⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-05-17 更新
3D-Fixup: Advancing Photo Editing with 3D Priors
Authors:Yen-Chi Cheng, Krishna Kumar Singh, Jae Shin Yoon, Alex Schwing, Liangyan Gui, Matheus Gadelha, Paul Guerrero, Nanxuan Zhao
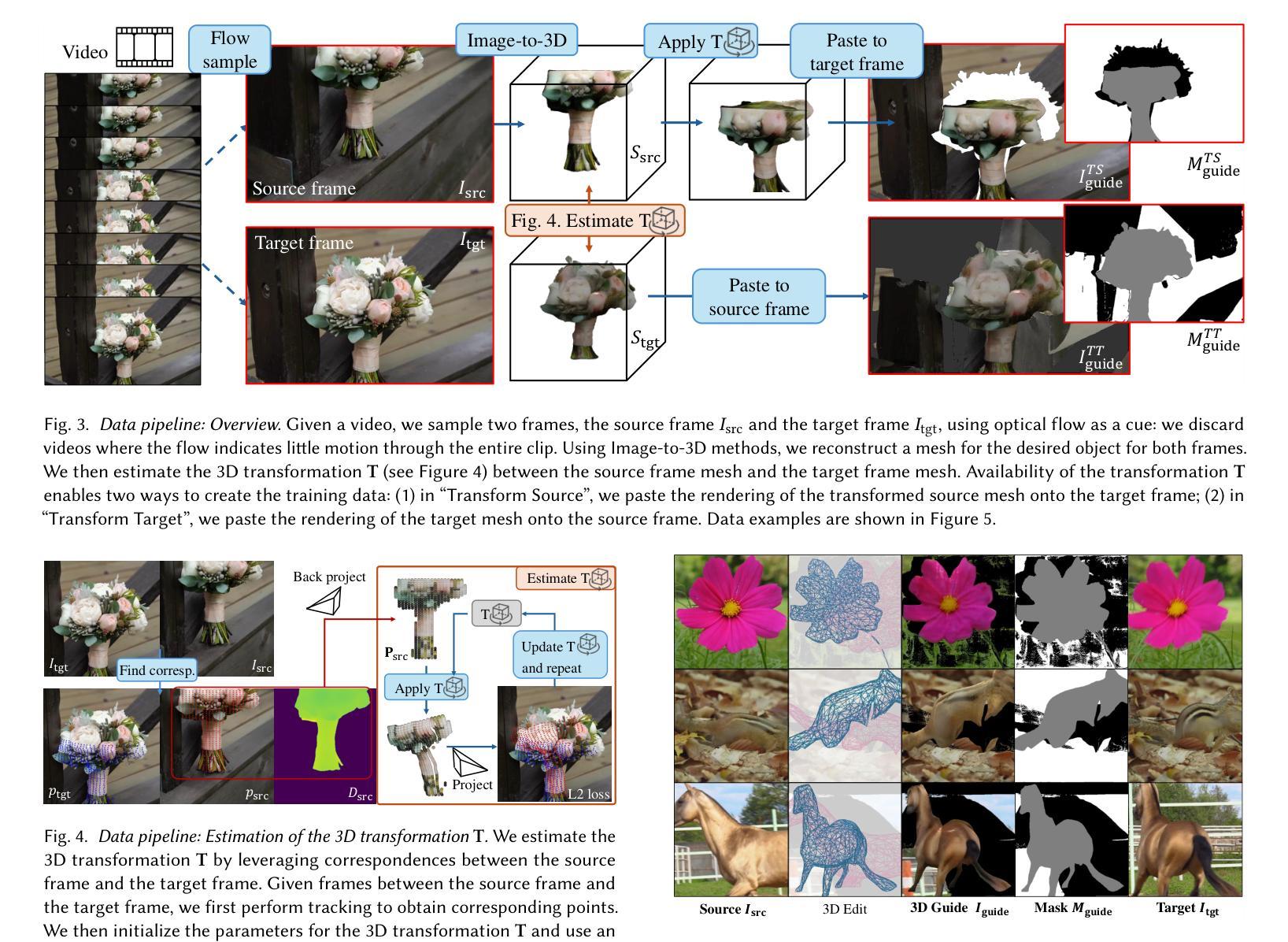
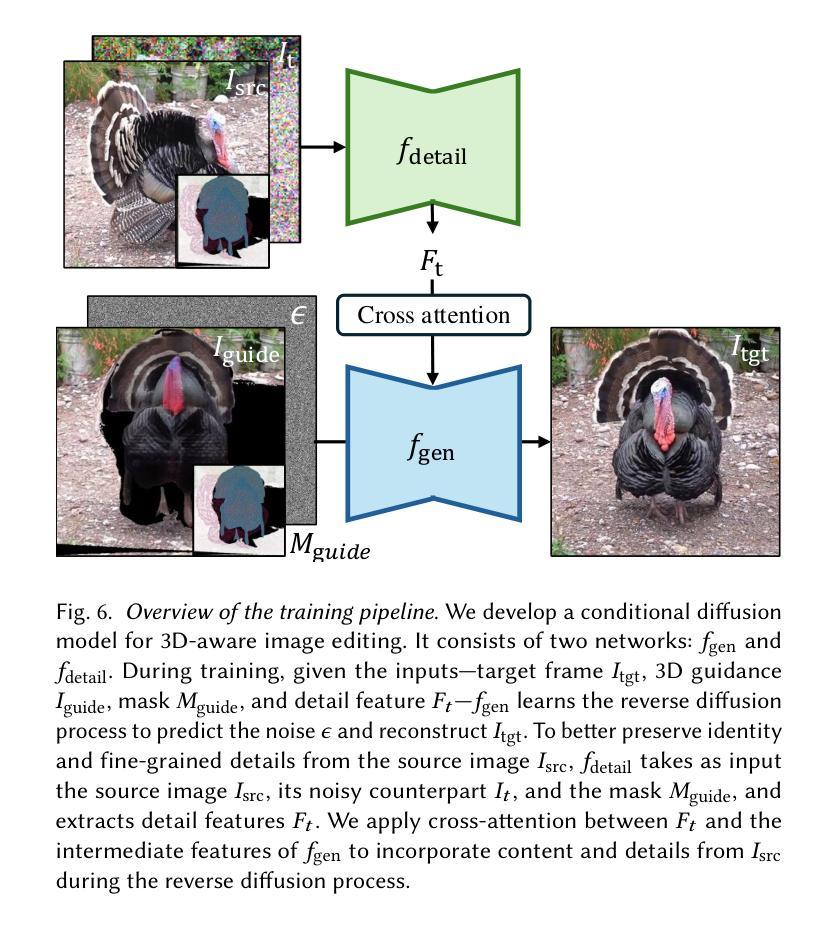
Despite significant advances in modeling image priors via diffusion models, 3D-aware image editing remains challenging, in part because the object is only specified via a single image. To tackle this challenge, we propose 3D-Fixup, a new framework for editing 2D images guided by learned 3D priors. The framework supports difficult editing situations such as object translation and 3D rotation. To achieve this, we leverage a training-based approach that harnesses the generative power of diffusion models. As video data naturally encodes real-world physical dynamics, we turn to video data for generating training data pairs, i.e., a source and a target frame. Rather than relying solely on a single trained model to infer transformations between source and target frames, we incorporate 3D guidance from an Image-to-3D model, which bridges this challenging task by explicitly projecting 2D information into 3D space. We design a data generation pipeline to ensure high-quality 3D guidance throughout training. Results show that by integrating these 3D priors, 3D-Fixup effectively supports complex, identity coherent 3D-aware edits, achieving high-quality results and advancing the application of diffusion models in realistic image manipulation. The code is provided at https://3dfixup.github.io/
尽管通过扩散模型对图像先验进行建模取得了重大进展,但由于物体仅通过单张图像指定,3D感知图像编辑仍然具有挑战性。为了应对这一挑战,我们提出了3D-Fixup,这是一个由学习到的3D先验引导编辑2D图像的新框架。该框架支持物体平移和3D旋转等复杂编辑情况。为了实现这一点,我们采用了一种基于训练的方法,利用扩散模型的生成能力。由于视频数据天然地编码了现实世界的物理动态,我们转向视频数据来生成训练数据对,即源帧和目标帧。我们并没有仅依赖单个训练模型来推断源帧和目标帧之间的转换,而是融入了来自Image-to-3D模型的3D指导,该模型通过显式地将2D信息投影到3D空间中,从而应对这一具有挑战性的任务。我们设计了一个数据生成管道,以确保在整个训练过程中提供高质量的3D指导。结果表明,通过整合这些3D先验知识,3D-Fixup有效地支持了复杂、身份一致的3D感知编辑,取得了高质量的结果,并推动了扩散模型在真实图像操作中的应用。相关代码已发布在https://3dfixup.github.io/上。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF SIGGRAPH 2025. Project page: https://3dfixup.github.io/
Summary
本文提出一种名为“3D-Fixup”的新框架,用于通过学到的3D先验知识来编辑二维图像。该框架支持物体平移和三维旋转等复杂编辑情况。它采用基于训练的方法,利用扩散模型的生成能力。借助视频数据编码的现实世界物理动态特性,生成训练数据对(即源帧和目标帧)。通过结合Image-to-3D模型的3D指导,显式地将二维信息投影到三维空间中,解决了源帧和目标帧之间转换的推断难题。通过整合这些3D先验知识,3D-Fixup有效支持复杂的、身份一致的3D感知编辑,实现高质量结果,推动扩散模型在真实图像操作中的应用。
Key Takeaways
- 3D-Fixup是一个新的框架,旨在通过学到的3D先验知识来解决仅通过单一图像指定物体的3D-aware图像编辑挑战。
- 框架支持物体平移和三维旋转等复杂编辑情况,利用扩散模型的生成能力。
- 采用视频数据生成训练数据对,包括源帧和目标帧,利用现实世界的物理动态特性。
- 结合Image-to-3D模型的3D指导,显式地将二维信息投影到三维空间中。
- 通过整合3D先验知识,3D-Fixup能实现高质量的复杂、身份一致的3D感知编辑。
- 该框架推动了扩散模型在真实图像操作中的应用。
点此查看论文截图


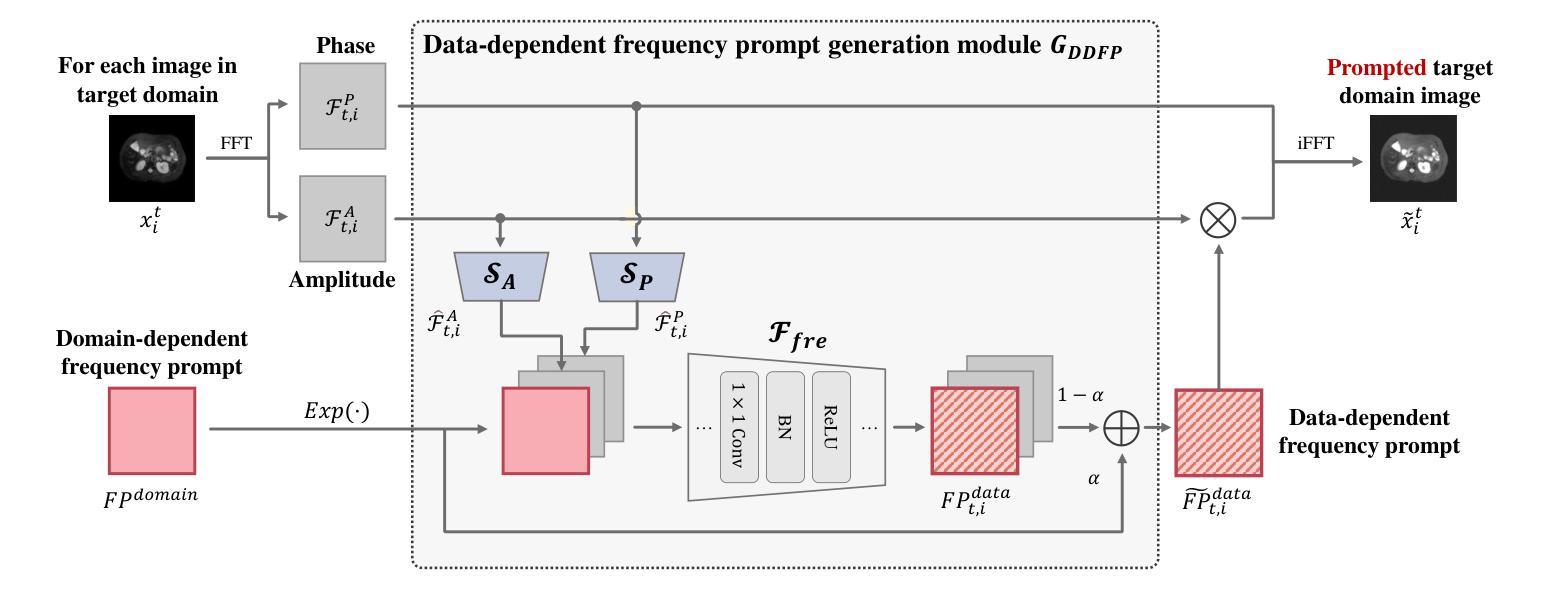
DDFP: Data-dependent Frequency Prompt for Source Free Domain Adaptation of Medical Image Segmentation
Authors:Siqi Yin, Shaolei Liu, Manning Wang
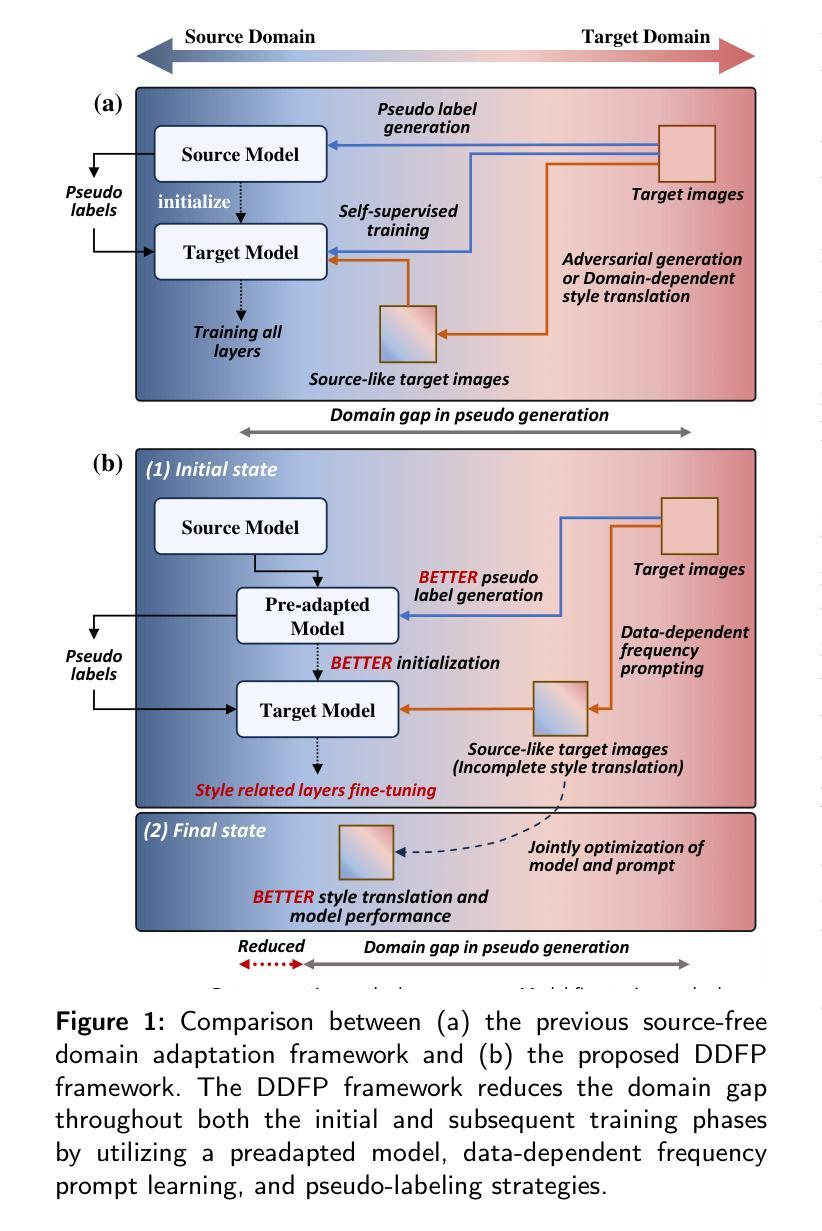
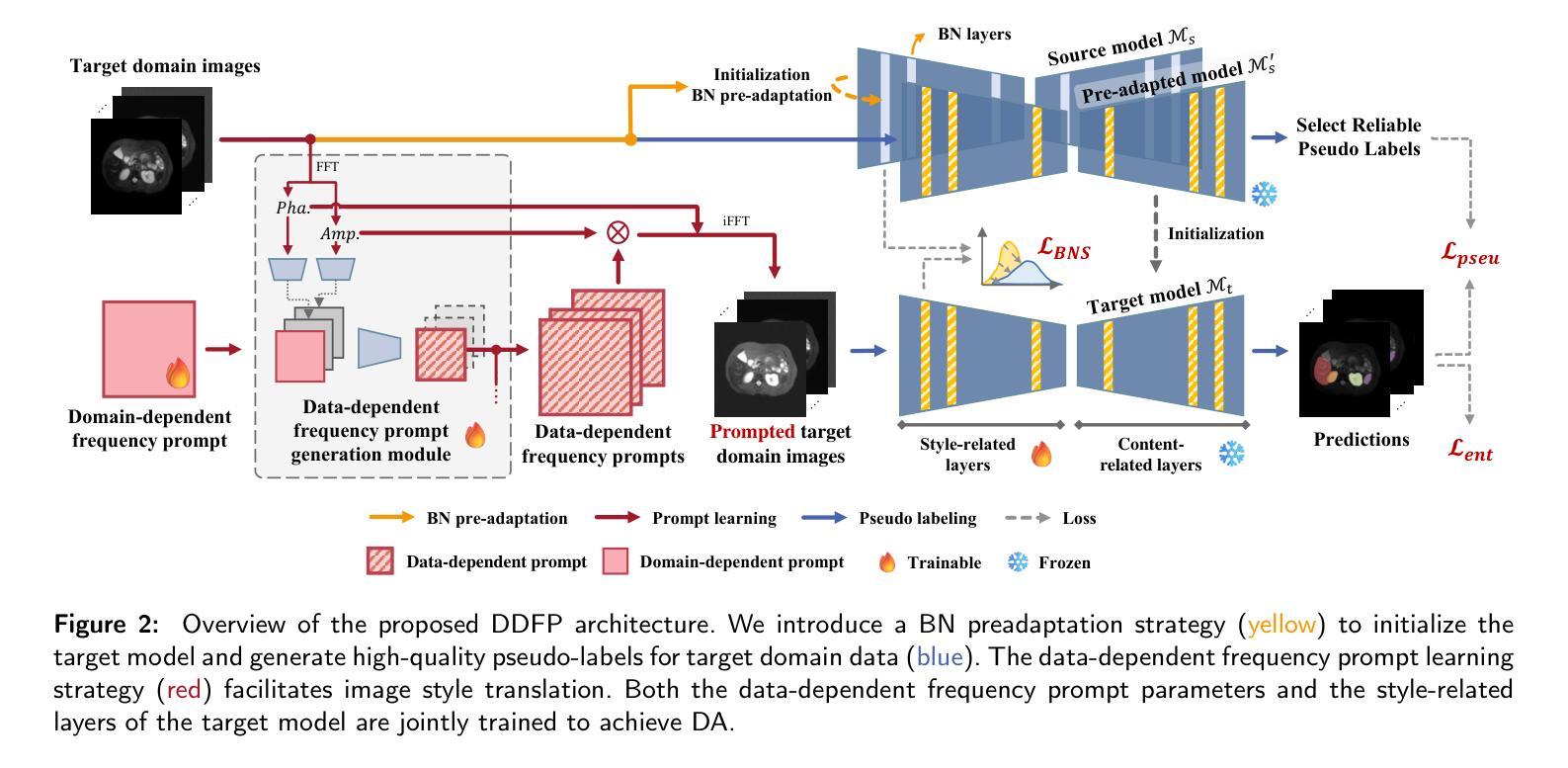
Domain adaptation addresses the challenge of model performance degradation caused by domain gaps. In the typical setup for unsupervised domain adaptation, labeled data from a source domain and unlabeled data from a target domain are used to train a target model. However, access to labeled source domain data, particularly in medical datasets, can be restricted due to privacy policies. As a result, research has increasingly shifted to source-free domain adaptation (SFDA), which requires only a pretrained model from the source domain and unlabeled data from the target domain data for adaptation. Existing SFDA methods often rely on domain-specific image style translation and self-supervision techniques to bridge the domain gap and train the target domain model. However, the quality of domain-specific style-translated images and pseudo-labels produced by these methods still leaves room for improvement. Moreover, training the entire model during adaptation can be inefficient under limited supervision. In this paper, we propose a novel SFDA framework to address these challenges. Specifically, to effectively mitigate the impact of domain gap in the initial training phase, we introduce preadaptation to generate a preadapted model, which serves as an initialization of target model and allows for the generation of high-quality enhanced pseudo-labels without introducing extra parameters. Additionally, we propose a data-dependent frequency prompt to more effectively translate target domain images into a source-like style. To further enhance adaptation, we employ a style-related layer fine-tuning strategy, specifically designed for SFDA, to train the target model using the prompted target domain images and pseudo-labels. Extensive experiments on cross-modality abdominal and cardiac SFDA segmentation tasks demonstrate that our proposed method outperforms existing state-of-the-art methods.
领域适应(Domain Adaptation)旨在解决因领域差异导致的模型性能下降的挑战。在典型的无监督领域适应设置中,使用来自源域的标注数据以及来自目标域的无标注数据来训练目标模型。然而,由于隐私政策,特别是医疗数据集的标注源域数据可能受到限制。因此,研究逐渐转向无源域适应(SFDA),它只需要源域的预训练模型以及目标域的无标注数据进行适应。现有的SFDA方法通常依赖于领域特定的图像风格转换和自我监督技术来弥合领域差距并训练目标域模型。然而,这些方法产生的领域特定风格转换图像和伪标签的质量仍有提升空间。此外,在有限的监督下,对整个模型进行适应训练可能效率低下。针对这些挑战,我们在本文中提出了一种新型的SFDA框架。具体来说,为了有效减轻初始训练阶段中的领域差距影响,我们引入预适应(preadaptation)来生成预适应模型,作为目标模型的初始化,并允许生成高质量的增强伪标签,而不会引入额外的参数。此外,我们提出了一种数据依赖的频率提示(frequency prompt),以更有效地将目标域图像转换为类似源域的风格。为了进一步增强适应,我们采用了一种针对SFDA设计的风格相关层微调策略,使用提示的目标域图像和伪标签训练目标模型。在跨模态腹部和心脏SFDA分割任务上的大量实验表明,我们提出的方法优于现有的最先进方法。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文提出了一个无需源域标签数据的新源自由域自适应(SFDA)框架,解决了模型性能因领域差异而下降的问题。该框架引入预适应生成预适应模型,减少领域差距的影响,利用数据依赖的频率提示翻译目标域图像,并使用针对SFDA设计的风格相关层微调策略训练目标模型。实验证明该方法在跨模态腹部和心脏SFDA分割任务上优于现有技术。
Key Takeaways
- 领域自适应是解决模型性能因领域差异而下降的挑战的一种方法。
- 源自由域自适应(SFDA)仅需要源域的预训练模型和来自目标域的无标签数据进行适应。
- 现有SFDA方法依赖于领域特定的图像风格翻译和自监督技术,但生成图像和伪标签的质量仍有提升空间。
- 本文引入预适应生成预适应模型,作为目标模型的初始化,减少领域差距的影响。
- 提出数据依赖的频率提示,更有效地将目标域图像翻译成类似源域的风格。
- 采用针对SFDA设计的风格相关层微调策略,利用提示的目标域图像和伪标签训练目标模型。
点此查看论文截图

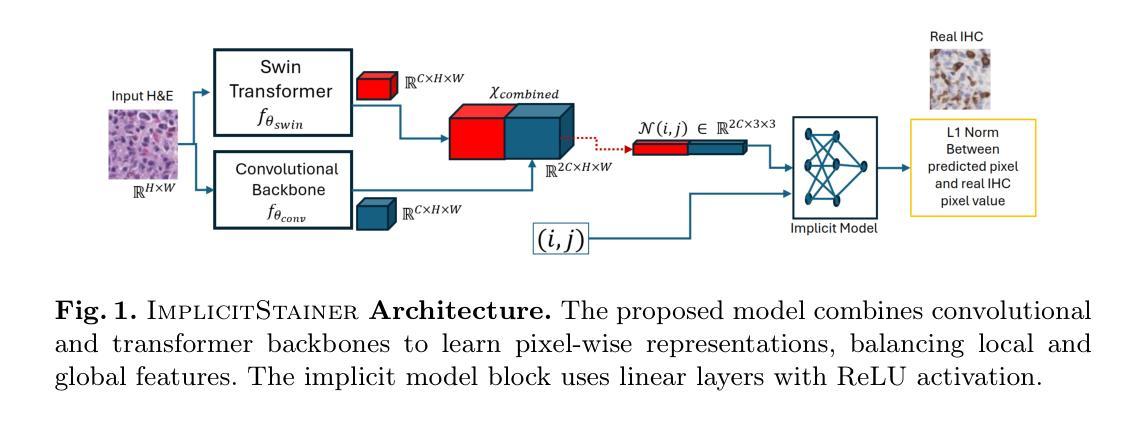
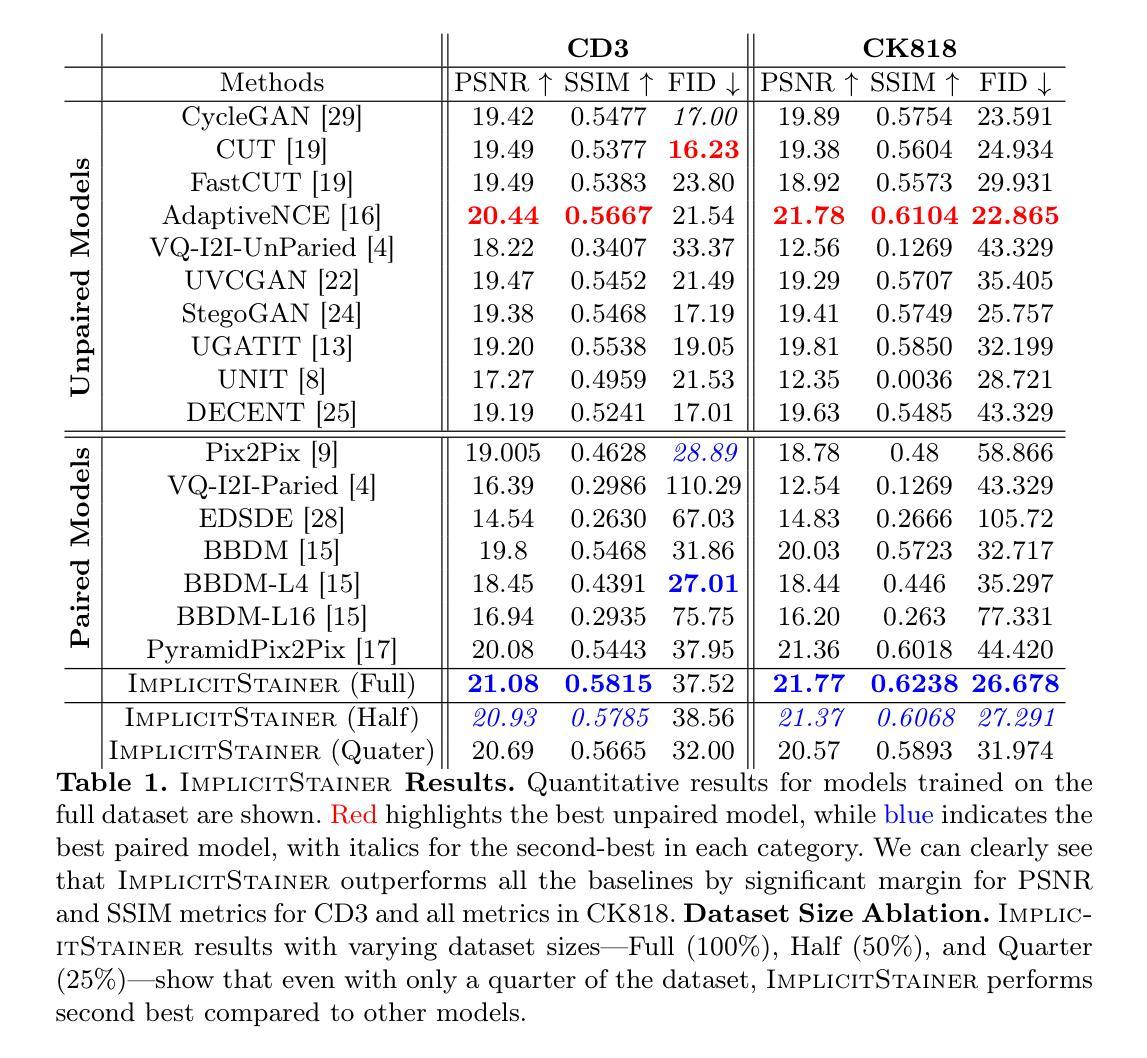
ImplicitStainer: Data-Efficient Medical Image Translation for Virtual Antibody-based Tissue Staining Using Local Implicit Functions
Authors:Tushar Kataria, Beatrice Knudsen, Shireen Y. Elhabian
Hematoxylin and eosin (H&E) staining is a gold standard for microscopic diagnosis in pathology. However, H&E staining does not capture all the diagnostic information that may be needed. To obtain additional molecular information, immunohistochemical (IHC) stains highlight proteins that mark specific cell types, such as CD3 for T-cells or CK8/18 for epithelial cells. While IHC stains are vital for prognosis and treatment guidance, they are typically only available at specialized centers and time consuming to acquire, leading to treatment delays for patients. Virtual staining, enabled by deep learning-based image translation models, provides a promising alternative by computationally generating IHC stains from H&E stained images. Although many GAN and diffusion based image to image (I2I) translation methods have been used for virtual staining, these models treat image patches as independent data points, which results in increased and more diverse data requirements for effective generation. We present ImplicitStainer, a novel approach that leverages local implicit functions to improve image translation, specifically virtual staining performance, by focusing on pixel-level predictions. This method enhances robustness to variations in dataset sizes, delivering high-quality results even with limited data. We validate our approach on two datasets using a comprehensive set of metrics and benchmark it against over fifteen state-of-the-art GAN- and diffusion based models. Full Code and models trained will be released publicly via Github upon acceptance.
苏木精和伊红(H&E)染色是病理学显微镜诊断的金标准。然而,H&E染色并不能捕捉到所有所需的诊断信息。为了获得额外的分子信息,免疫组织化学(IHC)染色会突出显示标记特定细胞类型的蛋白质,如T细胞的CD3或上皮细胞的CK8/18。虽然IHC染色对于预后和治疗指导至关重要,但它们通常仅在专业中心提供,且获取时间较长,导致患者治疗延迟。深度学习驱动的图像翻译模型启用了虚拟染色技术,该技术可以通过计算从H&E染色图像生成IHC染色。尽管许多生成对抗网络(GAN)和基于扩散的图像到图像(I2I)翻译方法已被用于虚拟染色,但这些模型将图像斑块视为独立的数据点,导致需要更多样化和增加的数据才能有效生成。我们提出了ImplicitStainer这一新方法,它利用局部隐函数来提高图像翻译,特别是虚拟染色性能,侧重于像素级预测。这种方法提高了对数据集大小变化的稳健性,即使在有限的数据下也能产生高质量的结果。我们在两个数据集上验证了我们的方法,使用了一套综合指标,并与超过十五种最先进的GAN和基于扩散的模型进行了基准测试。一旦接受,我们将通过GitHub公开发布完整的代码和训练好的模型。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary:
通过深度学习的图像翻译模型实现虚拟染色技术,能够从H&E染色图像中计算生成免疫组织化学染色,提高病理诊断的准确性和效率。然而,现有方法存在数据需求量大和处理图像补丁独立的问题。本研究提出了一种名为ImplicitStainer的新方法,利用局部隐函数提高图像翻译质量,尤其针对虚拟染色性能进行改进,通过像素级预测增强稳健性,在有限数据下也能获得高质量结果。
Key Takeaways:
- H&E染色是病理学显微镜诊断的金标准,但无法捕获所有诊断所需的信息。
- 免疫组织化学染色(IHC)对于预后和治疗指导至关重要,但获取过程复杂且耗时。
- 虚拟染色技术通过深度学习图像翻译模型为病理学诊断提供了新的选择。
- 当前虚拟染色方法存在数据需求量大和处理图像补丁独立的问题。
- ImplicitStainer方法利用局部隐函数提高图像翻译质量,特别针对虚拟染色性能优化。
- ImplicitStainer通过像素级预测增强稳健性,在有限数据下也能生成高质量结果。
点此查看论文截图