⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-05-22 更新
Automated Fetal Biometry Assessment with Deep Ensembles using Sparse-Sampling of 2D Intrapartum Ultrasound Images
Authors:Jayroop Ramesh, Valentin Bacher, Mark C. Eid, Hoda Kalabizadeh, Christian Rupprecht, Ana IL Namburete, Pak-Hei Yeung, Madeleine K. Wyburd, Nicola K. Dinsdale
The International Society of Ultrasound advocates Intrapartum Ultrasound (US) Imaging in Obstetrics and Gynecology (ISUOG) to monitor labour progression through changes in fetal head position. Two reliable ultrasound-derived parameters that are used to predict outcomes of instrumental vaginal delivery are the angle of progression (AoP) and head-symphysis distance (HSD). In this work, as part of the Intrapartum Ultrasounds Grand Challenge (IUGC) 2024, we propose an automated fetal biometry measurement pipeline to reduce intra- and inter-observer variability and improve measurement reliability. Our pipeline consists of three key tasks: (i) classification of standard planes (SP) from US videos, (ii) segmentation of fetal head and pubic symphysis from the detected SPs, and (iii) computation of the AoP and HSD from the segmented regions. We perform sparse sampling to mitigate class imbalances and reduce spurious correlations in task (i), and utilize ensemble-based deep learning methods for task (i) and (ii) to enhance generalizability under different US acquisition settings. Finally, to promote robustness in task iii) with respect to the structural fidelity of measurements, we retain the largest connected components and apply ellipse fitting to the segmentations. Our solution achieved ACC: 0.9452, F1: 0.9225, AUC: 0.983, MCC: 0.8361, DSC: 0.918, HD: 19.73, ASD: 5.71, $\Delta_{AoP}$: 8.90 and $\Delta_{HSD}$: 14.35 across an unseen hold-out set of 4 patients and 224 US frames. The results from the proposed automated pipeline can improve the understanding of labour arrest causes and guide the development of clinical risk stratification tools for efficient and effective prenatal care.
国际超声学会倡导在产科和妇科领域使用产时超声(US)成像技术,通过监测胎儿头部位置的变化来监控产程进展。预测器械分娩结果的两个可靠的超声参数是进展角度(AoP)和头骨盆入口距离(HSD)。在这项工作中,作为产时超声挑战赛(IUGC)2024的一部分,我们提出了一种自动化胎儿生物测量管道,旨在减少观察者内部和观察者之间的变异性,提高测量可靠性。我们的管道包含三个关键任务:(i)从超声视频中分类标准平面(SP),(ii)从检测到的SP中分割胎儿头部和耻骨弓,以及(iii)从分割区域计算AoP和HSD。我们通过稀疏采样缓解类别不平衡问题并减少任务(i)中的虚假相关性,并基于组合深度学习的方法应用于任务(i)和(ii),以增强在不同超声采集环境下的通用性。最后,为了促进任务iii的结构测量忠实性,我们保留最大的连通组件,并对分割应用椭圆拟合。我们的解决方案在未经训练的4位患者和224个超声帧的测试集上取得了以下成果:ACC:0.9452,F1:0.9225,AUC:0.983,MCC:0.8361,DSC:0.918,HD:19.73,ASD:5.71,ΔAoP:8.9 和ΔHSD:14.35。所提出的自动化管道的结果可以提高对产程停滞原因的理解,并有助于开发用于高效有效产前护理的临床风险分层工具。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Top 5 in MICCAI IUGC 2024: Intrapartum Ultrasound Grand Challenge & Runners up in Classification!
Summary
超声成像学会提倡在妇产科领域使用产时超声成像技术来监测产程进展。该研究提出一个自动化胎儿生物测量管道,用于减少观察者内部和外部的变异性,提高测量可靠性。该管道包括三个关键任务:从超声视频中分类标准平面、从检测到的标准平面中分割胎儿头部和耻骨联合,以及计算进展角和头骨距离。该研究采用稀疏采样技术缓解类别不平衡问题,并利用基于集成深度学习的方法提高任务的一般性。最终,该自动化管道提高了对产程停滞原因的理解,有助于开发临床风险分层工具,为高效有效的产前护理提供指导。
Key Takeaways
- 产时超声成像技术被用于监测产程进展。
- 一个自动化胎儿生物测量管道被提出,以减少观察者变异并提高测量可靠性。
- 该管道包含三个关键任务:从超声视频中分类标准平面、分割胎儿头部和耻骨联合,以及计算进展角和头骨距离。
- 稀疏采样技术用于缓解类别不平衡问题。
- 集成深度学习的方法用于提高任务的一般性。
- 自动化管道有助于理解产程停滞的原因。
点此查看论文截图

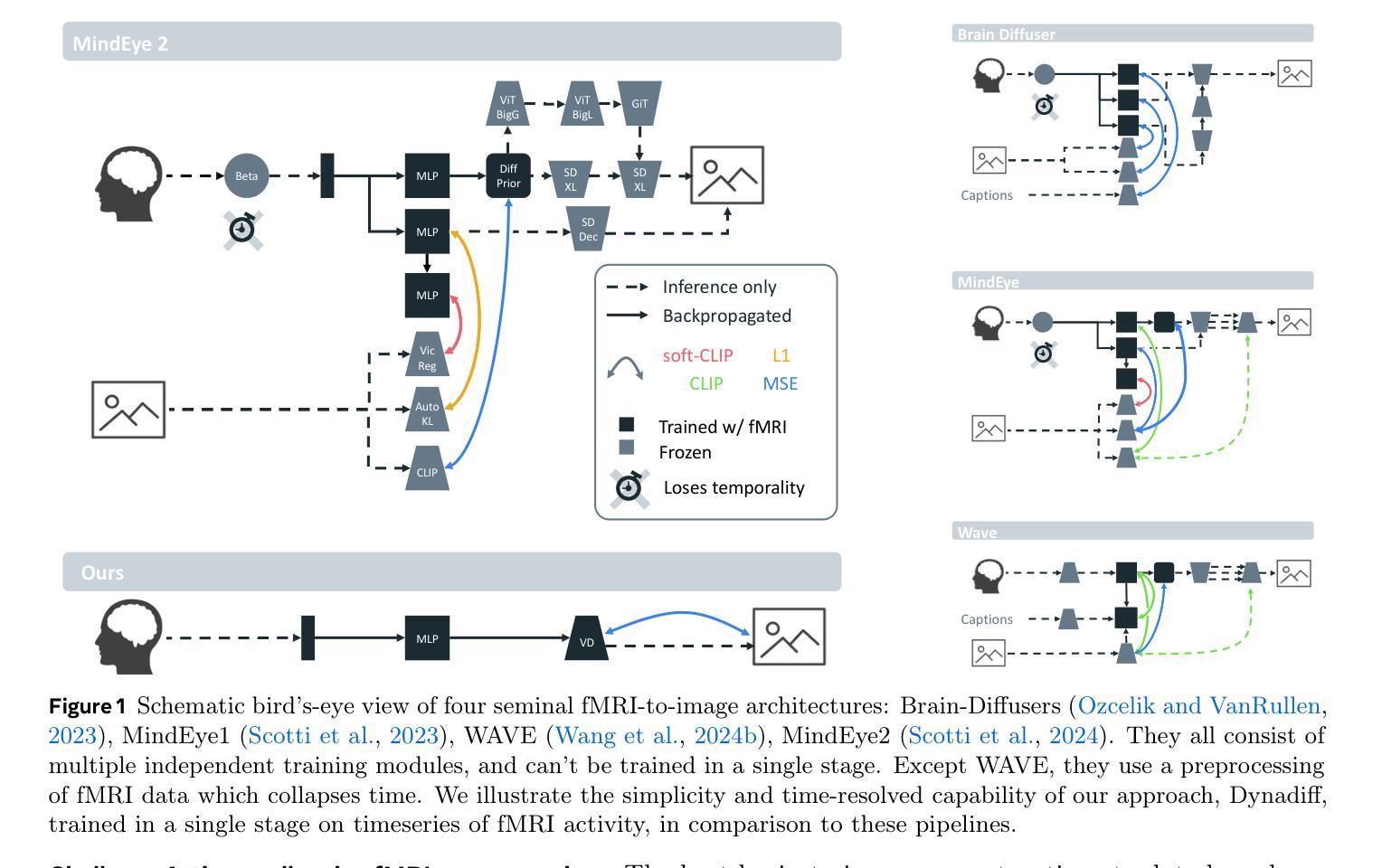
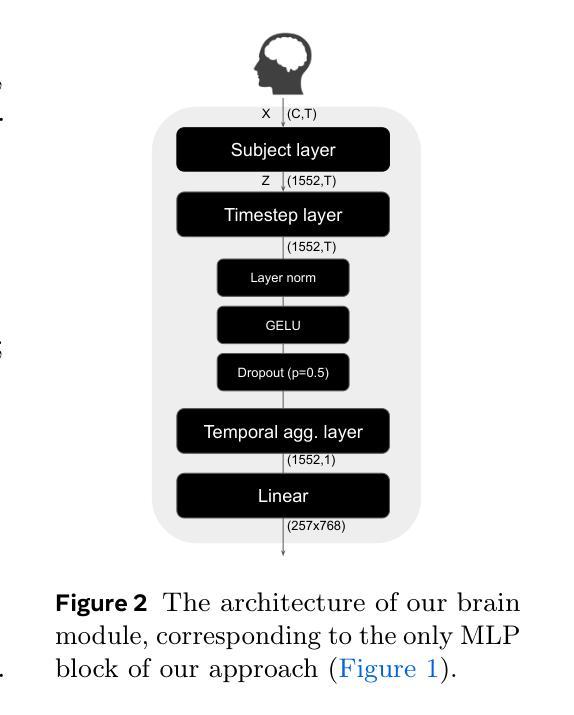
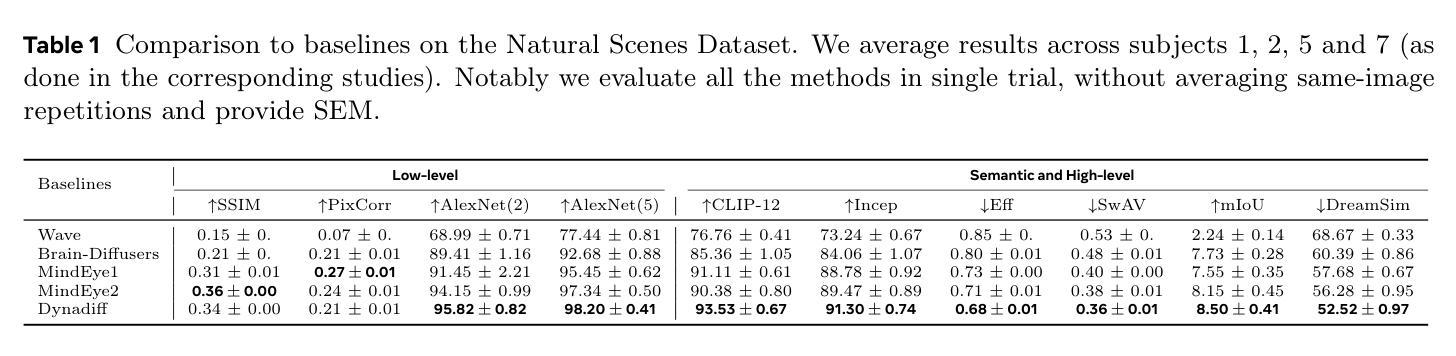
Dynadiff: Single-stage Decoding of Images from Continuously Evolving fMRI
Authors:Marlène Careil, Yohann Benchetrit, Jean-Rémi King
Brain-to-image decoding has been recently propelled by the progress in generative AI models and the availability of large ultra-high field functional Magnetic Resonance Imaging (fMRI). However, current approaches depend on complicated multi-stage pipelines and preprocessing steps that typically collapse the temporal dimension of brain recordings, thereby limiting time-resolved brain decoders. Here, we introduce Dynadiff (Dynamic Neural Activity Diffusion for Image Reconstruction), a new single-stage diffusion model designed for reconstructing images from dynamically evolving fMRI recordings. Our approach offers three main contributions. First, Dynadiff simplifies training as compared to existing approaches. Second, our model outperforms state-of-the-art models on time-resolved fMRI signals, especially on high-level semantic image reconstruction metrics, while remaining competitive on preprocessed fMRI data that collapse time. Third, this approach allows a precise characterization of the evolution of image representations in brain activity. Overall, this work lays the foundation for time-resolved brain-to-image decoding.
脑到图像的解码最近得到了生成式人工智能模型的进步和大型超高场功能磁共振成像(fMRI)的可用性推动。然而,当前的方法依赖于复杂的多阶段管道和预处理步骤,这些步骤通常会压缩脑记录的暂时维度,从而限制了时间解析的脑解码器。在这里,我们引入了Dynadiff(动态神经活动扩散图像重建),这是一种新的单阶段扩散模型,旨在从动态发展的fMRI记录中重建图像。我们的方法提供了三个主要的贡献。首先,与现有方法相比,Dynadiff简化了训练。其次,我们的模型在解析性fMRI信号上优于最新模型,特别是在高级语义图像重建指标上表现突出,同时在压缩时间的预处理fMRI数据上保持竞争力。第三,这种方法可以精确描述图像表示在脑活动中的演变。总体而言,这项工作为时间解析的脑到图像解码奠定了基础。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
大脑图像解码技术因生成式人工智能模型的进步和超高场功能磁共振成像(fMRI)的普及而得到推动。然而,当前方法依赖于复杂的多阶段管道和预处理步骤,通常会忽略脑记录的时间维度,从而限制了时间解析的大脑解码器。本文介绍了Dynadiff(用于图像重建的动态神经活动扩散),这是一种新的单阶段扩散模型,可从动态fMRI记录中重建图像。Dynadiff提供了三个主要贡献:简化训练、在时解析的fMRI信号上表现优于现有技术、准确刻画大脑活动中图像表示的变化。总体而言,这项工作为时间解析的大脑图像解码奠定了基础。
Key Takeaways
- 大脑图像解码技术受益于生成式人工智能模型的进步和超高场功能磁共振成像的普及。
- 当前方法存在复杂的多阶段管道和预处理步骤,导致忽略脑记录的时间维度。
- Dynadiff是一种新的单阶段扩散模型,可从动态fMRI记录中重建图像。
- Dynadiff简化了训练过程。
- Dynadiff在时解析的fMRI信号上的表现优于现有技术,特别是在高级语义图像重建指标上。
- Dynadiff在预处理忽略时间维度的fMRI数据上仍具有竞争力。
点此查看论文截图


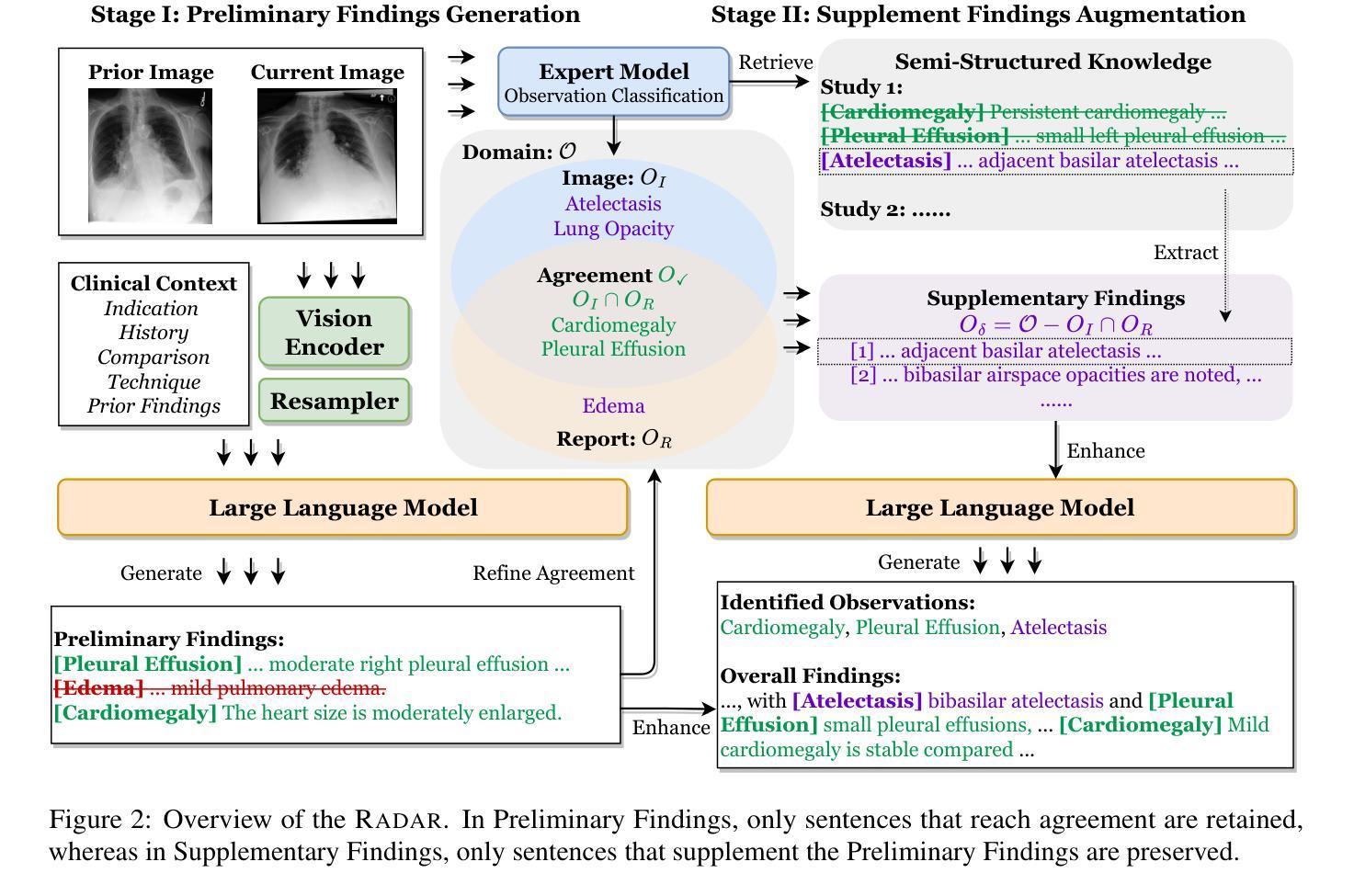
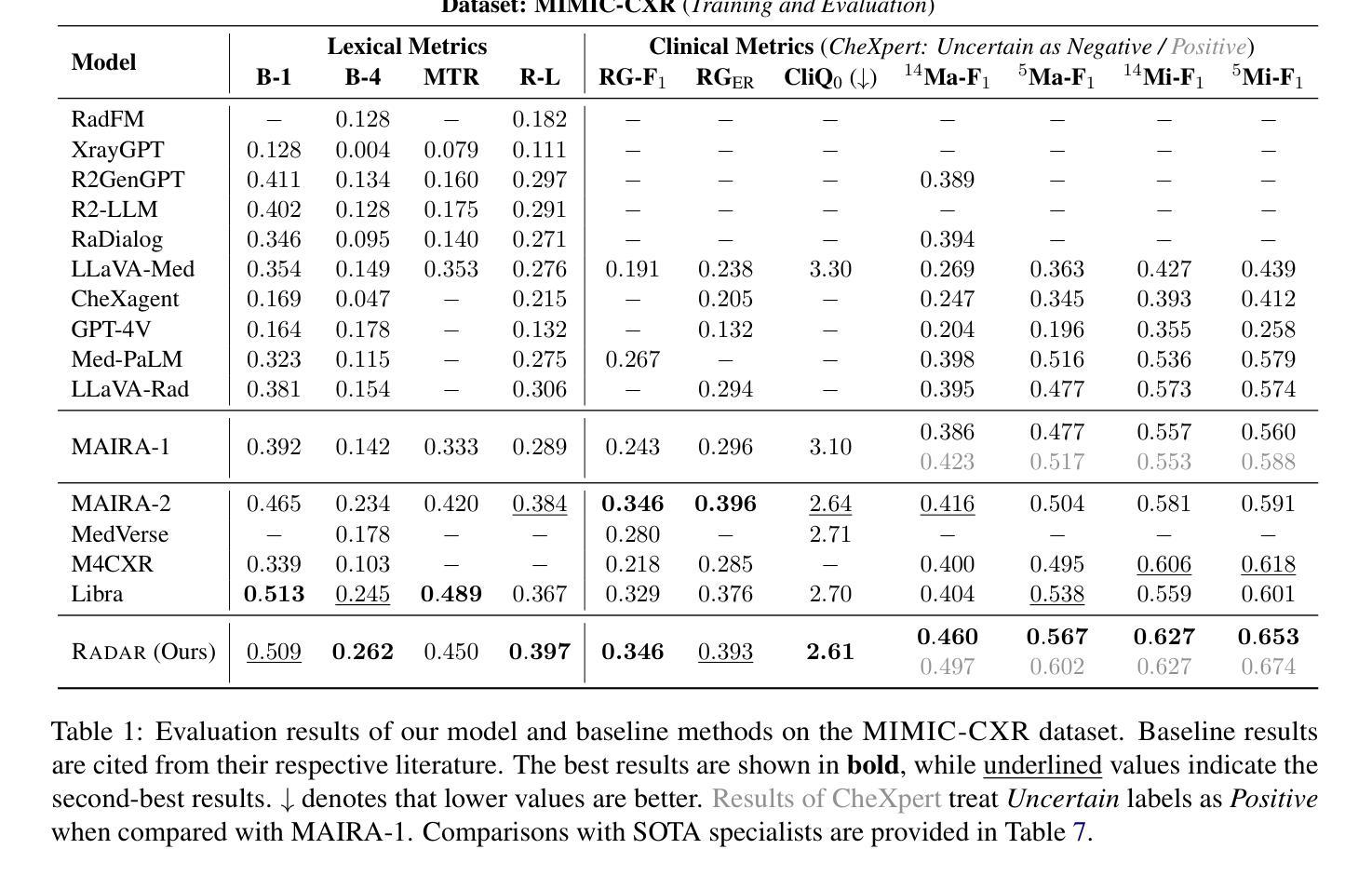
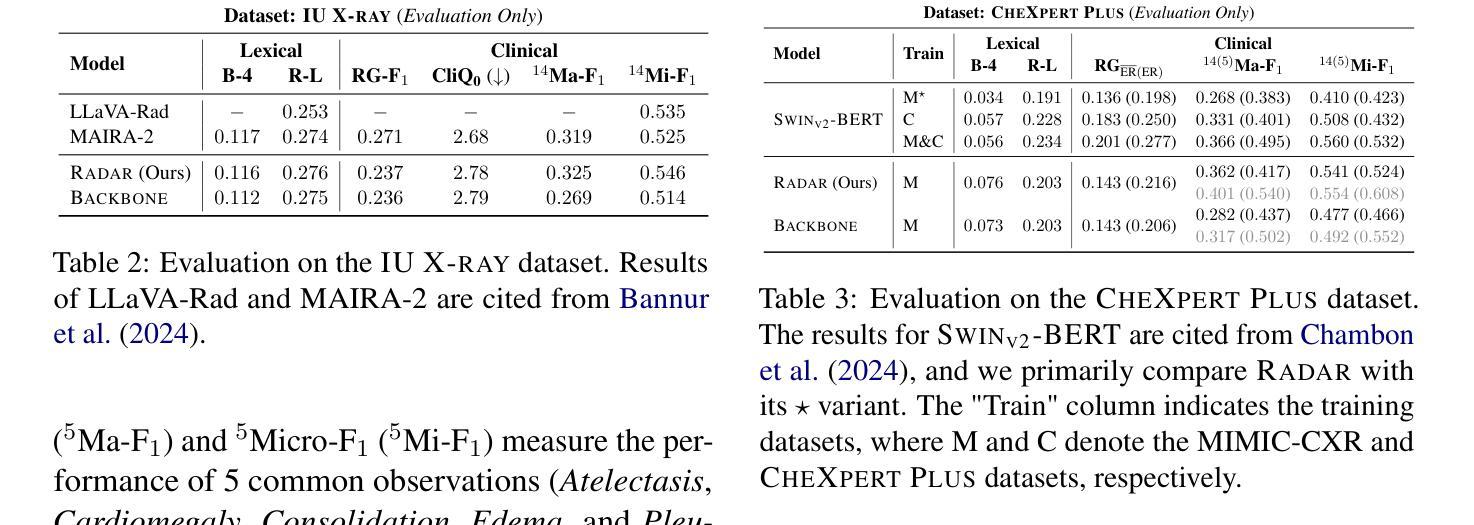
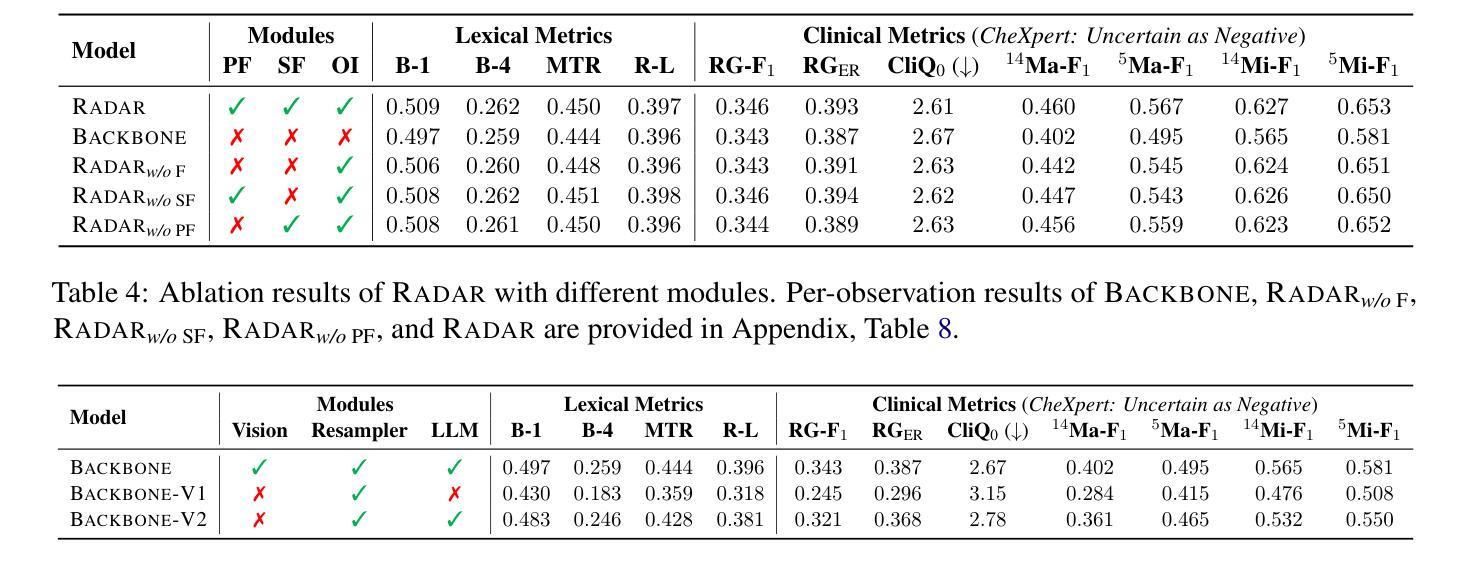
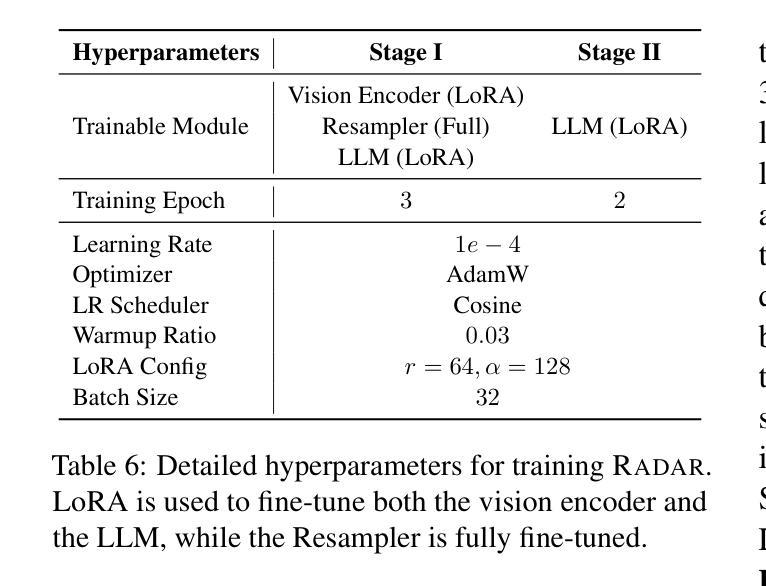
RADAR: Enhancing Radiology Report Generation with Supplementary Knowledge Injection
Authors:Wenjun Hou, Yi Cheng, Kaishuai Xu, Heng Li, Yan Hu, Wenjie Li, Jiang Liu
Large language models (LLMs) have demonstrated remarkable capabilities in various domains, including radiology report generation. Previous approaches have attempted to utilize multimodal LLMs for this task, enhancing their performance through the integration of domain-specific knowledge retrieval. However, these approaches often overlook the knowledge already embedded within the LLMs, leading to redundant information integration and inefficient utilization of learned representations. To address this limitation, we propose RADAR, a framework for enhancing radiology report generation with supplementary knowledge injection. RADAR improves report generation by systematically leveraging both the internal knowledge of an LLM and externally retrieved information. Specifically, it first extracts the model’s acquired knowledge that aligns with expert image-based classification outputs. It then retrieves relevant supplementary knowledge to further enrich this information. Finally, by aggregating both sources, RADAR generates more accurate and informative radiology reports. Extensive experiments on MIMIC-CXR, CheXpert-Plus, and IU X-ray demonstrate that our model outperforms state-of-the-art LLMs in both language quality and clinical accuracy
大型语言模型(LLMs)在多个领域,包括放射学报告生成方面,表现出了显著的能力。以前的方法试图使用多模式LLMs来完成此任务,通过整合特定领域的知识检索来增强它们的性能。然而,这些方法往往忽视了LLMs中已经嵌入的知识,导致冗余的信息集成和所学表示的利用效率低下。为了解决这一局限性,我们提出了RADAR,这是一个通过补充知识注入增强放射学报告生成的框架。RADAR通过系统地利用LLM的内部知识和外部检索信息来改善报告生成。具体来说,它首先提取与专家图像分类输出相符的模型获取的知识。然后,它检索相关的补充知识来进一步丰富这些信息。最后,通过聚合这两个来源,RADAR生成更准确和信息丰富的放射学报告。在MIMIC-CXR、CheXpert-Plus和IU X-ray上的广泛实验表明,我们的模型在语言质量和临床准确性方面都优于最新的LLMs。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
大规模语言模型(LLMs)在包括放射学报告生成在内的各领域展现出卓越的能力。尽管先前的方法尝试使用多模态LLMs并整合领域特定知识检索来提升性能,但它们往往忽视了LLMs内部已嵌入的知识,导致信息整合冗余和表征利用低效。为解决这个问题,我们提出RADAR框架,通过注入补充知识提升放射学报告生成。RADAR通过系统利用LLM的内部知识和外部检索信息来改善报告生成。它首先提取与专家图像分类输出对齐的模型习得知识,然后检索相关补充知识进一步丰富这些信息。最后,通过聚合这两部分知识,RADAR生成更准确和更具信息量的放射学报告。在MIMIC-CXR、CheXpert-Plus和IU X-ray上的广泛实验表明,我们的模型在语言质量和临床准确性方面均优于最新LLMs。
Key Takeaways
- LLMs已在包括放射学报告生成在内的多个领域展现强大能力。
- 现有方法虽尝试整合多模态LLMs和领域特定知识以提升性能,但忽视了LLMs内部知识,导致信息冗余和效率不高。
- RADAR框架旨在通过注入补充知识提升放射学报告生成,系统利用LLM的内部知识和外部检索信息。
- RADAR能提取与专家图像分类输出对齐的模型知识,并检索相关补充知识丰富这些信息。
- 通过结合内外部知识,RADAR能生成更准确和更具信息量的放射学报告。
- 在多个数据集上的实验表明,RADAR在语言和临床准确性方面超越现有LLMs。
- RADAR框架对于提高放射学报告生成任务的性能具有潜力。
点此查看论文截图

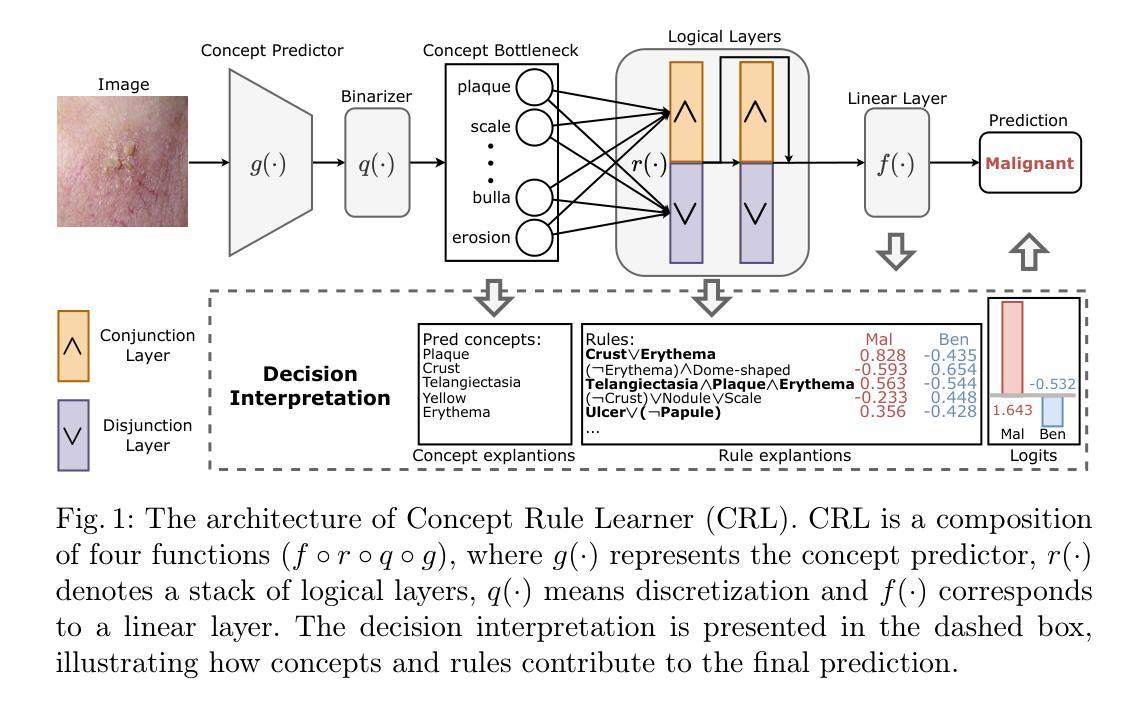
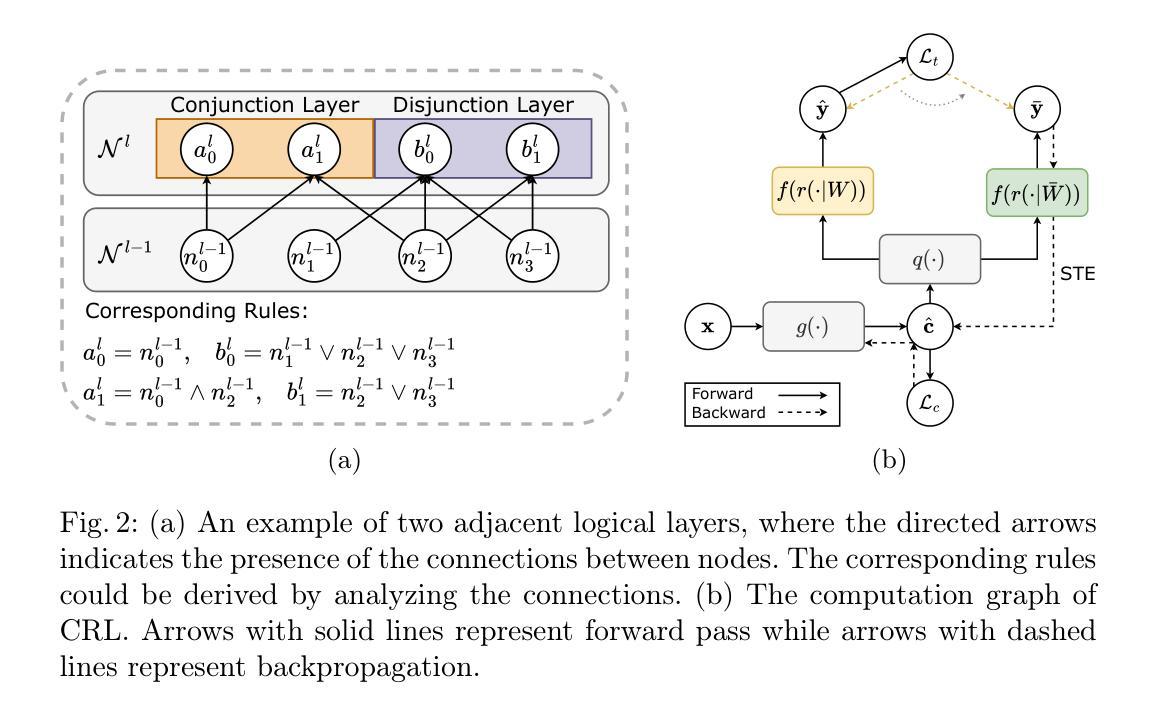
Learning Concept-Driven Logical Rules for Interpretable and Generalizable Medical Image Classification
Authors:Yibo Gao, Hangqi Zhou, Zheyao Gao, Bomin Wang, Shangqi Gao, Sihan Wang, Xiahai Zhuang
The pursuit of decision safety in clinical applications highlights the potential of concept-based methods in medical imaging. While these models offer active interpretability, they often suffer from concept leakages, where unintended information within soft concept representations undermines both interpretability and generalizability. Moreover, most concept-based models focus solely on local explanations (instance-level), neglecting the global decision logic (dataset-level). To address these limitations, we propose Concept Rule Learner (CRL), a novel framework to learn Boolean logical rules from binarized visual concepts. CRL employs logical layers to capture concept correlations and extract clinically meaningful rules, thereby providing both local and global interpretability. Experiments on two medical image classification tasks show that CRL achieves competitive performance with existing methods while significantly improving generalizability to out-of-distribution data. The code of our work is available at https://github.com/obiyoag/crl.
在临床应用中追求决策安全性凸显了基于概念的方法在医学成像中的潜力。虽然这些模型提供了积极的可解释性,但它们常常受到概念泄漏的影响,即软概念表示中的意外信息破坏了可解释性和泛化能力。此外,大多数基于概念模型只关注局部解释(实例级),忽略了全局决策逻辑(数据集级)。为了解决这些局限性,我们提出了概念规则学习者(CRL),这是一种从二元化视觉概念中学习布尔逻辑规则的新框架。CRL通过逻辑层捕捉概念相关性并提取具有临床意义的规则,从而提供局部和全局的可解释性。在两个医学图像分类任务上的实验表明,CRL在现有方法中表现良好,在分布外数据上显著提高泛化能力。我们的工作代码可在https://github.com/obiyoag/crl获取。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF early accepted by MICCAI 2025
Summary
医学成像中决策安全性的追求凸显了概念方法学的潜力。但概念模型存在概念泄露问题,且多关注局部解释(实例级),忽略全局决策逻辑(数据集级)。为此,我们提出Concept Rule Learner(CRL)框架,能从二元化视觉概念中学习布尔逻辑规则。CRL利用逻辑层捕捉概念相关性,提取临床意义规则,实现局部和全局双重解释性。实验表明,CRL在医学图像分类任务中具有竞争力,并能显著提高对分布外数据的泛化能力。
Key Takeaways
- 概念模型在医学成像中具有潜力,但需解决概念泄露问题。
- 大多数概念模型关注局部解释,忽略全局决策逻辑。
- 提出Concept Rule Learner(CRL)框架,能从二元化视觉概念中学习布尔逻辑规则。
- CRL通过逻辑层捕捉概念相关性,提供局部和全局双重解释性。
- CRL在医学图像分类任务中表现竞争力。
- CRL能提高对分布外数据的泛化能力。
点此查看论文截图

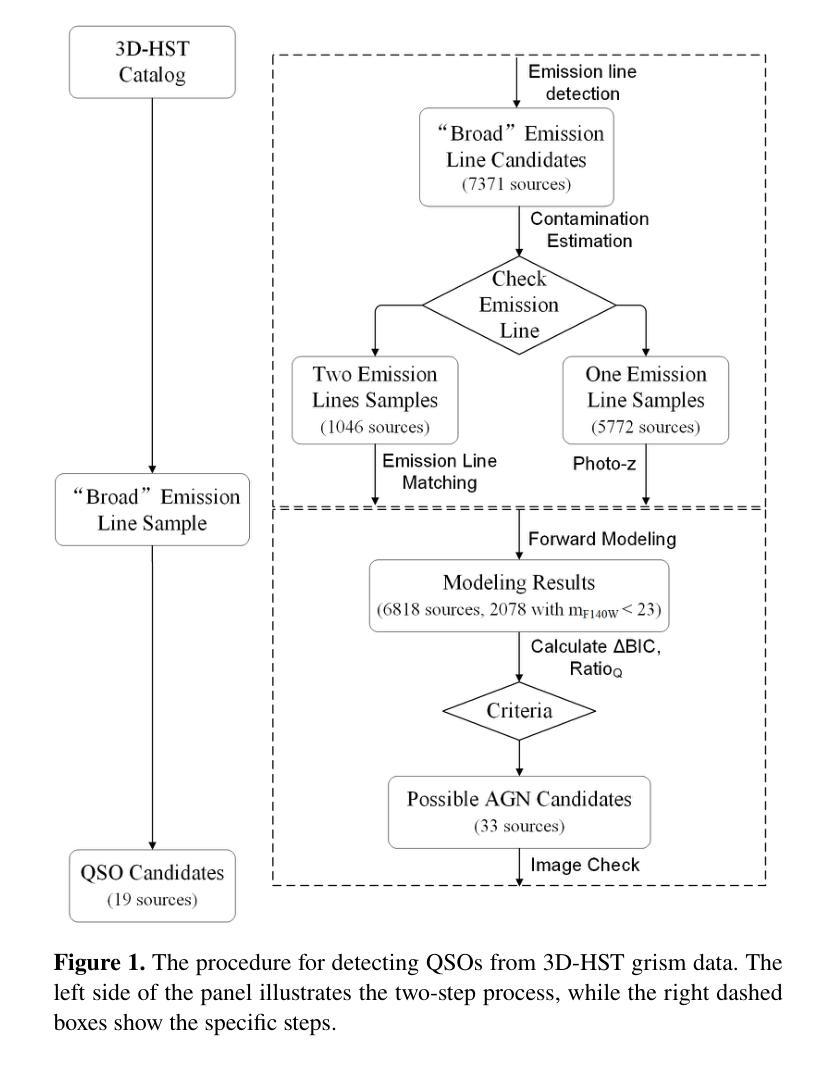
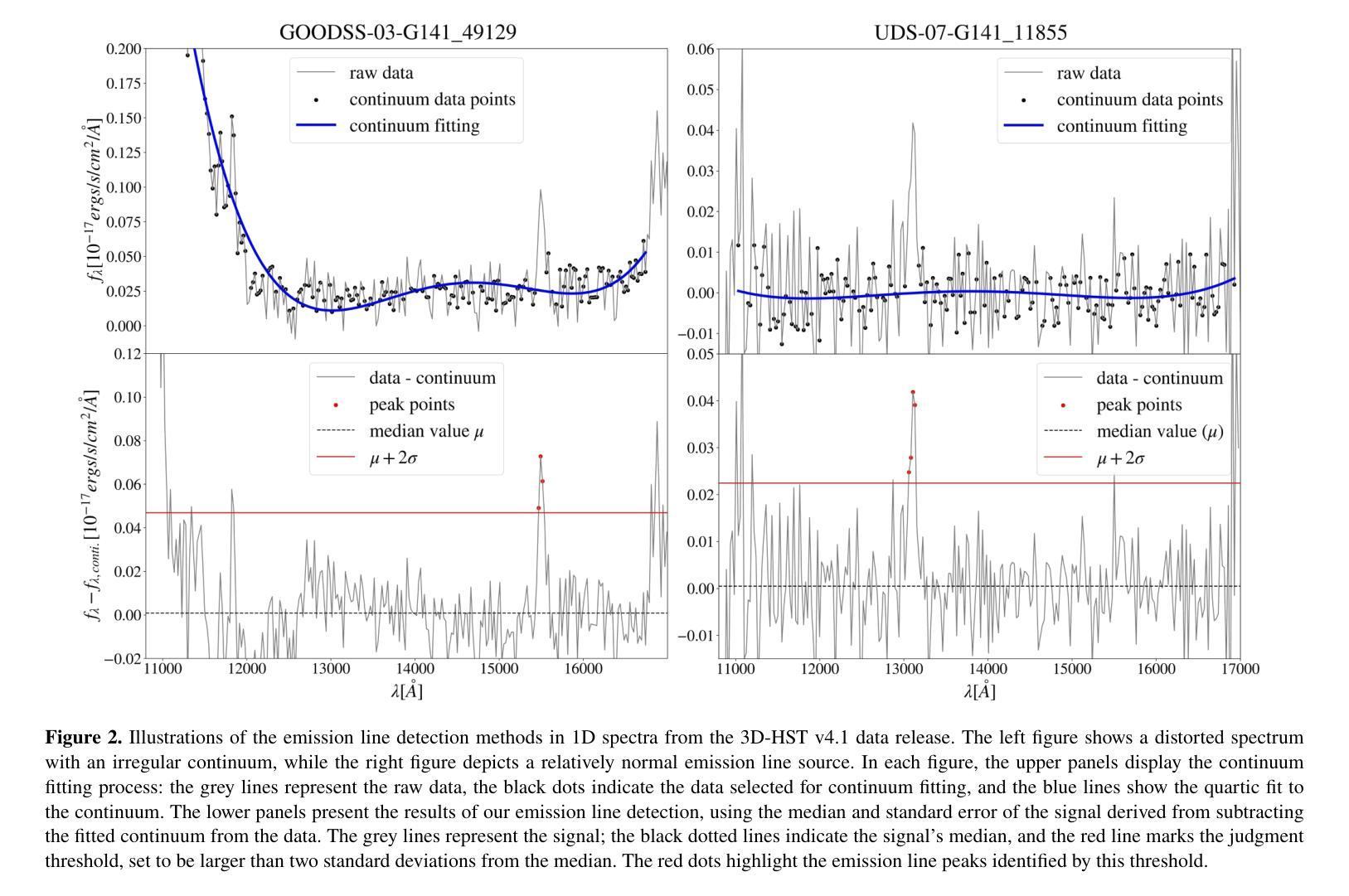
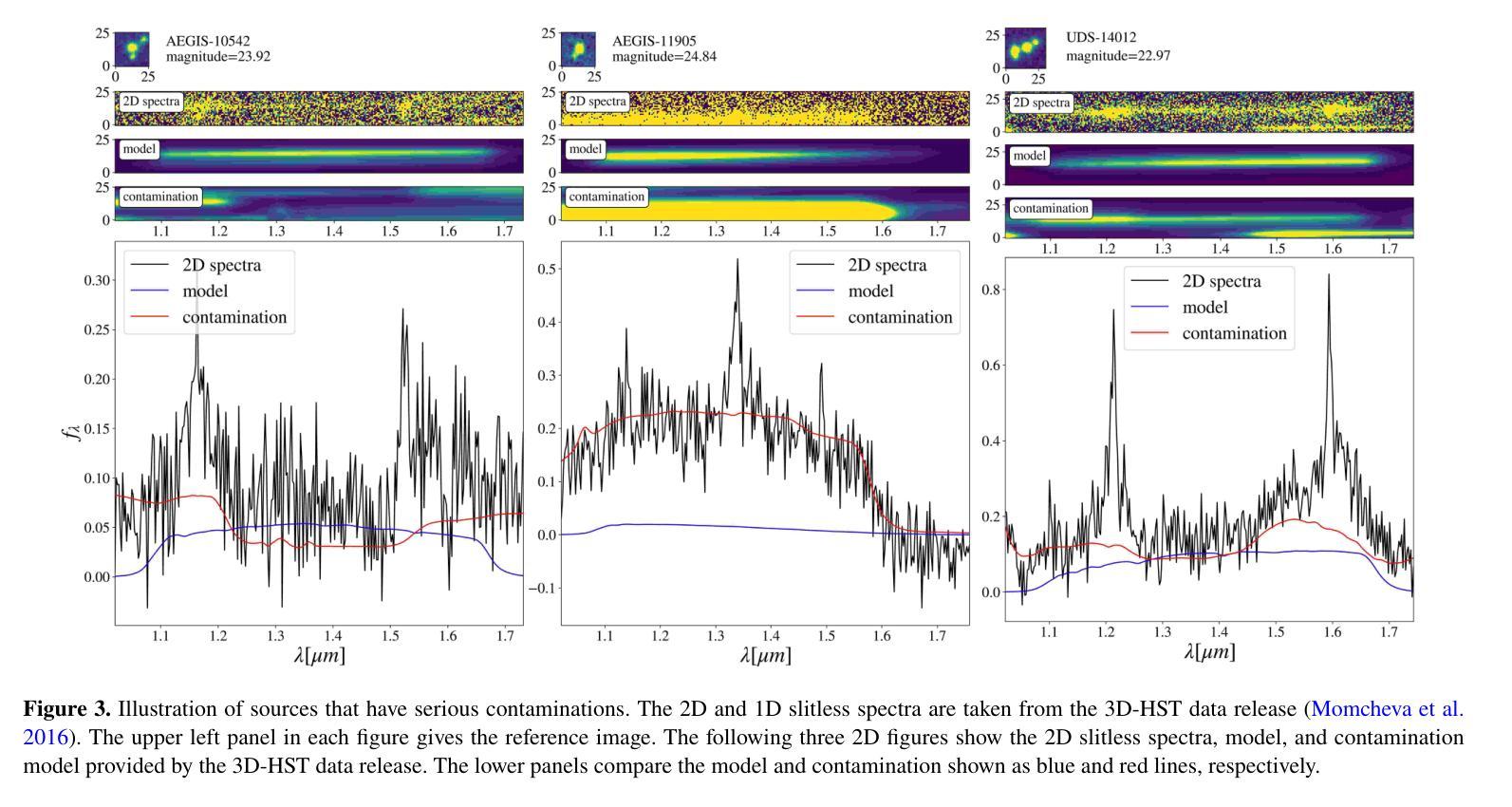
Quasar identifications from the slitless spectra: a test from 3D-HST
Authors:Yuxuan Pang, Xue-Bing Wu, Yuming Fu, Rui Zhu, Tao Ji, Qinchun Ma, Xiaotong Feng
Slitless spectroscopy is a traditional method for selecting quasars. In this paper, we develop a procedure for selecting quasars (QSOs) using the 3D-HST G141 slitless spectra. We initially identify over 6,000 sources with emission lines broader than those typically found in emission line galaxies (ELGs) by analyzing the 1D spectra. These ``broad’’ emission lines may originate from actual QSO broad lines ($\rm FWHM\geq1200~\rm km/s$) or the convolved narrow lines ($\rm FWHM = 200\sim 300\rm km/s$) in ELGs with effective radii $\geq$0.3” (2.5Kpc at z=1). We then propose a criterion based on the reliability of the QSO component in the forward modeling results. Using the known QSOs, ELGs, and simulation spectra, we find that our criterion successfully selects about 90% of known QSOs with H$\alpha$ or H$\beta$ line detection and point-like structures, with an ELG contamination rate of about 5%. We apply this method to emission line sources without significant contamination and select 19 QSO candidates at redshift $z=0.12-1.56$. 12 of these candidates have Chandra X-ray detections. This sample covers a broader range of the rest-frame UV colors and has redder optical slopes compared to the SDSS QSOs, yet it is more likely to be composed of normal QSOs rather than little red dots. Through spectral analysis, the estimated black hole masses of the sample are $10^{6.9}-10^{8.3} M_{\odot}$. Our new candidates improve the completeness of the QSO sample at $z=0.8-1.6$ in the 3D-HST field. The proposed method will also be helpful for QSO selections via slitless spectroscopy in Euclid and the Chinese Space Station Telescope.
无缝隙光谱法是选择类星体的传统方法。本文中,我们开发了一种利用3D-HST G141无缝隙光谱选择类星体(QSO)的程序。我们最初通过分析一维光谱,识别了6000多个光源,这些光源的发射线比通常出现在发射线星系(ELGs)中的发射线更宽。这些“宽”发射线可能来源于实际的QSO宽线(FWHM≥1200km/s)或是通过有效半径≥0.3”(在z=1时为2.5Kpc)的ELGs卷积后的窄线(FWHM=200~300km/s)。然后,我们提出了一个基于正向建模结果中类星体成分可靠性的标准。利用已知的类星体、发射线星系和模拟光谱,我们发现我们的标准成功选择了约90%具有Hα或Hβ线检测点和点状结构的已知类星体,且发射线星系的污染率约为5%。我们将这种方法应用于无明显污染的发射线光源,选择了19个红移范围为z=0.12-1.56的类星体候选者。其中12个候选者被Chandra X射线探测到。这个样本涵盖了更广泛的静止帧紫外线颜色,并且具有比SDSS类星体更红的光学斜率,但它更可能由正常的类星体组成,而不是小红点。通过光谱分析,样本估计的黑洞质量为$10^{6.9}-10^{8.3} M_{\odot}$。我们的新候选者提高了在红移z=0.8-1.6时在3D-HST场的类星体样本的完备性。所提出的方法也将有助于通过Euclid和中国空间站望远镜的无缝隙光谱法选择类星体。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 22 pages, 15 figures, accepted by MNRAS
Summary
利用无缝隙光谱法选择类星体(QSOs)的新方法,基于3D-HST G141无缝隙光谱进行分析。初步筛选出6,000多个源,具有比发射线星系(ELGs)更宽的发射线。提出基于正向建模结果中类星体成分可靠性的标准,成功选出约90%已知类星体,污染率约为5%。应用此方法筛选出19个红移z=0.12-1.56的类星体候选者,其中12个有Chandra X射线检测。此方法提高了在3D-HST字段上z=0.8-1.6的类星体样本的完整性。
Key Takeaways
- 利用3D-HST G141无缝隙光谱进行类星体(QSOs)选择。
- 通过分析1D光谱,初步筛选出具有比发射线星系(ELGs)更宽发射线的“宽”源。
- 提出基于正向建模结果中类星体成分可靠性的筛选标准。
- 成功选出约90%已知类星体,同时保持较低的ELG污染率(约5%)。
- 筛选出19个红移范围在z=0.12-1.56的类星体候选者,其中部分有Chandra X射线检测。
- 此类星体样本具有不同的静止帧UV颜色和光学斜率,但更可能由正常类星体组成。
点此查看论文截图

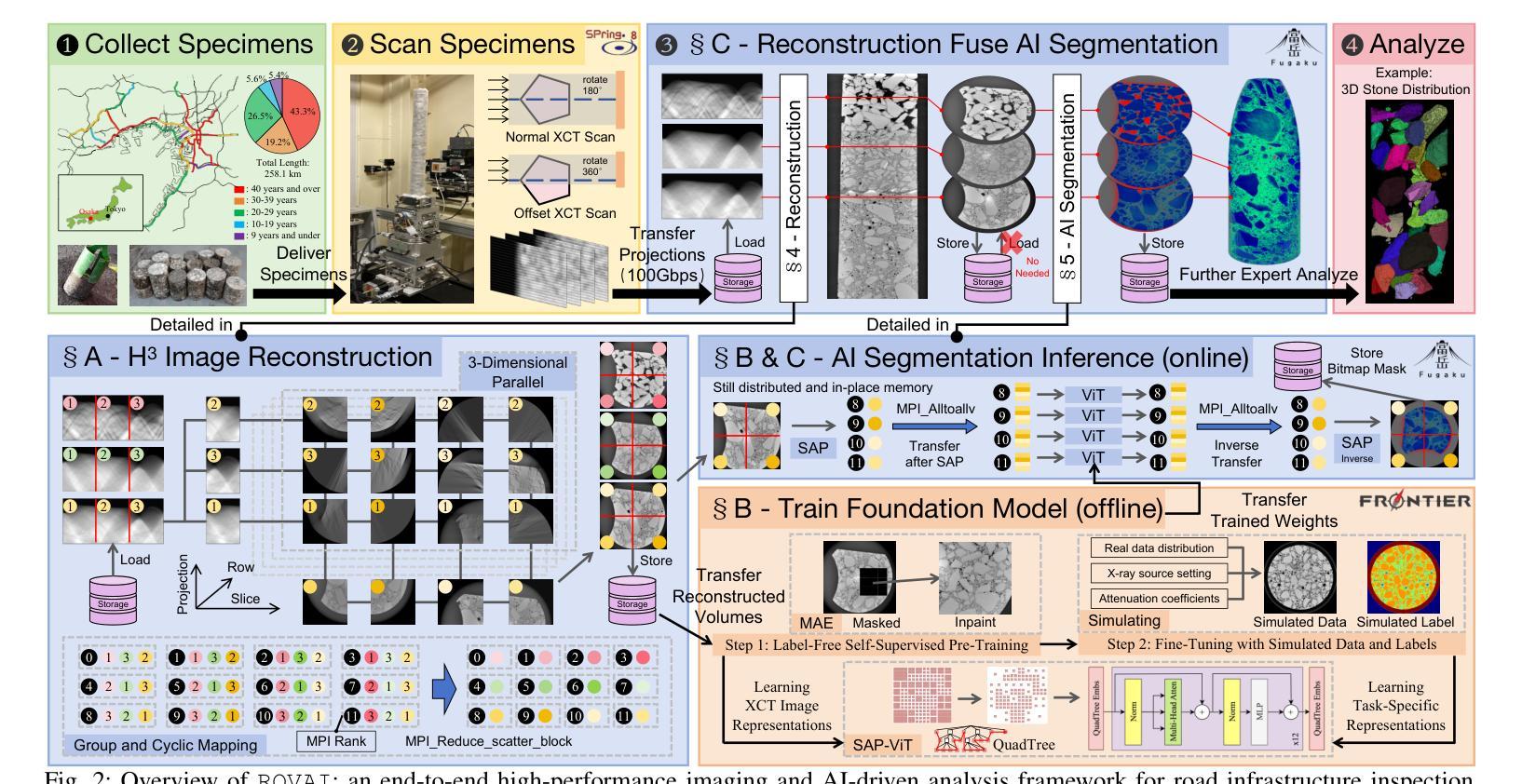
Paradigm Shift in Infrastructure Inspection Technology: Leveraging High-performance Imaging and Advanced AI Analytics to Inspect Road Infrastructure
Authors:Du Wu, Enzhi Zhang, Isaac Lyngaas, Xiao Wang, Amir Ziabari, Tao Luo, Peng Chen, Kento Sato, Fumiyoshi Shoji, Takaki Hatsui, Kentaro Uesugi, Akira Seo, Yasuhito Sakai, Toshio Endo, Tetsuya Ishikawa, Satoshi Matsuoka, Mohamed Wahib
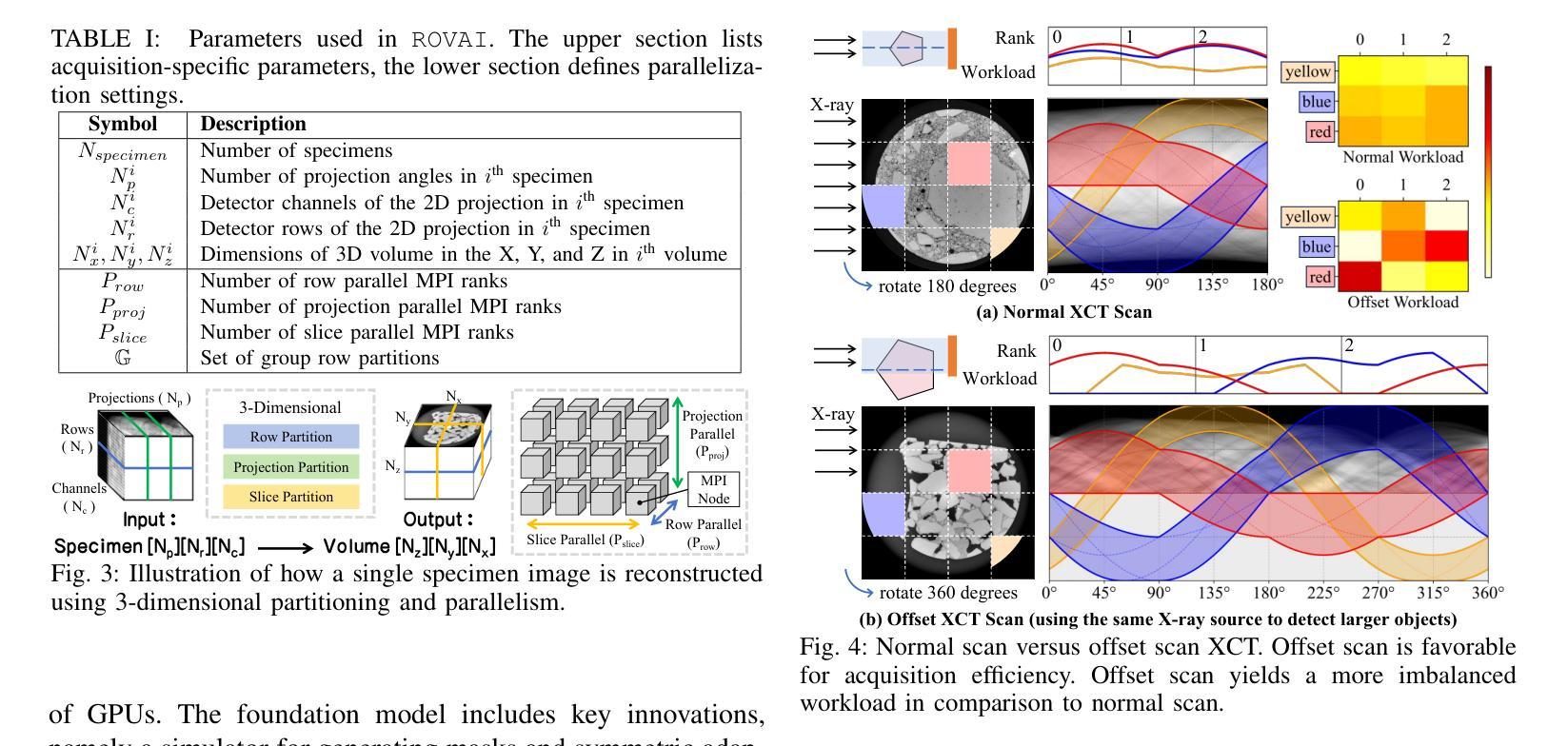
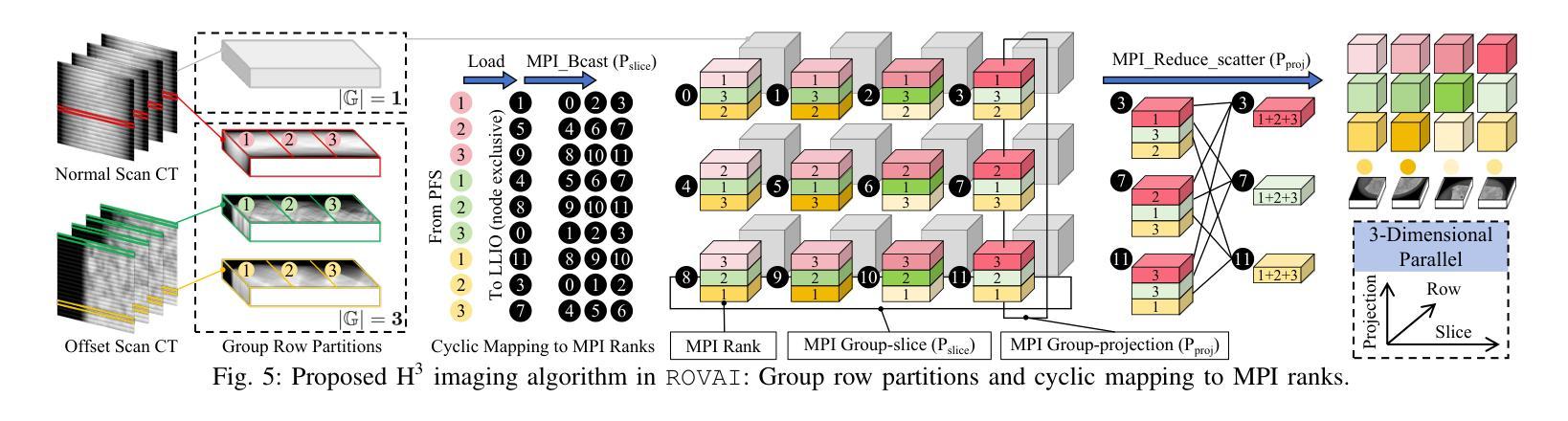
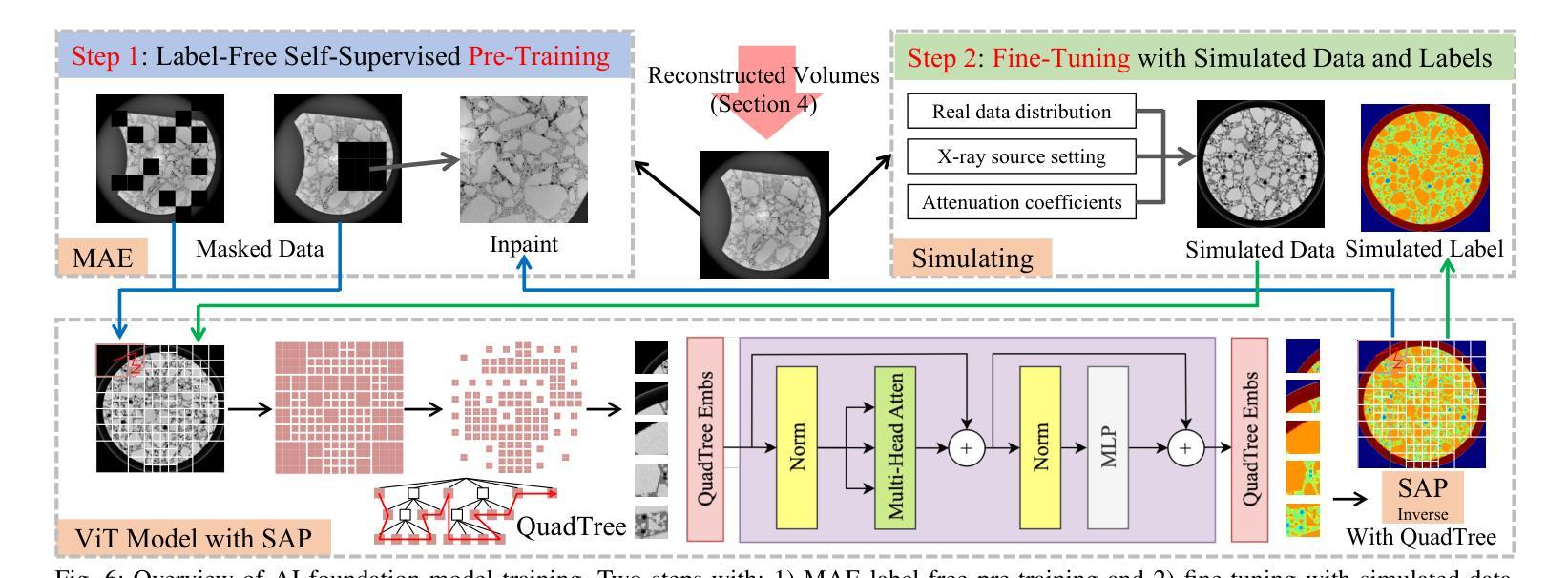
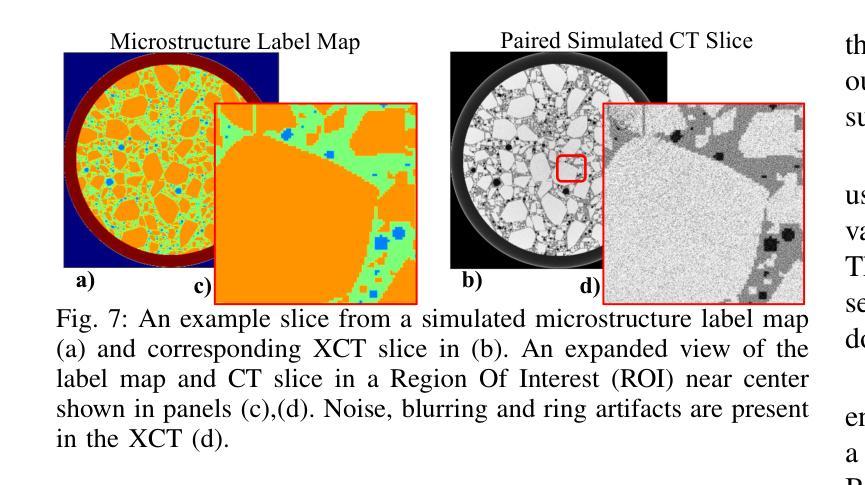
Effective road infrastructure management is crucial for modern society. Traditional manual inspection techniques remain constrained by cost, efficiency, and scalability, while camera and laser imaging methods fail to capture subsurface defects critical for long-term structural integrity. This paper introduces ROVAI, an end-to-end framework that integrates high-resolution X-ray computed tomography imaging and advanced AI-driven analytics, aiming to transform road infrastructure inspection technologies. By leveraging the computational power of world-leading supercomputers, Fugaku and Frontier, and SoTA synchrotron facility (Spring-8), ROVAI enables scalable and high-throughput processing of massive 3D tomographic datasets. Our approach overcomes key challenges, such as the high memory requirements of vision models, the lack of labeled training data, and storage I/O bottlenecks. This seamless integration of imaging and AI analytics facilitates automated defect detection, material composition analysis, and lifespan prediction. Experimental results demonstrate the effectiveness of ROVAI in real-world scenarios, setting a new standard for intelligent, data-driven infrastructure management.
在现代社会,有效的道路基础设施管理至关重要。传统的手动检查技术仍受到成本、效率和可扩展性的限制,而摄像和激光成像方法无法捕捉到对长期结构完整性至关重要的地下缺陷。本文介绍了ROVAI,这是一个端到端的框架,集成了高分辨率X射线计算机断层扫描成像和先进的AI驱动分析,旨在改变道路基础设施检查技术。通过利用世界领先的超级计算机Fugaku和Frontier以及SoTA同步加速器设施(Spring-8)的计算能力,ROVAI能够实现大规模3D断层数据集的可扩展性和高吞吐量处理。我们的方法克服了关键挑战,如视觉模型的高内存要求、缺乏标记的训练数据和存储I/O瓶颈。成像和AI分析的无缝集成促进了自动化缺陷检测、材料组成分析和寿命预测。实验结果表明,ROVAI在真实场景中的有效性,为智能、数据驱动的设施管理树立了新标准。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Submitting this work to be considered for the Gordon Bell Award in SC25
Summary
本论文提出了ROVAI这一端到端的框架,集成了高分辨率的X射线计算机断层扫描成像和先进的AI驱动分析技术,旨在改变传统的道路基础设施检测方式。利用超级计算机Fugaku和Frontier的计算能力,以及SoTA同步加速器设施(Spring-8),实现了大规模的三维断层数据集的高通量处理。此外,还克服了模型高内存要求等难题。整合成像与人工智能分析能够自动化进行缺陷检测、材料成分分析和寿命预测等。实验结果证明,ROVAI在实际场景中的应用效果卓越,为智能化数据驱动的基础设施管理设立了新标准。
Key Takeaways
- ROVAI框架结合了高分辨率X射线计算机断层扫描成像和AI驱动分析技术,用于道路基础设施检测。
- 利用超级计算机Fugaku和Frontier的高性能计算能力处理大规模三维断层数据集。
- ROVAI克服了模型高内存要求等难题。
- 通过整合成像与人工智能分析,实现自动化缺陷检测、材料成分分析和寿命预测等功能。
- ROVAI框架在真实场景中的实验效果显著,准确度高。
- ROVAI框架的应用有助于提升道路基础设施管理的智能化水平。
点此查看论文截图

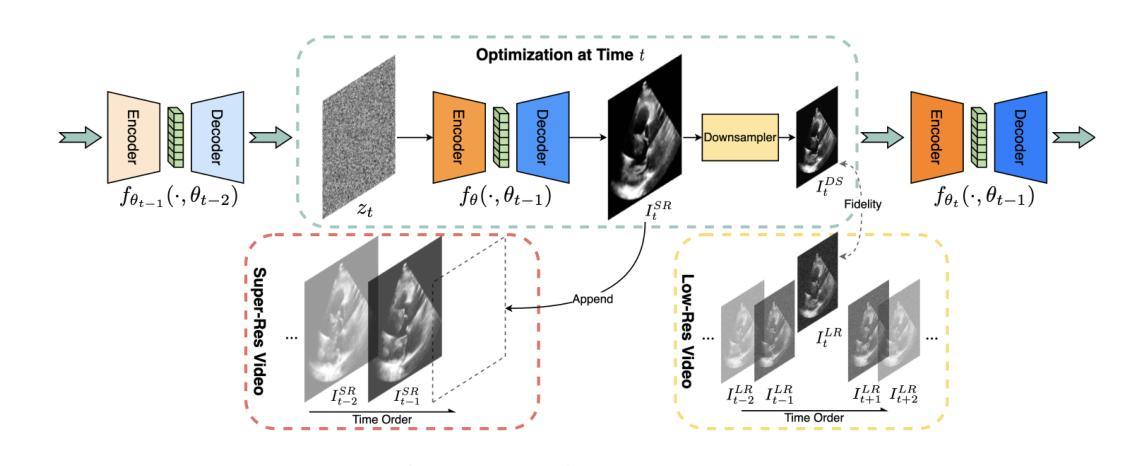
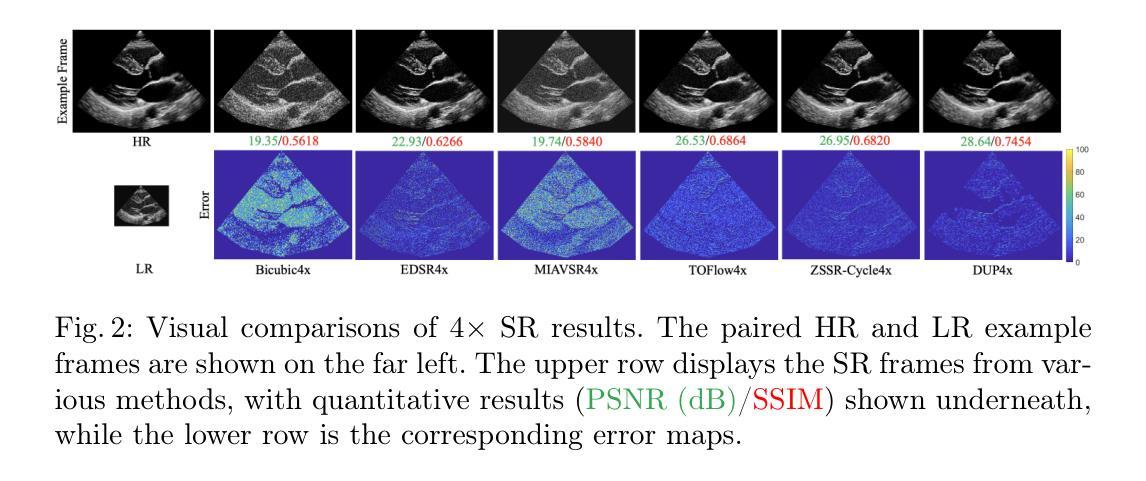
Blind Restoration of High-Resolution Ultrasound Video
Authors:Chu Chen, Kangning Cui, Pasquale Cascarano, Wei Tang, Elena Loli Piccolomini, Raymond H. Chan
Ultrasound imaging is widely applied in clinical practice, yet ultrasound videos often suffer from low signal-to-noise ratios (SNR) and limited resolutions, posing challenges for diagnosis and analysis. Variations in equipment and acquisition settings can further exacerbate differences in data distribution and noise levels, reducing the generalizability of pre-trained models. This work presents a self-supervised ultrasound video super-resolution algorithm called Deep Ultrasound Prior (DUP). DUP employs a video-adaptive optimization process of a neural network that enhances the resolution of given ultrasound videos without requiring paired training data while simultaneously removing noise. Quantitative and visual evaluations demonstrate that DUP outperforms existing super-resolution algorithms, leading to substantial improvements for downstream applications.
超声成像在临床实践中得到广泛应用,但超声视频常常存在信号噪声比(SNR)低和分辨率有限的问题,给诊断和治疗带来挑战。设备和采集设置的差异可能会进一步加剧数据分布和噪声水平的差异,降低预训练模型的通用性。这项工作提出了一种名为Deep Ultrasound Prior(DUP)的自监督超声视频超分辨率算法。DUP采用神经网络的视频自适应优化过程,可以在不需要配对训练数据的同时,提高给定超声视频的分辨率并去除噪声。定量和视觉评估表明,DUP优于现有的超分辨率算法,为下游应用带来了实质性的改进。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
该研究提出了一种名为Deep Ultrasound Prior(DUP)的自监督超声视频超分辨率算法。该算法采用神经网络视频自适应优化过程,能够在无需配对训练数据的情况下提高超声视频的分辨率并去除噪声。定量和视觉评估表明,DUP在超分辨率算法方面表现优异,为下游应用带来了实质性的改进。
Key Takeaways
- 超声成像在临床实践中应用广泛,但存在信号噪声比(SNR)低和分辨率有限的问题,对诊断和治疗带来挑战。
- 设备及采集设置的差异会进一步加剧数据分布和噪声水平的不同,降低预训练模型的通用性。
- Deep Ultrasound Prior(DUP)是一种自监督超声视频超分辨率算法,可提高超声视频的分辨率并消除噪声。
- DUP采用视频自适应优化过程的神经网络,无需配对训练数据。
- 与现有超分辨率算法相比,DUP表现出优越性。
- DUP能显著改善超声视频的分辨率和噪声水平,有助于提高诊断的准确性和分析的可靠性。
点此查看论文截图

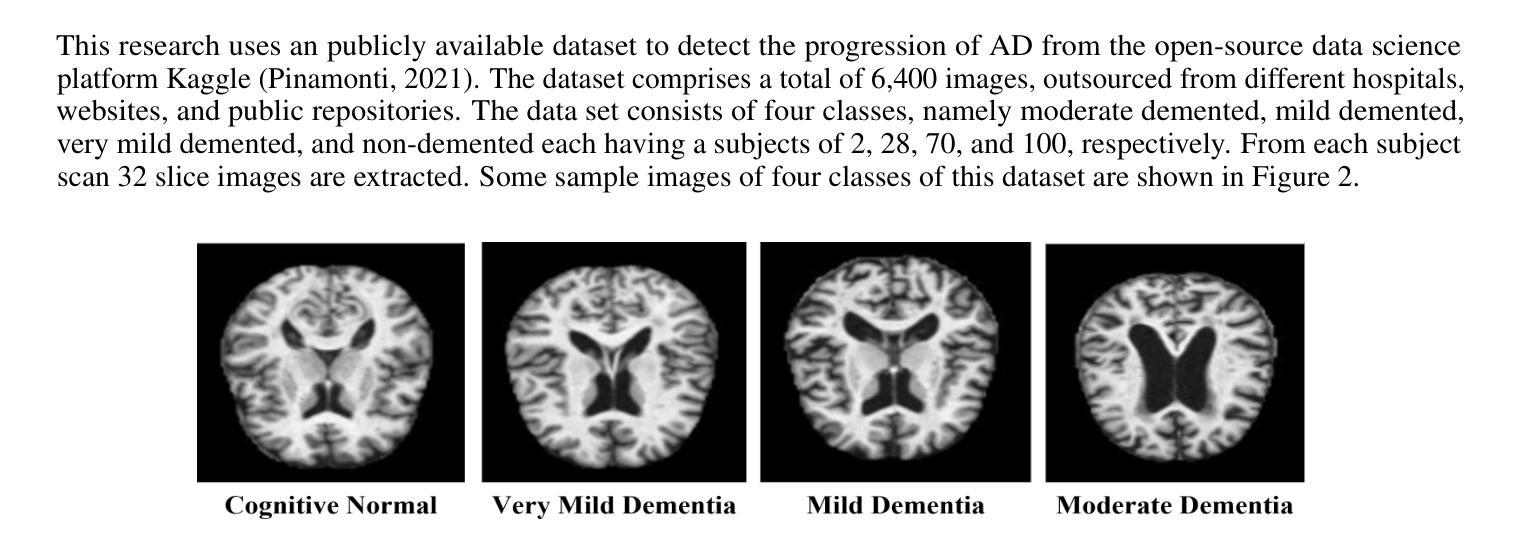
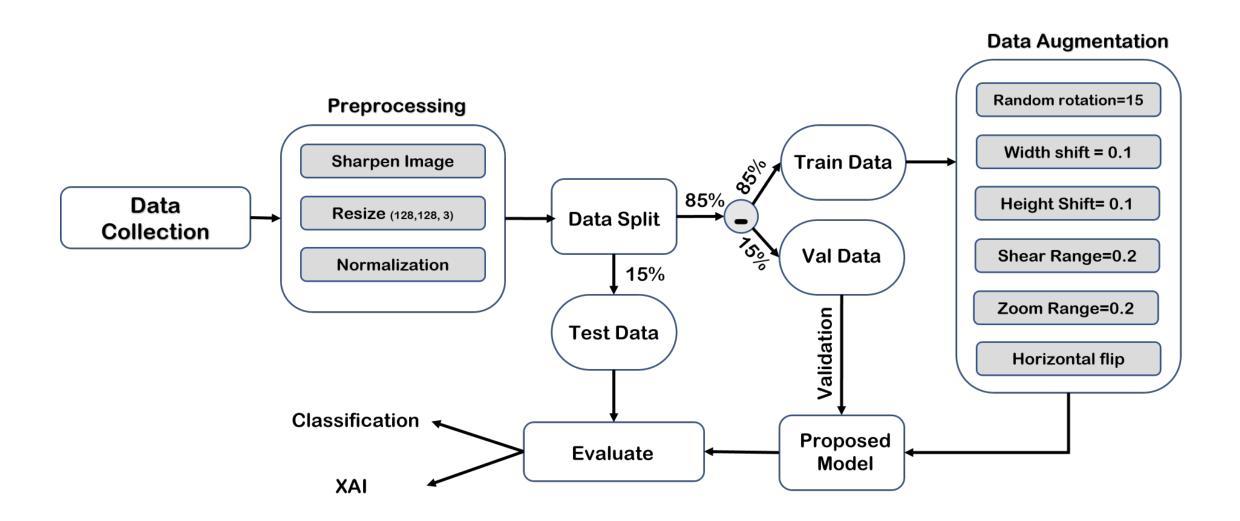
XDementNET: An Explainable Attention Based Deep Convolutional Network to Detect Alzheimer Progression from MRI data
Authors:Soyabul Islam Lincoln, Mirza Mohd Shahriar Maswood
A common neurodegenerative disease, Alzheimer’s disease requires a precise diagnosis and efficient treatment, particularly in light of escalating healthcare expenses and the expanding use of artificial intelligence in medical diagnostics. Many recent studies shows that the combination of brain Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) and deep neural networks have achieved promising results for diagnosing AD. Using deep convolutional neural networks, this paper introduces a novel deep learning architecture that incorporates multiresidual blocks, specialized spatial attention blocks, grouped query attention, and multi-head attention. The study assessed the model’s performance on four publicly accessible datasets and concentrated on identifying binary and multiclass issues across various categories. This paper also takes into account of the explainability of AD’s progression and compared with state-of-the-art methods namely Gradient Class Activation Mapping (GradCAM), Score-CAM, Faster Score-CAM, and XGRADCAM. Our methodology consistently outperforms current approaches, achieving 99.66% accuracy in 4-class classification, 99.63% in 3-class classification, and 100% in binary classification using Kaggle datasets. For Open Access Series of Imaging Studies (OASIS) datasets the accuracies are 99.92%, 99.90%, and 99.95% respectively. The Alzheimer’s Disease Neuroimaging Initiative-1 (ADNI-1) dataset was used for experiments in three planes (axial, sagittal, and coronal) and a combination of all planes. The study achieved accuracies of 99.08% for axis, 99.85% for sagittal, 99.5% for coronal, and 99.17% for all axis, and 97.79% and 8.60% respectively for ADNI-2. The network’s ability to retrieve important information from MRI images is demonstrated by its excellent accuracy in categorizing AD stages.
阿尔茨海默病是一种常见的神经退行性疾病,需要精确诊断和治疗,特别是在医疗保健费用不断增加和人工智能在医学诊断中广泛应用的情况下。最近的研究表明,结合脑部磁共振成像(MRI)和深度神经网络对AD的诊断取得了有希望的结果。本文介绍了一种新型深度学习架构,采用多残差块、专用空间注意力块、分组查询注意力和多头注意力。该研究在四个公开数据集上评估了模型性能,并专注于识别不同类别的二进制和多类别问题。本文还考虑了AD进展的解释性,并与最先进的方法进行了比较,即梯度类激活映射(GradCAM)、分数-CAM、更快的分数-CAM和XGRADCAM。我们的方法在Kaggle数据集上实现了四分类99.66%、三分类99.63%、二分类100%的准确率。对于开放访问成像研究系列(OASIS)数据集,准确率分别为99.92%、99.90%、和99.95%。在阿尔茨海默病神经影像学倡议-1(ADNI-1)数据集上进行的三个平面(轴向、矢状和冠状)以及所有平面的组合实验表明,准确率为轴向99.08%、矢状面99.85%、冠状面99.5%、所有轴平面组合为综合的准确率99.17%,对ADNI-2准确率分别实现了到达87%,证明了网络从MRI图像中提取重要信息的能力及其在分类AD阶段方面的出色准确性。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 20 pages, 12 figures,
Summary
本研究结合脑磁共振成像(MRI)和深度神经网络,提出一种新型深度学习架构,用于诊断阿尔茨海默病(AD)。该架构采用多残差块、专业空间注意力块、分组查询注意力和多头注意力等技术,在四个公开数据集上评估模型性能,并关注不同类别的二元和多类问题。此外,本研究还考虑了AD进展的解释性,并与Gradient Class Activation Mapping (GradCAM)、Score-CAM、Faster Score-CAM和XGRADCAM等最新方法进行比较。新型架构在分类AD阶段时表现出卓越准确性。
Key Takeaways
- 本研究结合脑MRI和深度神经网络诊断AD,提出新型深度学习架构。
- 新型架构采用多残差块、专业空间注意力块等技术,提高模型性能。
- 模型在四个公开数据集上表现优秀,包括二元和多类分类问题。
- 研究考虑了AD进展的解释性,并与多种最新方法进行比较。
- 新型架构在分类AD阶段时表现出卓越准确性,达到高准确率。
- 使用Kaggle数据集,4类分类准确率为99.66%,3类分类准确率为99.63%,二元分类准确率为100%。
点此查看论文截图

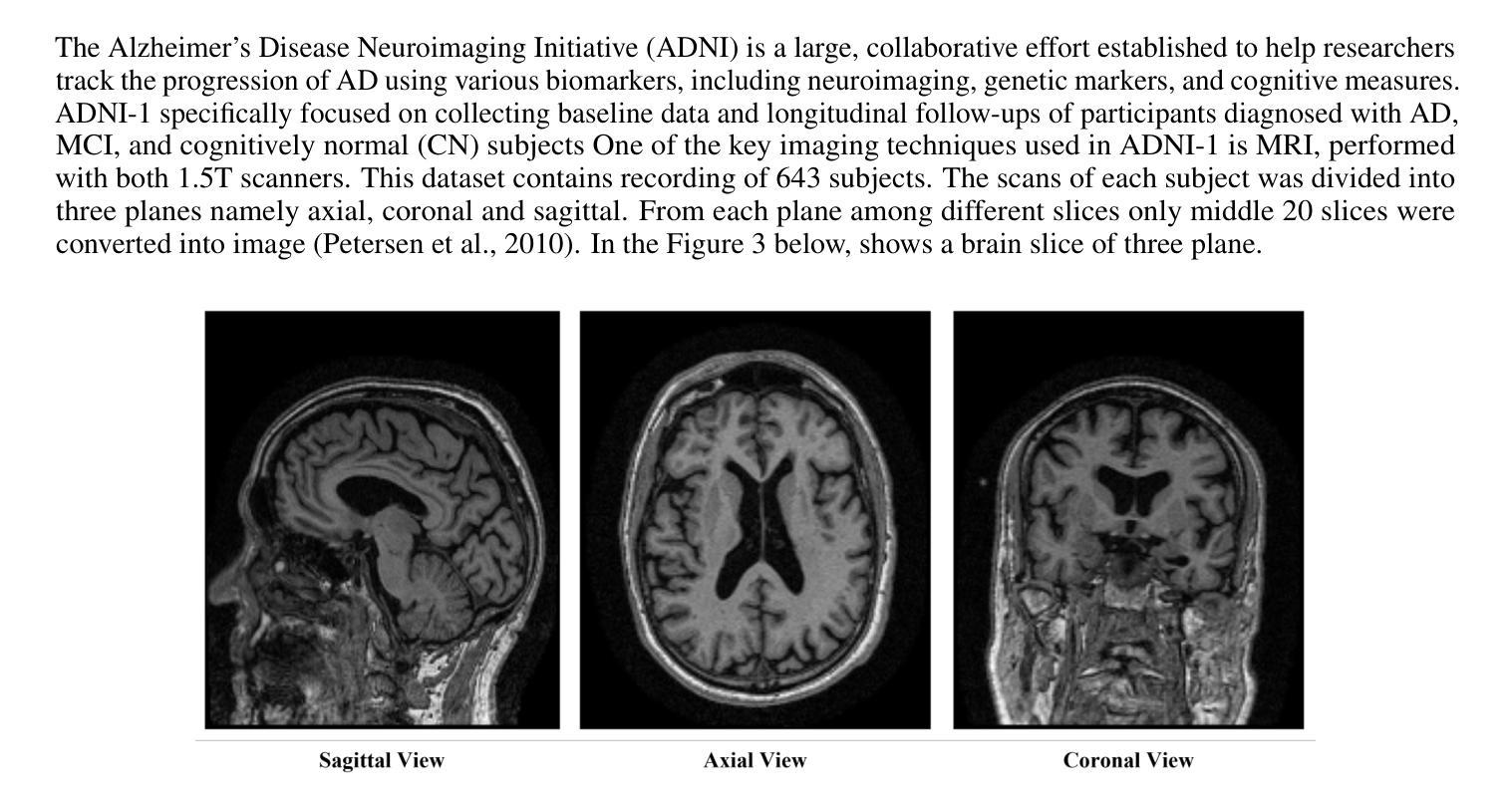
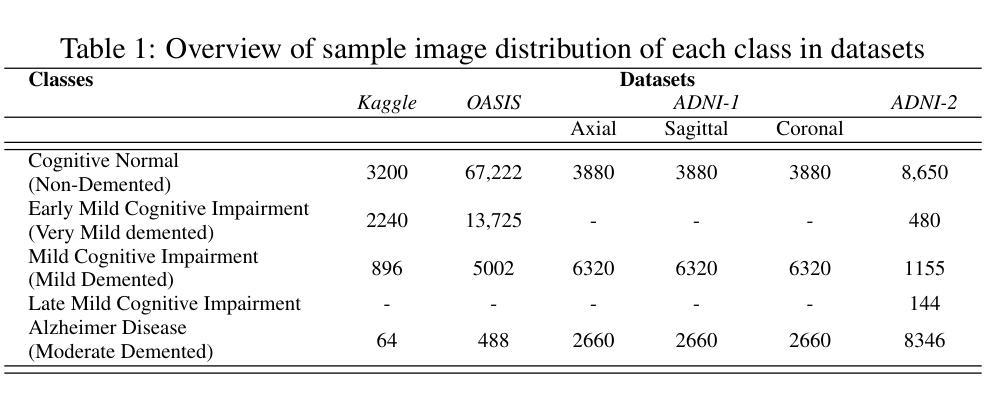
Orbital Phase-resolved Analysis of X-ray and Gamma-ray Observations of the High-Mass Gamma-ray Binary 4FGL J1405.1-6119
Authors:Alexander Lange, Robin H. D. Corbet, Joel B. Coley, Guillaume Dubus, Jeremy Hare, Nazma Islam, Jonathan Barnes
We present the results of multi-wavelength observations of the High-Mass Gamma-Ray Binary 4FGL J1405.1-6119. A pair of joint XMM-Newton and NuSTAR observations taken in 2019 (sampling the gamma-ray maximum and X-ray maximum) characterize the emission of soft and hard X-rays. We find variability of the hydrogen column density along our line of sight, $N_{\rm H}$, and photon index, $\Gamma$, and find no evidence of pulsations in X-rays. We also refine a new best-fit orbital period to $P=13.7157\pm0.0014$ days, the first orbital phase-resolved analysis based on nearly 16 years of Fermi–LAT observations of 4FGL J1405.1-6119 and the evolution of the spectral shape as a function of orbital phase. Finally, the X-ray and $\gamma$-ray spectra for the phases sampled in the new X-ray observations can be interpreted in the framework of the intrabinary shock model, previously applied to High-Mass Gamma-Ray binaries such as LS 5039.
我们对高质量伽马射线双星4FGL J1405.1-6119进行了多波长观测的结果展示。通过2019年联合XMM-牛顿和NuSTAR的观测(采样伽马射线最大值和X射线最大值),我们描述了软X射线和硬X射线的发射特征。我们发现视线方向的氢柱密度$N_{\rm H}$和光子指数$\Gamma$存在变化,且在X射线上未发现脉动证据。我们还对最佳拟合轨道周期进行了更新,为$P=13.7157\pm0.0014$天,这是基于近16年对4FGL J1405.1-6119的费米-LAT观测数据进行的首次轨道相位解析分析,以及谱形随轨道相位的演化。最后,新X射线观测中采样阶段的X射线和伽马射线光谱可以在双星内冲击模型的框架内进行解释,该模型之前已应用于高质量伽马射线双星,如LS 5039。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted for publication in the Astrophysical Journal
Summary
本文报告了高质能γ射线双星4FGL J1405.1-6119的多波长观测结果。通过联合XMM-Newton和NuSTAR在2019年的观测,发现其软、硬X射线的发射特征,并观察到视线上氢柱密度($N_{\rm H}$)和光子指数($\Gamma$)的变化。没有发现X射线脉冲,并精细测量了最佳拟合轨道周期为13.7157±0.0014天。此外,基于近16年的Fermi-LAT观测数据,首次进行了轨道相位解析分析,并研究了光谱形状随轨道相位的变化。最后,新观测阶段的X射线和γ射线光谱可在二体冲击模型的框架内进行解释,该模型已应用于其他高质能γ射线双星如LS 5039。
Key Takeaways
- 报告了高质能γ射线双星4FGL J1405.1-6119的XMM-Newton和NuSTAR联合观测结果。
- 观察到软、硬X射线的发射特征。
- 视线上氢柱密度($N_{\rm H}$)和光子指数($\Gamma$)存在变化。
- 没有发现X射线脉冲。
- 轨道周期被精细测量为13.7157±0.0014天。
- 基于近16年的Fermi-LAT观测数据进行了轨道相位解析分析。
点此查看论文截图

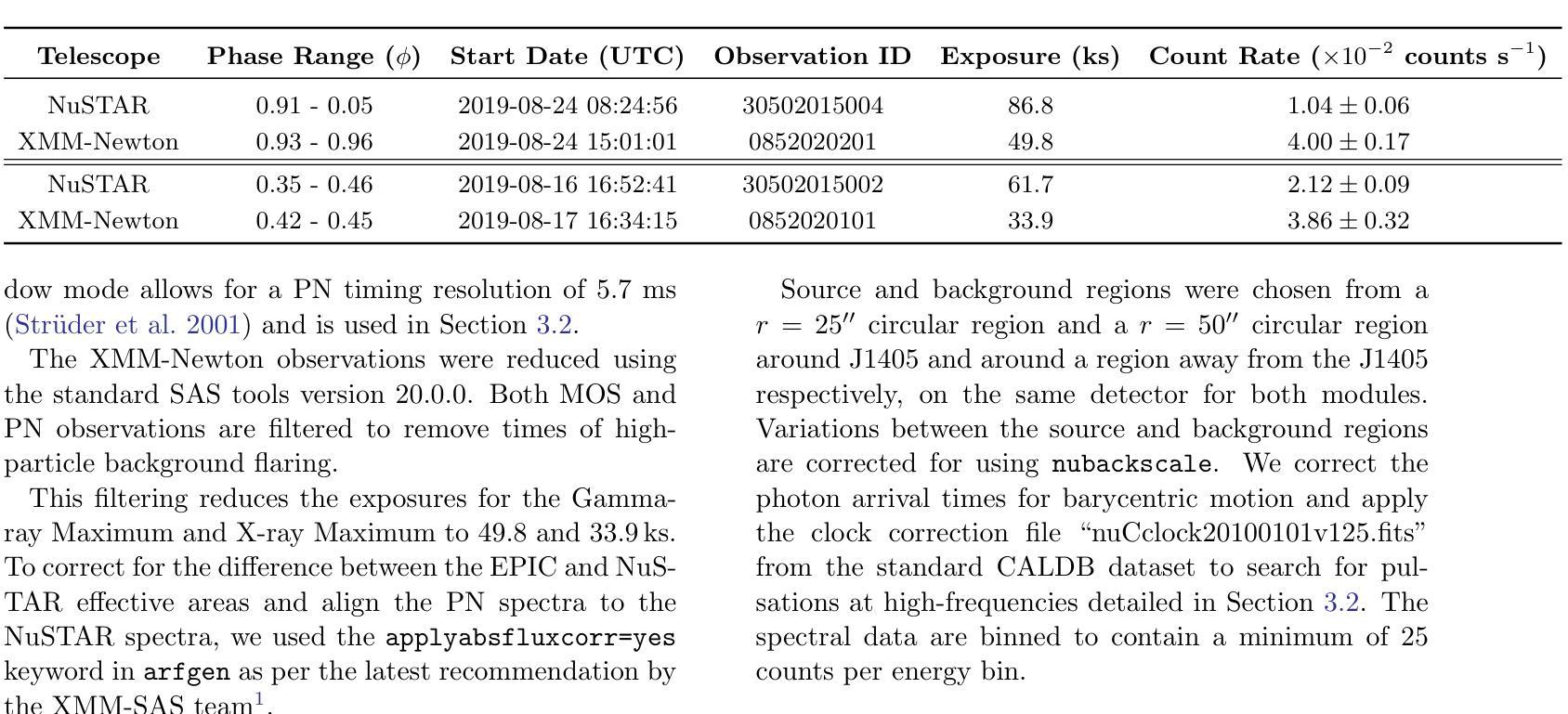
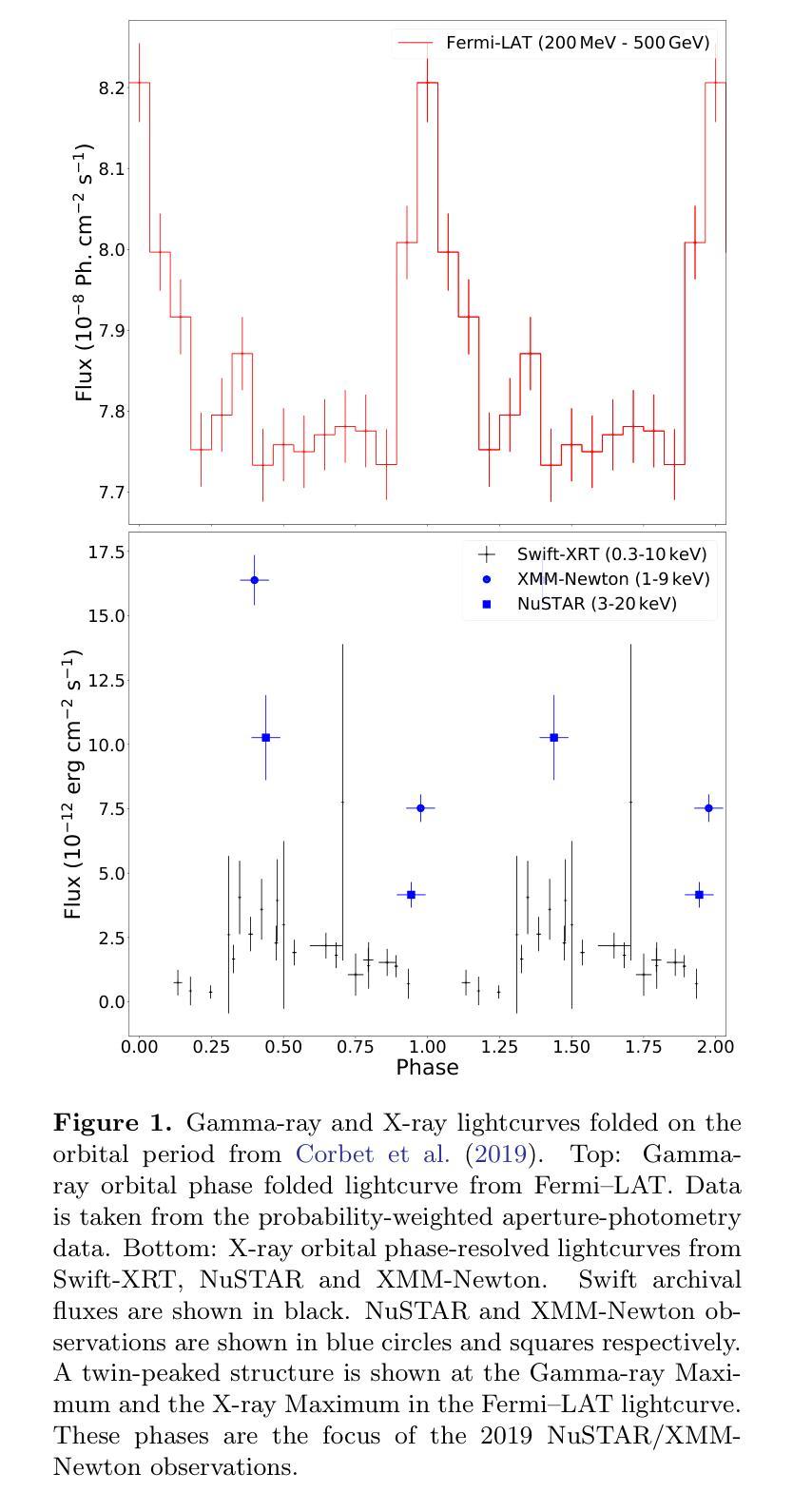
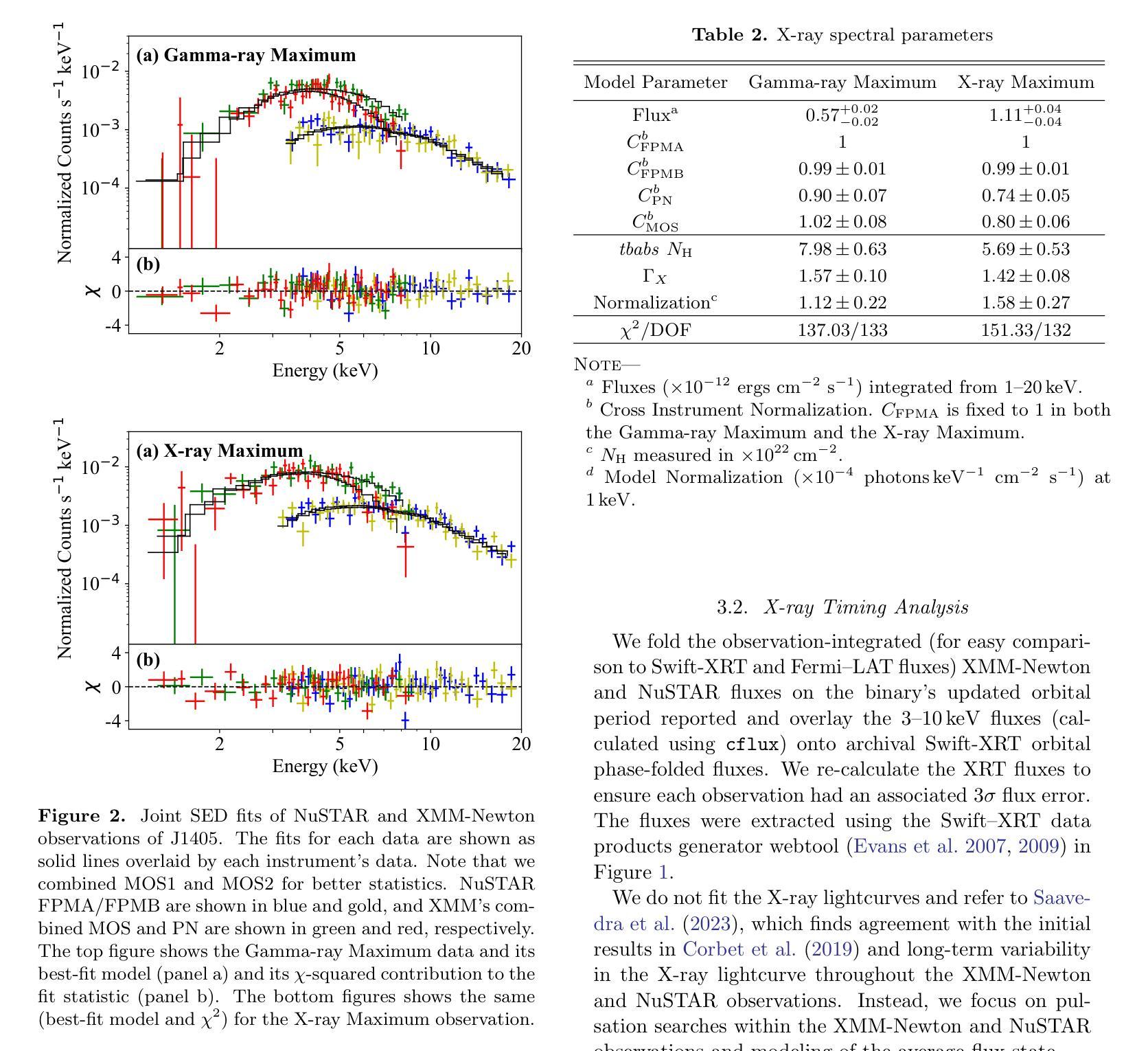
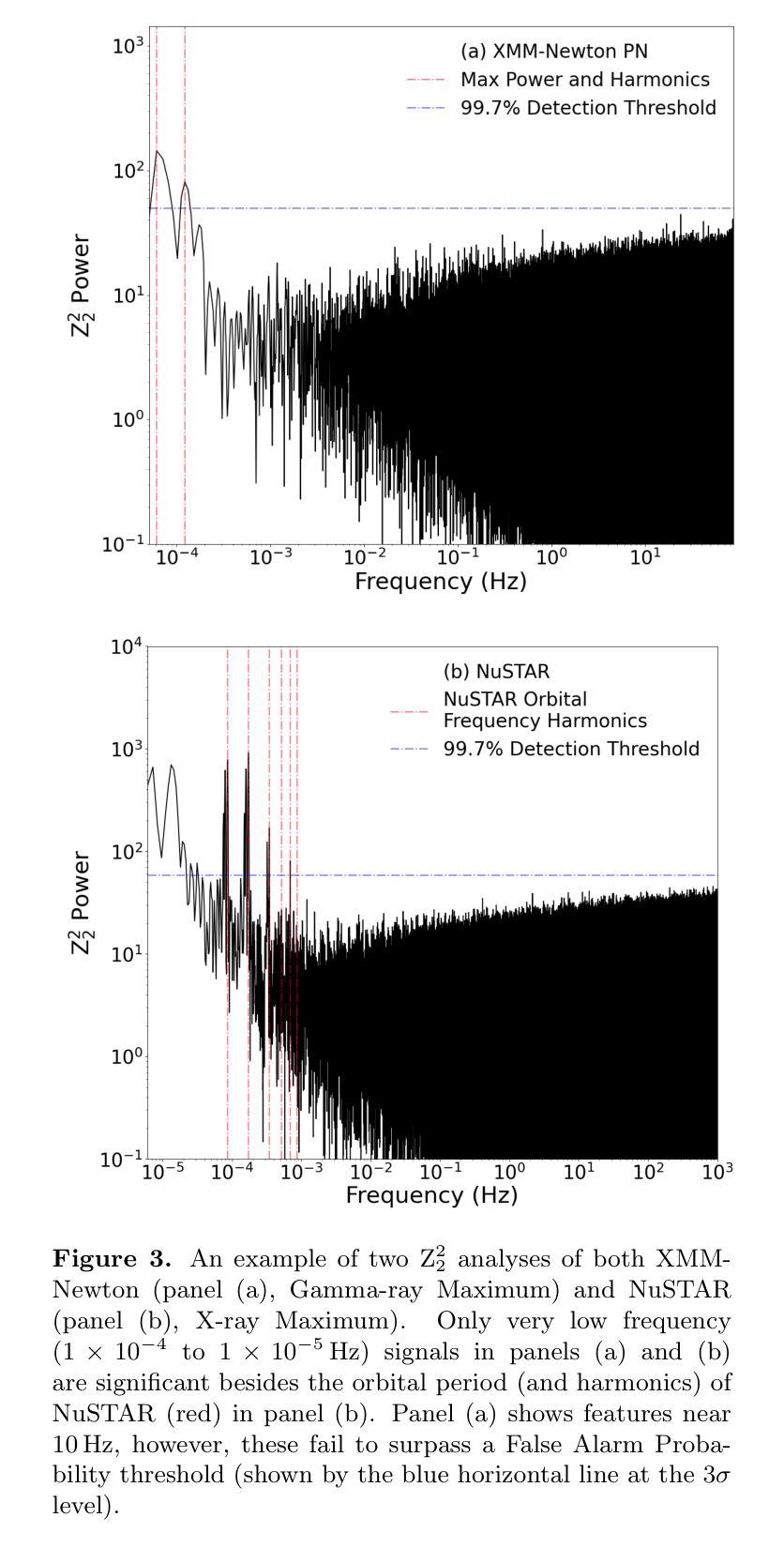
Origin of the X-ray emission in blazars through multiwavelength polarization
Authors:Ioannis Liodakis, Haocheng Zhang, Stella Boula, Riccardo Middei, Jorge Otero-Santos, Dmitry Blinov, Iván Agudo, Markus Böttcher, Chien-Ting Chen, Steven R. Ehlert, Svetlana G. Jorstad, Philip Kaaret, Henric Krawczynski, Abel L. Peirson, Roger W. Romani, Fabrizio Tavecchio, Martin C. Weisskopf, Pouya M. Kouch, Elina Lindfors, Kari Nilsson, Callum McCall, Helen E. Jermak, Iain A. Steele, Ioannis Myserlis, Mark Gurwell, Garrett K. Keating, Ramprasad Rao, Sincheol Kang, Sang-Sung Lee, Sanghyun Kim, Whee Yeon Cheong, Hyeon-Woo Jeong, Emmanouil Angelakis, Alexander Kraus, Francisco José Aceituno, Giacomo Bonnoli, Víctor Casanova, Juan Escudero, Beatriz Agís-González, Daniel Morcuende, Alfredo Sota, Rumen Bachev, Tatiana S. Grishina, Evgenia N. Kopatskaya, Elena G. Larionova, Daria A. Morozova, Sergey S. Savchenko, Ekaterina V. Shishkina, Ivan S. Troitskiy, Yulia V. Troitskaya, Andrey A. Vasilyev
The origin of the high-energy emission in astrophysical jets from black holes is a highly debated issue. This is particularly true for jets from supermassive black holes that are among the most powerful particle accelerators in the Universe. So far, the addition of new observations and new messengers have only managed to create more questions than answers. However, the newly available X-ray polarization observations promise to finally distinguish between emission models. We use extensive multiwavelength and polarization campaigns as well as state-of-the-art polarized spectral energy distribution models to attack this problem by focusing on two X-ray polarization observations of blazar BL Lacertae in flaring and quiescent $\gamma$-ray states. We find that regardless of the jet composition and underlying emission model, inverse-Compton scattering from relativistic electrons dominates at X-ray energies.
天文物理学中黑洞喷射的高能辐射来源是一个备受争议的话题。特别是来自超级大质量黑洞的喷射流,它们是宇宙中最为强大的粒子加速器之一。迄今为止,新的观测和信使的增加只是产生了更多的问题而非答案。然而,新可用的X射线偏振观测有望最终区分不同的发射模型。我们采用了广泛的多波长和偏振观测活动以及最先进的偏振谱能量分布模型,通过专注于处于耀发和静止伽马射线的BL Lacertae的两个X射线偏振观测来解决这个问题。我们发现,无论射流成分和底层发射模型如何,相对论性电子的逆康普顿散射在X射线能量中占主导地位。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 10 pages, 15 figures, 4 Tables, accepted for publication in A&A
Summary
探讨黑洞引起的天体物理学喷射流中高能量发射的起源是一个备受争议的问题,特别是来自超大质量黑洞的喷射流,它们被认为是宇宙中最强大的粒子加速器。新观测数据和新技术带来新的启发同时也产生了更多的问题。最新的X射线偏振观测可能为区分发射模型提供依据。通过全方位的多波长和偏振观测以及最先进的偏振谱能量分布模型,我们对耀斑状态和高静止γ射线状态下的BLLacertae的X射线偏振观测进行研究,发现无论喷射流组成和潜在发射模型如何,相对论性电子的逆康普顿散射在X射线能量段占主导地位。
Key Takeaways
- 高能天体物理学喷射流中黑洞引发的高能量发射起源是一个有争议的问题。
- 超大质量黑洞喷射流是最强大的粒子加速器之一。
- 新观测数据和新技术带来更多问题,X射线偏振观测可能为区分发射模型提供依据。
- 通过全方位的多波长和偏振观测以及先进的模型进行研究。
- 无论喷射流组成和潜在发射模型如何,X射线能量段的逆康普顿散射占主导地位。
- BLLacertae的X射线偏振观测是研究此问题的关键。
点此查看论文截图

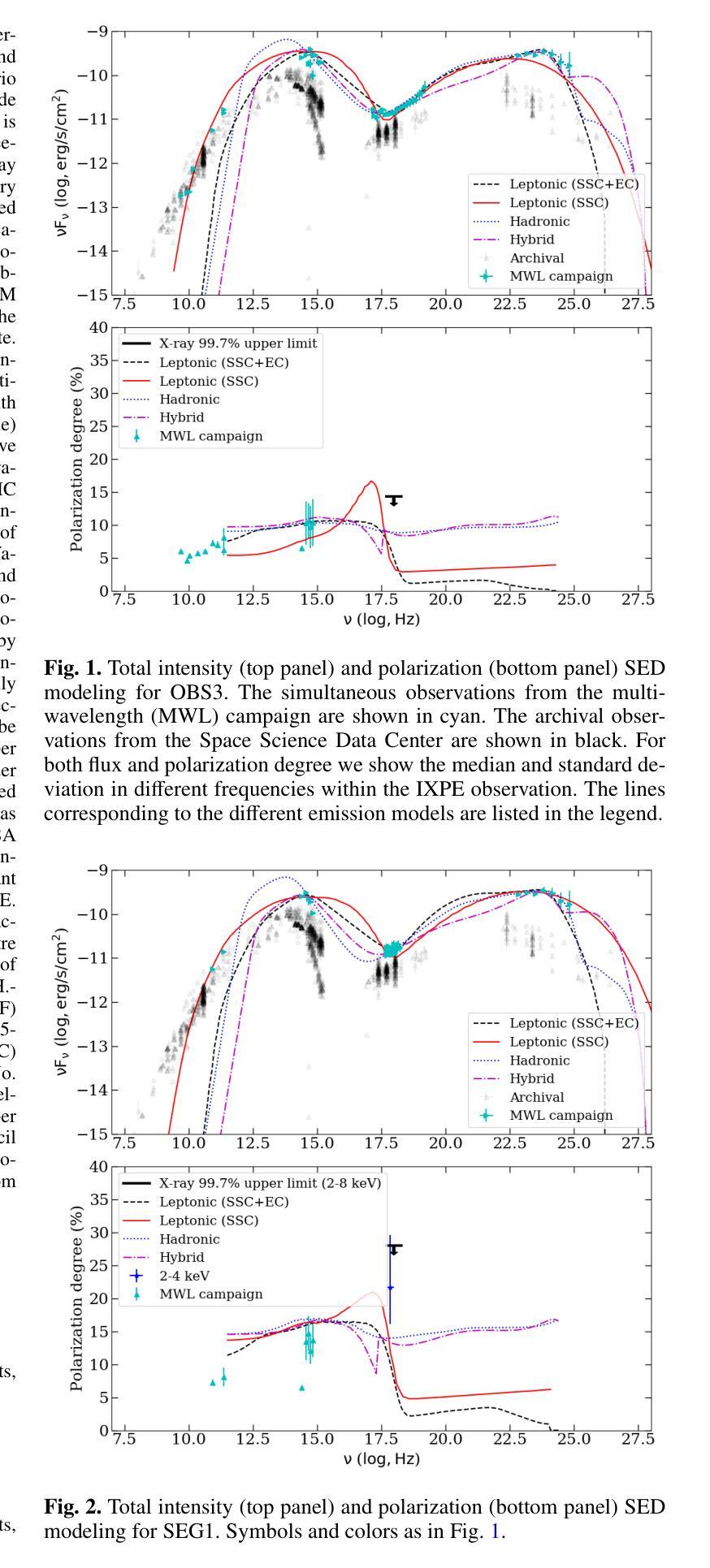
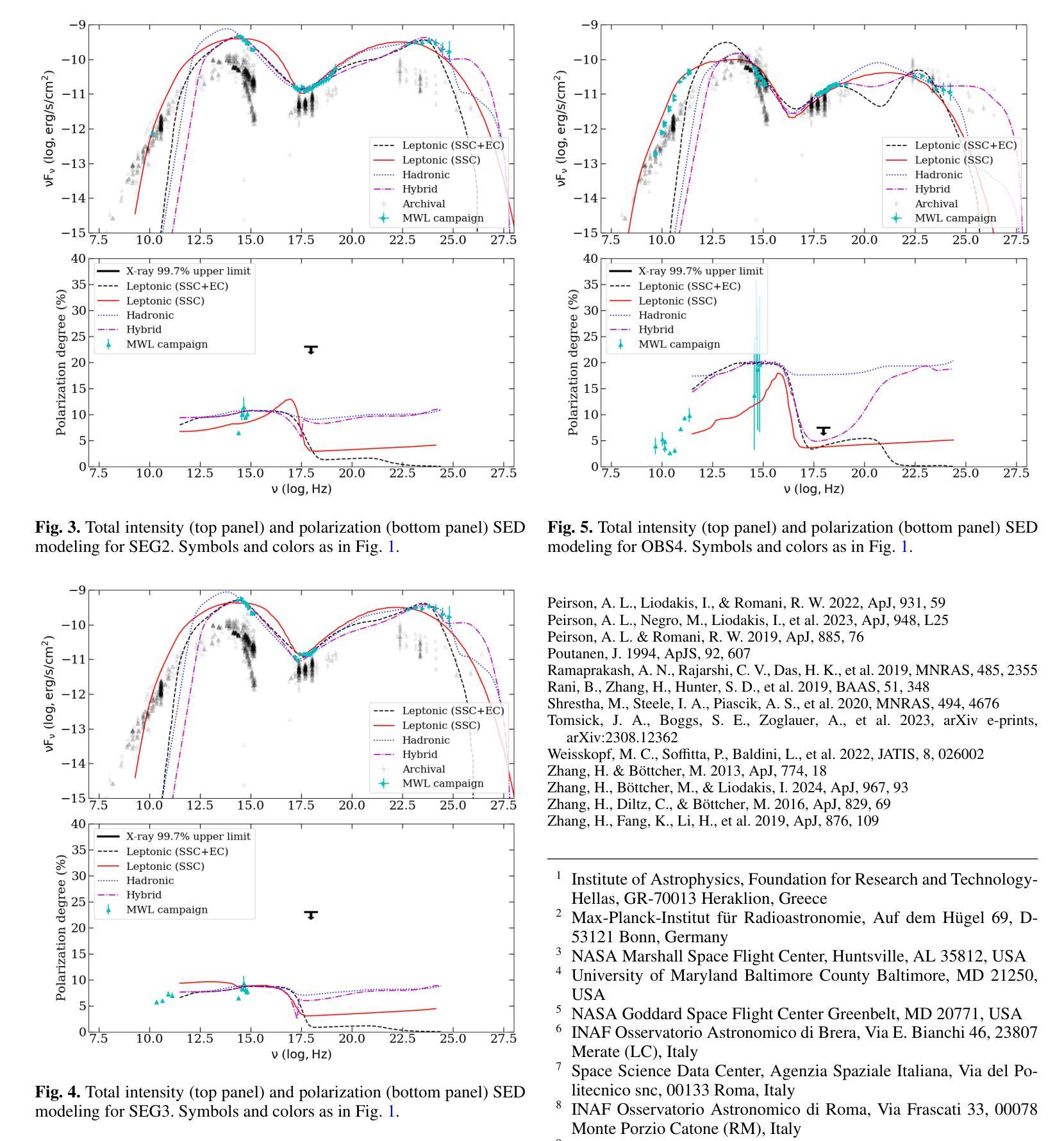
VTBench: Evaluating Visual Tokenizers for Autoregressive Image Generation
Authors:Huawei Lin, Tong Geng, Zhaozhuo Xu, Weijie Zhao
Autoregressive (AR) models have recently shown strong performance in image generation, where a critical component is the visual tokenizer (VT) that maps continuous pixel inputs to discrete token sequences. The quality of the VT largely defines the upper bound of AR model performance. However, current discrete VTs fall significantly behind continuous variational autoencoders (VAEs), leading to degraded image reconstructions and poor preservation of details and text. Existing benchmarks focus on end-to-end generation quality, without isolating VT performance. To address this gap, we introduce VTBench, a comprehensive benchmark that systematically evaluates VTs across three core tasks: Image Reconstruction, Detail Preservation, and Text Preservation, and covers a diverse range of evaluation scenarios. We systematically assess state-of-the-art VTs using a set of metrics to evaluate the quality of reconstructed images. Our findings reveal that continuous VAEs produce superior visual representations compared to discrete VTs, particularly in retaining spatial structure and semantic detail. In contrast, the degraded representations produced by discrete VTs often lead to distorted reconstructions, loss of fine-grained textures, and failures in preserving text and object integrity. Furthermore, we conduct experiments on GPT-4o image generation and discuss its potential AR nature, offering new insights into the role of visual tokenization. We release our benchmark and codebase publicly to support further research and call on the community to develop strong, general-purpose open-source VTs.
近期自回归(AR)模型在图像生成方面表现出强大的性能,其中关键组件是视觉令牌化器(VT),它将连续的像素输入映射到离散的令牌序列。VT的质量在很大程度上决定了AR模型性能的上限。然而,当前的离散VT明显落后于连续变分自编码器(VAEs),导致图像重建质量下降,细节和文本保留不足。现有的基准测试主要关注端到端的生成质量,并没有孤立地评估VT的性能。为了弥补这一空白,我们引入了VTBench,这是一个全面的基准测试,系统地评估了VT在三个核心任务中的表现:图像重建、细节保留和文本保留,涵盖了各种评估场景。我们使用一组度量指标系统地评估了最先进的VT在重建图像质量方面的表现。我们的研究发现,与离散VT相比,连续VAEs产生了更优越的视觉表示,特别是在保留空间结构和语义细节方面。相比之下,离散VT产生的退化表示经常导致重建失真、丢失细微纹理以及在保留文本和对象完整性方面的失败。此外,我们还对GPT-4o的图像生成进行了实验,并对其潜在的AR特性进行了讨论,为视觉令牌化作用提供了新的见解。我们公开发布了我们的基准测试和代码库,以支持进一步的研究,并呼吁社区开发强大、通用的开源VT。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 24 pages, 13 figures, 3 tables
Summary
基于最近自回归模型在图像生成中的表现,可视化令牌映射在生成连续像素输入离散序列方面发挥关键作用。尽管VT技术进展迅速,但与连续变分自编码器相比仍有所不足,导致图像重建质量下降,细节和文本保留不足。现有基准测试主要关注端到端的生成质量,忽略了VT性能。本文介绍了一个全面评估VT的系统性基准测试,通过三个核心任务系统地评估了最新的VT性能,包括图像重建、细节保留和文本保留。研究结果表明,连续变分自编码器在生成视觉表示方面优于离散VT,特别是在保留空间结构和语义细节方面。此外,本文还探讨了GPT-4o图像生成的潜在自回归性质。呼吁开发强大、通用的开源VT以支持进一步的研究。
Key Takeaways
- 自回归模型在图像生成中表现出强大的性能,其中可视化令牌映射是关键组件。
- 现有离散可视化令牌映射技术相较于连续变分自编码器存在性能差距,导致图像重建质量下降和细节丢失。
- 引入了一个新的基准测试VTBench,旨在系统地评估可视化令牌映射的性能,包括图像重建、细节保留和文本保留三个核心任务。
- 研究发现连续变分自编码器在生成视觉表示方面优于离散可视化令牌映射技术。
- GPT-4o图像生成具有潜在的自回归性质。
点此查看论文截图


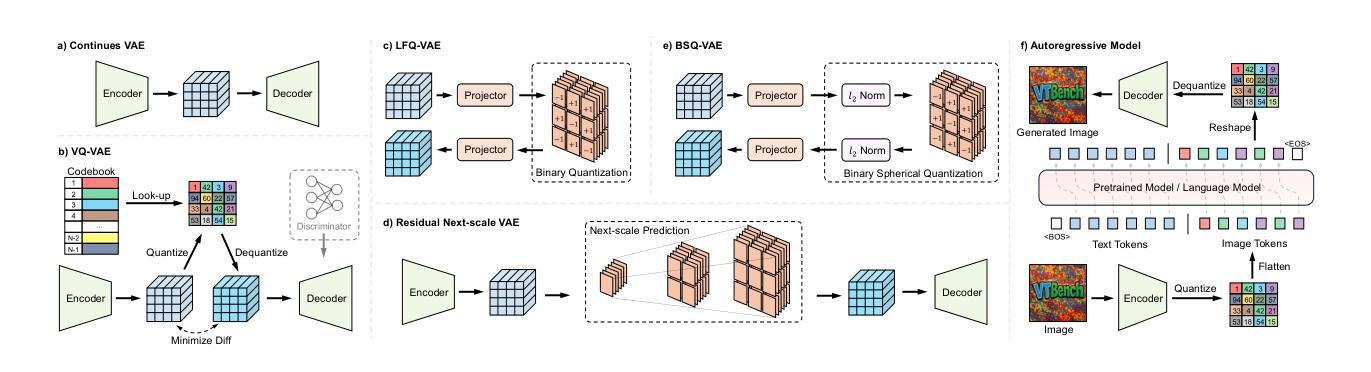


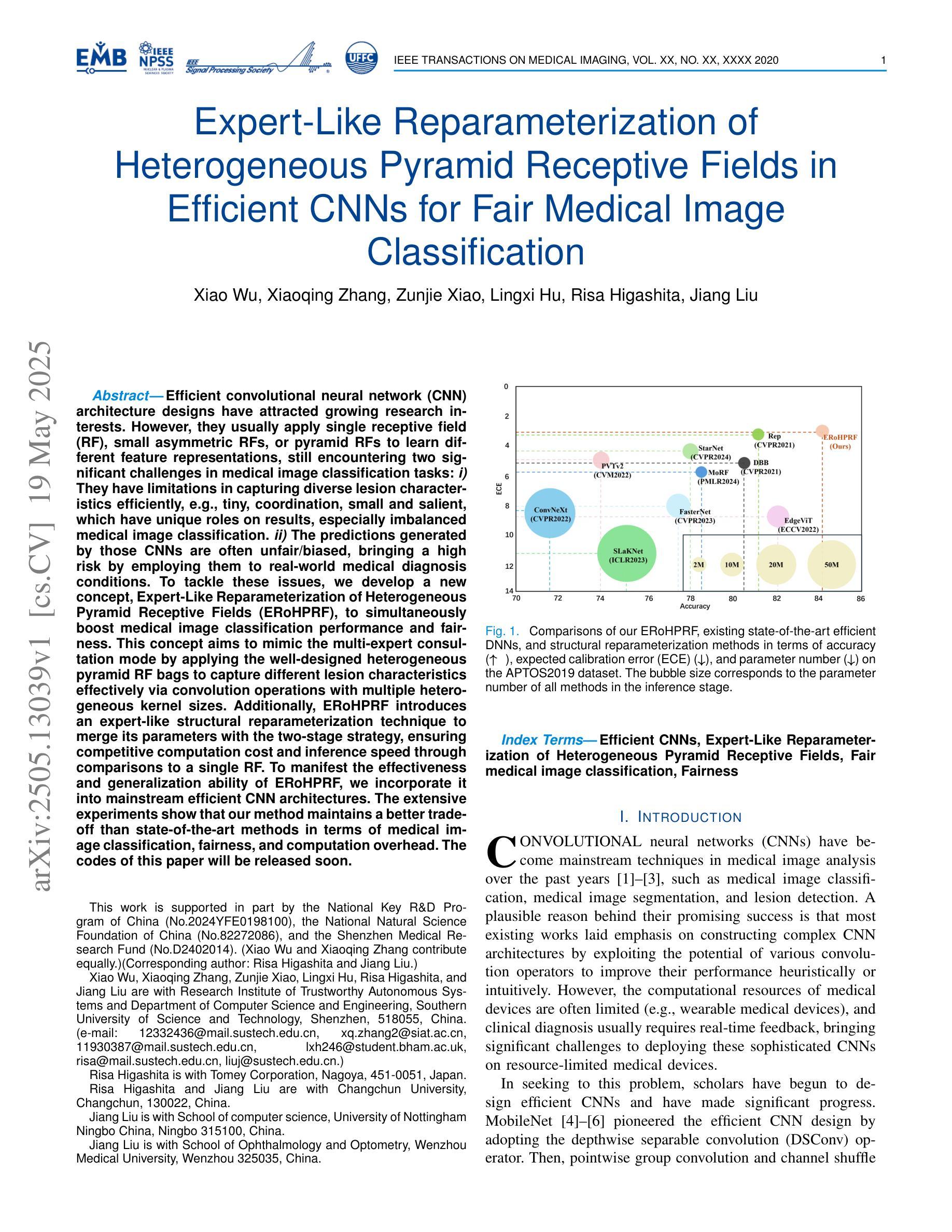
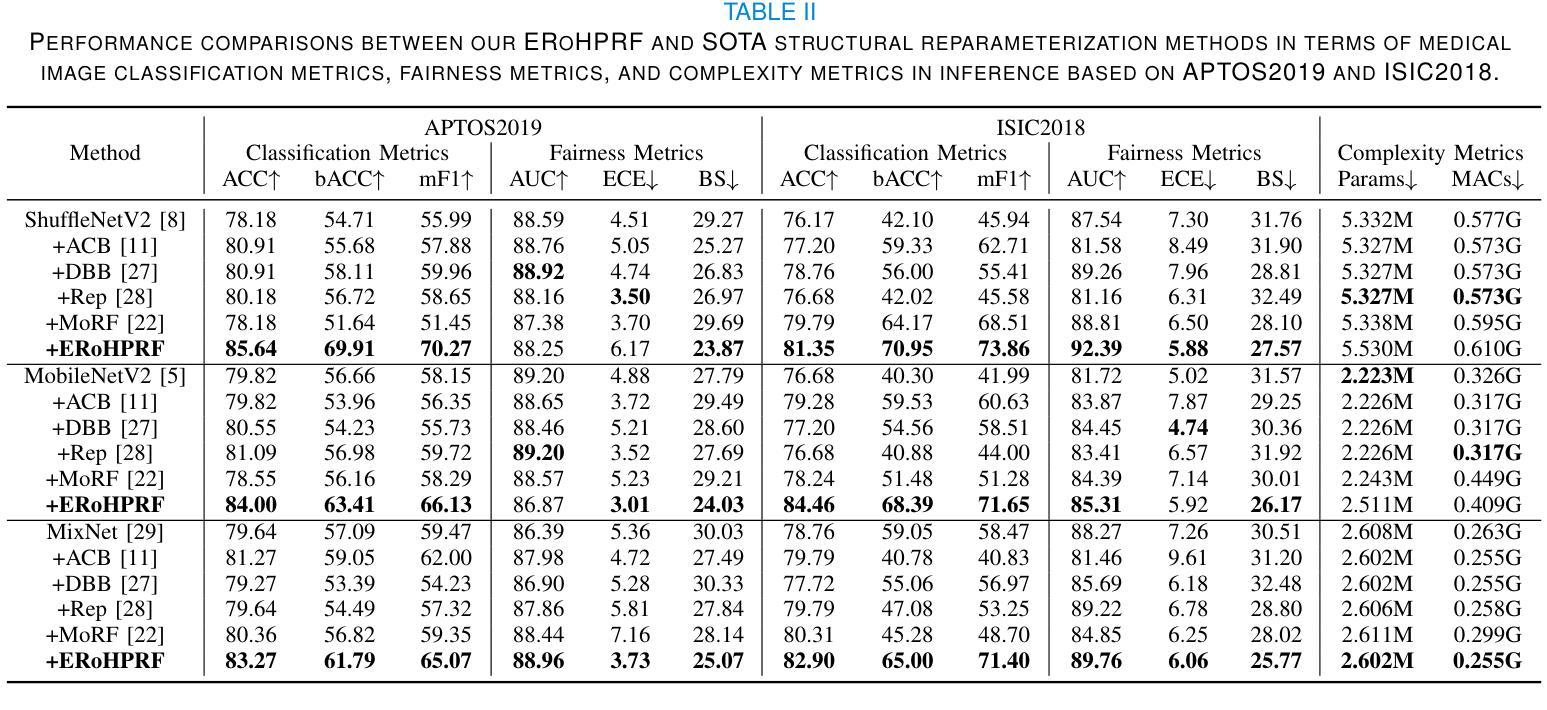
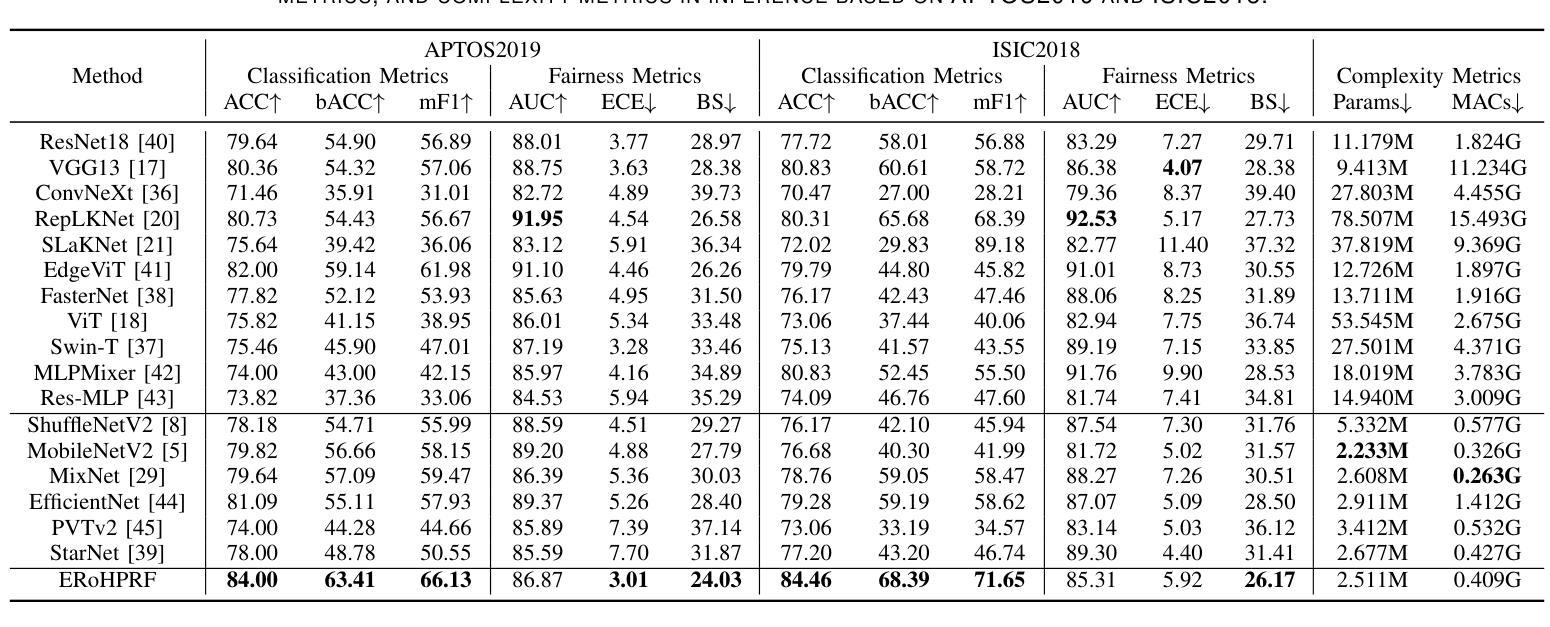
Expert-Like Reparameterization of Heterogeneous Pyramid Receptive Fields in Efficient CNNs for Fair Medical Image Classification
Authors:Xiao Wu, Xiaoqing Zhang, Zunjie Xiao, Lingxi Hu, Risa Higashita, Jiang Liu
Efficient convolutional neural network (CNN) architecture designs have attracted growing research interests. However, they usually apply single receptive field (RF), small asymmetric RFs, or pyramid RFs to learn different feature representations, still encountering two significant challenges in medical image classification tasks: 1) They have limitations in capturing diverse lesion characteristics efficiently, e.g., tiny, coordination, small and salient, which have unique roles on results, especially imbalanced medical image classification. 2) The predictions generated by those CNNs are often unfair/biased, bringing a high risk by employing them to real-world medical diagnosis conditions. To tackle these issues, we develop a new concept, Expert-Like Reparameterization of Heterogeneous Pyramid Receptive Fields (ERoHPRF), to simultaneously boost medical image classification performance and fairness. This concept aims to mimic the multi-expert consultation mode by applying the well-designed heterogeneous pyramid RF bags to capture different lesion characteristics effectively via convolution operations with multiple heterogeneous kernel sizes. Additionally, ERoHPRF introduces an expert-like structural reparameterization technique to merge its parameters with the two-stage strategy, ensuring competitive computation cost and inference speed through comparisons to a single RF. To manifest the effectiveness and generalization ability of ERoHPRF, we incorporate it into mainstream efficient CNN architectures. The extensive experiments show that our method maintains a better trade-off than state-of-the-art methods in terms of medical image classification, fairness, and computation overhead. The codes of this paper will be released soon.
高效的卷积神经网络(CNN)架构设计已引起越来越多的研究兴趣。然而,它们通常应用单个感受野(RF)、小型不对称RFs或金字塔RF来学习不同的特征表示,在医学图像分类任务中仍面临两个重大挑战:1)它们在有效捕获各种病变特征方面存在局限性,例如微小、协调、小而显著的特征在结果中具有独特作用,特别是在不平衡医学图像分类中。2)这些CNN生成的预测通常是不公平/有偏见的,将它们应用于现实世界的医学诊断条件会带来高风险。为了解决这些问题,我们提出了一个新的概念——异质金字塔感受野的专家型再参数化(ERoHPRF),以同时提高医学图像分类的性能和公平性。该概念旨在通过应用设计精良的异质金字塔RF包来模仿多专家咨询模式,通过具有多种异质内核大小的卷积操作有效捕获不同的病变特征。此外,ERoHPRF引入了一种类似于专家的结构化再参数化技术,将其参数与两阶段策略相结合,通过与单个RF的比较,确保具有竞争力的计算成本和推理速度。为了证明ERoHPRF的有效性和通用性,我们将其纳入主流的高效CNN架构中。广泛的实验表明,我们的方法在医学图像分类、公平性和计算开销方面达到了最先进的平衡。本文的代码将很快发布。
论文及项目相关链接
摘要
高效卷积神经网络(CNN)架构设计日益受到研究关注。然而,它们在医学图像分类任务中仍面临两大挑战:一是捕捉多样病灶特征效率有限;二是生成的预测常有偏见。为应对这些问题,我们提出了一个新的概念——异质金字塔感受野的专家型再参数化(ERoHPRF),旨在同时提高医学图像分类的性能和公平性。它旨在通过应用精心设计了的异质金字塔感受野袋来模仿多专家咨询模式,并通过多种异质内核大小的卷积操作有效捕捉不同的病灶特征。此外,ERoHPRF还引入了一种专家型结构再参数化技术,通过两阶段策略将其参数进行合并,以确保与单一感受野相比具有竞争力的计算成本和推理速度。实验表明,该方法在医学图像分类、公平性和计算开销方面达到了更好的权衡。
要点
- 高效CNN架构在医学图像分类中面临挑战,如捕捉多样病灶特征和预测公平性。
- 提出ERoHPRF概念,通过异质金字塔感受野袋有效捕捉不同病灶特征。
- ERoHPRF模仿多专家咨询模式,提高医学图像分类性能。
- 引入专家型结构再参数化技术,确保计算效率和推理速度。
- 实验表明,该方法在医学图像分类、公平性和计算开销方面优于现有方法。
- 代码将很快发布,以便其他研究者使用和改进。
点此查看论文截图
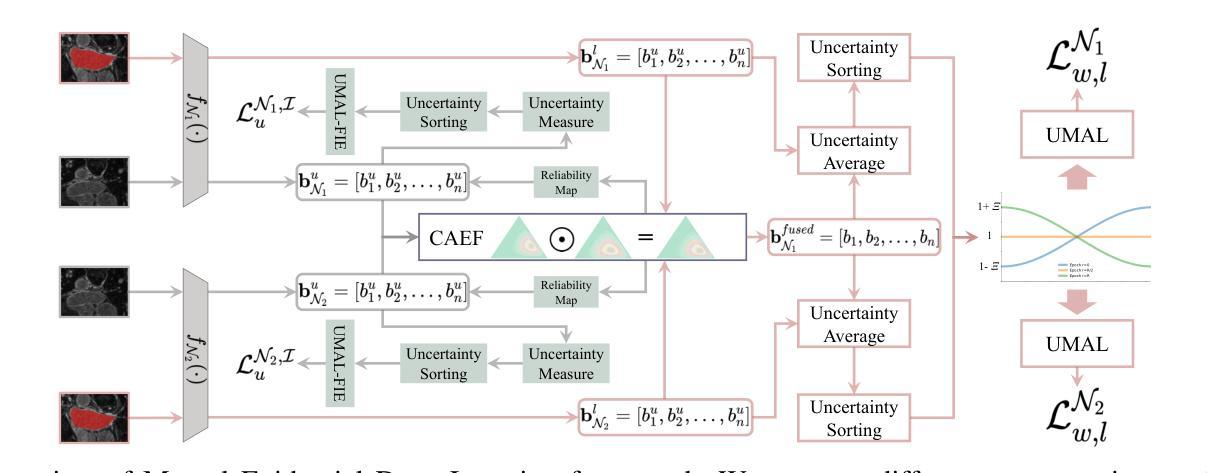
Mutual Evidential Deep Learning for Medical Image Segmentation
Authors:Yuanpeng He, Yali Bi, Lijian Li, Chi-Man Pun, Wenpin Jiao, Zhi Jin
Existing semi-supervised medical segmentation co-learning frameworks have realized that model performance can be diminished by the biases in model recognition caused by low-quality pseudo-labels. Due to the averaging nature of their pseudo-label integration strategy, they fail to explore the reliability of pseudo-labels from different sources. In this paper, we propose a mutual evidential deep learning (MEDL) framework that offers a potentially viable solution for pseudo-label generation in semi-supervised learning from two perspectives. First, we introduce networks with different architectures to generate complementary evidence for unlabeled samples and adopt an improved class-aware evidential fusion to guide the confident synthesis of evidential predictions sourced from diverse architectural networks. Second, utilizing the uncertainty in the fused evidence, we design an asymptotic Fisher information-based evidential learning strategy. This strategy enables the model to initially focus on unlabeled samples with more reliable pseudo-labels, gradually shifting attention to samples with lower-quality pseudo-labels while avoiding over-penalization of mislabeled classes in high data uncertainty samples. Additionally, for labeled data, we continue to adopt an uncertainty-driven asymptotic learning strategy, gradually guiding the model to focus on challenging voxels. Extensive experiments on five mainstream datasets have demonstrated that MEDL achieves state-of-the-art performance.
现有的半监督医学分割协同学习框架已经意识到,模型识别中的偏见会导致伪标签质量下降,进而影响模型性能。由于他们的伪标签集成策略的平均性质,他们无法探索从不同来源获得的伪标签的可靠性。在本文中,我们提出了一种互证深度学习(MEDL)框架,从两个角度为半监督学习中的伪标签生成提供了潜在可行的解决方案。首先,我们引入具有不同架构的网络,为未标记样本生成互补证据,并采用改进的分类感知证据融合来指导来自不同架构网络的证据预测的自信合成。其次,利用融合证据中的不确定性,我们设计了一种基于渐近费舍尔信息的证据学习策略。该策略使模型最初关注具有更可靠伪标签的未标记样本,逐渐将注意力转移到具有较低质量伪标签的样本上,同时避免在高数据不确定性样本中过度惩罚误标记的类别。此外,对于标记数据,我们继续采用基于不确定性的渐近学习策略,逐渐引导模型关注具有挑战性的体素。在五个主流数据集上的大量实验表明,MEDL达到了最新技术水平。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
半监督医学图像分割协同学习框架面临因伪标签质量导致的模型识别偏差问题,影响了模型性能。本文提出一种互证深度学习(MEDL)框架,从两个角度为解决伪标签生成问题提供潜在可行方案。首先,引入不同架构的网络为未标记样本生成互补证据,并采用改进的分类感知证据融合指导来自不同架构网络的证据预测的合成。其次,利用融合证据的不确定性,设计基于渐近Fisher信息的证据学习策略,使模型能关注伪标签更可靠的未标记样本,逐渐转向伪标签质量较低的样本,同时避免高数据不确定性样本中误标记类的过度惩罚。对五个主流数据集的大量实验表明,MEDL取得了最先进的性能。
Key Takeaways
- 半监督医学图像分割协同学习框架受伪标签质量影响,可能导致模型性能下降。
- 现有框架因平均伪标签整合策略,无法探索不同来源伪标签的可靠性。
- MEDL框架通过引入不同架构的网络生成互补证据,提高伪标签的质量。
- MEDL采用改进的证据融合方法和渐近Fisher信息证据学习策略,关注更可靠的未标记样本。
- MEDL框架能逐渐转向伪标签质量较低的样本,同时避免误标记类的过度惩罚。
- MEDL在五个主流数据集上实现了最先进的性能。
点此查看论文截图

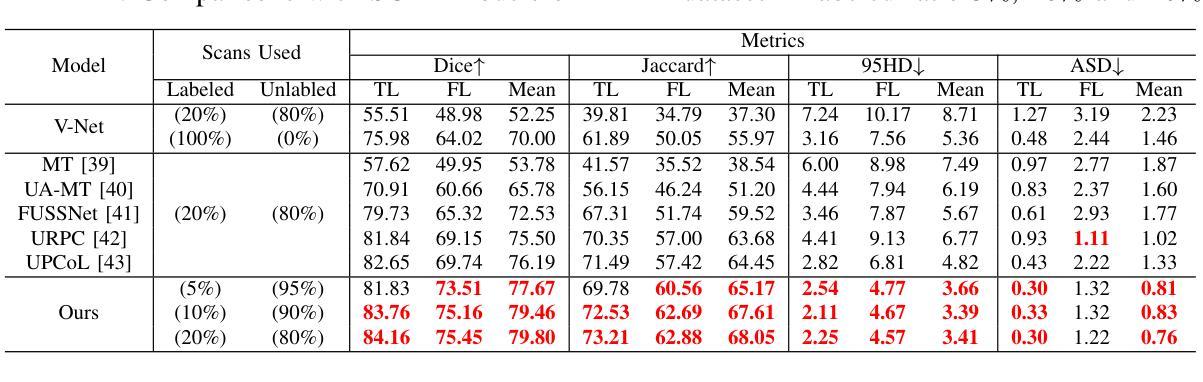
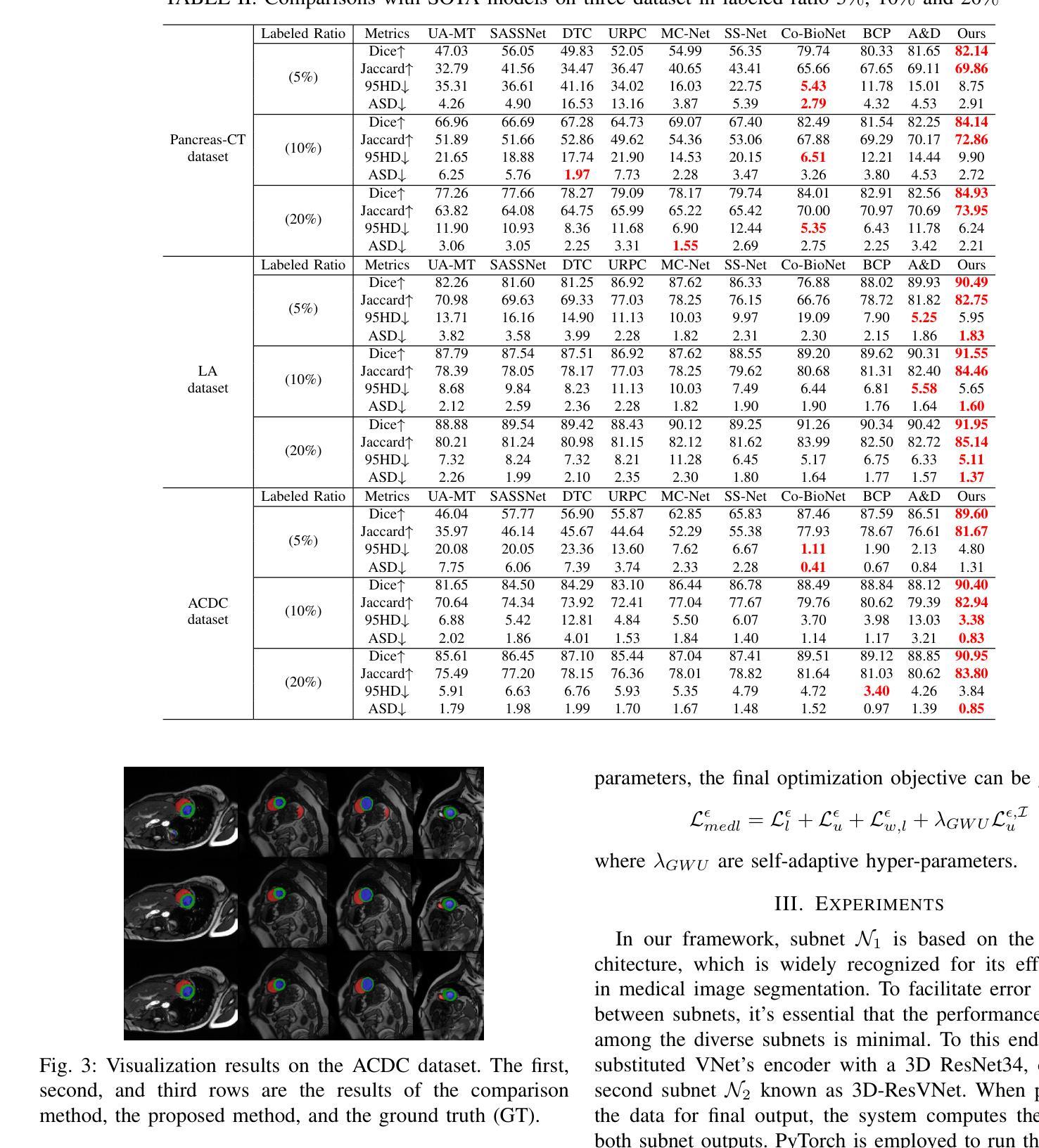
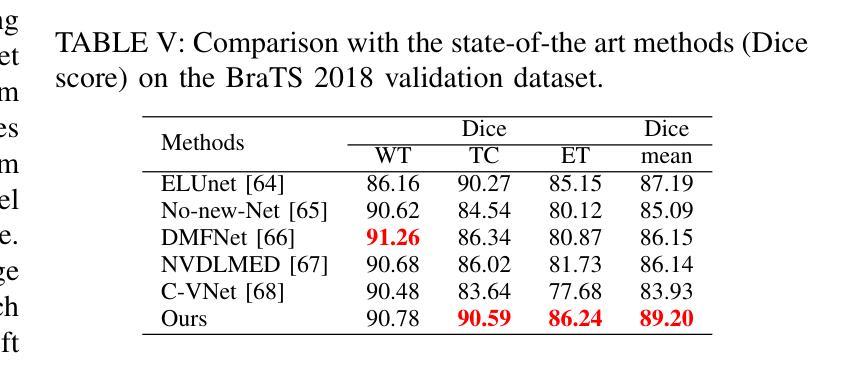
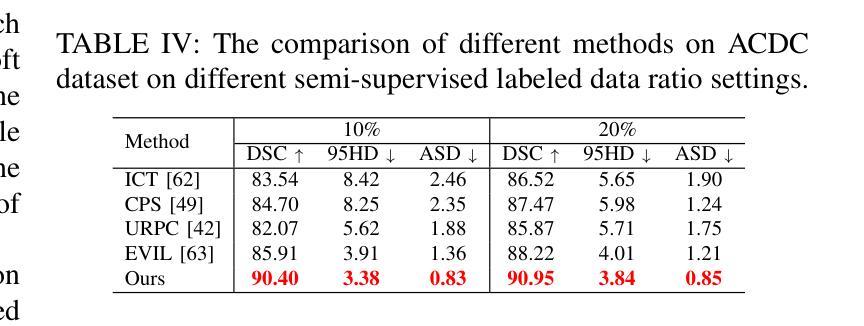
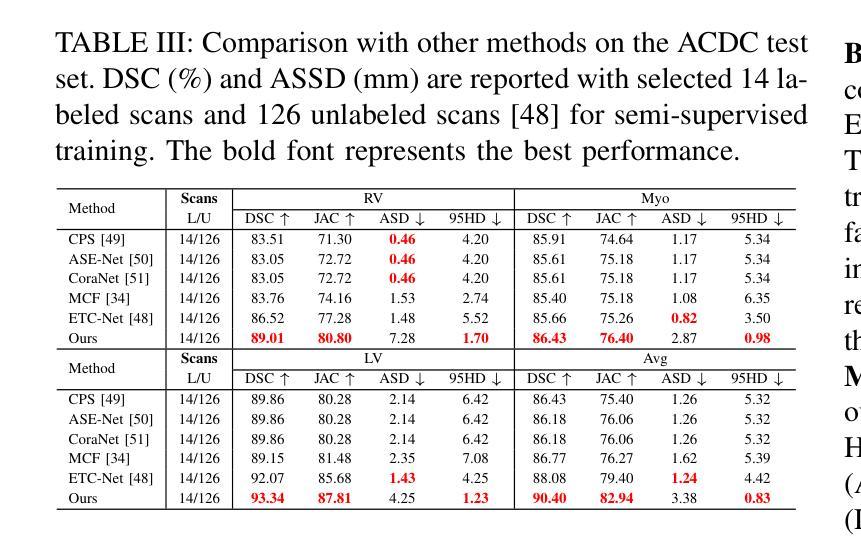
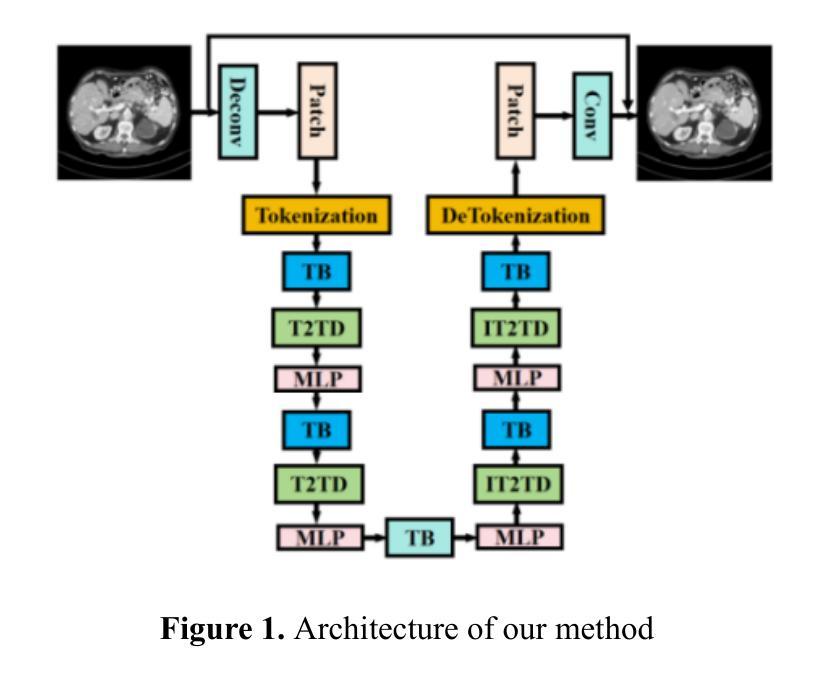
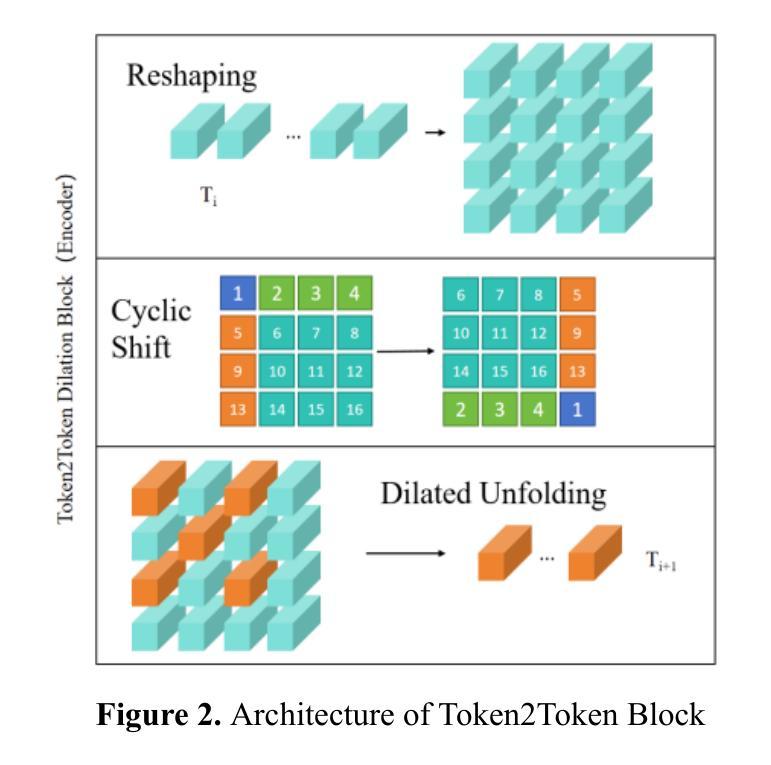
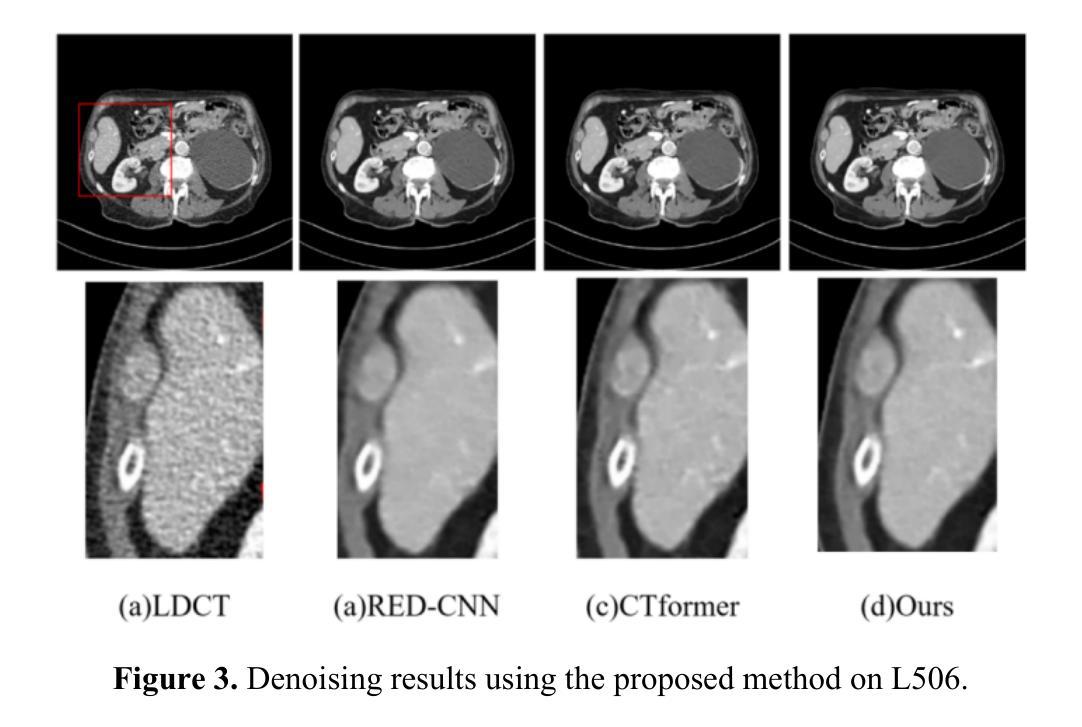
CTLformer: A Hybrid Denoising Model Combining Convolutional Layers and Self-Attention for Enhanced CT Image Reconstruction
Authors:Zhiting Zheng, Shuqi Wu, Wen Ding
Low-dose CT (LDCT) images are often accompanied by significant noise, which negatively impacts image quality and subsequent diagnostic accuracy. To address the challenges of multi-scale feature fusion and diverse noise distribution patterns in LDCT denoising, this paper introduces an innovative model, CTLformer, which combines convolutional structures with transformer architecture. Two key innovations are proposed: a multi-scale attention mechanism and a dynamic attention control mechanism. The multi-scale attention mechanism, implemented through the Token2Token mechanism and self-attention interaction modules, effectively captures both fine details and global structures at different scales, enhancing relevant features and suppressing noise. The dynamic attention control mechanism adapts the attention distribution based on the noise characteristics of the input image, focusing on high-noise regions while preserving details in low-noise areas, thereby enhancing robustness and improving denoising performance. Furthermore, CTLformer integrates convolutional layers for efficient feature extraction and uses overlapping inference to mitigate boundary artifacts, further strengthening its denoising capability. Experimental results on the 2016 National Institutes of Health AAPM Mayo Clinic LDCT Challenge dataset demonstrate that CTLformer significantly outperforms existing methods in both denoising performance and model efficiency, greatly improving the quality of LDCT images. The proposed CTLformer not only provides an efficient solution for LDCT denoising but also shows broad potential in medical image analysis, especially for clinical applications dealing with complex noise patterns.
低剂量CT(LDCT)图像往往伴随着显著的噪声,这会对图像质量和随后的诊断准确性产生负面影响。为了解决LDCT去噪中的多尺度特征融合和多样噪声分布模式的挑战,本文介绍了一种创新模型CTLformer,该模型结合了卷积结构和转换器架构。提出了两项关键创新:多尺度注意机制和动态注意控制机制。多尺度注意机制通过Token2Token机制和自注意交互模块实现,能够有效地捕捉不同尺度下的精细细节和全局结构,增强相关特征并抑制噪声。动态注意控制机制根据输入图像的噪声特性调整注意分布,关注高噪声区域的同时保持低噪声区域的细节,从而提高稳健性,改善去噪性能。此外,CTLformer集成了卷积层进行高效特征提取,并使用重叠推理来缓解边界伪影,进一步加强其去噪能力。在2016年国立卫生研究院AAPM梅奥诊所LDCT挑战赛数据集上的实验结果表明,CTLformer在降噪性能和模型效率方面都大大优于现有方法,极大地提高了LDCT图像的质量。所提出的CTLformer不仅为LDCT去噪提供了有效的解决方案,还显示出在医学图像分析中的广阔潜力,特别是在处理复杂噪声模式的临床应用方面。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了一种针对低剂量CT(LDCT)图像去噪的新模型CTLformer。该模型结合了卷积结构和变压器架构,通过多尺度注意机制和动态注意控制机制,有效捕捉不同尺度的精细细节和全局结构,并根据输入图像的噪声特性自适应调整注意力分布,从而提高稳健性和去噪性能。在NIH AAPM Mayo Clinic LDCT Challenge数据集上的实验结果表明,CTLformer在降噪性能和模型效率方面均显著优于现有方法,极大提高了LDCT图像的质量。
Key Takeaways
- LDCT图像常伴随显著噪声,影响图像质量和诊断准确性。
2.CTLformer模型结合卷积结构和变压器架构,旨在解决LDCT图像去噪中的多尺度特征融合和噪声分布多样性问题。 - 多尺度注意机制通过Token2Token机制和自注意交互模块,有效捕捉不同尺度的精细细节和全局结构。
- 动态注意控制机制根据输入图像的噪声特性自适应调整注意力分布,兼顾高噪声区域的关注与低噪声区域的细节保留。
- CTLformer通过卷积层进行高效特征提取,并使用重叠推理来减轻边界伪影,进一步增强去噪能力。
- 在NIH AAPM Mayo Clinic LDCT Challenge数据集上的实验结果表明,CTLformer在降噪性能和模型效率方面表现出卓越性能。
点此查看论文截图

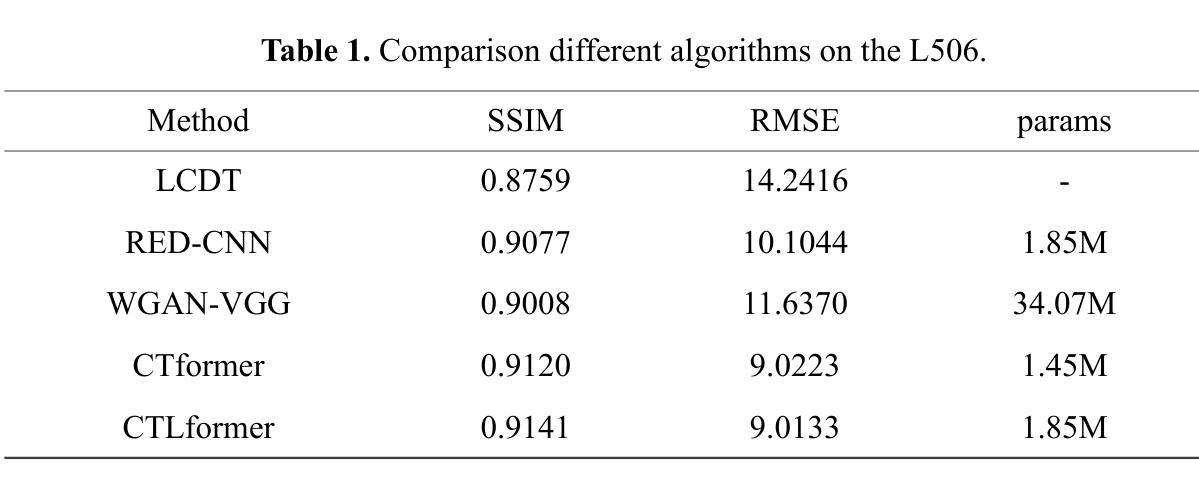
BenSParX: A Robust Explainable Machine Learning Framework for Parkinson’s Disease Detection from Bengali Conversational Speech
Authors:Riad Hossain, Muhammad Ashad Kabir, Arat Ibne Golam Mowla, Animesh Chandra Roy, Ranjit Kumar Ghosh
Parkinson’s disease (PD) poses a growing global health challenge, with Bangladesh experiencing a notable rise in PD-related mortality. Early detection of PD remains particularly challenging in resource-constrained settings, where voice-based analysis has emerged as a promising non-invasive and cost-effective alternative. However, existing studies predominantly focus on English or other major languages; notably, no voice dataset for PD exists for Bengali - posing a significant barrier to culturally inclusive and accessible healthcare solutions. Moreover, most prior studies employed only a narrow set of acoustic features, with limited or no hyperparameter tuning and feature selection strategies, and little attention to model explainability. This restricts the development of a robust and generalizable machine learning model. To address this gap, we present BenSparX, the first Bengali conversational speech dataset for PD detection, along with a robust and explainable machine learning framework tailored for early diagnosis. The proposed framework incorporates diverse acoustic feature categories, systematic feature selection methods, and state-of-the-art machine learning algorithms with extensive hyperparameter optimization. Furthermore, to enhance interpretability and trust in model predictions, the framework incorporates SHAP (SHapley Additive exPlanations) analysis to quantify the contribution of individual acoustic features toward PD detection. Our framework achieves state-of-the-art performance, yielding an accuracy of 95.77%, F1 score of 95.57%, and AUC-ROC of 0.982. We further externally validated our approach by applying the framework to existing PD datasets in other languages, where it consistently outperforms state-of-the-art approaches. To facilitate further research and reproducibility, the dataset has been made publicly available at https://github.com/Riad071/BenSParX.
帕金森病(PD)已成为全球日益严峻的健康挑战,孟加拉国的PD相关死亡率也显著上升。在资源有限的环境中,早期PD检测仍然是一项艰巨的任务。基于声音的分析作为一种有前景的非侵入性和低成本替代方法应运而生。然而,现有研究主要集中在英语或其他主要语言上;值得注意的是,尚无针对PD的孟加拉语语音数据集,这对包含文化特征的全面医疗解决方案构成了重大障碍。此外,大多数早期研究仅使用了有限的声学特征,并且很少有或没有超参数调整和特征选择策略,对模型解释性的关注也较少。这限制了稳健且可推广的机器学习模型的发展。为了弥补这一空白,我们推出了BenSparX,这是针对PD检测的首个孟加拉语对话语音数据集,以及一个用于早期诊断的稳健且可解释的机器学习框架。所提出的框架结合了多种声学特征类别、系统特征选择方法以及具有广泛超参数优化的最新机器学习算法。此外,为了提高对模型预测的解释性和信任度,该框架结合了SHAP(SHapley Additive exPlanations)分析,以量化单个声学特征对PD检测的贡献。我们的框架达到了最先进的表现水平,准确率达到了95.77%,F1分数为95.57%,AUC-ROC为0.982。我们进一步通过将该框架应用于其他语言的现有PD数据集来验证我们的方法,它在各种情况下均表现出超越现有先进方法的表现。为了便于进一步的研究和可重复性,数据集已在https://github.com/Riad071/BenSParX上公开提供。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 46 pages, 16 figures
Summary
本文介绍了孟加拉国帕金森病(PD)检测的新研究。针对资源受限环境中早期PD检测的挑战,提出了BenSparX——首个用于PD检测的孟加拉语对话语音数据集和一个稳健、可解释的机器学习框架。该框架结合多种声学特征、系统特征选择方法和优化超参数的机器学习算法,并采用SHAP分析提高模型预测的可解释性。研究取得卓越性能,准确率达95.77%,F1分数为95.57%,AUC-ROC为0.982,并在其他语言的数据集上表现优异。数据集已公开分享,以推动进一步研究和可重复性。
Key Takeaways
- 帕金森病(PD)在孟加拉国呈现上升趋势,早期检测面临挑战,特别是在资源受限的环境中。
- 语音分析为PD的早期非侵入性和成本效益高的检测提供了希望。
- 目前缺乏针对孟加拉语的PD语音数据集,阻碍了文化包容和可访问的医疗卫生解决方案的发展。
- BenSparX是首个为PD检测设计的孟加拉语对话语音数据集。
- 提出的机器学习框架结合多种声学特征、系统特征选择方法和先进的机器学习算法,进行超参数优化。
- 采用SHAP分析提高模型预测的可解释性。
- 研究取得卓越性能,并在其他语言的数据集上表现优异,数据集已公开分享。
点此查看论文截图

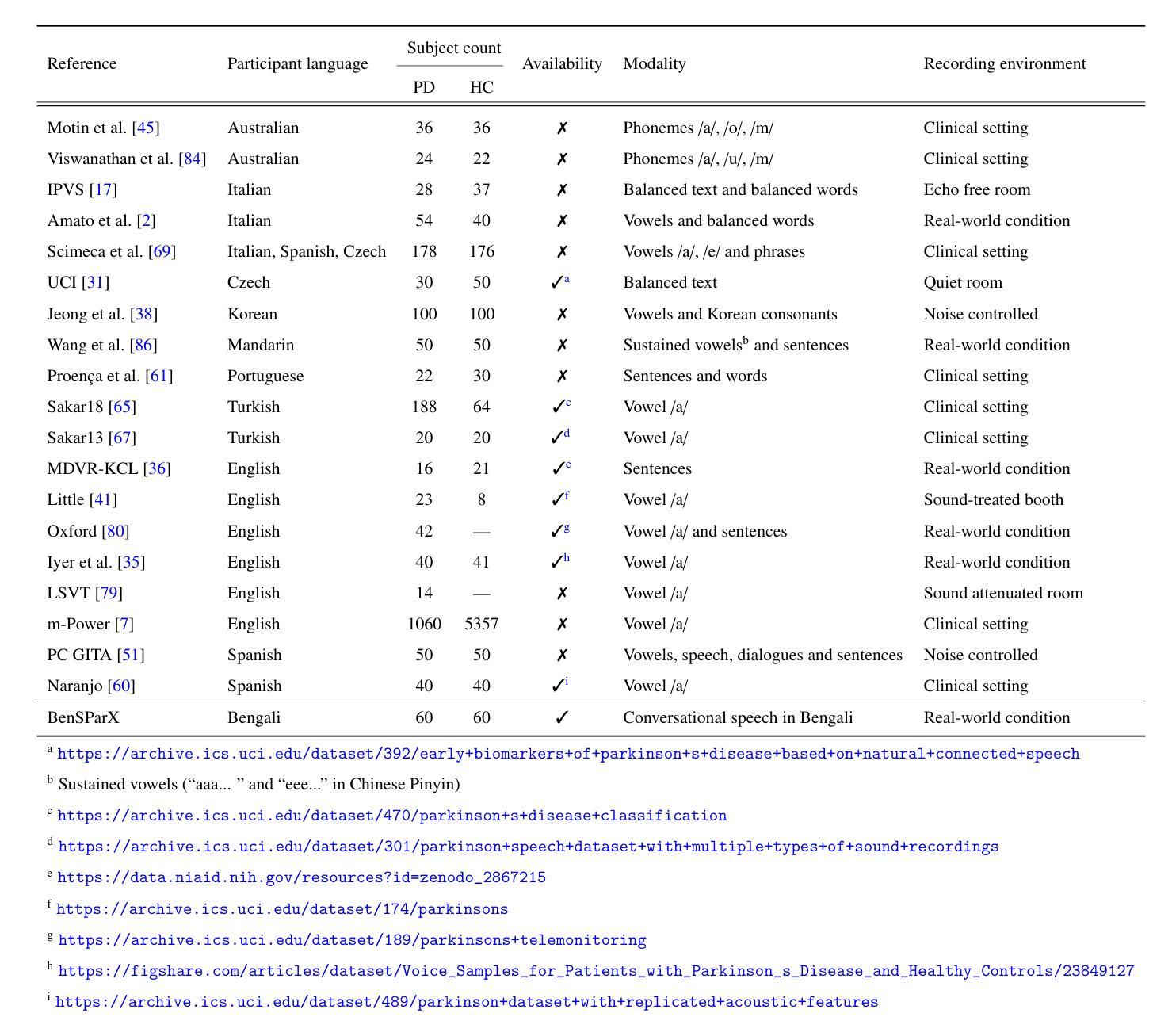
Multimodal Cancer Survival Analysis via Hypergraph Learning with Cross-Modality Rebalance
Authors:Mingcheng Qu, Guang Yang, Donglin Di, Tonghua Su, Yue Gao, Yang Song, Lei Fan
Multimodal pathology-genomic analysis has become increasingly prominent in cancer survival prediction. However, existing studies mainly utilize multi-instance learning to aggregate patch-level features, neglecting the information loss of contextual and hierarchical details within pathology images. Furthermore, the disparity in data granularity and dimensionality between pathology and genomics leads to a significant modality imbalance. The high spatial resolution inherent in pathology data renders it a dominant role while overshadowing genomics in multimodal integration. In this paper, we propose a multimodal survival prediction framework that incorporates hypergraph learning to effectively capture both contextual and hierarchical details from pathology images. Moreover, it employs a modality rebalance mechanism and an interactive alignment fusion strategy to dynamically reweight the contributions of the two modalities, thereby mitigating the pathology-genomics imbalance. Quantitative and qualitative experiments are conducted on five TCGA datasets, demonstrating that our model outperforms advanced methods by over 3.4% in C-Index performance.
多模态病理基因组学分析在癌症生存预测中越来越突出。然而,现有研究主要利用多实例学习来聚合补丁级别的特征,忽视了病理图像中上下文和层次细节的信息丢失。此外,病理和基因组之间数据粒度和维度的差异导致了明显的模态不平衡。病理数据的高空间分辨率使其在多模态融合中占据主导地位,掩盖了基因组学的作用。在本文中,我们提出了一种多模态生存预测框架,它结合了超图学习,可以有效地捕获病理图像中的上下文和层次细节。此外,它采用模态再平衡机制和交互对齐融合策略,动态地重新计算两种模态的贡献,从而缓解病理基因组学的不平衡问题。在五个TCGA数据集上进行的定量和定性实验表明,我们的模型的C-Index性能比先进的方法高出超过3.4%。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF accepted by IJCAI2025 Code: https://github.com/MCPathology/MRePath
Summary
医学图像多模态分析在癌症生存预测中越来越重要。现有研究主要通过多实例学习来聚合补丁级别的特征,但忽略了病理图像中的上下文和层次细节的丢失。同时,病理和基因组数据在粒度和维度上的差异导致模态不平衡。本文提出一种多模态生存预测框架,采用超图学习有效捕捉病理图像中的上下文和层次细节,并引入模态平衡机制和交互对齐融合策略,动态调整两种模态的贡献,缓解病理-基因组不平衡问题。在五个TCGA数据集上的定量和定性实验表明,该模型在C-Index性能上比先进方法高出3.4%以上。
Key Takeaways
- 多模态病理基因组分析在癌症生存预测中的重要性。
- 现有研究通过多实例学习聚合补丁级别特征,但忽略了上下文和层次细节的丢失。
- 病理和基因组数据在粒度和维度上的差异导致模态不平衡。
- 提出的框架采用超图学习捕捉病理图像中的上下文和层次细节。
- 引入模态平衡机制来缓解病理-基因组不平衡问题。
- 定量和定性实验在五个TCGA数据集上验证了模型的有效性。
点此查看论文截图

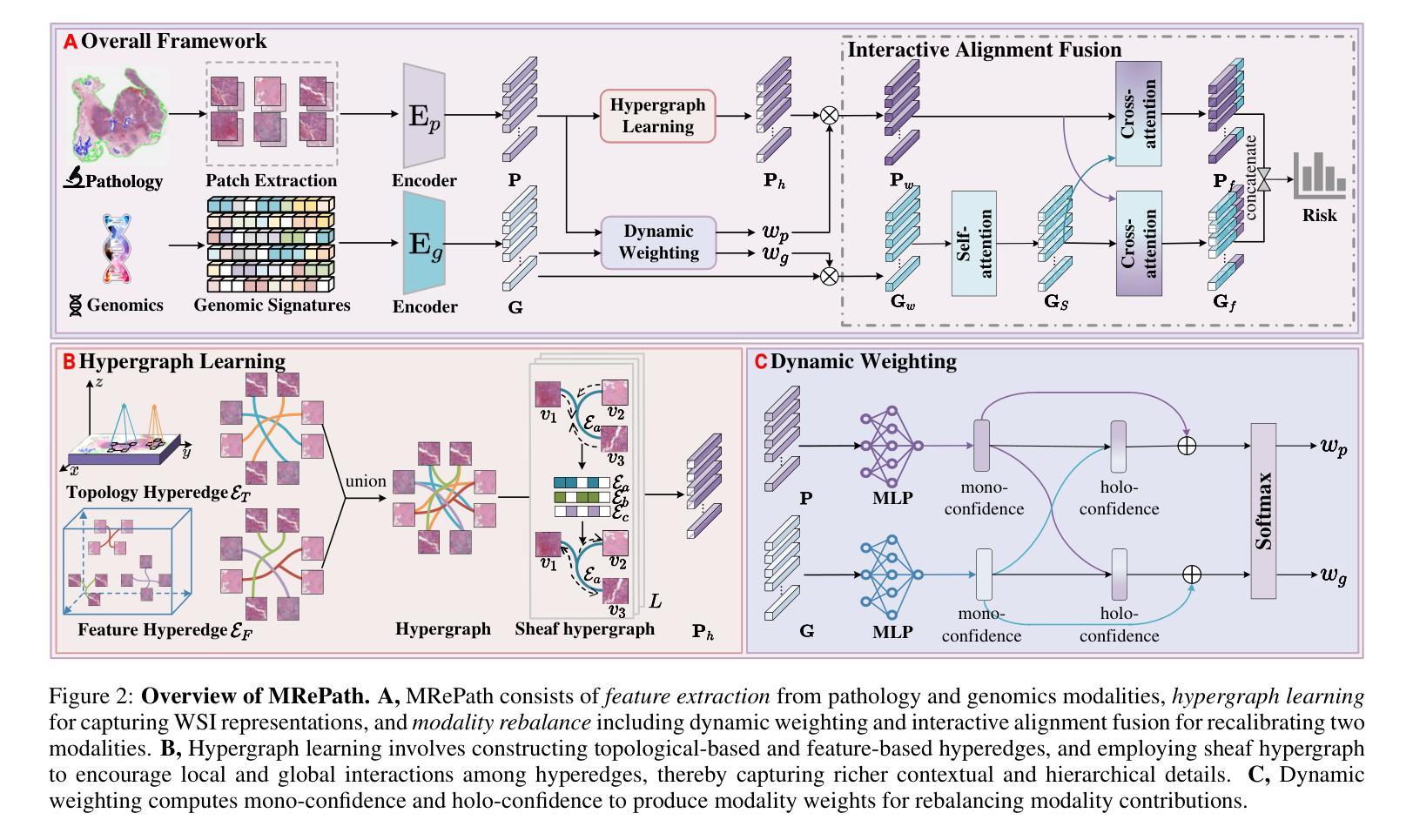
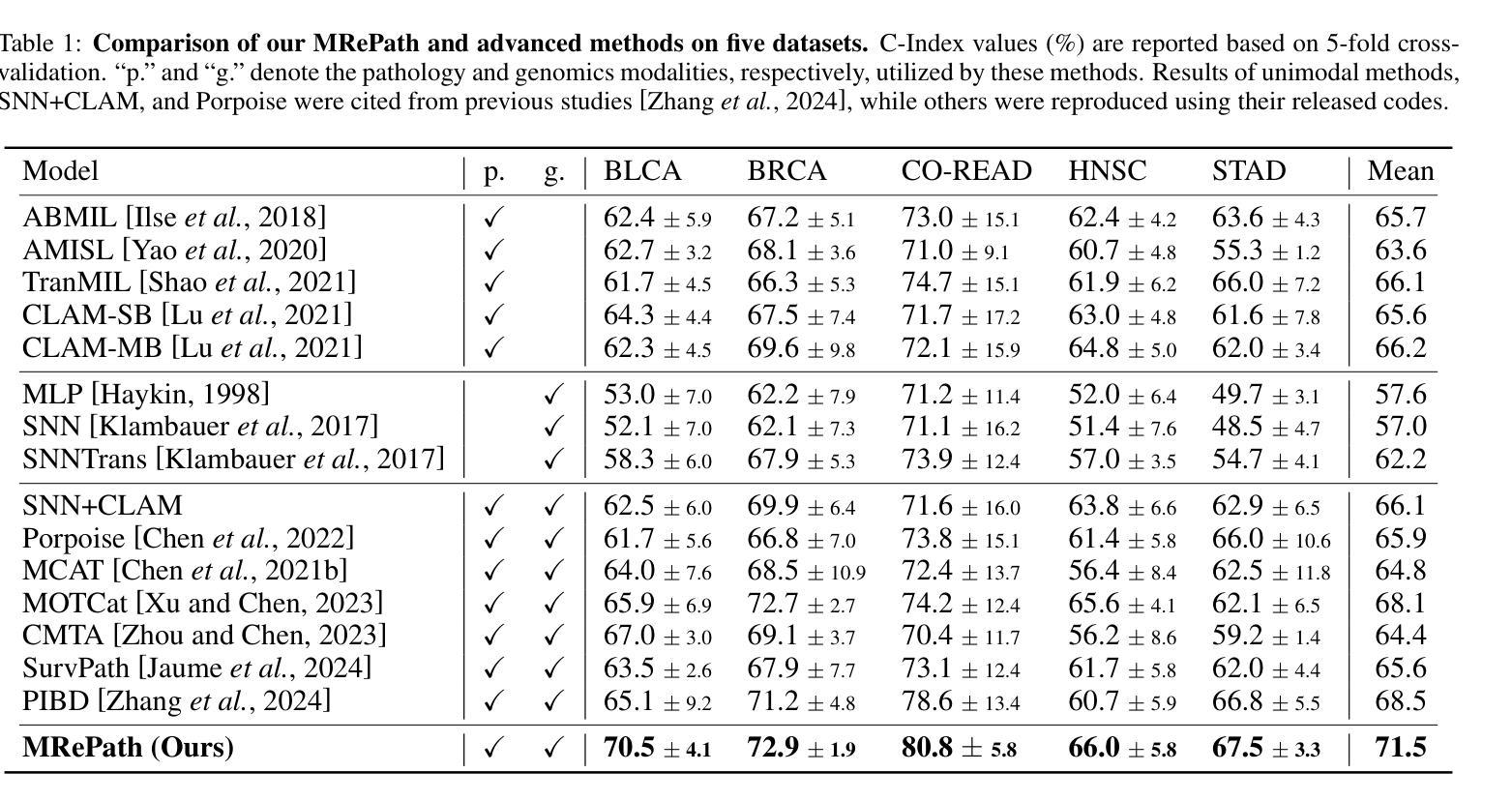
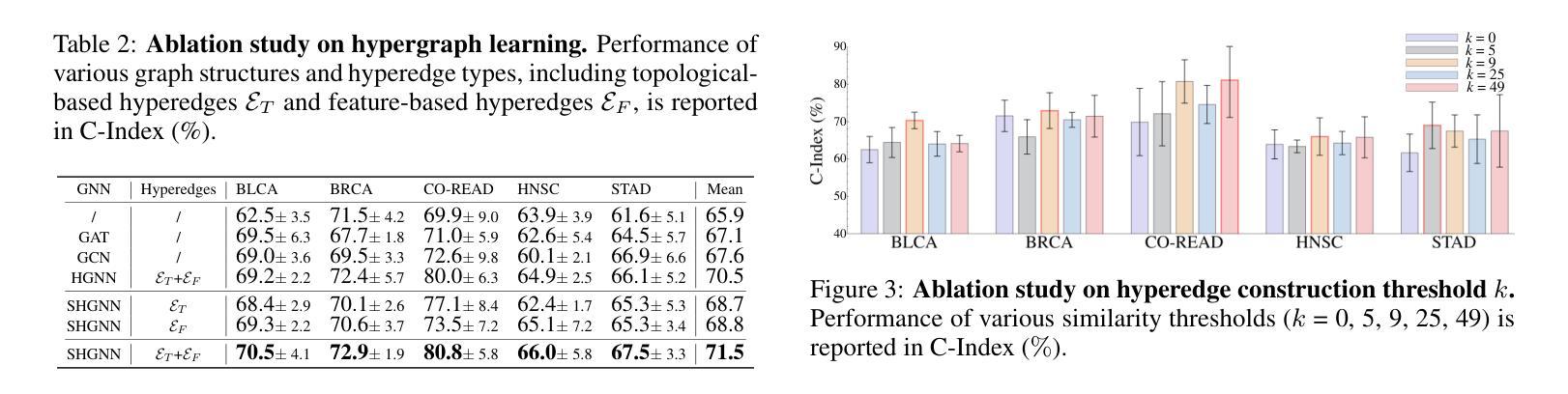
Online Iterative Self-Alignment for Radiology Report Generation
Authors:Ting Xiao, Lei Shi, Yang Zhang, HaoFeng Yang, Zhe Wang, Chenjia Bai
Radiology Report Generation (RRG) is an important research topic for relieving radiologist’ heavy workload. Existing RRG models mainly rely on supervised fine-tuning (SFT) based on different model architectures using data pairs of radiological images and corresponding radiologist-annotated reports. Recent research has shifted focus to post-training improvements, aligning RRG model outputs with human preferences using reinforcement learning (RL). However, the limited data coverage of high-quality annotated data poses risks of overfitting and generalization. This paper proposes a novel Online Iterative Self-Alignment (OISA) method for RRG that consists of four stages: self-generation of diverse data, self-evaluation for multi-objective preference data,self-alignment for multi-objective optimization and self-iteration for further improvement. Our approach allows for generating varied reports tailored to specific clinical objectives, enhancing the overall performance of the RRG model iteratively. Unlike existing methods, our frame-work significantly increases data quality and optimizes performance through iterative multi-objective optimization. Experimental results demonstrate that our method surpasses previous approaches, achieving state-of-the-art performance across multiple evaluation metrics.
医学影像报告生成(RRG)是缓解放射科医生繁重工作量的一项重要研究课题。现有的RRG模型主要依赖于基于不同模型架构的精细调整(SFT),使用放射图像和相应的放射科医生注释报告的数据对进行训练。最近的研究重点转向了对训练后的改进,通过使用强化学习(RL)使RRG模型的输出与人类偏好对齐。然而,高质量标注数据的有限覆盖范围带来了过拟合和泛化的风险。本文提出了一种新型的在线迭代自对齐(OISA)方法用于医学影像报告生成,包括四个阶段:多样化数据的自我生成,多目标偏好数据的自我评价,多目标优化的自我对齐以及进一步的自我迭代改进。我们的方法可以根据特定的临床目标生成多种报告,通过迭代方式提高医学影像报告生成模型的总体性能。不同于现有的方法,我们的框架通过迭代多目标优化显著提高了数据质量并优化了性能。实验结果表明,我们的方法在多个评价指标上超越了以前的方法,达到了最先进的性能水平。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by ACL 2025 Main
Summary
本文提出了一种新型的在线迭代自对齐(OISA)方法用于放射学报告生成(RRG),包括四个阶段:多样数据的自我生成、多目标偏好数据的自我评价、多目标优化的自我对齐以及进一步的自我迭代改进。该方法能够生成符合特定临床目标的多样化报告,通过迭代多目标优化提高RRG模型的总体性能。实验结果表明,该方法超越了以前的方法,在多个评估指标上达到了最先进的性能。
Key Takeaways
- RRG是缓解放射科医生繁重工作量的重要研究话题。
- 现有RRG模型主要依赖于使用图像和相应放射科医生注释报告的数据对进行有监督微调(SFT)。
- 最近的研究集中在训练后的改进上,使用强化学习(RL)使RRG模型输出与人类偏好对齐。
- 高质量注释数据的有限覆盖存在过拟合和泛化风险。
- 提出的OISA方法包括多样数据自我生成、多目标偏好自我评价、多目标优化自我对齐和进一步自我迭代改进四个阶段。
- OISA方法允许生成符合特定临床目标的多样化报告。
点此查看论文截图

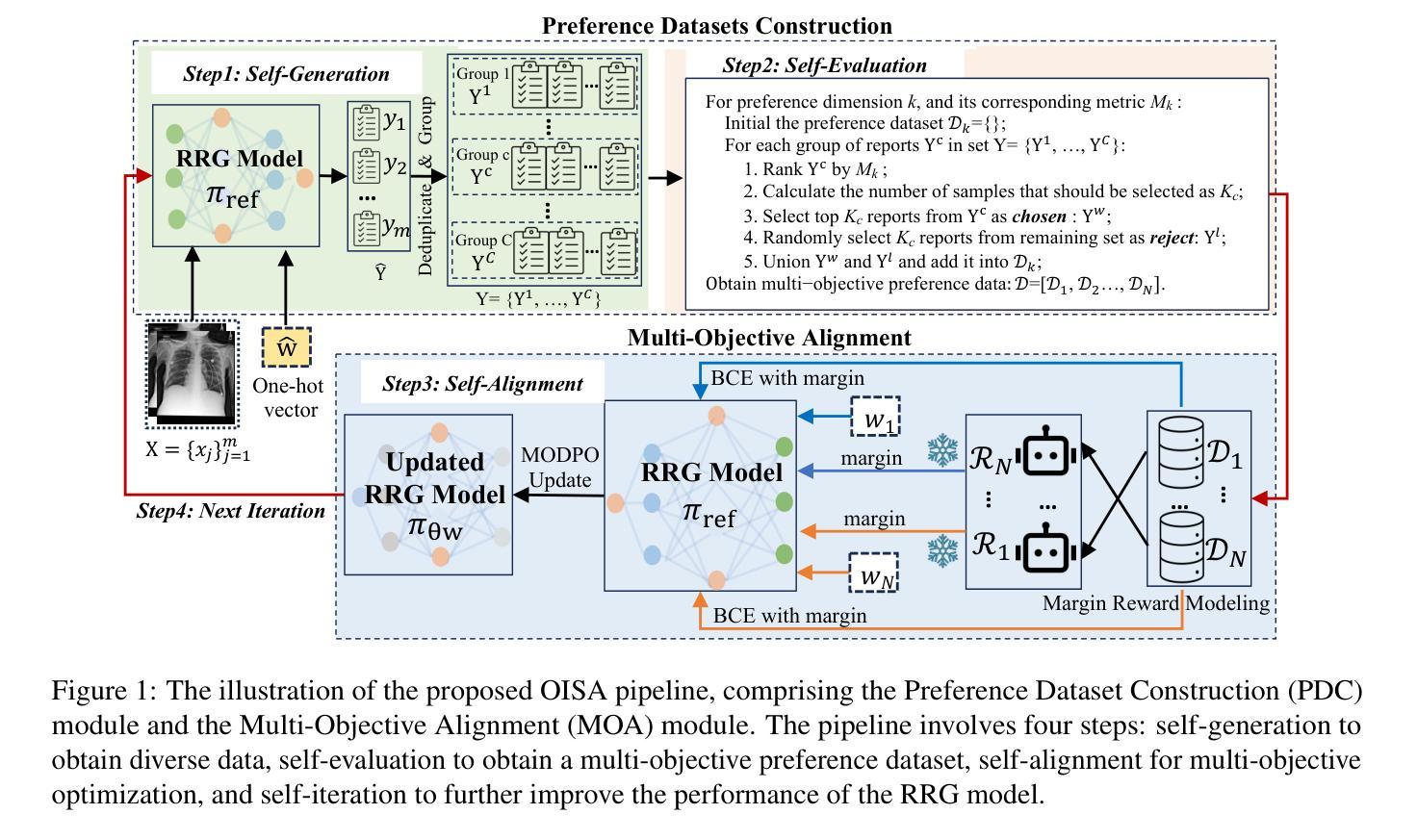
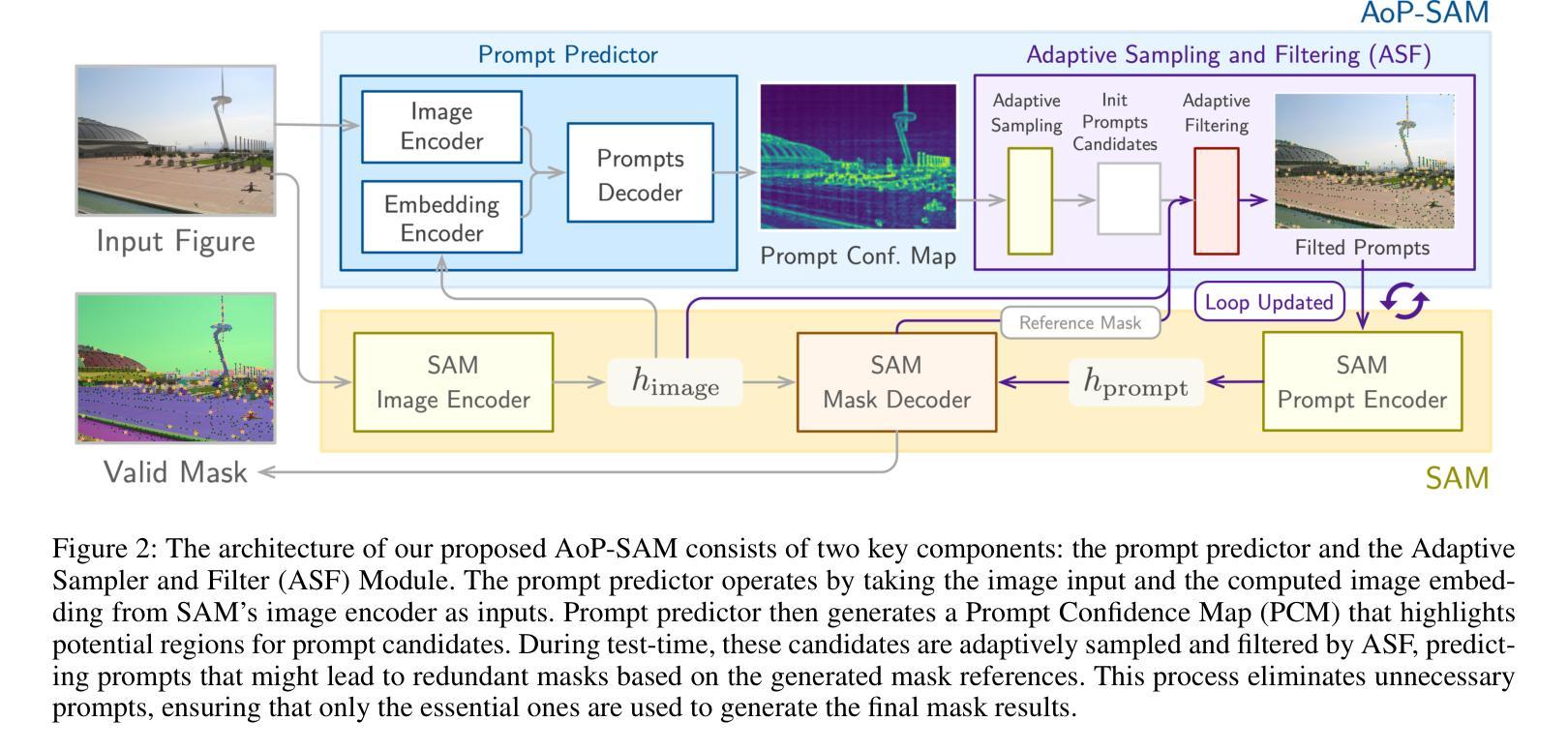
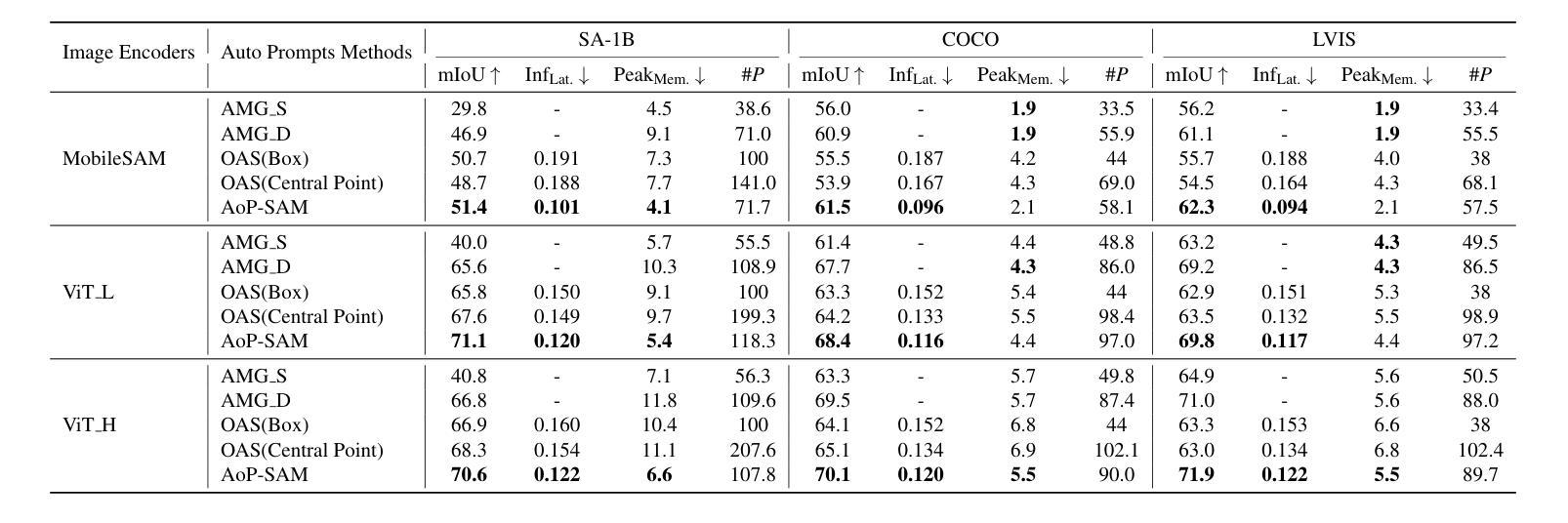
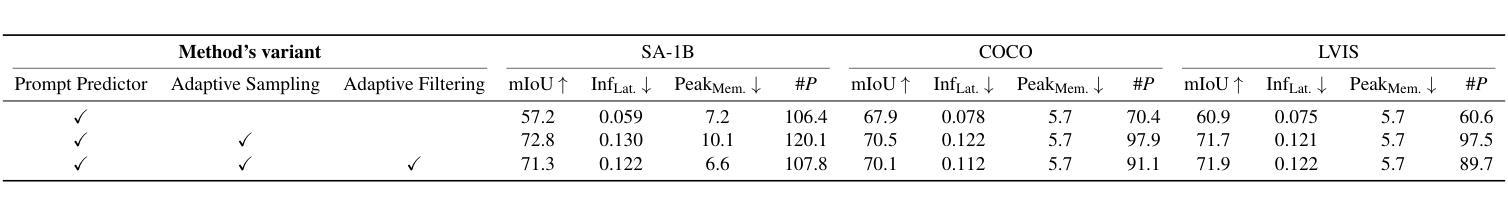
AoP-SAM: Automation of Prompts for Efficient Segmentation
Authors:Yi Chen, Mu-Young Son, Chuanbo Hua, Joo-Young Kim
The Segment Anything Model (SAM) is a powerful foundation model for image segmentation, showing robust zero-shot generalization through prompt engineering. However, relying on manual prompts is impractical for real-world applications, particularly in scenarios where rapid prompt provision and resource efficiency are crucial. In this paper, we propose the Automation of Prompts for SAM (AoP-SAM), a novel approach that learns to generate essential prompts in optimal locations automatically. AoP-SAM enhances SAM’s efficiency and usability by eliminating manual input, making it better suited for real-world tasks. Our approach employs a lightweight yet efficient Prompt Predictor model that detects key entities across images and identifies the optimal regions for placing prompt candidates. This method leverages SAM’s image embeddings, preserving its zero-shot generalization capabilities without requiring fine-tuning. Additionally, we introduce a test-time instance-level Adaptive Sampling and Filtering mechanism that generates prompts in a coarse-to-fine manner. This notably enhances both prompt and mask generation efficiency by reducing computational overhead and minimizing redundant mask refinements. Evaluations of three datasets demonstrate that AoP-SAM substantially improves both prompt generation efficiency and mask generation accuracy, making SAM more effective for automated segmentation tasks.
Segment Anything Model(SAM)是一个强大的图像分割基础模型,通过提示工程展示稳健的零样本泛化能力。然而,依赖手动提示对于实际应用来说并不实用,特别是在需要快速提供提示和资源效率至关重要的场景中。在本文中,我们提出了SAM的自动提示(AoP-SAM),这是一种新颖的方法,可以自动学习在最佳位置生成关键提示。AoP-SAM通过消除手动输入,提高了SAM的效率和可用性,使其更适合实际任务。我们的方法采用轻便高效的提示预测模型,该模型可以检测图像中的关键实体并识别放置提示候选人的最佳区域。这种方法利用SAM的图像嵌入,在不需要进行微调的情况下保留其零样本泛化能力。此外,我们引入了一种测试时实例级自适应采样和过滤机制,以粗细结合的方式生成提示。这显著提高了提示和蒙版生成效率,减少了计算开销和冗余蒙版修正。对三个数据集的评价表明,AoP-SAM大大提高了提示生成效率和蒙版生成准确性,使SAM在自动化分割任务中更加有效。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted at AAAI 2025
Summary
SAM模型通过提示工程技术实现了强大的图像分割功能,但手动提示在实际应用中不实用。本文提出自动化提示方法AoP-SAM,通过自动在最佳位置生成关键提示来增强SAM的效率和实用性。该方法使用轻量级且高效的提示预测器模型,在图像中检测关键实体并确定最佳提示区域。利用SAM的图像嵌入,无需微调即可保留其零样本泛化能力。此外,引入测试时实例级自适应采样和过滤机制,以粗到细的方式生成提示,提高提示和掩膜生成效率。在三个数据集上的评估表明,AoP-SAM显著提高了提示生成效率和掩膜生成准确性。
Key Takeaways
- SAM模型是一个强大的图像分割基础模型,具有零样本泛化能力,通过提示工程技术实现。
- 手动提示在实际应用中不实用,需要自动化提示方法。
- AoP-SAM方法自动在最佳位置生成关键提示,提高SAM的效率和实用性。
- 提示预测器模型用于检测图像中的关键实体并确定最佳提示区域。
- 利用SAM的图像嵌入,无需微调即可保留其零样本泛化能力。
- 引入测试时实例级自适应采样和过滤机制,提高提示和掩膜生成的效率。
点此查看论文截图

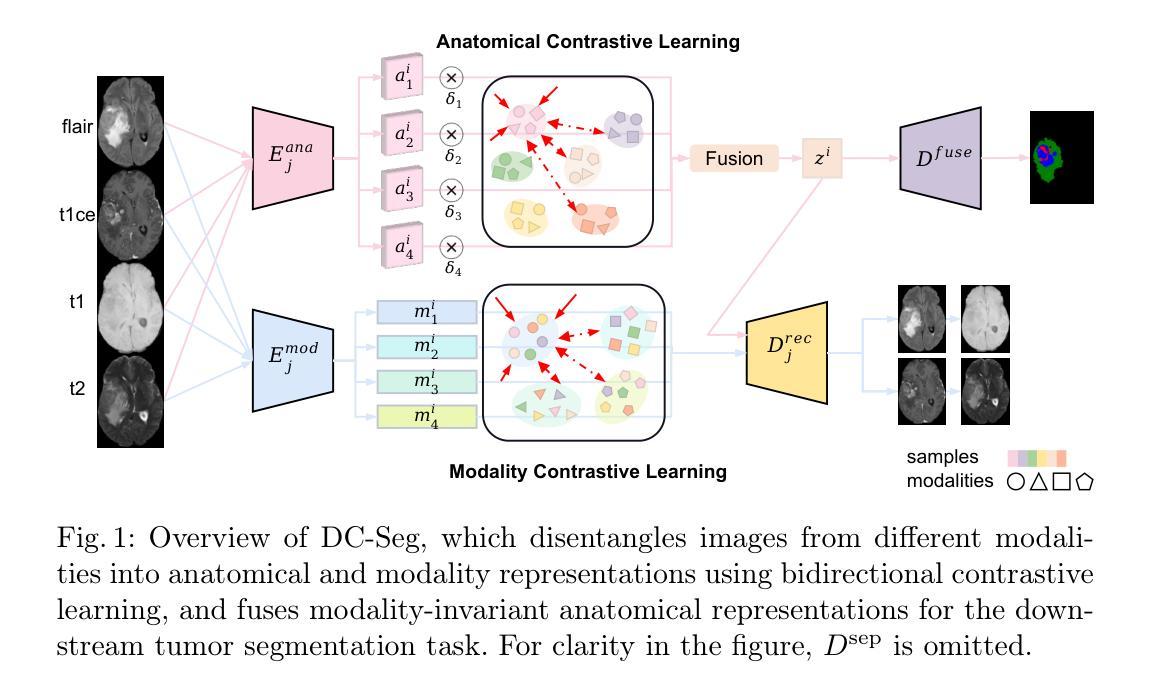
DC-Seg: Disentangled Contrastive Learning for Brain Tumor Segmentation with Missing Modalities
Authors:Haitao Li, Ziyu Li, Yiheng Mao, Zhengyao Ding, Zhengxing Huang
Accurate segmentation of brain images typically requires the integration of complementary information from multiple image modalities. However, clinical data for all modalities may not be available for every patient, creating a significant challenge. To address this, previous studies encode multiple modalities into a shared latent space. While somewhat effective, it remains suboptimal, as each modality contains distinct and valuable information. In this study, we propose DC-Seg (Disentangled Contrastive Learning for Segmentation), a new method that explicitly disentangles images into modality-invariant anatomical representation and modality-specific representation, by using anatomical contrastive learning and modality contrastive learning respectively. This solution improves the separation of anatomical and modality-specific features by considering the modality gaps, leading to more robust representations. Furthermore, we introduce a segmentation-based regularizer that enhances the model’s robustness to missing modalities. Extensive experiments on the BraTS 2020 and a private white matter hyperintensity(WMH) segmentation dataset demonstrate that DC-Seg outperforms state-of-the-art methods in handling incomplete multimodal brain tumor segmentation tasks with varying missing modalities, while also demonstrate strong generalizability in WMH segmentation. The code is available at https://github.com/CuCl-2/DC-Seg.
对脑图像的精确分割通常需要整合来自多种图像模态的互补信息。然而,并非每位患者的所有模态的临床数据都是可用的,这就形成了一个巨大的挑战。为了解决这一问题,之前的研究将多种模态编码到共享潜在空间中。虽然这种做法在某种程度上是有效的,但它仍然不够理想,因为每个模态都包含独特且有价值的信息。在本研究中,我们提出了DC-Seg(用于分割的解纠缠对比学习),这是一种新方法,通过分别使用解剖对比学习和模态对比学习,显式地将图像解纠缠成模态不变的解剖表示和模态特定的表示。此解决方案通过考虑模态间隙,提高了解剖和模态特定特征的分离,从而得到更稳健的表示。此外,我们还引入了一种基于分割的正则化器,增强了模型对缺失模态的鲁棒性。在BraTS 2020和私人白质高信号(WMH)分割数据集上的大量实验表明,DC-Seg在处理具有不同缺失模态的不完整多模态脑肿瘤分割任务方面优于最先进的方法,同时在WMH分割中表现出强大的泛化能力。代码可在https://github.com/CuCl-2/DC-Seg找到。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文提出了一种新的医学图像分割方法DC-Seg,该方法通过解耦对比学习显式地将图像分解为模态不变的结构表示和模态特定的表示,从而改进了结构特征和模态特征的分离。DC-Seg在处理不同缺失模态的不完整多模态脑肿瘤分割任务时表现出卓越的性能,同时在WMH分割中展现出强大的泛化能力。
Key Takeaways
- DC-Seg解决了多模态医学图像分割中可能存在的模态数据不完整的问题。
- 通过解耦对比学习,DC-Seg将图像分解为模态不变的结构表示和模态特定的表示,以改进特征分离。
- DC-Seg考虑了模态差异,增强了结构和模态特征的鲁棒性表示。
- 引入了一个新的分割正则化器,增强了模型对缺失模态的鲁棒性。
- 在BraTS 2020数据集和私有WMH分割数据集上的实验表明,DC-Seg在处理不完整多模态脑肿瘤分割任务时优于现有方法。
- DC-Seg在WMH分割中展现出强大的泛化能力。
点此查看论文截图

Bridging the Inter-Domain Gap through Low-Level Features for Cross-Modal Medical Image Segmentation
Authors:Pengfei Lyu, Pak-Hei Yeung, Xiaosheng Yu, Jing Xia, Jianning Chi, Chengdong Wu, Jagath C. Rajapakse
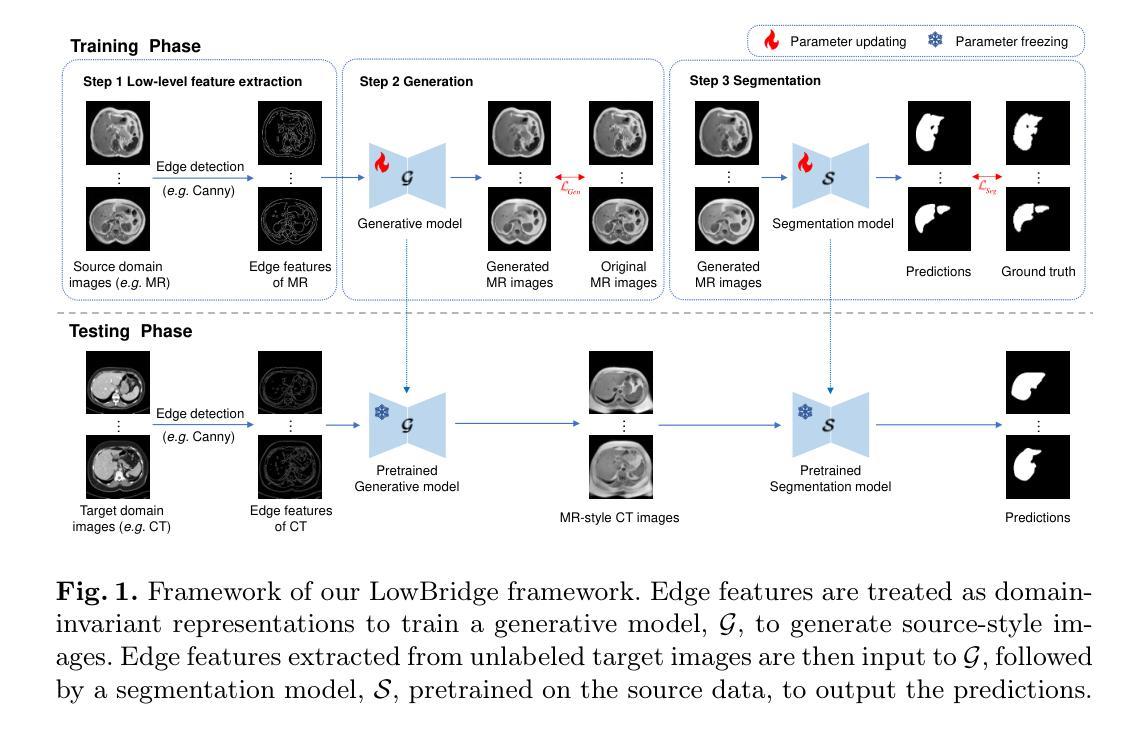
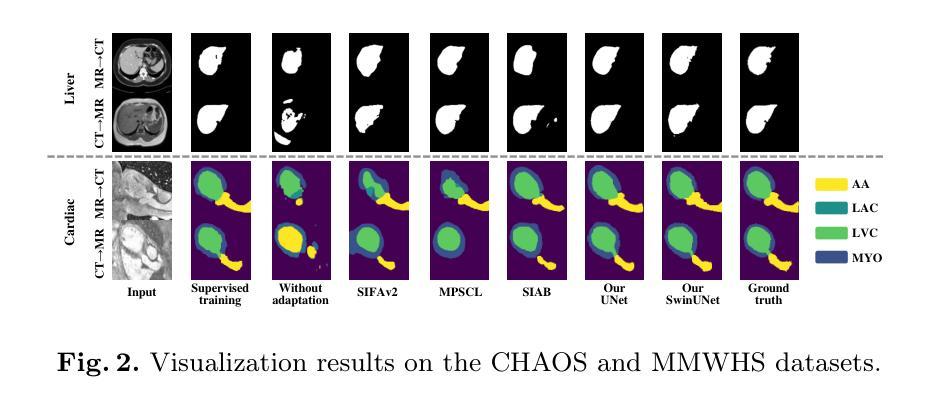
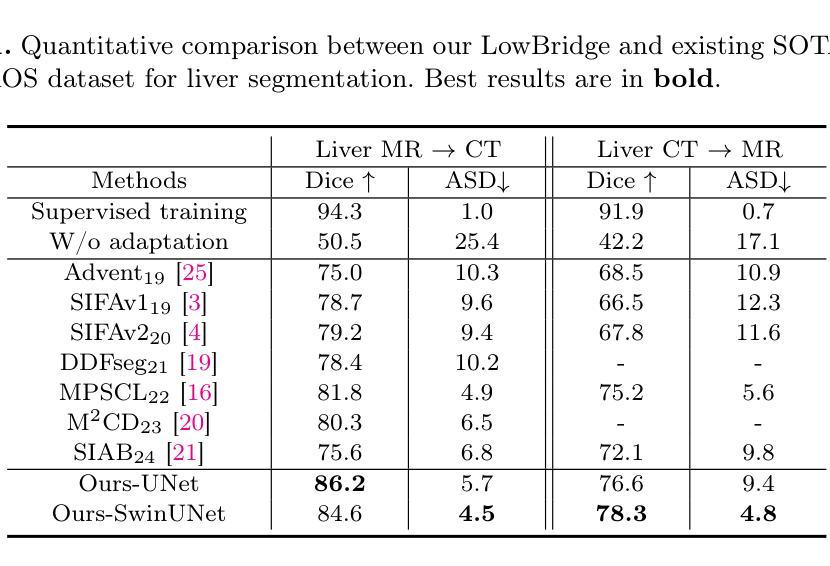
This paper addresses the task of cross-modal medical image segmentation by exploring unsupervised domain adaptation (UDA) approaches. We propose a model-agnostic UDA framework, LowBridge, which builds on a simple observation that cross-modal images share some similar low-level features (e.g., edges) as they are depicting the same structures. Specifically, we first train a generative model to recover the source images from their edge features, followed by training a segmentation model on the generated source images, separately. At test time, edge features from the target images are input to the pretrained generative model to generate source-style target domain images, which are then segmented using the pretrained segmentation network. Despite its simplicity, extensive experiments on various publicly available datasets demonstrate that \proposed achieves state-of-the-art performance, outperforming eleven existing UDA approaches under different settings. Notably, further ablation studies show that \proposed is agnostic to different types of generative and segmentation models, suggesting its potential to be seamlessly plugged with the most advanced models to achieve even more outstanding results in the future. The code is available at https://github.com/JoshuaLPF/LowBridge.
本文探讨了通过探索无监督域自适应(UDA)方法进行跨模态医学图像分割的任务。我们提出了一个模型无关的无监督域自适应框架LowBridge,该框架基于一种简单观察,即跨模态图像由于描述相同结构而共享一些相似的低级特征(例如边缘)。具体来说,我们首先训练一个生成模型,从边缘特征恢复源图像,然后分别在生成的源图像上训练一个分割模型。在测试时,将目标图像的边缘特征输入到预训练的生成模型中,以生成源风格的目标域图像,然后使用预训练的分割网络对其进行分割。尽管其简单性,在多个公开数据集上的大量实验表明,该方法达到了最先进的性能,在不同设置下超越了现有的十一种UDA方法。值得注意的是,进一步的消融研究表明,该方法对不同类型的生成和分割模型具有通用性,这表明它有可能与最先进的模型无缝集成,在未来实现更出色的结果。代码可在[https://github.com/JoshuaLPF/LowBridge找到。]
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 11 pages, 2 figures
Summary
医学图像跨模态分割任务通过探索无监督域自适应(UDA)方法进行研究。提出了一种模型通用的UDA框架LowBridge,它基于跨模态图像共享相同结构的一些相似低级别特征(如边缘)的简单观察。通过训练生成模型来从边缘特征恢复源图像,并单独训练分割模型。测试时,将目标图像的边缘特征输入预训练的生成模型,生成源风格的目标域图像,然后使用预训练的分割网络进行分割。尽管其简单性,在多个公开数据集上的实验表明,该方法达到了最先进的性能,在不同设置下优于十一种现有的UDA方法。代码可在链接找到。
Key Takeaways
- 该论文提出了一种模型通用的无监督域自适应(UDA)框架LowBridge,用于解决医学图像跨模态分割问题。
- LowBridge框架基于跨模态图像共享低级别特征的观察,如边缘。
- 该框架包括训练生成模型以从边缘特征恢复源图像,并单独训练分割模型。
- 在测试阶段,使用目标图像的边缘特征生成源风格的目标域图像,并使用预训练的分割网络进行分割。
- 论文在多个公开数据集上进行了实验,表明该方法达到了最先进的性能。
- 与多种现有的UDA方法相比,该方法在不同设置下具有优越性。
点此查看论文截图