⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-05-22 更新
Personalize Your Gaussian: Consistent 3D Scene Personalization from a Single Image
Authors:Yuxuan Wang, Xuanyu Yi, Qingshan Xu, Yuan Zhou, Long Chen, Hanwang Zhang
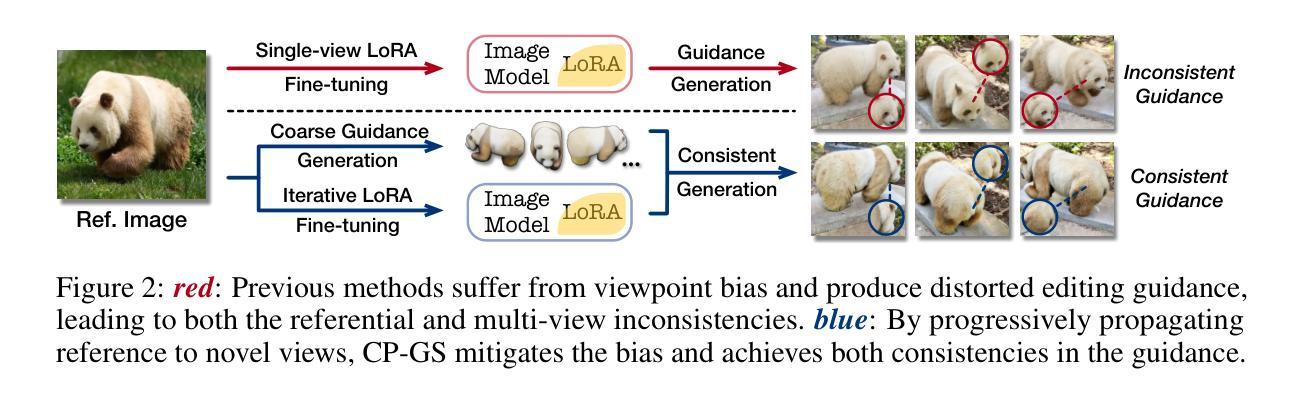
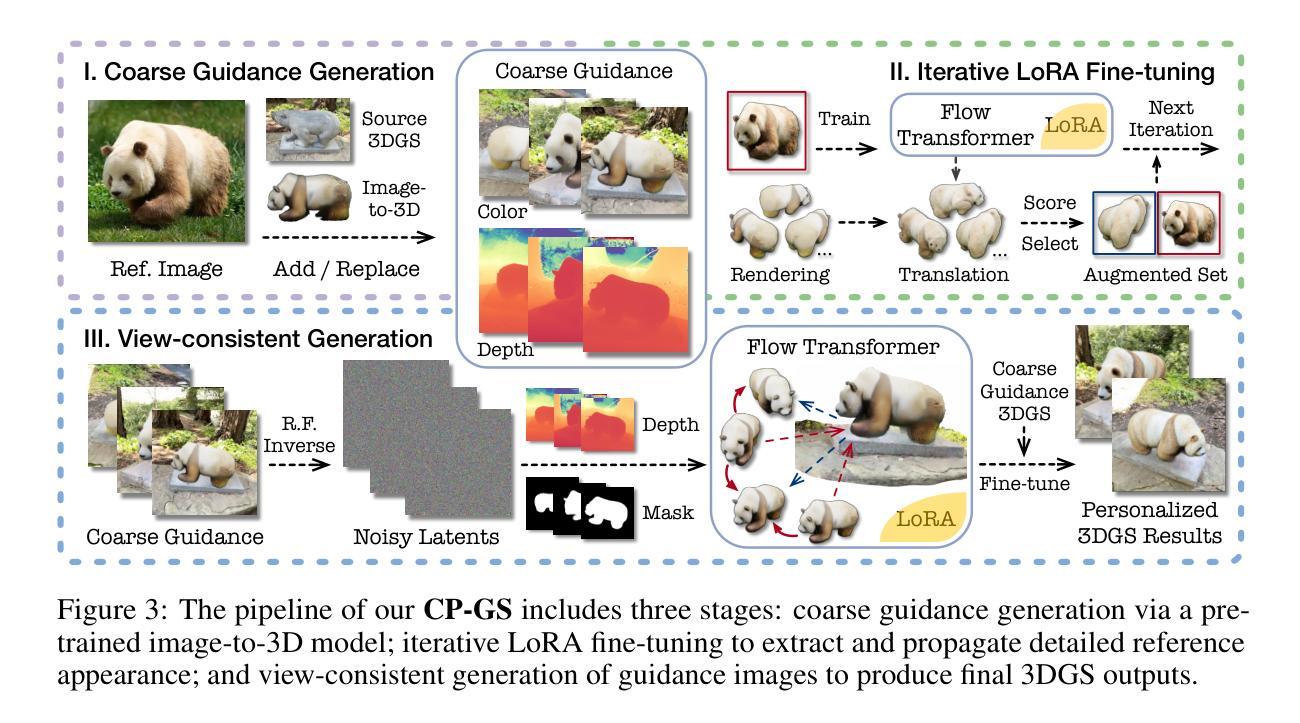
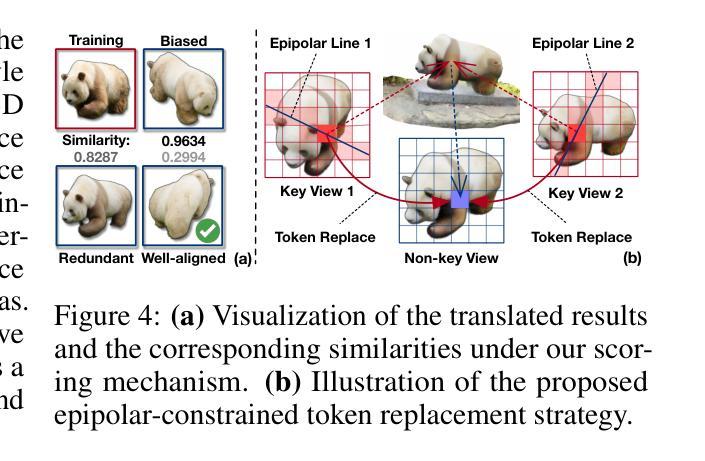
Personalizing 3D scenes from a single reference image enables intuitive user-guided editing, which requires achieving both multi-view consistency across perspectives and referential consistency with the input image. However, these goals are particularly challenging due to the viewpoint bias caused by the limited perspective provided in a single image. Lacking the mechanisms to effectively expand reference information beyond the original view, existing methods of image-conditioned 3DGS personalization often suffer from this viewpoint bias and struggle to produce consistent results. Therefore, in this paper, we present Consistent Personalization for 3D Gaussian Splatting (CP-GS), a framework that progressively propagates the single-view reference appearance to novel perspectives. In particular, CP-GS integrates pre-trained image-to-3D generation and iterative LoRA fine-tuning to extract and extend the reference appearance, and finally produces faithful multi-view guidance images and the personalized 3DGS outputs through a view-consistent generation process guided by geometric cues. Extensive experiments on real-world scenes show that our CP-GS effectively mitigates the viewpoint bias, achieving high-quality personalization that significantly outperforms existing methods. The code will be released at https://github.com/Yuxuan-W/CP-GS.
通过单一参考图像个性化3D场景,可实现直观的用户引导编辑,这要求在不同视角之间实现多视图一致性以及与输入图像的参照一致性。然而,由于单一图像提供的有限视角所导致的视点偏见,这些目标特别具有挑战性。缺乏在原始视图之外有效扩展参考信息的机制,现有的图像条件3DGS个性化方法通常受到这种视点偏见的影响,难以产生一致的结果。因此,本文提出了面向3D高斯拼贴的一致个性化(CP-GS)框架,该框架逐步传播单视图参考外观到新的视角。特别是,CP-GS集成了预训练的图像到3D生成和迭代LoRA微调,以提取和扩展参考外观,并最终通过几何线索引导的多视图一致性生成过程,生成忠实的多视图指导图像和个性化的3DGS输出。在真实场景上的大量实验表明,我们的CP-GS有效地减轻了视点偏见,实现了高质量的个性化,显著优于现有方法。代码将在https://github.com/Yuxuan-W/CP-GS发布。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 9 pages
Summary
本文提出一种名为CP-GS的框架,用于解决在单视角参考图像下的个性化三维场景建模问题。该框架通过逐步传播单视角参考外观到新的视角,实现了多视角一致性及个人化外观的保持。实验证明,CP-GS能有效缓解视角偏差问题,实现高质量的个人化三维建模,显著优于现有方法。
Key Takeaways
- 个人化三维场景建模需要从单视角参考图像实现用户引导的编辑,需要达到多视角一致性和与输入图像的参照一致性。
- 现有图像条件的三维场景生成方法因单一视角导致的视角偏差问题,难以实现一致性结果。
- CP-GS框架通过逐步传播单视角参考外观到新的视角,解决了视角偏差问题。
- CP-GS集成了预训练图像到三维生成的转换和迭代LoRA微调,以提取和扩展参考外观。
- CP-GS通过几何线索引导的一致视图生成过程,生成忠实的多视角指导图像和个人化的三维场景。
- 在真实场景的大量实验表明,CP-GS方法实现了高质量的个人化三维建模,显著优于现有方法。
点此查看论文截图

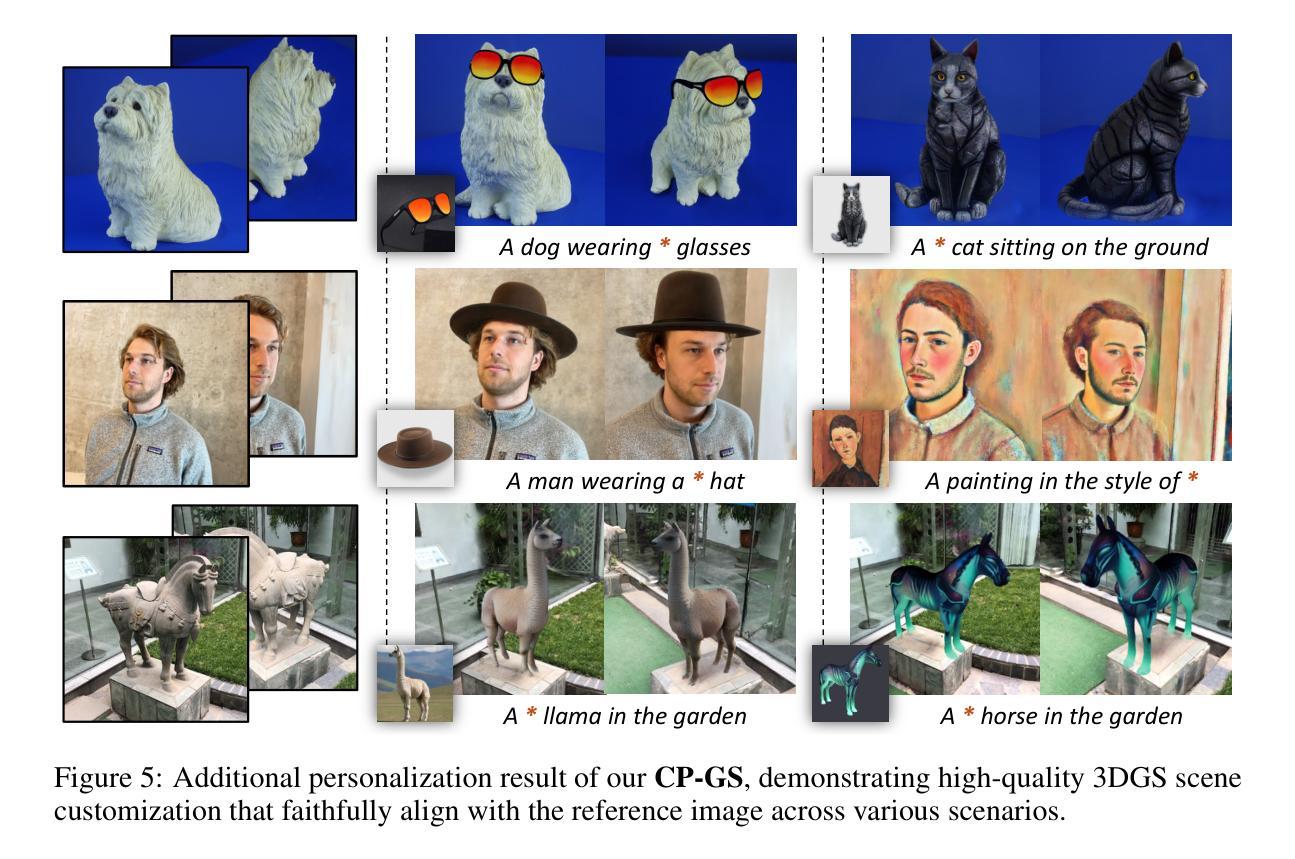
MGStream: Motion-aware 3D Gaussian for Streamable Dynamic Scene Reconstruction
Authors:Zhenyu Bao, Qing Li, Guibiao Liao, Zhongyuan Zhao, Kanglin Liu
3D Gaussian Splatting (3DGS) has gained significant attention in streamable dynamic novel view synthesis (DNVS) for its photorealistic rendering capability and computational efficiency. Despite much progress in improving rendering quality and optimization strategies, 3DGS-based streamable dynamic scene reconstruction still suffers from flickering artifacts and storage inefficiency, and struggles to model the emerging objects. To tackle this, we introduce MGStream which employs the motion-related 3D Gaussians (3DGs) to reconstruct the dynamic and the vanilla 3DGs for the static. The motion-related 3DGs are implemented according to the motion mask and the clustering-based convex hull algorithm. The rigid deformation is applied to the motion-related 3DGs for modeling the dynamic, and the attention-based optimization on the motion-related 3DGs enables the reconstruction of the emerging objects. As the deformation and optimization are only conducted on the motion-related 3DGs, MGStream avoids flickering artifacts and improves the storage efficiency. Extensive experiments on real-world datasets N3DV and MeetRoom demonstrate that MGStream surpasses existing streaming 3DGS-based approaches in terms of rendering quality, training/storage efficiency and temporal consistency. Our code is available at: https://github.com/pcl3dv/MGStream.
3D高斯扩展(3DGS)因其逼真的渲染能力和计算效率,在流式动态新视图合成(DNVS)中受到了广泛关注。尽管在提高渲染质量和优化策略方面取得了很大进展,但基于3DGS的流式动态场景重建仍然受到闪烁伪影和存储效率低下的困扰,并且在建模新生对象时面临困难。为了解决这个问题,我们引入了MGStream,它采用与运动相关的3D高斯(3DG)来重建动态场景,并采用普通的3DG来重建静态场景。与运动相关的3DG是根据运动掩码和基于聚类的凸包算法实现的。对与运动相关的3DG应用刚性变形来进行动态建模,对与运动相关的3DG进行基于注意力的优化,以实现新生对象的重建。由于变形和优化只在与运动相关的3DG上进行,MGStream避免了闪烁伪影,提高了存储效率。在真实世界数据集N3DV和MeetRoom上的大量实验表明,MGStream在渲染质量、训练/存储效率和时间一致性方面超越了现有的基于流式传输的3DGS方法。我们的代码可在以下网址找到:https://github.com/pcl3dv/MGStream。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
3DGS在流式动态场景重建领域备受关注,但仍存在闪烁伪影、存储效率低和难以建模新生物体等问题。为解决这些问题,MGStream采用运动相关的三维高斯(motion-related 3DGs)重建动态场景,静态场景使用普通三维高斯(vanilla 3DGs)。通过运动掩码和基于聚类的凸包算法实现运动相关三维高斯。对运动相关三维高斯进行刚性变形建模,采用基于注意力的优化技术重建新生物体。在真实世界数据集上的实验证明,MGStream在提高渲染质量、训练效率、存储效率和时间连贯性的同时,克服了现有流式传输3DGS方法存在的问题。
Key Takeaways
- MGStream通过使用不同的高斯处理方法来重建动态和静态场景。运动相关的高斯(motion-related 3DGs)用于动态场景的重建,而普通的高斯(vanilla 3DGs)用于静态场景的重建。
- MGStream引入基于运动掩码和聚类算法来实现运动相关的高斯表示方法。这使得它在建模动态场景时具有更好的适应性。
- 通过应用刚性变形和基于注意力的优化技术,MGStream可以有效地重建新生物体。这种策略增强了模型对于场景中的新元素的捕捉能力。
- MGStream能够解决现有的流式传输3DGS方法在渲染质量、训练效率、存储效率和时间连贯性等方面存在的问题。它避免了闪烁伪影并提高了存储效率。
点此查看论文截图

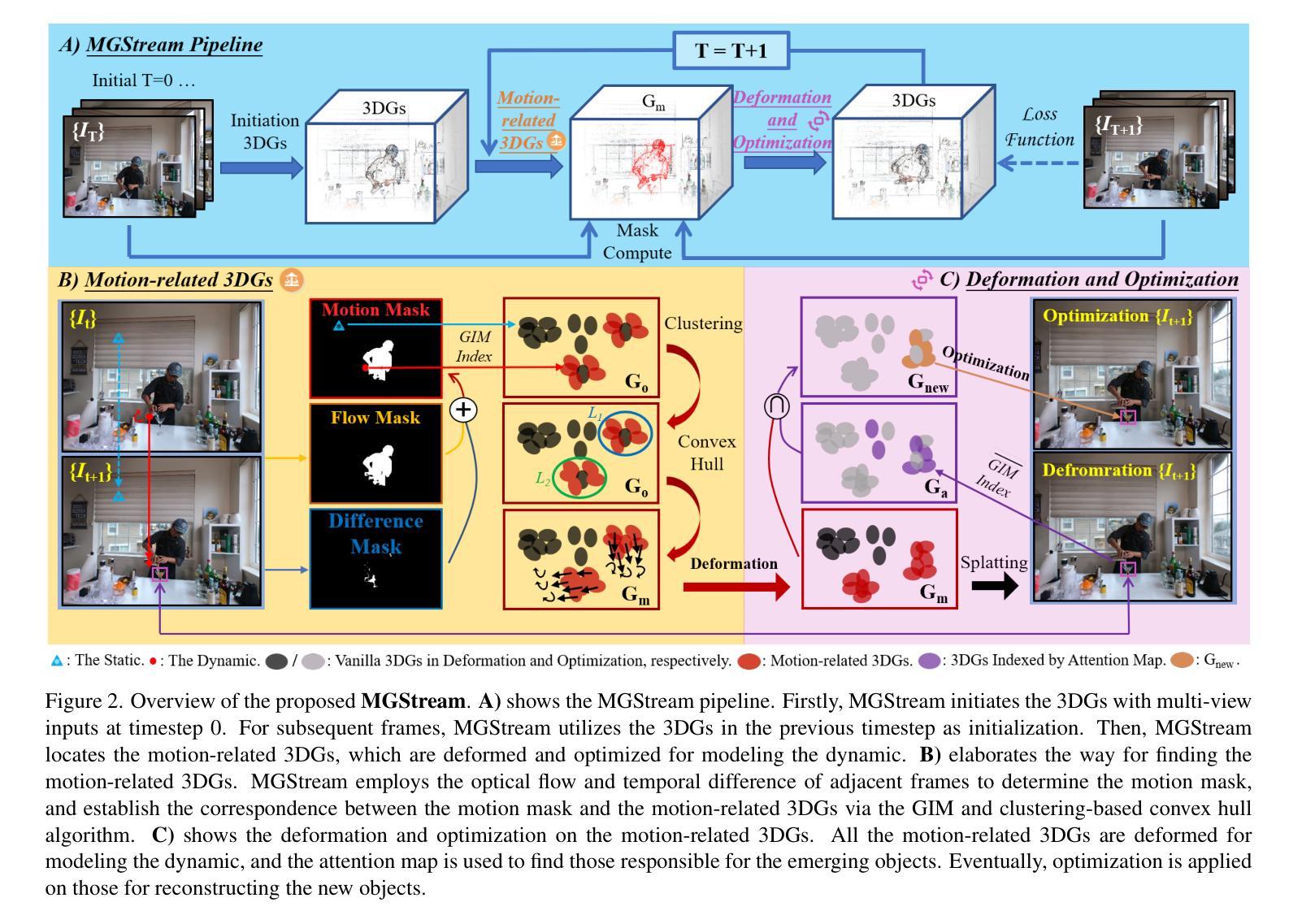



Recollection from Pensieve: Novel View Synthesis via Learning from Uncalibrated Videos
Authors:Ruoyu Wang, Yi Ma, Shenghua Gao
Currently almost all state-of-the-art novel view synthesis and reconstruction models rely on calibrated cameras or additional geometric priors for training. These prerequisites significantly limit their applicability to massive uncalibrated data. To alleviate this requirement and unlock the potential for self-supervised training on large-scale uncalibrated videos, we propose a novel two-stage strategy to train a view synthesis model from only raw video frames or multi-view images, without providing camera parameters or other priors. In the first stage, we learn to reconstruct the scene implicitly in a latent space without relying on any explicit 3D representation. Specifically, we predict per-frame latent camera and scene context features, and employ a view synthesis model as a proxy for explicit rendering. This pretraining stage substantially reduces the optimization complexity and encourages the network to learn the underlying 3D consistency in a self-supervised manner. The learned latent camera and implicit scene representation have a large gap compared with the real 3D world. To reduce this gap, we introduce the second stage training by explicitly predicting 3D Gaussian primitives. We additionally apply explicit Gaussian Splatting rendering loss and depth projection loss to align the learned latent representations with physically grounded 3D geometry. In this way, Stage 1 provides a strong initialization and Stage 2 enforces 3D consistency - the two stages are complementary and mutually beneficial. Extensive experiments demonstrate the effectiveness of our approach, achieving high-quality novel view synthesis and accurate camera pose estimation, compared to methods that employ supervision with calibration, pose, or depth information. The code is available at https://github.com/Dwawayu/Pensieve.
当前,几乎所有最先进的全新视角合成和重建模型都依赖于校准过的相机或额外的几何先验知识来进行训练。这些先决条件极大地限制了它们对大量未校准数据的适用性。为了缓解这一要求,并解锁在大型未校准视频上进行自我监督训练的潜力,我们提出了一种新颖的两阶段策略,仅从原始视频帧或多视角图像训练视角合成模型,而无需提供相机参数或其他先验知识。在第一阶段,我们学习在潜在空间中隐式重建场景,而不依赖于任何明确的3D表示。具体来说,我们预测每帧的潜在相机和场景上下文特征,并采用视角合成模型作为明确渲染的代理。这种预训练阶段大大降低了优化复杂度,并鼓励网络以自我监督的方式学习潜在的3D一致性。学到的潜在相机和隐式场景表示与真实的3D世界之间存在很大差距。为了减少这种差距,我们引入了第二阶段的训练,通过明确预测3D高斯基本体来实现。我们还应用了显式的高斯平铺渲染损失和深度投影损失,以使学到的潜在表示与物理基础的3D几何结构对齐。通过这种方式,第一阶段提供了强大的初始化,第二阶段强制实施3D一致性——两个阶段是互补的,相互受益。大量实验证明了我们的方法的有效性,与采用校准、姿态或深度信息进行监督的方法相比,我们实现了高质量的新视角合成和准确的相机姿态估计。代码可在https://github.com/Dwawayu/Pensieve获得。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 13 pages, 4 figures
Summary
本文提出一种新颖的两阶段策略,用于从原始视频帧或多视角图像训练视角合成模型,无需相机参数或其他先验知识。第一阶段学习在潜在空间中隐式重建场景,预测每帧的潜在相机和场景上下文特征,并采用视角合成模型作为显式渲染的代理。此预训练阶段降低了优化复杂度,鼓励网络以自监督的方式学习潜在的3D一致性。第二阶段通过显式预测3D高斯基本体来缩小学习到的潜在相机和隐式场景表示与真实3D世界之间的差距。通过显式高斯溅射渲染损失和深度投影损失来对齐学到的潜在表示与物理基础的3D几何结构。两个阶段互为补充,相互受益,实现高质量的新视角合成和准确的相机姿态估计。
Key Takeaways
- 提出一种新颖的两阶段策略,用于从原始视频或多视角图像训练视角合成模型,无需相机参数或其他先验知识。
- 第一阶段学习在潜在空间中隐式重建场景,预测每帧的潜在相机和场景上下文特征。
- 预训练阶段采用视角合成模型作为显式渲染的代理,降低优化复杂度并学习潜在的3D一致性。
- 第二阶段通过显式预测3D高斯基本体来缩小与真实3D世界的差距。
- 引入显式高斯溅射渲染损失和深度投影损失,对齐学到的潜在表示与物理基础的3D几何结构。
- 两阶段策略互为补充,相互受益。
点此查看论文截图

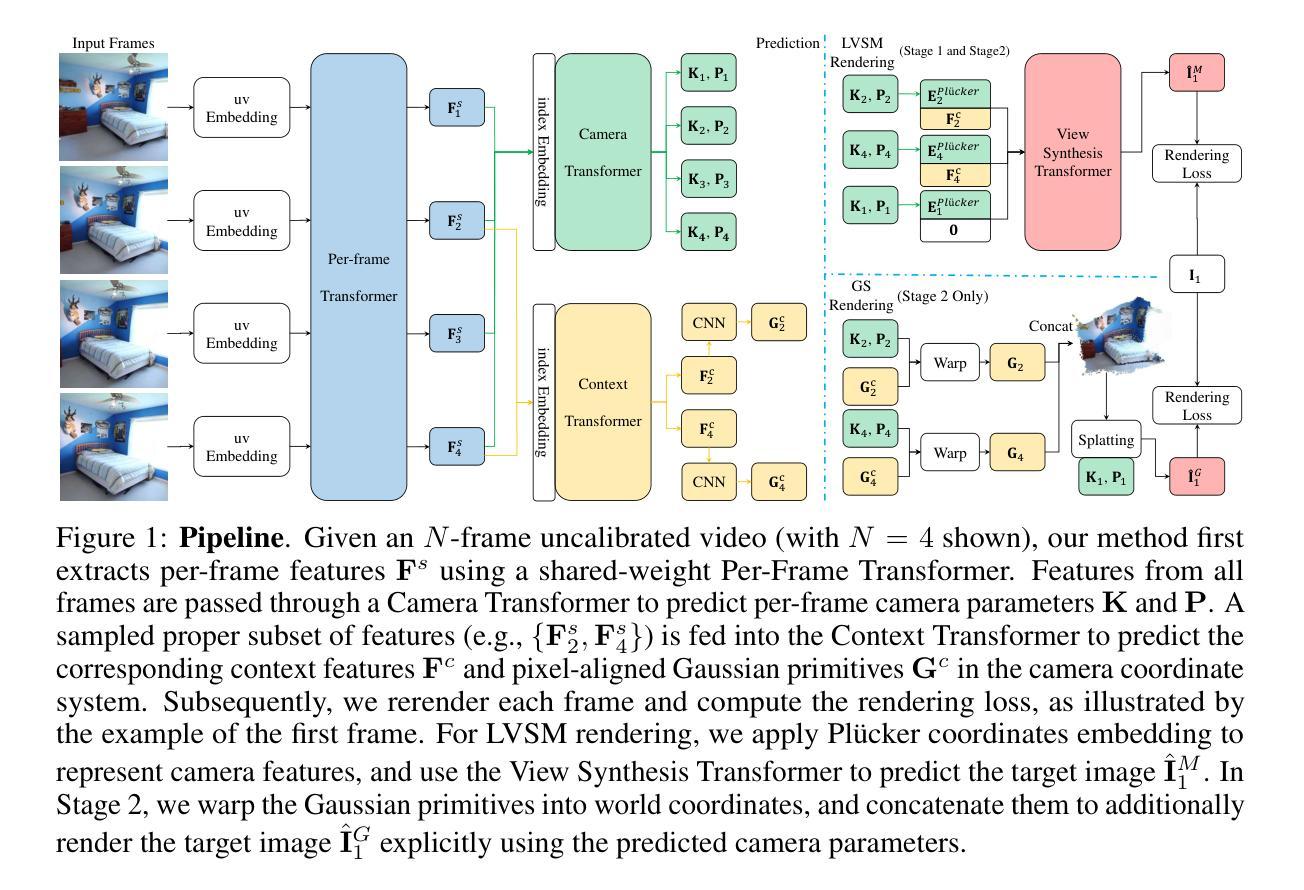
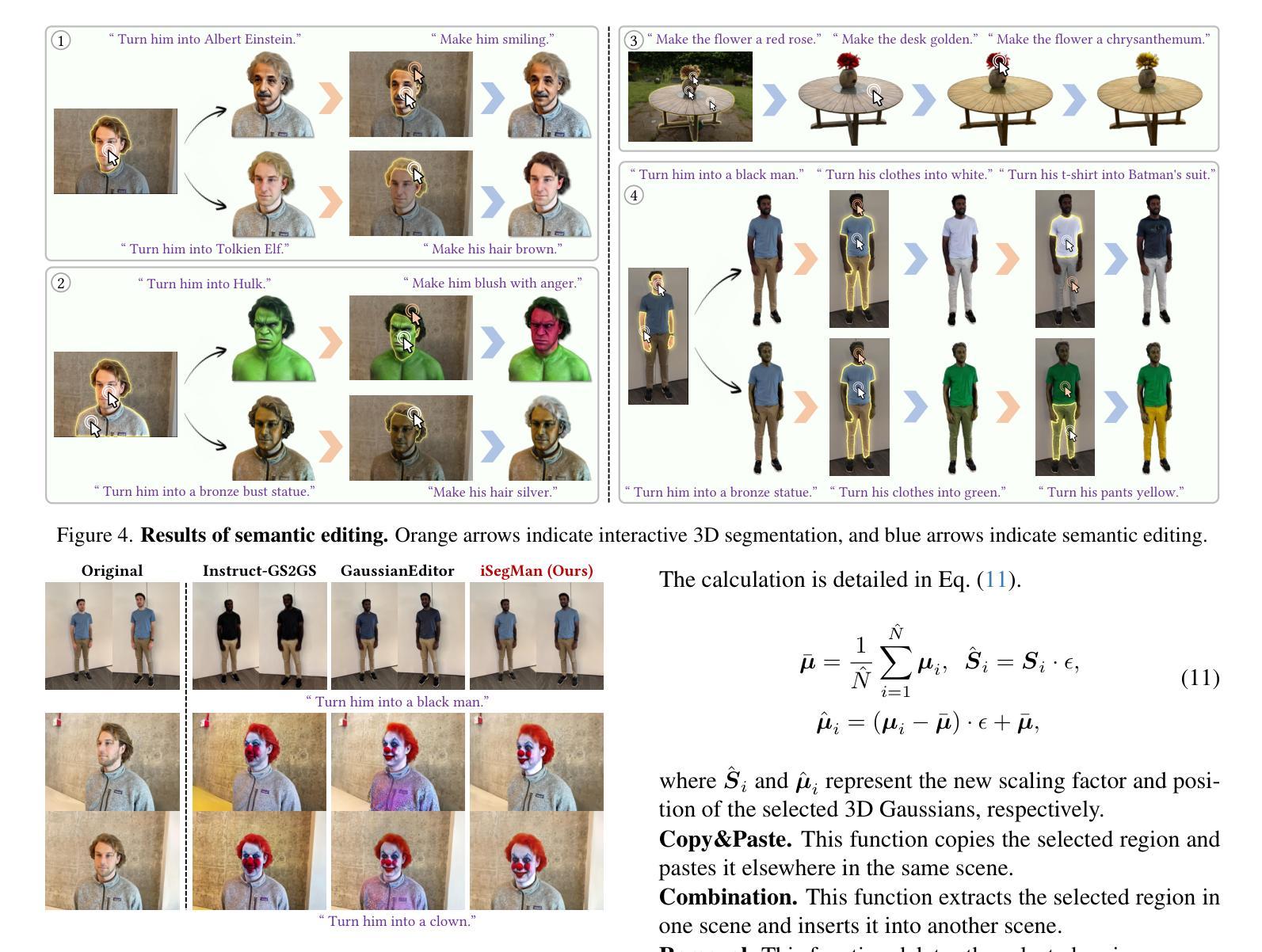
iSegMan: Interactive Segment-and-Manipulate 3D Gaussians
Authors:Yian Zhao, Wanshi Xu, Ruochong Zheng, Pengchong Qiao, Chang Liu, Jie Chen
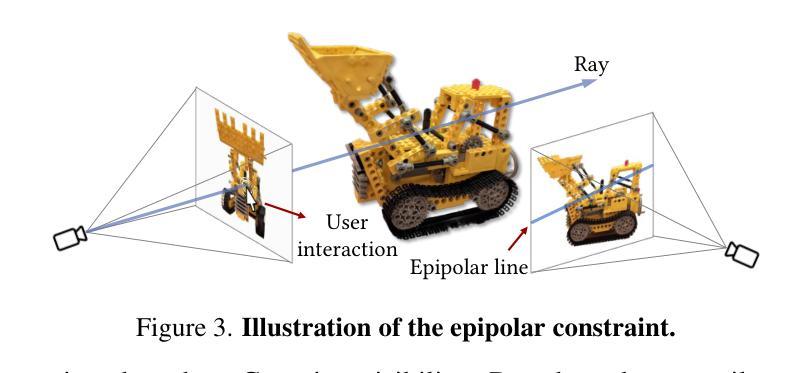
The efficient rendering and explicit nature of 3DGS promote the advancement of 3D scene manipulation. However, existing methods typically encounter challenges in controlling the manipulation region and are unable to furnish the user with interactive feedback, which inevitably leads to unexpected results. Intuitively, incorporating interactive 3D segmentation tools can compensate for this deficiency. Nevertheless, existing segmentation frameworks impose a pre-processing step of scene-specific parameter training, which limits the efficiency and flexibility of scene manipulation. To deliver a 3D region control module that is well-suited for scene manipulation with reliable efficiency, we propose interactive Segment-and-Manipulate 3D Gaussians (iSegMan), an interactive segmentation and manipulation framework that only requires simple 2D user interactions in any view. To propagate user interactions to other views, we propose Epipolar-guided Interaction Propagation (EIP), which innovatively exploits epipolar constraint for efficient and robust interaction matching. To avoid scene-specific training to maintain efficiency, we further propose the novel Visibility-based Gaussian Voting (VGV), which obtains 2D segmentations from SAM and models the region extraction as a voting game between 2D Pixels and 3D Gaussians based on Gaussian visibility. Taking advantage of the efficient and precise region control of EIP and VGV, we put forth a Manipulation Toolbox to implement various functions on selected regions, enhancing the controllability, flexibility and practicality of scene manipulation. Extensive results on 3D scene manipulation and segmentation tasks fully demonstrate the significant advantages of iSegMan. Project page is available at https://zhao-yian.github.io/iSegMan.
3DGS的高效渲染和明确性质促进了3D场景操作的发展。然而,现有方法通常在控制操作区域方面遇到挑战,并且无法为用户提供交互式反馈,这不可避免地导致意外结果。直观地看,加入交互式3D分割工具可以弥补这一缺陷。然而,现有的分割框架需要进行场景特定参数的预处理训练,这限制了场景操作的效率和灵活性。为了提供一个适合场景操作的可靠高效的3D区域控制模块,我们提出了交互式分割和操作3D高斯(iSegMan),这是一个交互式分割和操作框架,它只需要在任何视图中进行简单的2D用户交互。为了将用户交互传播到其他视图,我们提出了基于极点的交互传播(EIP),该创新性地利用极点约束来进行高效且稳定的交互匹配。为了避免特定场景的训练以维持效率,我们进一步提出了基于可见性的高斯投票(VGV)新方法,从SAM获取2D分割,并将区域提取建模为基于高斯可见性的2D像素和3D高斯之间的投票游戏。利用EIP和VGV的高效精确区域控制,我们推出了一款操作工具箱,可以在选定区域上实现各种功能,增强了场景操作的操控性、灵活性和实用性。在3D场景操作和分割任务上的大量结果充分证明了iSegMan的显著优势。项目页面可在https://zhao-yian.github.io/iSegMan访问。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF CVPR 2025
Summary
3DGS的高效渲染和明确性质推动了3D场景操作的发展。但现有方法控制操作区域时面临挑战,无法为用户提供交互反馈,导致意料之外的结果。通过结合直觉性的互动三维分割工具可以弥补这一缺陷。为提供适合场景操作的可靠高效的三维区域控制模块,提出了交互式分段与操作三维高斯(iSegMan)框架,只需在任何视图进行简单的二维用户交互。通过传播用户交互到其他视图,提出了基于极线的交互传播(EIP),利用极线约束实现高效稳定的交互匹配。为避免影响效率的特定场景训练,进一步提出基于可见性的高斯投票(VGV),从SAM获得二维分割,并将区域提取建模为二维像素与基于高斯可见性的三维高斯之间的投票游戏。利用EIP和VGV的高效精确区域控制,提供了一个操作工具箱,实现对选定区域的各种功能,增强了场景操作的操控性、灵活性和实用性。
Key Takeaways
- 3DGS的特性和挑战:高效渲染和明确性质推动3D场景操作发展,但现有方法控制操作区域时面临挑战。
- 交互式3D分割工具的融入:为改进现有方法的不足,引入了交互式3D分割工具。
- iSegMan框架:提出了一种交互式分段与操作三维高斯(iSegMan)框架,简化用户交互并提升场景操作的效率与灵活性。
- 基于极线的交互传播(EIP):实现用户交互在不同视图间的有效传播。
- 避免特定场景训练的解决方案:引入基于可见性的高斯投票(VGV),无需特定场景训练即可实现高效区域控制。
- 操作工具箱:提供多种功能以增强场景操作的实用性。
点此查看论文截图

GSFF-SLAM: 3D Semantic Gaussian Splatting SLAM via Feature Field
Authors:Zuxing Lu, Xin Yuan, Shaowen Yang, Jingyu Liu, Changyin Sun
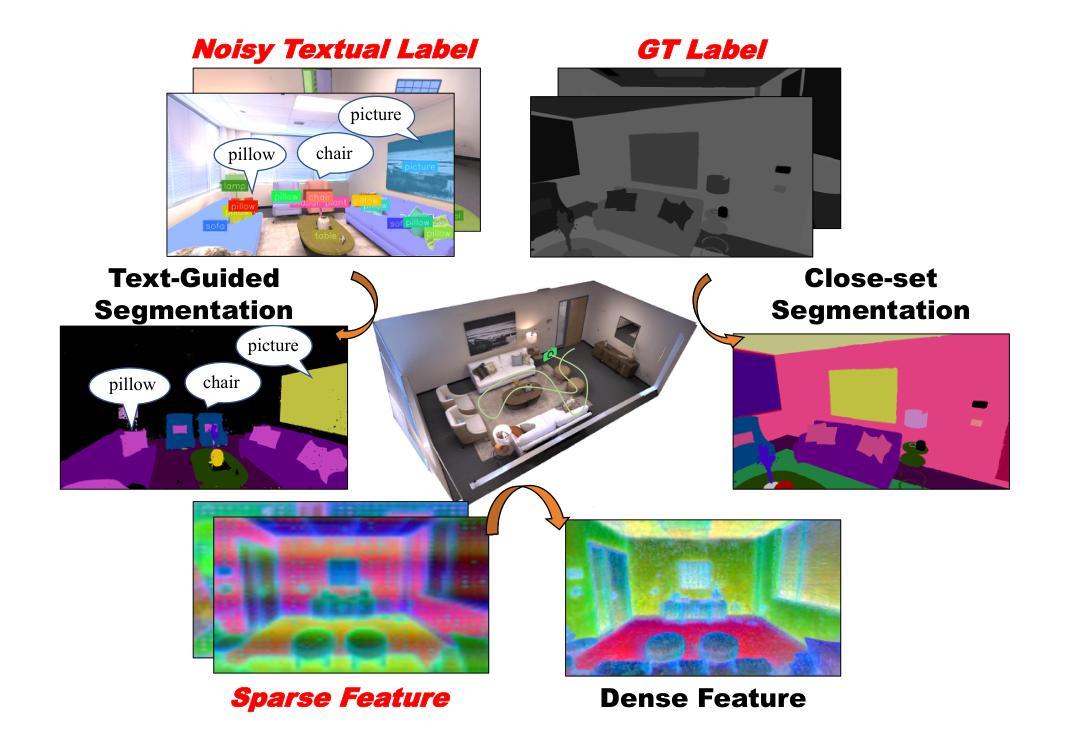
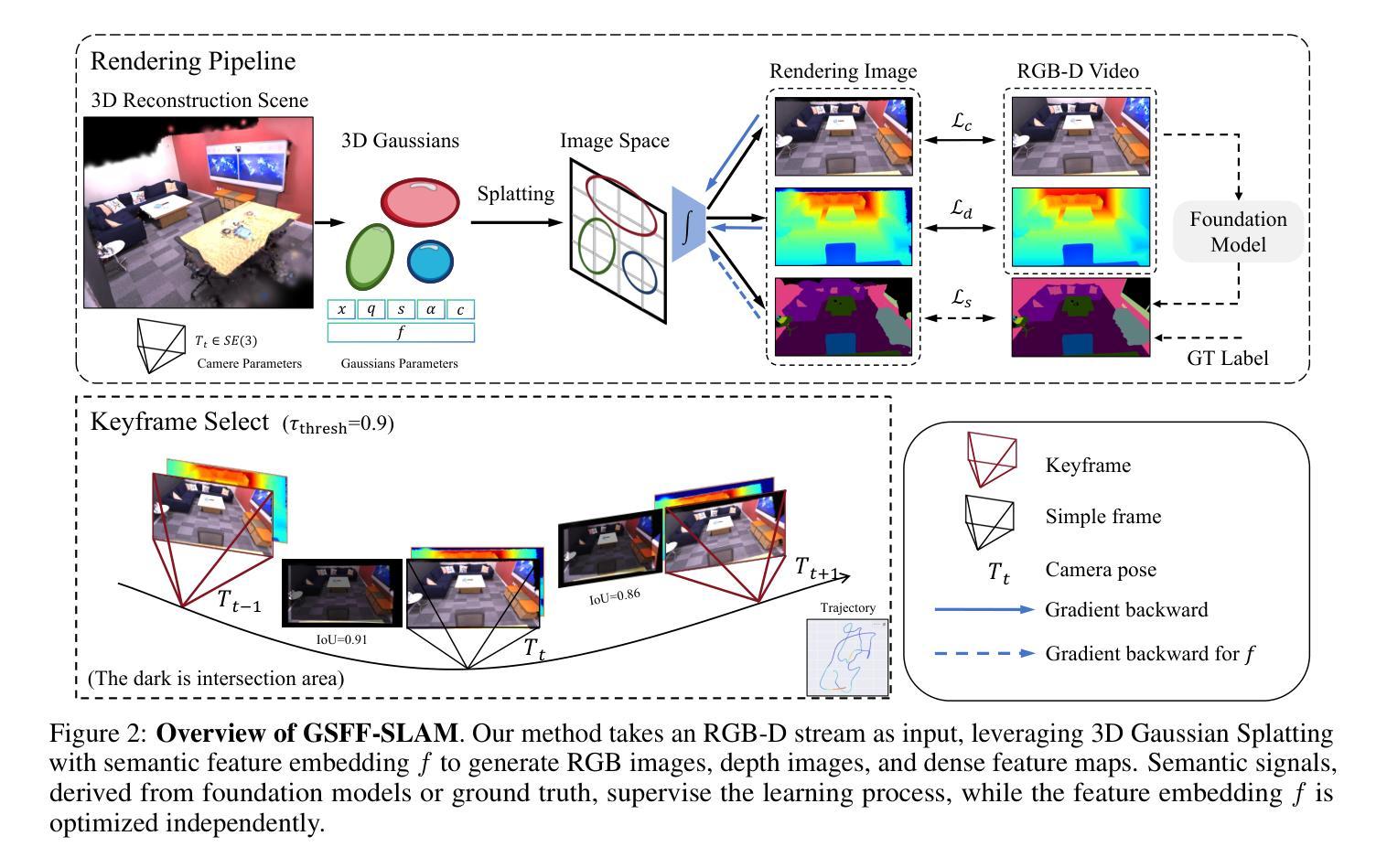
Semantic-aware 3D scene reconstruction is essential for autonomous robots to perform complex interactions. Semantic SLAM, an online approach, integrates pose tracking, geometric reconstruction, and semantic mapping into a unified framework, shows significant potential. However, existing systems, which rely on 2D ground truth priors for supervision, are often limited by the sparsity and noise of these signals in real-world environments. To address this challenge, we propose GSFF-SLAM, a novel dense semantic SLAM system based on 3D Gaussian Splatting that leverages feature fields to achieve joint rendering of appearance, geometry, and N-dimensional semantic features. By independently optimizing feature gradients, our method supports semantic reconstruction using various forms of 2D priors, particularly sparse and noisy signals. Experimental results demonstrate that our approach outperforms previous methods in both tracking accuracy and photorealistic rendering quality. When utilizing 2D ground truth priors, GSFF-SLAM achieves state-of-the-art semantic segmentation performance with 95.03% mIoU, while achieving up to 2.9$\times$ speedup with only marginal performance degradation.
语义感知的3D场景重建对于自主机器人执行复杂交互至关重要。语义SLAM作为一种在线方法,将姿态跟踪、几何重建和语义映射整合到一个统一框架中,显示出巨大的潜力。然而,现有系统通常依赖于2D真实先验进行监督,这在真实世界环境中受到这些信号的稀疏性和噪声的限制。为了应对这一挑战,我们提出了GSFF-SLAM,这是一种基于3D高斯拼贴的新颖密集语义SLAM系统,它利用特征场实现外观、几何和N维语义特征的联合渲染。通过独立优化特征梯度,我们的方法支持使用各种形式的2D先验进行语义重建,尤其是稀疏和嘈杂的信号。实验结果表明,我们的方法在跟踪精度和照片级渲染质量方面都优于以前的方法。当利用2D真实先验时,GSFF-SLAM以95.03%的mIoU达到最先进的语义分割性能,同时实现高达2.9倍的加速,且性能仅略有下降。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文探讨了自主机器人在进行复杂交互时,语义感知的3D场景重建的重要性。针对现有系统依赖的二维真实场景先验信号稀疏且含有噪声的问题,提出了一种基于高斯映射特征的语义分割密集系统GSFF-SLAM。该系统通过独立优化特征梯度,实现了对形态、几何和N维语义特征的联合渲染,并支持使用各种形式的二维先验进行语义重建,尤其适用于稀疏和噪声信号。实验结果显示,该方法在跟踪精度和逼真度渲染质量方面均优于先前方法,在利用二维真实场景先验的情况下实现了最先进水平的语义分割性能。
Key Takeaways
- 语义感知的3D场景重建对于自主机器人进行复杂交互至关重要。
- 一种新的在线方法GSFF-SLAM集成了姿态跟踪、几何重建和语义映射,解决现有系统面临的挑战。
- 现有系统依赖的二维真实场景先验信号存在稀疏性和噪声问题。
- GSFF-SLAM利用高斯映射特征实现了形态、几何和N维语义特征的联合渲染。
- 通过独立优化特征梯度,GSFF-SLAM支持使用各种形式的二维先验进行语义重建。
- 实验结果表明GSFF-SLAM在跟踪精度和渲染质量上表现优异,尤其在稀疏和噪声环境下。
点此查看论文截图

ELECTRA: A Cartesian Network for 3D Charge Density Prediction with Floating Orbitals
Authors:Jonas Elsborg, Luca Thiede, Alán Aspuru-Guzik, Tejs Vegge, Arghya Bhowmik
We present the Electronic Tensor Reconstruction Algorithm (ELECTRA) - an equivariant model for predicting electronic charge densities using floating orbitals. Floating orbitals are a long-standing concept in the quantum chemistry community that promises more compact and accurate representations by placing orbitals freely in space, as opposed to centering all orbitals at the position of atoms. Finding the ideal placement of these orbitals requires extensive domain knowledge, though, which thus far has prevented widespread adoption. We solve this in a data-driven manner by training a Cartesian tensor network to predict the orbital positions along with orbital coefficients. This is made possible through a symmetry-breaking mechanism that is used to learn position displacements with lower symmetry than the input molecule while preserving the rotation equivariance of the charge density itself. Inspired by recent successes of Gaussian Splatting in representing densities in space, we are using Gaussian orbitals and predicting their weights and covariance matrices. Our method achieves a state-of-the-art balance between computational efficiency and predictive accuracy on established benchmarks.
我们提出了电子张量重建算法(ELECTRA)——这是一种利用浮动轨道预测电子电荷密度的等价模型。浮动轨道是量子化学界的一个长期概念,它通过让轨道在空间中自由放置,而不是将所有轨道定位在原子位置,从而提供更为紧凑和准确的表示。然而,找到这些轨道的理想位置需要大量的专业知识,这迄今为止阻碍了其广泛应用。我们通过训练笛卡尔张量网络来预测轨道位置以及轨道系数来解决这个问题。这是通过一个对称破坏机制实现的,该机制用于学习具有比输入分子更低对称性的位置位移,同时保持电荷密度本身的旋转等价性。受到高斯涂绘法在空间中表示密度的最新成功的启发,我们使用高斯轨道并预测其权重和协方差矩阵。我们的方法在公认的标准测试上实现了计算效率和预测精度之间的最新平衡。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 10 pages, 4 figures, 2 tables
Summary
本文介绍了电子张量重建算法(ELECTRA),这是一种利用浮动轨道预测电子电荷密度的等价模型。浮动轨道是一个长期存在于量子化学领域中的概念,它通过让轨道在空间中自由放置,而非以原子位置为中心,提供了更紧凑和准确的表示。本文采用数据驱动的方式解决浮动轨道的理想放置问题,训练一个笛卡尔张量网络来预测轨道位置和轨道系数。通过采用对称破缺机制,可以在学习具有较低对称性的位置位移的同时保持电荷密度的旋转等价性。受到高斯分裂在空间密度表示方面的最新成功的启发,本文采用高斯轨道并预测其权重和协方差矩阵。该方法在计算效率和预测准确性之间达到了最新的平衡。
Key Takeaways
- ELECTRA算法利用浮动轨道预测电子电荷密度,该算法通过数据驱动的方式解决轨道的理想放置问题。
- 浮动轨道的概念允许轨道在空间中自由放置,提高表示的准确性和紧凑性。
- 通过训练笛卡尔张量网络来预测轨道位置和轨道系数。
- 采用对称破缺机制学习位置位移,同时保持电荷密度的旋转等价性。
- 受到高斯分裂成功的启发,采用高斯轨道并预测其权重和协方差矩阵。
- 该方法在计算效率和预测准确性之间达到了新的平衡。
点此查看论文截图

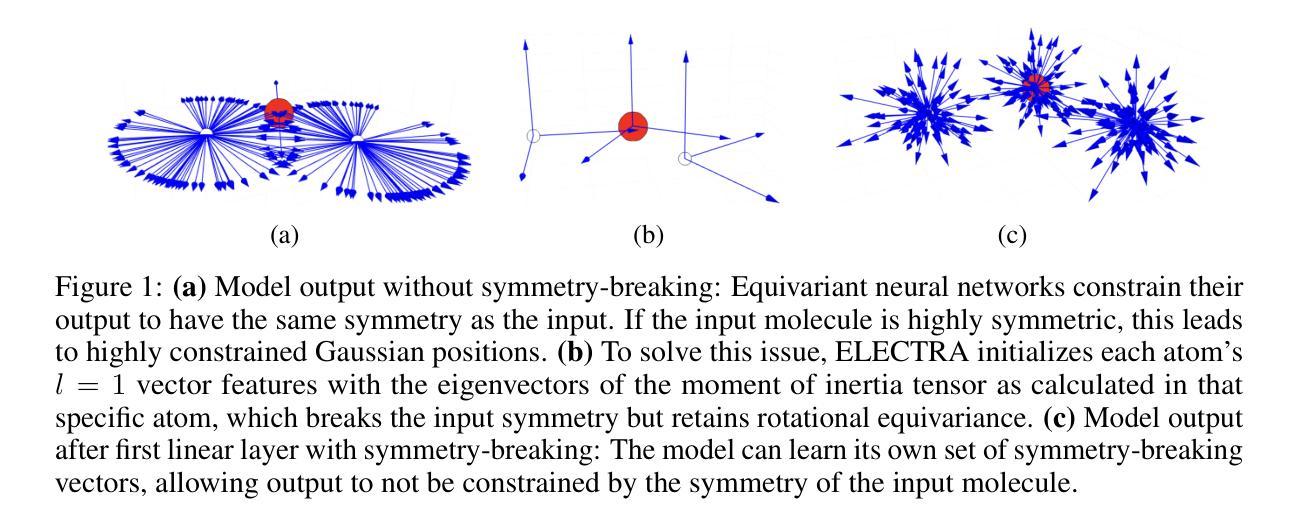
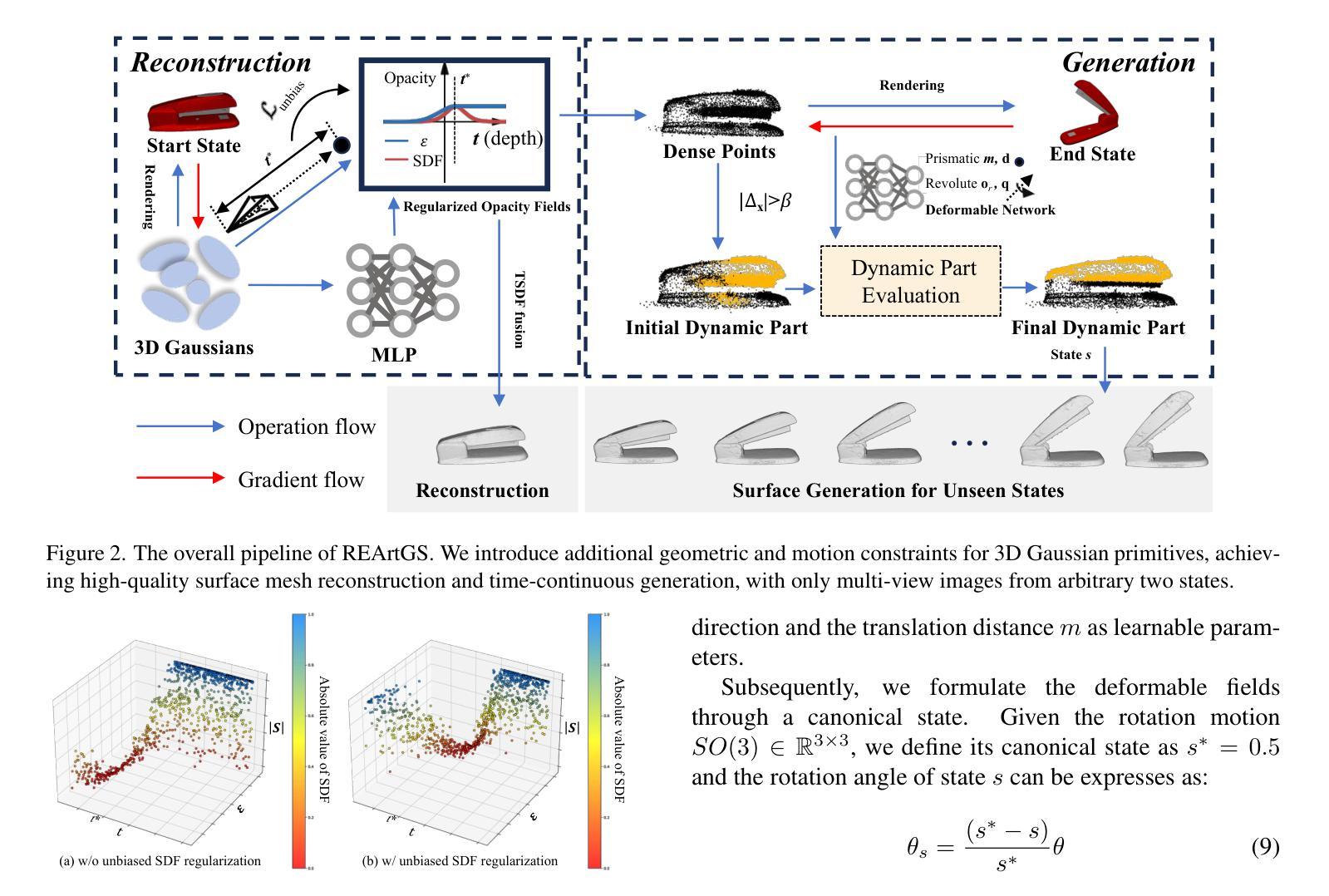
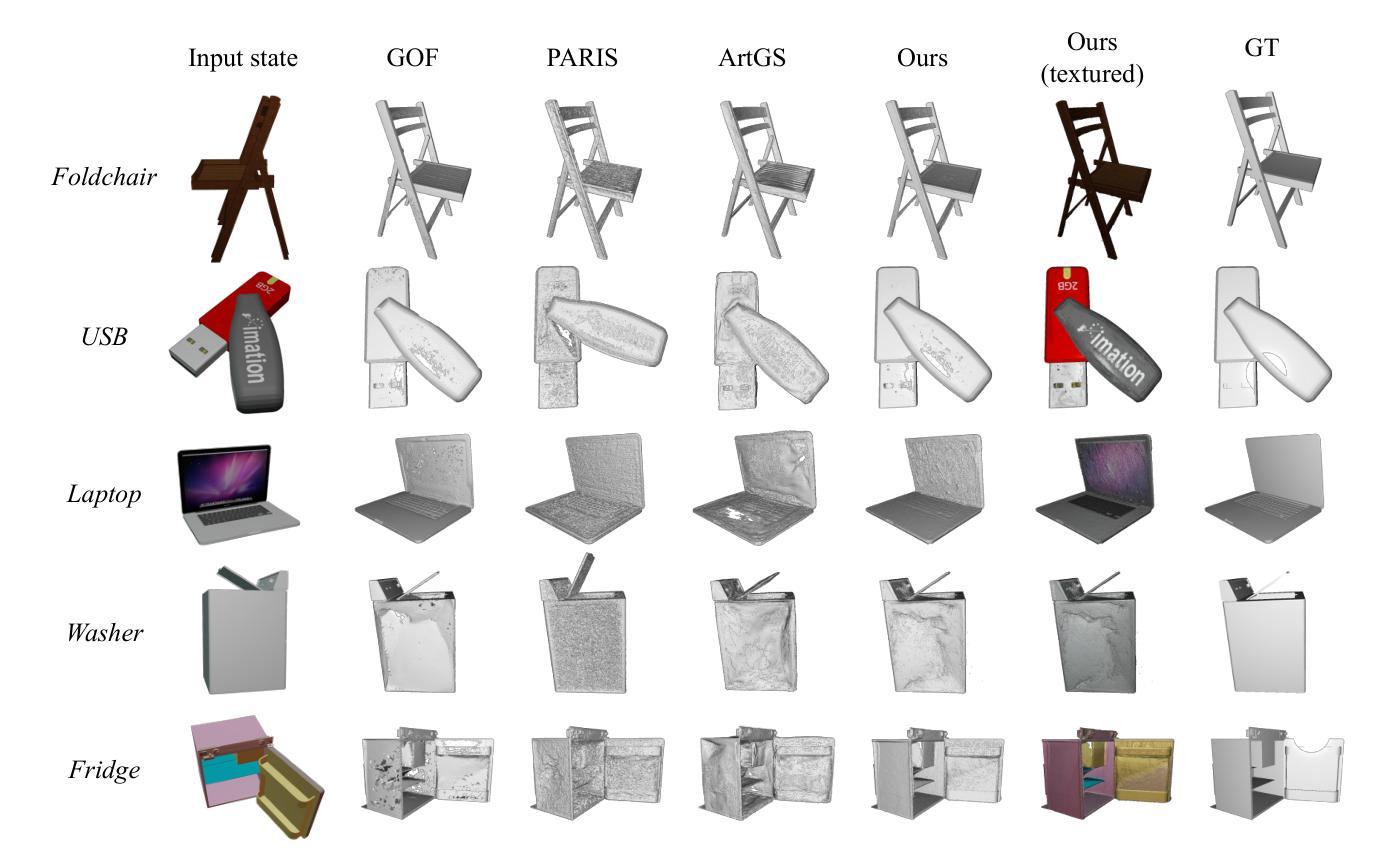
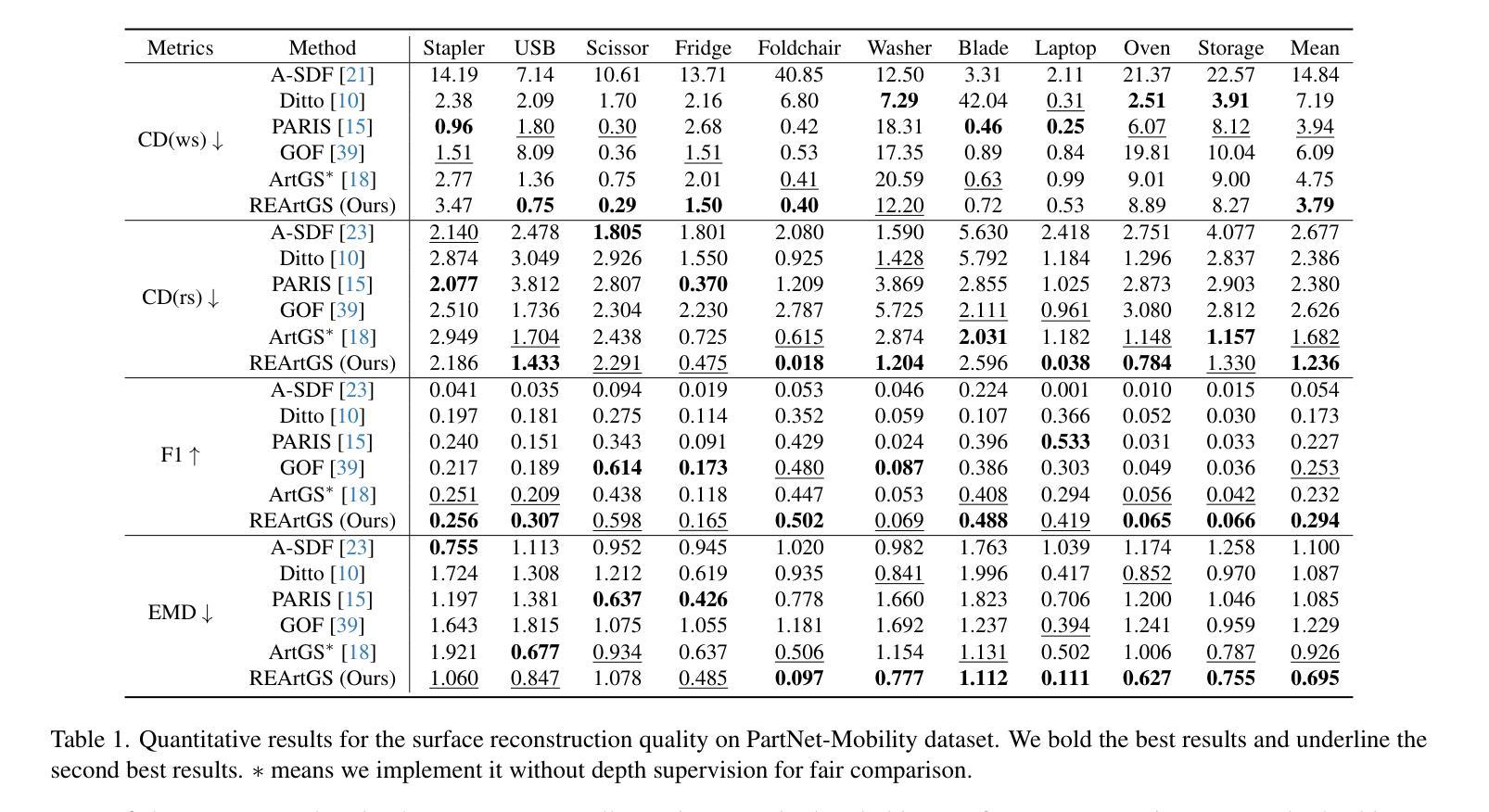
REArtGS: Reconstructing and Generating Articulated Objects via 3D Gaussian Splatting with Geometric and Motion Constraints
Authors:Di Wu, Liu Liu, Zhou Linli, Anran Huang, Liangtu Song, Qiaojun Yu, Qi Wu, Cewu Lu
Articulated objects, as prevalent entities in human life, their 3D representations play crucial roles across various applications. However, achieving both high-fidelity textured surface reconstruction and dynamic generation for articulated objects remains challenging for existing methods. In this paper, we present REArtGS, a novel framework that introduces additional geometric and motion constraints to 3D Gaussian primitives, enabling high-quality textured surface reconstruction and generation for articulated objects. Specifically, given multi-view RGB images of arbitrary two states of articulated objects, we first introduce an unbiased Signed Distance Field (SDF) guidance to regularize Gaussian opacity fields, enhancing geometry constraints and improving surface reconstruction quality. Then we establish deformable fields for 3D Gaussians constrained by the kinematic structures of articulated objects, achieving unsupervised generation of surface meshes in unseen states. Extensive experiments on both synthetic and real datasets demonstrate our approach achieves high-quality textured surface reconstruction for given states, and enables high-fidelity surface generation for unseen states. Codes will be released after acceptance and the project website is at https://sites.google.com/view/reartgs/home.
关节对象作为人类生活中普遍存在的实体,其3D表示在各种应用中扮演着至关重要的角色。然而,对于现有方法来说,实现关节对象的高保真纹理表面重建和动态生成仍然具有挑战性。在本文中,我们提出了REArtGS,一个引入3D高斯原始几何和动作约束的新框架,能够实现关节对象的高质量纹理表面重建和生成。具体来说,给定关节对象的两种任意状态的多视角RGB图像,我们首先引入无偏符号距离场(SDF)指导来规范高斯不透明度场,增强几何约束并提高表面重建质量。然后,我们根据关节对象的运动结构建立可变形的高斯场,实现未见状态的表面网格的无监督生成。在合成和真实数据集上的大量实验表明,我们的方法实现了给定状态的高质量纹理表面重建,并能对未见状态实现高保真表面生成。代码将在接受后发布,项目网站地址为https://sites.google.com/view/reartgs/home。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 11pages, 6 figures
Summary
本文介绍了REArtGS框架,通过引入额外的几何和运动约束到三维高斯原始模型,实现了高质量纹理表面重建和关节运动物体的动态生成。给定关节运动物体的两种状态的多视角RGB图像,采用无偏带符号距离场(SDF)指导来规范化高斯不透明度场,增强几何约束并提高表面重建质量。然后,根据关节运动物体的运动结构建立可变形的高斯场,实现未知状态下表面网格的无监督生成。实验证明,该方法在合成和真实数据集上均实现了高质量纹理表面重建,并为未知状态提供了高保真表面生成。
Key Takeaways
- REArtGS框架实现了高质量纹理表面重建和关节运动物体的动态生成。
- 通过引入额外的几何和运动约束到三维高斯原始模型,增强了关节运动物体的重建和生成效果。
- 采用无偏带符号距离场(SDF)指导来规范化高斯不透明度场,提高了表面重建质量。
- 建立可变形的高斯场,实现未知状态下表面网格的无监督生成。
- 该方法适用于多种关节运动物体,具备处理多视角RGB图像的能力。
- 实验证明,REArtGS在合成和真实数据集上都表现出优异的性能。
点此查看论文截图

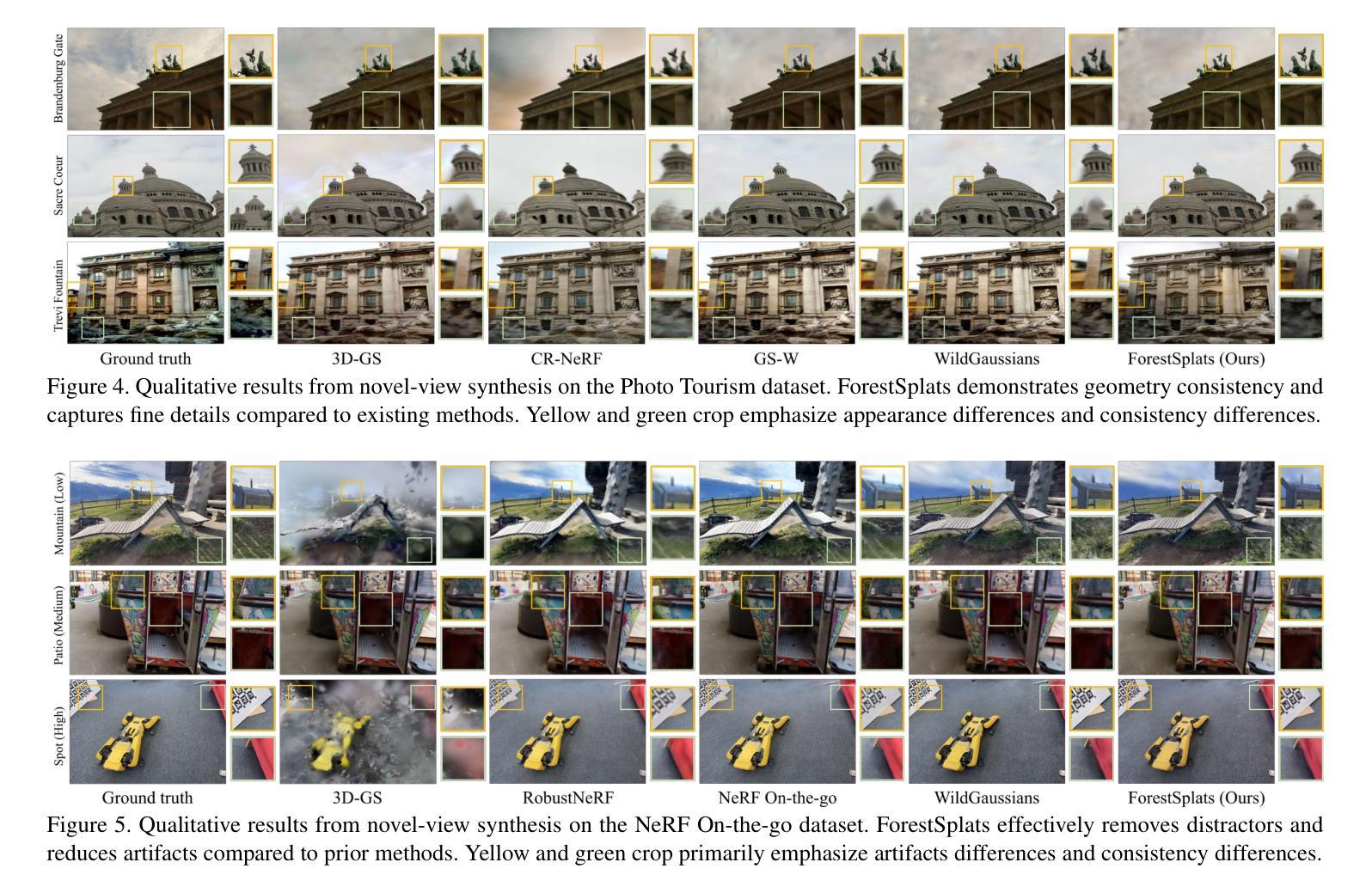
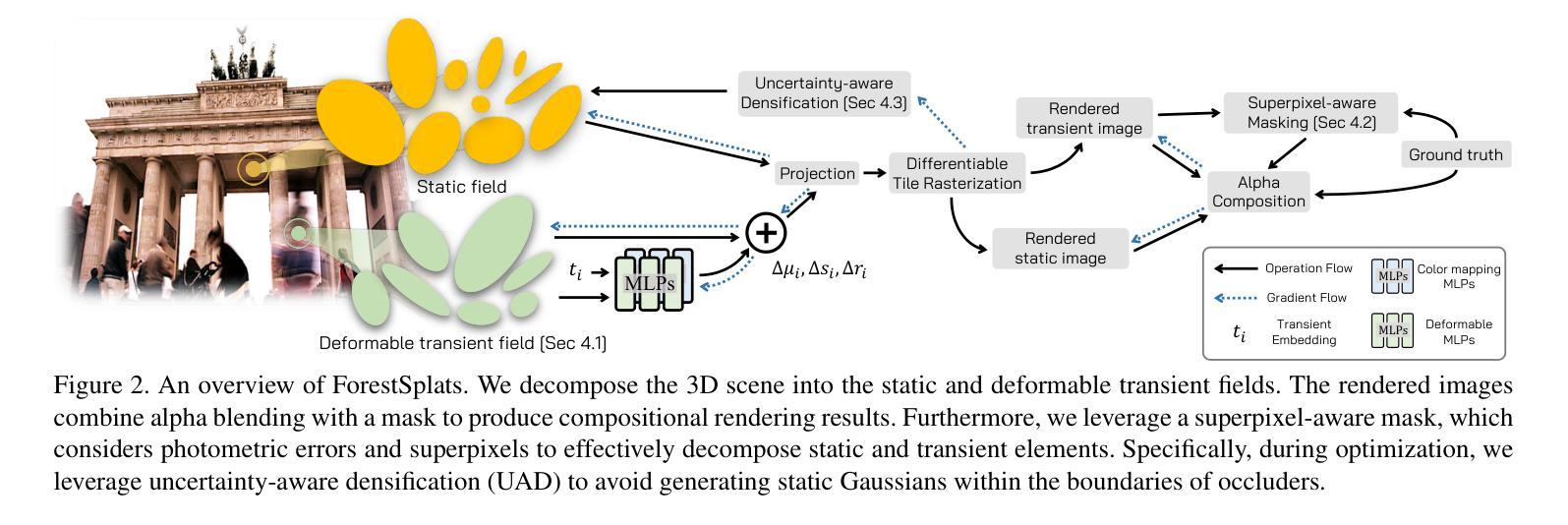
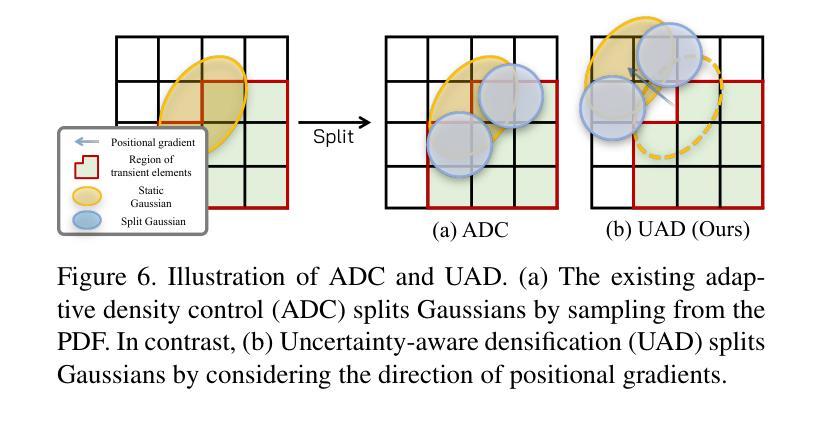
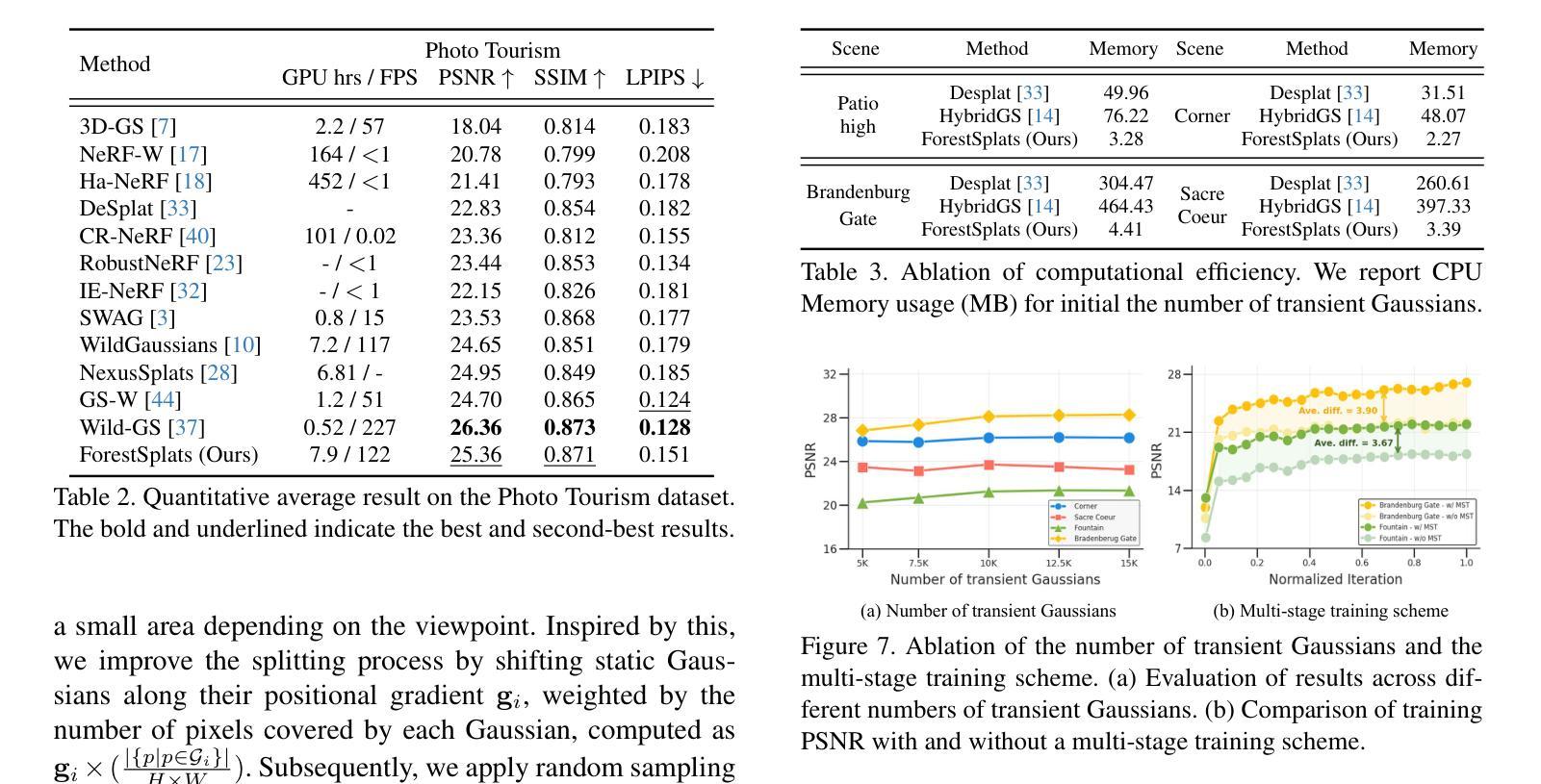
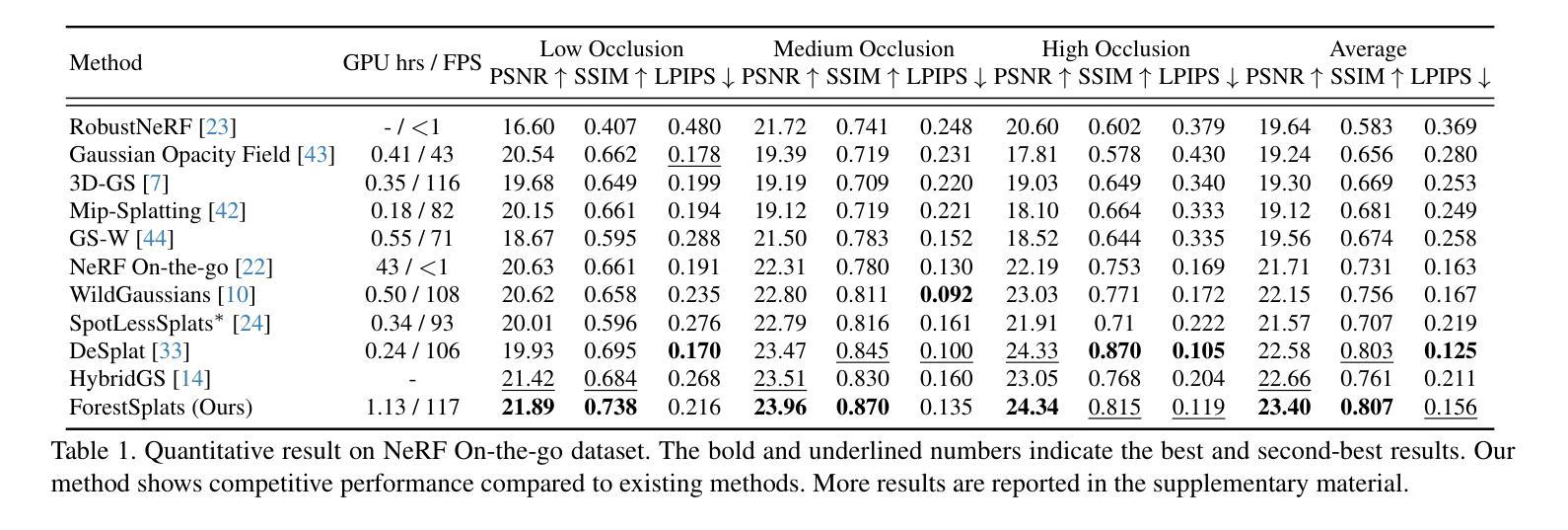
ForestSplats: Deformable transient field for Gaussian Splatting in the Wild
Authors:Wongi Park, Myeongseok Nam, Siwon Kim, Sangwoo Jo, Soomok Lee
Recently, 3D Gaussian Splatting (3D-GS) has emerged, showing real-time rendering speeds and high-quality results in static scenes. Although 3D-GS shows effectiveness in static scenes, their performance significantly degrades in real-world environments due to transient objects, lighting variations, and diverse levels of occlusion. To tackle this, existing methods estimate occluders or transient elements by leveraging pre-trained models or integrating additional transient field pipelines. However, these methods still suffer from two defects: 1) Using semantic features from the Vision Foundation model (VFM) causes additional computational costs. 2) The transient field requires significant memory to handle transient elements with per-view Gaussians and struggles to define clear boundaries for occluders, solely relying on photometric errors. To address these problems, we propose ForestSplats, a novel approach that leverages the deformable transient field and a superpixel-aware mask to efficiently represent transient elements in the 2D scene across unconstrained image collections and effectively decompose static scenes from transient distractors without VFM. We designed the transient field to be deformable, capturing per-view transient elements. Furthermore, we introduce a superpixel-aware mask that clearly defines the boundaries of occluders by considering photometric errors and superpixels. Additionally, we propose uncertainty-aware densification to avoid generating Gaussians within the boundaries of occluders during densification. Through extensive experiments across several benchmark datasets, we demonstrate that ForestSplats outperforms existing methods without VFM and shows significant memory efficiency in representing transient elements.
最近,3D高斯平滑技术(3D-GS)已经崭露头角,它在静态场景中实现了实时渲染速度和高品质结果。虽然3D-GS在静态场景中的表现很有效,但在真实世界环境中,由于瞬态物体、光照变化和遮挡程度的差异,它们的性能会显著下降。为了解决这个问题,现有方法通过利用预训练模型或集成额外的瞬态场管道来估计遮挡物或瞬态元素。然而,这些方法仍然存在两个缺陷:1)使用视觉基础模型(VFM)的语义特征会导致额外的计算成本。2)瞬态场需要处理大量的内存来应对具有视图的高斯分布的瞬态元素,并且仅仅依赖光度误差来定义遮挡物的清晰边界时非常困难。为了解决这些问题,我们提出了ForestSplats,这是一种利用可变形瞬态场和超像素感知掩膜的新方法,能够高效地在不受约束的图像集合中表示二维场景中的瞬态元素,并从没有VFM的瞬态干扰物中有效地分解静态场景。我们设计的瞬态场是可变形的,可以捕捉每个视图的瞬态元素。此外,我们引入了超像素感知掩膜,通过考虑光度误差和超像素来清晰地定义遮挡物的边界。另外,我们还提出了不确定性感知稠化技术,以避免在遮挡物的边界内生成高斯分布稠化期间的情况。通过几项基准数据集的广泛实验,我们证明了ForestSplats在不需要VFM的情况下优于现有方法,并且在表示瞬态元素方面表现出显著的内存效率。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了新兴的3D高斯展铺技术(ForestSplats)在处理真实世界环境中的动态场景时的优势。该技术通过利用可变形瞬态场和超像素感知掩膜,有效地表示二维场景中的瞬态元素,并分解静态场景中的干扰元素。相较于依赖视觉基础模型的方法,ForestSplats具有更高的计算效率和内存使用效率。
Key Takeaways
- 3D高斯展铺在静态场景中表现良好,但在真实世界环境下处理动态场景时性能下降。
- 现有方法尝试通过预训练模型或集成额外的瞬态场管道来估计遮挡物或瞬态元素,但存在计算成本高和内存使用效率低的问题。
- ForestSplats利用可变形瞬态场和超像素感知掩膜有效地表示和分解场景中的瞬态元素和遮挡物。
- ForestSplats相较于依赖视觉基础模型的方法具有更高的计算效率和内存使用效率。
- ForestSplats通过不确定性增密避免了在遮挡物边界内生成高斯分布。
点此查看论文截图



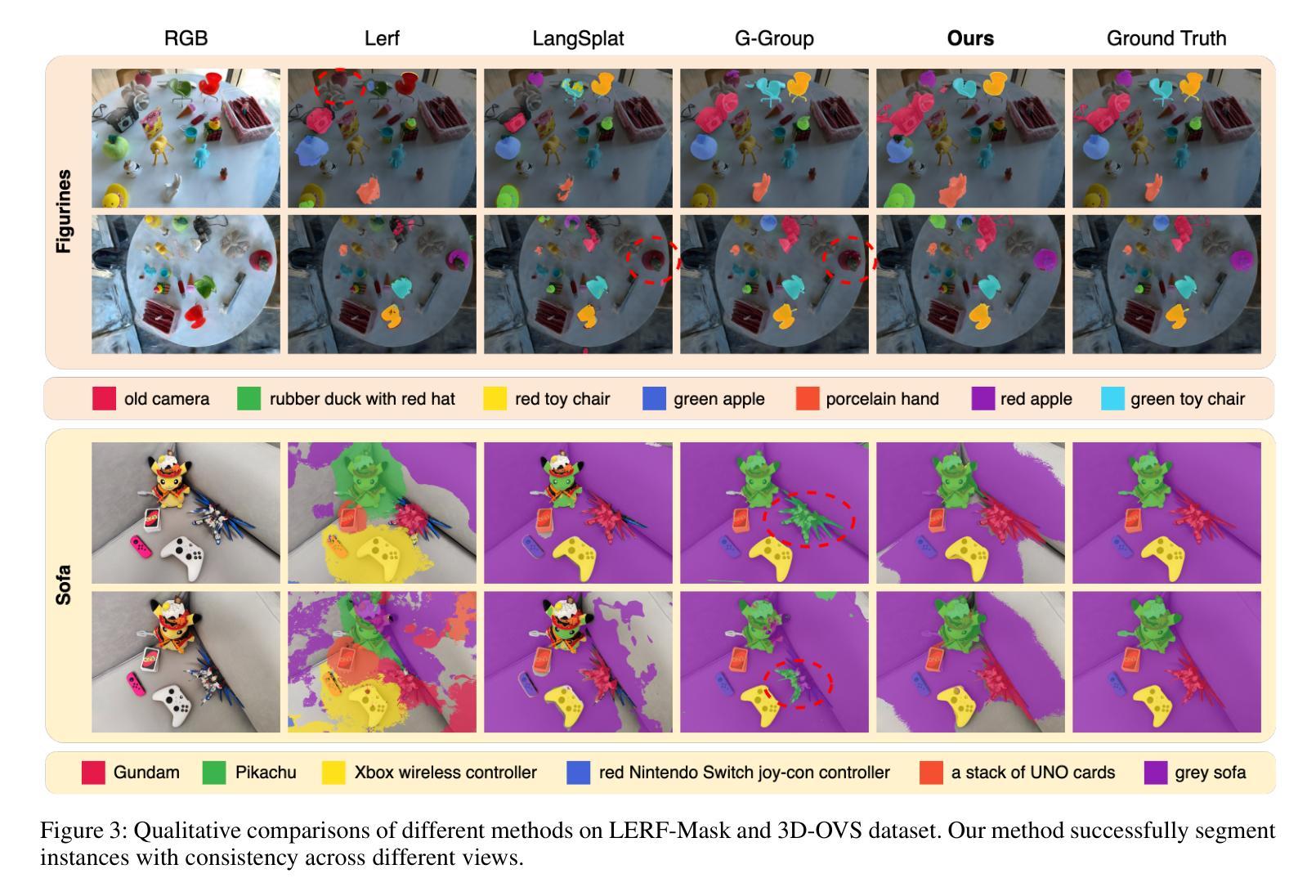
Bootstraping Clustering of Gaussians for View-consistent 3D Scene Understanding
Authors:Wenbo Zhang, Lu Zhang, Ping Hu, Liqian Ma, Yunzhi Zhuge, Huchuan Lu
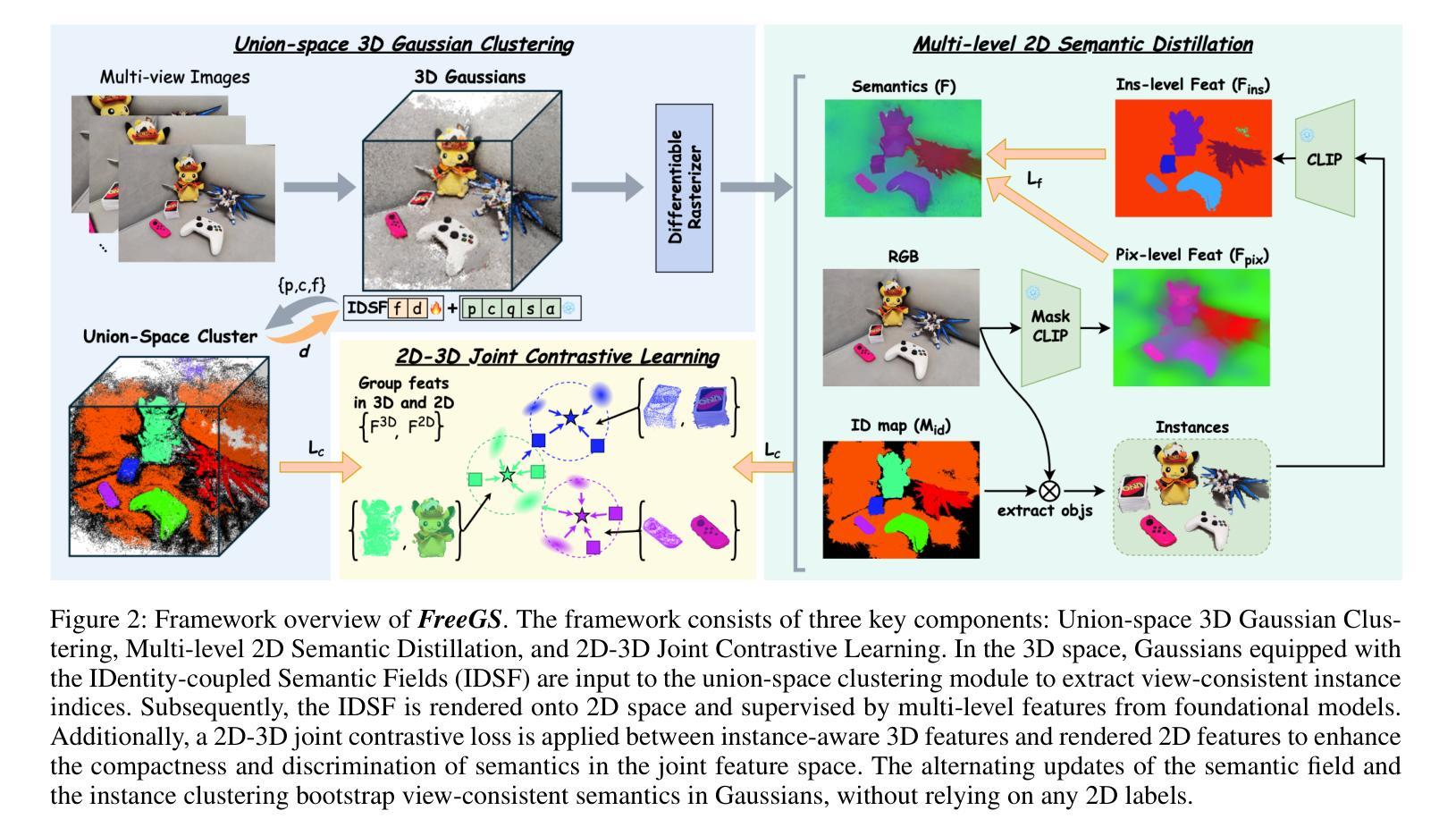
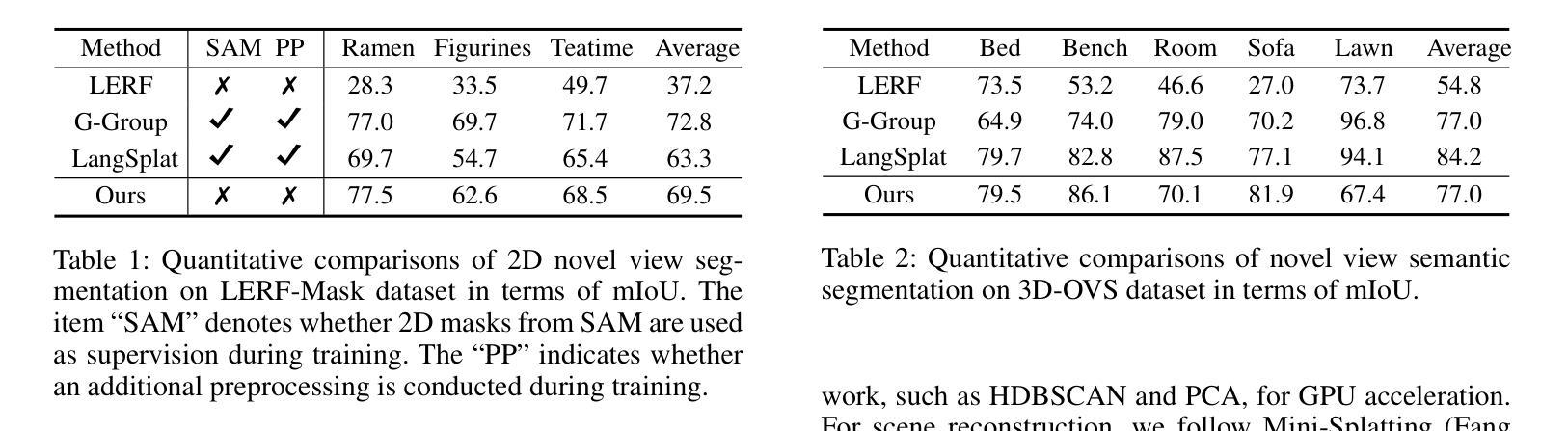
Injecting semantics into 3D Gaussian Splatting (3DGS) has recently garnered significant attention. While current approaches typically distill 3D semantic features from 2D foundational models (e.g., CLIP and SAM) to facilitate novel view segmentation and semantic understanding, their heavy reliance on 2D supervision can undermine cross-view semantic consistency and necessitate complex data preparation processes, therefore hindering view-consistent scene understanding. In this work, we present FreeGS, an unsupervised semantic-embedded 3DGS framework that achieves view-consistent 3D scene understanding without the need for 2D labels. Instead of directly learning semantic features, we introduce the IDentity-coupled Semantic Field (IDSF) into 3DGS, which captures both semantic representations and view-consistent instance indices for each Gaussian. We optimize IDSF with a two-step alternating strategy: semantics help to extract coherent instances in 3D space, while the resulting instances regularize the injection of stable semantics from 2D space. Additionally, we adopt a 2D-3D joint contrastive loss to enhance the complementarity between view-consistent 3D geometry and rich semantics during the bootstrapping process, enabling FreeGS to uniformly perform tasks such as novel-view semantic segmentation, object selection, and 3D object detection. Extensive experiments on LERF-Mask, 3D-OVS, and ScanNet datasets demonstrate that FreeGS performs comparably to state-of-the-art methods while avoiding the complex data preprocessing workload. Our code is publicly available at https://github.com/wb014/FreeGS.
将语义注入3D高斯映射(3DGS)近来引起了广泛关注。虽然当前的方法通常从二维基础模型(例如CLIP和SAM)中提炼出三维语义特征,以促进新视图分割和语义理解,但它们对二维监督的严重依赖可能会破坏跨视图的语义一致性,并需要复杂的数据准备过程,从而阻碍视图一致的场景理解。在这项工作中,我们提出了FreeGS,这是一个无监督的语义嵌入3DGS框架,它能够实现无需二维标签的视图一致的三维场景理解。我们不是直接学习语义特征,而是将身份耦合语义字段(IDSF)引入到3DGS中,该字段可以捕获每个高斯的三维语义表示和视图一致的实例索引。我们使用两步交替策略优化IDSF:语义有助于提取三维空间中的连贯实例,而生成的实例则对二维空间的稳定语义注入进行规范化。此外,我们采用二维-三维联合对比损失,以增强视图一致的三维几何和丰富语义之间的互补性,在启动过程中促进知识迁移学习训练的过程;从而令FreeGS统一完成新视图语义分割、对象选择和三维对象检测等任务。在LERF-Mask、3D-OVS和ScanNet数据集上的大量实验表明,FreeGS的性能与最先进的同类方法相当,同时避免了复杂的数据预处理工作量。我们的代码公开在https://github.com/wb014/FreeGS。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted to AAAI25
Summary
本文提出了FreeGS,这是一种无需二维标签的无监督语义嵌入三维高斯绘制(3DGS)框架,可实现跨视图一致的场景理解。通过引入身份耦合语义场(IDSF)捕获语义表示和视图一致的实例索引,采用两步交替优化策略,实现语义提取和实例正则化。此外,采用二维到三维的联合对比损失,增强了在启动过程中视图一致的几何形状和丰富语义之间的互补性。实验表明,FreeGS在新型视图语义分割、对象选择和三维对象检测等任务上表现优异。
Key Takeaways
- FreeGS是一个无监督的语义嵌入3DGS框架,无需二维标签即可实现跨视图一致的场景理解。
- 引入身份耦合语义场(IDSF),捕获语义表示和视图一致的实例索引。
- 采用两步交替优化策略:语义提取和实例正则化。
- 利用二维到三维的联合对比损失增强几何形状和语义的互补性。
- 在多个数据集上的实验证明FreeGS性能卓越,实现了新型视图语义分割、对象选择和三维对象检测等任务。
点此查看论文截图


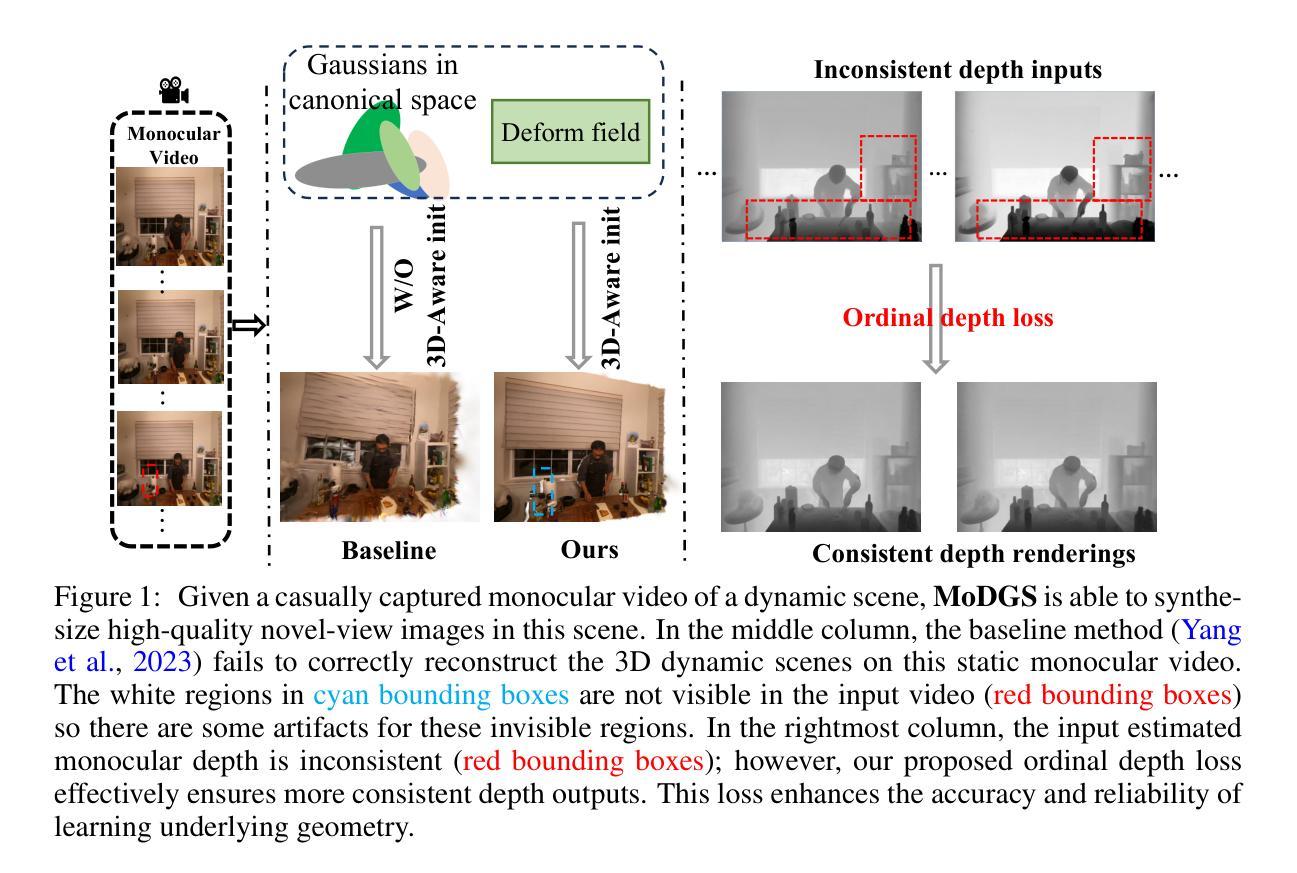
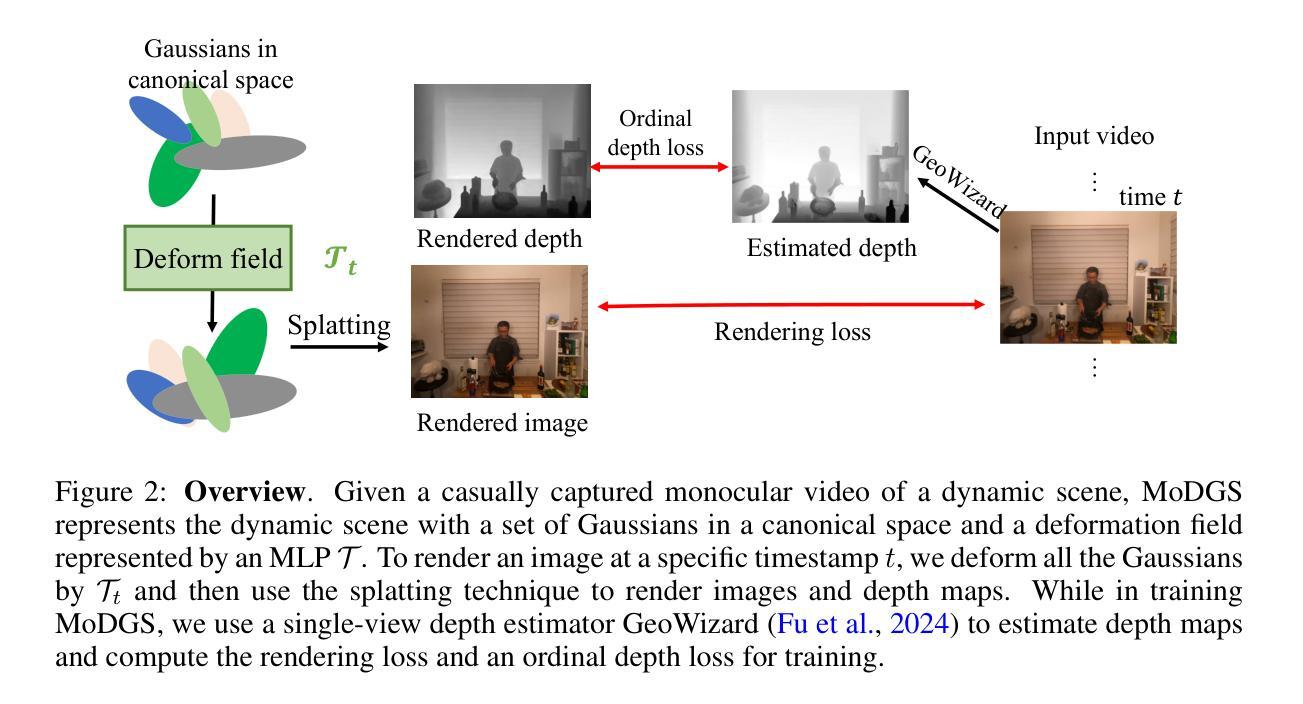
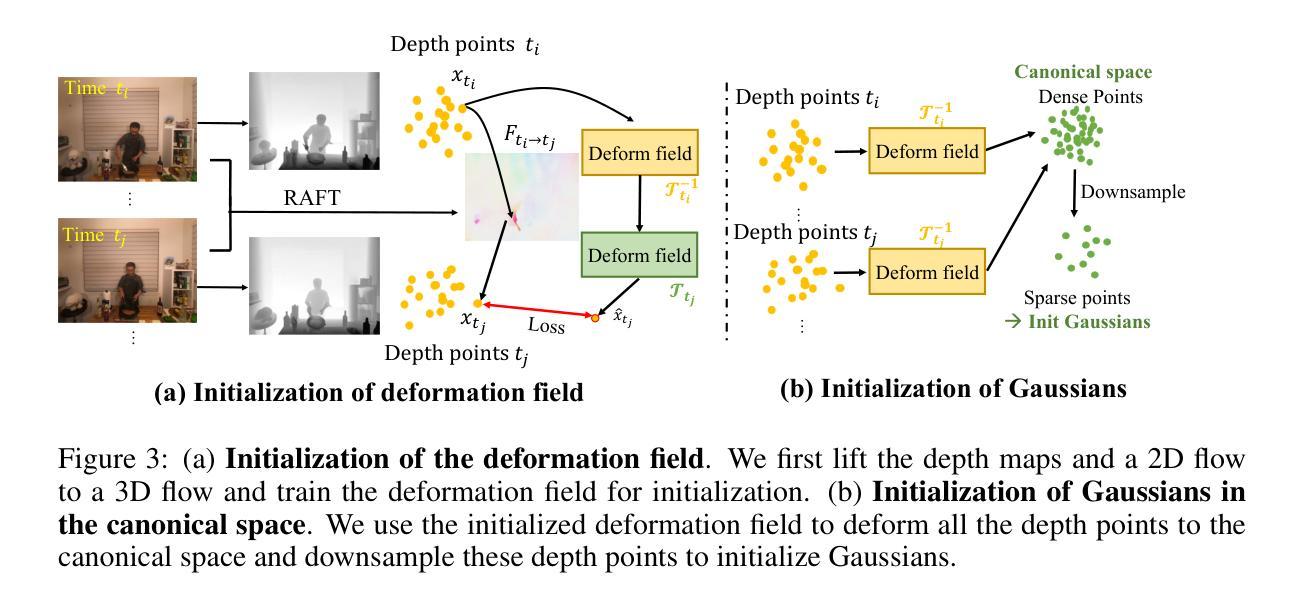
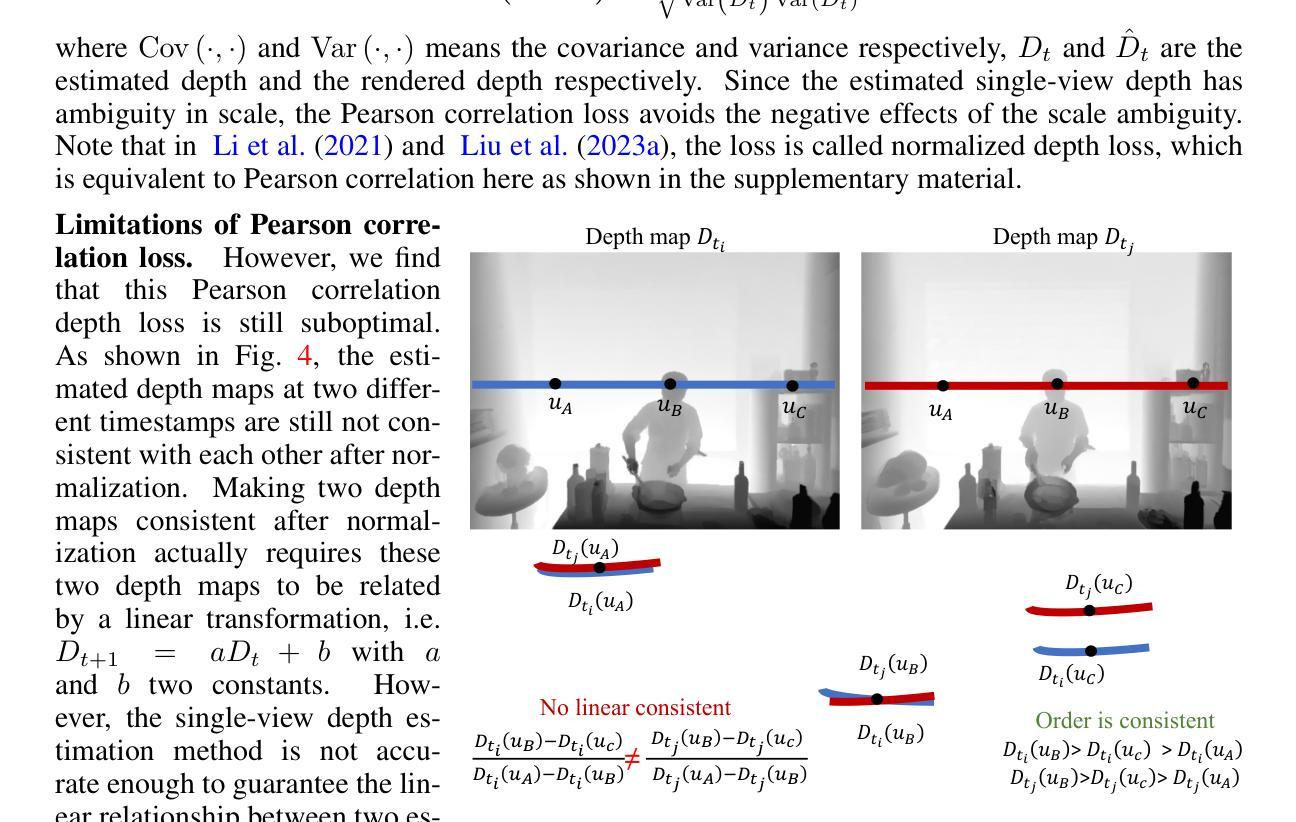
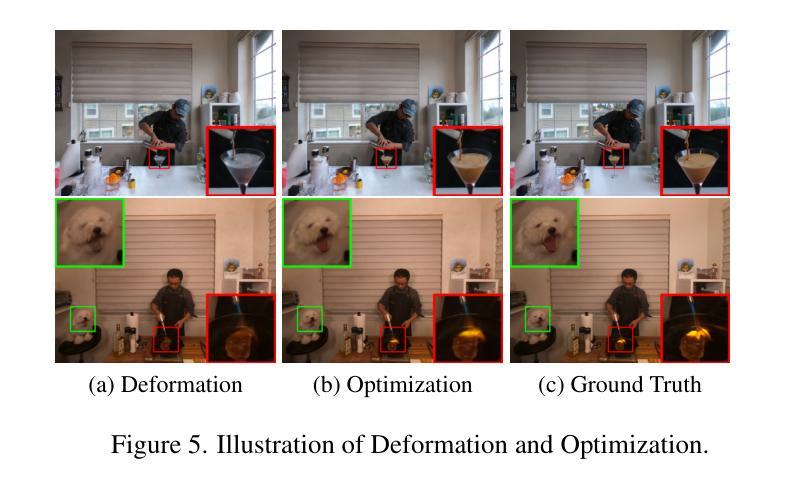
MoDGS: Dynamic Gaussian Splatting from Casually-captured Monocular Videos with Depth Priors
Authors:Qingming Liu, Yuan Liu, Jiepeng Wang, Xianqiang Lyv, Peng Wang, Wenping Wang, Junhui Hou
In this paper, we propose MoDGS, a new pipeline to render novel views of dy namic scenes from a casually captured monocular video. Previous monocular dynamic NeRF or Gaussian Splatting methods strongly rely on the rapid move ment of input cameras to construct multiview consistency but struggle to recon struct dynamic scenes on casually captured input videos whose cameras are either static or move slowly. To address this challenging task, MoDGS adopts recent single-view depth estimation methods to guide the learning of the dynamic scene. Then, a novel 3D-aware initialization method is proposed to learn a reasonable deformation field and a new robust depth loss is proposed to guide the learning of dynamic scene geometry. Comprehensive experiments demonstrate that MoDGS is able to render high-quality novel view images of dynamic scenes from just a casually captured monocular video, which outperforms state-of-the-art meth ods by a significant margin. The code will be publicly available.
在这篇论文中,我们提出了MoDGS,这是一种新的流程,用于从随意捕获的单目视频中呈现动态场景的新视图。之前的单目动态NeRF或高斯喷涂方法严重依赖于输入相机的快速移动来构建多视图一致性,但难以在随意捕获的输入视频上重建动态场景,这些视频的相机要么是静态的,要么是移动缓慢的。为了解决这一具有挑战性的任务,MoDGS采用最新的单视图深度估计方法来指导动态场景的学习。然后,提出了一种新的3D感知初始化方法,以学习合理的变形场,并提出了一种新的鲁棒深度损失来指导动态场景几何的学习。综合实验表明,MoDGS能够从随意捕获的单目视频中呈现高质量动态场景的新视图图像,显著优于现有方法。代码将公开可用。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted as a poster at ICLR. Project page: https://modgs.github.io
摘要
本文针对从单目视频中渲染动态场景的新视图的任务,提出了MoDGS这一新流程。以往的方法大多依赖于快速移动的输入相机来构建多视图一致性,但在处理随意拍摄的单目视频时面临困难,这些视频的相机往往是静态或缓慢移动的。MoDGS采用最新的单视图深度估计方法来指导动态场景的学习。接着,提出了一种新的3D感知初始化方法,用于学习合理的变形场,并提出了一种新的稳健深度损失来指导动态场景几何的学习。实验证明,MoDGS能够从简单的单目视频中渲染出高质量的动态场景新视图,并显著优于现有方法。
要点
- MoDGS是一个用于从单目视频中渲染动态场景新视图的新流程。
- 以往的monocular动态NeRF或高斯贴片方法依赖快速相机移动来构建多视图一致性,但在处理静态或缓慢移动的相机拍摄的视频时面临困难。
- MoDGS采用单视图深度估计方法来指导动态场景的学习。
- 提出了一种新的3D感知初始化方法,用于学习合理的变形场。
- 提出了一种新的稳健深度损失来指导动态场景几何的学习。
- MoDGS能够显著优于现有方法,从简单的单目视频中渲染出高质量的新视图。
点此查看论文截图