⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-05-21 更新
Unified Cross-modal Translation of Score Images, Symbolic Music, and Performance Audio
Authors:Jongmin Jung, Dongmin Kim, Sihun Lee, Seola Cho, Hyungjoon Soh, Irmak Bukey, Chris Donahue, Dasaem Jeong
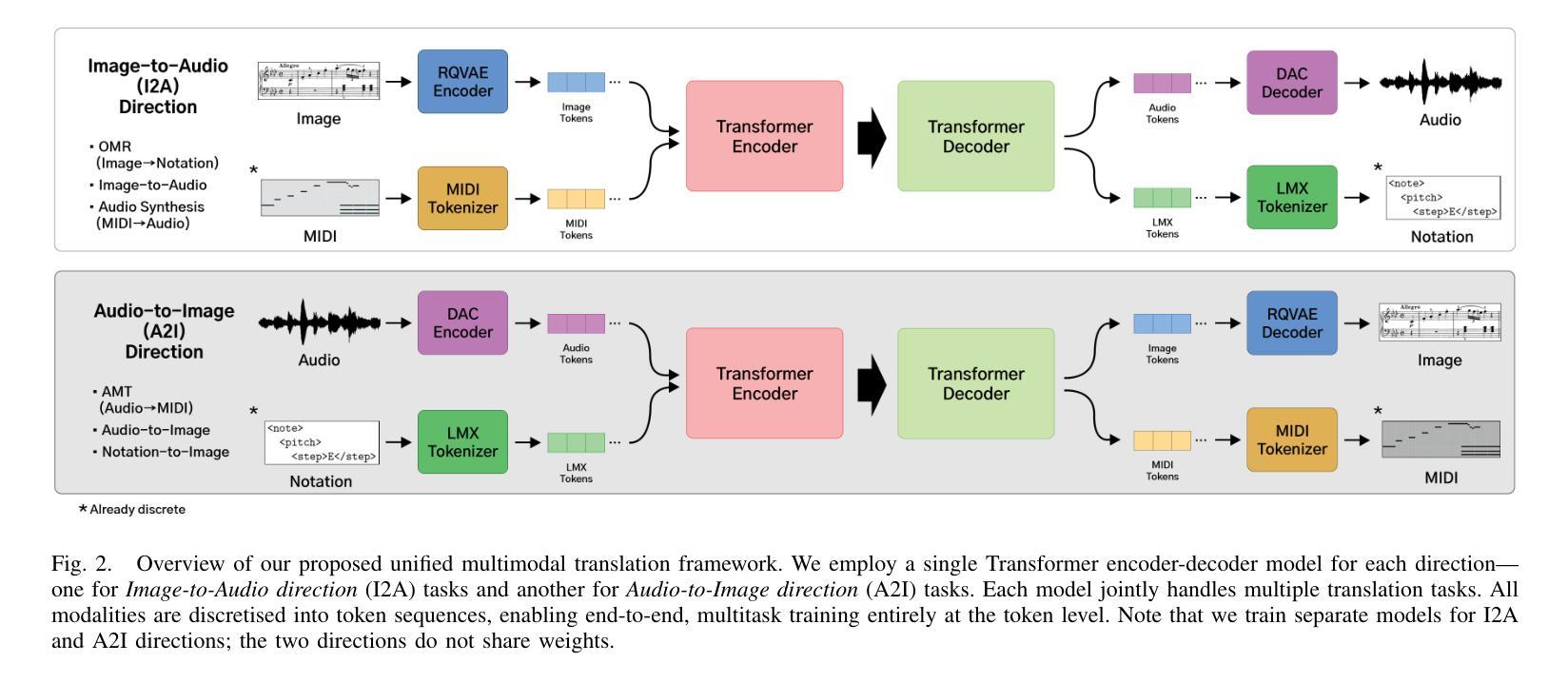
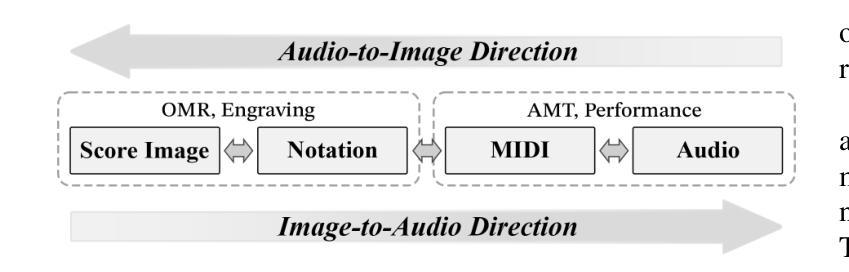
Music exists in various modalities, such as score images, symbolic scores, MIDI, and audio. Translations between each modality are established as core tasks of music information retrieval, such as automatic music transcription (audio-to-MIDI) and optical music recognition (score image to symbolic score). However, most past work on multimodal translation trains specialized models on individual translation tasks. In this paper, we propose a unified approach, where we train a general-purpose model on many translation tasks simultaneously. Two key factors make this unified approach viable: a new large-scale dataset and the tokenization of each modality. Firstly, we propose a new dataset that consists of more than 1,300 hours of paired audio-score image data collected from YouTube videos, which is an order of magnitude larger than any existing music modal translation datasets. Secondly, our unified tokenization framework discretizes score images, audio, MIDI, and MusicXML into a sequence of tokens, enabling a single encoder-decoder Transformer to tackle multiple cross-modal translation as one coherent sequence-to-sequence task. Experimental results confirm that our unified multitask model improves upon single-task baselines in several key areas, notably reducing the symbol error rate for optical music recognition from 24.58% to a state-of-the-art 13.67%, while similarly substantial improvements are observed across the other translation tasks. Notably, our approach achieves the first successful score-image-conditioned audio generation, marking a significant breakthrough in cross-modal music generation.
音乐存在于多种模态中,如乐谱图像、符号乐谱、MIDI和音乐音频。各种模态之间的翻译被确立为音乐信息检索的核心任务,如自动音乐转录(音频到MIDI)和乐谱识别(乐谱图像到符号乐谱)。然而,过去大多数关于多模态翻译的工作都是在单个翻译任务上训练特定模型。在本文中,我们提出了一种通用方法,即同时训练多个翻译任务的通用模型。两个关键因素使这种统一的方法可行:一是新的大规模数据集和每种模态的标记化。首先,我们提出了一个新的数据集,该数据集包含从YouTube视频收集的超过1300小时的配对音频乐谱图像数据,其规模是现有音乐模态翻译数据集的十倍。其次,我们的统一标记化框架将乐谱图像、音频、MIDI和MusicXML离散成一系列标记,使得单个编码器-解码器转换器能够作为一个连贯的序列到序列任务来处理多个跨模态翻译。实验结果证实,我们的多任务统一模型在几个关键领域优于单任务基线模型,特别是将乐谱识别的符号错误率从24.58%降低到最先进的13.67%,同时在其他翻译任务上也观察到了类似的显著改进。值得注意的是,我们的方法实现了首次乐谱图像条件下的音频生成,标志着跨模态音乐生成方面的一个重大突破。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Submitted to IEEE Transactions on Audio, Speech and Language Processing (TASLPRO)
Summary
本文提出一种统一的多模态音乐翻译方法,该方法使用一个通用模型同时处理多种翻译任务,包括音频转MIDI和乐谱图像转乐谱符号等。该研究创新点在于:一是构建了一个大规模的多模态音乐翻译数据集,包含超过1300小时的音频和乐谱图像配对数据;二是提出了一个统一的符号化框架,将乐谱图像、音频、MIDI和音乐XML等格式离散化为一系列符号序列,使得一个单一的编码解码器就能够处理多个跨模态翻译任务。实验结果显示,该统一多任务模型在多个关键领域优于单任务基准模型,如光学音乐识别的符号错误率从24.58%降低到最新的13.67%。此外,该研究还首次实现了基于乐谱图像条件的音频生成,标志着跨模态音乐生成领域的一个重大突破。
Key Takeaways
- 研究提出了一个统一的多模态音乐翻译方法,涵盖多种音乐模态之间的翻译任务。
- 构建了一个大规模的音乐模态翻译数据集,包含音频和乐谱图像配对数据。
- 提出了一个统一的符号化框架,将不同音乐模态转换为符号序列,为统一模型处理多模态翻译任务提供了可能。
- 统一多任务模型在跨模态音乐翻译任务上表现出优异性能,显著降低了光学音乐识别的符号错误率。
- 研究实现了首次基于乐谱图像条件的音频生成,标志着跨模态音乐生成的重要进展。
- 该研究为音乐信息检索中的多模态翻译任务提供了新的思路和方法。
点此查看论文截图



RoboFAC: A Comprehensive Framework for Robotic Failure Analysis and Correction
Authors:Weifeng Lu, Minghao Ye, Zewei Ye, Ruihan Tao, Shuo Yang, Bo Zhao
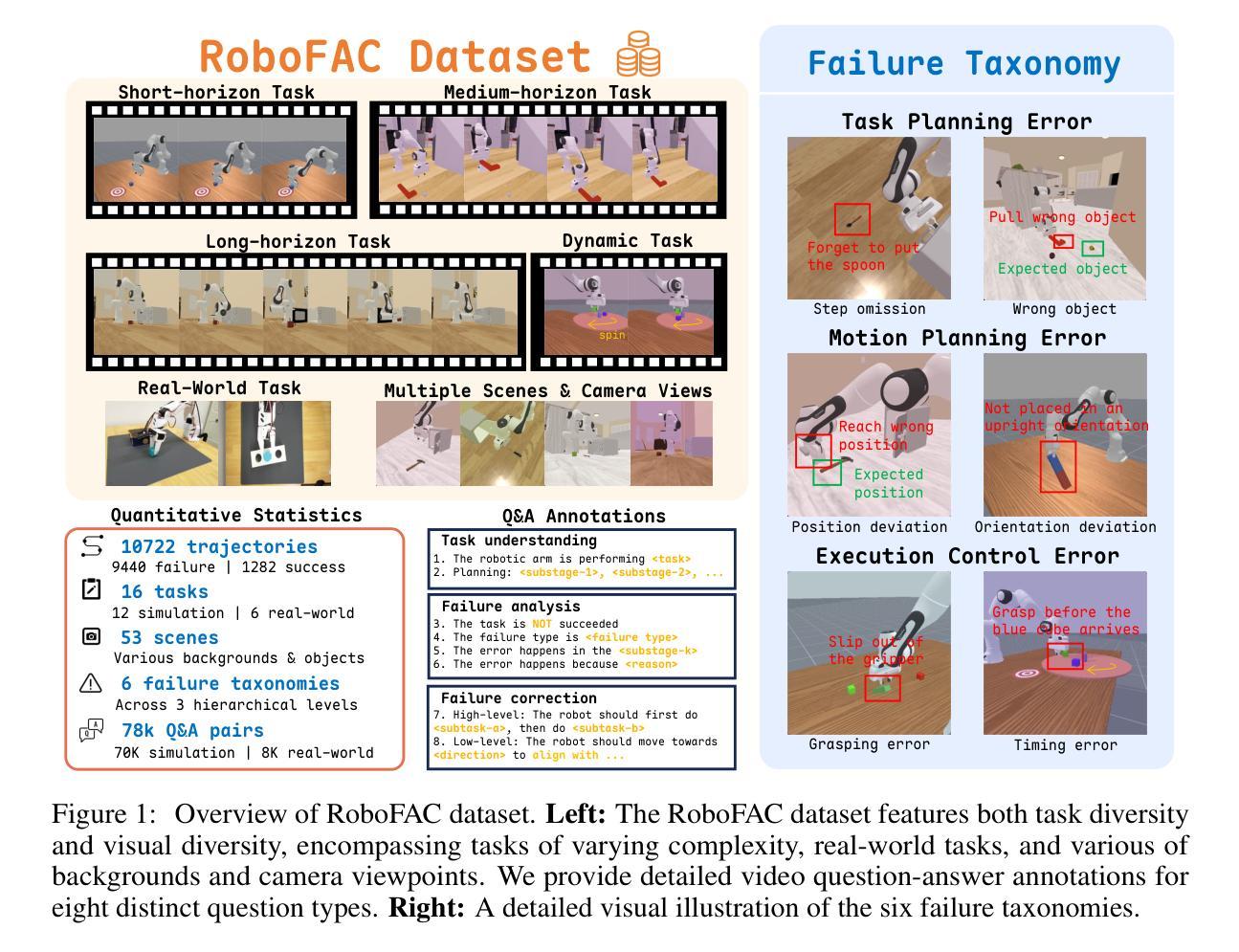
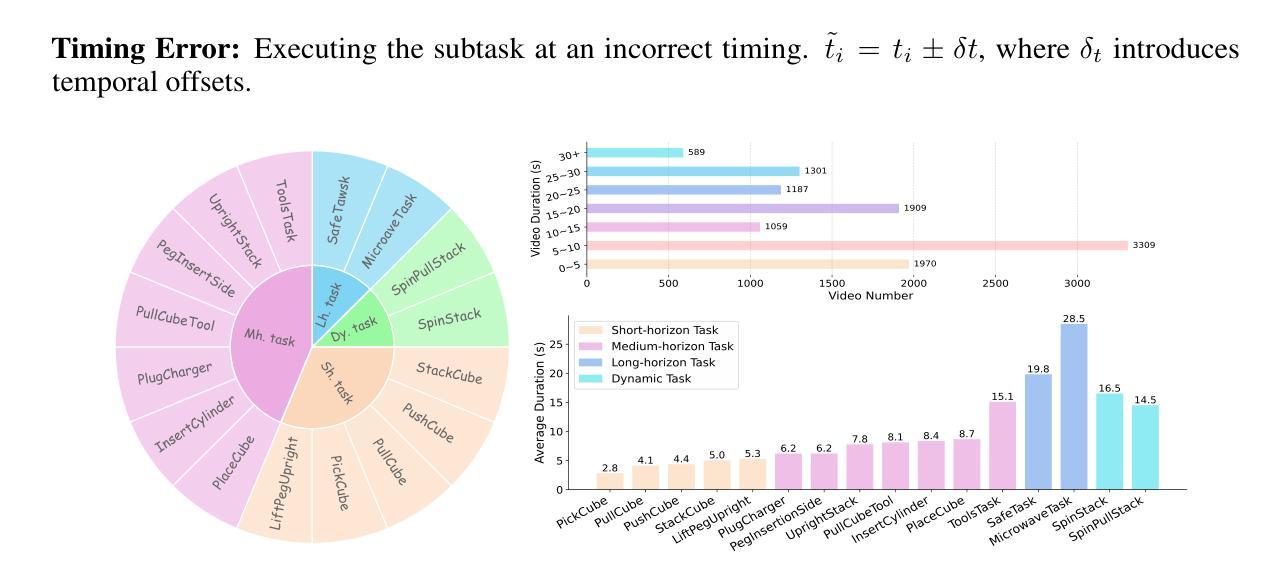
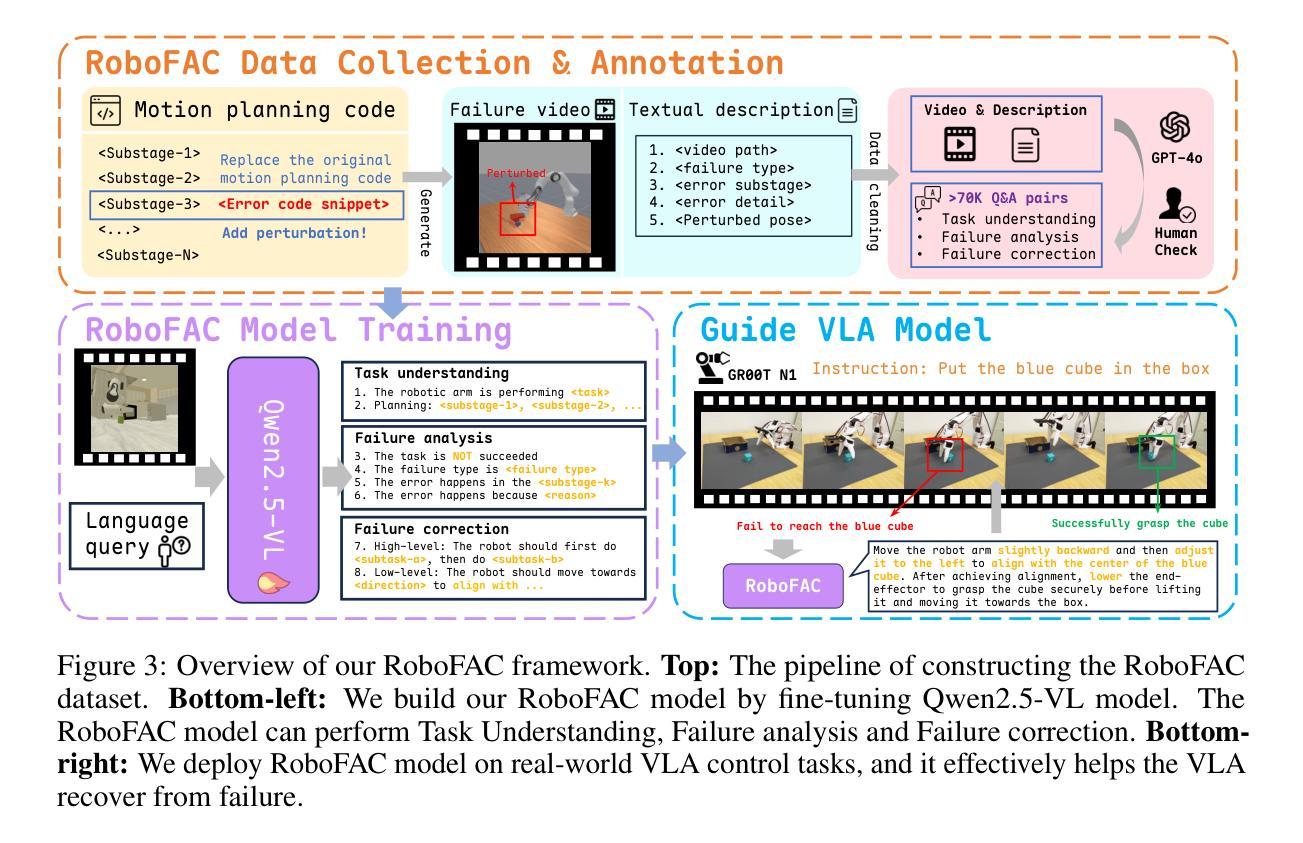
Vision-Language-Action (VLA) models have recently advanced robotic manipulation by translating natural-language instructions and image information into sequential control actions. However, these models often underperform in open-world scenarios, as they are predominantly trained on successful expert demonstrations and exhibit a limited capacity for failure recovery. In this work, we present a Robotic Failure Analysis and Correction (RoboFAC) framework to address this issue. Firstly, we construct RoboFAC dataset comprising 9,440 erroneous manipulation trajectories and 78,623 QA pairs across 16 diverse tasks and 53 scenes in both simulation and real-world environments. Leveraging our dataset, we develop RoboFAC model, which is capable of Task Understanding, Failure Analysis and Failure Correction. Experimental results demonstrate that the RoboFAC model outperforms GPT-4o by 34.1% on our evaluation benchmark. Furthermore, we integrate the RoboFAC model into a real-world VLA control pipeline as an external supervision providing correction instructions, yielding a 29.1% relative improvement on average on four real-world tasks. The results show that our RoboFAC framework effectively handles robotic failures and assists the VLA model in recovering from failures.
视觉语言动作(VLA)模型最近通过将自然语言指令和图像信息翻译成一系列控制动作,推动了机器人操作技术的发展。然而,这些模型在开放世界场景中往往表现不佳,因为它们主要基于成功的专家演示,并且在故障恢复方面能力有限。针对这一问题,我们在工作中提出了机器人故障分析与纠正(RoboFAC)框架。首先,我们构建了RoboFAC数据集,其中包含9440条错误的操作轨迹和78623对问答,涉及仿真和真实环境中的16个任务和53个场景。利用我们的数据集,我们开发了RoboFAC模型,具备任务理解、故障分析和故障纠正能力。实验结果表明,RoboFAC模型在我们的评估基准测试上的表现优于GPT-4o,达到34.1%。此外,我们将RoboFAC模型集成到现实世界中的VLA控制管道中,作为外部监督提供纠正指令,在四个真实任务上平均提高了29.1%的相对表现。结果表明,我们的RoboFAC框架有效地处理了机器人故障,并帮助VLA模型从故障中恢复。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
该研究提出了Robotic Failure Analysis and Correction(RoboFAC)框架,以解决Vision-Language-Action(VLA)模型在开放世界场景下性能不足的问题。该框架构建了包含错误操作轨迹和问答对的RoboFAC数据集,并开发了具备任务理解、故障分析和故障纠正能力的RoboFAC模型。实验结果表明,RoboFAC模型在评估基准测试上优于GPT-4o达34.1%,并且集成到真实世界的VLA控制管道中后,平均相对改进率为29.1%。
Key Takeaways
- VLA模型通过将自然语言指令和图像信息翻译为连续的控制动作,推动了机器人操作的发展。
- VLA模型在开放世界场景中的性能有待提高,尤其对于错误恢复的能力有限。
- 研究人员构建了RoboFAC数据集,包含错误操作轨迹和跨不同任务和场景的问答对。
- 开发出的RoboFAC模型具备任务理解、故障分析和纠正功能。
- 实验显示,RoboFAC模型在评估基准测试上的性能优于GPT-4o达34.1%。
- 在真实世界的VLA控制管道中集成RoboFAC模型后,实现了平均相对改进率29.1%。
点此查看论文截图


Evaluation and optimization of deep learning models for enhanced detection of brain cancer using transmission optical microscopy of thin brain tissue samples
Authors:Mohnish Sao, Mousa Alrubayan, Prabhakar Pradhan
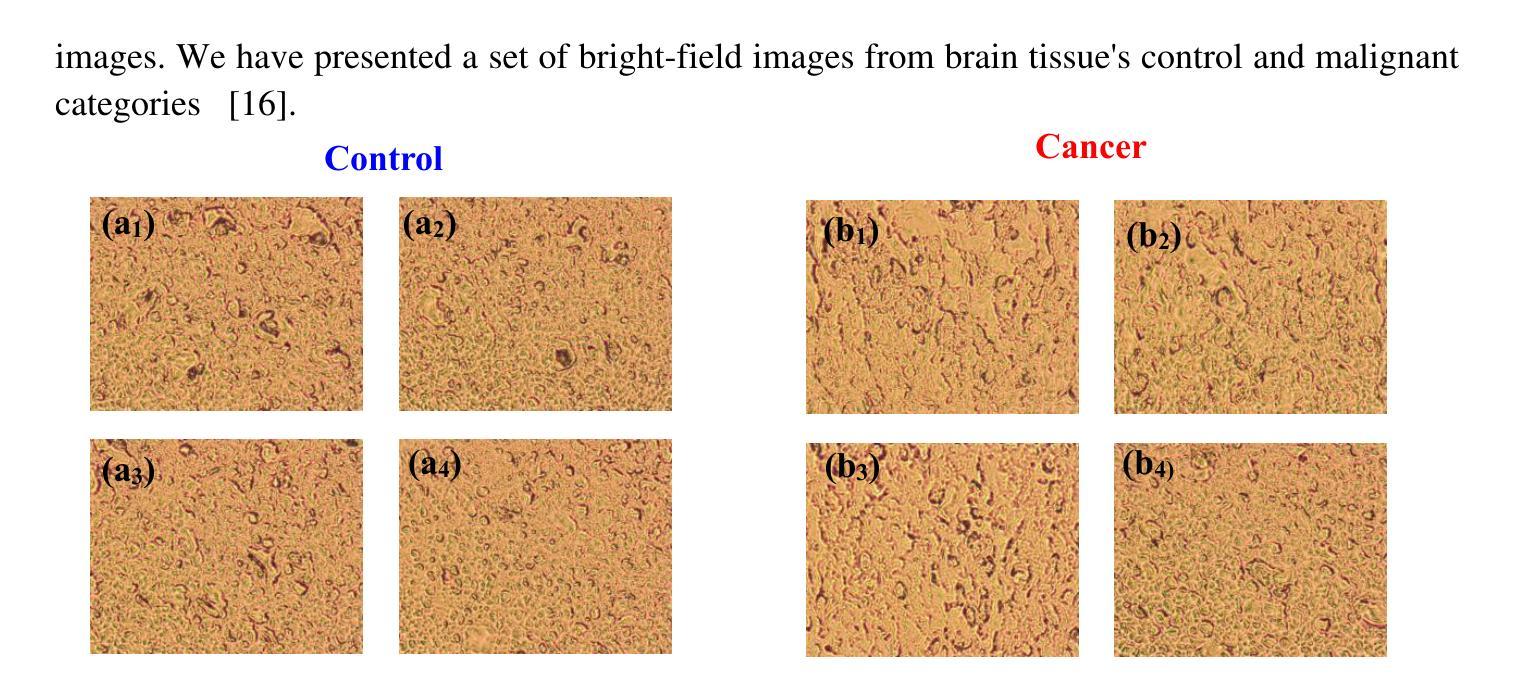
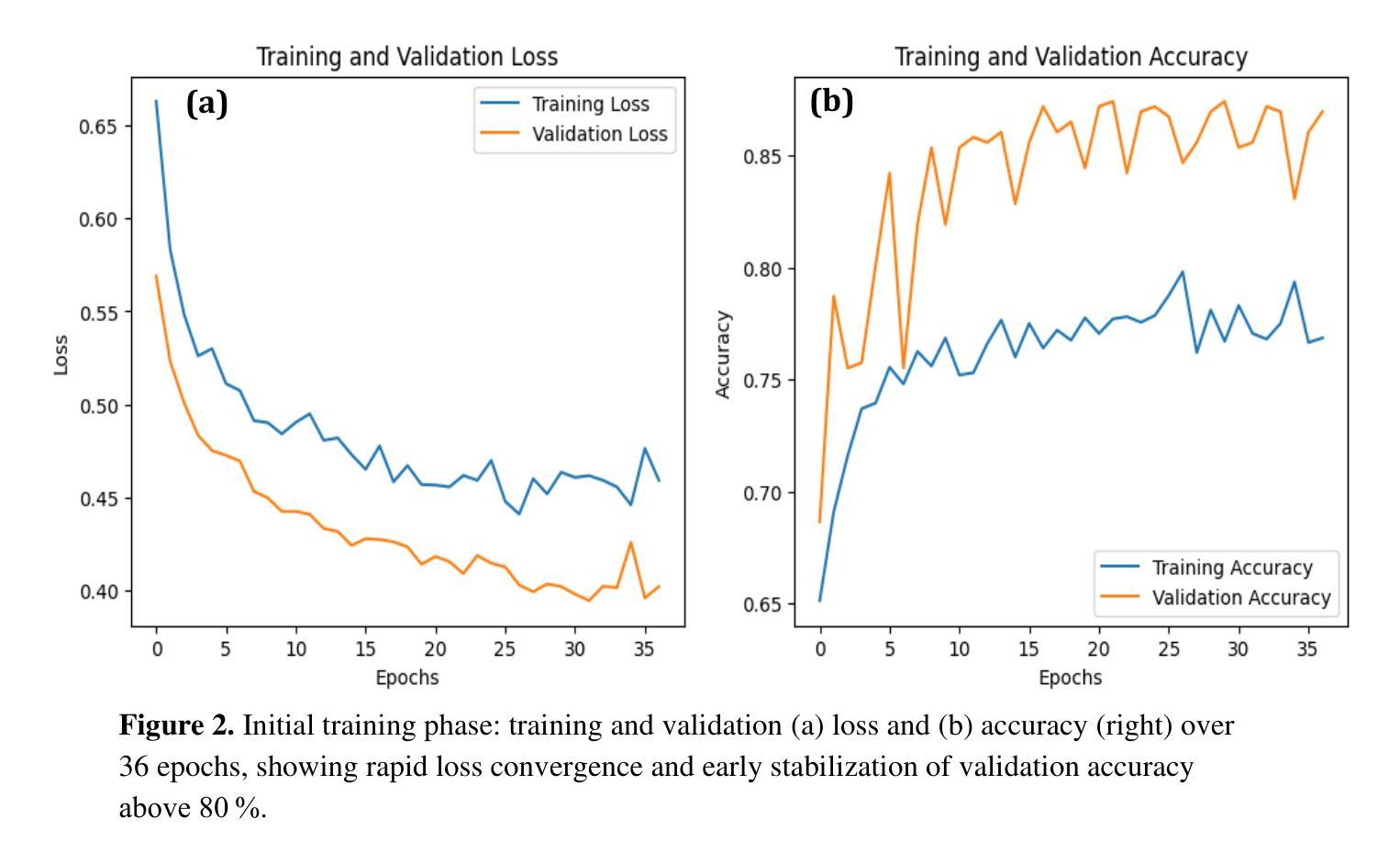
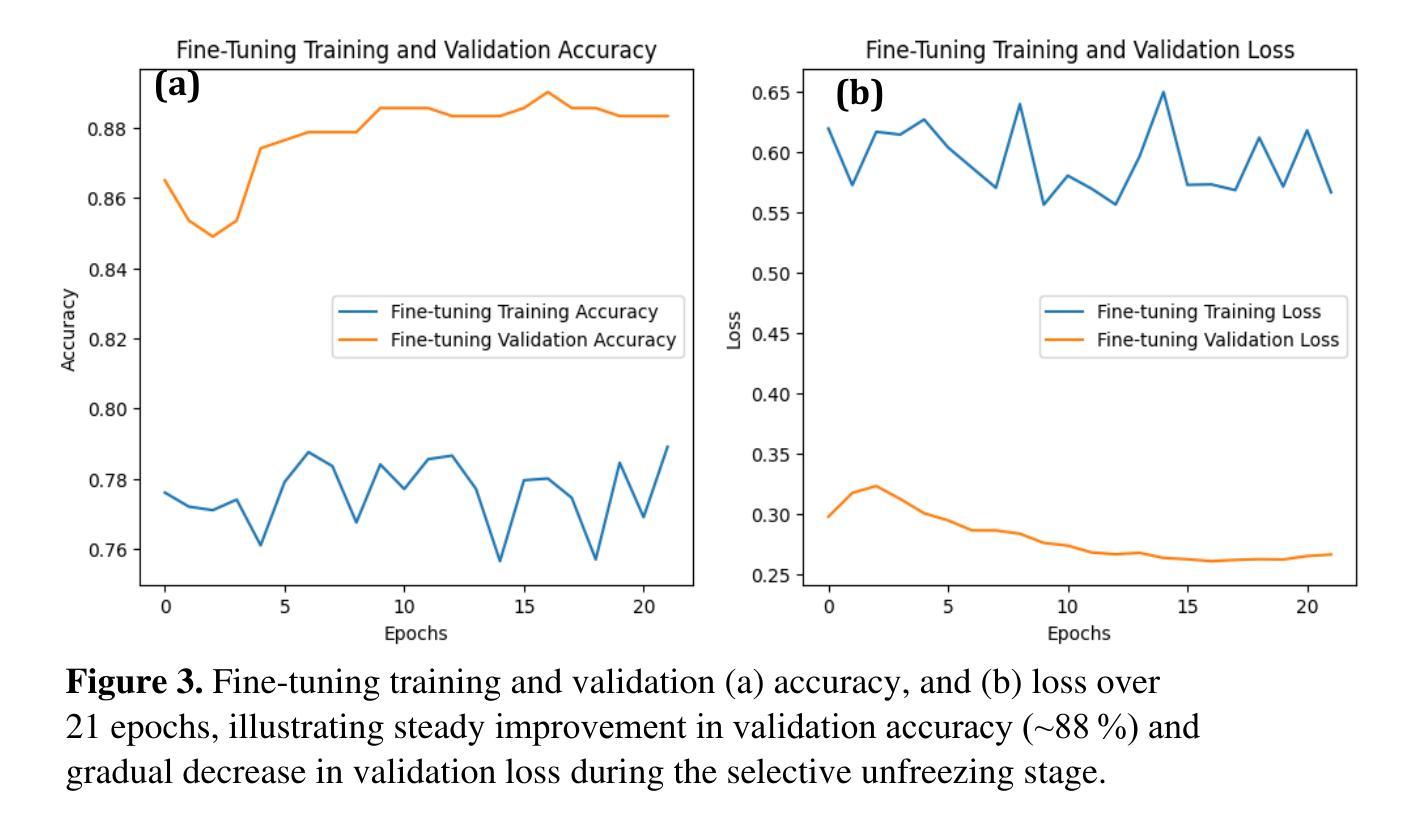
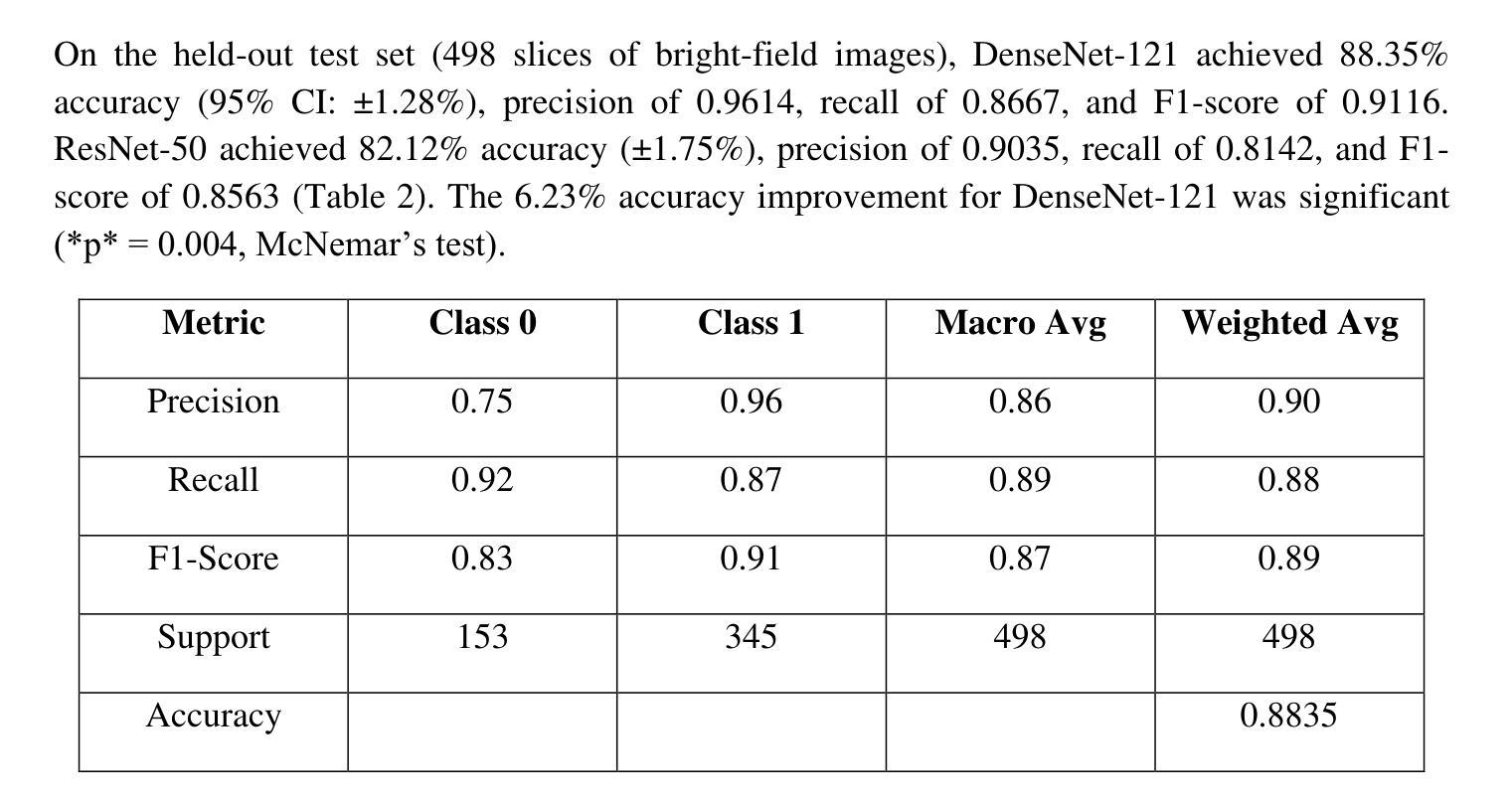
Optical transmission spectroscopy is one method to understand brain tissue structural properties from brain tissue biopsy samples, yet manual interpretation is resource intensive and prone to inter observer variability. Deep convolutional neural networks (CNNs) offer automated feature learning directly from raw brightfield images. Here, we evaluate ResNet50 and DenseNet121 on a curated dataset of 2,931 bright-field transmission optical microscopy images of thin brain tissue, split into 1,996 for training, 437 for validation, and 498 for testing. Our two stage transfer learning protocol involves initial training of a classifier head on frozen pretrained feature extractors, followed by fine tuning of deeper convolutional blocks with extensive data augmentation (rotations, flips, intensity jitter) and early stopping. DenseNet121 achieves 88.35 percent test accuracy, 0.9614 precision, 0.8667 recall, and 0.9116 F1 score the best performance compared to ResNet50 (82.12 percent, 0.9035, 0.8142, 0.8563). Detailed analysis of confusion matrices, training and validation curves, and classwise prediction distributions illustrates robust convergence and minimal bias. These findings demonstrate the superior generalization of dense connectivity on limited medical datasets and outline future directions for multi-class tumor grading and clinical translation.
光学传输光谱法是一种通过脑组织活检样本了解脑组织结构性质的方法,但人工解读需要耗费大量资源,并且容易因观察者之间差异而导致结果差异。深度卷积神经网络(CNN)可以直接从原始明场图像中实现自动化特征学习。在此,我们对包含有用于训练的1996张图像、用于验证的437张图像以及用于测试的498张图像的精选数据集进行了ResNet50和DenseNet121评估。我们的两阶段迁移学习协议涉及首先在冻结的预训练特征提取器上训练分类器头部,然后通过丰富的数据增强(旋转、翻转、强度抖动)进行更深的卷积块的微调并使用早期停止策略。DenseNet121在测试集上取得了最佳性能,测试准确度为88.35%,精确度、召回率和F1分数分别为0.9614、0.8667和0.9116。与ResNet50(测试准确度为82.12%,精确度、召回率和F1分数分别为0.9035、0.8142和0.8563)相比具有优势。通过对混淆矩阵、训练和验证曲线以及类别预测分布进行详细分析,显示出稳健的收敛性和较小的偏差。这些结果表明密集连接在有限的医学数据集上具有优越的一般化能力,并概述了未来多类肿瘤分级和临床转化的方向。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 10 pages, 5 figures
Summary:利用光学传输光谱法了解脑组织活检样本的结构特性,但手动解读需要大量资源且易出现观察者间差异。本研究采用深度卷积神经网络(CNN)直接从原始明场图像中学习特征,对ResNet50和DenseNet121进行评估。在精选的包含2931张薄脑组织明场透射光学显微镜图像的数据集上,应用两阶段迁移学习协议,实现分类器头部的初步训练以及对冻结的预训练特征提取器的精细调整。通过数据增强(旋转、翻转、强度抖动)和早期停止策略,DenseNet121取得了最佳性能,测试准确度为88.35%,精确度、召回率和F1分数分别为0.9614、0.8667和0.9116。而ResNet50的性能稍逊,准确率为82.12%。研究结果表明DenseNet具有优越的泛化能力,未来有望应用于多类肿瘤分级和临床转化研究。
Key Takeaways:
- 本研究使用深度卷积神经网络(CNN)从薄脑组织明场透射光学显微镜图像中自动学习特征。
- 通过两阶段迁移学习协议,DenseNet121在数据集上取得了最佳性能。
- DenseNet121的测试准确度达到88.35%,并且具有较高的精确度、召回率和F1分数。
- 研究表明DenseNet具有优越的泛化能力,尤其在有限的医学数据集上。
点此查看论文截图

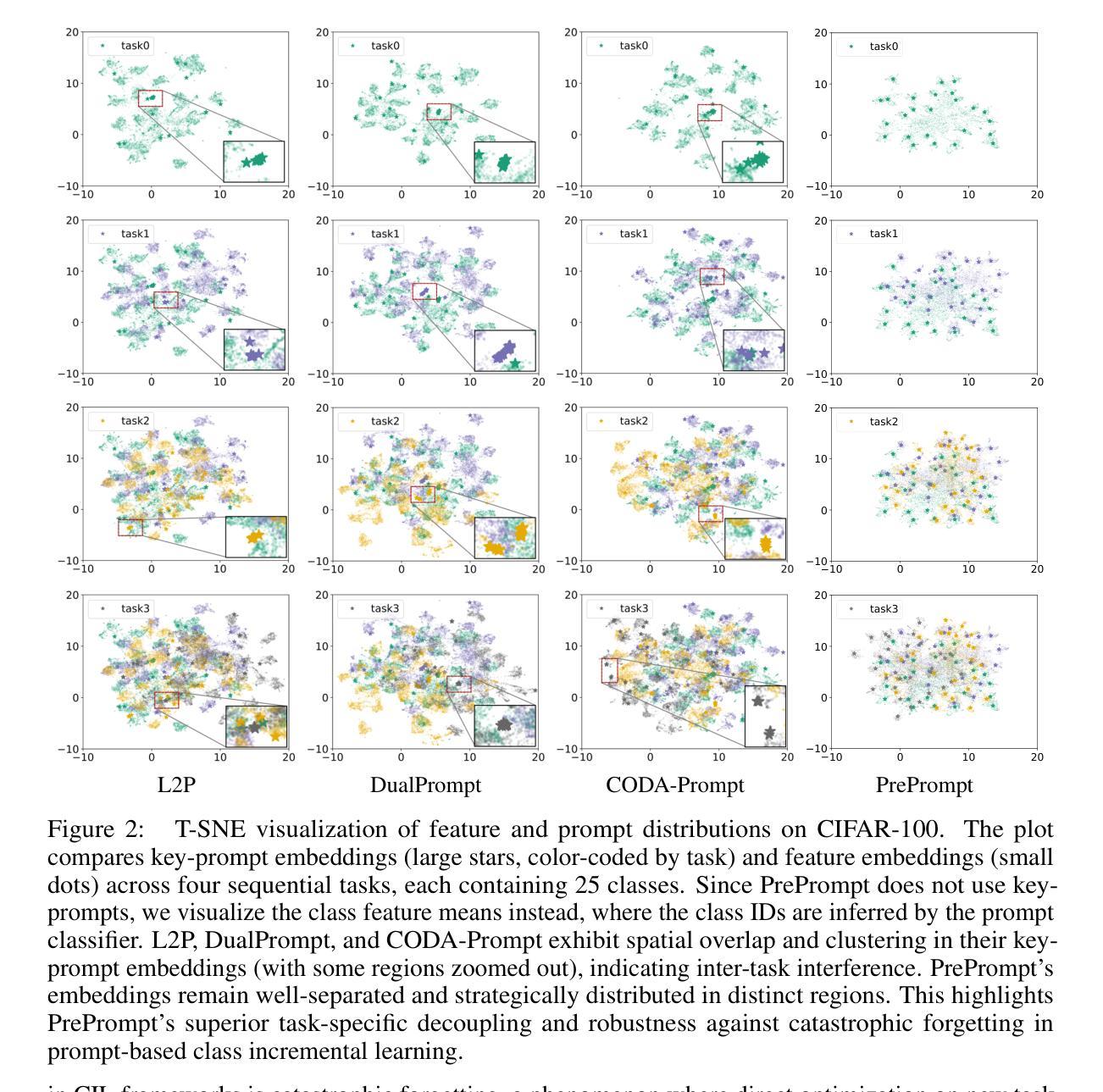
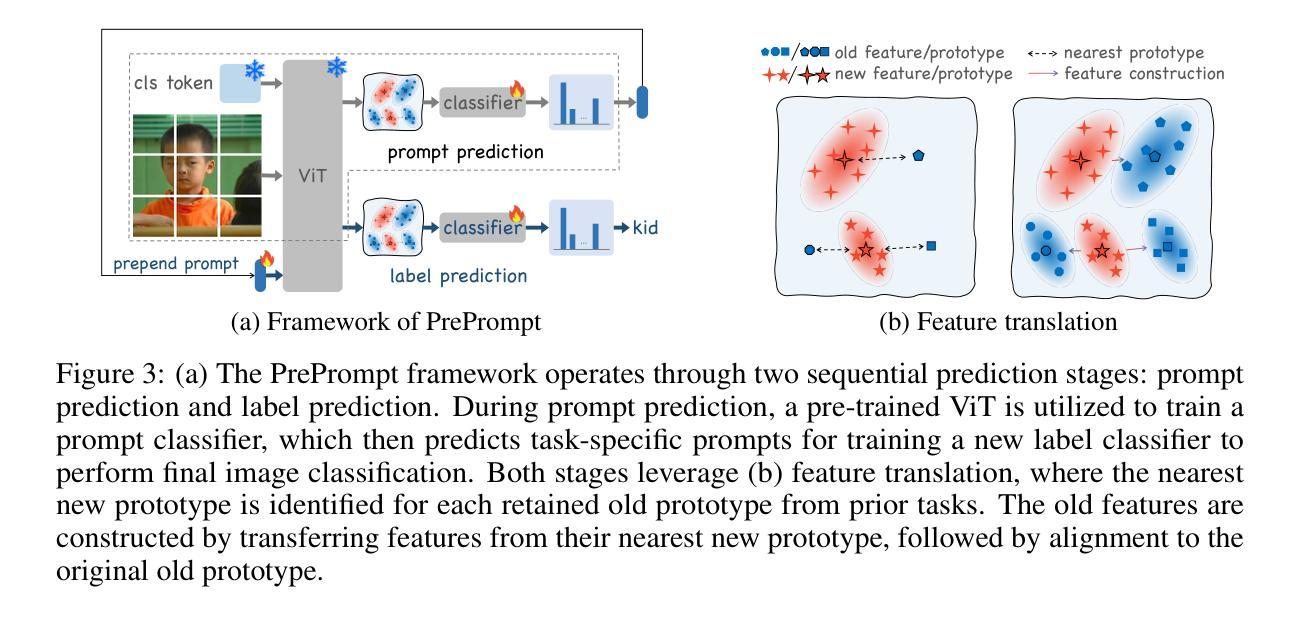
PrePrompt: Predictive prompting for class incremental learning
Authors:Libo Huang, Zhulin An, Chuanguang Yang, Boyu Diao, Fei Wang, Yan Zeng, Zhifeng Hao, Yongjun Xu
Class Incremental Learning (CIL) based on pre-trained models offers a promising direction for open-world continual learning. Existing methods typically rely on correlation-based strategies, where an image’s classification feature is used as a query to retrieve the most related key prompts and select the corresponding value prompts for training. However, these approaches face an inherent limitation: fitting the entire feature space of all tasks with only a few trainable prompts is fundamentally challenging. We propose Predictive Prompting (PrePrompt), a novel CIL framework that circumvents correlation-based limitations by leveraging pre-trained models’ natural classification ability to predict task-specific prompts. Specifically, PrePrompt decomposes CIL into a two-stage prediction framework: task-specific prompt prediction followed by label prediction. While theoretically appealing, this framework risks bias toward recent classes due to missing historical data for older classifier calibration. PrePrompt then mitigates this by incorporating feature translation, dynamically balancing stability and plasticity. Experiments across multiple benchmarks demonstrate PrePrompt’s superiority over state-of-the-art prompt-based CIL methods. Code available at \href{github.com/libo-huang/preprompt}{github.com/libo-huang/preprompt}.
基于预训练模型的类增量学习(CIL)为开放世界持续学习提供了有前景的方向。现有方法通常依赖于基于关联的策略,其中使用图像的分类特征作为查询来检索最相关的关键提示,并选择相应的值提示进行训练。然而,这些方法面临一个固有的局限性:用少数可训练提示来适应所有任务的整体特征空间具有根本挑战性。我们提出了预测提示(PrePrompt),这是一种新型CIL框架,它通过利用预训练模型的天然分类能力来预测特定任务的提示,从而避免了基于关联的限制。具体来说,PrePrompt将CIL分解为一个两阶段预测框架:特定任务的提示预测,然后是标签预测。虽然这在理论上很有吸引力,但由于缺少旧分类器的历史数据进行校准,这个框架可能偏向最近的类别。PrePrompt通过结合特征翻译来减轻这一问题,动态平衡稳定性和可塑性。在多个基准测试上的实验表明,PrePrompt优于最先进的基于提示的CIL方法。代码可在github.com/libo-huang/preprompt找到。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 16 pages, 29 figures, conference
Summary
基于预训练模型的类增量学习(CIL)为开放世界持续学习提供了有前景的方向。现有方法通常依赖于基于关联的策略,使用图像的识别特征作为查询来检索最相关的关键提示,并选择对应的值提示进行训练。然而,这些方法面临内在局限:用少量可训练提示来拟合所有任务的整个特征空间具有根本挑战性。我们提出预测提示(PrePrompt)这一新型CIL框架,通过利用预训练模型的天然分类能力来预测任务特定提示,从而规避了基于关联的限制。PrePrompt将CIL分解为两个阶段:任务特定提示预测和标签预测。尽管理论上具有吸引力,但由于缺少对旧分类器的校准历史数据,此框架可能偏向最近的类别。PrePrompt通过引入特征翻译来平衡稳定性和可塑性,从而缓解这一问题。在多个基准测试上的实验表明,PrePrompt优于最新的提示式CIL方法。
Key Takeaways
- 类增量学习(CIL)是开放世界持续学习的一个有前途的方向。
- 现有方法主要依赖基于关联的策略,使用图像分类特征作为查询来检索提示。
- 基于预训练模型的PrePrompt框架通过预测任务特定提示来规避关联限制。
- PrePrompt将CIL分解为任务特定提示预测和标签预测两个阶段。
- PrePrompt可能偏向最近的类别,因为缺少旧分类器的校准历史数据。
- 特征翻译被引入到PrePrompt中以平衡稳定性和可塑性。
点此查看论文截图

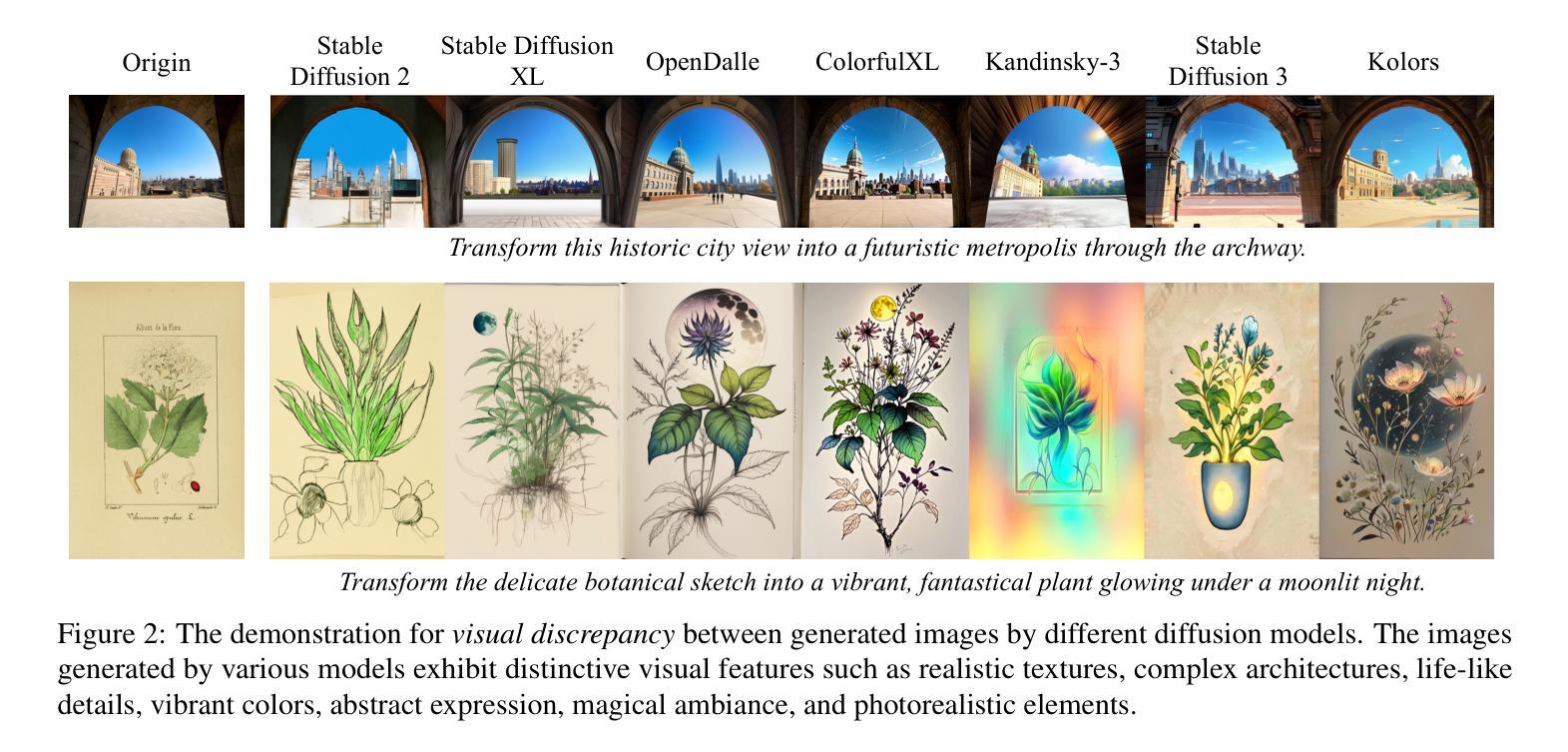
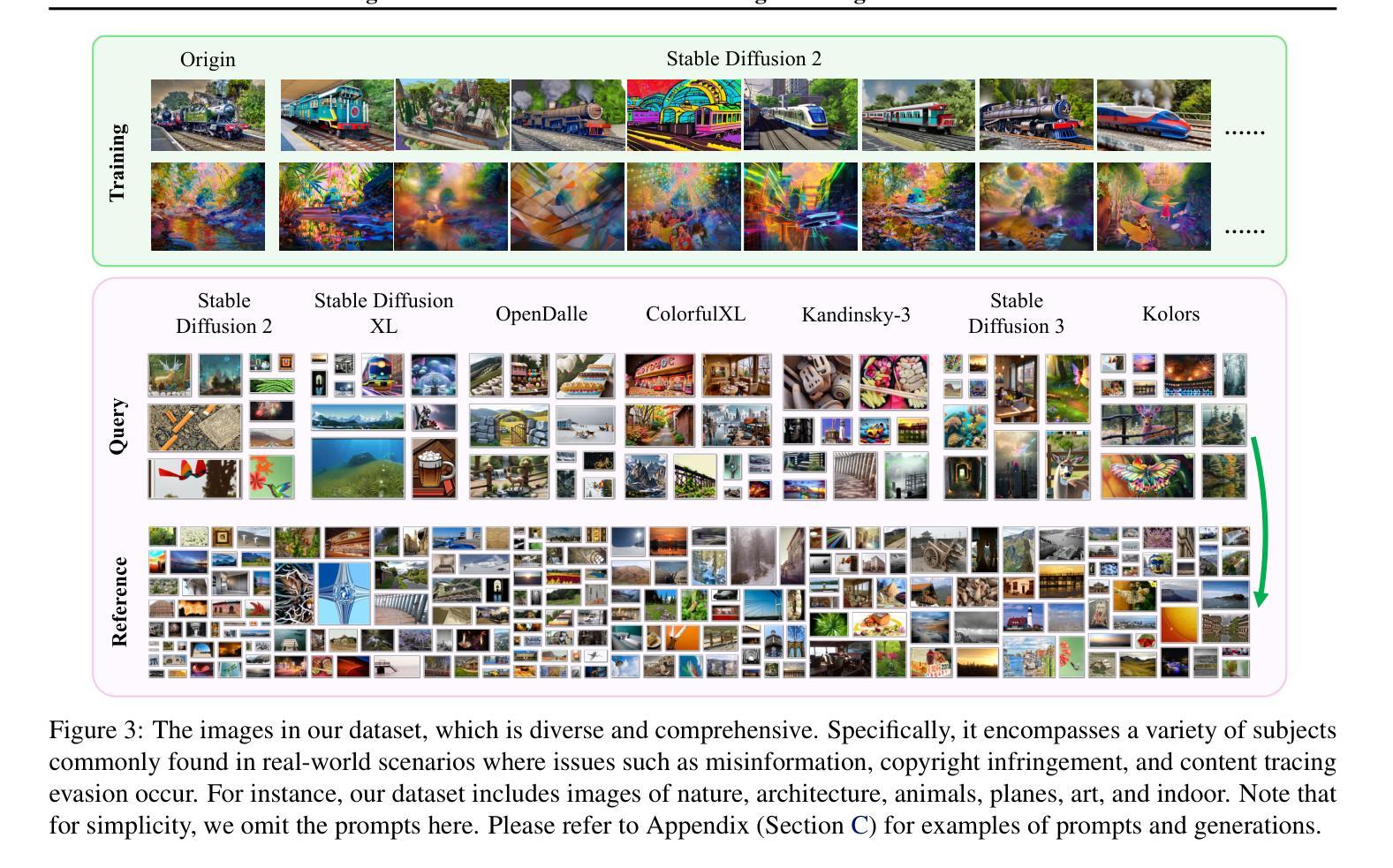
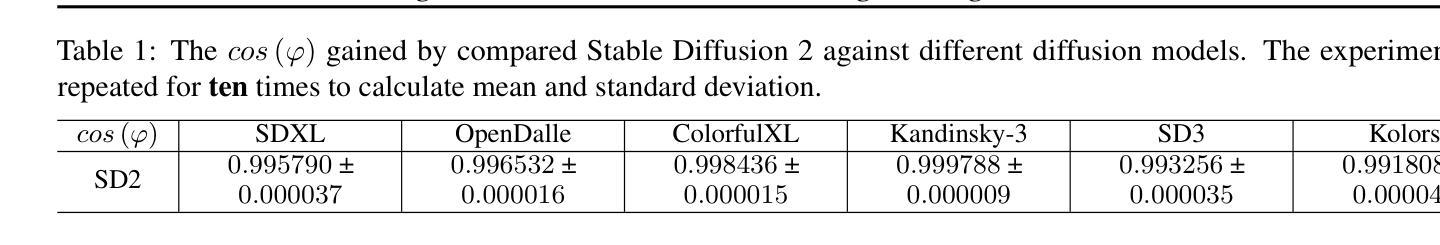
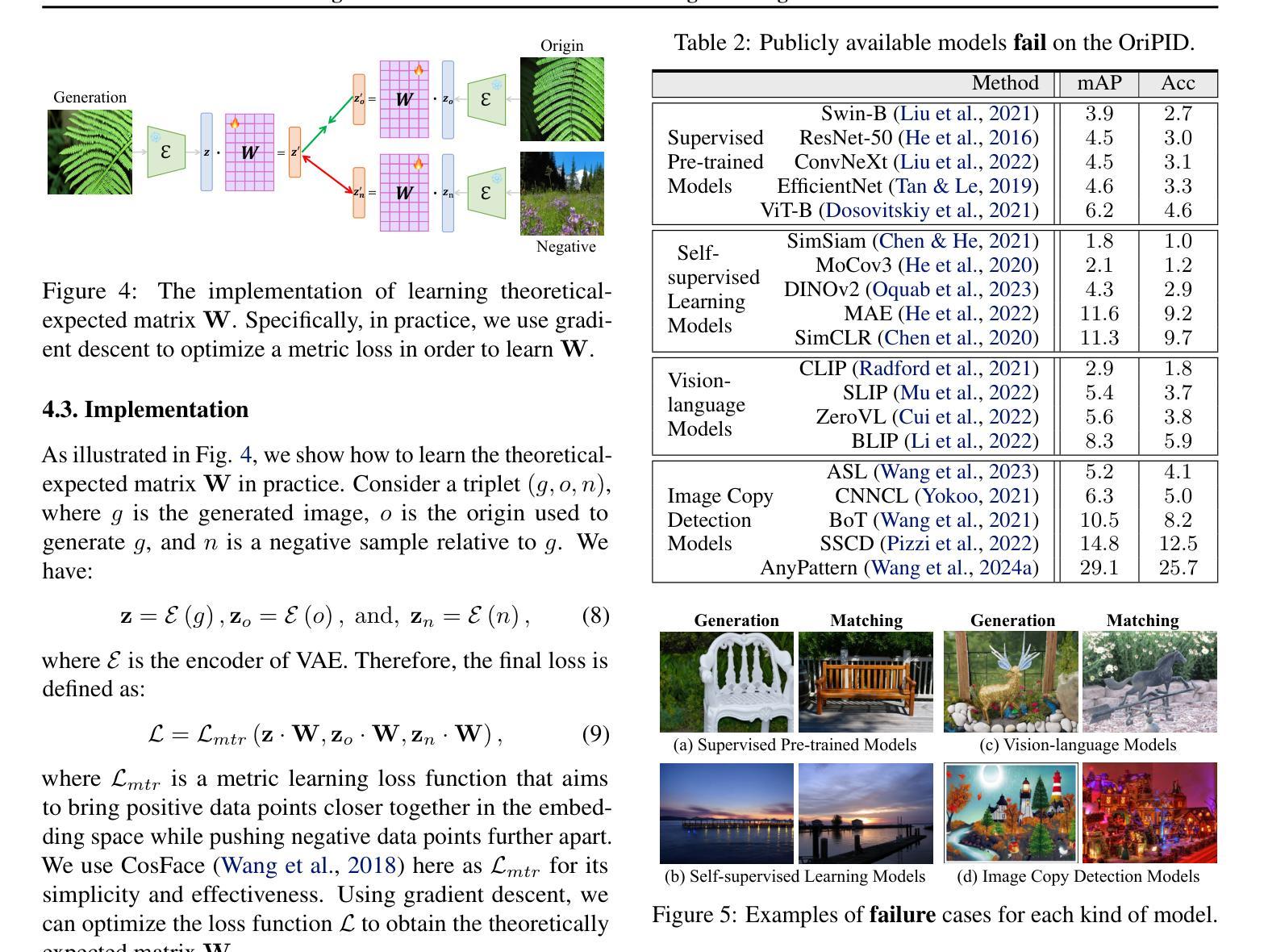
Origin Identification for Text-Guided Image-to-Image Diffusion Models
Authors:Wenhao Wang, Yifan Sun, Zongxin Yang, Zhentao Tan, Zhengdong Hu, Yi Yang
Text-guided image-to-image diffusion models excel in translating images based on textual prompts, allowing for precise and creative visual modifications. However, such a powerful technique can be misused for spreading misinformation, infringing on copyrights, and evading content tracing. This motivates us to introduce the task of origin IDentification for text-guided Image-to-image Diffusion models (ID$^2$), aiming to retrieve the original image of a given translated query. A straightforward solution to ID$^2$ involves training a specialized deep embedding model to extract and compare features from both query and reference images. However, due to visual discrepancy across generations produced by different diffusion models, this similarity-based approach fails when training on images from one model and testing on those from another, limiting its effectiveness in real-world applications. To solve this challenge of the proposed ID$^2$ task, we contribute the first dataset and a theoretically guaranteed method, both emphasizing generalizability. The curated dataset, OriPID, contains abundant Origins and guided Prompts, which can be used to train and test potential IDentification models across various diffusion models. In the method section, we first prove the existence of a linear transformation that minimizes the distance between the pre-trained Variational Autoencoder (VAE) embeddings of generated samples and their origins. Subsequently, it is demonstrated that such a simple linear transformation can be generalized across different diffusion models. Experimental results show that the proposed method achieves satisfying generalization performance, significantly surpassing similarity-based methods ($+31.6%$ mAP), even those with generalization designs. The project is available at https://id2icml.github.io.
文本引导的图像到图像扩散模型在根据文本提示进行图像转换方面表现出色,可以进行精确和创造性的视觉修改。然而,这种强大的技术可能会被误用,用于传播错误信息、侵犯版权和规避内容追踪。这促使我们引入针对文本引导的图像到图像扩散模型的起源识别任务(ID$^2$),旨在检索给定翻译查询的原始图像。一种解决ID$^2$的直观方法是通过训练专门的深度嵌入模型来提取和比较查询图像和参考图像的特征。然而,由于不同扩散模型产生的各代图像之间的视觉差异,这种基于相似度的方法在用一个模型训练而在另一个模型测试时会失败,从而限制了其在现实世界应用中的有效性。为了解决所提出的ID$^2$任务的这一挑战,我们提供了第一个数据集和一种理论上有保证的方法,两者都强调通用性。我们精心制作的数据集OriPID包含丰富的起源和引导提示,可用于训练和测试各种扩散模型的潜在识别模型。在方法部分,我们首先证明存在一个线性变换可以最小化预训练变分自编码器(VAE)生成的样本嵌入与其原始样本之间的距离。随后,演示了这种简单的线性变换可以在不同的扩散模型之间进行泛化。实验结果表明,所提出的方法达到了令人满意的泛化性能,显著超越了基于相似度的方法(提高31.6%的mAP),甚至是那些具有泛化设计的方法。该项目在https://id2icml.github.io可用。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by ICML 2025
Summary:文本引导的图像到图像扩散模型能够根据文本提示进行精确而富有创意的图像修改。但该技术可能会被误用,如传播误导信息、侵犯版权和规避内容追踪。为此,提出了针对文本引导的图像到图像扩散模型的起源识别任务(ID$^2$),旨在检索给定翻译查询的原始图像。我们为此任务贡献第一个数据集和一种理论上有保证的方法,都强调通用性。数据集包含丰富的起源和引导提示,可用于训练和测试跨各种扩散模型的潜在识别模型。方法部分证明存在一个线性变换可以最小化生成样本的预训练变分自编码器嵌入与其起源之间的距离,这种简单的线性变换可以在不同的扩散模型中进行泛化。实验结果验证了该方法的良好泛化性能,显著优于基于相似度的方法(提高31.6%的mAP)。
Key Takeaways:
- 文本引导的图像到图像扩散模型可以根据文本提示进行精确和创意的图像修改。
- 这种技术可能被误用,导致传播误导信息、侵犯版权和规避内容追踪等问题。
- 针对此问题,提出了起源识别任务(ID$^2$),旨在检索给定翻译查询的原始图像。
- 贡献了一个针对ID$^2$任务的数据集(OriPID),包含用于训练和测试的起源和引导提示。
- 提出了一种理论上有保证的方法,通过线性变换来最小化生成样本与其起源之间的距离,并在不同的扩散模型中进行泛化。
- 实验结果表明该方法具有良好的泛化性能,显著优于基于相似度的方法。
点此查看论文截图

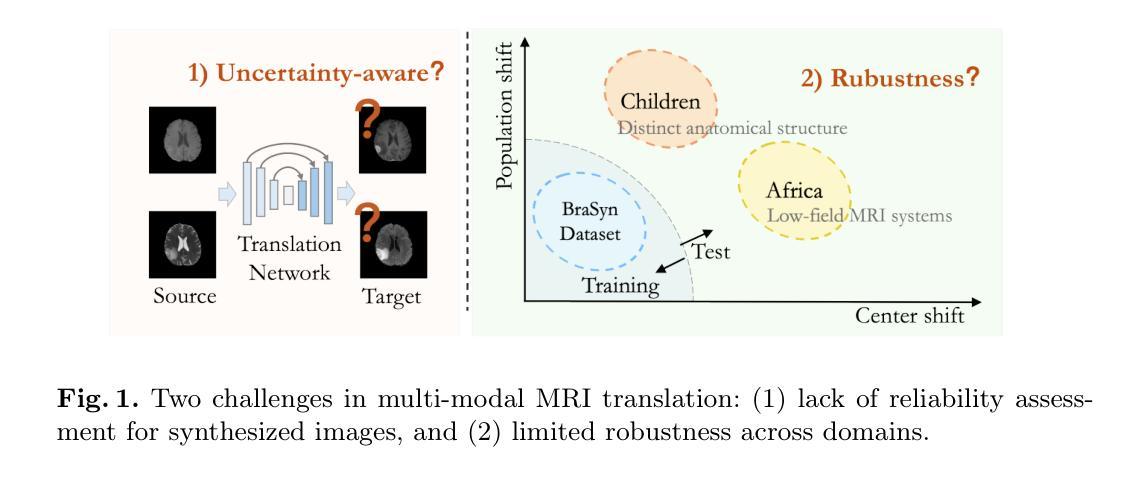
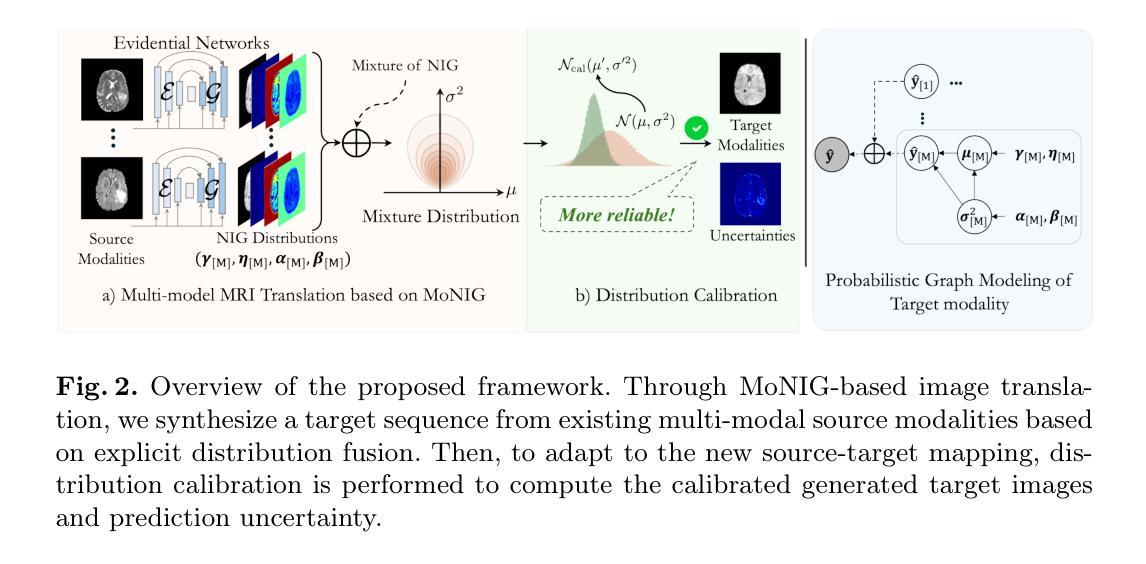
Multi-modal MRI Translation via Evidential Regression and Distribution Calibration
Authors:Jiyao Liu, Shangqi Gao, Yuxin Li, Lihao Liu, Xin Gao, Zhaohu Xing, Junzhi Ning, Yanzhou Su, Xiao-Yong Zhang, Junjun He, Ningsheng Xu, Xiahai Zhuang
Multi-modal Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) translation leverages information from source MRI sequences to generate target modalities, enabling comprehensive diagnosis while overcoming the limitations of acquiring all sequences. While existing deep-learning-based multi-modal MRI translation methods have shown promising potential, they still face two key challenges: 1) lack of reliable uncertainty quantification for synthesized images, and 2) limited robustness when deployed across different medical centers. To address these challenges, we propose a novel framework that reformulates multi-modal MRI translation as a multi-modal evidential regression problem with distribution calibration. Our approach incorporates two key components: 1) an evidential regression module that estimates uncertainties from different source modalities and an explicit distribution mixture strategy for transparent multi-modal fusion, and 2) a distribution calibration mechanism that adapts to source-target mapping shifts to ensure consistent performance across different medical centers. Extensive experiments on three datasets from the BraTS2023 challenge demonstrate that our framework achieves superior performance and robustness across domains.
多模态磁共振成像(MRI)翻译技术利用源MRI序列的信息来生成目标模态,从而实现全面诊断,同时克服了获取所有序列的局限性。虽然现有的基于深度学习的多模态MRI翻译方法已显示出有前途的潜力,但它们仍面临两个关键挑战:一是合成图像缺乏可靠的不确定性量化,二是在不同医疗中心部署时的稳健性有限。为了解决这些挑战,我们提出了一种新的框架,它将多模态MRI翻译重新表述为一个具有分布校准的多模态证据回归问题。我们的方法包含两个关键组成部分:一是证据回归模块,用于估计来自不同源模态的不确定性,并给出一个透明的多模态融合显式分布混合策略;二是分布校准机制,该机制能够适应源目标映射变化,以确保在不同医疗中心之间的性能一致性。在BraTS2023挑战的三个数据集上的广泛实验表明,我们的框架在跨域性能方面表现出卓越的性能和稳健性。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Early accepted by MICCAI 2025
Summary
多模态磁共振成像(MRI)转换利用源MRI序列的信息生成目标模态,实现全面诊断,同时克服获取所有序列的限制。针对现有深度学习多模态MRI转换方法面临的挑战,包括合成图像的不确定性量化不足和不同医疗中心部署的鲁棒性有限,我们提出了一种新的框架。该框架将多模态MRI转换重新构建为多模态证据回归问题,并引入分布校准机制。通过证据回归模块估计不同源模态的不确定性,并采用透明多模态融合策略进行分布校准。实验表明,该框架在BraTS2023挑战赛的三个数据集上表现出卓越的性能和跨域鲁棒性。
Key Takeaways
- 多模态MRI转换利用源MRI序列信息生成目标模态,促进全面诊断。
- 现有深度学习多模态MRI转换方法面临两个主要挑战:缺乏合成图像的不确定性量化以及跨不同医疗中心的鲁棒性有限。
- 新框架将多模态MRI转换重新构建为多模态证据回归问题,以处理源MRI序列的不确定性。
- 新框架引入证据回归模块,从多种源模态估计不确定性,并采用透明的多模态融合策略。
- 分布校准机制能够适应源-目标映射变化,确保在不同医疗中心之间的一致性能。
- 在BraTS2023挑战赛的数据集上进行的大量实验表明,新框架在性能和鲁棒性方面表现出优越性。
点此查看论文截图