⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-05-22 更新
IPENS:Interactive Unsupervised Framework for Rapid Plant Phenotyping Extraction via NeRF-SAM2 Fusion
Authors:Wentao Song, He Huang, Youqiang Sun, Fang Qu, Jiaqi Zhang, Longhui Fang, Yuwei Hao, Chenyang Peng
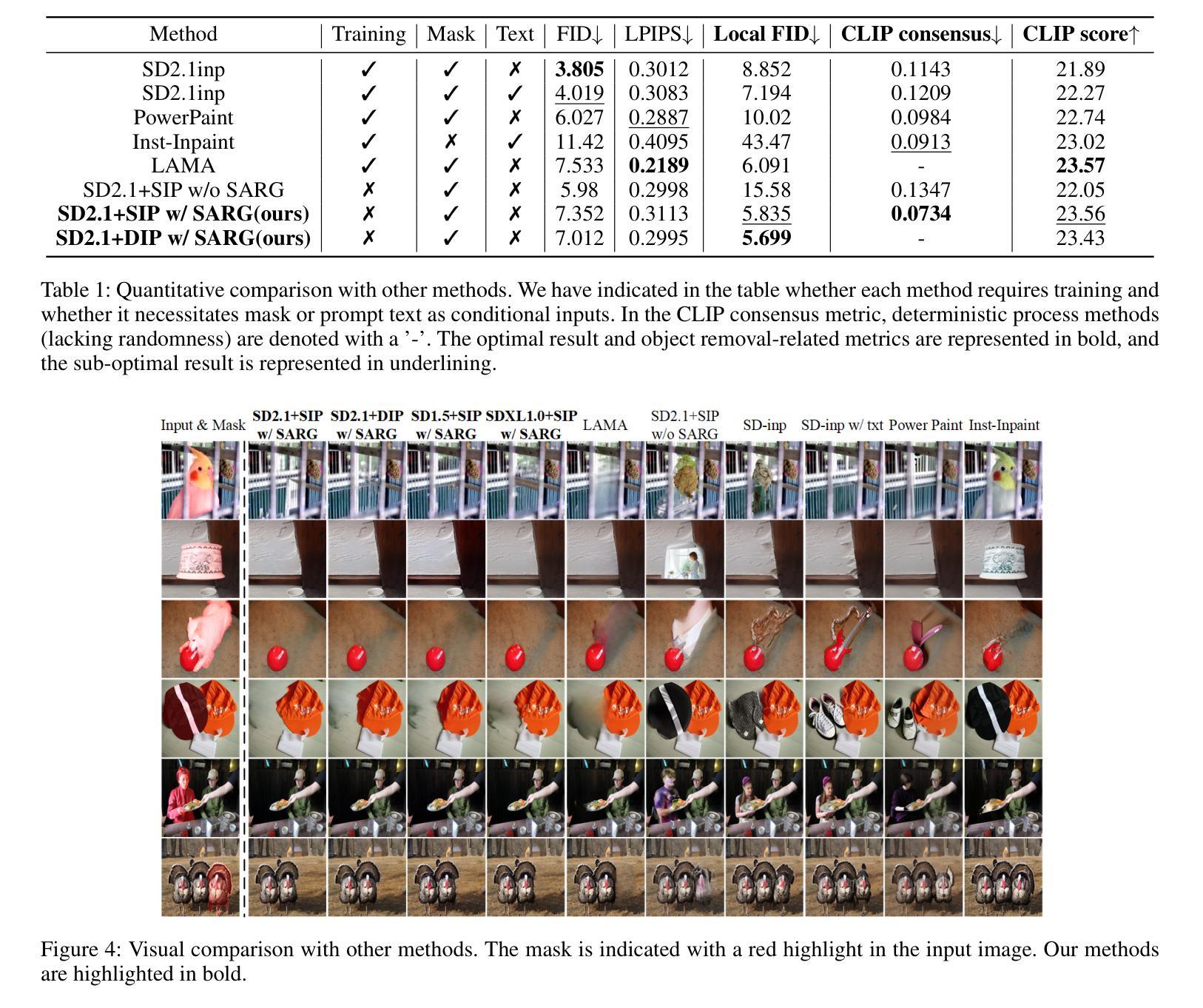
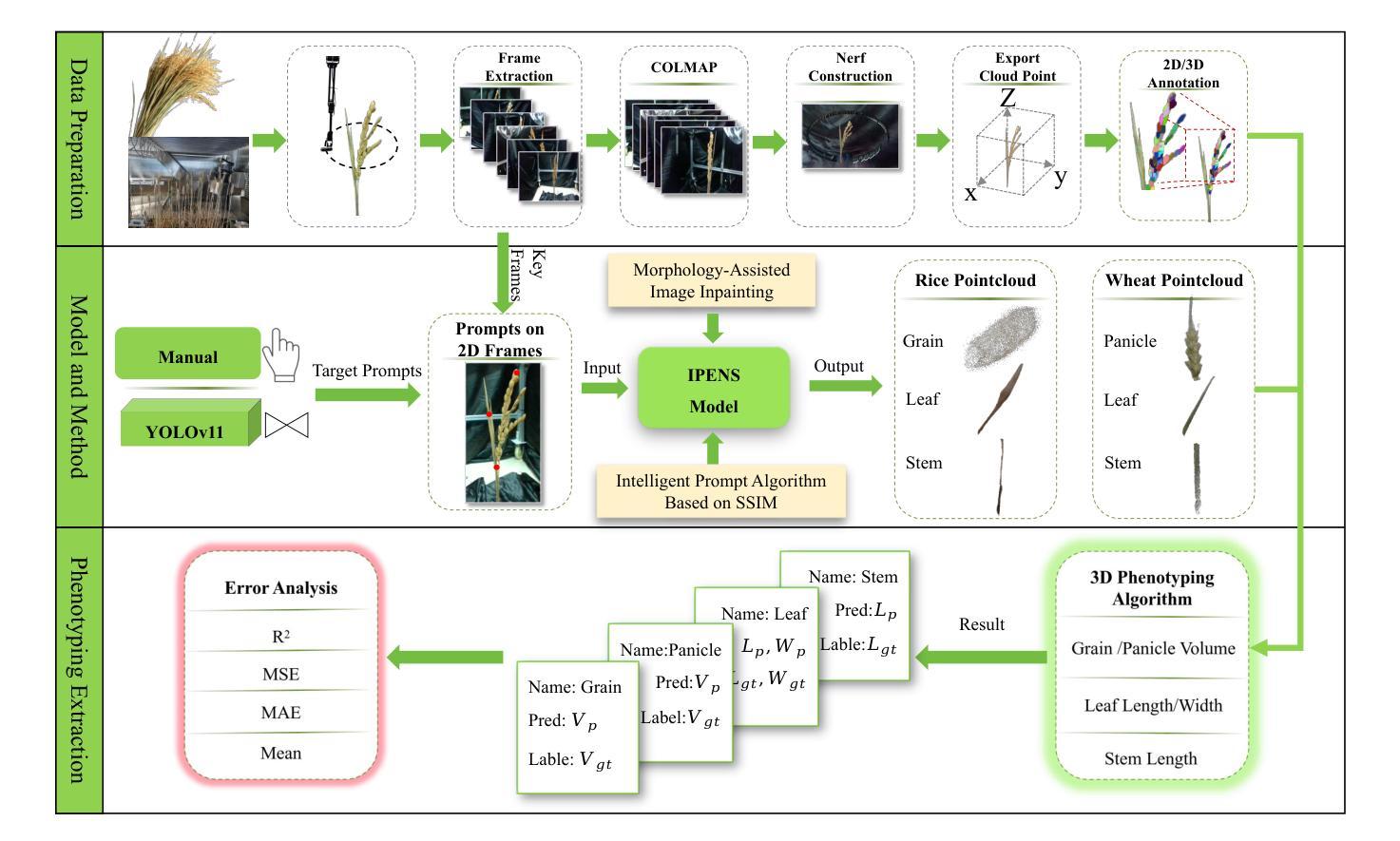
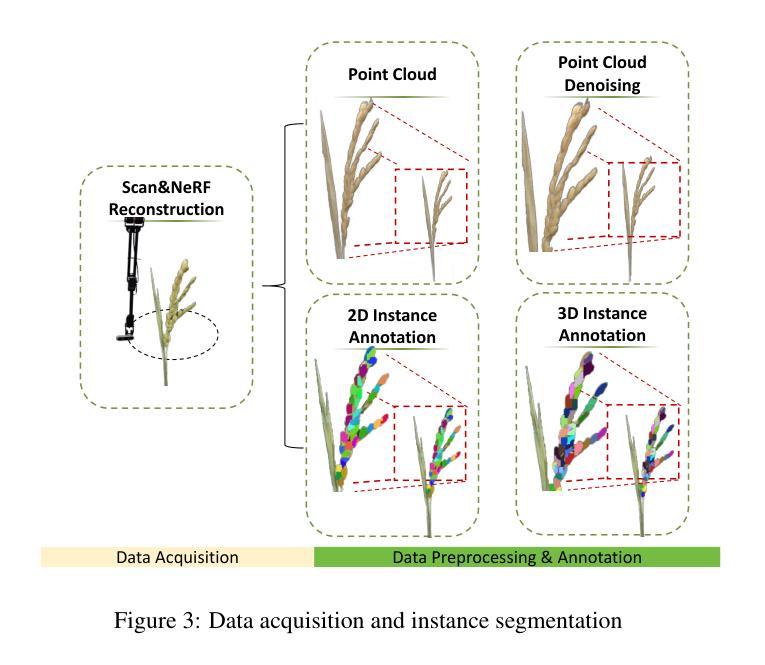
Advanced plant phenotyping technologies play a crucial role in targeted trait improvement and accelerating intelligent breeding. Due to the species diversity of plants, existing methods heavily rely on large-scale high-precision manually annotated data. For self-occluded objects at the grain level, unsupervised methods often prove ineffective. This study proposes IPENS, an interactive unsupervised multi-target point cloud extraction method. The method utilizes radiance field information to lift 2D masks, which are segmented by SAM2 (Segment Anything Model 2), into 3D space for target point cloud extraction. A multi-target collaborative optimization strategy is designed to effectively resolve the single-interaction multi-target segmentation challenge. Experimental validation demonstrates that IPENS achieves a grain-level segmentation accuracy (mIoU) of 63.72% on a rice dataset, with strong phenotypic estimation capabilities: grain volume prediction yields R2 = 0.7697 (RMSE = 0.0025), leaf surface area R2 = 0.84 (RMSE = 18.93), and leaf length and width predictions achieve R2 = 0.97 and 0.87 (RMSE = 1.49 and 0.21). On a wheat dataset,IPENS further improves segmentation accuracy to 89.68% (mIoU), with equally outstanding phenotypic estimation performance: spike volume prediction achieves R2 = 0.9956 (RMSE = 0.0055), leaf surface area R2 = 1.00 (RMSE = 0.67), and leaf length and width predictions reach R2 = 0.99 and 0.92 (RMSE = 0.23 and 0.15). This method provides a non-invasive, high-quality phenotyping extraction solution for rice and wheat. Without requiring annotated data, it rapidly extracts grain-level point clouds within 3 minutes through simple single-round interactions on images for multiple targets, demonstrating significant potential to accelerate intelligent breeding efficiency.
先进植物表型技术对于目标性状的改良和智能育种的加速起着至关重要的作用。由于植物物种的多样性,现有方法严重依赖于大规模高精度手动注释数据。对于粒级自遮挡对象,无监督方法往往证明无效。本研究提出了一种交互式无监督多目标点云提取方法IPENS。该方法利用辐射场信息,将SAM2(任何分割模型2)分割的2D遮罩提升到3D空间,用于目标点云提取。设计了一种多目标协同优化策略,有效解决单次交互多目标分割挑战。实验验证表明,IPENS在稻米数据集上达到了粒级分割准确率(mIoU)63.72%,具有很强的表型估计能力:粒体积预测R2=0.7697(RMSE=0.0025),叶表面积R2=0.84(RMSE=18.93),叶长和叶宽预测达到R2=0.97和0.87(RMSE=1.49和0.21)。在小麦数据集上,IPENS进一步提高了分割精度至89.68%(mIoU),同样表现出卓越的表型估计性能:穗体积预测达到R2=0.9956(RMSE=0.0055),叶表面积R2=1.00(RMSE=0.67),叶长和叶宽预测达到R2=0.99和0.92(RMSE=0.23和0.15)。该方法为水稻和小麦提供了非侵入式、高质量的表型提取解决方案。它无需注释数据,通过简单的单轮图像交互,在3分钟内即可为多目标快速提取粒级点云,显示出加速智能育种效率的显著潜力。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本研究提出一种交互式无监督多目标点云提取方法IPENS,利用辐射场信息将二维掩膜提升到三维空间进行目标点云提取,解决植物自遮挡对象的分割问题。在稻类与小麦数据测试集上表现优秀,实现了高效的智能育种加速潜力。
Key Takeaways
- IPENS利用辐射场信息将二维掩膜提升到三维空间进行目标点云提取,用于植物表型分析。
- 无需大量高精度标注数据,仅通过简单单轮交互即可在几分钟内提取出谷粒级点云。
- IPENS在稻类数据集上实现了谷粒级别的分割精度(mIoU)为63.72%,并且具有较强的表型估计能力。
- 在小麦数据集上,IPENS进一步提高了分割精度(mIoU达到89.68%),并展现出出色的表型估计性能。
- IPENS具有潜力加速智能育种效率,为稻类和麦类作物的非侵入式高质量表型提取提供了解决方案。
- IPENS通过多目标协同优化策略解决了单交互多目标分割挑战。
点此查看论文截图


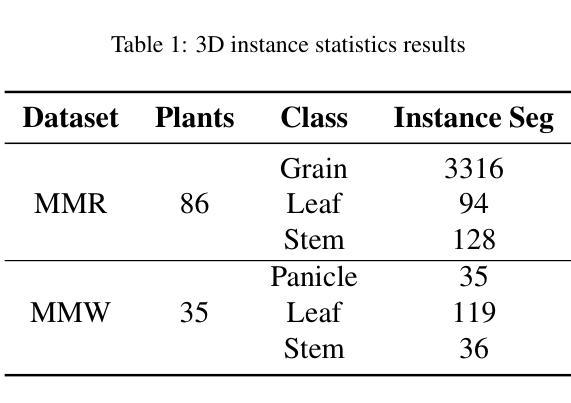
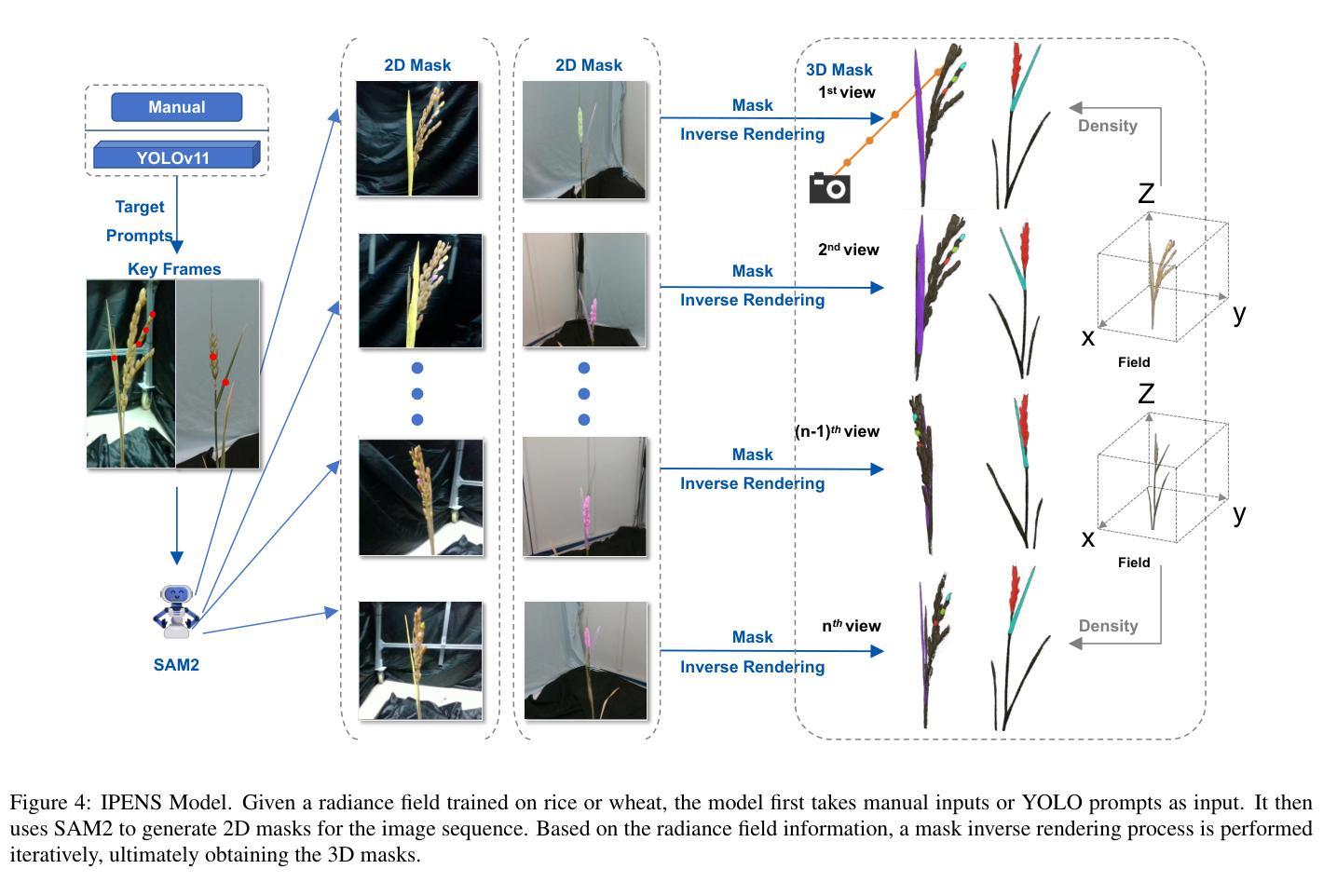
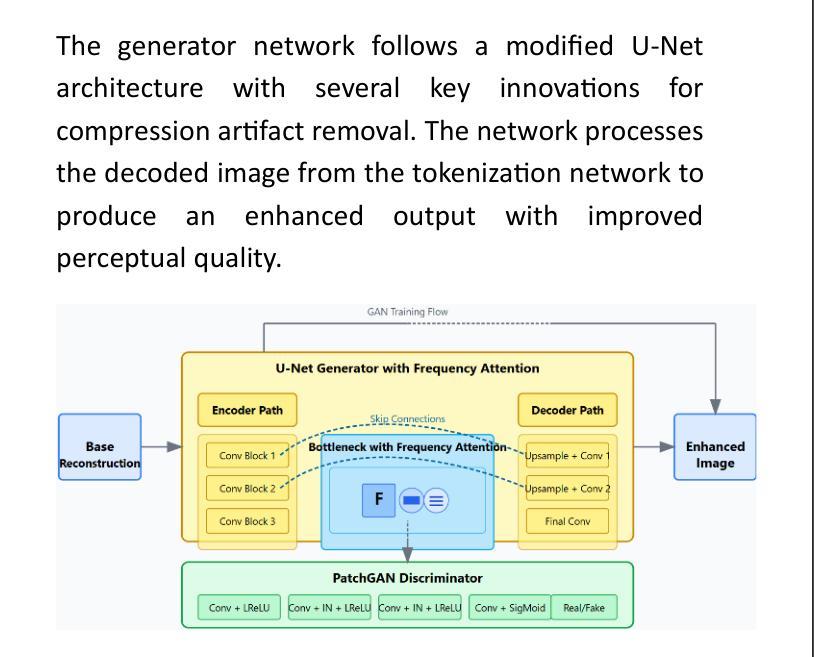
GANCompress: GAN-Enhanced Neural Image Compression with Binary Spherical Quantization
Authors:Karthik Sivakoti
The exponential growth of visual data in digital communications has intensified the need for efficient compression techniques that balance rate-distortion performance with computational feasibility. While recent neural compression approaches have shown promise, they still struggle with fundamental challenges: preserving perceptual quality at high compression ratios, computational efficiency, and adaptability to diverse visual content. This paper introduces GANCompress, a novel neural compression framework that synergistically combines Binary Spherical Quantization (BSQ) with Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs) to address these challenges. Our approach employs a transformer-based autoencoder with an enhanced BSQ bottleneck that projects latent representations onto a hypersphere, enabling efficient discretization with bounded quantization error. This is followed by a specialized GAN architecture incorporating frequency-domain attention and color consistency optimization. Experimental results demonstrate that GANCompress achieves substantial improvement in compression efficiency – reducing file sizes by up to 100x with minimal visual distortion. Our method outperforms traditional codecs like H.264 by 12-15% in perceptual metrics while maintaining comparable PSNR/SSIM values, with 2.4x faster encoding and decoding speeds. On standard benchmarks including ImageNet-1k and COCO2017, GANCompress sets a new state-of-the-art, reducing FID from 0.72 to 0.41 (43% improvement) compared to previous methods while maintaining higher throughput. This work presents a significant advancement in neural compression technology with promising applications for real-time visual communication systems.
数字通信中视觉数据的指数级增长,使得需要一种能够在速率失真性能和计算可行性之间取得平衡的压缩技术。虽然最近的神经压缩方法显示出了一定的潜力,但它们仍然面临着一些基本挑战:在高压缩率下保持感知质量、计算效率和适应各种视觉内容的能力。本文介绍了GANCompress,这是一种新颖的神经压缩框架,它通过二进制球面量化(BSQ)与生成对抗网络(GANs)的结合来解决这些挑战。我们的方法采用基于变压器的自动编码器,并使用增强的BSQ瓶颈将潜在表示投影到超球体上,实现具有有界量化误差的有效离散化。随后是一个结合了频域注意力和颜色一致性优化的专用GAN架构。实验结果表明,GANCompress在压缩效率方面取得了显著改进,通过高达100倍的压缩比例减小文件大小,同时实现最小的视觉失真。我们的方法在感知度量上优于H.264等传统编解码器,同时保持相当的峰值信噪比(PSNR)/结构相似性度量(SSIM)值,编码和解码速度提高了2.4倍。在包括ImageNet-1k和COCO2017在内的标准基准测试中,GANCompress达到了业界最新的领先水平,与以前的方法相比,在保持较高吞吐量的同时,将无监督离散化指标(FID)从0.72降低到0.41(提高了43%)。这项工作代表了神经压缩技术的一个重大进展,对实时视觉通信系统具有潜在的应用价值。
论文及项目相关链接
摘要
神经网络压缩技术GANCompress结合了二进制球面量化(BSQ)与生成对抗网络(GANs),解决了高压缩比下的感知质量保存、计算效率以及对各种视觉内容的适应性等挑战。采用基于变压器的自编码器与增强BSQ瓶颈,将潜在表示投影到超球体上,实现了具有有界量化误差的高效离散化。之后采用具有频域注意力和颜色一致性优化的专用GAN架构。实验结果表明,GANCompress在压缩效率方面取得了重大改进,文件大小减少了高达100倍,视觉失真最小。在ImageNet-1k和COCO2017等标准基准测试中,与先前方法相比,FID从0.72降低到0.41(提高了43%),同时保持较高的吞吐量,为实时视觉通信系统提供了有前途的应用前景。本研究标志着神经网络压缩技术的重大进展。
关键见解
- GANCompress结合了二进制球面量化(BSQ)和生成对抗网络(GANs),解决了神经网络压缩中的多重挑战。
- 采用基于变压器的自编码器与增强BSQ方法实现高效离散化和有界量化误差。
- GAN架构具有频域注意力和颜色一致性优化功能。
- GANCompress实现了高达100倍的文件大小缩减,视觉失真极小。
- 与传统编解码器H.264相比,GANCompress在感知指标上提高了12-15%,同时保持相当的PSNR/SSIM值。
- 在标准基准测试中,与先前方法相比,FID降低了43%,同时保持较高的吞吐量。
点此查看论文截图

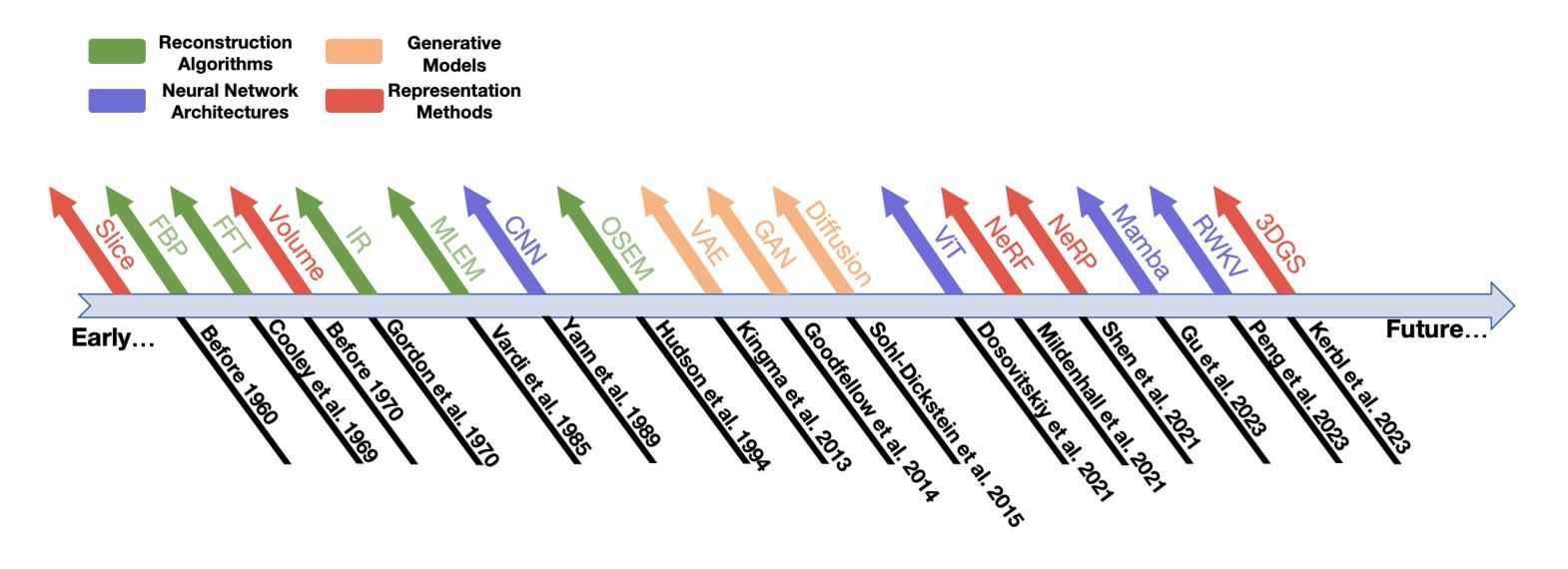
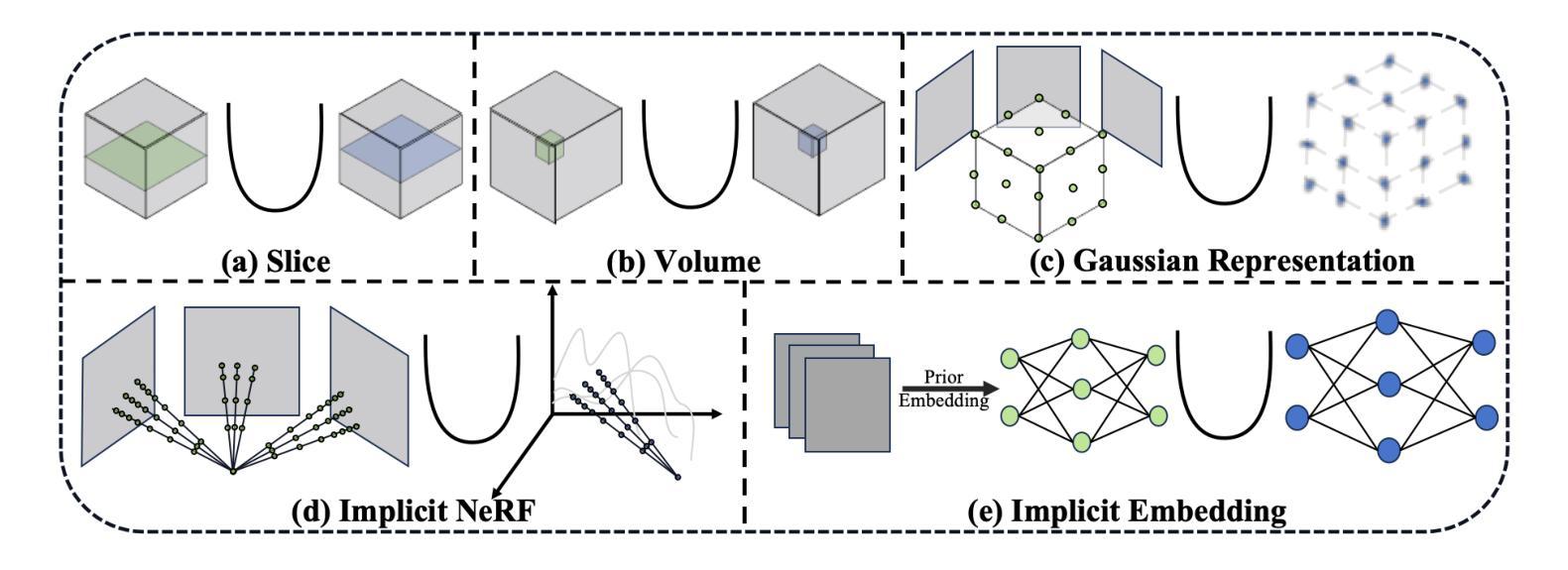
Explicit and Implicit Representations in AI-based 3D Reconstruction for Radiology: A Systematic Review
Authors:Yuezhe Yang, Boyu Yang, Yaqian Wang, Yang He, Xingbo Dong, Zhe Jin
The demand for high-quality medical imaging in clinical practice and assisted diagnosis has made 3D reconstruction in radiological imaging a key research focus. Artificial intelligence (AI) has emerged as a promising approach to enhancing reconstruction accuracy while reducing acquisition and processing time, thereby minimizing patient radiation exposure and discomfort and ultimately benefiting clinical diagnosis. This review explores state-of-the-art AI-based 3D reconstruction algorithms in radiological imaging, categorizing them into explicit and implicit approaches based on their underlying principles. Explicit methods include point-based, volume-based, and Gaussian representations, while implicit methods encompass implicit prior embedding and neural radiance fields. Additionally, we examine commonly used evaluation metrics and benchmark datasets. Finally, we discuss the current state of development, key challenges, and future research directions in this evolving field. Our project available on: https://github.com/Bean-Young/AI4Radiology.
临床实践和对辅助诊断的高质量医学成像的需求使得放射成像中的三维重建成为关键的研究重点。人工智能(AI)作为一种有前景的方法,在提高重建精度、减少采集和处理时间方面显示出巨大的潜力,从而减少了患者的辐射暴露和不适感,最终有益于临床诊断。本文综述了基于人工智能的放射成像三维重建算法的最新进展,根据它们的基本原理将其分为显式方法和隐式方法。显式方法包括点基、体积基和高斯表示法,而隐式方法包括隐式先验嵌入和神经辐射场。此外,我们还研究了常用的评估指标和基准数据集。最后,我们讨论了该领域的当前发展状态、关键挑战和未来研究方向。我们的项目可在以下网址找到:https://github.com/Bean-Young/AI4Radiology。
论文及项目相关链接
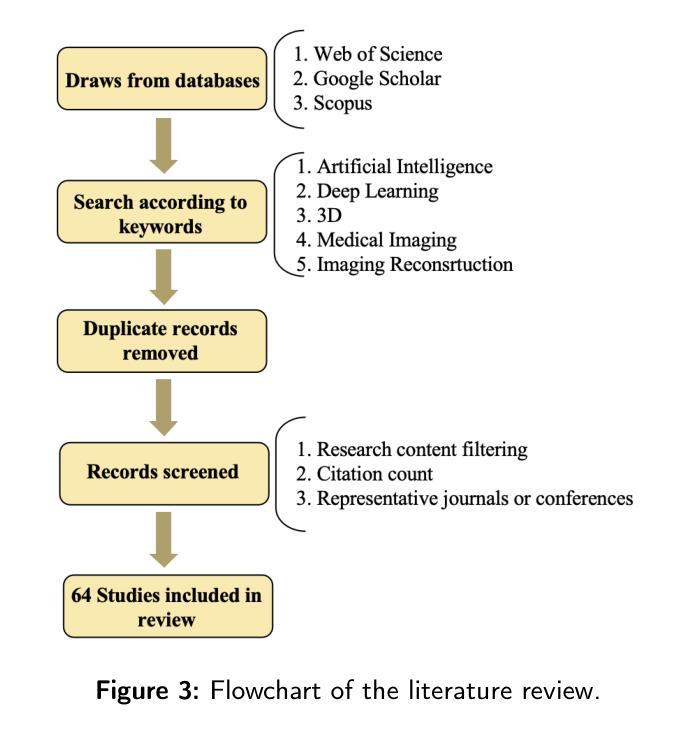
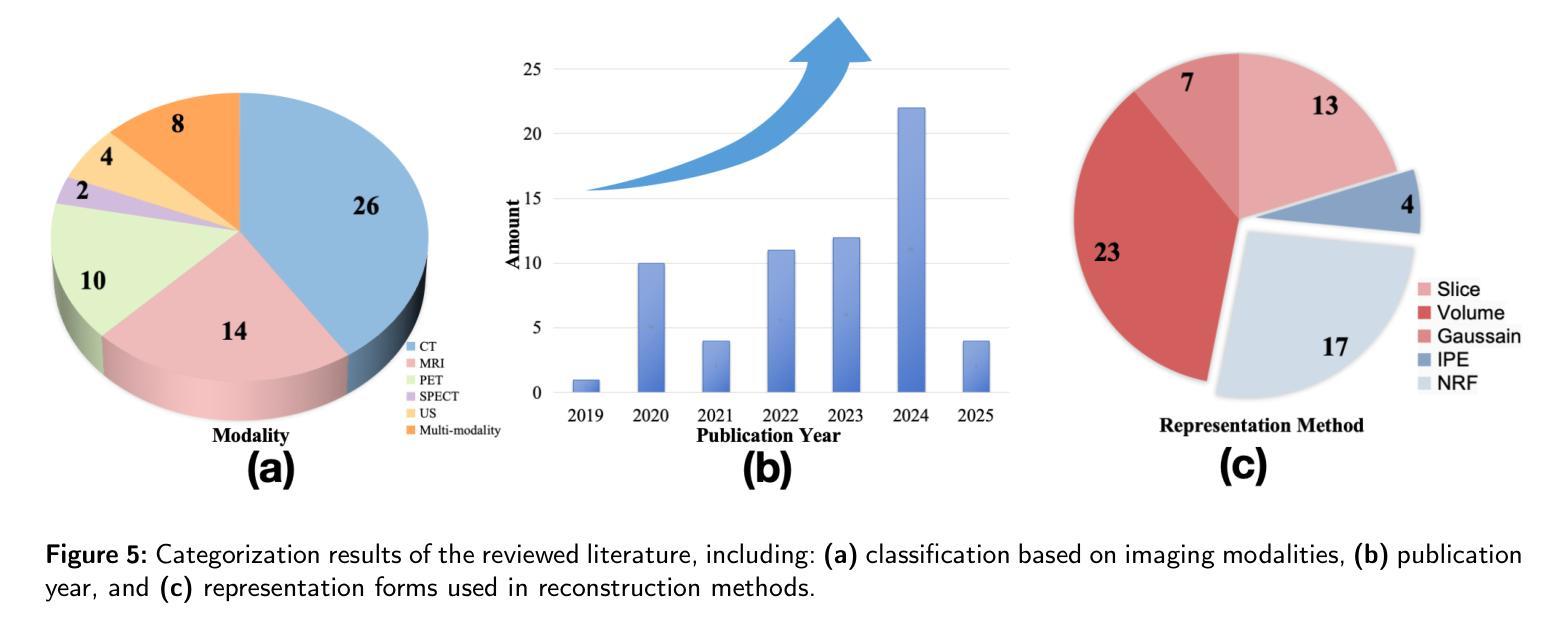
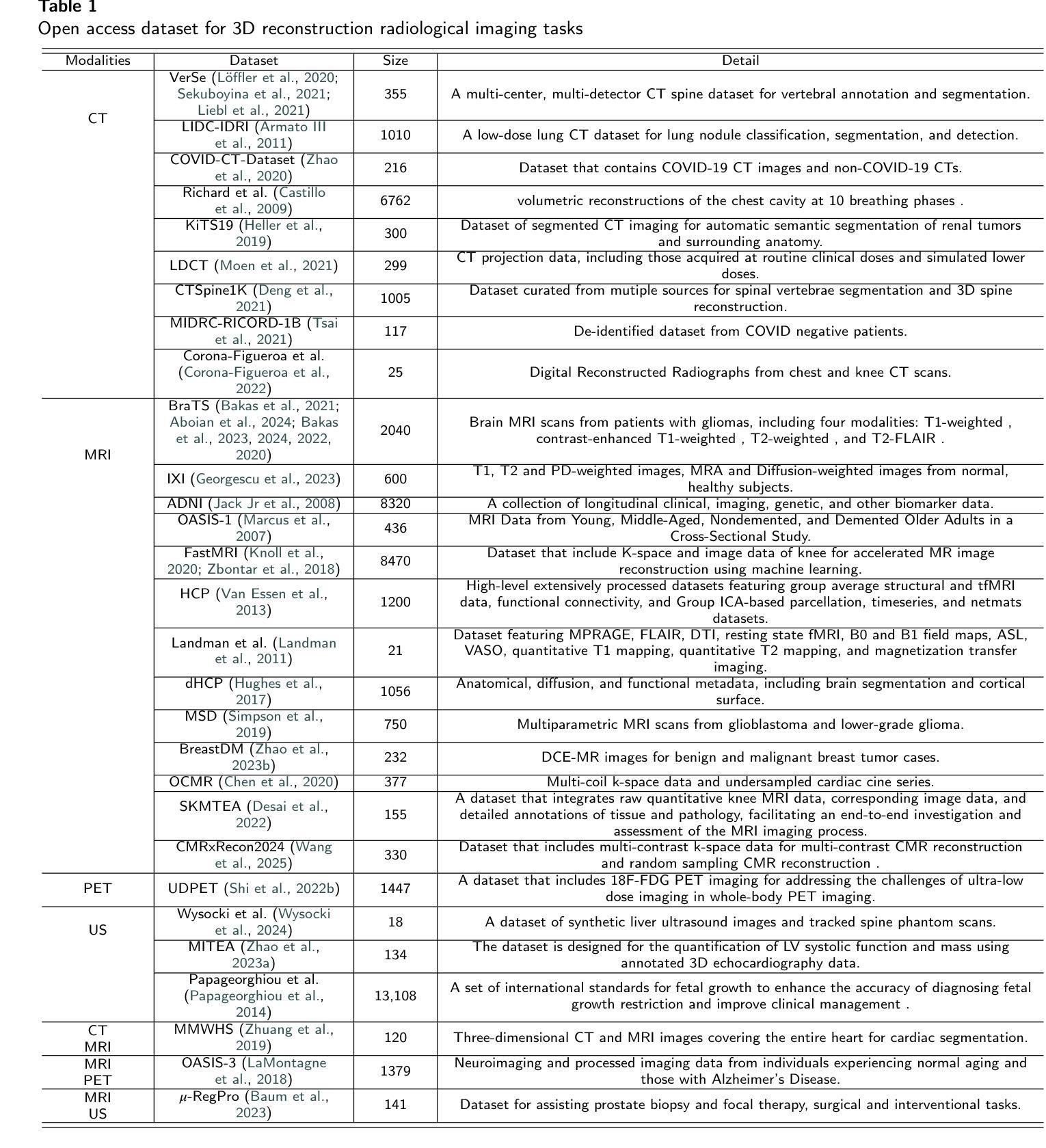
PDF 20 pages, 5 figures, submit to Medical Image Analysis
Summary
本文介绍了人工智能在放射学成像中的三维重建技术。文章讨论了当前最前沿的人工智能三维重建算法,将其分为显式方法和隐式方法两类。显式方法包括点基、体积基和基于高斯表示的方法,而隐式方法则涵盖隐式先验嵌入和神经辐射场技术。文章还探讨了常用的评估指标和基准数据集,并讨论了当前领域的发展状况、关键挑战和未来研究方向。项目代码可通过链接访问:https://github.com/Bean-Young/AI4Radiology。
Key Takeaways
- 人工智能在放射学成像中的三维重建技术对于临床实践及辅助诊断至关重要。
- 当前主流的人工智能三维重建算法分为显式方法和隐式方法两种。
- 显式方法主要包括点基、体积基和基于高斯表示的技术。
- 隐式方法涵盖隐式先验嵌入和神经辐射场技术。
- 人工智能在三维重建中的应用有助于提升重建精度,减少采集和处理时间,降低患者辐射暴露和不适感,对临床诊断具有积极影响。
- 文章还探讨了评估三维重建技术的常用指标和基准数据集。
点此查看论文截图

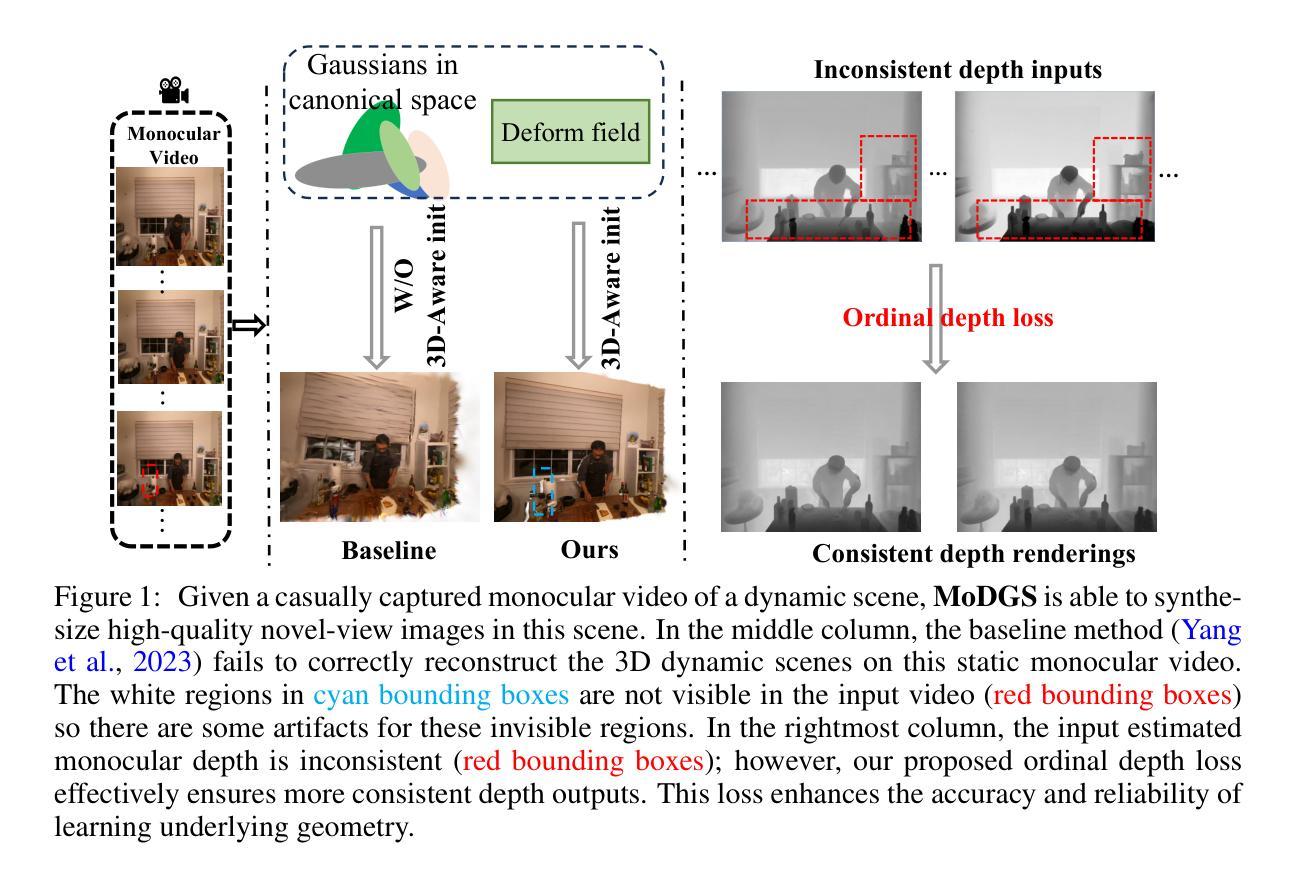
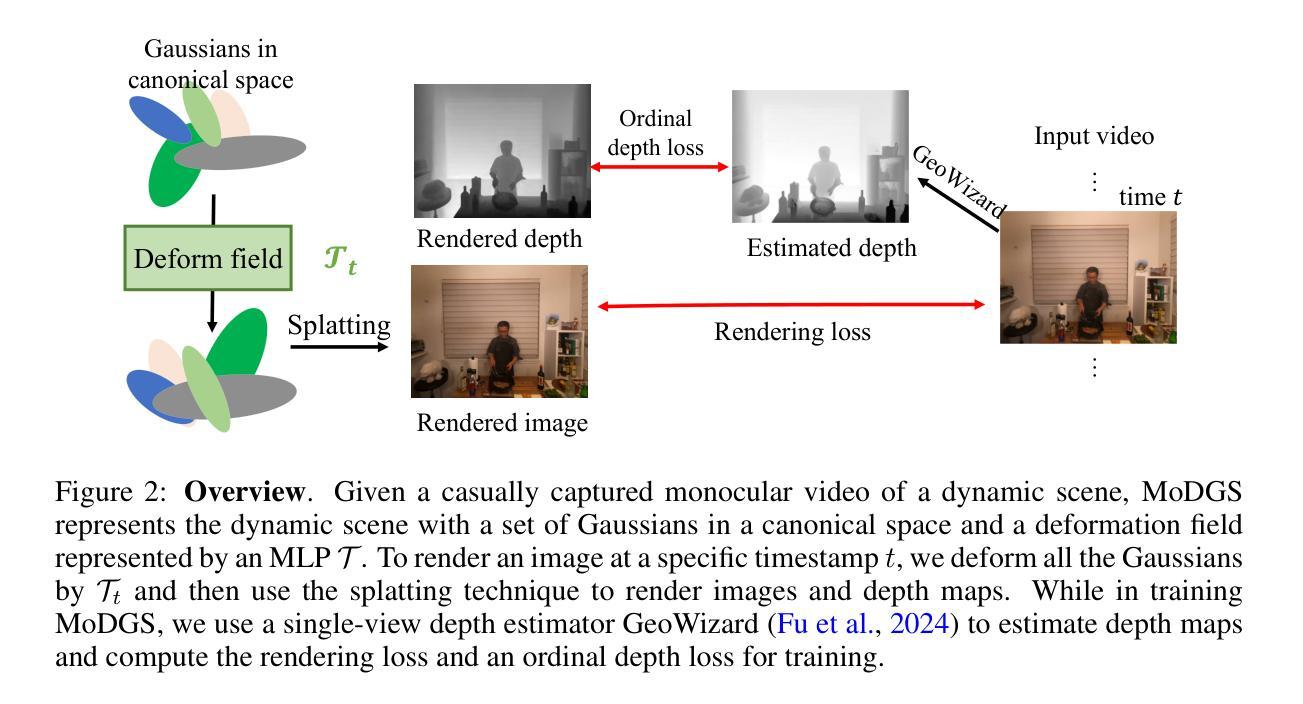
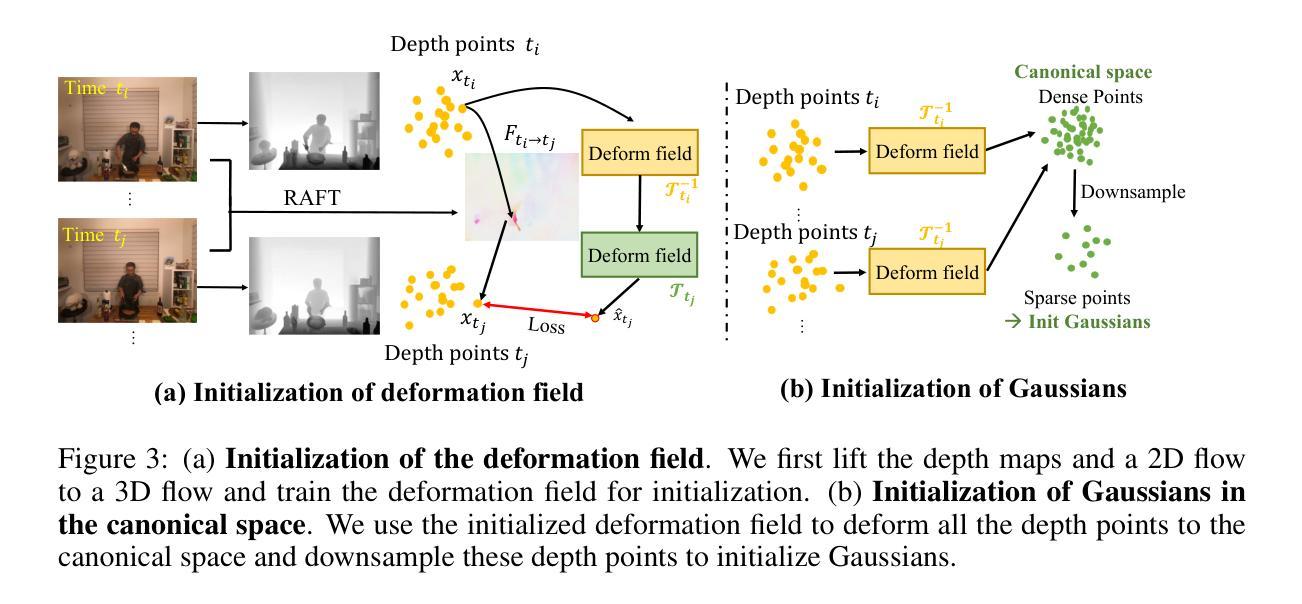
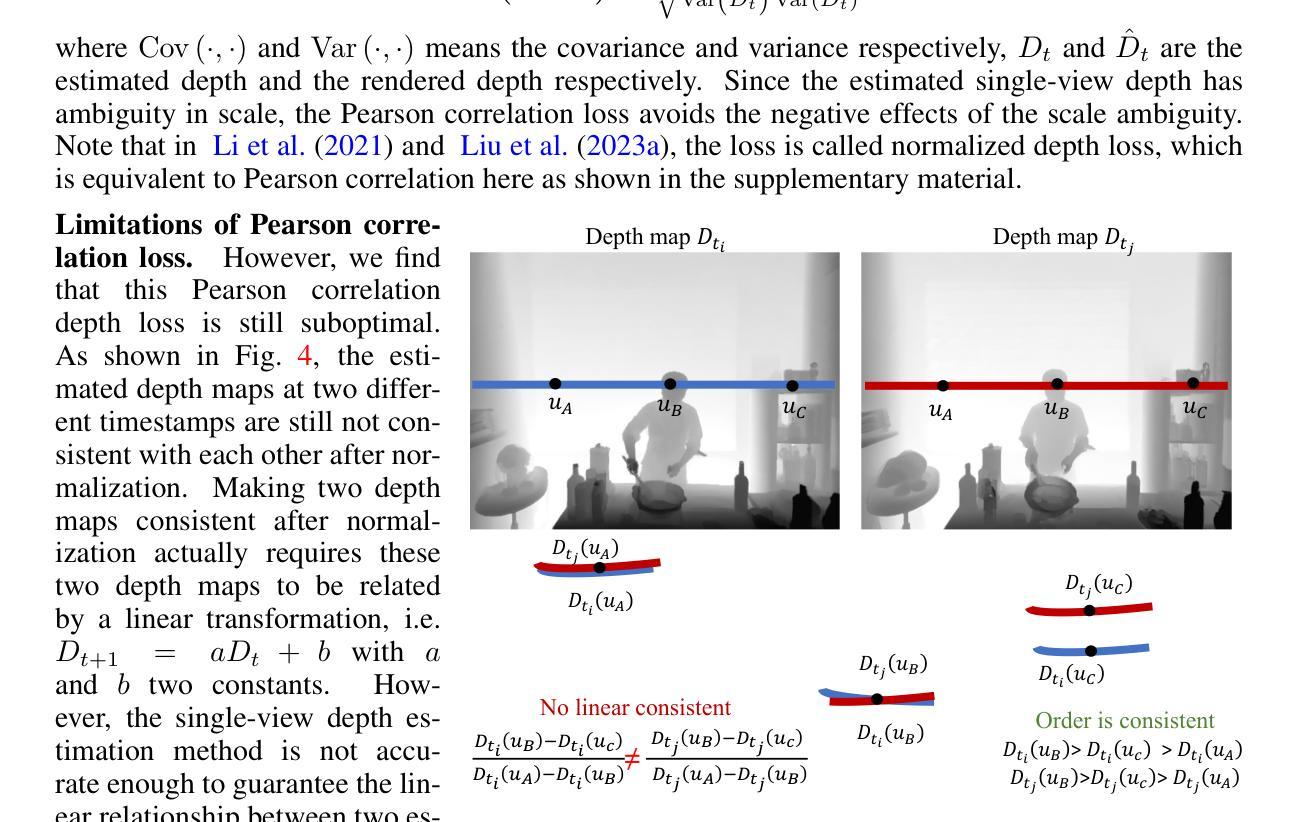
MoDGS: Dynamic Gaussian Splatting from Casually-captured Monocular Videos with Depth Priors
Authors:Qingming Liu, Yuan Liu, Jiepeng Wang, Xianqiang Lyv, Peng Wang, Wenping Wang, Junhui Hou
In this paper, we propose MoDGS, a new pipeline to render novel views of dy namic scenes from a casually captured monocular video. Previous monocular dynamic NeRF or Gaussian Splatting methods strongly rely on the rapid move ment of input cameras to construct multiview consistency but struggle to recon struct dynamic scenes on casually captured input videos whose cameras are either static or move slowly. To address this challenging task, MoDGS adopts recent single-view depth estimation methods to guide the learning of the dynamic scene. Then, a novel 3D-aware initialization method is proposed to learn a reasonable deformation field and a new robust depth loss is proposed to guide the learning of dynamic scene geometry. Comprehensive experiments demonstrate that MoDGS is able to render high-quality novel view images of dynamic scenes from just a casually captured monocular video, which outperforms state-of-the-art meth ods by a significant margin. The code will be publicly available.
在这篇论文中,我们提出了MoDGS,这是一种新的流程,可以从随意捕获的单目视频中呈现动态场景的新视角。之前的单目动态NeRF或高斯涂抹方法强烈依赖于输入相机的快速移动来构建多视角一致性,但在处理随意捕获的输入视频(其相机静止或移动缓慢)时,很难重建动态场景。针对这一具有挑战性的任务,MoDGS采用了最新的单视图深度估计方法来指导动态场景的学习。然后,提出了一种新颖的3D感知初始化方法,用于学习合理的变形场,并提出了一种新的稳健深度损失来指导动态场景几何的学习。综合实验表明,MoDGS能够从随意捕获的单目视频中呈现高质量动态场景的新视角图像,显著优于当前最先进的方法。代码将公开可用。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted as a poster at ICLR. Project page: https://modgs.github.io
摘要
这篇论文提出了一种名为MoDGS的新方法,能够从偶然捕获的单目视频中渲染动态场景的新视角。相较于以往依赖快速相机移动来实现多视角一致性的动态NeRF或高斯拼贴方法,MoDGS针对偶然捕获的输入视频(相机静止或移动缓慢)进行改进。它采用最新的单视图深度估计方法来指导动态场景的学习。接着,提出了一种新的3D感知初始化方法,用于学习合理的变形场,并引入了一种新的稳健深度损失来指导动态场景几何的学习。综合实验表明,MoDGS能够从偶然捕获的单目视频中高质量地渲染动态场景的新视角图像,显著优于现有方法。
要点
- MoDGS是一种从单目视频中渲染动态场景新视角的方法。
- 它解决了在相机静止或缓慢移动的情况下,渲染动态场景的难题。
- MoDGS采用单视图深度估计方法来指导动态场景的学习。
- 提出了一种新的3D感知初始化方法,用于学习合理的变形场。
- 引入了一种新的稳健深度损失,以更好地指导动态场景几何的学习。
- 综合实验证明MoDGS显著优于现有方法,能够高质量地渲染动态场景的新视角。
点此查看论文截图