⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-05-17 更新
Logos as a Well-Tempered Pre-train for Sign Language Recognition
Authors:Ilya Ovodov, Petr Surovtsev, Karina Kvanchiani, Alexander Kapitanov, Alexander Nagaev
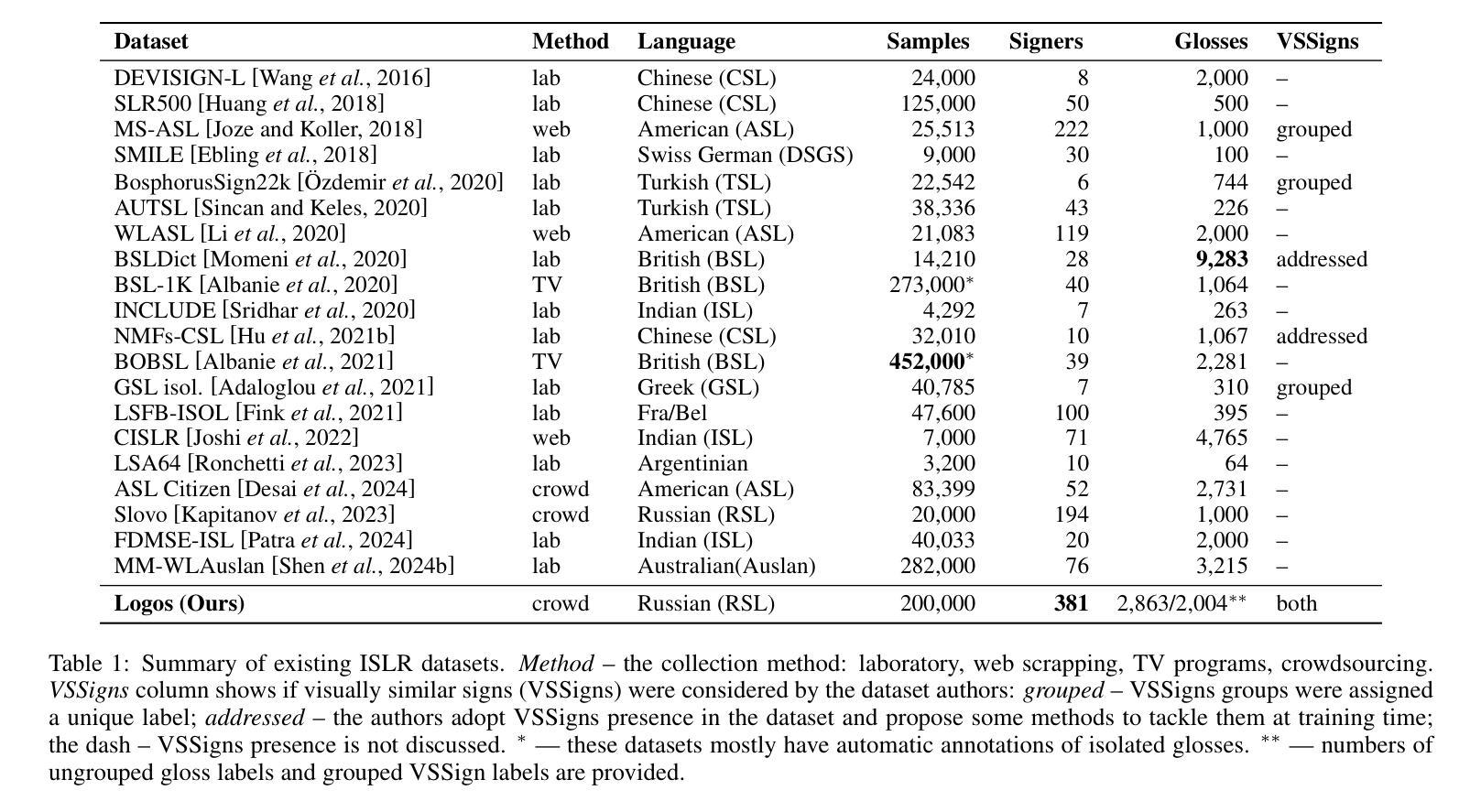
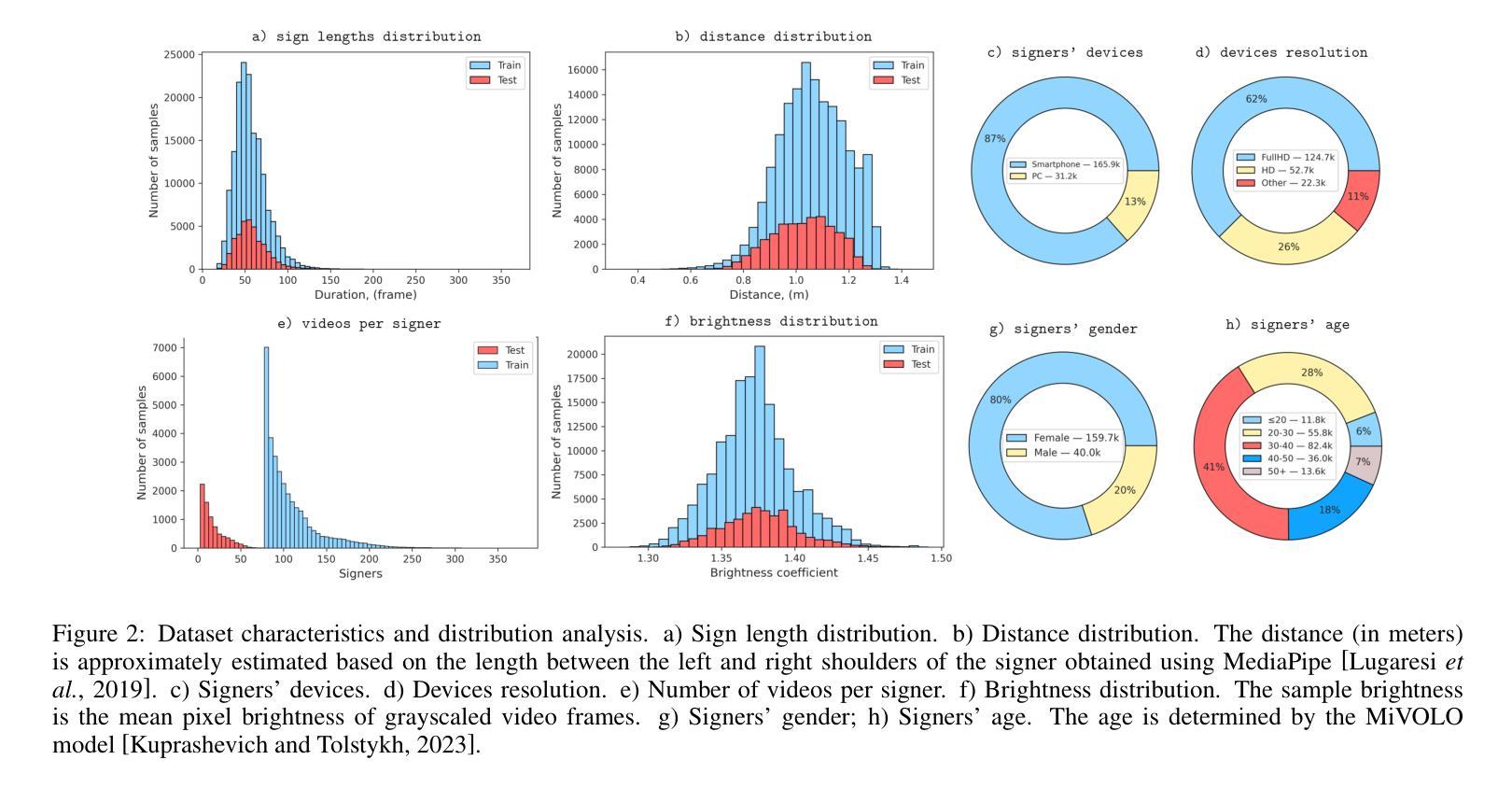
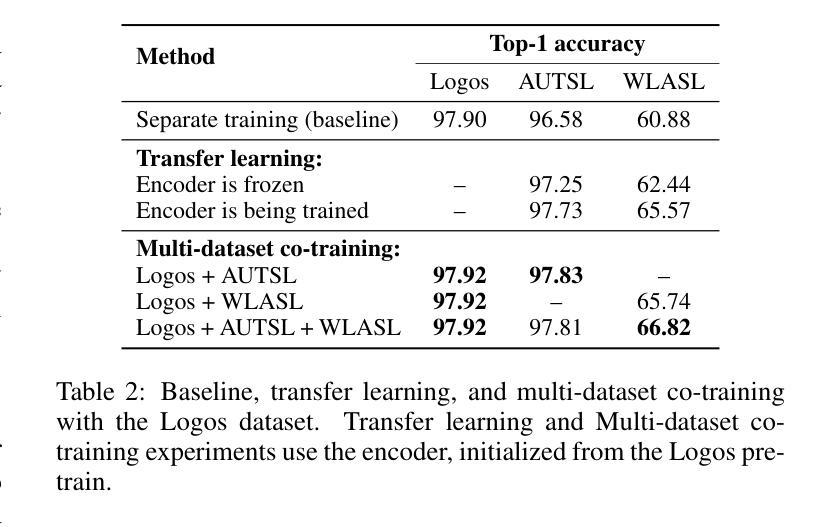
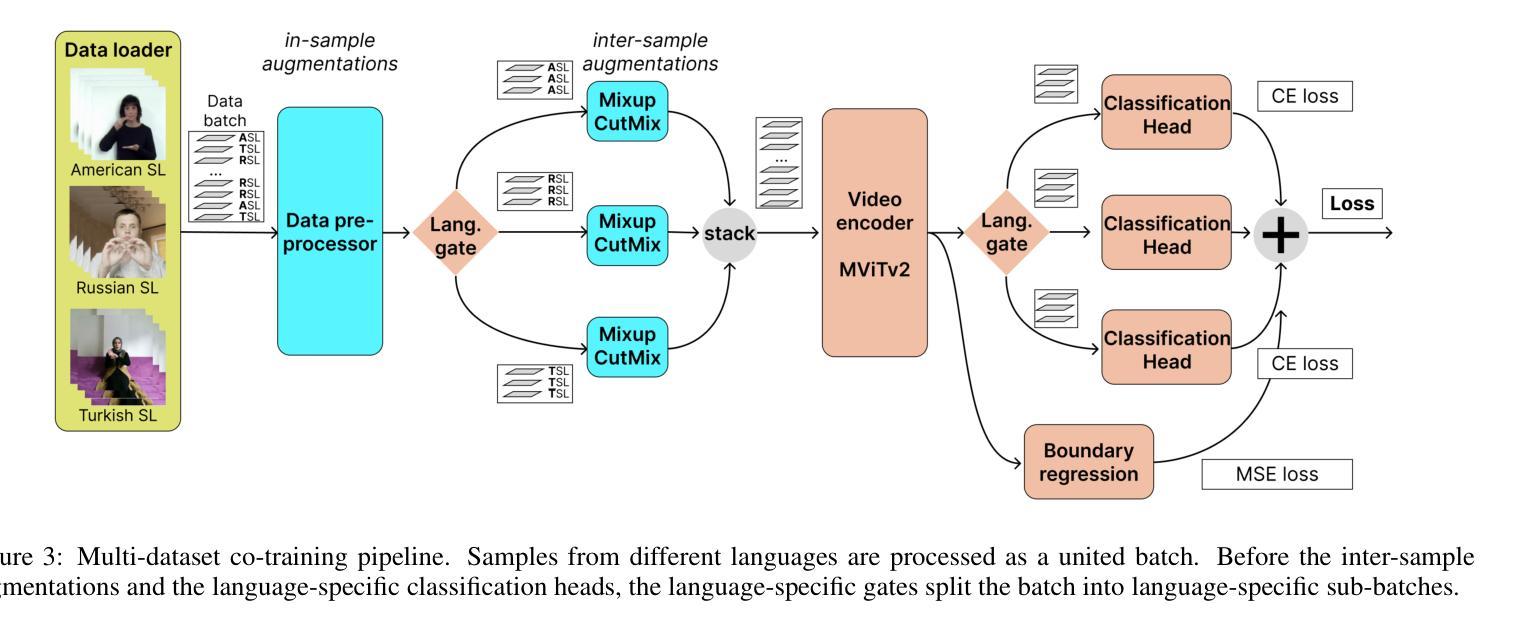
This paper examines two aspects of the isolated sign language recognition (ISLR) task. First, despite the availability of a number of datasets, the amount of data for most individual sign languages is limited. It poses the challenge of cross-language ISLR model training, including transfer learning. Second, similar signs can have different semantic meanings. It leads to ambiguity in dataset labeling and raises the question of the best policy for annotating such signs. To address these issues, this study presents Logos, a novel Russian Sign Language (RSL) dataset, the most extensive ISLR dataset by the number of signers and one of the largest available datasets while also the largest RSL dataset in size and vocabulary. It is shown that a model, pre-trained on the Logos dataset can be used as a universal encoder for other language SLR tasks, including few-shot learning. We explore cross-language transfer learning approaches and find that joint training using multiple classification heads benefits accuracy for the target lowresource datasets the most. The key feature of the Logos dataset is explicitly annotated visually similar sign groups. We show that explicitly labeling visually similar signs improves trained model quality as a visual encoder for downstream tasks. Based on the proposed contributions, we outperform current state-of-the-art results for the WLASL dataset and get competitive results for the AUTSL dataset, with a single stream model processing solely RGB video. The source code, dataset, and pre-trained models are publicly available.
本文探讨了孤立手语识别(ISLR)任务的两个方面。首先,尽管有许多数据集可用,但大多数个别手语的数据量是有限的。这提出了跨语言ISLR模型训练的挑战,包括迁移学习。其次,相似的符号可能有不同的语义。这导致了数据集标签的模糊性,并引发了标注此类符号的最佳策略的问题。为了解决这些问题,本研究提出了Logos,这是一个新的俄罗斯手语(RSL)数据集,它是按签约人数计算的最广泛的ISLR数据集之一,也是可用数据中规模最大的数据集之一,同时在大小和词汇量方面也是最大的RSL数据集。研究表明,在Logos数据集上预训练的模型可以用作其他语言SLR任务(包括小样学习)的通用编码器。我们探索了跨语言迁移学习方法,发现使用多个分类头进行联合训练最有利于目标低资源数据集的准确性。Logo数据集的关键特点是明确注释了视觉上相似的符号组。我们证明,明确标注视觉上相似的符号作为下游任务的视觉编码器可以提高训练模型的质量。基于所提出的贡献,我们在WLASL数据集上取得了最先进的性能,并在使用仅处理RGB视频的单流模型的情况下,为AUTSL数据集获得了具有竞争力的结果。源代码、数据集和预训练模型均可公开获得。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文探讨了孤立手语识别(ISLR)任务的两个方面。首先,虽然存在许多数据集,但大多数个别手语的数据量有限,这带来了跨语言ISLR模型训练的挑战,包括迁移学习。其次,相似的手势可能有不同的语义含义,这导致了数据集标签的模糊性,并引发了如何标注此类手势的最佳策略问题。为解决这些问题,本文提出了Logos,一个新型俄罗斯手语(RSL)数据集,它是按签名者数量而言最全面的ISLR数据集之一,也是目前可用的大型数据集之一,同时在大小和词汇量方面也是最大的RSL数据集。研究表明,预训练在Logos数据集上的模型可作为其他语言SLR任务(包括小样学习)的通用编码器使用。本研究探讨了跨语言迁移学习方法,发现使用多个分类头进行联合训练最有利于目标低资源数据集的准确性。Logos数据集的关键特点是显式注释的视觉相似符号组。研究结果表明,显式标注视觉相似的符号作为下游任务的视觉编码器可以提高训练模型的质量。基于所提出的贡献,我们在WLASL数据集上超越了当前最先进的成果,对于仅处理RGB视频的AUTSL数据集也获得了有竞争力的结果。
Key Takeaways
- 孤立手语识别(ISLR)面临数据限制和跨语言模型训练挑战。
- Logos数据集是俄罗斯手语(RSL)最大的数据集,包含大量签名者和词汇。
- 预训练在Logos数据集上的模型可作为其他语言SLR任务的通用编码器。
- 跨语言迁移学习方法中,联合训练使用多个分类头能显著提高目标低资源数据集的准确性。
- Logos数据集显式标注视觉相似符号组,这有助于提高训练模型的质量。
- 该研究在WLASL数据集上表现优于现有技术,并在AUTSL数据集上取得有竞争力的结果。
点此查看论文截图

Comparing LLM Text Annotation Skills: A Study on Human Rights Violations in Social Media Data
Authors:Poli Apollinaire Nemkova, Solomon Ubani, Mark V. Albert
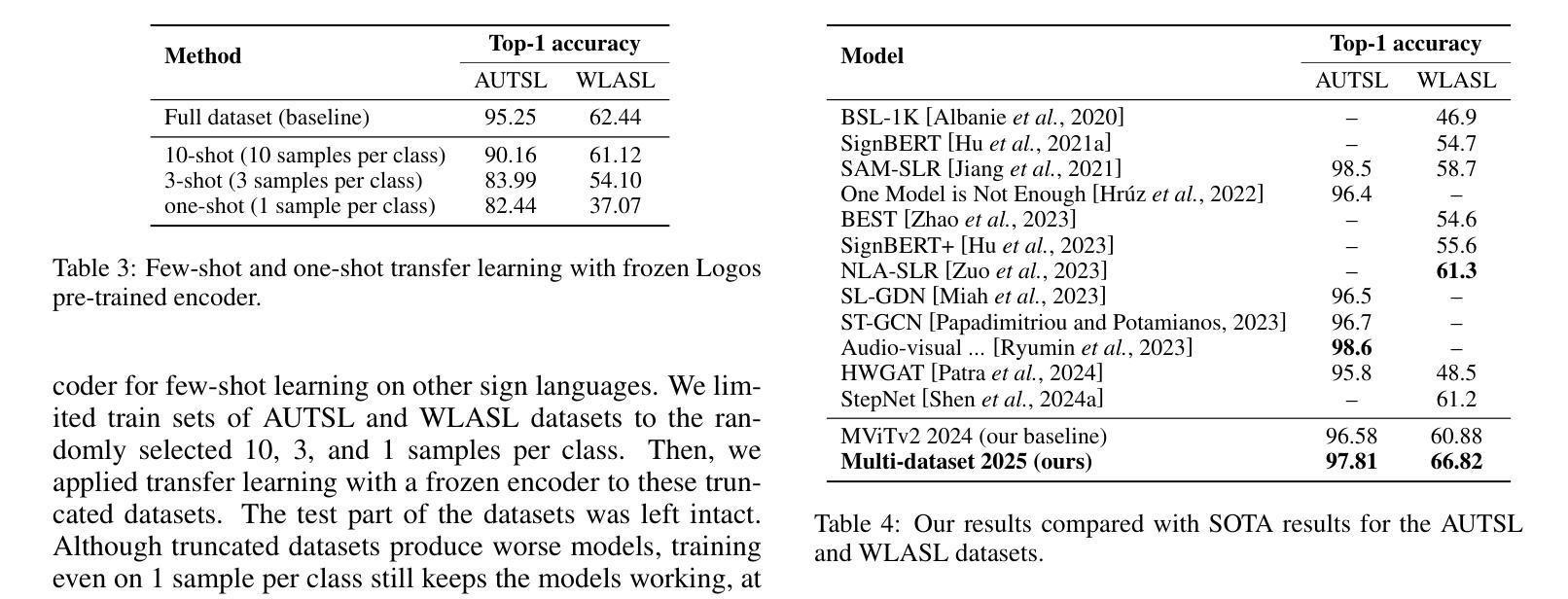
In the era of increasingly sophisticated natural language processing (NLP) systems, large language models (LLMs) have demonstrated remarkable potential for diverse applications, including tasks requiring nuanced textual understanding and contextual reasoning. This study investigates the capabilities of multiple state-of-the-art LLMs - GPT-3.5, GPT-4, LLAMA3, Mistral 7B, and Claude-2 - for zero-shot and few-shot annotation of a complex textual dataset comprising social media posts in Russian and Ukrainian. Specifically, the focus is on the binary classification task of identifying references to human rights violations within the dataset. To evaluate the effectiveness of these models, their annotations are compared against a gold standard set of human double-annotated labels across 1000 samples. The analysis includes assessing annotation performance under different prompting conditions, with prompts provided in both English and Russian. Additionally, the study explores the unique patterns of errors and disagreements exhibited by each model, offering insights into their strengths, limitations, and cross-linguistic adaptability. By juxtaposing LLM outputs with human annotations, this research contributes to understanding the reliability and applicability of LLMs for sensitive, domain-specific tasks in multilingual contexts. It also sheds light on how language models handle inherently subjective and context-dependent judgments, a critical consideration for their deployment in real-world scenarios.
随着自然语言处理(NLP)系统的日益成熟,大型语言模型(LLM)在各种应用中展现出巨大的潜力,包括需要微妙文本理解和上下文推理的任务。本研究旨在探讨多款先进的大型语言模型——GPT-3.5、GPT-4、LLAMA3、Mistral 7B和Claude-2在零样本和少样本注释复杂文本数据集方面的能力,该数据集包含俄语和乌克兰语的社会媒体帖子。具体来说,关注的是数据集中识别侵犯人权参考的二元分类任务。为了评估这些模型的性能,它们的注释与基于1000个样本的人类双重注释标签的黄金标准集进行了比较。分析包括在不同提示条件下评估注释性能,提示以英语和俄语两种语言提供。此外,该研究还探讨了每个模型特有的错误和分歧模式,深入了解它们的力量、局限性和跨语言适应性。通过将LLM输出与人类注释进行对照,本研究有助于了解LLM在多元语言环境中的敏感性和特定领域的任务的可信度和适用性。它还揭示了语言模型如何处理固有的主观性和上下文相关的判断,这对于它们在现实场景中的部署是一个重要的考量。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
在本研究中,针对包含俄罗斯和乌克兰社交媒体帖子的复杂文本数据集,评估了多款先进的自然语言处理模型(包括GPT-3.5、GPT-4、LLAMA3、Mistral 7B和Claude-2)进行零样本和少样本标注的能力。研究重点是在数据集中识别涉及人权侵犯内容的二进制分类任务。通过对比这些模型标注与人类双重标注标签的结果,评估了模型性能。研究还探讨了每个模型的独特错误模式和分歧,并探讨了模型的优缺点以及跨语言适应性。本研究有助于了解语言模型在多语言环境中的可靠性及在敏感领域的适用性,并为语言模型如何处理主观性和上下文依赖的判断提供了见解。
Key Takeaways
- 本研究评估了多款先进的自然语言处理模型在零样本和少样本标注方面的能力。
- 研究集中在识别涉及人权侵犯内容的二进制分类任务上。
- 模型性能通过对比与人类双重标注标签的结果进行评估。
- 研究探讨了每个模型的独特错误模式和分歧。
- 探讨了模型的优缺点以及跨语言适应性。
- 本研究有助于了解语言模型在多语言环境中的可靠性及在敏感领域的适用性。
点此查看论文截图

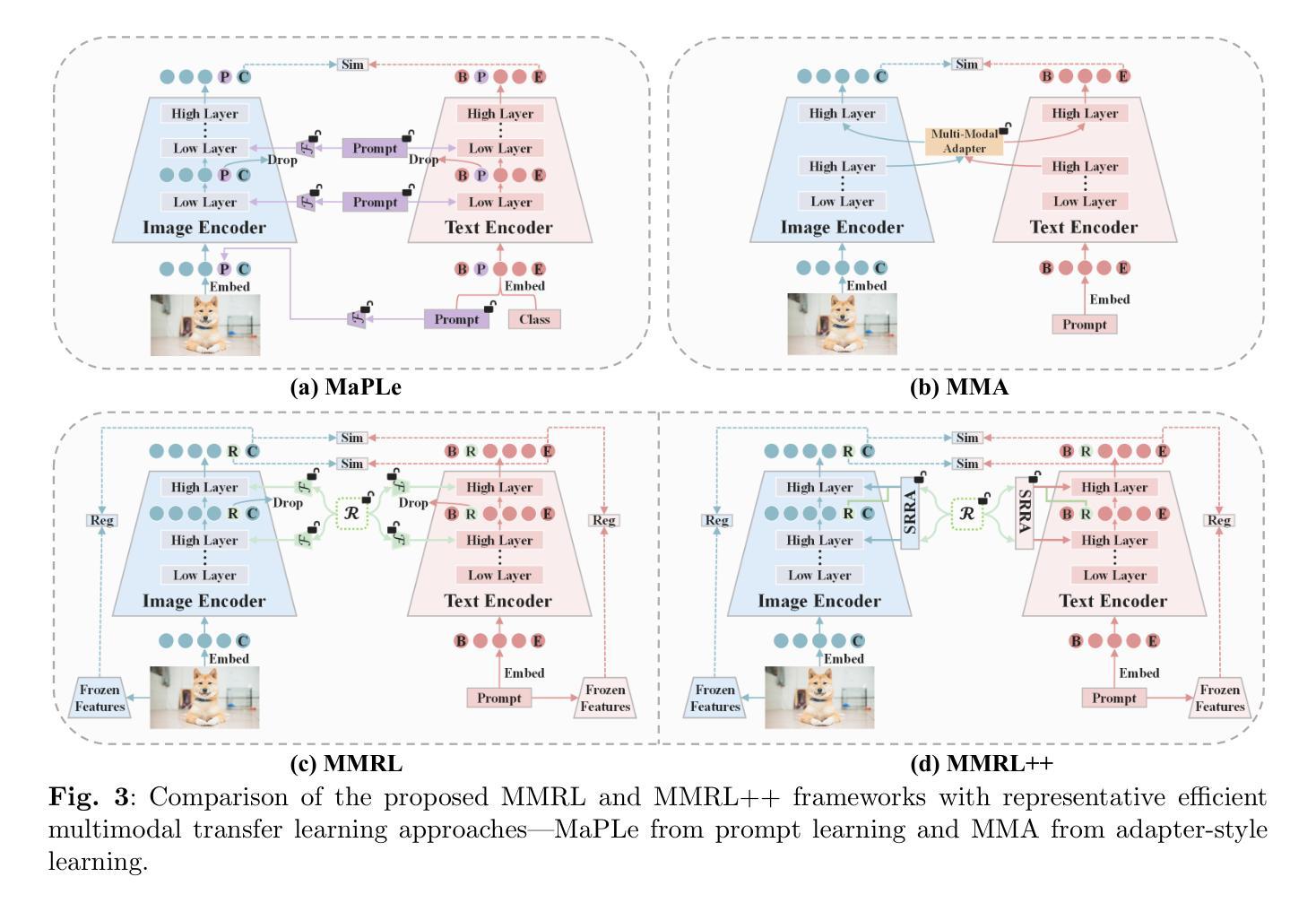
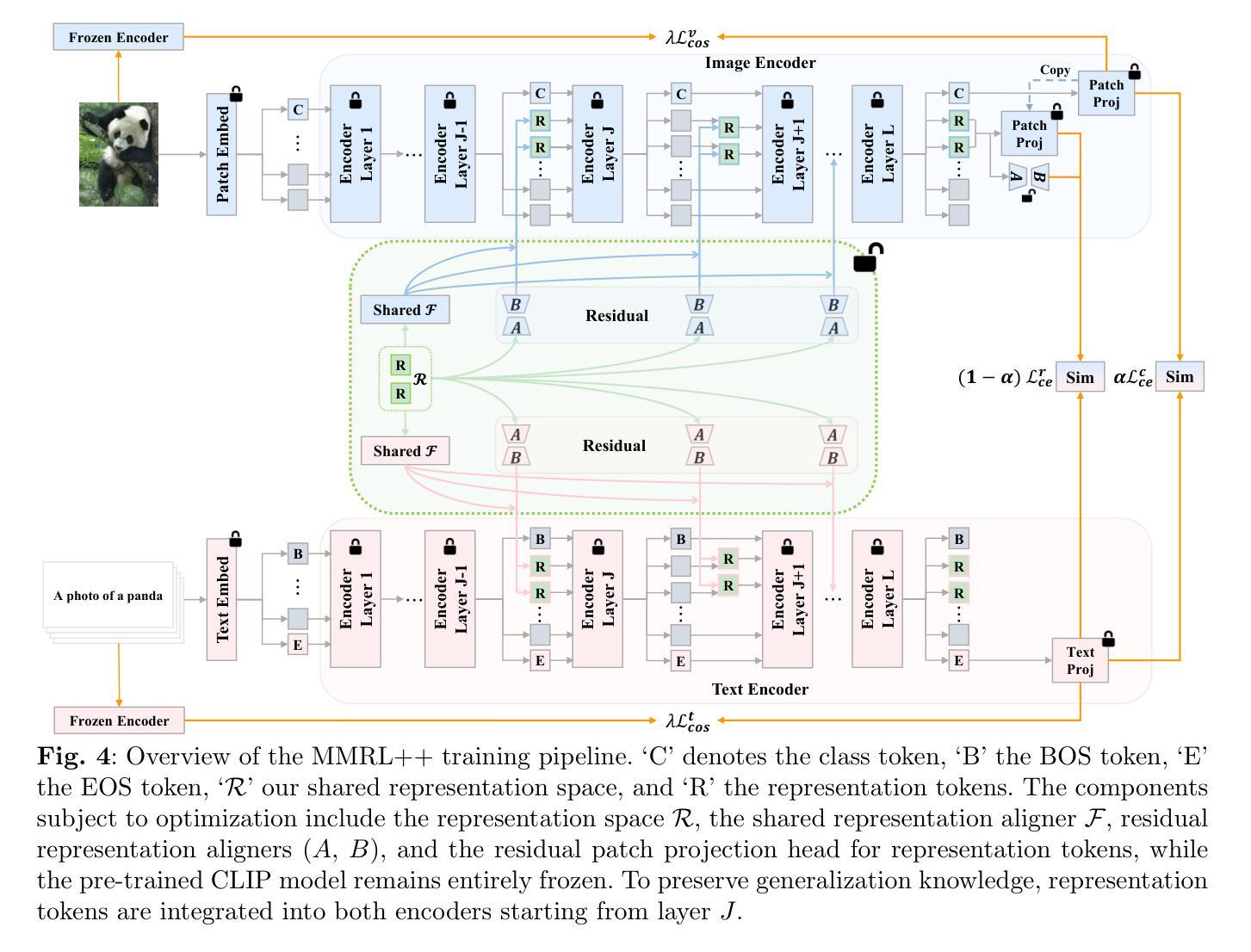
MMRL++: Parameter-Efficient and Interaction-Aware Representation Learning for Vision-Language Models
Authors:Yuncheng Guo, Xiaodong Gu
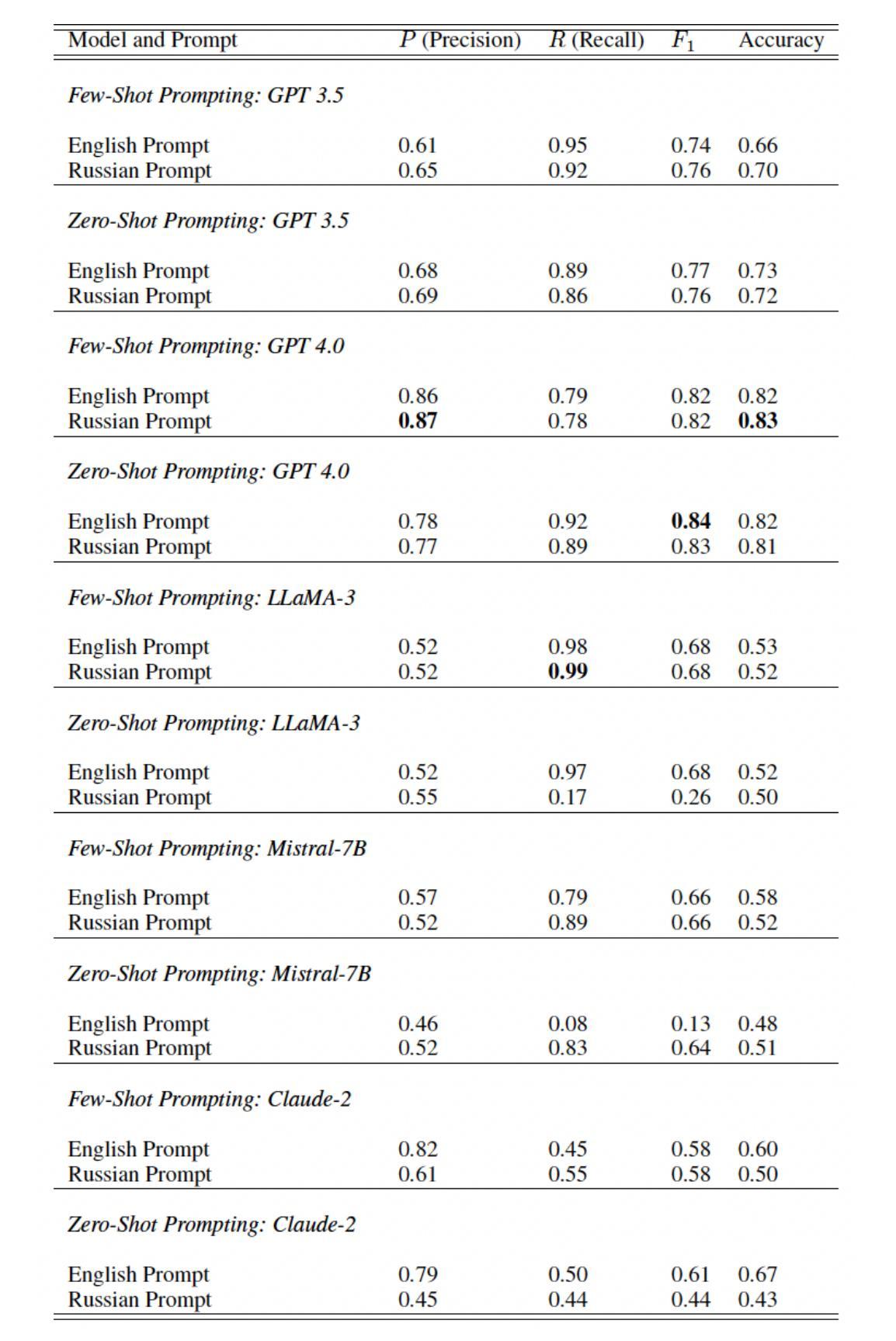
Large-scale pre-trained Vision-Language Models (VLMs) have significantly advanced transfer learning across diverse tasks. However, adapting these models with limited few-shot data often leads to overfitting, undermining their ability to generalize to new tasks. To address this, we propose Multi-Modal Representation Learning (MMRL), which introduces a shared, learnable, modality-agnostic representation space. MMRL generates space tokens projected into both text and image encoders as representation tokens, enabling more effective cross-modal interactions. Unlike prior methods that mainly optimize class token features, MMRL inserts representation tokens into higher encoder layers–where task-specific features are more prominent–while preserving general knowledge in the lower layers. During training, both class and representation features are jointly optimized: a trainable projection layer is applied to representation tokens for task adaptation, while the projection layer for class token remains frozen to retain pre-trained knowledge. To further promote generalization, we introduce a regularization term aligning class and text features with the frozen VLM’s zero-shot features. At inference, a decoupling strategy uses both class and representation features for base tasks, but only class features for novel tasks due to their stronger generalization. Building upon this, we propose MMRL++, a parameter-efficient and interaction-aware extension that significantly reduces trainable parameters and enhances intra-modal interactions–particularly across the layers of representation tokens–allowing gradient sharing and instance-specific information to propagate more effectively through the network. Extensive experiments on 15 datasets demonstrate that MMRL and MMRL++ consistently outperform state-of-the-art methods, achieving a strong balance between task-specific adaptation and generalization.
大规模预训练视觉语言模型(VLMs)已经显著推动了不同任务的迁移学习。然而,用有限的少量数据适应这些模型往往会导致过拟合,损害其推广到新任务的能力。为了解决这个问题,我们提出了多模态表示学习(MMRL),它引入了一个共享的、可学习的、模态无关的表示空间。MMRL生成空间令牌,将其投射到文本和图像编码器中以作为表示令牌,从而实现更有效的跨模态交互。与主要优化类别令牌特征的前期方法不同,MMRL将表示令牌插入到更高级别的编码器层中(任务特定特征更为突出),同时在较低层次上保留一般知识。在训练过程中,类别和表示特征会共同进行优化:一个可训练的投影层应用于表示令牌以进行任务适配,而类别令牌的投影层保持冻结以保留预训练知识。为了进一步促进泛化,我们引入了一个正则化项,将类别和文本特征与冻结的VLM的零样本特征对齐。在推理过程中,采用了解耦策略,对于基础任务同时使用类别和表示特征,但对于新型任务仅使用类别特征,因为它们的泛化能力更强。在此基础上,我们提出了MMRL++,一个参数高效、交互感知的扩展,它显著减少了可训练参数,增强了内部模态交互——特别是在表示令牌的层次之间——允许梯度共享和实例特定信息更有效地通过网络传播。在15个数据集上的广泛实验表明,MMRL和MMRL++始终优于最先进的方法,在任务特定适应性和泛化之间取得了强大的平衡。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Due to the limitation “The abstract field cannot be longer than 1,920 characters”, the abstract appearing here is slightly shorter than that in the PDF file
Summary
大规模预训练视觉语言模型(VLMs)在多种任务迁移学习上取得了显著进展,但在有限小样数据下适应这些模型常常会导致过拟合,影响其在新任务上的泛化能力。为解决这一问题,我们提出了多模态表示学习(MMRL)方法,它引入了一个共享、可学习、模态无关的表示空间。MMRL生成空间令牌并投影到文本和图像编码器作为表示令牌,实现更有效的跨模态交互。与主要优化类别令牌特征的前人方法不同,MMRL将表示令牌插入到更突出的编码器层中,同时在下层保留一般知识。在训练过程中,类别和表示特征是联合优化的:可训练的投影层应用于表示令牌以进行任务适应,而类别令牌的投影层保持不变以保留预训练知识。为了进一步促进泛化,我们引入了一个正则化项,将类别和文本特征与VLM的零样本特征的冻结对齐。在推理过程中,采用解耦策略,对于基础任务同时使用类别和表示特征,但对于新任务仅使用类别特征,因为其具有更强的泛化能力。在此基础上,我们提出了MMRL++,一个参数高效、交互感知的扩展,显著减少了可训练参数,增强了内部模态交互,特别是在表示令牌的各层之间,允许梯度共享和实例特定信息更有效地通过网络传播。在15个数据集上的广泛实验表明,MMRL和MMRL++始终优于最先进的方法,在任务特定适应和泛化之间取得了强大的平衡。
Key Takeaways
- 大规模预训练视觉语言模型(VLMs)在迁移学习上表现优异,但在小样数据下适应易出现过度拟合。
- 提出多模态表示学习(MMRL)方法,引入共享、可学习、模态无关的表示空间来解决这一问题。
- MMRL通过生成空间令牌并投影到文本和图像编码器,促进跨模态交互。
- MMRL在训练过程中联合优化类别和表示特征,同时保留预训练知识。
- 引入正则化项对齐类别和文本特征与VLM的零样本特征,提升泛化能力。
- 在推理过程中采用解耦策略,区分基础任务和新任务的特征使用。
点此查看论文截图

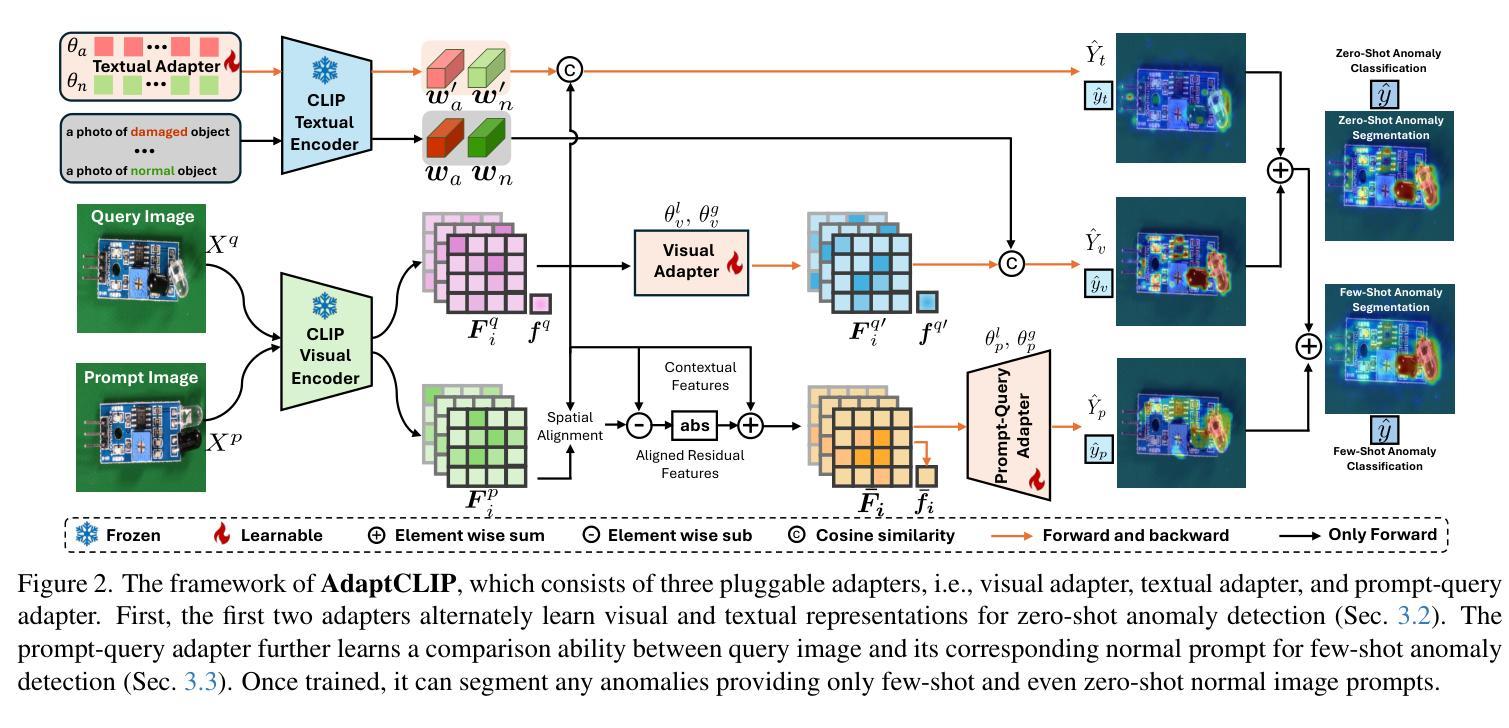
AdaptCLIP: Adapting CLIP for Universal Visual Anomaly Detection
Authors:Bin-Bin Gao, Yue Zhu, Jiangtao Yan, Yuezhi Cai, Weixi Zhang, Meng Wang, Jun Liu, Yong Liu, Lei Wang, Chengjie Wang
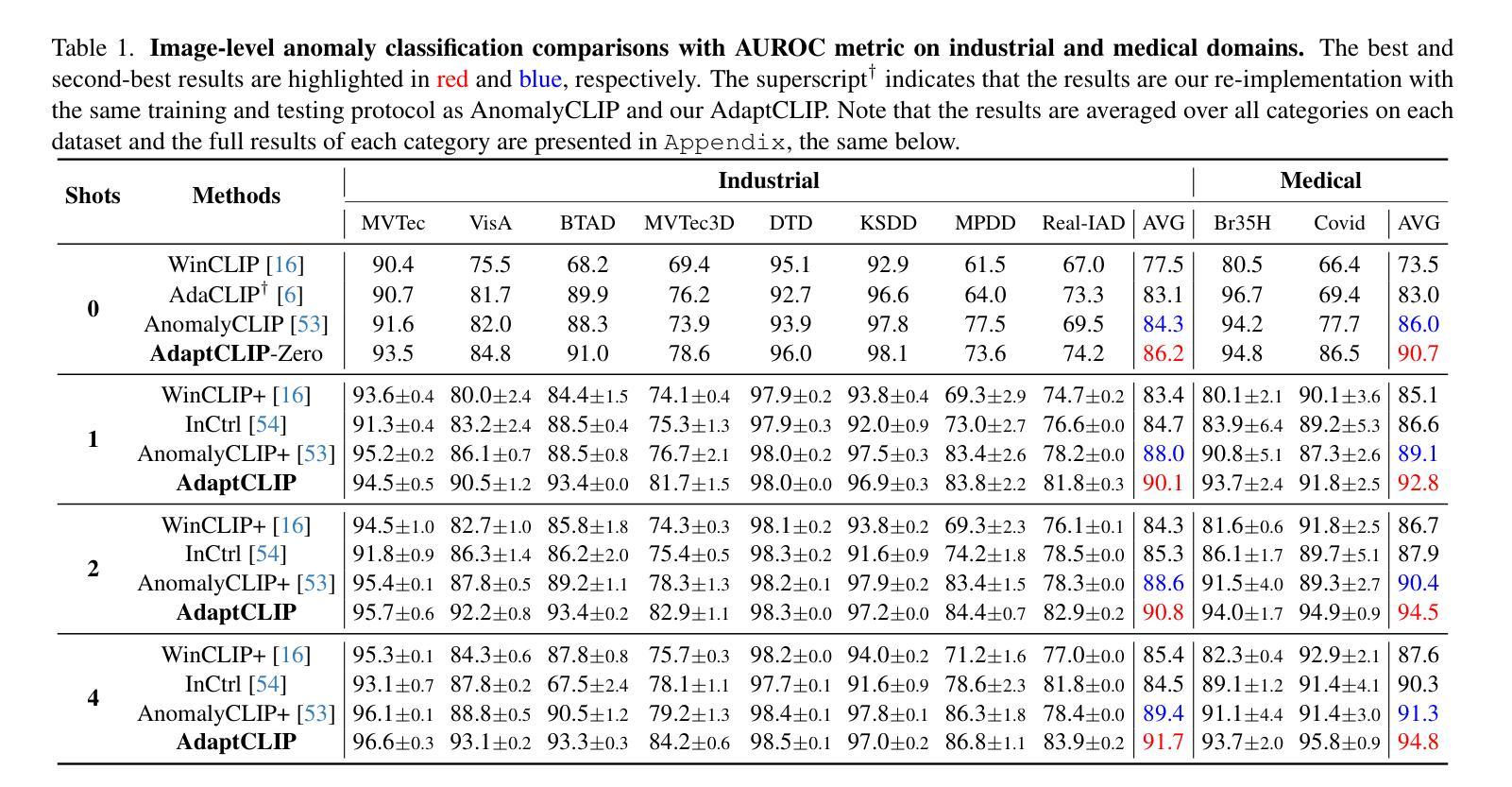
Universal visual anomaly detection aims to identify anomalies from novel or unseen vision domains without additional fine-tuning, which is critical in open scenarios. Recent studies have demonstrated that pre-trained vision-language models like CLIP exhibit strong generalization with just zero or a few normal images. However, existing methods struggle with designing prompt templates, complex token interactions, or requiring additional fine-tuning, resulting in limited flexibility. In this work, we present a simple yet effective method called AdaptCLIP based on two key insights. First, adaptive visual and textual representations should be learned alternately rather than jointly. Second, comparative learning between query and normal image prompt should incorporate both contextual and aligned residual features, rather than relying solely on residual features. AdaptCLIP treats CLIP models as a foundational service, adding only three simple adapters, visual adapter, textual adapter, and prompt-query adapter, at its input or output ends. AdaptCLIP supports zero-/few-shot generalization across domains and possesses a training-free manner on target domains once trained on a base dataset. AdaptCLIP achieves state-of-the-art performance on 12 anomaly detection benchmarks from industrial and medical domains, significantly outperforming existing competitive methods. We will make the code and model of AdaptCLIP available at https://github.com/gaobb/AdaptCLIP.
通用视觉异常检测旨在从新型或未见过的视觉领域识别异常值,这在开放场景中至关重要,而无需进行额外的微调。最近的研究表明,像CLIP这样的预训练视觉语言模型仅通过零张或少数几张正常图像就能展现出强大的泛化能力。然而,现有方法在设计提示模板、复杂的令牌交互或需要额外的微调方面存在困难,导致灵活性有限。在这项工作中,我们提出了一种简单有效的方法,称为AdaptCLIP,它基于两个关键见解。首先,应该交替学习自适应的视觉和文本表示,而不是联合学习。其次,查询和正常图像提示之间的比较学习应融入上下文和对齐的残差特征,而不是仅依赖残差特征。AdaptCLIP将CLIP模型作为基础服务,仅在输入或输出端添加三个简单的适配器,即视觉适配器、文本适配器和提示查询适配器。AdaptCLIP支持跨领域的零/少镜头泛化,一旦在基础数据集上进行训练,它在目标领域上采用无训练方式。AdaptCLIP在来自工业和医疗领域的12个异常检测基准测试上实现了最佳性能,显著优于现有的竞争方法。我们将在https://github.com/gaobb/AdaptCLIP上提供AdaptCLIP的代码和模型。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 27 pages, 15 figures, 22 tables
Summary
基于CLIP模型的AdaptCLIP方法实现了零样本或少样本的视觉异常检测。它通过交替学习视觉和文本表示,结合上下文和对齐残差特征进行比对学习,仅通过添加三个简单的适配器就实现了强大的泛化能力。AdaptCLIP在多个工业和医疗领域的异常检测基准测试中取得了最佳性能。
Key Takeaways
- AdaptCLIP是一种简单有效的零样本或少样本视觉异常检测方法。
- 该方法基于CLIP模型,结合上下文和对齐残差特征进行对比学习。
- 通过交替学习视觉和文本表示,增强了模型的泛化能力。
- 仅通过添加三个适配器(视觉适配器、文本适配器和提示查询适配器)就实现了强大的性能。
- AdaptCLIP在多个工业和医疗领域的异常检测基准测试中取得了最佳表现。
- 该方法支持跨域泛化,对目标域的训练是免费的。
点此查看论文截图


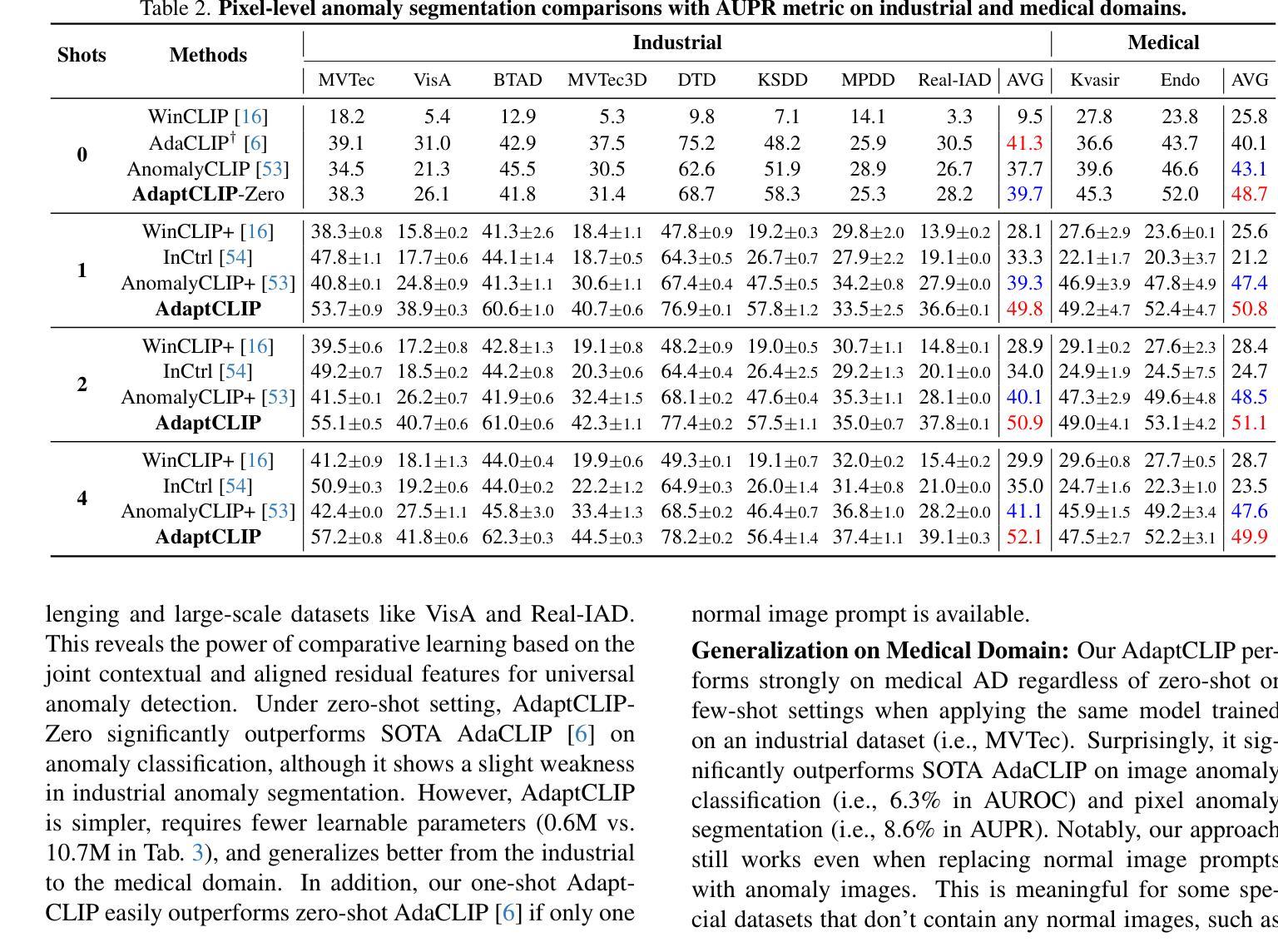
Few-Shot Learning of Visual Compositional Concepts through Probabilistic Schema Induction
Authors:Andrew Jun Lee, Taylor Webb, Trevor Bihl, Keith Holyoak, Hongjing Lu
The ability to learn new visual concepts from limited examples is a hallmark of human cognition. While traditional category learning models represent each example as an unstructured feature vector, compositional concept learning is thought to depend on (1) structured representations of examples (e.g., directed graphs consisting of objects and their relations) and (2) the identification of shared relational structure across examples through analogical mapping. Here, we introduce Probabilistic Schema Induction (PSI), a prototype model that employs deep learning to perform analogical mapping over structured representations of only a handful of examples, forming a compositional concept called a schema. In doing so, PSI relies on a novel conception of similarity that weighs object-level similarity and relational similarity, as well as a mechanism for amplifying relations relevant to classification, analogous to selective attention parameters in traditional models. We show that PSI produces human-like learning performance and outperforms two controls: a prototype model that uses unstructured feature vectors extracted from a deep learning model, and a variant of PSI with weaker structured representations. Notably, we find that PSI’s human-like performance is driven by an adaptive strategy that increases relational similarity over object-level similarity and upweights the contribution of relations that distinguish classes. These findings suggest that structured representations and analogical mapping are critical to modeling rapid human-like learning of compositional visual concepts, and demonstrate how deep learning can be leveraged to create psychological models.
学习新视觉概念的能力是人类认知的标志性特征之一。传统的类别学习模型将每个示例表示为无结构的特征向量,而组合概念学习则依赖于(1)示例的结构化表示(例如,由对象及其关系组成的定向图)和(2)通过类比映射识别跨示例的共享关系结构。在这里,我们引入了概率模式归纳(PSI),这是一种原型模型,它利用深度学习仅通过少量示例的结构化表示进行类比映射,形成称为模式的组合概念。通过这种方式,PSI依赖于一种新型相似性概念,该概念权衡对象级相似性和关系相似性,以及一种类似于传统模型中的选择性注意参数的放大与分类相关的关系的机制。我们表明PSI能产生与人类类似的学习性能,并优于两个对照组:一个使用从深度学习模型中提取的无结构特征向量的原型模型,以及一个具有较弱结构化表示的PSI变体。值得注意的是,我们发现PSI的人类化性能是由一种自适应策略驱动的,该策略增加了关系相似性并超越了对象级别的相似性,并增加了区分类别的关系的贡献。这些发现表明,结构化表示和类比映射对于模拟人类快速学习组合视觉概念至关重要,并展示了如何利用深度学习来创建心理模型。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Lee, A. J., Webb, T., Bihl, T., Holyoak, K. J., & Lu, H. (2025). Few-shot learning of visual compositional concepts through probabilistic schema induction. In A. Ruggeri, D. Barner, C. Walker, & N. Bramley (Eds.), Proceedings of the 47th Annual Conference of the Cognitive Science Society. Cognitive Science Society
Summary
本文介绍了概率模式归纳(PSI)这一原型模型,该模型利用深度学习对有限的结构化表示示例进行类比映射,形成称为模式的组合概念。PSI依赖于新的相似性概念,既考虑对象层面的相似性,又考虑关系层面的相似性,同时提供一种放大与分类相关的关系的机制。研究表明,PSI实现了与人类类似的学习性能,并优于使用深度学习的无结构化特征向量的原型模型和PSI的弱结构化表示变体。这表明结构化表示和类比映射对于模拟人类快速学习组合视觉概念至关重要。
Key Takeaways
- PSI模型利用深度学习进行类比映射,处理有限的结构化示例表示。
- PSI依赖于对象层面和关系层面的相似性度量。
- PSI模型采用一种放大与分类相关关系的机制,类似于传统模型中的选择性注意参数。
- PSI实现了与人类类似的学习性能。
- PSI模型优于使用无结构化特征向量的原型模型和弱结构化表示的PSI变体。
- 结构化表示和类比映射对于模拟人类快速学习组合视觉概念至关重要。
点此查看论文截图

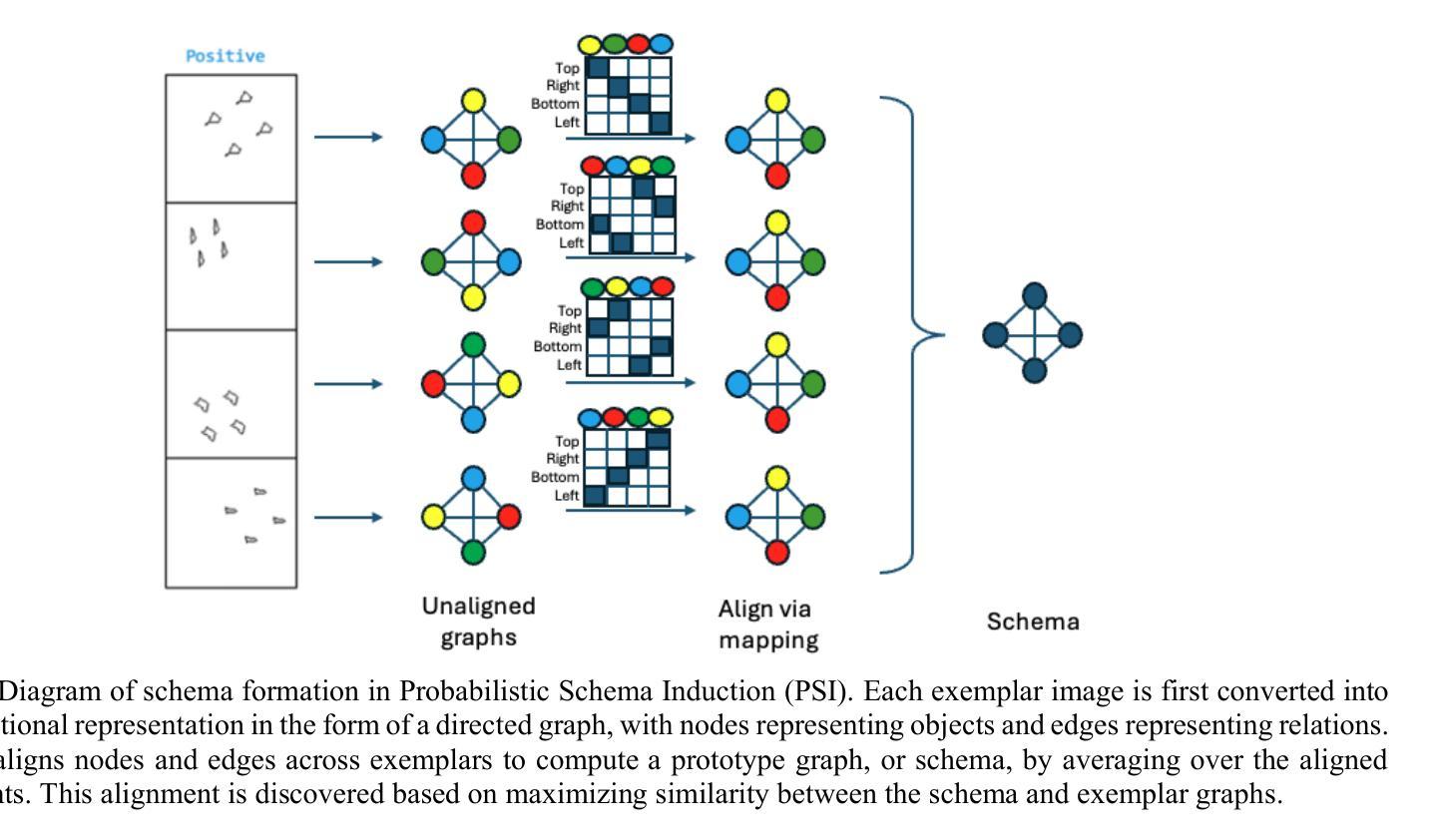
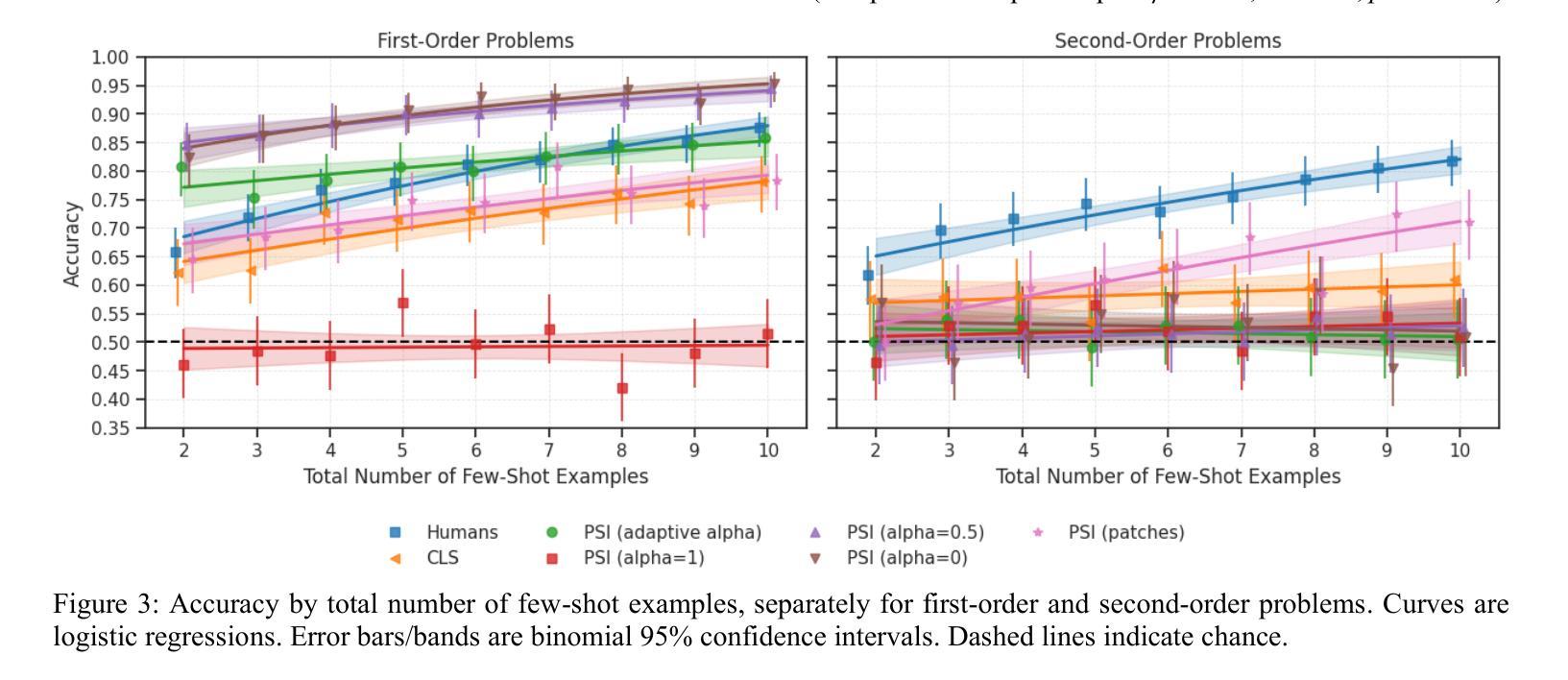
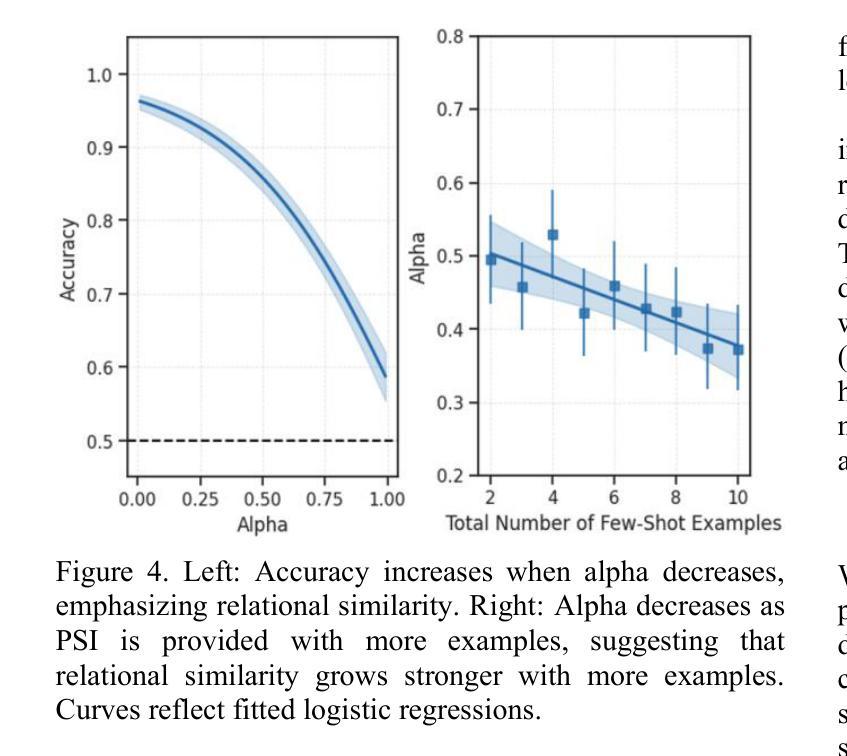
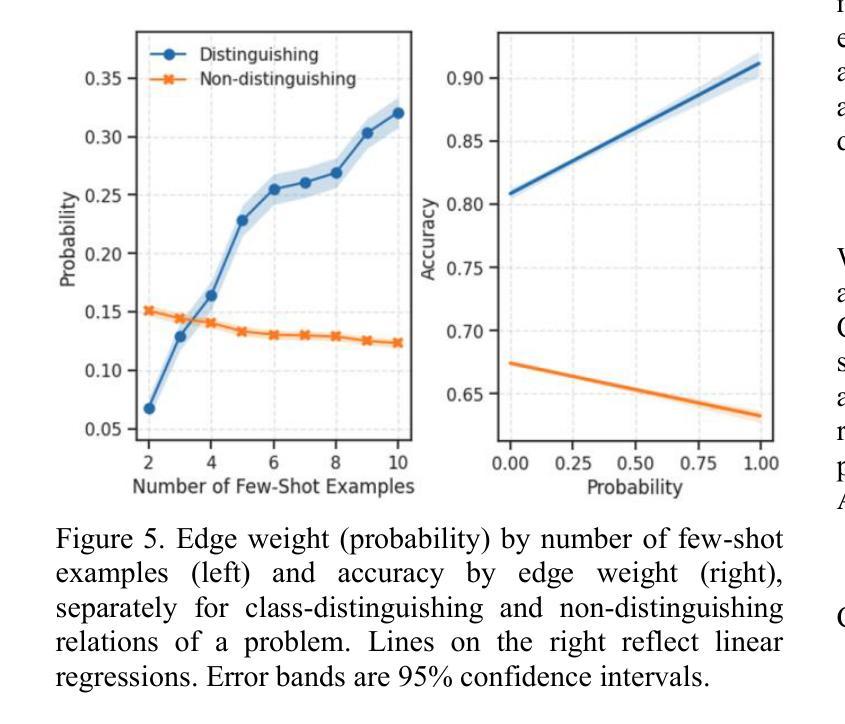
Fast and Robust: Task Sampling with Posterior and Diversity Synergies for Adaptive Decision-Makers in Randomized Environments
Authors:Yun Qu, Qi Cheems Wang, Yixiu Mao, Yiqin Lv, Xiangyang Ji
Task robust adaptation is a long-standing pursuit in sequential decision-making. Some risk-averse strategies, e.g., the conditional value-at-risk principle, are incorporated in domain randomization or meta reinforcement learning to prioritize difficult tasks in optimization, which demand costly intensive evaluations. The efficiency issue prompts the development of robust active task sampling to train adaptive policies, where risk-predictive models are used to surrogate policy evaluation. This work characterizes the optimization pipeline of robust active task sampling as a Markov decision process, posits theoretical and practical insights, and constitutes robustness concepts in risk-averse scenarios. Importantly, we propose an easy-to-implement method, referred to as Posterior and Diversity Synergized Task Sampling (PDTS), to accommodate fast and robust sequential decision-making. Extensive experiments show that PDTS unlocks the potential of robust active task sampling, significantly improves the zero-shot and few-shot adaptation robustness in challenging tasks, and even accelerates the learning process under certain scenarios. Our project website is at https://thu-rllab.github.io/PDTS_project_page.
任务鲁棒性适应是序列决策制定中一个长期追求的目标。一些风险规避策略,例如条件风险价值原则,被纳入领域随机化或元强化学习中,以优化中的优先困难任务为目标,这些任务需要进行昂贵的密集评估。效率问题促使开发鲁棒的主动任务采样以训练自适应策略,其中风险预测模型用于替代策略评估。这项工作将鲁棒的主动任务采样的优化管道特征化为马尔可夫决策过程,提出了理论和实践见解,并构成了风险规避场景中的稳健性概念。重要的是,我们提出了一种易于实施的方法,称为后验和多样性协同任务采样(PDTS),以实现快速和稳健的序列决策制定。大量实验表明,PDTS释放了鲁棒的主动任务采样的潜力,显著提高了挑战性任务的零样本和少样本适应稳健性,甚至在特定场景下加速了学习过程。我们的项目网站是https://thu-rllab.github.io/PDTS_project_page。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF ICML 2025
Summary
风险规避策略在决策序列中进行了长期的适应性改造,面临挑战和成本高昂的任务需求评估。本文介绍了通过将风险规避策略纳入领域随机化或元强化学习来解决效率问题的方法。为解决这些问题,引入了风险预测模型替代政策评估。这项研究对优化流程进行了特征刻画并提出了理论与实践的见解。通过开发易于实施的名为PDTS(后验与多样性协同任务采样)的方法,实现了快速而稳健的决策序列优化。实验证明,PDTS可以显著提高在具有挑战性的任务中的零镜适应性和少数次适应性适应性稳健性,甚至可以在某些场景下加速学习过程。相关项目网址:https://thu-rllab.github.io/PDTS_project_page。
Key Takeaways
- 风险规避策略被纳入领域随机化或元强化学习中以优化决策序列的适应性改造过程。
- 效率问题促使发展稳健主动任务采样,以训练自适应策略。
- 风险预测模型用于替代政策评估以提高决策效率和准确性。
- PDTS方法结合了后验与多样性协同采样技术来解决优化问题。
- PDTS能显著提高零镜和少数次适应性稳健性。实验证明了其在解决复杂任务方面的优势。
- PDTS方法有助于加速学习过程,特别是在某些特定场景下。
点此查看论文截图

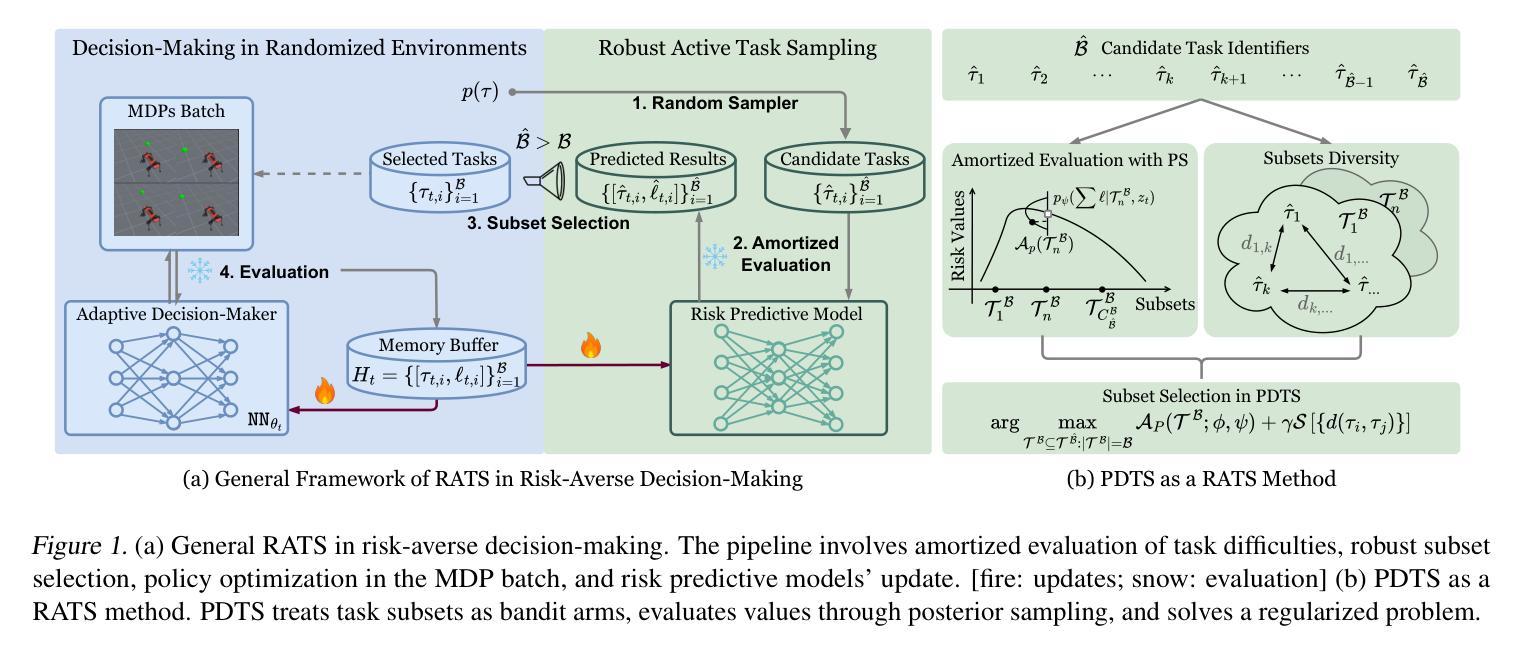
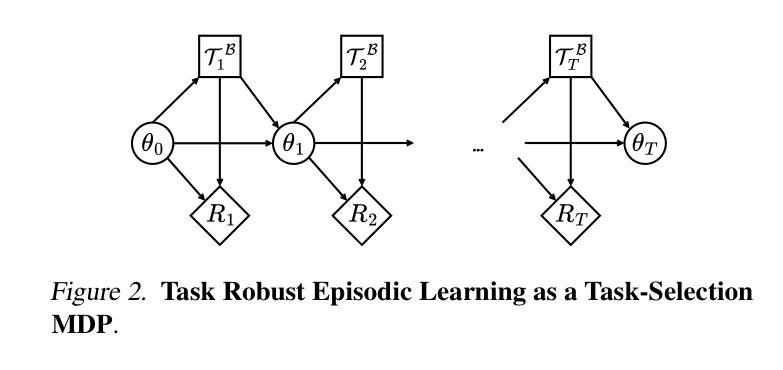
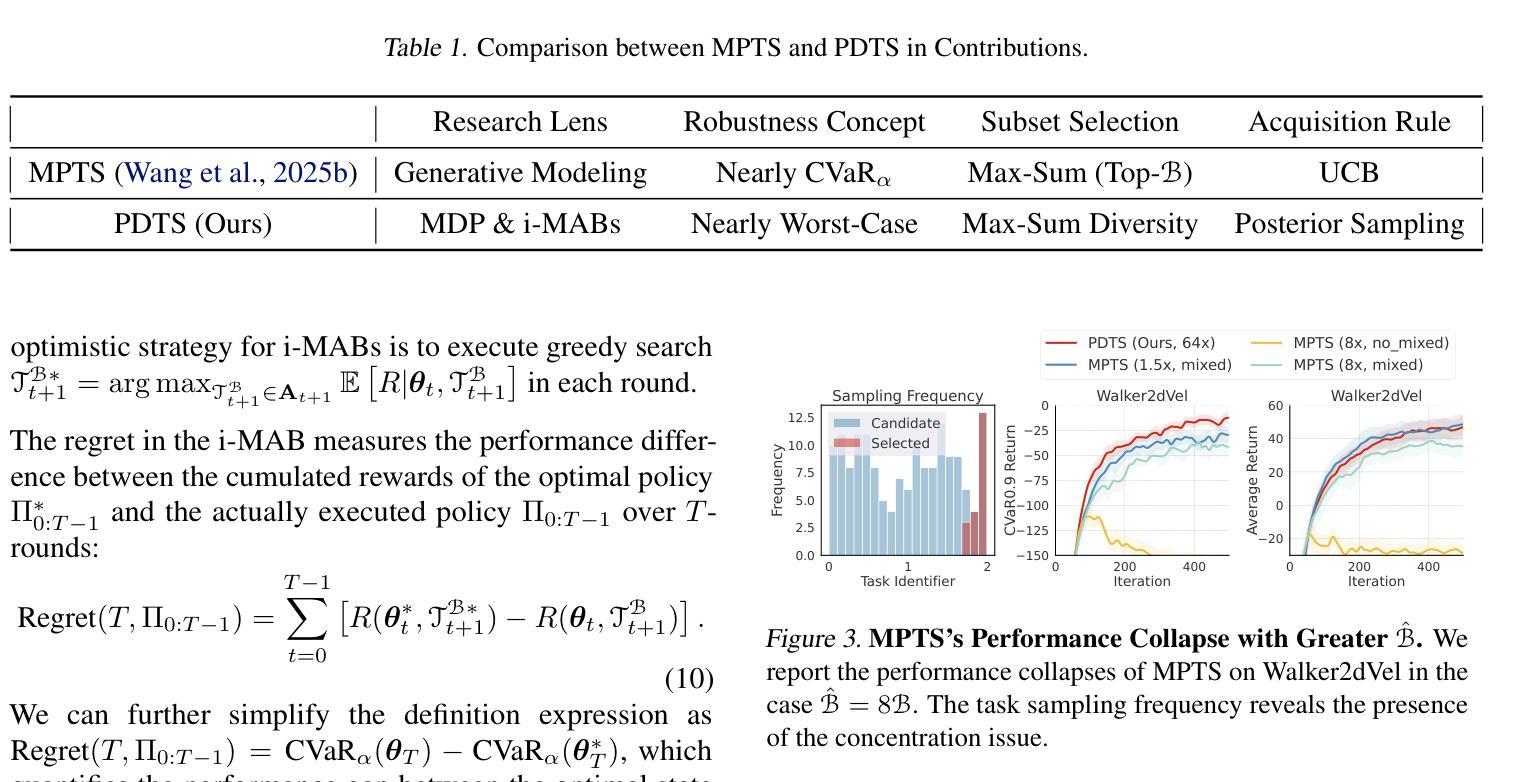
Benchmarking Generative AI for Scoring Medical Student Interviews in Objective Structured Clinical Examinations (OSCEs)
Authors:Jadon Geathers, Yann Hicke, Colleen Chan, Niroop Rajashekar, Justin Sewell, Susannah Cornes, Rene F. Kizilcec, Dennis Shung
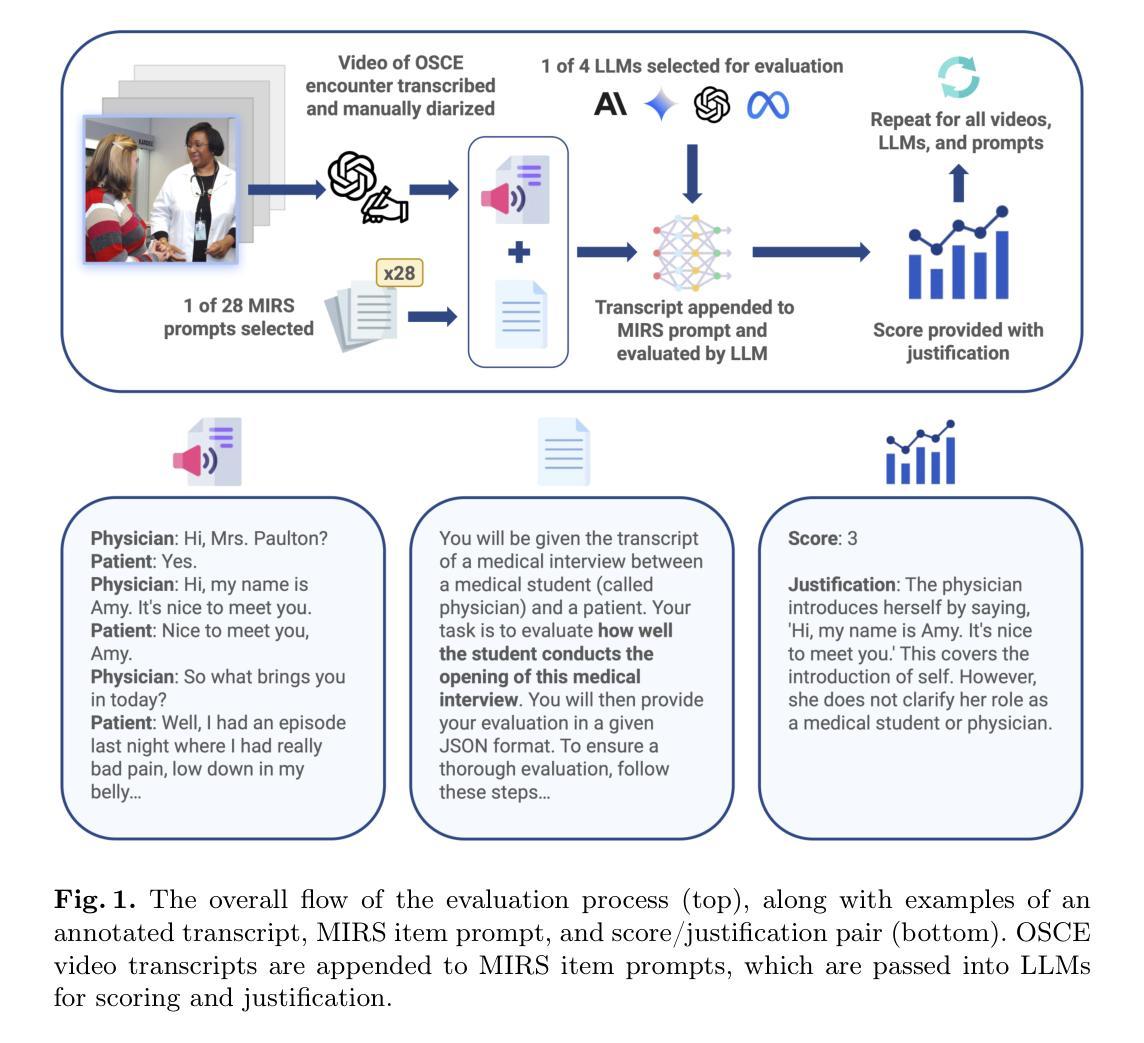
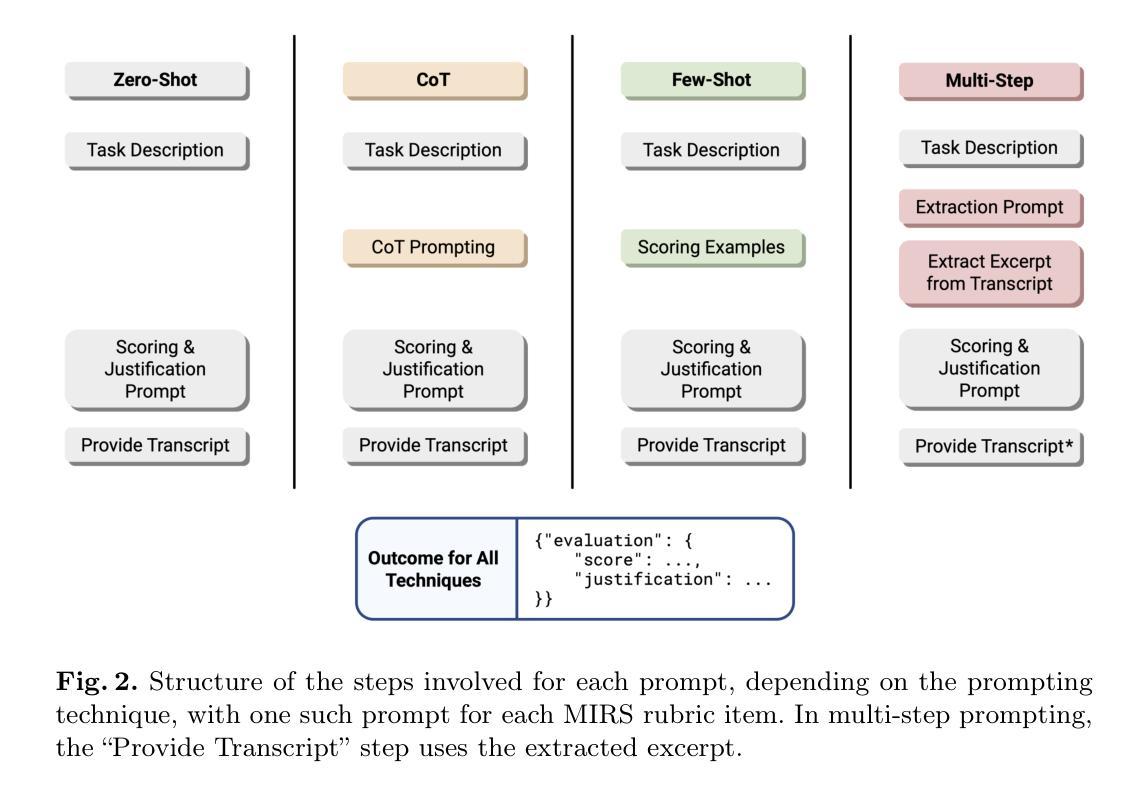
Objective Structured Clinical Examinations (OSCEs) are widely used to assess medical students’ communication skills, but scoring interview-based assessments is time-consuming and potentially subject to human bias. This study explored the potential of large language models (LLMs) to automate OSCE evaluations using the Master Interview Rating Scale (MIRS). We compared the performance of four state-of-the-art LLMs (GPT-4o, Claude 3.5, Llama 3.1, and Gemini 1.5 Pro) in evaluating OSCE transcripts across all 28 items of the MIRS under the conditions of zero-shot, chain-of-thought (CoT), few-shot, and multi-step prompting. The models were benchmarked against a dataset of 10 OSCE cases with 174 expert consensus scores available. Model performance was measured using three accuracy metrics (exact, off-by-one, thresholded). Averaging across all MIRS items and OSCE cases, LLMs performed with low exact accuracy (0.27 to 0.44), and moderate to high off-by-one accuracy (0.67 to 0.87) and thresholded accuracy (0.75 to 0.88). A zero temperature parameter ensured high intra-rater reliability ({\alpha} = 0.98 for GPT-4o). CoT, few-shot, and multi-step techniques proved valuable when tailored to specific assessment items. The performance was consistent across MIRS items, independent of encounter phases and communication domains. We demonstrated the feasibility of AI-assisted OSCE evaluation and provided benchmarking of multiple LLMs across multiple prompt techniques. Our work provides a baseline performance assessment for LLMs that lays a foundation for future research into automated assessment of clinical communication skills.
客观结构化临床考试(OSCEs)被广泛用于评估医学生的沟通技巧,但基于面试的评估打分耗时且存在人为偏见。本研究探讨了大型语言模型(LLMs)使用主面试评分表(MIRS)自动进行OSCE评估的潜力。我们比较了四种最新LLMs(GPT-4o、Claude 3.5、Llama 3.1和Gemini 1.5 Pro)在评估OSCE记录时的表现,涵盖了MIRS的所有28项内容,包括零样本、思维链(CoT)、小样本和多步提示的情况。这些模型是以10个OSCE病例数据集为基准,共有174个专家共识分数可供使用。模型性能采用三种准确性指标(精确、离一、阈值)进行测量。在所有MIRS项目和OSCE病例上的平均精确性较低(0.27至0.44),离一准确率和阈值准确率则处于中等至高水平(分别为0.67至0.87和0.75至0.88)。零温度参数确保了高的内部一致性(GPT-4o的α=0.98)。针对特定的评估项目,思维链、小样本和多步技术证明是有价值的。性能在MIRS项目上表现一致,不受遇到阶段和沟通领域的影响。我们证明了人工智能辅助OSCE评估的可行性,并提供了多种LLMs在多种提示技术上的基准测试。我们的工作为LLMs提供了基线性能评估,为未来研究自动化评估临床沟通技巧奠定了基础。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 12 pages + 3 pages of references, 4 figures
摘要
本研究探索了大语言模型(LLMs)在利用“大师面试评分量表”(MIRS)自动评估临床沟通技能考试(OSCEs)方面的潜力。对比了四款先进LLM在MIRS的28个项目中对OSCE文稿的零样本、思维链(CoT)、少样本和多步提示下的评估表现。以包含174个专家共识分数的数据集为基准,评估模型的性能。LLMs的平均表现显示,在精确准确性方面表现较低(0.27至0.44),但在宽松准确率和阈值准确率方面表现中度至高度(0.67至0.87)。零温度参数确保了高度的内部一致性(GPT-4o的α= 0.98)。针对特定的评估项目,思维链、少样本和多步技术证明是有价值的。性能在MIRS项目中表现一致,不受遇到阶段和沟通领域的影响。本研究证明了AI辅助OSCE评估的可行性,并为多种LLMs在多种提示技术上的表现提供了基准测试。本研究为未来临床沟通技能自动化评估的研究提供了基础性能评估。
关键见解
- 研究探索了大语言模型(LLMs)在自动评估医疗临床沟通技能考试(OSCEs)方面的潜力。
- 对比了四款先进LLM在多种提示技术下的评估表现。
- LLMs在精确准确性方面表现较低,但在宽松准确率和阈值准确率方面表现较好。
- 零温度参数确保了高度的内部一致性。
- 思维链、少样本和多步技术对于特定评估项目具有价值。
- LLMs的性能在MIRS项目中表现一致,不受遇到阶段和沟通领域的影响。
点此查看论文截图

FitCF: A Framework for Automatic Feature Importance-guided Counterfactual Example Generation
Authors:Qianli Wang, Nils Feldhus, Simon Ostermann, Luis Felipe Villa-Arenas, Sebastian Möller, Vera Schmitt
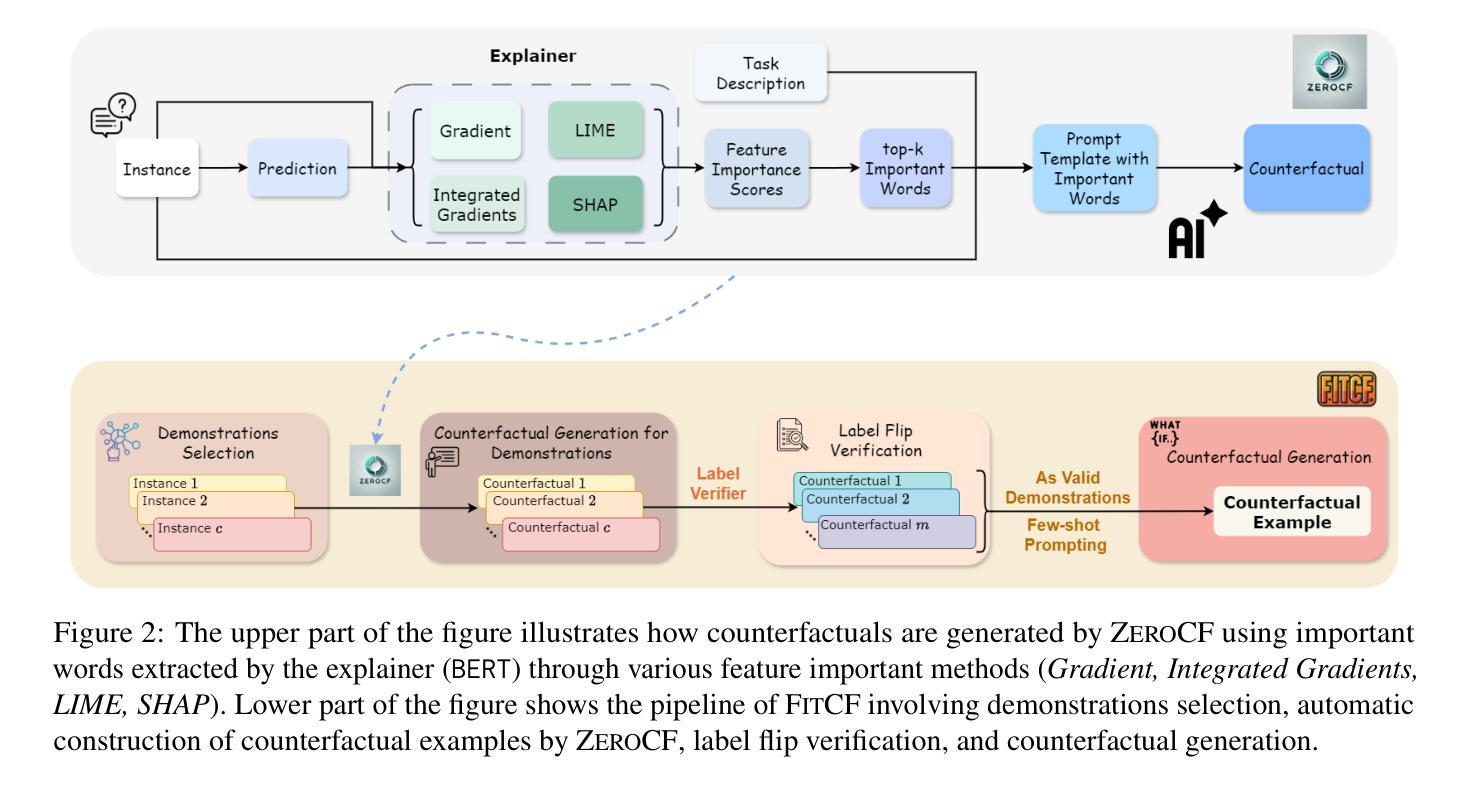
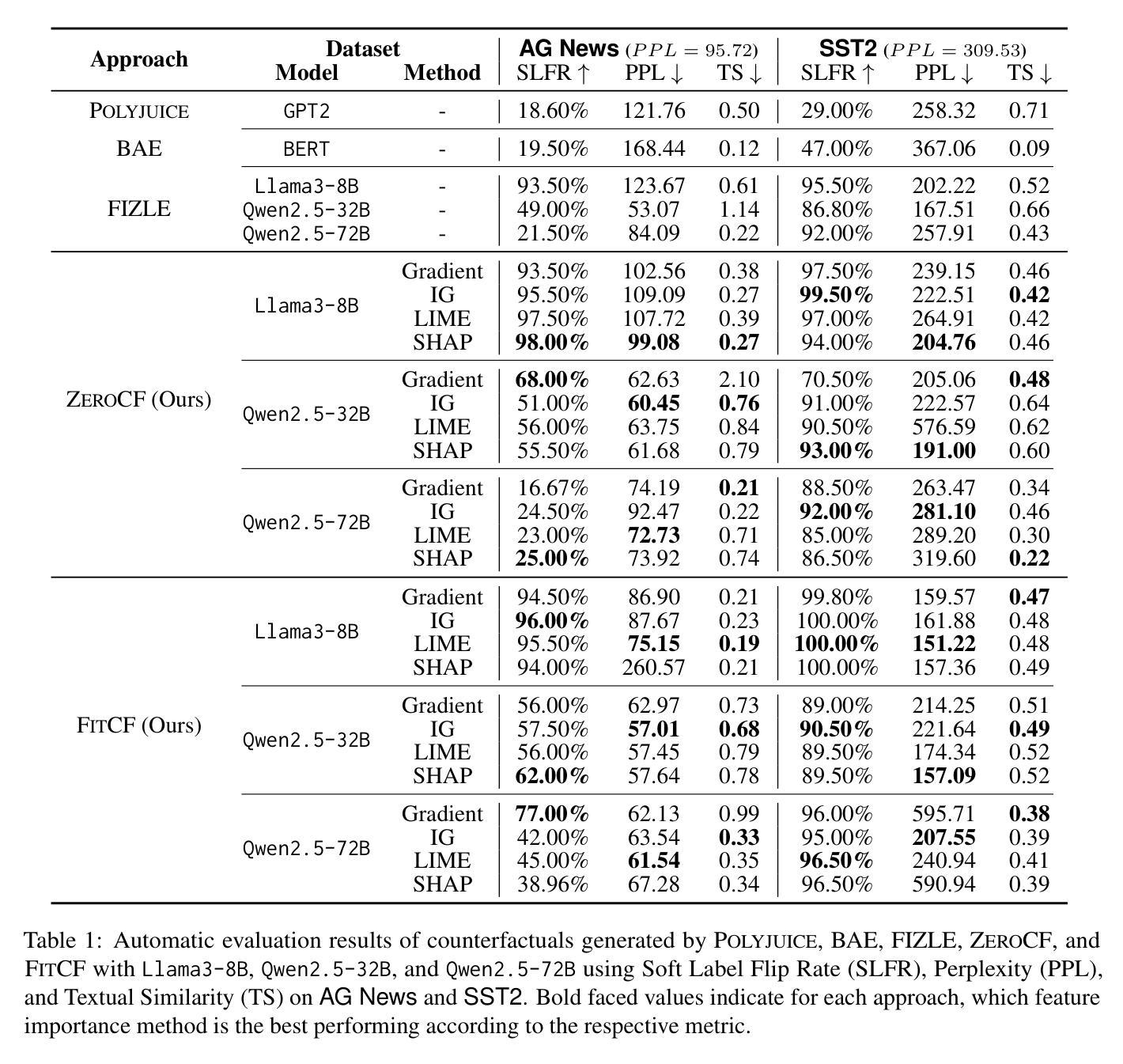
Counterfactual examples are widely used in natural language processing (NLP) as valuable data to improve models, and in explainable artificial intelligence (XAI) to understand model behavior. The automated generation of counterfactual examples remains a challenging task even for large language models (LLMs), despite their impressive performance on many tasks. In this paper, we first introduce ZeroCF, a faithful approach for leveraging important words derived from feature attribution methods to generate counterfactual examples in a zero-shot setting. Second, we present a new framework, FitCF, which further verifies aforementioned counterfactuals by label flip verification and then inserts them as demonstrations for few-shot prompting, outperforming two state-of-the-art baselines. Through ablation studies, we identify the importance of each of FitCF’s core components in improving the quality of counterfactuals, as assessed through flip rate, perplexity, and similarity measures. Furthermore, we show the effectiveness of LIME and Integrated Gradients as backbone attribution methods for FitCF and find that the number of demonstrations has the largest effect on performance. Finally, we reveal a strong correlation between the faithfulness of feature attribution scores and the quality of generated counterfactuals.
在自然语言处理(NLP)中,反事实例子被广泛应用于提升模型价值的数据,并且在可解释人工智能(XAI)中用于理解模型行为。尽管大型语言模型(LLM)在许多任务上表现出令人印象深刻的性能,但自动生成反事实例子仍然是一个具有挑战性的任务。在本文中,我们首先介绍了ZeroCF,这是一种忠实的方法,利用从特征归因方法派生出的重要单词,在无射击环境中生成反事实例子。其次,我们提出了一个新的框架FitCF,它通过标签翻转验证进一步验证了上述反事实,然后将它们作为演示用于小样本提示,表现优于两种最新基线。通过废除研究,我们确定了FitCF每个核心组件在提高反事实质量方面的重要性,通过翻转率、困惑度和相似性度量进行评估。此外,我们展示了LIME和集成梯度作为FitCF的骨干归因方法的有效性,并发现演示的数量对性能的影响最大。最后,我们发现特征归因分数的忠实性与生成的反事实质量之间存在强烈的相关性。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF ACL 2025 Findings; camera-ready version
Summary
本文介绍了在自然语言处理(NLP)和可解释人工智能(XAI)中广泛应用的反事实示例。文章提出了ZeroCF方法,利用特征归属方法生成零样本环境下的反事实示例。此外,还提出了FitCF框架,通过标签翻转验证进行反事实验证,并将其作为示范用于少量提示。此方法超越了两种最先进的基线方法。文章还通过消融研究确定了FitCF的核心组件在提高反事实质量方面的重要性,并展示了LIME和集成梯度作为FitCF的骨干归属方法的有效性。同时,文章揭示了特征归属分数与生成反事实质量之间的强相关性。
Key Takeaways
- ZeroCF方法利用特征归属方法中的关键单词,在零样本环境下生成反事实示例。
- FitCF框架通过标签翻转验证来验证反事实,并将其作为示范用于少量提示,表现出超越现有方法的性能。
- 消融研究确定了FitCF的核心组件在改善反事实质量方面的重要性。
- LIME和集成梯度作为FitCF的骨干归属方法表现出有效性。
- 文中对比了两种先进的基线方法,显示了FitCF的优越性。
- 反事实示例在自然语言处理和可解释人工智能领域有广泛应用。
点此查看论文截图

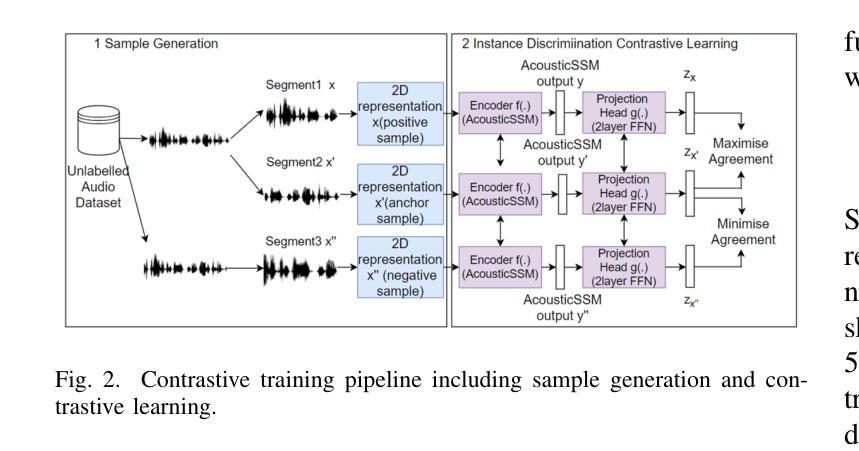
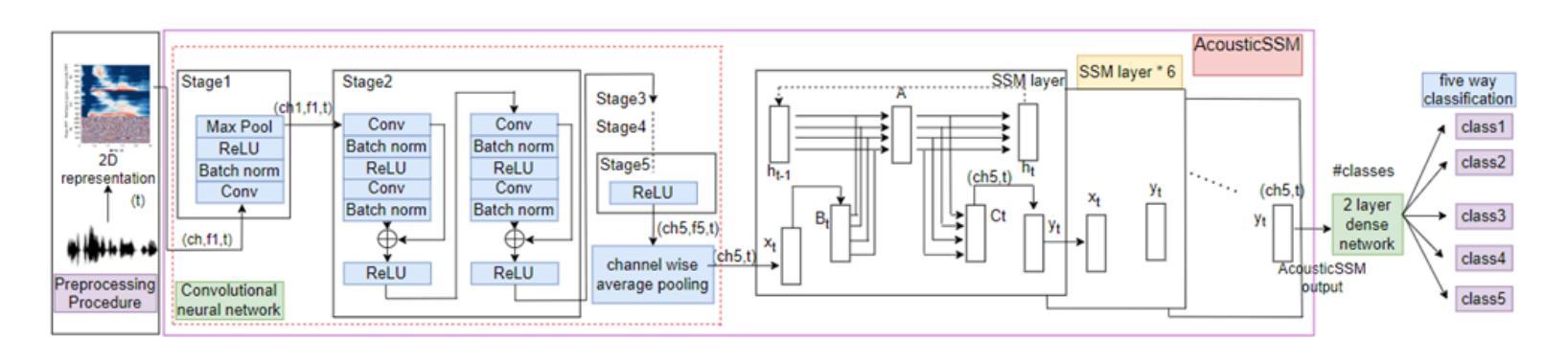
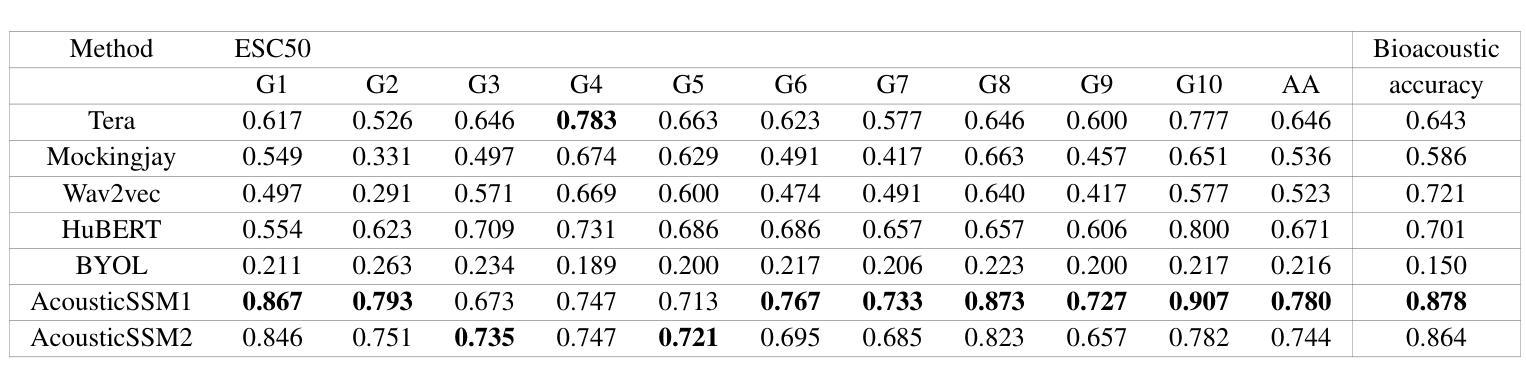
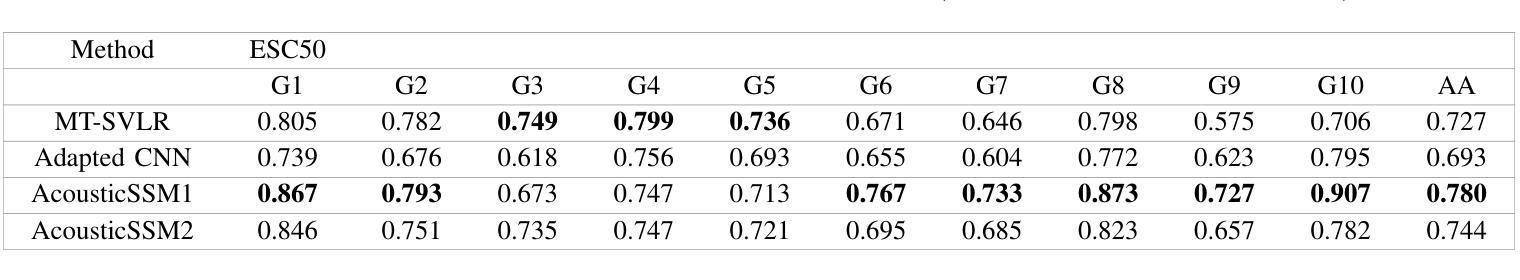
Self-supervised Learning for Acoustic Few-Shot Classification
Authors:Jingyong Liang, Bernd Meyer, Isaac Ning Lee, Thanh-Toan Do
Labelled data are limited and self-supervised learning is one of the most important approaches for reducing labelling requirements. While it has been extensively explored in the image domain, it has so far not received the same amount of attention in the acoustic domain. Yet, reducing labelling is a key requirement for many acoustic applications. Specifically in bioacoustic, there are rarely sufficient labels for fully supervised learning available. This has led to the widespread use of acoustic recognisers that have been pre-trained on unrelated data for bioacoustic tasks. We posit that training on the actual task data and combining self-supervised pre-training with few-shot classification is a superior approach that has the ability to deliver high accuracy even when only a few labels are available. To this end, we introduce and evaluate a new architecture that combines CNN-based preprocessing with feature extraction based on state space models (SSMs). This combination is motivated by the fact that CNN-based networks alone struggle to capture temporal information effectively, which is crucial for classifying acoustic signals. SSMs, specifically S4 and Mamba, on the other hand, have been shown to have an excellent ability to capture long-range dependencies in sequence data. We pre-train this architecture using contrastive learning on the actual task data and subsequent fine-tuning with an extremely small amount of labelled data. We evaluate the performance of this proposed architecture for ($n$-shot, $n$-class) classification on standard benchmarks as well as real-world data. Our evaluation shows that it outperforms state-of-the-art architectures on the few-shot classification problem.
标注数据有限,自监督学习是降低标注要求的最重要方法之一。虽然它在图像领域已经得到了广泛的研究,但在声学领域尚未得到相同程度的关注。然而,减少标注是许多声学应用的关键需求。特别是在生物声学领域,几乎很少有完全监督学习的充足标签。这导致了预训练于非相关数据的声学识别器在生物声学任务中的广泛使用。我们认为,在实际任务数据上进行训练,并将自监督预训练与少量样本分类相结合是一种更优越的方法,即使在只有少量标签的情况下,也有能力实现高准确性。为此,我们引入并评估了一种新架构,该架构结合了基于CNN的预处理和基于状态空间模型(SSM)的特征提取。这种结合是由这样一个事实驱动的:仅基于CNN的网络难以有效地捕获时间信息,这对于分类声学信号至关重要。另一方面,SSM,特别是S4和Mamba,已被证明在捕获序列数据的长期依赖性方面具有出色的能力。我们使用对比学习在实际任务数据上对此架构进行预训练,随后用极少量的标记数据进行微调。我们在标准基准测试以及真实世界数据上评估了该提议架构在(n-shot,n-class)分类中的性能。我们的评估结果表明,它在小样本分类问题上优于现有最先进的架构。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本摘要针对标注数据有限的问题,提出一种结合自监督预训练和少样本分类的新架构。该架构结合了CNN的预处理和基于状态空间模型(SSM)的特征提取,旨在提高在声学信号分类中的准确性,特别是在生物声学领域。通过对比学习在实际任务数据上进行预训练,并随后用极少量的标记数据进行微调。在标准基准测试和真实世界数据上的评估显示,该架构在少样本分类问题上优于现有技术。
Key Takeaways
- 标注数据有限是许多声学应用面临的挑战,自监督学习是减少标注需求的重要方法之一。
- 在生物声学领域,预训练于非相关数据的声学识别器广泛使用,但使用实际任务数据进行训练和结合自监督预训练的方法可能更优。
- 提出的新架构结合了CNN和SSM,旨在有效捕捉声学信号的时空信息。
- 对比学习用于在实际任务数据上进行预训练。
- 该架构通过微调,使用极少量标记数据即可达到高准确性。
- 在标准基准测试和真实世界数据上的评估显示,该架构在少样本分类问题上表现优异。
- 该方法弥补了图像领域自监督学习的广泛应用与声学领域相对忽视之间的鸿沟。
点此查看论文截图

Towards Foundation Model for Chemical Reactor Modeling: Meta-Learning with Physics-Informed Adaptation
Authors:Zihao Wang, Zhe Wu
Developing accurate models for chemical reactors is often challenging due to the complexity of reaction kinetics and process dynamics. Traditional approaches require retraining models for each new system, limiting generalizability and efficiency. In this work, we take a step toward foundation models for chemical reactor modeling by introducing a neural network framework that generalizes across diverse reactor types and rapidly adapts to new chemical processes. Our approach leverages meta-learning to pretrain the model on a broad set of reactor dynamics, enabling efficient adaptation to unseen reactions with minimal data. To further enhance generalizability, we incorporate physics-informed fine-tuning, ensuring physically consistent adaptation to new reactor conditions. Our framework is evaluated across three integer-order fundamental reactor types - continuous stirred tank reactors, batch reactors, and plug flow reactors - demonstrating superior few-shot adaptation compared to conventional data-driven, physics-informed, and transfer learning approaches. By combining meta-learning with physics-informed adaptation, this work lays the foundation for a generalizable modeling framework, advancing the development of foundation models for chemical engineering applications. Source code is available at https://github.com/killingbear999/chemical-reactor-foundation-model.
针对化学反应器和过程动力学复杂性的特点,开发精确的反应器模型往往面临挑战。传统方法需要为每个新系统重新训练模型,这限制了模型的通用性和效率。在这项工作中,我们朝着构建化学反应堆基础模型的方向迈出了一步,通过引入一种神经网络框架,该框架可广泛应用于各种反应堆类型,并能快速适应新的化学过程。我们的方法利用元学习在广泛的反应堆动力学上对模型进行预训练,使得其能够使用最少的数据快速适应未见过的反应。为了进一步提高模型的通用性,我们采用了基于物理的微调方法,确保新反应器条件下的物理一致性适应。我们的框架在三种整数阶基本反应堆类型(连续搅拌罐反应器、间歇反应器和塞流反应器)上进行了评估,展示了与传统数据驱动、物理知情和迁移学习等方法相比的优异少样本适应能力。通过将元学习与物理知情适应相结合,这项工作为通用建模框架奠定了基础,推动了化学工程应用基础模型的开发。相关源代码可在 https://github.com/killingbear999/chemical-reactor-foundation-model 上获取。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Chemical Engineering Research and Design
Summary
本文引入了一种神经网络框架,用于建立通用的化学反应堆模型,该框架可快速适应新的化学反应过程。该研究利用元学习对模型进行预训练,使其在广泛的反应器动力学上具备一般性,并能以最小的数据快速适应未见过的反应。为提高模型的通用性,研究结合了物理信息微调技术,确保对新反应器条件的适应具有物理一致性。该研究在三种基本反应器类型上评估了其框架的效能,展示了与传统数据驱动、物理信息驱动和迁移学习等方法相比的优异性能。该研究为建立通用的建模框架奠定了基础,推动了化学工程应用中的基础模型的发展。
Key Takeaways
- 引入神经网络框架用于化学反应堆建模,实现快速适应新化学反应过程。
- 利用元学习对模型进行预训练,提高模型在广泛反应器动力学上的通用性。
- 借助物理信息微调技术增强模型的适应性,确保对新反应器条件的适应具有物理一致性。
- 在三种基本反应器类型上进行了框架评估,展示优越性能。
- 对比了传统数据驱动、物理信息驱动和迁移学习方法,显示出其优势。
- 建立了通用的建模框架,推动了化学工程应用中的基础模型发展。
点此查看论文截图

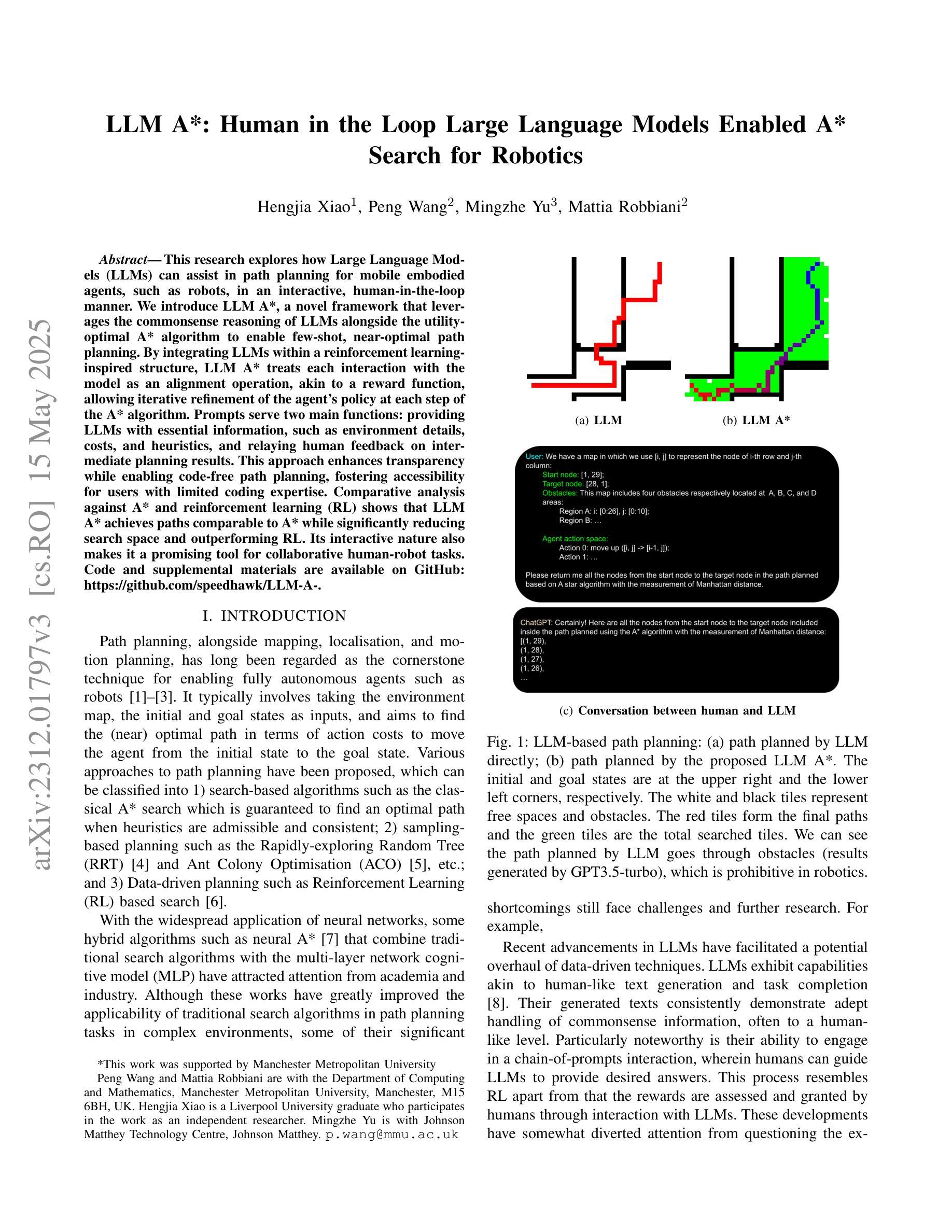
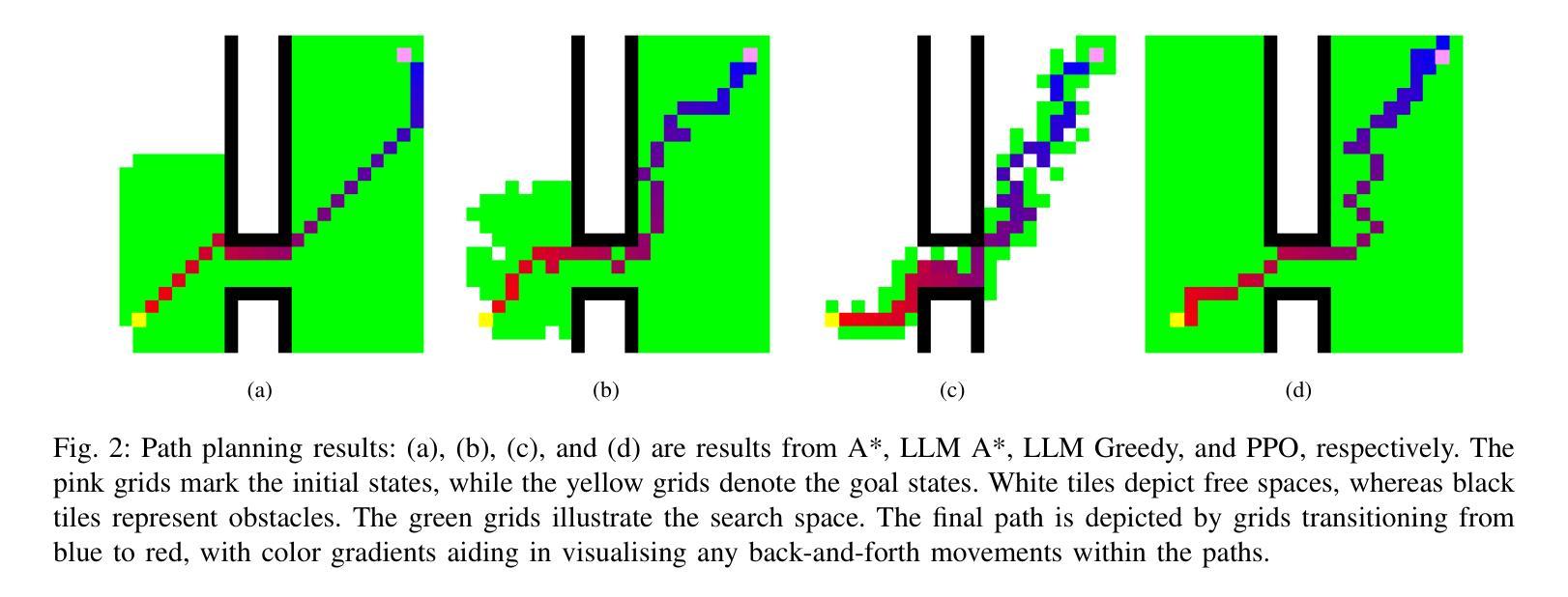
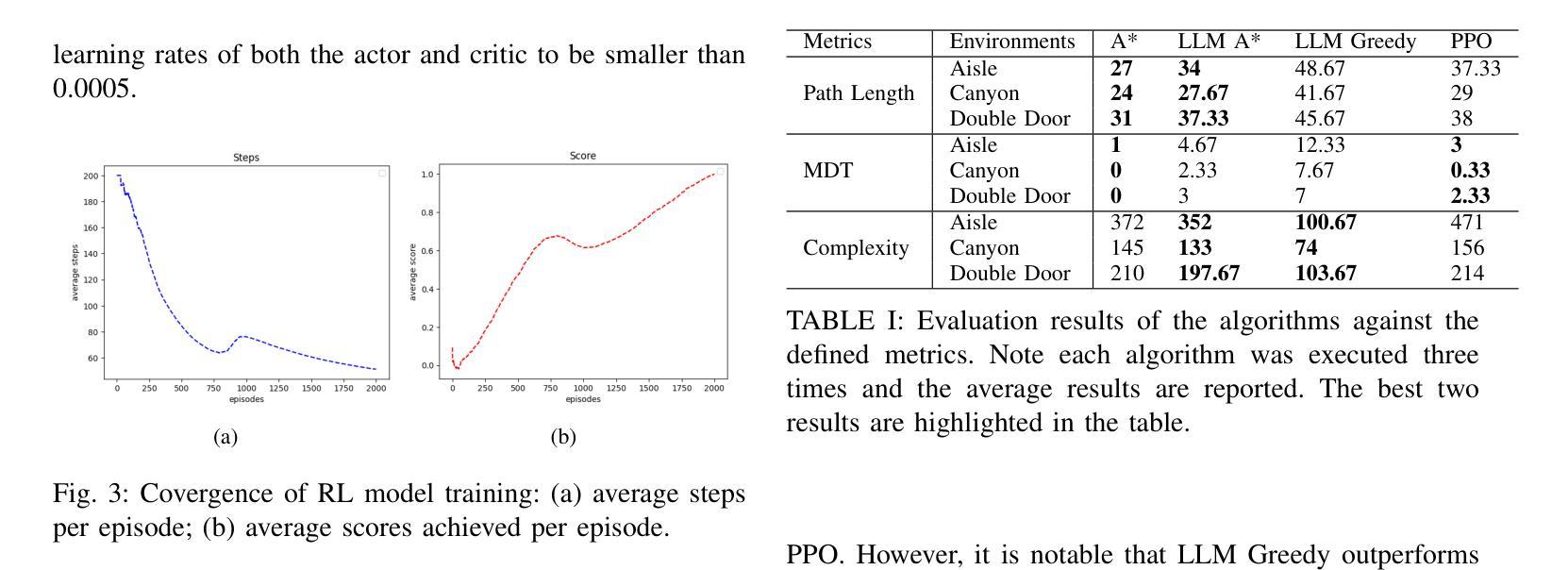
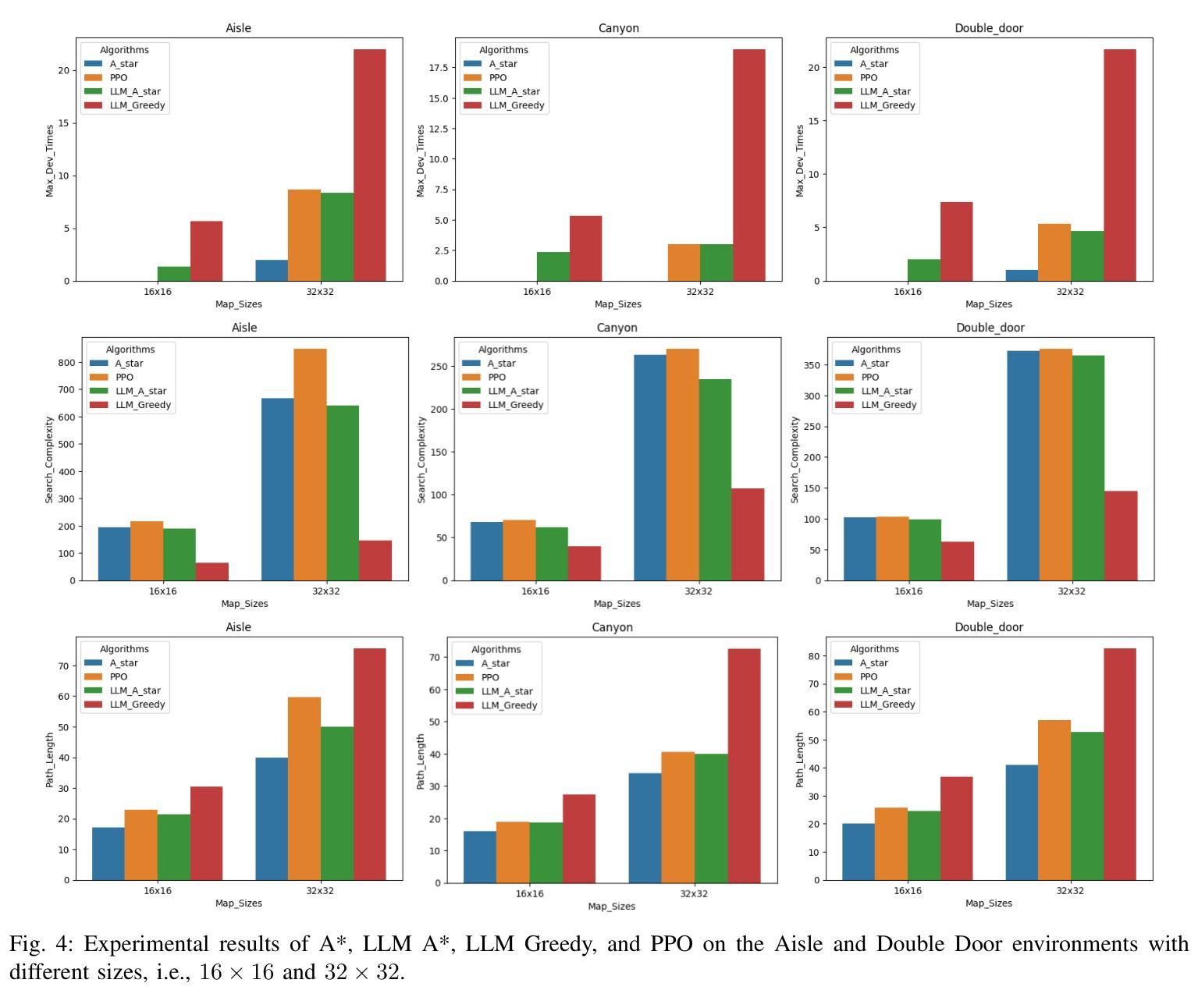
LLM A*: Human in the Loop Large Language Models Enabled A* Search for Robotics
Authors:Hengjia Xiao, Peng Wang, Mingzhe Yu, Mattia Robbiani
This research focuses on how Large Language Models (LLMs) can help with (path) planning for mobile embodied agents such as robots, in a human-in-the-loop and interactive manner. A novel framework named LLM A*, aims to leverage the commonsense of LLMs, and the utility-optimal A* is proposed to facilitate few-shot near-optimal path planning. Prompts are used for two main purposes: 1) to provide LLMs with essential information like environments, costs, heuristics, etc.; 2) to communicate human feedback on intermediate planning results to LLMs. This approach takes human feedback on board and renders the entire planning process transparent (akin to a `white box’) to humans. Moreover, it facilitates code-free path planning, thereby fostering the accessibility and inclusiveness of artificial intelligence techniques to communities less proficient in coding. Comparative analysis against A* and RL demonstrates that LLM A* exhibits greater efficiency in terms of search space and achieves paths comparable to A* while outperforming RL. The interactive nature of LLM A* also makes it a promising tool for deployment in collaborative human-robot tasks. Codes and Supplemental Materials can be found at GitHub: https://github.com/speedhawk/LLM-A-.
本文重点研究大型语言模型(LLM)如何以人机循环和交互的方式,为移动实体代理(如机器人)进行(路径)规划提供帮助。提出了一种名为LLM A的新型框架,旨在利用LLM的常识,并提出了实用最优A,以促进少数最优路径规划。提示用于两个主要目的:1)为LLM提供环境、成本、启发式等基本信息;2)对LLM传达中间规划结果的人类反馈。这种方法接受人类反馈,使整个规划过程对人类透明(类似于“白盒”)。此外,它促进了无需编码的路径规划,从而提高了编码能力不足的社区对人工智能技术的可及性和包容性。与A和强化学习(RL)的对比分析表明,LLM A在搜索空间方面表现出更高的效率,实现的路径与A相当但优于RL。LLM A的交互性也使其成为在人机协作任务中部署的有前途的工具。代码和补充材料可在GitHub上找到:https://github.com/speedhawk/LLM-A-。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 7 figures, 8 pages
Summary:该研究探讨如何利用大型语言模型(LLM)辅助移动实体(如机器人)进行路径规划。提出一种名为LLM A的新框架,通过利用LLM的常识知识和A算法实现少样本近优路径规划。通过提示实现人机互动反馈,使规划过程透明化,并促进非编码用户参与路径规划,提高人工智能技术的普及性和包容性。与A和强化学习相比,LLM A在搜索空间上具有更高的效率,且路径规划效果与A*相当,优于强化学习。
Key Takeaways:
- LLM A*框架结合大型语言模型(LLM)进行移动实体路径规划,促进人机互动。
- 利用提示(prompt)实现环境信息提供和人类反馈的双向交流。
- LLM A*框架使路径规划过程透明化,便于人类理解。
- 非编码用户也能利用LLM A*参与路径规划,提高了人工智能技术的普及性和包容性。
- LLM A*相比传统算法在搜索空间上具有更高的效率。
- LLM A的路径规划效果与A算法相当。
点此查看论文截图