⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-05-21 更新
FlowCut: Unsupervised Video Instance Segmentation via Temporal Mask Matching
Authors:Alp Eren Sari, Paolo Favaro
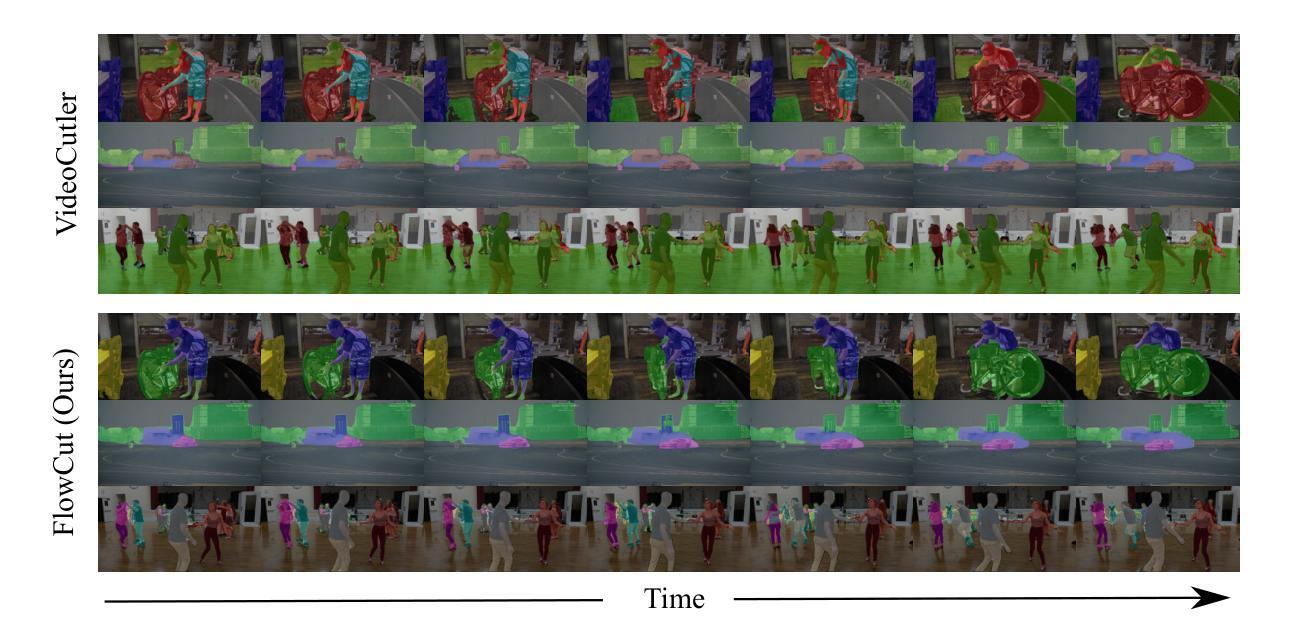
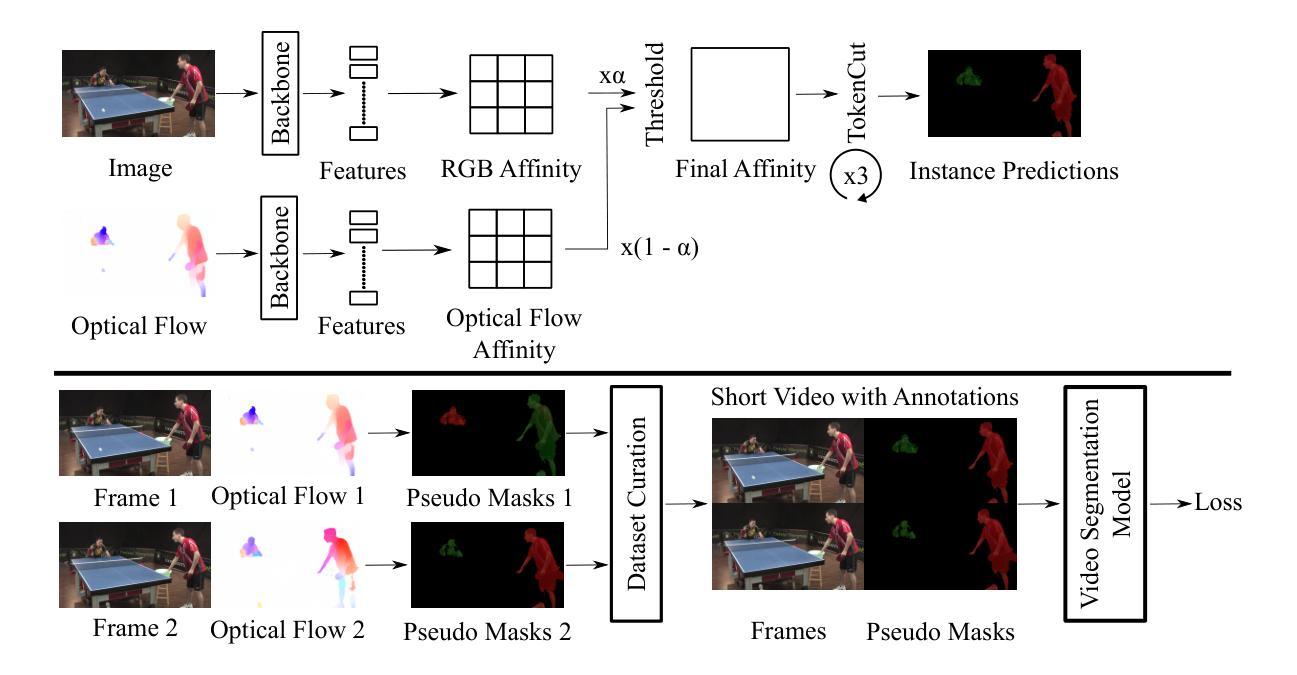
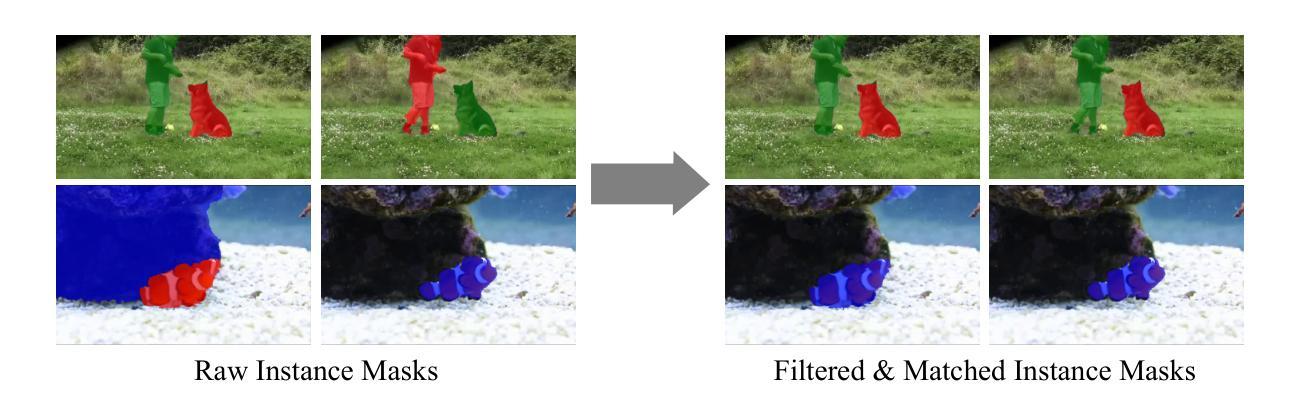
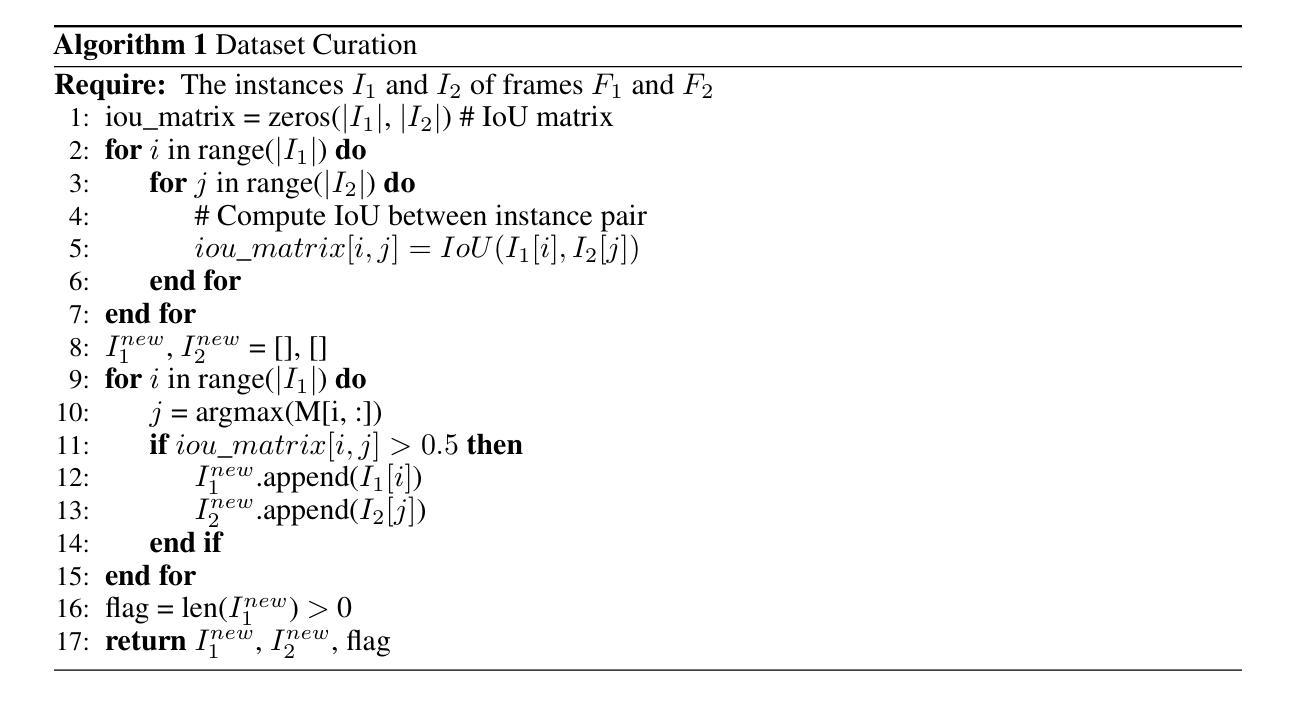
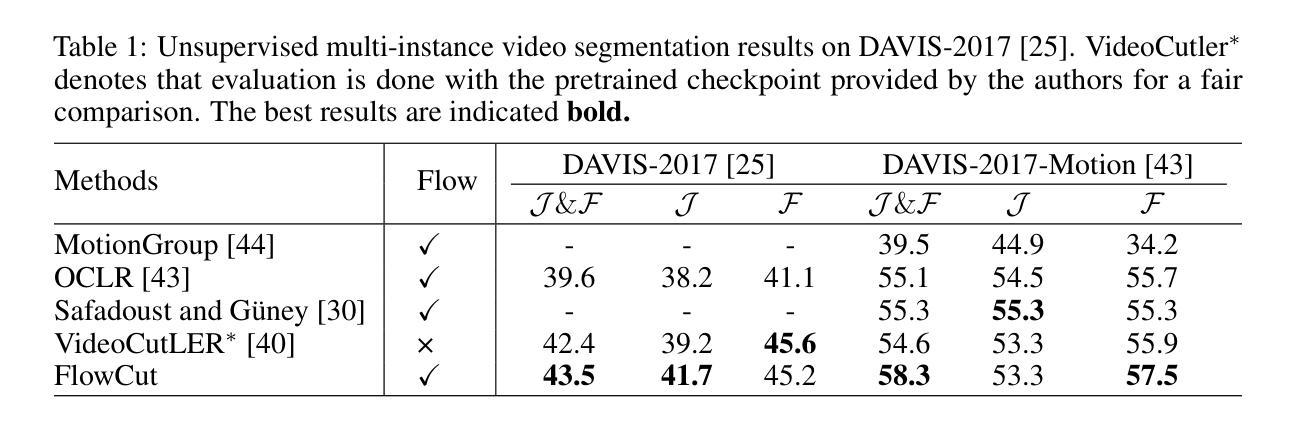
We propose FlowCut, a simple and capable method for unsupervised video instance segmentation consisting of a three-stage framework to construct a high-quality video dataset with pseudo labels. To our knowledge, our work is the first attempt to curate a video dataset with pseudo-labels for unsupervised video instance segmentation. In the first stage, we generate pseudo-instance masks by exploiting the affinities of features from both images and optical flows. In the second stage, we construct short video segments containing high-quality, consistent pseudo-instance masks by temporally matching them across the frames. In the third stage, we use the YouTubeVIS-2021 video dataset to extract our training instance segmentation set, and then train a video segmentation model. FlowCut achieves state-of-the-art performance on the YouTubeVIS-2019, YouTubeVIS-2021, DAVIS-2017, and DAVIS-2017 Motion benchmarks.
我们提出了FlowCut方法,这是一种用于无监督视频实例分割的简单而有效的方法,它由一个三阶段框架构成,用于构建带有伪标签的高质量视频数据集。据我们所知,我们的工作是首次尝试为无监督视频实例分割制作带有伪标签的视频数据集。在第一阶段,我们通过利用图像和光流特征的亲和力生成伪实例掩膜。在第二阶段,我们构建包含高质量、一致的伪实例掩膜的短视频片段,通过跨帧进行时间匹配。在第三阶段,我们使用YouTubeVIS-2021视频数据集提取训练实例分割集,然后训练视频分割模型。FlowCut在YouTubeVIS-2019、YouTubeVIS-2021、DAVIS-2017和DAVIS-2017运动基准测试上达到了最先进的性能。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文提出了FlowCut方法,这是一种用于无监督视频实例分割的简单而有效的方法,包括三阶段框架,用于构建带有伪标签的高质量视频数据集。该方法首先生成伪实例掩膜,然后构建包含高质量、一致的伪实例掩膜的视频片段,并在YouTubeVIS-2021视频数据集上提取训练实例分割集进行模型训练。FlowCut在YouTubeVIS-2019、YouTubeVIS-2021、DAVIS-2017和DAVIS-2017运动基准测试中达到了最先进的性能。
Key Takeaways
- FlowCut是一种用于无监督视频实例分割的三阶段方法。
- 该方法利用图像和光学流特征之间的亲和力生成伪实例掩膜。
- 通过时间匹配跨帧构建高质量的视频片段。
- 使用YouTubeVIS-2021视频数据集进行训练实例分割集提取。
- FlowCut在多个基准测试中达到了最先进的性能。
- 该方法首次尝试使用伪标签构建视频数据集进行无监督视频实例分割。
点此查看论文截图

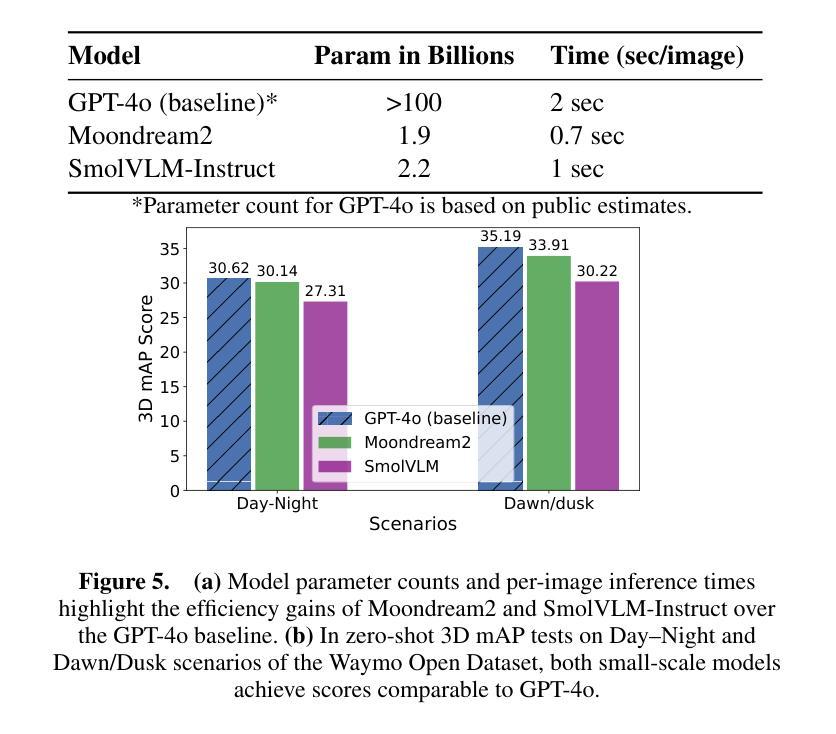
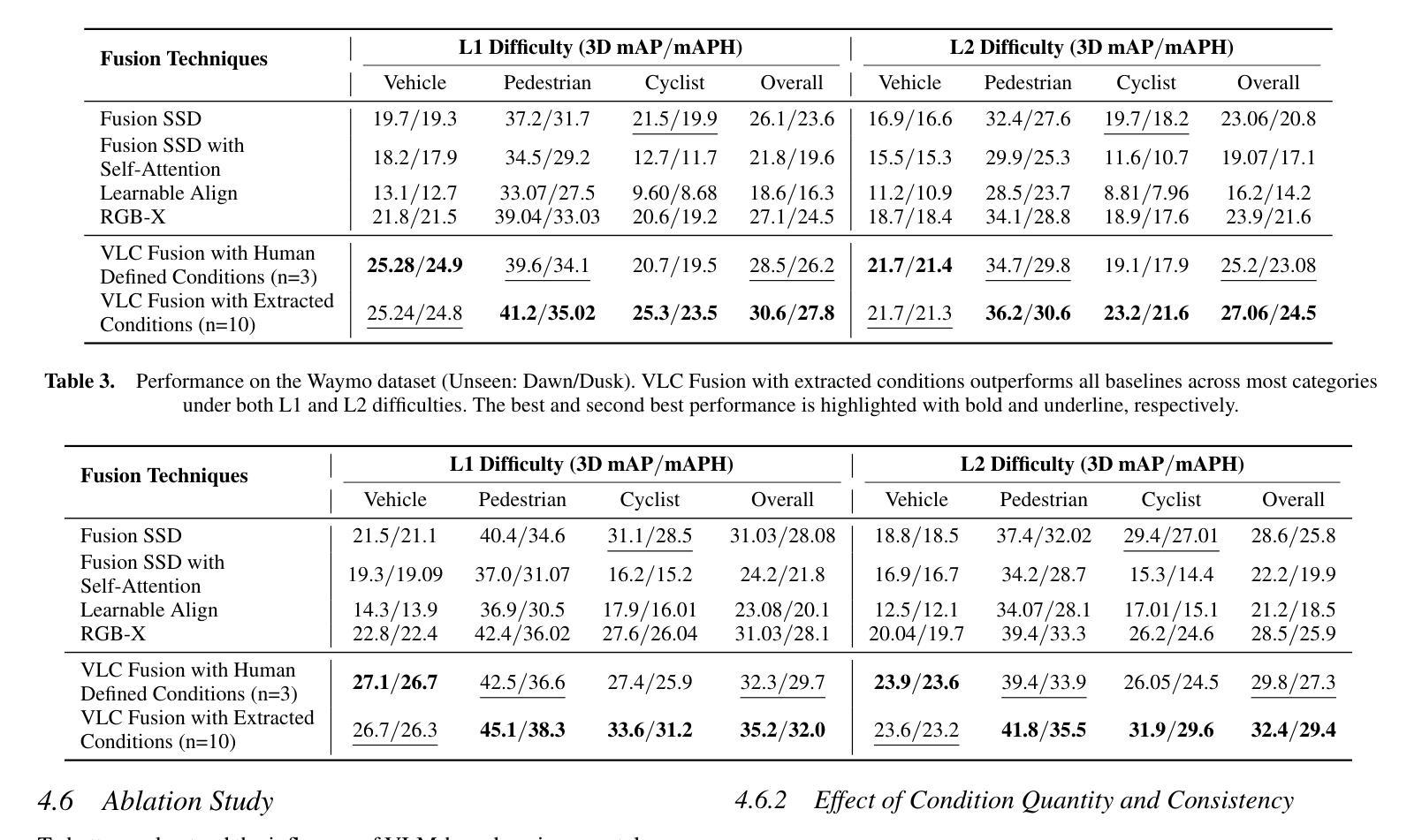
VLC Fusion: Vision-Language Conditioned Sensor Fusion for Robust Object Detection
Authors:Aditya Taparia, Noel Ngu, Mario Leiva, Joshua Shay Kricheli, John Corcoran, Nathaniel D. Bastian, Gerardo Simari, Paulo Shakarian, Ransalu Senanayake
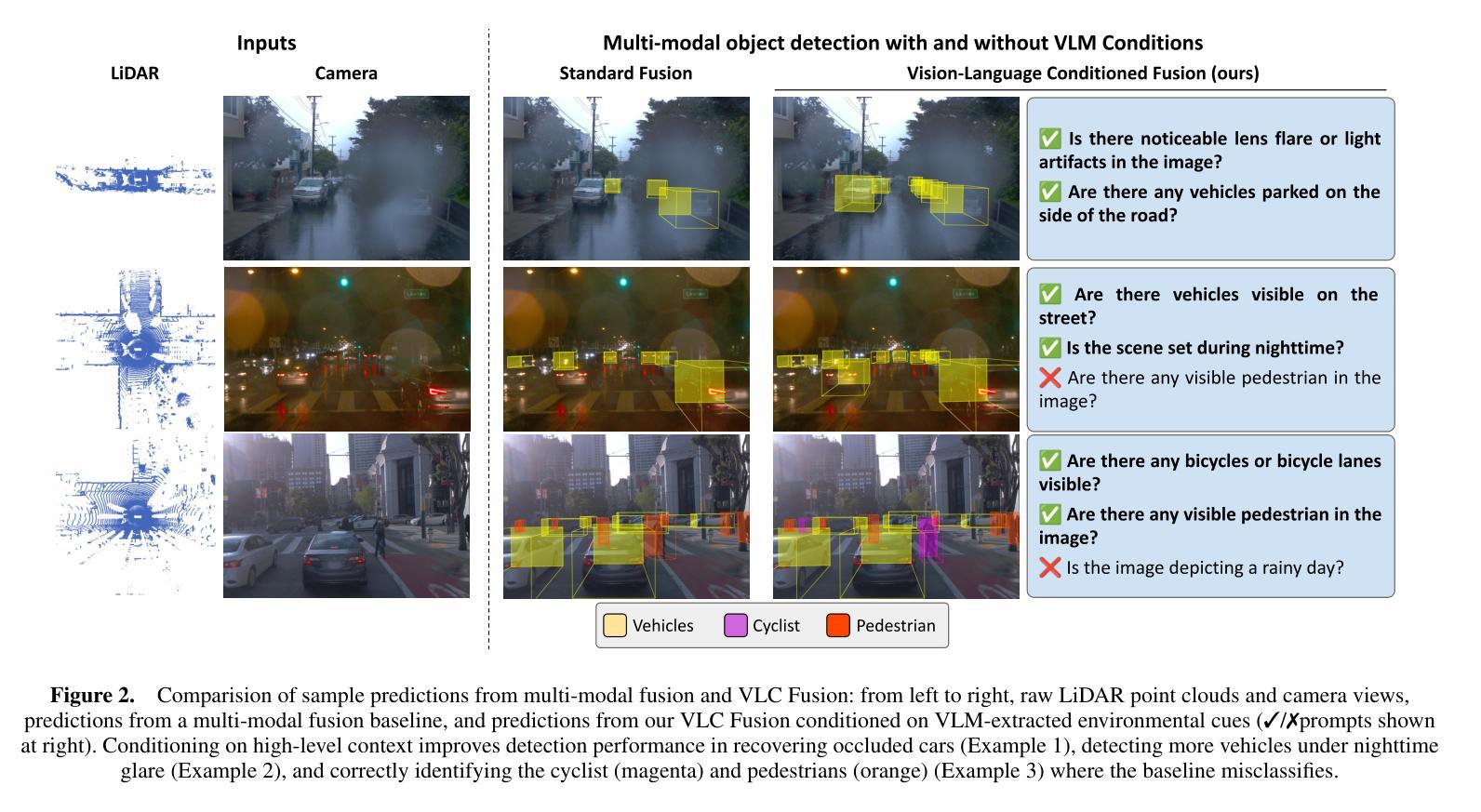
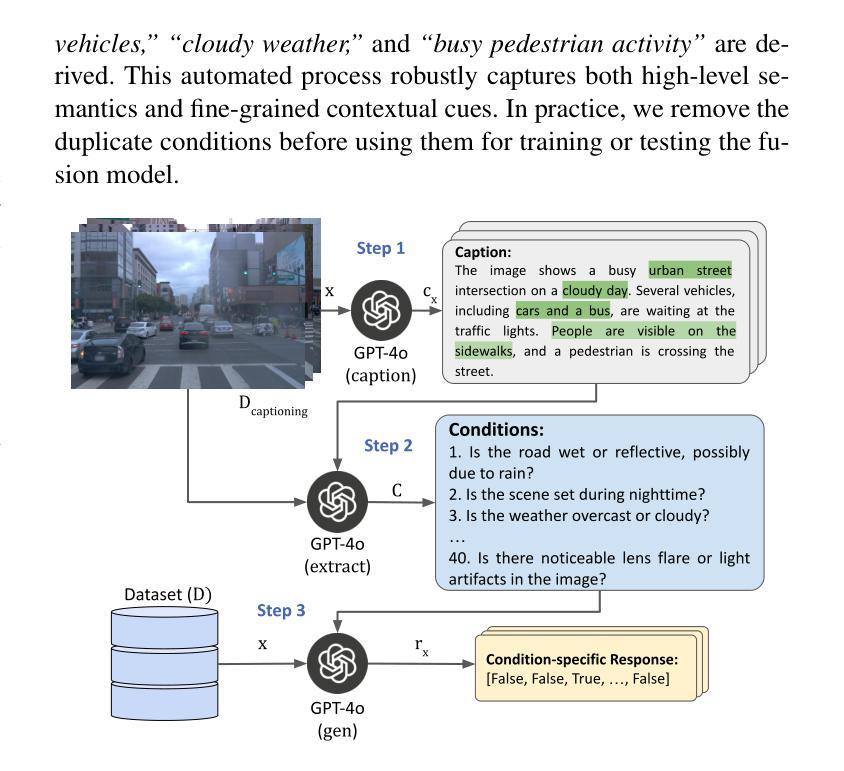
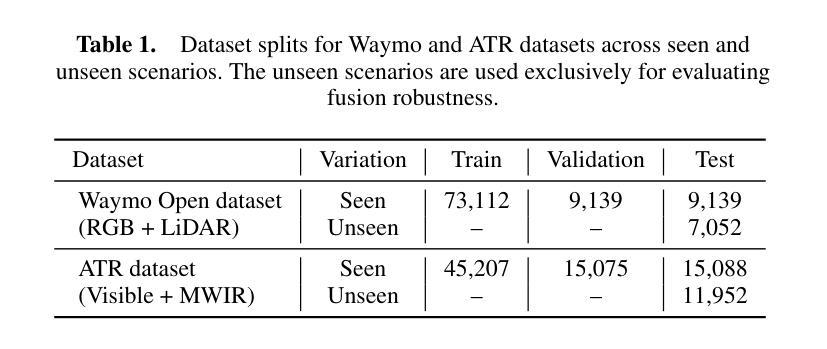
Although fusing multiple sensor modalities can enhance object detection performance, existing fusion approaches often overlook subtle variations in environmental conditions and sensor inputs. As a result, they struggle to adaptively weight each modality under such variations. To address this challenge, we introduce Vision-Language Conditioned Fusion (VLC Fusion), a novel fusion framework that leverages a Vision-Language Model (VLM) to condition the fusion process on nuanced environmental cues. By capturing high-level environmental context such as as darkness, rain, and camera blurring, the VLM guides the model to dynamically adjust modality weights based on the current scene. We evaluate VLC Fusion on real-world autonomous driving and military target detection datasets that include image, LIDAR, and mid-wave infrared modalities. Our experiments show that VLC Fusion consistently outperforms conventional fusion baselines, achieving improved detection accuracy in both seen and unseen scenarios.
虽然融合多种传感器模式可以提高目标检测性能,但现有的融合方法往往忽略了环境条件和传感器输入之间的细微差异。因此,它们在面对这些差异时,很难自适应地权衡每个模式的权重。为了应对这一挑战,我们引入了视觉语言条件融合(VLC Fusion)这一新型融合框架,它利用视觉语言模型(VLM)根据微妙的环境线索对融合过程进行条件化。通过捕捉如黑暗、雨天、相机模糊等高级环境上下文信息,VLM引导模型根据当前场景动态调整模式权重。我们在现实世界的自动驾驶和军事目标检测数据集上评估了VLC Fusion的性能,这些数据集包括图像、激光雷达和中波红外模式。实验表明,VLC Fusion持续超越传统的融合基线,在已知和未知场景中均实现了更高的检测精度。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 12 pages, 19 figures
Summary
基于多传感器融合技术的物体检测性能得到了提升,但现有融合方法忽略了环境条件和传感器输入的细微变化,难以自适应调整不同模态的权重。为解决这一问题,本文提出Vision-Language Conditioned Fusion(VLC Fusion)融合框架,借助Vision-Language Model(VLM)对环境特征进行感知分析。在高层次环境信息引导下(如光线不足、雨水及相机失真),动态调整模态权重,以实现最佳场景化适配。在真实世界自动驾驶和军事目标检测数据集上的实验表明,VLC Fusion在可见和未见场景中的检测精度均优于传统融合方法。
Key Takeaways
- 多传感器融合技术能提高物体检测性能。
- 现有融合方法难以适应环境条件和传感器输入的细微变化。
- Vision-Language Conditioned Fusion(VLC Fusion)框架被提出,利用Vision-Language Model(VLM)感知环境特征。
- VLM能捕捉高层次的环境信息,如黑暗、雨水和相机失真等。
- VLC Fusion能根据场景动态调整不同模态的权重。
- 在真实世界的数据集上,VLC Fusion在物体检测方面的表现优于传统融合方法。
点此查看论文截图



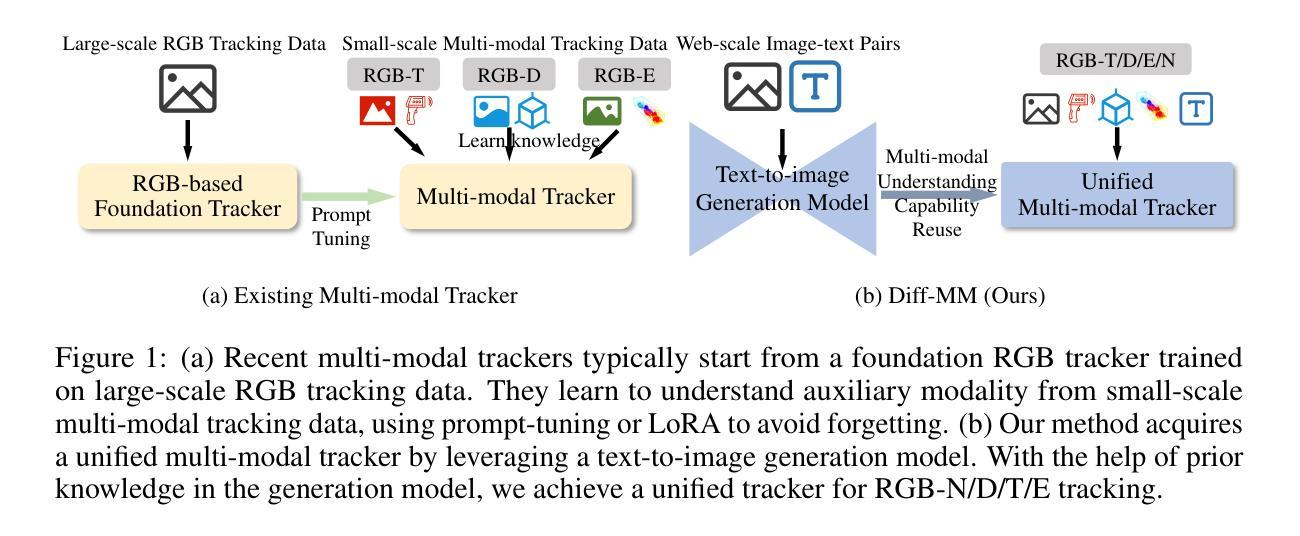
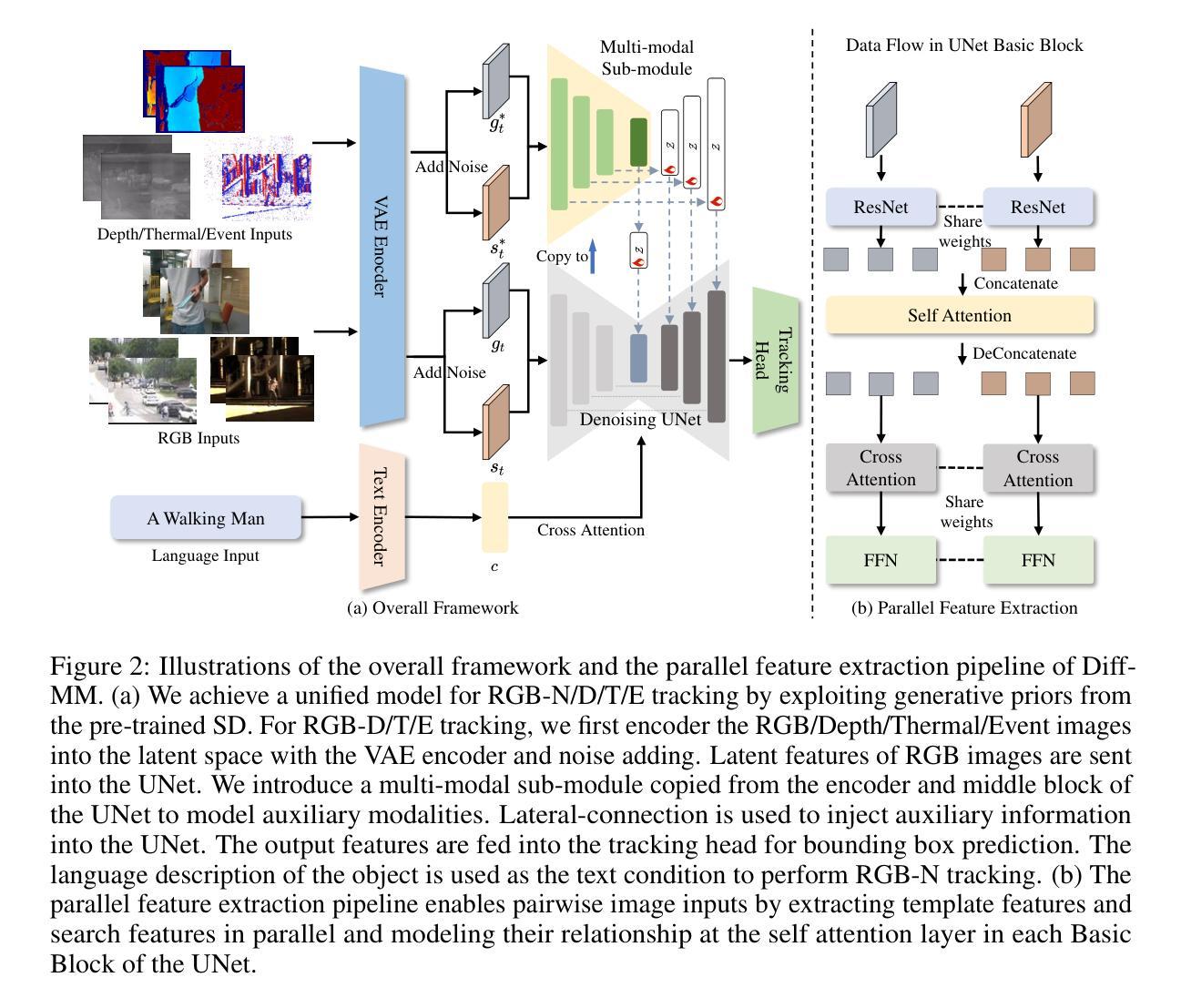
Diff-MM: Exploring Pre-trained Text-to-Image Generation Model for Unified Multi-modal Object Tracking
Authors:Shiyu Xuan, Zechao Li, Jinhui Tang
Multi-modal object tracking integrates auxiliary modalities such as depth, thermal infrared, event flow, and language to provide additional information beyond RGB images, showing great potential in improving tracking stabilization in complex scenarios. Existing methods typically start from an RGB-based tracker and learn to understand auxiliary modalities only from training data. Constrained by the limited multi-modal training data, the performance of these methods is unsatisfactory. To alleviate this limitation, this work proposes a unified multi-modal tracker Diff-MM by exploiting the multi-modal understanding capability of the pre-trained text-to-image generation model. Diff-MM leverages the UNet of pre-trained Stable Diffusion as a tracking feature extractor through the proposed parallel feature extraction pipeline, which enables pairwise image inputs for object tracking. We further introduce a multi-modal sub-module tuning method that learns to gain complementary information between different modalities. By harnessing the extensive prior knowledge in the generation model, we achieve a unified tracker with uniform parameters for RGB-N/D/T/E tracking. Experimental results demonstrate the promising performance of our method compared with recently proposed trackers, e.g., its AUC outperforms OneTracker by 8.3% on TNL2K.
多模态目标跟踪结合了深度、热红外、事件流和语言等辅助模态,为RGB图像以外的信息提供了额外的信息来源,在复杂场景中显示出巨大的提高跟踪稳定性的潜力。现有的方法大多从基于RGB的跟踪器开始,仅从训练数据中学习理解辅助模态。由于有限的多模态训练数据的限制,这些方法的性能并不令人满意。为了缓解这一局限性,这项工作提出了一个统一的多模态跟踪器Diff-MM,通过利用预训练的文本到图像生成模型的多模态理解能力。Diff-MM利用预训练的Stable Diffusion的UNet作为跟踪特征提取器,通过提出的并行特征提取管道实现成对图像输入进行目标跟踪。我们进一步引入了一种多模态子模块调整方法,该方法能够学习不同模态之间的互补信息。通过利用生成模型中的丰富先验知识,我们实现了具有统一参数的RGB-N/D/T/E跟踪的统一跟踪器。实验结果证明,与最近提出的跟踪器相比,我们的方法具有令人鼓舞的表现,例如在TNL2K上,其AUC值较OneTracker高出8.3%。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了多模态对象跟踪技术,该技术结合深度、热红外、事件流和语言等辅助模态信息,提高在复杂场景下的跟踪稳定性。针对现有方法受限于多模态训练数据不足的问题,本文提出一种基于预训练文本到图像生成模型的统一多模态跟踪器Diff-MM。该跟踪器通过并行特征提取管道利用UNet进行特征提取,并引入多模态子模块调节方法来学习不同模态之间的互补信息,实现了RGB-N/D/T/E统一跟踪。实验结果表明,该方法在TNL2K数据集上的AUC性能优于现有跟踪器,如OneTracker。
Key Takeaways
- 多模态对象跟踪结合了多种辅助模态信息以提高跟踪稳定性。
- 现有方法主要基于RGB图像进行训练,受限于多模态数据的缺乏。
- 本文提出一种基于预训练文本到图像生成模型的统一多模态跟踪器Diff-MM。
- Diff-MM利用UNet进行特征提取,并引入并行特征提取管道来处理成对的图像输入。
- 提出了多模态子模块调节方法,学习不同模态之间的互补信息。
- 利用生成模型中的先验知识,实现了RGB-N/D/T/E统一跟踪。
点此查看论文截图

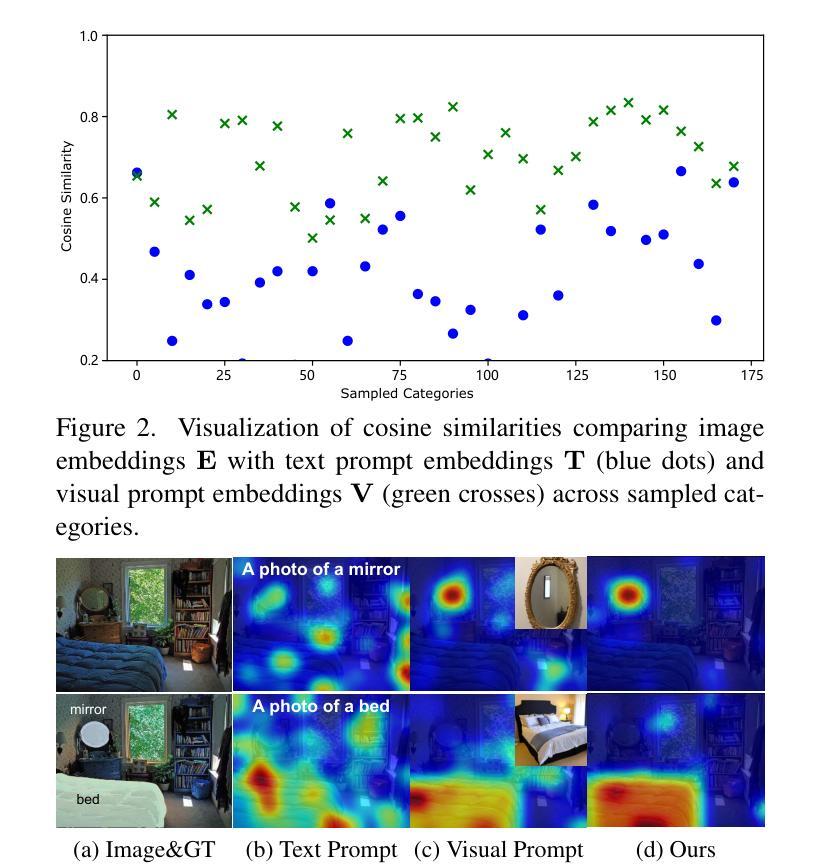
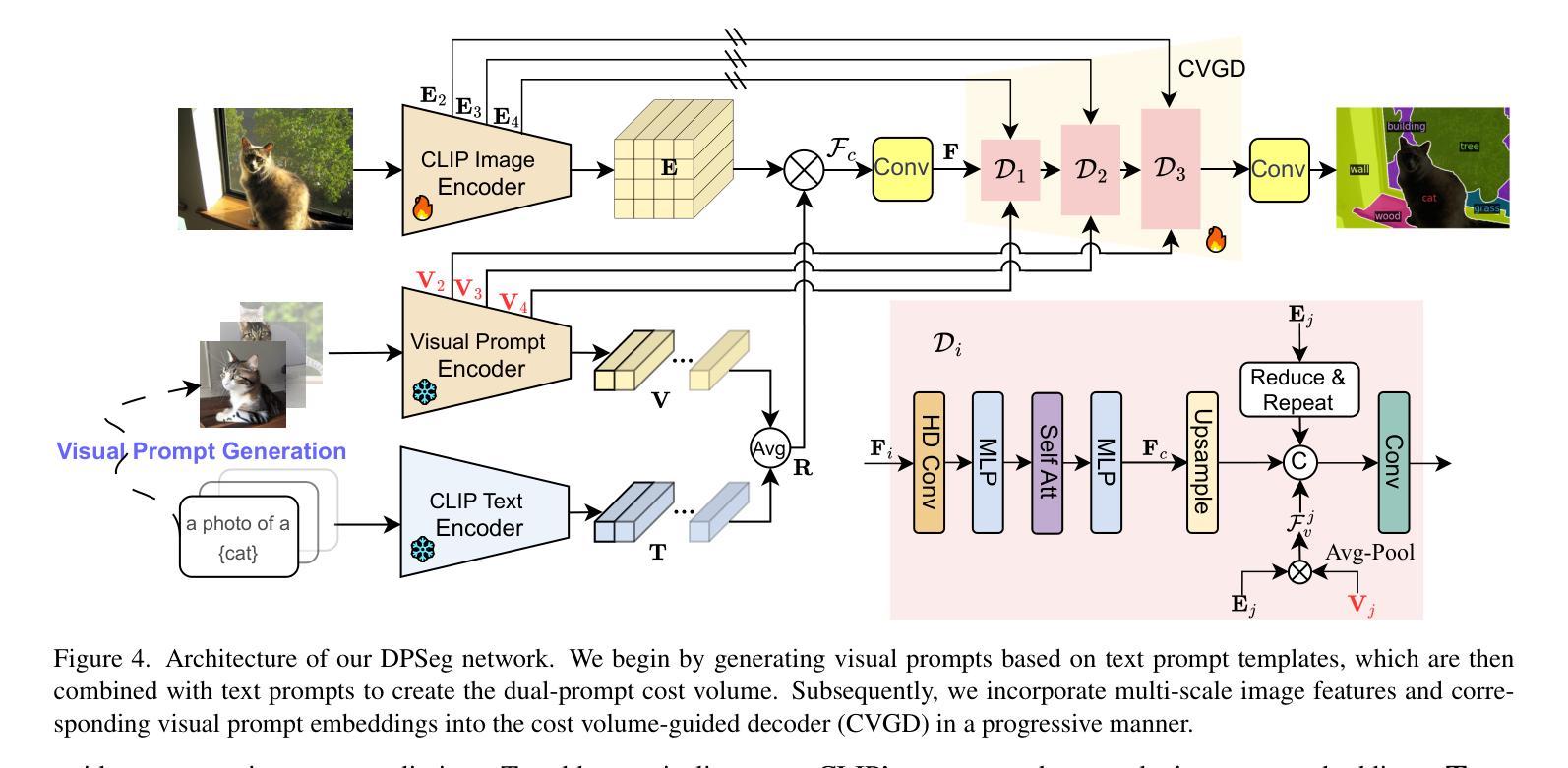
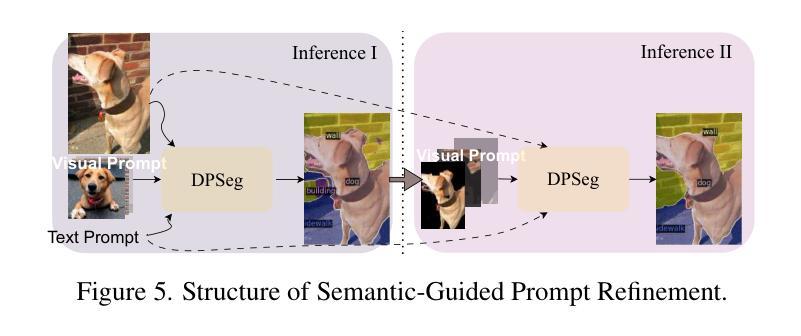
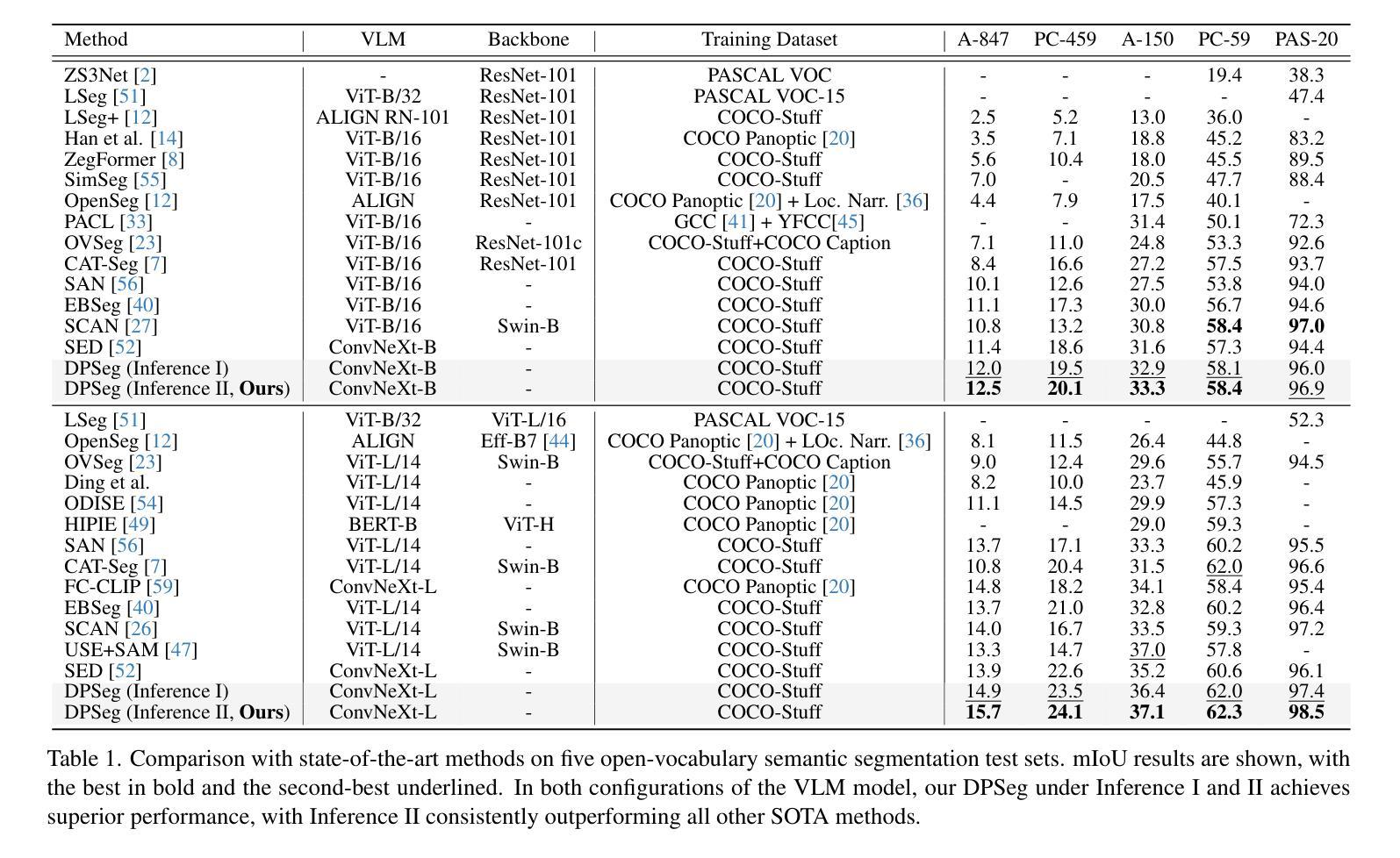
DPSeg: Dual-Prompt Cost Volume Learning for Open-Vocabulary Semantic Segmentation
Authors:Ziyu Zhao, Xiaoguang Li, Linjia Shi, Nasrin Imanpour, Song Wang
Open-vocabulary semantic segmentation aims to segment images into distinct semantic regions for both seen and unseen categories at the pixel level. Current methods utilize text embeddings from pre-trained vision-language models like CLIP but struggle with the inherent domain gap between image and text embeddings, even after extensive alignment during training. Additionally, relying solely on deep text-aligned features limits shallow-level feature guidance, which is crucial for detecting small objects and fine details, ultimately reducing segmentation accuracy. To address these limitations, we propose a dual prompting framework, DPSeg, for this task. Our approach combines dual-prompt cost volume generation, a cost volume-guided decoder, and a semantic-guided prompt refinement strategy that leverages our dual prompting scheme to mitigate alignment issues in visual prompt generation. By incorporating visual embeddings from a visual prompt encoder, our approach reduces the domain gap between text and image embeddings while providing multi-level guidance through shallow features. Extensive experiments demonstrate that our method significantly outperforms existing state-of-the-art approaches on multiple public datasets.
开放词汇语义分割旨在将图像分割成像素级别的不同语义区域,包括已知和未知类别。当前的方法利用预训练的视觉语言模型(如CLIP)的文本嵌入,但在图像和文本嵌入之间的固有领域差距上仍然面临挑战,即使在训练过程中进行了大量的对齐也是如此。此外,仅依赖深度文本对齐特征限制了浅层特征指导,这对于检测小物体和精细细节至关重要,最终会降低分割精度。为了解决这些局限性,我们针对此任务提出了双提示框架DPSeg。我们的方法结合了双提示成本体积生成、成本体积引导解码器和语义引导提示优化策略,利用我们的双提示方案来缓解视觉提示生成中的对齐问题。通过结合视觉提示编码器的视觉嵌入,我们的方法缩小了文本和图像嵌入之间的领域差距,同时通过浅层特征提供了多级指导。大量实验表明,我们的方法在多个公共数据集上显著优于现有的最先进的方法。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by CVPR2025
Summary
本文提出了一种新型的开放词汇语义分割方法,即DPSeg双提示框架。该框架旨在解决图像和文本嵌入之间的领域差距问题,并通过结合视觉提示编码器产生的视觉嵌入,提供多层次指导,从而提高分割准确性。实验证明,该方法在多公共数据集上的性能显著优于现有先进技术。
Key Takeaways
- 开放词汇语义分割旨在将图像分割成不同语义区域,涵盖已知和未知类别,且分割在像素级别进行。
- 当前方法使用如CLIP等预训练视觉语言模型的文本嵌入,但面临图像和文本嵌入之间的领域差距问题。
- 单纯依赖深度文本对齐特征忽视了浅层特征指导,这对检测小物体和精细细节至关重要,从而降低了分割精度。
- DPSeg框架通过结合双提示成本体积生成、成本体积引导解码器和语义引导提示优化策略,解决了对齐问题。
- DPSeg利用视觉提示编码器的视觉嵌入,缩小了文本和图像嵌入之间的领域差距。
- DPSeg通过多层次指导提高了分割准确性。
点此查看论文截图

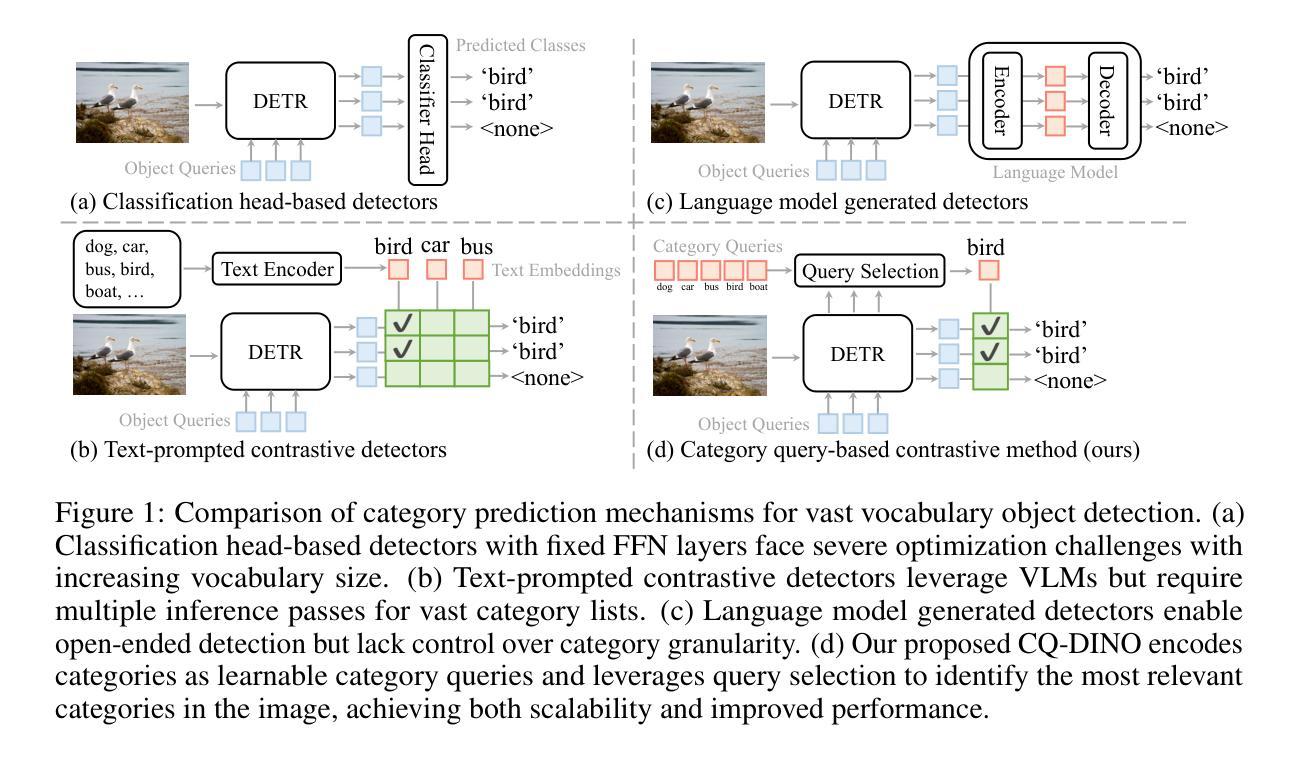
CQ-DINO: Mitigating Gradient Dilution via Category Queries for Vast Vocabulary Object Detection
Authors:Zhichao Sun, Huazhang Hu, Yidong Ma, Gang Liu, Nemo Chen, Xu Tang, Yao Hu, Yongchao Xu
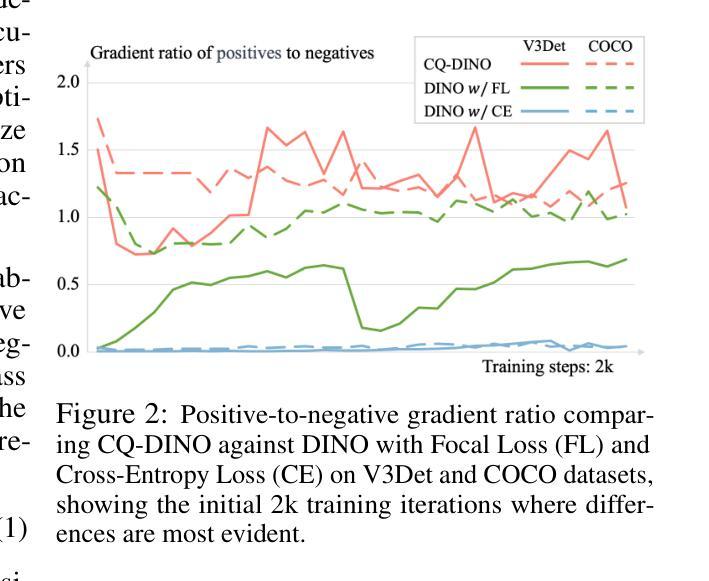
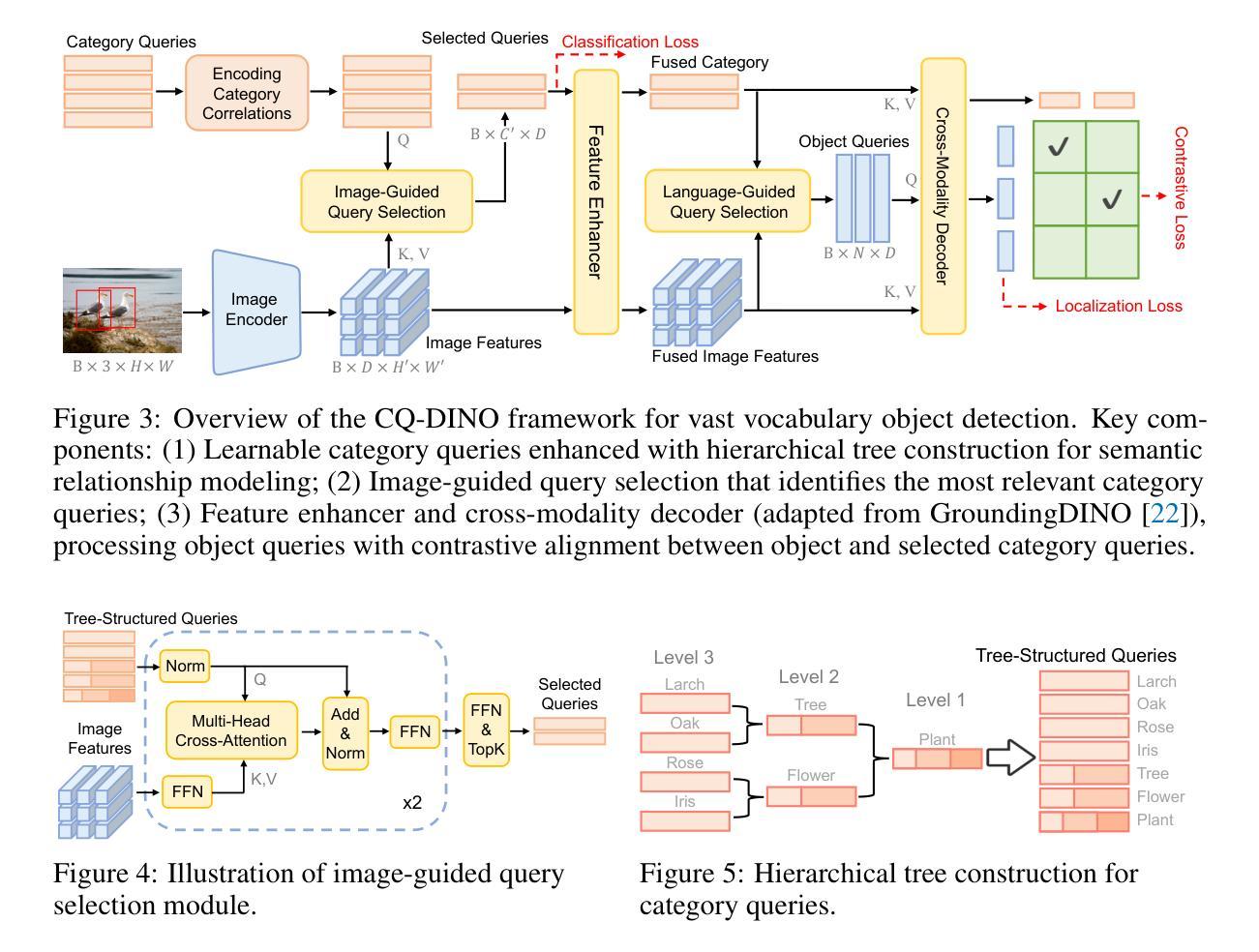
With the exponential growth of data, traditional object detection methods are increasingly struggling to handle vast vocabulary object detection tasks effectively. We analyze two key limitations of classification-based detectors: positive gradient dilution, where rare positive categories receive insufficient learning signals, and hard negative gradient dilution, where discriminative gradients are overwhelmed by numerous easy negatives. To address these challenges, we propose CQ-DINO, a category query-based object detection framework that reformulates classification as a contrastive task between object queries and learnable category queries. Our method introduces image-guided query selection, which reduces the negative space by adaptively retrieving top-K relevant categories per image via cross-attention, thereby rebalancing gradient distributions and facilitating implicit hard example mining. Furthermore, CQ-DINO flexibly integrates explicit hierarchical category relationships in structured datasets (e.g., V3Det) or learns implicit category correlations via self-attention in generic datasets (e.g., COCO). Experiments demonstrate that CQ-DINO achieves superior performance on the challenging V3Det benchmark (surpassing previous methods by 2.1% AP) while maintaining competitiveness in COCO. Our work provides a scalable solution for real-world detection systems requiring wide category coverage. The code is publicly at https://github.com/RedAIGC/CQ-DINO.
随着数据的指数级增长,传统目标检测方法在应对大规模词汇目标检测任务时越来越困难。我们分析了基于分类的检测器的两个关键局限性:正向梯度稀释,即罕见的正类别接收到的学习信号不足;以及难以应对的负梯度稀释,即区分梯度被大量简单的负样本所淹没。为了应对这些挑战,我们提出了基于类别查询的目标检测框架CQ-DINO。它将分类重新表述为目标查询与可学习类别查询之间的对比任务。我们的方法引入了图像引导查询选择,通过跨注意力自适应地检索每张图像的前K个相关类别,从而减少负空间,从而重新平衡梯度分布并促进隐式硬样本挖掘。此外,CQ-DINO可以灵活地集成结构化数据集(例如V3Det)中的显式层次类别关系,或通过通用数据集(例如COCO)中的自注意力学习隐式类别相关性。实验表明,CQ-DINO在具有挑战性的V3Det基准测试上取得了优于其他方法(超过2.1%的AP)的性能,同时在COCO中保持竞争力。我们的工作为需要广泛类别覆盖的真实世界检测系统提供了可扩展的解决方案。代码公开在https://github.com/RedAIGC/CQ-DINO。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文探讨了数据指数增长背景下,传统目标检测方法的局限性,特别是在处理大规模词汇目标检测任务时的挑战。为解决这些问题,提出了一种基于类别查询的目标检测框架CQ-DINO,该框架通过对比对象查询和可学习类别查询来重新制定分类任务。同时引入了图像引导查询选择机制,通过跨注意力自适应地检索每幅图像的前K个相关类别,从而减少负空间,平衡梯度分布,促进隐性硬样本挖掘。实验表明,CQ-DINO在具有挑战性的V3Det基准测试上表现卓越,超过了以前的方法(提高2.1%的AP),同时在COCO等通用数据集上也具有竞争力。为需要广泛类别覆盖的真实世界检测系统提供了可扩展的解决方案。
Key Takeaways
- 数据量的指数增长使传统目标检测方法在处理大规模词汇目标检测任务时面临挑战。
- 现有分类检测器的两个主要局限性是正向梯度稀释和硬负梯度稀释。
- CQ-DINO框架通过对比对象查询和类别查询来改革分类任务,解决上述问题。
- 图像引导查询选择机制能够自适应地检索每幅图像的前K个相关类别,减少负空间,平衡梯度分布。
- CQ-DINO在V3Det基准测试上表现优越,超过先前方法2.1%的AP,同时在COCO等数据集上保持竞争力。
- CQ-DINO框架为需要广泛类别覆盖的真实世界检测系统提供了可扩展的解决方案。
点此查看论文截图