⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-05-21 更新
DC-Seg: Disentangled Contrastive Learning for Brain Tumor Segmentation with Missing Modalities
Authors:Haitao Li, Ziyu Li, Yiheng Mao, Zhengyao Ding, Zhengxing Huang
Accurate segmentation of brain images typically requires the integration of complementary information from multiple image modalities. However, clinical data for all modalities may not be available for every patient, creating a significant challenge. To address this, previous studies encode multiple modalities into a shared latent space. While somewhat effective, it remains suboptimal, as each modality contains distinct and valuable information. In this study, we propose DC-Seg (Disentangled Contrastive Learning for Segmentation), a new method that explicitly disentangles images into modality-invariant anatomical representation and modality-specific representation, by using anatomical contrastive learning and modality contrastive learning respectively. This solution improves the separation of anatomical and modality-specific features by considering the modality gaps, leading to more robust representations. Furthermore, we introduce a segmentation-based regularizer that enhances the model’s robustness to missing modalities. Extensive experiments on the BraTS 2020 and a private white matter hyperintensity(WMH) segmentation dataset demonstrate that DC-Seg outperforms state-of-the-art methods in handling incomplete multimodal brain tumor segmentation tasks with varying missing modalities, while also demonstrate strong generalizability in WMH segmentation. The code is available at https://github.com/CuCl-2/DC-Seg.
精确地分割脑图像通常需要整合来自多种图像模态的互补信息。然而,并非每位患者都有所有模态的临床数据,这构成了一大挑战。为了解决这一问题,先前的研究将多种模态编码到共享潜在空间中。虽然这种做法有一定效果,但仍然是次优的,因为每个模态都包含独特且有价值的信息。在本研究中,我们提出了DC-Seg(基于分割的解纠缠对比学习),这是一种新的方法,通过分别使用解剖对比学习和模态对比学习,将图像显式地解纠缠为模态不变的解剖表示和模态特定的表示。这个解决方案通过考虑模态间隙,改进了解剖和模态特定特征的分离,从而得到更稳健的表示。此外,我们还引入了一种基于分割的正则化器,提高了模型对缺失模态的鲁棒性。在BraTS 2020和私有白质高信号(WMH)分割数据集上的大量实验表明,DC-Seg在处理具有不同缺失模态的不完整多模态脑肿瘤分割任务方面优于最先进的方法,同时在WMH分割中表现出强大的泛化能力。代码可在https://github.com/CuCl-2/DC-Seg中找到。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
多模态大脑图像分割面临因缺少数据造成的挑战。为解决这一问题,该研究提出了DC-Seg方法,通过解耦对比学习将图像分为模态不变的结构表示和模态特定的表示,并引入分割正则化器增强模型对缺失模态的鲁棒性。在BraTS 2020和私有WMH分割数据集上的实验表明,DC-Seg在处理不同缺失模态的不完全多模态脑肿瘤分割任务时表现优于最新方法,同时具有较强的泛化能力。
Key Takeaways
- DC-Seg解决了多模态大脑图像分割中因缺少某些模态数据带来的挑战。
- DC-Seg通过将图像分为模态不变的结构表示和模态特定的表示,提高了模型的性能。
- 解耦对比学习在DC-Seg中用于增强模型的鲁棒性和泛化能力。
- 分割正则化器在DC-Seg中增强了模型对缺失模态的鲁棒性。
- DC-Seg在BraTS 2020数据集上的表现优于其他最新方法。
- DC-Seg在处理WMH分割任务时显示出强大的泛化能力。
点此查看论文截图

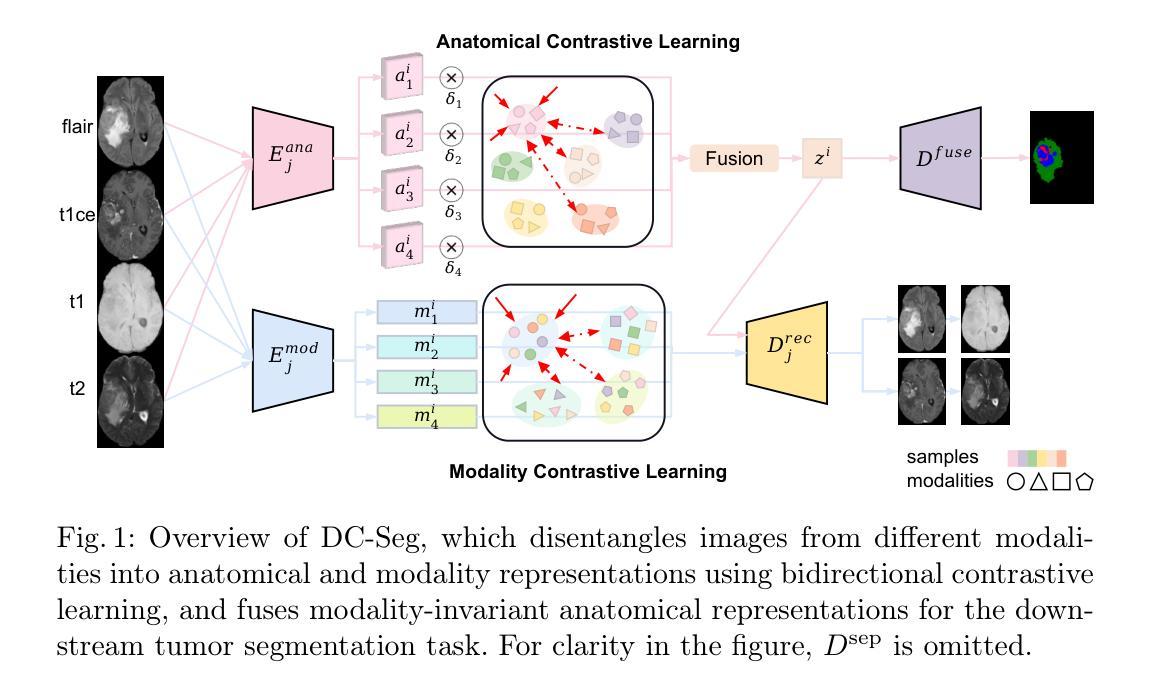
Rethinking Image Forgery Detection via Soft Contrastive Learning and Unsupervised Clustering
Authors:Haiwei Wu, Yiming Chen, Jiantao Zhou, Yuanman Li
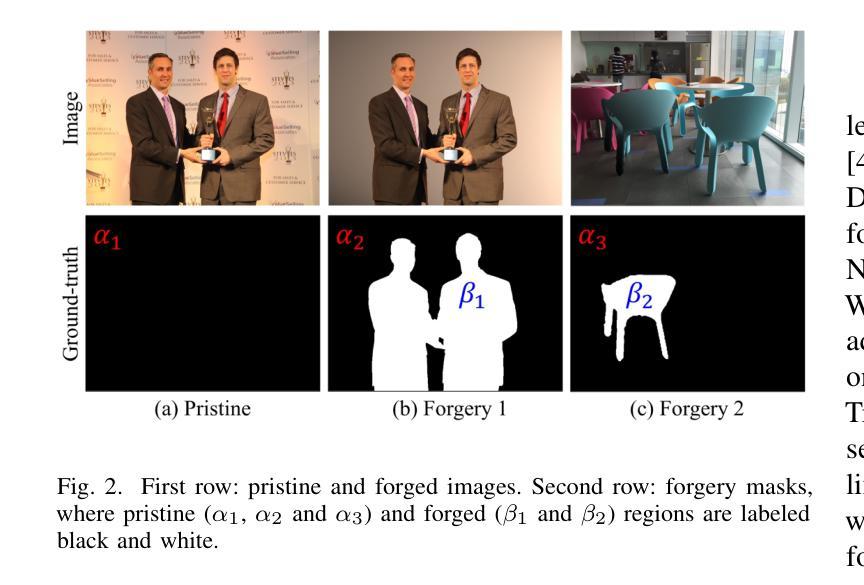
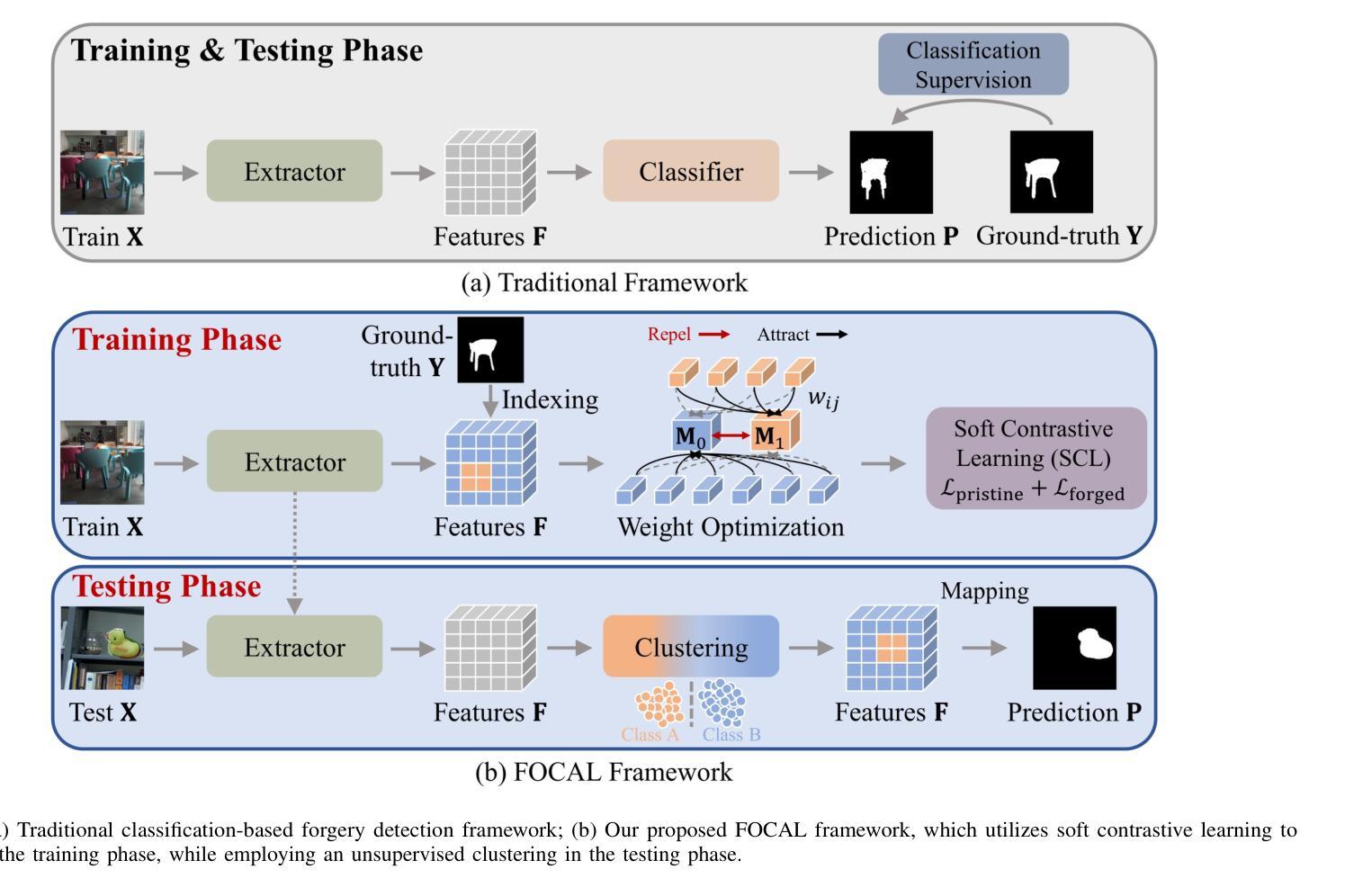
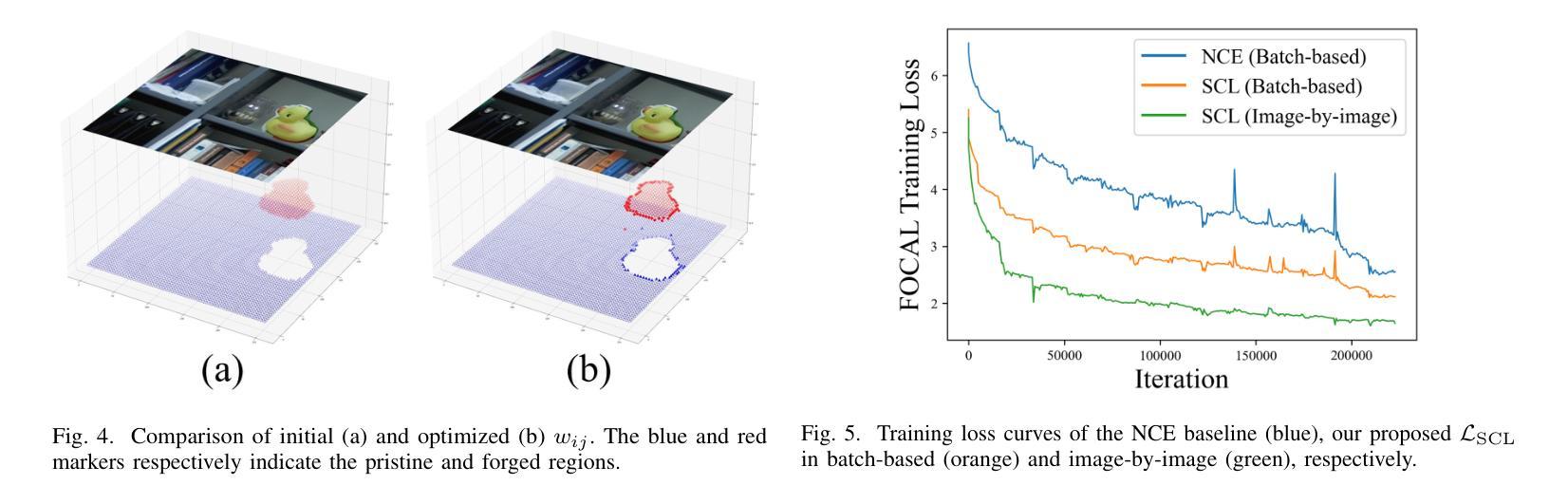
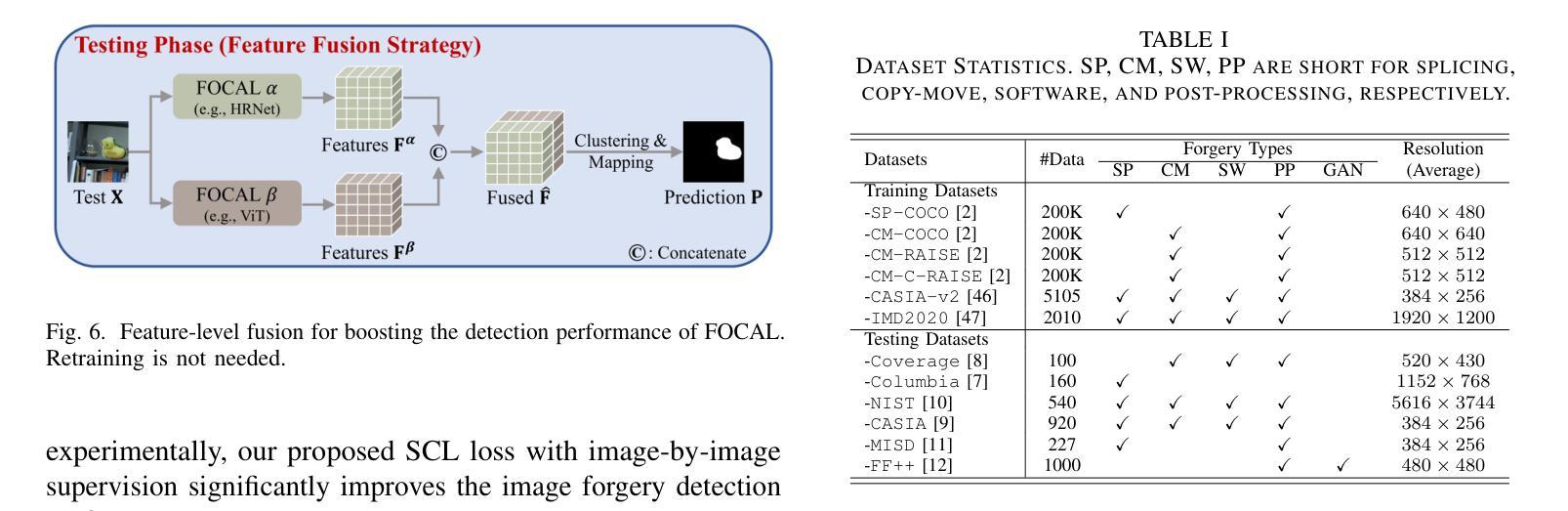
Image forgery detection aims to detect and locate forged regions in an image. Most existing forgery detection algorithms formulate classification problems to classify pixels into forged or pristine. However, the definition of forged and pristine pixels is only relative within one single image, e.g., a forged region in image A is actually a pristine one in its source image B (splicing forgery). Such a relative definition has been severely overlooked by existing methods, which unnecessarily mix forged (pristine) regions across different images into the same category. To resolve this dilemma, we propose the FOrensic ContrAstive cLustering (FOCAL) method, a novel, simple yet very effective paradigm based on soft contrastive learning and unsupervised clustering for the image forgery detection. Specifically, FOCAL 1) designs a soft contrastive learning (SCL) to supervise the high-level forensic feature extraction in an image-by-image manner, explicitly reflecting the above relative definition; 2) employs an on-the-fly unsupervised clustering algorithm (instead of a trained one) to cluster the learned features into forged/pristine categories, further suppressing the cross-image influence from training data; and 3) allows to further boost the detection performance via simple feature-level concatenation without the need of retraining. Extensive experimental results over six public testing datasets demonstrate that our proposed FOCAL significantly outperforms the state-of-the-art competitors by big margins: +24.8% on Coverage, +18.9% on Columbia, +17.3% on FF++, +15.3% on MISD, +15.0% on CASIA and +10.5% on NIST in terms of IoU (see also Fig. 1). The paradigm of FOCAL could bring fresh insights and serve as a novel benchmark for the image forgery detection task. The code is available at https://github.com/HighwayWu/FOCAL.
图像伪造检测旨在检测和定位图像中的伪造区域。现有的大多数伪造检测算法将问题设定为分类问题,将像素分类为伪造或原始像素。然而,伪造和原始像素的定义只在单张图像内相对存在,例如在图像A中的伪造区域在其源图像B中实际上是原始的(拼接伪造)。现有方法严重忽视了这种相对定义,它们不必要地将不同图像的伪造(原始)区域混合到同一类别中。为了解决这一困境,我们提出了基于软对比学习和无监督聚类的图像伪造检测新范式——FOrensic ContrAstive cLustering(FOCAL)。具体来说,FOCAL 1)设计了一种软对比学习(SCL)以图像为方式对高级取证特征进行有监督提取,明确反映了上述相对定义;2)采用实时无监督聚类算法(而不是预训练的算法)对学习的特征进行伪造/原始类别聚类,进一步抑制训练数据中跨图像的影响;并且3)通过简单的特征级拼接进一步提高检测性能,而无需重新训练。在六个公开测试数据集上的广泛实验结果表明,我们提出的FOCAL在IoU方面显著优于最新竞争对手:在Coverage上高出+24.8%,在Columbia上高出+18.9%,在FF++上高出+17.3%,在MISD上高出+15.3%,在CASIA上高出+15.0%,在NIST上高出+10.5%(也见图1)。FOCAL的范式可以为图像伪造检测任务带来全新见解,并可作为新的基准测试。代码可在https://github.com/HighwayWu/FOCAL找到。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
提出的FOCAL方法基于软对比学习和无监督聚类,用于图像伪造检测。该方法通过软对比学习监督高级别取证特征提取,采用在线无监督聚类算法对特征进行分类,进一步提高检测性能,无需重新训练。在六个公开测试数据集上的实验结果表明,FOCAL显著优于最新竞争对手,在IoU方面有较大提高。
Key Takeaways
- 图像伪造检测旨在检测和定位图像中的伪造区域。
- 现有伪造检测算法大多将问题制定为像素分类问题,但存在相对定义的问题,即伪造和原始像素的定义是相对于单张图像而言的。
- FOCAL方法基于软对比学习和无监督聚类,解决了现有方法忽视相对定义的问题。
- FOCAL通过软对比学习监督高级别取证特征提取,并采用在线无监督聚类算法对特征进行聚类,以区分伪造和原始区域。
- FOCAL提高了检测性能,且通过简单的特征级拼接即可实现,无需重新训练。
- 在多个公开测试数据集上的实验结果表明,FOCAL显著优于其他方法,在IoU方面有较大提升。
点此查看论文截图