⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-05-21 更新
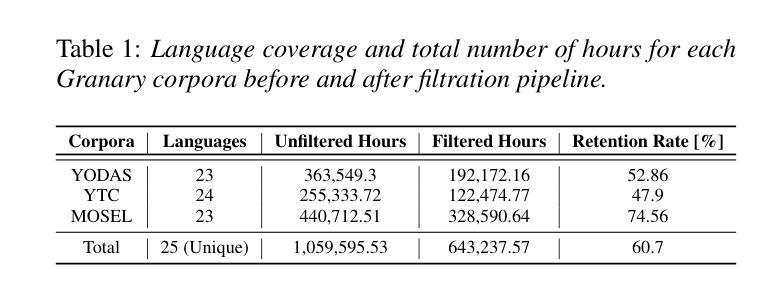
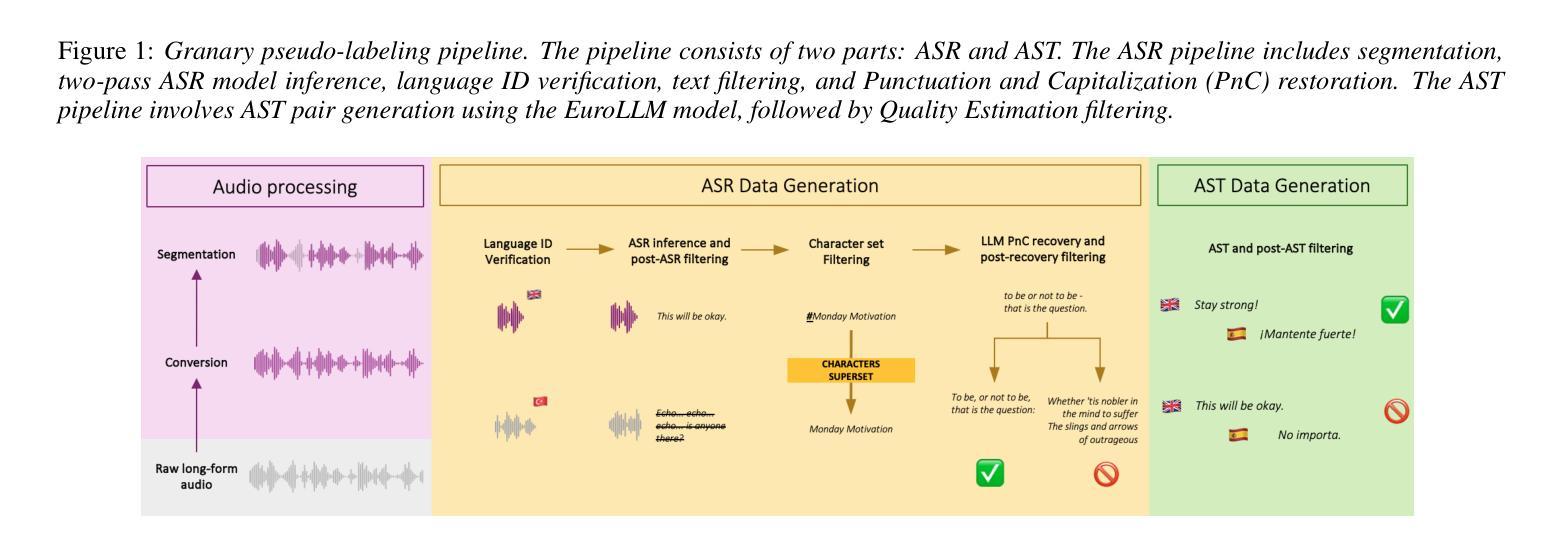
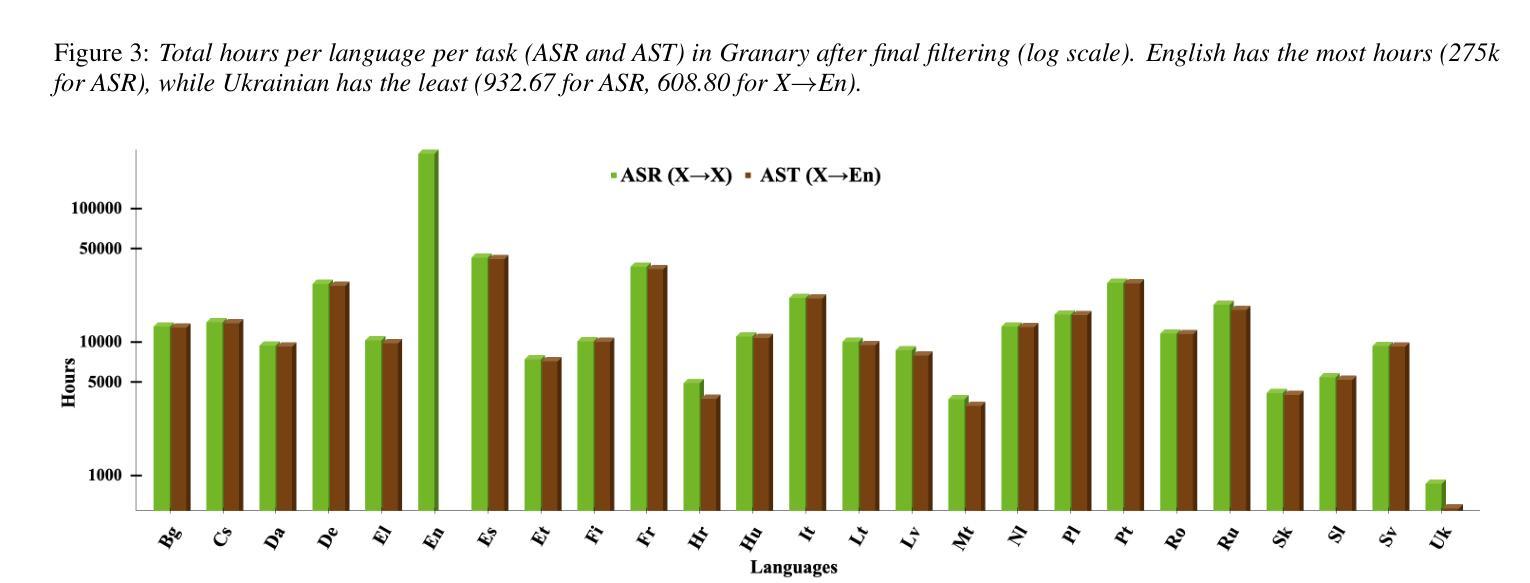
Granary: Speech Recognition and Translation Dataset in 25 European Languages
Authors:Nithin Rao Koluguri, Monica Sekoyan, George Zelenfroynd, Sasha Meister, Shuoyang Ding, Sofia Kostandian, He Huang, Nikolay Karpov, Jagadeesh Balam, Vitaly Lavrukhin, Yifan Peng, Sara Papi, Marco Gaido, Alessio Brutti, Boris Ginsburg
Multi-task and multilingual approaches benefit large models, yet speech processing for low-resource languages remains underexplored due to data scarcity. To address this, we present Granary, a large-scale collection of speech datasets for recognition and translation across 25 European languages. This is the first open-source effort at this scale for both transcription and translation. We enhance data quality using a pseudo-labeling pipeline with segmentation, two-pass inference, hallucination filtering, and punctuation restoration. We further generate translation pairs from pseudo-labeled transcriptions using EuroLLM, followed by a data filtration pipeline. Designed for efficiency, our pipeline processes vast amount of data within hours. We assess models trained on processed data by comparing their performance on previously curated datasets for both high- and low-resource languages. Our findings show that these models achieve similar performance using approx. 50% less data. Dataset will be made available at https://hf.co/datasets/nvidia/Granary
多任务和多语言方法对于大型模型有益,但由于数据稀缺,针对低资源语言的语音处理仍然被忽视。为了解决这个问题,我们推出了Granary,这是一个涵盖25种欧洲语言的语音数据集的大规模集合,用于识别和翻译。这是用于转录和翻译的此类规模的首次开源尝试。我们使用伪标签管道提高数据质量,包括分段、两阶段推断、幻觉过滤和标点恢复。我们进一步使用EuroLLM从伪标签转录中生成翻译对,随后进行数据处理管道。我们的设计注重效率,能在数小时内处理大量数据。我们通过在针对高资源和低资源语言的先前整理的数据集上比较性能来评估经过处理的数据训练的模型。我们的研究结果表明,这些模型在大约减少50%的数据的情况下实现了类似的性能。数据集将在https://hf.co/datasets/nvidia/Granary上提供。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted at Interspeech 2025
Summary
大规模多语种语音数据集Granary发布,包含25种欧洲语言的语音识别和翻译数据。采用伪标签流水线提高数据质量,并使用EuroLLM生成翻译配对。训练在此数据上的模型在高低资源语言上的性能表现良好,仅使用约50%的数据便达到了相似的效果。
Key Takeaways
- Granary是一个大规模的多语种语音数据集,涵盖25种欧洲语言,旨在解决低资源语言语音处理的数据稀缺问题。
- 通过伪标签流水线提高数据质量,包括分段、两阶段推断、幻觉过滤和标点恢复。
- 使用EuroLLM从伪标签转录生成翻译配对。
- 设计了高效的数据处理流水线,可在数小时内处理大量数据。
- 在已整理的高、低资源语言数据集上评估训练模型的性能。
- 模型在减少约50%数据的情况下实现了相似的性能表现。
点此查看论文截图

Time-Frequency-Based Attention Cache Memory Model for Real-Time Speech Separation
Authors:Guo Chen, Kai Li, Runxuan Yang, Xiaolin Hu
Existing causal speech separation models often underperform compared to non-causal models due to difficulties in retaining historical information. To address this, we propose the Time-Frequency Attention Cache Memory (TFACM) model, which effectively captures spatio-temporal relationships through an attention mechanism and cache memory (CM) for historical information storage. In TFACM, an LSTM layer captures frequency-relative positions, while causal modeling is applied to the time dimension using local and global representations. The CM module stores past information, and the causal attention refinement (CAR) module further enhances time-based feature representations for finer granularity. Experimental results showed that TFACM achieveed comparable performance to the SOTA TF-GridNet-Causal model, with significantly lower complexity and fewer trainable parameters. For more details, visit the project page: https://cslikai.cn/TFACM/.
现有的因果语音分离模型由于难以保留历史信息,通常与非因果模型相比表现不佳。为了解决这一问题,我们提出了时间-频率注意力缓存内存(TFACM)模型,该模型通过注意力机制和缓存内存(CM)有效捕捉时空关系,用于历史信息的存储。在TFACM中,LSTM层捕获频率相对位置,而因果建模则应用于时间维度,使用局部和全局表示。CM模块存储过去的信息,因果注意力细化(CAR)模块进一步增强了基于时间的特征表示,以实现更精细的粒度。实验结果表明,TFACM模型在性能上达到了最新技术TF-GridNet-Causal模型的水平,同时复杂度更低,可训练参数更少。如需更多详细信息,请访问项目页面:https://cslikai.cn/TFACM/。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary:
现有因果语音分离模型因难以保留历史信息而性能不足。我们提出TFACM模型,它通过注意力机制和缓存存储器捕捉时空关系来有效地解决这个问题。TFACM使用LSTM层捕捉频率相对位置,并在时间维度上应用因果建模。缓存存储器存储过去信息,因果注意力细化模块进一步提高了时间特征的精细度。实验结果表明,TFACM模型性能与SOTA TF-GridNet-Causal模型相当,但复杂度更低,可训练参数更少。更多详情访问项目页面:链接地址。
Key Takeaways:
- 现有因果语音分离模型由于难以保留历史信息而性能受限。
- TFACM模型通过注意力机制和缓存存储器捕捉时空关系来解决这一问题。
- LSTM层用于捕捉频率相对位置信息。
- 时间维度上应用了因果建模,采用局部和全局表示。
- 缓存存储器模块用于存储过去信息。
- 因果注意力细化模块提高了时间特征的精细度。
点此查看论文截图

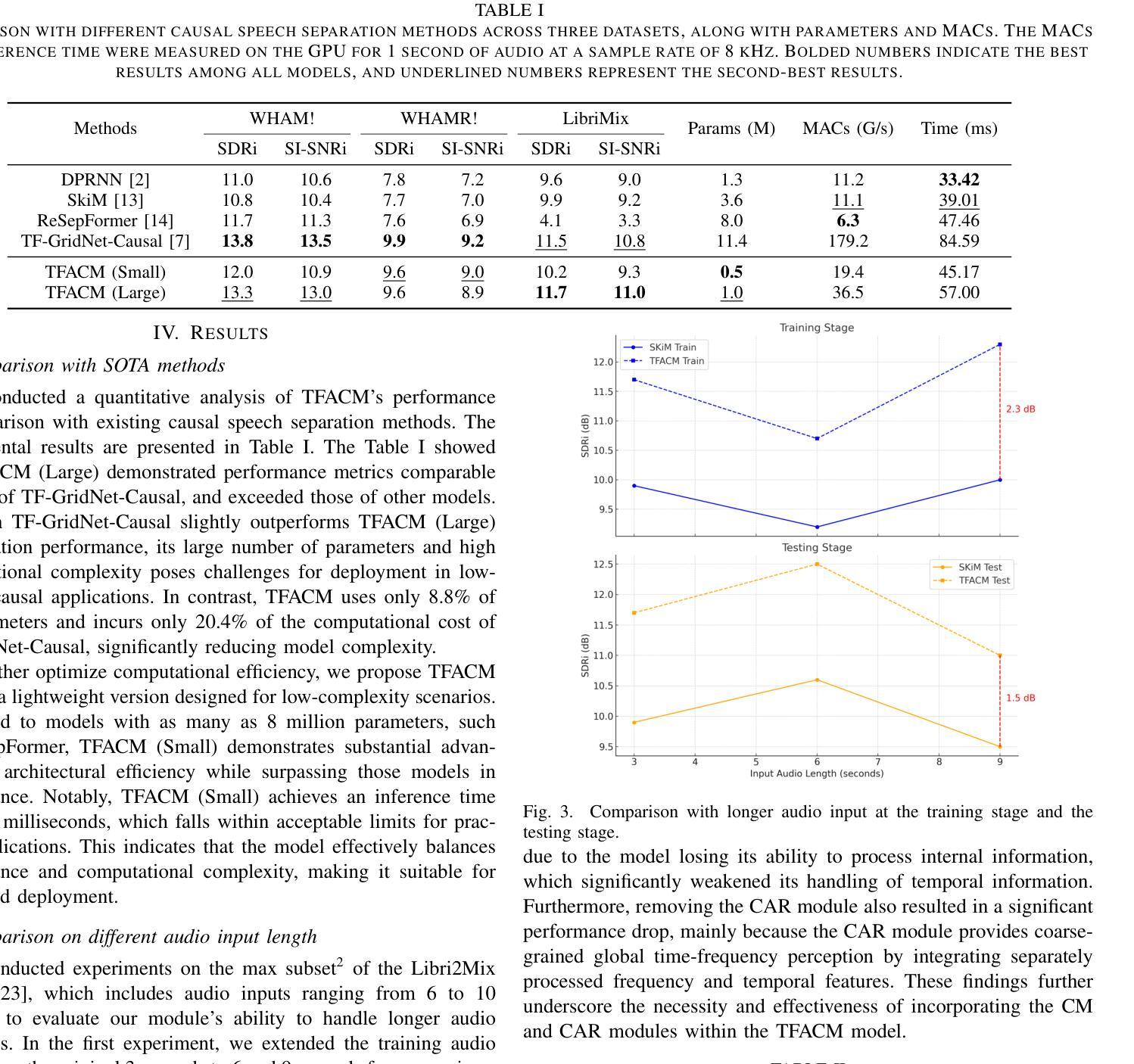
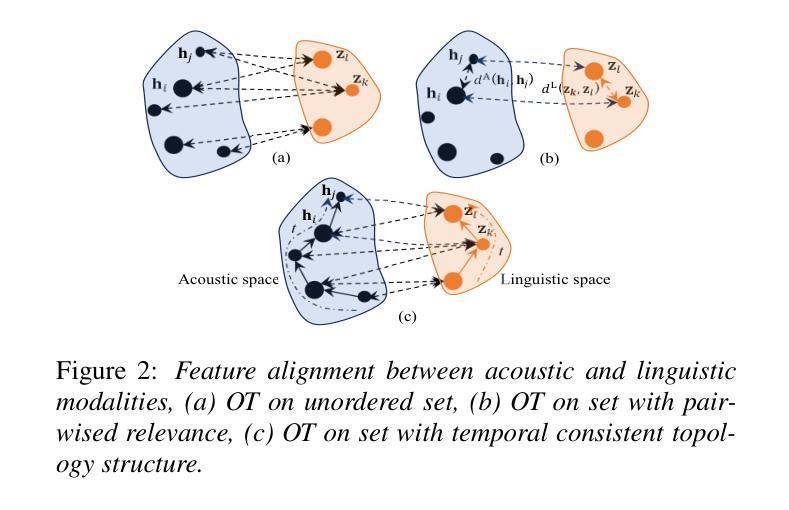
Cross-modal Knowledge Transfer Learning as Graph Matching Based on Optimal Transport for ASR
Authors:Xugang Lu, Peng Shen, Yu Tsao, Hisashi Kawai
Transferring linguistic knowledge from a pretrained language model (PLM) to acoustic feature learning has proven effective in enhancing end-to-end automatic speech recognition (E2E-ASR). However, aligning representations between linguistic and acoustic modalities remains a challenge due to inherent modality gaps. Optimal transport (OT) has shown promise in mitigating these gaps by minimizing the Wasserstein distance (WD) between linguistic and acoustic feature distributions. However, previous OT-based methods overlook structural relationships, treating feature vectors as unordered sets. To address this, we propose Graph Matching Optimal Transport (GM-OT), which models linguistic and acoustic sequences as structured graphs. Nodes represent feature embeddings, while edges capture temporal and sequential relationships. GM-OT minimizes both WD (between nodes) and Gromov-Wasserstein distance (GWD) (between edges), leading to a fused Gromov-Wasserstein distance (FGWD) formulation. This enables structured alignment and more efficient knowledge transfer compared to existing OT-based approaches. Theoretical analysis further shows that prior OT-based methods in linguistic knowledge transfer can be viewed as a special case within our GM-OT framework. We evaluate GM-OT on Mandarin ASR using a CTC-based E2E-ASR system with a PLM for knowledge transfer. Experimental results demonstrate significant performance gains over state-of-the-art models, validating the effectiveness of our approach.
将预训练语言模型(PLM)中的语言知识转移到声学特征学习,已被证明可以增强端到端自动语音识别(E2E-ASR)的效果。然而,由于固有的模态差距,语言模态和声音模态之间的表示对齐仍然是一个挑战。最优传输(OT)通过最小化语言特征和声音特征分布之间的Wasserstein距离(WD)来弥补这些差距,显示出良好前景。然而,之前的基于OT的方法忽视了结构关系,将特征向量视为无序集合。为了解决这个问题,我们提出了图匹配最优传输(GM-OT),它将语言特征和声音序列建模为结构图。节点代表特征嵌入,而边缘捕捉时序和顺序关系。GM-OT同时最小化节点之间的WD和边缘之间的Gromov-Wasserstein距离(GWD),从而形成了融合Gromov-Wasserstein距离(FGWD)的公式。这使得结构对齐和知识转移与现有的基于OT的方法相比更加高效。理论分析进一步表明,先前的语言知识转移中的基于OT的方法可以被视为我们GM-OT框架内的特殊情况。我们在使用基于CTC的E2E-ASR系统对普通话ASR上评估GM-OT进行知识转移的效果。实验结果表明,与最新模型相比,我们的方法实现了显著的性能提升,验证了其有效性。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF To appear in Interspeech 2025
Summary
本文探讨了将预训练语言模型(PLM)的语言知识转移到声学特征学习以提升端到端自动语音识别(E2E-ASR)性能的方法。针对语言与声学模态间存在的表示对齐问题,本文提出了图匹配最优传输(GM-OT)方法。该方法将语言与声学序列建模为结构图,通过最小化节点间的Wasserstein距离(WD)和边缘间的Gromov-Wasserstein距离(GWD),实现结构化对齐和更高效的知识转移。实验结果表明,GM-OT在汉语语音识别任务中取得了显著的性能提升。
Key Takeaways
- 预训练语言模型(PLM)的语言知识转移对提升端到端自动语音识别(E2E-ASR)性能有效。
- 对齐语言与声学模态的表示是一个挑战,因为两种模态之间存在固有的差距。
- 现有基于最优传输(OT)的方法忽视了结构关系,将特征向量视为无序集合。
- 图匹配最优传输(GM-OT)方法被提出,将语言与声学序列建模为结构图,实现结构化对齐。
- GM-OT通过最小化节点间的Wasserstein距离(WD)和边缘间的Gromov-Wasserstein距离(GWD),实现更高效的知识转移。
- 理论分析显示,先前的基于OT的语言知识转移方法可以作为GM-OT框架的特例。
点此查看论文截图

Suicide Risk Assessment Using Multimodal Speech Features: A Study on the SW1 Challenge Dataset
Authors:Ambre Marie, Ilias Maoudj, Guillaume Dardenne, Gwenolé Quellec
The 1st SpeechWellness Challenge conveys the need for speech-based suicide risk assessment in adolescents. This study investigates a multimodal approach for this challenge, integrating automatic transcription with WhisperX, linguistic embeddings from Chinese RoBERTa, and audio embeddings from WavLM. Additionally, handcrafted acoustic features – including MFCCs, spectral contrast, and pitch-related statistics – were incorporated. We explored three fusion strategies: early concatenation, modality-specific processing, and weighted attention with mixup regularization. Results show that weighted attention provided the best generalization, achieving 69% accuracy on the development set, though a performance gap between development and test sets highlights generalization challenges. Our findings, strictly tied to the MINI-KID framework, emphasize the importance of refining embedding representations and fusion mechanisms to enhance classification reliability.
第一届SpeechWellness挑战赛凸显了青少年语音自杀风险评估的必要性。本研究针对这一挑战,采用多模式方法,将自动转录与WhisperX、中文RoBERTa的语言嵌入和WavLM的音频嵌入相结合。此外,还结合了手工制作的声学特征,包括MFCCs、谱对比和音高相关统计。我们探索了三种融合策略:早期连接、模态特定处理和带混合正则化的加权注意力。结果表明,加权注意力提供了最佳泛化能力,在开发集上达到69%的准确率,但开发集和测试集之间的性能差距突出了泛化挑战。我们的发现严格与MINI-KID框架相关,强调改进嵌入表示和融合机制的重要性,以提高分类可靠性。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Submitted to the SpeechWellness Challenge at Interspeech 2025; 5 pages, 2 figures, 2 tables
Summary
语音健康挑战凸显青少年自杀风险评估的重要性。本研究通过整合自动转录技术与多模态方法,运用WhisperX实现语音识别和多模态评估。研究采用了来自中文RoBERTa的语言嵌入与来自WavLM的音频嵌入,并结合手工制作的声音特征如MFCCs、谱对比以及音高统计。实验探讨了早期拼接、模态特定处理和加权注意力与mixup正则化三种融合策略。结果显示,加权注意力策略在开发集上取得了最佳泛化性能,准确率达到了69%,但在开发集和测试集之间的性能差距也反映了泛化的挑战。基于MINI-KID框架的结果强调了精炼嵌入表达和融合机制对提升分类可靠性的重要性。
Key Takeaways
- 第一项“语音健康挑战”传达了评估青少年自杀风险的需求。
- 研究采用多模态方法应对挑战,结合了自动语音识别技术与多种特征处理技术。
- 研究采用WhisperX进行语音识别和中文RoBERTa提供的语言嵌入以及WavLM提供的音频嵌入技术。
- 手工制作的声学特征如MFCCs、谱对比和音高统计被纳入研究中。
- 研究探讨了三种融合策略,其中加权注意力策略表现最佳,开发集上准确率达到了69%。
- 存在泛化挑战,表现在开发集和测试集之间的性能差距上。
点此查看论文截图

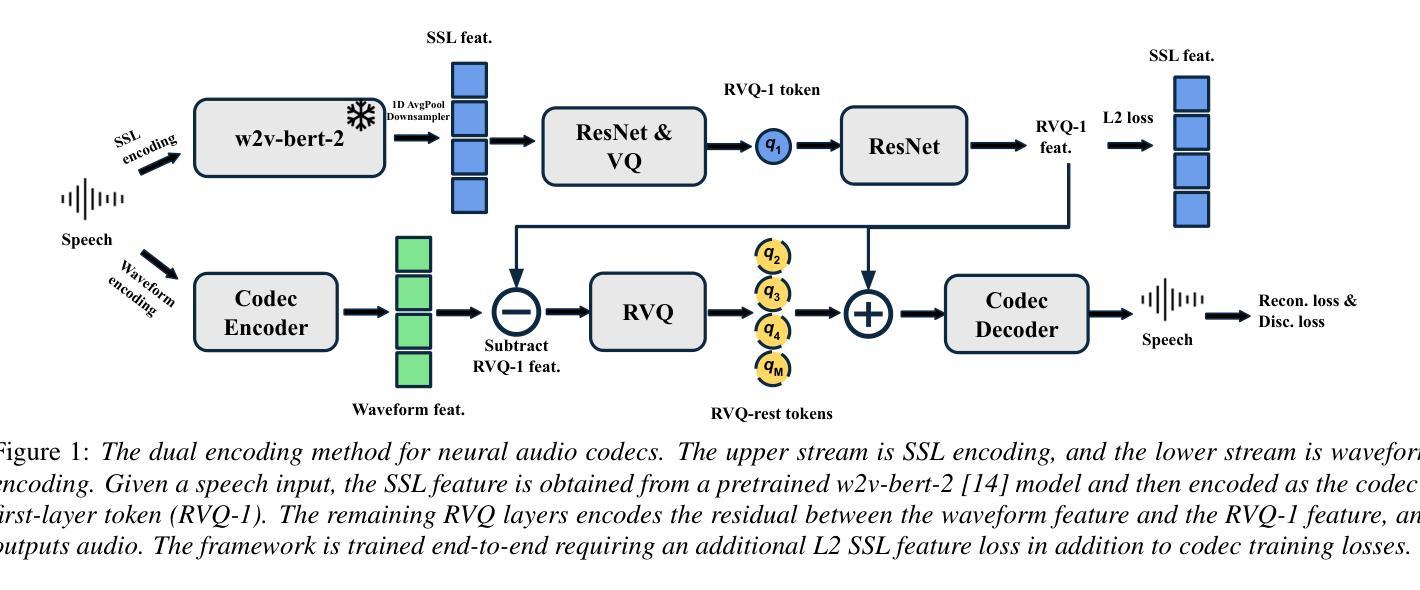
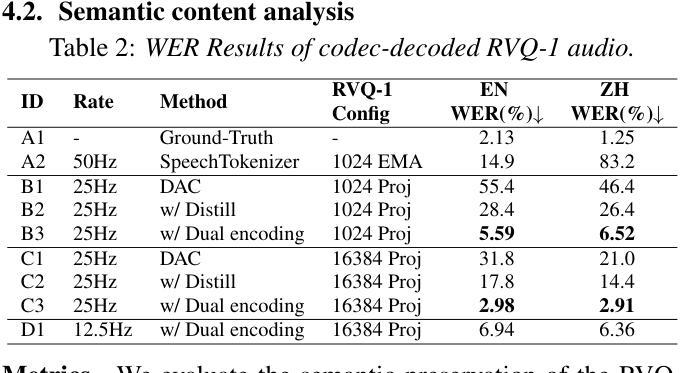
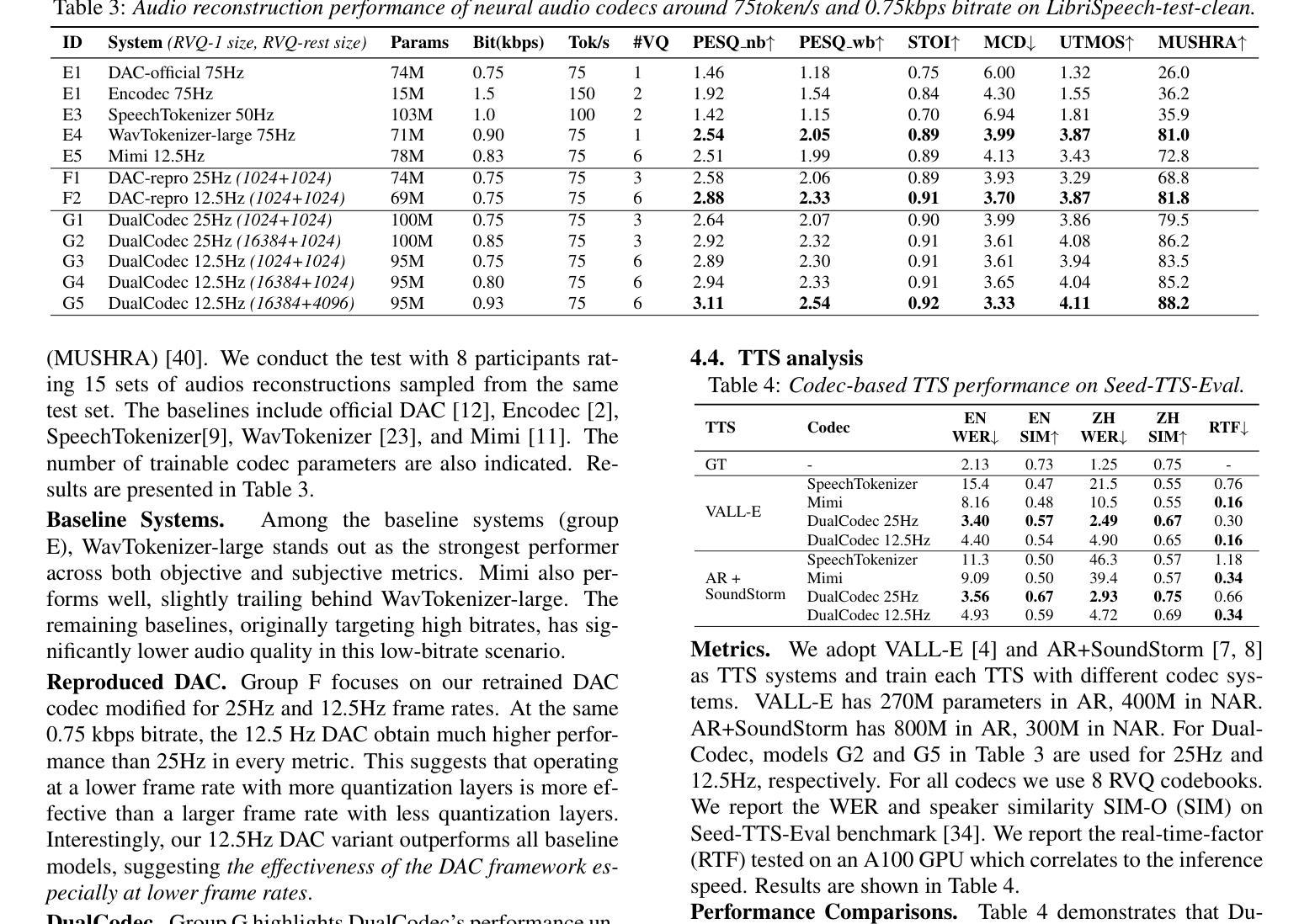
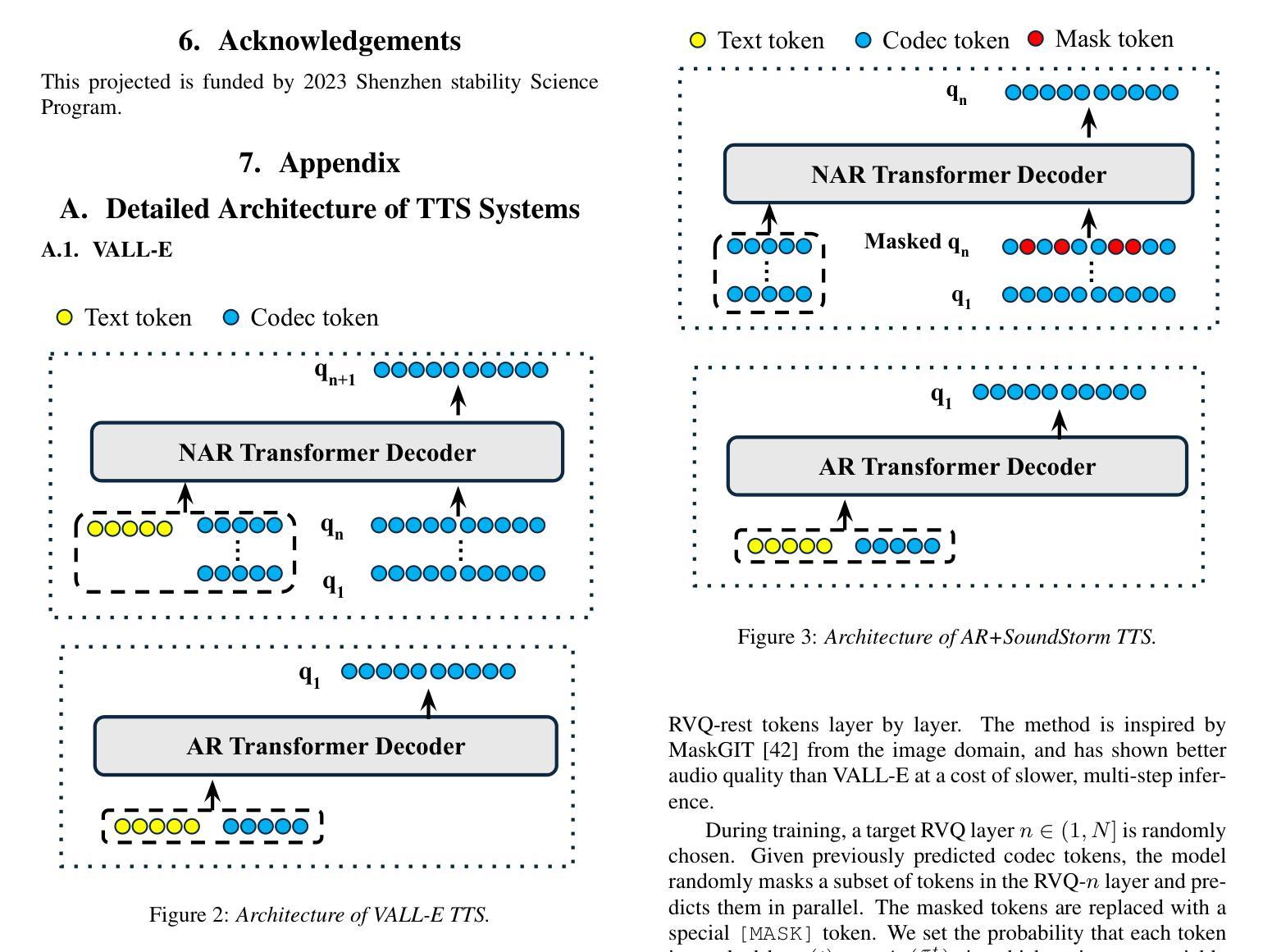
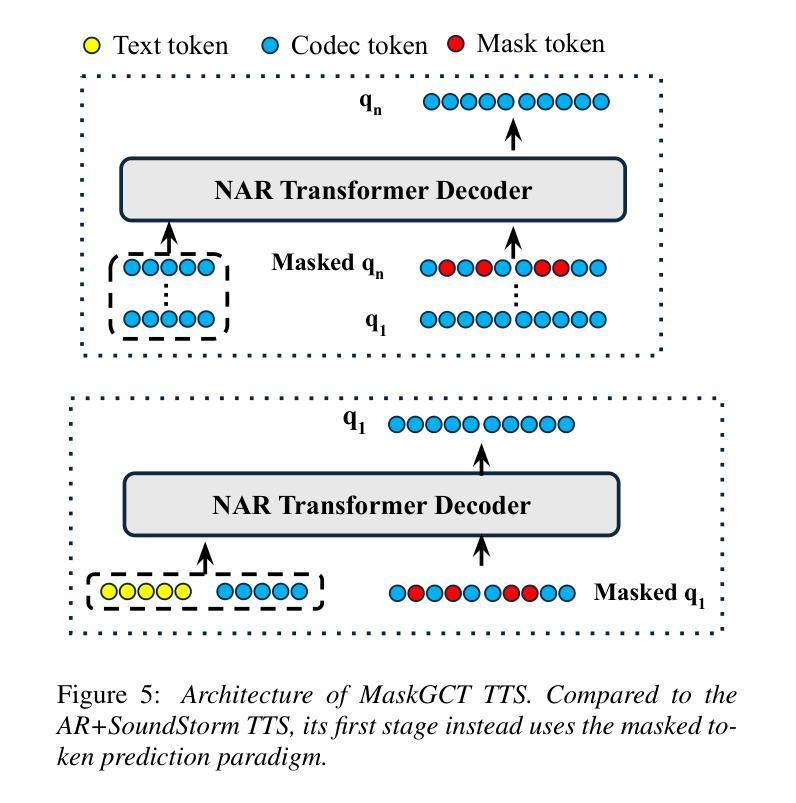
DualCodec: A Low-Frame-Rate, Semantically-Enhanced Neural Audio Codec for Speech Generation
Authors:Jiaqi Li, Xiaolong Lin, Zhekai Li, Shixi Huang, Yuancheng Wang, Chaoren Wang, Zhenpeng Zhan, Zhizheng Wu
Neural audio codecs form the foundational building blocks for language model (LM)-based speech generation. Typically, there is a trade-off between frame rate and audio quality. This study introduces a low-frame-rate, semantically enhanced codec model. Existing approaches distill semantically rich self-supervised (SSL) representations into the first-layer codec tokens. This work proposes DualCodec, a dual-stream encoding approach that integrates SSL and waveform representations within an end-to-end codec framework. In this setting, DualCodec enhances the semantic information in the first-layer codec and enables the codec system to maintain high audio quality while operating at a low frame rate. Note that a low-frame-rate codec improves the efficiency of speech generation. Experimental results on audio codec and speech generation tasks confirm the effectiveness of the proposed DualCodec compared to state-of-the-art codec systems, such as Mimi Codec, SpeechTokenizer, DAC, and Encodec. Demos and codes are available at: https://dualcodec.github.io
神经音频编解码器是语言模型(LM)为基础语音生成的基石构建块。通常,帧率和音频质量之间存在权衡。本研究引入了一种低帧率、语义增强的编解码器模型。现有方法将语义丰富的自监督(SSL)表示形式蒸馏到第一层编解码器令牌中。这项工作提出了DualCodec,一种双流编码方法,它在一个端到端的编解码器框架内集成了SSL和波形表示形式。在这种设置下,DualCodec增强了第一层编解码器的语义信息,使编解码器系统能够在低帧率下保持高音频质量。请注意,低帧率的编解码器提高了语音生成的效率。在音频编解码器和语音生成任务上的实验结果证实了与最新编解码器系统(如Mimi Codec、SpeechTokenizer、DAC和Encodec)相比,所提出的DualCodec的有效性。演示和代码可在:https://dualcodec.github.io 上找到。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted to Interspeech 2025. Github: https://github.com/jiaqili3/dualcodec
Summary
神经网络音频编码解码器为基于语言模型的语音生成提供了基础构建块。本文提出一种低帧率、语义增强的编码解码器模型,该模型将语义丰富的自监督表示融入第一层编码解码器标记中。实验结果表明,相较于现有的一流编码解码器系统,如Mimi Codec、SpeechTokenizer、DAC和Encodec等,本文提出的DualCodec在低帧率下能维持较高的音频质量并提升语音生成的效率。更多演示和代码可访问:https://dualcodec.github.io。
Key Takeaways
- 神经网络音频编码解码器为语音生成提供了基础框架。
- 当前技术中帧率和音频质量存在权衡问题。
- 本文提出了DualCodec模型,集成了自监督表示和波形表示。
- DualCodec在低帧率下增强第一层编码解码器的语义信息并维持较高音频质量。
- 与其他先进编码解码器系统相比,DualCodec能有效提升语音生成的效率。
- DualCodec演示和代码可在线访问。
点此查看论文截图

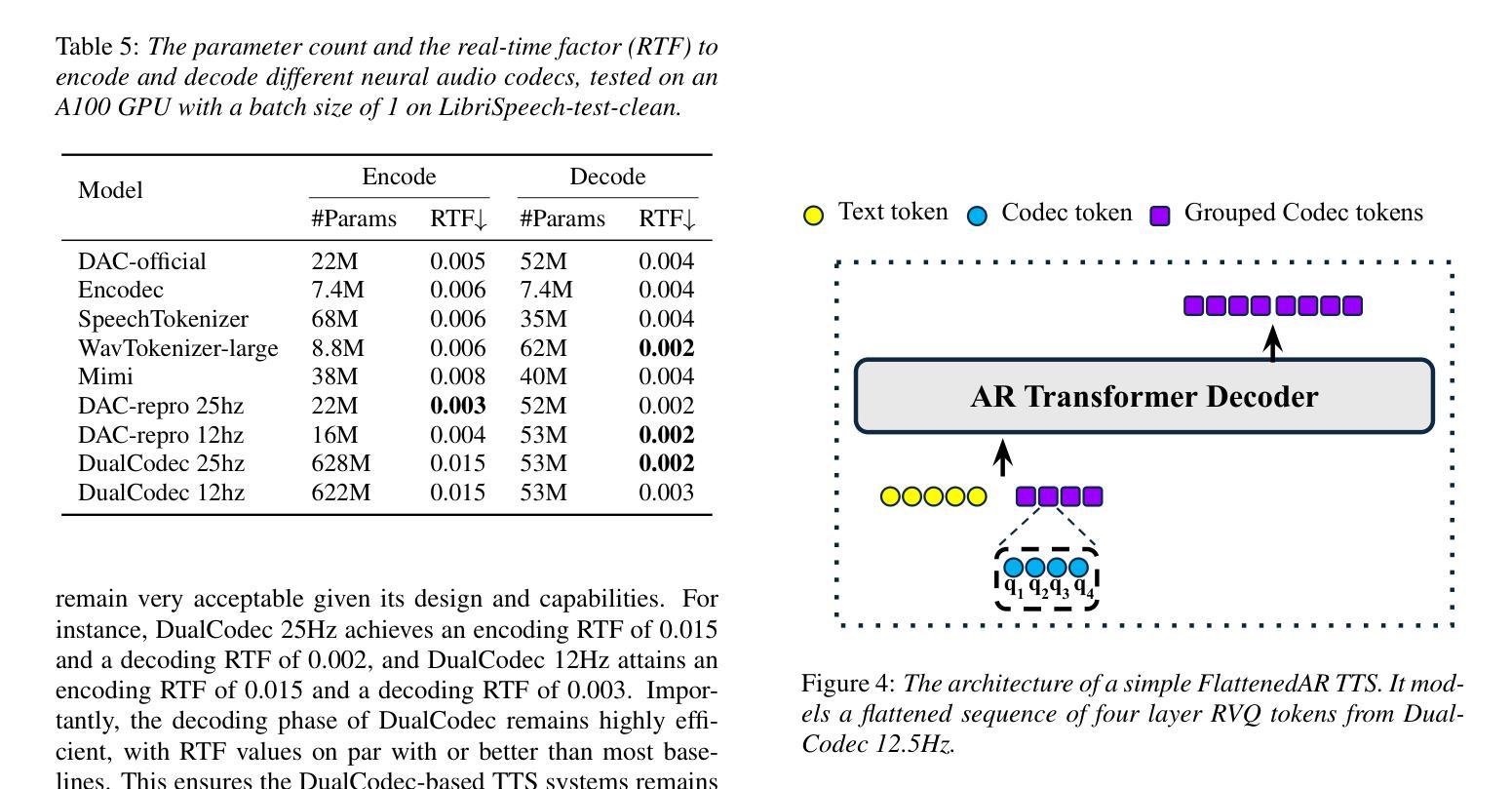
Calm-Whisper: Reduce Whisper Hallucination On Non-Speech By Calming Crazy Heads Down
Authors:Yingzhi Wang, Anas Alhmoud, Saad Alsahly, Muhammad Alqurishi, Mirco Ravanelli
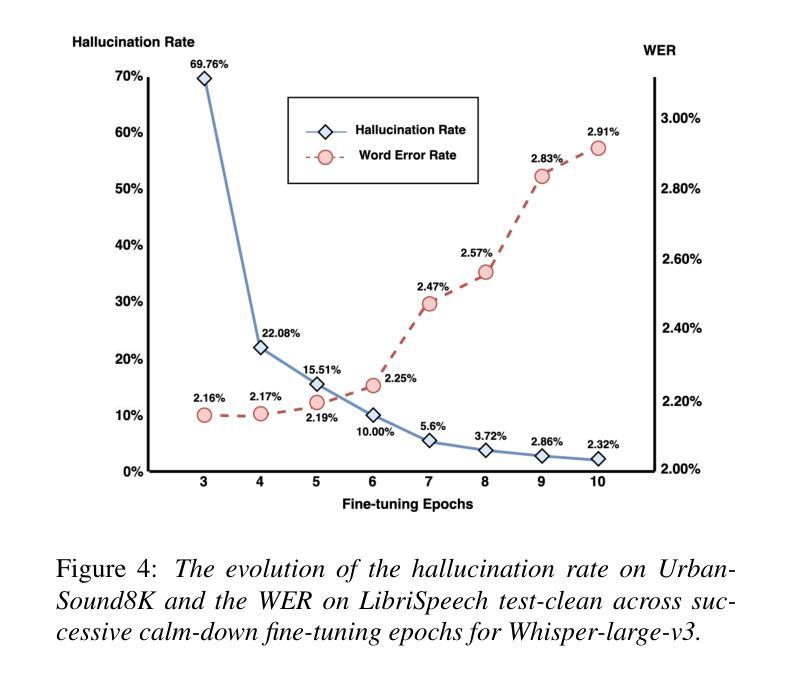
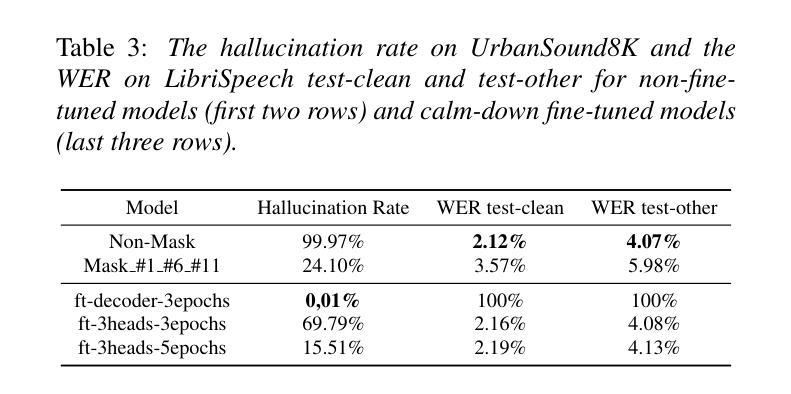
OpenAI’s Whisper has achieved significant success in Automatic Speech Recognition. However, it has consistently been found to exhibit hallucination issues, particularly in non-speech segments, which limits its broader application in complex industrial settings. In this paper, we introduce a novel method to reduce Whisper’s hallucination on non-speech segments without using any pre- or post-possessing techniques. Specifically, we benchmark the contribution of each self-attentional head in the Whisper-large-v3 decoder to the hallucination problem by performing a head-wise mask. Our findings reveal that only 3 of the 20 heads account for over 75% of the hallucinations on the UrbanSound dataset. We then fine-tune these three crazy heads using a collection of non-speech data. The results show that our best fine-tuned model, namely Calm-Whisper, achieves over 80% reduction in non-speech hallucination with only less than 0.1% WER degradation on LibriSpeech test-clean and test-other.
OpenAI的Whisper在自动语音识别方面取得了巨大成功。然而,人们发现它存在幻觉问题,特别是在非语音片段中,这限制了其在复杂工业环境中的更广泛应用。在本文中,我们介绍了一种新方法,可以在不使用任何预处理或后处理技术的情军下减少Whisper在非语音片段上的幻觉。具体来说,我们通过执行头向掩码,对Whisper-large-v3解码器中每个自注意力头的幻觉问题贡献进行基准测试。我们的研究发现,仅有3个头在UrbanSound数据集上的幻觉贡献超过75%。然后,我们使用非语音数据的集合对这三个疯狂的头部进行微调。结果表明,我们最佳调整后的模型——Calm-Whisper,在非语音幻觉方面实现了超过80%的减少,同时在LibriSpeech测试清洁和测试其他方面的话语错误率降低不到0.1%。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted to Interspeech 2025
摘要
OpenAI的Whisper在语音识别领域取得了巨大成功,但在非语音片段中存在幻觉问题,限制了其在复杂工业环境中的广泛应用。本文引入了一种新方法,无需使用任何预处理或后处理技巧,即可减少Whisper在非语音片段上的幻觉。通过对面头进行逐一分析,我们发现在UrbanSound数据集上,仅有三个头部导致超过75%的幻觉。通过精细调整这三个异常头,并利用非语音数据进行训练,得到的最佳模型Calm-Whisper在非语音幻觉上减少了超过80%,同时LibriSpeech测试集的词错误率仅增加不到0.1%。
关键见解
- OpenAI的Whisper在语音识别领域取得了显著成功,但在非语音片段中存在幻觉问题。
- 在处理非语音片段时,仅少数头部贡献了大部分的幻觉问题。
- 通过精细调整导致幻觉的主要头部,可以有效减少幻觉现象。
- 使用非语音数据对模型进行训练,有助于提高模型的性能并减少非语音幻觉。
- Calm-Whisper模型在非语音幻觉方面表现出卓越性能,减少了超过80%的幻觉。
- 尽管在非语音片段上取得了显著改进,但Calm-Whisper在LibriSpeech测试集的词错误率增加很少(不到0.1%)。
点此查看论文截图

OZSpeech: One-step Zero-shot Speech Synthesis with Learned-Prior-Conditioned Flow Matching
Authors:Hieu-Nghia Huynh-Nguyen, Ngoc Son Nguyen, Huynh Nguyen Dang, Thieu Vo, Truong-Son Hy, Van Nguyen
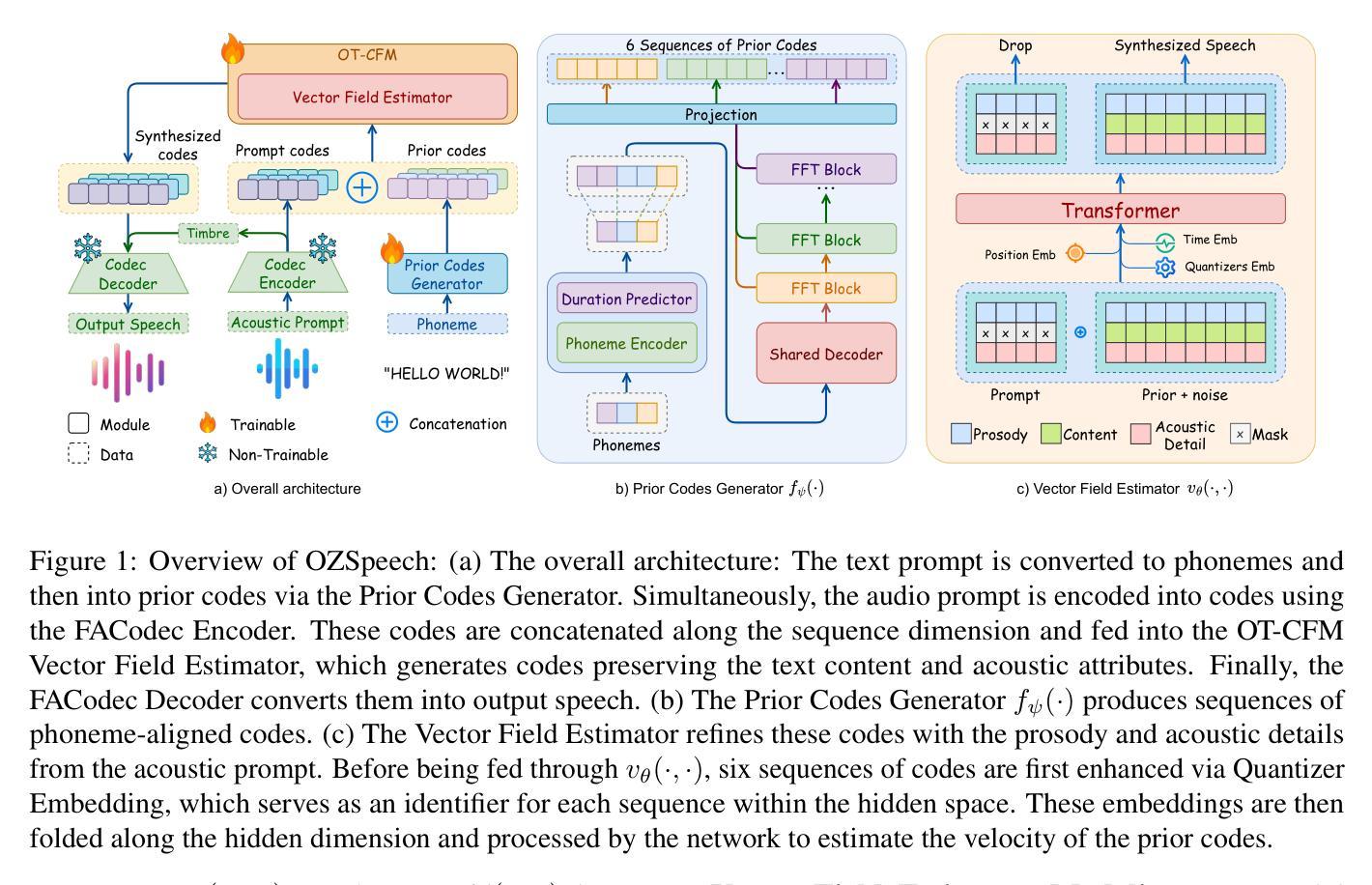
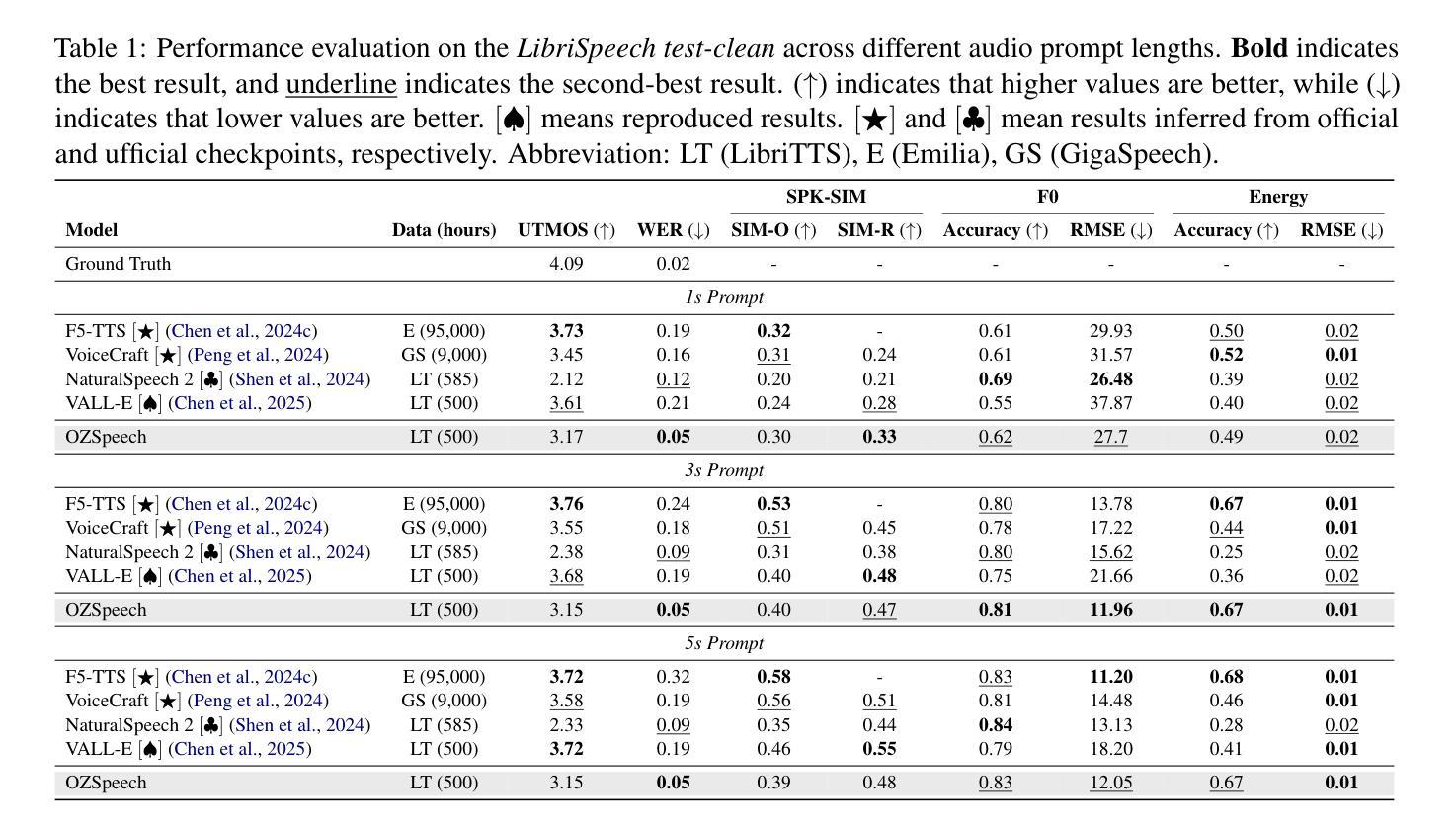
Text-to-speech (TTS) systems have seen significant advancements in recent years, driven by improvements in deep learning and neural network architectures. Viewing the output speech as a data distribution, previous approaches often employ traditional speech representations, such as waveforms or spectrograms, within the Flow Matching framework. However, these methods have limitations, including overlooking various speech attributes and incurring high computational costs due to additional constraints introduced during training. To address these challenges, we introduce OZSpeech, the first TTS method to explore optimal transport conditional flow matching with one-step sampling and a learned prior as the condition, effectively disregarding preceding states and reducing the number of sampling steps. Our approach operates on disentangled, factorized components of speech in token format, enabling accurate modeling of each speech attribute, which enhances the TTS system’s ability to precisely clone the prompt speech. Experimental results show that our method achieves promising performance over existing methods in content accuracy, naturalness, prosody generation, and speaker style preservation. Audio samples are available at our demo page https://ozspeech.github.io/OZSpeech_Web/.
文本转语音(TTS)系统在近年来取得了重大进展,这一进展得益于深度学习和神经网络架构的改进。将输出语音视为数据分布,之前的方法经常在流匹配框架中使用传统的语音表示方法,例如波形或频谱图。然而,这些方法具有局限性,包括忽略了各种语音属性以及在训练过程中引入的额外约束导致的计算成本高昂。为了解决这些挑战,我们引入了OZSpeech,这是第一种探索最优传输条件流匹配的TTS方法,采用一步采样和学到的先验作为条件,有效地忽略了先前的状态并减少了采样步骤的数量。我们的方法运行在令牌格式的语音解纠缠、分解的组件上,能够对每个语音属性进行精确建模,这增强了TTS系统精确克隆提示语音的能力。实验结果表明,我们的方法在内容准确性、自然度、语调生成和说话人风格保持方面均实现了优于现有方法的有前途的性能。音频样本可在我们的演示页面https://ozspeech.github.io/OZSpeech_Web/上找到。
论文及项目相关链接
摘要
文本转语音(TTS)系统近年来取得显著进展,得益于深度学习和神经网络架构的改进。本文提出OZSpeech方法,首次在TTS领域中探索最优传输条件流匹配,采用一步采样和学习的先验条件,有效忽略先前状态,减少采样步骤数量。该方法在语音的分解组件上进行操作,能准确建模各种语音特征,提高了TTS系统在内容准确性、自然度、语调生成和说话人风格保持方面的性能。
关键见解
- TTS系统近年来有显著进步,得益于深度学习和神经网络的发展。
- 之前的TTS方法常使用传统语音表示,如波形或频谱图,在流匹配框架内存在局限性。
- OZSpeech是首个在TTS中探索最优传输条件流匹配的方法。
- OZSpeech采用一步采样和学习的先验条件,忽略先前状态,减少采样步骤。
- OZSpeech方法在语音分解组件上操作,能准确建模各种语音特征。
- 实验结果表明,OZSpeech在内容准确性、自然度、语调生成和说话人风格保持等方面性能优越。
- 可通过https://ozspeech.github.io/OZSpeech_Web/体验音频样本。
点此查看论文截图

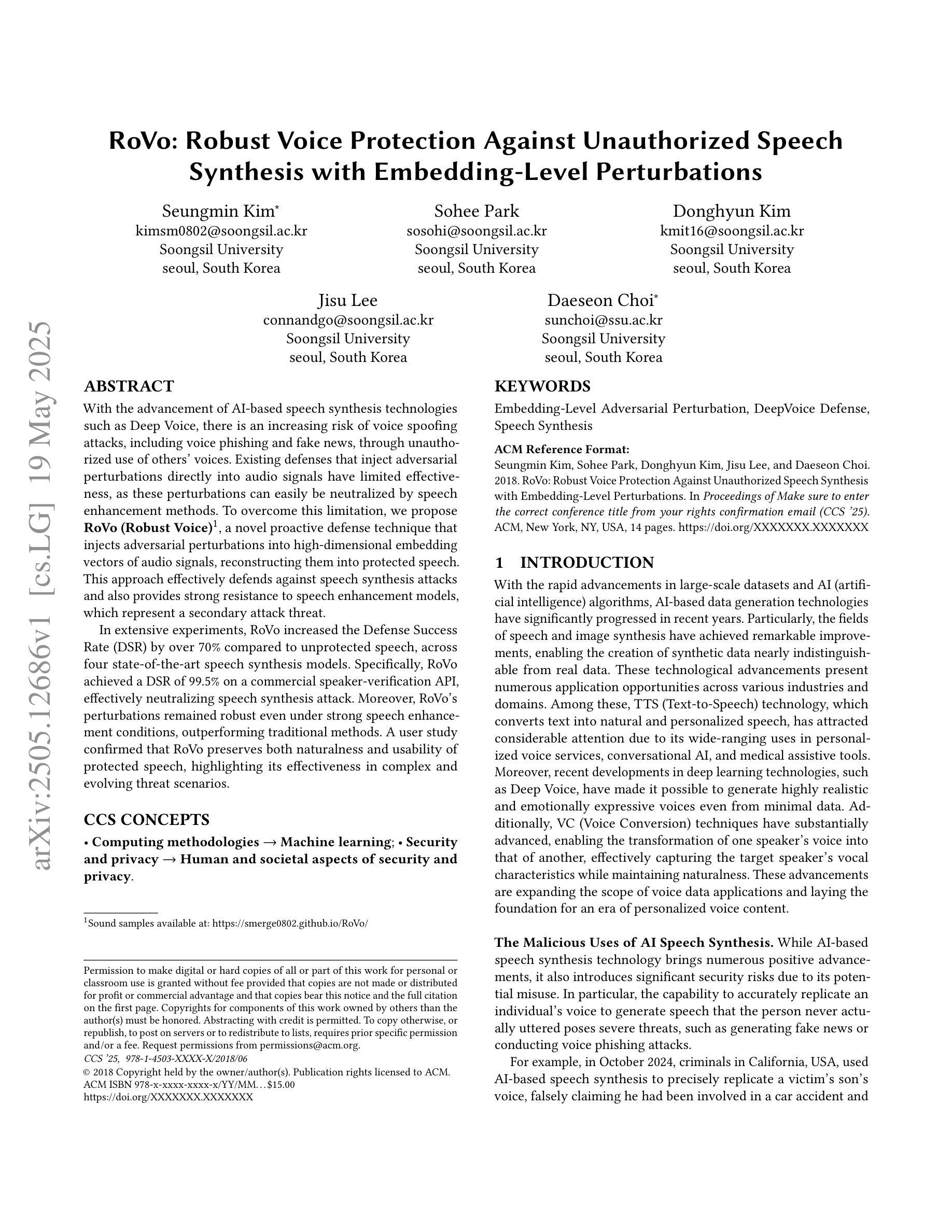
RoVo: Robust Voice Protection Against Unauthorized Speech Synthesis with Embedding-Level Perturbations
Authors:Seungmin Kim, Sohee Park, Donghyun Kim, Jisu Lee, Daeseon Choi
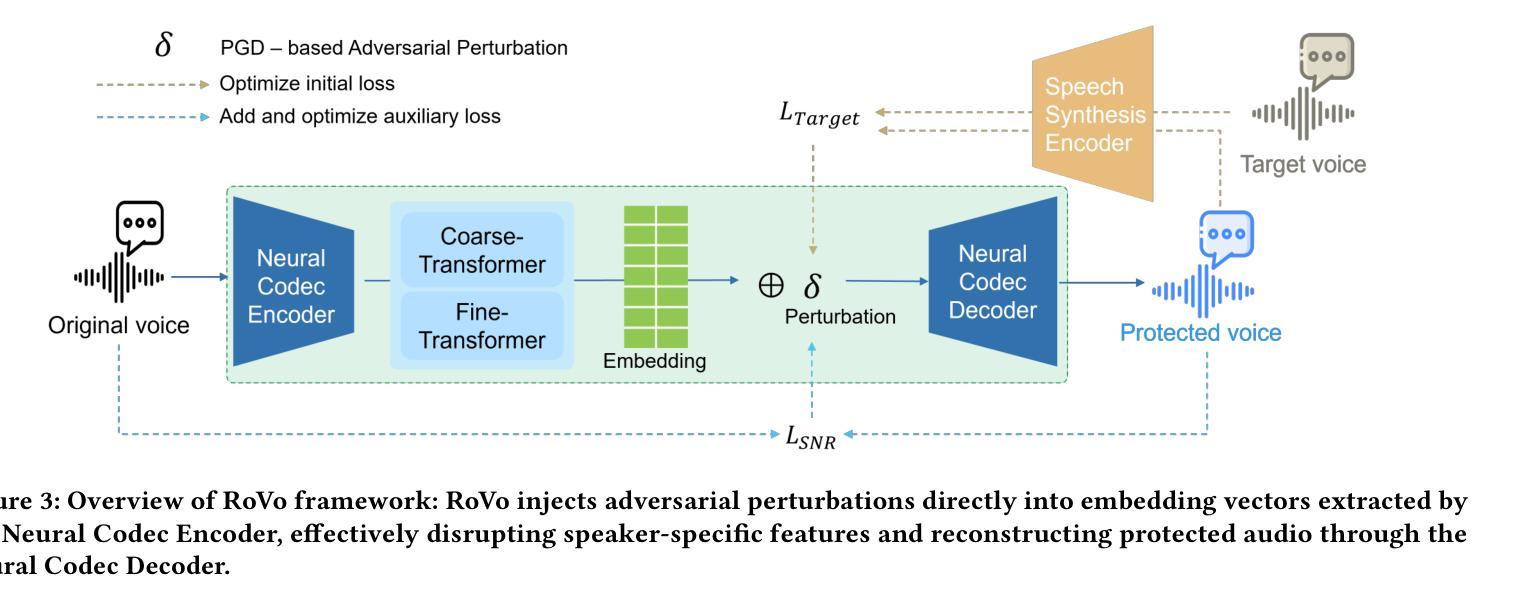
With the advancement of AI-based speech synthesis technologies such as Deep Voice, there is an increasing risk of voice spoofing attacks, including voice phishing and fake news, through unauthorized use of others’ voices. Existing defenses that inject adversarial perturbations directly into audio signals have limited effectiveness, as these perturbations can easily be neutralized by speech enhancement methods. To overcome this limitation, we propose RoVo (Robust Voice), a novel proactive defense technique that injects adversarial perturbations into high-dimensional embedding vectors of audio signals, reconstructing them into protected speech. This approach effectively defends against speech synthesis attacks and also provides strong resistance to speech enhancement models, which represent a secondary attack threat. In extensive experiments, RoVo increased the Defense Success Rate (DSR) by over 70% compared to unprotected speech, across four state-of-the-art speech synthesis models. Specifically, RoVo achieved a DSR of 99.5% on a commercial speaker-verification API, effectively neutralizing speech synthesis attack. Moreover, RoVo’s perturbations remained robust even under strong speech enhancement conditions, outperforming traditional methods. A user study confirmed that RoVo preserves both naturalness and usability of protected speech, highlighting its effectiveness in complex and evolving threat scenarios.
随着基于深度声音等AI语音合成技术的进步,通过未经授权的他人声音进行语音欺骗攻击(包括语音钓鱼和虚假新闻)的风险日益增加。直接在音频信号中注入对抗性干扰的现有防御措施效果有限,因为这些干扰很容易被语音增强方法所中和。为了克服这一局限性,我们提出了RoVo(Robust Voice),这是一种新型主动防御技术,将对抗性干扰注入音频信号的高维嵌入向量中,然后重建为受保护的语音。该方法有效防御语音合成攻击,并对代表次要攻击威胁的语音增强模型提供了强大的抵抗力。在广泛的实验中,与未受保护的语音相比,RoVo将防御成功率(DSR)提高了70%以上,涵盖了四种最先进的语音合成模型。具体来说,在商用语音识别API上,RoVo的DSR达到了99.5%,有效地中和了语音合成攻击。此外,即使在强烈的语音增强条件下,RoVo的干扰仍然稳健,优于传统方法。用户研究证实,RoVo保留了受保护语音的自然性和可用性,突显其在复杂和不断发展的威胁场景中的有效性。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了基于AI的语音合成技术如Deep Voice的快速发展带来的语音欺骗攻击风险,包括语音钓鱼和假新闻。现有的直接在音频信号中注入对抗性扰动的防御方法效果有限,容易被语音增强方法中和。为此,本文提出RoVo(Robust Voice)这一新型主动防御技术,将对抗性扰动注入音频信号的高维嵌入向量中,重构为保护语音。此方法有效抵御语音合成攻击,并对语音增强模型表现出强大的抵抗力。实验表明,RoVo相较于未保护的语音,在四种先进的语音合成模型上的防御成功率(DSR)提高了70%以上。特别是在商业语音识别API上,RoVo的DSR达到99.5%。此外,用户研究表明,RoVo既保持了保护语音的自然性,又保证了可用性。
Key Takeaways
- AI语音合成技术如Deep Voice的进步增加了语音欺骗攻击的风险。
- 目前直接的音频信号对抗性扰动防御方法容易被语音增强方法中和。
- RoVo是一种新型主动防御技术,将扰动注入音频信号的高维嵌入向量中。
- RoVo有效抵御语音合成攻击和语音增强模型的威胁。
- RoVo在多种先进的语音合成模型上的防御成功率显著提高。
- 商业语音识别API上,RoVo的防御成功率达到99.5%。
点此查看论文截图
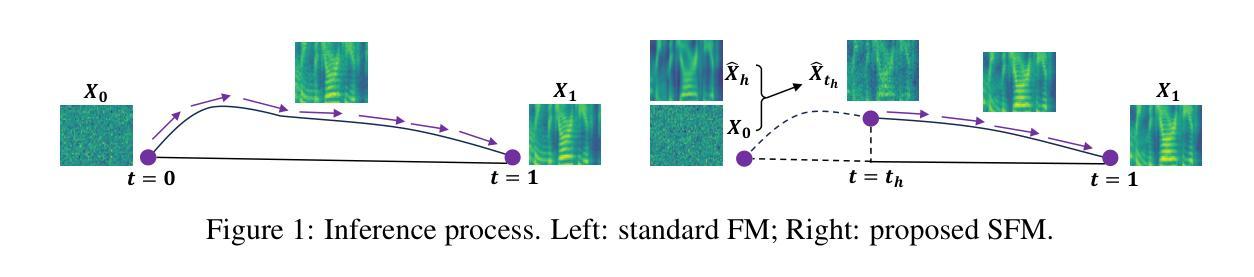
Shallow Flow Matching for Coarse-to-Fine Text-to-Speech Synthesis
Authors:Dong Yang, Yiyi Cai, Yuki Saito, Lixu Wang, Hiroshi Saruwatari
We propose a shallow flow matching (SFM) mechanism to enhance flow matching (FM)-based text-to-speech (TTS) models within a coarse-to-fine generation paradigm. SFM constructs intermediate states along the FM paths using coarse output representations. During training, we introduce an orthogonal projection method to adaptively determine the temporal position of these states, and apply a principled construction strategy based on a single-segment piecewise flow. The SFM inference starts from the intermediate state rather than pure noise and focuses computation on the latter stages of the FM paths. We integrate SFM into multiple TTS models with a lightweight SFM head. Experiments show that SFM consistently improves the naturalness of synthesized speech in both objective and subjective evaluations, while significantly reducing inference when using adaptive-step ODE solvers. Demo and codes are available at https://ydqmkkx.github.io/SFMDemo/.
我们提出了一种浅流匹配(SFM)机制,以在粗到细生成范式内增强基于流匹配(FM)的文本到语音(TTS)模型。SFM利用粗输出表示构建FM路径中的中间状态。在训练过程中,我们引入了一种正交投影方法来自适应地确定这些状态的时间位置,并基于单段分段流应用了一种有原则的构建策略。SFM推理从中间状态开始,而不是从纯噪声开始,并将计算重点放在FM路径的后期阶段。我们将SFM集成到多个TTS模型中,使用轻量级的SFM头。实验表明,无论是在客观还是主观评估中,SFM都能持续提高合成语音的自然度,同时在采用自适应步长ODE求解器时,能显著降低推理时间。演示和代码可通过https://ydqmkkx.github.io/SFMDemo/获取。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文提出了一种浅流匹配(SFM)机制,用于在粗到细生成范式中增强基于流匹配(FM)的文本到语音(TTS)模型。SFM通过在FM路径上构建中间状态,利用粗输出表示。在训练过程中,引入正交投影方法自适应确定这些状态的时间位置,并基于单段分段流应用有原则的构建策略。SFM推理从中间状态开始,而非纯噪声,并将计算重点放在FM路径的后期阶段。实验表明,SFM在客观和主观评估中均提高了合成语音的自然度,在使用自适应步长ODE求解器时,显著减少了推理时间。
Key Takeaways
- 提出了浅流匹配(SFM)机制,用于增强基于流匹配(FM)的文本到语音(TTS)模型的性能。
- SFM在FM路径上构建中间状态,利用粗输出表示。
- 训练过程中,通过正交投影方法自适应确定中间状态的时间位置。
- 采用单段分段流的策略进行有原则的构建。
- SFM推理从中间状态开始,提高语音合成的自然度。
- 实验表明,SFM在客观和主观评估中均有效,且能显著减少推理时间。
- 提供了演示和代码链接,方便用户了解和实现该机制。
点此查看论文截图

BenSParX: A Robust Explainable Machine Learning Framework for Parkinson’s Disease Detection from Bengali Conversational Speech
Authors:Riad Hossain, Muhammad Ashad Kabir, Arat Ibne Golam Mowla, Animesh Chandra Roy, Ranjit Kumar Ghosh
Parkinson’s disease (PD) poses a growing global health challenge, with Bangladesh experiencing a notable rise in PD-related mortality. Early detection of PD remains particularly challenging in resource-constrained settings, where voice-based analysis has emerged as a promising non-invasive and cost-effective alternative. However, existing studies predominantly focus on English or other major languages; notably, no voice dataset for PD exists for Bengali - posing a significant barrier to culturally inclusive and accessible healthcare solutions. Moreover, most prior studies employed only a narrow set of acoustic features, with limited or no hyperparameter tuning and feature selection strategies, and little attention to model explainability. This restricts the development of a robust and generalizable machine learning model. To address this gap, we present BenSparX, the first Bengali conversational speech dataset for PD detection, along with a robust and explainable machine learning framework tailored for early diagnosis. The proposed framework incorporates diverse acoustic feature categories, systematic feature selection methods, and state-of-the-art machine learning algorithms with extensive hyperparameter optimization. Furthermore, to enhance interpretability and trust in model predictions, the framework incorporates SHAP (SHapley Additive exPlanations) analysis to quantify the contribution of individual acoustic features toward PD detection. Our framework achieves state-of-the-art performance, yielding an accuracy of 95.77%, F1 score of 95.57%, and AUC-ROC of 0.982. We further externally validated our approach by applying the framework to existing PD datasets in other languages, where it consistently outperforms state-of-the-art approaches. To facilitate further research and reproducibility, the dataset has been made publicly available at https://github.com/Riad071/BenSParX.
帕金森病(PD)是一个日益严重的全球健康挑战,孟加拉国的PD相关死亡率也出现了显著上升。在资源有限的环境中,PD的早期检测仍然是一项艰巨的挑战,基于声音的分析已出现为前景广阔的微创且成本效益高的替代方案。然而,现有的研究主要集中在英语或其他主要语言上;值得注意的是,尚未存在用于PD检测的孟加拉语语音数据集,这对包含文化和可访问性的医疗保健解决方案造成了重大障碍。此外,大多数早期研究仅使用有限的声学特征,有限的或没有超参数调整和特征选择策略,并且很少关注模型的可解释性。这限制了稳健且可推广的机器学习模型的发展。为了弥补这一差距,我们推出了BenSparX,这是用于PD检测的第一个孟加拉语对话语音数据集,以及一个针对早期诊断量身定制的稳健且可解释的机器学习框架。所提出的框架结合了多种声学特征类别、系统的特征选择方法以及先进的机器学习算法进行广泛的超参数优化。此外,为了提高模型预测的解释性和可信度,该框架结合了SHAP(SHapley Additive exPlanations)分析,以量化单个声学特征对PD检测的贡献。我们的框架达到了业界领先水平,准确率为95.77%,F1分数为95.57%,AUC-ROC为0.982。我们进一步通过将该框架应用于其他语言的现有PD数据集来验证我们的方法,在大多数情况下它都优于业界领先的方法。为了便于进一步的研究和可重复性,该数据集已在https://github.com/Riad071/BenSParX上公开提供。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 46 pages, 16 figures
摘要
帕金森病(PD)全球挑战日益严峻,孟加拉国PD相关死亡率显著上升。在资源有限的环境中,早期发现PD尤为困难,基于声音的分析成为了一种有前景的非侵入性和经济有效的替代方案。但目前的研究主要集中在英语或其他主要语言上,孟加拉语的PD语音数据集尚不存在,这成为实现包容性和可访问性医疗保健解决方案的重大障碍。此外,大多数先前的研究仅使用有限的声学特征,缺乏超参数调整和特征选择策略,且对模型解释性的关注很少,这限制了稳健且可推广的机器学习模型的发展。为解决此问题,我们推出了BenSparX,这是首个用于PD检测的孟加拉语会话语音数据集,以及一个用于早期诊断的稳健且可解释的机器学习框架。该框架纳入各类声学特征、系统的特征选择方法和带有广泛超参数优化的先进机器学习算法。此外,为提高模型预测的解释性和可信度,框架结合了SHAP(SHapley Additive exPlanations)分析,以量化个人声学特征对PD检测的贡献。我们的框架达到了先进的表现水平,准确率95.77%,F1分数95.57%,AUC-ROC为0.982。通过将该框架应用于其他语言的现有PD数据集进行外部验证,证实其始终优于最先进的方法。为便于进一步研究和可重复性,数据集已在https://github.com/Riad071/BenSParx上公开提供。
要点
- 帕金森病(PD)在全球范围内构成重大挑战,孟加拉国的死亡率显著上升。
- 在资源有限的环境中早期发现PD具有挑战性,声音分析成为了一种有前途的替代方案。
- 目前缺乏针对孟加拉语的PD语音数据集,限制了包容性和可访问性医疗保健解决方案的实现。
- 提出的BenSparX数据集和机器学习框架结合了多种声学特征、系统特征选择方法和先进的机器学习算法,具有广泛的超参数优化。
- 机器学习框架利用SHAP分析提高模型预测的解释性。
- 框架达到了先进的表现水平,并在外部验证中表现出优异的性能。
点此查看论文截图

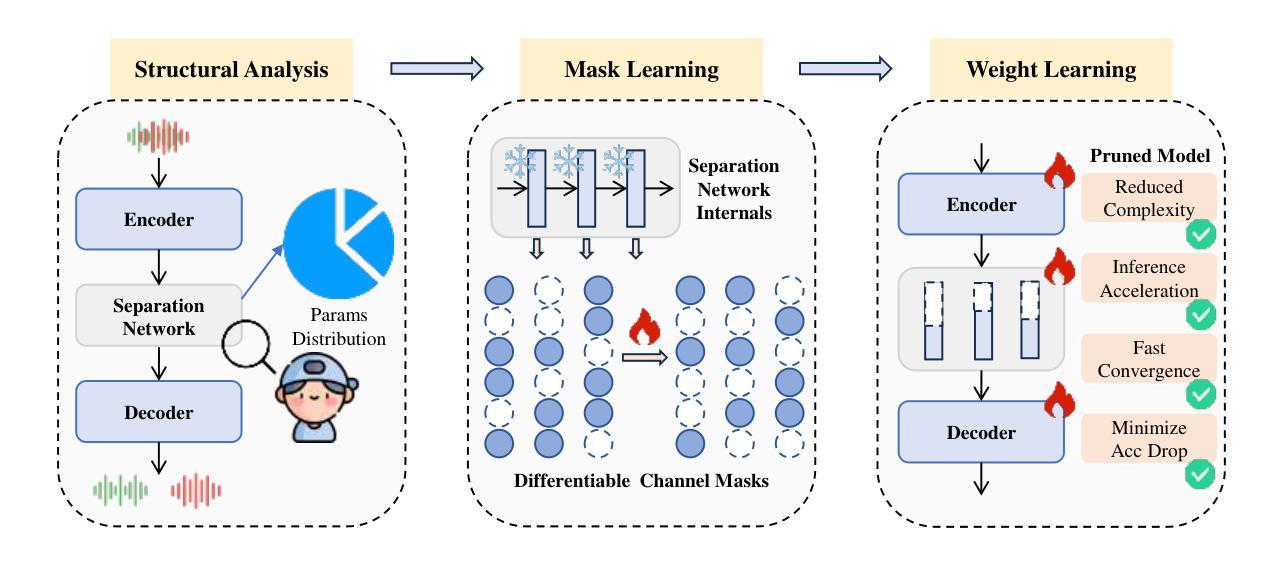
SepPrune: Structured Pruning for Efficient Deep Speech Separation
Authors:Yuqi Li, Kai Li, Xin Yin, Zhifei Yang, Junhao Dong, Zeyu Dong, Chuanguang Yang, Yingli Tian, Yao Lu
Although deep learning has substantially advanced speech separation in recent years, most existing studies continue to prioritize separation quality while overlooking computational efficiency, an essential factor for low-latency speech processing in real-time applications. In this paper, we propose SepPrune, the first structured pruning framework specifically designed to compress deep speech separation models and reduce their computational cost. SepPrune begins by analyzing the computational structure of a given model to identify layers with the highest computational burden. It then introduces a differentiable masking strategy to enable gradient-driven channel selection. Based on the learned masks, SepPrune prunes redundant channels and fine-tunes the remaining parameters to recover performance. Extensive experiments demonstrate that this learnable pruning paradigm yields substantial advantages for channel pruning in speech separation models, outperforming existing methods. Notably, a model pruned with SepPrune can recover 85% of the performance of a pre-trained model (trained over hundreds of epochs) with only one epoch of fine-tuning, and achieves convergence 36$\times$ faster than training from scratch. Code is available at https://github.com/itsnotacie/SepPrune.
尽管深度学习在近年来已经极大地推动了语音分离技术的发展,但大多数现有研究仍然优先重视分离质量,而忽视了计算效率这一实时应用中低延迟语音处理的关键因素。在本文中,我们提出了SepPrune,这是首个专为压缩深度语音分离模型而设计的结构化剪枝框架,旨在降低其计算成本。SepPrune首先分析给定模型的计算结构,以识别计算负担最高的层。然后,它引入了一种可微分的掩码策略,以实现梯度驱动的通道选择。基于学习的掩码,SepPrune剪去冗余通道并对剩余参数进行微调以恢复性能。大量实验表明,这种可学习的剪枝范式在语音分离模型的通道剪枝方面具有显著优势,优于现有方法。值得注意的是,使用SepPrune修剪的模型只需一个周期的微调就可以恢复预训练模型(经过数百个周期的训练)的85%性能,并且收敛速度比从头开始训练快36倍。代码可在https://github.com/itsnotacie/SepPrune找到。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文提出SepPrune,一个专为深度语音分离模型设计的结构化剪枝框架,旨在提高计算效率并降低计算成本。它通过分析模型的计算结构来识别计算负担最高的层,引入可微掩码策略进行梯度驱动的通道选择。实验表明,SepPrune的剪枝策略在语音分离模型中表现优异,能快速恢复模型的性能,并提高收敛速度。
Key Takeaways
- SepPrune是首个专为深度语音分离模型设计的结构化剪枝框架。
- 该框架旨在提高语音分离模型的计算效率,并降低计算成本。
- SepPrune通过分析模型的计算结构来识别负担最高的层。
- 使用可微掩码策略进行梯度驱动的通道选择。
- SepPrune的剪枝策略在语音分离模型中表现优异,能快速恢复模型的性能。
- 相较于预训练模型,经过SepPrune的模型只需一个epoch的微调即可恢复85%的性能。
点此查看论文截图

Enhanced Multimodal Hate Video Detection via Channel-wise and Modality-wise Fusion
Authors:Yinghui Zhang, Tailin Chen, Yuchen Zhang, Zeyu Fu
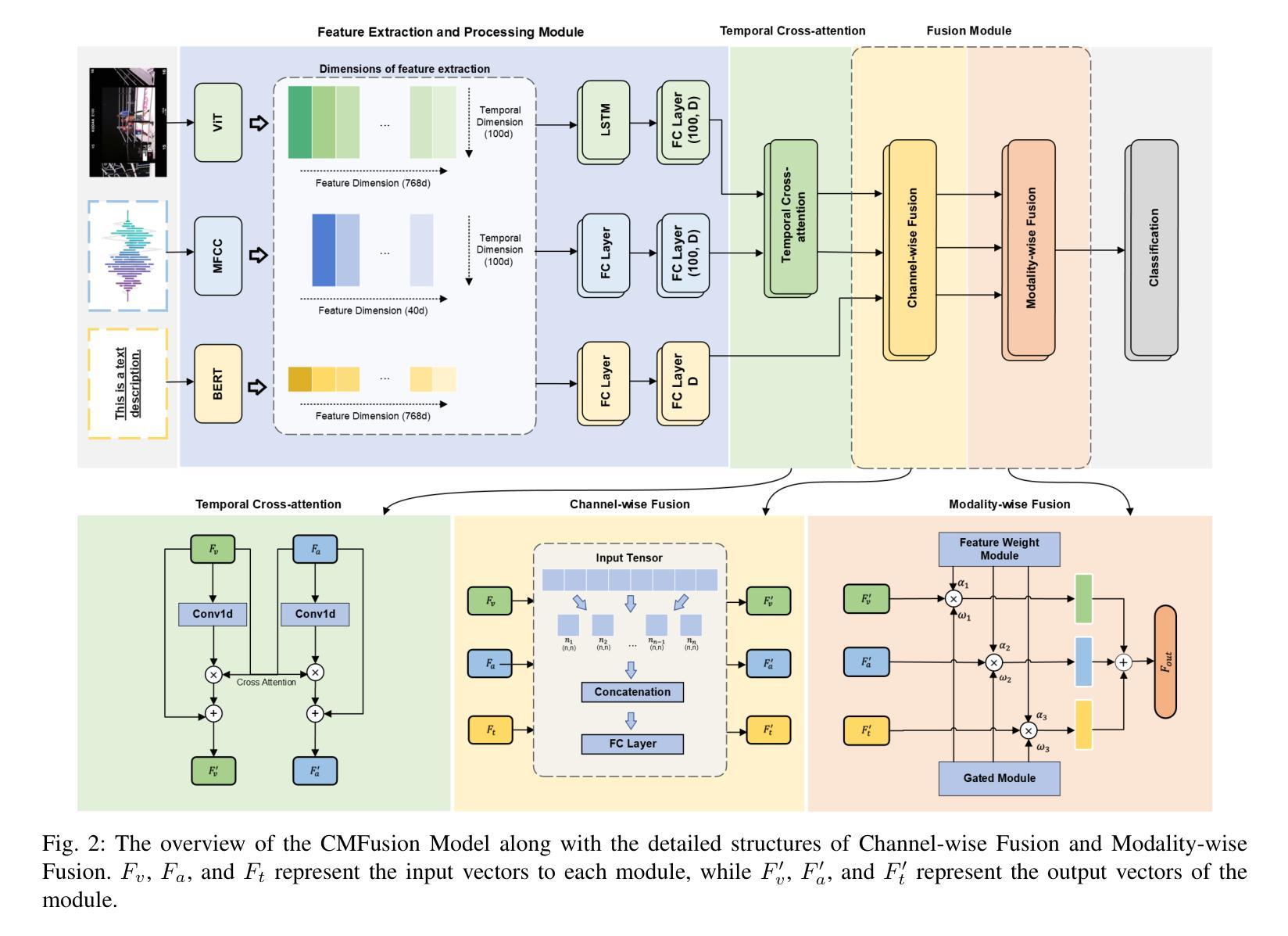
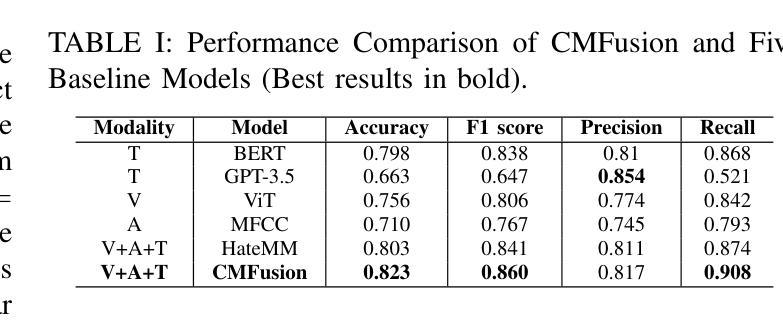
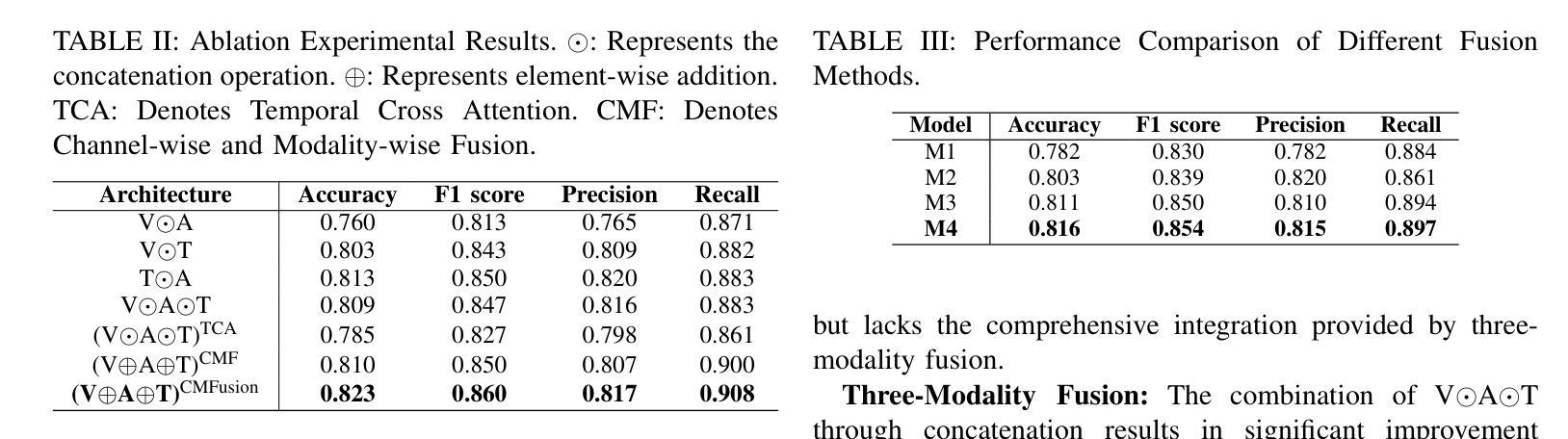
The rapid rise of video content on platforms such as TikTok and YouTube has transformed information dissemination, but it has also facilitated the spread of harmful content, particularly hate videos. Despite significant efforts to combat hate speech, detecting these videos remains challenging due to their often implicit nature. Current detection methods primarily rely on unimodal approaches, which inadequately capture the complementary features across different modalities. While multimodal techniques offer a broader perspective, many fail to effectively integrate temporal dynamics and modality-wise interactions essential for identifying nuanced hate content. In this paper, we present CMFusion, an enhanced multimodal hate video detection model utilizing a novel Channel-wise and Modality-wise Fusion Mechanism. CMFusion first extracts features from text, audio, and video modalities using pre-trained models and then incorporates a temporal cross-attention mechanism to capture dependencies between video and audio streams. The learned features are then processed by channel-wise and modality-wise fusion modules to obtain informative representations of videos. Our extensive experiments on a real-world dataset demonstrate that CMFusion significantly outperforms five widely used baselines in terms of accuracy, precision, recall, and F1 score. Comprehensive ablation studies and parameter analyses further validate our design choices, highlighting the model’s effectiveness in detecting hate videos. The source codes will be made publicly available at https://github.com/EvelynZ10/cmfusion.
随着TikTok和YouTube等平台视频内容的迅速崛起,信息传播的方式已经发生了变革,但同时也促进了有害内容的扩散,特别是仇恨视频。尽管在打击仇恨言论方面付出了巨大努力,但由于仇恨视频的隐晦性,检测这些视频仍然是一个挑战。当前的检测方法主要依赖于单模态方法,这些方法无法充分捕捉不同模态之间的互补特征。虽然多模态技术提供了更广泛的视角,但许多技术在整合识别仇恨内容所必需的时间动态和模态间交互方面效果不佳。在本文中,我们提出了CMFusion,这是一种采用新型通道级和模态级融合机制的高级多模态仇恨视频检测模型。CMFusion首先使用预训练模型从文本、音频和视频模态中提取特征,然后采用时间交叉注意机制来捕捉视频和音频流之间的依赖关系。然后,通过通道级和模态级融合模块处理所学习到的特征,以获取视频的信息化表示。我们在真实世界数据集上进行的广泛实验表明,与五个广泛使用的基线相比,CMFusion在准确性、精确度、召回率和F1分数方面均表现出显著优势。全面的消融研究和参数分析进一步验证了我们的设计选择,突显了该模型在检测仇恨视频方面的有效性。源代码将在https://github.com/EvelynZ10/cmfusion上公开。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF ICDMW 2024, Github: https://github.com/EvelynZ10/cmfusion
Summary
本文探讨视频平台上仇恨视频的传播问题,提出了一种新的多媒体仇恨视频检测模型CMFusion。该模型通过融合文本、音频和视频等多模态信息,结合时间交叉注意力机制,有效捕捉视频和音频流之间的依赖关系。实验结果表明,CMFusion在真实数据集上的准确率、精确度、召回率和F1分数等方面均优于五种广泛使用的基线方法。
Key Takeaways
- 视频内容在TikTok和YouTube等平台上迅速崛起,改变了信息传播方式,同时也促进了有害内容的扩散,特别是仇恨视频。
- 当前仇恨视频检测方法主要依赖于单模态方法,无法充分捕捉不同模态的互补特征。
- 多模态技术虽然提供了更广泛的视角,但许多方法未能有效地结合时间动态和模态间交互,这对于识别微妙的仇恨内容至关重要。
- CMFusion是一种增强的多媒体仇恨视频检测模型,通过渠道和模态融合机制,提取文本、音频和视频特征,并捕捉视频和音频流之间的依赖关系。
- CMFusion模型在真实数据集上的性能显著优于五种广泛使用的基线方法。
- 消融研究和参数分析验证了CMFusion模型设计的有效性。
点此查看论文截图

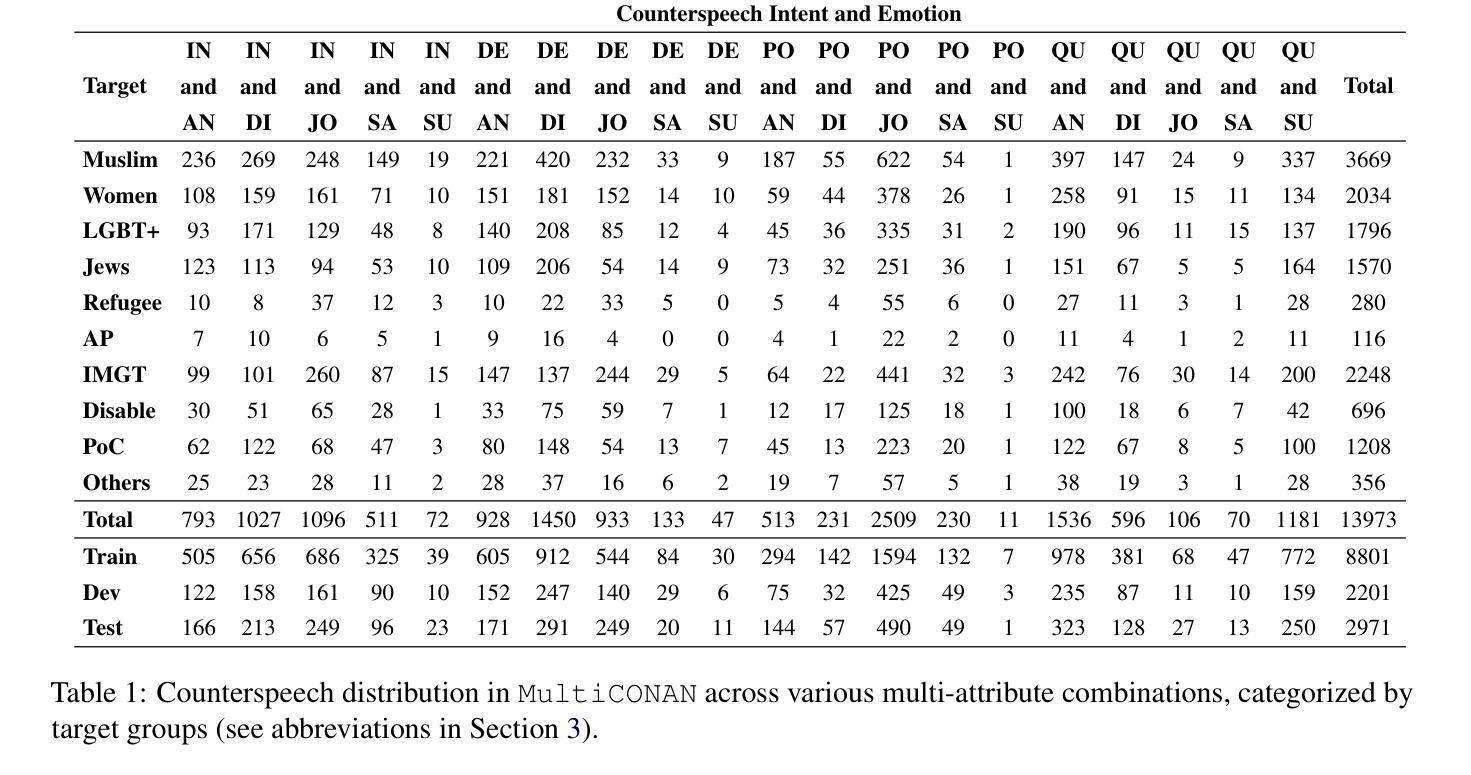
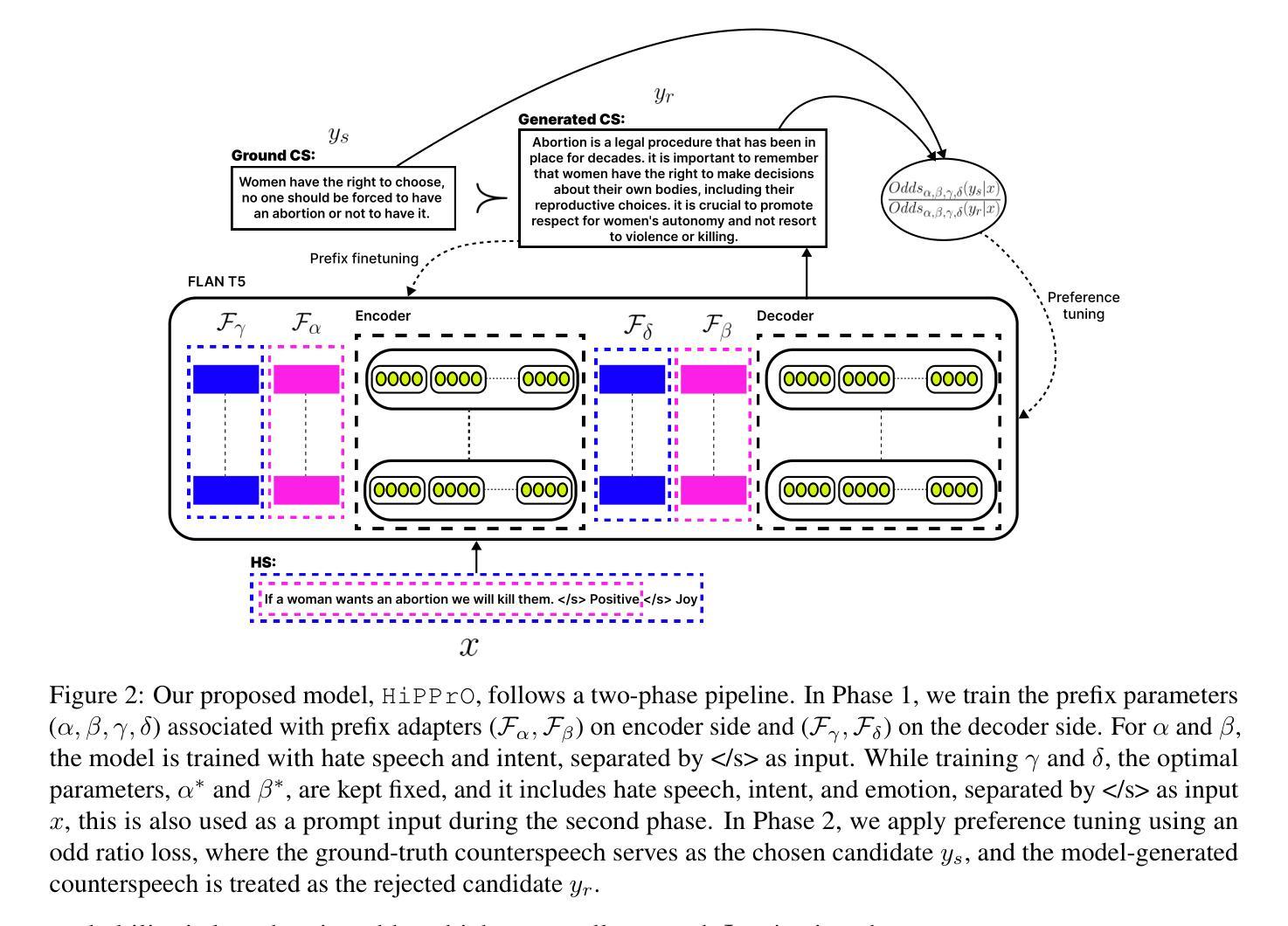
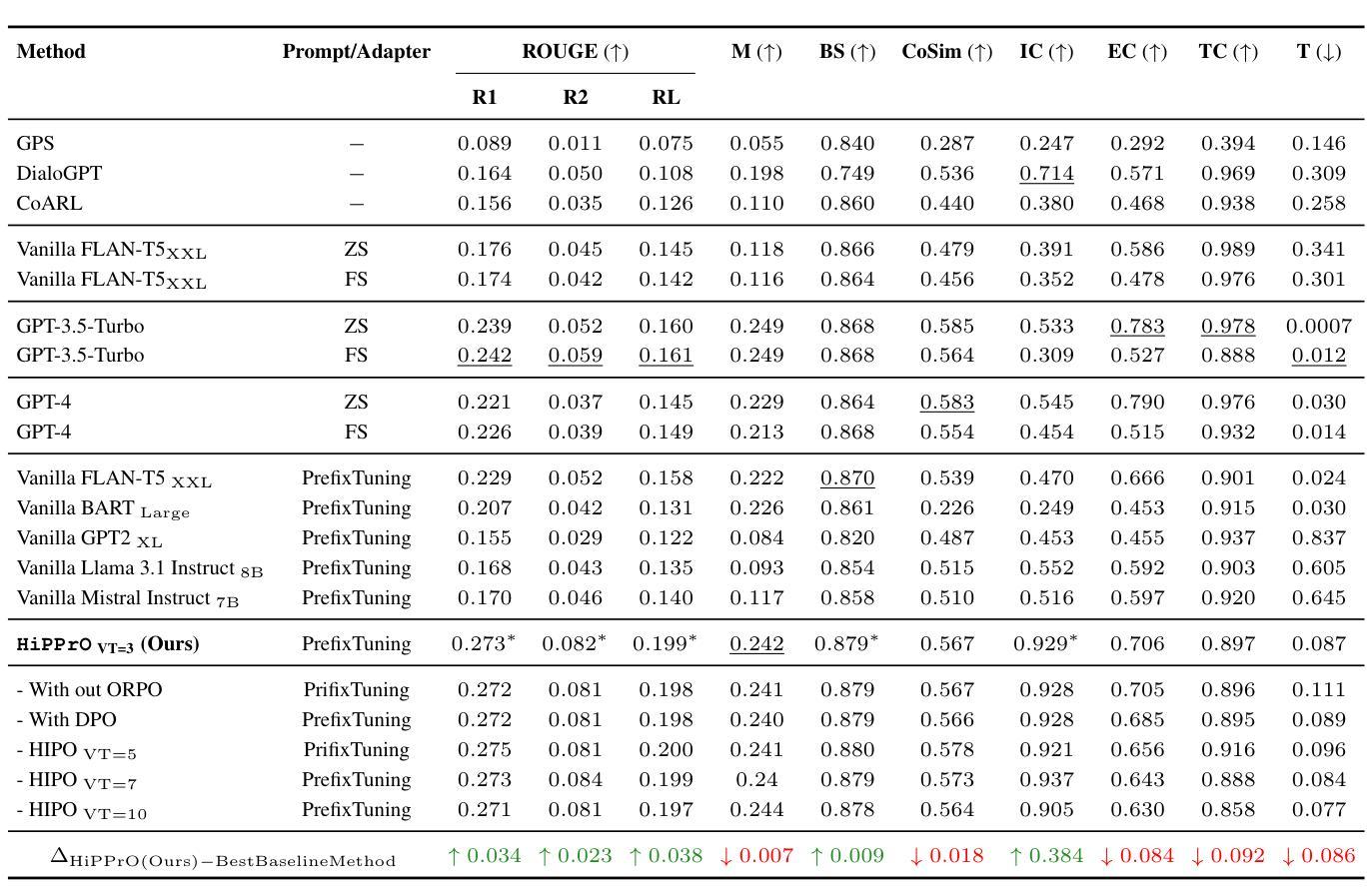
Counterspeech the ultimate shield! Multi-Conditioned Counterspeech Generation through Attributed Prefix Learning
Authors:Aswini Kumar Padhi, Anil Bandhakavi, Tanmoy Chakraborty
Counterspeech has proven to be a powerful tool to combat hate speech online. Previous studies have focused on generating counterspeech conditioned only on specific intents (single attributed). However, a holistic approach considering multiple attributes simultaneously can yield more nuanced and effective responses. Here, we introduce HiPPrO, Hierarchical Prefix learning with Preference Optimization, a novel two-stage framework that utilizes the effectiveness of attribute-specific prefix embedding spaces hierarchically optimized during the counterspeech generation process in the first phase. Thereafter, we incorporate both reference and reward-free preference optimization to generate more constructive counterspeech. Furthermore, we extend IntentCONANv2 by annotating all 13,973 counterspeech instances with emotion labels by five annotators. HiPPrO leverages hierarchical prefix optimization to integrate these dual attributes effectively. An extensive evaluation demonstrates that HiPPrO achieves a ~38 % improvement in intent conformity and a ~3 %, ~2 %, ~3 % improvement in Rouge-1, Rouge-2, and Rouge-L, respectively, compared to several baseline models. Human evaluations further substantiate the superiority of our approach, highlighting the enhanced relevance and appropriateness of the generated counterspeech. This work underscores the potential of multi-attribute conditioning in advancing the efficacy of counterspeech generation systems.
对抗性言论已被证明是网上打击仇恨言论的有力工具。之前的研究主要集中在仅根据特定意图(单一属性)生成对抗性言论。然而,考虑多个属性同时的全面方法可能会产生更细致和有效的回应。在这里,我们介绍了HiPPrO,即带有偏好优化的层次前缀学习(Hierarchical Prefix learning with Preference Optimization),这是一种新的两阶段框架。它利用特定属性前缀嵌入空间在生成对抗性言论过程中的有效性进行层次优化。之后,我们结合了参考和无奖励偏好优化,以生成更具建设性的对抗性言论。此外,我们对所有13973个对抗性言论实例进行了情感标签标注,由五位标注者完成。HiPPrO利用层次前缀优化有效地整合了这些双重属性。一项广泛评估表明,HiPPrO在意图一致性方面取得了约38%的改进,并且在Rouge-1、Rouge-2和Rouge-L方面分别取得了约3%、约2%、约3%的改进,相较于几个基准模型。人类评估进一步证实了我们方法的优越性,突出了生成对抗性言论的增强关联性和恰当性。这项工作突显了多属性条件在提升对抗性言论生成系统效率方面的潜力。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了对抗网络仇恨言论的有效工具——反语。以往的研究主要关注于基于特定意图的反语生成,而本文提出一种综合考虑多种属性的全面方法,以产生更精细和有效的回应。为此,本文引入了HiPPrO框架,该框架利用属性特定的前缀嵌入空间进行分层优化,并在反语生成过程中进行改进。实验证明,HiPPrO方法在意图符合性和评价指数方面相比基线模型有显著提升,显示出多属性条件在提升反语生成系统效能方面的潜力。
Key Takeaways
- 反语是网络上对抗仇恨言论的有力工具。
- 以往研究主要关注基于单一意图的反语生成,而全面考虑多种属性的方法能生成更精细和有效的回应。
- 引入HiPPrO框架,通过分层前缀学习并结合偏好优化进行反语生成。
- HiPPrO在意图符合性和评价指数方面较基线模型有显著改善。
- 人类评估进一步证明了HiPPrO方法的优越性,强调了其在生成反语的相关性。
- 情感标签在反语生成过程中的作用被重视,并进行了相应的研究。
点此查看论文截图

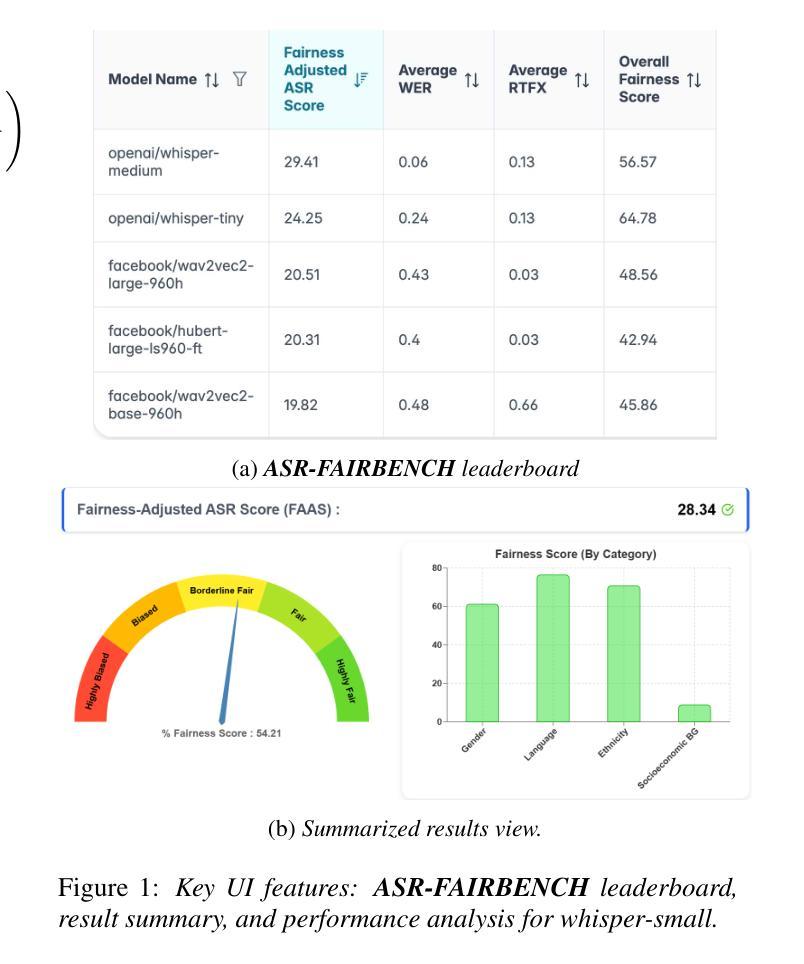
ASR-FAIRBENCH: Measuring and Benchmarking Equity Across Speech Recognition Systems
Authors:Anand Rai, Satyam Rahangdale, Utkarsh Anand, Animesh Mukherjee
Automatic Speech Recognition (ASR) systems have become ubiquitous in everyday applications, yet significant disparities in performance across diverse demographic groups persist. In this work, we introduce the ASR-FAIRBENCH leaderboard which is designed to assess both the accuracy and equity of ASR models in real-time. Leveraging the Meta’s Fair-Speech dataset, which captures diverse demographic characteristics, we employ a mixed-effects Poisson regression model to derive an overall fairness score. This score is integrated with traditional metrics like Word Error Rate (WER) to compute the Fairness Adjusted ASR Score (FAAS), providing a comprehensive evaluation framework. Our approach reveals significant performance disparities in SOTA ASR models across demographic groups and offers a benchmark to drive the development of more inclusive ASR technologies.
自动语音识别(ASR)系统在日常应用中已经无处不在,但在不同人口群体中的性能仍存在显著差异。在这项工作中,我们推出了ASR-FAIRBENCH排行榜,旨在实时评估ASR模型的准确性和公平性。我们利用Meta的Fair-Speech数据集,该数据集捕捉了多样化的人口特征,采用混合效应泊松回归模型得出整体公平分数。该分数与词错误率(WER)等传统指标相结合,计算出公平调整后的ASR分数(FAAS),提供了一个全面的评估框架。我们的方法揭示了最先进ASR模型在不同人口群体中的性能差异,并为开发更具包容性的ASR技术提供了基准。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Paper accepted at INTERSPEECH 2025
Summary:自动语音识别(ASR)系统在日常应用中已普及,但不同人群性能差距显著。本研究引入了ASR-FAIRBENCH排行榜,旨在实时评估ASR模型的准确性和公平性。利用Meta的Fair-Speech数据集,该数据集捕捉了多种人口特征,我们采用混合效应Poisson回归模型得出整体公平得分。该得分与词错误率(WER)等传统指标相结合,计算出公平调整后的ASR得分(FAAS),为全面评估框架提供依据。本研究揭示了顶尖ASR模型在不同人群中的性能差距,并为开发更具包容性的ASR技术提供了基准。
Key Takeaways:
- ASR系统在普及应用中仍存在不同人群的性能差异问题。
- 引入了ASR-FAIRBENCH排行榜以评估ASR模型的准确性和公平性。
- 利用Fair-Speech数据集来捕捉多种人口特征。
- 采用混合效应Poisson回归模型评估ASR模型的公平性。
- 结合传统指标如词错误率(WER)和公平得分,提出公平调整后的ASR得分(FAAS)。
- 研究揭示了现有顶尖ASR模型在不同人群中的性能差距。
- 为开发更包容的ASR技术提供了基准和评估工具。
点此查看论文截图

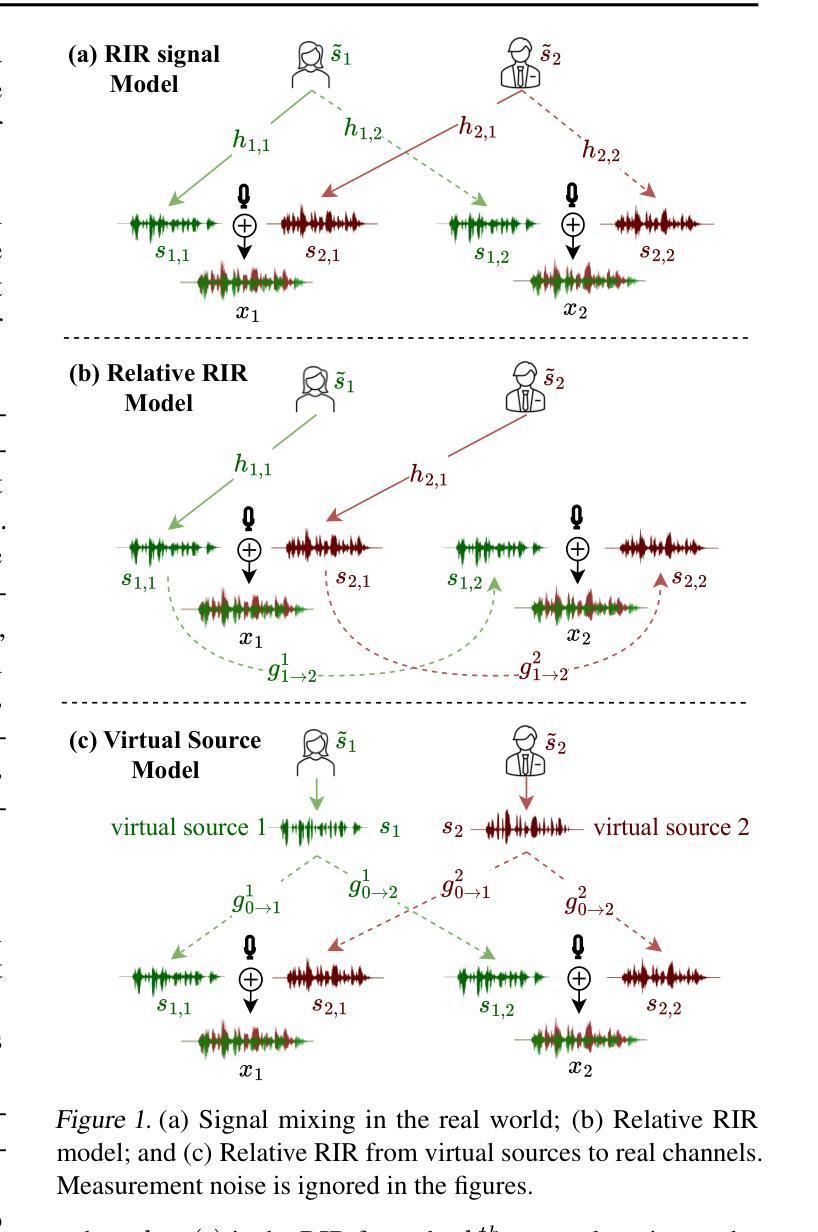
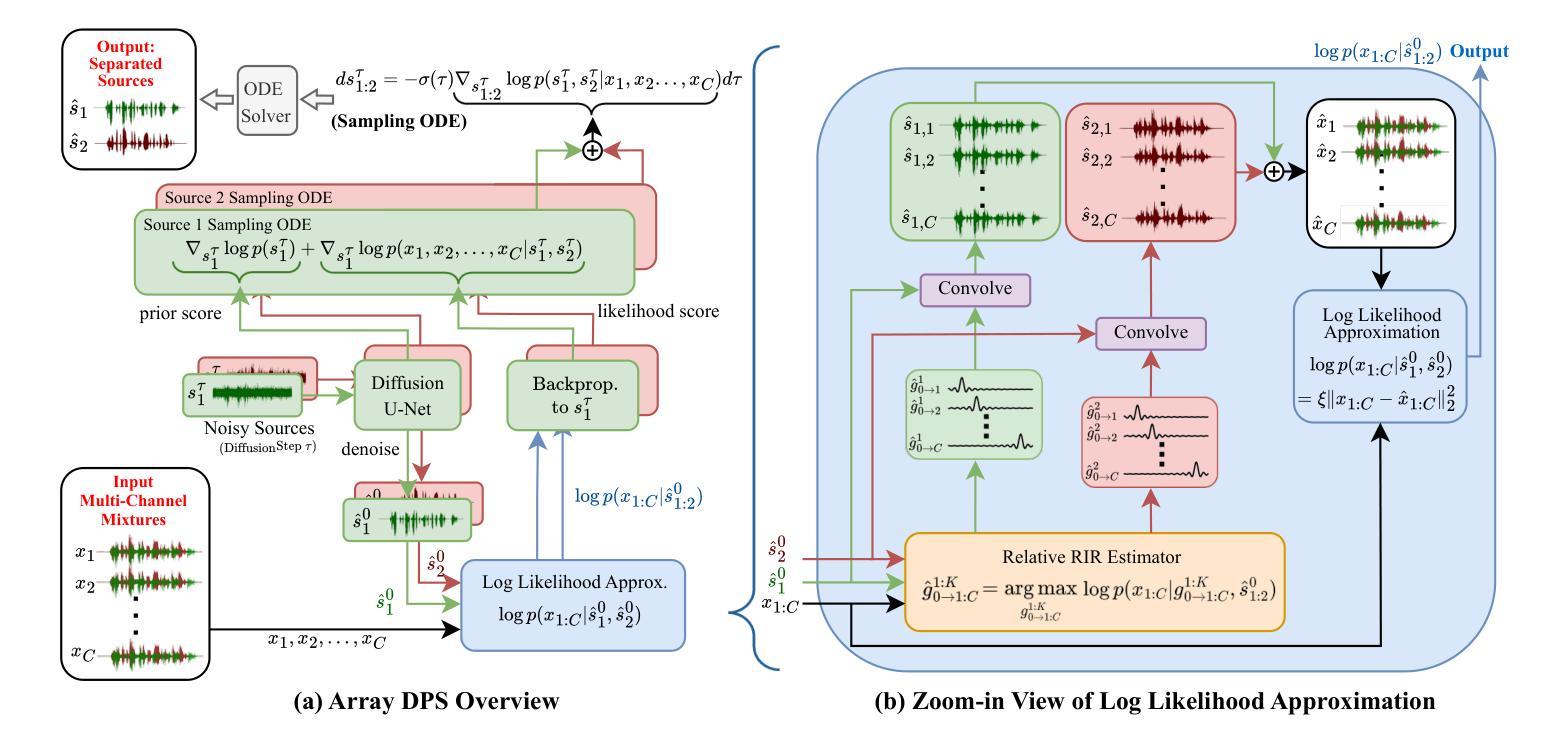
ArrayDPS: Unsupervised Blind Speech Separation with a Diffusion Prior
Authors:Zhongweiyang Xu, Xulin Fan, Zhong-Qiu Wang, Xilin Jiang, Romit Roy Choudhury
Blind Speech Separation (BSS) aims to separate multiple speech sources from audio mixtures recorded by a microphone array. The problem is challenging because it is a blind inverse problem, i.e., the microphone array geometry, the room impulse response (RIR), and the speech sources, are all unknown. We propose ArrayDPS to solve the BSS problem in an unsupervised, array-agnostic, and generative manner. The core idea builds on diffusion posterior sampling (DPS), but unlike DPS where the likelihood is tractable, ArrayDPS must approximate the likelihood by formulating a separate optimization problem. The solution to the optimization approximates room acoustics and the relative transfer functions between microphones. These approximations, along with the diffusion priors, iterate through the ArrayDPS sampling process and ultimately yield separated voice sources. We only need a simple single-speaker speech diffusion model as a prior along with the mixtures recorded at the microphones; no microphone array information is necessary. Evaluation results show that ArrayDPS outperforms all baseline unsupervised methods while being comparable to supervised methods in terms of SDR. Audio demos are provided at: https://arraydps.github.io/ArrayDPSDemo/.
盲语音分离(BSS)旨在从麦克风阵列记录的音频混合中分离出多个语音源。这个问题具有挑战性,因为它是一个盲逆问题,即麦克风阵列的几何形状、房间冲击响应(RIR)和语音源都是未知的。我们提出ArrayDPS以无监督、阵列无关和生成的方式解决BSS问题。核心理念建立在扩散后采样(DPS)的基础上,但不同于DPS中可能性是可追踪的,ArrayDPS必须通过制定一个单独的优化问题来近似可能性。优化的解决方案近似于房间声学以及麦克风之间的相对传递函数。这些近似值,连同扩散先验,在ArrayDPS采样过程中进行迭代,并最终产生分离的语音源。我们只需要一个简单的单说话人语音扩散模型作为先验,以及麦克风记录的混合声音;无需麦克风阵列信息。评估结果表明,ArrayDPS在SDR方面优于所有基线无监督方法,同时与有监督方法相当。音频演示请访问:https://arraydps.github.io/ArrayDPSDemo/。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Paper Accepted at ICML2025 Demo: https://arraydps.github.io/ArrayDPSDemo/ Code: https://github.com/ArrayDPS/ArrayDPS
Summary
盲语音分离(BSS)是从麦克风阵列录制的音频混合中分离多个语音源的问题。我们提出ArrayDPS以无监督、阵列无关和生成的方式解决BSS问题。其核心思想基于扩散后采样(DPS),但不同于DPS中的似然性可以计算,ArrayDPS必须通过构建单独的优化问题来近似似然性。该优化的解决方案近似于房间声学以及麦克风之间的相对传递函数。这些近似值与扩散先验值一起,在ArrayDPS采样过程中进行迭代,最终产生分离的语音源。我们仅需要一个简单的单说话人语音扩散模型作为先验值,以及麦克风录制的混合声音,无需知道麦克风阵列的信息。评估结果显示,ArrayDPS在无人监督的方法中表现最佳,同时在SDR方面与有监督的方法相当。
Key Takeaways
- 盲语音分离(BSS)是从麦克风阵列录制的音频中分离多个语音源的问题,具有挑战性。
- ArrayDPS以无监督、阵列无关和生成的方式解决BSS问题。
- ArrayDPS的核心思想基于扩散后采样(DPS),但需要近似似然性。
- 该优化的解决方案近似于房间声学及麦克风间的相对传递函数。
- ArrayDPS结合了扩散先验与优化的解决方案进行迭代采样,最终产生分离的语音源。
- 仅需简单的单说话人语音扩散模型作为先验,以及混合录音,无需知道麦克风阵列的具体信息。
点此查看论文截图


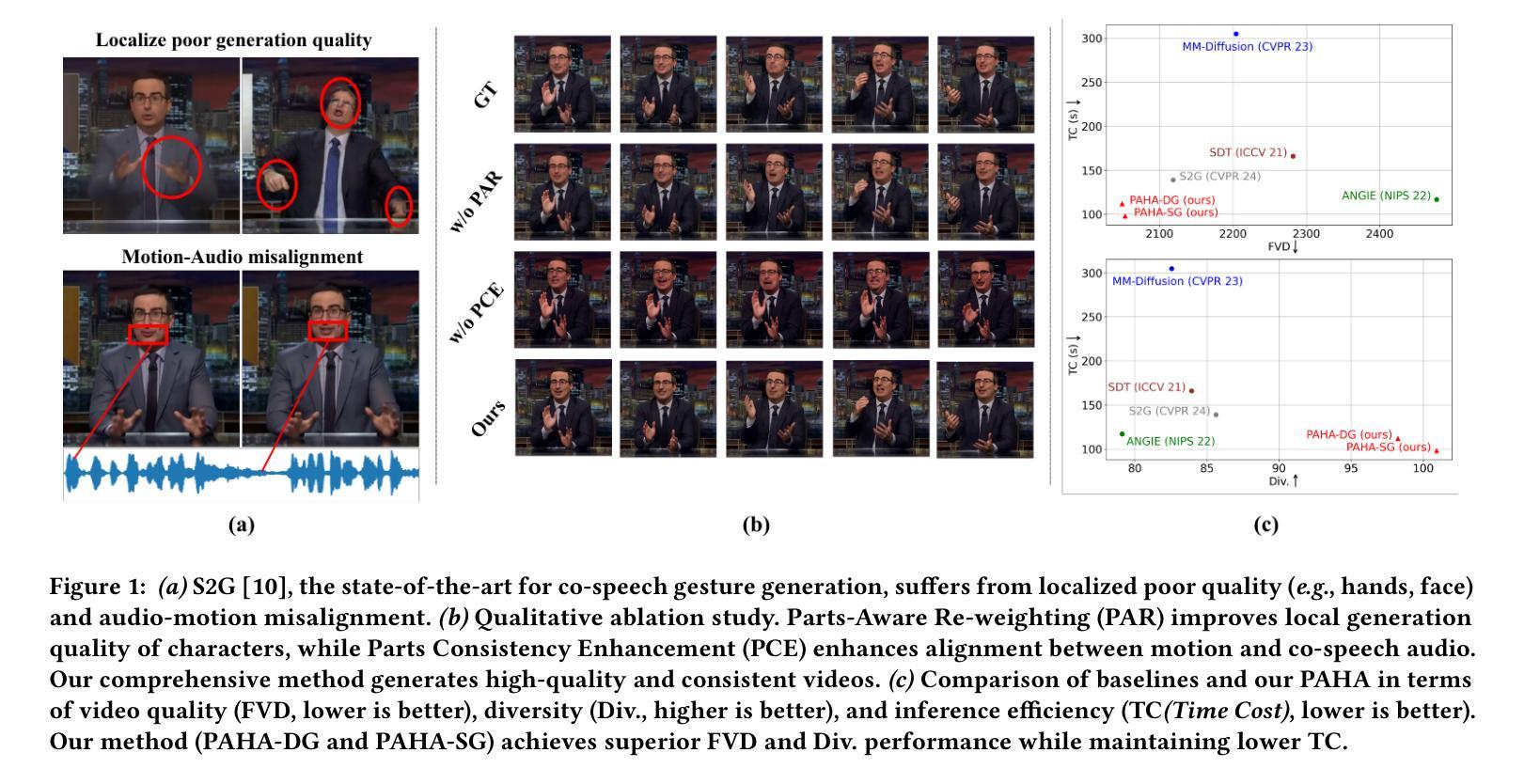
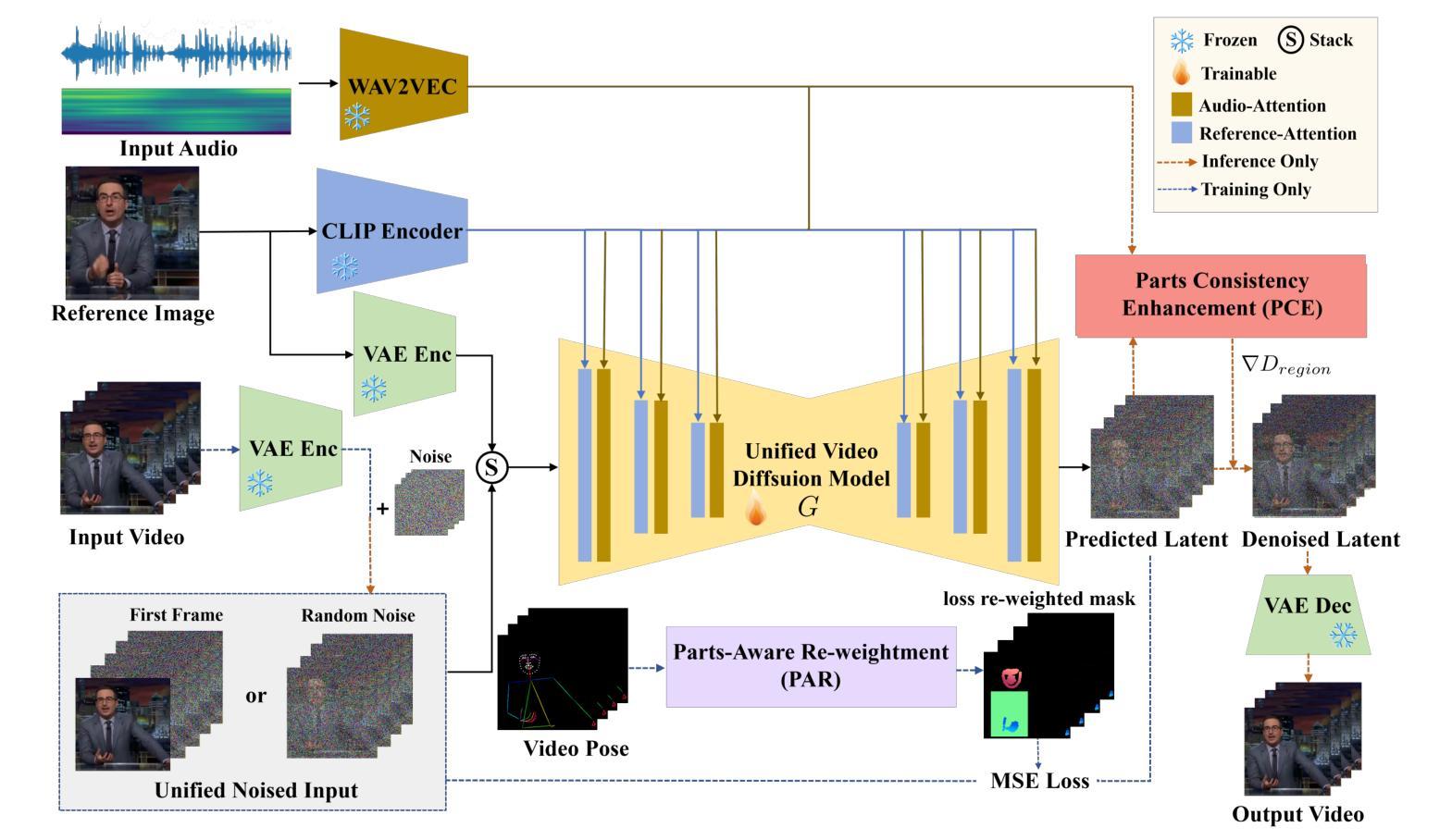
PAHA: Parts-Aware Audio-Driven Human Animation with Diffusion Model
Authors:S. Z. Zhou, Y. B. Wang, J. F. Wu, T. Hu, J. N. Zhang, Z. J. Li, Y. Liu
Audio-driven human animation technology is widely used in human-computer interaction, and the emergence of diffusion models has further advanced its development. Currently, most methods rely on multi-stage generation and intermediate representations, resulting in long inference time and issues with generation quality in specific foreground regions and audio-motion consistency. These shortcomings are primarily due to the lack of localized fine-grained supervised guidance. To address above challenges, we propose PAHA, an end-to-end audio-driven upper-body human animation framework with diffusion model. We introduce two key methods: Parts-Aware Re-weighting (PAR) and Parts Consistency Enhancement (PCE). PAR dynamically adjusts regional training loss weights based on pose confidence scores, effectively improving visual quality. PCE constructs and trains diffusion-based regional audio-visual classifiers to improve the consistency of motion and co-speech audio. Afterwards, we design two novel inference guidance methods for the foregoing classifiers, Sequential Guidance (SG) and Differential Guidance (DG), to balance efficiency and quality respectively. Additionally, we build CNAS, the first public Chinese News Anchor Speech dataset, to advance research and validation in this field. Extensive experimental results and user studies demonstrate that PAHA significantly outperforms existing methods in audio-motion alignment and video-related evaluations. The codes and CNAS dataset will be released upon acceptance.
音频驱动的人形动画技术广泛应用于人机交互领域,扩散模型的出现进一步推动了其发展。当前,大多数方法依赖于多阶段生成和中间表示,导致推理时间长,特定前景区域生成质量和音画同步问题。这些缺点主要是由于缺乏局部精细监督指导。为了解决上述挑战,我们提出了PAHA,这是一个基于扩散模型的端到端音频驱动人体上半部分动画框架。我们介绍了两种关键方法:零件感知重加权(PAR)和零件一致性增强(PCE)。PAR根据姿态置信度分数动态调整区域训练损失权重,有效提高视觉质量。PCE构建并训练基于扩散的区域音视频分类器,以提高运动和语音音频的一致性。之后,我们为前述分类器设计了两种新颖推理指导方法,即顺序指导(SG)和差异指导(DG),以分别平衡效率和质量。此外,我们构建了CNAS,首个公开的中文新闻主播语音数据集,以推动该领域的研究和验证。大量的实验和用户研究表明,PAHA在音频运动对齐和视频相关评估方面显著优于现有方法。代码和CNAS数据集将在接受后发布。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了音频驱动的人体动画技术在人机交互中的广泛应用,以及扩散模型的出现对其发展的进一步推动。针对当前方法存在的长期推理时间、特定前景区域生成质量和音频运动一致性等问题,提出了一个端到端的音频驱动上身人体动画框架PAHA,并引入了Parts-Aware Re-weighting(PAR)和Parts Consistency Enhancement(PCE)两种关键方法。通过构建和训练基于扩散的区域音频视觉分类器,提高了运动一致性及与语音的协调性。同时,设计了两种新型推理指导方法,Sequential Guidance(SG)和Differential Guidance(DG),以平衡效率和质量。此外,建立了首个中文新闻主播语音数据集CNAS,以推动该领域的研究和验证。实验和用户研究结果表明,PAHA在音频运动对齐和视频相关评估方面显著优于现有方法。
Key Takeaways
- 音频驱动的人体动画技术在人机交互中有广泛应用,扩散模型的出现进一步推动了其发展。
- 当前方法存在长期推理时间、生成质量及音频运动一致性问题。
- PAHA框架通过引入PAR和PCE方法,提高了视觉质量及运动与音频的一致性。
- 设计了SG和DG两种推理指导方法,以平衡效率和质量。
- 建立了首个中文新闻主播语音数据集CNAS,用于研究和验证。
- 实验和用户研究结果显示PAHA显著优于现有方法。
点此查看论文截图

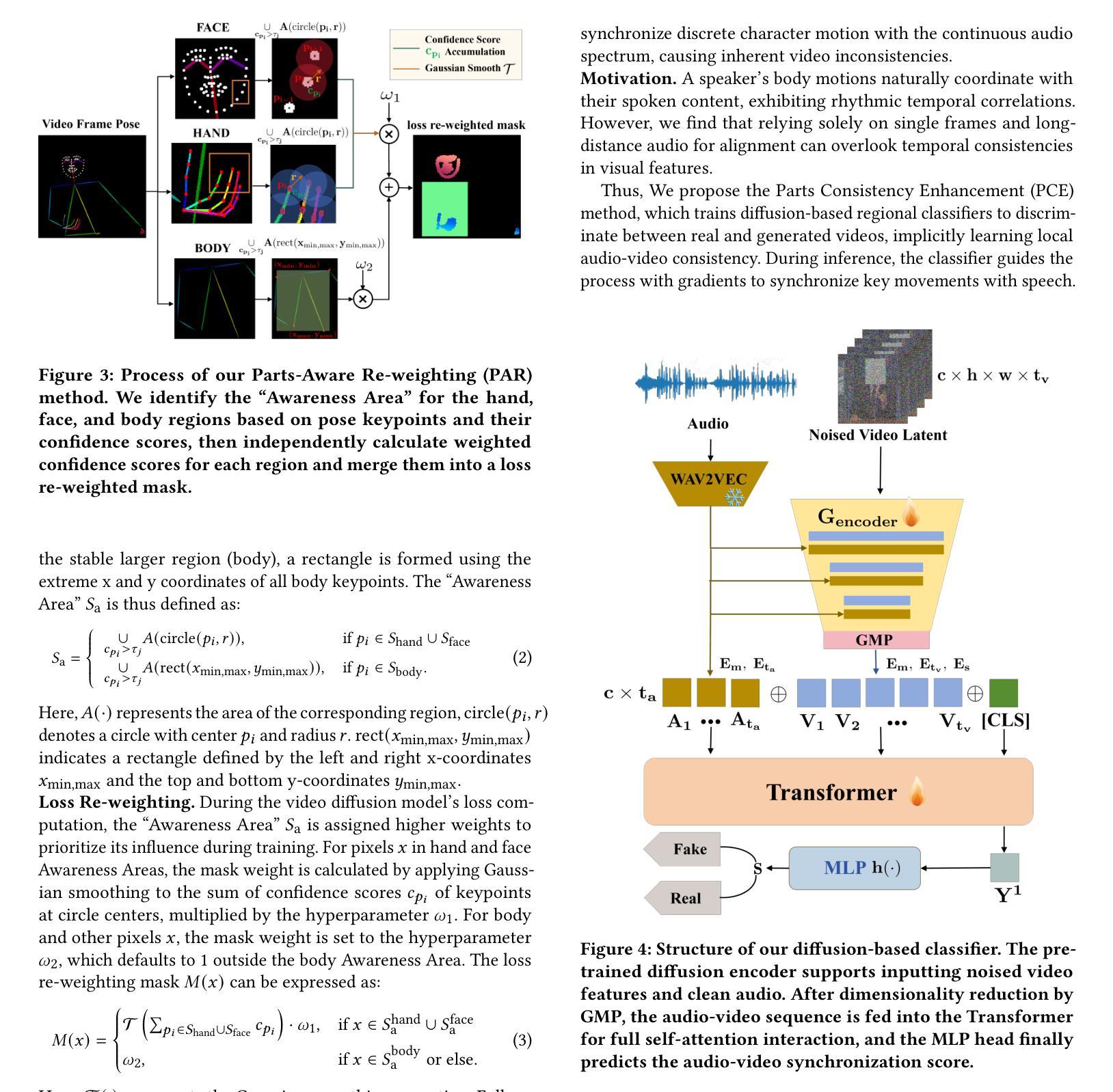
USpeech: Ultrasound-Enhanced Speech with Minimal Human Effort via Cross-Modal Synthesis
Authors:Luca Jiang-Tao Yu, Running Zhao, Sijie Ji, Edith C. H. Ngai, Chenshu Wu
Speech enhancement is crucial for ubiquitous human-computer interaction. Recently, ultrasound-based acoustic sensing has emerged as an attractive choice for speech enhancement because of its superior ubiquity and performance. However, due to inevitable interference from unexpected and unintended sources during audio-ultrasound data acquisition, existing solutions rely heavily on human effort for data collection and processing. This leads to significant data scarcity that limits the full potential of ultrasound-based speech enhancement. To address this, we propose USpeech, a cross-modal ultrasound synthesis framework for speech enhancement with minimal human effort. At its core is a two-stage framework that establishes the correspondence between visual and ultrasonic modalities by leveraging audio as a bridge. This approach overcomes challenges from the lack of paired video-ultrasound datasets and the inherent heterogeneity between video and ultrasound data. Our framework incorporates contrastive video-audio pre-training to project modalities into a shared semantic space and employs an audio-ultrasound encoder-decoder for ultrasound synthesis. We then present a speech enhancement network that enhances speech in the time-frequency domain and recovers the clean speech waveform via a neural vocoder. Comprehensive experiments show USpeech achieves remarkable performance using synthetic ultrasound data comparable to physical data, outperforming state-of-the-art ultrasound-based speech enhancement baselines. USpeech is open-sourced at https://github.com/aiot-lab/USpeech/.
语音增强对于无处不在的人机交互至关重要。最近,基于超声的声学感知因其普遍的适用性和卓越的性能而成为语音增强的一个吸引人的选择。然而,在音频超声数据采集过程中,不可避免地会存在来自意外和非预期源的干扰,现有的解决方案严重依赖于人工的数据收集和处理。这导致了数据严重匮乏,限制了基于超声的语音增强的潜力。为了解决这一问题,我们提出了USpeech,这是一个跨模态超声合成框架,用于语音增强,只需最小的人工干预。其核心是一个两阶段框架,通过音频作为桥梁,建立视觉和超声模态之间的对应关系。这种方法克服了缺乏配对视频超声数据集和视频与超声数据之间固有的异质性的挑战。我们的框架结合了对比视频音频预训练,将模态投影到共享语义空间,并采用了音频超声编码器-解码器进行超声合成。然后,我们提出了一种语音增强网络,该网络在时频域增强语音,并通过神经vocoder恢复干净的语音波形。综合实验表明,USpeech使用合成超声数据实现了与物理数据相当的卓越性能,超越了最先进的基于超声的语音增强基线。USpeech已在https://github.com/aiot-lab/USpeech/开源。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by Proceedings of the ACM on Interactive, Mobile, Wearable and Ubiquitous Technologies (ACM IMWUT/UbiComp 2025)
摘要
本文提出了USpeech,一种利用跨模态超声合成技术的语音增强框架,几乎无需人工干预。该框架通过建立视频与超声波之间的对应关系来解决缺乏配套的视频-超声波数据集的问题,借助音频作为媒介来解决这种内在的差异。框架中包含对比视频-音频预训练以及一个用于合成超声波的音频-超声波编码器解码器。同时,引入语音增强网络在时频域内增强语音,并通过神经网络vocoder恢复清洁语音波形。实验证明,使用合成超声波数据的USpeech性能卓越,与物理数据相比表现优异,超越了现有的基于超声波的语音增强基线技术。USpeech已开源。
关键见解
- 语音增强对于普遍的人机交互至关重要。
- 超声波在语音增强中展现出色的普及性和性能,成为新兴的选择。
- 由于音频和超声波数据采集过程中的干扰和误配对,现有解决方案需要大量人工数据收集和处理,导致数据稀缺问题。
- 提出了一种新型的跨模态超声合成框架USpeech,旨在以最小的手工努力进行语音增强。
点此查看论文截图

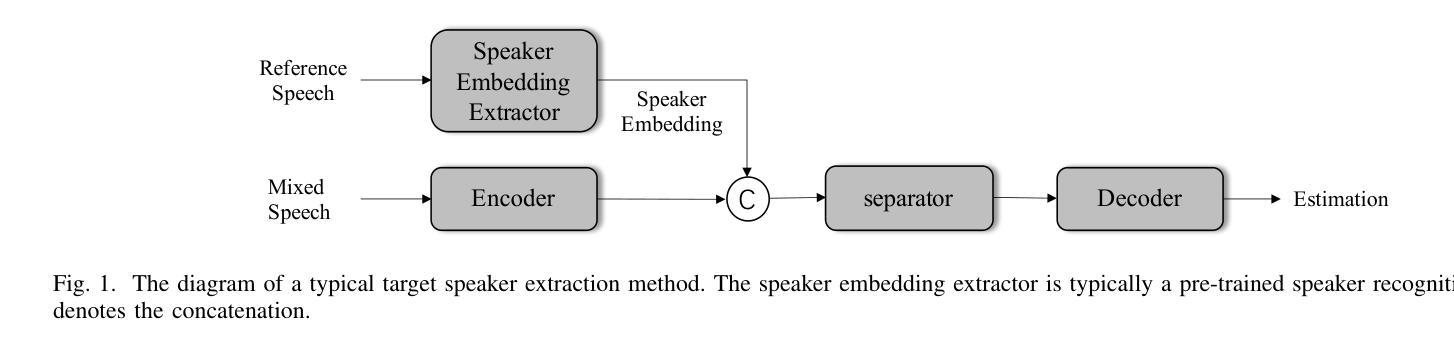
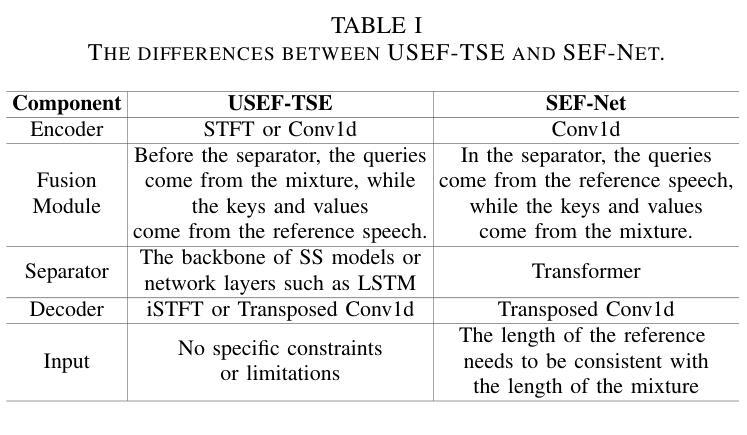
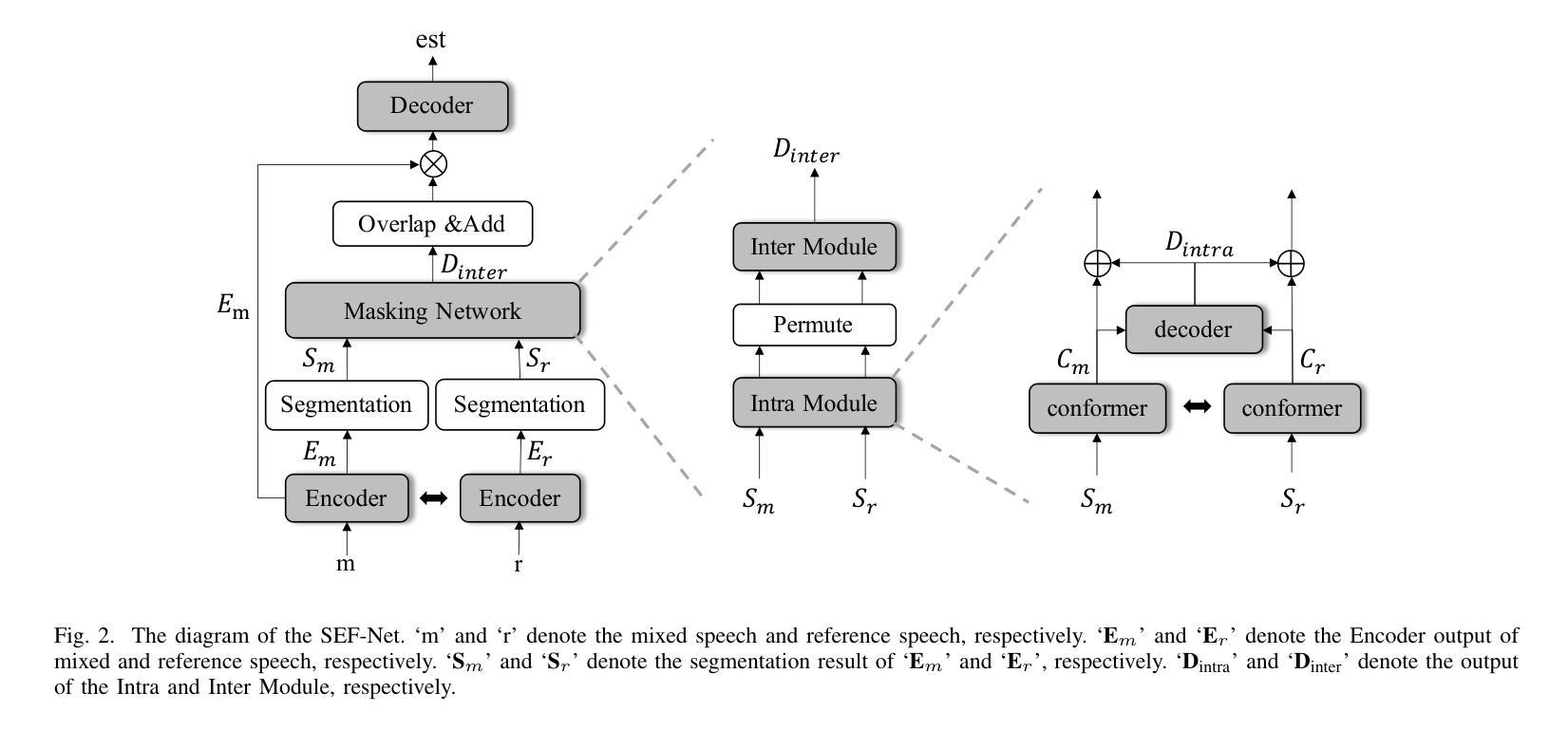
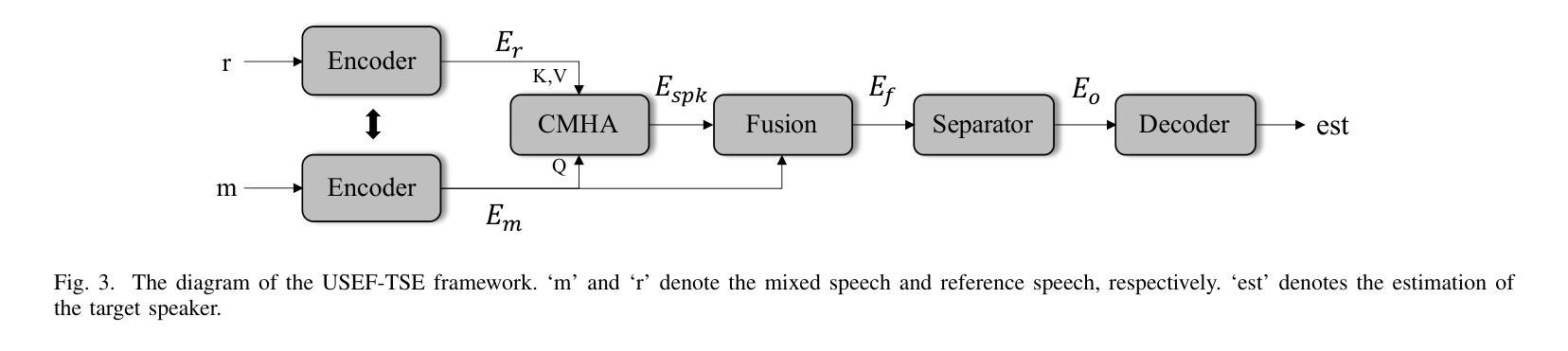
USEF-TSE: Universal Speaker Embedding Free Target Speaker Extraction
Authors:Bang Zeng, Ming Li
Target speaker extraction aims to separate the voice of a specific speaker from mixed speech. Traditionally, this process has relied on extracting a speaker embedding from a reference speech, in which a speaker recognition model is required. However, identifying an appropriate speaker recognition model can be challenging, and using the target speaker embedding as reference information may not be optimal for target speaker extraction tasks. This paper introduces a Universal Speaker Embedding-Free Target Speaker Extraction (USEF-TSE) framework that operates without relying on speaker embeddings. USEF-TSE utilizes a multi-head cross-attention mechanism as a frame-level target speaker feature extractor. This innovative approach allows mainstream speaker extraction solutions to bypass the dependency on speaker recognition models and better leverage the information available in the enrollment speech, including speaker characteristics and contextual details. Additionally, USEF-TSE can seamlessly integrate with other time-domain or time-frequency domain speech separation models to achieve effective speaker extraction. Experimental results show that our proposed method achieves state-of-the-art (SOTA) performance in terms of Scale-Invariant Signal-to-Distortion Ratio (SI-SDR) on the WSJ0-2mix, WHAM!, and WHAMR! datasets, which are standard benchmarks for monaural anechoic, noisy and noisy-reverberant two-speaker speech separation and speaker extraction. The results on the LibriMix and the blind test set of the ICASSP 2023 DNS Challenge demonstrate that the model performs well on more diverse and out-of-domain data. For access to the source code, please visit: https://github.com/ZBang/USEF-TSE.
目标说话人提取旨在从混合语音中分离出特定说话人的声音。传统上,这一过程依赖于从参考语音中提取说话人嵌入,这需要说话人识别模型。然而,识别合适的说话人识别模型可能具有挑战性,并且使用目标说话人嵌入作为参考信息可能不是针对目标说话人提取任务的最佳选择。本文介绍了一种无通用说话人嵌入目标说话人提取(USEF-TSE)框架,该框架无需依赖说话人嵌入即可运行。USEF-TSE利用多头交叉注意机制作为帧级目标说话人特征提取器。这种创新方法允许主流说话人提取解决方案绕过对说话人识别模型的依赖,并更好地利用报名语音中的信息,包括说话人特征和上下文细节。此外,USEF-TSE可以无缝集成到其他时域或时频域语音分离模型,以实现有效的说话人提取。实验结果表明,我们提出的方法在WSJ0-2mix、WHAM!和WHAMR!数据集上达到了最新的性能水平。这些数据集是单核消声、噪声和噪声混响双声道语音分离和说话人提取的标准基准测试。在LibriMix和ICASSP 2023 DNS挑战的盲测试集上的结果表明,该模型在更多样化和领域外的数据上表现良好。如需访问源代码,请访问:https://github.com/ZBang/USEF-TSE。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by IEEE Transactions on Audio, Speech and Language Processing (TASLP)
摘要
目标说话人提取旨在从混合语音中分离特定说话人的声音。本文提出了一种无通用说话人嵌入目标说话人提取(USEF-TSE)框架,该框架无需依赖说话人嵌入即可运作。USEF-TSE使用多头交叉注意机制作为帧级目标说话人特征提取器,使主流说话人提取解决方案绕过对说话人识别模型的依赖,更好地利用报名语音中的信息,包括说话人特征和上下文细节。此外,USEF-TSE可以无缝集成到其他时域或时频域语音分离模型,以实现有效的说话人提取。实验结果表明,该方法在WSJ0-2mix、WHAM!和WHAMR!数据集上的尺度不变信号失真比(SI-SDR)方面达到了最新水平。该模型在更多样化和非域数据的LibriMix和ICASSP 2023 DNS Challenge的盲测试集上的表现良好。
关键见解
- 目标说话人提取旨在从混合语音中分离特定说话人的声音。
- 传统的说话人提取方法依赖于从参考语音中提取说话人嵌入,这需要使用说话人识别模型,但识别合适的模型具有挑战性。
- USEF-TSE框架提出了一种不依赖通用说话人嵌入的方法,通过多头交叉注意机制进行目标说话人特征提取。
- 该方法绕过了对说话人识别模型的依赖,并更好地利用了报名语音中的信息。
- USEF-TSE框架可以与其他语音分离模型无缝集成,实现有效的说话人提取。
- 实验结果表明,USEF-TSE在多个数据集上达到了最新水平的性能。
- 模型在多样化和非域数据上的表现良好,源代码已公开发布。
点此查看论文截图

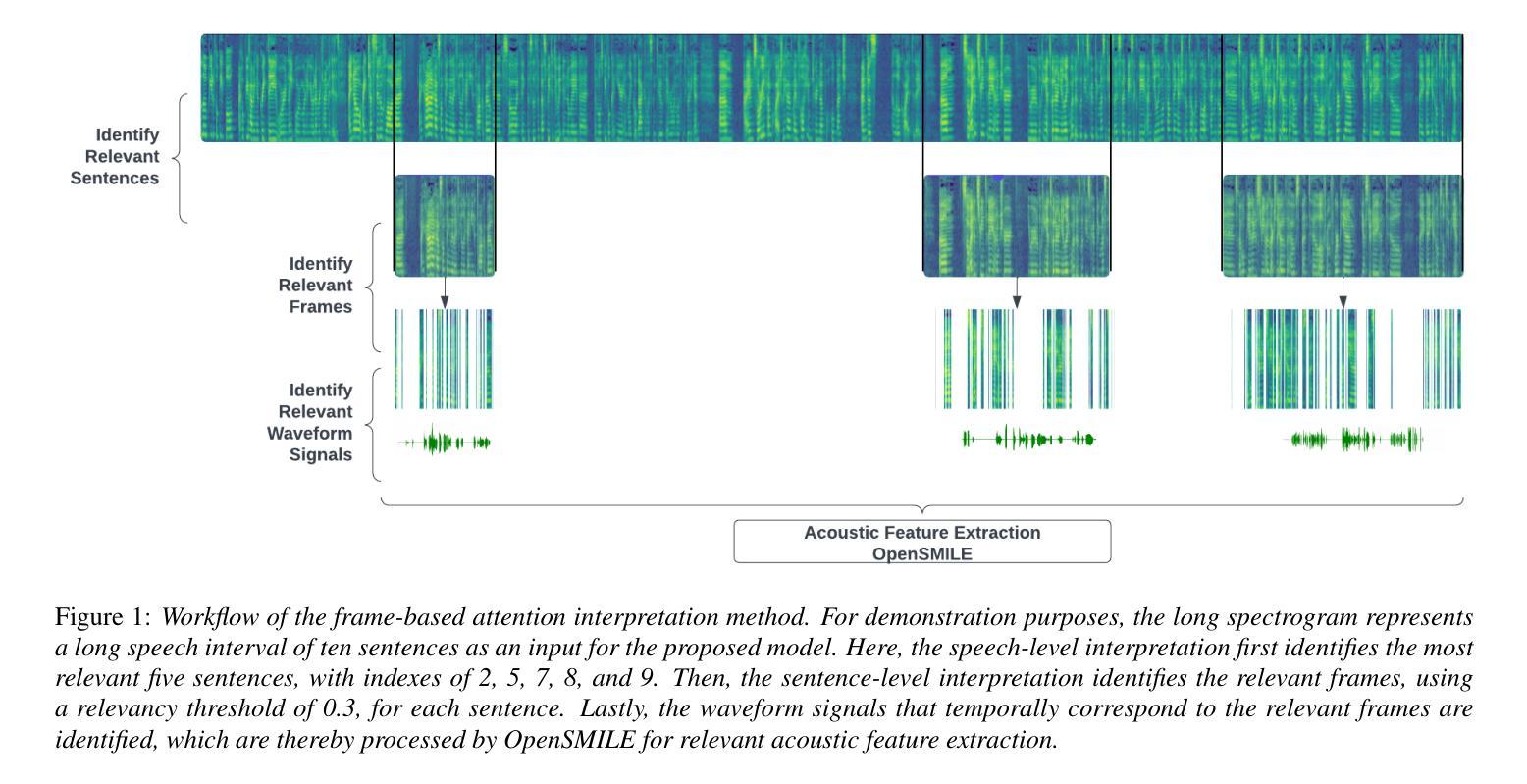
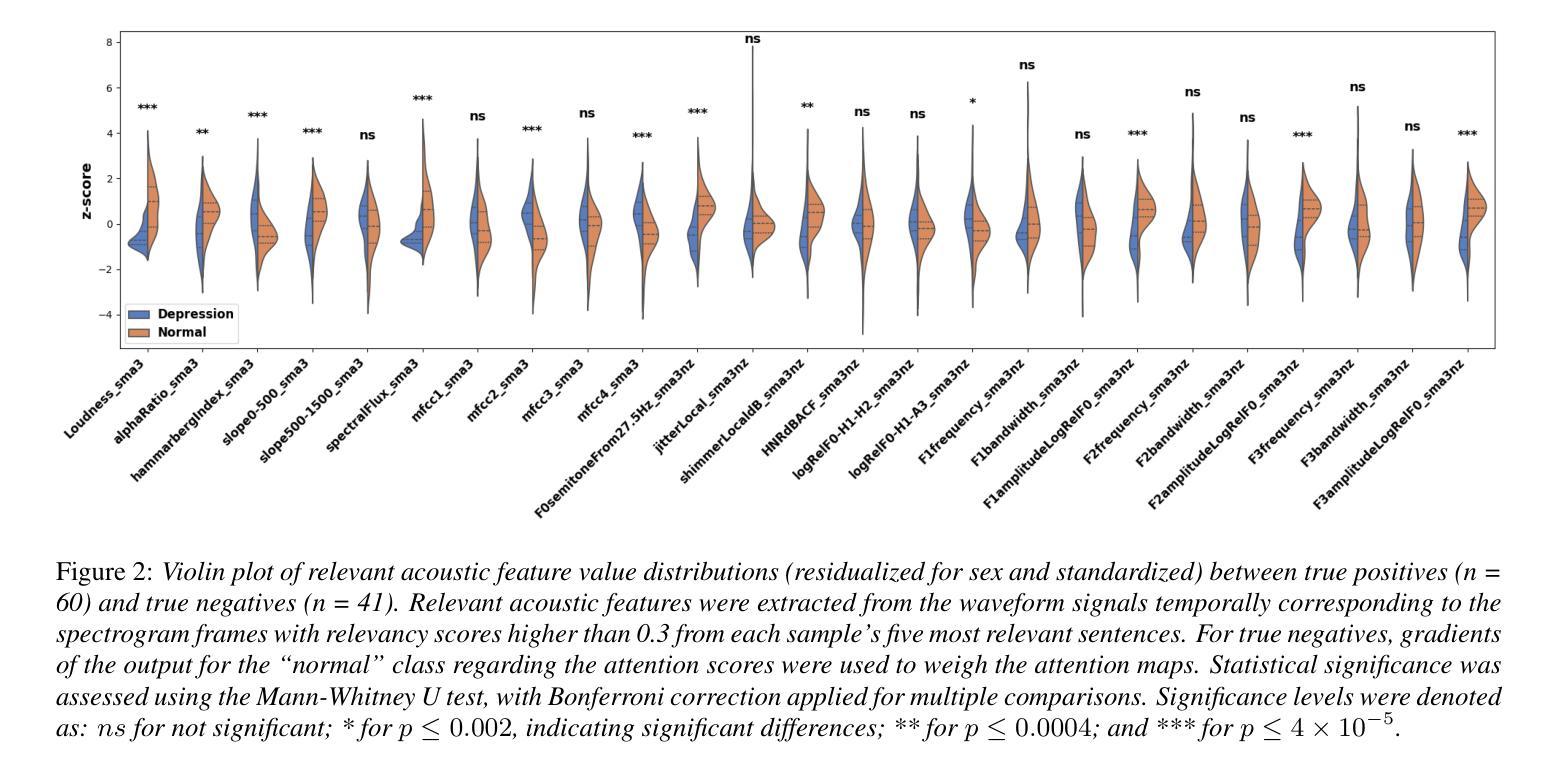
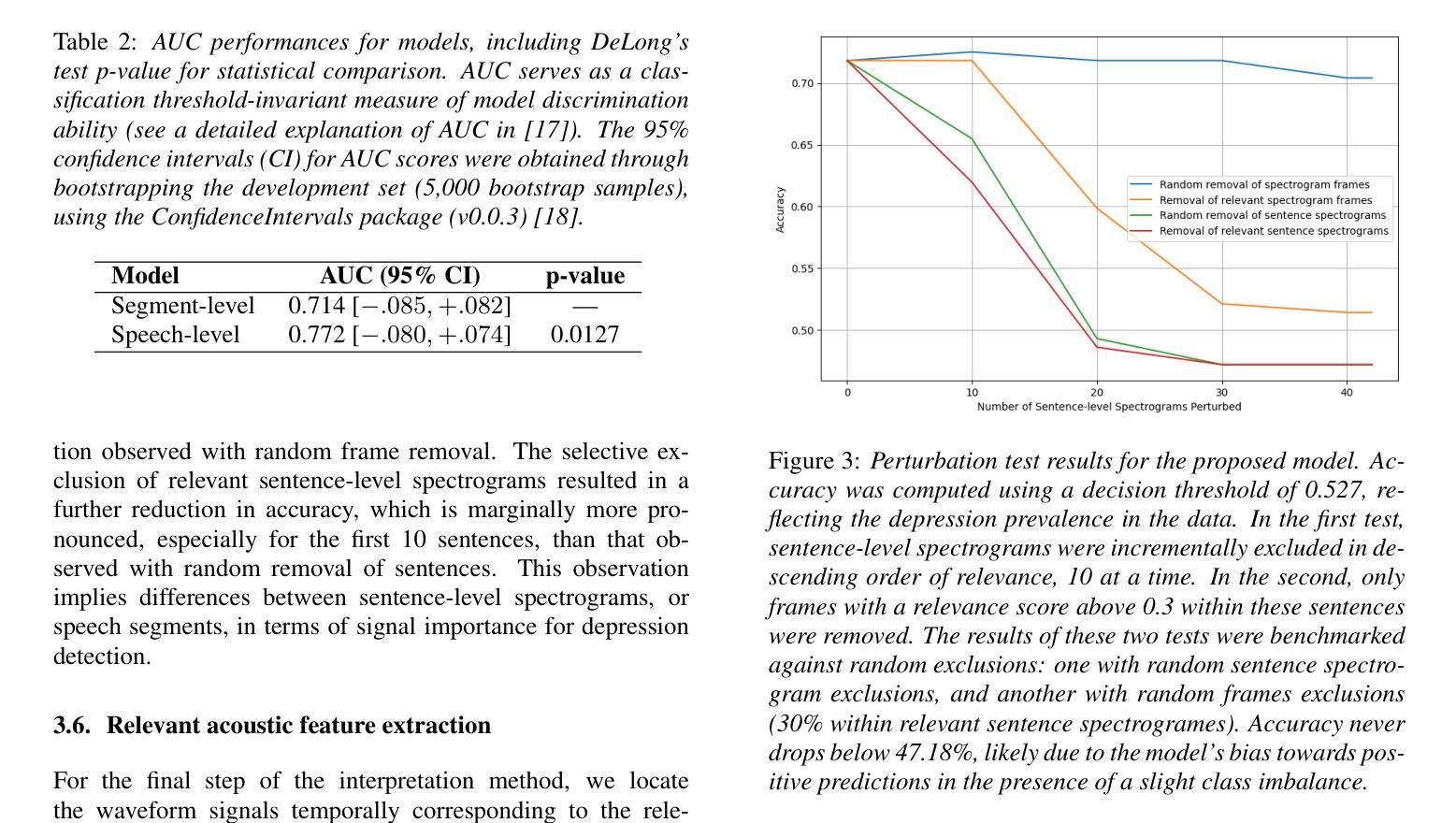
An interpretable speech foundation model for depression detection by revealing prediction-relevant acoustic features from long speech
Authors:Qingkun Deng, Saturnino Luz, Sofia de la Fuente Garcia
Speech-based depression detection tools could aid early screening. Here, we propose an interpretable speech foundation model approach to enhance the clinical applicability of such tools. We introduce a speech-level Audio Spectrogram Transformer (AST) to detect depression using long-duration speech instead of short segments, along with a novel interpretation method that reveals prediction-relevant acoustic features for clinician interpretation. Our experiments show the proposed model outperforms a segment-level AST, highlighting the impact of segment-level labelling noise and the advantage of leveraging longer speech duration for more reliable depression detection. Through interpretation, we observe our model identifies reduced loudness and F0 as relevant depression signals, aligning with documented clinical findings. This interpretability supports a responsible AI approach for speech-based depression detection, rendering such tools more clinically applicable.
基于语音的抑郁症检测工具有助于早期筛查。在这里,我们提出了一种可解释的语音基础模型方法,以提高此类工具的临床适用性。我们引入了一种语音级别的音频频谱图转换器(AST)来检测抑郁症,使用长时语音而不是短片段,以及一种新的解释方法,揭示与预测相关的声学特征,供临床医生解释。我们的实验表明,该模型的表现优于片段级别的AST,突出了片段级别标签噪声的影响,以及利用更长的语音持续时间进行更可靠的抑郁症检测的优势。通过解释,我们发现我们的模型识别出降低的响度和F0与抑郁症相关,这与临床发现相吻合。这种可解释性支持了基于语音的抑郁症检测的负责任的人工智能方法,使这类工具更适用于临床实践。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 5 pages, 3 figures. arXiv admin note: substantial text overlap with arXiv:2309.13476
总结
语音基础的抑郁症检测工具可辅助早期筛查。本文提出了一种可解释的语音基础模型方法,以提高此类工具的临床适用性。我们引入了基于语音层面的音频频谱图转换器(AST)来检测抑郁症,使用长时语音而非短片段进行检测。此外,我们还提出了一种新的解释方法,揭示与预测相关的声学特征,以供临床医生解读。实验表明,所提出的模型优于基于片段级别的AST模型,凸显了片段级别标签噪声的影响以及利用较长语音时长进行更可靠的抑郁症检测的优势。通过解读,我们发现模型识别出的低沉音量和F0与抑郁症有关的声音信号是一致的,这与临床发现相吻合。这种可解释性支持了面向语音的抑郁症检测责任AI方法,使此类工具更具临床适用性。
关键见解
- 语音基础的抑郁症检测工具具有早期筛查的潜力。
- 提出了一种可解释的语音基础模型方法,以增强临床适用性。
- 引入了基于语音层面的Audio Spectrogram Transformer(AST)来检测抑郁症。
- 提出的新解释方法有助于揭示预测相关的声学特征,支持医生解读。
- 实验显示,所提出的模型性能优于基于片段级别的AST模型。
- 模型识别出的声音特征与临床发现相符,如降低的音量和F0变化。
点此查看论文截图