⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-05-20 更新
QVGen: Pushing the Limit of Quantized Video Generative Models
Authors:Yushi Huang, Ruihao Gong, Jing Liu, Yifu Ding, Chengtao Lv, Haotong Qin, Jun Zhang
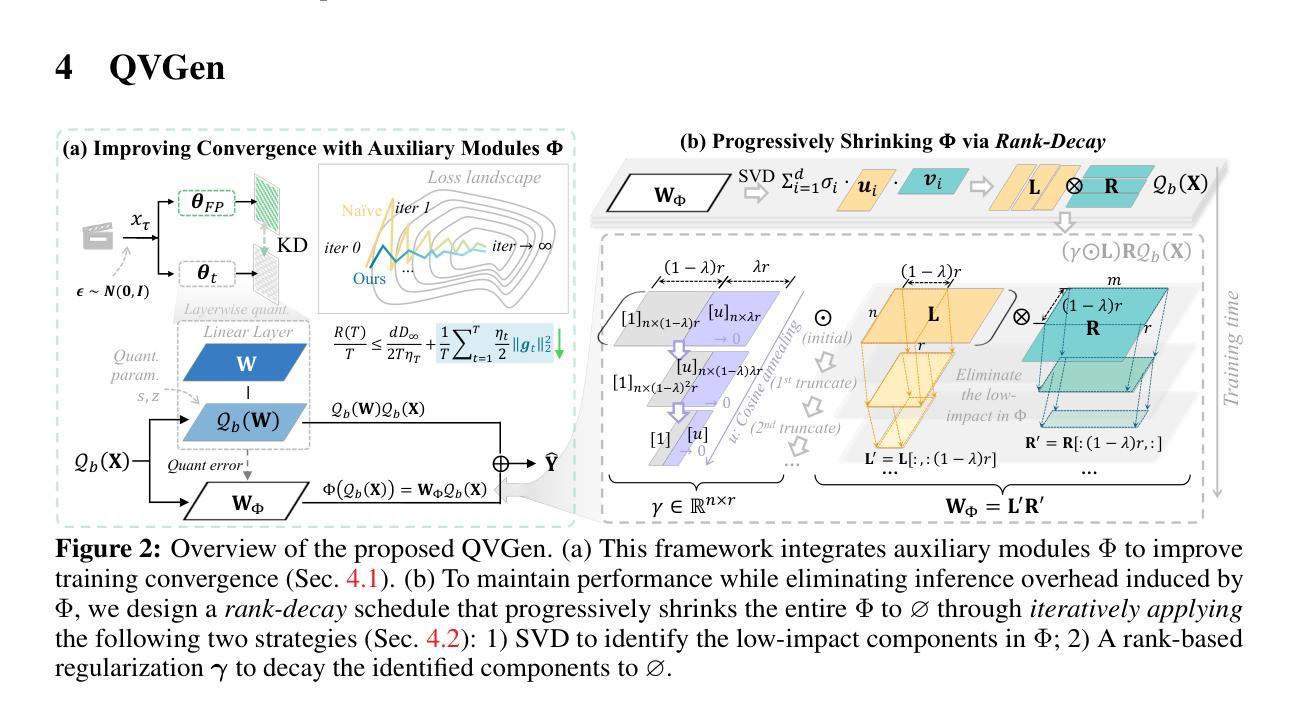
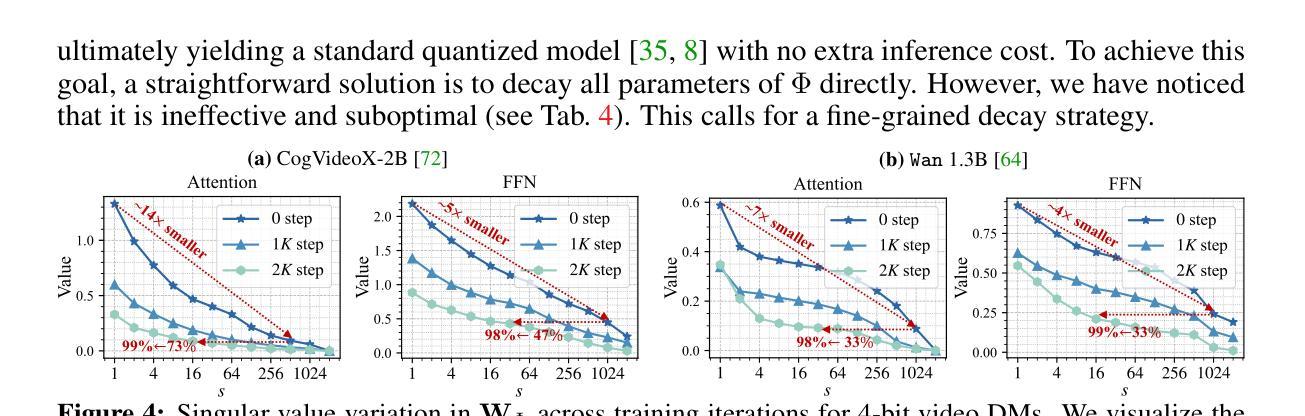
Video diffusion models (DMs) have enabled high-quality video synthesis. Yet, their substantial computational and memory demands pose serious challenges to real-world deployment, even on high-end GPUs. As a commonly adopted solution, quantization has proven notable success in reducing cost for image DMs, while its direct application to video DMs remains ineffective. In this paper, we present QVGen, a novel quantization-aware training (QAT) framework tailored for high-performance and inference-efficient video DMs under extremely low-bit quantization (e.g., 4-bit or below). We begin with a theoretical analysis demonstrating that reducing the gradient norm is essential to facilitate convergence for QAT. To this end, we introduce auxiliary modules ($\Phi$) to mitigate large quantization errors, leading to significantly enhanced convergence. To eliminate the inference overhead of $\Phi$, we propose a rank-decay strategy that progressively eliminates $\Phi$. Specifically, we repeatedly employ singular value decomposition (SVD) and a proposed rank-based regularization $\mathbf{\gamma}$ to identify and decay low-contributing components. This strategy retains performance while zeroing out inference overhead. Extensive experiments across $4$ state-of-the-art (SOTA) video DMs, with parameter sizes ranging from $1.3$B $\sim14$B, show that QVGen is the first to reach full-precision comparable quality under 4-bit settings. Moreover, it significantly outperforms existing methods. For instance, our 3-bit CogVideoX-2B achieves improvements of $+25.28$ in Dynamic Degree and $+8.43$ in Scene Consistency on VBench.
视频扩散模型(DMs)已经能够实现高质量的视频合成。然而,其巨大的计算和内存需求对实际部署带来了严峻挑战,即使在高端GPU上也是如此。作为一种常用的解决方案,量化在降低图像DM的成本方面取得了显著的成效,而直接应用于视频DM则仍然无效。在本文中,我们介绍了QVGen,这是一个针对极端低比特量化(例如4位及以下)下高性能和推理效率的视频DM定制的新型量化感知训练(QAT)框架。我们从理论分析开始,证明降低梯度范数是促进QAT收敛的关键。为此,我们引入了辅助模块(Φ)来缓解大量的量化误差,从而显著增强了收敛性。为了消除Φ的推理开销,我们提出了一种等级衰减策略,该策略逐步消除Φ。具体来说,我们反复使用奇异值分解(SVD)和提出的基于等级的规则γ来识别和衰减贡献较小的成分。此策略在消除推理开销的同时保留了性能。在4种最先进的视频DMs上的广泛实验,参数大小从1.3B到14B不等,表明QVGen首次在4位设置下达到全精度相当的质量,并且显著优于现有方法。例如,我们的3位CogVideoX-2B在VBench上的动态度和场景一致性分别提高了+25.28和+8.43。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Our code will be released upon acceptance
Summary
视频扩散模型(DMs)能够实现高质量视频合成,但其巨大的计算和内存需求对实际部署带来了挑战。针对视频DMs的量化训练框架QVGen被提出,该框架针对极低比特量化(如4位及以下)进行优化,通过引入辅助模块和排名衰减策略提高性能和推理效率。实验证明,QVGen在多种先进视频DMs中实现了全精度相当的质量,并显著优于现有方法。
Key Takeaways
- 视频扩散模型(DMs)可实现高质量视频合成,但计算和内存需求巨大,对实际部署带来挑战。
- QVGen是一种针对视频DMs的量化训练框架,旨在提高性能和推理效率,尤其适用于极低比特量化。
- QVGen通过引入辅助模块来减轻量化误差,并通过理论分析和实验验证其有效性。
- QVGen采用排名衰减策略消除辅助模块在推理过程中的开销,通过奇异值分解和基于排名的正则化策略逐步消除低贡献组件。
- QVGen在多种先进视频DMs中实现了全精度相当的质量,并在某些指标上显著优于现有方法。
- QVGen为视频DMs的实用部署提供了新的可能性和解决方案。
点此查看论文截图


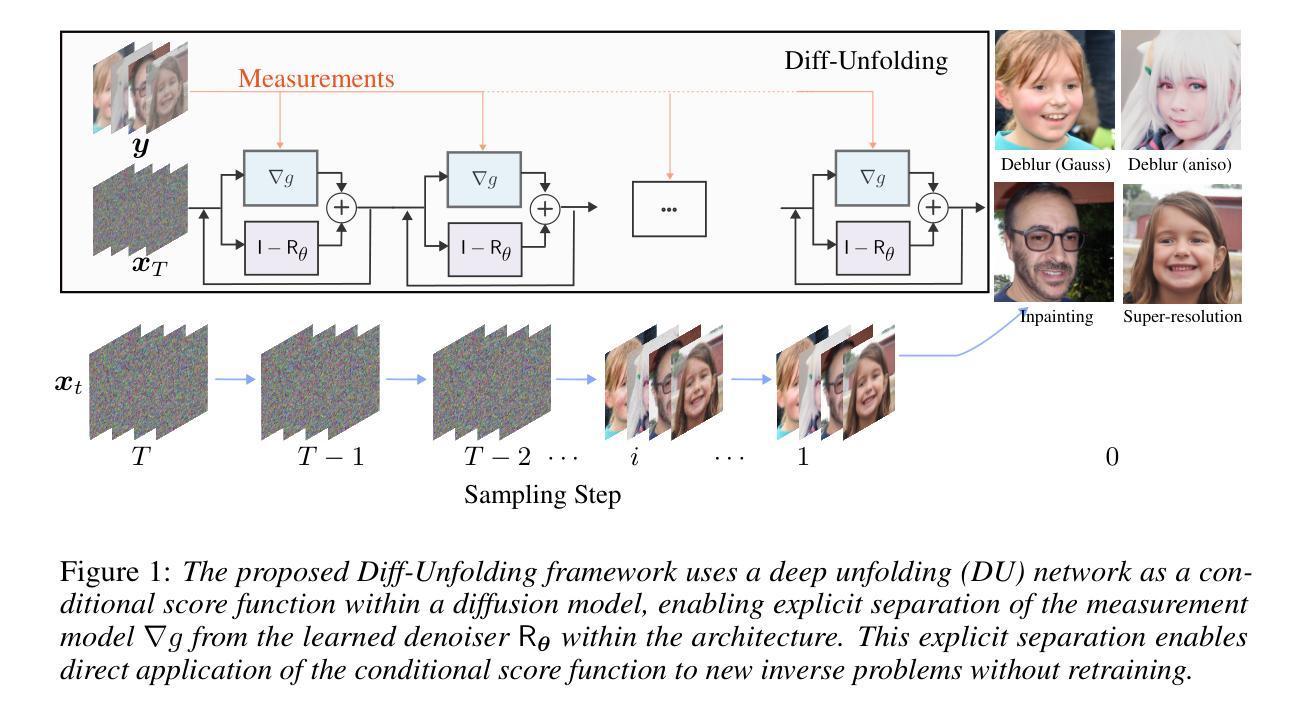
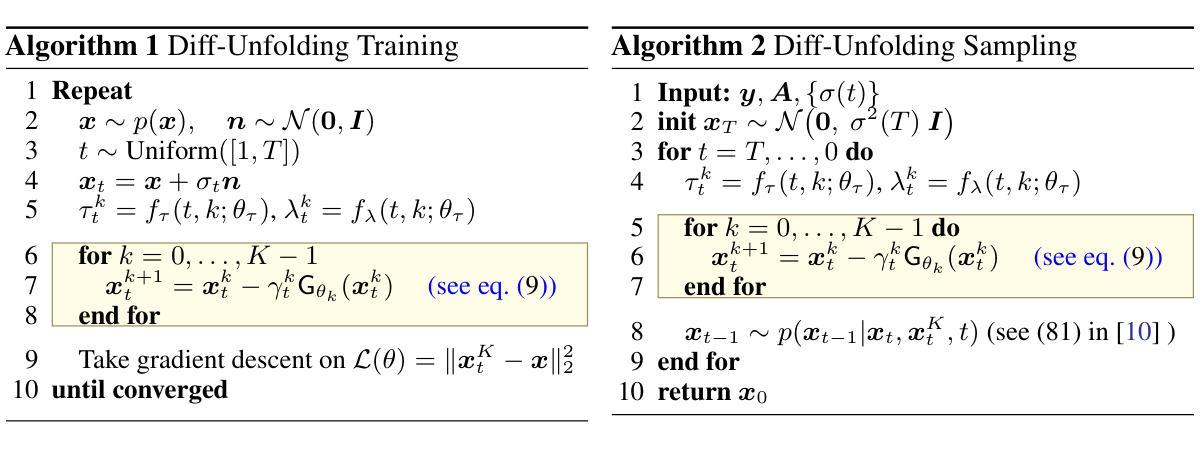
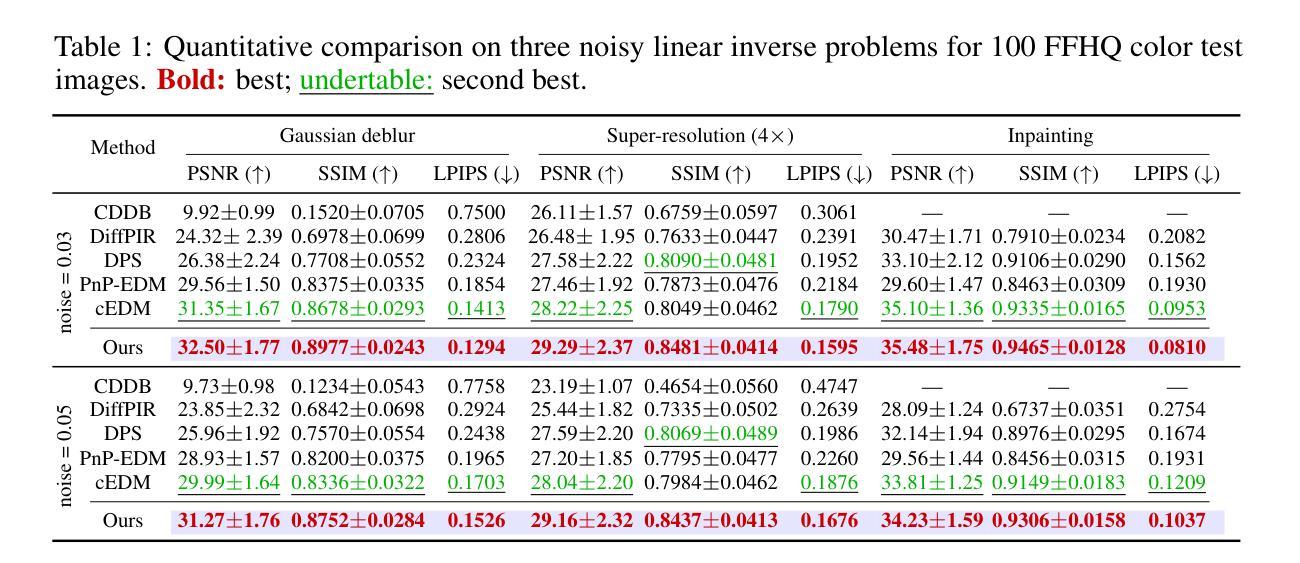
Diff-Unfolding: A Model-Based Score Learning Framework for Inverse Problems
Authors:Yuanhao Wang, Shirin Shoushtari, Ulugbek S. Kamilov
Diffusion models are extensively used for modeling image priors for inverse problems. We introduce \emph{Diff-Unfolding}, a principled framework for learning posterior score functions of \emph{conditional diffusion models} by explicitly incorporating the physical measurement operator into a modular network architecture. Diff-Unfolding formulates posterior score learning as the training of an unrolled optimization scheme, where the measurement model is decoupled from the learned image prior. This design allows our method to generalize across inverse problems at inference time by simply replacing the forward operator without retraining. We theoretically justify our unrolling approach by showing that the posterior score can be derived from a composite model-based optimization formulation. Extensive experiments on image restoration and accelerated MRI show that Diff-Unfolding achieves state-of-the-art performance, improving PSNR by up to 2 dB and reducing LPIPS by $22.7%$, while being both compact (47M parameters) and efficient (0.72 seconds per $256 \times 256$ image). An optimized C++/LibTorch implementation further reduces inference time to 0.63 seconds, underscoring the practicality of our approach.
扩散模型被广泛用于逆向问题的图像先验建模。我们介绍了Diff-Unfolding,这是一种通过明确地将物理测量算子融入模块化网络架构来学习条件扩散模型的后验得分函数的原理性框架。Diff-Unfolding将后验得分学习制定为展开优化方案的训练,其中测量模型与学习的图像先验解耦。这种设计使得我们的方法能够在推理时通过简单地替换正向算子来泛化到各种逆向问题,而无需重新训练。我们通过显示后验得分可以从基于模型的组合优化公式中得出,从理论上证明了我们的展开方法。在图像恢复和加速MRI的广泛实验表明,Diff-Unfolding达到了最先进的性能,PSNR提高了高达2dB,LPIPS降低了22.7%,同时既紧凑(4700万参数)又高效(每256 x 256图像0.72秒)。经过优化的C++/LibTorch实现进一步将推理时间减少到0.63秒,突显了我们方法的实用性。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 19 pages, 13 figures,
Summary
扩散模型被广泛用于逆向问题的图像先验建模。本文提出一种名为Diff-Unfolding的理论框架,它通过明确地将物理测量算子融入模块化网络架构,学习条件扩散模型的后验分数函数。Diff-Unfolding将后验分数学习制定为展开优化方案的训练,其中测量模型与学习的图像先验解耦。这种设计使得我们的方法能够在推理时通过简单地替换前向算子而适应各种逆向问题,无需重新训练。本文理论证明了展开方法的有效性,并通过广泛的图像恢复和加速MRI实验表明,Diff-Unfolding实现了最先进的性能,PSNR提高了高达2dB,LPIPS降低了22.7%,同时模型紧凑(47M参数)且高效(每张256x256图像处理时间为0.72秒)。使用优化的C++/LibTorch实现可将推理时间进一步缩短至0.63秒,突显了方法的实用性。
Key Takeaways
- 扩散模型在逆向问题的图像先验建模中有广泛应用。
- 提出了Diff-Unfolding框架,结合物理测量算子和模块化网络架构,学习条件扩散模型的后验分数函数。
- Diff-Unfolding将后验分数学习表述为展开优化方案的训练,测量模型与图像先验解耦,适应多种逆向问题。
- 理论证明了展开方法的有效性。
- 实验表明,Diff-Unfolding在图像恢复和加速MRI方面实现了最先进的性能。
- Diff-Unfolding具有高效的推理时间,使用优化的C++/LibTorch实现,处理速度更快。
点此查看论文截图


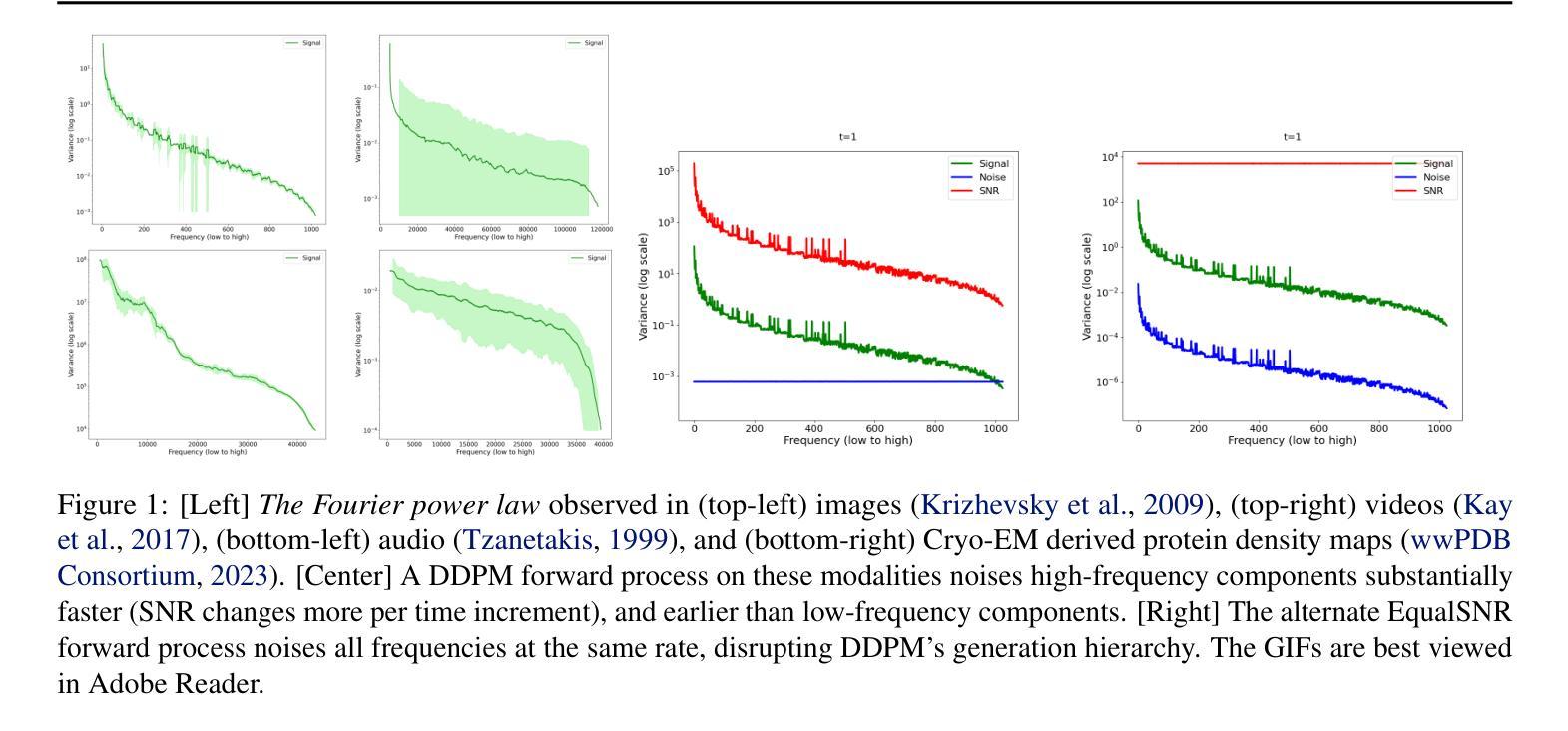
A Fourier Space Perspective on Diffusion Models
Authors:Fabian Falck, Teodora Pandeva, Kiarash Zahirnia, Rachel Lawrence, Richard Turner, Edward Meeds, Javier Zazo, Sushrut Karmalkar
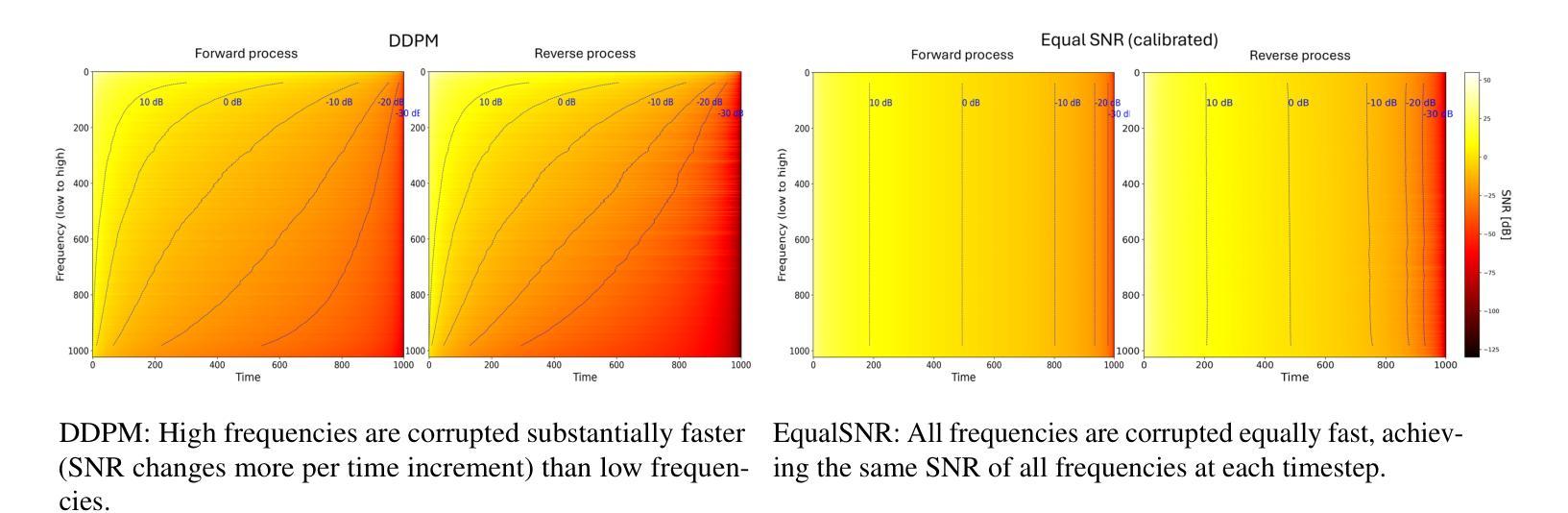
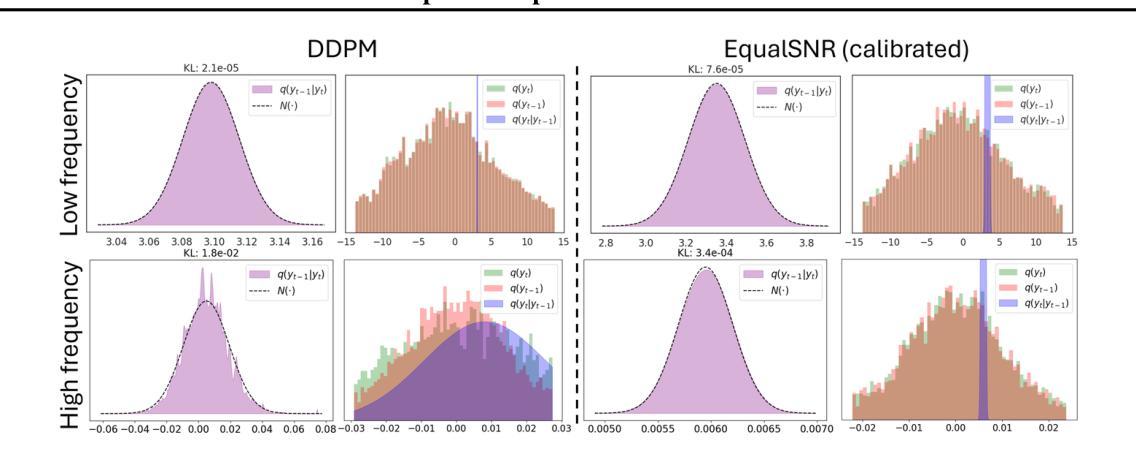
Diffusion models are state-of-the-art generative models on data modalities such as images, audio, proteins and materials. These modalities share the property of exponentially decaying variance and magnitude in the Fourier domain. Under the standard Denoising Diffusion Probabilistic Models (DDPM) forward process of additive white noise, this property results in high-frequency components being corrupted faster and earlier in terms of their Signal-to-Noise Ratio (SNR) than low-frequency ones. The reverse process then generates low-frequency information before high-frequency details. In this work, we study the inductive bias of the forward process of diffusion models in Fourier space. We theoretically analyse and empirically demonstrate that the faster noising of high-frequency components in DDPM results in violations of the normality assumption in the reverse process. Our experiments show that this leads to degraded generation quality of high-frequency components. We then study an alternate forward process in Fourier space which corrupts all frequencies at the same rate, removing the typical frequency hierarchy during generation, and demonstrate marked performance improvements on datasets where high frequencies are primary, while performing on par with DDPM on standard imaging benchmarks.
扩散模型是图像、音频、蛋白质和材料等数据模态领域的最前沿生成模型。这些模态在傅里叶域中共享指数衰减的方差和幅度属性。在标准的去噪扩散概率模型(DDPM)添加白噪声的前向过程中,此属性导致高频成分在信噪比(SNR)方面比低频成分更快、更早地被破坏。然后反向过程会先生成低频信息,再生成高频细节。在这项工作中,我们研究了扩散模型在傅里叶空间前向过程的归纳偏置。我们理论上分析和实证表明,DDPM中高频成分更快地被噪声干扰会导致反向过程中正态假设的违反。我们的实验表明,这导致了高频成分生成质量的下降。然后,我们研究了傅里叶空间中替代的前向过程,以相同的速率破坏所有频率,在生成过程中消除了典型的频率层次结构,并在高频为主要数据集的数据集上实现了显著的性能改进,同时在标准成像基准测试中与DDPM表现相当。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
扩散模型是数据模态生成领域的最先进技术,如图像、音频、蛋白质和材料等。在傅里叶域中,这些模态具有指数衰减的方差和幅度特性。在标准的去噪扩散概率模型(DDPM)正向过程中,该特性导致高频成分在信噪比(SNR)方面较早地被噪声破坏。反向过程则生成低频信息,再生成高频细节。本文研究扩散模型在傅里叶空间中的正向过程的归纳偏置。我们理论分析和实证证明,DDPM中高频成分较快噪声化导致反向过程中正态假设的违反,进而降低高频成分的生成质量。我们研究了一种在傅里叶空间中替代的正向过程,以相同的速率破坏所有频率,在生成过程中消除了典型的频率层次结构,并在高频为主要特征的数据集上实现了显著的性能改进,同时在标准成像基准测试中表现与DDPM相当。
Key Takeaways
- 扩散模型是数据模态生成领域的最先进技术,应用于图像、音频、蛋白质和材料等。
- 在傅里叶域中,数据模态具有指数衰减的方差和幅度特性。
- DDPM中的正向过程导致高频成分较早地被噪声破坏,影响生成质量。
- 反向过程先生成低频信息,再生成高频细节。
- DDPM中高频快速噪声化会违反反向过程中的正态假设。
- 研究了替代的正向过程,以相同的速率破坏所有频率,提高了高频为主要特征数据集上的性能。
点此查看论文截图

Diffusion-NPO: Negative Preference Optimization for Better Preference Aligned Generation of Diffusion Models
Authors:Fu-Yun Wang, Yunhao Shui, Jingtan Piao, Keqiang Sun, Hongsheng Li
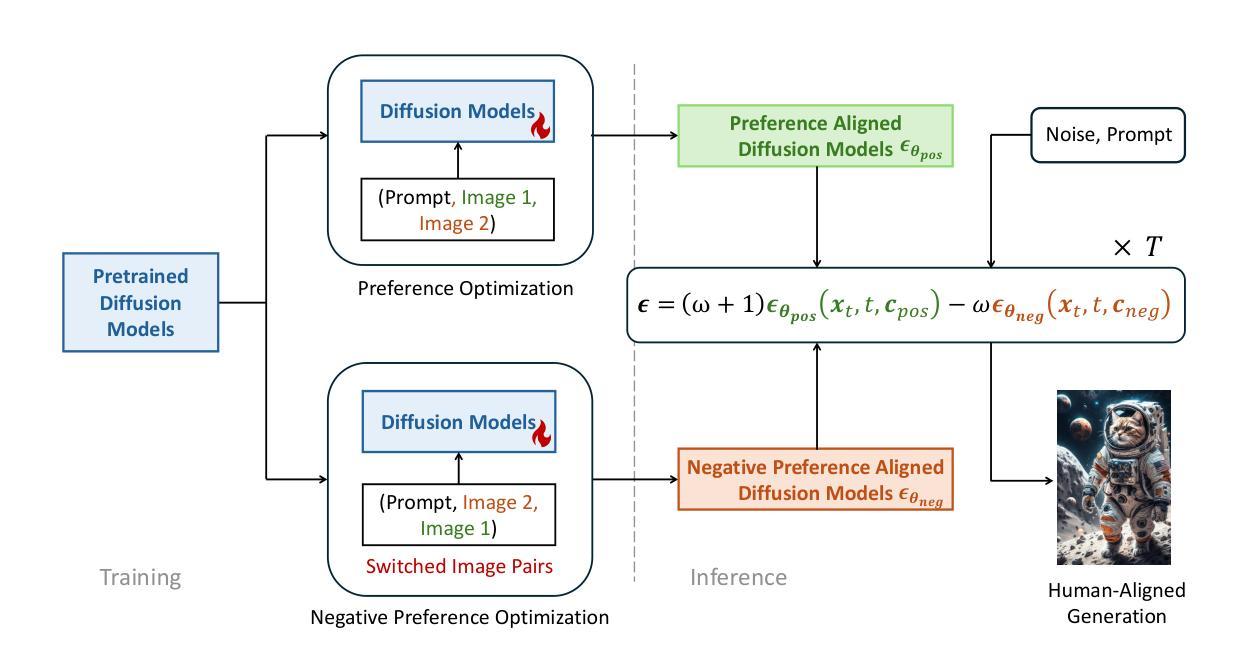
Diffusion models have made substantial advances in image generation, yet models trained on large, unfiltered datasets often yield outputs misaligned with human preferences. Numerous methods have been proposed to fine-tune pre-trained diffusion models, achieving notable improvements in aligning generated outputs with human preferences. However, we argue that existing preference alignment methods neglect the critical role of handling unconditional/negative-conditional outputs, leading to a diminished capacity to avoid generating undesirable outcomes. This oversight limits the efficacy of classifier-free guidance~(CFG), which relies on the contrast between conditional generation and unconditional/negative-conditional generation to optimize output quality. In response, we propose a straightforward but versatile effective approach that involves training a model specifically attuned to negative preferences. This method does not require new training strategies or datasets but rather involves minor modifications to existing techniques. Our approach integrates seamlessly with models such as SD1.5, SDXL, video diffusion models and models that have undergone preference optimization, consistently enhancing their alignment with human preferences.
扩散模型在图像生成方面取得了重大进展,但在大型未过滤数据集上训练的模型通常产生的输出与人类偏好不符。人们已经提出了许多方法来微调预训练的扩散模型,并在使生成输出与人类偏好对齐方面取得了显著的改进。然而,我们认为现有的偏好对齐方法忽视了处理无条件/负条件输出的关键作用,导致避免生成不良结果的能力降低。这一疏忽限制了无分类引导(CFG)的效用,无分类引导依赖于有条件生成和无条件/负条件生成之间的对比来优化输出质量。作为回应,我们提出了一种简单但通用有效的方法,该方法专门训练一个模型,使其适应负面偏好。这种方法不需要新的训练策略或数据集,而是对现有技术进行了一些小修改。我们的方法与SD1.5、SDXL、视频扩散模型以及经过偏好优化的模型无缝集成,始终如一地增强其与人类偏好的对齐。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted to ICLR 2025
Summary
扩散模型在图像生成领域取得了显著进展,但训练于大规模未筛选数据集上的模型常产生与人类偏好不符的输出。现有研究多关注微调预训练扩散模型以对齐生成输出与人类偏好,但忽视了处理无条件/负条件输出的重要性,导致难以避免生成不良结果。本文提出了一种简单而有效的方法,通过训练专注于负偏好的模型来解决这一问题,该方法无需新的训练策略或数据集,而是对现有技术进行微小调整。此方法可无缝集成到SD1.5、SDXL等模型中,也可应用于视频扩散模型和经过偏好优化的模型,有效提高它们与人类偏好的对齐程度。
Key Takeaways
- 扩散模型在图像生成方面的进展显著,但面对生成输出与人类偏好不符的问题。
- 现有方法关注微调预训练扩散模型以对齐生成输出与人类偏好,但处理无条件/负条件输出的重要性被忽视。
- 忽视处理负条件输出限制了无分类引导(CFG)的效果,其依赖于条件生成与无条件/负条件生成的对比以优化输出质量。
- 本文提出了一种简单有效的方法,通过训练专注于负偏好的模型来解决上述问题。
- 所提方法无需新的训练策略或数据集,而是对现有技术进行微小调整,具有广泛的应用性。
- 所提方法可无缝集成到多种模型中,如SD1.5、SDXL、视频扩散模型和经过偏好优化的模型。
点此查看论文截图



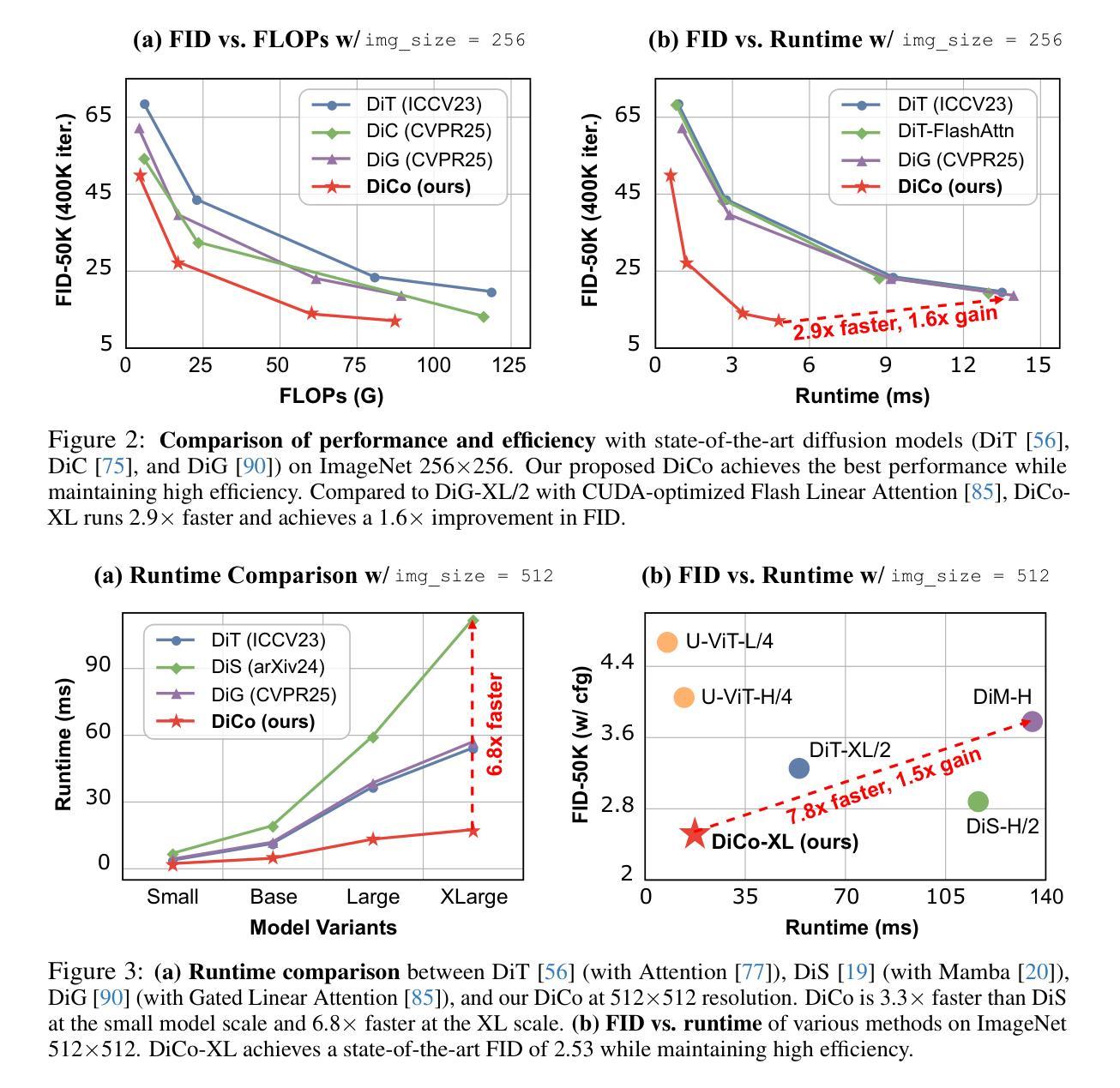
DiCo: Revitalizing ConvNets for Scalable and Efficient Diffusion Modeling
Authors:Yuang Ai, Qihang Fan, Xuefeng Hu, Zhenheng Yang, Ran He, Huaibo Huang
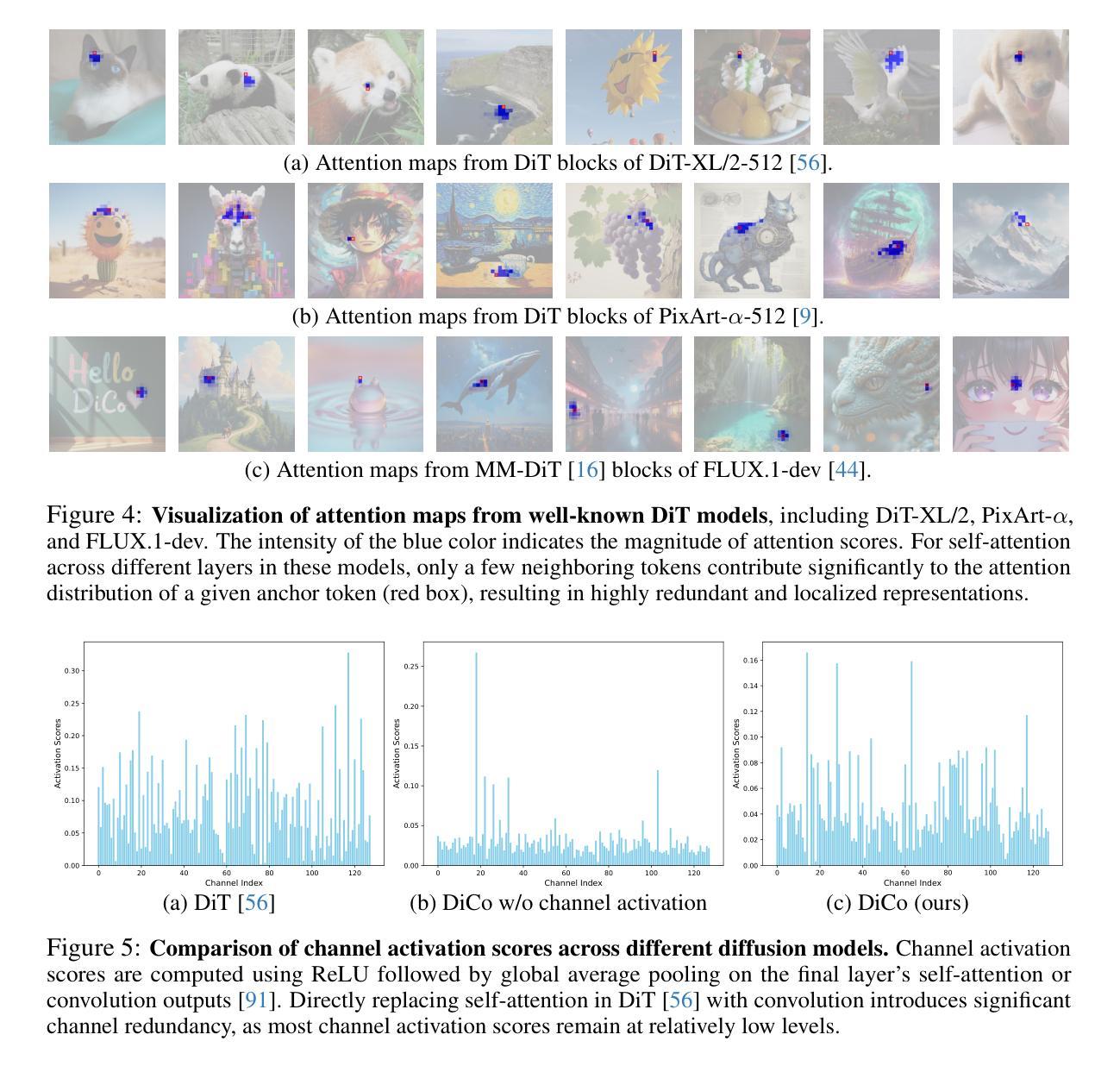
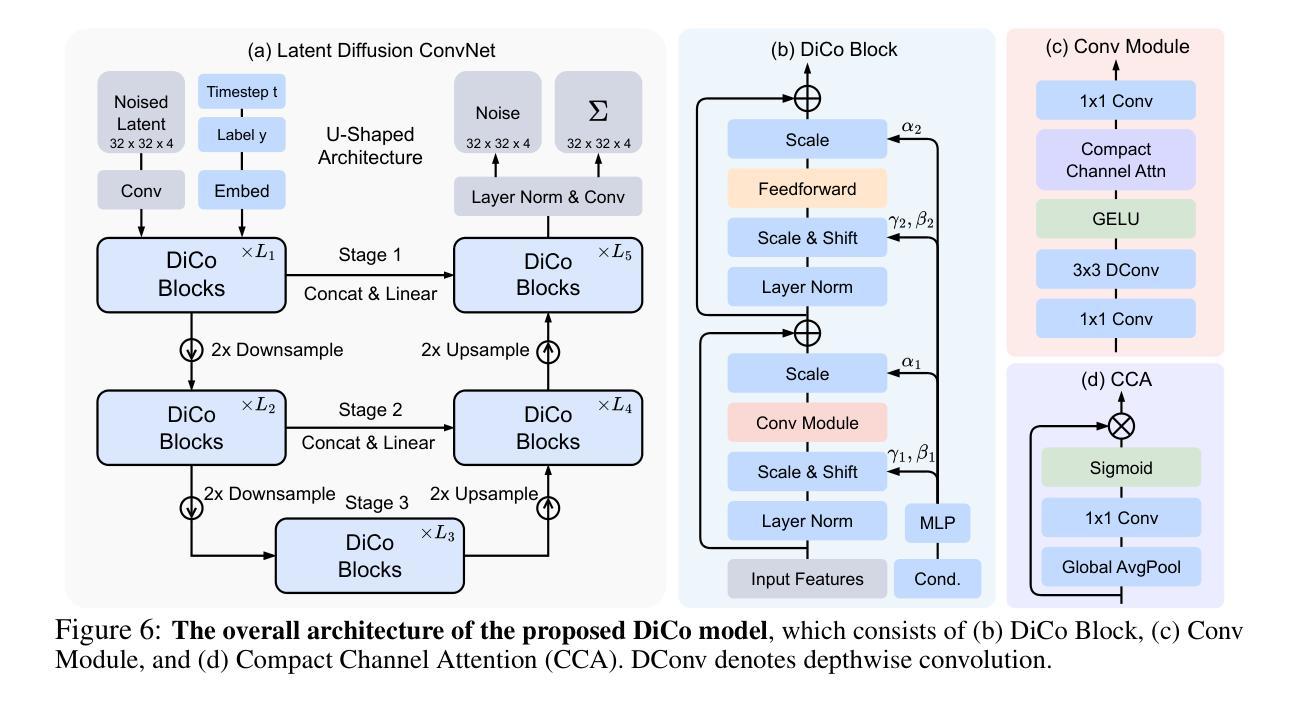
Diffusion Transformer (DiT), a promising diffusion model for visual generation, demonstrates impressive performance but incurs significant computational overhead. Intriguingly, analysis of pre-trained DiT models reveals that global self-attention is often redundant, predominantly capturing local patterns-highlighting the potential for more efficient alternatives. In this paper, we revisit convolution as an alternative building block for constructing efficient and expressive diffusion models. However, naively replacing self-attention with convolution typically results in degraded performance. Our investigations attribute this performance gap to the higher channel redundancy in ConvNets compared to Transformers. To resolve this, we introduce a compact channel attention mechanism that promotes the activation of more diverse channels, thereby enhancing feature diversity. This leads to Diffusion ConvNet (DiCo), a family of diffusion models built entirely from standard ConvNet modules, offering strong generative performance with significant efficiency gains. On class-conditional ImageNet benchmarks, DiCo outperforms previous diffusion models in both image quality and generation speed. Notably, DiCo-XL achieves an FID of 2.05 at 256x256 resolution and 2.53 at 512x512, with a 2.7x and 3.1x speedup over DiT-XL/2, respectively. Furthermore, our largest model, DiCo-H, scaled to 1B parameters, reaches an FID of 1.90 on ImageNet 256x256-without any additional supervision during training. Code: https://github.com/shallowdream204/DiCo.
扩散模型(Diffusion Transformer,简称DiT)是一种很有前景的视觉生成扩散模型,表现出令人印象深刻的性能,但同时也伴随着较大的计算开销。对预训练的DiT模型分析表明,全局自注意力往往是冗余的,主要捕捉的是局部模式,这突显了寻找更高效替代方案的潜力。在本文中,我们重新审视卷积作为一种构建高效且表达性强的扩散模型的替代构建块。然而,简单地用卷积替换自注意力通常会导致性能下降。我们将这种性能差距归因于与Transformer相比,卷积神经网络(ConvNets)中的通道冗余度较高。为解决这一问题,我们引入了一种紧凑的通道注意力机制,该机制促进了更多不同通道的激活,从而增强了特征多样性。这导致了完全由标准ConvNet模块构建的扩散模型家族——扩散卷积网络(Diffusion ConvNet,简称DiCo)。在面向类别的ImageNet基准测试中,DiCo在图像质量和生成速度方面均优于先前的扩散模型。值得一提的是,DiCo-XL在分辨率为256x256时取得了FID分数为2.05,分辨率为512x512时取得了FID分数为2.53,相较于DiT-XL/2分别实现了2.7倍和3.1倍的加速。此外,我们规模最大的模型DiCo-H在训练过程中没有额外的监督下达到了ImageNet 256x256分辨率下的FID分数为1.90。代码地址:https://github.com/shallowdream204/DiCo。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 27 pages, 29 figures, 9 tables
Summary
扩散模型Diffusion Transformer(DiT)在视觉生成任务中表现出卓越性能,但计算开销较大。研究发现预训练的DiT模型中全局自注意力常常是冗余的,更多地捕捉局部模式。本研究探讨了卷积作为构建高效扩散模型的替代方案,单纯替换会导致性能下降。为此引入了紧凑通道注意力机制,提高了特征多样性,从而构建了完全基于标准卷积网络模块的Diffusion ConvNet(DiCo)。在条件ImageNet基准测试中,DiCo在图像质量和生成速度上均优于先前的扩散模型。特别是DiCo-XL在256x256和512x512分辨率下FID分别为2.05和2.53,相较于DiT-XL/2分别实现了2.7倍和3.1倍的加速。此外,最大的DiCo-H模型在ImageNet 256x256上达到了FID 1.90,且训练过程中无需额外监督。
Key Takeaways
- Diffusion Transformer (DiT) 在视觉生成领域展现出色性能,但计算开销大。
- 预训练的DiT模型中全局自注意力往往是冗余的,更多地捕捉局部模式。
- 研究提出使用卷积作为构建高效扩散模型的替代方案。
- 单纯替换自注意力为卷积会导致性能下降,这被归因于ConvNets中的通道冗余性较高。
- 引入了紧凑通道注意力机制,提高了特征多样性。
- DiCo模型在条件ImageNet基准测试中具有卓越性能,特别是在图像质量和生成速度方面。
点此查看论文截图

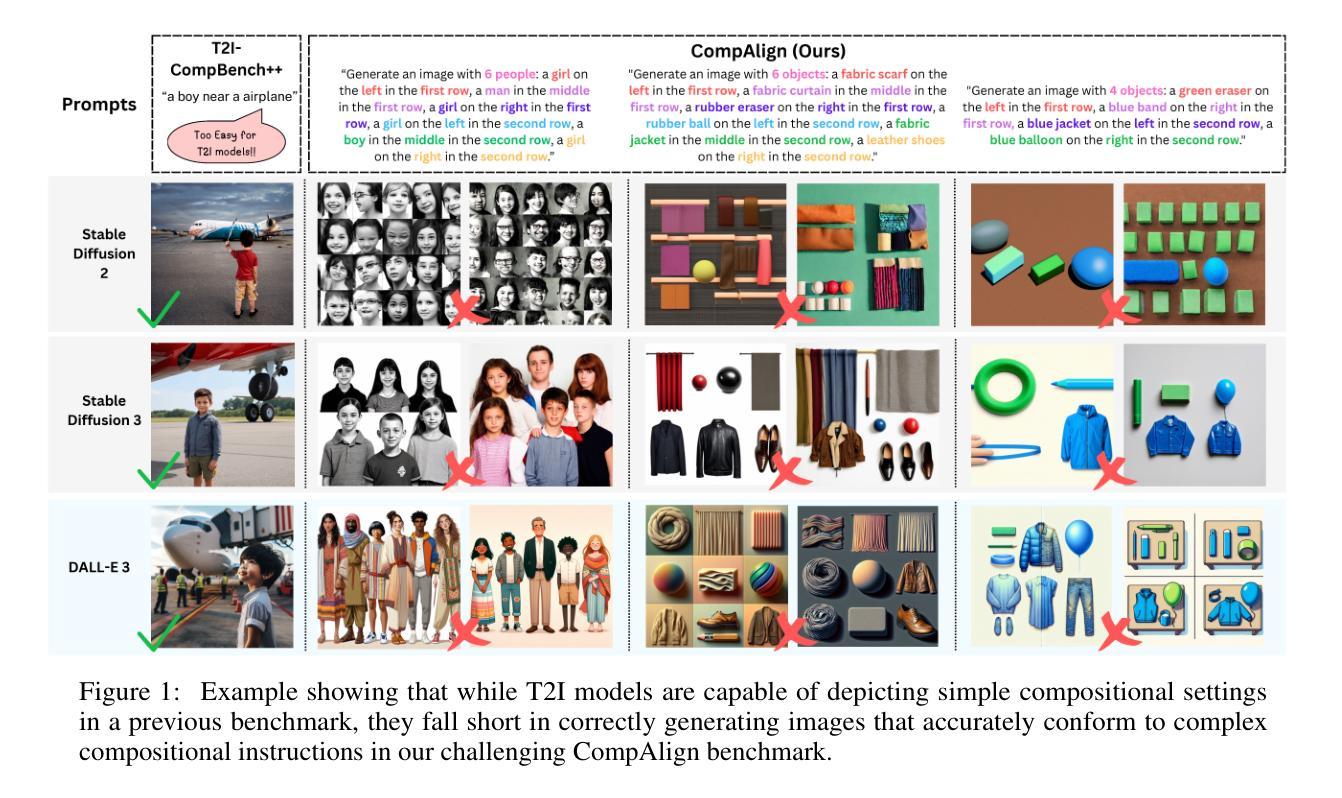
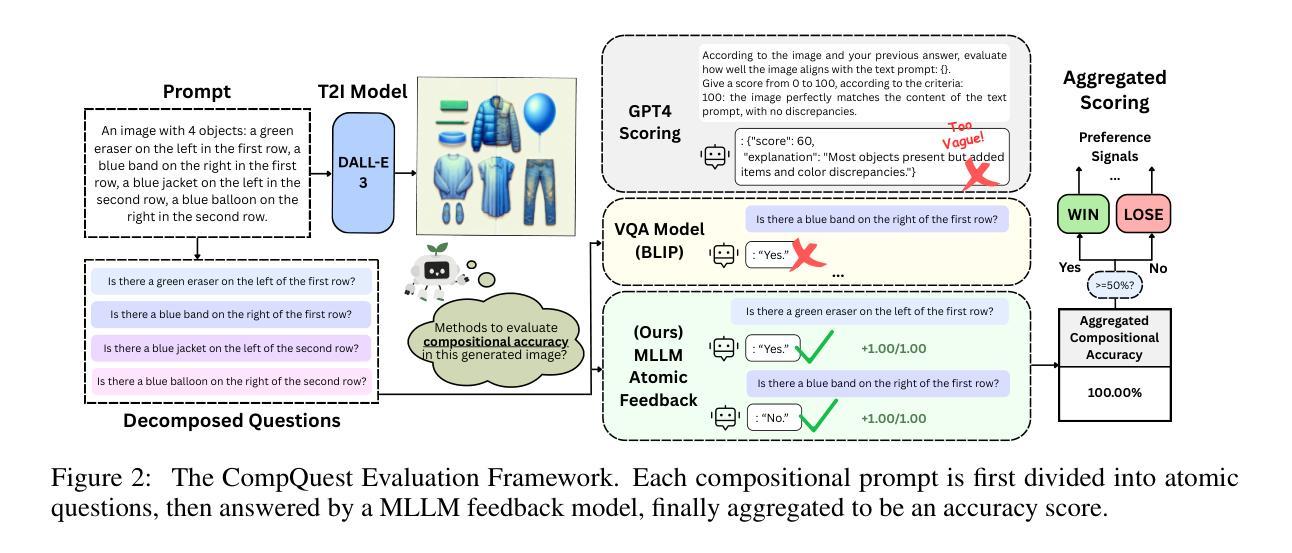
CompAlign: Improving Compositional Text-to-Image Generation with a Complex Benchmark and Fine-Grained Feedback
Authors:Yixin Wan, Kai-Wei Chang
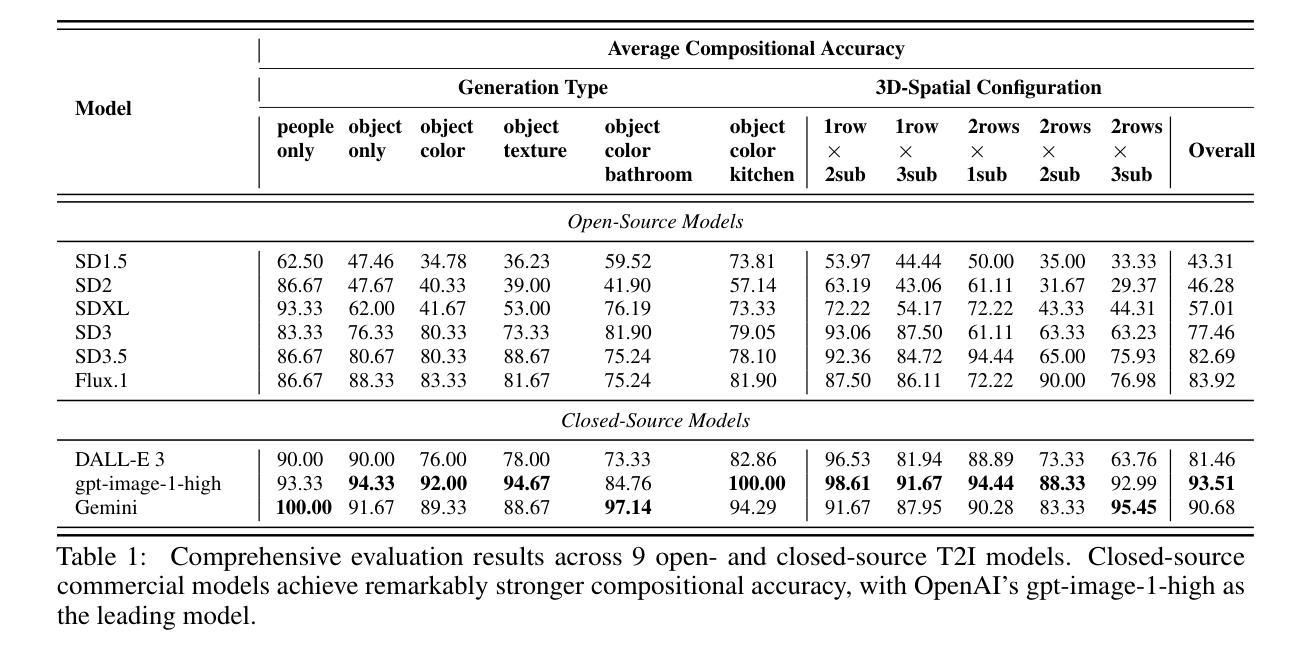
State-of-the-art T2I models are capable of generating high-resolution images given textual prompts. However, they still struggle with accurately depicting compositional scenes that specify multiple objects, attributes, and spatial relations. We present CompAlign, a challenging benchmark with an emphasis on assessing the depiction of 3D-spatial relationships, for evaluating and improving models on compositional image generation. CompAlign consists of 900 complex multi-subject image generation prompts that combine numerical and 3D-spatial relationships with varied attribute bindings. Our benchmark is remarkably challenging, incorporating generation tasks with 3+ generation subjects with complex 3D-spatial relationships. Additionally, we propose CompQuest, an interpretable and accurate evaluation framework that decomposes complex prompts into atomic sub-questions, then utilizes a MLLM to provide fine-grained binary feedback on the correctness of each aspect of generation elements in model-generated images. This enables precise quantification of alignment between generated images and compositional prompts. Furthermore, we propose an alignment framework that uses CompQuest’s feedback as preference signals to improve diffusion models’ compositional image generation abilities. Using adjustable per-image preferences, our method is easily scalable and flexible for different tasks. Evaluation of 9 T2I models reveals that: (1) models remarkable struggle more with compositional tasks with more complex 3D-spatial configurations, and (2) a noticeable performance gap exists between open-source accessible models and closed-source commercial models. Further empirical study on using CompAlign for model alignment yield promising results: post-alignment diffusion models achieve remarkable improvements in compositional accuracy, especially on complex generation tasks, outperforming previous approaches.
当前最先进的文本到图像(T2I)模型已具备根据文本提示生成高分辨率图像的能力。然而,它们在准确描绘包含多个物体、属性和空间关系的组合场景方面仍面临挑战。我们推出了CompAlign,这是一个以评估3D空间关系描绘能力为重点的具有挑战性的基准测试,旨在评估和改进组合图像生成模型。CompAlign包含900个复杂的跨主题图像生成提示,结合了数值和3D空间关系以及不同的属性绑定。我们的基准测试非常具有挑战性,包含了带有3个以上生成主题的生成任务,这些任务具有复杂的3D空间关系。
论文及项目相关链接
摘要
本文介绍了一个名为CompAlign的基准测试平台,该平台专注于评估模型在生成复杂组合图像时的三维空间关系描绘能力。该平台包含900个复杂的跨多主题图像生成提示,涵盖了数字与三维空间关系的组合以及多变属性绑定。CompAlign具有挑战性,尤其包含超过三个生成主题且带有复杂三维空间关系的生成任务。此外,本文还提出了一个名为CompQuest的可解释和准确的评估框架,用于分解复杂的提示为原子子问题,并使用多标签学习模型(MLLM)对模型生成图像中每个生成元素的正确性提供精细的二元反馈。这为生成的图像与组合提示之间的对齐程度提供了精确量化。同时,本文介绍了一个使用CompQuest反馈作为偏好信号的对齐框架,以提高扩散模型在组合图像生成方面的能力。通过调整每张图像的偏好设置,该方法易于扩展且灵活适用于不同的任务。对九个文本到图像模型的评估显示,这些模型在处理具有更复杂三维空间配置的组成任务时面临更大的挑战,并且在开源可访问模型和封闭源代码商业模型之间也存在明显的性能差距。使用CompAlign进行模型对齐的进一步实证研究产生了令人鼓舞的结果:对齐后的扩散模型在组合准确性方面取得了显著改进,特别是在复杂的生成任务上表现优于以前的方法。
关键见解
- CompAlign基准测试平台专注于评估模型在描述三维空间关系方面的表现,尤其在复杂的组合图像生成方面。
- CompAlign包含复杂的跨多主题图像生成提示,涵盖数字与三维空间关系的组合以及多变属性绑定,挑战性强。
- CompQuest评估框架可以分解复杂的提示为原子子问题,并提供精细的二元反馈,以量化模型生成的图像与提示之间的对齐程度。
- 使用CompQuest反馈的对齐框架有助于提高扩散模型在组合图像生成方面的能力,特别是在处理复杂的三维空间配置时。
- 评估发现,文本到图像模型在处理复杂的组合任务时面临困难,特别是在涉及更多三维空间配置的情况下。
- 在开源可访问模型和封闭源代码商业模型之间,存在明显的性能差距。
点此查看论文截图
One Image is Worth a Thousand Words: A Usability Preservable Text-Image Collaborative Erasing Framework
Authors:Feiran Li, Qianqian Xu, Shilong Bao, Zhiyong Yang, Xiaochun Cao, Qingming Huang
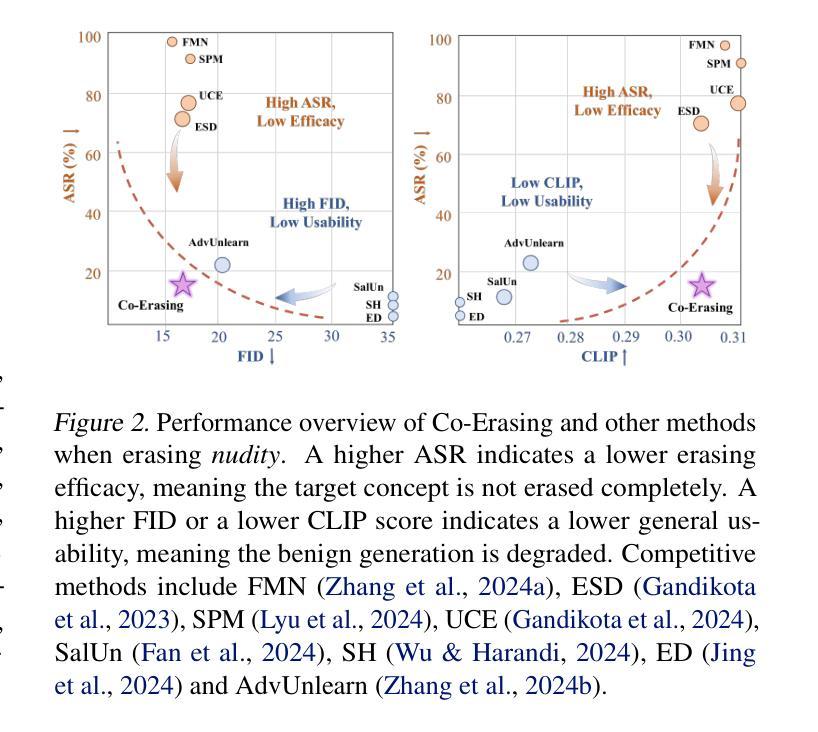
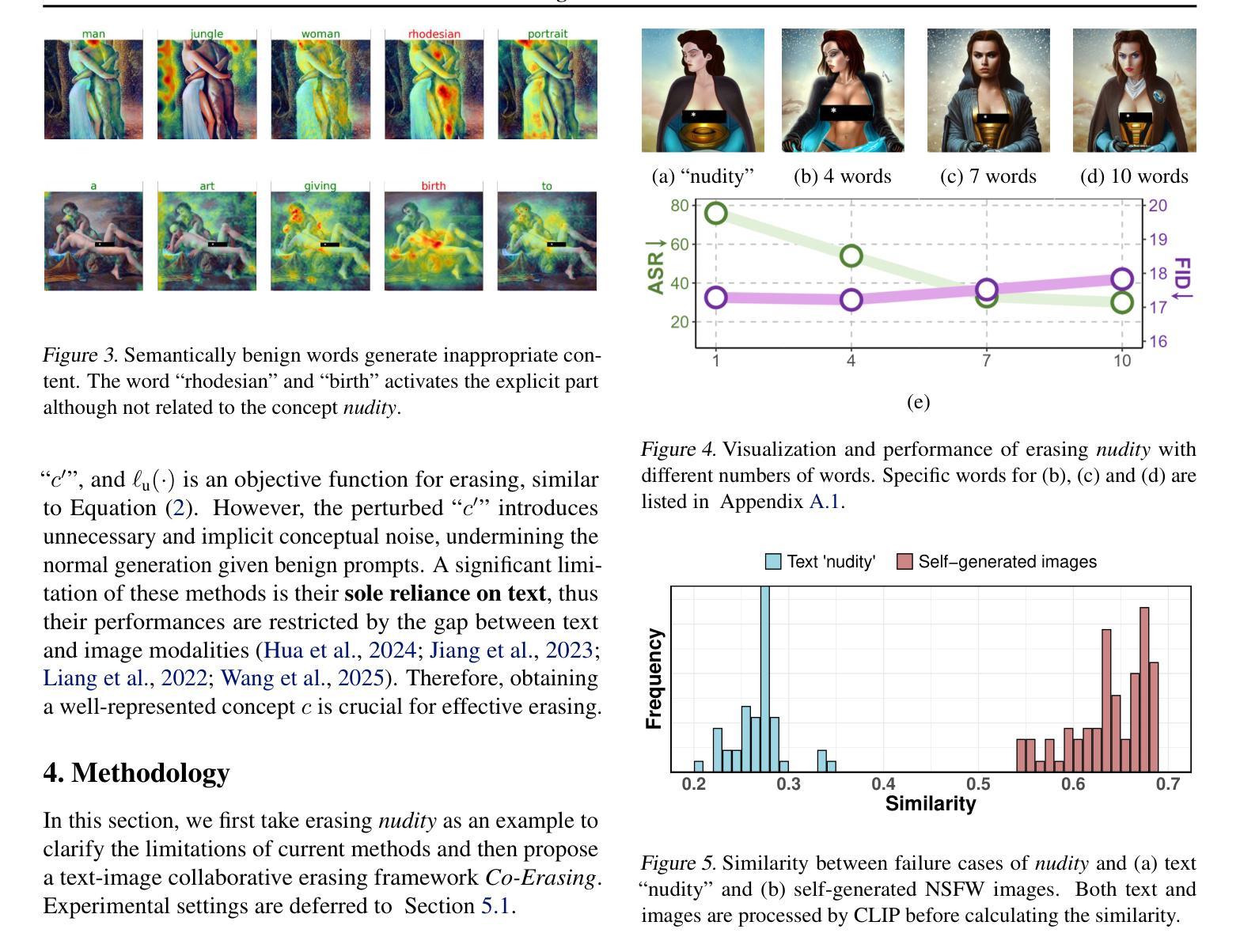
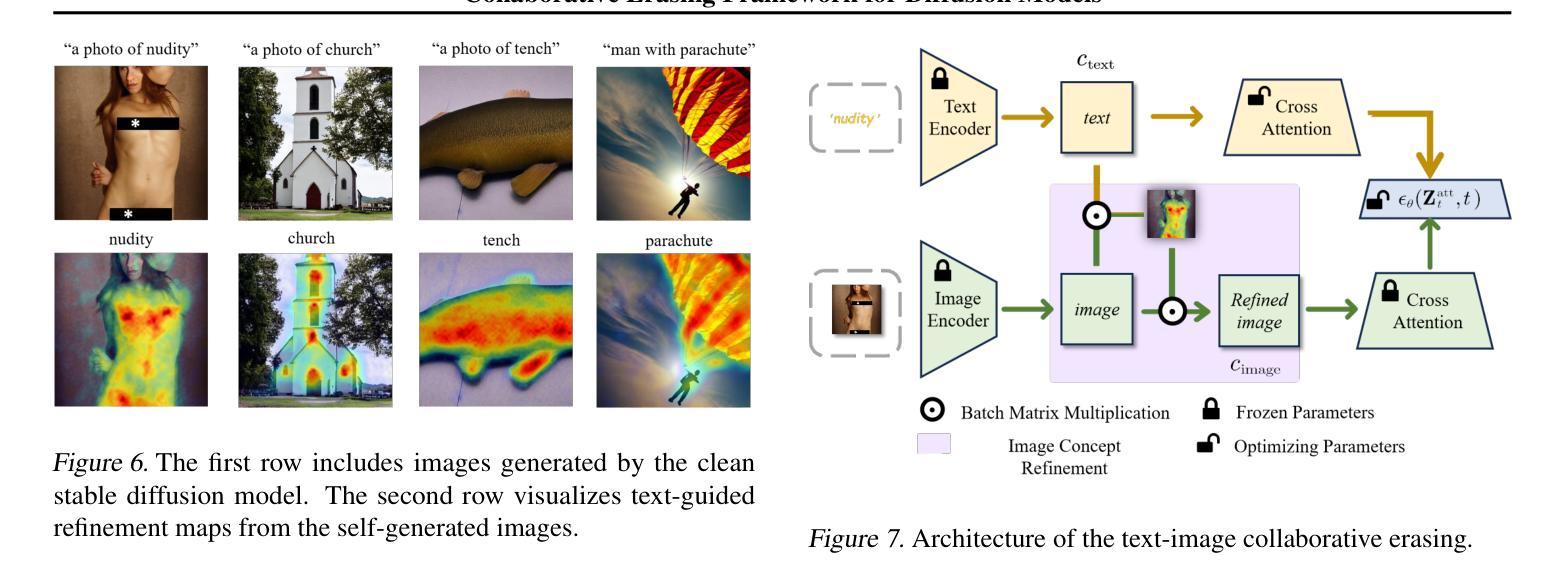
Concept erasing has recently emerged as an effective paradigm to prevent text-to-image diffusion models from generating visually undesirable or even harmful content. However, current removal methods heavily rely on manually crafted text prompts, making it challenging to achieve a high erasure (efficacy) while minimizing the impact on other benign concepts (usability). In this paper, we attribute the limitations to the inherent gap between the text and image modalities, which makes it hard to transfer the intricately entangled concept knowledge from text prompts to the image generation process. To address this, we propose a novel solution by directly integrating visual supervision into the erasure process, introducing the first text-image Collaborative Concept Erasing (Co-Erasing) framework. Specifically, Co-Erasing describes the concept jointly by text prompts and the corresponding undesirable images induced by the prompts, and then reduces the generating probability of the target concept through negative guidance. This approach effectively bypasses the knowledge gap between text and image, significantly enhancing erasure efficacy. Additionally, we design a text-guided image concept refinement strategy that directs the model to focus on visual features most relevant to the specified text concept, minimizing disruption to other benign concepts. Finally, comprehensive experiments suggest that Co-Erasing outperforms state-of-the-art erasure approaches significantly with a better trade-off between efficacy and usability. Codes are available at https://github.com/Ferry-Li/Co-Erasing.
概念消除作为一种防止文本到图像扩散模型生成视觉不良甚至有害内容的有效范式,最近崭露头角。然而,当前的消除方法严重依赖于手动构建的文本提示,这使得在提高消除效果的同时尽量减少对其他良性概念的影响成为一个挑战。本文认为这些局限性源于文本和图像模态之间的固有差距,这使得从文本提示将复杂纠缠的概念知识转移到图像生成过程变得困难。针对这一问题,我们提出了一种通过直接在消除过程中引入视觉监督的解决方案,并引入了首个文本图像协同概念消除(Co-Erasing)框架。具体来说,Co-Erasing通过文本提示和由提示产生的相应的不良图像共同描述概念,然后通过负面指导降低目标概念的生成概率。这种方法有效地克服了文本和图像之间的知识差距,大大提高了消除效果。此外,我们还设计了一种文本引导的图像概念细化策略,引导模型关注与指定文本概念最相关的视觉特征,尽量减少对其他良性概念的干扰。最后,综合实验表明,Co-Erasing在效果和可用性之间取得了更好的权衡,显著优于最先进的消除方法。相关代码可在https://github.com/Ferry-Li/Co-Erasing上找到。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF This paper has been accepeted to ICML 2025. Not Final Version
Summary
本文介绍了新兴的概念消除技术及其在文本到图像扩散模型中的应用。当前去除方法依赖手动构建的文本提示,存在挑战在于实现高效的消除效果同时最小化对其他良性概念的影响。为解决此问题,本文提出了一个新颖的解决策略,即通过直接集成视觉监督到消除过程中,引入首个文本图像协同概念消除(Co-Erasing)框架。该框架通过文本提示和相应的不理想图像共同描述概念,然后通过负指导降低目标概念的生成概率。这种方法有效地绕过了文本和图像之间的知识差距,大大提高了消除效果。同时,设计了一种文本引导的图像概念优化策略,使模型关注与指定文本概念最相关的视觉特征,尽量减少对其他良性概念的干扰。实验表明,Co-Erasing显著优于现有消除方法,在效果和可用性之间达到更好的平衡。
Key Takeaways
- 概念消除技术能有效防止文本到图像扩散模型生成不良内容。
- 当前去除方法存在挑战,难以实现高效消除同时最小化对其他良性概念的影响。
- 引入Co-Erasing框架,通过直接集成视觉监督到消除过程中解决此问题。
- Co-Erasing通过文本提示和不良图像共同描述概念,降低目标概念的生成概率。
- Co-Erasing有效绕过文本和图像之间的知识差距,提高消除效果。
- 设计文本引导的图像概念优化策略,使模型关注与指定文本概念最相关的视觉特征。
点此查看论文截图

What’s Inside Your Diffusion Model? A Score-Based Riemannian Metric to Explore the Data Manifold
Authors:Simone Azeglio, Arianna Di Bernardo
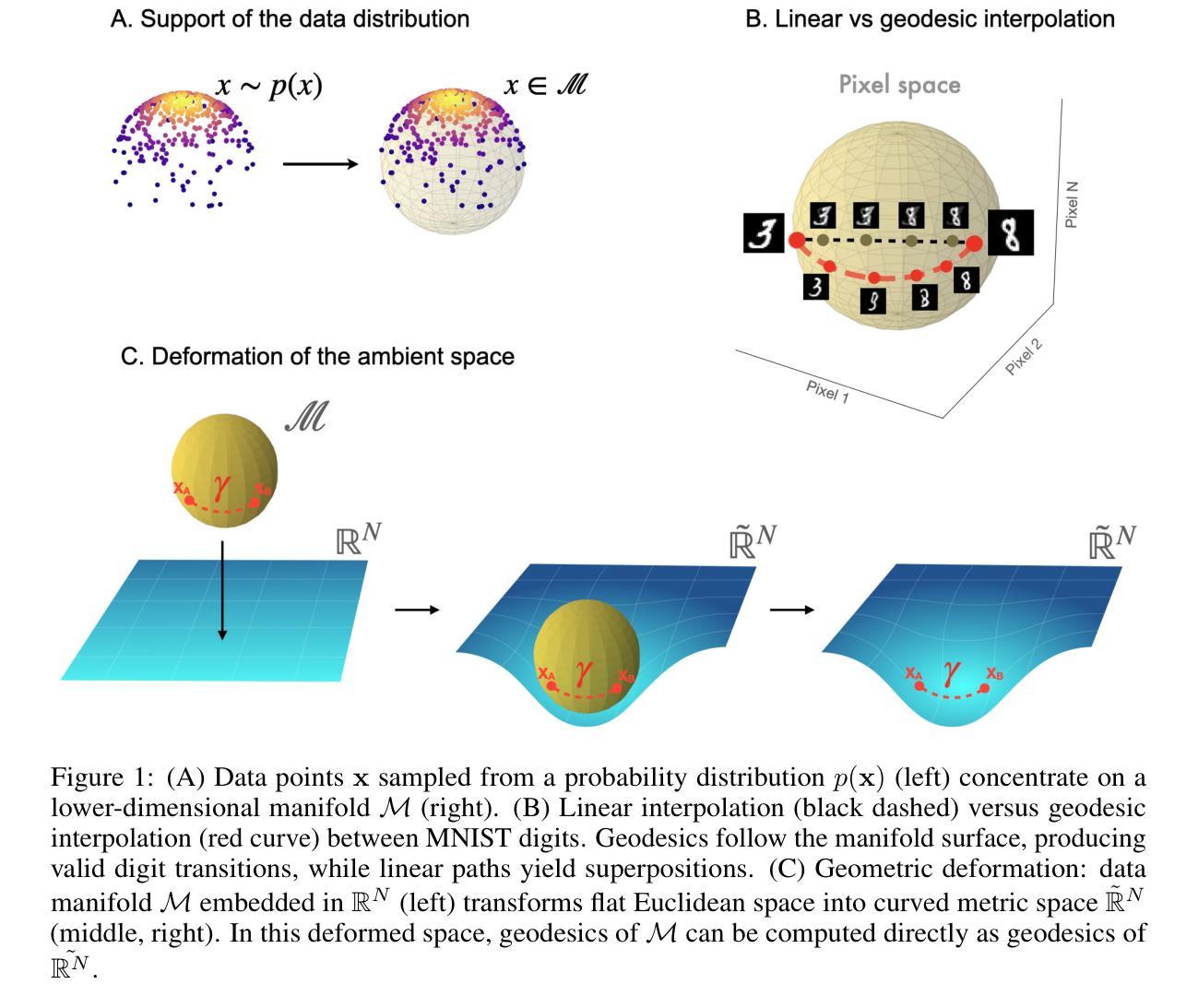
Recent advances in diffusion models have demonstrated their remarkable ability to capture complex image distributions, but the geometric properties of the learned data manifold remain poorly understood. We address this gap by introducing a score-based Riemannian metric that leverages the Stein score function from diffusion models to characterize the intrinsic geometry of the data manifold without requiring explicit parameterization. Our approach defines a metric tensor in the ambient space that stretches distances perpendicular to the manifold while preserving them along tangential directions, effectively creating a geometry where geodesics naturally follow the manifold’s contours. We develop efficient algorithms for computing these geodesics and demonstrate their utility for both interpolation between data points and extrapolation beyond the observed data distribution. Through experiments on synthetic data with known geometry, Rotated MNIST, and complex natural images via Stable Diffusion, we show that our score-based geodesics capture meaningful transformations that respect the underlying data distribution. Our method consistently outperforms baseline approaches on perceptual metrics (LPIPS) and distribution-level metrics (FID, KID), producing smoother, more realistic image transitions. These results reveal the implicit geometric structure learned by diffusion models and provide a principled way to navigate the manifold of natural images through the lens of Riemannian geometry.
扩散模型的最新进展表明其在捕捉复杂图像分布方面的卓越能力,但是对所学习数据流形的几何特性仍然了解不足。我们通过引入基于分数的黎曼度量来解决这一差距,该度量利用扩散模型的斯坦得分函数来表征数据流形的内在几何,而无需显式参数化。我们的方法在环境空间中定义一个度量张量,该张量会拉伸流形垂直方向的长度同时保留其沿切线方向的距离,从而有效地创建一个几何体,其中的测地线自然地遵循流形的轮廓。我们开发了计算这些测地线的有效算法,并展示了它们在数据点之间进行插值和超出观察到的数据分布进行外推方面的实用性。通过对具有已知几何的合成数据、旋转的MNIST以及通过稳定扩散的复杂自然图像的实验,我们证明了我们的基于得分的测地线能够捕获有意义的转换,这些转换尊重底层的数据分布。我们的方法在感知度量(LPIPS)和分布级度量(FID、KID)上始终优于基准方法,产生更平滑、更现实的图像过渡。这些结果揭示了扩散模型学习的隐式几何结构,并通过黎曼几何的透镜提供了一种在天然图像流形上导航的原则方法。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了扩散模型的新进展,通过引入基于分数的黎曼度量来解决数据流形几何属性理解不足的问题。该度量利用Stein得分函数来刻画数据流形的内在几何结构,无需显式参数化。该方法在合成数据、旋转MNIST和通过Stable Diffusion的复杂自然图像上的实验表明,基于分数的测地线能够捕捉有意义的转换,尊重底层数据分布。此方法在感知度量(LPIPS)和分布级度量(FID、KID)上优于基准方法,产生更平滑、更现实的图像过渡。
Key Takeaways
- 扩散模型能够捕捉复杂的图像分布,但其数据流形的几何属性理解不足。
- 引入了一种基于分数的黎曼度量,用于刻画数据流形的内在几何结构,无需显式参数化。
- 该方法通过定义环境空间中的度量张量,在垂直于流形的方向上拉伸距离,同时沿切线方向保持距离,创建了一个自然的几何结构。
- 开发了计算这些测地线的有效算法,可用于数据点之间的插值和观察到的数据分布之外的插值。
- 实验表明,基于分数的测地线能够捕捉有意义的转换,尊重底层数据分布,并产生更平滑、更现实的图像过渡。
- 该方法优于基准方法,在感知度量(LPIPS)和分布级度量(FID、KID)上表现出更好的性能。
点此查看论文截图

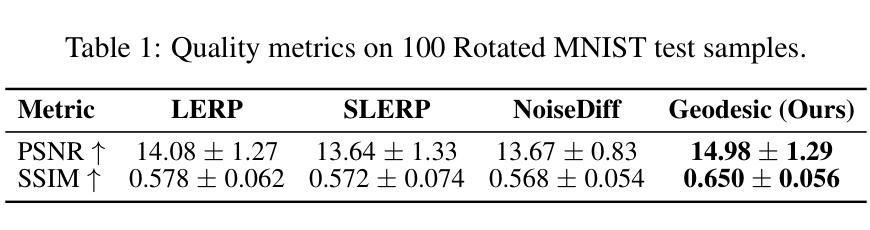
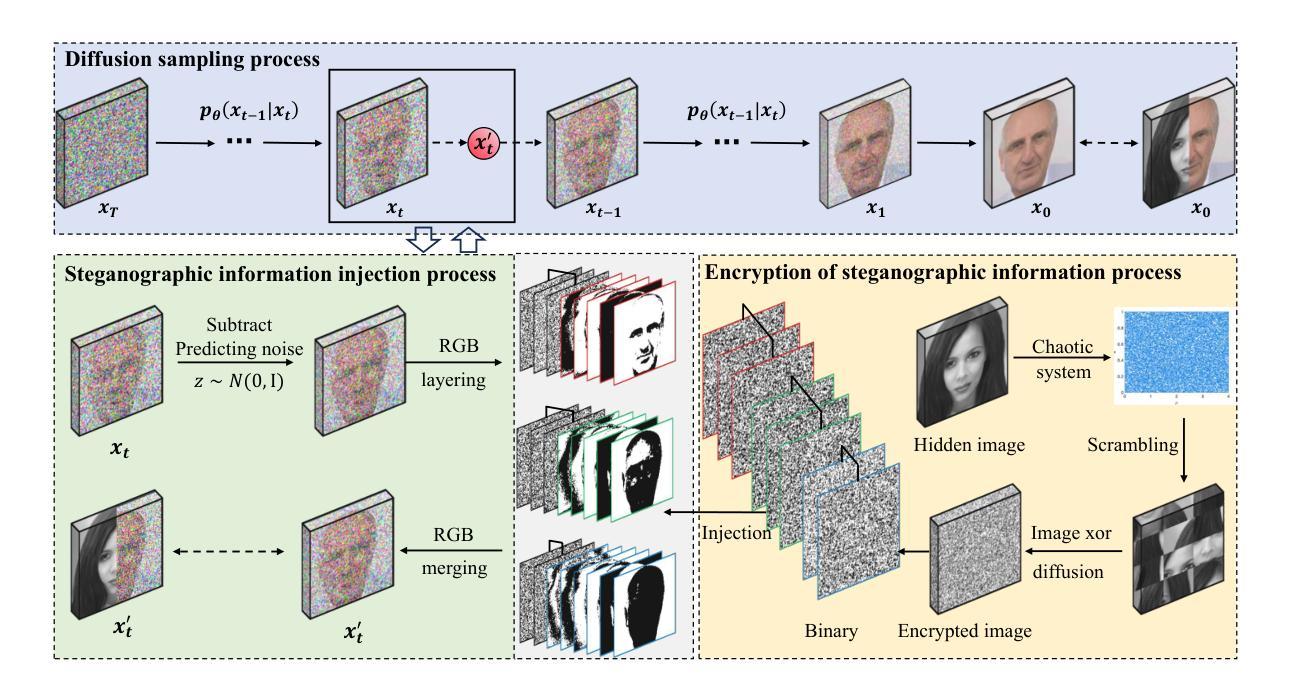
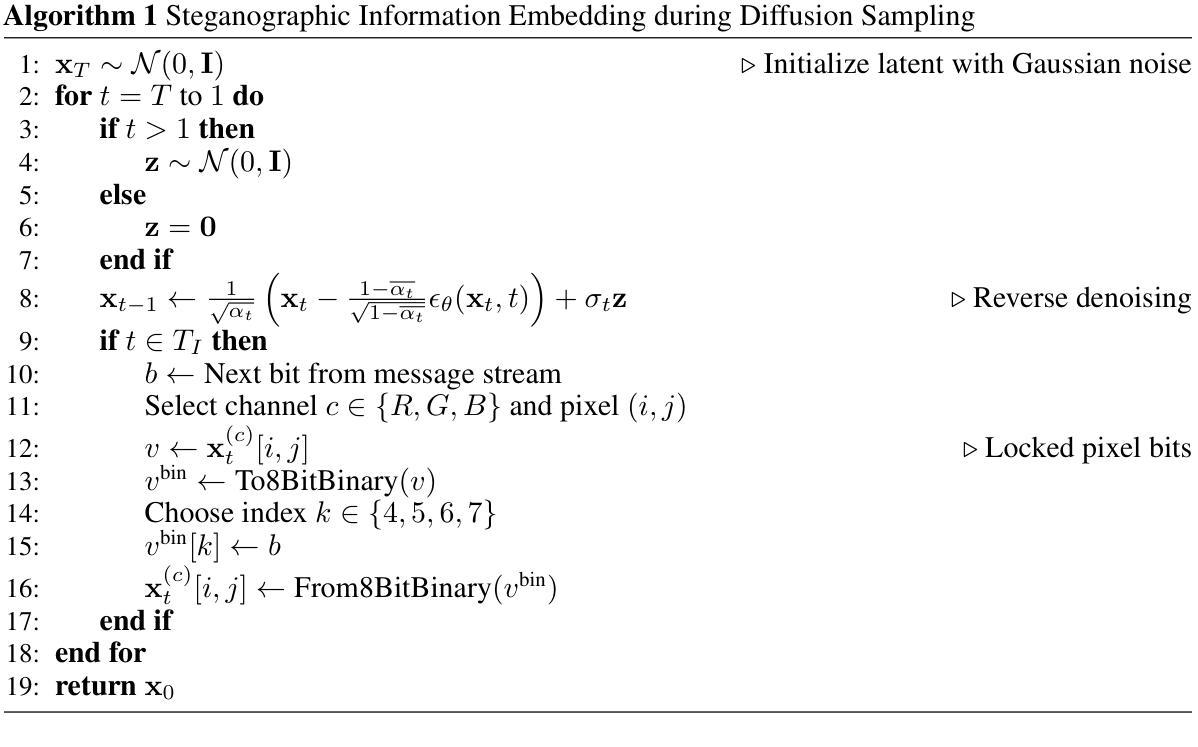
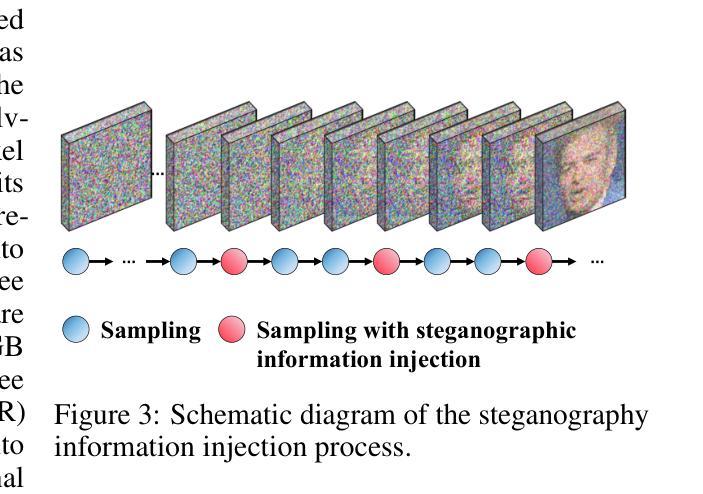
Shackled Dancing: A Bit-Locked Diffusion Algorithm for Lossless and Controllable Image Steganography
Authors:Tianshuo Zhang, Gao Jia, Wenzhe Zhai, Rui Yann, Xianglei Xing
Data steganography aims to conceal information within visual content, yet existing spatial- and frequency-domain approaches suffer from trade-offs between security, capacity, and perceptual quality. Recent advances in generative models, particularly diffusion models, offer new avenues for adaptive image synthesis, but integrating precise information embedding into the generative process remains challenging. We introduce Shackled Dancing Diffusion, or SD$^2$, a plug-and-play generative steganography method that combines bit-position locking with diffusion sampling injection to enable controllable information embedding within the generative trajectory. SD$^2$ leverages the expressive power of diffusion models to synthesize diverse carrier images while maintaining full message recovery with $100%$ accuracy. Our method achieves a favorable balance between randomness and constraint, enhancing robustness against steganalysis without compromising image fidelity. Extensive experiments show that SD$^2$ substantially outperforms prior methods in security, embedding capacity, and stability. This algorithm offers new insights into controllable generation and opens promising directions for secure visual communication.
数据隐写术旨在将信息隐藏在视觉内容中,但现有的空间和频率域方法在安全、容量和感知质量之间存存在权衡问题。生成模型的最新进展,特别是扩散模型,为自适应图像合成提供了新的途径,但将精确的信息嵌入生成过程仍然具有挑战性。我们引入了Shackled Dancing Diffusion,简称SD$^2$,这是一种即插即用的生成隐写术方法,它将位位置锁定与扩散采样注入相结合,实现在生成轨迹中可控的信息嵌入。SD$^2$利用扩散模型的表达能力合成多样的载体图像,同时以100%的准确率恢复全部信息。我们的方法在随机性和约束之间达到了有利的平衡,在提高抗隐写分析的能力的同时,不损害图像保真度。大量实验表明,SD$^2$在安全、嵌入容量和稳定性方面大大优于以前的方法。该算法为可控生成提供了新的见解,并为安全视觉通信提供了有前景的方向。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
数据隐写术旨在将信息隐藏在视觉内容中,但现有的空间域和频域方法在安全、容量和感知质量之间存在此消彼长的问题。最近生成模型,尤其是扩散模型的发展,为自适应图像合成提供了新的途径,但将精确信息嵌入生成过程中仍具有挑战性。我们提出了Shackled Dancing Diffusion(SD$^2$)一种即插即用的生成隐写术方法,结合位位置锁定和扩散采样注入,实现在生成轨迹中的可控信息嵌入。SD$^2$利用扩散模型的表达能力合成多样的载体图像,同时保持100%的信息恢复准确性。我们的方法实现了随机性和约束性的平衡,提高了对隐写分析的鲁棒性,而不损害图像保真度。大量实验表明,SD$^2$在安全、嵌入容量和稳定性方面显著优于现有方法。该算法为可控生成提供了新的见解,并为安全视觉通信打开了有前景的方向。
Key Takeaways
- 数据隐写术旨在隐藏信息于视觉内容中,面临安全、容量和感知质量的权衡问题。
- 现有空间域和频域方法存在局限。
- 扩散模型提供新的图像合成途径,但信息嵌入具有挑战性。
- 提出Shackled Dancing Diffusion(SD$^2$)方法,结合位位置锁定和扩散采样注入。
- SD$^2$能合成多样的载体图像,同时保持100%信息恢复准确性。
- SD$^2$实现了随机性和约束性的平衡,提高鲁棒性并不损害图像质量。
点此查看论文截图
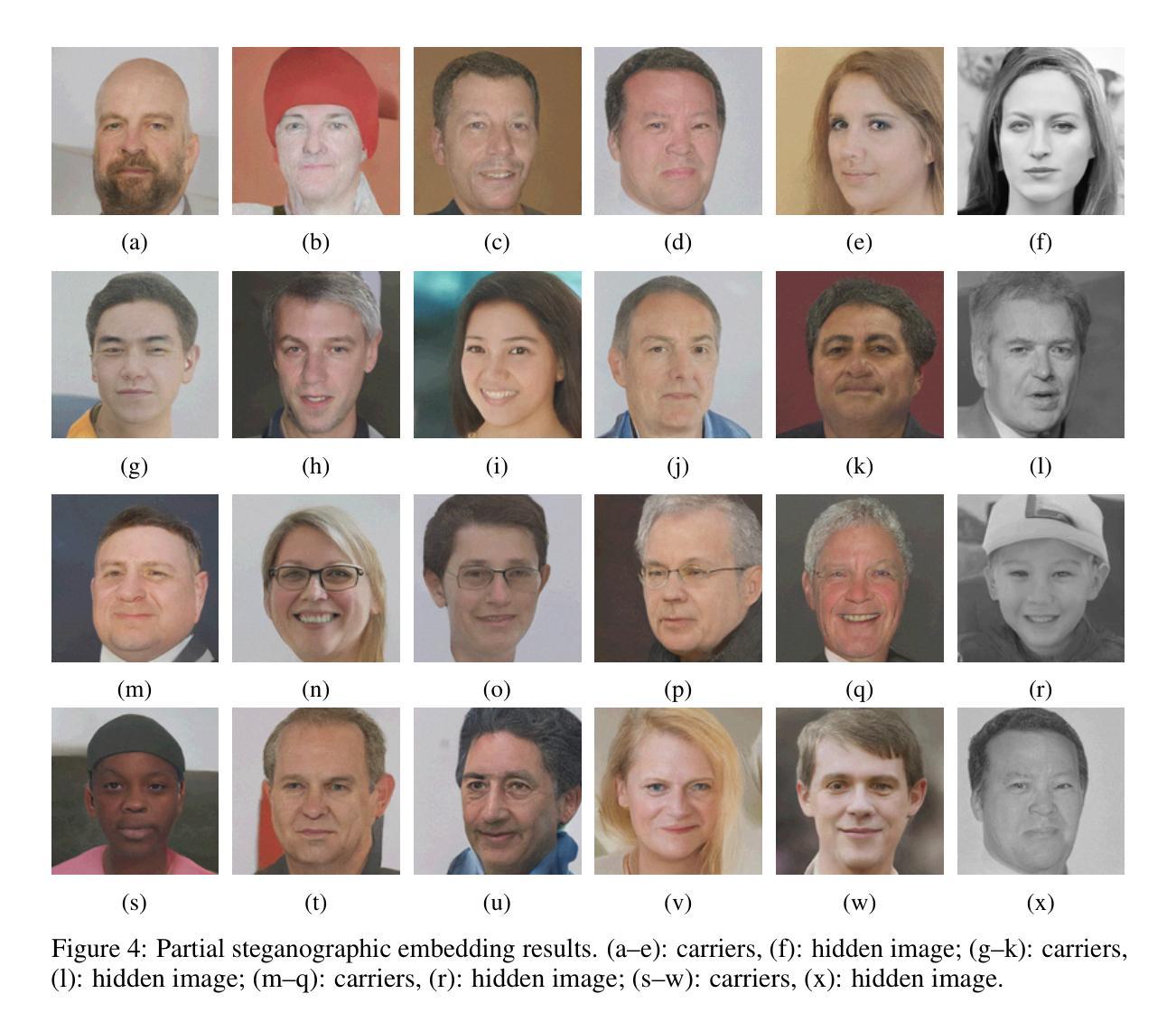


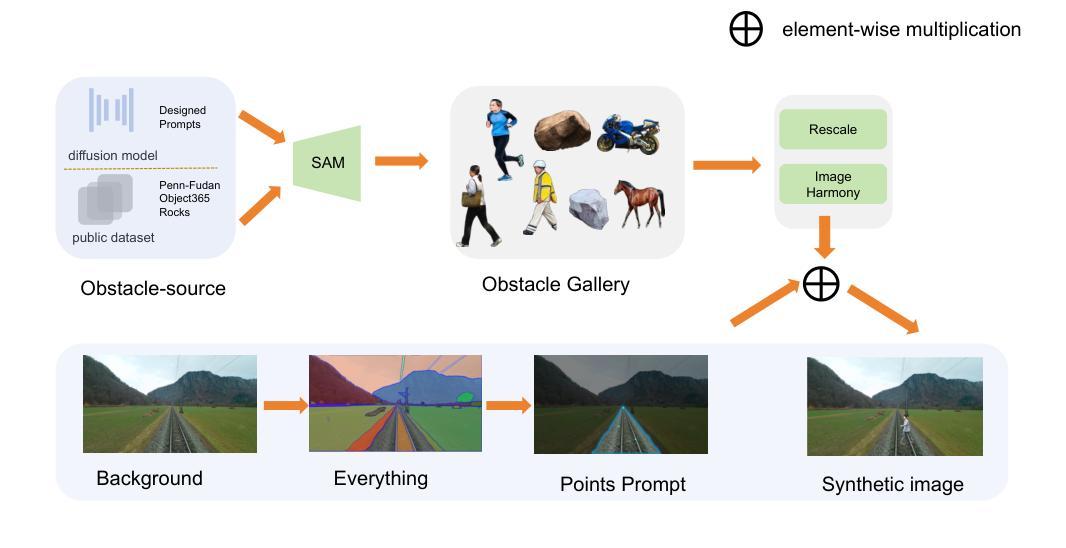
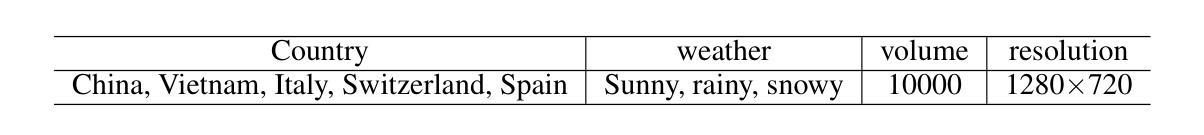
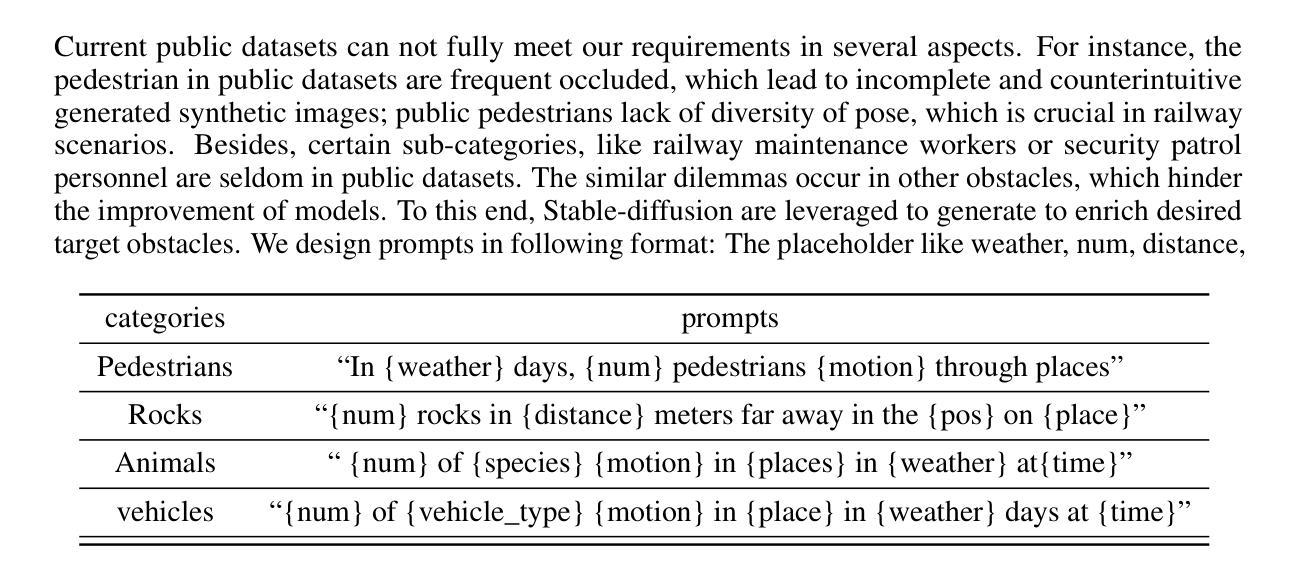
SynRailObs: A Synthetic Dataset for Obstacle Detection in Railway Scenarios
Authors:Qiushi Guo, Jason Rambach
Detecting potential obstacles in railway environments is critical for preventing serious accidents. Identifying a broad range of obstacle categories under complex conditions requires large-scale datasets with precisely annotated, high-quality images. However, existing publicly available datasets fail to meet these requirements, thereby hindering progress in railway safety research. To address this gap, we introduce SynRailObs, a high-fidelity synthetic dataset designed to represent a diverse range of weather conditions and geographical features. Furthermore, diffusion models are employed to generate rare and difficult-to-capture obstacles that are typically challenging to obtain in real-world scenarios. To evaluate the effectiveness of SynRailObs, we perform experiments in real-world railway environments, testing on both ballasted and ballastless tracks across various weather conditions. The results demonstrate that SynRailObs holds substantial potential for advancing obstacle detection in railway safety applications. Models trained on this dataset show consistent performance across different distances and environmental conditions. Moreover, the model trained on SynRailObs exhibits zero-shot capabilities, which are essential for applications in security-sensitive domains. The data is available in https://www.kaggle.com/datasets/qiushi910/synrailobs.
在铁路环境中检测潜在障碍对于预防严重事故至关重要。在复杂条件下识别广泛障碍类别需要大规模数据集,其中包含精确标注的高质量图像。然而,现有公开数据集无法满足这些要求,从而阻碍了铁路安全研究的进展。为解决这一差距,我们推出了SynRailObs这一高保真合成数据集,旨在代表各种天气条件和地理特征。此外,还使用了扩散模型来生成罕见且难以捕获的障碍,这些障碍在真实场景中通常难以获得。为了评估SynRailObs的有效性,我们在真实铁路环境中进行实验,在多种天气条件下对球轨和无球轨轨道进行测试。结果表明,SynRailObs在铁路安全应用的障碍物检测方面具有巨大潜力。在此数据集上训练的模型在不同距离和环境条件下表现一致。此外,在SynRailObs上训练的模型具有零样本能力,这对于安全敏感领域的应用至关重要。数据可在https://www.kaggle.com/datasets/qiushi910/synrailobs找到。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
在铁路环境中检测潜在障碍对于预防严重事故至关重要。为满足复杂条件下广泛障碍类别的识别需求,需要大规模、精确标注、高质量图像的数据集。然而,现有公开数据集无法满足这些要求,阻碍了铁路安全研究的进展。为解决这一缺口,我们推出SynRailObs高保真合成数据集,旨在代表各种天气和地理特征。此外,采用扩散模型生成罕见且难以捕获的障碍,这些障碍在真实场景中通常难以获取。通过真实铁路环境实验验证SynRailObs的有效性,在球粒和无球粒轨道上测试各种天气条件下的性能。结果表明,SynRailObs在铁路安全应用中的障碍检测方面具有巨大潜力。模型在此数据集上的表现距离和环境条件均表现一致。此外,在安全性敏感领域的应用中,经过SynRailObs训练的模型具有零射击能力。数据可在https://www.kaggle.com/datasets/qiushi910/synrailobs上获取。
Key Takeaways
- 铁路障碍检测对于预防事故至关重要,但现有数据集无法满足复杂条件下的多样障碍识别需求。
- SynRailObs是一个高保真合成数据集,旨在代表各种天气和地理特征的障碍情况。
- 扩散模型被用于生成真实场景中难以捕获的罕见障碍。
- SynRailObs数据集通过真实铁路环境实验验证其有效性。
- 模型在SynRailObs数据集上的表现稳定,能够适应不同距离和环境条件。
- 经过SynRailObs训练的模型具有零射击能力,这在安全性敏感领域的应用中至关重要。
点此查看论文截图


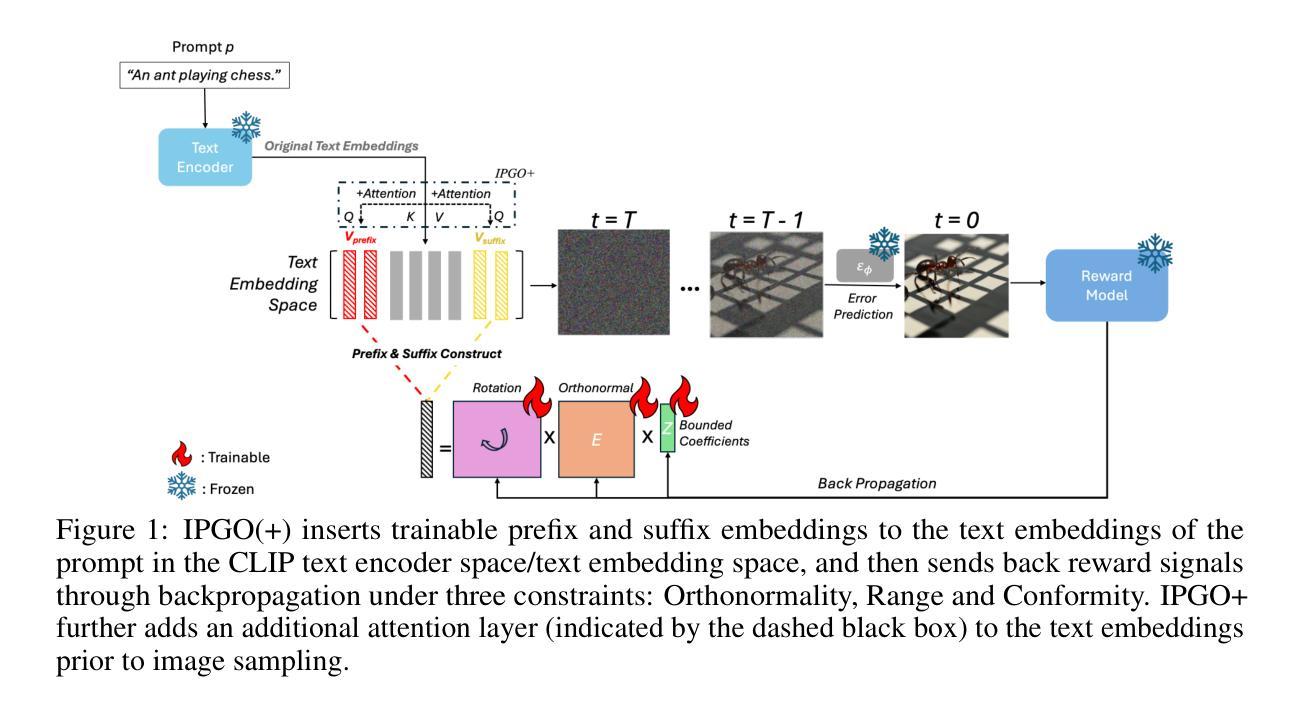
IPGO: Indirect Prompt Gradient Optimization for Parameter-Efficient Prompt-level Fine-Tuning on Text-to-Image Models
Authors:Jianping Ye, Michel Wedel, Kunpeng Zhang
Text-to-Image Diffusion models excel at generating images from text prompts but often exhibit suboptimal alignment with content semantics, aesthetics, and human preferences. To address these limitations, this study proposes a novel parameter-efficient framework, Indirect Prompt Gradient Optimization (IPGO), for prompt-level diffusion model fine-tuning. IPGO enhances prompt embeddings by injecting continuously differentiable embeddings at the beginning and end of the prompt embeddings, leveraging low-rank structures with the flexibility and nonlinearity from rotations. This approach enables gradient-based optimization of injected embeddings under range, orthonormality, and conformity constraints, effectively narrowing the search space, promoting a stable solution, and ensuring alignment between the embeddings of the injected embeddings and the original prompt. Its extension IPGO+ adds a parameter-free cross-attention mechanism on the prompt embedding to enforce dependencies between the original prompt and the inserted embeddings. We conduct extensive evaluations through prompt-wise (IPGO) and prompt-batch (IPGO+) training using three reward models of image aesthetics, image-text alignment, and human preferences across three datasets of varying complexity. The results show that IPGO consistently outperforms SOTA benchmarks, including stable diffusion v1.5 with raw prompts, text-embedding-based methods (TextCraftor), training-based methods (DRaFT and DDPO), and training-free methods (DPO-Diffusion, Promptist, and ChatGPT-4o). Specifically, IPGO achieves a win-rate exceeding 99% in prompt-wise learning, and IPGO+ achieves a comparable, but often better performance against current SOTAs (a 75% win rate) in prompt-batch learning. Moreover, we illustrate IPGO’s generalizability and its capability to significantly enhance image quality while requiring minimal data and resources.
文本转图像扩散模型擅长根据文本提示生成图像,但在内容语义、美学和人类偏好方面的对齐常常不够理想。为了解决这个问题,本研究提出了一种新的参数高效框架——间接提示梯度优化(IPGO),用于提示级扩散模型的微调。IPGO通过注入连续可微的嵌入来增强提示嵌入,这些嵌入位于提示嵌入的开始和结束处,利用低阶结构,同时拥有旋转的灵活性和非线性。这种方法允许在范围、正交性和一致性约束下对注入的嵌入进行基于梯度的优化,有效地缩小了搜索空间,促进了稳定解决方案的出现,并确保了注入嵌入的嵌入与原始提示之间的对齐。其扩展版IPGO+在提示嵌入上增加了一种无参数交叉注意机制,以强制执行原始提示和插入的嵌入之间的依赖关系。我们通过提示(IPGO)和提示批次(IPGO+)训练,使用三种图像美学、图像文本对齐和人类偏好奖励模型,在三个不同复杂度的数据集上进行了广泛评估。结果表明,IPGO一致地超越了最新基准,包括使用原始提示的稳定扩散v1.5、基于文本嵌入的方法(TextCraftor)、基于训练的方法(DRaFT和DDPO)和免训练方法(DPO-Diffusion、Promptist和ChatGPT-4o)。具体来说,IPGO在提示级学习中实现了超过99%的胜率,而IPGO+在提示批次学习中达到了与当前最新技术相当(75%的胜率)但往往更好的性能。此外,我们还展示了IPGO的通用性以及其在需要大量数据和资源的情况下显著提高图像质量的能力。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 9 pages, 2 figures, 4 tables
摘要
文本到图像扩散模型能够根据文本提示生成图像,但在内容语义、美学和人类偏好方面的对齐性常常不够理想。为解决这些问题,本研究提出了一种新型的参数高效框架——间接提示梯度优化(IPGO),用于扩散模型的提示级别微调。IPGO通过注入连续可微分的嵌入,增强提示嵌入,利用旋转的灵活性和非线性性,在提示嵌入的开头和结尾处进行注入。此方法能够实现注入嵌入的梯度优化,在范围、正交性和一致性约束下有效缩小搜索空间,促进稳定解决方案的出现,并确保注入嵌入与原始提示嵌入之间的对齐。其扩展版IPGO+在提示嵌入上增加了一种无参数交叉注意力机制,以强制执行原始提示和插入嵌入之间的依赖关系。我们通过使用三种奖励模型(图像美学、图像文本对齐和人类偏好)和三个不同复杂度的数据集进行提示(IPGO)和提示批次(IPGO+)的广泛评估。结果表明,IPGO在多个场景下表现超过其他尖端方法,包括原始提示的稳定扩散v1.5方法、基于文本嵌入的方法(TextCraftor)、基于训练的方法(DRaFT和DDPO)和无训练的方法(DPO-Diffusion、Promptist和ChatGPT-4o)。具体而言,IPGO在提示级学习中取得超过99%的胜率,而IPGO+在提示批次学习中取得了与当前最佳做法相当的(有时更好)表现,达到75%的胜率。此外,我们展示了IPGO的泛化能力及其增强图像质量的能力,同时需要最少的数据和资源。
关键见解
- 文本到图像扩散模型在根据文本提示生成图像方面表现出色,但在语义对齐、美学和人类偏好方面存在局限性。
- IPGO框架通过注入连续可微分的嵌入增强提示嵌入,提高了扩散模型的性能。
- IPGO利用低阶结构和旋转的灵活性和非线性性进行优化,确保嵌入之间的对齐并促进稳定解决方案的出现。
- IPGO+通过添加交叉注意力机制进一步增强了IPGO的性能,强化了原始提示和插入嵌入之间的依赖关系。
- 使用三种奖励模型进行广泛评估表明IPGO在各种场景下均表现出色,与其他方法的比较显示出其优越性。
- IPGO在提示级学习中取得显著成果,而IPGO+在提示批次学习中也表现出强大的性能。
点此查看论文截图