⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-05-20 更新
MutualNeRF: Improve the Performance of NeRF under Limited Samples with Mutual Information Theory
Authors:Zifan Wang, Jingwei Li, Yitang Li, Yunze Liu
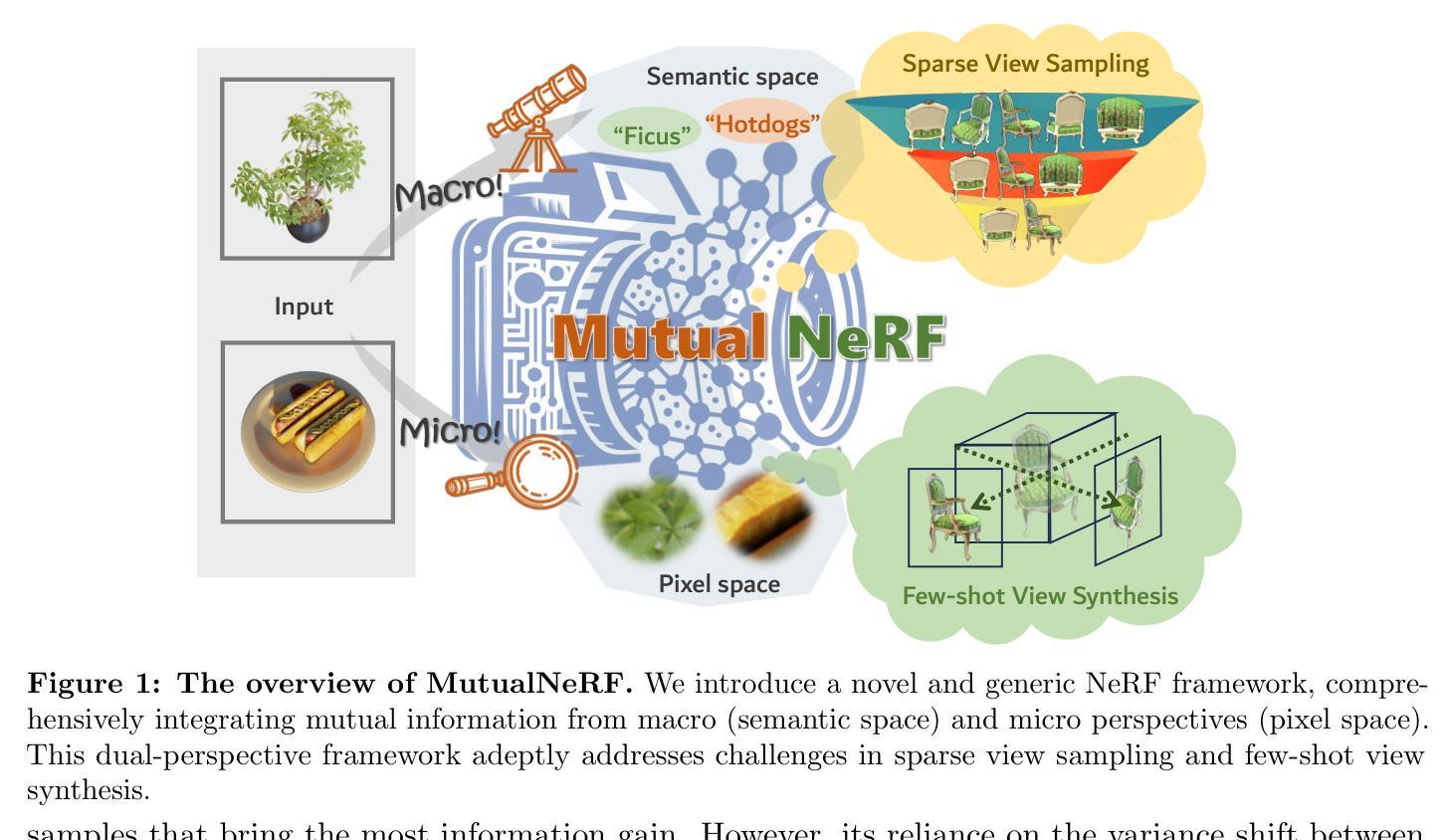
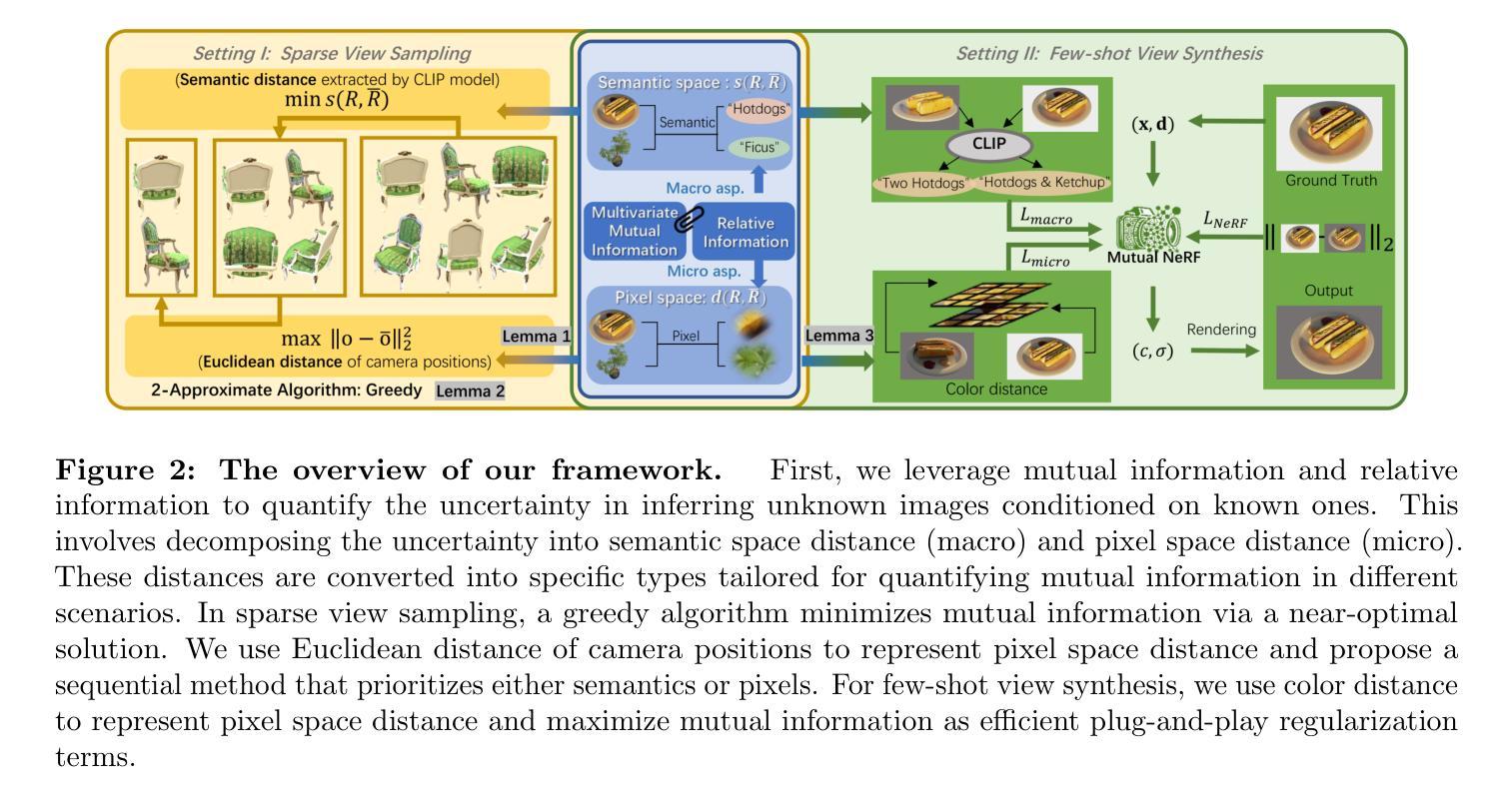
This paper introduces MutualNeRF, a framework enhancing Neural Radiance Field (NeRF) performance under limited samples using Mutual Information Theory. While NeRF excels in 3D scene synthesis, challenges arise with limited data and existing methods that aim to introduce prior knowledge lack theoretical support in a unified framework. We introduce a simple but theoretically robust concept, Mutual Information, as a metric to uniformly measure the correlation between images, considering both macro (semantic) and micro (pixel) levels. For sparse view sampling, we strategically select additional viewpoints containing more non-overlapping scene information by minimizing mutual information without knowing ground truth images beforehand. Our framework employs a greedy algorithm, offering a near-optimal solution. For few-shot view synthesis, we maximize the mutual information between inferred images and ground truth, expecting inferred images to gain more relevant information from known images. This is achieved by incorporating efficient, plug-and-play regularization terms. Experiments under limited samples show consistent improvement over state-of-the-art baselines in different settings, affirming the efficacy of our framework.
本文介绍了MutualNeRF框架,该框架利用互信息理论在有限样本下增强神经辐射场(NeRF)的性能。虽然NeRF在3D场景合成方面表现出色,但在数据有限的情况下仍然面临挑战,而现有的旨在引入先验知识的方法在统一框架中缺乏理论支持。我们引入了一个简单但理论上稳健的概念——互信息,作为一个指标来统一测量图像之间的关联,同时考虑宏观(语义)和微观(像素)级别。针对稀疏视图采样,我们通过最小化互信息,事先不了解真实图像的情况下,有针对性地选择包含更多非重叠场景信息的额外视点。我们的框架采用贪心算法,提供接近最优的解决方案。在少量视图合成中,我们在推断图像和真实图像之间最大化互信息,期望推断图像从已知图像中获得更多相关信息。这是通过融入高效、即插即用的正则化项来实现的。在有限样本下的实验表明,在不同设置下,我们的框架始终改进了最新技术的基线,证实了其有效性。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
该论文提出一种名为MutualNeRF的框架,它利用互信息理论来提升有限样本下的神经辐射场(NeRF)性能。针对NeRF在面临有限数据时面临的挑战,引入互信息作为衡量图像间关联性的统一度量标准,涉及宏观语义和微观像素层面。通过稀疏视图采样,利用互信息最小化策略性地选择包含更多非重叠场景信息的额外视角。针对少样本视图合成,通过最大化推断图像与地面真实之间的互信息,使推断图像从已知图像中获得更多相关信息。实验证明,该框架在有限样本下不同设置中均优于现有技术基线。
Key Takeaways
- MutualNeRF框架基于互信息理论提升NeRF在有限样本下的性能。
- 互信息被用作衡量图像间关联性的统一度量,涵盖宏观和微观层面。
- 在稀疏视图采样中,通过最小化互信息策略性地选择额外视角。
- 在少样本视图合成中,通过最大化推断图像与真实图像之间的互信息,提高推断图像的质量。
- 该框架采用贪婪算法,提供近似的最优解决方案。
- 实验证明,该框架在有限样本下的不同设置中都优于现有的技术基线。
- MutualNeRF框架具有广泛的应用前景,特别是在3D场景合成和计算机视觉领域。
点此查看论文截图

SafeTrans: LLM-assisted Transpilation from C to Rust
Authors:Muhammad Farrukh, Smeet Shah, Baris Coskun, Michalis Polychronakis
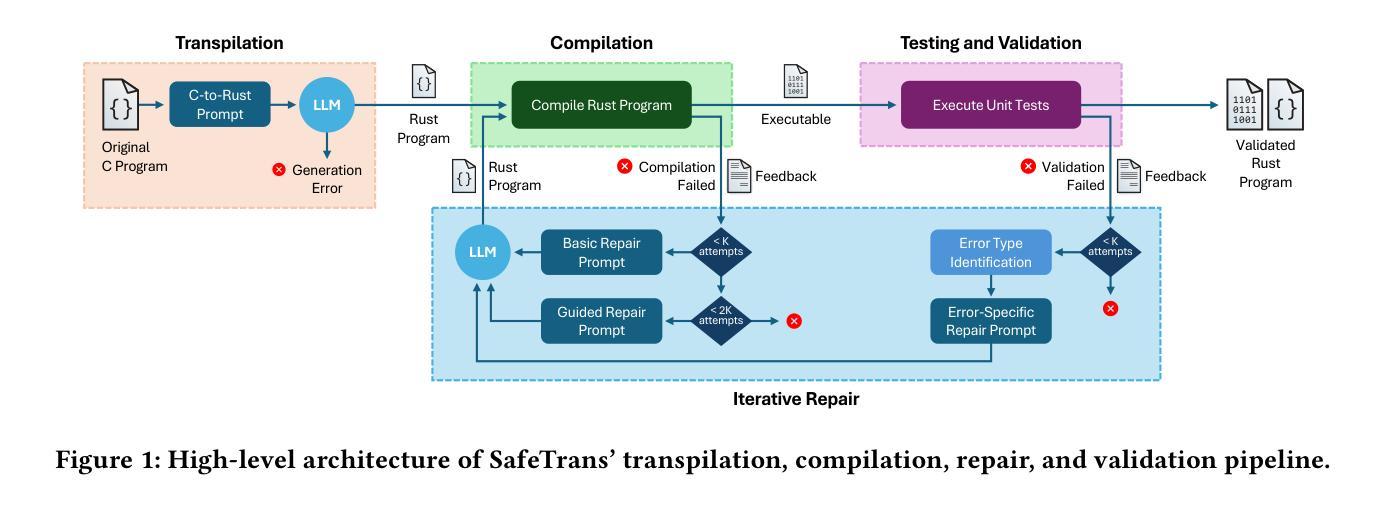
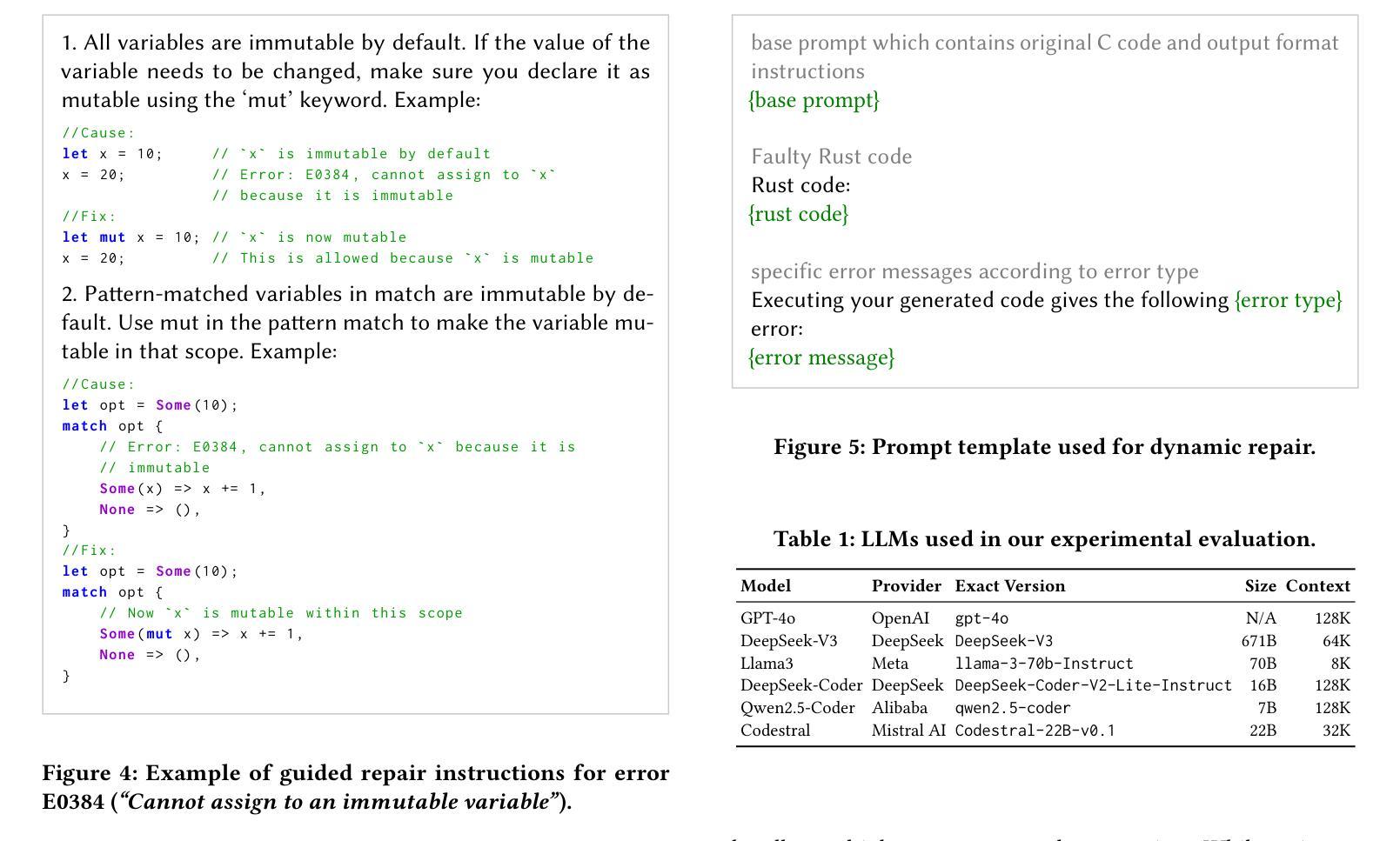
Rust is a strong contender for a memory-safe alternative to C as a “systems” programming language, but porting the vast amount of existing C code to Rust is a daunting task. In this paper, we evaluate the potential of large language models (LLMs) to automate the transpilation of C code to idiomatic Rust, while ensuring that the generated code mitigates any memory-related vulnerabilities present in the original code. To that end, we present the design and implementation of SafeTrans, a framework that uses LLMs to i) transpile C code into Rust and ii) iteratively fix any compilation and runtime errors in the resulting code. A key novelty of our approach is the introduction of a few-shot guided repair technique for translation errors, which provides contextual information and example code snippets for specific error types, guiding the LLM toward the correct solution. Another novel aspect of our work is the evaluation of the security implications of the transpilation process, i.e., whether potential vulnerabilities in the original C code have been properly addressed in the translated Rust code. We experimentally evaluated SafeTrans with six leading LLMs and a set of 2,653 C programs accompanied by comprehensive unit tests, which were used for validating the correctness of the translated code. Our results show that our iterative repair strategy improves the rate of successful translations from 54% to 80% for the best-performing LLM (GPT-4o), and that all types of identified vulnerabilities in the original C code are effectively mitigated in the translated Rust code.
Rust作为系统编程语言,是C语言内存安全替代品的强劲竞争者,但将大量现有的C代码移植到Rust是一项艰巨的任务。在本文中,我们评估了大型语言模型(LLM)在自动将C代码编译成地道的Rust代码方面的潜力,同时确保生成的代码能够缓解原始代码中存在的任何内存相关漏洞。为此,我们介绍了SafeTrans的设计与实施,这是一个利用LLM将C代码编译成Rust的框架,并迭代修复生成代码中的任何编译和运行时错误。我们的方法的一个关键新颖之处在于引入了一种基于少量样本的修复翻译错误的技术,该技术为特定错误类型提供上下文信息和示例代码片段,引导LLM走向正确的解决方案。我们工作的另一个新颖之处在于评估编译过程中的安全影响,即原始C代码中的潜在漏洞是否已在翻译的Rust代码中得到了适当处理。我们通过实验使用领先的六个LLM和一组包含综合单元测试的2653个C程序对SafeTrans进行了评估,用于验证翻译代码的准确性。结果表明,对于表现最佳的LLM(GPT-4o),我们的迭代修复策略将成功翻译率从54%提高到80%,并且原始C代码中识别的所有类型的漏洞在翻译的Rust代码中均得到有效缓解。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
Rust是替代C语言作为系统编程语言的内存安全选择的有力竞争者,但将大量现有C代码移植到Rust是一项艰巨的任务。本文评估了大型语言模型(LLMs)在自动将C代码转换为地道的Rust代码方面的潜力,同时确保生成的代码消除原始代码中的任何内存相关漏洞。为此,我们展示了SafeTrans的设计与实施,这是一个利用LLMs将C代码转换为Rust代码的框架,并迭代修复结果代码中的任何编译和运行时错误。SafeTrans的关键创新之处在于引入了一种基于少量指导的修复翻译错误的技术,该技术提供上下文信息和针对特定错误类型的示例代码片段,引导LLM走向正确的解决方案。此外,我们还评估了翻译过程的安全影响,即原始C代码中的潜在漏洞是否已在翻译的Rust代码中得到了妥善解决。实验表明,我们的迭代修复策略提高了最佳表现的大型语言模型(GPT-4o)的成功翻译率,从54%提高到80%,且原始C代码中识别的所有类型的漏洞在翻译的Rust代码中均得到有效缓解。
Key Takeaways
- Rust被视为C语言的安全替代系统编程语言的有力竞争者。
- 大型语言模型(LLMs)在自动化C代码向Rust代码的转换方面展现潜力。
- SafeTrans框架用于实现自动化的语言转换并确保消除原始代码中的内存漏洞。
- SafeTrans框架的关键创新包括少量指导的修复技术和对翻译过程安全影响的评估。
- 实验结果表明迭代修复策略能有效提高翻译成功率并减少潜在的安全漏洞。
- 通过对比多种大型语言模型的性能,发现GPT-4o在翻译任务中表现最佳。
点此查看论文截图


CLIP Embeddings for AI-Generated Image Detection: A Few-Shot Study with Lightweight Classifier
Authors:Ziyang Ou
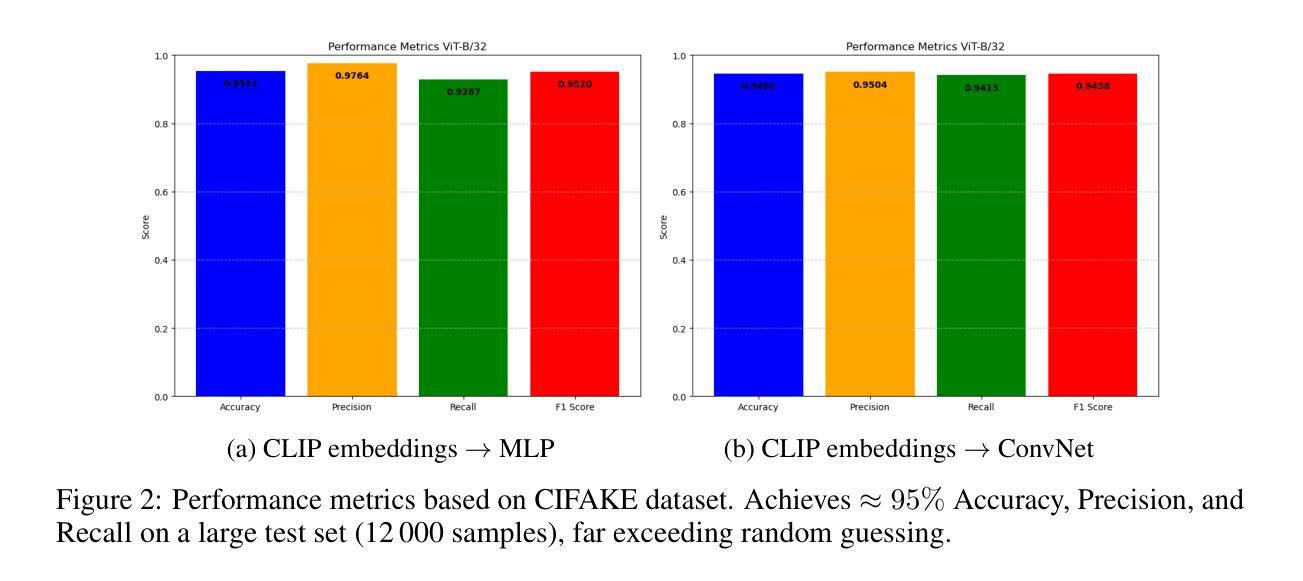
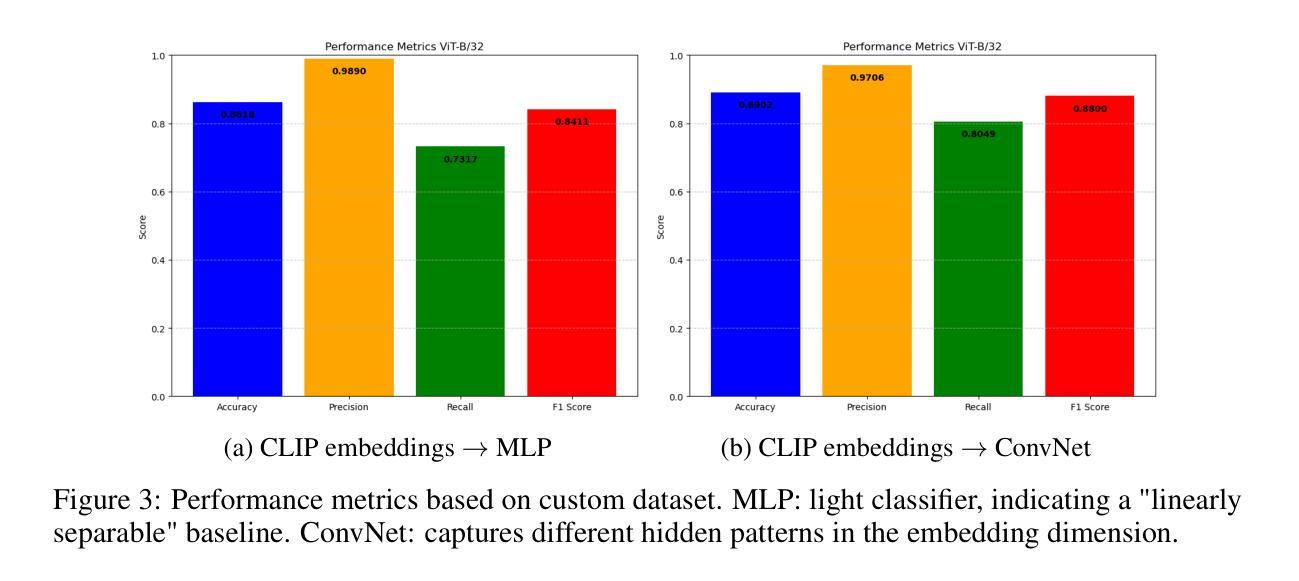
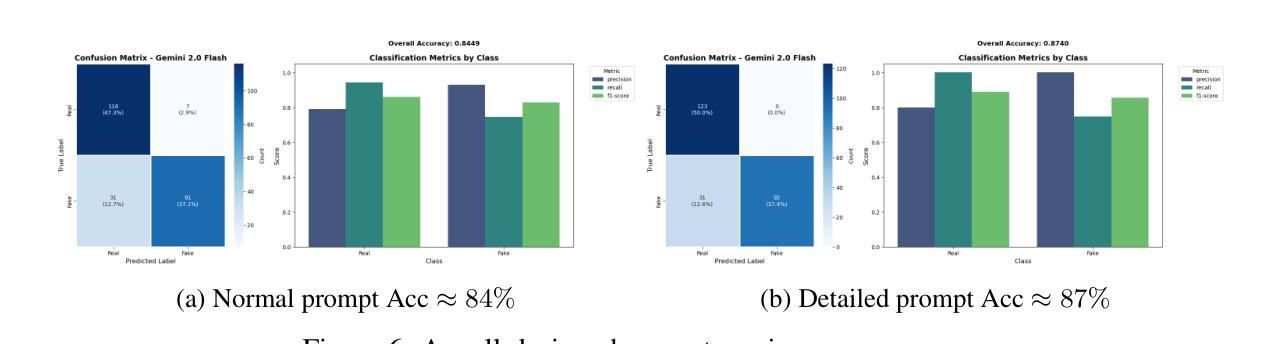
Verifying the authenticity of AI-generated images presents a growing challenge on social media platforms these days. While vision-language models (VLMs) like CLIP outdo in multimodal representation, their capacity for AI-generated image classification is underexplored due to the absence of such labels during the pre-training process. This work investigates whether CLIP embeddings inherently contain information indicative of AI generation. A proposed pipeline extracts visual embeddings using a frozen CLIP model, feeds its embeddings to lightweight networks, and fine-tunes only the final classifier. Experiments on the public CIFAKE benchmark show the performance reaches 95% accuracy without language reasoning. Few-shot adaptation to curated custom with 20% of the data results in performance to 85%. A closed-source baseline (Gemini-2.0) has the best zero-shot accuracy yet fails on specific styles. Notably, some specific image types, such as wide-angle photographs and oil paintings, pose significant challenges to classification. These results indicate previously unexplored difficulties in classifying certain types of AI-generated images, revealing new and more specific questions in this domain that are worth further investigation.
验证AI生成图片的真实性如今在社交媒体平台上呈现出一个日益增长的挑战。虽然像CLIP这样的视觉语言模型在多模态表示方面表现出色,但由于预训练过程中缺少相应的标签,它们在AI生成图像分类方面的能力尚未得到充分探索。本研究旨在调查CLIP嵌入是否内在包含指示AI生成的信息。提出的流程使用冻结的CLIP模型提取视觉嵌入,将其嵌入轻量级网络,并仅对最终分类器进行微调。在公共CIFAKE基准测试集上的实验表明,性能达到了不使用语言推理的95%准确率。使用少量数据对精选的自定义数据集进行适应,仅使用20%的数据即可达到85%的性能。一个封闭的基线(Gemini-2.0)具有最佳的零准确率,但在特定风格上仍然失败。值得注意的是,某些特定的图像类型,如广角照片和油画,对分类构成了重大挑战。这些结果表明在分类某些类型的AI生成图像时存在以前未探索的困难,揭示了这个领域新的更具体的问题值得进一步调查。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 8 pages, 5 figures, not submitted to any conference
Summary
本文探讨了使用CLIP等视觉语言模型对AI生成的图像进行真伪验证的挑战。研究团队提出了一种利用预训练的CLIP模型提取图像嵌入信息,通过轻量级网络进行分类的方法,并在CIFAKE公开数据集上实现了高达95%的分类准确率,且无需语言推理能力。此外,该研究还展示了少量数据定制模型的性能表现,并指出了某些特定类型的图像(如广角照片和油画)的分类难度。该研究揭示了该领域值得进一步探讨的新问题和特定性。
Key Takeaways
- CLIP等视觉语言模型在AI生成的图像真伪验证方面存在潜力。
- 预训练的CLIP模型可用于提取图像嵌入信息,辅助进行AI生成图像的分类。
- 轻量级网络结合预训练模型嵌入信息,在CIFAKE数据集上实现了高准确率分类。
- 无需语言推理能力即可完成分类任务。
- 少量数据定制模型的性能表现良好,但在某些特定类型的图像上仍存在挑战。
- 特定风格的AI生成图像(如广角照片和油画)的分类存在难度。
点此查看论文截图





MetaSym: A Symplectic Meta-learning Framework for Physical Intelligence
Authors:Pranav Vaidhyanathan, Aristotelis Papatheodorou, Mark T. Mitchison, Natalia Ares, Ioannis Havoutis
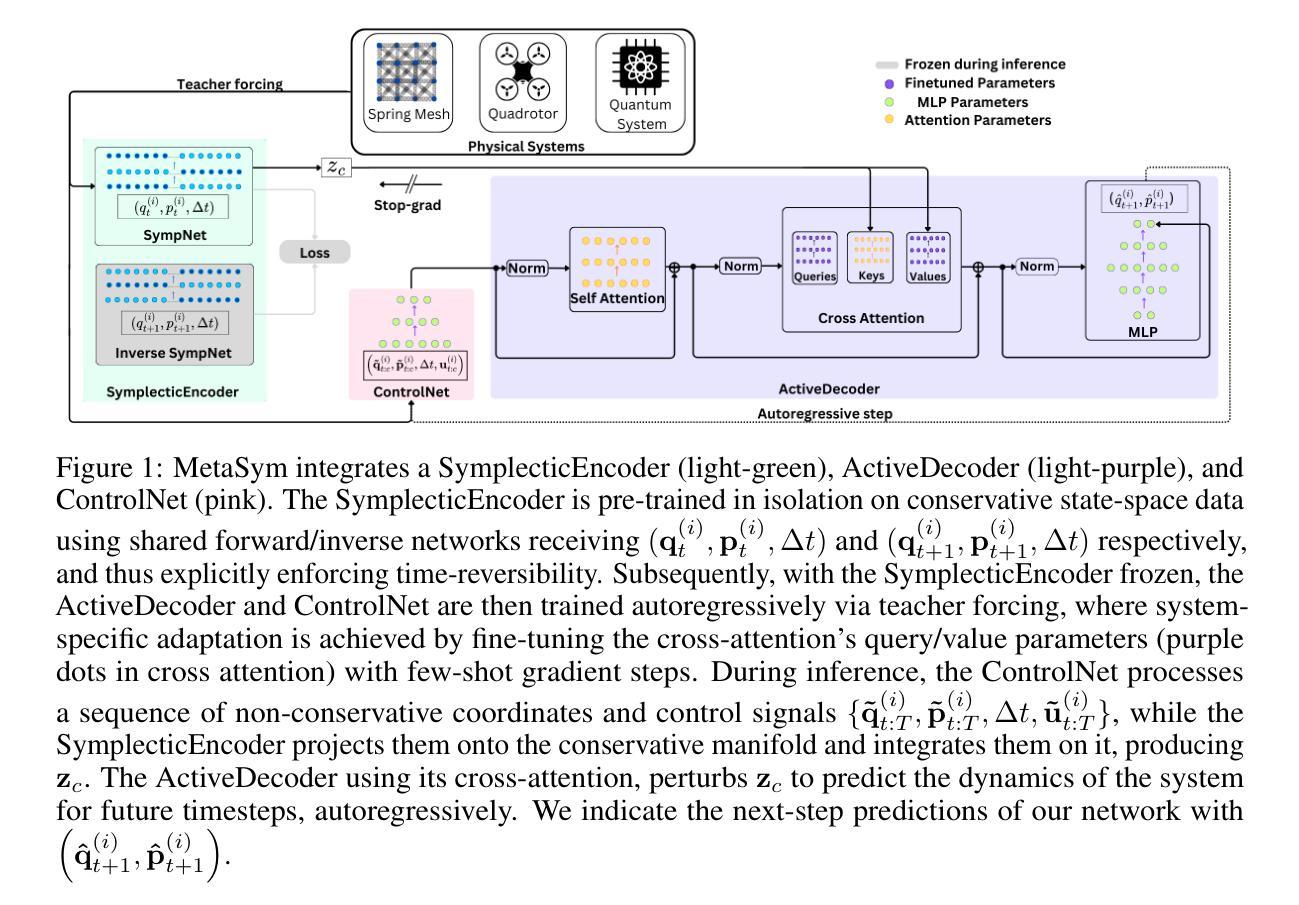
Scalable and generalizable physics-aware deep learning has long been considered a significant challenge with various applications across diverse domains ranging from robotics to molecular dynamics. Central to almost all physical systems are symplectic forms, the geometric backbone that underpins fundamental invariants like energy and momentum. In this work, we introduce a novel deep learning framework, MetaSym. In particular, MetaSym combines a strong symplectic inductive bias obtained from a symplectic encoder, and an autoregressive decoder with meta-attention. This principled design ensures that core physical invariants remain intact, while allowing flexible, data-efficient adaptation to system heterogeneities. We benchmark MetaSym with highly varied and realistic datasets, such as a high-dimensional spring-mesh system (Otness et al., 2021), an open quantum system with dissipation and measurement backaction, and robotics-inspired quadrotor dynamics. Our results demonstrate superior performance in modeling dynamics under few-shot adaptation, outperforming state-of-the-art baselines that use larger models.
可扩展和通用的物理感知深度学习长期以来被视为一项具有重大挑战的任务,其在从机器人技术到分子动力学等多个领域都有广泛的应用。几乎所有物理系统的核心都是辛形式,它是支撑能量和动量等基本不变量的几何骨架。在这项工作中,我们引入了一种新型深度学习框架MetaSym。特别是,MetaSym结合了由辛编码器获得的强大辛归纳偏见和带有元注意的自动生成解码器。这种有原则的设计确保核心物理不变量保持完整,同时允许灵活、高效地对系统异质性进行适应。我们以高度多样化和现实的数据集对MetaSym进行基准测试,例如高维弹簧网格系统(Otness等人,2021年)、具有耗散和测量反作用的开放量子系统,以及受机器人技术启发的四旋翼飞行器动力学。我们的结果表明,在少量适应的情况下,对动力学进行建模时表现出卓越的性能,超越了使用更大模型的最新基线水平。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 10 + 11 pages, 5 figures, 8 tables
摘要
本研究引入了一种新型深度学习框架MetaSym,结合了强大的辛几何先验知识和具有元注意力的自回归解码器。该框架能够保持核心物理不变性,同时灵活、高效地适应系统异质性。MetaSym在多种实际应用场景中表现出卓越性能,如在高维弹簧网格系统、开放量子系统和模拟机器人动力学中实现了少样本适应建模的优异表现,超越了使用更大模型的最先进基线。
关键见解
- MetaSym框架结合了辛几何的先验知识,这是物理系统的基础。
- 该框架通过辛编码器获得强大的辛归纳偏见。
- MetaSym采用具有元注意力的自回归解码器设计。
- 通过高度多样化和现实的基准测试数据集(如高维弹簧网格系统、开放量子系统和模拟机器人动力学),验证了MetaSym的性能。
- MetaSym在少样本适应建模方面表现出卓越性能。
- 该框架允许灵活、高效地适应系统异质性。
点此查看论文截图

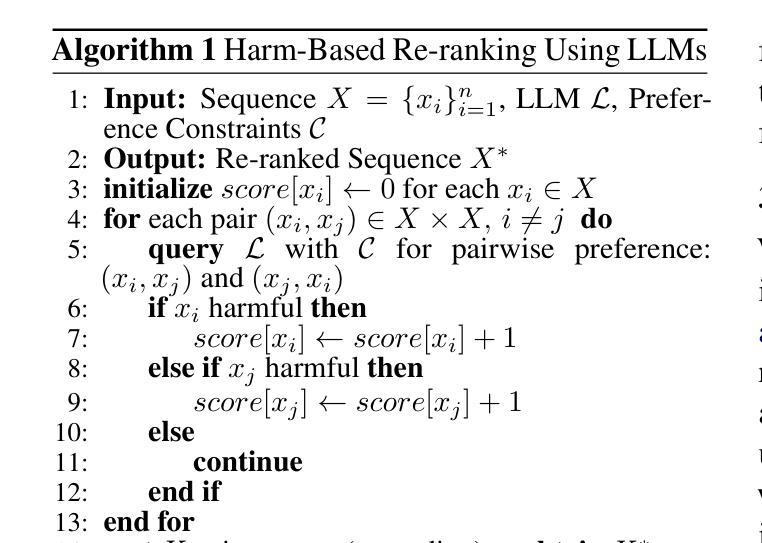
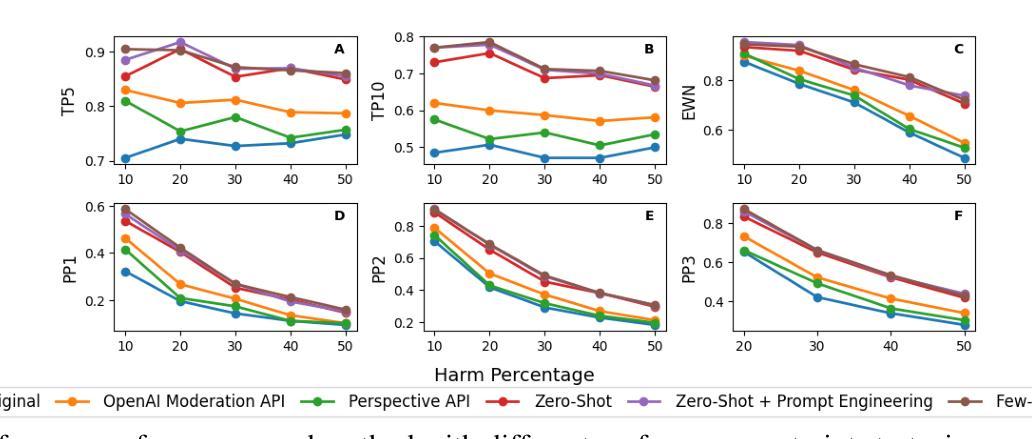
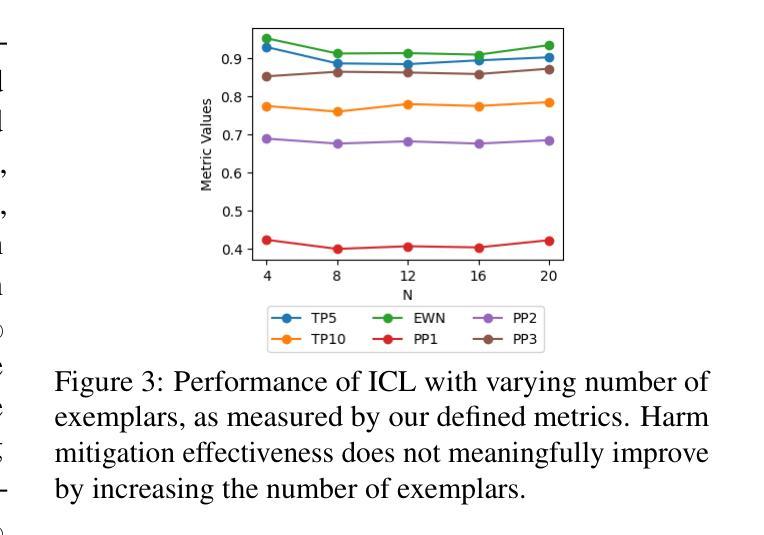
Re-ranking Using Large Language Models for Mitigating Exposure to Harmful Content on Social Media Platforms
Authors:Rajvardhan Oak, Muhammad Haroon, Claire Jo, Magdalena Wojcieszak, Anshuman Chhabra
Social media platforms utilize Machine Learning (ML) and Artificial Intelligence (AI) powered recommendation algorithms to maximize user engagement, which can result in inadvertent exposure to harmful content. Current moderation efforts, reliant on classifiers trained with extensive human-annotated data, struggle with scalability and adapting to new forms of harm. To address these challenges, we propose a novel re-ranking approach using Large Language Models (LLMs) in zero-shot and few-shot settings. Our method dynamically assesses and re-ranks content sequences, effectively mitigating harmful content exposure without requiring extensive labeled data. Alongside traditional ranking metrics, we also introduce two new metrics to evaluate the effectiveness of re-ranking in reducing exposure to harmful content. Through experiments on three datasets, three models and across three configurations, we demonstrate that our LLM-based approach significantly outperforms existing proprietary moderation approaches, offering a scalable and adaptable solution for harm mitigation.
社交媒体平台利用机器学习和人工智能驱动的推荐算法来最大限度地提高用户参与度,这可能会导致无意间接触到有害内容。当前依赖于使用大量人工注释数据训练的分类器的审核工作,在可扩展性和适应新形式的危害方面遇到了挑战。为了解决这些挑战,我们提出了一种新的再排序方法,该方法使用零样本和少样本设置中的大型语言模型(LLM)。我们的方法可以动态地评估和重新排序内容序列,有效地减少有害内容的暴露,而无需大量的标记数据。除传统的排名指标外,我们还引入了两个新指标来评估重新排序在减少接触有害内容方面的有效性。通过在三个数据集、三个模型和三组配置上的实验,我们证明了基于LLM的方法显著优于现有的专有审核方法,为危害缓解提供了可扩展和可适应的解决方案。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted to ACL 2025 Main Conference
Summary:社交媒体平台利用机器学习(ML)和人工智能(AI)驱动的推荐算法最大化用户参与度,这可能导致用户无意中接触到有害内容。针对当前依赖大量人工标注数据训练的分类器在可扩展性和适应新形式的危害方面的挑战,我们提出了一种新的使用大规模语言模型(LLM)的零样本和少样本环境下的重新排名方法。该方法动态评估和重新排名内容序列,在不需要大量标记数据的情况下有效减少有害内容的暴露。除了传统的排名指标外,我们还引入了两个新指标来评估重新排名在减少有害内容暴露方面的有效性。通过三个数据集、三个模型和三种配置的实验,我们证明基于LLM的方法显著优于现有的专有内容管理策略,为危害缓解提供了可扩展和适应性强的解决方案。
Key Takeaways:
- 社交媒体平台使用ML和AI驱动的推荐算法以提高用户参与度,但可能导致用户接触到有害内容。
- 当前的内容管理策略在扩展性和适应新形式的危害方面存在挑战。
- 提出了一种基于LLM的新颖重新排名方法,以动态评估和重新排名内容序列。
- 该方法可在不需要大量标记数据的情况下有效减少有害内容的暴露。
- 除了传统排名指标外,还引入了两个新指标来评估重新排名的有效性。
- 在三个数据集、三个模型和三种配置的实验中,LLM方法显著优于现有策略。
点此查看论文截图