⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-05-21 更新
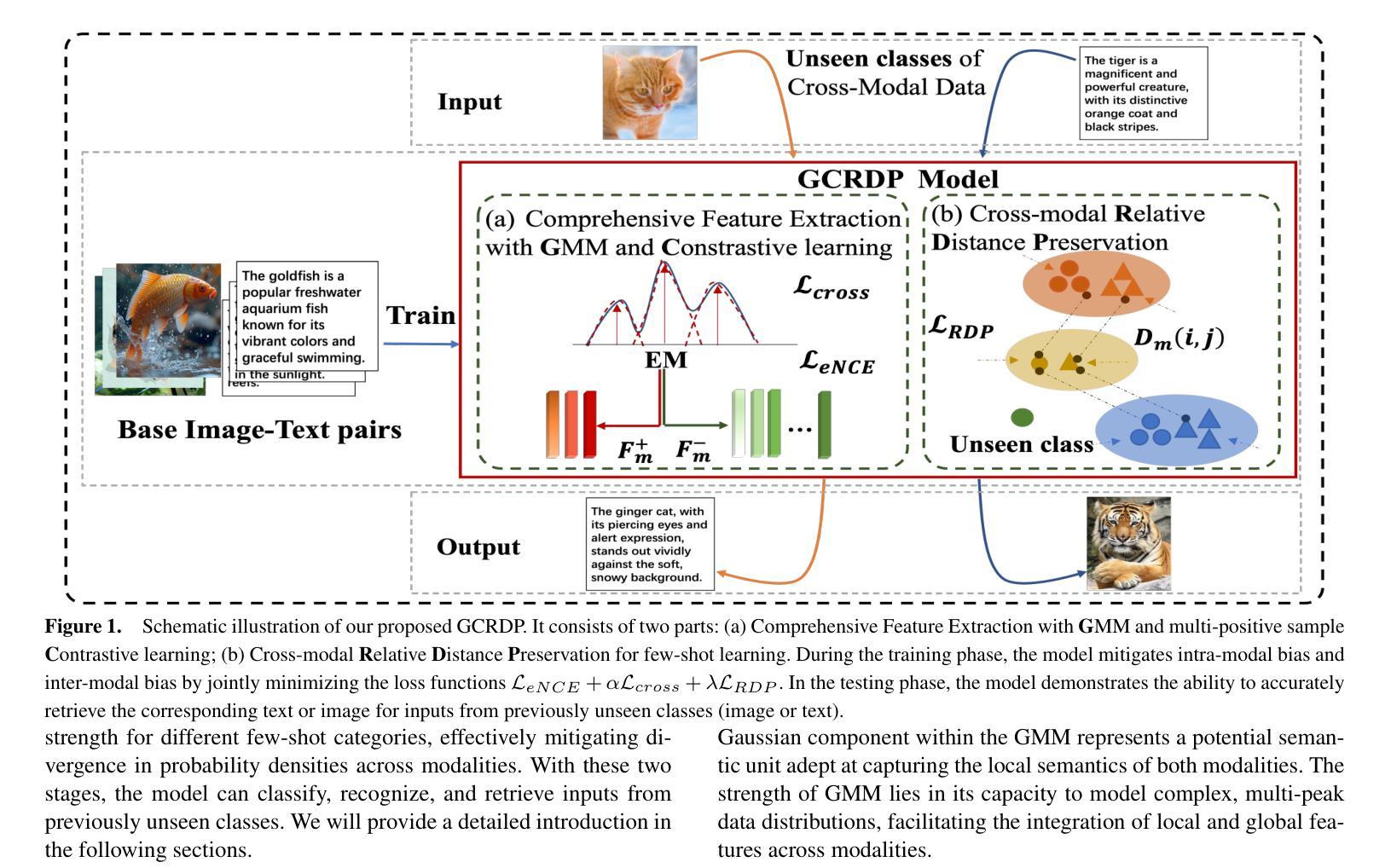
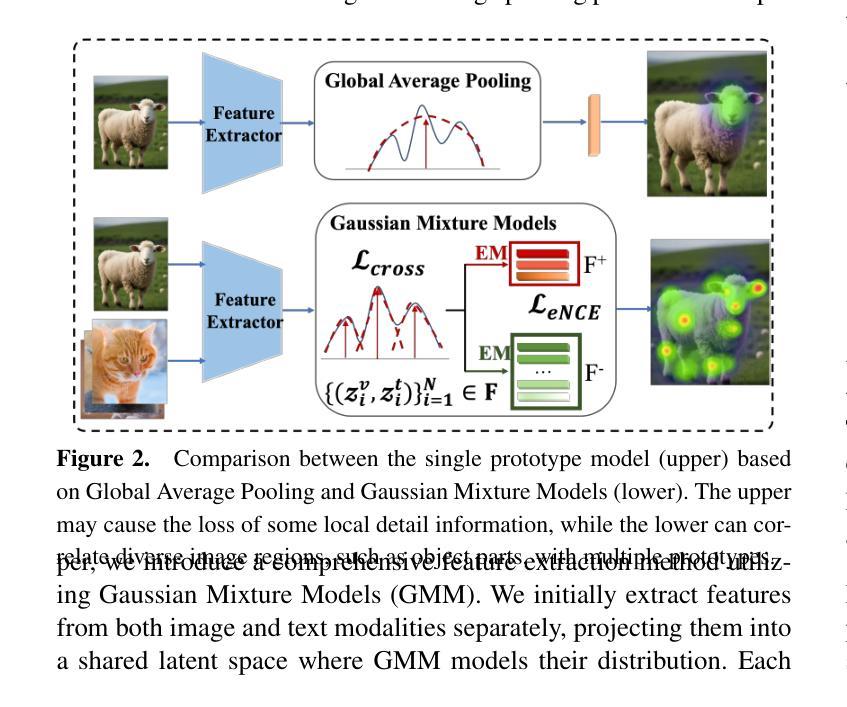
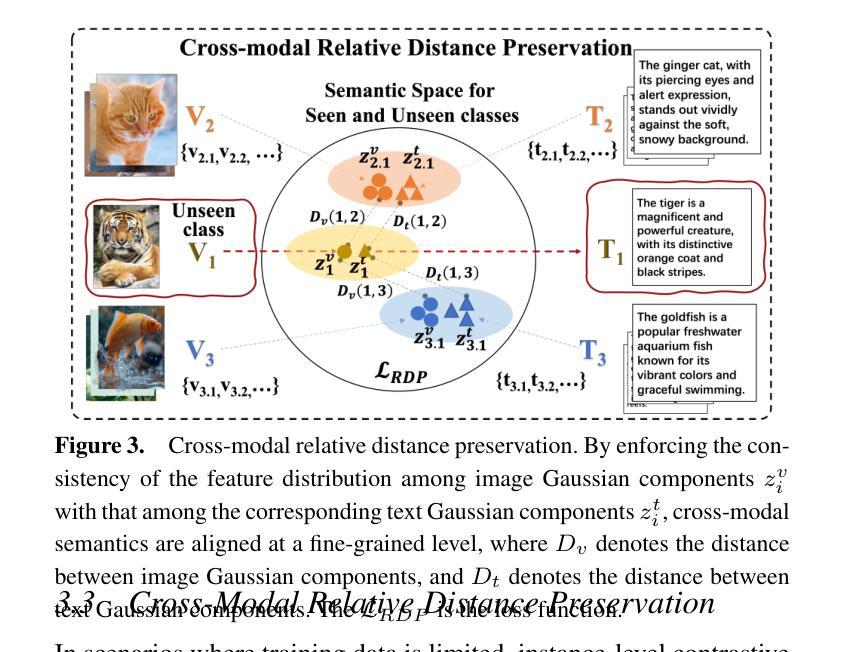
GMM-Based Comprehensive Feature Extraction and Relative Distance Preservation For Few-Shot Cross-Modal Retrieval
Authors:Chengsong Sun, Weiping Li, Xiang Li, Yuankun Liu, Lianlei Shan
Few-shot cross-modal retrieval focuses on learning cross-modal representations with limited training samples, enabling the model to handle unseen classes during inference. Unlike traditional cross-modal retrieval tasks, which assume that both training and testing data share the same class distribution, few-shot retrieval involves data with sparse representations across modalities. Existing methods often fail to adequately model the multi-peak distribution of few-shot cross-modal data, resulting in two main biases in the latent semantic space: intra-modal bias, where sparse samples fail to capture intra-class diversity, and inter-modal bias, where misalignments between image and text distributions exacerbate the semantic gap. These biases hinder retrieval accuracy. To address these issues, we propose a novel method, GCRDP, for few-shot cross-modal retrieval. This approach effectively captures the complex multi-peak distribution of data using a Gaussian Mixture Model (GMM) and incorporates a multi-positive sample contrastive learning mechanism for comprehensive feature modeling. Additionally, we introduce a new strategy for cross-modal semantic alignment, which constrains the relative distances between image and text feature distributions, thereby improving the accuracy of cross-modal representations. We validate our approach through extensive experiments on four benchmark datasets, demonstrating superior performance over six state-of-the-art methods.
少量样本跨模态检索致力于在有限的训练样本上学习跨模态表示,使模型能够在推理过程中处理未见过的类别。与传统假设训练和测试数据具有相同类别分布的跨模态检索任务不同,少量样本检索涉及到跨模态的稀疏表示数据。现有方法往往无法充分建模少量样本跨模态数据的多峰分布,导致潜在语义空间中存在两个主要偏见:模态内偏见,其中稀疏样本无法捕捉类内多样性;模态间偏见,其中图像和文本分布之间的错位加剧了语义鸿沟。这些偏见阻碍了检索的准确性。为了解决这些问题,我们提出了一种用于少量样本跨模态检索的新方法GCRDP。该方法使用高斯混合模型(GMM)有效地捕获了数据的复杂多峰分布,并采用了多阳性样本对比学习机制进行特征的综合建模。此外,我们还引入了一种新的跨模态语义对齐策略,约束图像和文本特征分布之间的相对距离,从而提高了跨模态表示的准确性。我们在四个基准数据集上进行了大量实验,验证了我们的方法,显示出其优于六种最先进的方法。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了小样本的跨模态检索技术,它使用有限样本学习跨模态表示,可以处理推断期间未见过的类别。文章提出了一种新的方法GCRDP来解决小样本的跨模态检索问题,该方法利用高斯混合模型(GMM)有效地捕捉数据的复杂多峰分布,采用多阳性样本对比学习机制进行特征建模,并引入新的跨模态语义对齐策略,约束图像和文本特征分布之间的相对距离,提高跨模态表示的准确性。实验证明该方法在四个基准数据集上优于六种最新的方法。
Key Takeaways
- Few-shot cross-modal retrieval关注使用有限样本学习跨模态表示,以处理未见过的类别。
- 传统跨模态检索任务假定训练和测试数据具有相同的类别分布,而few-shot检索涉及跨模态数据的稀疏表示。
- 现有方法往往不能充分建模跨模态数据的多峰分布,导致潜伏语义空间中的两种偏见:同模态偏见和跨模态偏见。
- 文章提出的GCRDP方法利用高斯混合模型(GMM)捕捉数据的复杂多峰分布。
- GCRDP采用多阳性样本对比学习机制进行特征建模,并引入新的跨模态语义对齐策略。
- 实验证明GCRDP在四个基准数据集上的性能优于六种最新的方法。
点此查看论文截图

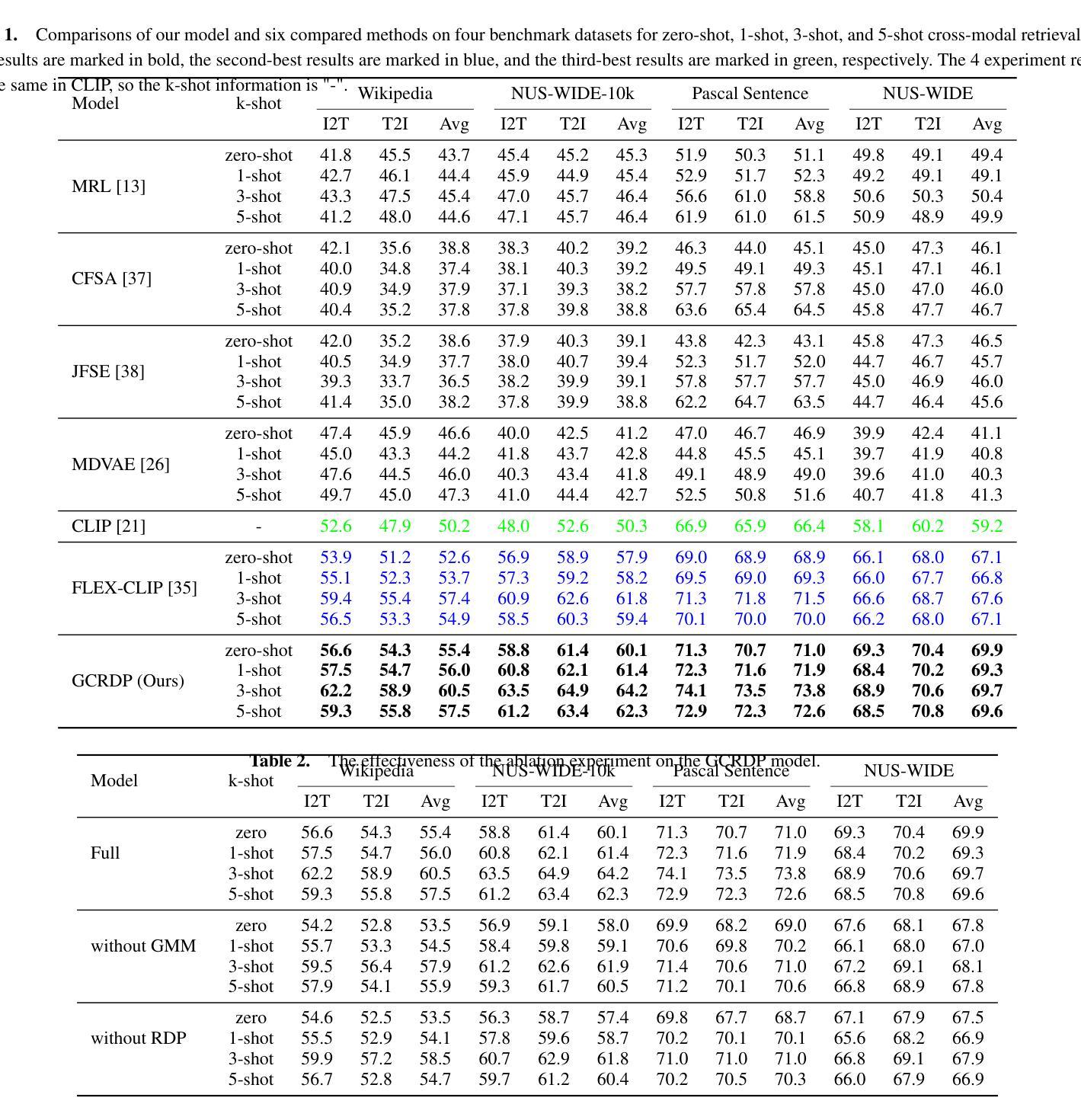
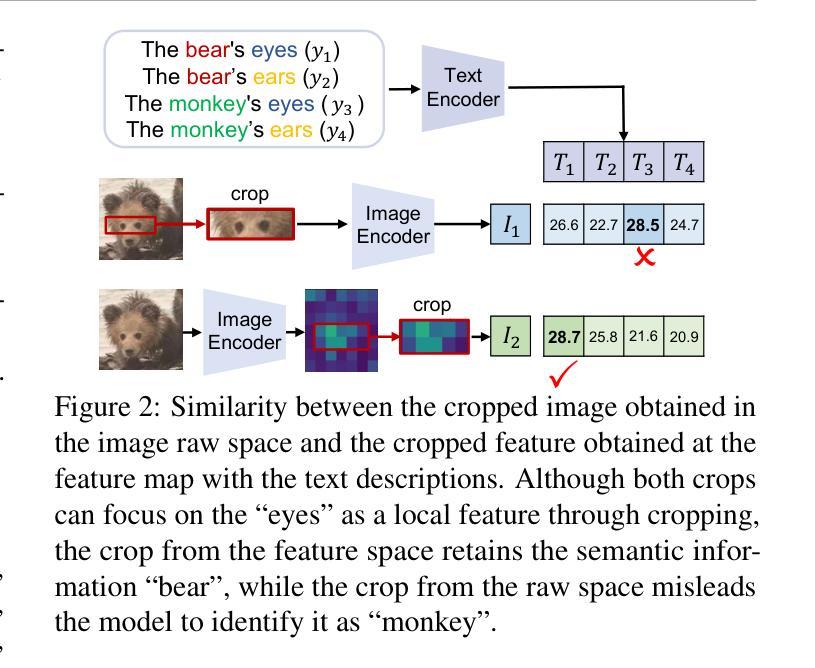
From Local Details to Global Context: Advancing Vision-Language Models with Attention-Based Selection
Authors:Lincan Cai, Jingxuan Kang, Shuang Li, Wenxuan Ma, Binhui Xie, Zhida Qin, Jian Liang
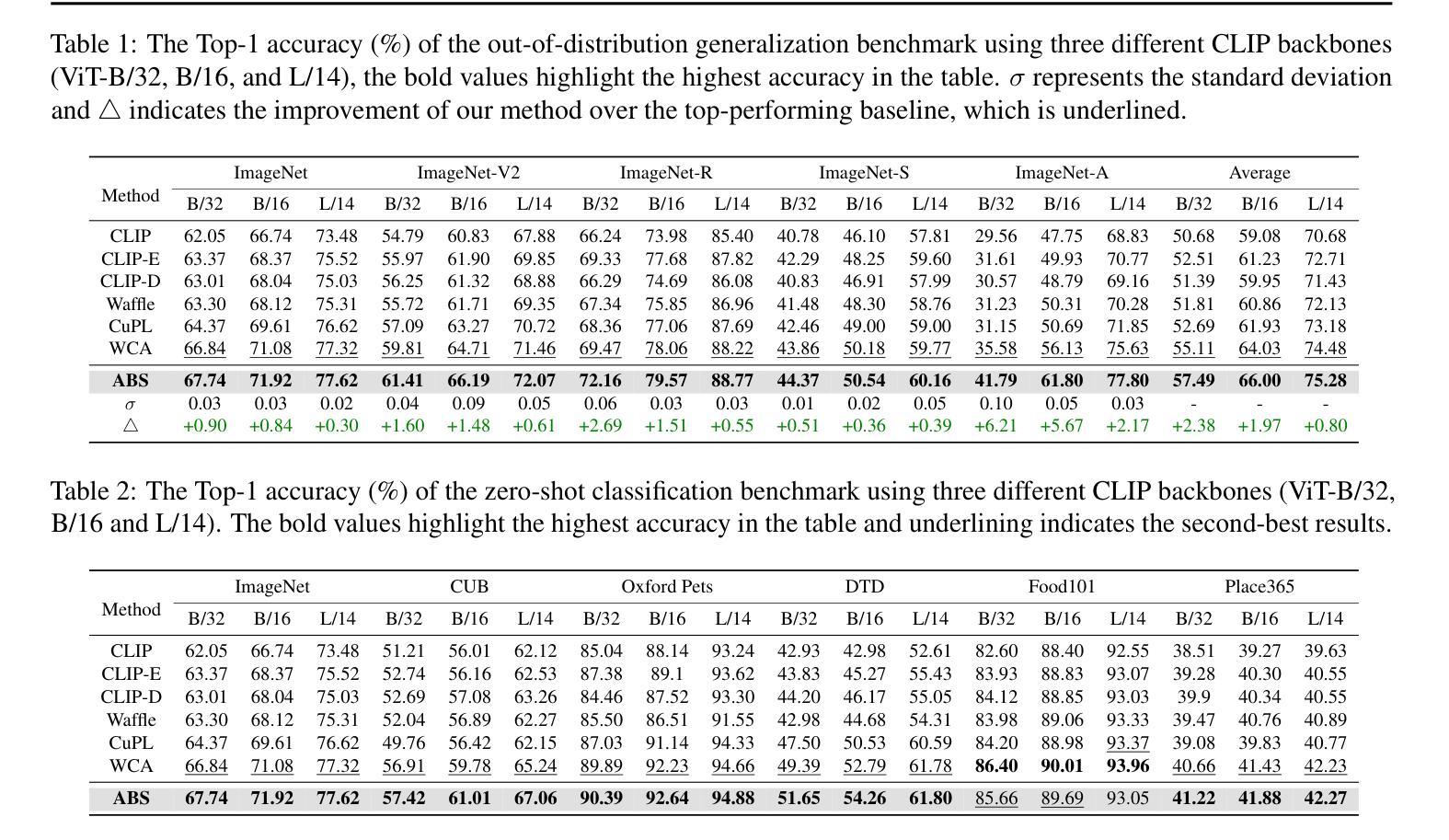
Pretrained vision-language models (VLMs), e.g., CLIP, demonstrate impressive zero-shot capabilities on downstream tasks. Prior research highlights the crucial role of visual augmentation techniques, like random cropping, in alignment with fine-grained class descriptions generated by large language models (LLMs), significantly enhancing zero-shot performance by incorporating multi-view information. However, the inherent randomness of these augmentations can inevitably introduce background artifacts and cause models to overly focus on local details, compromising global semantic understanding. To address these issues, we propose an \textbf{A}ttention-\textbf{B}ased \textbf{S}election (\textbf{ABS}) method from local details to global context, which applies attention-guided cropping in both raw images and feature space, supplement global semantic information through strategic feature selection. Additionally, we introduce a soft matching technique to effectively filter LLM descriptions for better alignment. \textbf{ABS} achieves state-of-the-art performance on out-of-distribution generalization and zero-shot classification tasks. Notably, \textbf{ABS} is training-free and even rivals few-shot and test-time adaptation methods. Our code is available at \href{https://github.com/BIT-DA/ABS}{\textcolor{darkgreen}{https://github.com/BIT-DA/ABS}}.
预训练的视觉语言模型(如CLIP)在下游任务中展现出令人印象深刻的零样本能力。早期研究突出了视觉增强技术(如随机裁剪)与由大型语言模型生成的精细类别描述对齐的关键作用,通过融入多视图信息,显著提高了零样本性能。然而,这些增强的固有随机性不可避免地会引入背景伪影,导致模型过度关注局部细节,从而损害全局语义理解。为了解决这些问题,我们提出了一种从局部细节到全局上下文的注意力基础选择(ABS)方法。该方法在原始图像和特征空间中应用注意力引导裁剪,通过战略特征选择来补充全局语义信息。此外,我们还引入了一种软匹配技术,以有效地过滤LLM描述,以更好地对齐。ABS在超出分布泛化和零样本分类任务上达到了最新性能水平。值得注意的是,ABS无需训练,甚至与少数样本和测试时间适应方法相匹敌。我们的代码可在https://github.com/BIT-DA/ABS处获得。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
预训练视觉语言模型(如CLIP)在下游任务中展现出强大的零样本能力。研究强调视觉增强技术与大型语言模型生成的精细类别描述相结合的重要性,通过融入多视角信息显著提高零样本性能。然而,增强技术的随机性可能引入背景伪影,导致模型过度关注局部细节,影响全局语义理解。为此,我们提出一种基于注意力的选择(ABS)方法,从局部细节转向全局上下文。该方法在原始图像和特征空间应用注意力引导裁剪,通过策略性特征选择补充全局语义信息。同时,引入软匹配技术有效过滤LLM描述,实现更好的对齐。ABS在超出分布泛化和零样本分类任务上达到最新性能水平,且无需训练,甚至可与少样本和测试时适应方法相抗衡。
Key Takeaways
- 预训练视觉语言模型(VLMs)如CLIP在下游任务中表现出强大的零样本能力。
- 视觉增强技术与LLM生成的精细类别描述相结合能显著提高零样本性能。
- 增强技术的随机性可能引入背景伪影和过度关注局部细节的问题。
- 提出的ABS方法从局部细节转向全局上下文,通过注意力机制在原始图像和特征空间进行裁剪。
- ABS通过策略性特征选择补充全局语义信息。
- ABS采用软匹配技术过滤LLM描述,实现更好的模型对齐。
- ABS方法在超出分布泛化和零样本分类任务上表现优秀,且无需训练,具有实际应用潜力。
点此查看论文截图

SynDec: A Synthesize-then-Decode Approach for Arbitrary Textual Style Transfer via Large Language Models
Authors:Han Sun, Zhen Sun, Zongmin Zhang, Linzhao Jia, Wei Shao, Min Zhang
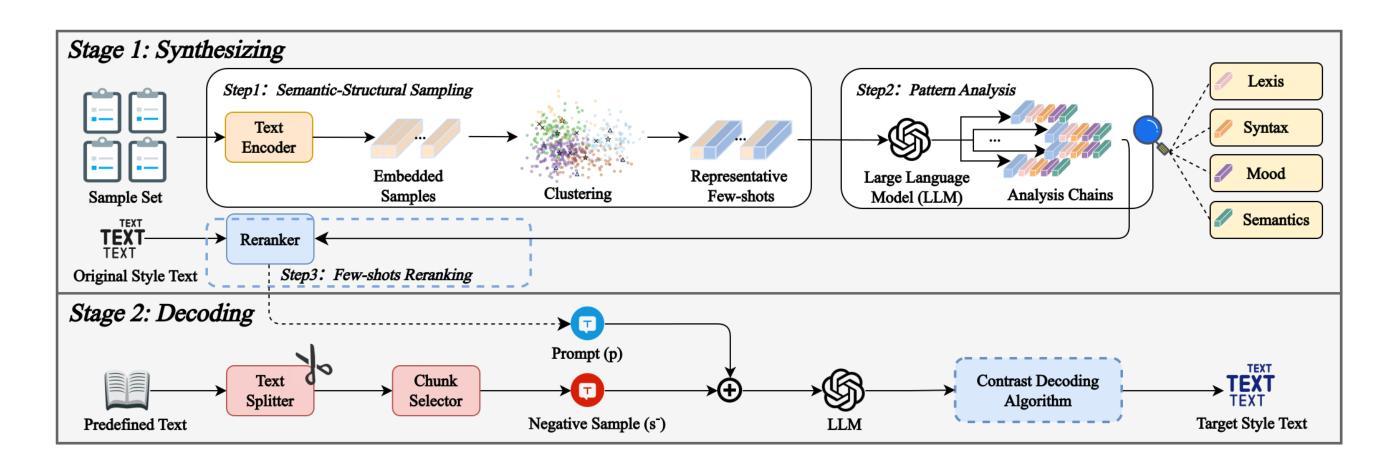
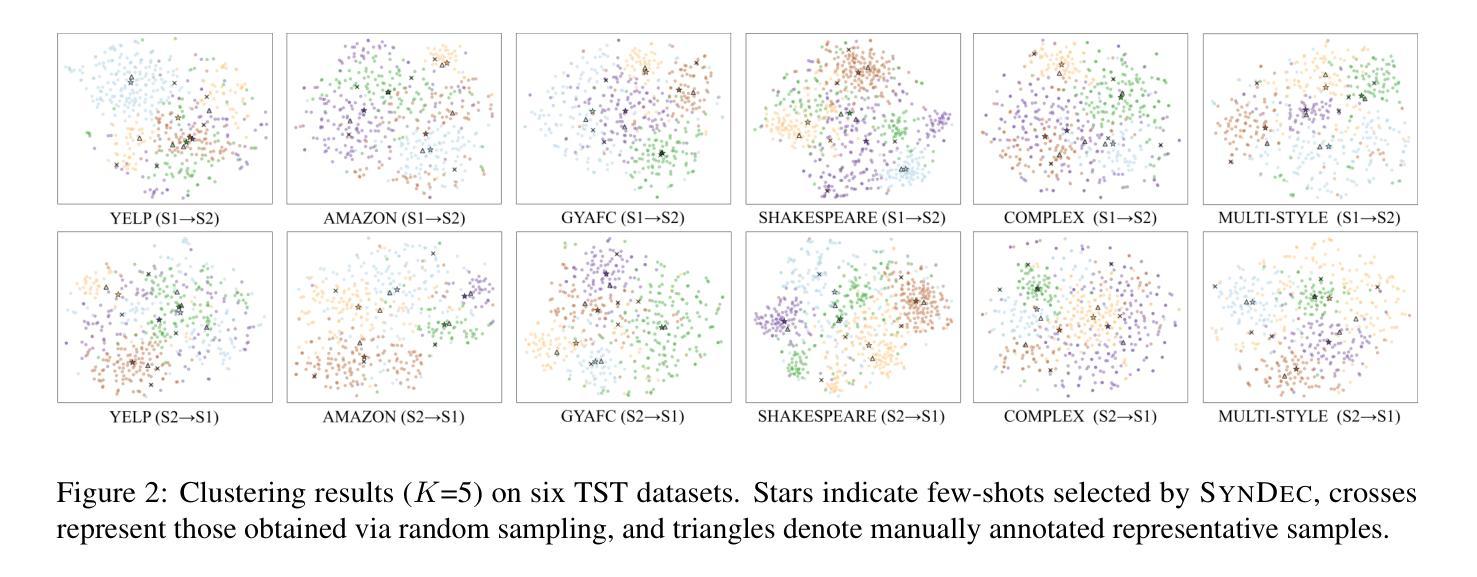
Large Language Models (LLMs) are emerging as dominant forces for textual style transfer. However, for arbitrary style transfer, LLMs face two key challenges: (1) considerable reliance on manually-constructed prompts and (2) rigid stylistic biases inherent in LLMs. In this paper, we propose a novel Synthesize-then-Decode (SynDec) approach, which automatically synthesizes high-quality prompts and amplifies their roles during decoding process. Specifically, our approach synthesizes prompts by selecting representative few-shot samples, conducting a four-dimensional style analysis, and reranking the candidates. At LLM decoding stage, the TST effect is amplified by maximizing the contrast in output probabilities between scenarios with and without the synthesized prompt, as well as between prompts and negative samples. We conduct extensive experiments and the results show that SynDec outperforms existing state-of-the-art LLM-based methods on five out of six benchmarks (e.g., achieving up to a 9% increase in accuracy for modern-to-Elizabethan English transfer). Detailed ablation studies further validate the effectiveness of SynDec.
大型语言模型(LLM)正在成为文本风格转换的主导力量。然而,对于任意风格转换,LLM面临两个关键挑战:(1)严重依赖手动构建的提示;(2)LLM中固有的僵化风格偏见。在本文中,我们提出了一种新型的先合成后解码(SynDec)方法,该方法可以自动合成高质量提示,并在解码过程中放大其作用。具体来说,我们的方法通过选择具有代表性的少量样本、进行四维风格分析以及重新排序候选项来合成提示。在LLM解码阶段,通过最大化有合成提示和无提示场景之间的输出概率对比,以及提示和负样本之间的对比,放大了TST效应。我们进行了大量实验,结果表明,在六个基准测试中的五个上,SynDec优于现有的基于LLM的最先进方法(例如,在现代到伊丽莎白时代的英语转换中,准确率提高了高达9%)。详细的消融研究进一步验证了SynDec的有效性。
论文及项目相关链接
摘要
LLMs在自然语言风格迁移领域表现出极大的潜力,但仍面临两大挑战:依赖手动构建的提示和LLMs本身的风格偏见。本文提出了一种新颖的Synthesize-then-Decode(SynDec)方法,该方法能够自动合成高质量提示并在解码过程中放大其作用。具体来说,我们的方法通过选择代表性的少量样本、进行四维风格分析以及重新排序候选者来合成提示。在LLM解码阶段,通过最大化有合成提示与无提示场景的输出概率对比,以及提示与负样本之间的对比,放大了TST效应。实验表明,SynDec在五个基准测试中的表现优于现有的一流LLM方法(例如在从现代英语到伊丽莎白时代英语的迁移中准确率提高了高达9%)。详细的消融研究进一步验证了SynDec的有效性。
关键见解
- LLMs在自然语言风格迁移方面展现出强大的潜力,但仍面临依赖手动提示和固有风格偏见两大挑战。
- 提出的Synthesize-then-Decode(SynDec)方法能够自动合成高质量提示并在解码过程中放大其作用。
- SynDec方法通过选择代表性样本、进行四维风格分析和重新排序候选者来合成提示。
- 在LLM解码阶段,SynDec通过最大化有提示与无提示场景的输出概率对比来放大效果。
- 实验表明,SynDec在多数基准测试中的表现优于其他方法,如在特定风格迁移任务中准确率有显著提高。
- 消融研究验证了SynDec方法的有效性。
点此查看论文截图

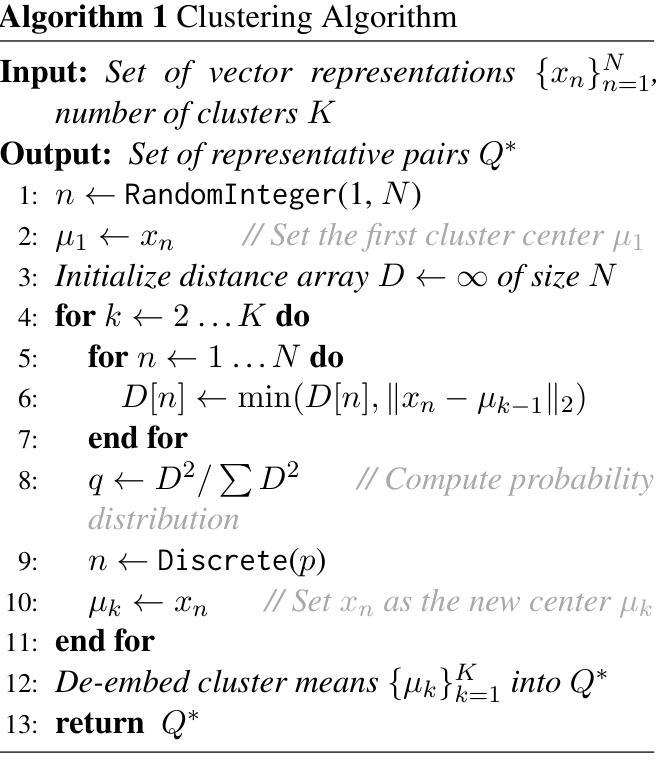
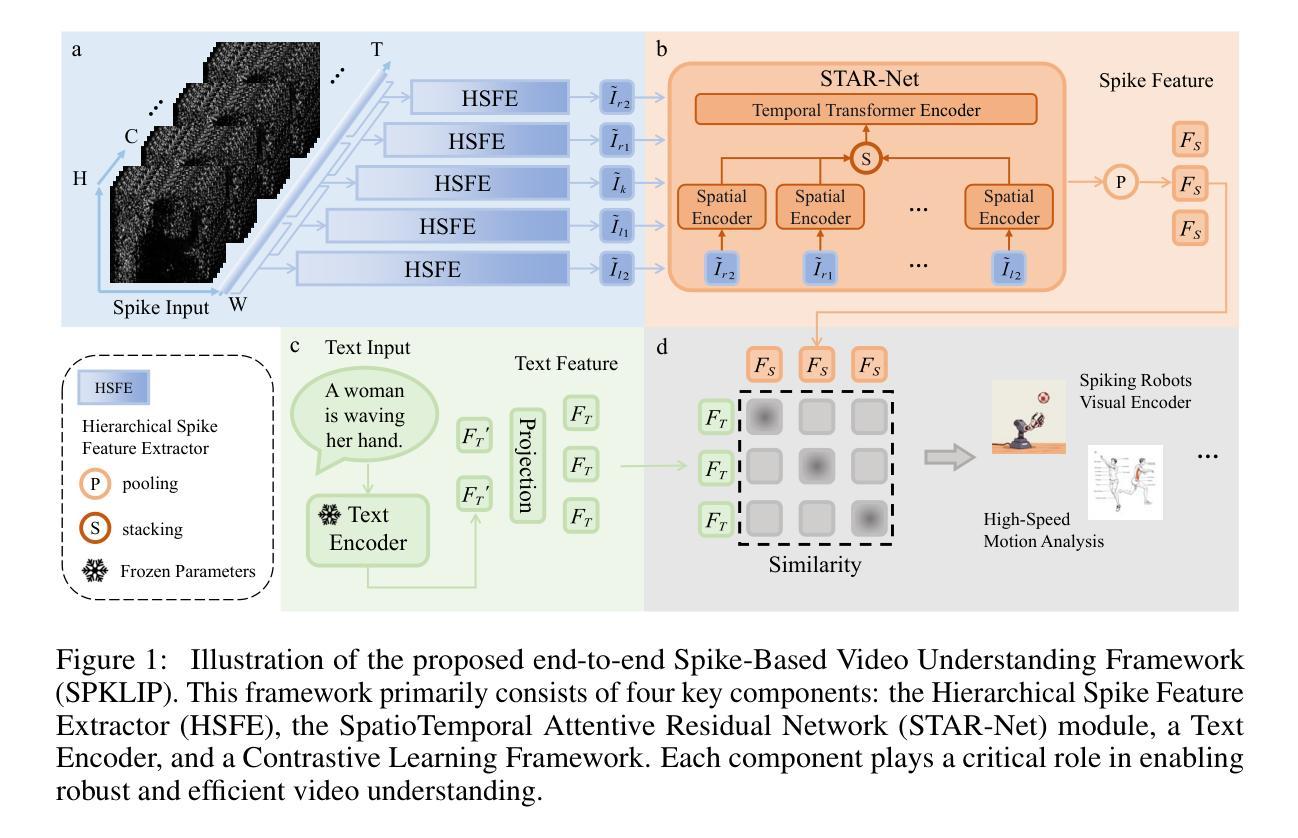
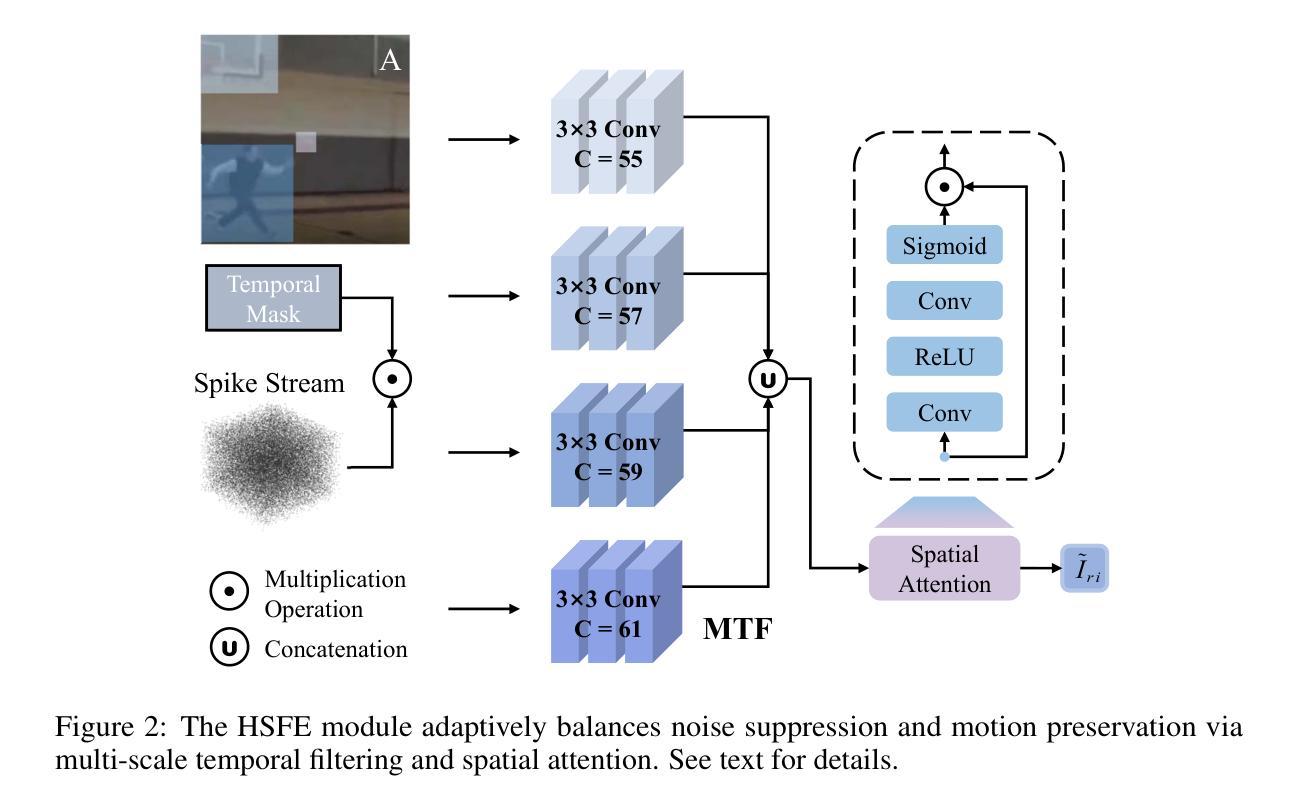
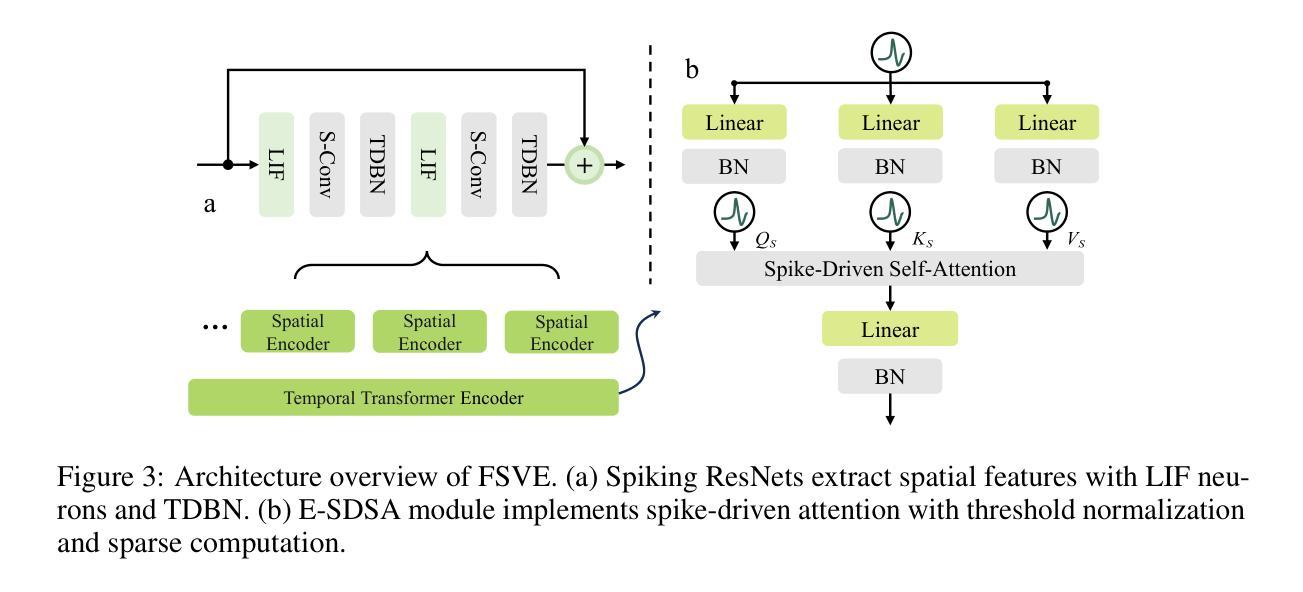
SPKLIP: Aligning Spike Video Streams with Natural Language
Authors:Yongchang Gao, Meiling Jin, Zhaofei Yu, Tiejun Huang, Guozhang Chen
Spike cameras offer unique sensing capabilities but their sparse, asynchronous output challenges semantic understanding, especially for Spike Video-Language Alignment (Spike-VLA) where models like CLIP underperform due to modality mismatch. We introduce SPKLIP, the first architecture specifically for Spike-VLA. SPKLIP employs a hierarchical spike feature extractor that adaptively models multi-scale temporal dynamics in event streams, and uses spike-text contrastive learning to directly align spike video with language, enabling effective few-shot learning. A full-spiking visual encoder variant, integrating SNN components into our pipeline, demonstrates enhanced energy efficiency. Experiments show state-of-the-art performance on benchmark spike datasets and strong few-shot generalization on a newly contributed real-world dataset. SPKLIP’s energy efficiency highlights its potential for neuromorphic deployment, advancing event-based multimodal research. The source code and dataset are available at [link removed for anonymity].
脉冲摄像头提供了独特的感知能力,但其稀疏、异步的输出给语义理解带来了挑战,特别是在脉冲视频语言对齐(Spike-VLA)方面,CLIP等模型由于模态不匹配而表现不佳。我们引入了专为Spike-VLA设计的第一个架构SPKLIP。SPKLIP采用分层脉冲特征提取器,自适应地模拟事件流中的多尺度时间动态,并使用脉冲文本对比学习直接对齐脉冲视频和语言,从而实现有效的少样本学习。一种全脉冲视觉编码器变体,将SNN组件集成到我们的流程中,展示了增强的能源效率。实验表明,在基准脉冲数据集上表现卓越,在新贡献的现实数据集上具有很强的少样本泛化能力。SPKLIP的能源效率凸显了其用于神经形态部署的潜力,推动了基于事件的多媒体研究的发展。源代码和数据集可在(为保密而删除的链接)获取。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了针对脉冲视频语言对齐(Spike-VLA)的新的架构SPKLIP。SPKLIP采用分层脉冲特征提取器,自适应地模拟事件流中的多尺度时间动态,并通过脉冲文本对比学习直接对齐脉冲视频和语言,从而实现有效的少样本学习。引入全脉冲视觉编码器变体,将脉冲神经网络组件集成到我们的管道中,提高了能效。实验表明,该模型在脉冲数据集上表现最佳,并在新贡献的真实世界数据集上实现了强大的少样本泛化能力。
Key Takeaways
- SPKLIP是针对脉冲视频语言对齐(Spike-VLA)的首个专门架构。
- SPKLIP使用分层脉冲特征提取器,该提取器能够自适应地模拟事件流中的多尺度时间动态。
- 通过脉冲文本对比学习,SPKLIP实现了脉冲视频与语言的直接对齐。
- SPKLIP支持有效的少样本学习。
- 全脉冲视觉编码器变体的引入提高了能效,显示出在神经形态部署中的潜力。
- 实验表明SPKLIP在脉冲数据集上表现最佳。
点此查看论文截图

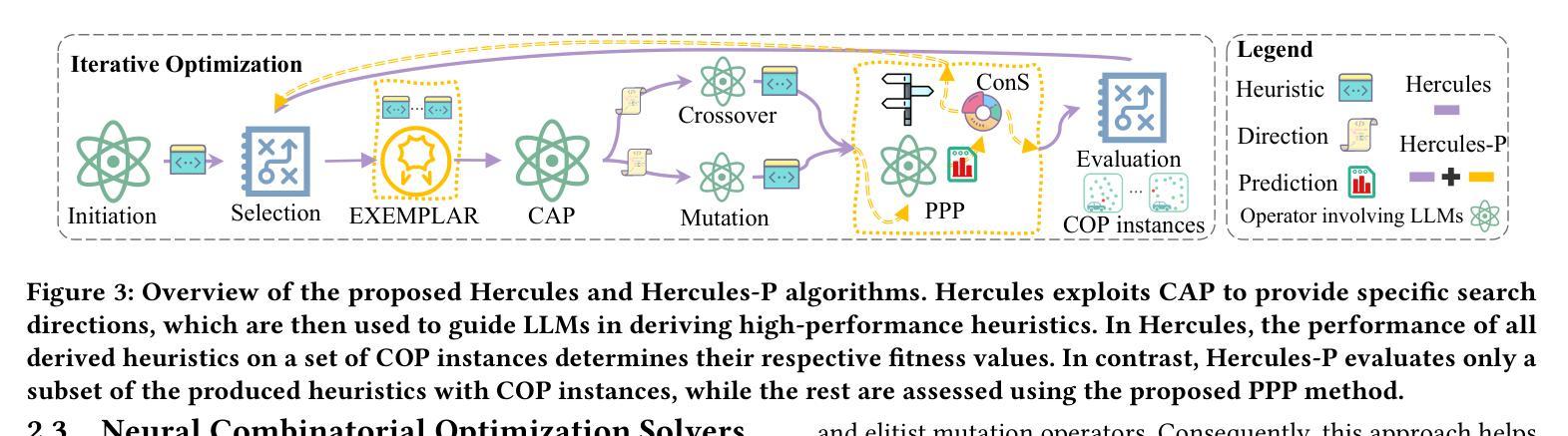
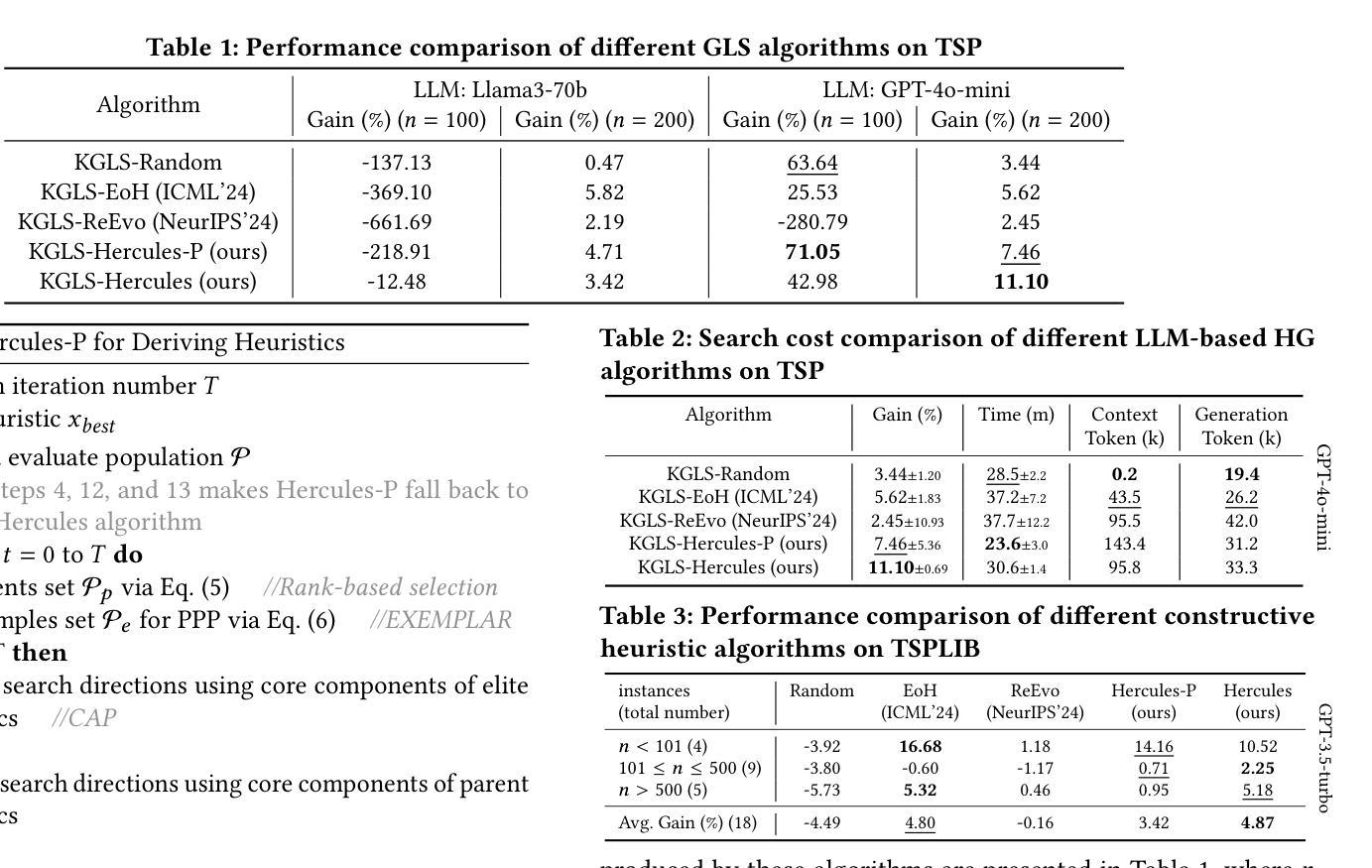
Efficient Heuristics Generation for Solving Combinatorial Optimization Problems Using Large Language Models
Authors:Xuan Wu, Di Wang, Chunguo Wu, Lijie Wen, Chunyan Miao, Yubin Xiao, You Zhou
Recent studies exploited Large Language Models (LLMs) to autonomously generate heuristics for solving Combinatorial Optimization Problems (COPs), by prompting LLMs to first provide search directions and then derive heuristics accordingly. However, the absence of task-specific knowledge in prompts often leads LLMs to provide unspecific search directions, obstructing the derivation of well-performing heuristics. Moreover, evaluating the derived heuristics remains resource-intensive, especially for those semantically equivalent ones, often requiring omissible resource expenditure. To enable LLMs to provide specific search directions, we propose the Hercules algorithm, which leverages our designed Core Abstraction Prompting (CAP) method to abstract the core components from elite heuristics and incorporate them as prior knowledge in prompts. We theoretically prove the effectiveness of CAP in reducing unspecificity and provide empirical results in this work. To reduce computing resources required for evaluating the derived heuristics, we propose few-shot Performance Prediction Prompting (PPP), a first-of-its-kind method for the Heuristic Generation (HG) task. PPP leverages LLMs to predict the fitness values of newly derived heuristics by analyzing their semantic similarity to previously evaluated ones. We further develop two tailored mechanisms for PPP to enhance predictive accuracy and determine unreliable predictions, respectively. The use of PPP makes Hercules more resource-efficient and we name this variant Hercules-P. Extensive experiments across four HG tasks, five COPs, and eight LLMs demonstrate that Hercules outperforms the state-of-the-art LLM-based HG algorithms, while Hercules-P excels at minimizing required computing resources. In addition, we illustrate the effectiveness of CAP, PPP, and the other proposed mechanisms by conducting relevant ablation studies.
最近的研究利用大型语言模型(LLM)自主生成解决组合优化问题(COP)的启发式方法,通过提示LLM首先提供搜索方向,然后据此推导启发式。然而,提示中缺乏特定任务的知识往往导致LLM提供非特定的搜索方向,阻碍推导高性能的启发式方法。此外,评估推导出的启发式方法仍然需要消耗大量资源,特别是对于语义等价的方法,通常需要大量的资源支出。为了使LLM能够提供特定的搜索方向,我们提出了赫拉克斯算法(Hercules),该算法利用我们设计的核心抽象提示法(CAP),从优秀启发式方法中提取核心组件并将其作为先验知识纳入提示中。我们从理论上证明了CAP在减少非特异性方面的有效性,并在本文中提供了实证结果。为了降低评估派生启发式方法所需的计算资源,我们提出了开创性的性能预测提示法(PPP),这是启发式生成任务中的一种新方法。PPP利用LLM通过分析其与已评估启发式方法的语义相似性来预测新派生启发式方法的适应度值。我们进一步为PPP开发了两个定制机制,分别用于提高预测精度和确定不可靠的预测。PPP的使用使赫拉克斯算法更加高效,我们将这种变体命名为赫拉克斯-P。在四个启发式生成任务、五个组合优化问题和八个大型语言模型上进行的广泛实验表明,赫拉克斯算法优于最新的基于大型语言模型的HG算法,而赫拉克斯-P则擅长最小化所需的计算资源。此外,我们通过进行相关的消融研究,说明了核心抽象提示法(CAP)、性能预测提示法(PPP)以及其他提议机制的有效性。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by SIGKDD 2025
Summary
本文研究了利用大型语言模型(LLMs)自主生成解决组合优化问题(COPs)的启发式方法。针对LLMs在提供搜索方向时缺乏任务特定知识的问题,提出了Heracles算法,该算法通过设计核心抽象提示(CAP)方法,从优秀启发式中提取核心组件,并将其作为先验知识融入提示中,从而减少非特异性。为减少评估衍生启发式所需的计算资源,本文首次提出了性能预测提示(PPP)方法,通过语义相似性预测新启发式的适应度值。通过广泛的实验和消融研究,证明Heracles及其改进版Heracles-P在效率和性能上的优越性。
Key Takeaways
- 大型语言模型(LLMs)被用于自主生成解决组合优化问题(COPs)的启发式方法。
- LLMs在提供搜索方向时因缺乏任务特定知识而面临挑战。
- 提出了Heracles算法,通过核心抽象提示(CAP)方法融入优秀启发式中的核心组件作为先验知识。
- CAP理论上减少了非特异性,并通过实验证明了其有效性。
- 为减少评估衍生启发式所需的计算资源,首次提出了性能预测提示(PPP)方法。
- PPP通过语义相似性预测新启发式的适应度值,提高了Heracles的资源效率,形成了Heracles-P。
点此查看论文截图



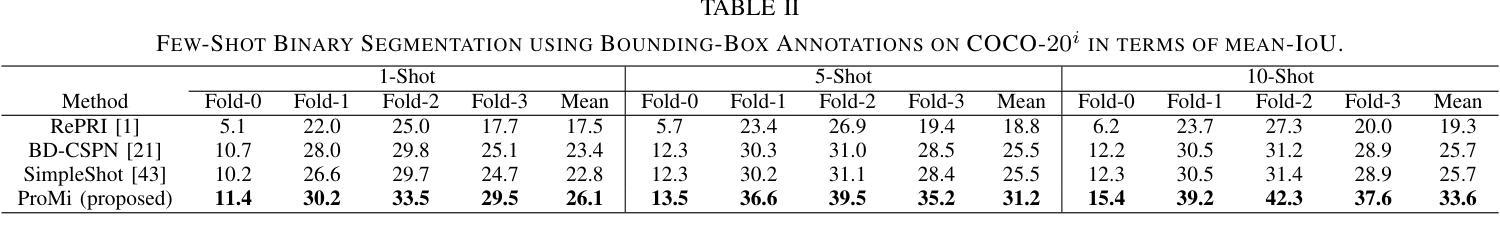
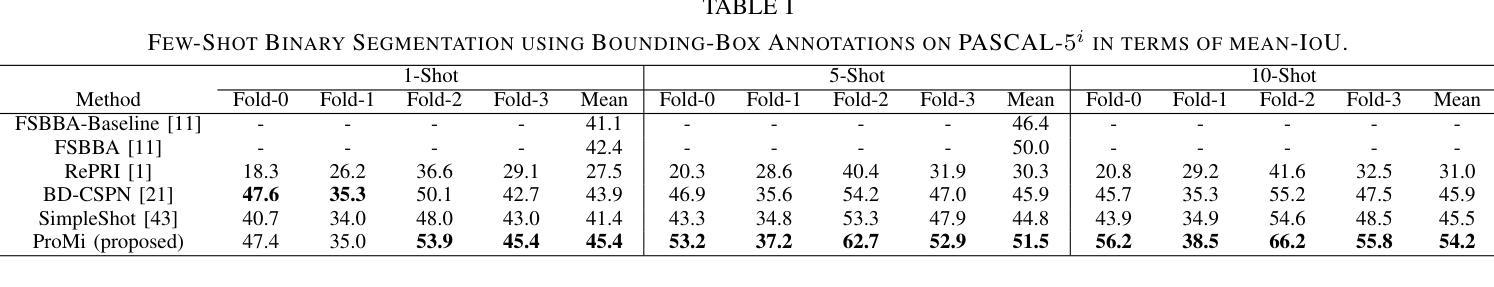
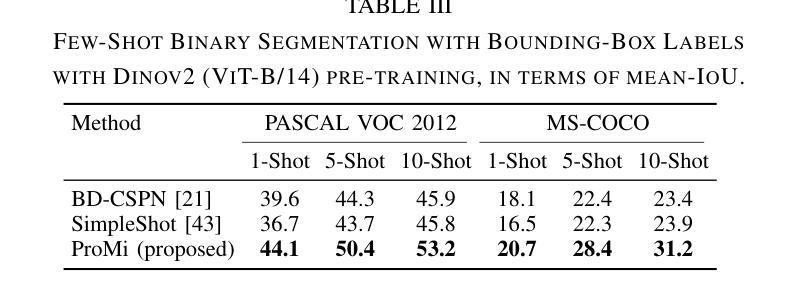
ProMi: An Efficient Prototype-Mixture Baseline for Few-Shot Segmentation with Bounding-Box Annotations
Authors:Florent Chiaroni, Ali Ayub, Ola Ahmad
In robotics applications, few-shot segmentation is crucial because it allows robots to perform complex tasks with minimal training data, facilitating their adaptation to diverse, real-world environments. However, pixel-level annotations of even small amount of images is highly time-consuming and costly. In this paper, we present a novel few-shot binary segmentation method based on bounding-box annotations instead of pixel-level labels. We introduce, ProMi, an efficient prototype-mixture-based method that treats the background class as a mixture of distributions. Our approach is simple, training-free, and effective, accommodating coarse annotations with ease. Compared to existing baselines, ProMi achieves the best results across different datasets with significant gains, demonstrating its effectiveness. Furthermore, we present qualitative experiments tailored to real-world mobile robot tasks, demonstrating the applicability of our approach in such scenarios. Our code: https://github.com/ThalesGroup/promi.
在机器人应用中,小样分割(few-shot segmentation)至关重要,因为它允许机器人在少量训练数据的情况下执行复杂的任务,促进其适应多样化的现实世界环境。然而,即使是少量图像的像素级注释也是极其耗时和昂贵的。在本文中,我们提出了一种基于边界框注释的新型小样二进制分割方法,而不是像素级标签。我们介绍了ProMi,这是一种基于原型混合的有效方法,它将背景类视为分布的混合物。我们的方法简单、无需训练且有效,可以轻松适应粗略注释。与现有基线相比,ProMi在不同数据集上取得了最佳结果,并显示出显著的收益,证明了其有效性。此外,我们还针对现实世界中的移动机器人任务进行了定制定性实验,展示了我们的方法在此类场景中的应用性。我们的代码:https://github.com/ThalesGroup/promi。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
该论文提出了一种基于边界框标注的新型少样本二元分割方法ProMi,用于机器人应用中。该方法解决了像素级标注耗时耗力的问题,通过将背景类视为混合分布来实现训练免费的简单有效方法,能轻松适应粗略标注。实验表明,相较于现有基线方法,ProMi在不同数据集上取得了最佳效果,尤其在真实世界移动机器人任务中的应用展示了其适用性。
Key Takeaways
- 该论文提出了一种基于边界框标注的少样本二元分割方法ProMi,适用于机器人应用。
- ProMi解决了像素级标注成本高和耗时的问题。
- ProMi通过将背景类视为混合分布来实现其方法。
- ProMi是简单且训练免费的,并能轻松适应粗略标注。
- ProMi相较于现有方法在多个数据集上取得了最佳效果。
- 该方法特别适用于真实世界的移动机器人任务。
点此查看论文截图

Relation Extraction or Pattern Matching? Unravelling the Generalisation Limits of Language Models for Biographical RE
Authors:Varvara Arzt, Allan Hanbury, Michael Wiegand, Gábor Recski, Terra Blevins
Analysing the generalisation capabilities of relation extraction (RE) models is crucial for assessing whether they learn robust relational patterns or rely on spurious correlations. Our cross-dataset experiments find that RE models struggle with unseen data, even within similar domains. Notably, higher intra-dataset performance does not indicate better transferability, instead often signaling overfitting to dataset-specific artefacts. Our results also show that data quality, rather than lexical similarity, is key to robust transfer, and the choice of optimal adaptation strategy depends on the quality of data available: while fine-tuning yields the best cross-dataset performance with high-quality data, few-shot in-context learning (ICL) is more effective with noisier data. However, even in these cases, zero-shot baselines occasionally outperform all cross-dataset results. Structural issues in RE benchmarks, such as single-relation per sample constraints and non-standardised negative class definitions, further hinder model transferability.
关系抽取(RE)模型的一般化能力分析对于评估模型是学会稳健的关系模式,还是依赖于偶然的关联至关重要。我们的跨数据集实验发现,RE模型在处理未见过的数据时面临困难,即使在类似的领域内也是如此。值得注意的是,较高的数据集内部性能并不表明更好的可转移性,反而通常表明对特定数据集的过度拟合。我们的结果还表明,数据质量而非词汇相似性才是实现稳健转移的关键,而最佳适应策略的选择取决于可用的数据质量:虽然在高质量数据的情况下,微调(fine-tuning)提供了最佳跨数据集性能,但在噪声数据的情况下,以少数样本进行上下文学习(ICL)更加有效。然而,即使在这种情况下,零射击(zero-shot)基线有时超过了所有跨数据集的结果。RE基准测试中的结构性问题(如每个样本的单关系约束和非标准化的负类定义)进一步阻碍了模型的可迁移性。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary:关系抽取模型(RE)的泛化能力对于评估模型是否学习稳健的关系模式至关重要。研究发现RE模型在处理未见数据时存在困难,且高数据集内部性能并不一定意味着良好的迁移能力。数据质量对稳健迁移至关重要,最佳适应策略的选择取决于可用数据的质量。此外,结构问题如RE基准测试中的单一关系样本限制和非标准化负面类别定义进一步阻碍模型的可迁移性。
Key Takeaways:
- 关系抽取模型在未见数据上表现不佳,泛化能力有待提高。
- 高数据集内部性能并不保证良好的跨数据集迁移能力,可能存在过拟合现象。
- 数据质量对模型稳健迁移至关重要,优质数据更适合精细调整模型。
- 噪声数据更适合采用少量上下文学习(ICL)策略。
- 零样本基线在某些情况下表现最佳,超出所有跨数据集结果。
- RE基准测试存在结构问题,如单一关系样本限制和非标准化负面类别定义。
点此查看论文截图

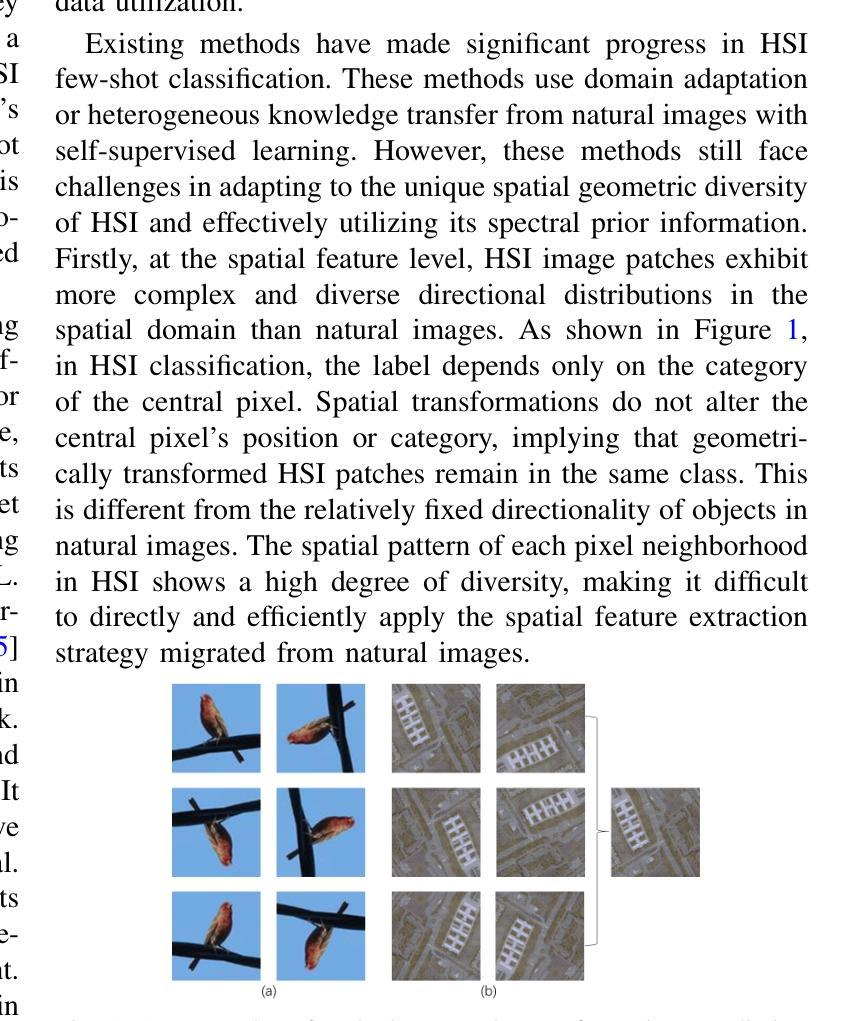
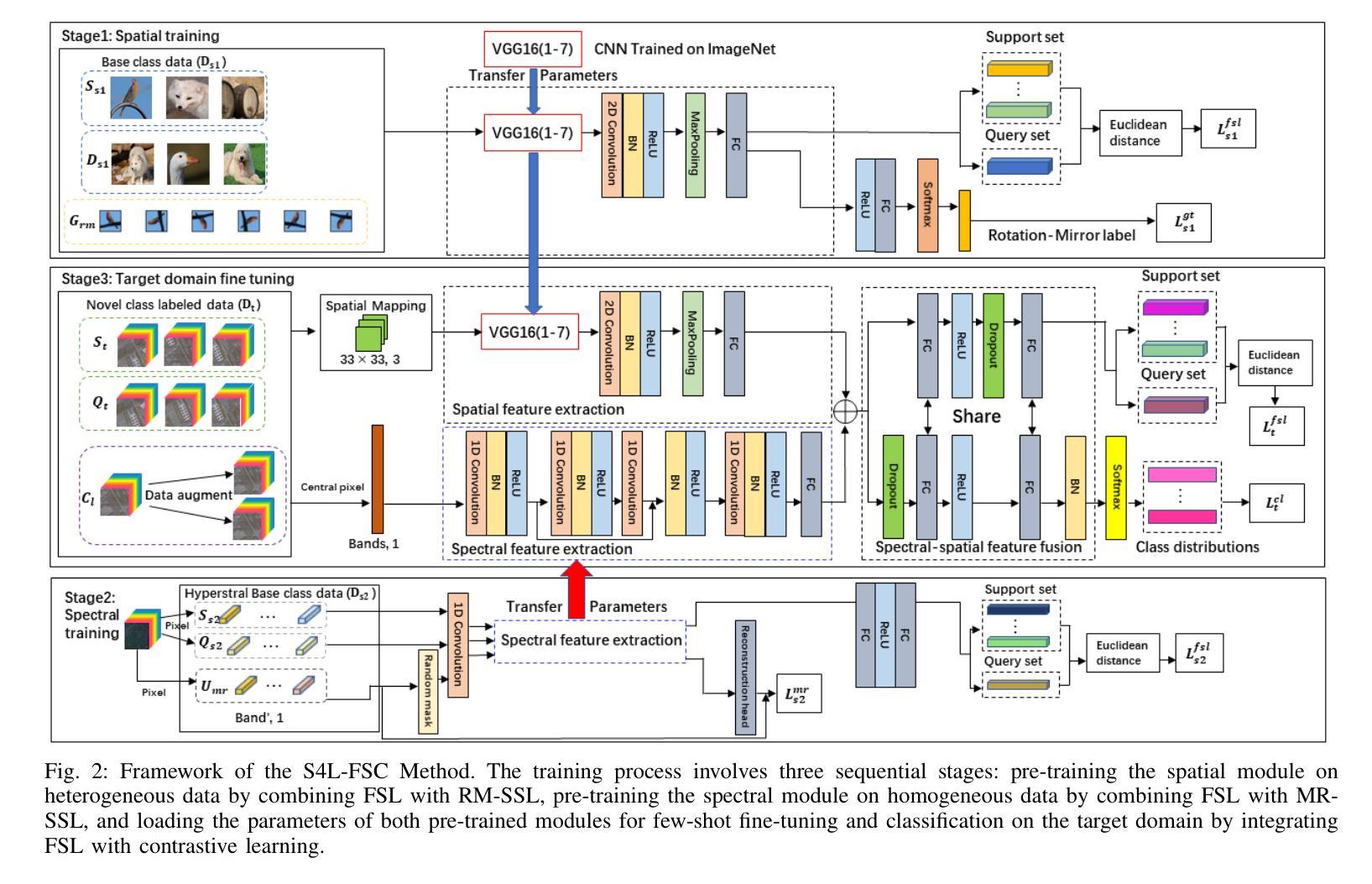
Spectral-Spatial Self-Supervised Learning for Few-Shot Hyperspectral Image Classification
Authors:Wenchen Chen, Yanmei Zhang, Zhongwei Xiao, Jianping Chu, Xingbo Wang
Few-shot classification of hyperspectral images (HSI) faces the challenge of scarce labeled samples. Self-Supervised learning (SSL) and Few-Shot Learning (FSL) offer promising avenues to address this issue. However, existing methods often struggle to adapt to the spatial geometric diversity of HSIs and lack sufficient spectral prior knowledge. To tackle these challenges, we propose a method, Spectral-Spatial Self-Supervised Learning for Few-Shot Hyperspectral Image Classification (S4L-FSC), aimed at improving the performance of few-shot HSI classification. Specifically, we first leverage heterogeneous datasets to pretrain a spatial feature extractor using a designed Rotation-Mirror Self-Supervised Learning (RM-SSL) method, combined with FSL. This approach enables the model to learn the spatial geometric diversity of HSIs using rotation and mirroring labels as supervisory signals, while acquiring transferable spatial meta-knowledge through few-shot learning. Subsequently, homogeneous datasets are utilized to pretrain a spectral feature extractor via a combination of FSL and Masked Reconstruction Self-Supervised Learning (MR-SSL). The model learns to reconstruct original spectral information from randomly masked spectral vectors, inferring spectral dependencies. In parallel, FSL guides the model to extract pixel-level discriminative features, thereby embedding rich spectral priors into the model. This spectral-spatial pretraining method, along with the integration of knowledge from heterogeneous and homogeneous sources, significantly enhances model performance. Extensive experiments on four HSI datasets demonstrate the effectiveness and superiority of the proposed S4L-FSC approach for few-shot HSI classification.
高光谱图像(HSI)的few-shot分类面临的一个挑战是标注样本稀缺。自监督学习(SSL)和few-shot学习(FSL)为解决这一问题提供了有前景的途径。然而,现有的方法往往难以适应高光谱图像的空间几何多样性,并且缺乏足够的谱先验知识。为了应对这些挑战,我们提出了一种针对高光谱图像few-shot分类的方法,名为谱空间自监督学习(Spectral-Spatial Self-Supervised Learning for Few-Shot Hyperspectral Image Classification,简称S4L-FSC),旨在提高few-shot HSI分类的性能。具体来说,我们首先利用异质数据集预训练一个空间特征提取器,采用设计的旋转镜像自监督学习方法(RM-SSL)与few-shot学习相结合。这种方法使模型能够利用旋转和镜像标签作为监督信号来学习高光谱图像的空间几何多样性,同时通过few-shot学习获得可转移的空间元知识。然后,使用同质数据集预训练一个谱特征提取器,结合few-shot学习和掩码重建自监督学习(MR-SSL)。模型学习从随机掩码的谱向量中重建原始谱信息,推断谱依赖性。同时,few-shot学习指导模型提取像素级别的判别特征,从而将丰富的谱先验嵌入模型中。这种谱空间预训练方法,以及来自异质和同质源的知识的整合,显著提高了模型的性能。在四个HSI数据集上的广泛实验证明了所提出的S4L-FSC方法在few-shot HSI分类中的有效性和优越性。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF https://github.com/Wenchen-Chen/S4L-FSC
Summary
该文本介绍了针对高光谱图像(HSI)的少量样本分类问题,通过结合自监督学习(SSL)和少量学习(FSL)方法提出的一种新的解决方案——光谱空间自监督学习用于少量高光谱图像分类(S4L-FSC)。该方法通过利用异质数据集进行空间特征提取器的预训练,并结合旋转镜像自监督学习和少量学习,使模型学会高光谱图像的空间几何多样性。接着使用同质数据集进行光谱特征提取器的预训练,结合少量学习和掩膜重建自监督学习,使模型学习重建原始光谱信息并提取像素级判别特征。通过整合来自异质和同质来源的知识,S4L-FSC方法能显著提高模型性能,在四个HSI数据集上的实验证明了其有效性和优越性。
Key Takeaways
- 面对高光谱图像(HSI)的少量样本分类挑战,自监督学习(SSL)和少量学习(FSL)是有效的解决方法。
- 现有方法往往难以适应HSIs的空间几何多样性,缺乏足够的谱先验知识。
- 提出的S4L-FSC方法通过结合空间特征提取和谱特征提取,旨在提高少样本HSI分类的性能。
- 利用异质数据集进行空间特征提取器的预训练,结合旋转镜像自监督学习和少量学习,使模型学会空间几何多样性。
- 利用同质数据集进行光谱特征提取器的预训练,结合少量学习和掩膜重建自监督学习,使模型学习重建原始光谱信息和提取像素级判别特征。
- S4L-FSC方法整合来自异质和同质来源的知识,显著提高模型性能。
点此查看论文截图

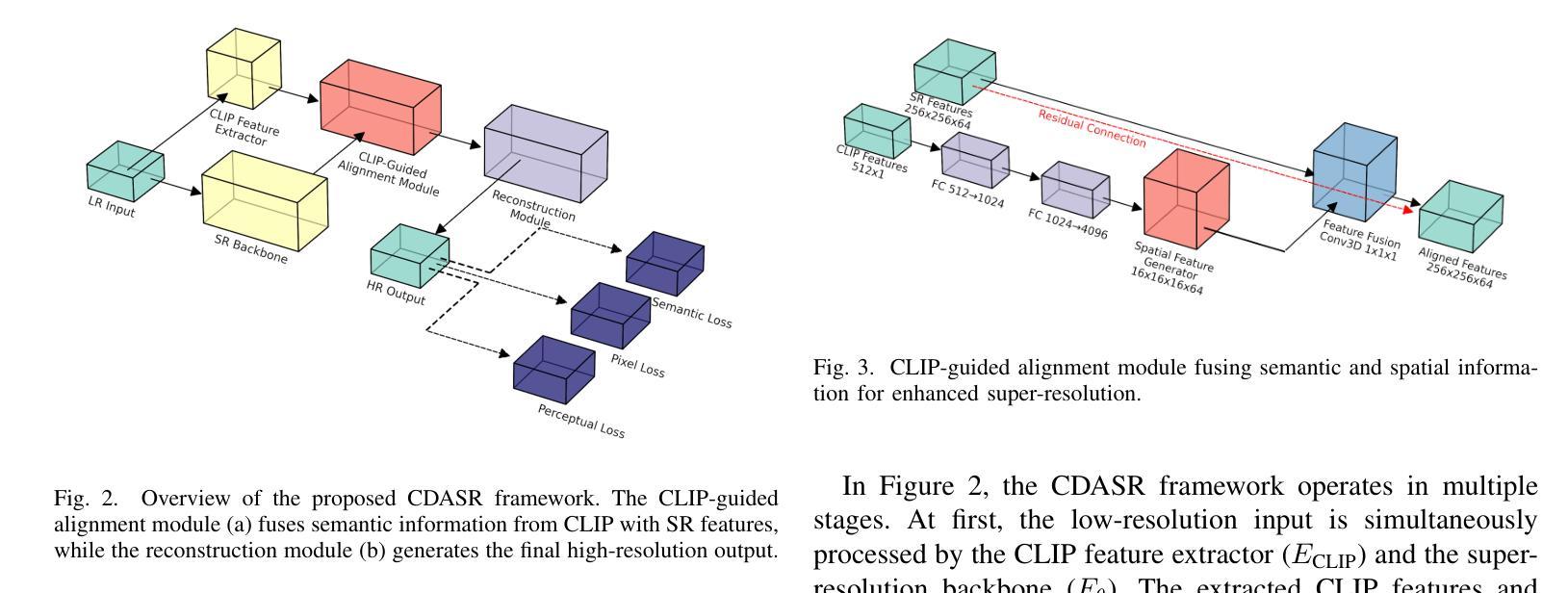
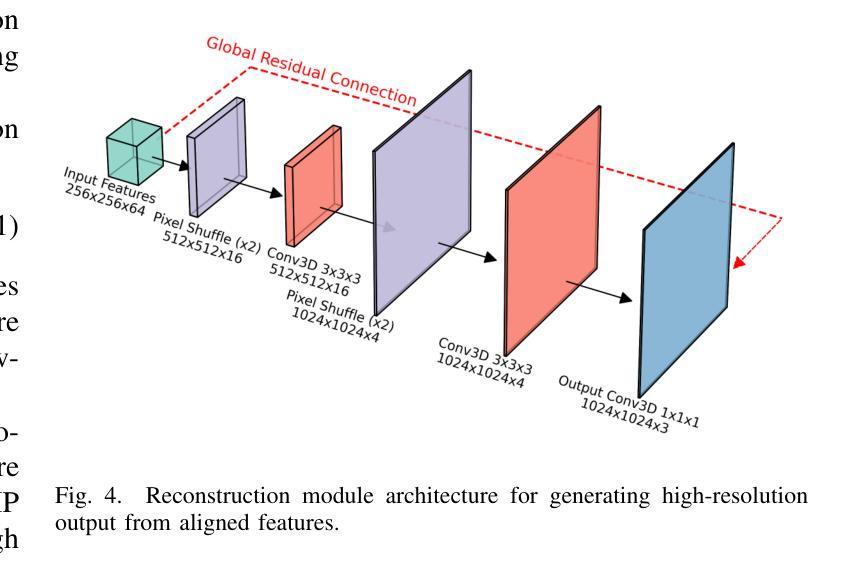
CLIP-aware Domain-Adaptive Super-Resolution
Authors:Zhengyang Lu, Qian Xia, Weifan Wang, Feng Wang
This work introduces CLIP-aware Domain-Adaptive Super-Resolution (CDASR), a novel framework that addresses the critical challenge of domain generalization in single image super-resolution. By leveraging the semantic capabilities of CLIP (Contrastive Language-Image Pre-training), CDASR achieves unprecedented performance across diverse domains and extreme scaling factors. The proposed method integrates CLIP-guided feature alignment mechanism with a meta-learning inspired few-shot adaptation strategy, enabling efficient knowledge transfer and rapid adaptation to target domains. A custom domain-adaptive module processes CLIP features alongside super-resolution features through a multi-stage transformation process, including CLIP feature processing, spatial feature generation, and feature fusion. This intricate process ensures effective incorporation of semantic information into the super-resolution pipeline. Additionally, CDASR employs a multi-component loss function that combines pixel-wise reconstruction, perceptual similarity, and semantic consistency. Extensive experiments on benchmark datasets demonstrate CDASR’s superiority, particularly in challenging scenarios. On the Urban100 dataset at $\times$8 scaling, CDASR achieves a significant PSNR gain of 0.15dB over existing methods, with even larger improvements of up to 0.30dB observed at $\times$16 scaling.
本文介绍了CLIP感知域自适应超分辨率(CDASR)这一新型框架,该框架解决了单图像超分辨率领域中的域泛化这一关键挑战。通过利用CLIP(对比语言图像预训练)的语义能力,CDASR在不同域和极端缩放因子上实现了前所未有的性能。所提出的方法将CLIP引导的特征对齐机制与受元学习启发的少样本自适应策略相结合,实现了高效的知识转移和快速适应目标域。一个定制的域自适应模块通过多阶段转换过程处理CLIP特征和超分辨率特征,包括CLIP特征处理、空间特征生成和特征融合。这一精细的过程确保了语义信息有效地融入超分辨率管道。此外,CDASR采用多组件损失函数,结合了像素级的重建、感知相似性和语义一致性。在基准数据集上的大量实验证明了CDASR的优越性,特别是在具有挑战性的场景中。在Urban100数据集上,以×8的缩放比例,CDASR较现有方法实现了0.15dB的PSNR增益,而在×16的缩放比例下,甚至观察到了高达0.30dB的更大改进。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
该工作提出了CLIP感知域自适应超分辨率(CDASR)框架,解决了单图像超分辨率中的域泛化问题。结合CLIP(对比语言图像预训练)的语义能力,CDASR在不同域和极端缩放因子上实现了前所未有的性能。该框架通过CLIP引导的特征对齐机制和元学习驱动的小样本自适应策略,实现了高效的知识转移和快速适应目标域的能力。多阶段转换过程包括CLIP特征处理、空间特征生成和特征融合,确保语义信息有效地融入超分辨率管道中。此外,CDASR采用多组件损失函数,结合像素级重建、感知相似性和语义一致性。在基准数据集上的实验表明,CDASR在具有挑战性的场景中表现卓越,特别是在Urban100数据集上放大八倍时,与现有方法相比,PSNR增益提高了高达0.15dB。在放大倍数更高时,如放大十六倍时,其性能提升更大。
Key Takeaways
- CLIP感知域自适应超分辨率(CDASR)框架解决了单图像超分辨率中的域泛化挑战。
- 利用CLIP的语义能力实现跨不同域的出色性能。
- 通过CLIP引导的特征对齐和元学习驱动的小样本自适应策略实现快速适应目标域。
- 多阶段转换过程确保语义信息融入超分辨率处理中。
- 采用多组件损失函数,平衡像素级重建、感知相似性和语义一致性。
- 在基准数据集上的实验证明CDASR在挑战性的场景中表现优越。
点此查看论文截图


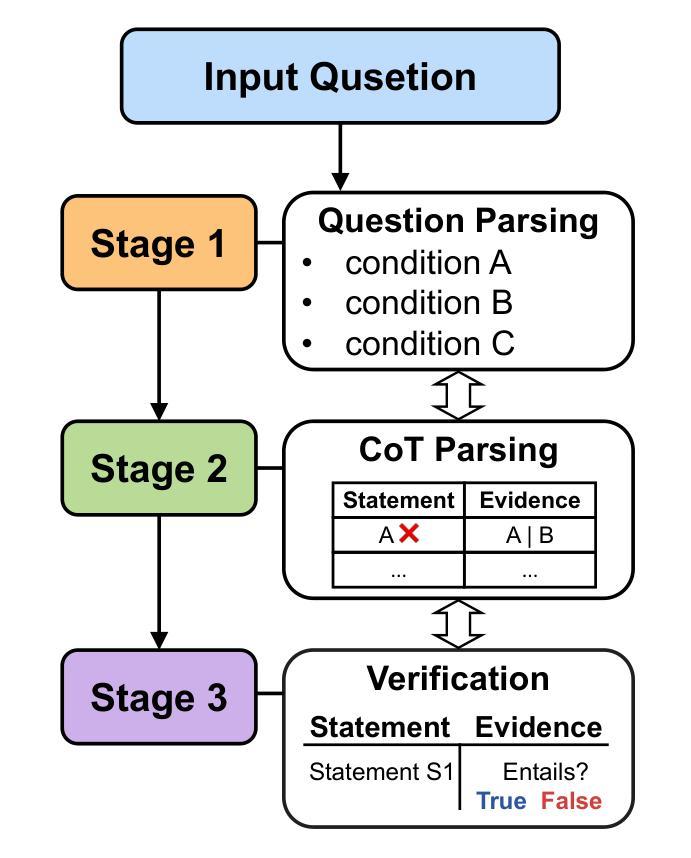
LLMSR@XLLM25: An Empirical Study of LLM for Structural Reasoning
Authors:Xinye Li, Mingqi Wan, Dianbo Sui
We present Team asdfo123’s submission to the LLMSR@XLLM25 shared task, which evaluates large language models on producing fine-grained, controllable, and interpretable reasoning processes. Systems must extract all problem conditions, decompose a chain of thought into statement-evidence pairs, and verify the logical validity of each pair. Leveraging only the off-the-shelf Meta-Llama-3-8B-Instruct, we craft a concise few-shot, multi-turn prompt that first enumerates all conditions and then guides the model to label, cite, and adjudicate every reasoning step. A lightweight post-processor based on regular expressions normalises spans and enforces the official JSON schema. Without fine-tuning, external retrieval, or ensembling, our method ranks 5th overall, achieving macro F1 scores on par with substantially more complex and resource-consuming pipelines. We conclude by analysing the strengths and limitations of our approach and outlining directions for future research in structural reasoning with LLMs. Our code is available at https://github.com/asdfo123/LLMSR-asdfo123.
我们在此介绍Team asdfo123在LLMSR@XLLM25共享任务中的提交内容。该任务旨在评估大型语言模型在生成精细、可控、可解释推理过程方面的能力。系统必须提取所有问题条件,将思维链条分解成陈述-证据对,并验证每对逻辑的有效性。我们仅利用现成的Meta-Llama-3-8B-Instruct,设计了一个简洁的少量多轮提示,首先列举所有条件,然后引导模型对每一步进行标注、引用和裁决。基于正则表达式的轻量级后处理器用于标准化跨度并强制执行官方JSON模式。我们的方法无需微调、外部检索或集成,总体排名第五,宏观F1分数与更复杂和资源密集型的管道相当。最后,我们分析了我们方法的优点和局限性,并概述了未来在结构推理中使用大型语言模型的研究方向。我们的代码可在https://github.com/asdfo123/LLMSR-asdfo123找到。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
团队asdfo123在LLMSR@XLLM25共享任务中的提交内容,展示了大型语言模型在生成精细粒度、可控且可解释推理过程方面的评估。团队利用现成的Meta-Llama-3-8B-Instruct模型,通过简洁的少量多轮提示,列举所有条件,并指导模型对每一步推理进行标注、引用和裁决。基于正则表达式轻量级后处理器对跨度进行标准化并强制执行官方JSON模式。无需微调、外部检索或集成技术,该方法总体排名第五,宏观F1分数与更复杂和资源密集型的管道相当。
Key Takeaways
- 团队asdfo123在LLMSR@XLLM25任务中展示了其使用大型语言模型的推理能力。
- 他们利用Meta-Llama-3-8B-Instruct模型,通过少量多轮提示进行推理。
- 系统必须提取问题条件,分解思维链成语句证据对,并验证每对的逻辑有效性。
- 团队使用基于正则表达式的轻量级后处理器来标准化输出并遵守官方JSON模式。
- 该方法无需微调、外部检索或集成技术,总体排名第五。
- 宏观F1分数显示,该方法性能与更复杂的管道相当。
点此查看论文截图

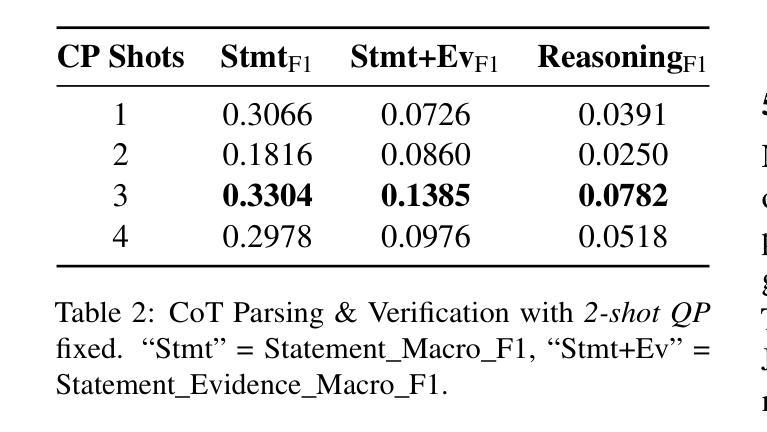
Bridging Generative and Discriminative Learning: Few-Shot Relation Extraction via Two-Stage Knowledge-Guided Pre-training
Authors:Quanjiang Guo, Jinchuan Zhang, Sijie Wang, Ling Tian, Zhao Kang, Bin Yan, Weidong Xiao
Few-Shot Relation Extraction (FSRE) remains a challenging task due to the scarcity of annotated data and the limited generalization capabilities of existing models. Although large language models (LLMs) have demonstrated potential in FSRE through in-context learning (ICL), their general-purpose training objectives often result in suboptimal performance for task-specific relation extraction. To overcome these challenges, we propose TKRE (Two-Stage Knowledge-Guided Pre-training for Relation Extraction), a novel framework that synergistically integrates LLMs with traditional relation extraction models, bridging generative and discriminative learning paradigms. TKRE introduces two key innovations: (1) leveraging LLMs to generate explanation-driven knowledge and schema-constrained synthetic data, addressing the issue of data scarcity; and (2) a two-stage pre-training strategy combining Masked Span Language Modeling (MSLM) and Span-Level Contrastive Learning (SCL) to enhance relational reasoning and generalization. Together, these components enable TKRE to effectively tackle FSRE tasks. Comprehensive experiments on benchmark datasets demonstrate the efficacy of TKRE, achieving new state-of-the-art performance in FSRE and underscoring its potential for broader application in low-resource scenarios. \footnote{The code and data are released on https://github.com/UESTC-GQJ/TKRE.
面向小样本关系抽取(FSRE)依然是一个充满挑战的任务,原因在于标注数据的稀缺以及现有模型的泛化能力有限。尽管大型语言模型(LLM)通过上下文学习(ICL)在FSRE中显示出潜力,但它们的一般性训练目标往往导致针对特定任务的关系抽取性能不佳。为了克服这些挑战,我们提出了TKRE(关系抽取的两阶段知识引导预训练),这是一个整合LLM和传统关系抽取模型的新型框架,融合了生成式和判别式学习范式。TKRE引入了两个关键创新点:(1)利用LLM生成解释驱动的知识和模式约束的合成数据,解决数据稀缺的问题;(2)结合掩码跨度语言建模(MSLM)和跨度级别对比学习(SCL)的两阶段预训练策略,以增强关系推理和泛化能力。这些组件共同作用,使TKRE能够有效应对FSRE任务。在基准数据集上进行的综合实验证明了TKRE的有效性,取得了FSRE的最新 state-of-the-art 性能,并突显了其在低资源场景中的更广泛应用潜力。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 13 pages, 6 figures, Appear on IJCAI 2025
Summary
该文本提出了一种名为TKRE的新的关系提取框架,它通过整合大型语言模型与传统关系提取模型,克服了数据稀缺和模型泛化能力有限的挑战。TKRE引入了两项关键创新:利用大型语言模型生成解释驱动的知识和模式约束的合成数据,以及结合遮罩跨度语言建模和跨度级别对比学习的两阶段预训练策略。这些组件共同使TKRE能够有效解决少量射击关系提取任务,并在基准数据集上实现了新的最先进的性能。
Key Takeaways
- TKRE是一个新的关系提取框架,结合了大型语言模型与传统关系提取模型的优点。
- LLMs在TKRE中用于生成解释驱动的知识和模式约束的合成数据,以解决数据稀缺问题。
- TKRE采用两阶段预训练策略,包括遮罩跨度语言建模和跨度级别对比学习。
- 这些策略增强了TKRE的关系推理和泛化能力。
- TKRE在基准数据集上实现了新的最先进的性能,表明其在少量射击关系提取任务中的有效性。
- TKRE的潜在应用不仅限于关系提取,还可应用于低资源场景中的更广泛任务。
点此查看论文截图

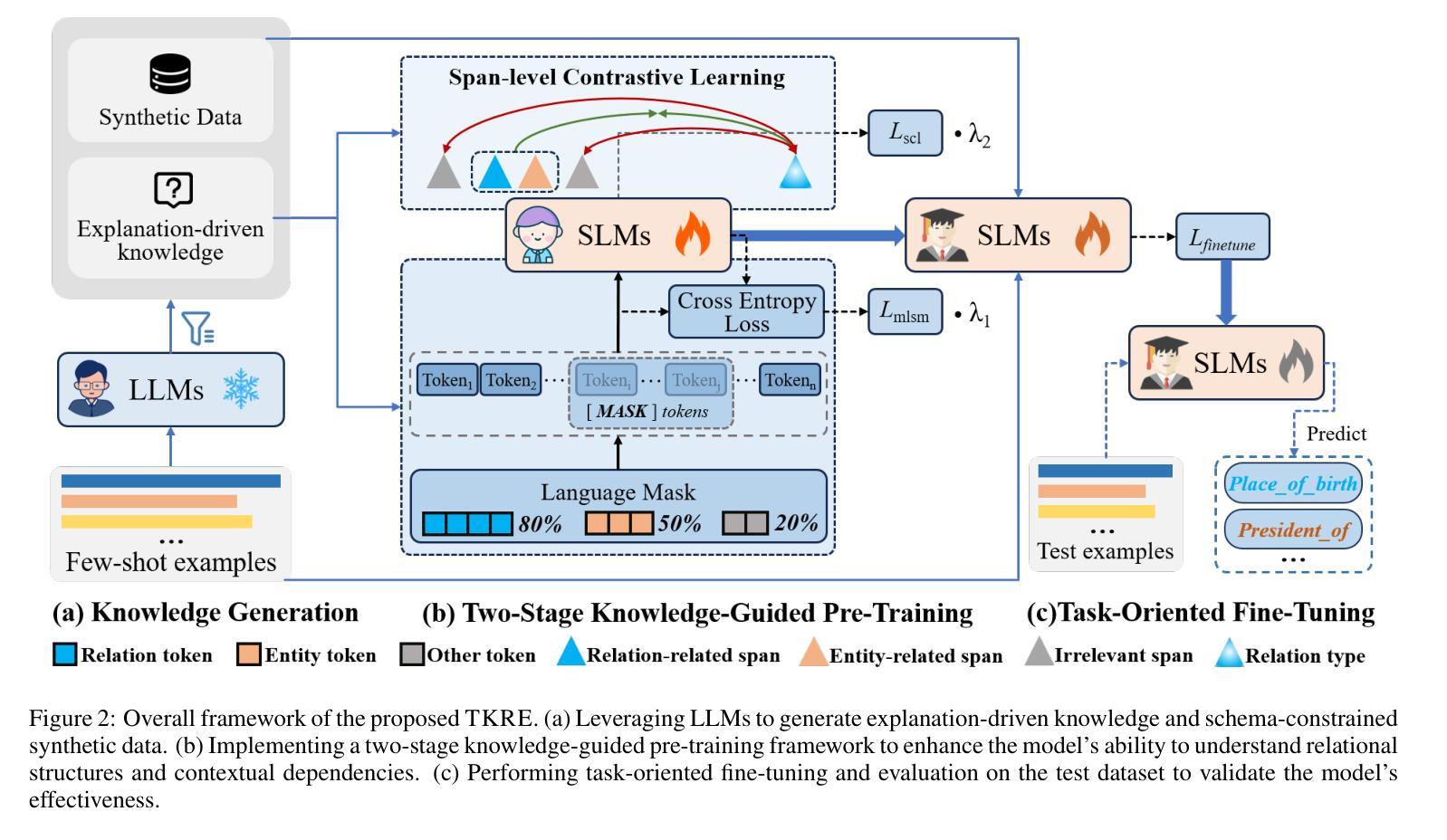


Data Whisperer: Efficient Data Selection for Task-Specific LLM Fine-Tuning via Few-Shot In-Context Learning
Authors:Shaobo Wang, Ziming Wang, Xiangqi Jin, Jize Wang, Jiajun Zhang, Kaixin Li, Zichen Wen, Zhong Li, Conghui He, Xuming Hu, Linfeng Zhang
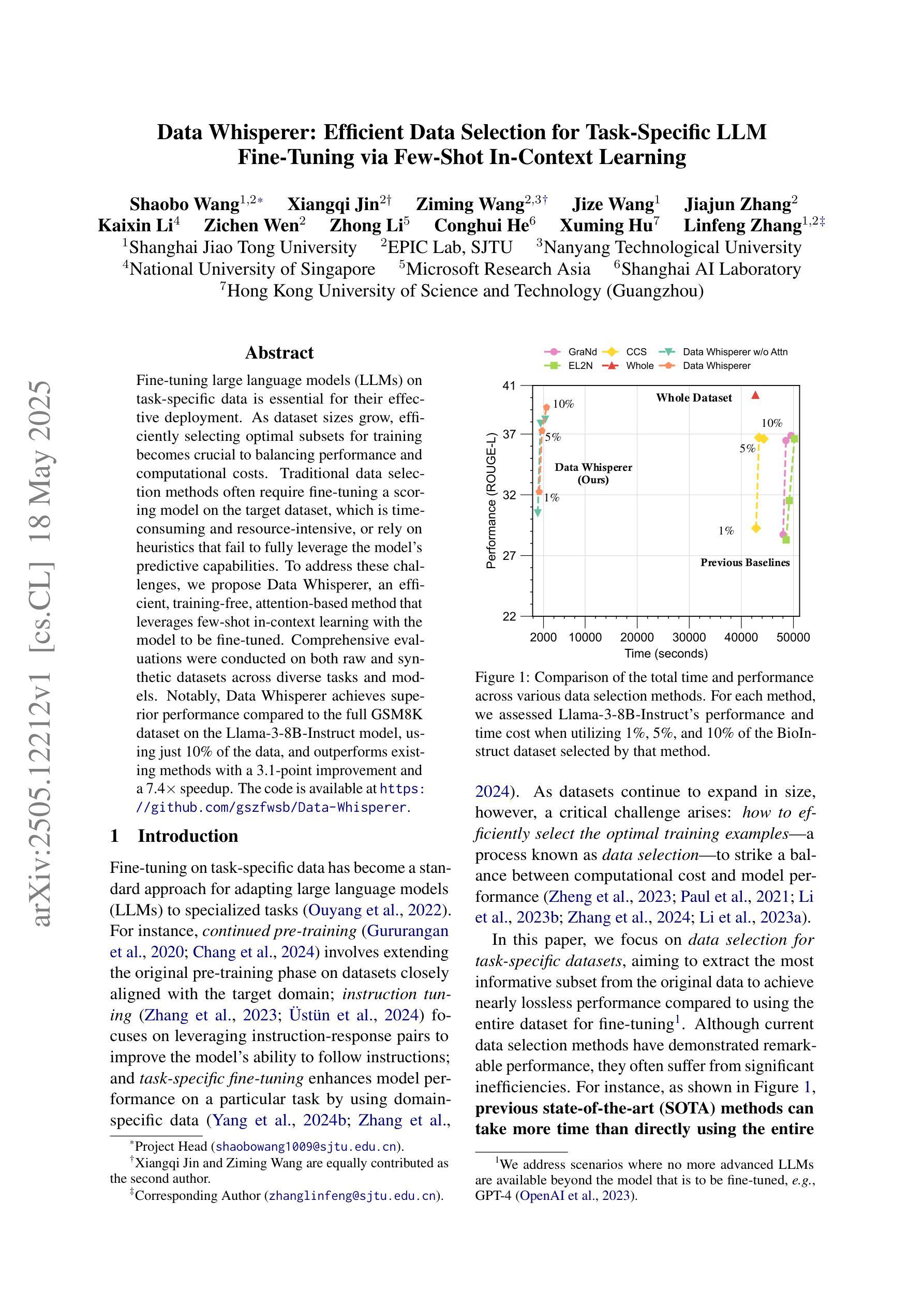
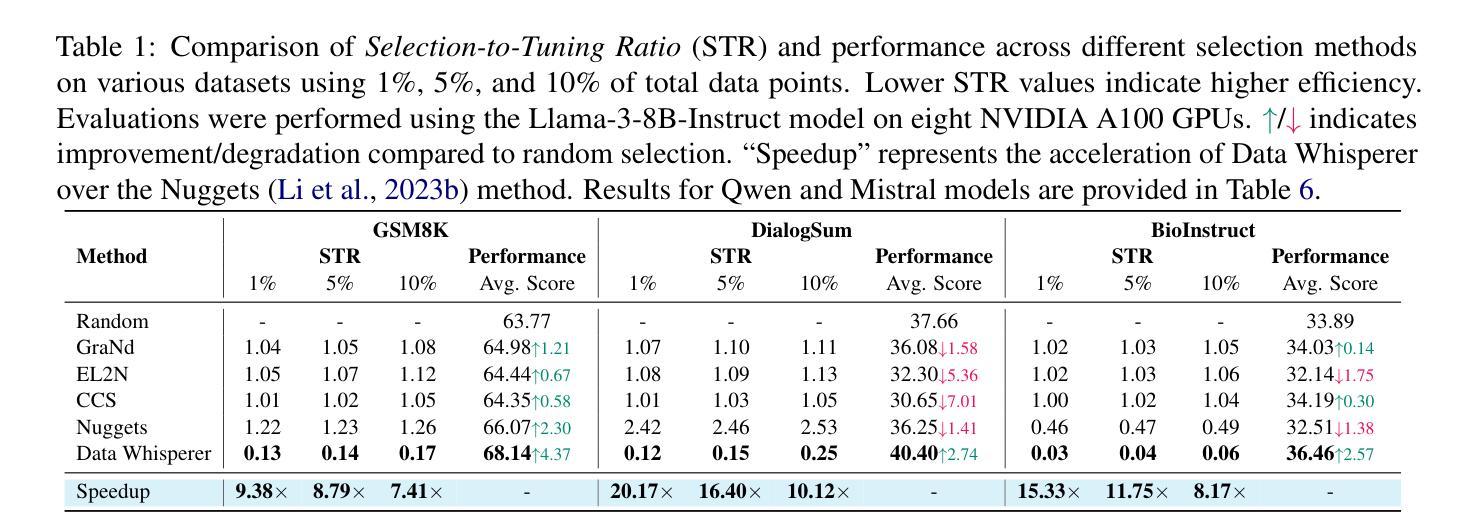
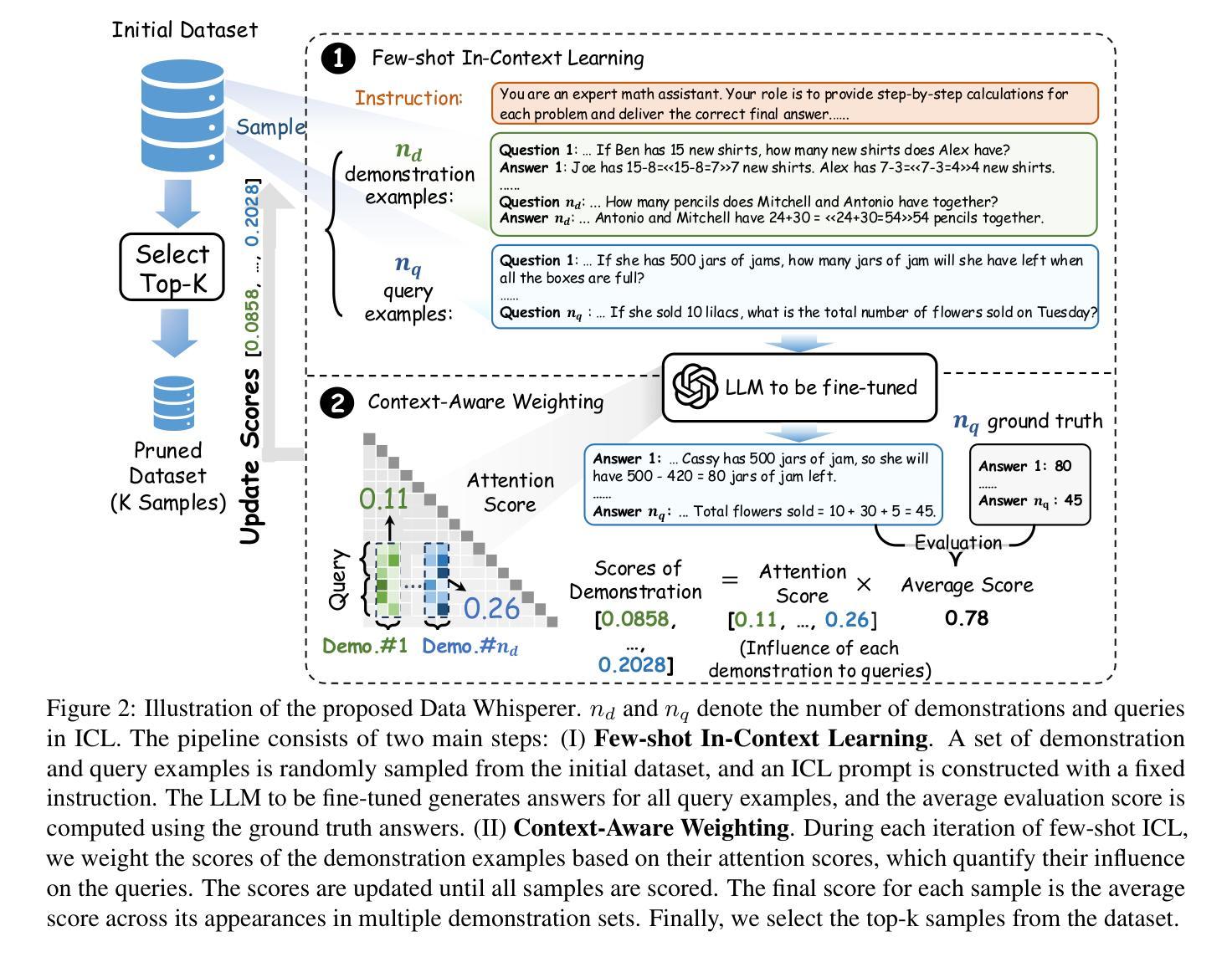
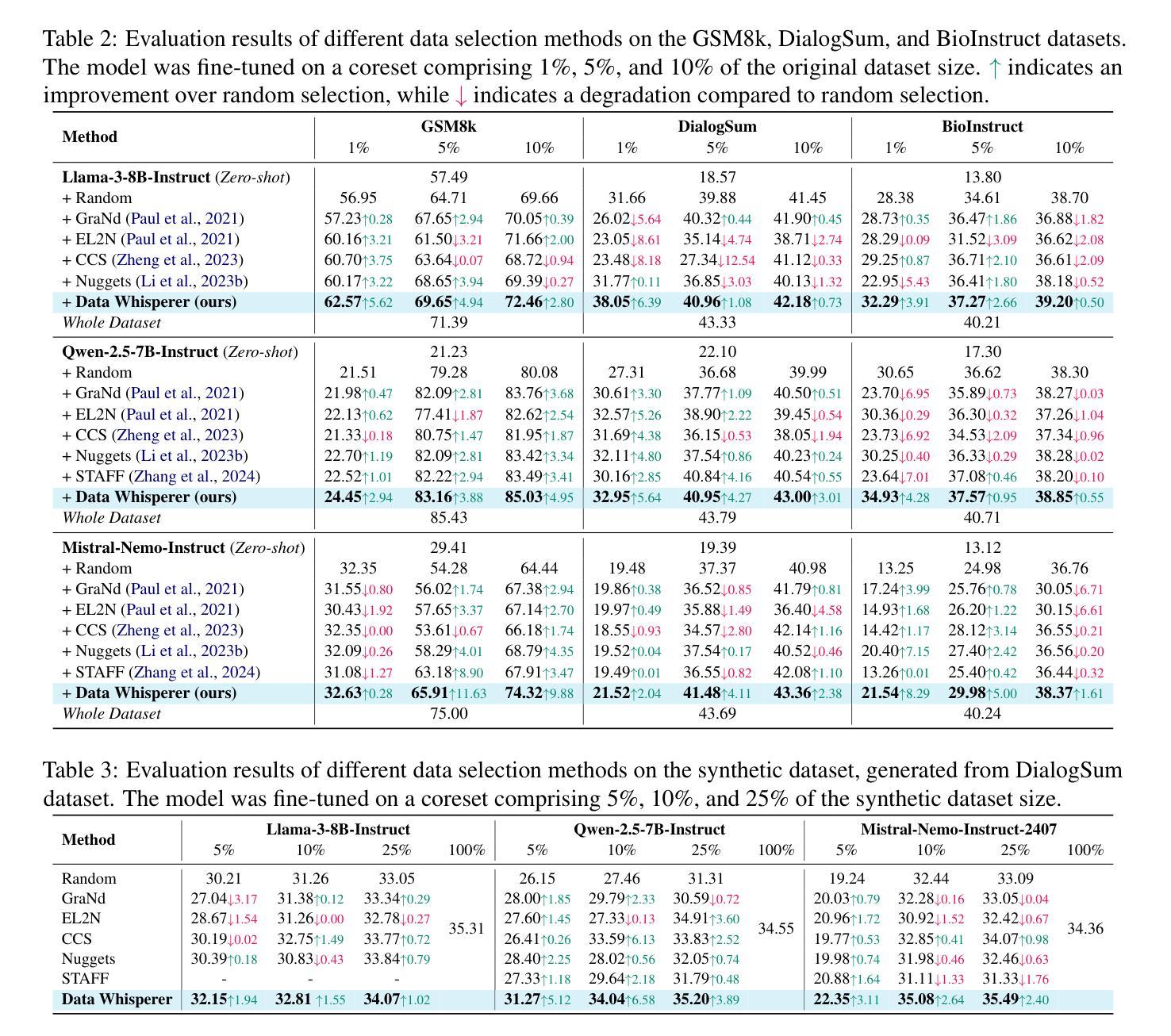
Fine-tuning large language models (LLMs) on task-specific data is essential for their effective deployment. As dataset sizes grow, efficiently selecting optimal subsets for training becomes crucial to balancing performance and computational costs. Traditional data selection methods often require fine-tuning a scoring model on the target dataset, which is time-consuming and resource-intensive, or rely on heuristics that fail to fully leverage the model’s predictive capabilities. To address these challenges, we propose Data Whisperer, an efficient, training-free, attention-based method that leverages few-shot in-context learning with the model to be fine-tuned. Comprehensive evaluations were conducted on both raw and synthetic datasets across diverse tasks and models. Notably, Data Whisperer achieves superior performance compared to the full GSM8K dataset on the Llama-3-8B-Instruct model, using just 10% of the data, and outperforms existing methods with a 3.1-point improvement and a 7.4$\times$ speedup.
对大型语言模型(LLM)进行针对特定任务的微调是有效部署它们的关键。随着数据集规模的扩大,高效选择最佳子集进行训练对于平衡性能和计算成本至关重要。传统数据选择方法通常需要针对目标数据集对评分模型进行微调,这不仅耗时而且资源密集,或者依赖于无法充分利用模型预测能力的启发式方法。为了解决这些挑战,我们提出了Data Whisperer,这是一种高效、无需训练、基于注意力的方法,它利用少量上下文内学习来对要进行微调模型的。我们在原始和合成数据集上进行了多样化的任务和模型的全面评估。值得注意的是,Data Whisperer仅使用10%的数据便在Llama-3-8B-Instruct模型上实现了相较于GSM8K数据集的更佳性能,并且相对于现有方法实现了3.1个点的提升和7.4倍的加速。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by ACL 2025 main, 18 pages, 8 figures, 6 tables
Summary
大型语言模型(LLM)在特定任务数据上进行微调对于其有效部署至关重要。随着数据集规模的扩大,为了平衡性能和计算成本,选择最佳的子集进行训练变得尤为重要。针对传统数据选择方法中存在的问题,本文提出了Data Whisperer方法,这是一种高效、无需训练、基于注意力的方法,利用少量数据结合待微调模型进行上下文学习。通过在不同的任务和模型上进行的综合评估显示,Data Whisperer在仅使用少量数据的情况下,相较于GSM8K数据集实现了更佳性能提升。尤其是在对Llama-3-8B-Instruct模型的评估中,使用仅10%的数据实现了显著超越,相较于现有方法实现了3.1点的性能提升和高达7.4倍的提速。这一新方法既快速又有效。
Key Takeaways
- 大型语言模型在特定任务上的微调至关重要,但数据集规模的扩大带来了平衡性能和计算成本的挑战。
- 传统数据选择方法需要长时间精细调整评分模型或依赖不能充分利用模型预测能力的启发式方法。
- Data Whisperer是一种高效、无需训练、基于注意力的方法,通过利用待微调模型的上下文学习进行少量数据训练。
点此查看论文截图
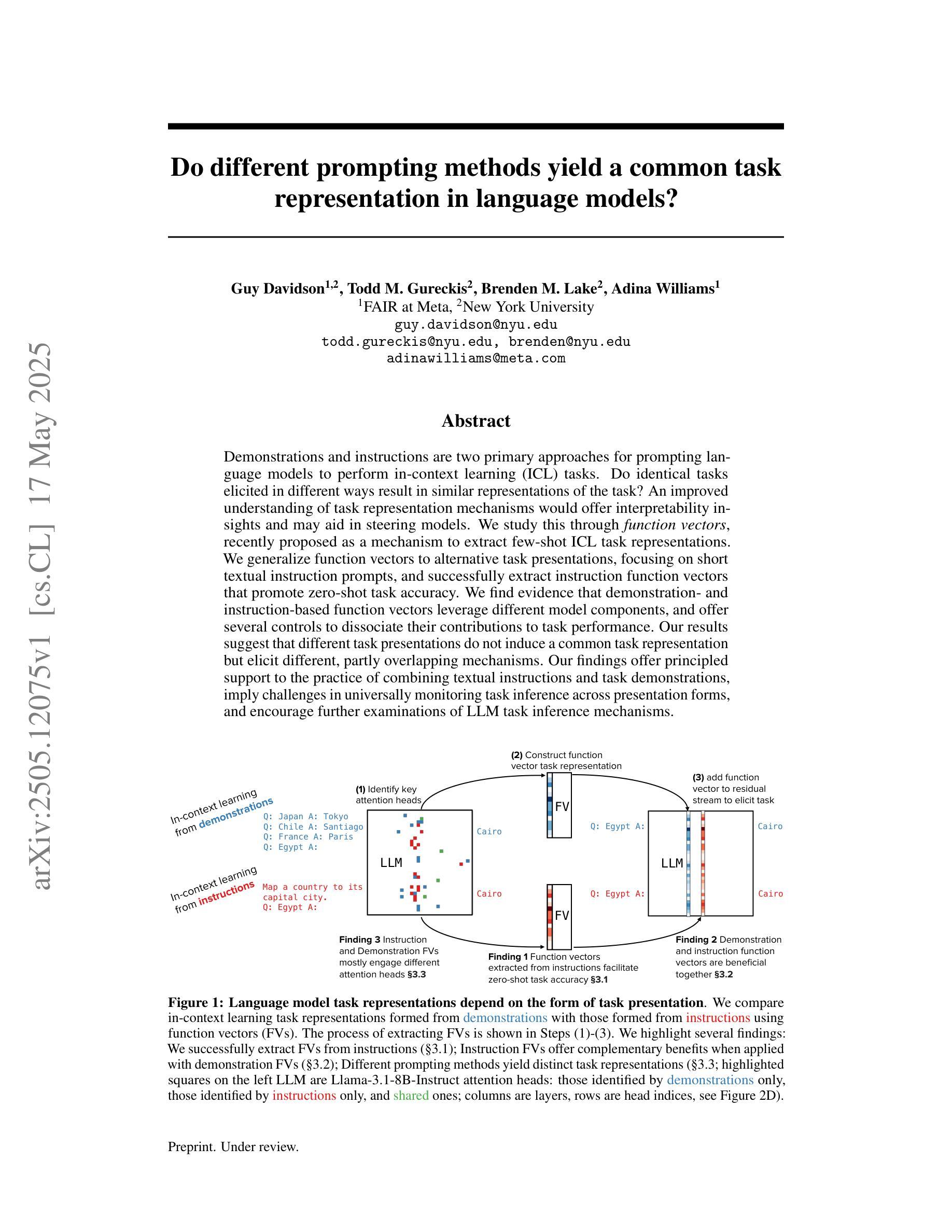
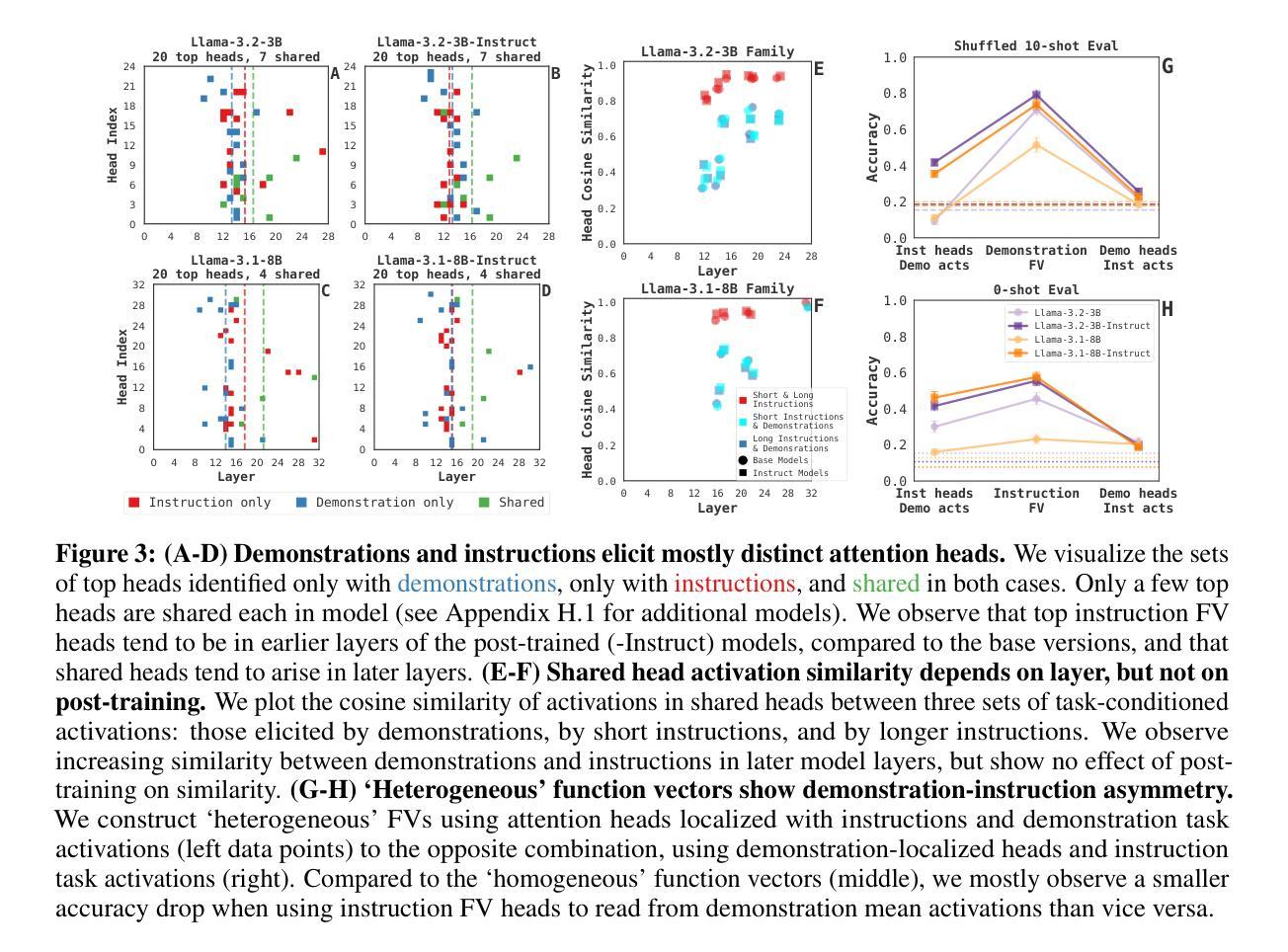
Do different prompting methods yield a common task representation in language models?
Authors:Guy Davidson, Todd M. Gureckis, Brenden M. Lake, Adina Williams
Demonstrations and instructions are two primary approaches for prompting language models to perform in-context learning (ICL) tasks. Do identical tasks elicited in different ways result in similar representations of the task? An improved understanding of task representation mechanisms would offer interpretability insights and may aid in steering models. We study this through function vectors, recently proposed as a mechanism to extract few-shot ICL task representations. We generalize function vectors to alternative task presentations, focusing on short textual instruction prompts, and successfully extract instruction function vectors that promote zero-shot task accuracy. We find evidence that demonstration- and instruction-based function vectors leverage different model components, and offer several controls to dissociate their contributions to task performance. Our results suggest that different task presentations do not induce a common task representation but elicit different, partly overlapping mechanisms. Our findings offer principled support to the practice of combining textual instructions and task demonstrations, imply challenges in universally monitoring task inference across presentation forms, and encourage further examinations of LLM task inference mechanisms.
演示和指令是促使语言模型执行上下文学习(ICL)任务的主要两种方法。通过不同的方式呈现相同的任务是否会导致任务表示的相似性?对任务表示机制有更好的理解可以提供解释性洞察,并可能有助于引导模型。我们通过功能向量进行研究,该功能向量最近被提出作为提取少量ICL任务表示的机制。我们将功能向量推广到替代任务展示,侧重于简短的文本指令提示,并成功提取出指令功能向量,提高了零射击任务准确性。我们发现,基于演示和指令的功能向量利用不同的模型组件,并提供了一些控制方法来分离它们对任务性能的贡献。我们的结果表明,不同的任务展示并没有形成通用的任务表示,而是引发了部分重叠的不同机制。我们的研究为结合文本指令和任务演示的实践提供了原则支持,暗示了在各种呈现形式中普遍监测任务推断的挑战性,并鼓励进一步考察LLM的任务推断机制。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 9 pages, 4 figures; under review
Summary
该文本研究了通过不同方式呈现相同任务时,语言模型的上下文学习(ICL)任务表现。通过功能向量这一机制,对基于演示和指令的任务表示进行了深入研究,并成功提取了指令功能向量,提高了零样本任务准确性。研究发现,基于演示和指令的功能向量利用不同的模型组件,对任务性能做出了不同的贡献。结果暗示不同的任务呈现方式不会形成共同的任务表示,而是激发部分重叠的机制。
Key Takeaways
- 演示和指令是两种主要方法,用于引导语言模型执行上下文学习任务(ICL)。
- 通过功能向量机制,研究了不同任务呈现方式对语言模型任务表现的影响。
- 成功提取了指令功能向量,提高了零样本任务准确性。
- 演示和指令基于的功能向量利用不同的模型组件。
- 不同的任务呈现方式不会形成共同的任务表示,而是激发部分重叠的机制。
- 结合文本指令和任务演示的实践得到了支持。
点此查看论文截图

Cross-Model Transfer of Task Vectors via Few-Shot Orthogonal Alignment
Authors:Kazuhiko Kawamoto, Atsuhiro Endo, Hiroshi Kera
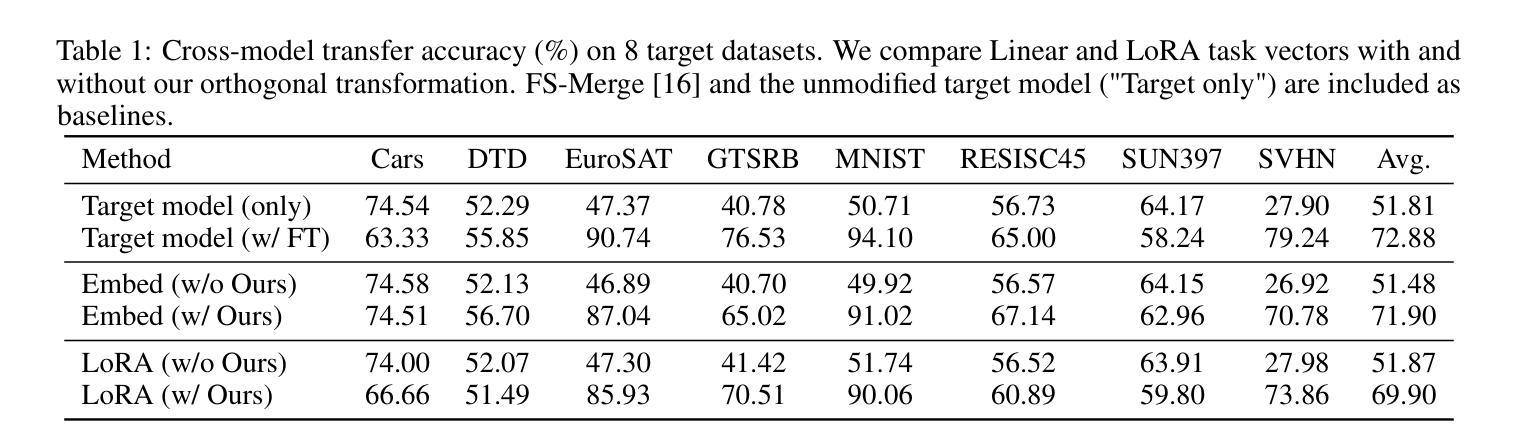
Task arithmetic enables efficient model editing by representing task-specific changes as vectors in parameter space. Task arithmetic typically assumes that the source and target models are initialized from the same pre-trained parameters. This assumption limits its applicability in cross-model transfer settings, where models are independently pre-trained on different datasets. To address this challenge, we propose a method based on few-shot orthogonal alignment, which aligns task vectors to the parameter space of a differently pre-trained target model. These transformations preserve key properties of task vectors, such as norm and rank, and are learned using only a small number of labeled examples. We evaluate the method using two Vision Transformers pre-trained on YFCC100M and LAION400M, and test on eight classification datasets. Experimental results show that our method improves transfer accuracy over direct task vector application and achieves performance comparable to few-shot fine-tuning, while maintaining the modularity and reusability of task vectors. Our code is available at https://github.com/kawakera-lab/CrossModelTransfer.
任务算术通过表示特定任务的改变为参数空间中的向量来实现高效的模型编辑。任务算术通常假设源模型和目标模型都是从相同的预训练参数进行初始化的。这一假设限制了其在跨模型迁移设置中的应用,其中模型在不同的数据集上进行独立预训练。为了应对这一挑战,我们提出了一种基于少量正交对齐的方法,该方法将任务向量对齐到不同预训练的目标模型的参数空间。这些转换保留了任务向量的关键属性,例如范数和等级,并且仅使用少量标记样本进行学习。我们使用两个在YFCC100M和LAION400M上预训练的视觉转换器进行评估,并在八个分类数据集上进行测试。实验结果表明,我们的方法改进了直接应用任务向量的迁移精度,并实现了与少量微调相当的性能,同时保持了任务向量的模块化和可重用性。我们的代码可在https://github.com/kawakera-lab/CrossModelTransfer处获取。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 8 pages
Summary
任务算术通过参数空间中的向量表示特定任务的变化,从而实现模型的快速编辑。当源模型和目标模型使用相同的预训练参数初始化时,任务算术效果很好。然而,在跨模型迁移设置中,模型在不同的数据集上进行独立预训练,这一假设限制了其适用性。为了应对这一挑战,我们提出了基于少样本正交对齐的方法,该方法将任务向量对齐到不同预训练目标模型的参数空间。这些转换保留了任务向量的关键属性,如范数和秩,并且仅使用少量标记样本进行学习。实验结果表明,我们的方法在跨模型迁移中提高了任务向量的应用效果,实现了与少样本微调相当的性能,同时保持了任务向量的模块化和可重用性。
Key Takeaways
- 任务算术通过参数空间中的向量表示特定任务的变化,用于高效模型编辑。
- 源模型和目标模型的预训练参数初始化影响任务算术的应用范围。
- 在跨模型迁移设置中,需要新的方法来应用任务算术,因为模型在不同的数据集上进行独立预训练。
- 提出了基于少样本正交对齐的方法,将任务向量对齐到不同预训练目标模型的参数空间。
- 转换保留了任务向量的关键属性,如范数和秩。
- 使用少量标记样本进行学习的效果良好。
点此查看论文截图


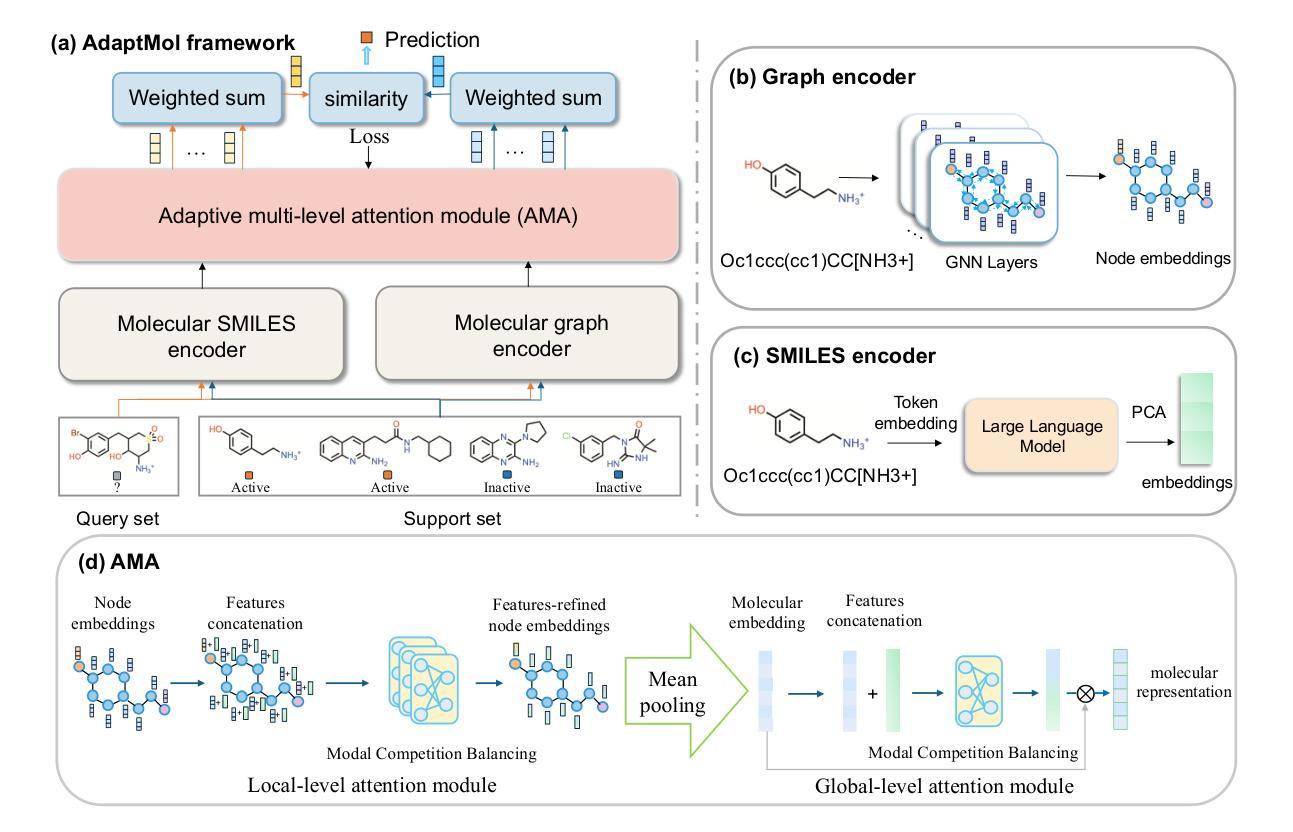
AdaptMol: Adaptive Fusion from Sequence String to Topological Structure for Few-shot Drug Discovery
Authors:Yifan Dai, Xuanbai Ren, Tengfei Ma, Qipeng Yan, Yiping Liu, Yuansheng Liu, Xiangxiang Zeng
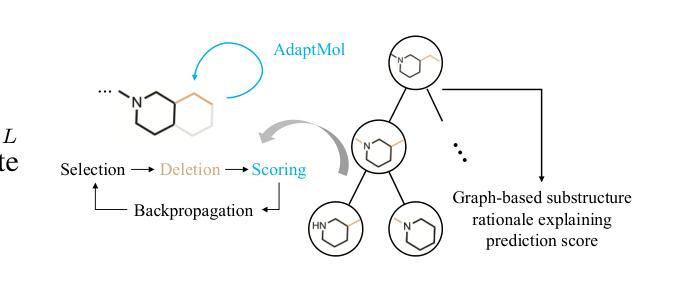
Accurate molecular property prediction (MPP) is a critical step in modern drug development. However, the scarcity of experimental validation data poses a significant challenge to AI-driven research paradigms. Under few-shot learning scenarios, the quality of molecular representations directly dictates the theoretical upper limit of model performance. We present AdaptMol, a prototypical network integrating Adaptive multimodal fusion for Molecular representation. This framework employs a dual-level attention mechanism to dynamically integrate global and local molecular features derived from two modalities: SMILES sequences and molecular graphs. (1) At the local level, structural features such as atomic interactions and substructures are extracted from molecular graphs, emphasizing fine-grained topological information; (2) At the global level, the SMILES sequence provides a holistic representation of the molecule. To validate the necessity of multimodal adaptive fusion, we propose an interpretable approach based on identifying molecular active substructures to demonstrate that multimodal adaptive fusion can efficiently represent molecules. Extensive experiments on three commonly used benchmarks under 5-shot and 10-shot settings demonstrate that AdaptMol achieves state-of-the-art performance in most cases. The rationale-extracted method guides the fusion of two modalities and highlights the importance of both modalities.
精确分子属性预测(MPP)是现代药物开发中的关键步骤。然而,实验验证数据的稀缺性对AI驱动的研究模式构成了重大挑战。在少量学习场景下,分子表示的质量直接决定了模型性能的理论上限。我们提出了AdaptMol,这是一个结合自适应多模式融合的原型网络进行分子表示。该框架采用双重层次的注意机制,动态融合全局和局部分子特征,这些特征来自两种模式:SMILES序列和分子图形。(1)在局部层面,从分子图中提取结构特征,如原子相互作用和子结构,强调精细的拓扑信息;(2)在全局层面,SMILES序列为分子提供了整体表示。为了验证多模式自适应融合的必要性,我们提出了一种基于识别分子活性子结构的可解释方法,证明多模式自适应融合可以有效地代表分子。在5次和10次设置下,对三个常用基准测试进行的广泛实验表明,AdaptMol在大多数情况下都达到了最新技术性能。所提取的理性方法指导了两种模式的融合,并强调了两种模式的重要性。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 15 pages, 6 figures
Summary
适应分子表示的多模态融合方法,旨在解决现代药物开发中准确分子属性预测(MPP)面临的挑战。通过引入原型网络并结合自适应多模态融合技术,提出一种名为AdaptMol的框架。该框架采用双级注意力机制,动态融合全局和局部分子特征,特征来源于SMILES序列和分子图两种模式。局部层面强调精细的拓扑信息,如原子相互作用和子结构;全局层面则提供分子的整体表示。通过可解释的识别分子活性子结构的方法验证了多模态自适应融合的必要性。在三个常用基准数据集上的实验表明,AdaptMol在5-shot和10-shot设置下取得了最先进的性能表现。
Key Takeaways
- Accurate分子属性预测(MPP)是现代药物开发的关键步骤,缺乏实验验证数据对AI研究造成挑战。
- AdaptMol框架结合了自适应多模态融合技术和原型网络。
- 该框架采用双级注意力机制,动态融合全局和局部分子特征。
- 局部层面关注精细的拓扑信息,如原子相互作用和子结构;全局层面提供分子整体表示。
- 通过识别分子活性子结构的方法验证了多模态自适应融合的必要性。
- 在多个数据集上的实验表明,AdaptMol在few-shot设置下实现了卓越性能。
点此查看论文截图

Generalizable Vision-Language Few-Shot Adaptation with Predictive Prompts and Negative Learning
Authors:Sriram Mandalika
Few-shot adaptation remains a core challenge for vision-language models (VLMs), especially under limited supervision and noisy support samples. We propose PromptFuseNL, a unified framework that enhances few-shot generalization by combining predictive prompt tuning with dual-branch positive and negative learning. The method refines class prototypes through task-conditioned residuals, multi-stage cross-modal coordination, and semantic hard negative mining. To address label noise, we introduce an unsupervised instance reweighting strategy that downweights unreliable support examples without requiring additional labels or structural changes. PromptFuseNL fuses visual and textual cues through lightweight modules for efficient and discriminative prediction. Evaluated across 15 benchmarks, it consistently surpasses existing prompt- and adapter-based methods in all shot settings while remaining highly efficient, achieving up to 300x faster training and 1000x lower FLOPs compared to full prompt tuning, achieving a new state-of-the-art for robust and scalable few-shot vision-language adaptation.
在视觉语言模型(VLMs)中,尤其是在有限的监督和噪声样本的支持下,小样本适应仍然是一个核心挑战。我们提出了PromptFuseNL这一统一框架,它通过预测提示调整与双分支正负学习相结合,提高了小样本泛化能力。该方法通过任务条件残差、多阶段跨模态协调和语义硬负挖掘来优化类原型。为了解决标签噪声问题,我们引入了一种无监督的实例重加权策略,该策略可以在不需要额外标签或结构更改的情况下降低不可靠的支持样本的权重。PromptFuseNL通过轻量级模块融合视觉和文本线索,以实现高效和鉴别性预测。在15个基准测试上的评估表明,它在所有射击设置中都超过了现有的基于提示和适配器的方法,同时保持了高效率,与全提示调整相比,训练速度提高了300倍,FLOPs降低了1000倍,为实现稳健且可扩展的小样本视觉语言适应达到了最新水平。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
少数样本适应仍是视觉语言模型(VLMs)的核心挑战,特别是在有限监督与噪声样本的支持下。我们提出PromptFuseNL统一框架,通过预测提示调整与正负样本学习的双分支结合,提高少样本泛化能力。此方法通过任务条件残差、多阶段跨模态协调和语义硬负样本挖掘来优化类原型。为解决标签噪声问题,我们引入无监督实例重加权策略,在不需额外标签或结构更改的情况下降低不可靠支持样本的权重。PromptFuseNL通过轻量级模块融合视觉和文本线索,实现高效和鉴别性预测。在15个基准测试中,相较于现有的提示和适配器方法,它在所有射击设置中都表现优异,并且高度高效,与完整提示调整相比实现了高达300倍的更快训练和高达更低的FLOPs数量,成为新的少样本视觉语言适应技术的杰出代表。
Key Takeaways
- PromptFuseNL是一个统一框架,旨在提高视觉语言模型在有限监督与噪声样本下的少样本泛化能力。
- 通过预测提示调整与正负样本学习的结合来提升模型性能。
- 通过任务条件残差、多阶段跨模态协调和语义硬负样本挖掘来优化类原型。
- 引入无监督实例重加权策略来解决标签噪声问题。
- PromptFuseNL框架实现了高效和鉴别性的预测,通过轻量级模块融合视觉和文本线索。
- 在多个基准测试中表现优异,相较于其他方法具有更高的效率和准确性。
点此查看论文截图

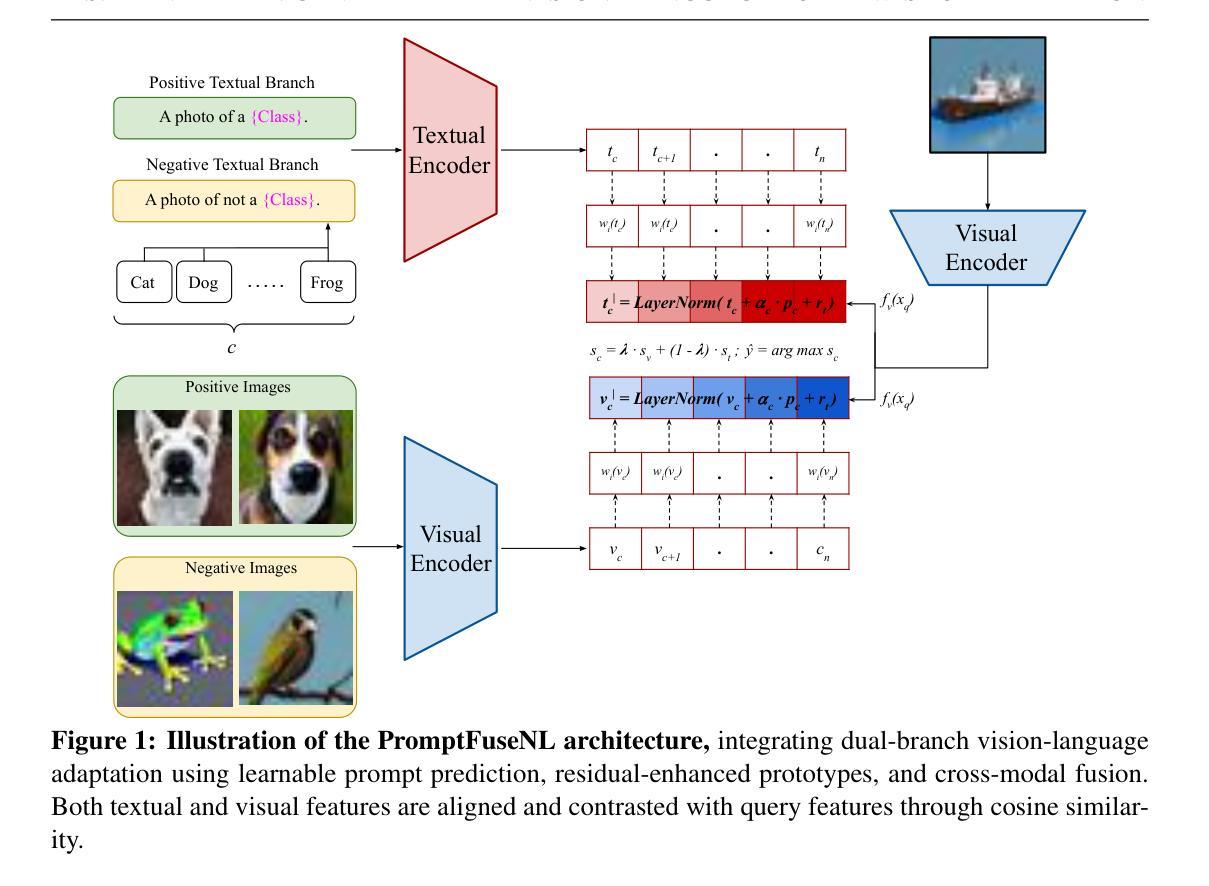
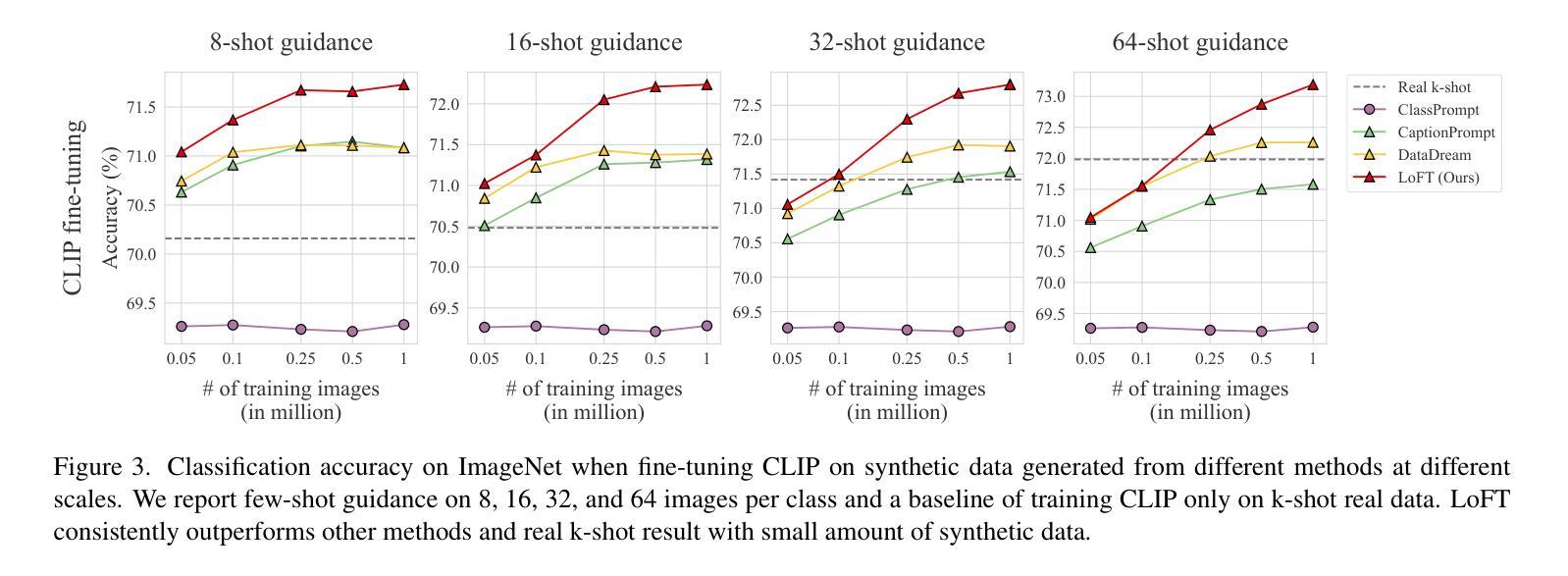
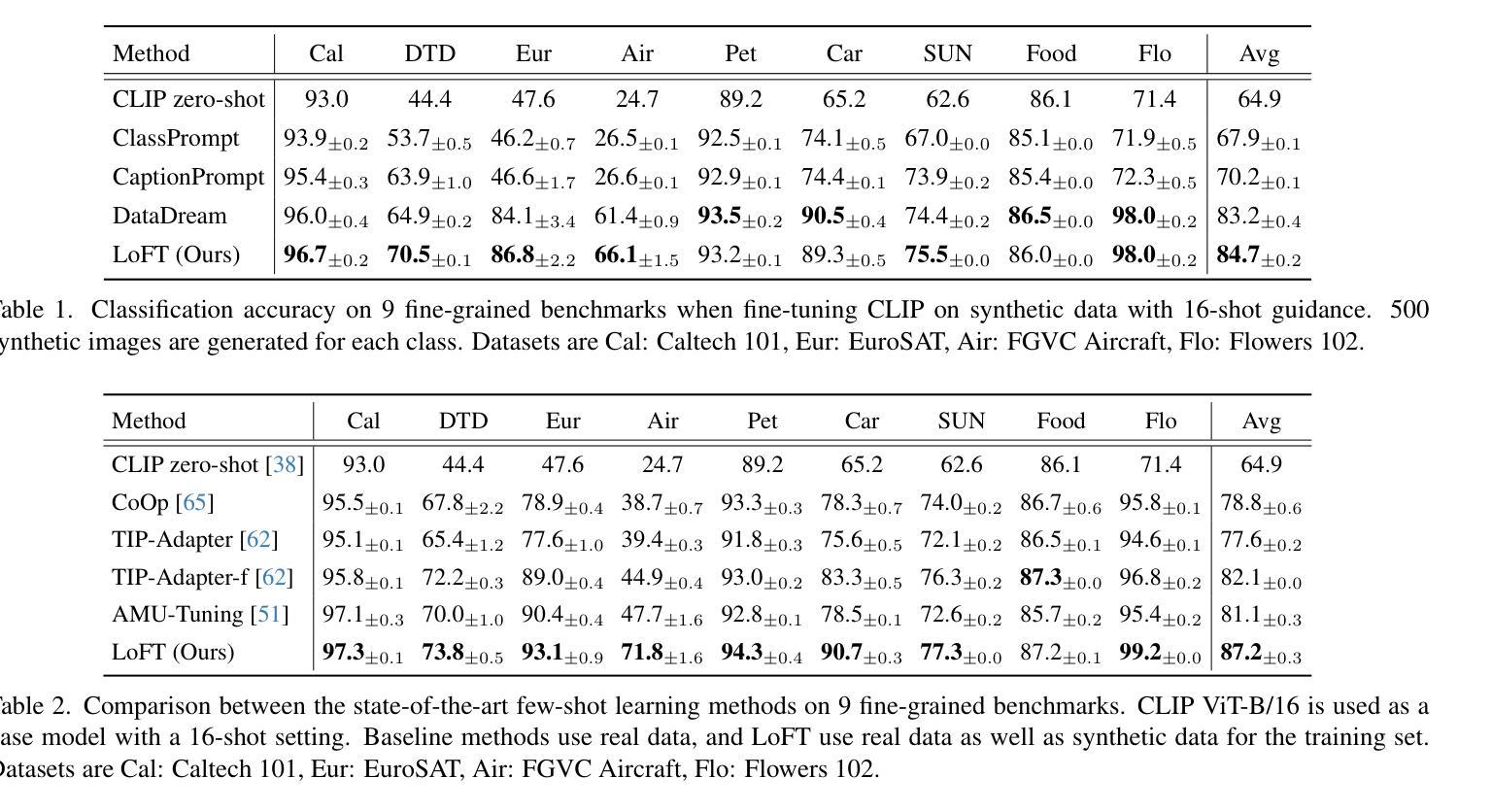
LoFT: LoRA-fused Training Dataset Generation with Few-shot Guidance
Authors:Jae Myung Kim, Stephan Alaniz, Cordelia Schmid, Zeynep Akata
Despite recent advances in text-to-image generation, using synthetically generated data seldom brings a significant boost in performance for supervised learning. Oftentimes, synthetic datasets do not faithfully recreate the data distribution of real data, i.e., they lack the fidelity or diversity needed for effective downstream model training. While previous work has employed few-shot guidance to address this issue, existing methods still fail to capture and generate features unique to specific real images. In this paper, we introduce a novel dataset generation framework named LoFT, LoRA-Fused Training-data Generation with Few-shot Guidance. Our method fine-tunes LoRA weights on individual real images and fuses them at inference time, producing synthetic images that combine the features of real images for improved diversity and fidelity of generated data. We evaluate the synthetic data produced by LoFT on 10 datasets, using 8 to 64 real images per class as guidance and scaling up to 1000 images per class. Our experiments show that training on LoFT-generated data consistently outperforms other synthetic dataset methods, significantly increasing accuracy as the dataset size increases. Additionally, our analysis demonstrates that LoFT generates datasets with high fidelity and sufficient diversity, which contribute to the performance improvement. The code is available at https://github.com/ExplainableML/LoFT.
尽管最近在文本到图像生成方面取得了进展,但使用合成数据很少能显著提高监督学习的性能。通常,合成数据集无法真实地重现真实数据的数据分布,即它们缺乏有效下游模型训练所需的保真度或多样性。虽然之前的工作已经采用小样本指导来解决这个问题,但现有方法仍然无法捕获并生成特定真实图像所独有的特征。在本文中,我们介绍了一种新型数据集生成框架,名为LoFT(融合小样本指导的LoRA训练数据生成)。我们的方法通过微调每个真实图像的LoRA权重并在推理时间进行融合,生成合成图像,这些图像结合了真实图像的特征,提高了生成数据的多样性和保真度。我们在10个数据集上评估了LoFT生成的合成数据,使用每类8到64张真实图像作为指导,并扩展到每类1000张图像。我们的实验表明,在LoFT生成的数据上进行训练始终优于其他合成数据集方法,随着数据集规模的增加,准确率显著提高。此外,我们的分析表明,LoFT生成的数据集具有高保真和足够的多样性,这有助于性能改进。代码可在https://github.com/ExplainableML/LoFT获取。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了一种名为LoFT的新型数据集生成框架,该框架采用少样本指导,通过微调LoRA权重并融合真实图像,生成合成图像。实验表明,使用LoFT生成的数据进行训练优于其他合成数据集方法,并且在数据集规模增大时,准确性显著提高。
Key Takeaways
- LoFT是一种新型数据集生成框架,采用少样本指导策略。
- LoFT通过微调LoRA权重并融合真实图像来生成合成图像。
- LoFT生成的合成数据在多个数据集上的表现均优于其他合成数据集方法。
- 随着数据集规模的增加,使用LoFT生成的数据进行训练的准确性显著提高。
- LoFT生成的数据集具有高保真度和足够的多样性。
- LoFT框架的代码已公开可访问。
点此查看论文截图

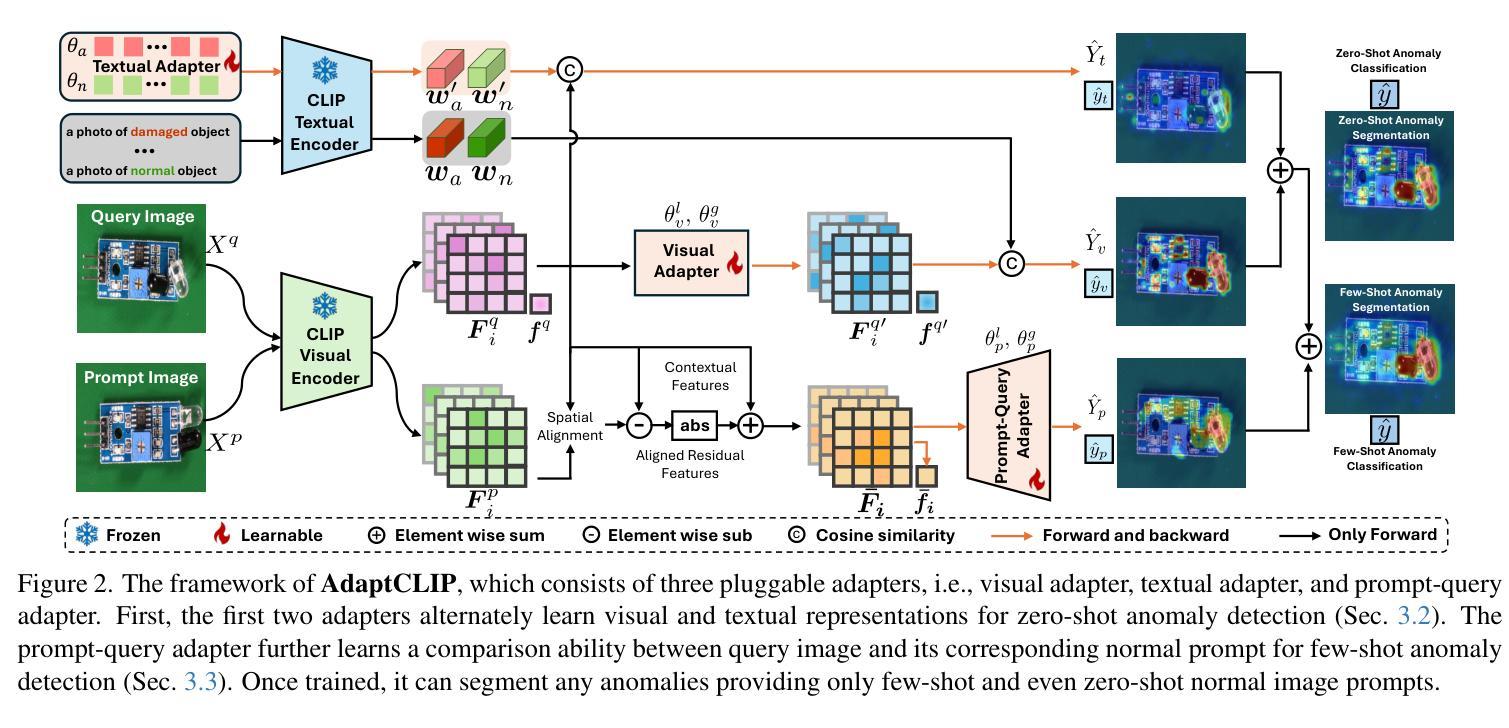
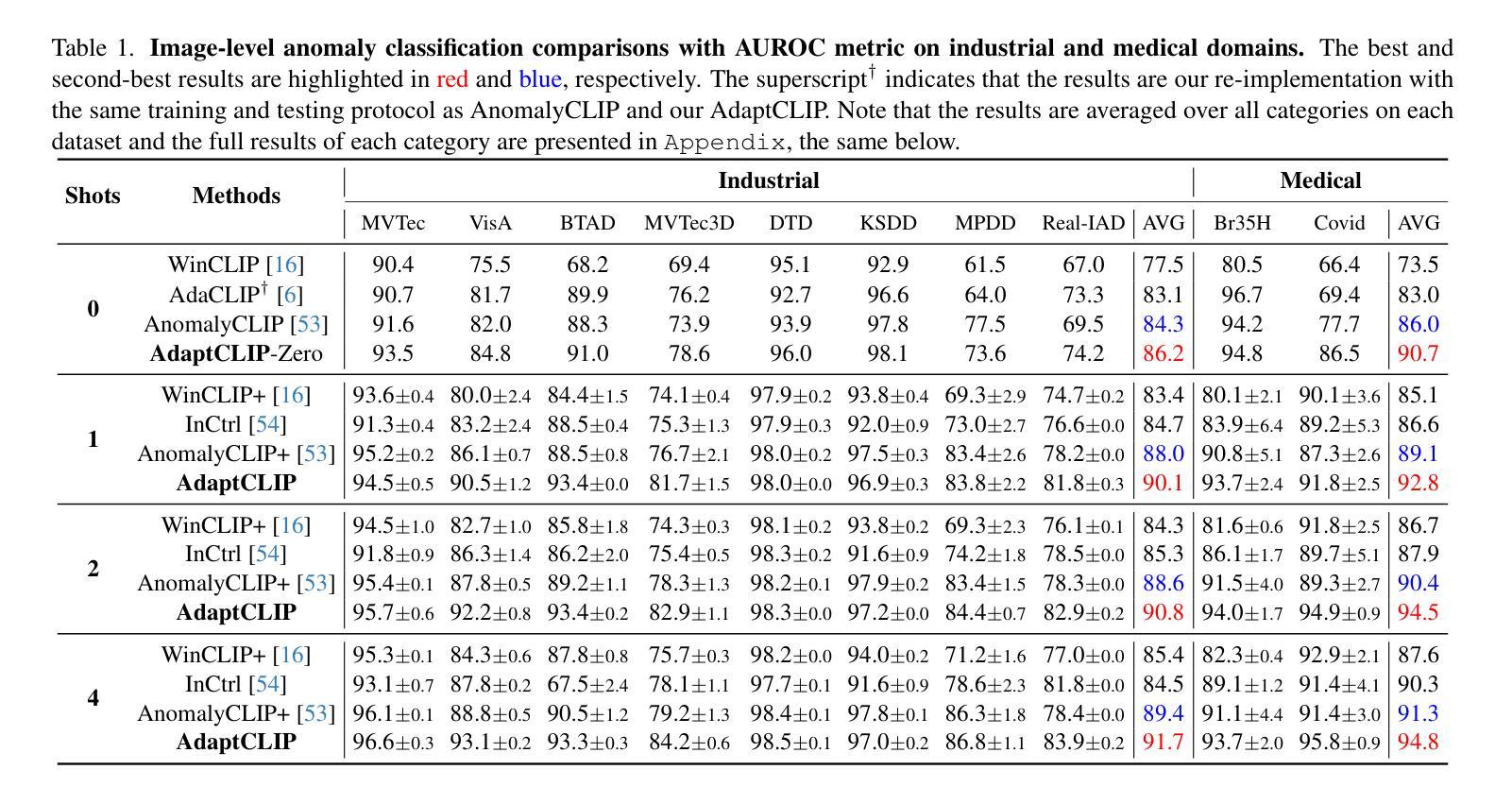
AdaptCLIP: Adapting CLIP for Universal Visual Anomaly Detection
Authors:Bin-Bin Gao, Yue Zhou, Jiangtao Yan, Yuezhi Cai, Weixi Zhang, Meng Wang, Jun Liu, Yong Liu, Lei Wang, Chengjie Wang
Universal visual anomaly detection aims to identify anomalies from novel or unseen vision domains without additional fine-tuning, which is critical in open scenarios. Recent studies have demonstrated that pre-trained vision-language models like CLIP exhibit strong generalization with just zero or a few normal images. However, existing methods struggle with designing prompt templates, complex token interactions, or requiring additional fine-tuning, resulting in limited flexibility. In this work, we present a simple yet effective method called AdaptCLIP based on two key insights. First, adaptive visual and textual representations should be learned alternately rather than jointly. Second, comparative learning between query and normal image prompt should incorporate both contextual and aligned residual features, rather than relying solely on residual features. AdaptCLIP treats CLIP models as a foundational service, adding only three simple adapters, visual adapter, textual adapter, and prompt-query adapter, at its input or output ends. AdaptCLIP supports zero-/few-shot generalization across domains and possesses a training-free manner on target domains once trained on a base dataset. AdaptCLIP achieves state-of-the-art performance on 12 anomaly detection benchmarks from industrial and medical domains, significantly outperforming existing competitive methods. We will make the code and model of AdaptCLIP available at https://github.com/gaobb/AdaptCLIP.
通用视觉异常检测旨在从新颖或未见过的视觉领域识别异常值,无需额外的微调,这在开放场景中至关重要。最近的研究表明,仅使用零张或少数几张正常图像进行训练的预训练视觉语言模型(如CLIP)具有很强的泛化能力。然而,现有方法在设计提示模板、复杂的令牌交互或需要额外的微调方面存在困难,导致灵活性有限。在这项工作中,我们提出了一种简单有效的方法,称为基于两个关键见解的AdaptCLIP。首先,应交替学习自适应的视觉和文本表示,而不是联合学习。其次,查询和正常图像提示之间的比较学习应融入上下文和对齐的残差特征,而不是仅依赖残差特征。AdaptCLIP将CLIP模型作为基础服务,仅在输入或输出端添加三个简单的适配器:视觉适配器、文本适配器和提示查询适配器。AdaptCLIP支持跨领域的零/少镜头泛化,一旦在基础数据集上进行训练,它在目标领域上采用无训练方式。AdaptCLIP在来自工业和医疗领域的12个异常检测基准测试上达到了最先进的性能表现,显著优于现有的竞争方法。我们将在https://github.com/gaobb/AdaptCLIP上提供AdaptCLIP的代码和模型。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 27 pages, 15 figures, 22 tables
Summary
基于CLIP模型的AdaptCLIP方法,通过交替学习视觉和文本表示,结合上下文和余弦特征的对比学习,实现了无需额外精细调整的跨域零样本或少样本异常检测。此方法只需在输入或输出端添加少量适配器即可支持目标域的推广。AdaptCLIP在多个工业和医疗领域的异常检测基准测试中表现卓越。
Key Takeaways
- AdaptCLIP旨在实现跨未知视觉领域的异常检测,无需额外精细调整。
- 基于CLIP模型的强大泛化能力,仅使用零样本或少样本正常图像。
- AdaptCLIP采用交替学习视觉和文本表示的方式,增强模型的灵活性。
- 引入对比学习机制,结合上下文和余弦特征进行异常检测。
- 仅通过添加三个简单适配器(视觉适配器、文本适配器和提示查询适配器)来增强CLIP模型的功能。
- AdaptCLIP在多个异常检测基准测试中表现最佳,显著优于现有方法。
点此查看论文截图


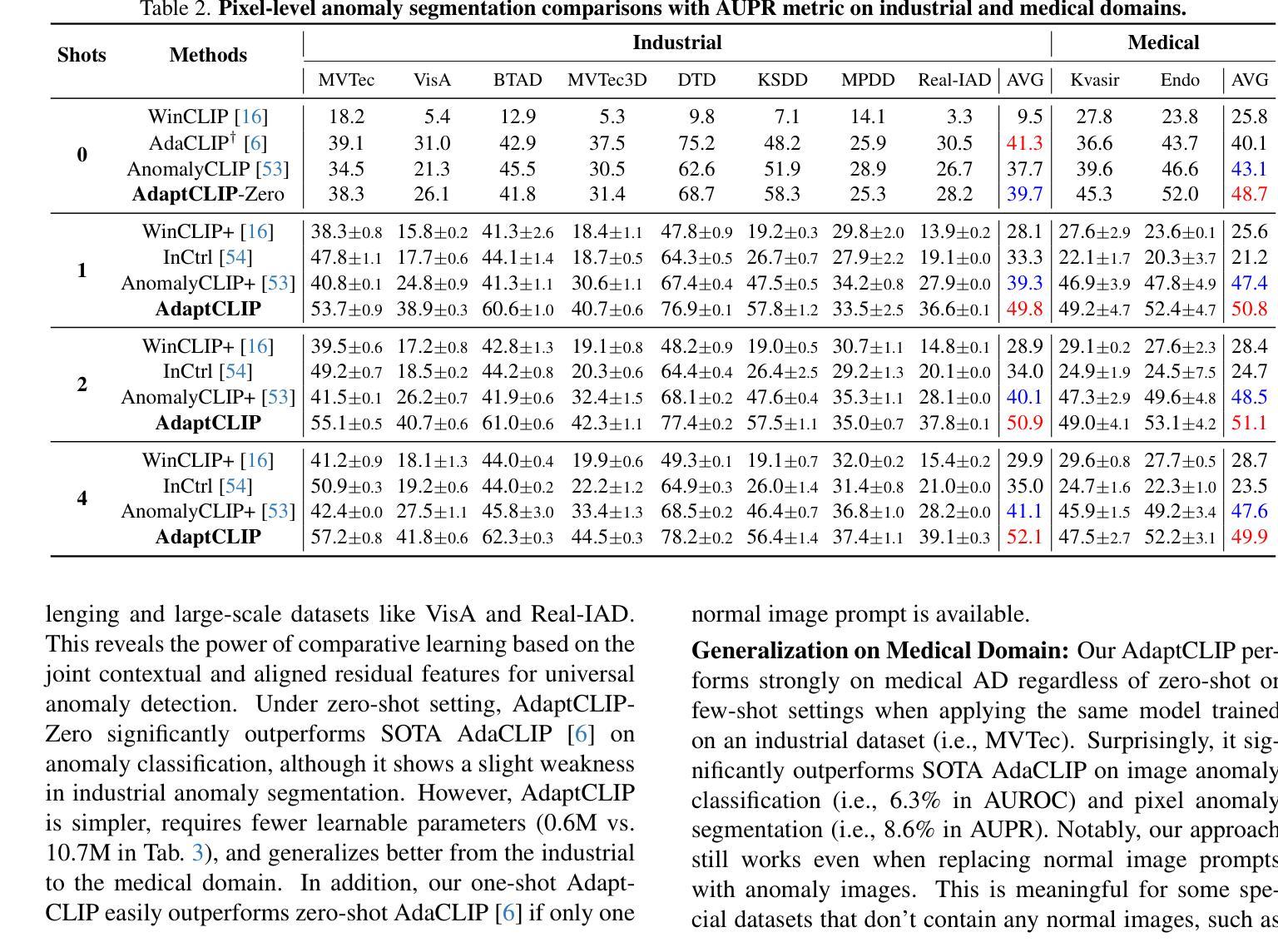
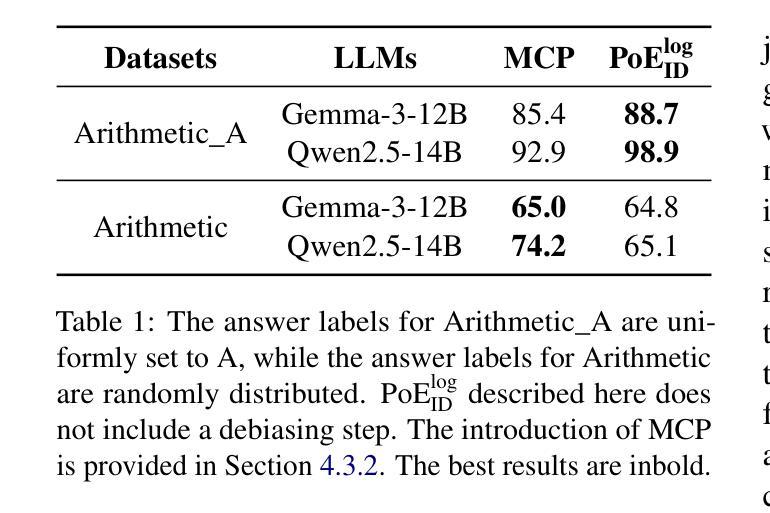
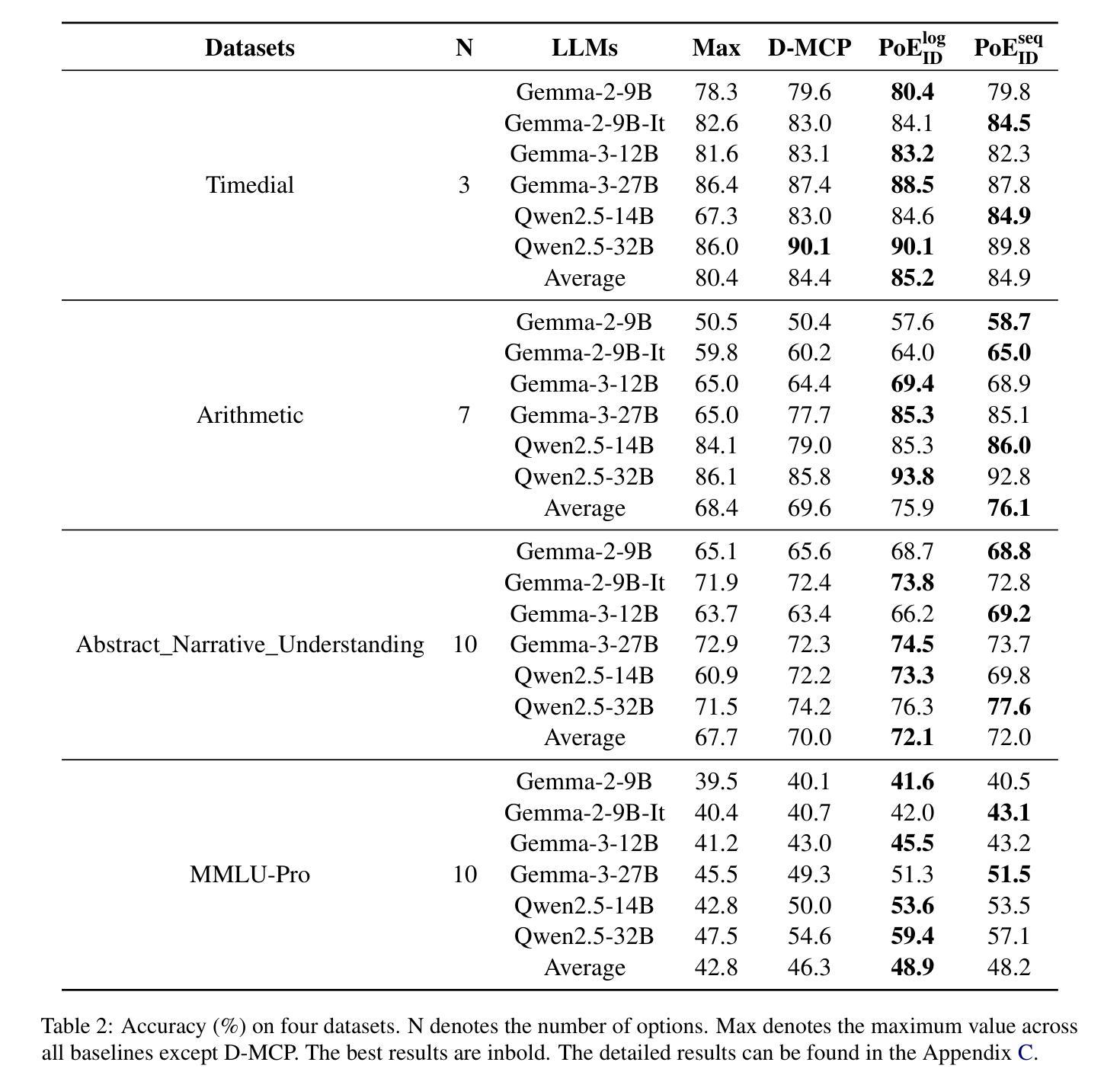
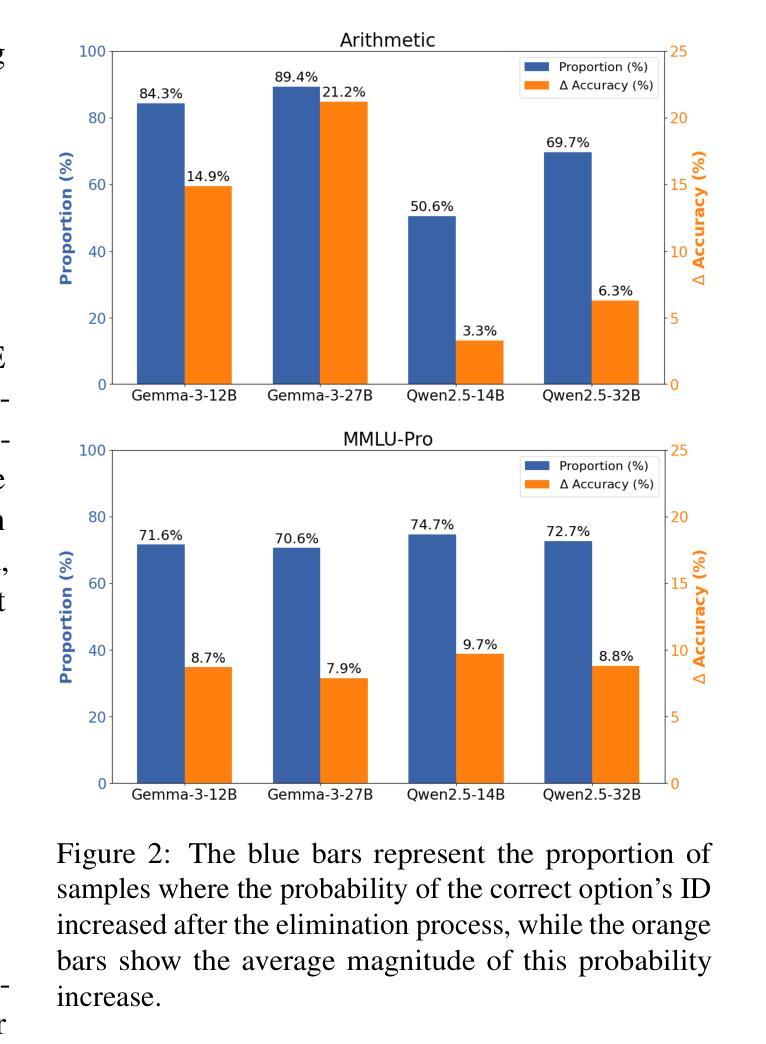
Option-ID Based Elimination For Multiple Choice Questions
Authors:Zhenhao Zhu, Bulou Liu, Qingyao Ai, Yiqun Liu
Multiple choice questions (MCQs) are a popular and important task for evaluating large language models (LLMs). Based on common strategies people use when answering MCQs, the process of elimination (PoE) has been proposed as an effective problem-solving method. Existing PoE methods typically either have LLMs directly identify incorrect options or score options and replace lower-scoring ones with [MASK]. However, both methods suffer from inapplicability or suboptimal performance. To address these issues, this paper proposes a novel option-ID based PoE ($\text{PoE}{\text{ID}}$). $\text{PoE}{\text{ID}}$ critically incorporates a debiasing technique to counteract LLMs token bias, enhancing robustness over naive ID-based elimination. It features two strategies: $\text{PoE}{\text{ID}}^{\text{log}}$, which eliminates options whose IDs have log probabilities below the average threshold, and $\text{PoE}{\text{ID}}^{\text{seq}}$, which iteratively removes the option with the lowest ID probability. We conduct extensive experiments with 6 different LLMs on 4 diverse datasets. The results demonstrate that $\text{PoE}{\text{ID}}$, especially $\text{PoE}{\text{ID}}^{\text{log}}$, significantly improves zero-shot and few-shot MCQs performance, particularly in datasets with more options. Our analyses demonstrate that $\text{PoE}_{\text{ID}}^{\text{log}}$ enhances the LLMs’ confidence in selecting the correct option, and the option elimination strategy outperforms methods relying on [MASK] replacement. We further investigate the limitations of LLMs in directly identifying incorrect options, which stem from their inherent deficiencies.
多项选择题(MCQs)是评估大型语言模型(LLM)流行且重要的任务。基于人们回答选择题时常用的策略,提出了基于排除法(PoE)作为一种有效的解决问题的方法。现有的PoE方法通常要么让LLM直接识别错误选项,要么对选项进行评分并将得分较低的选项替换为[MASK]。然而,这两种方法都存在不适用或性能不佳的问题。为了解决这些问题,本文提出了一种基于选项ID的PoE(PoE ID)。PoE ID巧妙地融入了去偏技术来对抗LLM令牌偏差,相对于简单的基于ID的消除方法增强了稳健性。它包含两种策略:PoE ID log,它消除那些ID对数概率低于平均阈值的选项;PoE ID seq,它迭代地移除具有最低ID概率的选项。我们在四个不同的数据集上对六个不同的LLM进行了大量实验。结果表明,特别是PoE ID log,在零样本和少样本选择题上显著提高性能,尤其是在有更多选项的数据集上。我们的分析表明,PoE ID log增强了LLM在选择正确选项时的信心,并且基于选项消除的策略优于依赖于[MASK]替换的方法。我们还进一步探讨了LLM在直接识别错误选项方面的局限性,这些局限性源于其固有的缺陷。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
基于人们在回答选择题时的常用策略,提出了一种有效的解题方法——排除法(PoE)。现有的PoE方法要么直接让大型语言模型(LLM)识别错误选项,要么对选项进行评分并用[MASK]替换低分选项。然而,这两种方法都存在不适用或性能不佳的问题。针对这些问题,本文提出了一种基于选项ID的PoE($\text{PoE}{\text{ID}}$)。$\text{PoE}{\text{ID}}$巧妙地融入了一种去偏技术,以抵消LLM的令牌偏置,提高了对基于单纯ID消除的稳健性。它包含两种策略:$\text{PoE}{\text{ID}}^{\text{log}}$,消除ID对数概率低于平均阈值的选项;以及$\text{PoE}{\text{ID}}^{\text{seq}}$,迭代移除ID概率最低的选择项。实验表明,特别是在选项较多的数据集上,$\text{PoE}{\text{ID}}$,尤其是$\text{PoE}{\text{ID}}^{\text{log}}$,能显著提高零样本和少样本选择题的表现。
Key Takeaways
- 排除法(PoE)被提出作为解决大型语言模型(LLM)在选择题任务中的问题的一种有效方法。
- 现有PoE方法存在不适用或性能不佳的问题。
- 论文提出了一种新的基于选项ID的PoE方法($\text{PoE}{\text{ID}}$),包含两种策略:$\text{PoE}{\text{ID}}^{\text{log}}$和$\text{PoE}_{\text{ID}}^{\text{seq}}$。
- $\text{PoE}_{\text{ID}}$通过融入去偏技术,提高了LLM在选择题任务中的性能。
- 在多个LLM和多种数据集上的实验表明,$\text{PoE}{\text{ID}}$特别是$\text{PoE}{\text{ID}}^{\text{log}}$表现优异。
- $\text{PoE}_{\text{ID}}^{\text{log}}$增强了LLM选择正确选项的信心。
点此查看论文截图

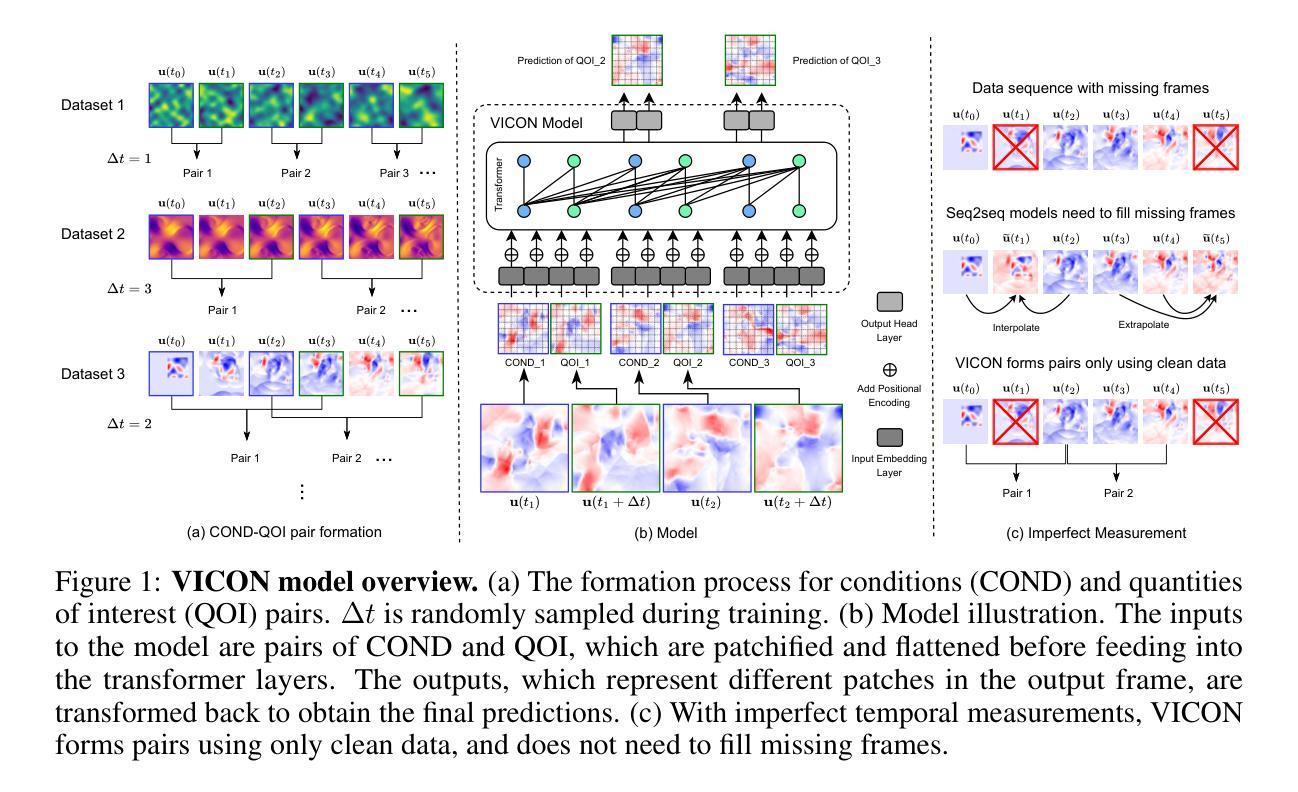
VICON: Vision In-Context Operator Networks for Multi-Physics Fluid Dynamics Prediction
Authors:Yadi Cao, Yuxuan Liu, Liu Yang, Rose Yu, Hayden Schaeffer, Stanley Osher
In-Context Operator Networks (ICONs) have demonstrated the ability to learn operators across diverse partial differential equations using few-shot, in-context learning. However, existing ICONs process each spatial point as an individual token, severely limiting computational efficiency when handling dense data in higher spatial dimensions. We propose Vision In-Context Operator Networks (VICON), which integrates vision transformer architectures to efficiently process 2D data through patch-wise operations while preserving ICON’s adaptability to multiphysics systems and varying timesteps. Evaluated across three fluid dynamics benchmarks, VICON significantly outperforms state-of-the-art baselines: DPOT and MPP, reducing the averaged last-step rollout error by 37.9% compared to DPOT and 44.7% compared to MPP, while requiring only 72.5% and 34.8% of their respective inference times. VICON naturally supports flexible rollout strategies with varying timestep strides, enabling immediate deployment in imperfect measurement systems where sampling frequencies may differ or frames might be dropped - common challenges in real-world settings - without requiring retraining or interpolation. In these realistic scenarios, VICON exhibits remarkable robustness, experiencing only 24.41% relative performance degradation compared to 71.37%-74.49% degradation in baseline methods, demonstrating its versatility for deploying in realistic applications. Our scripts for processing datasets and code are publicly available at https://github.com/Eydcao/VICON.
In-Context Operator Networks(ICONs)已证明具备在少数情境下学习多种偏微分方程操作符的能力。然而,现有ICON将每个空间点视为单个标记,在处理高维空间中的密集数据时,计算效率受到严重限制。我们提出Vision In-Context Operator Networks(VICON),它结合了视觉转换器架构,通过块操作高效处理二维数据,同时保留ICON对多物理系统和不同时间步长的适应性。在三个流体动力学基准测试中评估显示,VICON显著优于最新基线技术DPOT和MPP,与DPOT相比减少了平均最后一步滚动误差的百分比达到37.9%,与MPP相比减少了平均最后一步滚动误差的百分比达到44.7%,同时仅需要其各自推理时间的百分比达到分别为72.5%和34.8%。VICON自然支持灵活的时间步长滚动策略,能够在测量系统不完美的情况下即时部署,其中采样频率可能有所不同或帧可能会丢失——现实场景中常见的问题——无需进行再次训练或插值处理。在这些实际场景中,与基线方法相比VICON展现出显著的稳健性,相对性能下降仅为24.41%,而基线方法性能下降为介于71.37%-74.49%,证明了其在现实应用中的通用性。我们的数据集处理脚本和代码公开可在https://github.com/Eydcao/VICON获取。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF update 1 more baseline + 1 more experiment setup (performance for temporal measurements with dropped frames); updated to Nueral IPS format. Refined writing and presentations
Summary
VICON是一种基于Vision Transformer架构的In-Context Operator Networks(ICONs)的改进版本,旨在高效处理二维数据,同时保留ICONs在多物理系统和不同时间步长的适应性。在三个流体动力学基准测试中,VICON显著优于现有技术基准线,减少了平均最后一步滚动误差,并提供了灵活的滚动策略以应对不同的时间步长跨度。VICON在处理现实世界中的不完美测量系统时展现出出色的稳健性,且在数据集处理和代码已公开发布以供使用。
Key Takeaways
- VICON整合了Vision Transformer架构,旨在提高处理二维数据时的计算效率。
- VICON保留了ICONs对多物理系统和不同时间步长的适应性。
- 在三个流体动力学基准测试中,VICON显著优于现有技术基准线。
- VICON减少了平均最后一步滚动误差,相较于其他方法表现更优。
- VICON支持灵活的滚动策略,适应不同的时间步长跨度,适用于不完美测量系统。
- 在现实世界的挑战中,VICON展现出强大的稳健性。
点此查看论文截图