图像指定物体进行编辑的挑战。
- 利用扩散模型的生成能力和视频数据生成训练数据对,实现源帧和目标帧之间的转换推断。
- 融入Image-to-3D模型的3D指导,显式地将二维信息投影到三维空间。
- 设计了数据生成管道,确保在整个训练过程中获得高质量的3D指导。
- 3D-Fixup支持复杂的、连贯的三维感知编辑。
点此查看论文截图


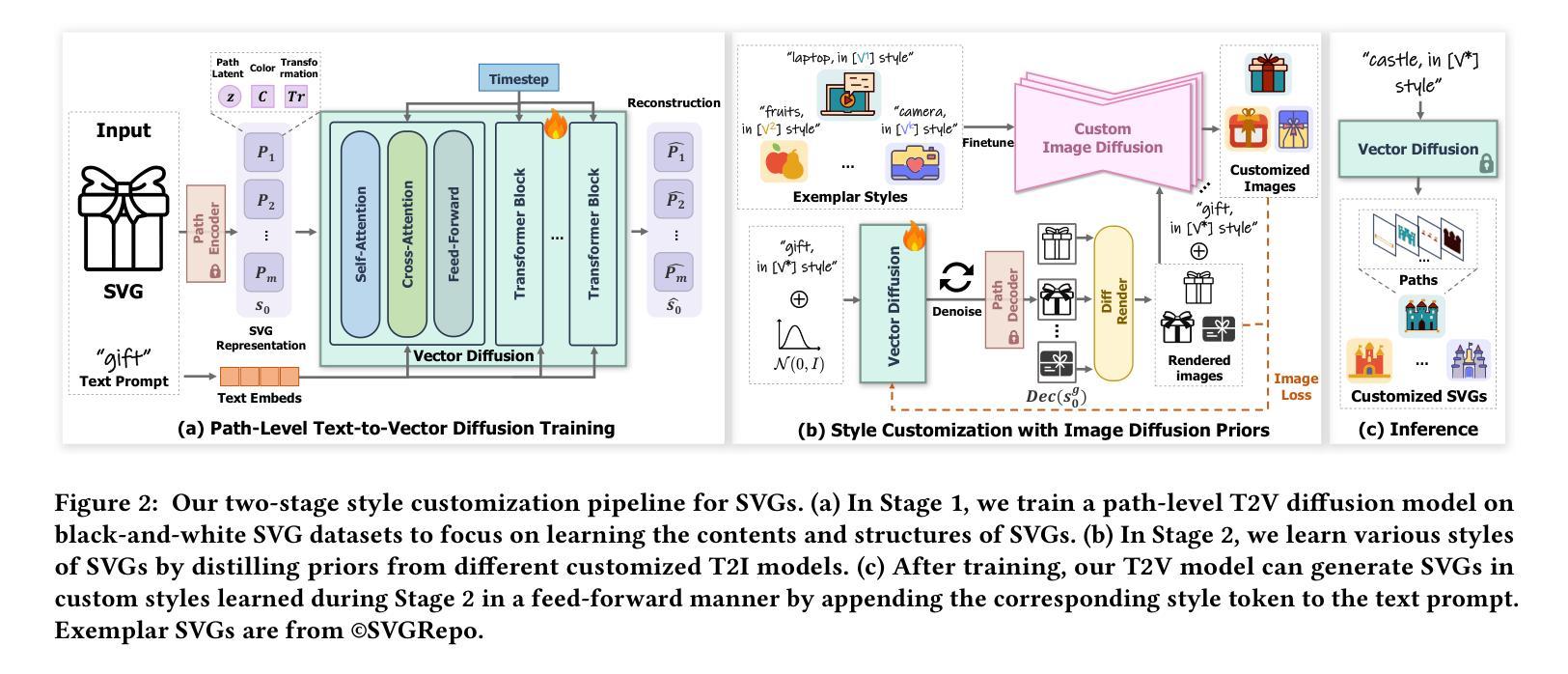
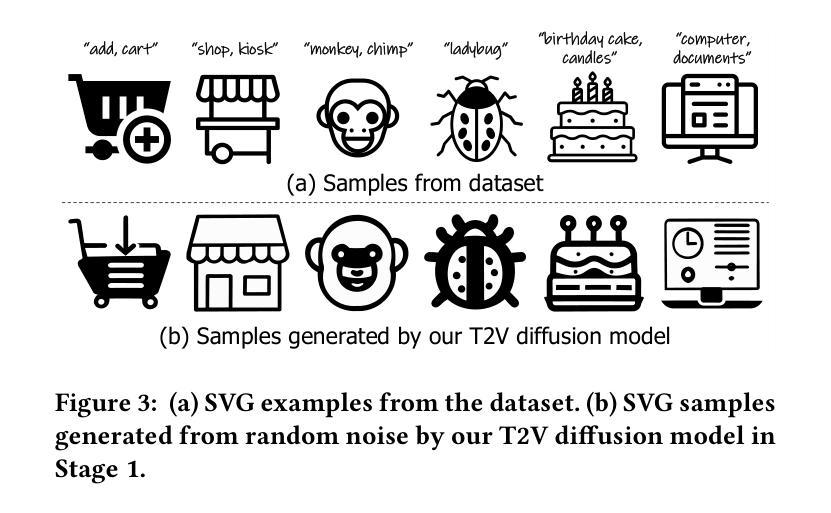
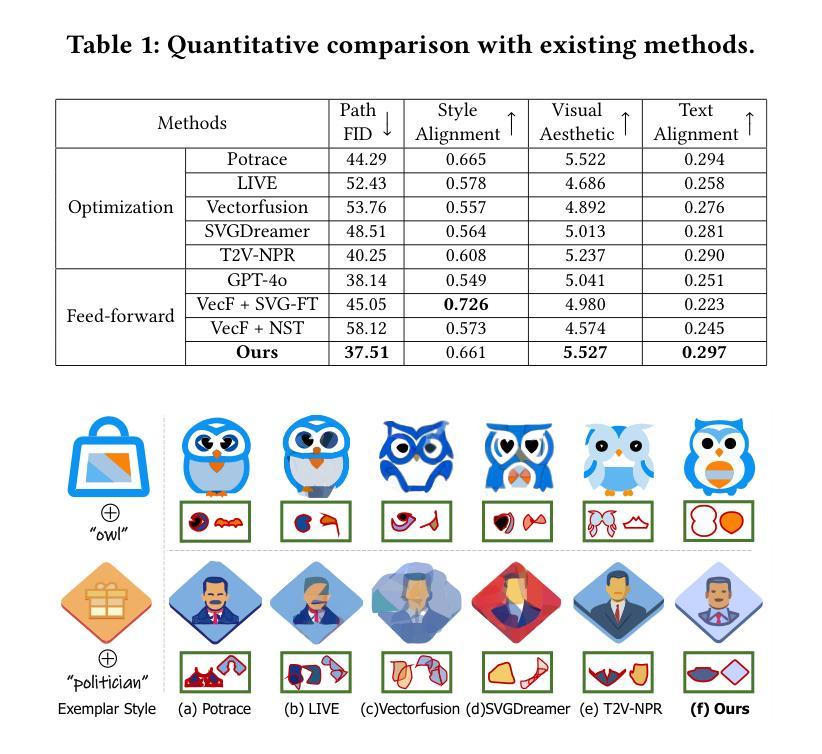
Style Customization of Text-to-Vector Generation with Image Diffusion Priors
Authors:Peiying Zhang, Nanxuan Zhao, Jing Liao
Scalable Vector Graphics (SVGs) are highly favored by designers due to their resolution independence and well-organized layer structure. Although existing text-to-vector (T2V) generation methods can create SVGs from text prompts, they often overlook an important need in practical applications: style customization, which is vital for producing a collection of vector graphics with consistent visual appearance and coherent aesthetics. Extending existing T2V methods for style customization poses certain challenges. Optimization-based T2V models can utilize the priors of text-to-image (T2I) models for customization, but struggle with maintaining structural regularity. On the other hand, feed-forward T2V models can ensure structural regularity, yet they encounter difficulties in disentangling content and style due to limited SVG training data. To address these challenges, we propose a novel two-stage style customization pipeline for SVG generation, making use of the advantages of both feed-forward T2V models and T2I image priors. In the first stage, we train a T2V diffusion model with a path-level representation to ensure the structural regularity of SVGs while preserving diverse expressive capabilities. In the second stage, we customize the T2V diffusion model to different styles by distilling customized T2I models. By integrating these techniques, our pipeline can generate high-quality and diverse SVGs in custom styles based on text prompts in an efficient feed-forward manner. The effectiveness of our method has been validated through extensive experiments. The project page is https://customsvg.github.io.
可扩展矢量图形(SVG)因其分辨率独立和层次结构清晰而深受设计师喜爱。尽管现有的文本到矢量(T2V)生成方法可以根据文本提示生成SVG,但它们往往忽略了实际应用中的一个重要需求:样式定制。这对于生产具有一致外观和连贯美学的矢量图形集合至关重要。对现有的T2V方法进行样式定制扩展面临一定的挑战。基于优化的T2V模型可以利用文本到图像(T2I)模型的先验知识进行定制,但在保持结构规律性方面存在困难。另一方面,前馈T2V模型可以确保结构规律性,但由于SVG训练数据的有限,它们在解开内容和样式时遇到困难。为了解决这些挑战,我们提出了一种用于SVG生成的两阶段样式定制管道,利用前馈T2V模型和T2I图像先验的优势。在第一阶段,我们训练了一个具有路径级别表示的T2V扩散模型,以确保SVG的结构规律性,同时保留多样的表达能力。在第二阶段,我们通过蒸馏定制T2I模型来定制T2V扩散模型的不同风格。通过整合这些技术,我们的管道能够以高效的前馈方式,基于文本提示生成高质量和多样化的定制样式SVG。我们的方法的有效性已经通过大量的实验得到了验证。项目页面是https://customsvg.github.io。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by SIGGRAPH 2025 (Conference Paper). Project page: https://customsvg.github.io
Summary
本文介绍了SVG设计的重要性以及现有文本转矢量(T2V)生成方法的局限性。针对实际应用中的样式定制需求,提出了一种基于扩散模型的两阶段SVG样式定制流程。第一阶段训练带有路径级别表示的T2V扩散模型,确保SVG的结构规律性和丰富的表达能力。第二阶段通过蒸馏定制化的T2I模型对T2V扩散模型进行风格定制。该项目实现了高效的前馈方式生成高质量、多样化的定制风格SVG。
Key Takeaways
- SVG因其分辨率独立性和分层结构受到设计师青睐。
- 现有文本转矢量(T2V)生成方法虽能从文本提示生成SVG,但忽略了样式定制的重要性。
- 样式定制对于生产具有一致外观和连贯美学的矢量图形至关重要。
- 优化基于文本转图像(T2I)模型的T2V方法存在保持结构规律性的挑战。
- 馈前T2V模型能保证结构规律性,但在内容与样式解耦方面遇到困难,因SVG训练数据有限。
- 提出的两阶段样式定制流程结合了T2V扩散模型和T2I图像先验的优势。
- 第一阶段训练T2V扩散模型确保SVG的结构规律性和丰富表达力;第二阶段通过蒸馏定制化T2I模型进行风格定制。
点此查看论文截图


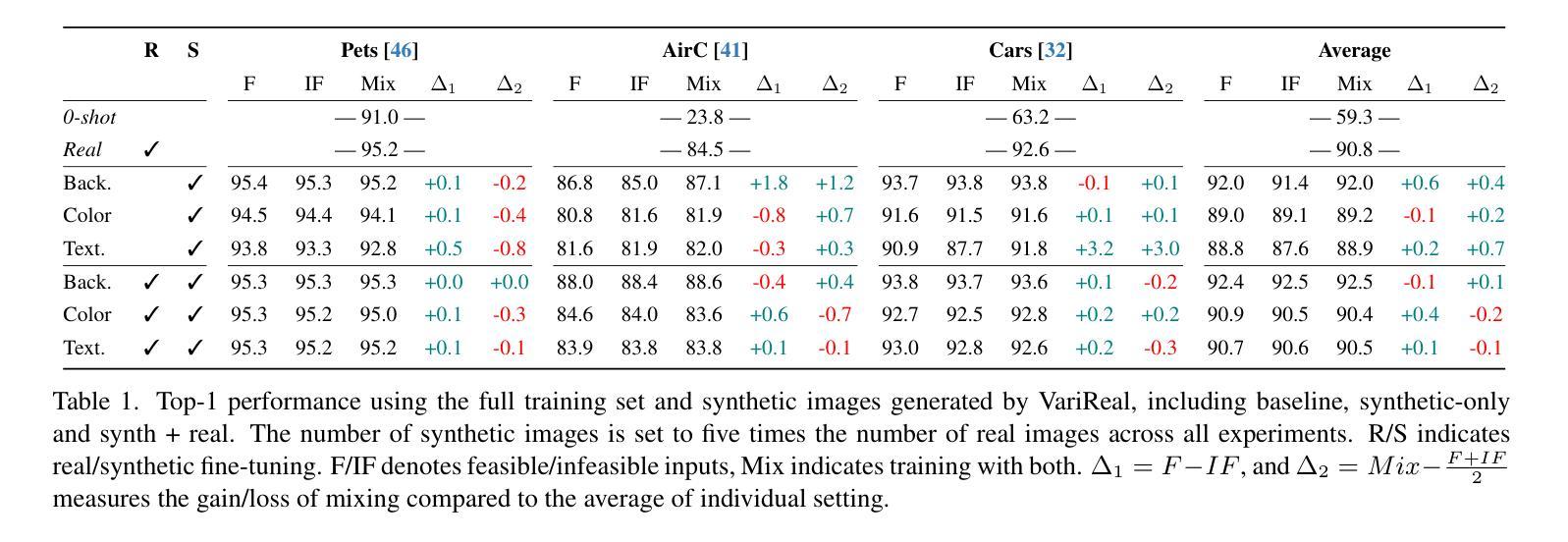
Does Feasibility Matter? Understanding the Impact of Feasibility on Synthetic Training Data
Authors:Yiwen Liu, Jessica Bader, Jae Myung Kim
With the development of photorealistic diffusion models, models trained in part or fully on synthetic data achieve progressively better results. However, diffusion models still routinely generate images that would not exist in reality, such as a dog floating above the ground or with unrealistic texture artifacts. We define the concept of feasibility as whether attributes in a synthetic image could realistically exist in the real-world domain; synthetic images containing attributes that violate this criterion are considered infeasible. Intuitively, infeasible images are typically considered out-of-distribution; thus, training on such images is expected to hinder a model’s ability to generalize to real-world data, and they should therefore be excluded from the training set whenever possible. However, does feasibility really matter? In this paper, we investigate whether enforcing feasibility is necessary when generating synthetic training data for CLIP-based classifiers, focusing on three target attributes: background, color, and texture. We introduce VariReal, a pipeline that minimally edits a given source image to include feasible or infeasible attributes given by the textual prompt generated by a large language model. Our experiments show that feasibility minimally affects LoRA-fine-tuned CLIP performance, with mostly less than 0.3% difference in top-1 accuracy across three fine-grained datasets. Also, the attribute matters on whether the feasible/infeasible images adversarially influence the classification performance. Finally, mixing feasible and infeasible images in training datasets does not significantly impact performance compared to using purely feasible or infeasible datasets.
随着超真实扩散模型的发展,部分或完全在合成数据上训练的模型取得了越来越好的结果。然而,扩散模型仍然经常生成在现实中不存在的图像,例如漂浮在地面上方的狗或具有不现实的纹理瑕疵。我们定义可行性的概念为合成图像中的属性是否能在现实世界中真实存在;含有违反这一标准的属性的合成图像被视为不可行。直观地说,不可行的图像通常被认为是离群值;因此,在这样的图像上进行训练会阻碍模型对真实世界数据的泛化能力,因此应尽可能从训练集中排除。但是,可行性真的重要吗?在本文中,我们研究了在生成基于CLIP的分类器的合成训练数据时是否必须强制执行可行性,重点关注三个目标属性:背景、颜色和纹理。我们引入了VariReal,一个管道,它稍微编辑给定的源图像以包含由大型语言模型生成的文本提示所给出的可行或不可行的属性。我们的实验表明,可行性对使用LoRA微调CLIP的性能影响甚微,在三个精细数据集上top-1准确率差异大多不到0.3%。此外,属性很重要,可行或不可行的图像是否会不利于影响分类性能。最后,与纯粹使用可行或不可行的数据集相比,在训练数据集中混合可行和不可行的图像并不会显著影响性能。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF CVPRW 2025
Summary
本文探讨了基于CLIP分类器的合成训练数据生成中可行性概念的重要性。研究发现,对于背景、颜色和纹理等目标属性,强制实施可行性对LoRA微调后的CLIP性能影响甚微。混合可行与不可行的图像在训练数据集中对性能的影响并不显著。
Key Takeaways
- 合成数据在训练扩散模型时逐渐取得更好的结果,但仍会生成与现实不符的图像。
- 定义了“可行性”概念,即合成图像中的属性是否能在现实世界中存在。
- 不可行的图像通常被认为是离群值,训练时可能阻碍模型对真实世界数据的泛化能力,应尽量避免用于训练。
- 在基于CLIP的分类器中,强制实施可行性对性能影响较小。
- 在使用大型语言模型生成的文本提示时,可行或不可行的属性对图像进行最小限度的编辑。
- 在三个精细数据集上,LoRA微调后的CLIP性能在可行性与不可行性图像之间的差异大多小于0.3%。
点此查看论文截图



ORL-LDM: Offline Reinforcement Learning Guided Latent Diffusion Model Super-Resolution Reconstruction
Authors:Shijie Lyu
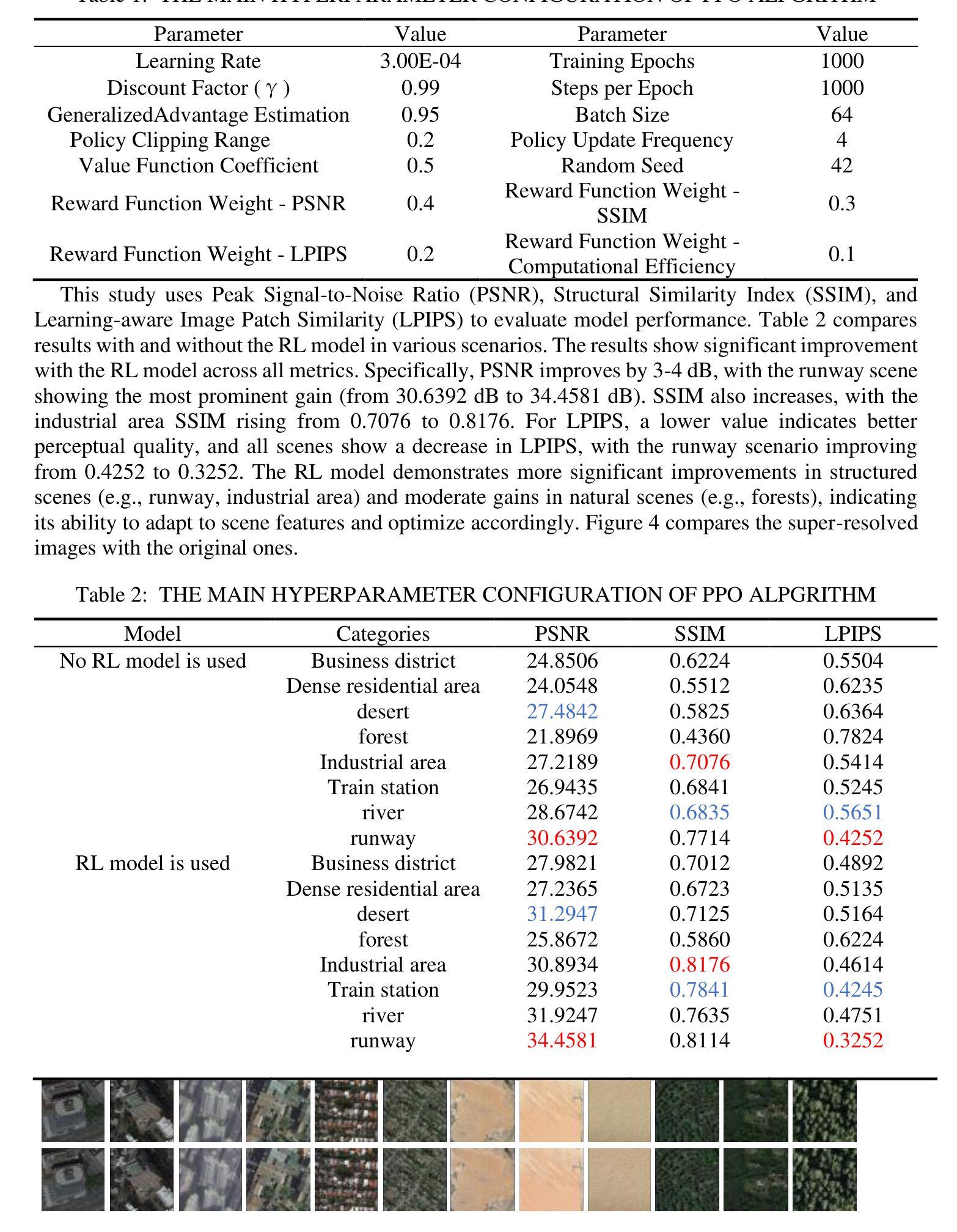
With the rapid advancement of remote sensing technology, super-resolution image reconstruction is of great research and practical significance. Existing deep learning methods have made progress but still face limitations in handling complex scenes and preserving image details. This paper proposes a reinforcement learning-based latent diffusion model (LDM) fine-tuning method for remote sensing image super-resolution. The method constructs a reinforcement learning environment with states, actions, and rewards, optimizing decision objectives through proximal policy optimization (PPO) during the reverse denoising process of the LDM model. Experiments on the RESISC45 dataset show significant improvements over the baseline model in PSNR, SSIM, and LPIPS, with PSNR increasing by 3-4dB, SSIM improving by 0.08-0.11, and LPIPS reducing by 0.06-0.10, particularly in structured and complex natural scenes. The results demonstrate the method’s effectiveness in enhancing super-resolution quality and adaptability across scenes.
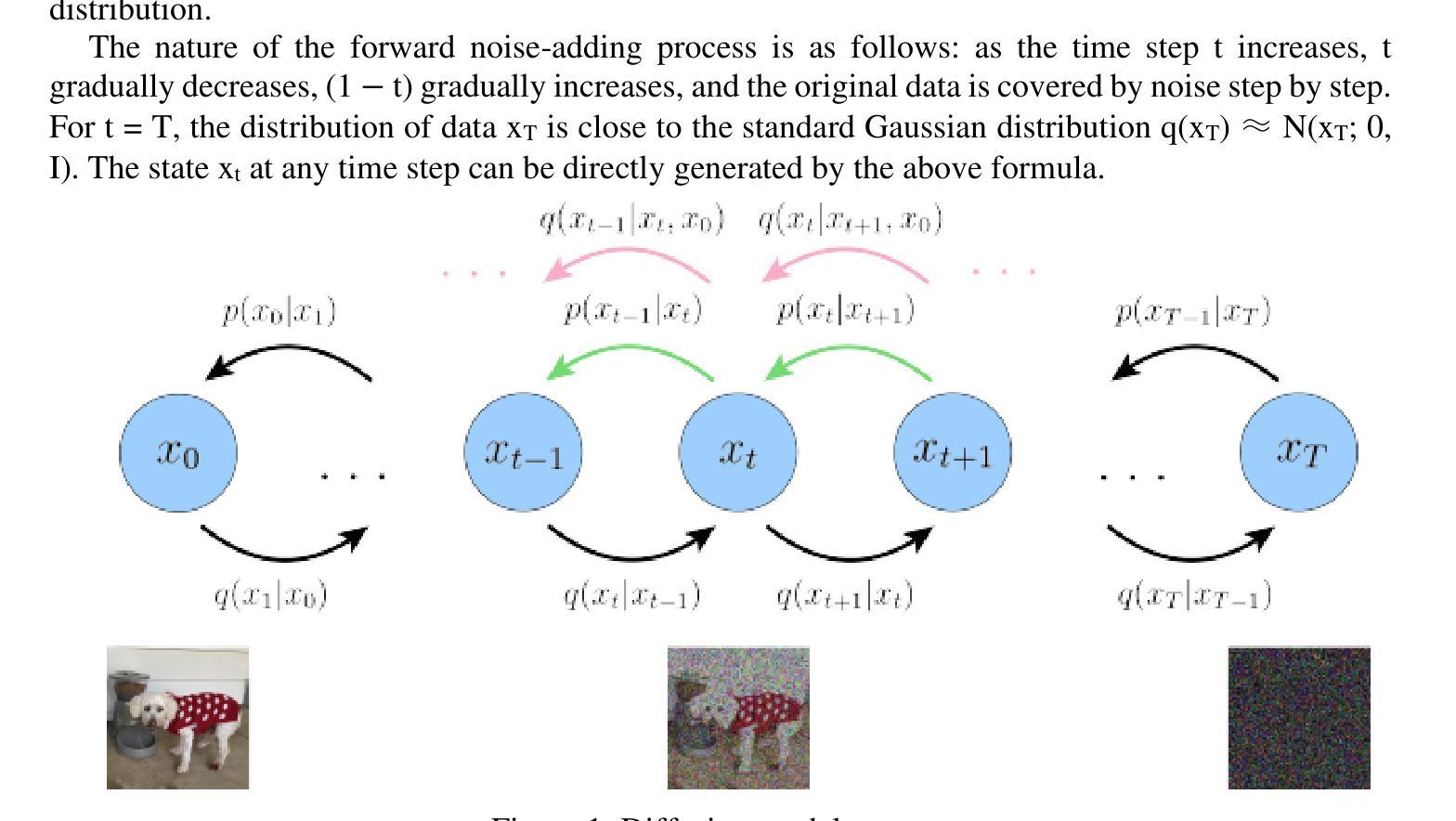
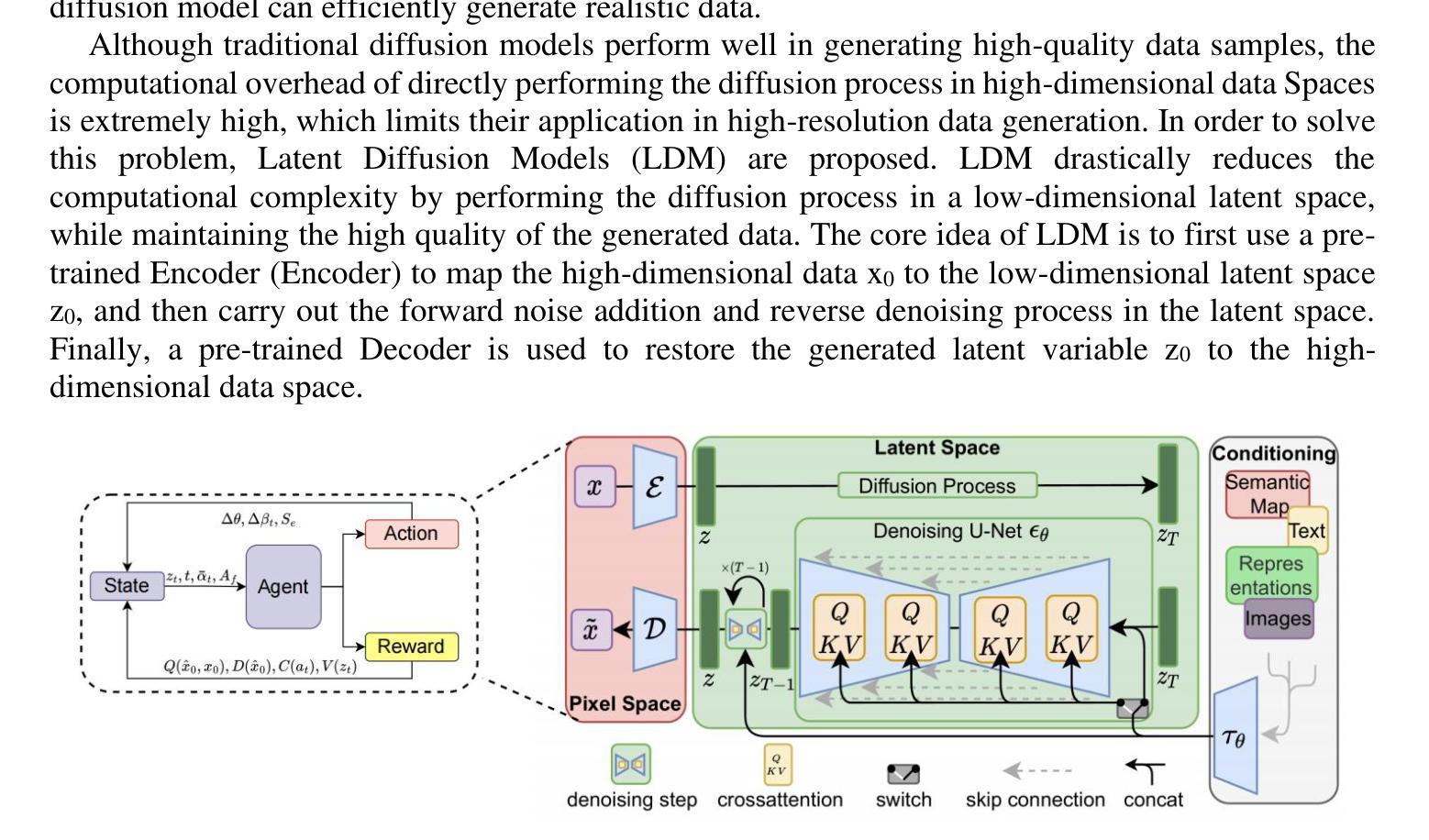
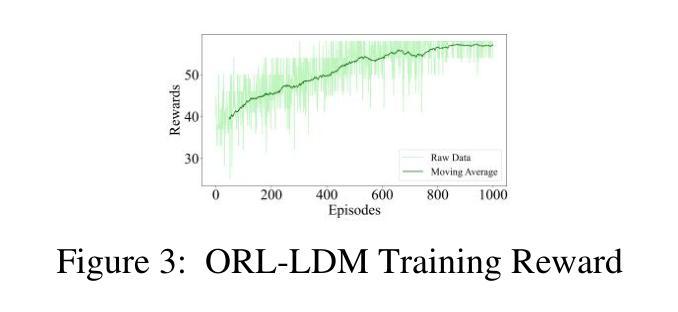
随着遥感技术的快速发展,超分辨率图像重建在研究和实际应用中具有重要意义。现有的深度学习算法虽已取得进展,但在处理复杂场景和保留图像细节方面仍存在局限性。本文提出了一种基于强化学习的潜在扩散模型(LDM)微调方法,用于遥感图像超分辨率。该方法构建了一个强化学习环境,包括状态、行为和奖励,在LDM模型的反向去噪过程中通过近端策略优化(PPO)优化决策目标。在RESISC45数据集上的实验表明,该方法在峰值信噪比(PSNR)、结构相似性(SSIM)和局部感知图像相似性(LPIPS)等指标上较基线模型有明显改进,其中PSNR提高了3-4分贝,SSIM提高了0.08-0.11,LPIPS降低了0.06-0.10。特别是在结构化及复杂的自然场景下,该方法的超分辨率质量提升效果显著,场景适应性较强。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by the 4th International Conference on Computing Innovation and Applied Physics (CONF-CIAP 2025), and will be published in EAI Community Research Series-CORE or Theoretical and Natural Science (TNS)
Summary
超分辨率图像重建具有极大的研究和实践意义,随着遥感技术的快速发展,现有的深度学习方法虽有所进展,但在处理复杂场景和保留图像细节方面仍存在局限。本文提出一种基于强化学习的潜在扩散模型(LDM)精细调整方法,用于遥感图像超分辨率重建。该方法构建了一个强化学习环境,包括状态、行为和奖励,在LDM模型的逆向去噪过程中通过近端策略优化(PPO)优化决策目标。在RESISC45数据集上的实验表明,该方法在峰值信噪比(PSNR)、结构相似性(SSIM)和局部感知图像相似性(LPIPS)等指标上较基线模型有显著改善,特别是针对结构化及复杂自然场景。结果证明了该方法在提高超分辨率质量和场景适应性方面的有效性。
Key Takeaways
- 遥感图像超分辨率重建具有重大研究和实践价值,随着遥感技术的快速发展,现有方法仍面临处理复杂场景和保留图像细节的挑战。
- 本文提出了一种基于强化学习的潜在扩散模型(LDM)精细调整方法,旨在改进遥感图像的超分辨率重建。
- 该方法构建了一个强化学习环境,包括状态、行为和奖励,优化决策目标。
- 实验采用RESISC45数据集,在峰值信噪比(PSNR)、结构相似性(SSIM)和局部感知图像相似性(LPIPS)等指标上较基线模型有显著改善。
- 方法在结构化及复杂自然场景的超分辨率重建中表现出良好的增强效果和适应性。
- 强化学习和潜在扩散模型的结合为遥感图像超分辨率重建提供了新的思路和方法。
点此查看论文截图

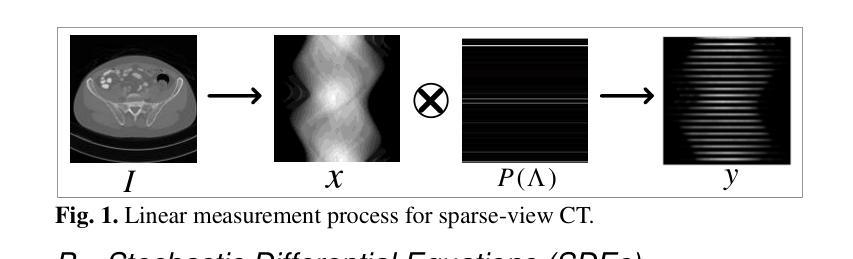
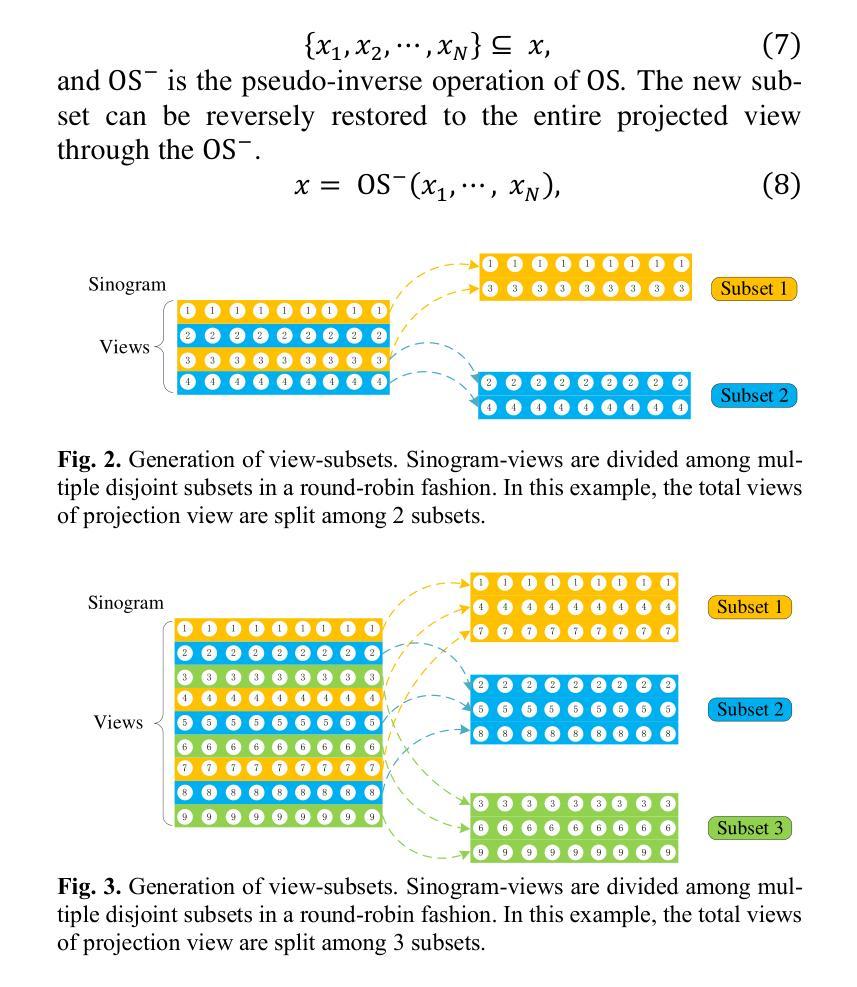
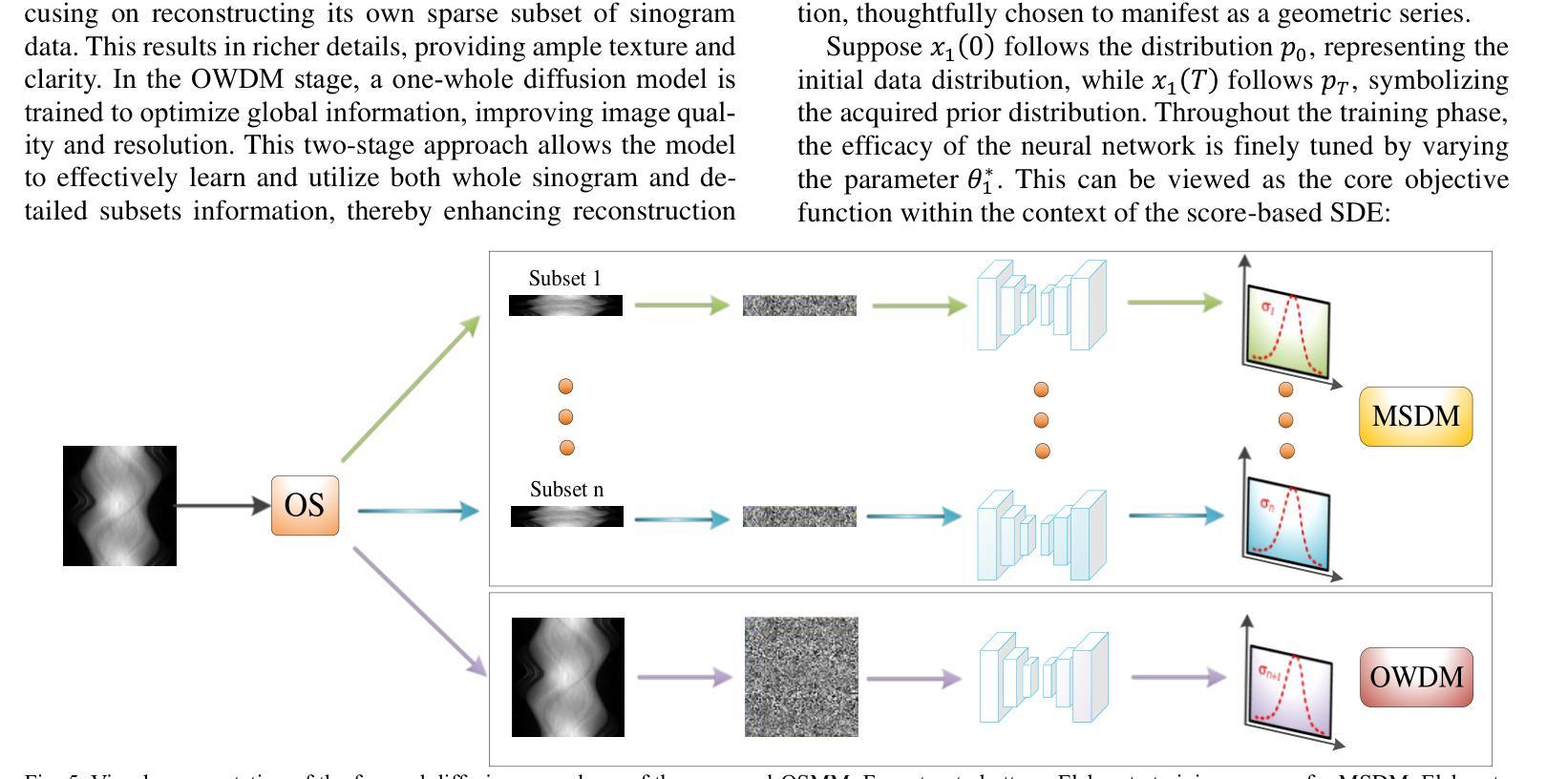
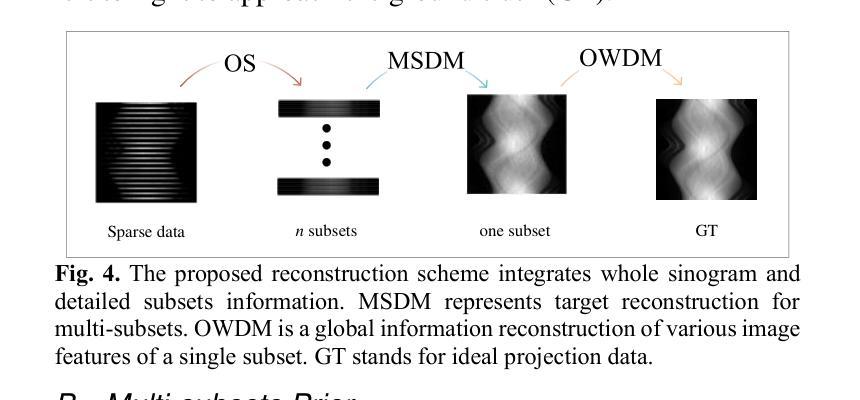
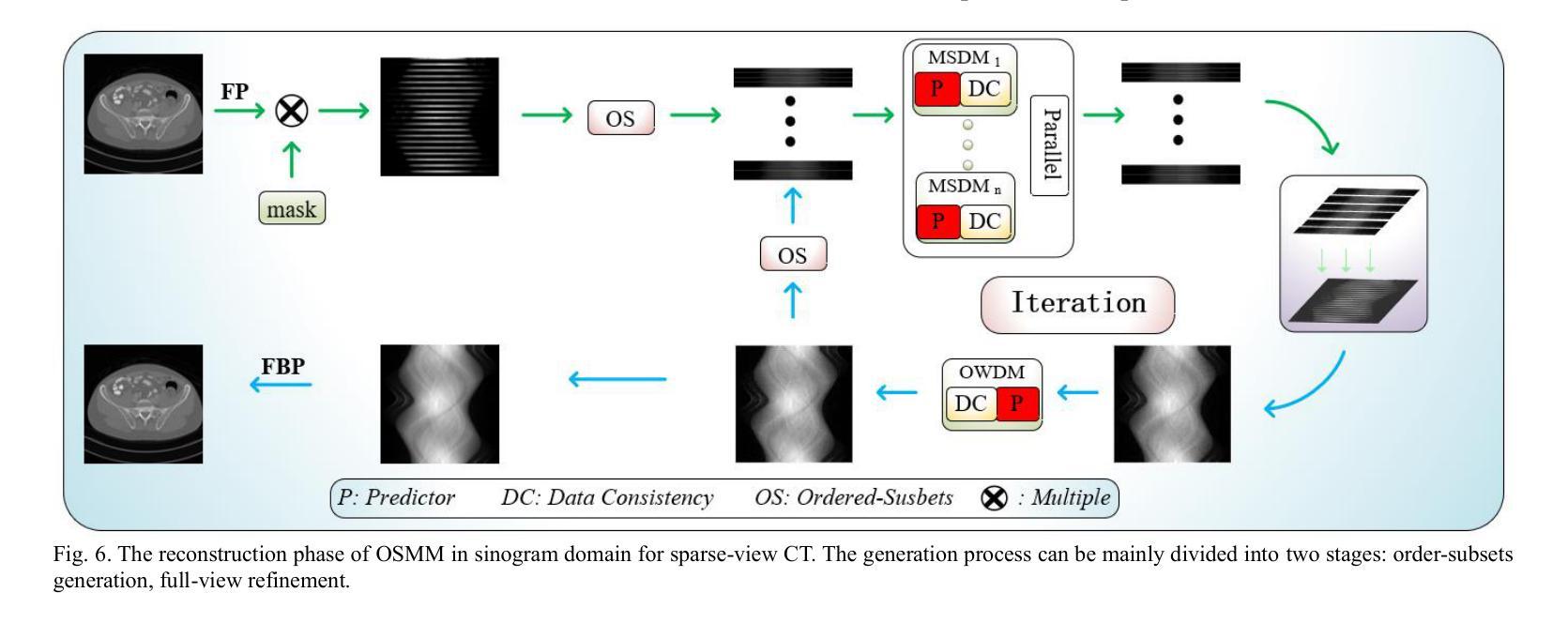
Ordered-subsets Multi-diffusion Model for Sparse-view CT Reconstruction
Authors:Pengfei Yu, Bin Huang, Minghui Zhang, Weiwen Wu, Shaoyu Wang, Qiegen Liu
Score-based diffusion models have shown significant promise in the field of sparse-view CT reconstruction. However, the projection dataset is large and riddled with redundancy. Consequently, applying the diffusion model to unprocessed data results in lower learning effectiveness and higher learning difficulty, frequently leading to reconstructed images that lack fine details. To address these issues, we propose the ordered-subsets multi-diffusion model (OSMM) for sparse-view CT reconstruction. The OSMM innovatively divides the CT projection data into equal subsets and employs multi-subsets diffusion model (MSDM) to learn from each subset independently. This targeted learning approach reduces complexity and enhances the reconstruction of fine details. Furthermore, the integration of one-whole diffusion model (OWDM) with complete sinogram data acts as a global information constraint, which can reduce the possibility of generating erroneous or inconsistent sinogram information. Moreover, the OSMM’s unsupervised learning framework provides strong robustness and generalizability, adapting seamlessly to varying sparsity levels of CT sinograms. This ensures consistent and reliable performance across different clinical scenarios. Experimental results demonstrate that OSMM outperforms traditional diffusion models in terms of image quality and noise resilience, offering a powerful and versatile solution for advanced CT imaging in sparse-view scenarios.
基于得分的扩散模型在稀疏视图CT重建领域显示出巨大的潜力。然而,投影数据集庞大且存在冗余。因此,将扩散模型应用于未处理的数据导致学习效率低下和学习难度增加,经常导致重建的图像缺乏细节。为了解决这些问题,我们提出了有序子集多扩散模型(OSMM)用于稀疏视图CT重建。OSMM创新地将CT投影数据分成相等的子集,并采用多子集扩散模型(MSDM)从每个子集中独立学习。这种有针对性的学习方法降低了复杂性,提高了细节重建的能力。此外,将整体扩散模型(OWDM)与完整辛氏图数据相结合,作为全局信息约束,降低了产生错误或不一致辛氏图信息的可能性。而且,OSMM的无监督学习框架提供了强大的鲁棒性和通用性,能够无缝适应不同CT辛氏图的稀疏水平。这确保了在不同临床场景中的一致和可靠性能。实验结果表明,OSMM在图像质量和噪声韧性方面优于传统扩散模型,为稀疏视图场景下的高级CT成像提供了强大而通用的解决方案。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
基于分数扩散模型在稀疏视图CT重建领域展现出良好前景。但由于投影数据集庞大且存在冗余信息,直接使用扩散模型处理未经处理的数据会导致学习效率低下,重建图像缺失细节的问题。为此,提出有序子集多扩散模型(OSMM)。它将CT投影数据分成若干子集,采用多子集扩散模型(MSDM)独立学习每个子集,降低复杂度并提升细节重建效果。结合全扩散模型(OWDM)与完整辛恩格图数据作为全局信息约束,减少错误或不一致辛恩格图信息的生成可能。OSMM的无监督学习框架表现出强大的鲁棒性和泛化性,能适应不同CT辛恩格图稀疏水平,确保在各种临床场景下的稳定可靠性能。实验结果证明OSMM在图像质量和噪声韧性方面优于传统扩散模型,为稀疏视图场景下的先进CT成像提供了强大而通用的解决方案。
Key Takeaways
- 分数扩散模型在稀疏视图CT重建中有良好前景。
- 直接应用扩散模型处理未经处理的数据会导致学习效率低下和图像细节缺失。
- 提出有序子集多扩散模型(OSMM)解决上述问题,将CT投影数据分成子集进行独立学习。
- OSMM采用多子集扩散模型(MSDM)降低学习复杂度并提升细节重建效果。
- 结合全扩散模型(OWDM)与完整辛恩格图数据作为全局信息约束。
- OSMM的无监督学习框架适应不同CT辛恩格图稀疏水平,表现稳定可靠。
点此查看论文截图

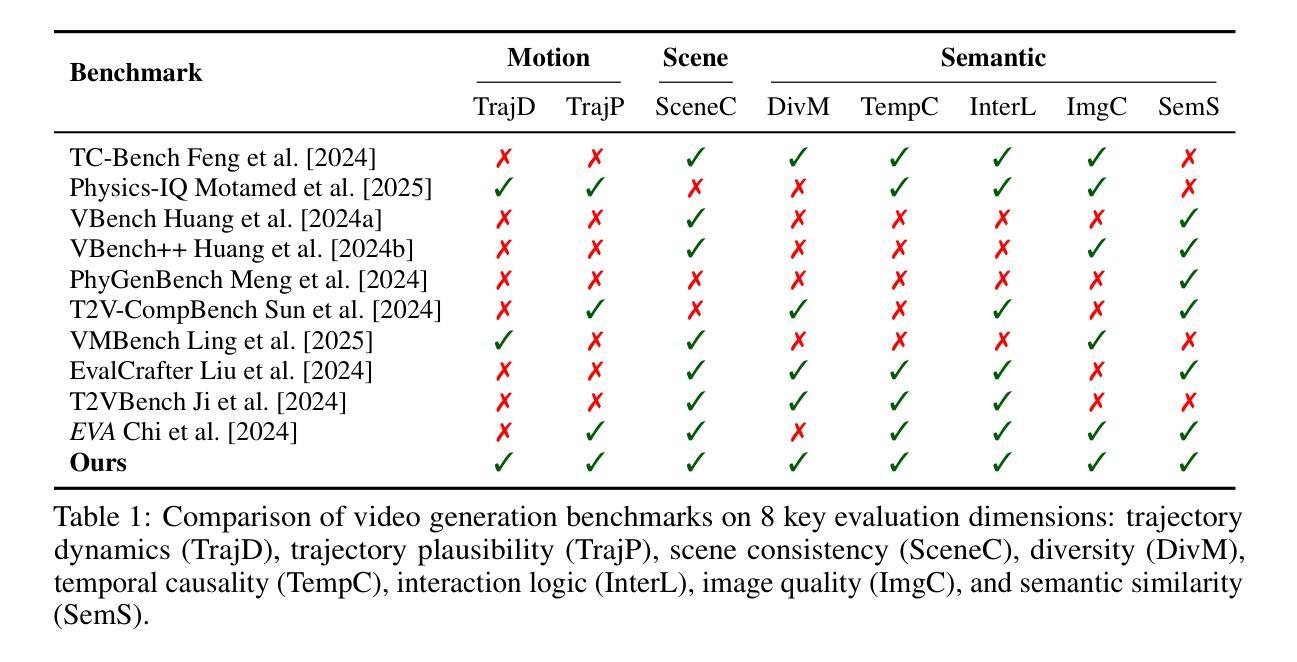
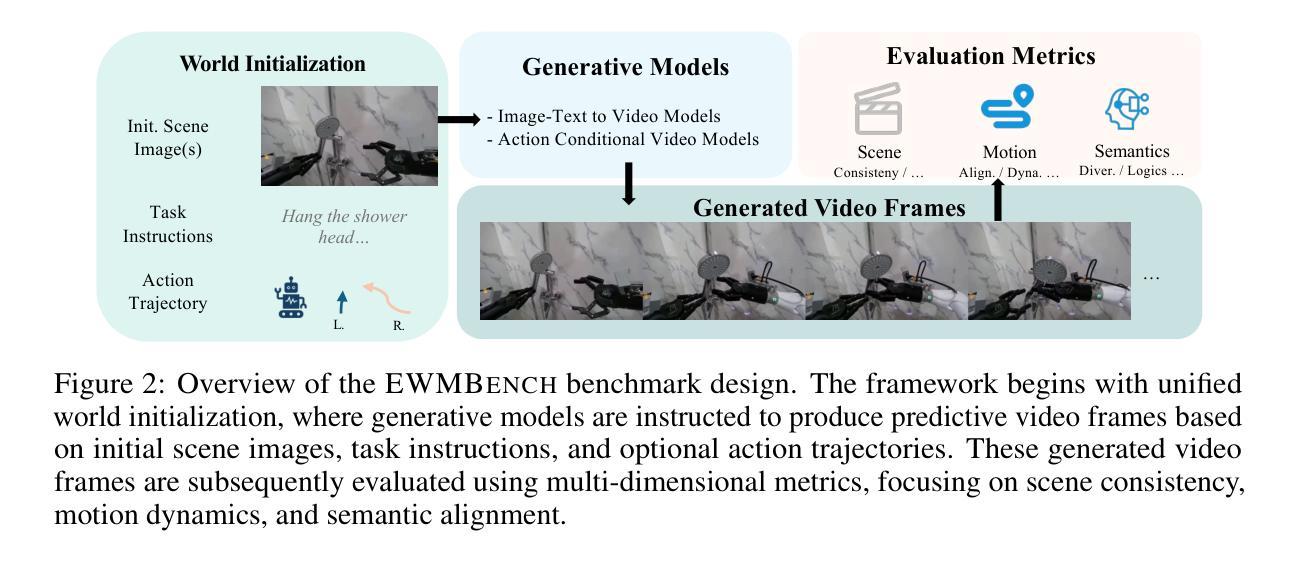
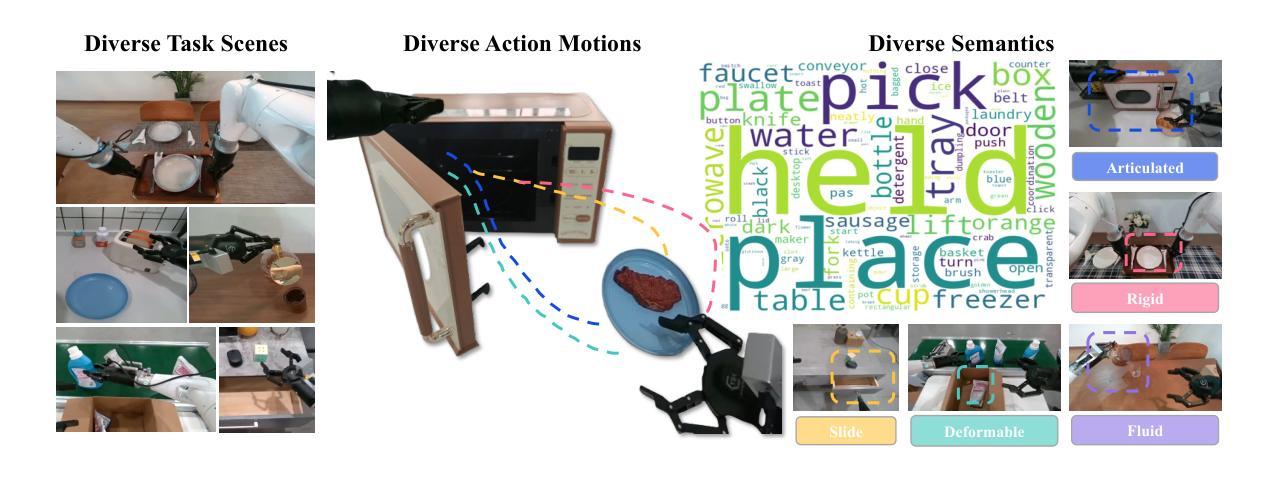
EWMBench: Evaluating Scene, Motion, and Semantic Quality in Embodied World Models
Authors:Hu Yue, Siyuan Huang, Yue Liao, Shengcong Chen, Pengfei Zhou, Liliang Chen, Maoqing Yao, Guanghui Ren
Recent advances in creative AI have enabled the synthesis of high-fidelity images and videos conditioned on language instructions. Building on these developments, text-to-video diffusion models have evolved into embodied world models (EWMs) capable of generating physically plausible scenes from language commands, effectively bridging vision and action in embodied AI applications. This work addresses the critical challenge of evaluating EWMs beyond general perceptual metrics to ensure the generation of physically grounded and action-consistent behaviors. We propose the Embodied World Model Benchmark (EWMBench), a dedicated framework designed to evaluate EWMs based on three key aspects: visual scene consistency, motion correctness, and semantic alignment. Our approach leverages a meticulously curated dataset encompassing diverse scenes and motion patterns, alongside a comprehensive multi-dimensional evaluation toolkit, to assess and compare candidate models. The proposed benchmark not only identifies the limitations of existing video generation models in meeting the unique requirements of embodied tasks but also provides valuable insights to guide future advancements in the field. The dataset and evaluation tools are publicly available at https://github.com/AgibotTech/EWMBench.
最近,创意人工智能的进展使得能够根据语言指令生成高保真图像和视频成为可能。在此基础上,文本到视频扩散模型已经演变为体世界模型(EWMs),能够从语言命令中生成物理上合理的场景,从而在实体人工智能应用中有效地实现视觉和行动的桥梁。本研究解决了评估EWMs的关键挑战,不仅限于一般的感知指标,以确保生成物理上可靠且行动一致的行为。我们提出了体世界模型基准测试(EWMBench),这是一个专门设计的框架,基于三个方面评估EWMs:视觉场景一致性、运动正确性和语义对齐。我们的方法利用精心挑选的数据集,涵盖各种场景和运动模式,以及全面的多维评估工具包,来评估和比较候选模型。所提出的基准测试不仅发现了现有视频生成模型在满足实体任务独特要求方面的局限性,而且为未来的领域发展提供了有价值的见解。数据集和评估工具可在https://github.com/AgibotTech/EWMBench公开访问。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Website: https://github.com/AgibotTech/EWMBench
Summary
本文介绍了创意AI的最新进展,特别是文本到视频扩散模型(Text-to-Video Diffusion Models)在生成物理上合理场景方面的能力。为解决评估这些模型在生成符合物理规律和行为一致性的挑战,提出了Embodied World Model Benchmark(EWMBench)评估框架。该框架基于视觉场景一致性、运动正确性和语义对齐三个关键方面来评估模型,并利用精心编制的包含多样场景和运动模式的数据集和全面的多维度评估工具包来评估和比较候选模型。该基准不仅揭示了现有视频生成模型在应对独特任务要求方面的局限性,而且为未来该领域的发展提供了宝贵见解。
Key Takeaways
- 文本到视频扩散模型已进化为体现世界模型(EWMs),能够从语言指令生成物理上合理的场景。
- EWMs在创意AI应用中实现了视觉和行为的桥梁。
- 评估EWMs的挑战在于确保生成内容的物理合理性和行为一致性。
- 提出Embodied World Model Benchmark(EWMBench)框架,基于视觉场景一致性、运动正确性和语义对齐三个关键方面来评估EWMs。
- EWMBench利用多样场景和运动模式的数据集和全面的多维度评估工具包。
- 现有视频生成模型在应对特定任务要求方面存在局限性。
点此查看论文截图

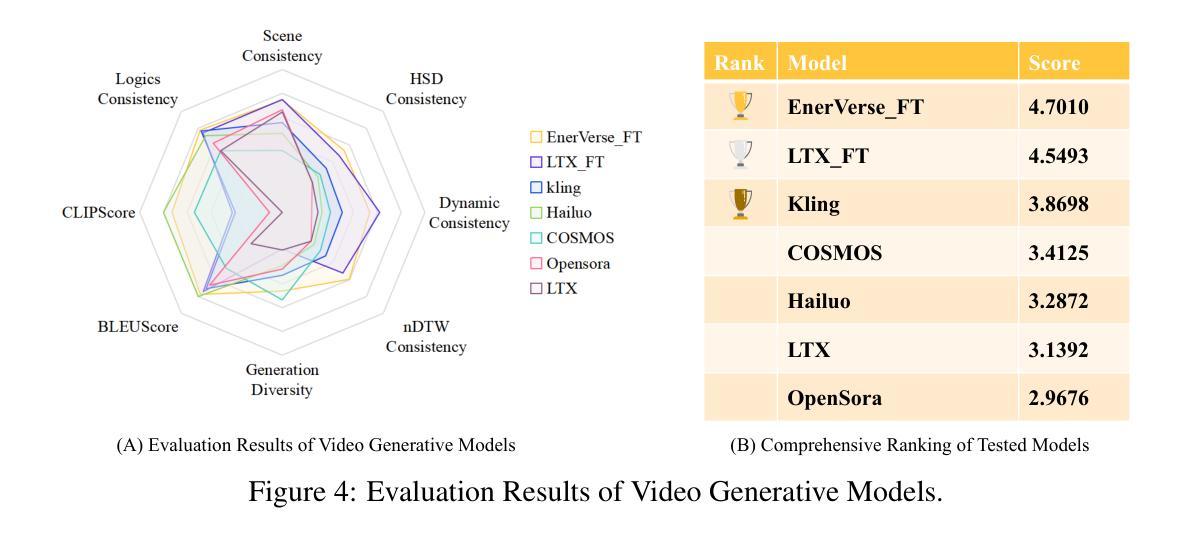
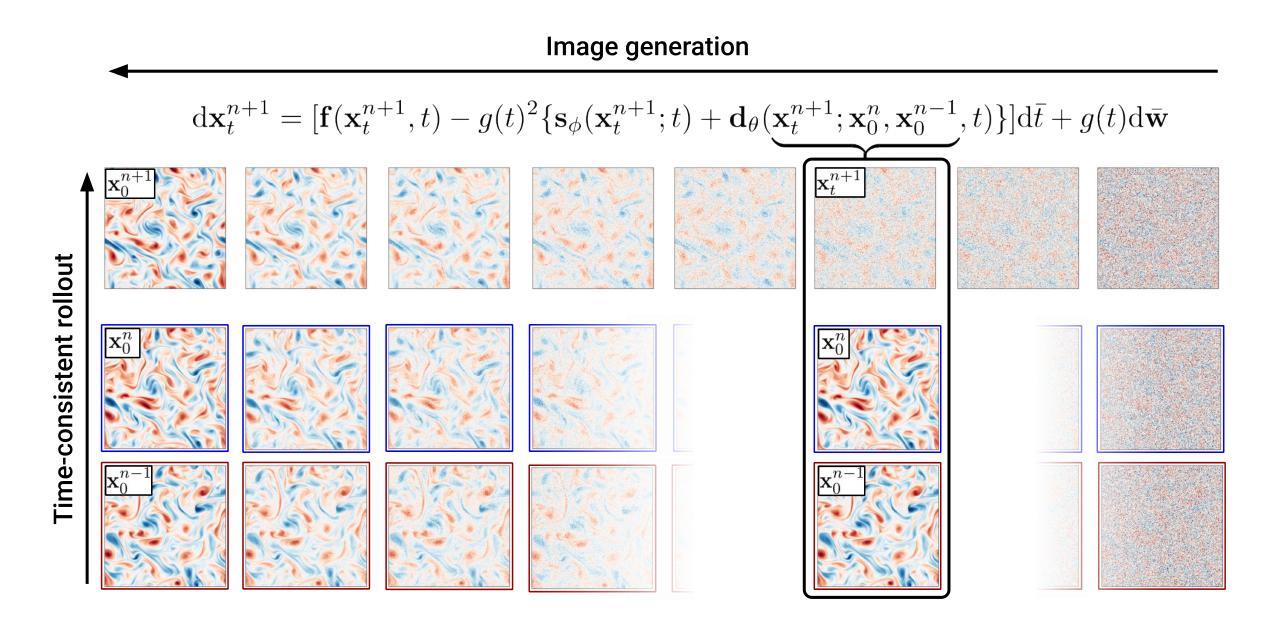
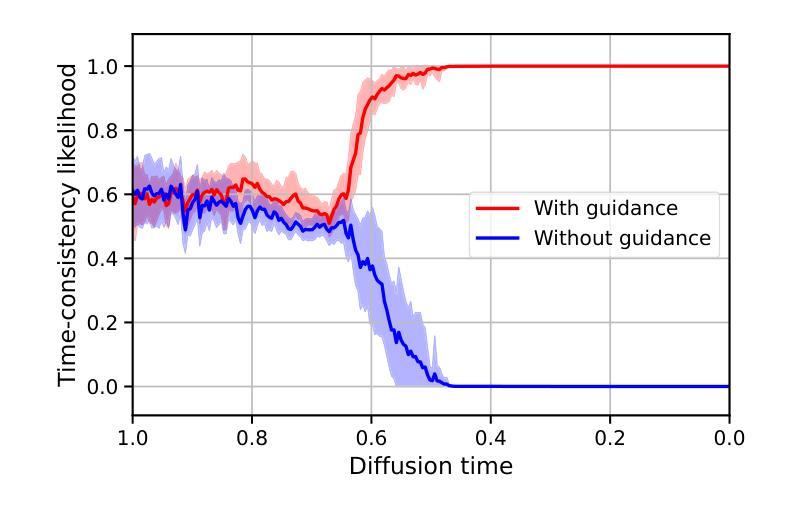
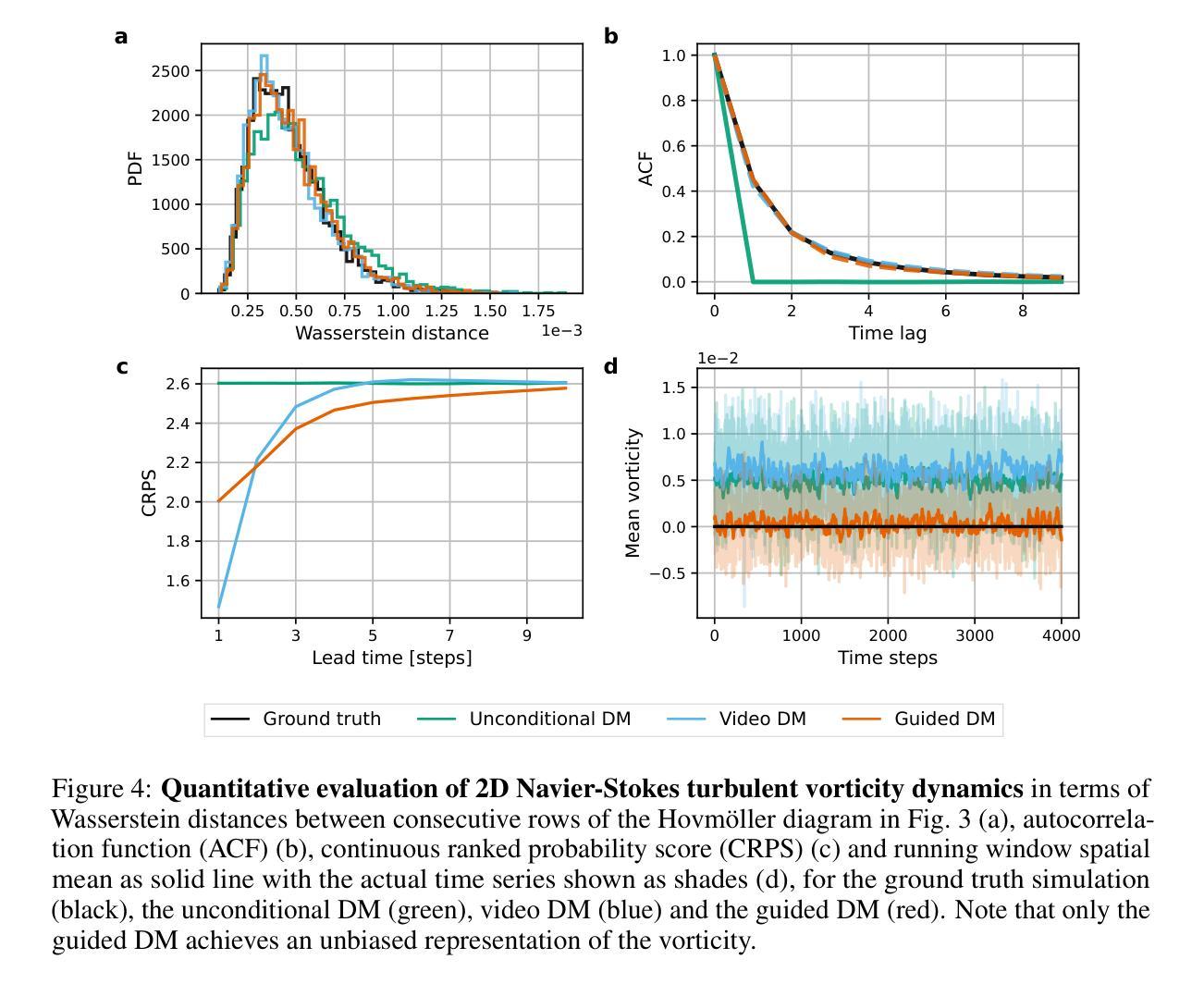
Generating time-consistent dynamics with discriminator-guided image diffusion models
Authors:Philipp Hess, Maximilian Gelbrecht, Christof Schötz, Michael Aich, Yu Huang, Shangshang Yang, Niklas Boers
Realistic temporal dynamics are crucial for many video generation, processing and modelling applications, e.g. in computational fluid dynamics, weather prediction, or long-term climate simulations. Video diffusion models (VDMs) are the current state-of-the-art method for generating highly realistic dynamics. However, training VDMs from scratch can be challenging and requires large computational resources, limiting their wider application. Here, we propose a time-consistency discriminator that enables pretrained image diffusion models to generate realistic spatiotemporal dynamics. The discriminator guides the sampling inference process and does not require extensions or finetuning of the image diffusion model. We compare our approach against a VDM trained from scratch on an idealized turbulence simulation and a real-world global precipitation dataset. Our approach performs equally well in terms of temporal consistency, shows improved uncertainty calibration and lower biases compared to the VDM, and achieves stable centennial-scale climate simulations at daily time steps.
对于许多视频生成、处理和建模应用(例如计算流体动力学、天气预报或长期气候模拟)来说,实现逼真的时间动态至关重要。视频扩散模型(VDM)是目前生成高度逼真动态的最先进方法。然而,从头开始训练VDM可能会面临挑战,并需要巨大的计算资源,这限制了其更广泛的应用。在这里,我们提出了一种时间一致性鉴别器,它可以让预训练的图像扩散模型生成逼真的时空动态。鉴别器引导采样推理过程,不需要扩展或微调图像扩散模型。我们将我们的方法与在理想化的湍流模拟和真实世界全球降水数据集上从头开始训练的VDM进行比较。我们的方法在时间一致性方面表现同样出色,与VDM相比,显示出改进的不确定性校准和更低的偏见,并以每日时间步长实现稳定的气候模拟(世纪规模)。
论文及项目相关链接
摘要
文章强调现实的时间动态对于视频生成、处理和建模应用的重要性,如计算流体动力学、天气预报或长期气候模拟等。视频扩散模型(VDMs)是目前生成高度现实动态的最先进方法,但其从头训练具有挑战性,需要大量计算资源,限制了其广泛应用。本文提出了一种时间一致性鉴别器,它能使预训练的图像扩散模型生成现实的时空动态。鉴别器引导采样推理过程,不需要图像扩散模型的扩展或微调。我们的方法与在理想化的湍流模拟和真实全球降水数据集上进行从头训练的VDM进行比较。我们的方法在时间一致性方面表现同样出色,显示出改进的不确定性校准和更低的偏见,且在每日时间步长下实现了稳定的气候模拟。
要点
- 现实的时间动态在视频生成、处理和建模应用中至关重要。
- 视频扩散模型(VDMs)是生成高度现实动态的最先进方法。
- 从头训练VDM具有挑战性,需要大量计算资源。
- 提出了一种时间一致性鉴别器,使预训练的图像扩散模型能生成现实的时空动态。
- 鉴别器引导采样推理过程,无需图像扩散模型的扩展或微调。
- 与VDM相比,我们的方法在时间一致性方面表现优秀,具有改进的不确定性校准和更低的偏见。
点此查看论文截图

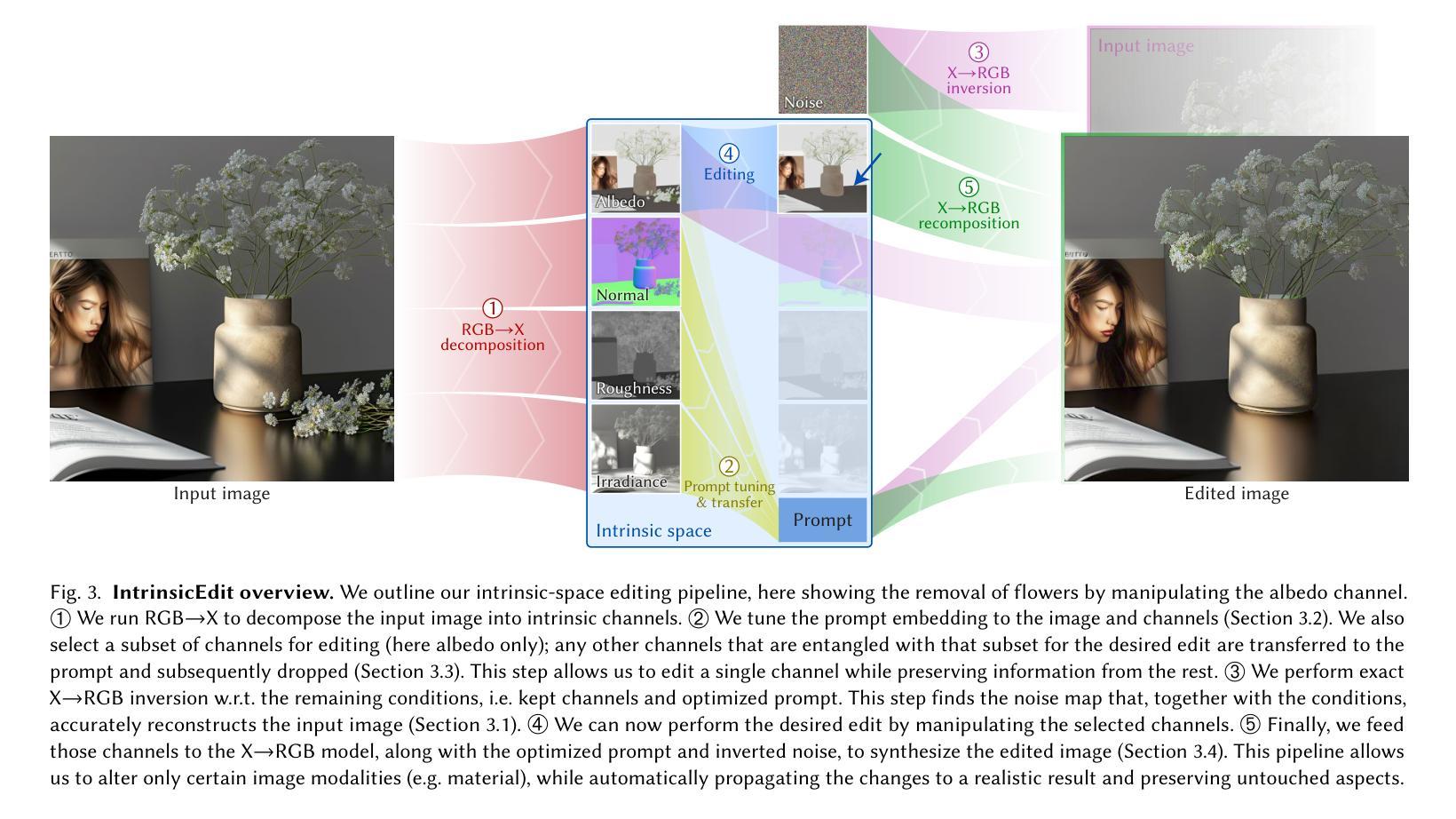
IntrinsicEdit: Precise generative image manipulation in intrinsic space
Authors:Linjie Lyu, Valentin Deschaintre, Yannick Hold-Geoffroy, Miloš Hašan, Jae Shin Yoon, Thomas Leimkühler, Christian Theobalt, Iliyan Georgiev
Generative diffusion models have advanced image editing with high-quality results and intuitive interfaces such as prompts and semantic drawing. However, these interfaces lack precise control, and the associated methods typically specialize on a single editing task. We introduce a versatile, generative workflow that operates in an intrinsic-image latent space, enabling semantic, local manipulation with pixel precision for a range of editing operations. Building atop the RGB-X diffusion framework, we address key challenges of identity preservation and intrinsic-channel entanglement. By incorporating exact diffusion inversion and disentangled channel manipulation, we enable precise, efficient editing with automatic resolution of global illumination effects – all without additional data collection or model fine-tuning. We demonstrate state-of-the-art performance across a variety of tasks on complex images, including color and texture adjustments, object insertion and removal, global relighting, and their combinations.
生成式扩散模型通过高质量结果和直观界面(如提示和语义绘图)推动了图像编辑的发展。然而,这些界面缺乏精确控制,相关方法通常专注于单一编辑任务。我们引入了一种通用、生成式工作流程,它在内在图像潜在空间中进行操作,能够对一系列编辑操作进行语义、局部操纵,具有像素精度。基于RGB-X扩散框架,我们解决了身份保留和内在通道纠缠的关键挑战。通过结合精确扩散反演和分离通道操纵,我们实现了精确、高效的编辑,自动解决全局照明效果问题——所有这一切无需额外收集数据或微调模型。我们在复杂图像的各种任务上展示了最先进的性能,包括颜色和纹理调整、对象插入和删除、全局重新照明及其组合。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF SIGGRAPH 2025 Journal track
Summary
本文介绍了基于RGB-X扩散框架的通用生成工作流程,该流程在内在图像潜在空间中进行操作,能够实现各种编辑操作的语义局部操纵,具有像素精度。通过引入精确扩散反转和分离通道操纵技术,解决了身份保留和内在通道纠缠的关键挑战,实现了复杂图像各种任务的卓越性能,包括颜色和纹理调整、对象插入和删除、全局重新照明及其组合。
Key Takeaways
- 生成性扩散模型在图像编辑方面取得了高质量结果,通过提示和语义绘图等直观界面进行操作。
- 现有界面缺乏精确控制,且相关方法通常专注于单个编辑任务。
- 引入了一种通用生成工作流程,在内在图像潜在空间中进行操作,实现多种编辑操作的语义局部操纵,具有像素精度。
- 基于RGB-X扩散框架,解决了身份保留和内在通道纠缠的关键挑战。
- 通过精确扩散反转和分离通道操纵,能够在不收集额外数据或微调模型的情况下,实现精确、高效的编辑,自动解决全局照明效果。
- 在复杂图像的各种任务上展示了卓越的性能,包括颜色和纹理调整、对象插入和删除、全局重新照明及其组合。
点此查看论文截图


Generative AI for Autonomous Driving: Frontiers and Opportunities
Authors:Yuping Wang, Shuo Xing, Cui Can, Renjie Li, Hongyuan Hua, Kexin Tian, Zhaobin Mo, Xiangbo Gao, Keshu Wu, Sulong Zhou, Hengxu You, Juntong Peng, Junge Zhang, Zehao Wang, Rui Song, Mingxuan Yan, Walter Zimmer, Xingcheng Zhou, Peiran Li, Zhaohan Lu, Chia-Ju Chen, Yue Huang, Ryan A. Rossi, Lichao Sun, Hongkai Yu, Zhiwen Fan, Frank Hao Yang, Yuhao Kang, Ross Greer, Chenxi Liu, Eun Hak Lee, Xuan Di, Xinyue Ye, Liu Ren, Alois Knoll, Xiaopeng Li, Shuiwang Ji, Masayoshi Tomizuka, Marco Pavone, Tianbao Yang, Jing Du, Ming-Hsuan Yang, Hua Wei, Ziran Wang, Yang Zhou, Jiachen Li, Zhengzhong Tu
Generative Artificial Intelligence (GenAI) constitutes a transformative technological wave that reconfigures industries through its unparalleled capabilities for content creation, reasoning, planning, and multimodal understanding. This revolutionary force offers the most promising path yet toward solving one of engineering’s grandest challenges: achieving reliable, fully autonomous driving, particularly the pursuit of Level 5 autonomy. This survey delivers a comprehensive and critical synthesis of the emerging role of GenAI across the autonomous driving stack. We begin by distilling the principles and trade-offs of modern generative modeling, encompassing VAEs, GANs, Diffusion Models, and Large Language Models (LLMs). We then map their frontier applications in image, LiDAR, trajectory, occupancy, video generation as well as LLM-guided reasoning and decision making. We categorize practical applications, such as synthetic data workflows, end-to-end driving strategies, high-fidelity digital twin systems, smart transportation networks, and cross-domain transfer to embodied AI. We identify key obstacles and possibilities such as comprehensive generalization across rare cases, evaluation and safety checks, budget-limited implementation, regulatory compliance, ethical concerns, and environmental effects, while proposing research plans across theoretical assurances, trust metrics, transport integration, and socio-technical influence. By unifying these threads, the survey provides a forward-looking reference for researchers, engineers, and policymakers navigating the convergence of generative AI and advanced autonomous mobility. An actively maintained repository of cited works is available at https://github.com/taco-group/GenAI4AD.
生成式人工智能(GenAI)构成了一场变革性的技术浪潮,它通过无与伦比的内容创建、推理、规划和多模式理解能力,重新配置各行业。这股革命力量为解决工程领域最宏伟的挑战之一——实现可靠、全自动的自动驾驶,特别是追求实现第五级自主驾驶,提供了最有希望的途径。这篇综述全面深入地探讨了GenAI在自动驾驶堆栈中的新兴角色。我们首先提炼了现代生成建模的原理和权衡,包括变分自编码器、生成对抗网络、扩散模型和大语言模型。然后,我们将这些前沿技术应用于图像、激光雷达、轨迹、占用、视频生成以及大语言模型引导的推理和决策制定。我们分类了实际应用,如合成数据流、端到端驾驶策略、高保真数字孪生系统、智能交通网络和跨域转移到实体人工智能等。我们确定了关键障碍和可能性,如全面概括罕见情况、评估和安全检查、预算有限的实现、法规合规、道德关注和环境影响,同时就理论保证、信任指标、交通集成和社会技术影响提出研究计划。通过统一这些线索,这篇综述为研究人员、工程师和政策制定者在生成式人工智能和先进的自动驾驶技术融合方面提供了前瞻性的参考。所引用的作品的一个活跃维护仓库可在https://github.com/taco-group/GenAI4AD找到。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
生成式人工智能(GenAI)重构行业的技术浪潮正兴起,凭借其强大的内容创作、推理、规划和多模态理解能力,为实现可靠的自动驾驶带来最有希望的路径。本文综述了GenAI在自动驾驶领域的新兴角色,介绍了现代生成模型的原则和权衡,包括变分自编码器、生成对抗网络、扩散模型和大语言模型,并探讨了它们在图像、激光雷达、轨迹、占用、视频生成以及大语言模型引导的推理和决策制定等前沿应用。同时,本文还总结了关键障碍和可能性,并提出了理论保证、信任指标、运输整合和社会技术影响等方面的研究计划。本文旨在为研究人员、工程师和政策制定者提供前瞻性参考。
Key Takeaways
- 生成式人工智能(GenAI)成为变革性技术,具备内容创建、推理、规划和多模态理解能力。
- GenAI在自动驾驶领域具有新兴和重要的角色,涵盖多个技术层面。
- 现代生成模型的原则和权衡,包括VAEs、GANs、Diffusion Models和LLMs的介绍。
- GenAI在图像、LiDAR、轨迹、占用、视频生成等前沿应用中的实际应用。
- LLMs在推理和决策制定中的引导角色。
- 实现自动驾驶的关键障碍包括全面概括罕见情况、评估和安全检查、预算有限的实施、法规合规、道德关切和环境影响。
点此查看论文截图

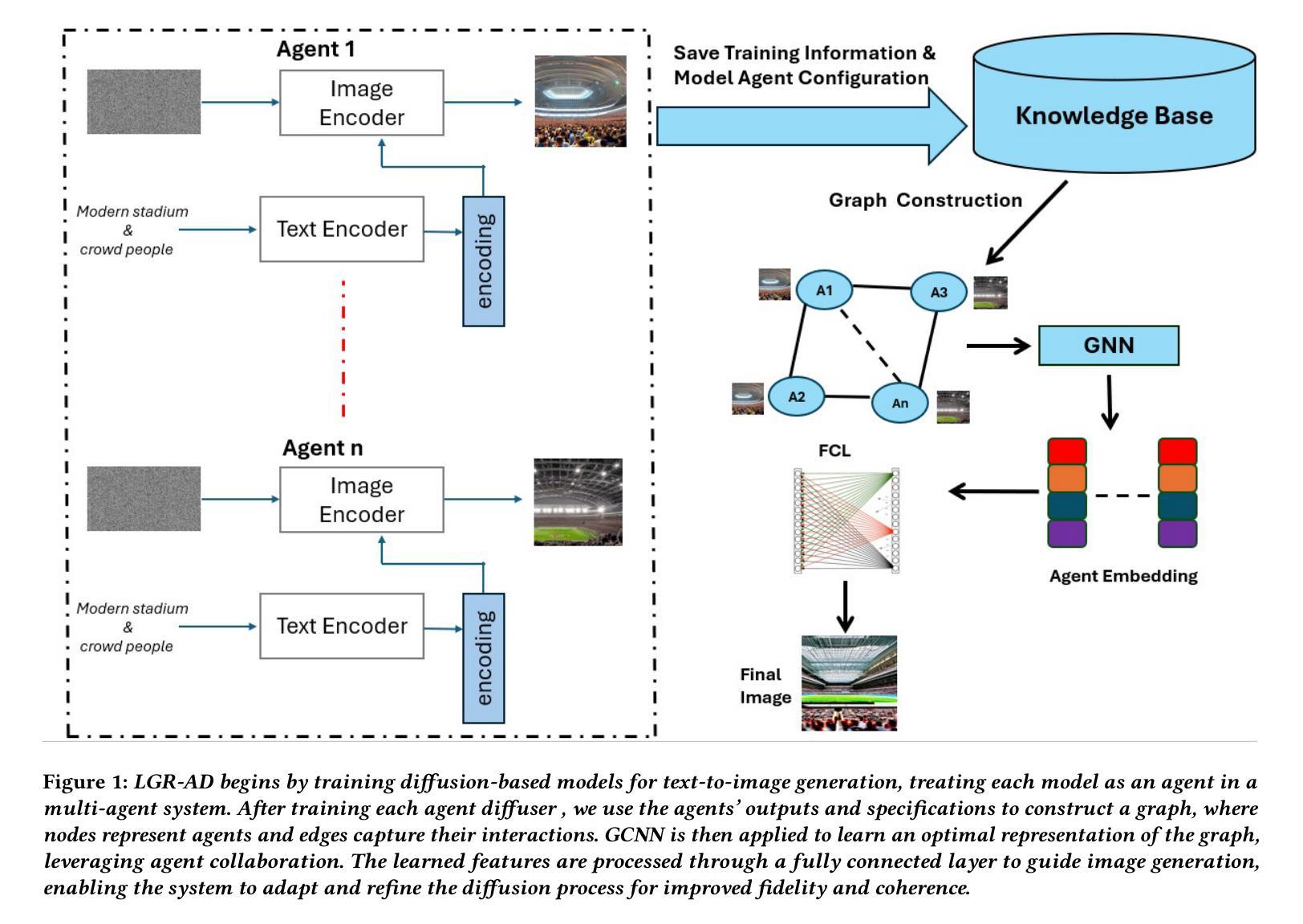
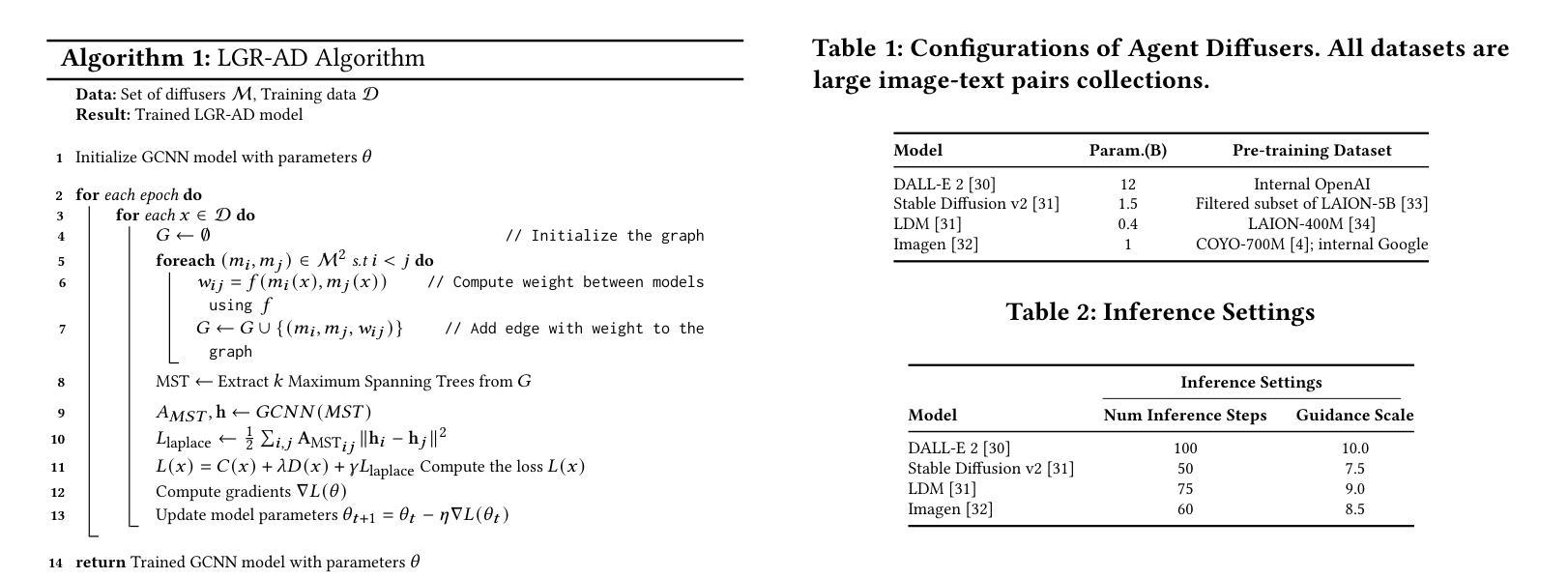
Learning Graph Representation of Agent Diffusers
Authors:Youcef Djenouri, Nassim Belmecheri, Tomasz Michalak, Jan Dubiński, Ahmed Nabil Belbachir, Anis Yazidi
Diffusion-based generative models have significantly advanced text-to-image synthesis, demonstrating impressive text comprehension and zero-shot generalization. These models refine images from random noise based on textual prompts, with initial reliance on text input shifting towards enhanced visual fidelity over time. This transition suggests that static model parameters might not optimally address the distinct phases of generation. We introduce LGR-AD (Learning Graph Representation of Agent Diffusers), a novel multi-agent system designed to improve adaptability in dynamic computer vision tasks. LGR-AD models the generation process as a distributed system of interacting agents, each representing an expert sub-model. These agents dynamically adapt to varying conditions and collaborate through a graph neural network that encodes their relationships and performance metrics. Our approach employs a coordination mechanism based on top-$k$ maximum spanning trees, optimizing the generation process. Each agent’s decision-making is guided by a meta-model that minimizes a novel loss function, balancing accuracy and diversity. Theoretical analysis and extensive empirical evaluations show that LGR-AD outperforms traditional diffusion models across various benchmarks, highlighting its potential for scalable and flexible solutions in complex image generation tasks. Code is available at: https://github.com/YousIA/LGR_AD
基于扩散的生成模型在文本到图像合成方面取得了显著的进步,展示了令人印象深刻的文本理解和零样本泛化能力。这些模型根据文本提示从随机噪声中细化图像,最初依赖文本输入,随着时间的推移,对视觉逼真度的要求逐渐增强。这种转变表明,静态模型参数可能无法最佳地应对生成的不同阶段。我们引入了LGR-AD(学习代理扩散图表示),这是一个新型的多代理系统,旨在提高动态计算机视觉任务的适应性。LGR-AD将生成过程建模为相互作用的代理的分布式系统,每个代理代表一个专家子模型。这些代理能够动态适应各种条件,并通过编码其关系和性能指标的图神经网络进行协作。我们的方法采用基于top-k最大生成树的协调机制,优化生成过程。每个代理的决策由元模型指导,该模型最小化新型损失函数,在准确性和多样性之间取得平衡。理论分析和广泛的实证研究均表明,在各种基准测试中,LGR-AD超越了传统扩散模型,凸显其在复杂图像生成任务中可扩展和灵活解决方案的潜力。代码可通过以下链接获取:https://github.com/YousIA/LGR_AD
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted at AAMAS2025 International Conference on Autonomous Agents and Multiagent Systems
Summary
文本介绍了基于扩散的生成模型在文本到图像合成方面的重大进展,它们能够根据文本提示从随机噪声中优化图像。为改善动态计算机视觉任务的适应性,提出了一种新型多智能体系统LGR-AD。LGR-AD将生成过程建模为智能体间的交互系统,每个智能体代表一个专家子模型,通过图神经网络进行协作与适应。采用基于最大生成树的协调机制优化生成过程。理论分析和大量实验评估表明,LGR-AD在多种基准测试中优于传统扩散模型,展现出其在复杂图像生成任务中的可扩展性和灵活性潜力。
Key Takeaways
- 扩散模型在文本到图像合成中取得显著进展,具备出色的文本理解和零样本泛化能力。
- 静态模型参数可能无法最佳地处理生成的不同阶段。
- LGR-AD是一种新型多智能体系统,旨在改善动态计算机视觉任务的适应性。
- LGR-AD将生成过程建模为智能体间的交互系统,每个智能体代表一个专家子模型。
- 通过图神经网络编码智能体之间的关系和性能度量,实现智能体间的动态适应和协作。
- LGR-AD采用基于最大生成树的协调机制优化生成过程。
- LGR-AD在多种基准测试中表现优于传统扩散模型,展现出其在复杂图像生成任务中的潜力。
点此查看论文截图

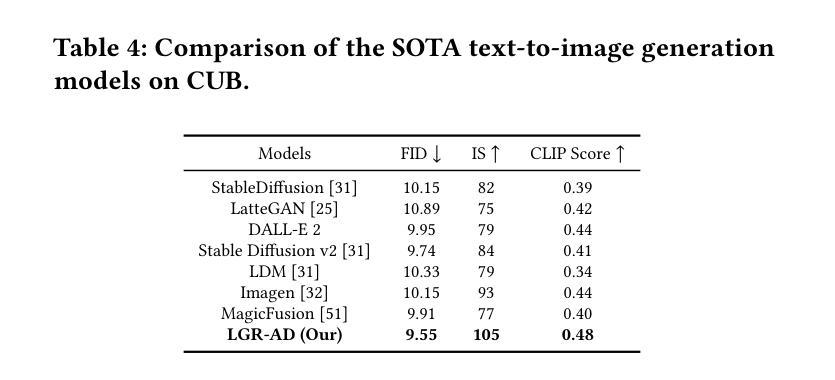
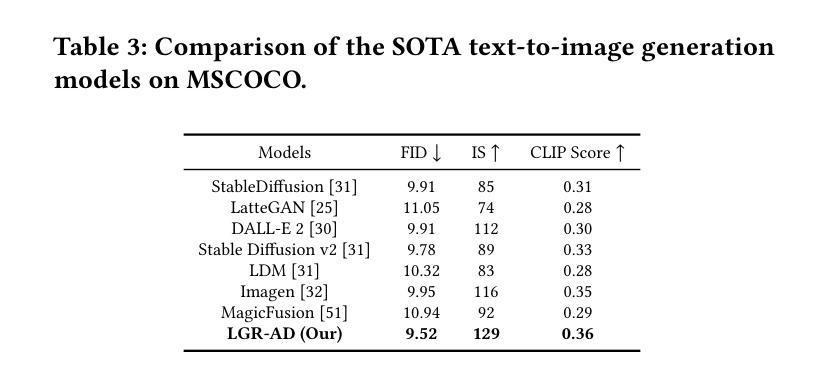
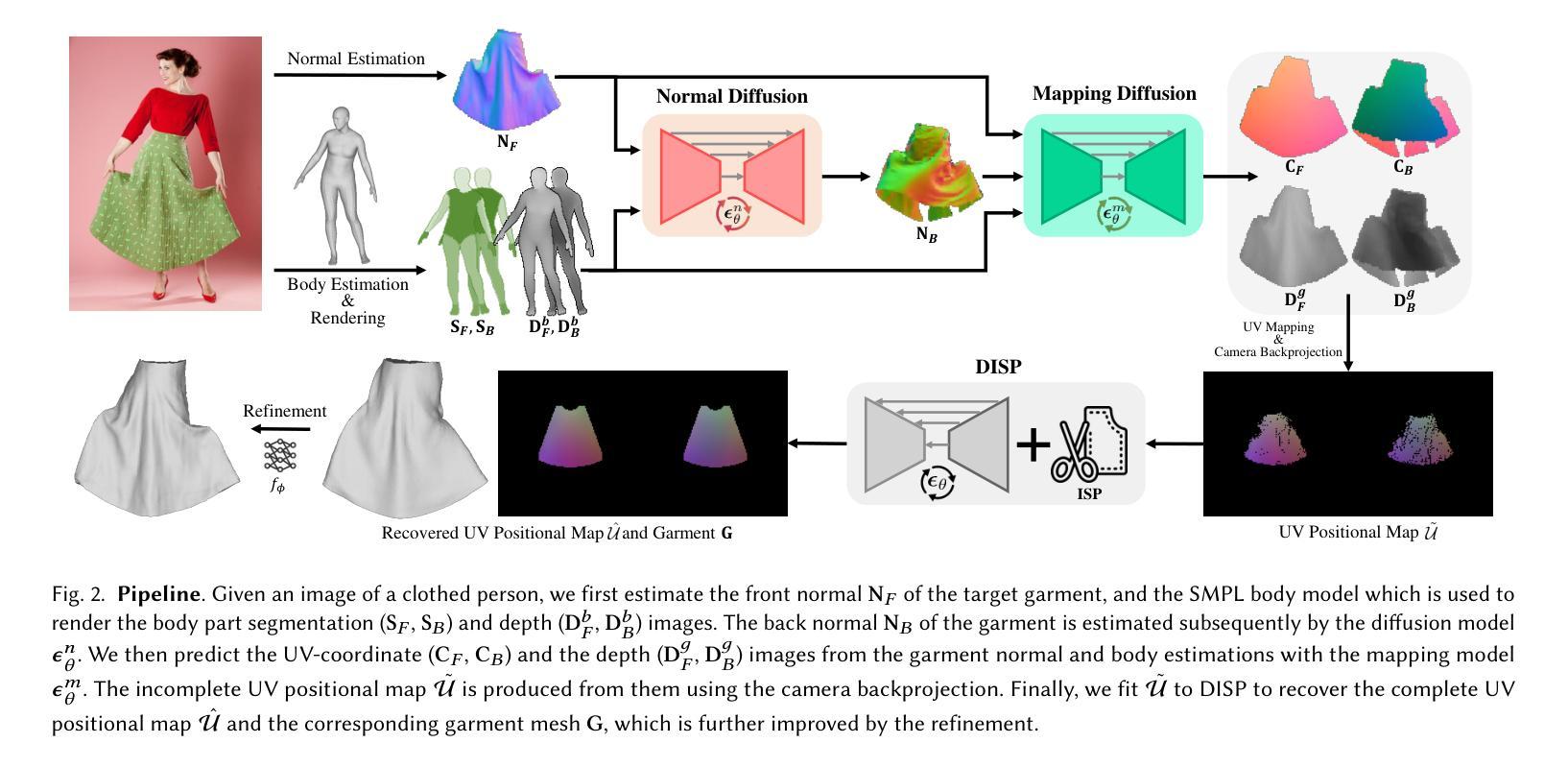
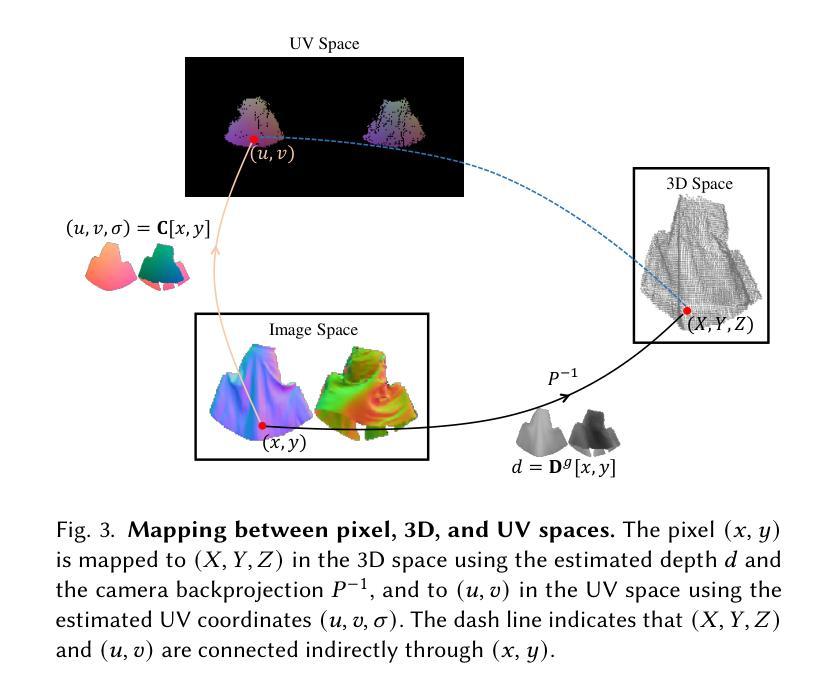
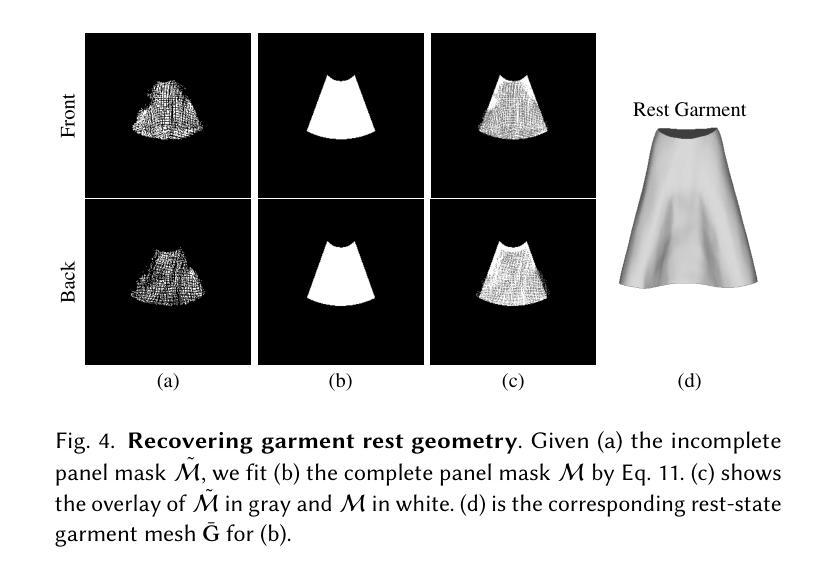
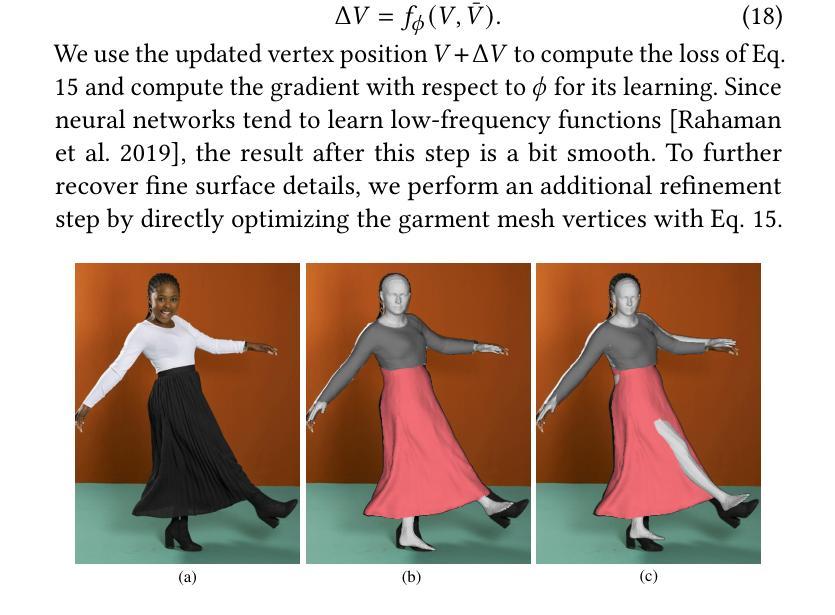
Single View Garment Reconstruction Using Diffusion Mapping Via Pattern Coordinates
Authors:Ren Li, Cong Cao, Corentin Dumery, Yingxuan You, Hao Li, Pascal Fua
Reconstructing 3D clothed humans from images is fundamental to applications like virtual try-on, avatar creation, and mixed reality. While recent advances have enhanced human body recovery, accurate reconstruction of garment geometry – especially for loose-fitting clothing – remains an open challenge. We present a novel method for high-fidelity 3D garment reconstruction from single images that bridges 2D and 3D representations. Our approach combines Implicit Sewing Patterns (ISP) with a generative diffusion model to learn rich garment shape priors in a 2D UV space. A key innovation is our mapping model that establishes correspondences between 2D image pixels, UV pattern coordinates, and 3D geometry, enabling joint optimization of both 3D garment meshes and the corresponding 2D patterns by aligning learned priors with image observations. Despite training exclusively on synthetically simulated cloth data, our method generalizes effectively to real-world images, outperforming existing approaches on both tight- and loose-fitting garments. The reconstructed garments maintain physical plausibility while capturing fine geometric details, enabling downstream applications including garment retargeting and texture manipulation.
从图像重建3D着装人体对于虚拟试穿、角色创建和混合现实等应用至关重要。虽然最近的进步增强了人体恢复能力,但衣物几何形状的精确重建——尤其是宽松衣物——仍然是一个待解决的难题。我们提出了一种从单幅图像进行高保真3D衣物重建的新方法,该方法结合了隐式缝纫模式(ISP)和生成扩散模型,在二维UV空间中学习丰富的衣物形状先验知识。我们的一个关键创新是映射模型,该模型建立了二维图像像素、UV模式坐标和三维几何之间的对应关系,通过优化图像观察和学习的先验知识,实现对三维衣物网格和相应二维模式的联合优化。尽管仅在合成模拟的织物数据进行训练,但我们的方法对于真实世界图像的推广效果很好,在紧身和宽松衣物上都优于现有方法。重建的衣物在保持物理合理性的同时捕捉了精细的几何细节,可实现下游应用,包括衣物重新定位和纹理操作。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF SIGGRAPH 2025
Summary
本文介绍了一种从单张图像进行高保真3D服装重建的新方法,该方法结合了隐式缝纫模式(ISP)和生成性扩散模型,在二维UV空间学习丰富的服装形状先验。通过建立二维图像像素、UV模式坐标和三维几何之间的对应关系,实现了对三维服装网格和相应二维模式的联合优化。尽管仅在合成模拟的布料数据上进行训练,但该方法在真实图像上的表现却非常出色,对于紧身和宽松服装的重建都有出色的表现。重建的服装既保持了物理上的可信度,又能捕捉精细的几何细节,为下游应用如服装重定向和纹理操作提供了可能。
Key Takeaways
- 文中提出了一种新的从单张图像进行高保真3D服装重建的方法。
- 结合了隐式缝纫模式(ISP)和生成性扩散模型,在二维UV空间学习服装形状先验。
- 建立了一种映射模型,实现了二维图像像素、UV模式坐标和三维几何之间的对应关系。
- 方法能够在真实图像上实现有效的重建,适用于紧身和宽松服装。
- 重建的服装保持了物理上的可信度,并能捕捉精细的几何细节。
- 该方法可为下游应用如服装重定向和纹理操作提供支持。
- 尽管只在合成模拟的布料数据上进行训练,但该方法具有很好的泛化性能。
点此查看论文截图

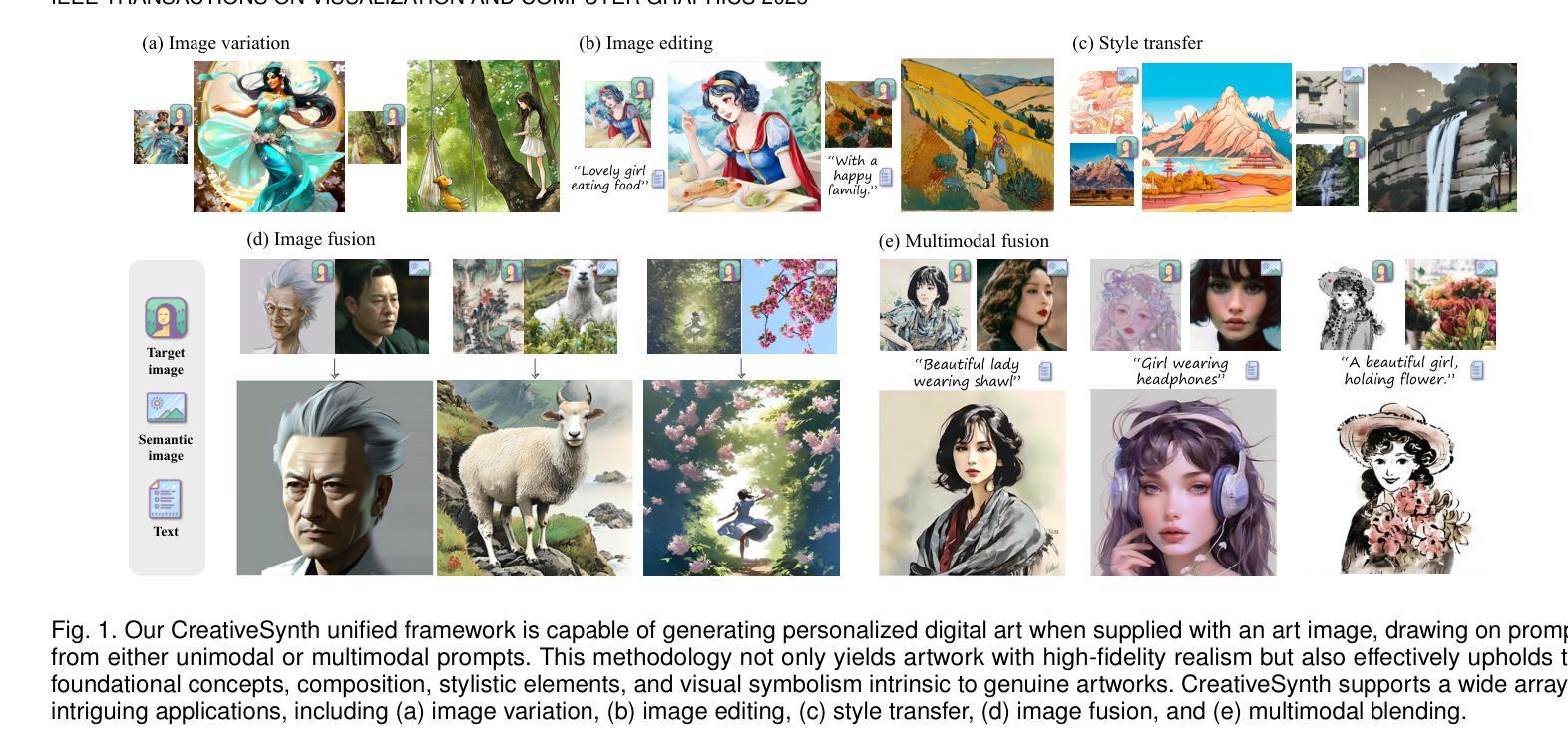
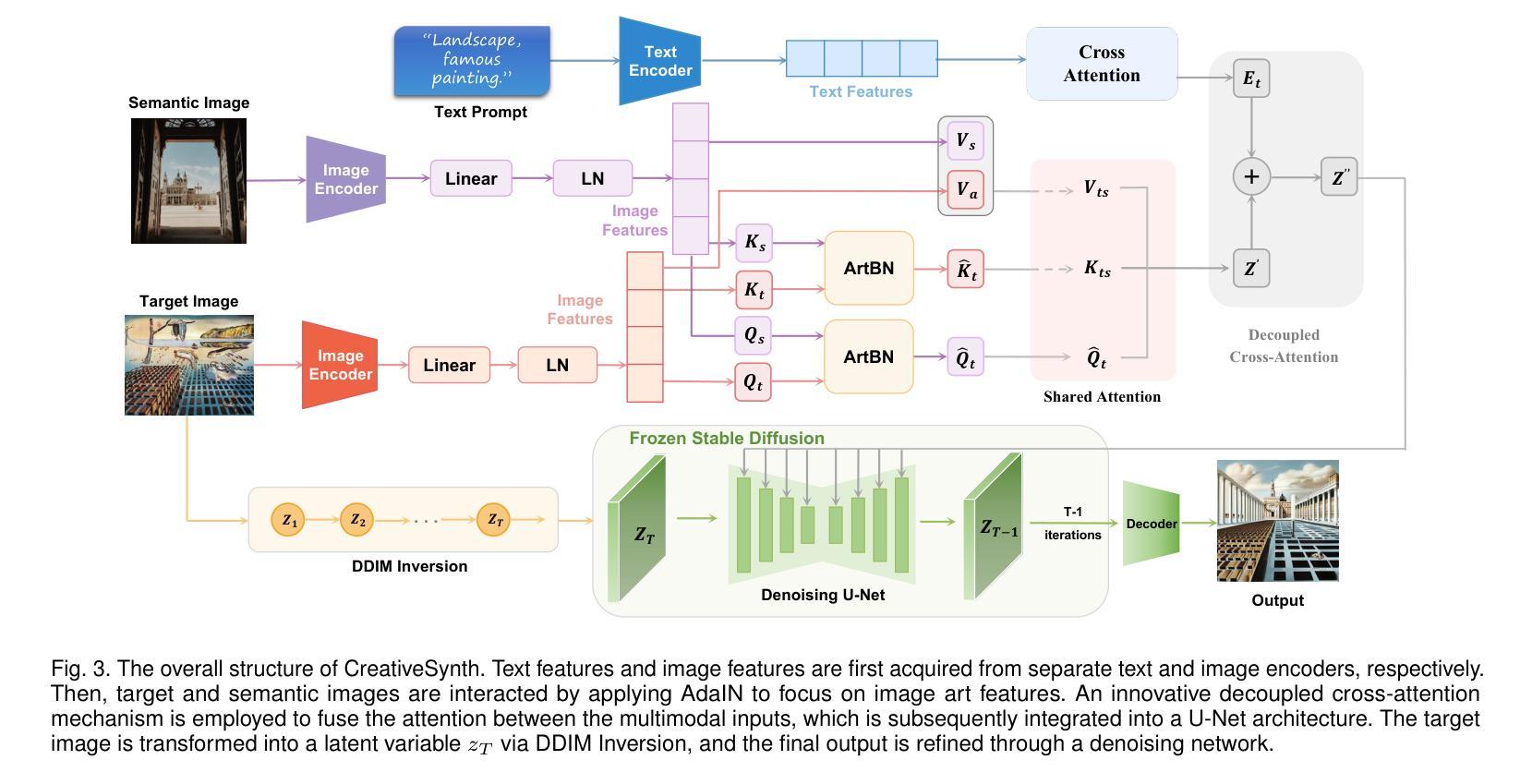
CreativeSynth: Cross-Art-Attention for Artistic Image Synthesis with Multimodal Diffusion
Authors:Nisha Huang, Weiming Dong, Yuxin Zhang, Fan Tang, Ronghui Li, Chongyang Ma, Xiu Li, Tong-Yee Lee, Changsheng Xu
Although remarkable progress has been made in image style transfer, style is just one of the components of artistic paintings. Directly transferring extracted style features to natural images often results in outputs with obvious synthetic traces. This is because key painting attributes including layout, perspective, shape, and semantics often cannot be conveyed and expressed through style transfer. Large-scale pretrained text-to-image generation models have demonstrated their capability to synthesize a vast amount of high-quality images. However, even with extensive textual descriptions, it is challenging to fully express the unique visual properties and details of paintings. Moreover, generic models often disrupt the overall artistic effect when modifying specific areas, making it more complicated to achieve a unified aesthetic in artworks. Our main novel idea is to integrate multimodal semantic information as a synthesis guide into artworks, rather than transferring style to the real world. We also aim to reduce the disruption to the harmony of artworks while simplifying the guidance conditions. Specifically, we propose an innovative multi-task unified framework called CreativeSynth, based on the diffusion model with the ability to coordinate multimodal inputs. CreativeSynth combines multimodal features with customized attention mechanisms to seamlessly integrate real-world semantic content into the art domain through Cross-Art-Attention for aesthetic maintenance and semantic fusion. We demonstrate the results of our method across a wide range of different art categories, proving that CreativeSynth bridges the gap between generative models and artistic expression. Code and results are available at https://github.com/haha-lisa/CreativeSynth.
虽然图像风格转换已经取得了显著的进展,但风格仅仅是艺术作品组件之一。直接将提取的风格特征转移到自然图像上,往往会导致输出结果带有明显的合成痕迹。这是因为布局、透视、形状和语义等关键绘画属性往往无法通过风格转换来传达和表达。大规模预训练的文本到图像生成模型已经证明了它们合成大量高质量图像的能力。然而,即使使用详细的文本描述,也很难充分表达绘画的独特视觉属性和细节。此外,通用模型在修改特定区域时往往会破坏整体的艺术效果,使艺术作品中实现统一美学更加复杂。我们的主要新思想是将多模态语义信息作为合成指南整合到艺术作品中,而不是将风格转移到现实世界。我们还旨在减少了对艺术作品和谐度的破坏,同时简化了指导条件。具体来说,我们提出了一种基于扩散模型、能够协调多模态输入的创新多任务统一框架,名为CreativeSynth。CreativeSynth结合多模态特征和自定义注意力机制,通过跨艺术注意力机制无缝整合现实世界语义内容到艺术领域,以维持审美和语义融合。我们的方法在广泛的不同艺术类别中得到了验证,证明了CreativeSynth在生成模型和艺术表达之间的桥梁作用。相关代码和结果可通过https://github.com/haha-lisa/CreativeSynth获取。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文提出一种基于扩散模型的多任务统一框架CreativeSynth,该框架结合跨艺术注意力的多模态语义信息,将现实世界语义内容无缝集成到艺术领域,旨在促进艺术作品的合成和美学维护。通过整合布局、透视、形状和语义等关键绘画属性,CreativeSynth在各类艺术类别中展现出强大的表现力,缩小了生成模型与艺术创作之间的差距。
Key Takeaways
- 当前图像风格转换存在合成痕迹明显的问题,因为关键绘画属性如布局、透视、形状和语义等难以通过风格转换表达。
- 大规模预训练文本到图像生成模型虽能合成高质量图像,但难以完全表达绘画的独特视觉属性和细节。
- 集成多模态语义信息作为合成指南,而非将风格转移到现实世界,有助于解决艺术效果中断和美学统一性问题。
- 提出的CreativeSynth框架基于扩散模型,能协调多模态输入,结合定制注意力机制和跨艺术注意力,实现语义融合和美学维护。
- CreativeSynth在多种艺术类别中展现出强大的表现力,有效缩小了生成模型与艺术创作之间的差距。
- CreativeSynth的方法和结果可通过在线代码库(https://github.com/haha-lisa/CreativeSynth)进行访问。
点此查看论文截图