⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-05-20 更新
GOUHFI: a novel contrast- and resolution-agnostic segmentation tool for Ultra-High Field MRI
Authors:Marc-Antoine Fortin, Anne Louise Kristoffersen, Michael Staff Larsen, Laurent Lamalle, Ruediger Stirnberg, Paal Erik Goa
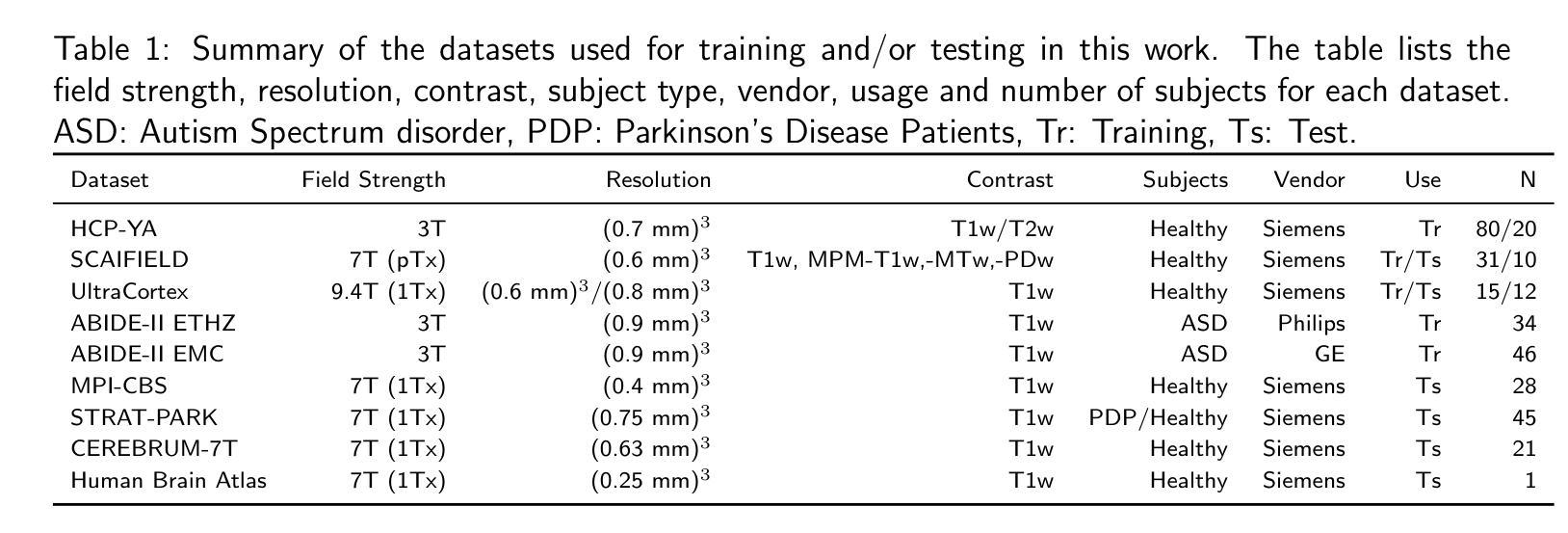
Recently, Ultra-High Field MRI (UHF-MRI) has become more available and one of the best tools to study the brain. One common step in quantitative neuroimaging is the brain segmentation. However, the differences between UHF-MRI and 1.5-3T images are such that the automatic segmentation techniques optimized at these field strengths usually produce unsatisfactory segmentation results for UHF images. It has been particularly challenging to perform quantitative analyses as typically done with 1.5-3T data, considerably limiting the potential of UHF-MRI. Hence, we propose a novel Deep Learning (DL)-based segmentation technique called GOUHFI: Generalized and Optimized segmentation tool for Ultra-High Field Images, designed to segment UHF images of various contrasts and resolutions. For training, we used a total of 206 label maps from four datasets acquired at 3T, 7T and 9.4T. In contrast to most DL strategies, we used a previously proposed domain randomization approach, where synthetic images generated from the label maps were used for training a 3D U-Net. GOUHFI was tested on seven different datasets and compared to techniques like FastSurferVINN and CEREBRUM-7T. GOUHFI was able to the segment six contrasts and seven resolutions tested at 3T, 7T and 9.4T. Average Dice-Sorensen Similarity Coefficient (DSC) scores of 0.87, 0.84, 0.91 were computed against the ground truth segmentations at 3T, 7T and 9.4T. Moreover, GOUHFI demonstrated impressive resistance to the typical inhomogeneities observed at UHF-MRI, making it a new powerful segmentation tool that allows to apply the usual quantitative analysis pipelines also at UHF. Ultimately, GOUHFI is a promising new segmentation tool, being the first of its kind proposing a contrast- and resolution-agnostic alternative for UHF-MRI, making it the forthcoming alternative for neuroscientists working with UHF-MRI or even lower field strengths.
最近,超高场磁共振成像(UHF-MRI)变得越来越普及,已成为研究大脑的最佳工具之一。定量神经影像学中的一个常见步骤是大脑分割。然而,UHF-MRI与1.5-3T图像之间的差异使得针对这些场强优化的自动分割技术通常会产生令人不满意的UHF图像分割结果。使用通常用于1.5-3T数据的定量分析方法具有挑战性,这极大地限制了UHF-MRI的潜力。因此,我们提出了一种新型的基于深度学习的分割技术,称为GOUHFI:适用于超高场图像的通用优化分割工具,旨在分割具有各种对比度和分辨率的UHF图像。为了训练,我们使用了从3T、7T和9.4T采集的四个数据集的共206个标签图。与大多数深度学习策略不同,我们采用了先前提出的域随机化方法,其中根据标签图生成的合成图像用于训练3D U-Net。GOUHFI在七个不同的数据集上进行了测试,并与FastSurferVINN和CEREBRUM-7T等技术进行了比较。GOUHFI能够在3T、7T和9.4T测试的六种对比度和七种分辨率下进行分割。与3T、7T和9.4T的基准分割相比,计算出的平均Dice-Sorensen相似系数(DSC)分数分别为0.87、0.84、0.91。此外,GOUHFI对UHF-MRI中常见的非均匀性表现出了令人印象深刻的抗性,成为了一种强大的新分割工具,允许在UHF上应用通常的定量分析流水线。最终,GOUHFI是一种有前途的新分割工具,它是第一个提出适用于UHF-MRI的对比度和分辨率无关替代方案的工具,使其成为从事UHF-MRI研究的神经科学家或甚至使用较低场强的科学家的未来替代方案。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 45 pages, 9 Figures, 6 Tables, Submitted to Imaging Neuroscience on 16-05-25
Summary
本文介绍了一种基于深度学习的新型超高频磁共振成像(UHF-MRI)分割工具GOUHFI。该工具可用于对各种对比度和分辨率的UHF图像进行分割,并通过使用合成图像进行训练来提高性能。在多个数据集上测试后,GOUHFI展现出良好的分割效果,并具有较高的抵抗UHF-MRI常见的不均匀性能力。它为神经科学家提供了一种有前途的新工具,可作为超高频和较低场强的MRI的替代方案。
Key Takeaways
- UHF-MRI已成为研究大脑的最佳工具之一,但在定量分析中面临挑战。
- 自动分割技术在超高场MRI上优化通常产生不满意的分割结果。
- GOUHFI是一个基于深度学习的新型分割工具,旨在解决UHF图像的分割问题。
- GOUHFI可用于多种对比度和分辨率的UHF图像分割。
- 使用合成图像进行训练,提高GOUHFI的性能。
- GOUHFI在多个数据集上表现出良好的分割效果,并具有较高的抵抗UHF-MRI不均匀性的能力。
- GOUHFI为神经科学家提供了一种有前途的新工具,可应用于超高频和较低场强的MRI分析。
点此查看论文截图

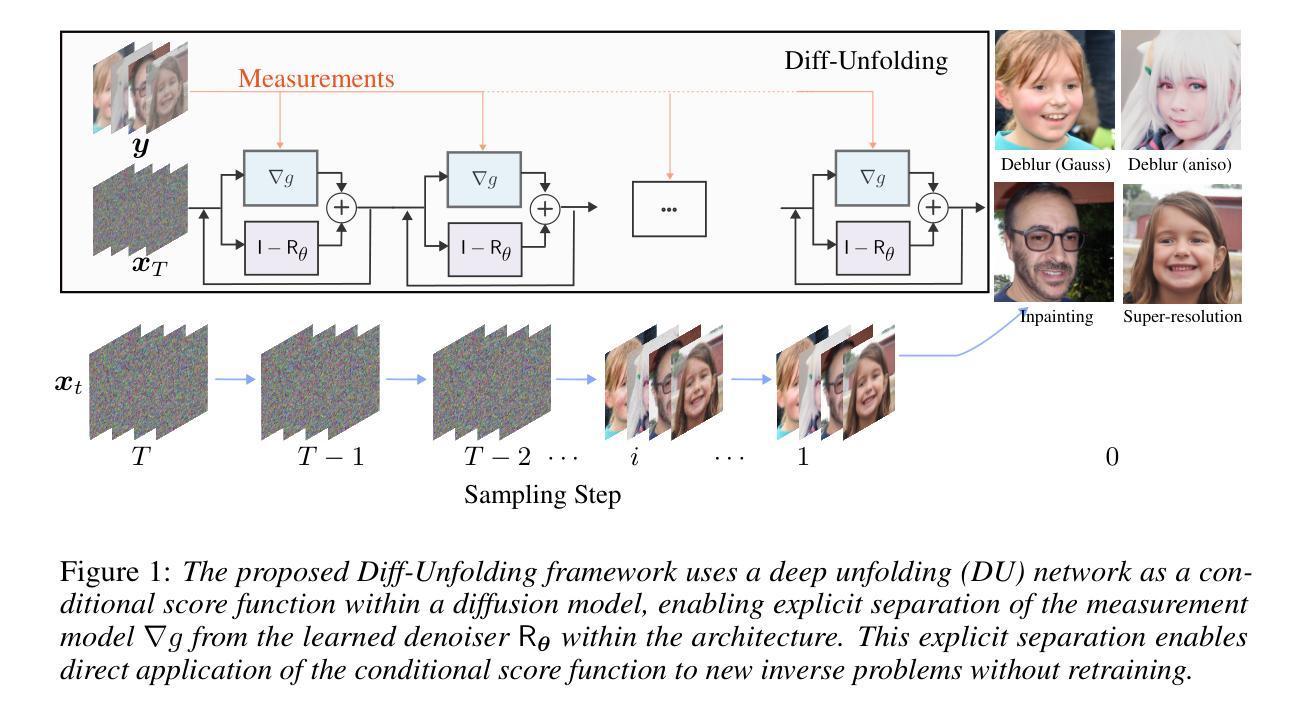
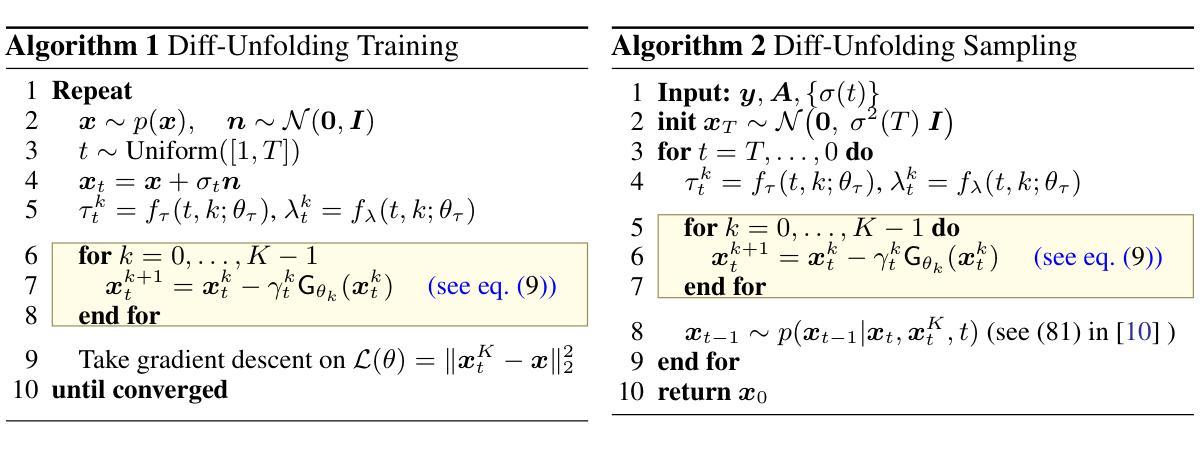
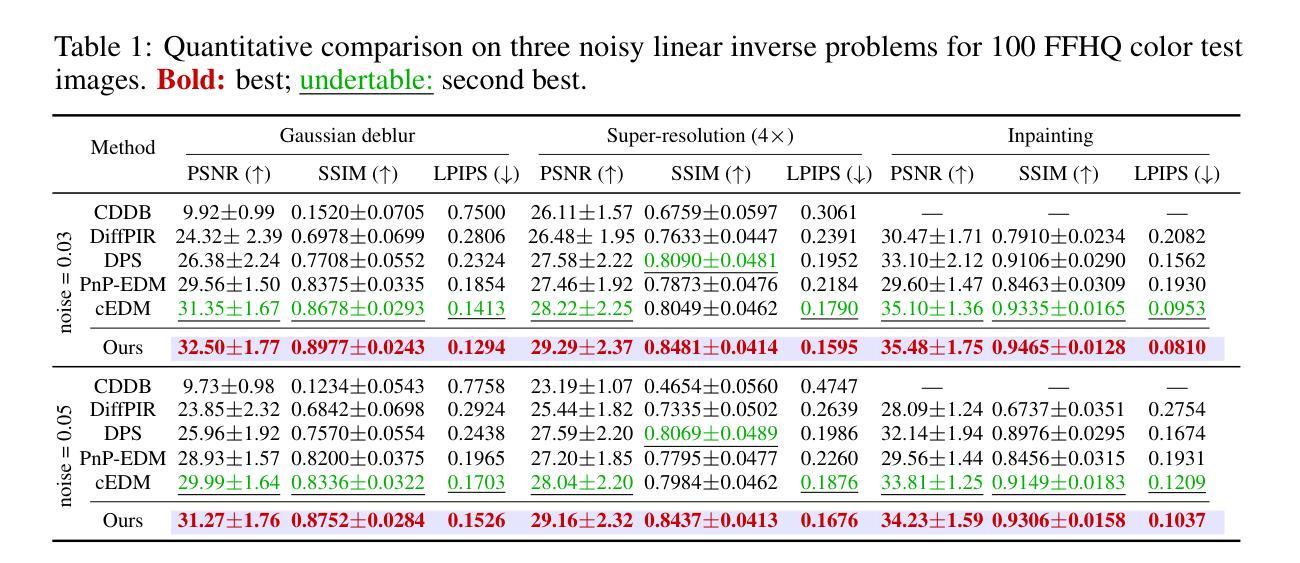
Diff-Unfolding: A Model-Based Score Learning Framework for Inverse Problems
Authors:Yuanhao Wang, Shirin Shoushtari, Ulugbek S. Kamilov
Diffusion models are extensively used for modeling image priors for inverse problems. We introduce \emph{Diff-Unfolding}, a principled framework for learning posterior score functions of \emph{conditional diffusion models} by explicitly incorporating the physical measurement operator into a modular network architecture. Diff-Unfolding formulates posterior score learning as the training of an unrolled optimization scheme, where the measurement model is decoupled from the learned image prior. This design allows our method to generalize across inverse problems at inference time by simply replacing the forward operator without retraining. We theoretically justify our unrolling approach by showing that the posterior score can be derived from a composite model-based optimization formulation. Extensive experiments on image restoration and accelerated MRI show that Diff-Unfolding achieves state-of-the-art performance, improving PSNR by up to 2 dB and reducing LPIPS by $22.7%$, while being both compact (47M parameters) and efficient (0.72 seconds per $256 \times 256$ image). An optimized C++/LibTorch implementation further reduces inference time to 0.63 seconds, underscoring the practicality of our approach.
扩散模型被广泛用于逆向问题的图像先验建模。我们介绍了”Diff-Unfolding”,这是一种通过明确地将物理测量算子融入模块化网络架构来学习”条件扩散模型”的后验评分函数的原理性框架。Diff-Unfolding将后验评分学习制定为展开优化方案的训练,其中测量模型与学习的图像先验解耦。这种设计使我们的方法能够在推理时通过简单地替换正向算子而泛化到各种逆向问题,而无需重新训练。我们通过理论证明,从基于复合模型的优化公式中可以推导出后验评分,从而证明我们的展开方法是合理的。在图像恢复和加速MRI的广泛实验表明,Diff-Unfolding达到了最先进的性能,PSNR提高了高达2分贝,LPIPS降低了22.7%,同时既紧凑(47M参数)又高效(每张256x256图像0.72秒)。经过优化的C++/LibTorch实现进一步将推理时间缩短至0.63秒,凸显了我们方法的实用性。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 19 pages, 13 figures,
Summary
扩散模型广泛用于图像先验建模中的反问题。本文提出一种名为Diff-Unfolding的理论框架,它通过明确地将物理测量算子融入模块化网络架构,学习条件扩散模型的后验得分函数。Diff-Unfolding将后验得分学习公式化为一种展开的优化方案训练,将测量模型与学习的图像先验解耦。这种设计使我们在推理时能灵活应对不同的反问题,只需替换前向算子而无需重新训练。本文理论证明了展开方法的合理性,即通过复合模型为基础的优化公式推导后验得分。在图像恢复和加速MRI的广泛实验表明,Diff-Unfolding达到了最先进的性能,PSNR提高了高达2分贝,LPIPS降低了22.7%,同时模型紧凑(47M参数)且高效(每处理一张256x256图像需0.72秒)。使用优化的C++/LibTorch实现进一步将推理时间缩短至0.63秒,凸显了方法的实用性。
Key Takeaways
- 扩散模型广泛应用于图像先验建模中的反问题。
- 提出了Diff-Unfolding框架,通过结合物理测量算子学习条件扩散模型的后验得分函数。
- Diff-Unfolding将后验得分学习表述为一种展开的优化方案,实现了测量模型与图像先验的解耦。
- 该方法在推理阶段能灵活应用于多种反问题,只需替换前向算子。
- 理论证明了展开方法的合理性,即通过复合模型优化公式推导后验得分。
- 在图像恢复和加速MRI的实验中,Diff-Unfolding表现出卓越性能,PSNR和LPIPS指标均有显著改善。
点此查看论文截图


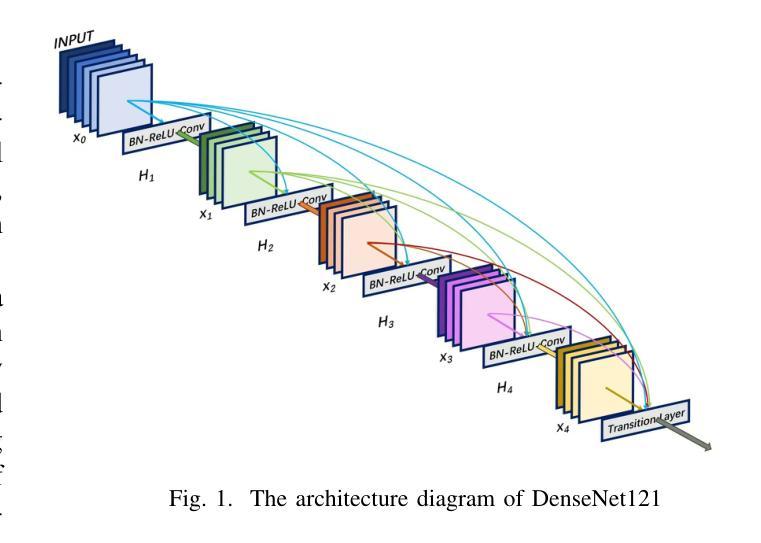
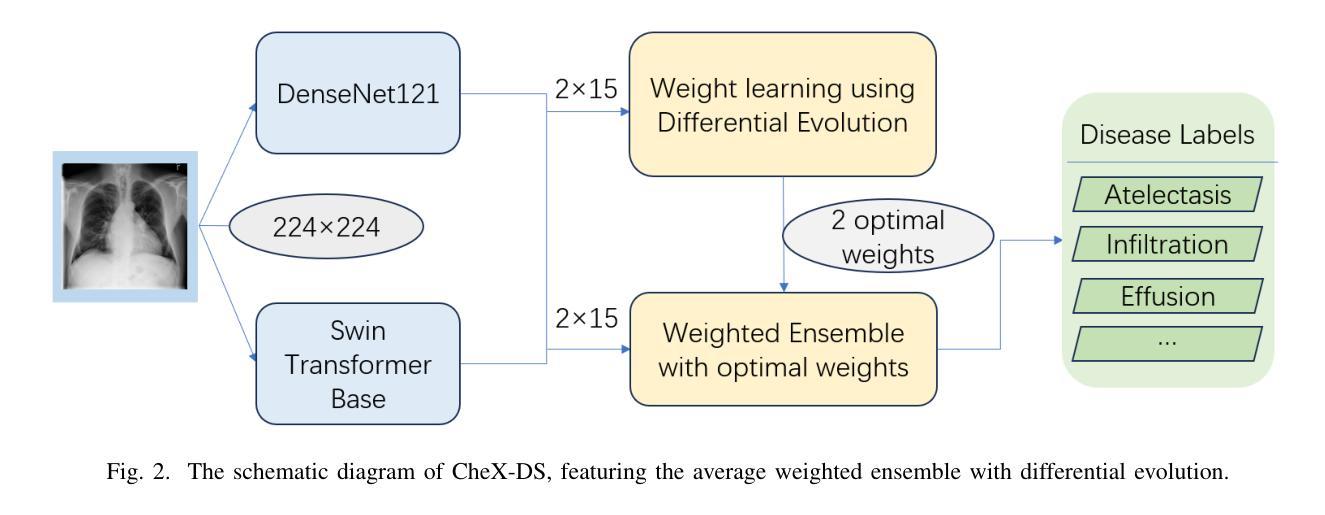
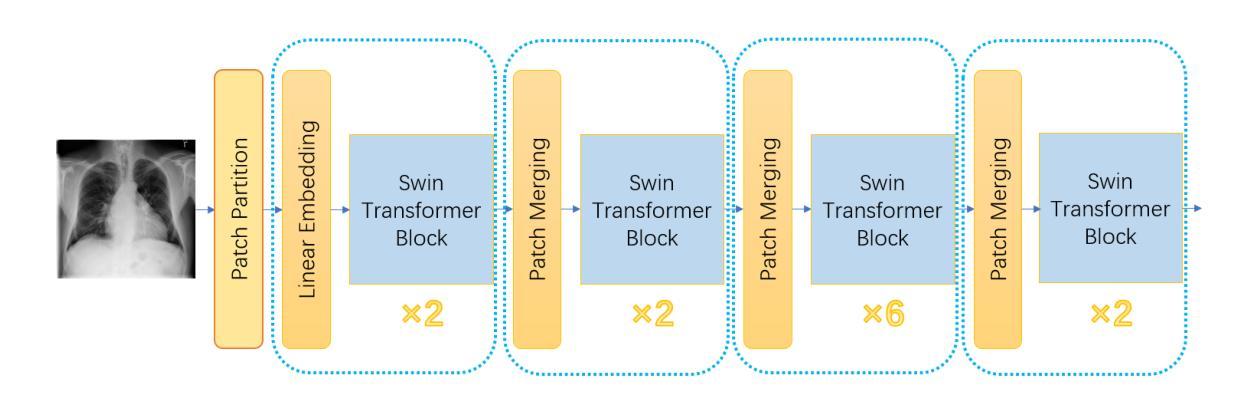
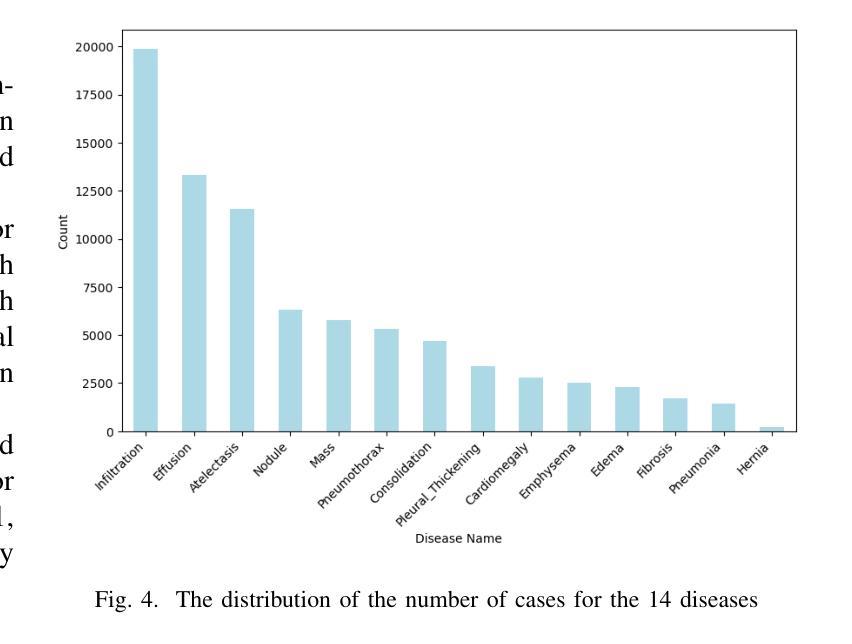
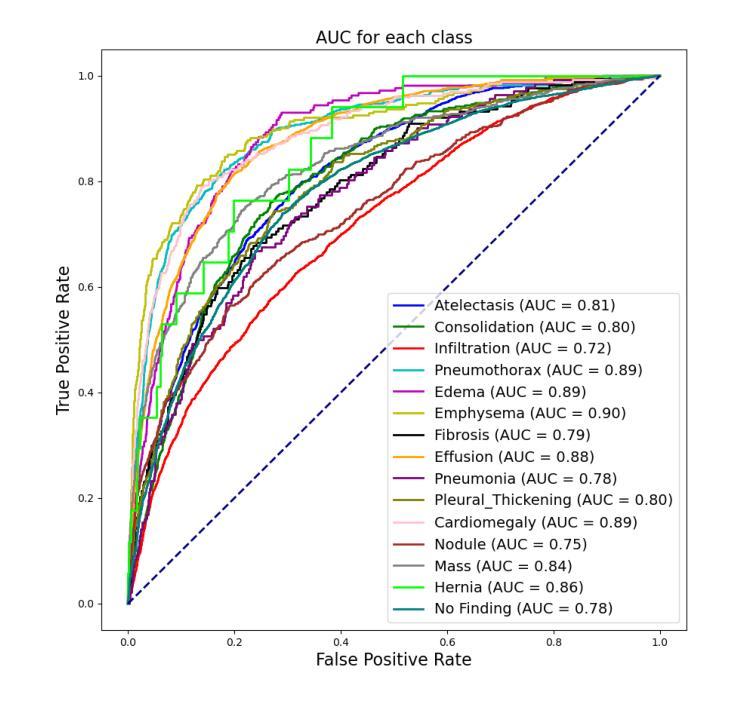
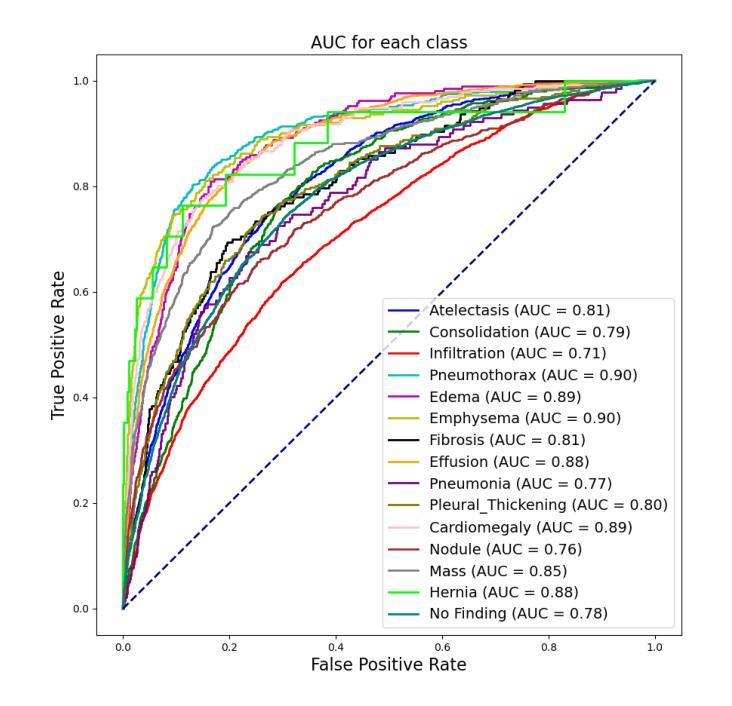
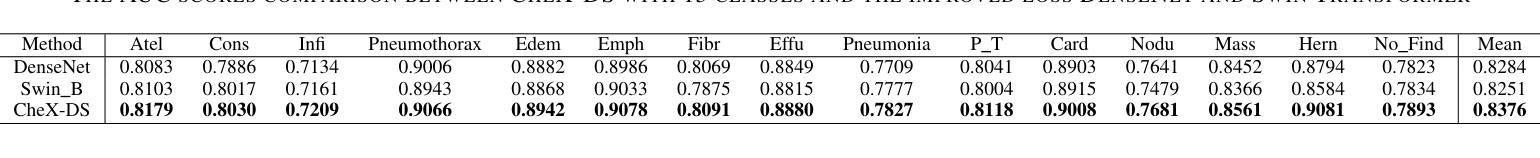
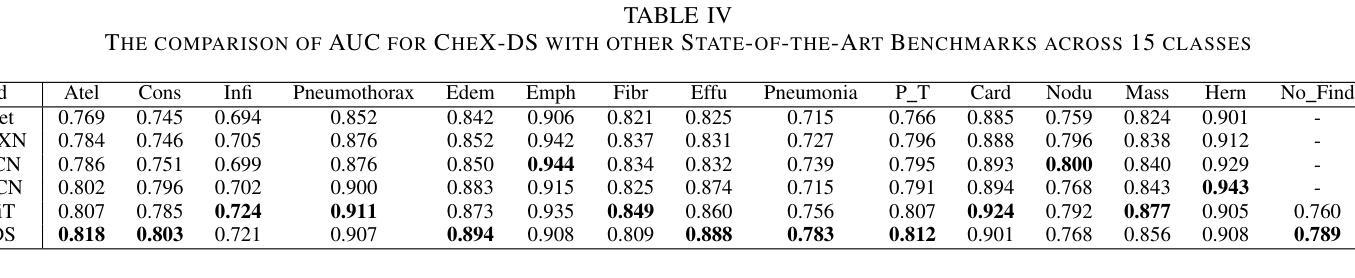
CheX-DS: Improving Chest X-ray Image Classification with Ensemble Learning Based on DenseNet and Swin Transformer
Authors:Xinran Li, Yu Liu, Xiujuan Xu, Xiaowei Zhao
The automatic diagnosis of chest diseases is a popular and challenging task. Most current methods are based on convolutional neural networks (CNNs), which focus on local features while neglecting global features. Recently, self-attention mechanisms have been introduced into the field of computer vision, demonstrating superior performance. Therefore, this paper proposes an effective model, CheX-DS, for classifying long-tail multi-label data in the medical field of chest X-rays. The model is based on the excellent CNN model DenseNet for medical imaging and the newly popular Swin Transformer model, utilizing ensemble deep learning techniques to combine the two models and leverage the advantages of both CNNs and Transformers. The loss function of CheX-DS combines weighted binary cross-entropy loss with asymmetric loss, effectively addressing the issue of data imbalance. The NIH ChestX-ray14 dataset is selected to evaluate the model’s effectiveness. The model outperforms previous studies with an excellent average AUC score of 83.76%, demonstrating its superior performance.
胸部疾病的自动诊断是一项受欢迎且具有挑战性的任务。当前大多数方法都是基于卷积神经网络(CNNs),这些网络专注于局部特征而忽略了全局特征。最近,计算机视觉领域引入了自注意力机制,表现出了卓越的性能。因此,本文提出了一种有效的模型CheX-DS,用于医学领域胸部X射线长尾多标签数据的分类。该模型基于优秀的医学成像DenseNet模型和目前流行的Swin Transformer模型,采用集成深度学习技术结合这两种模型的优势,充分利用CNN和Transformer的优点。CheX-DS的损失函数结合了加权二元交叉熵损失和不对称损失,有效地解决了数据不平衡的问题。选用NIH ChestX-ray14数据集对模型的有效性进行评估。该模型的平均AUC得分高达83.76%,表现出优异的性能,超过了以前的研究。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF BIBM
Summary
基于卷积神经网络(CNNs)的局限性,本文提出了一种新的模型CheX-DS,用于诊断胸部疾病。该模型结合了DenseNet和Swin Transformer模型的优势,利用集成深度学习技术进行分类。模型的损失函数结合了加权二元交叉熵损失和不对称损失,以解决数据不平衡问题。在NIH ChestX-ray14数据集上的实验结果表明,该模型具有出色的平均AUC得分,表现出卓越的性能。
Key Takeaways
- 当前诊断胸部疾病的方法大多基于卷积神经网络(CNNs),但忽略了全局特征。
- 自注意力机制在计算机视觉领域被引入,表现出卓越的性能。
- CheX-DS模型结合了DenseNet模型和Swin Transformer模型的优势。
- CheX-DS模型的损失函数结合了加权二元交叉熵损失和不对称损失,以解决数据不平衡问题。
- CheX-DS模型在NIH ChestX-ray14数据集上的平均AUC得分为83.76%,表现出卓越的性能。
- 该模型可以有效地处理医学领域的长尾多标签数据。
点此查看论文截图

Controlling spatial correlation in k-space interpolation networks for MRI reconstruction: denoising versus apparent blurring
Authors:Istvan Homolya, Peter Dawood, Jannik Stebani, Felix Breuer, Grit Hein, Matthias Gamer, Florian Knoll, Martin Blaimer
Purpose: To improve the interpretability of noise amplification and apparent blurring of k-space interpolation networks, and to optimize for them in the loss function as a model-based regularizer in k-space interpolation networks. Methods: Network is subjected to noise amplification analysis through automatic differentiation of the input with respect to the input. Noise variance maps are decomposed into terms accounting for the linear and nonlinear characteristics of the network. Variance maps are derived in each iteration, allowing for runtime quality monitoring. Maximum variance (eigenpixel) and residual variance maps (pixel contamination) are introduced, which describe the network noise amplification and apparent blurring, respectively. By including the variance maps in the training, the loss function is enriched with a model-based regularizer beyond the k-space data consistency term. Accordingly, the proposed g-factor-informed RAKI (GIF-RAKI) establishes a recurrent flow of noise and apparent blurring information into the training, that drives the denoising via the trainable nonlinear activation function. Results: GIF-RAKI outperforms other RAKI implementations, supported by difference maps, and image quality metrics. Eigenpixel and pixel contamination maps provide quantitative metrics for noise amplification and apparent blurring, respectively, without the need for a gold standard reference. RAKI with tuneable Leaky ReLU is capable of adjusting its own nonlinearity automatically. Conclusion: The additional model-based loss terms allow to optimize for the trade-off between denoising and apparent blurring during RAKI training. This has the potential to eliminate the need for heuristic hyperparameter tweaking.
目的:旨在提高k空间插值网络的噪声放大和明显模糊度的可解释性,并在损失函数中对它们进行优化,作为k空间插值网络的基于模型的正规化器。方法:网络通过输入相对于自身的自动微分来进行噪声放大分析。噪声方差图被分解成反映网络线性特征和非线性特征的项。每次迭代都会推导出方差图,从而实现运行时质量监控。引入了最大方差(特征像素)和残差方差图(像素污染),分别描述网络噪声放大和明显模糊度。通过将方差图纳入训练,损失函数除了k空间数据一致性项之外,还包含了基于模型的正规化器。因此,所提出的g因子信息RAKI(GIF-RAKI)将噪声和明显模糊度信息不断融入训练,通过可训练的非线性激活函数驱动去噪。结果:GIF-RAKI在其他RAKI实现中表现出色,这得到了差异图和图像质量指标的支持。特征像素和像素污染图分别为噪声放大和明显模糊度提供了定量指标,而无需金标准参考。具有可调泄漏ReLU的RAKI能够自动调整其非线性。结论:额外的基于模型的损失项允许在RAKI训练过程中优化去噪和明显模糊度之间的权衡。这有可能消除对启发式超参数调整的需求。
论文及项目相关链接
摘要
该研究旨在改善和提升k空间插值网络的噪声放大和模糊表现的解释性,并在损失函数中对其进行优化作为模型正则化器。通过自动区分网络输入,进行噪声放大分析,分解噪声方差图以考虑网络的线性和非线性特征。在每个迭代过程中推导方差图,实现运行时质量监控。引入最大方差(特征像素)和残差方差图(像素污染)来描述网络噪声放大和模糊现象。通过将方差图纳入训练,损失函数除了k空间数据一致性项外还加入了基于模型的正规化器。因此,所提出的基于g因子的RAKI(GIF-RAKI)将噪声和模糊信息不断融入训练,通过可训练的非线性激活函数驱动去噪。
关键见解
- 研究旨在提高k空间插值网络中的噪声放大和模糊表现的解释性,并对其进行优化。
- 通过自动区分网络输入进行噪声放大分析,并分解噪声方差图。
- 在每个迭代过程中推导方差图,实现运行时质量监控,引入最大方差和残差方差图来描述网络噪声放大和模糊现象。
- 将方差图纳入训练,丰富损失函数,包括基于模型的正规化器。
- GIF-RAKI建立了一个将噪声和模糊信息不断融入训练的流程,通过可训练的非线性激活函数驱动去噪。
- GIF-RAKI在其他RAKI实现中表现出优越性能,并提供定量指标来衡量噪声放大和模糊现象。
点此查看论文截图

In silico tool for identification of colorectal cancer from cell-free DNA biomarkers
Authors:Kartavya Mathur, Shipra Jain, Nisha Bajiya, Nishant Kumar, Gajendra P. S. Raghava
Colorectal cancer remains a major global health concern, with early detection being pivotal for improving patient outcomes. In this study, we leveraged high throughput methylation profiling of cellfree DNA to identify and validate diagnostic biomarkers for CRC. The GSE124600 study data were downloaded from the Gene Expression Omnibus, as the discovery cohort, comprising 142 CRC and 132 normal cfDNA methylation profiles obtained via MCTA seq. After preprocessing and filtering, 97,863 CpG sites were retained for further analysis. Differential methylation analysis using statistical tests identified 30,791 CpG sites as significantly altered in CRC samples, where p is less than 0.05. Univariate scoring enabled the selection of top ranking features, which were further refined using multiple feature selection algorithms, including Recursive Feature Elimination, Sequential Feature Selection, and SVC L1. Various machine learning models such as Logistic Regression, Support Vector Machines, Random Forest, and Multi layer Perceptron were trained and tested using independent validation datasets. The best performance was achieved with an MLP model trained on 25 features selected by RFE, reaching an AUROC of 0.89 and MCC of 0.78 on validation data. Additionally, a deep learning based convolutional neural network achieved an AUROC of 0.78. Functional annotation of the most predictive CpG sites identified several genes involved in key cellular processes, some of which were validated for differential expression in CRC using the GEPIA2 platform. Our study highlights the potential of cfDNA methylation markers combined with ML and DL models for noninvasive and accurate CRC detection, paving the way for clinically relevant diagnostic tools.
结直肠癌仍然是一个全球性的重大健康问题,早期发现对于改善患者预后至关重要。在这项研究中,我们利用细胞游离DNA的高通量甲基化谱分析技术,来识别和验证CRC的诊断生物标志物。GSE124600研究数据从基因表达综合数据库下载,作为发现队列,包含142例CRC和132例正常cfDNA甲基化谱,通过MCTA seq获得。经过预处理和筛选后,保留了97,863个CpG位点用于进一步分析。使用统计测试进行差异甲基化分析,确定了30,791个在CRC样本中显著改变的CpG位点(p < 0.05)。单变量评分使得能够选择排名靠前的特征,这些特征进一步使用多种特征选择算法进行精炼,包括递归特征消除、序列特征选择和SVC L1。使用独立验证数据集训练和测试了各种机器学习模型,如逻辑回归、支持向量机、随机森林和多层感知器。使用RFE选择的25个特征训练的MLP模型表现最佳,在验证数据上的AUROC达到0.89,MCC达到0.78。此外,基于深度学习的卷积神经网络达到了AUROC为0.78。预测性最高的CpG位点的功能注释确定了涉及关键细胞过程的几个基因,其中一些基因在CRC中的差异表达已通过GEPIA2平台进行验证。我们的研究强调了cfDNA甲基化标志物结合机器学习和深度学习模型在无创且准确的CRC检测中的潜力,为开发临床相关的诊断工具奠定了基础。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本研究利用细胞游离DNA的高通量甲基化谱分析技术,成功鉴定并验证了结直肠癌(CRC)的诊断生物标志物。研究采用GSE124600数据,通过差异甲基化分析和机器学习模型,筛选关键特征并构建模型,其中多层感知器模型表现最佳,验证数据集的受试者工作特征曲线下面积达到0.89,显示cfDNA甲基化标记结合机器学习在结直肠癌无创检测中的潜力。
Key Takeaways
- 研究利用细胞游离DNA的高通量甲基化谱分析技术,旨在鉴定结直肠癌(CRC)的诊断生物标志物。
- 通过差异甲基化分析,确定了30,791个在CRC样本中显著改变的CpG位点。
- 使用多种机器学习模型进行训练和测试,其中多层感知器模型表现最佳,验证数据集的受试者工作特征曲线下面积达到0.89。
- 深度学习卷积神经网络也表现出良好的诊断潜力,其受试者工作特征曲线下面积达到0.78。
- 最具预测性的CpG位点的功能注释显示,涉及关键细胞过程的几个基因被确定,并在CRC中验证了其差异表达。
- 研究结果强调了细胞游离DNA甲基化标记与机器学习结合在结直肠癌无创检测中的潜力。
点此查看论文截图

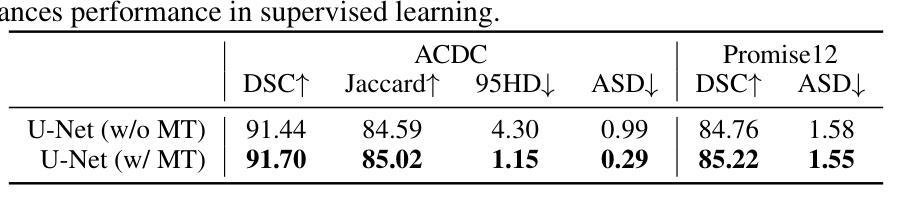
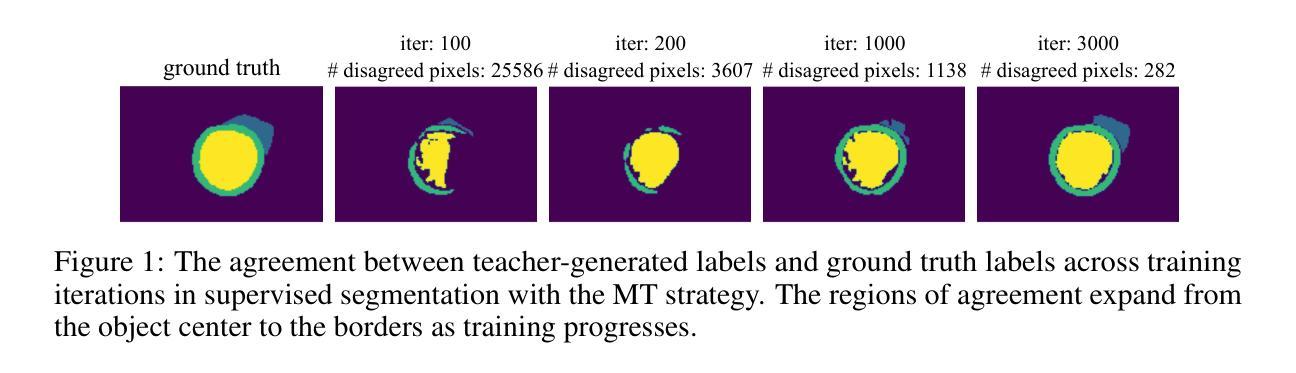
Rethinking the Mean Teacher Strategy from the Perspective of Self-paced Learning
Authors:Pengchen Zhang, Alan J. X. Guo, Sipin Luo, Zhe Han, Lin Guo
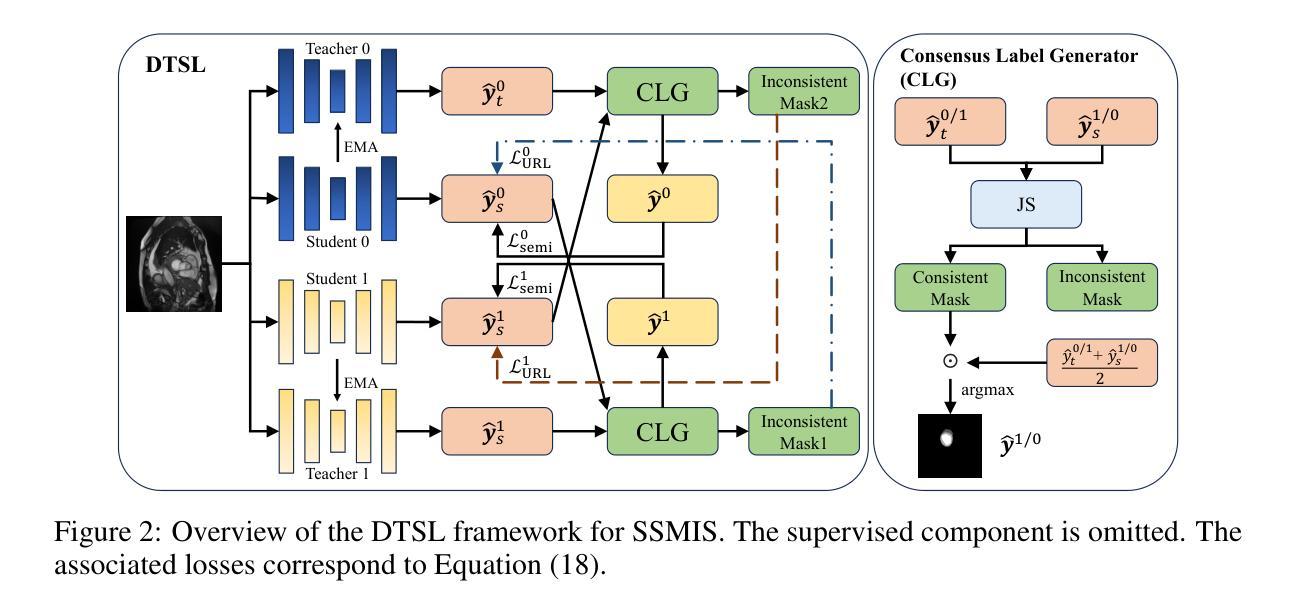
Semi-supervised medical image segmentation has attracted significant attention due to its potential to reduce manual annotation costs. The mean teacher (MT) strategy, commonly understood as introducing smoothed, temporally lagged consistency regularization, has demonstrated strong performance across various tasks in this field. In this work, we reinterpret the MT strategy on supervised data as a form of self-paced learning, regulated by the output agreement between the temporally lagged teacher model and the ground truth labels. This idea is further extended to incorporate agreement between a temporally lagged model and a cross-architectural model, which offers greater flexibility in regulating the learning pace and enables application to unlabeled data. Specifically, we propose dual teacher-student learning (DTSL), a framework that introduces two groups of teacher-student models with different architectures. The output agreement between the cross-group teacher and student models is used as pseudo-labels, generated via a Jensen-Shannon divergence-based consensus label generator (CLG). Extensive experiments on popular datasets demonstrate that the proposed method consistently outperforms existing state-of-the-art approaches. Ablation studies further validate the effectiveness of the proposed modules.
半监督医学图像分割因其降低手动标注成本的潜力而受到广泛关注。均值教师(Mean Teacher,简称MT)策略,通常理解为引入平滑、时间滞后一致性正则化,在该领域各种任务中表现出强大的性能。在这项工作中,我们将MT策略在监督数据上的应用重新解释为一种自我节奏学习,受时间滞后教师模型与真实标签之间输出协议的控制。这个想法进一步扩展到包含时间滞后模型与跨架构模型之间的协议,这为调节学习进度提供了更大的灵活性,并使其能够应用于无标签数据。具体来说,我们提出了双教师学生学习(Dual Teacher-Student Learning,简称DTSL)框架,该框架引入了两组不同架构的教师-学生模型。跨组教师和学生模型之间的输出协议作为通过Jensen-Shannon散度共识标签生成器(CLG)生成的伪标签。在流行数据集上的大量实验表明,所提出的方法始终优于现有的最先进的方法。消融研究进一步验证了所提出模块的有效性。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
半监督医学图像分割中,均值教师(MT)策略被重新解释为一种由输出协议监管的自我进度学习方式,并扩展应用于无标签数据。提出双教师学生学习(DTSL)框架,引入两组不同架构的教师-学生模型,通过基于Jensen-Shannon散度的共识标签生成器(CLG)生成伪标签。实验证明该方法优于现有先进技术。
Key Takeaways
- 半监督医学图像分割旨在降低手动注释成本。
- 均值教师(MT)策略被重新解释为自我进度学习,由输出协议监管。
- 扩展MT策略以纳入不同架构模型之间的协议,提供更灵活的学习速度调控。
- 提出双教师学生学习(DTSL)框架,包含两组不同架构的教师-学生模型。
- 使用基于Jensen-Shannon散度的共识标签生成器(CLG)生成伪标签。
- 在流行数据集上的广泛实验证明该方法优于现有技术。
点此查看论文截图

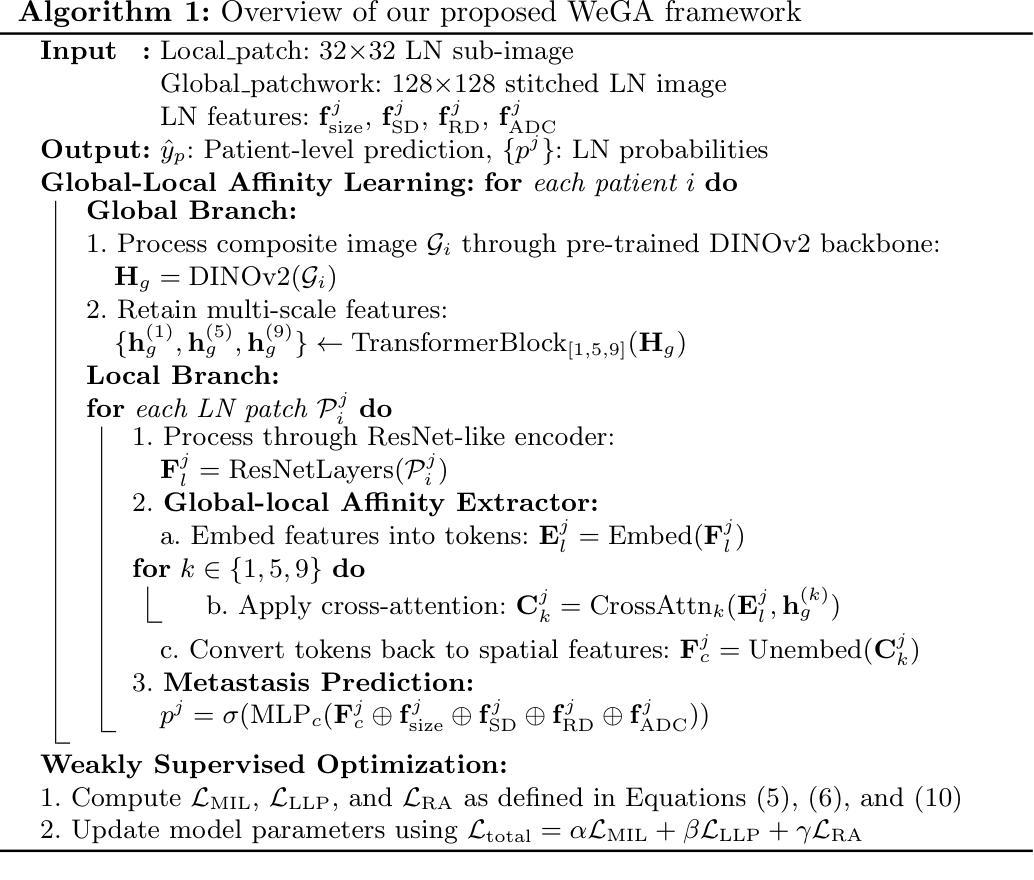
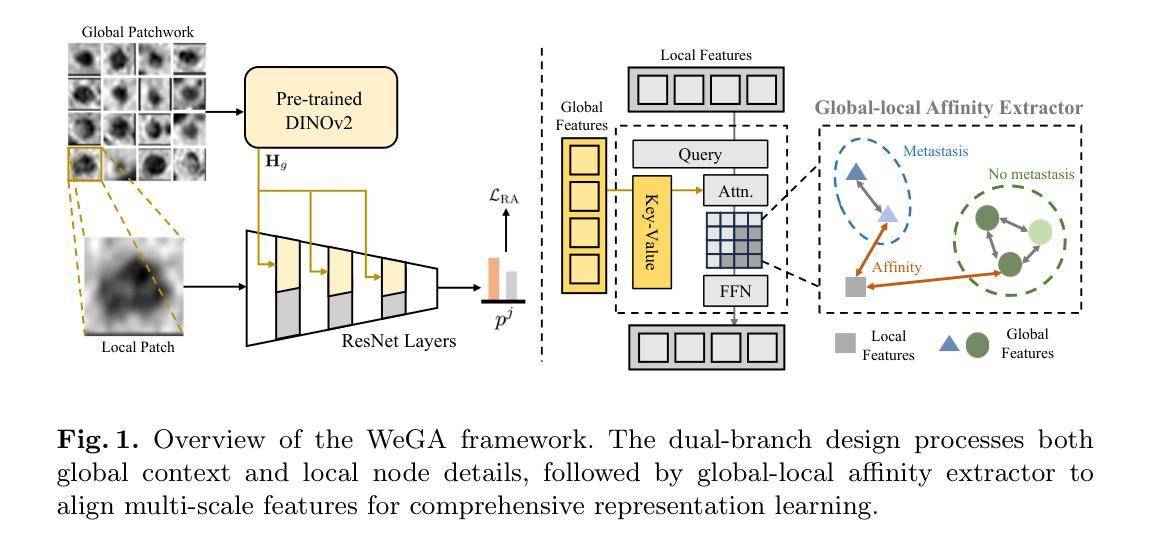
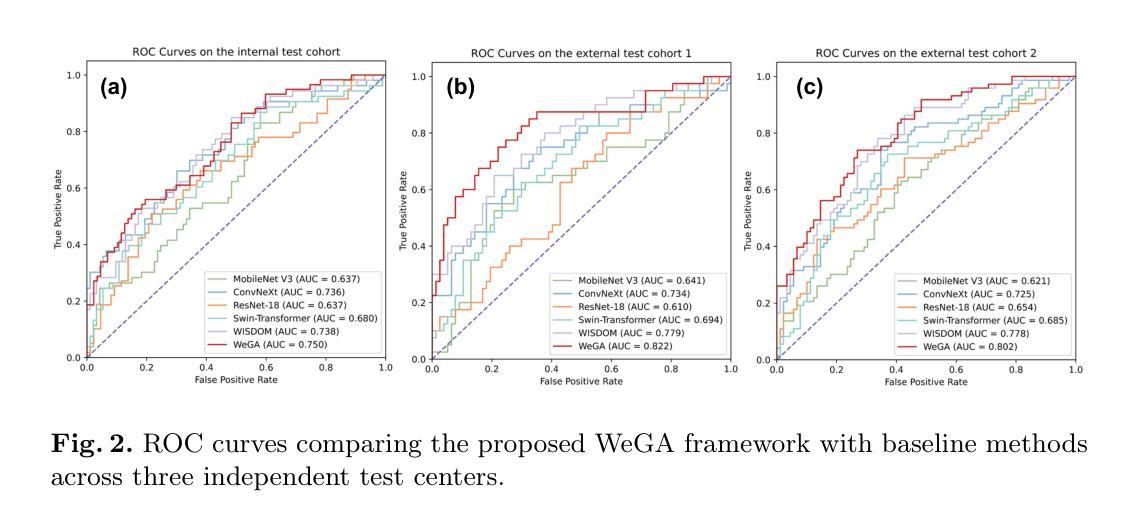
WeGA: Weakly-Supervised Global-Local Affinity Learning Framework for Lymph Node Metastasis Prediction in Rectal Cancer
Authors:Yifan Gao, Yaoxian Dong, Wenbin Wu, Chaoyang Ge, Feng Yuan, Jiaxi Sheng, Haoyue Li, Xin Gao
Accurate lymph node metastasis (LNM) assessment in rectal cancer is essential for treatment planning, yet current MRI-based evaluation shows unsatisfactory accuracy, leading to suboptimal clinical decisions. Developing automated systems also faces significant obstacles, primarily the lack of node-level annotations. Previous methods treat lymph nodes as isolated entities rather than as an interconnected system, overlooking valuable spatial and contextual information. To solve this problem, we present WeGA, a novel weakly-supervised global-local affinity learning framework that addresses these challenges through three key innovations: 1) a dual-branch architecture with DINOv2 backbone for global context and residual encoder for local node details; 2) a global-local affinity extractor that aligns features across scales through cross-attention fusion; and 3) a regional affinity loss that enforces structural coherence between classification maps and anatomical regions. Experiments across one internal and two external test centers demonstrate that WeGA outperforms existing methods, achieving AUCs of 0.750, 0.822, and 0.802 respectively. By effectively modeling the relationships between individual lymph nodes and their collective context, WeGA provides a more accurate and generalizable approach for lymph node metastasis prediction, potentially enhancing diagnostic precision and treatment selection for rectal cancer patients.
对直肠癌淋巴结转移(LNM)的准确评估是治疗计划的关键,但目前的MRI评估准确性不佳,可能导致临床决策失误。自动系统的开发也面临重大障碍,主要是缺乏节点级别的注释。以往的方法将淋巴结视为孤立的实体,而不是相互关联的系统,从而忽略了宝贵的空间和上下文信息。为了解决这一问题,我们提出了WeGA,这是一种新型的弱监督全局-局部亲和力学习框架,通过以下三个关键创新解决了这些挑战:1)具有DINOv2主干和残差编码器的双分支架构,用于全局上下文和局部节点细节;2)全局-局部亲和力提取器,通过跨注意力融合来对齐跨尺度的特征;3)区域亲和力损失,在分类图和解剖区域之间强制执行结构一致性。在一个内部和两个外部测试中心的实验表明,WeGA优于现有方法,分别实现了AUC值为0.750、0.822和0.802。通过有效地建模单个淋巴结之间的关系及其集体上下文,WeGA为淋巴结转移预测提供了更准确和可推广的方法,可能提高了直肠癌患者的诊断精度和治疗选择。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文提出一种新型的弱监督全局局部亲和力学习框架WeGA,用于准确评估直肠癌淋巴结节转移情况。该方法通过融合全局上下文和局部节点细节、跨尺度特征对齐以及结构连贯性,提高了预测准确性和泛化能力。
Key Takeaways
- 直肠癌中淋巴节点转移(LNM)的准确评估对治疗计划至关重要。
- 当前MRI评估存在准确性问题,导致临床决策失误。
- 开发自动化系统的难点在于缺乏节点级别的注释。
- 现有方法忽略淋巴节点的相互关联性和空间上下文信息。
- WeGA通过全局和局部分支架构、全局局部亲和力提取器和区域亲和力损失来解决这些问题。
- 实验结果表明,WeGA在内部和外部测试中心均表现出优异性能,提高了预测准确性。
点此查看论文截图

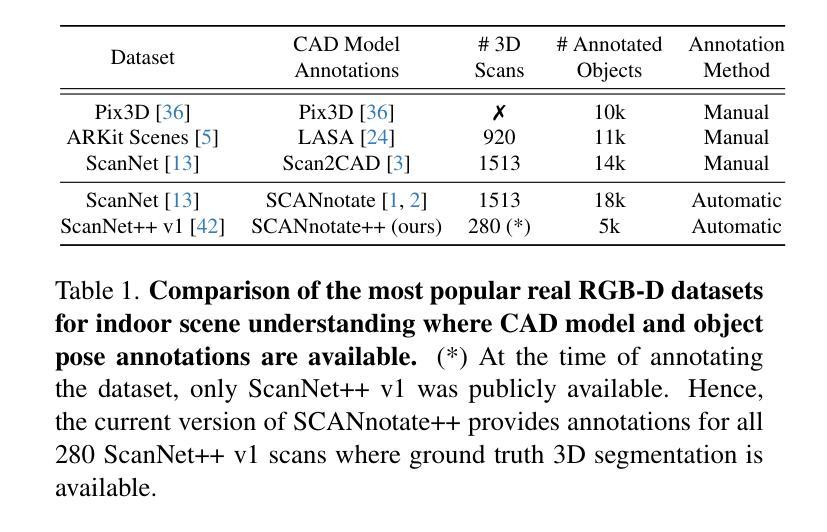
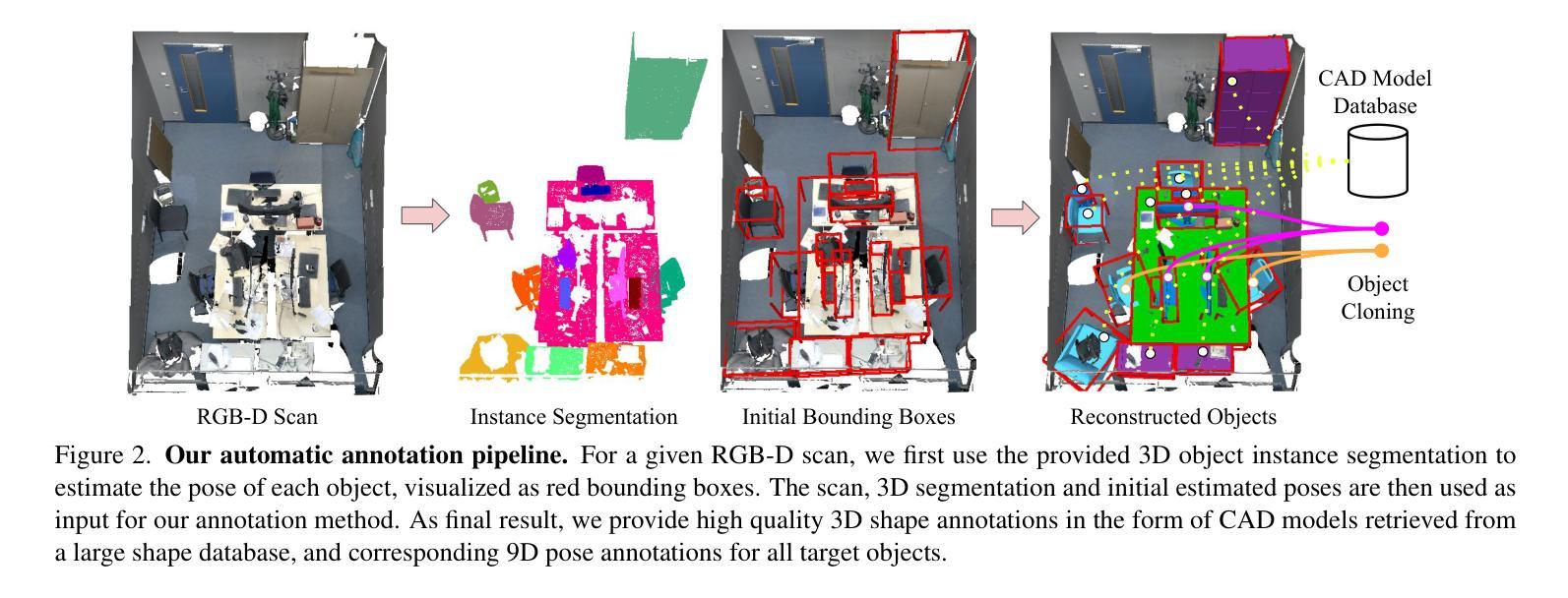
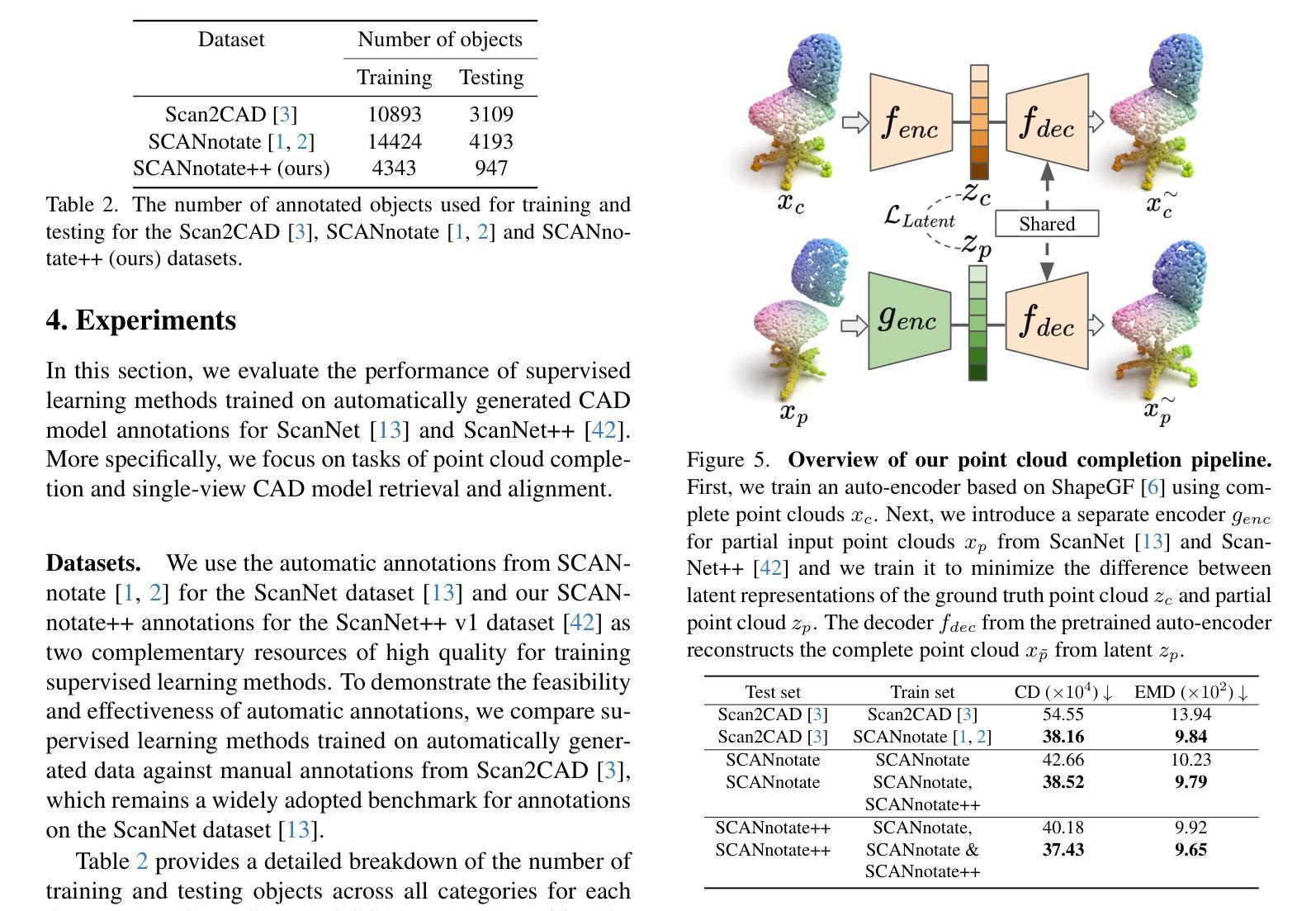
Leveraging Automatic CAD Annotations for Supervised Learning in 3D Scene Understanding
Authors:Yuchen Rao, Stefan Ainetter, Sinisa Stekovic, Vincent Lepetit, Friedrich Fraundorfer
High-level 3D scene understanding is essential in many applications. However, the challenges of generating accurate 3D annotations make development of deep learning models difficult. We turn to recent advancements in automatic retrieval of synthetic CAD models, and show that data generated by such methods can be used as high-quality ground truth for training supervised deep learning models. More exactly, we employ a pipeline akin to the one previously used to automatically annotate objects in ScanNet scenes with their 9D poses and CAD models. This time, we apply it to the recent ScanNet++ v1 dataset, which previously lacked such annotations. Our findings demonstrate that it is not only possible to train deep learning models on these automatically-obtained annotations but that the resulting models outperform those trained on manually annotated data. We validate this on two distinct tasks: point cloud completion and single-view CAD model retrieval and alignment. Our results underscore the potential of automatic 3D annotations to enhance model performance while significantly reducing annotation costs. To support future research in 3D scene understanding, we will release our annotations, which we call SCANnotate++, along with our trained models.
高级别的三维场景理解在许多应用中至关重要。然而,生成准确的三维标注的挑战使得开发深度学习模型变得困难。我们转向最近自动检索合成CAD模型的进展,并证明由这些方法生成的数据可以用作高质量的真实标签,用于训练有监督的深度学习模型。更确切地说,我们采用了一种类似于之前用于ScanNet场景中自动标注对象的管道,这些对象带有其9D姿态和CAD模型。这次,我们将其应用于最新的ScanNet++ v1数据集,该数据集之前缺乏此类注释。我们的研究结果表明,不仅可以在这些自动获得的注释上训练深度学习模型,而且所得模型的性能优于手动注释数据训练的模型。我们在两个不同的任务上对此进行了验证:点云补全和单视图CAD模型检索与对齐。我们的结果强调了自动三维标注在提高模型性能的同时显著降低标注成本的潜力。为了支持未来对三维场景理解的研究,我们将发布我们的注释,我们称之为SCANnotate++,以及我们训练的模型。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Project page: https://stefan-ainetter.github.io/SCANnotatepp; CVPR’25 Workshop
Summary
这篇文本介绍了自动检索合成CAD模型的新进展,并将其应用于ScanNet++ v1数据集的自动标注。研究结果表明,使用自动获得的标注训练深度模型不仅可行,而且其性能优于使用手动标注数据训练的模型。该研究为增强模型性能并显著降低标注成本提供了潜力,并将发布其标注和训练模型以支持未来研究。
Key Takeaways
- 自动检索合成CAD模型技术被应用于ScanNet++ v1数据集的标注,为深度学习任务提供了高质量的地标数据。
- 使用自动获得的标注训练的深度模型性能优于使用手动标注数据训练的模型。
- 自动进行3D标注的方法显著降低了标注成本。
- 通过应用类似ScanNet场景的自动标注技术,实现了对物体进行精确标注的目标。
- 研究结果验证了自动进行3D场景理解的可行性,并展示了其在多个应用中的潜力。
- 研究结果强调了自动获取高质量标注的重要性,特别是在缺乏手动标注数据的场景中。
点此查看论文截图


Resolving the Ambiguity of Complete-to-Partial Point Cloud Registration for Image-Guided Liver Surgery with Patches-to-Partial Matching
Authors:Zixin Yang, Jon S. Heiselman, Cheng Han, Kelly Merrell, Richard Simon, Cristian. A. Linte
In image-guided liver surgery, the initial rigid alignment between preoperative and intraoperative data, often represented as point clouds, is crucial for providing sub-surface information from preoperative CT/MRI images to the surgeon during the procedure. Currently, this alignment is typically performed using semi-automatic methods, which, while effective to some extent, are prone to errors that demand manual correction. Point cloud correspondence-based registration methods are promising to serve as a fully automatic solution. However, they may struggle in scenarios with limited intraoperative surface visibility, a common challenge in liver surgery, particularly in laparoscopic procedures, which we refer to as complete-to-partial ambiguity. We first illustrate this ambiguity by evaluating the performance of state-of-the-art learning-based point cloud registration methods on our carefully constructed in silico and in vitro datasets. Then, we propose a patches-to-partial matching strategy as a plug-and-play module to resolve the ambiguity, which can be seamlessly integrated into learning-based registration methods without disrupting their end-to-end structure. It has proven effective and efficient in improving registration performance for cases with limited intraoperative visibility. The constructed benchmark and the proposed module establish a solid foundation for advancing applications of point cloud correspondence-based registration methods in image-guided liver surgery.
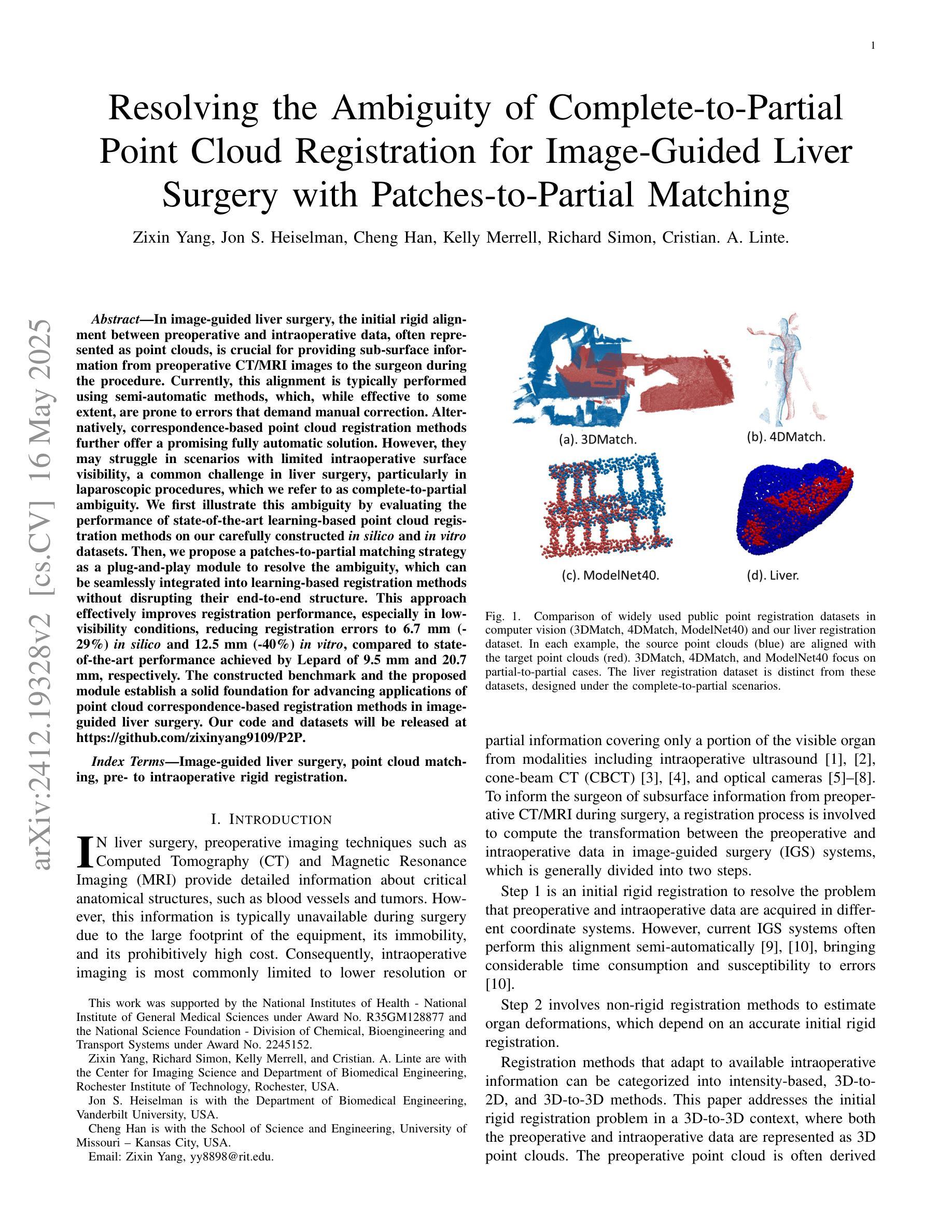
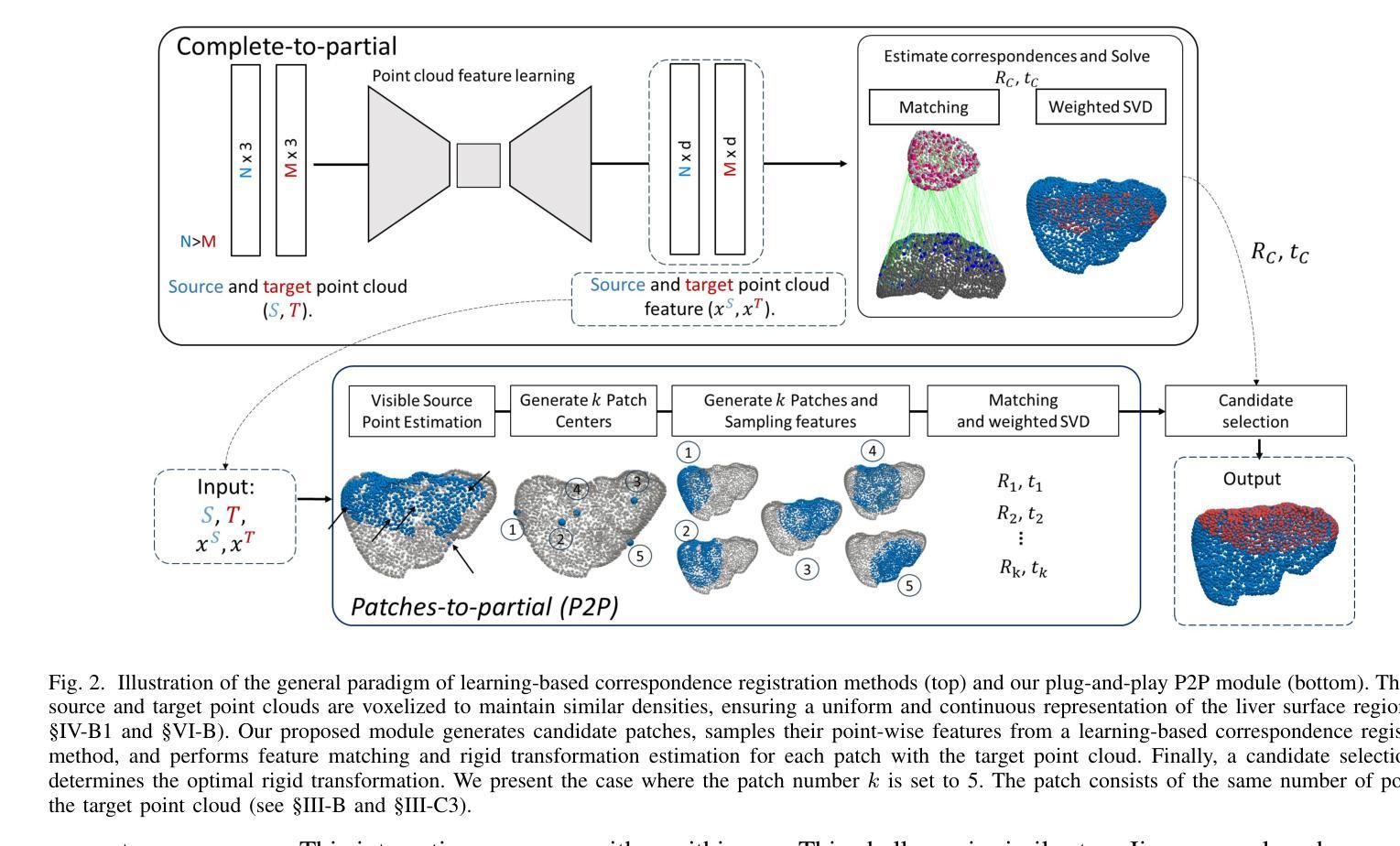
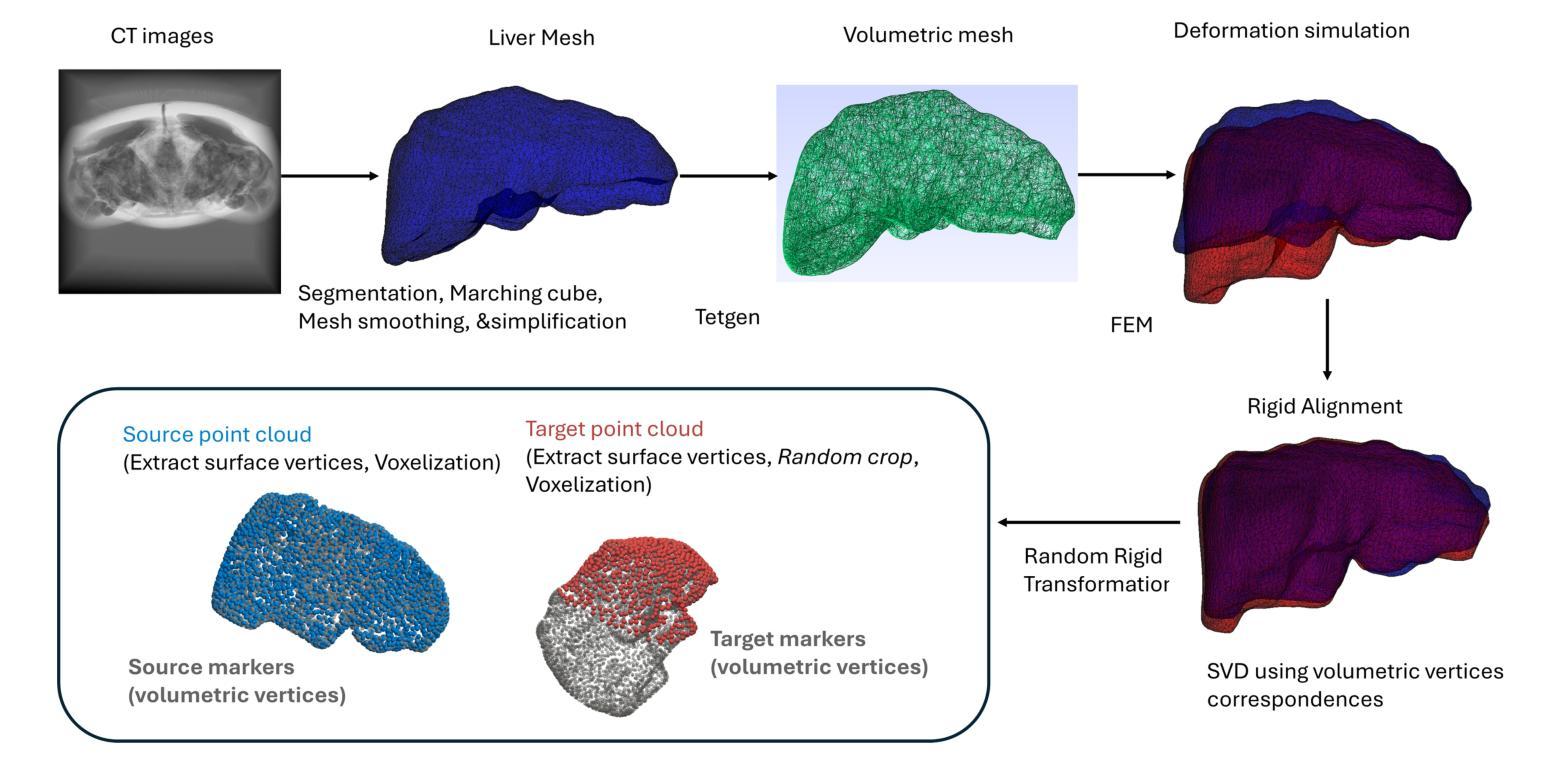
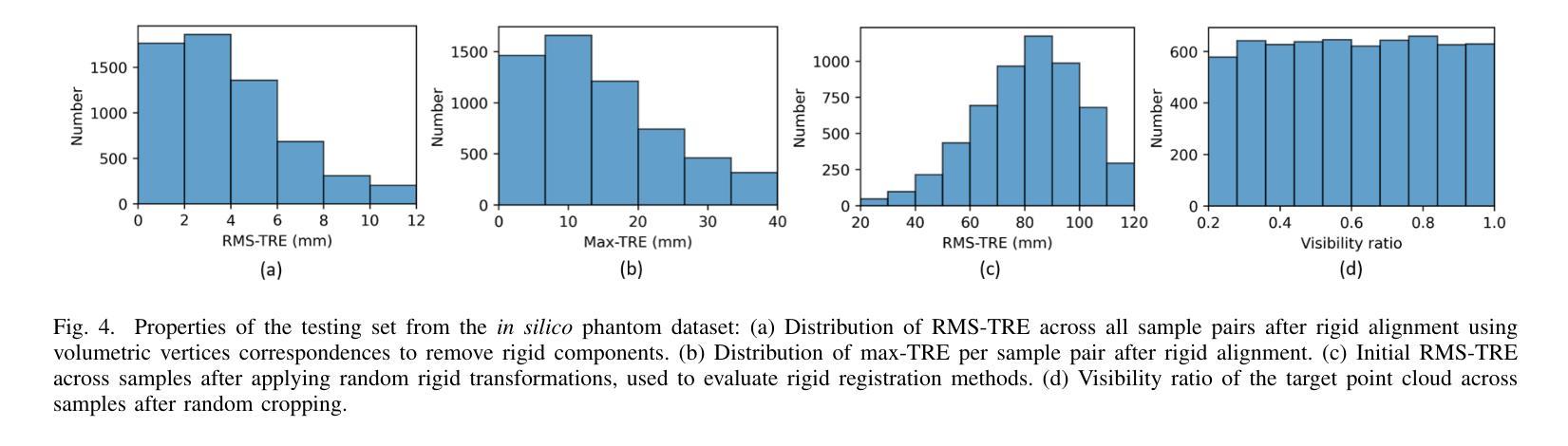
在图像引导下的肝脏手术中,术前和术中数据之间的初始刚性对齐至关重要。这些数据通常以点云的形式呈现,以便为外科医生提供从术前CT/MRI图像中获得的亚表面信息。目前,这种对齐通常使用半自动方法执行,这些方法尽管在一定程度上有效,但仍容易出现需要手动纠正的错误。基于点云对应的注册方法有望成为全自动解决方案。然而,在肝内表面可见性有限的场景中,它们可能会遇到困难,这是肝脏手术中常见的挑战,特别是在腹腔镜手术中,我们称之为完全到部分的模糊性。我们首先通过评估最先进的学习型点云注册方法在精心构建的体内和体外数据集上的表现来说明这种模糊性。然后,我们提出了一种补丁到部分的匹配策略,作为一种即插即用的模块来解决模糊性问题。它可以无缝集成到基于学习的注册方法中,而不会破坏其端到端的结构。对于术中视野有限的病例,该策略已被证明能够有效提高注册性能。构建的基准测试和提出的模块为推进点云对应注册方法在图像引导肝脏手术中的应用奠定了坚实的基础。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
在图像引导下的肝脏手术中,对术前和术中数据进行初步精确对齐极为关键,此过程常表现为点云形式,旨在向手术医生提供来自术前CT/MRI图像的表面下信息。当前,通常采用半自动方法进行此对齐,虽然在一定程度上有效,但易出现错误需要人工校正。基于点云对应的注册方法有望成为全自动解决方案,但在术中表面可见性有限的情况下可能会遇到困难,这在肝脏手术中尤为常见,特别是在腹腔镜手术中我们称之为完整到部分的歧义性。为解决此歧义性,本文提出一种即插即用的“补丁到部分”匹配策略,该策略可无缝集成到基于学习的注册方法中,且不影响其端到端的结构。对于术中可见性有限的情况,该策略在改善注册性能方面被证明是有效且高效的。本文构建的基准和提出的模块为推进点云对应注册方法在图像引导肝脏手术中的应用奠定了坚实基础。
Key Takeaways
- 在图像引导肝脏手术中,术前与术中数据的初始精确对齐至关重要,为手术医生提供来自术前影像的表面下信息。
- 当前的对齐方法主要依赖半自动技术,尽管有效,但存在需要人工校正的错误风险。
- 点云对应的注册方法被视为全自动解决方案的候选,但在术中表面可见性有限的情况下可能会遭遇挑战。
- 本文定义了完整到部分的歧义性问题,尤其在腹腔镜肝脏手术中尤为突出。
- 为解决上述歧义性,提出了一种“补丁到部分”匹配策略,可无缝集成到现有基于学习的注册方法中。
- 此策略在改善注册性能上被证实有效且高效,特别是在术中可见性有限的情况下。
点此查看论文截图
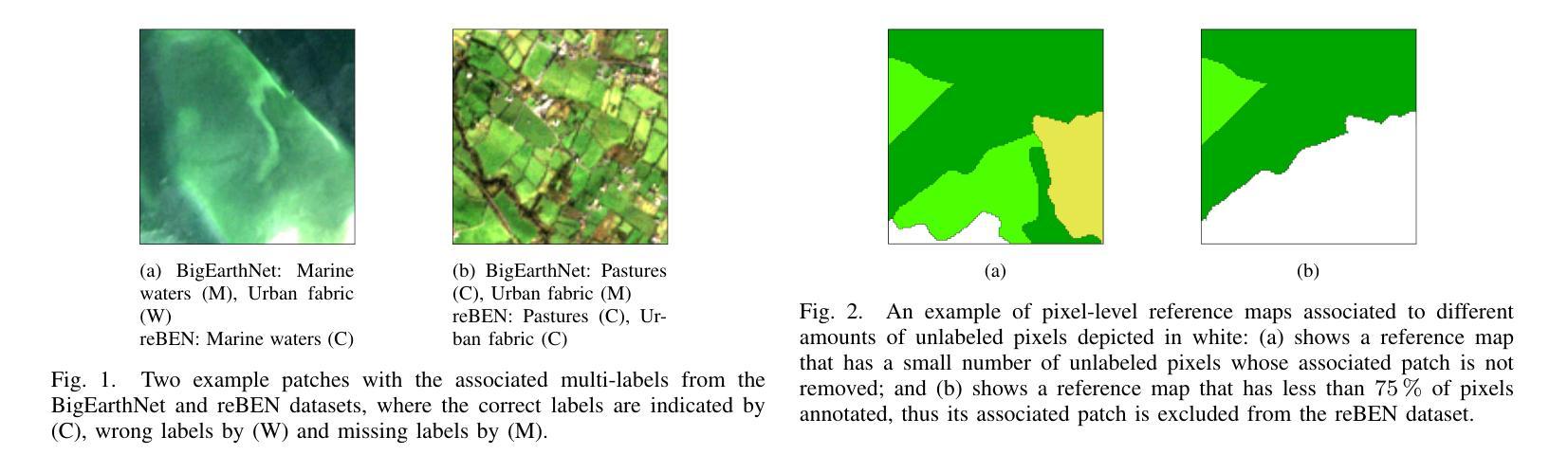
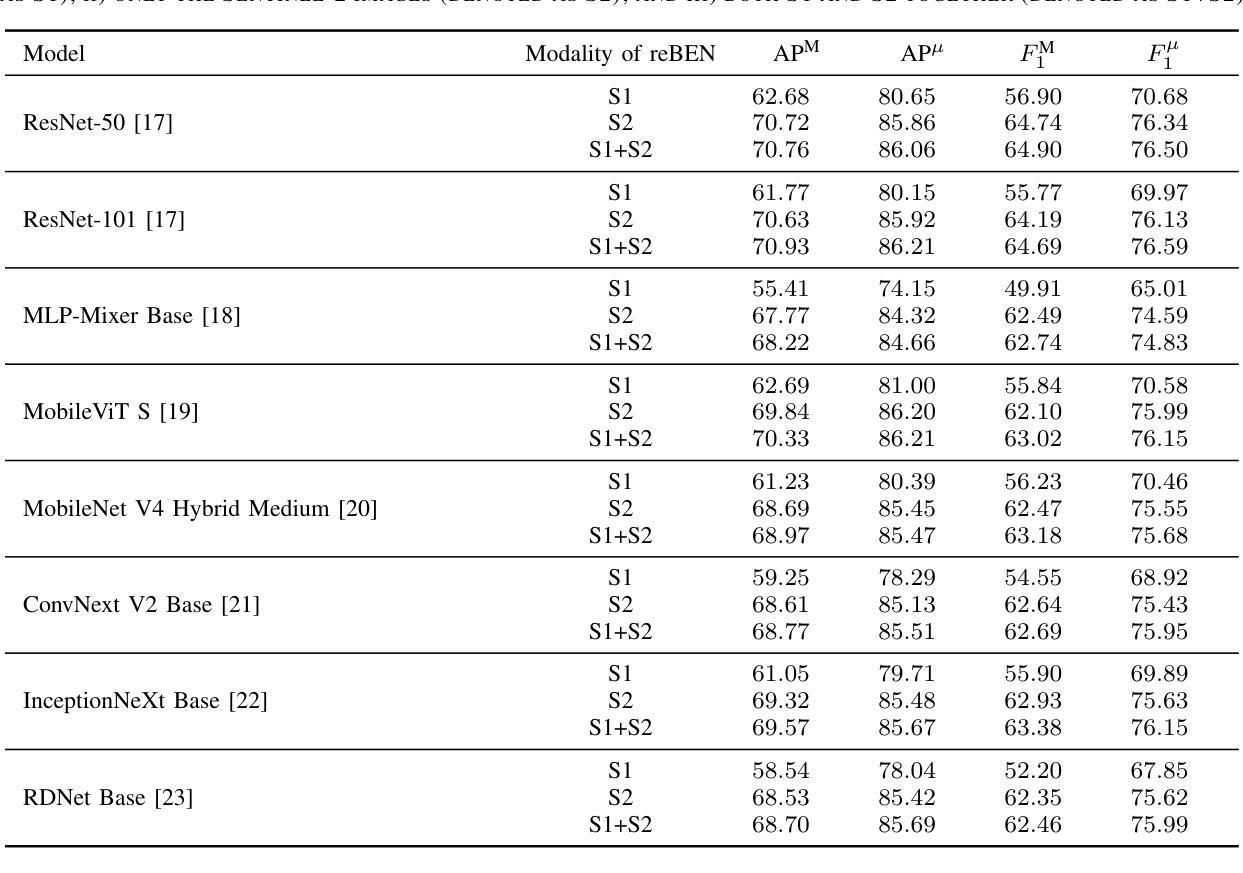
reBEN: Refined BigEarthNet Dataset for Remote Sensing Image Analysis
Authors:Kai Norman Clasen, Leonard Hackel, Tom Burgert, Gencer Sumbul, Begüm Demir, Volker Markl
This paper presents refined BigEarthNet (reBEN) that is a large-scale, multi-modal remote sensing dataset constructed to support deep learning (DL) studies for remote sensing image analysis. The reBEN dataset consists of 549,488 pairs of Sentinel-1 and Sentinel-2 image patches. To construct reBEN, we initially consider the Sentinel-1 and Sentinel-2 tiles used to construct the BigEarthNet dataset and then divide them into patches of size 1200 m x 1200 m. We apply atmospheric correction to the Sentinel-2 patches using the latest version of the sen2cor tool, resulting in higher-quality patches compared to those present in BigEarthNet. Each patch is then associated with a pixel-level reference map and scene-level multi-labels. This makes reBEN suitable for pixel- and scene-based learning tasks. The labels are derived from the most recent CORINE Land Cover (CLC) map of 2018 by utilizing the 19-class nomenclature as in BigEarthNet. The use of the most recent CLC map results in overcoming the label noise present in BigEarthNet. Furthermore, we introduce a new geographical-based split assignment algorithm that significantly reduces the spatial correlation among the train, validation, and test sets with respect to those present in BigEarthNet. This increases the reliability of the evaluation of DL models. To minimize the DL model training time, we introduce software tools that convert the reBEN dataset into a DL-optimized data format. In our experiments, we show the potential of reBEN for multi-modal multi-label image classification problems by considering several state-of-the-art DL models. The pre-trained model weights, associated code, and complete dataset are available at https://bigearth.net.
本文介绍了精细化的BigEarthNet(reBEN),这是一个大规模、多模态的遥感数据集,旨在支持用于遥感图像分析的深度学习(DL)研究。reBEN数据集包含549,488对Sentinel-1和Sentinel-2图像斑块。为了构建reBEN,我们首先考虑用于构建BigEarthNet数据集的Sentinel-1和Sentinel-2瓦片,然后将其划分为大小为1200米x 1200米的斑块。我们对Sentinel-2斑块应用大气校正,使用sen2cor工具的最新版本,从而得到与BigEarthNet中现有的斑块相比质量更高的斑块。然后,每个斑块都与像素级参考地图和场景级多标签相关联。这使得reBEN适合用于基于像素和场景的学习任务。标签是通过使用与BigEarthNet相同的19类命名法,从最新的2018年CORINE土地覆盖(CLC)地图中得出的。使用最新的CLC地图克服了BigEarthNet中存在的标签噪声。此外,我们引入了一种新的基于地理的分割分配算法,该算法显著减少了训练集、验证集和测试集之间的空间相关性,与BigEarthNet中的相关性相比。这增加了深度学习模型评估的可靠性。为了最小化深度学习模型训练时间,我们引入了将reBEN数据集转换为深度学习优化数据格式的软件工具。在我们的实验中,我们通过考虑一些最先进的深度学习模型,展示了reBEN在多模态多标签图像分类问题上的潜力。预训练模型权重、相关代码和完整数据集可在https://bigearth.net上找到。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted at IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium (IGARSS) 2025. Our code is available at https://github.com/rsim-tu-berlin/bigearthnet-pipeline
摘要
本论文推出精细化BigEarthNet(reBEN),这是一套大型、多模式遥感数据集,专为支持遥感图像分析的深度学习(DL)研究而构建。reBEN数据集包含549,488对Sentinel-1和Sentinel-2图像补丁。相较于BigEarthNet,reBEN通过应用大气校正技术提高了补丁质量,并引入新的地理分割分配算法以增加评估深度学习模型的可靠性。此外,为缩短深度学习模型训练时间,我们提供软件工具将reBEN数据集转换为优化的数据格式。实验显示,reBEN在多模态多标签图像分类问题方面具有潜力。预训练模型权重、相关代码和完整数据集可在https://bigearth.net访问。
关键见解
- reBEN是一个大型、多模式遥感数据集,专为支持深度学习研究而构建。
- reBEN包含经过大气校正的高质量图像补丁,适用于像素和场景基础学习任务。
- 利用最新的CORINE Land Cover地图克服BigEarthNet中的标签噪声问题。
- 引入新的地理分割分配算法以提高评估深度学习模型的可信度。
- 提供软件工具以优化深度学习模型的训练时间。
- 实验证明reBEN在多模态多标签图像分类问题上的潜力。
点此查看论文截图