⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-05-17 更新
FlexSpeech: Towards Stable, Controllable and Expressive Text-to-Speech
Authors:Linhan Ma, Dake Guo, He Wang, Jin Xu, Lei Xie
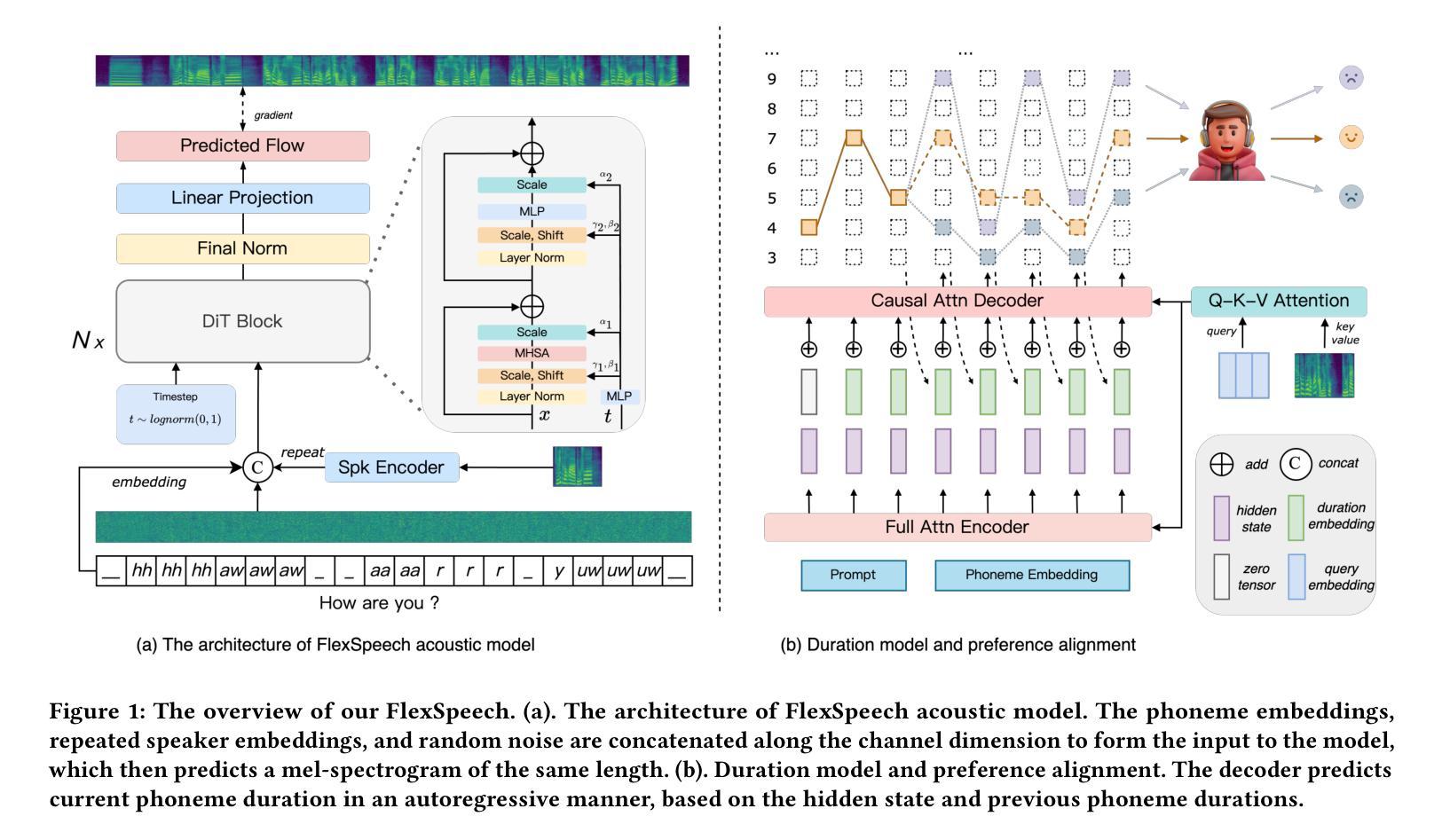
Current speech generation research can be categorized into two primary classes: non-autoregressive and autoregressive. The fundamental distinction between these approaches lies in the duration prediction strategy employed for predictable-length sequences. The NAR methods ensure stability in speech generation by explicitly and independently modeling the duration of each phonetic unit. Conversely, AR methods employ an autoregressive paradigm to predict the compressed speech token by implicitly modeling duration with Markov properties. Although this approach improves prosody, it does not provide the structural guarantees necessary for stability. To simultaneously address the issues of stability and naturalness in speech generation, we propose FlexSpeech, a stable, controllable, and expressive TTS model. The motivation behind FlexSpeech is to incorporate Markov dependencies and preference optimization directly on the duration predictor to boost its naturalness while maintaining explicit modeling of the phonetic units to ensure stability. Specifically, we decompose the speech generation task into two components: an AR duration predictor and a NAR acoustic model. The acoustic model is trained on a substantial amount of data to learn to render audio more stably, given reference audio prosody and phone durations. The duration predictor is optimized in a lightweight manner for different stylistic variations, thereby enabling rapid style transfer while maintaining a decoupled relationship with the specified speaker timbre. Experimental results demonstrate that our approach achieves SOTA stability and naturalness in zero-shot TTS. More importantly, when transferring to a specific stylistic domain, we can accomplish lightweight optimization of the duration module solely with about 100 data samples, without the need to adjust the acoustic model, thereby enabling rapid and stable style transfer.
目前的语音生成研究可以主要分为两大类:非自回归和自回归。这两种方法之间的根本区别在于它们用于预测长度序列的持续预测策略。NAR方法通过明确且独立地对每个语音单元的持续时间进行建模,确保了语音生成的稳定性。相反,AR方法采用自回归范式,通过隐式地利用马尔可夫属性来预测压缩的语音标记。尽管这种方法改善了韵律,但它并没有提供保证稳定性的结构保障。为了解决语音生成中的稳定性和自然性问题,我们提出了FlexSpeech,这是一种稳定、可控、表达力强的TTS模型。FlexSpeech的动机是在持续时间预测器上直接融入马尔可夫依赖和偏好优化,以提升其自然性,同时保持对语音单元的显式建模以确保稳定性。具体来说,我们将语音生成任务分解为两个组成部分:AR持续时间预测器和NAR声学模型。声学模型经过大量数据训练,能够在给定参考音频韵律和电话持续时间的情况下,学习更稳定地呈现音频。持续时间预测器以轻巧的方式进行优化,以适应不同的风格变化,从而在保持与指定演讲者音色解耦的同时,实现快速风格转换。实验结果表明,我们的方法在实现零TTS时的稳定性和自然性方面达到了最新水平。更重要的是,在转移到特定风格领域时,我们仅使用约100个数据样本对持续时间模块进行轻量级优化,无需调整声学模型,从而实现了快速稳定的风格转换。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 10 pages, 5 figures
Summary
本文主要介绍了两种主要的语音生成方法:非自回归(NAR)和自回归(AR)。NAR方法通过显式独立建模每个语音单元的持续时间来保证语音生成的稳定性。而AR方法则采用自回归范式,通过隐式建模持续时间(如马尔可夫属性)来预测压缩语音符号,虽可以改善韵律,但缺乏结构稳定性保障。为解决这两大问题,本文提出了FlexSpeech模型,这是一种稳定、可控且表现力强的文本转语音模型。FlexSpeech通过直接在持续时间预测器上引入马尔可夫依赖关系和偏好优化,在保持语音单元显式建模的同时,提高了其自然度。实验结果证明,该方法在零样本TTS中实现了先进稳定性和自然度的结合。尤其是在特定风格领域的迁移中,仅通过约100个数据样本对持续时间模块进行轻量化优化,无需调整声学模型,实现了快速稳定的风格迁移。
Key Takeaways
- 当前语音生成研究主要分为非自回归和自回归两种方法。两者在预测时长序列时采用不同策略。
- 非自回归方法(NAR)侧重于通过显式建模每个语音单元的持续时间来保证语音生成的稳定性。
- 自回归方法(AR)虽然能提高韵律,但在结构稳定性方面存在不足。
- FlexSpeech是一个稳定、可控且表现力强的TTS模型,结合了非自回归和自回归的优势。
- FlexSpeech通过优化持续时间预测器,实现了自然度和稳定性的平衡。
- FlexSpeech将语音生成任务分为两个组件:自回归持续时间预测器和非自回归声学模型。
点此查看论文截图