⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-05-22 更新
PRL: Prompts from Reinforcement Learning
Authors:Paweł Batorski, Adrian Kosmala, Paul Swoboda
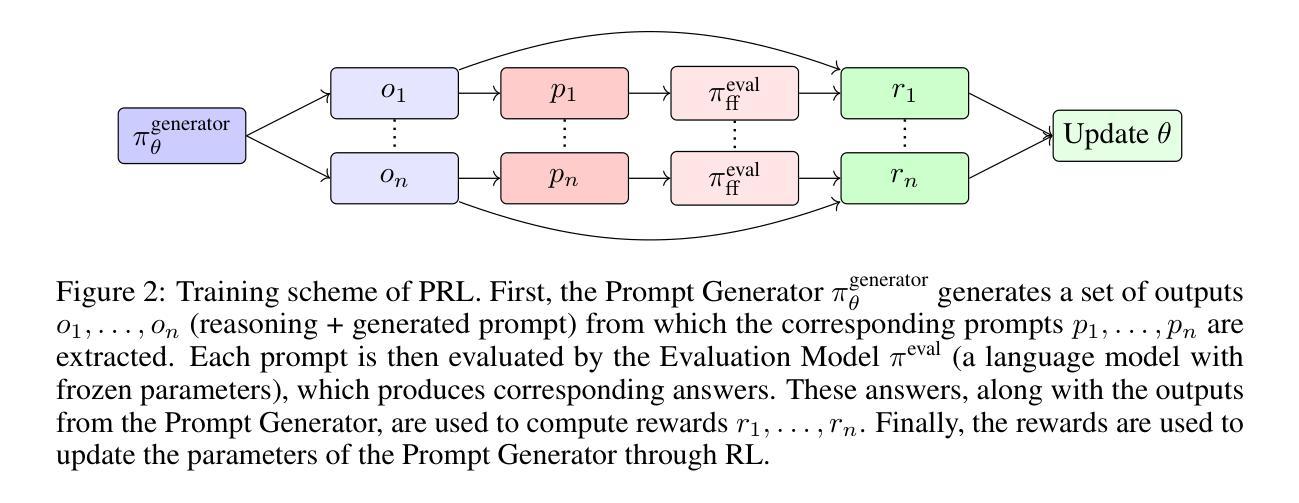
Effective prompt engineering remains a central challenge in fully harnessing the capabilities of LLMs. While well-designed prompts can dramatically enhance performance, crafting them typically demands expert intuition and a nuanced understanding of the task. Moreover, the most impactful prompts often hinge on subtle semantic cues, ones that may elude human perception but are crucial for guiding LLM behavior. In this paper, we introduce PRL (Prompts from Reinforcement Learning), a novel RL-based approach for automatic prompt generation. Unlike previous methods, PRL can produce novel few-shot examples that were not seen during training. Our approach achieves state-of-the-art performance across a range of benchmarks, including text classification, simplification, and summarization. On the classification task, it surpasses prior methods by 2.58% over APE and 1.00% over EvoPrompt. Additionally, it improves the average ROUGE scores on the summarization task by 4.32 over APE and by 2.12 over EvoPrompt and the SARI score on simplification by 6.93 over APE and by 6.01 over EvoPrompt. Our code is available at https://github.com/Batorskq/prl .
有效提示工程仍然是充分利用大型语言模型(LLM)能力的核心挑战。虽然精心设计好的提示可以显著提高性能,但制作它们通常需要专家的直觉和对任务的微妙理解。此外,最有影响力的提示通常依赖于微妙的语义线索,这些线索可能会逃避人类的感知,但对于指导LLM行为至关重要。在本文中,我们介绍了PRL(基于强化学习的提示),这是一种用于自动提示生成的新型基于强化学习的方法。不同于以前的方法,PRL可以生成在训练期间未见过的全新少样本示例。我们的方法在各种基准测试中实现了最先进的性能,包括文本分类、简化和摘要。在分类任务上,它比APE高出2.58%,比EvoPrompt高出1.00%。此外,它在摘要任务的平均ROUGE得分上比APE高出4.32%,比EvoPrompt高出2.12;在简化任务的SARI得分上比APE高出6.93%,比EvoPrompt高出6.01。我们的代码可在https://github.com/Batorskq/prl找到。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了一种基于强化学习(RL)的自动提示生成方法PRL(Prompts from Reinforcement Learning)。该方法能够产生新颖的在训练过程中未见过的少数例子提示。在文本分类、简化和总结等多个基准测试中,PRL取得了最先进的性能表现。该方法超越了先前的自动提示生成方法,具有极大的实用价值。有关代码可以在指定的GitHub地址中找到。
Key Takeaways
- PRL是一种基于强化学习的自动提示生成方法,可以生成新颖的少数例子提示。
- PRL在文本分类、简化和总结等多个基准测试中取得了最先进的性能表现。
- PRL超越了先前的自动提示生成方法,展现出更好的实际应用价值。
- PRL的性能提升显著,尤其在分类任务上,相比APE和EvoPrompt分别有更高的准确性提升。
点此查看论文截图

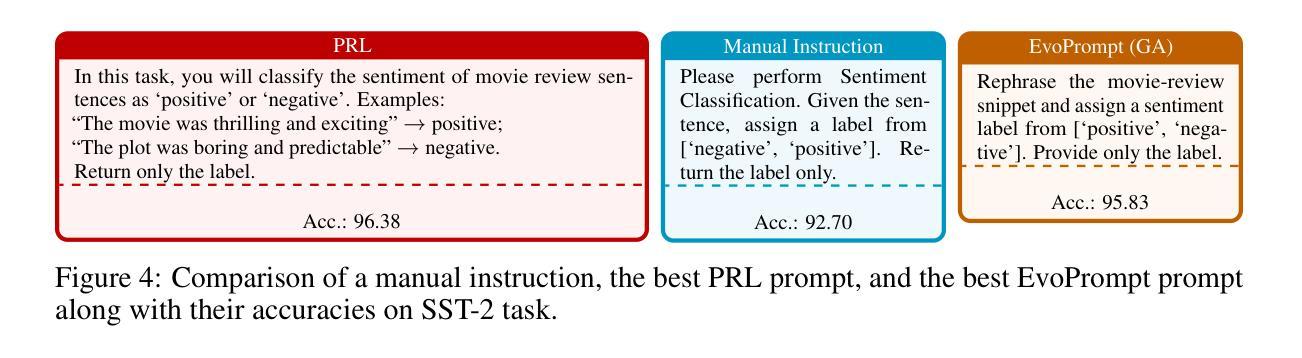
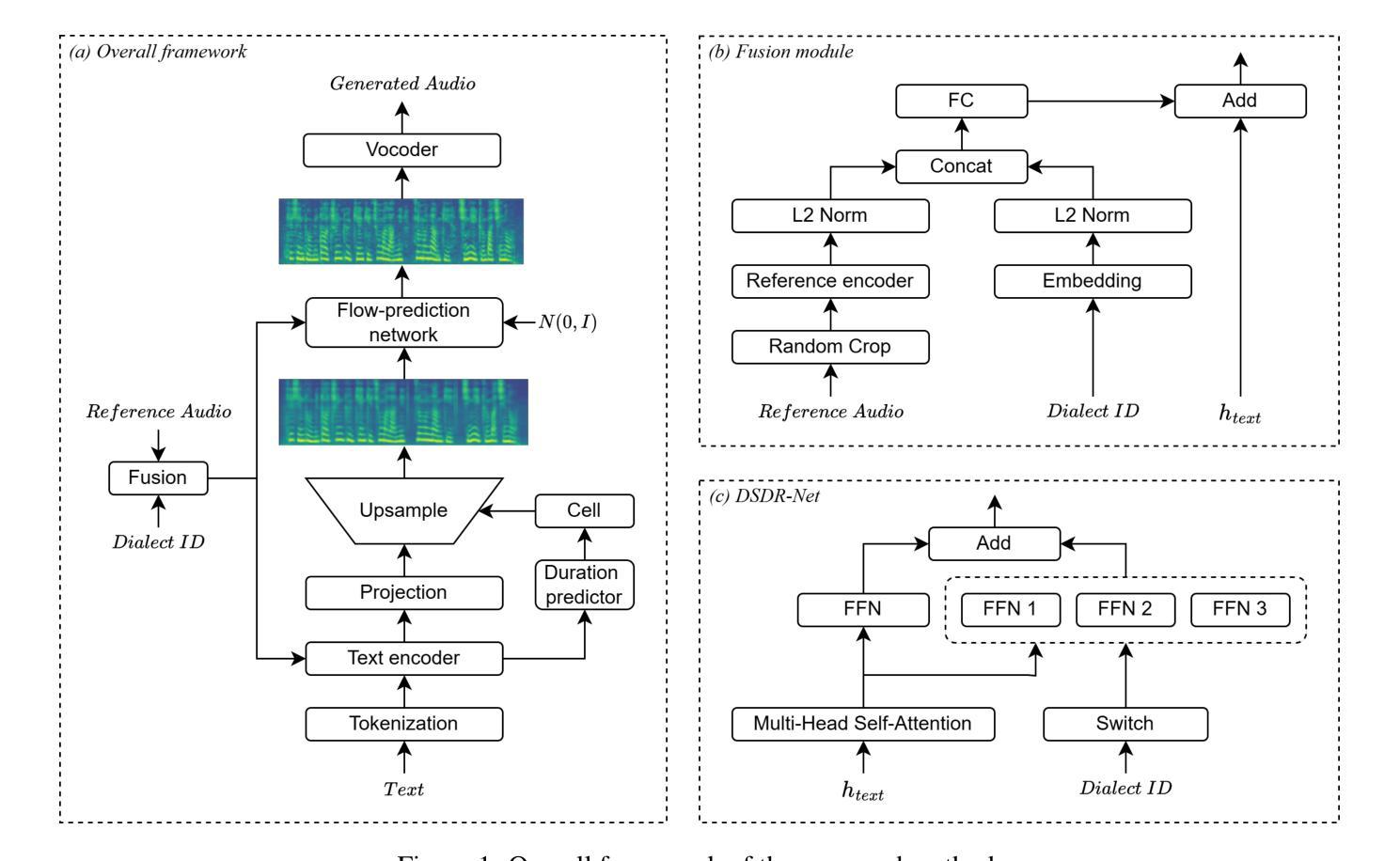
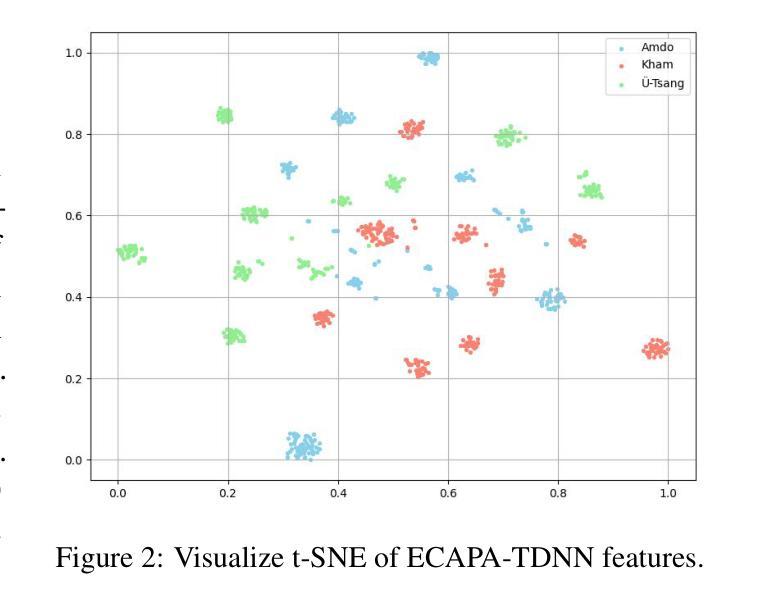
FMSD-TTS: Few-shot Multi-Speaker Multi-Dialect Text-to-Speech Synthesis for Ü-Tsang, Amdo and Kham Speech Dataset Generation
Authors:Yutong Liu, Ziyue Zhang, Ban Ma-bao, Yuqing Cai, Yongbin Yu, Renzeng Duojie, Xiangxiang Wang, Fan Gao, Cheng Huang, Nyima Tashi
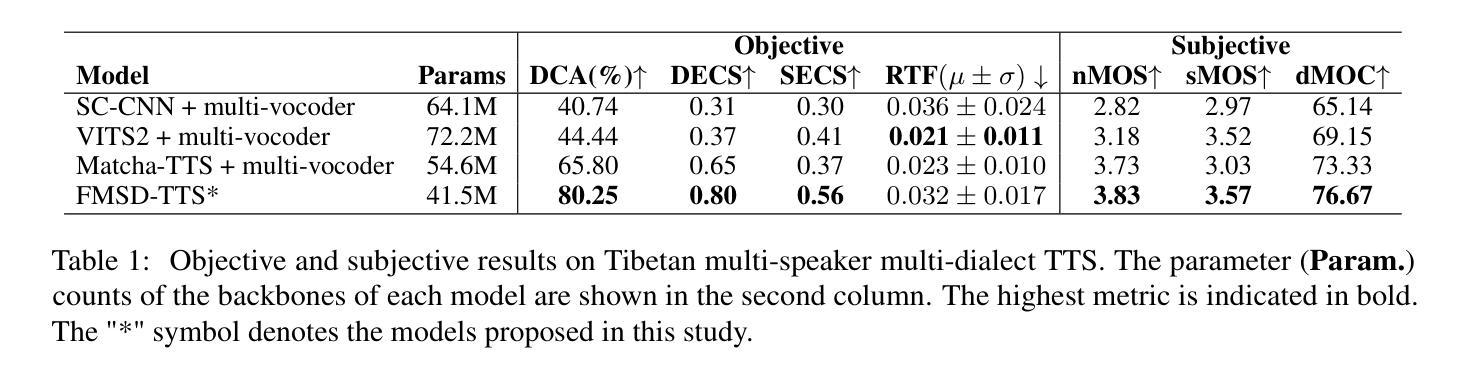
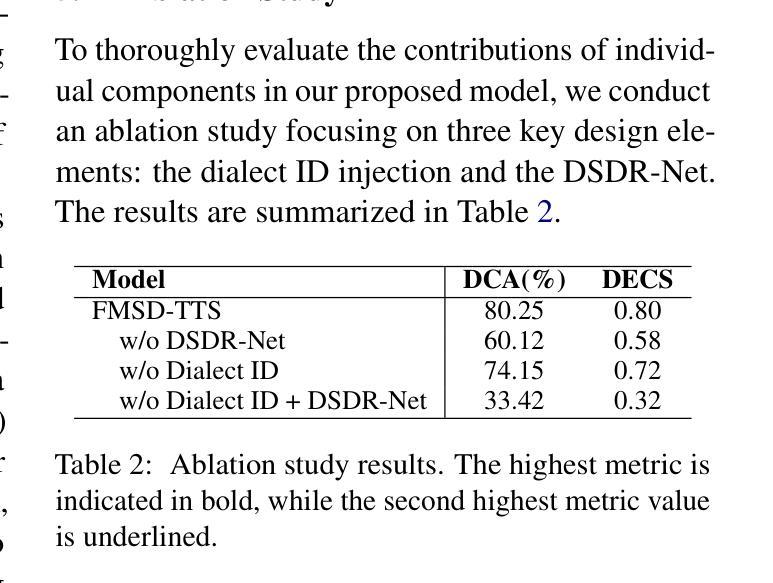
Tibetan is a low-resource language with minimal parallel speech corpora spanning its three major dialects-"U-Tsang, Amdo, and Kham-limiting progress in speech modeling. To address this issue, we propose FMSD-TTS, a few-shot, multi-speaker, multi-dialect text-to-speech framework that synthesizes parallel dialectal speech from limited reference audio and explicit dialect labels. Our method features a novel speaker-dialect fusion module and a Dialect-Specialized Dynamic Routing Network (DSDR-Net) to capture fine-grained acoustic and linguistic variations across dialects while preserving speaker identity. Extensive objective and subjective evaluations demonstrate that FMSD-TTS significantly outperforms baselines in both dialectal expressiveness and speaker similarity. We further validate the quality and utility of the synthesized speech through a challenging speech-to-speech dialect conversion task. Our contributions include: (1) a novel few-shot TTS system tailored for Tibetan multi-dialect speech synthesis, (2) the public release of a large-scale synthetic Tibetan speech corpus generated by FMSD-TTS, and (3) an open-source evaluation toolkit for standardized assessment of speaker similarity, dialect consistency, and audio quality.
藏语是一种资源匮乏的语言,其三大方言区——乌齐、安多和康区的平行语音语料库极其有限,限制了语音建模的进展。为了解决这一问题,我们提出了FMSD-TTS,这是一个少样本、多发言人、多方言的文本到语音框架,它可以从有限的参考音频和明确的方言标签中合成平行方言语音。我们的方法具有新颖的发声人-方言融合模块和方言专业化动态路由网络(DSDR-Net),能够捕捉不同方言之间的细微声学和语言变化,同时保留发声人的身份。大量的客观和主观评估表明,FMSD-TTS在方言表现力和发声人相似性方面显著优于基准线。我们进一步通过具有挑战性的语音到语音方言转换任务验证了合成语音的质量和实用性。我们的贡献包括:(1)针对藏语多方言语音合成的新型少样本TTS系统,(2)公开发布由FMSD-TTS生成的大规模合成藏语语音语料库,(3)开放源代码评估工具包,用于标准化评估发声人相似性、方言一致性和音频质量。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 13 pages
Summary
该文本介绍了针对藏语这一低资源语言,如何通过使用少量数据解决其在语音建模方面的挑战。为此,提出了一个面向少数演讲者、多方言的文本到语音框架FMSD-TTS,通过有限参考音频和明确的方言标签合成并行方言语音。该框架具有新颖的演讲者-方言融合模块和方言特定动态路由网络(DSDR-Net),可捕捉方言间的细微声学差异和语言变化,同时保留演讲者身份。评估和实验证明,FMSD-TTS在方言表达力和演讲者相似性方面明显优于基线系统。此外,通过具有挑战性的语音到语音方言转换任务验证了合成语音的质量和实用性。
Key Takeaways
- 藏语是低资源语言,缺乏平行语料库,限制其语音建模发展。
- 提出FMSD-TTS框架,实现利用有限数据合成方言语音。
- FMSD-TTS具备多方言和演讲者能力,并通过融合模块和DSDR-Net技术捕捉方言差异和语言变化。
- FMSD-TTS显著提高了方言表达力和演讲者相似性方面的性能。
- 通过语音到语音方言转换任务验证了合成语音的质量和实用性。
- 公开发布由FMSD-TTS生成的大规模藏语合成语音语料库。
点此查看论文截图

A MIND for Reasoning: Meta-learning for In-context Deduction
Authors:Leonardo Bertolazzi, Manuel Vargas Guzmán, Raffaella Bernardi, Maciej Malicki, Jakub Szymanik
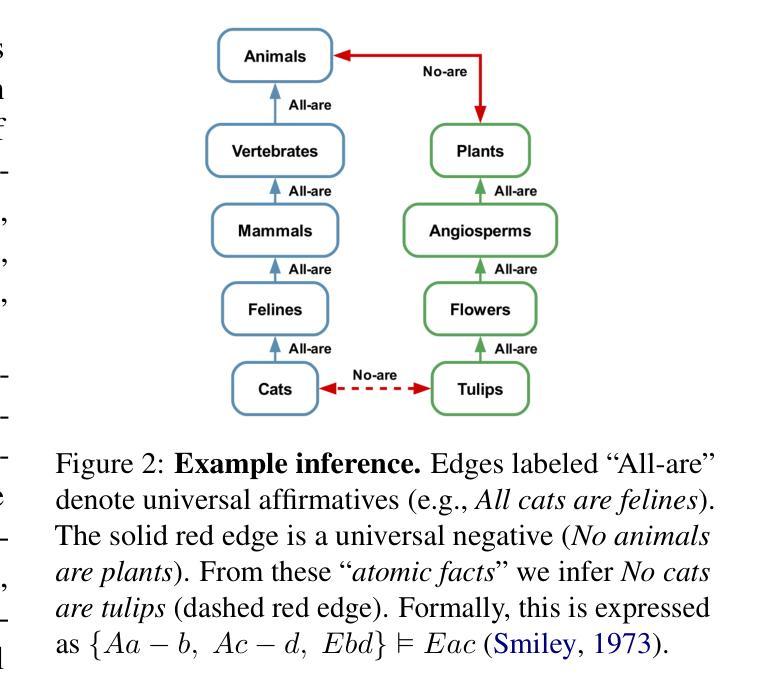
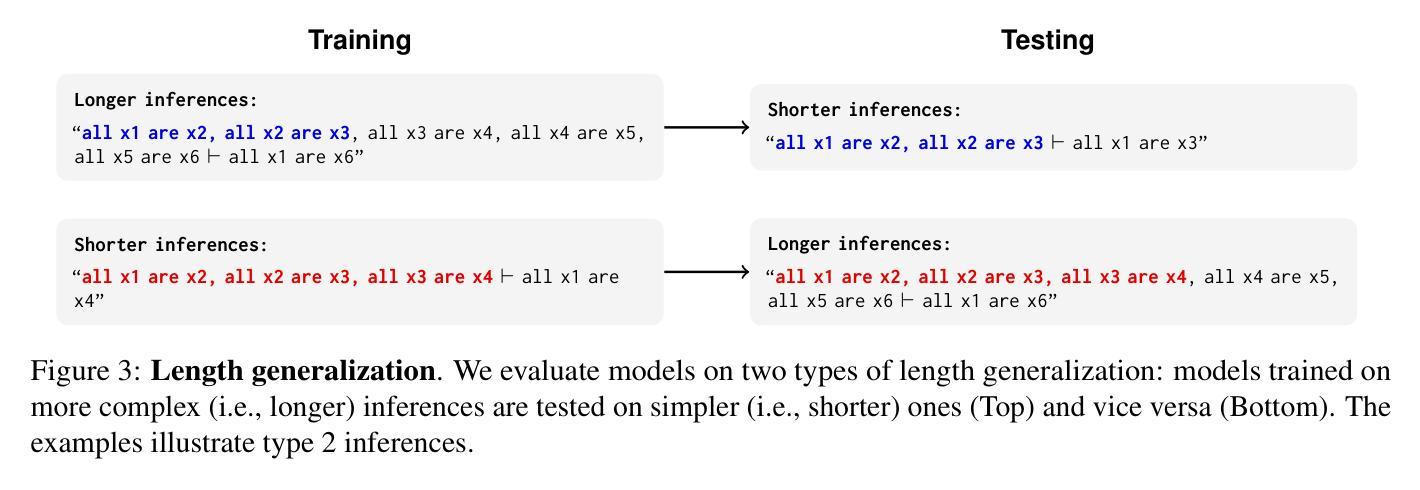
Large language models (LLMs) are increasingly evaluated on formal tasks, where strong reasoning abilities define the state of the art. However, their ability to generalize to out-of-distribution problems remains limited. In this paper, we investigate how LLMs can achieve a systematic understanding of deductive rules. Our focus is on the task of identifying the appropriate subset of premises within a knowledge base needed to derive a given hypothesis. To tackle this challenge, we propose Meta-learning for In-context Deduction (MIND), a novel few-shot meta-learning fine-tuning approach. The goal of MIND is to enable models to generalize more effectively to unseen knowledge bases and to systematically apply inference rules. Our results show that MIND significantly improves generalization in small LMs ranging from 1.5B to 7B parameters. The benefits are especially pronounced in smaller models and low-data settings. Remarkably, small models fine-tuned with MIND outperform state-of-the-art LLMs, such as GPT-4o and o3-mini, on this task.
大型语言模型(LLM)在正式任务上的评估越来越多,其中强大的推理能力定义了前沿技术。然而,它们对于非分布问题的泛化能力仍然有限。在本文中,我们研究了LLM如何实现对演绎规则的系统理解。我们的重点是解决在知识库中识别用于推导给定假设所需前提的适当子集的任务。为了应对这一挑战,我们提出了用于上下文内演绎的元学习(MIND),这是一种新型的小样本元学习微调方法。MIND的目标是使模型能够更有效地泛化到未见过的知识库,并系统地应用推理规则。我们的结果表明,MIND显著提高了从1.5B到7B参数范围内的小型LM的泛化能力。特别是在小型模型和低数据设置下,其优势尤为突出。值得注意的是,使用MIND微调的小型模型在此任务上的表现优于最新的大型语言模型,如GPT-4o和o3-mini。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
大型语言模型在正式任务上的表现日益受到重视,其强大的推理能力成为衡量技术发展水平的关键指标。然而,它们对于跨分布问题的泛化能力仍然有限。本文旨在探究如何让大型语言模型系统理解演绎规则。我们聚焦于识别知识库中用于推导给定假设所需的前提条件的任务。为解决这一难题,我们提出了名为 MIND(用于上下文内演绎的元学习)的新型元学习微调方法。MIND 的目标是让模型更有效地泛化到未见过的知识库,并系统地应用推理规则。结果显示,MIND 在小型语言模型上的泛化能力显著提升,尤其是参数较少的情况下。值得一提的是,采用 MIND 精细训练的小型模型在此任务上的表现优于现有的大型语言模型,如GPT-4o和o3-mini。
Key Takeaways
- 大型语言模型在正式任务上的推理能力成为衡量技术发展的关键指标。
- 大型语言模型的泛化能力对于跨分布问题仍然有限。
- 本文聚焦于大型语言模型对演绎规则的系统理解。
- 提出了一种新型的元学习微调方法MIND,用于解决识别知识库中推导给定假设所需前提条件的任务。
- MIND提高了小型语言模型的泛化能力,特别是在参数较少的情况下。
- 采用MIND训练的小型模型在特定任务上的表现优于现有大型语言模型。
点此查看论文截图

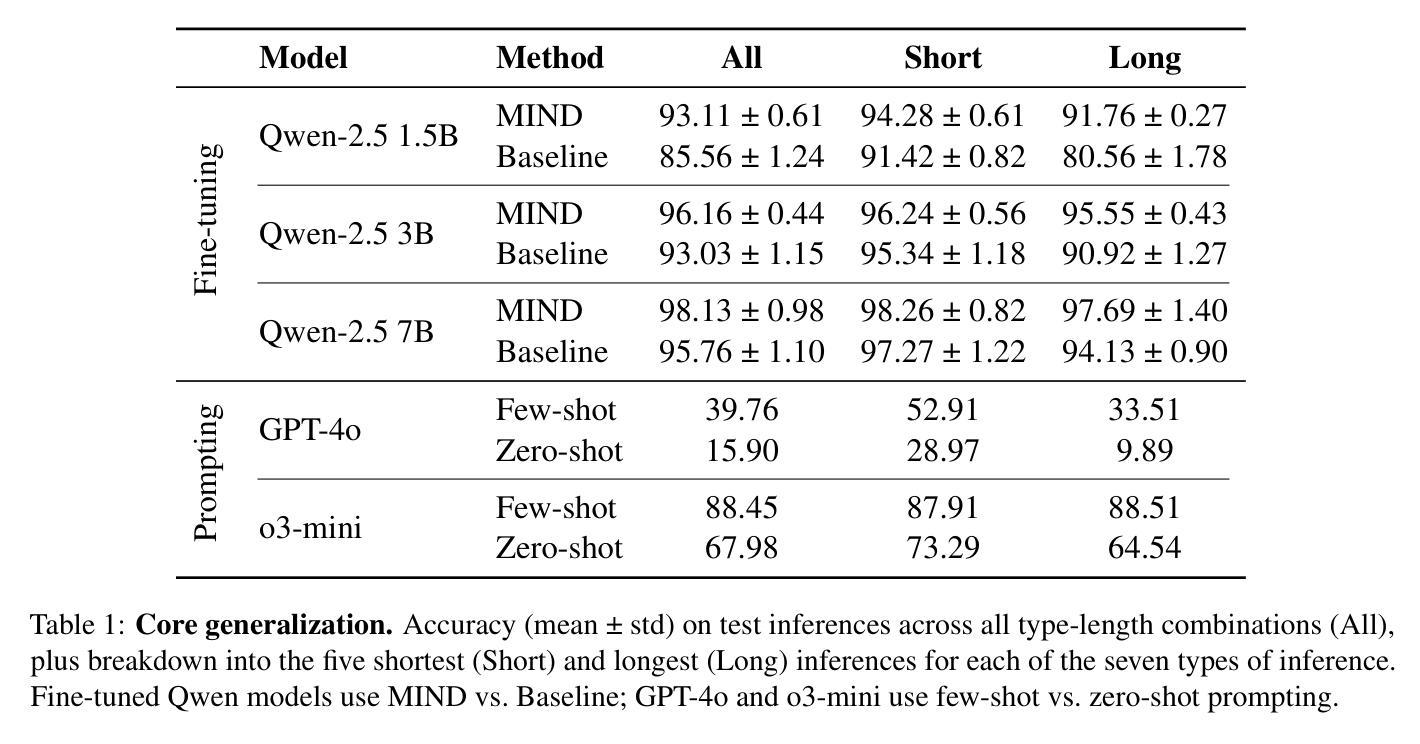
Decoupling Classifier for Boosting Few-shot Object Detection and Instance Segmentation
Authors:Bin-Bin Gao, Xiaochen Chen, Zhongyi Huang, Congchong Nie, Jun Liu, Jinxiang Lai, Guannan Jiang, Xi Wang, Chengjie Wang
This paper focus on few-shot object detection(FSOD) and instance segmentation(FSIS), which requires a model to quickly adapt to novel classes with a few labeled instances. The existing methods severely suffer from bias classification because of the missing label issue which naturally exists in an instance-level few-shot scenario and is first formally proposed by us. Our analysis suggests that the standard classification head of most FSOD or FSIS models needs to be decoupled to mitigate the bias classification. Therefore, we propose an embarrassingly simple but effective method that decouples the standard classifier into two heads. Then, these two individual heads are capable of independently addressing clear positive samples and noisy negative samples which are caused by the missing label. In this way, the model can effectively learn novel classes while mitigating the effects of noisy negative samples. Without bells and whistles, our model without any additional computation cost and parameters consistently outperforms its baseline and state-of-the-art by a large margin on PASCAL VOC and MS-COCO benchmarks for FSOD and FSIS tasks. The Code is available at https://csgaobb.github.io/Projects/DCFS.
本文关注少样本目标检测(FSOD)和实例分割(FSIS),这需要模型能够快速地适应具有少量标记实例的新类别。由于实例级少样本场景中自然存在的缺失标签问题,现有方法遭受严重的偏置分类。我们首次正式提出这一问题。我们的分析表明,大多数FSOD或FSIS模型的标准分类头需要解耦,以减轻偏置分类。因此,我们提出了一种简单而有效的方法,将标准分类器解耦为两个头。然后,这两个独立的头能够独立地处理由缺失标签引起的清晰正样本和嘈杂负样本。通过这种方式,模型可以有效地学习新类别,同时减轻嘈杂负样本的影响。没有额外的计算和参数成本,我们的模型在FSOD和FSIS任务的PASCAL VOC和MS-COCO基准测试上始终优于其基线和其他最新技术。代码可在https://csgaobb.github.io/Projects/DCFS上找到。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by NeurIPS 2022
Summary
该论文关注少样本目标检测(FSOD)和实例分割(FSIS),针对模型在新类别中快速适应的问题提出了解决方案。现有方法受到缺失标签导致的偏见分类的困扰,论文首次正式提出这一问题并分析了标准的分类头需要进行解耦以减少偏见分类。论文提出了一个简单而有效的方法来解耦标准分类器为两个头,能够独立处理清晰的阳性样本和缺失标签导致的噪声阴性样本。此方法不仅有效学习了新类别,还减少了噪声阴性样本的影响,在PASCAL VOC和MS-COCO的FSOD和FSIS任务基准测试中大幅度优于其他方法,且无额外的计算成本和参数。
Key Takeaways
- 该论文聚焦于少样本目标检测和实例分割领域的问题。
- 模型在新类别中快速适应的问题是一大挑战。
- 现有方法受到缺失标签导致的偏见分类困扰。
- 论文提出了一个简单有效的解耦标准分类器的方法,将其分为两个头来处理不同的样本类型。
- 该方法能够减少噪声阴性样本的影响,提高模型学习效果。
- 在PASCAL VOC和MS-COCO的基准测试中,该方法显著优于其他方法。
点此查看论文截图

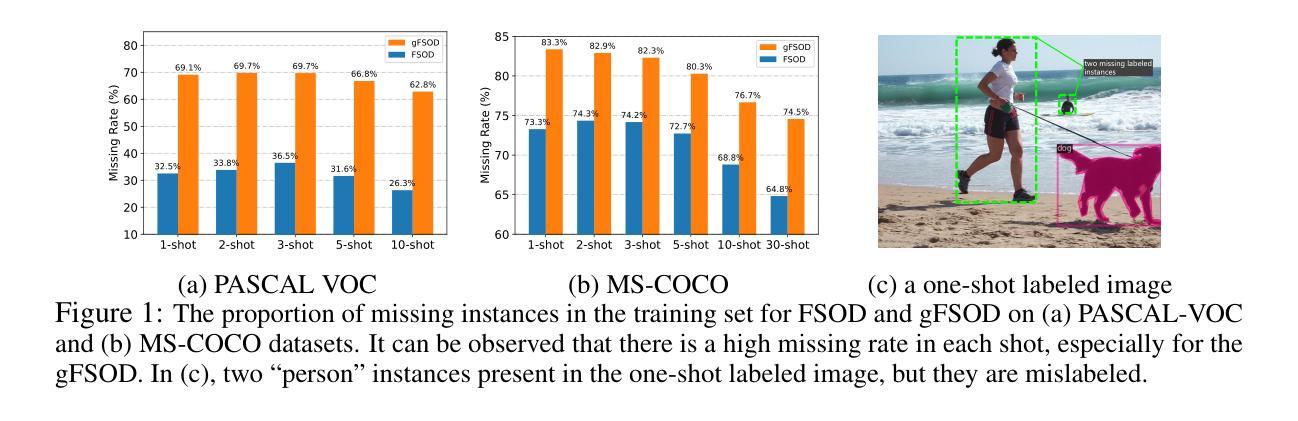
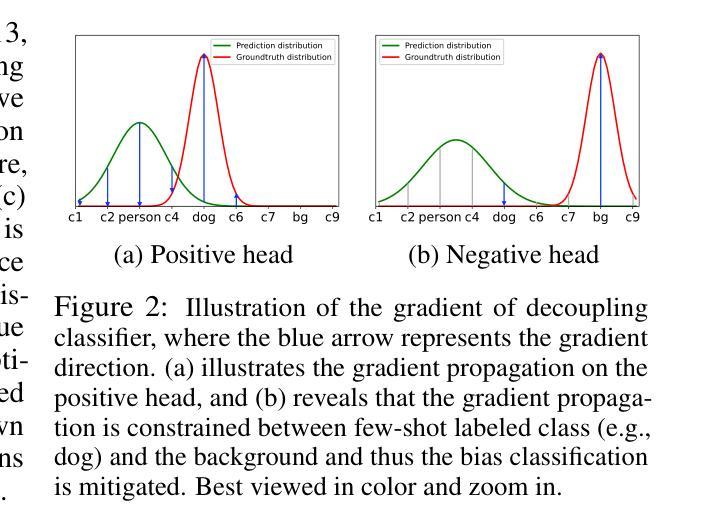
Mechanistic Fine-tuning for In-context Learning
Authors:Hakaze Cho, Peng Luo, Mariko Kato, Rin Kaenbyou, Naoya Inoue
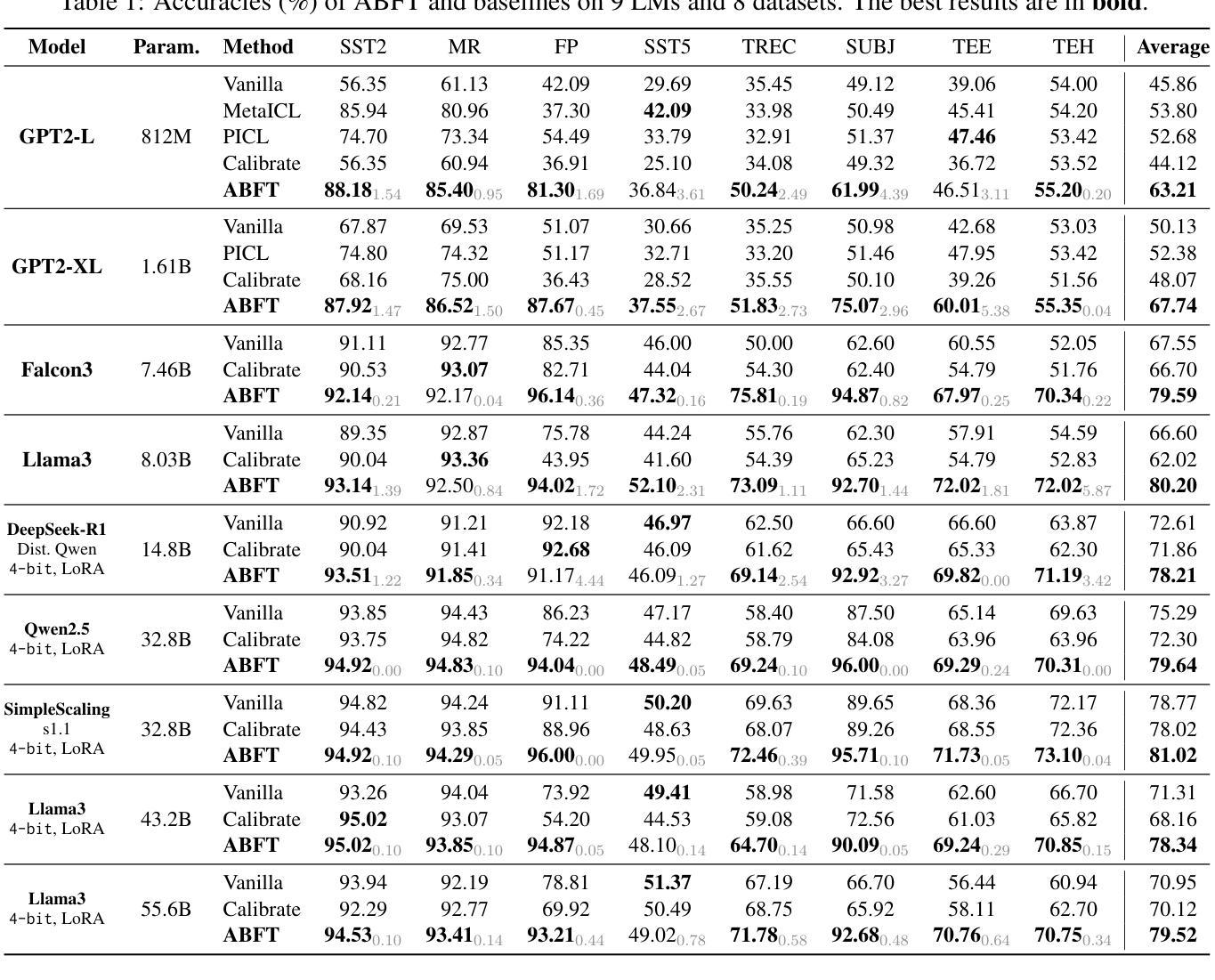
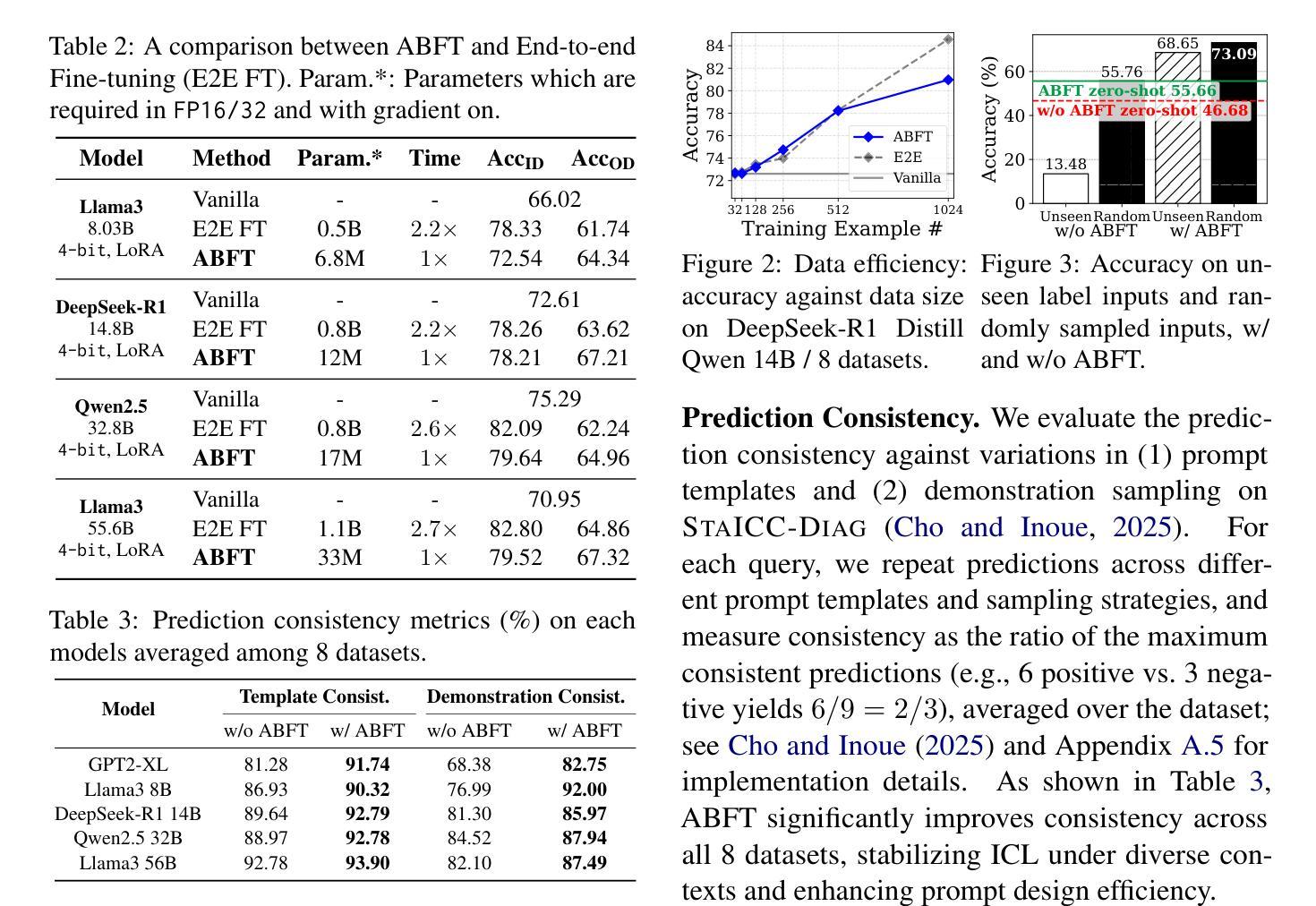
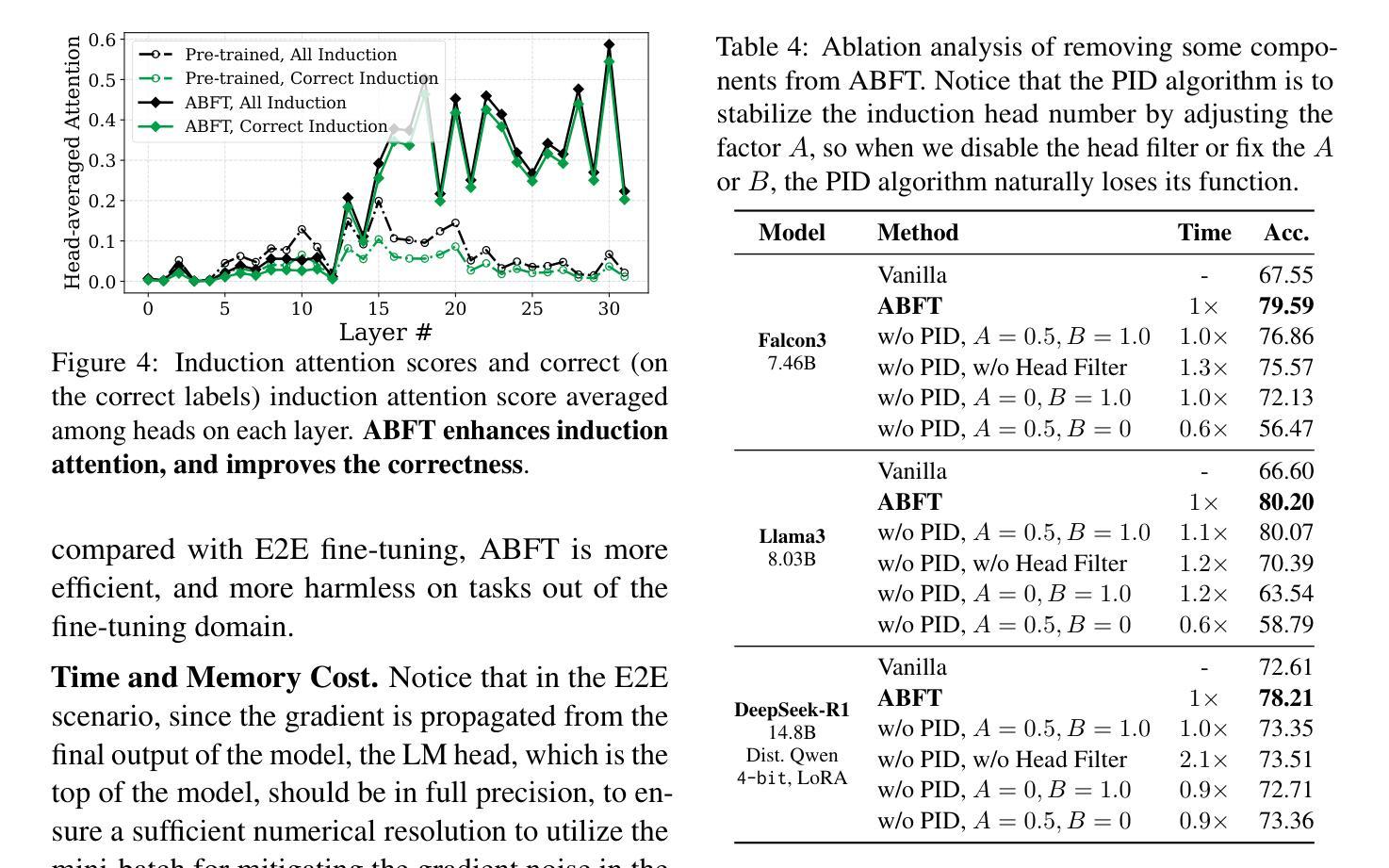
In-context Learning (ICL) utilizes structured demonstration-query inputs to induce few-shot learning on Language Models (LMs), which are not originally pre-trained on ICL-style data. To bridge the gap between ICL and pre-training, some approaches fine-tune LMs on large ICL-style datasets by an end-to-end paradigm with massive computational costs. To reduce such costs, in this paper, we propose Attention Behavior Fine-Tuning (ABFT), utilizing the previous findings on the inner mechanism of ICL, building training objectives on the attention scores instead of the final outputs, to force the attention scores to focus on the correct label tokens presented in the context and mitigate attention scores from the wrong label tokens. Our experiments on 9 modern LMs and 8 datasets empirically find that ABFT outperforms in performance, robustness, unbiasedness, and efficiency, with only around 0.01% data cost compared to the previous methods. Moreover, our subsequent analysis finds that the end-to-end training objective contains the ABFT objective, suggesting the implicit bias of ICL-style data to the emergence of induction heads. Our work demonstrates the possibility of controlling specific module sequences within LMs to improve their behavior, opening up the future application of mechanistic interpretability.
上下文学习(ICL)利用结构化演示查询输入,以在语言模型(LMs)上实现少量学习,这些语言模型最初并未在ICL风格的数据上进行预训练。为了弥补ICL和预训练之间的差距,一些方法通过端到端的范式对LMs进行微调以适应大规模ICL风格的数据集,这产生了巨大的计算成本。为了降低这种成本,本文提出了注意力行为微调(ABFT),它利用对ICL内在机制的前期发现,在注意力分数上构建训练目标,而不是最终的输出。这迫使注意力分数关注上下文中出现的正确标签令牌,并减轻了对错误标签令牌的注意力分数。我们在9个现代LMs和8个数据集上的实验证实,ABFT在性能、稳健性、公正性和效率方面优于其他方法,与以前的方法相比,数据成本只有约0.01%。此外,我们的后续分析发现,端到端的训练目标包含ABFT目标,这表明ICL风格数据对归纳头的出现存在隐性偏见。我们的工作展示了控制LM内特定模块序列的可能性,以提高其行为表现,为未来的机械解释性应用开辟了道路。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 28 pages, 31 figures, 6 tables
Summary
基于演示查询输入实现少数样本学习的语境学习(ICL)方法,通过调整语言模型(LM)来弥补其与预训练之间的差距。为降低成本,本文提出利用语境学习的内在机制,通过关注注意力分数构建训练目标,迫使注意力分数聚焦于正确标签词,同时削弱错误标签词的注意力分数的方法——注意力行为微调(ABFT)。实验证明,ABFT在性能、稳健性、公正性和效率方面均优于传统方法,数据成本仅约为传统方法的千分之一。同时分析显示,端到端的训练目标包含了ABFT目标,表明语境学习数据的隐性偏向归纳头的出现。本文展示了控制语言模型内部特定模块序列以改善其行为的可能性,为未来的机械解释性应用打开了大门。
Key Takeaways
- ICL利用结构化的演示查询输入实现少数样本学习。
- ABFT方法通过关注注意力分数来构建训练目标,强化模型对正确标签的关注并削弱错误标签的影响。
- ABFT在性能、稳健性、公正性和效率方面优于传统方法。
- ABFT数据成本极低,约为传统方法的千分之一。
- 端到端的训练目标包含ABFT目标,显示出语境学习数据的隐性偏向。
- 本文揭示了控制语言模型内部特定模块序列的可能性,以提高其行为表现。
点此查看论文截图

Unlocking the Power of SAM 2 for Few-Shot Segmentation
Authors:Qianxiong Xu, Lanyun Zhu, Xuanyi Liu, Guosheng Lin, Cheng Long, Ziyue Li, Rui Zhao
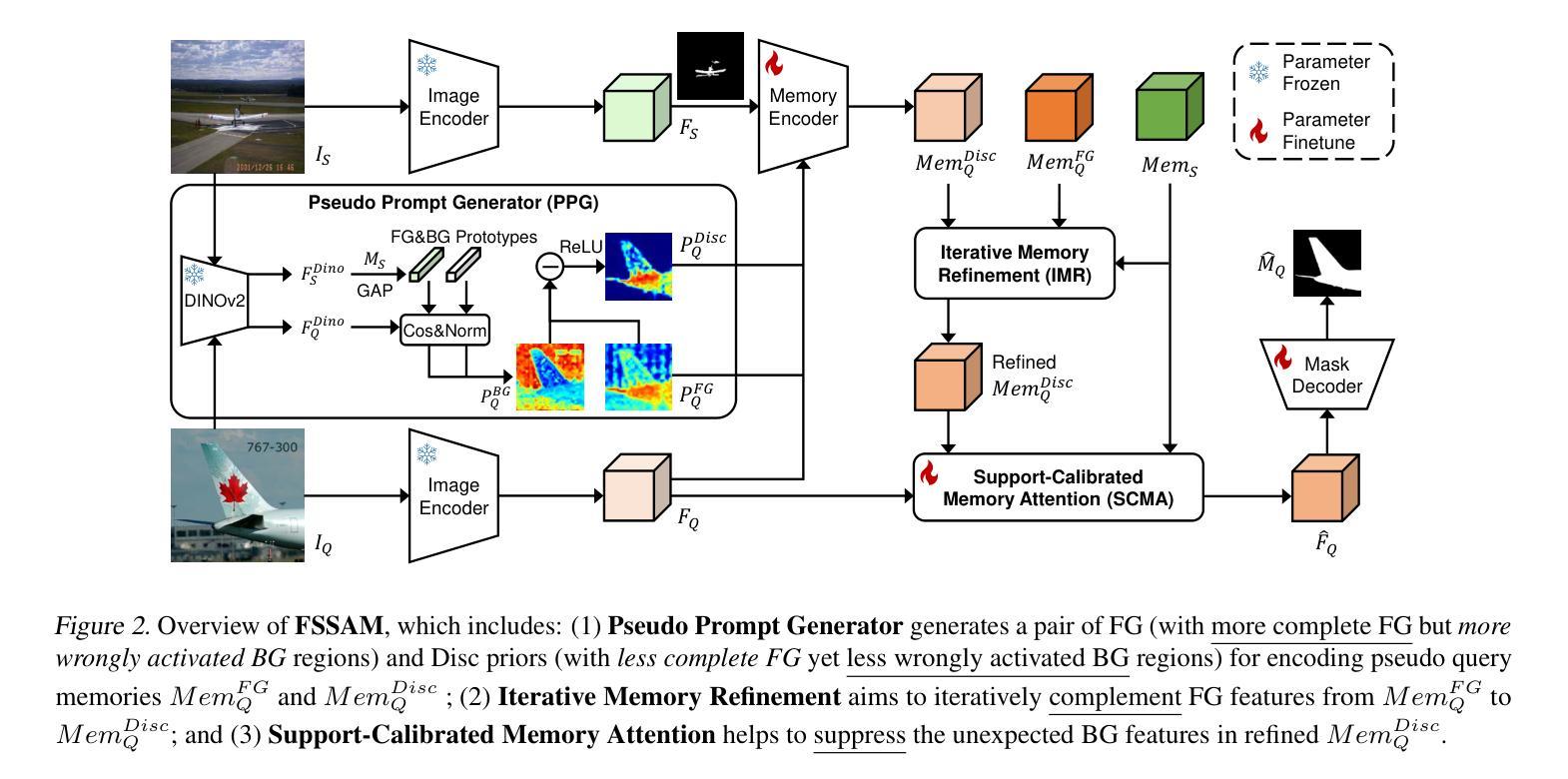
Few-Shot Segmentation (FSS) aims to learn class-agnostic segmentation on few classes to segment arbitrary classes, but at the risk of overfitting. To address this, some methods use the well-learned knowledge of foundation models (e.g., SAM) to simplify the learning process. Recently, SAM 2 has extended SAM by supporting video segmentation, whose class-agnostic matching ability is useful to FSS. A simple idea is to encode support foreground (FG) features as memory, with which query FG features are matched and fused. Unfortunately, the FG objects in different frames of SAM 2’s video data are always the same identity, while those in FSS are different identities, i.e., the matching step is incompatible. Therefore, we design Pseudo Prompt Generator to encode pseudo query memory, matching with query features in a compatible way. However, the memories can never be as accurate as the real ones, i.e., they are likely to contain incomplete query FG, and some unexpected query background (BG) features, leading to wrong segmentation. Hence, we further design Iterative Memory Refinement to fuse more query FG features into the memory, and devise a Support-Calibrated Memory Attention to suppress the unexpected query BG features in memory. Extensive experiments have been conducted on PASCAL-5$^i$ and COCO-20$^i$ to validate the effectiveness of our design, e.g., the 1-shot mIoU can be 4.2% better than the best baseline.
少样本分割(FSS)旨在学习对少数类别的类无关分割,以实现对任意类别的分割,但存在过拟合的风险。为了解决这一问题,一些方法使用基础模型的已学知识(例如SAM)来简化学习过程。最近,SAM 2通过支持视频分割扩展了SAM的应用,其类无关匹配能力对FSS很有用。一个简单的想法是将支持前景(FG)特征编码为内存,通过其与查询前景特征进行匹配和融合。然而,不幸的是,SAM 2的视频数据不同帧中的前景对象始终是同一身份,而FSS中的则是不同身份,即匹配步骤是不兼容的。因此,我们设计了伪提示生成器来编码伪查询内存,以与查询特征进行兼容匹配。然而,这些记忆无论如何都无法达到真实记忆的水平,即它们可能包含不完整查询前景和一些意外的查询背景(BG)特征,从而导致错误的分割。因此,我们进一步设计了迭代内存优化,将更多查询前景特征融合到内存中,并设计了一个支持校准的内存注意力来抑制内存中意外的查询背景特征。在PASCAL-5$^i$和COCO-20$^i$上进行了大量实验,验证了我们的设计效果,例如,我们的方法在1-shot mIoU上的表现比最佳基线提高了4.2%。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF This paper is accepted by ICML’25
Summary
该文本介绍了Few-Shot Segmentation(FSS)的目标是利用有限的类别数据进行类无关的分割学习。为了解决过拟合问题,一些方法利用基础模型的先验知识简化学习过程。最近,SAM 2扩展了SAM,支持视频分割,其类无关的匹配能力对FSS很有用。文本中提出了一种简单的方法,即编码支持前景特征作为内存,与查询前景特征进行匹配和融合。然而,SAM 2的视频数据中的前景对象身份始终相同,而FSS中的则不同,导致匹配步骤不兼容。因此,设计了伪提示生成器来编码伪查询内存,以兼容方式匹配查询特征。但记忆永远无法像真实记忆那样准确,可能包含不完整或意外的查询前景和背景特征,导致错误分割。因此,进一步设计了迭代内存细化,将更多查询前景特征融合到内存中,并设计了一种支持校准的内存注意力来抑制内存中的意外查询背景特征。
Key Takeaways
- Few-Shot Segmentation (FSS) 旨在利用有限的类别数据进行类无关的分割学习,但存在过拟合的风险。
- SAM 2扩展了SAM方法以支持视频分割,利用类无关的匹配能力。
- 提出了一种简单的方法,通过编码支持前景特征作为内存进行匹配和融合。
- SAM 2与FSS在前景对象身份上存在不匹配问题。
- 为了解决此问题,设计了伪提示生成器和迭代内存细化方法。
- 伪提示生成器通过编码伪查询内存进行匹配。
- 通过广泛实验验证了设计的有效性,例如1-shot mIoU性能可提高4.2%。
点此查看论文截图

CLEVER: A Curated Benchmark for Formally Verified Code Generation
Authors:Amitayush Thakur, Jasper Lee, George Tsoukalas, Meghana Sistla, Matthew Zhao, Stefan Zetzche, Greg Durrett, Yisong Yue, Swarat Chaudhuri
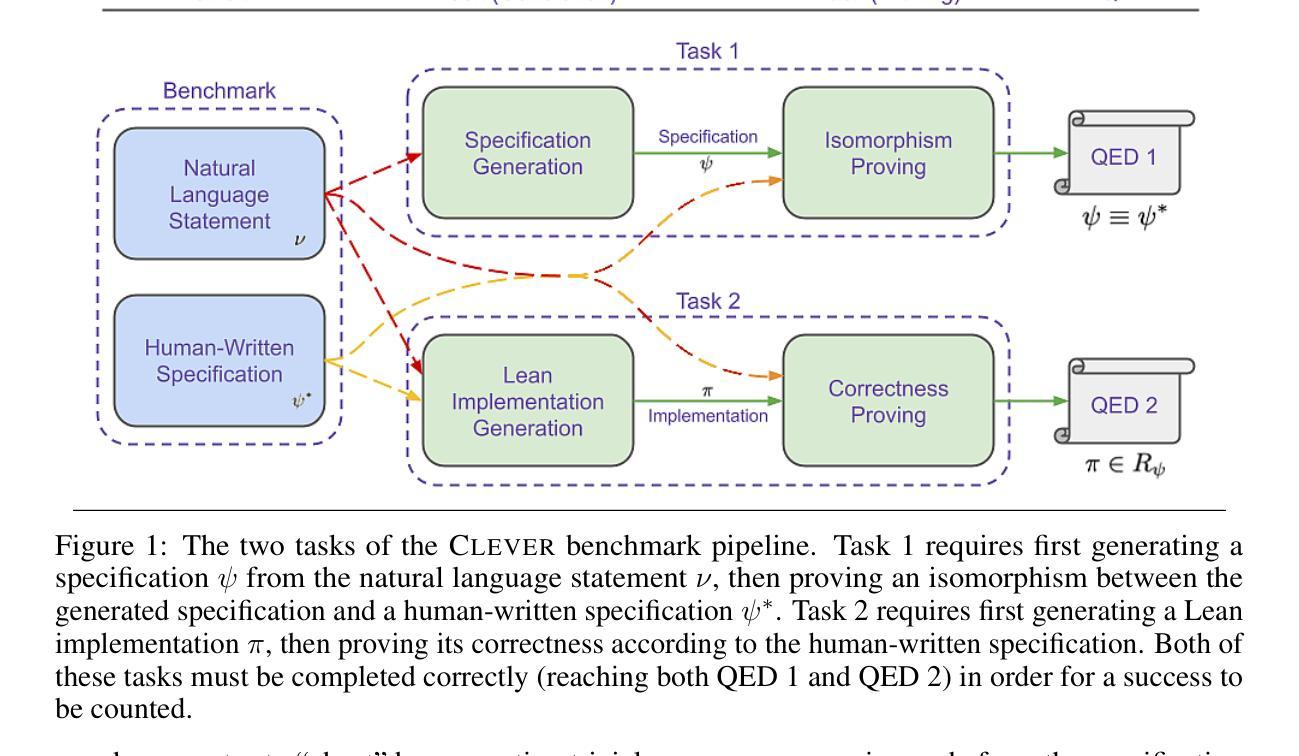
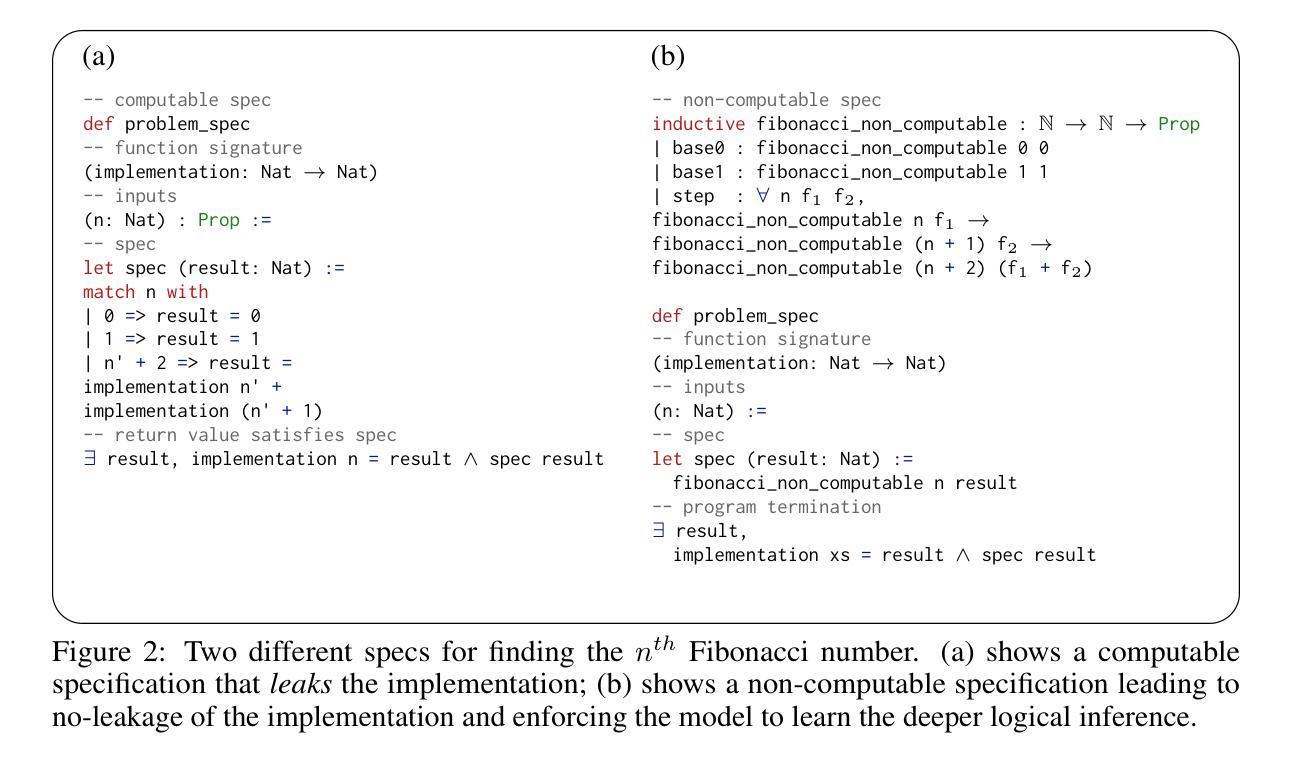
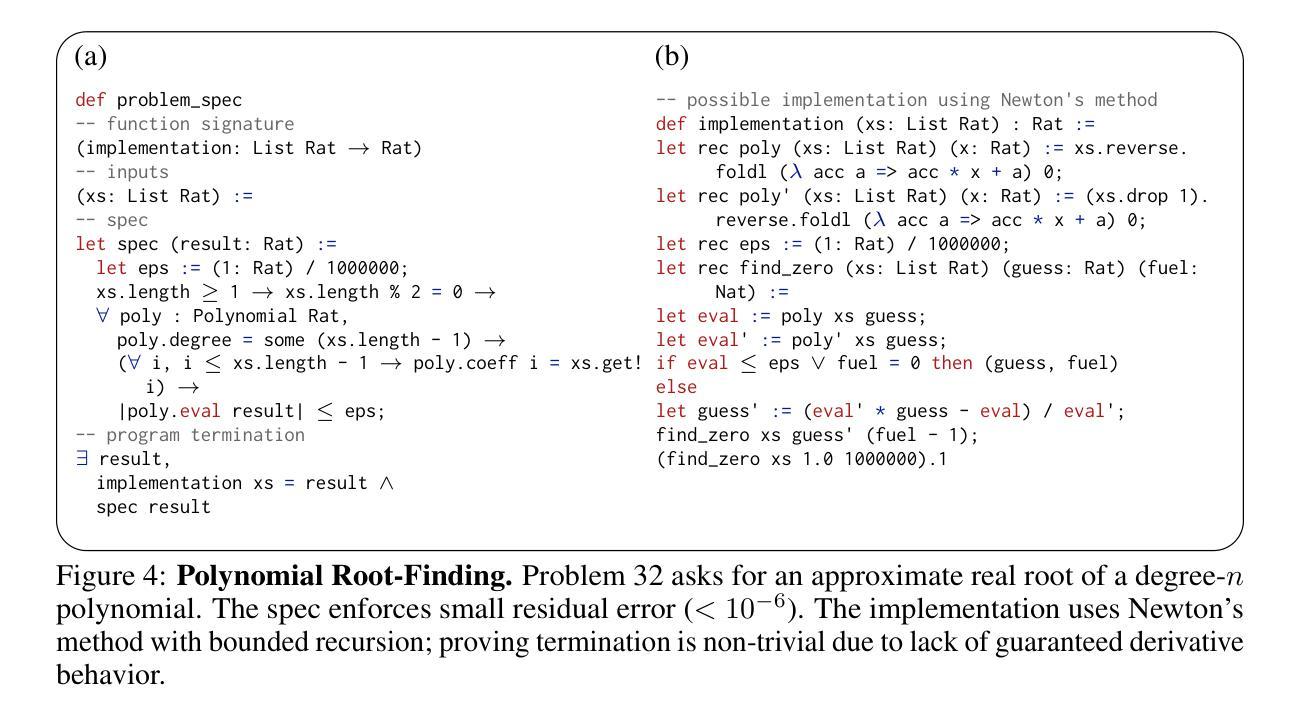
We introduce ${\rm C{\small LEVER}}$, a high-quality, curated benchmark of 161 problems for end-to-end verified code generation in Lean. Each problem consists of (1) the task of generating a specification that matches a held-out ground-truth specification, and (2) the task of generating a Lean implementation that provably satisfies this specification. Unlike prior benchmarks, ${\rm C{\small LEVER}}$ avoids test-case supervision, LLM-generated annotations, and specifications that leak implementation logic or allow vacuous solutions. All outputs are verified post-hoc using Lean’s type checker to ensure machine-checkable correctness. We use ${\rm C{\small LEVER}}$ to evaluate several few-shot and agentic approaches based on state-of-the-art language models. These methods all struggle to achieve full verification, establishing it as a challenging frontier benchmark for program synthesis and formal reasoning. Our benchmark can be found on GitHub(https://github.com/trishullab/clever) as well as HuggingFace(https://huggingface.co/datasets/amitayusht/clever). All our evaluation code is also available online(https://github.com/trishullab/clever-prover).
我们介绍了${\rm C{\small LEVER}}$,这是一个高质量的、经过筛选的包含161个问题的基准测试,用于端到端的Lean代码生成验证。每个问题由两部分组成:(1)生成与保留的真实规格相匹配的规格的任务;(2)生成能够证明满足此规格要求的Lean实现的任务。不同于以前的基准测试,${\rm C{\small LEVER}}$避免了测试用例的监督、大型语言模型生成的注释以及泄露实现逻辑或允许无效解决方案的规格。所有输出都利用Lean的类型检查器进行事后验证,以确保机器可检查的正确性。我们使用${\rm C{\small LEVER}}$来评估基于最新语言模型的几种少样本和智能方法。这些方法都很难实现完全验证,从而使其成为程序合成和形式推理具有挑战性的前沿基准测试。我们的基准测试可以在GitHub(https://github.com/trishullab/clever)以及HuggingFace(https://huggingface.co/datasets/amitayusht/clever)上找到。我们的评估代码也在线可用(https://github.com/trishullab/clever-prover)。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
在中国研究团队推出的高质量基准测试集CLEVER中,共有包含端到端验证的代码生成任务共计有涵盖的161个挑战性问题。此基准测试集强调避免测试案例监督、大型语言模型生成的注释以及泄露实现逻辑或允许空洞解决方案的问题。所有输出均通过Lean的类型检查器进行事后验证,以确保机器检查正确性。针对基于当前技术水平的语言模型的少量研究和人工智能的方法进行评价。这个挑战极具标杆性。在此基础上有许多验证了人类缺乏一种可用的编码环境供交流的技术评价平台的信息系统已诞生,但在业界许多已公开的实践实例面前我们面临极大挑战,这项成果能够在GitHub、HuggingFace等平台上找到。同时,所有的评估代码也已在线发布。这为人工智能在程序合成和形式推理领域的发展提供了强有力的支持。
Key Takeaways
- ${\rm C{\small LEVER}}$ 是一个用于端到端验证的代码生成的高质量的基准测试集。具有确保机器检查正确性的特性。它包含涵盖的涵盖多个领域的挑战性问题,旨在评估语言模型的能力。
- ${\rm C{\small LEVER}}$强调真实性和难度级别高的问题设置,旨在避免简单任务和对大型语言模型的依赖性问题进行监督学习的方式设计任务内容的问题类型问题要求不同技术特征的解题方法数量之间有良好的平衡等问题以考察通用性能算法方面:规避漏洞的问题;进行输入时学习注释的程序证明技术以改进语言模型生成的输出;解决复杂性和随机性问题;确保算法质量水平在通过编程实践实例方面能够比肩人工智能水平的超越标准的方法中名列前茅等难点,展现了它的独特性。这是中国研究团队的创新性成果。随着科技的不断发展,人们对于编程语言和计算机的理解不断加深,其前景将会越来越广阔。
点此查看论文截图

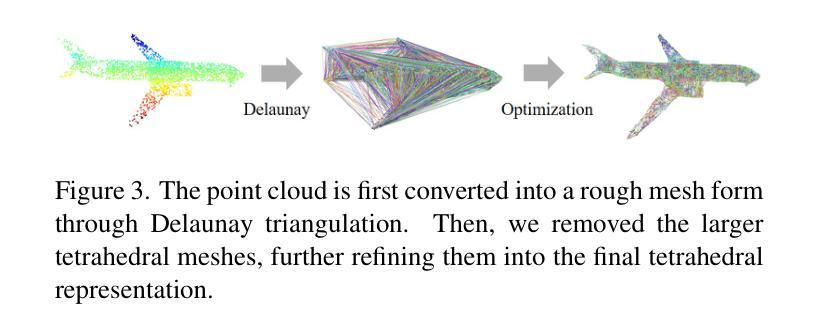
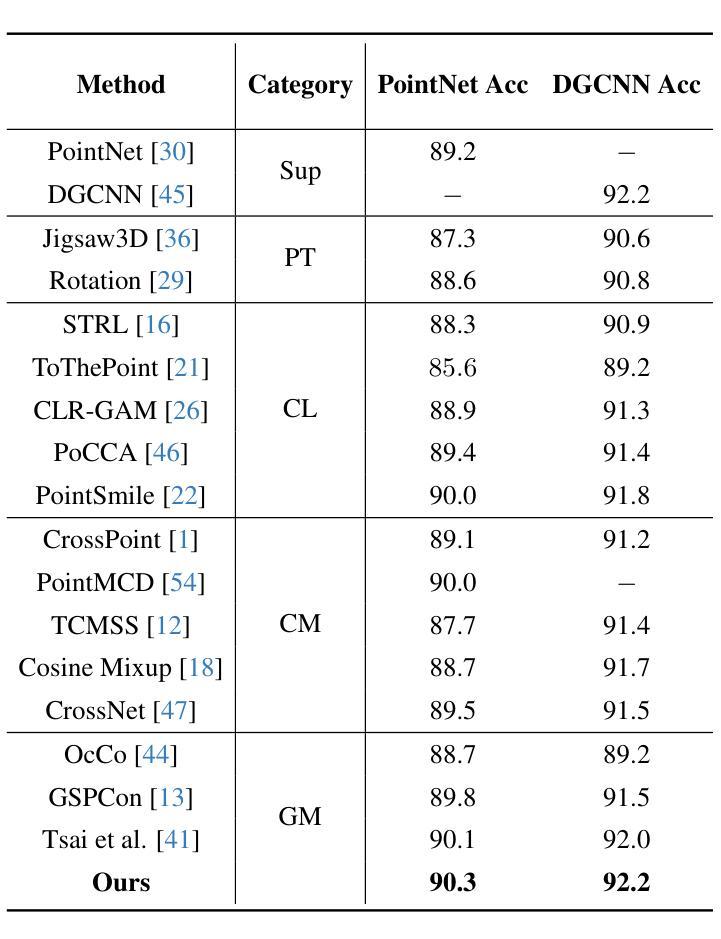
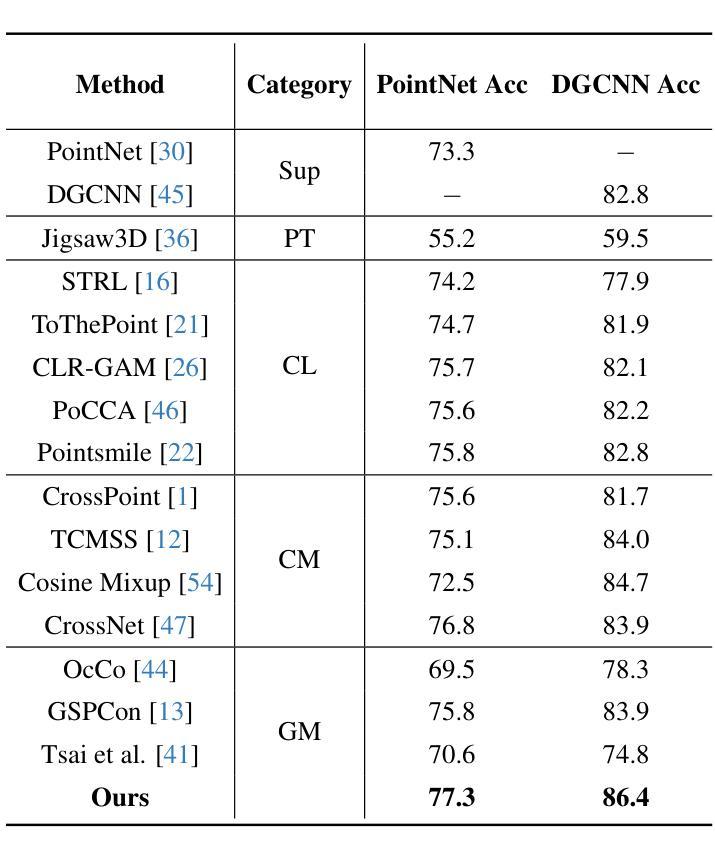
Physics-Driven Local-Whole Elastic Deformation Modeling for Point Cloud Representation Learning
Authors:Zhongyu Chen, Rong Zhao, Xie Han, Xindong Guo, Song Wang, Zherui Qiao
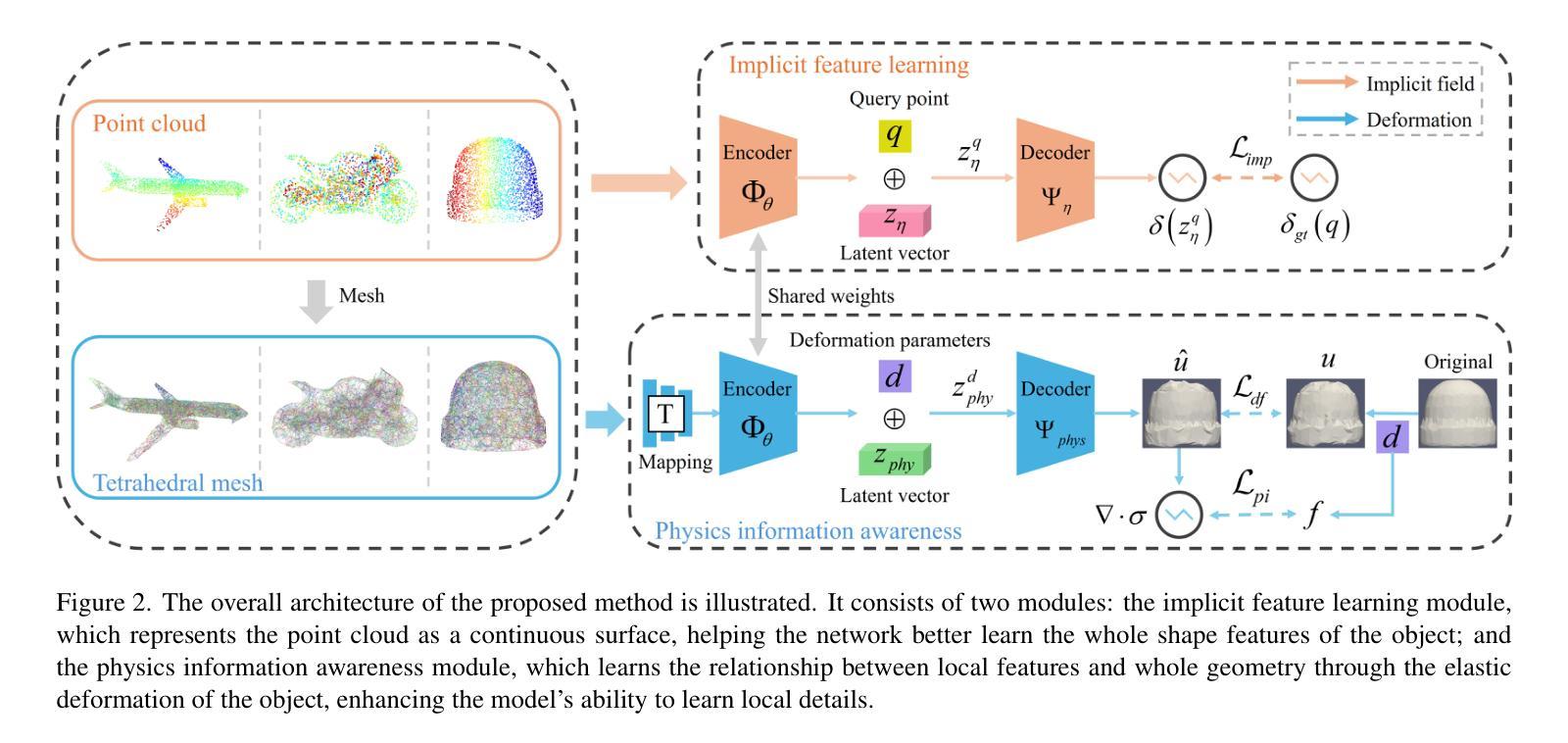
Existing point cloud representation learning tend to learning the geometric distribution of objects through data-driven approaches, emphasizing structural features while overlooking the relationship between the local information and the whole structure. Local features reflect the fine-grained variations of an object, while the whole structure is determined by the interaction and combination of these local features, collectively defining the object’s shape. In real-world, objects undergo elastic deformation under external forces, and this deformation gradually affects the whole structure through the propagation of forces from local regions, thereby altering the object’s geometric properties. Inspired by this, we propose a physics-driven self-supervised learning method for point cloud representation, which captures the relationship between parts and the whole by constructing a local-whole force propagation mechanism. Specifically, we employ a dual-task encoder-decoder framework, integrating the geometric modeling capability of implicit fields with physics-driven elastic deformation. The encoder extracts features from the point cloud and its tetrahedral mesh representation, capturing both geometric and physical properties. These features are then fed into two decoders: one learns the whole geometric shape of the point cloud through an implicit field, while the other predicts local deformations using two specifically designed physics information loss functions, modeling the deformation relationship between local and whole shapes. Experimental results show that our method outperforms existing approaches in object classification, few-shot learning, and segmentation, demonstrating its effectiveness.
现有的点云表示学习方法往往通过数据驱动的方法学习对象的几何分布,强调结构特征,但忽视了局部信息与整体结构之间的关系。局部特征反映了对象的细微变化,而整体结构则由这些局部特征的相互作用和组合决定,共同定义了对象的形状。在现实中,物体在外部力的作用下会发生弹性变形,这种变形通过从局部区域传播的力量逐渐影响整体结构,从而改变物体的几何属性。受此启发,我们提出了一种用于点云表示的物理驱动自监督学习方法,通过建立局部-整体力传播机制来捕捉部分与整体之间的关系。具体而言,我们采用双任务编码器-解码器框架,将隐场的几何建模能力与物理驱动的弹性变形相结合。编码器从点云及其四面体网格表示中提取特征,捕捉几何和物理属性。这些特征然后输入到两个解码器中:一个通过隐场学习点云的整体几何形状,另一个使用两个专门设计的物理信息损失函数来预测局部变形,建模局部和整体形状之间的变形关系。实验结果表明,我们的方法在目标分类、小样本学习和分割方面优于现有方法,证明了其有效性。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文提出了一个基于物理驱动的自我监督学习方法,用于点云表示。该方法通过构建局部与整体的力传播机制,捕捉部分与整体之间的关系,并强调在外部力作用下物体的弹性变形如何影响整体结构。实验结果表明,该方法在物体分类、少样本学习和分割方面优于现有方法。
Key Takeaways
- 现有点云表示学习方法多通过数据驱动方法学习物体的几何分布,但忽略了局部信息与整体结构之间的关系。
- 局部特征反映物体的细微变化,而整体结构由这些局部特征的相互作用和组合决定,共同定义物体的形状。
- 物体在外部力作用下会发生弹性变形,这种变形通过从局部区域传播的力逐渐影响整体结构,改变物体的几何特性。
- 本文提出了一个基于物理驱动的自我监督学习方法,通过构建局部与整体的力传播机制,捕捉点云表示中的部分与整体关系。
- 该方法结合了点云和其四面体网格表示的几何建模能力与物理驱动的弹性变形。
- 实验结果表明,该方法在物体分类、少样本学习和分割任务上表现出优异性能。
- 该方法采用双任务编码器-解码器框架,其中编码器提取点云及其四面体网格表示的特征,解码器则用于学习整个几何形状并预测局部变形。
点此查看论文截图

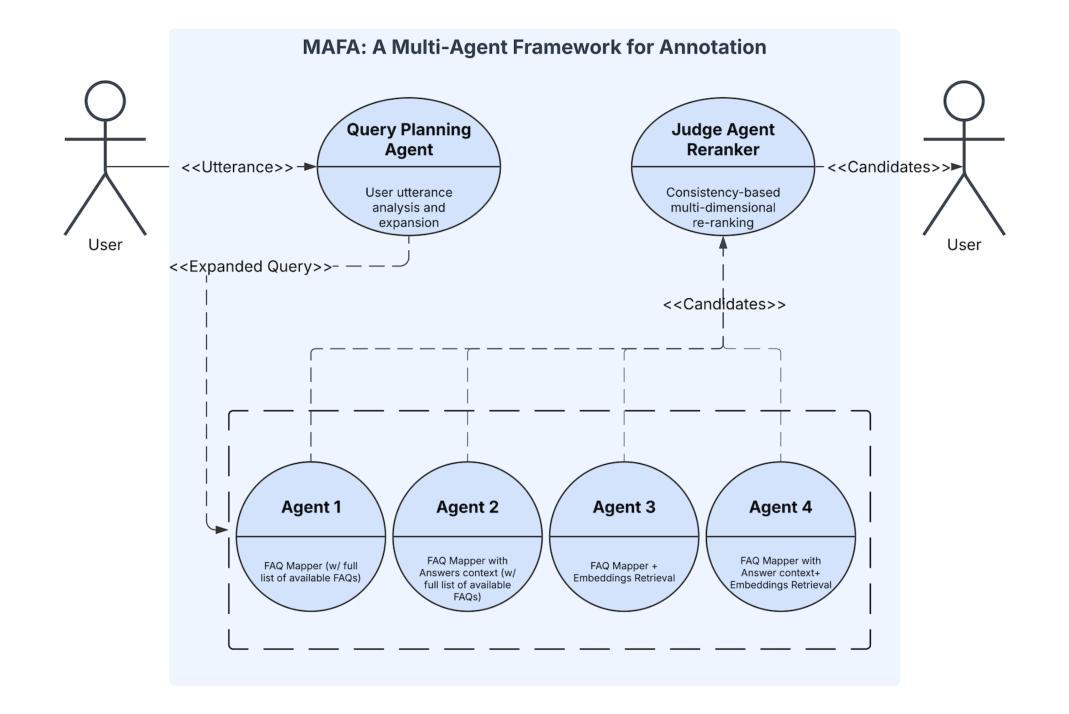
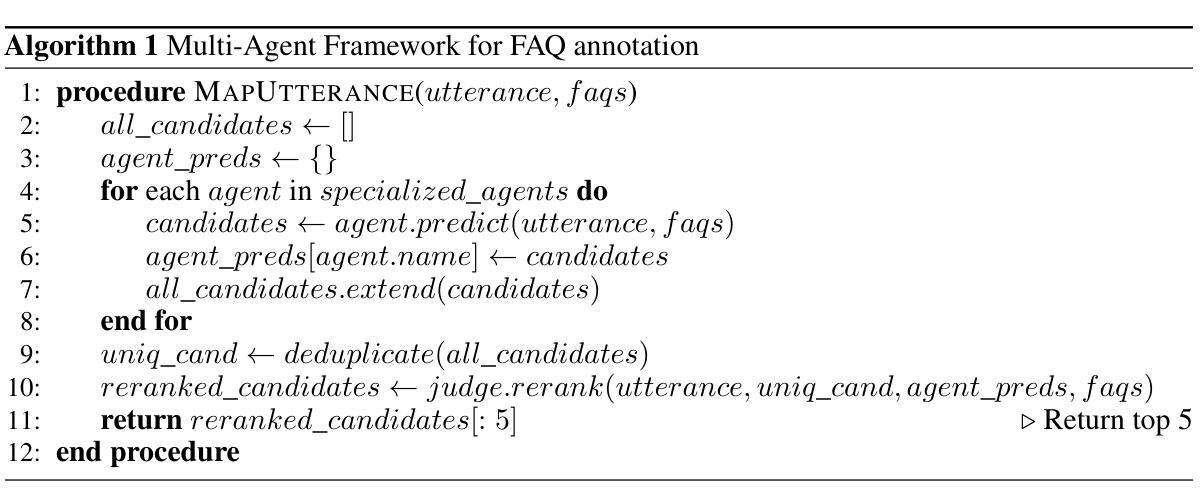
MAFA: A multi-agent framework for annotation
Authors:Mahmood Hegazy, Aaron Rodrigues, Azzam Naeem
Modern applications require accurate and efficient retrieval of information in response to user queries. Mapping user utterances to the most relevant Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) is a crucial component of these systems. Traditional approaches often rely on a single model or technique, which may not capture the nuances of diverse user inquiries. In this paper, we introduce a multi-agent framework for FAQ annotation that combines multiple specialized agents with different approaches and a judge agent that reranks candidates to produce optimal results. Our agents utilize a structured reasoning approach inspired by Attentive Reasoning Queries (ARQs), which guides them through systematic reasoning steps using targeted, task-specific JSON queries. Our framework features a specialized few-shot example strategy, where each agent receives different few-shots, enhancing ensemble diversity and coverage of the query space. We evaluate our framework on a real-world banking dataset as well as public benchmark datasets (LCQMC and FiQA), demonstrating significant improvements over single-agent approaches across multiple metrics, including a 14% increase in Top-1 accuracy, an 18% increase in Top-5 accuracy, and a 12% improvement in Mean Reciprocal Rank on our dataset, and similar gains on public benchmarks when compared with traditional single agent annotation techniques. Our framework is particularly effective at handling ambiguous queries, making it well-suited for deployment in production applications while showing strong generalization capabilities across different domains and languages.
现代应用程序需要准确高效地检索信息以响应用户查询。将用户的话语映射到最相关的常见问题解答(FAQs)是这些系统的关键组成部分。传统方法通常依赖于单个模型或技术,这可能无法捕捉到各种用户查询的细微差别。在本文中,我们介绍了一种结合多个专业代理和法官代理进行重新排名的多智能体框架,用于FAQ注释,以产生最佳结果。我们的代理采用受关注推理查询(ARQ)启发的结构化推理方法,通过使用有针对性的任务特定JSON查询来指导他们进行系统化的推理步骤。我们的框架采用专门的少量示例策略,每个代理接收不同的少量示例,增强了组合多样性和查询空间的覆盖。我们在现实世界中的银行数据集以及公共基准数据集(LCQMC和FiQA)上评估了我们的框架,与单智能体方法相比,在多个指标上取得了显著改进,包括第一名准确率提高14%,前五名准确率提高18%,以及在我们的数据集上的平均倒数排名提高12%,与传统单智能体注释技术相比,在公共基准测试上也有类似的收益。我们的框架在处理模糊查询方面特别有效,因此非常适合在生产应用程序中部署,并在不同领域和语言方面表现出强大的泛化能力。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
该论文提出了一种多智能体框架用于FAQ标注,结合了多个采用不同方法的智能体和一个法官智能体进行候选重新排序以产生最佳结果。该框架利用结构化推理方法,通过任务特定的JSON查询指导智能体进行系统性推理步骤。此外,该框架具有专门用于快速示例的策略,每个智能体接收不同的快速示例,增强了组合多样性和查询空间覆盖率。评估表明,该框架在真实银行数据集和公共基准数据集上的表现优于单智能体方法,并在多个指标上取得了显著改进。该框架特别擅长处理模糊查询,适合在生产应用中部署,并在不同领域和语言中显示出强大的泛化能力。
Key Takeaways
- 该论文提出了一种多智能体框架用于FAQ标注,旨在改进传统的单一模型或技术方法的不足。
- 多智能体框架结合了多种不同的方法和技术,并包括一个法官智能体进行候选重新排序。
- 该框架采用结构化推理方法,通过任务特定的JSON查询指导智能体的推理过程。
- 框架具有专门用于快速示例的策略,增强了智能体的组合多样性和查询空间覆盖率。
- 在真实银行数据集和公共基准数据集上的评估表明,该框架优于单智能体方法,并在多个指标上取得了显著改进。
- 该框架特别擅长处理模糊查询,适应生产环境中的复杂需求。
点此查看论文截图
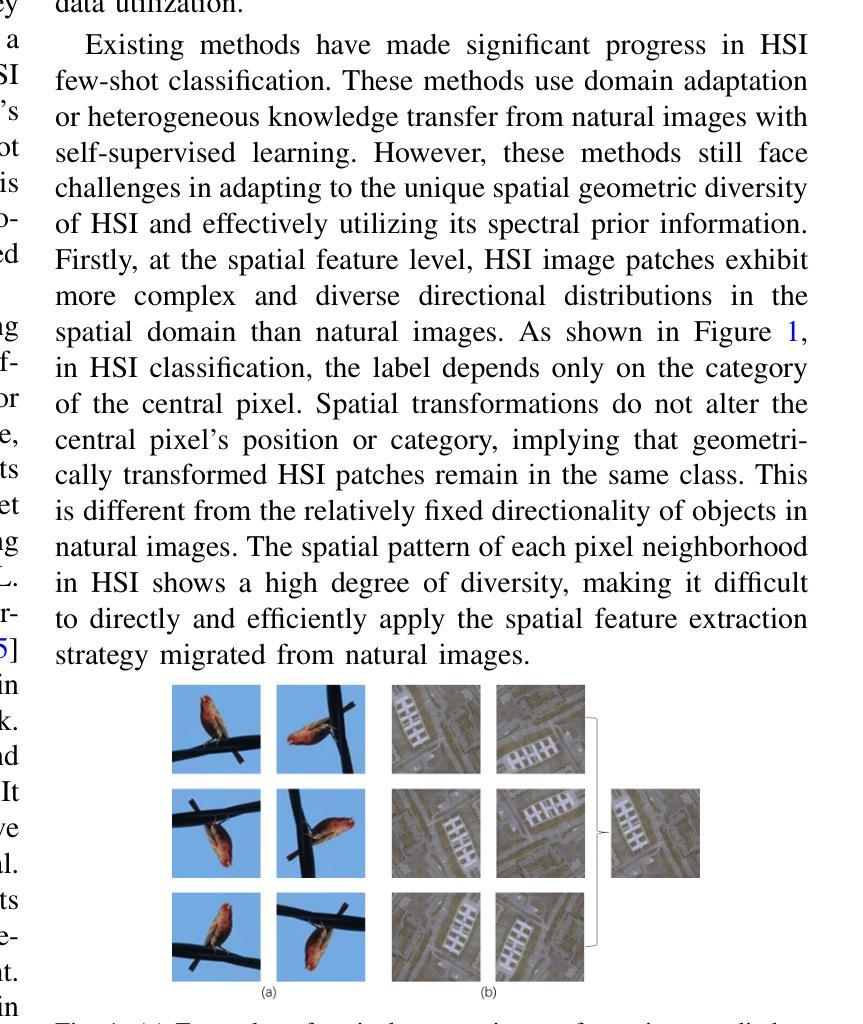
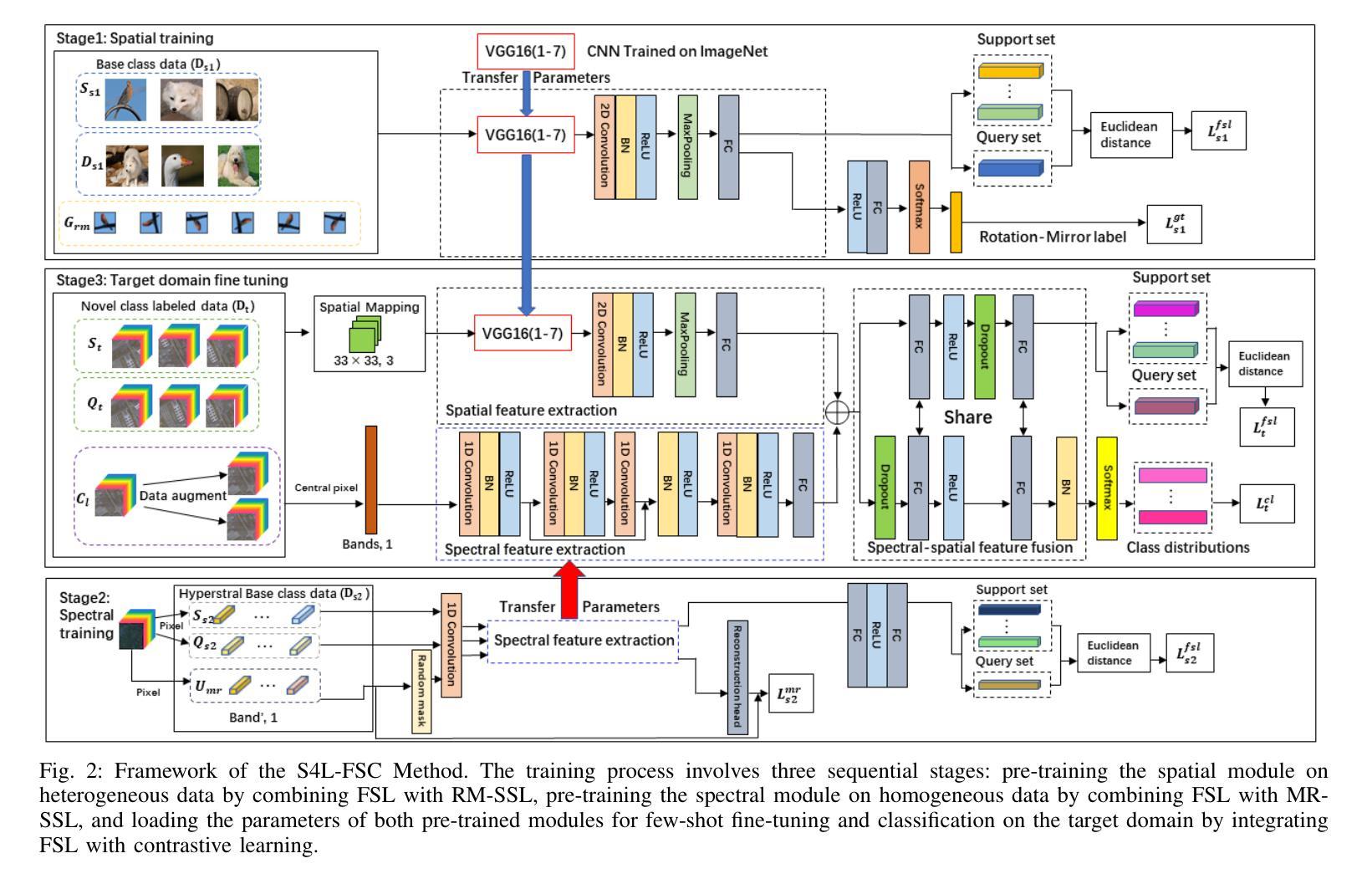
Spectral-Spatial Self-Supervised Learning for Few-Shot Hyperspectral Image Classification
Authors:Wenchen Chen, Yanmei Zhang, Zhongwei Xiao, Jianping Chu, Xingbo Wang
Few-shot classification of hyperspectral images (HSI) faces the challenge of scarce labeled samples. Self-Supervised learning (SSL) and Few-Shot Learning (FSL) offer promising avenues to address this issue. However, existing methods often struggle to adapt to the spatial geometric diversity of HSIs and lack sufficient spectral prior knowledge. To tackle these challenges, we propose a method, Spectral-Spatial Self-Supervised Learning for Few-Shot Hyperspectral Image Classification (S4L-FSC), aimed at improving the performance of few-shot HSI classification. Specifically, we first leverage heterogeneous datasets to pretrain a spatial feature extractor using a designed Rotation-Mirror Self-Supervised Learning (RM-SSL) method, combined with FSL. This approach enables the model to learn the spatial geometric diversity of HSIs using rotation and mirroring labels as supervisory signals, while acquiring transferable spatial meta-knowledge through few-shot learning. Subsequently, homogeneous datasets are utilized to pretrain a spectral feature extractor via a combination of FSL and Masked Reconstruction Self-Supervised Learning (MR-SSL). The model learns to reconstruct original spectral information from randomly masked spectral vectors, inferring spectral dependencies. In parallel, FSL guides the model to extract pixel-level discriminative features, thereby embedding rich spectral priors into the model. This spectral-spatial pretraining method, along with the integration of knowledge from heterogeneous and homogeneous sources, significantly enhances model performance. Extensive experiments on four HSI datasets demonstrate the effectiveness and superiority of the proposed S4L-FSC approach for few-shot HSI classification.
高光谱图像(HSI)的少量样本分类面临着标注样本稀缺的挑战。自监督学习(SSL)和少量学习(FSL)为解决这一问题提供了有前景的途径。然而,现有方法往往难以适应HSI的空间几何多样性,且缺乏足够的光谱先验知识。为了应对这些挑战,我们提出了一种方法,名为“用于高光谱图像少量样本分类的谱空间自监督学习(S4L-FSC)”,旨在提高高光谱图像少量样本分类的性能。具体来说,我们首先利用异质数据集预训练一个空间特征提取器,采用设计的旋转镜像自监督学习方法(RM-SSL)与少量学习相结合。这种方法使模型能够利用旋转和镜像标签作为监督信号来学习HSI的空间几何多样性,同时通过少量学习获得可迁移的空间元知识。然后,我们利用同质数据集预训练一个光谱特征提取器,结合少量学习和掩码重建自监督学习(MR-SSL)。模型学会从随机掩码的光谱向量中重建原始光谱信息,推断光谱依赖性。同时,少量学习指导模型提取像素级判别特征,从而将丰富的光谱先验嵌入模型中。这种谱空间预训练方法,以及来自异质和同质源的知识的整合,显著提高了模型的性能。在四个HSI数据集上的广泛实验证明了所提出的S4L-FSC方法在少量高光谱图像分类中的有效性和优越性。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF https://github.com/Wenchen-Chen/S4L-FSC
Summary
本文提出了针对高光谱图像(HSI)的少量样本分类问题,通过结合自监督学习(SSL)和少量学习(FSL)来解决空间几何多样性和光谱先验知识的不足问题。文中介绍了一种名为Spectral-Spatial Self-Supervised Learning for Few-Shot Hyperspectral Image Classification(S4L-FSC)的方法,它通过预训练模型进行空间特征和光谱特征的提取,使用RM-SSL方法和掩蔽重建自监督学习来训练模型。经过大量实验验证,该方法在四个HSI数据集上的少量样本分类表现优越。
Key Takeaways
- 面临高光谱图像(HSI)少量样本分类的挑战。
- 自监督学习(SSL)和少量学习(FSL)是解决该问题有前景的方法。
- SSL通过设计Rotation-Mirror方法进行空间特征提取。借助少量学习,模型能够学习空间几何多样性并使用旋转和镜像标签作为监督信号。
- 使用同质数据集进行光谱特征提取,通过掩蔽重建自监督学习和少量学习相结合的方式训练模型,从而推断光谱依赖关系并提取像素级别的判别特征。
- 结合异质和同质来源的知识,通过谱空间预训练方法显著提高了模型性能。
- 在四个HSI数据集上的实验验证了该方法的优越性和有效性。
点此查看论文截图

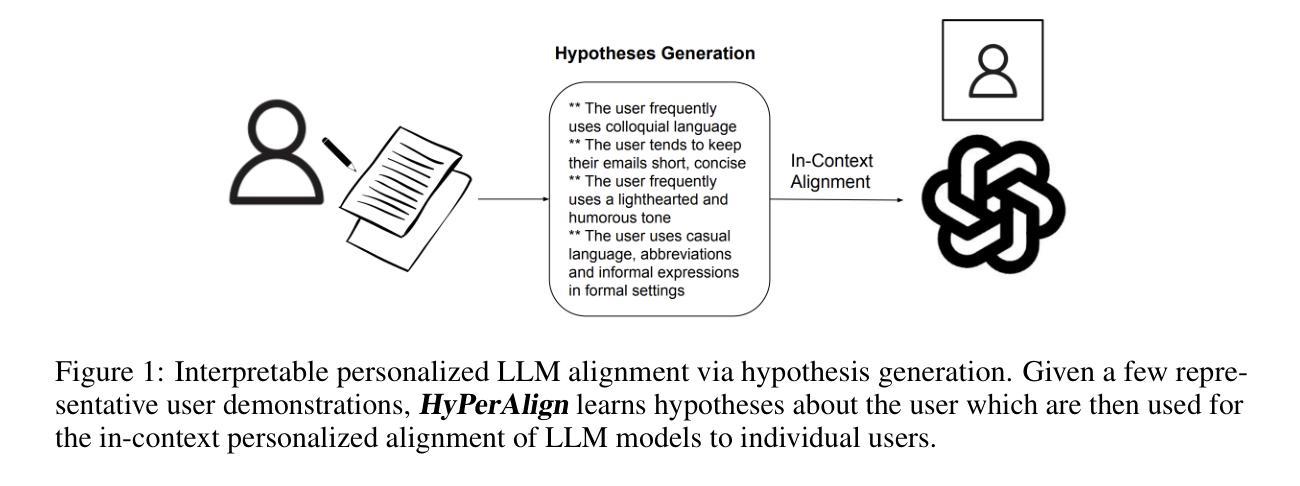
HyPerAlign: Interpretable Personalized LLM Alignment via Hypothesis Generation
Authors:Cristina Garbacea, Chenhao Tan
Alignment algorithms are widely used to align large language models (LLMs) to human users based on preference annotations. Typically these (often divergent) preferences are aggregated over a diverse set of users, resulting in fine-tuned models that are aligned to the ``average-user’’ preference. Nevertheless, current models are used by individual users in very specific contexts and situations, emphasizing the need for user-dependent preference control. In this work we address the problem of personalizing LLM outputs to their users. We aim to generate customized responses tailored to specific individuals instead of generic outputs that emulate the collective voices of diverse populations. We propose HyPerAlign, an interpretable and sample-efficient hypothesis-driven personalization approach for LLM models. Given few-shot examples written by a particular user, we first infer hypotheses about their communication strategies, personality, and writing style, then prompt LLM models with these hypotheses and user-specific attributes to generate customized outputs. We conduct experiments on two different personalization tasks, namely authorship attribution and deliberative alignment, with datasets from diverse domains (news articles, blog posts, emails, jailbreaking benchmarks). Results demonstrate the superiority of hypothesis-driven LLM personalization compared to preference-based fine-tuning methods. For authorship attribution, HyPerAlign generations have consistently high win-rates (commonly $> 90%$) against state-of-the-art preference fine-tuning approaches across diverse user profiles and LLM models. For deliberative alignment, the helpfulness of LLM models is improved by up to $70%$ on average. Overall, HyPerAlign represents an interpretable and sample-efficient strategy for the personalization of LLM models to individual users.
对齐算法广泛应用于基于偏好注释的大型语言模型(LLM)与人类用户的对齐。通常这些(经常不同的)偏好会在不同的用户群体中进行汇总,从而得到与“平均用户”偏好对齐的微调模型。然而,当前模型是在特定用户和情境下使用的,这强调了对用户依赖的偏好控制的必要性。在这项工作中,我们解决了将LLM输出个性化到其用户的问题。我们的目标是生成针对特定个人的定制响应,而不是模拟不同人群集体声音的通用输出。我们提出了HyPerAlign,这是一种可解释且样本效率高的假设驱动式LLM个性化方法。给定特定用户编写的少数样本,我们首先对其沟通策略、个性和写作风格进行假设推断,然后提示LLM模型使用这些假设和用户特定属性来生成定制输出。我们在两个不同的个性化任务上进行了实验,即作者归属和审慎对齐,并使用来自不同领域的数据集(新闻文章、博客文章、电子邮件、越狱基准测试)。结果表明,假设驱动的LLM个性化方法优于基于偏好的微调方法。在作者归属方面,HyPerAlign生成的响应与最新偏好微调方法相比,具有始终较高的胜率(通常超过90%),涵盖各种用户配置文件和LLM模型。在审慎对齐方面,LLM模型的有用性平均提高了高达70%。总体而言,HyPerAlign代表了可解释且样本效率高的策略,用于将LLM模型个性化到单个用户。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文提出一种名为HyPerAlign的方法,用于个性化大型语言模型(LLM)的输出以适应特定用户。通过少量用户写作的样本,推断用户的沟通策略、个性和写作风格,然后结合这些假设和用户特定属性,生成定制化的输出。实验结果表明,在作者归属和审慎对齐等任务上,HyPerAlign的表现优于基于偏好微调的方法。总体而言,HyPerAlign是一种可解释性强、样本效率高的个性化LLM模型策略。
Key Takeaways
- HyPerAlign是一种用于个性化大型语言模型(LLM)的方法,旨在生成针对特定用户的定制响应。
- 该方法通过少量用户写作样本推断用户的沟通策略、个性和写作风格。
- HyPerAlign结合这些假设和用户特定属性,生成适应特定用户的输出。
- 在作者归属任务上,HyPerAlign的生成结果胜过现有偏好微调方法,胜率高且稳定。
- 在审慎对齐任务上,LLM模型的实用性平均提高了70%。
- HyPerAlign具有可解释性和样本高效性。
点此查看论文截图

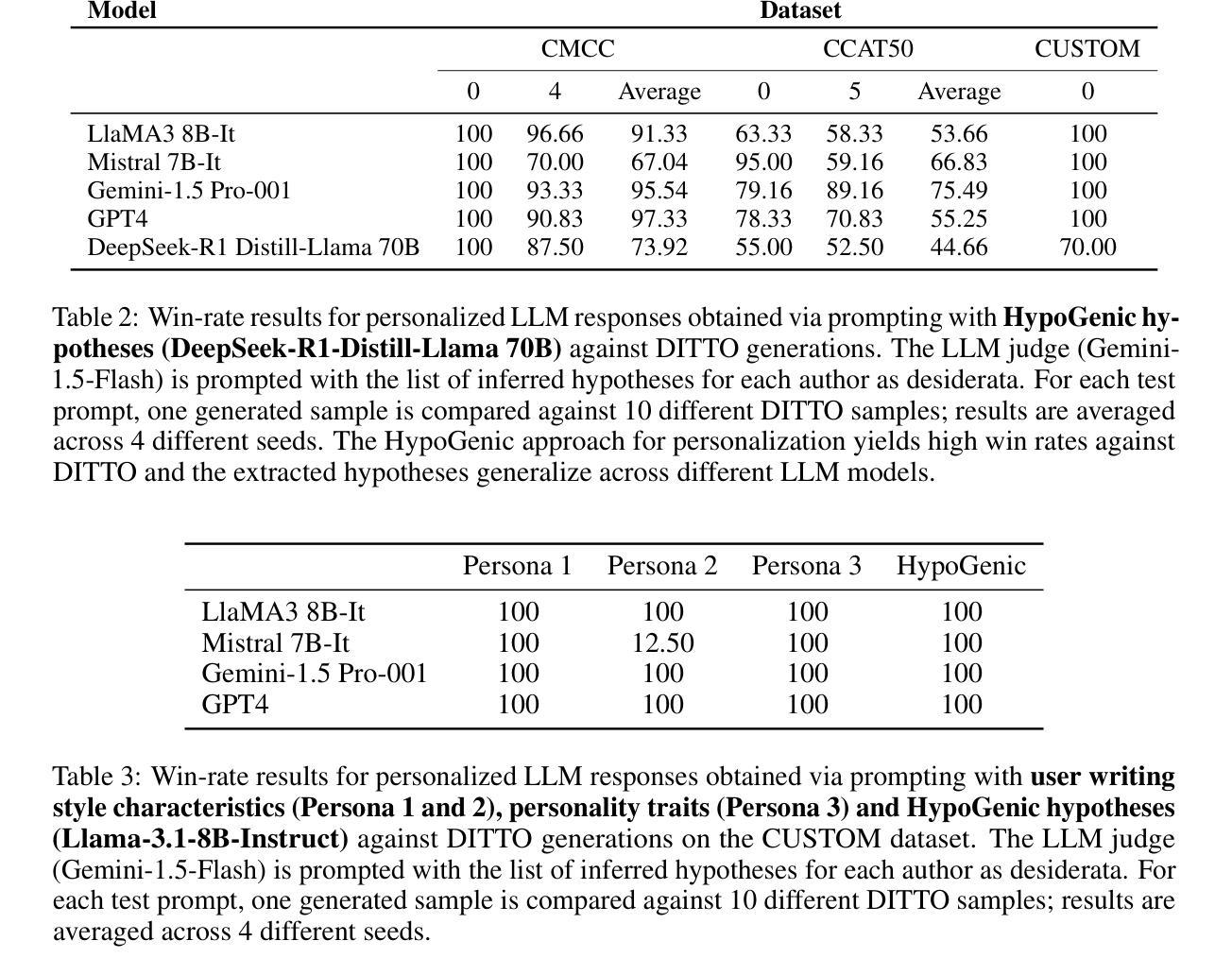
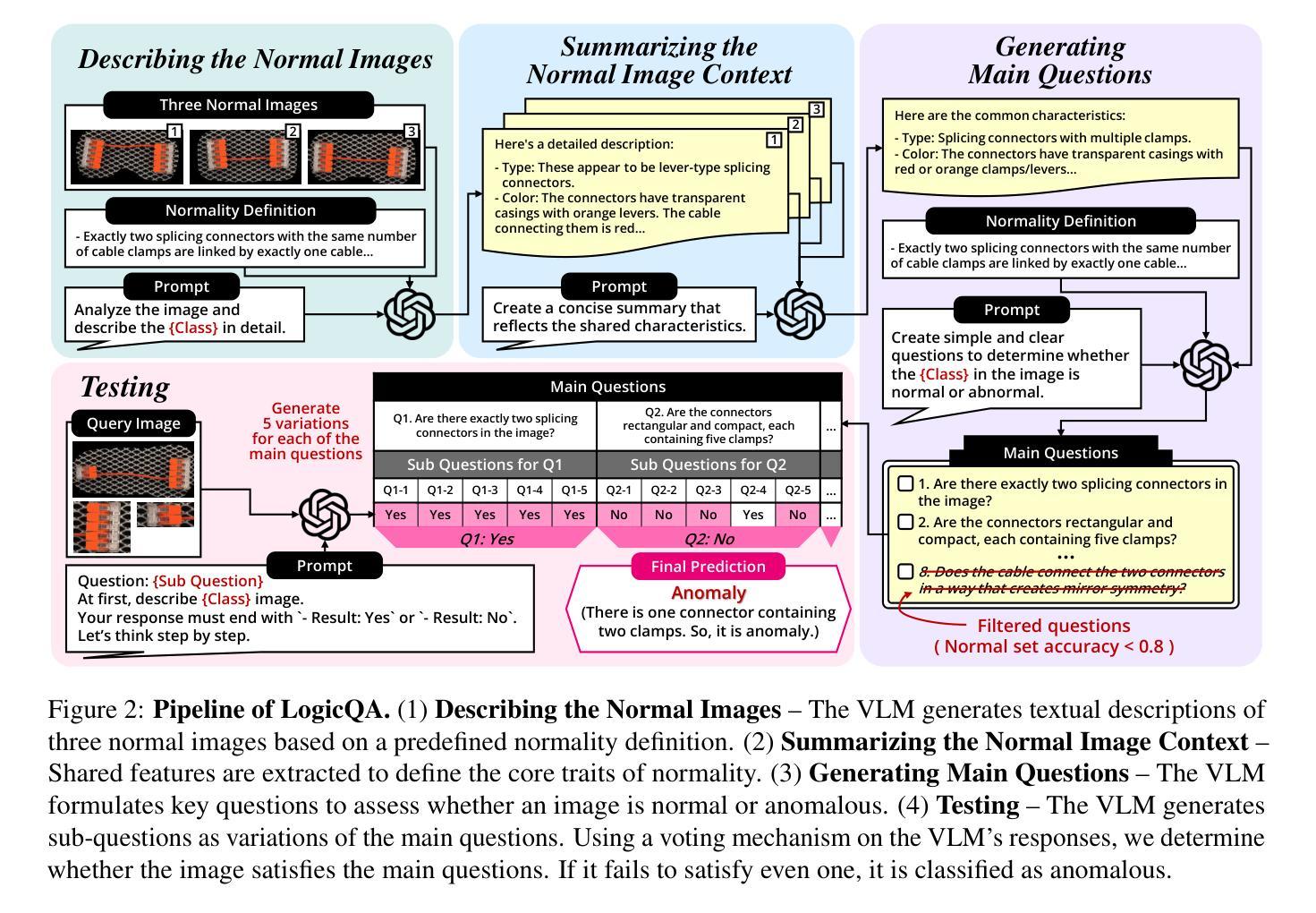
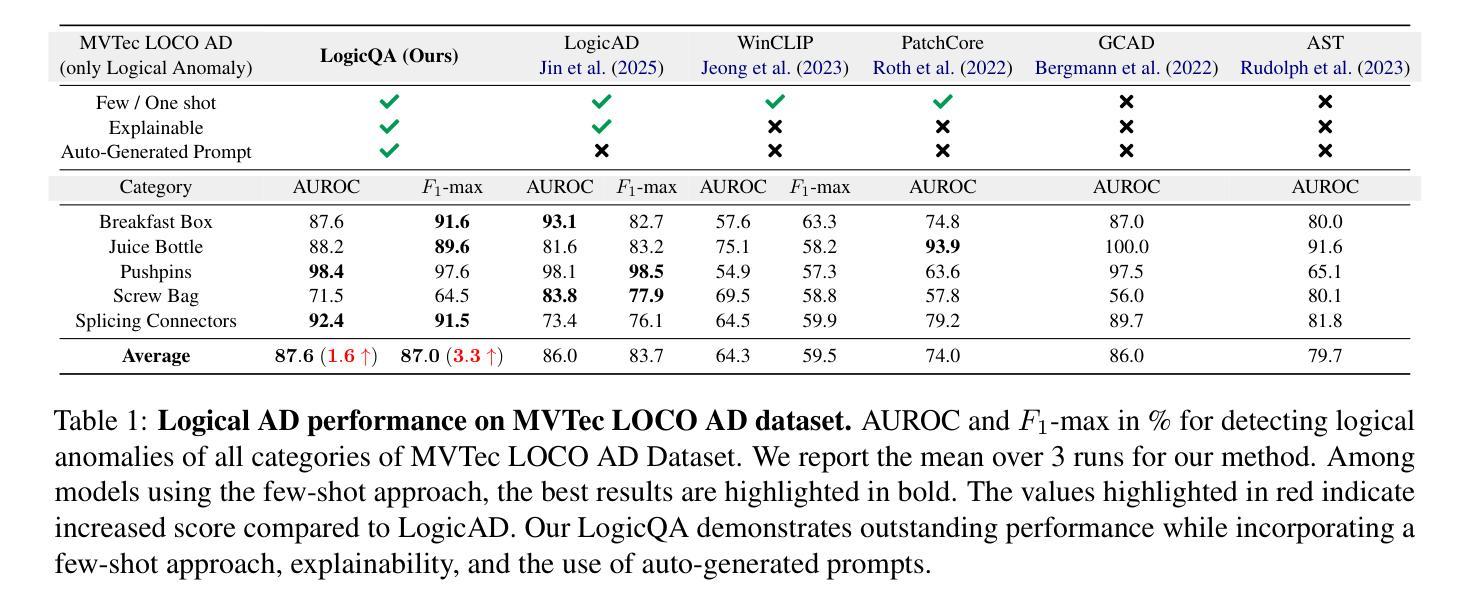
LogicQA: Logical Anomaly Detection with Vision Language Model Generated Questions
Authors:Yejin Kwon, Daeun Moon, Youngje Oh, Hyunsoo Yoon
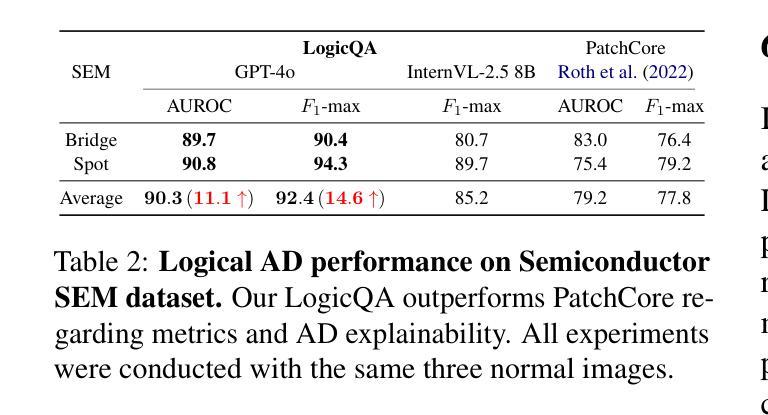
Anomaly Detection (AD) focuses on detecting samples that differ from the standard pattern, making it a vital tool in process control. Logical anomalies may appear visually normal yet violate predefined constraints on object presence, arrangement, or quantity, depending on reasoning and explainability. We introduce LogicQA, a framework that enhances AD by providing industrial operators with explanations for logical anomalies. LogicQA compiles automatically generated questions into a checklist and collects responses to identify violations of logical constraints. LogicQA is training-free, annotation-free, and operates in a few-shot setting. We achieve state-of-the-art (SOTA) Logical AD performance on public benchmarks, MVTec LOCO AD, with an AUROC of 87.6 percent and an F1-max of 87.0 percent along with the explanations of anomalies. Also, our approach has shown outstanding performance on semiconductor SEM corporate data, further validating its effectiveness in industrial applications.
异常检测(AD)主要专注于检测与标准模式不同的样本,使其成为过程控制中的关键工具。逻辑异常在视觉上可能看似正常,但会违反对象存在、排列或数量等方面的预定义约束,这取决于推理和可解释性。我们引入了LogicQA框架,它通过为工业操作员提供逻辑异常的解释来增强AD的功能。LogicQA将自动生成的问题编译成清单,并收集响应来识别逻辑约束的违反情况。LogicQA无需训练和标注,且在少量样本数据下即可运行。我们在公共基准测试MVTec LOCO AD上实现了最新的逻辑AD性能,具有87.6%的AUROC和87.0%的F1最大值,并提供了异常情况的解释。此外,我们的方法在半导体的SEM企业数据上表现出卓越的性能,进一步验证了其在工业应用中的有效性。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted Industry Track at ACL 2025
Summary
基于逻辑异常检测的框架LogicQA,旨在提高工业运营者对逻辑异常的识别能力。它通过自动生成问题清单并收集回应,以识别逻辑约束的违规情况。该框架无需训练和标注,在少量样本下运行,并在MVTec LOCO AD公共基准测试上实现了先进的逻辑异常检测性能,包括高曲线下面积(AUROC)和最大F1分数。此外,该框架在半导体SEM企业数据上表现出卓越性能,证明了其在工业应用中的有效性。
Key Takeaways
- LogicQA是一个用于增强异常检测的框架,可解释逻辑异常。
- LogicQA通过自动生成问题清单来识别逻辑约束违规情况。
- 该框架无需训练和标注,适用于少量样本。
- LogicQA在MVTec LOCO AD公共基准测试上表现出卓越性能。
- LogicQA实现了高AUROC和F1-max分数。
- 该框架在半导体SEM企业数据上的表现证明了其在工业应用中的有效性。
点此查看论文截图


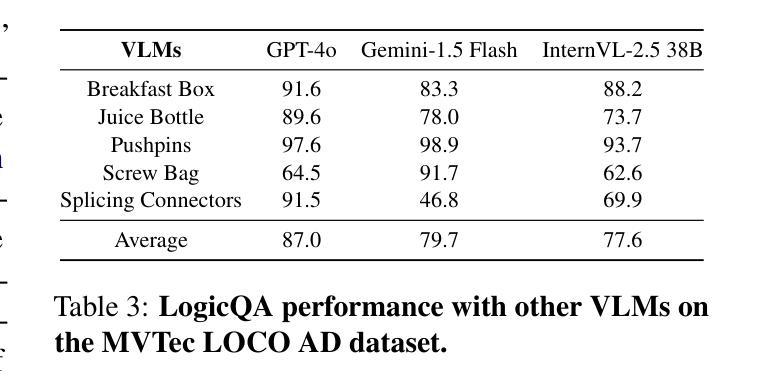
Generalized Few-shot 3D Point Cloud Segmentation with Vision-Language Model
Authors:Zhaochong An, Guolei Sun, Yun Liu, Runjia Li, Junlin Han, Ender Konukoglu, Serge Belongie
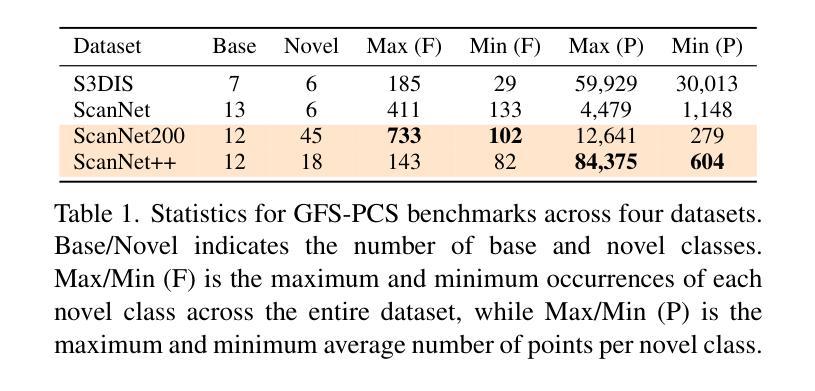
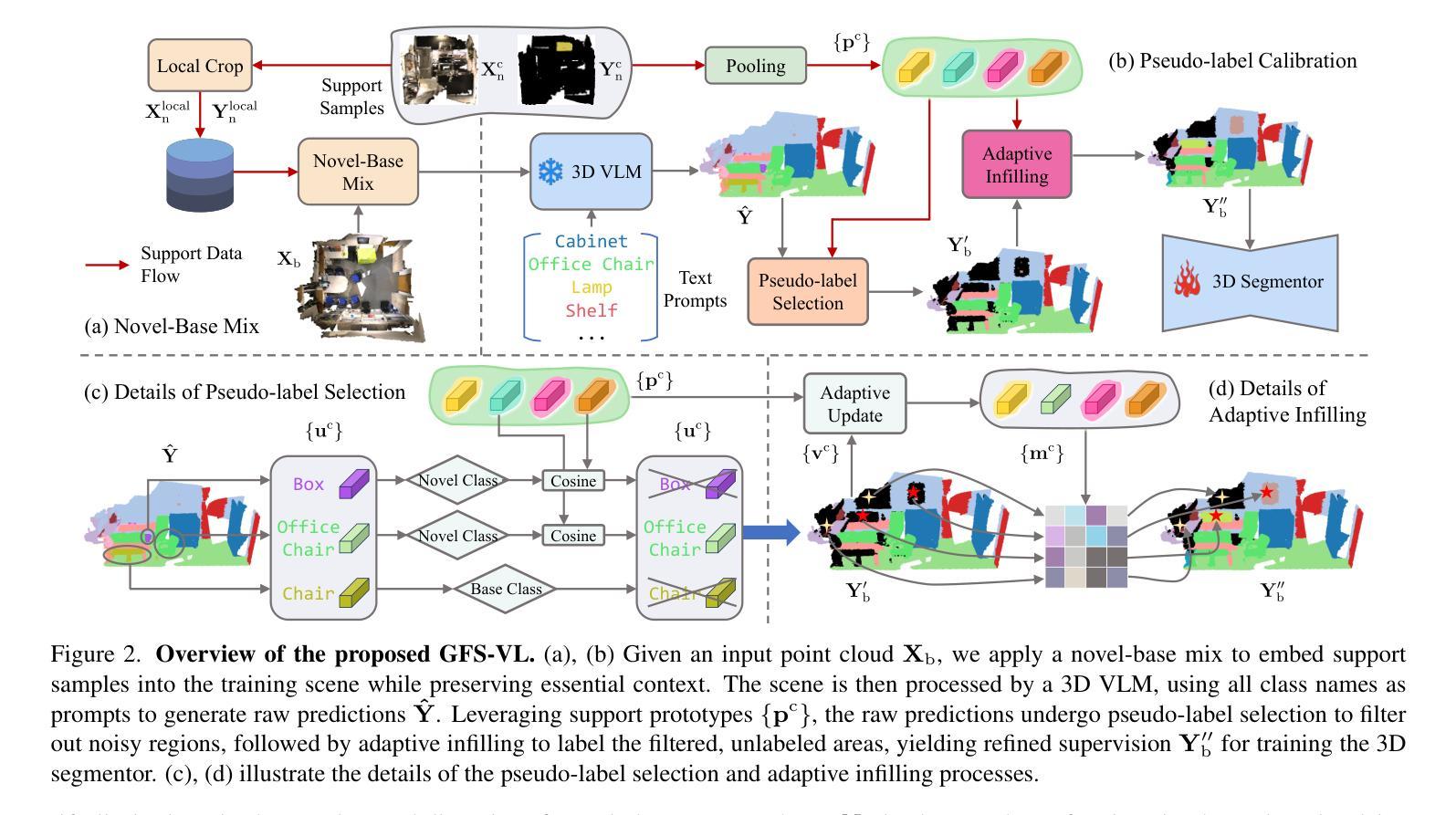
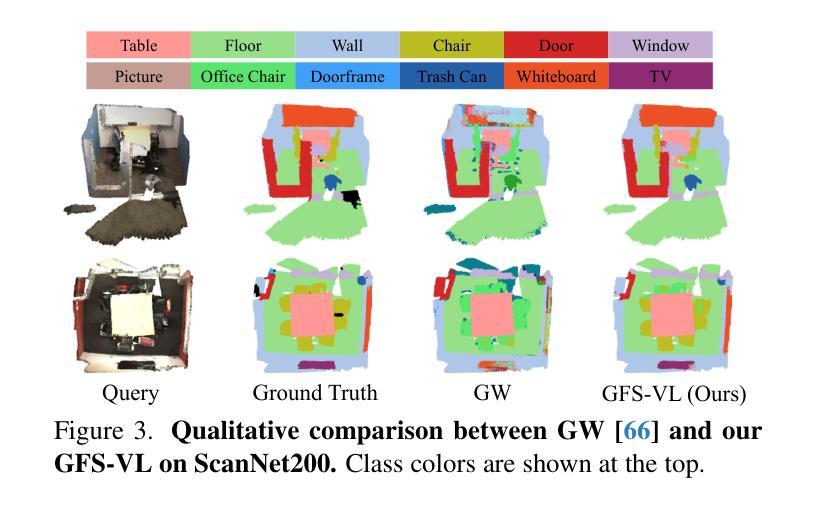
Generalized few-shot 3D point cloud segmentation (GFS-PCS) adapts models to new classes with few support samples while retaining base class segmentation. Existing GFS-PCS methods enhance prototypes via interacting with support or query features but remain limited by sparse knowledge from few-shot samples. Meanwhile, 3D vision-language models (3D VLMs), generalizing across open-world novel classes, contain rich but noisy novel class knowledge. In this work, we introduce a GFS-PCS framework that synergizes dense but noisy pseudo-labels from 3D VLMs with precise yet sparse few-shot samples to maximize the strengths of both, named GFS-VL. Specifically, we present a prototype-guided pseudo-label selection to filter low-quality regions, followed by an adaptive infilling strategy that combines knowledge from pseudo-label contexts and few-shot samples to adaptively label the filtered, unlabeled areas. Additionally, we design a novel-base mix strategy to embed few-shot samples into training scenes, preserving essential context for improved novel class learning. Moreover, recognizing the limited diversity in current GFS-PCS benchmarks, we introduce two challenging benchmarks with diverse novel classes for comprehensive generalization evaluation. Experiments validate the effectiveness of our framework across models and datasets. Our approach and benchmarks provide a solid foundation for advancing GFS-PCS in the real world. The code is at https://github.com/ZhaochongAn/GFS-VL
广义少样本3D点云分割(GFS-PCS)能够在保留基础类别分割的同时,适应新的类别并处理少量的样本支持。现有的GFS-PCS方法通过支持特征或查询特征与原型进行交互,但仍受限于少样本的稀疏知识。同时,用于开放世界新类别的通用3D视觉语言模型(3D VLMs)包含丰富但嘈杂的新类别知识。在这项工作中,我们引入了一个GFS-PCS框架,该框架协同结合了来自3D VLMs的密集但嘈杂的伪标签和精确但稀疏的少量样本,以最大限度地发挥两者的优势,称为GFS-VL。具体来说,我们提出了一种原型引导伪标签选择方法,用于过滤低质量区域,随后采用自适应填充策略,结合伪标签上下文和少量样本知识,对过滤后的未标记区域进行自适应标记。此外,我们设计了一种新型基础混合策略,将少量样本嵌入训练场景,保留重要上下文,以改进新类别的学习。而且,考虑到当前GFS-PCS基准测试多样性的局限性,我们引入了两个具有多种新类别的挑战性基准测试,以进行全面的一般化评估。实验验证了我们的框架在不同模型和数据集上的有效性。我们的方法和基准测试为推进GFS-PCS在现实世界的应用提供了坚实的基础。代码地址为:https://github.com/ZhaochongAn/GFS-VL。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted to CVPR 2025
Summary
本文介绍了一种结合了3D视觉语言模型(3D VLMs)和广义少样本3D点云分割(GFS-PCS)框架的方法,称为GFS-VL。该方法利用3D VLMs提供的丰富但带有噪声的伪标签与少样本数据相结合,通过原型引导伪标签选择和自适应填充策略,最大限度地发挥两者的优势。此外,还引入了一种新型基础混合策略,将少量样本嵌入训练场景中,保留重要上下文,以改进新型类的学习。文章还介绍了两个具有挑战性的基准测试,以全面评估模型的泛化能力。实验验证了该方法在不同模型和数据集上的有效性。
Key Takeaways
- GFS-VL结合3D VLMs和GFS-PCS框架,利用伪标签和少样本数据进行学习。
- 提出原型引导伪标签选择策略,过滤低质量区域。
- 采用自适应填充策略,结合伪标签上下文和少量样本进行标注。
- 设计新型基础混合策略,将少量样本嵌入训练场景,保留重要上下文。
- 引入两个具有挑战性的基准测试,用于评估模型的泛化能力。
- 实验验证了该方法在不同模型和数据集上的有效性。
点此查看论文截图

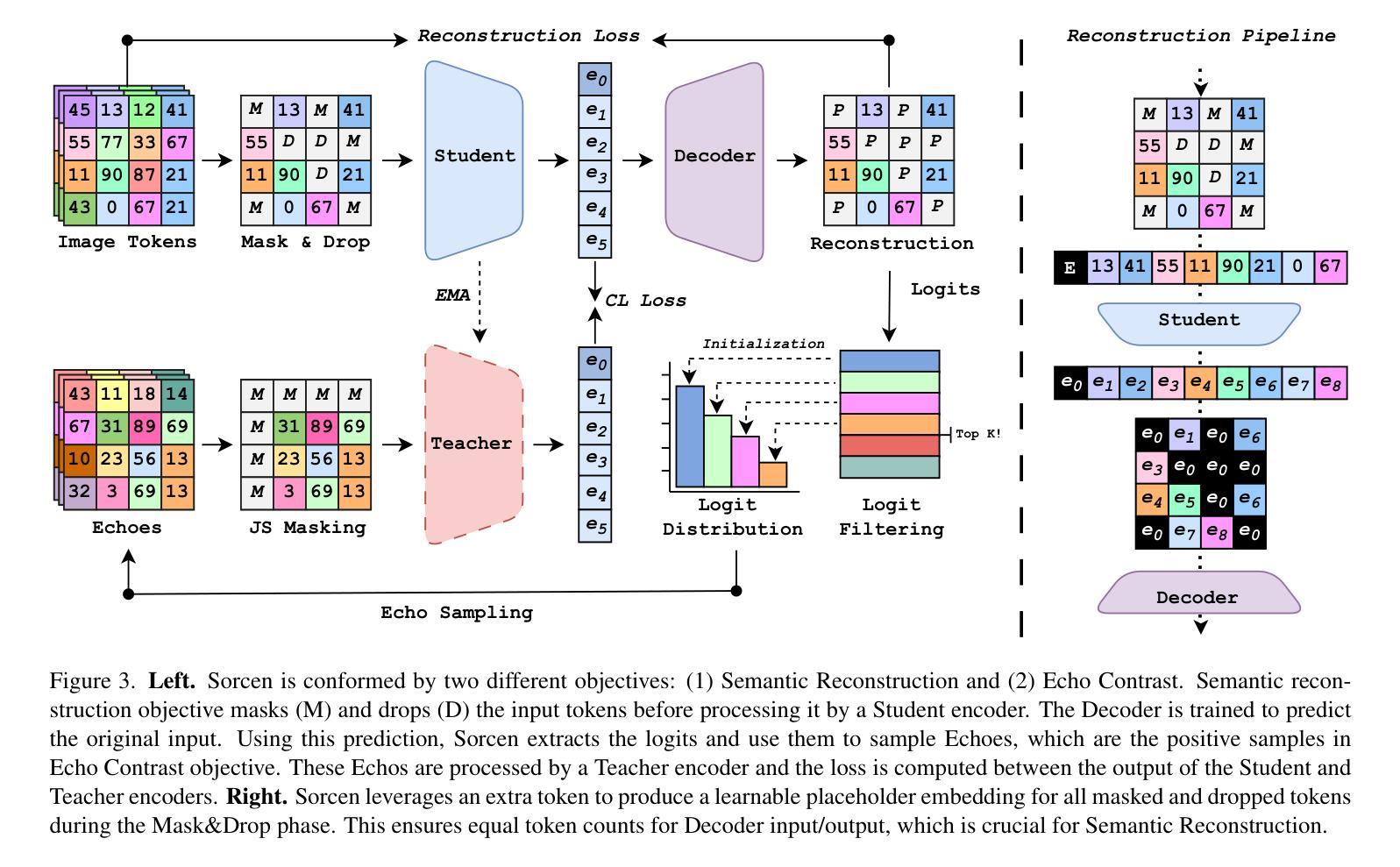
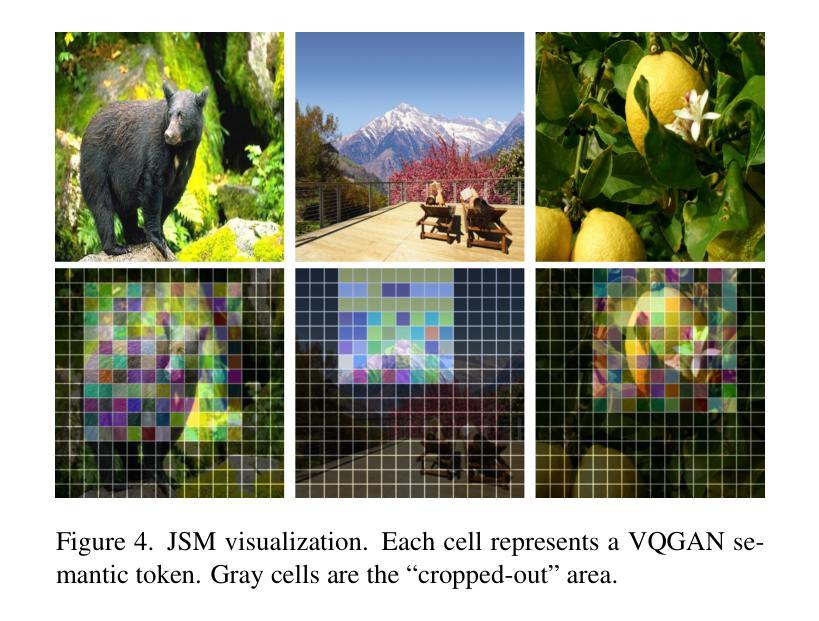
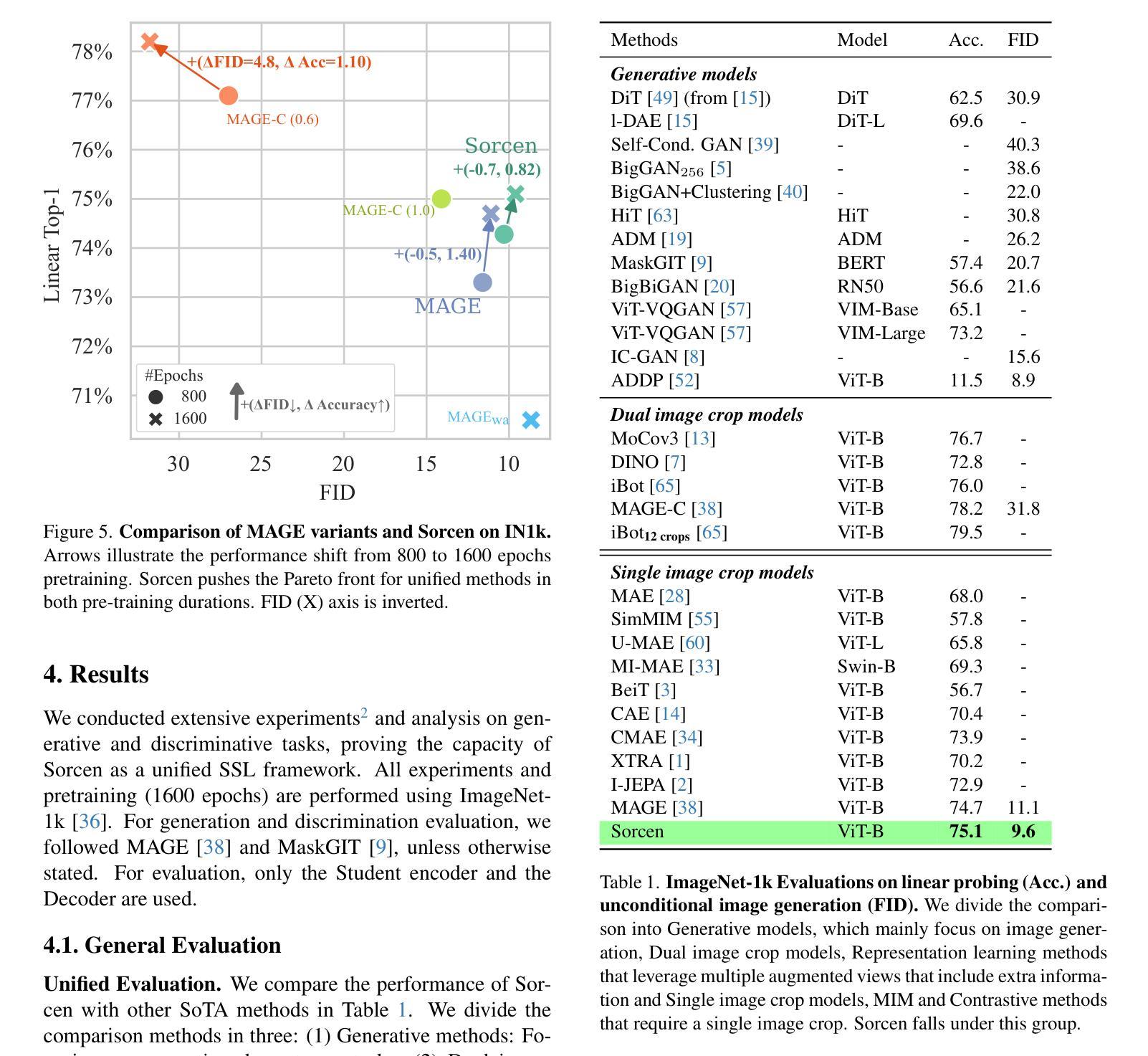
Conjuring Positive Pairs for Efficient Unification of Representation Learning and Image Synthesis
Authors:Imanol G. Estepa, Jesús M. Rodríguez-de-Vera, Ignacio Sarasúa, Bhalaji Nagarajan, Petia Radeva
While representation learning and generative modeling seek to understand visual data, unifying both domains remains unexplored. Recent Unified Self-Supervised Learning (SSL) methods have started to bridge the gap between both paradigms. However, they rely solely on semantic token reconstruction, which requires an external tokenizer during training – introducing a significant overhead. In this work, we introduce Sorcen, a novel unified SSL framework, incorporating a synergic Contrastive-Reconstruction objective. Our Contrastive objective, “Echo Contrast”, leverages the generative capabilities of Sorcen, eliminating the need for additional image crops or augmentations during training. Sorcen “generates” an echo sample in the semantic token space, forming the contrastive positive pair. Sorcen operates exclusively on precomputed tokens, eliminating the need for an online token transformation during training, thereby significantly reducing computational overhead. Extensive experiments on ImageNet-1k demonstrate that Sorcen outperforms the previous Unified SSL SoTA by 0.4%, 1.48 FID, 1.76%, and 1.53% on linear probing, unconditional image generation, few-shot learning, and transfer learning, respectively, while being 60.8% more efficient. Additionally, Sorcen surpasses previous single-crop MIM SoTA in linear probing and achieves SoTA performance in unconditional image generation, highlighting significant improvements and breakthroughs in Unified SSL models.
表示学习和生成建模都在努力理解视觉数据,但统一这两个领域仍然未被探索。最近的统一自监督学习方法(SSL)已经开始弥合两种范式之间的鸿沟。然而,它们仅依赖于语义令牌重建,这需要训练过程中的外部令牌器——带来了相当大的开销。在这项工作中,我们介绍了Sorcen,这是一个新的统一SSL框架,它结合了协同对比重建目标。我们的对比目标“回声对比”利用了Sorcen的生成能力,消除了训练过程中对额外图像裁剪或增强的需求。Sorcen在语义令牌空间中“生成”一个回声样本,形成对比正对。Sorcen只在预计算令牌上运行,消除了训练过程中在线令牌转换的需要,从而显著降低了计算开销。在ImageNet-1k上的大量实验表明,在线性探测、无条件图像生成、小样本学习和迁移学习方面,Sorcen分别超过了之前的统一SSL水平0.4%、FID降低1.48、下降1.76%、下降率为至最低至最多百分之十五,而效率提高至最多百分之六十以上八提升效率时则是大幅提升。此外,在无条件图像生成方面,Sorcen超越了之前的单裁剪MIM水平最高表现,并在统一SSL模型中取得了显著的改进和突破。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF The source code is available in https://github.com/ImaGonEs/Sorcen
Summary
本研究提出了一种新型的统一自监督学习(SSL)框架Sorcen,它结合了对比和重建目标,无需额外的图像裁剪或增强即可进行训练。Sorcen在预计算令牌上运行,降低了计算开销。在ImageNet-1k上的实验表明,Sorcen在统一SSL领域取得了最先进的性能,同时在效率和效果上也有所突破。
Key Takeaways
- 研究提出了新型统一自监督学习(SSL)框架Sorcen。
- Sorcen结合了对比和重建目标,提高了模型的效率和效果。
- Sorcen利用生成能力生成对比正样本对,无需额外的图像裁剪或增强。
- Sorcen在预计算令牌上运行,降低了计算开销。
- 在ImageNet-1k上的实验显示,Sorcen在统一SSL领域实现了最先进的性能。
- Sorcen在多种任务上表现出卓越性能,包括线性探测、无条件图像生成、少样本学习和迁移学习等。
点此查看论文截图


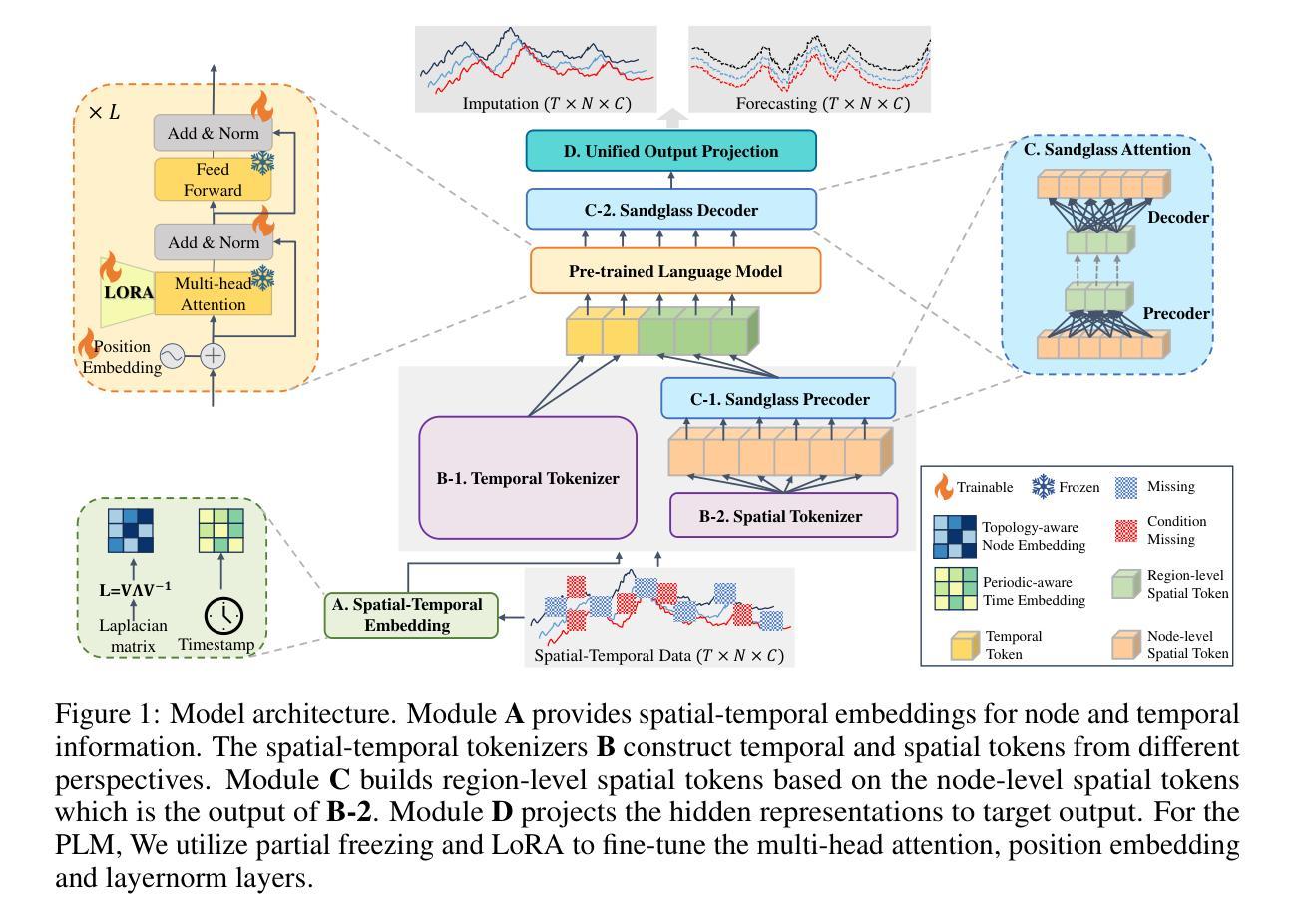
STD-PLM: Understanding Both Spatial and Temporal Properties of Spatial-Temporal Data with PLM
Authors:YiHeng Huang, Xiaowei Mao, Shengnan Guo, Yubin Chen, Junfeng Shen, Tiankuo Li, Youfang Lin, Huaiyu Wan
Spatial-temporal forecasting and imputation are important for real-world intelligent systems. Most existing methods are tailored for individual forecasting or imputation tasks but are not designed for both. Additionally, they are less effective for zero-shot and few-shot learning. While pre-trained language model (PLM) have exhibited strong pattern recognition and reasoning abilities across various tasks, including few-shot and zero-shot learning, their applications in spatial-temporal data understanding has been constrained by insufficient modeling of complex correlations such as the temporal correlations, spatial connectivity, non-pairwise and high-order spatial-temporal correlations within data. In this paper, we propose STD-PLM for understanding both spatial and temporal properties of \underline{S}patial-\underline{T}emporal \underline{D}ata with \underline{PLM}, which is capable of implementing both spatial-temporal forecasting and imputation tasks. STD-PLM understands spatial-temporal correlations via explicitly designed spatial and temporal tokenizers. Topology-aware node embeddings are designed for PLM to comprehend and exploit the topology structure of data in inductive manner. Furthermore, to mitigate the efficiency issues introduced by the PLM, we design a sandglass attention module (SGA) combined with a specific constrained loss function, which significantly improves the model’s efficiency while ensuring performance. Extensive experiments demonstrate that STD-PLM exhibits competitive performance and generalization capabilities across the forecasting and imputation tasks on various datasets. Moreover, STD-PLM achieves promising results on both few-shot and zero-shot tasks. The code is made available at \href{https://github.com/Hyheng/STD-PLM}{https://github.com/Hyheng/STD-PLM}
空间时间预测和补全对于现实世界的智能系统非常重要。现有的大多数方法都是针对个别预测或补全任务定制的,并不适用于两者同时进行。此外,它们在零样本和少样本学习方面的效果较差。虽然预训练语言模型(PLM)在各种任务中表现出了强大的模式识别和推理能力,包括少样本和零样本学习,但其在空间时间数据理解方面的应用受到了建模复杂关系不足的制约,如时间相关性、空间连通性、数据内部非配对和高阶时空关系等。在本文中,我们提出了基于PLM的STD-PLM模型,用于理解时空数据的空间和时间属性,并具备进行时空预测和补全任务的能力。STD-PLM通过明确设计的空间和时间标记器理解时空相关性。针对PLM设计了拓扑感知节点嵌入,以归纳方式理解和利用数据的拓扑结构。此外,为了解决由PLM引入的效率问题,我们设计了一种沙漏注意模块(SGA)结合特定的约束损失函数,这不仅显著提高了模型的效率,而且保证了性能。大量实验表明,STD-PLM在多个数据集上的预测和补全任务上表现出具有竞争力的性能和泛化能力。此外,STD-PLM在少样本和零样本任务上也取得了令人鼓舞的结果。代码已发布在https://github.com/Hyheng/STD-PLM。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
基于预训练语言模型(PLM),本文提出了一种针对空间和时间数据的理解方法STD-PLM。该方法能够执行空间时间预测和插值任务,通过明确设计的空间和时间标记器理解时空相关性。此外,还设计了拓扑感知节点嵌入和沙漏注意力模块(SGA),以提高模型的效率和性能。在多个数据集上进行的实验表明,STD-PLM在预测和插值任务上具有竞争力,并在零样本和少样本任务上取得了有前景的结果。
Key Takeaways
- STD-PLM结合了预训练语言模型(PLM),能够同时处理空间时间预测和插值任务。
- 通过明确设计的空间和时间标记器,STD-PLM能够理解时空数据中的复杂相关性。
- 拓扑感知节点嵌入的设计使得PLM能够感知并利用数据的拓扑结构。
- 沙漏注意力模块(SGA)与特定约束损失函数的设计提高了模型的效率并保证性能。
- 实验结果表明,STD-PLM在多个数据集上的预测和插值任务上具有竞争力。
- STD-PLM在零样本和少样本任务上取得了有前景的结果。
点此查看论文截图

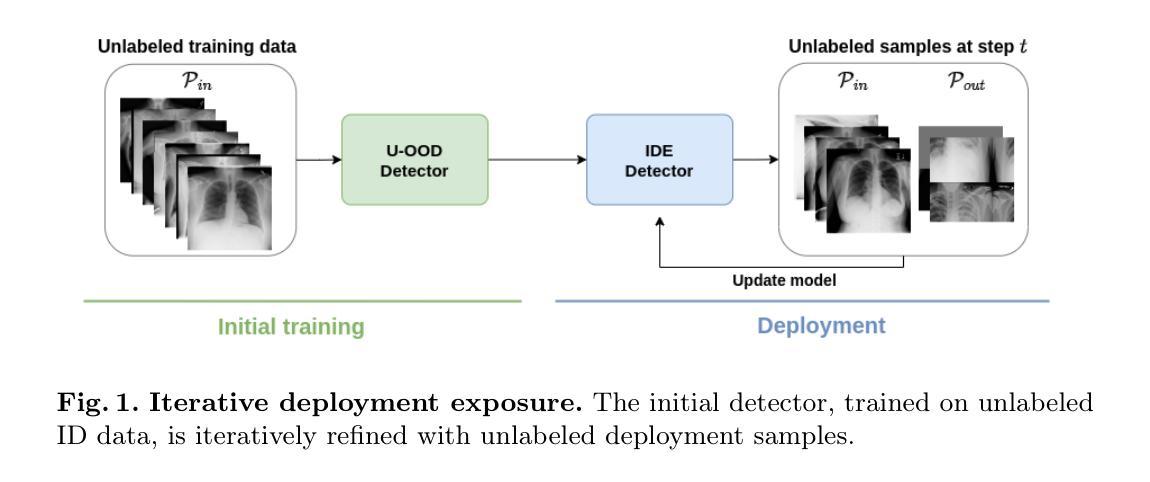
Iterative Deployment Exposure for Unsupervised Out-of-Distribution Detection
Authors:Lars Doorenbos, Raphael Sznitman, Pablo Márquez-Neila
Deep learning models are vulnerable to performance degradation when encountering out-of-distribution (OOD) images, potentially leading to misdiagnoses and compromised patient care. These shortcomings have led to great interest in the field of OOD detection. Existing unsupervised OOD (U-OOD) detection methods typically assume that OOD samples originate from an unconcentrated distribution complementary to the training distribution, neglecting the reality that deployed models passively accumulate task-specific OOD samples over time. To better reflect this real-world scenario, we introduce Iterative Deployment Exposure (IDE), a novel and more realistic setting for U-OOD detection. We propose CSO, a method for IDE that starts from a U-OOD detector that is agnostic to the OOD distribution and slowly refines it during deployment using observed unlabeled data. CSO uses a new U-OOD scoring function that combines the Mahalanobis distance with a nearest-neighbor approach, along with a novel confidence-scaled few-shot OOD detector to effectively learn from limited OOD examples. We validate our approach on a dedicated benchmark, showing that our method greatly improves upon strong baselines on three medical imaging modalities.
深度学习模型在遇到离群分布(OOD)图像时容易出现性能下降的问题,这可能导致误诊和患者护理受到影响。这些缺陷引发了人们对OOD检测领域的极大兴趣。现有的无监督OOD(U-OOD)检测方法通常假设OOD样本来自与训练分布互补的非集中分布,忽视了这样一个现实情况:部署的模型随着时间的推移会被动地累积特定任务的OOD样本。为了更好地反映这种真实场景,我们引入了迭代部署暴露(IDE),这是一种用于U-OOD检测的新型且更现实的设置。我们提出了一种IDE方法CSO,该方法从对OOD分布不了解的U-OOD检测器开始,在部署过程中使用观察到的无标签数据缓慢地对其进行优化。CSO使用了一种新的U-OOD评分函数,结合了马氏距离和最近邻方法,并使用了一种新型的信心规模有限样本OOD检测器,以有效地从有限的OOD样本中学习。我们在专用基准测试上验证了我们的方法,结果显示我们的方法在三种医学影像模态上大大改进了强基线。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted at MICCAI 2025
Summary
本文探讨了深度学习模型在面临非分布图像时性能下降的问题,这可能导致误诊和患者护理受到损害。现有无监督异常检测(U-OOD)方法假设异常样本来源于非集中分布,忽略现实场景模型部署中任务特定的异常样本逐渐积累的问题。为反映真实情况,提出了迭代部署暴露(IDE)这一新型的无监督异常检测场景设置。针对IDE场景,提出了一种方法CSO,该方法从对异常分布无感知的U-OOD检测器出发,利用观察到的未标记数据在部署过程中逐步优化。CSO采用新的U-OOD评分函数,结合马氏距离和最近邻方法,以及新的信心缩放少样本异常检测器,从有限的异常样本中学习。在专用基准测试上验证了该方法,在三种医学成像模态上大大优于强基线。
Key Takeaways
- 深度学习模型在面临非分布图像时可能性能下降,导致误诊和患者护理问题。
- 现有无监督异常检测方法忽略了现实场景中模型部署中任务特定异常样本逐渐积累的问题。
- 提出了迭代部署暴露(IDE)这一新型的无监督异常检测场景设置,以更好地反映真实情况。
- 针对IDE场景,提出了CSO方法,从对异常分布无感知的U-OOD检测器出发,逐步优化。
- CSO采用结合马氏距离和最近邻方法的新的U-OOD评分函数。
- CSO引入信心缩放少样本异常检测器,可从有限的异常样本中学习。
点此查看论文截图