⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-05-22 更新
Vox-Profile: A Speech Foundation Model Benchmark for Characterizing Diverse Speaker and Speech Traits
Authors:Tiantian Feng, Jihwan Lee, Anfeng Xu, Yoonjeong Lee, Thanathai Lertpetchpun, Xuan Shi, Helin Wang, Thomas Thebaud, Laureano Moro-Velazquez, Dani Byrd, Najim Dehak, Shrikanth Narayanan
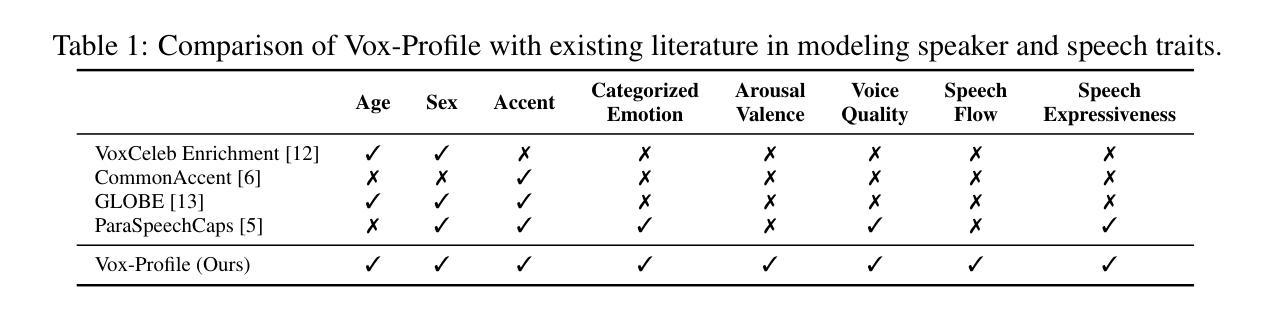
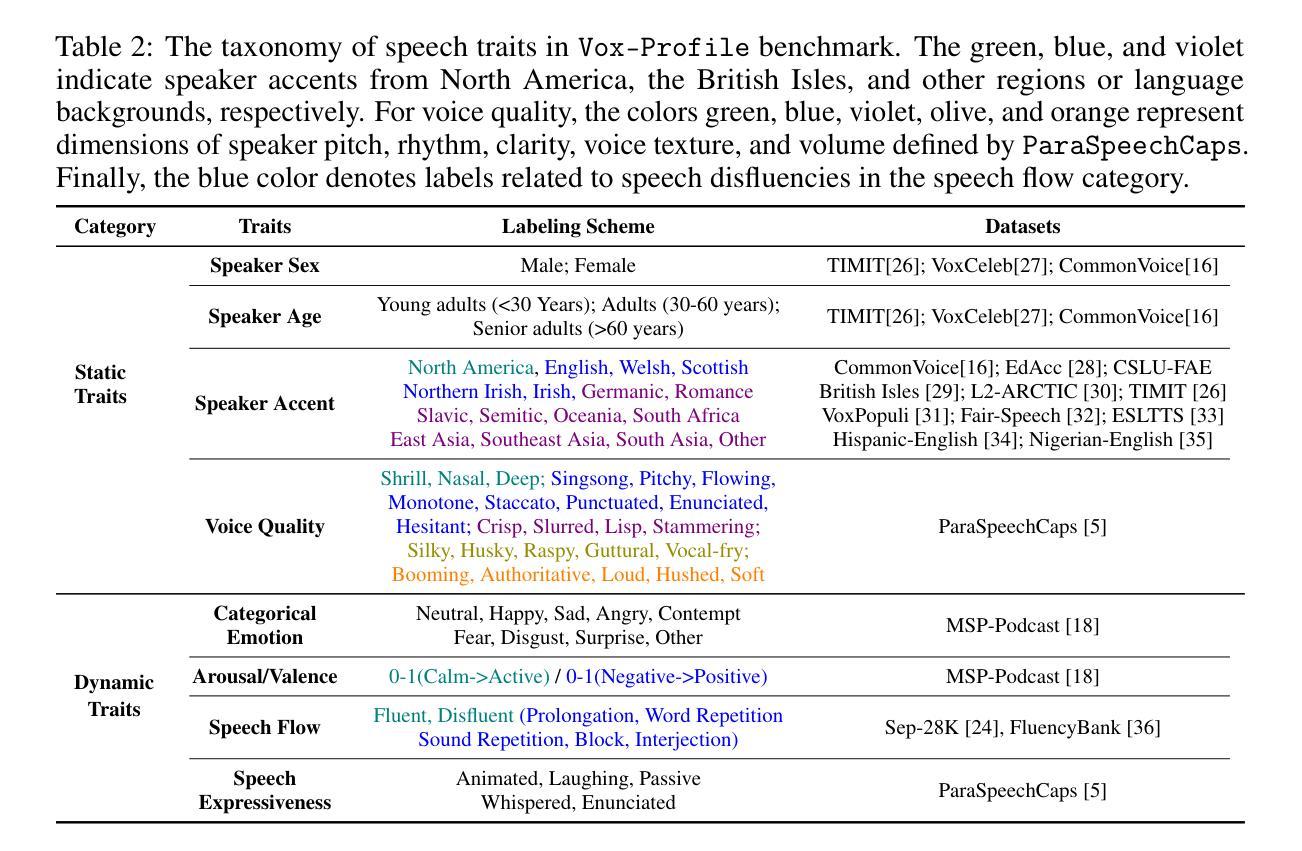
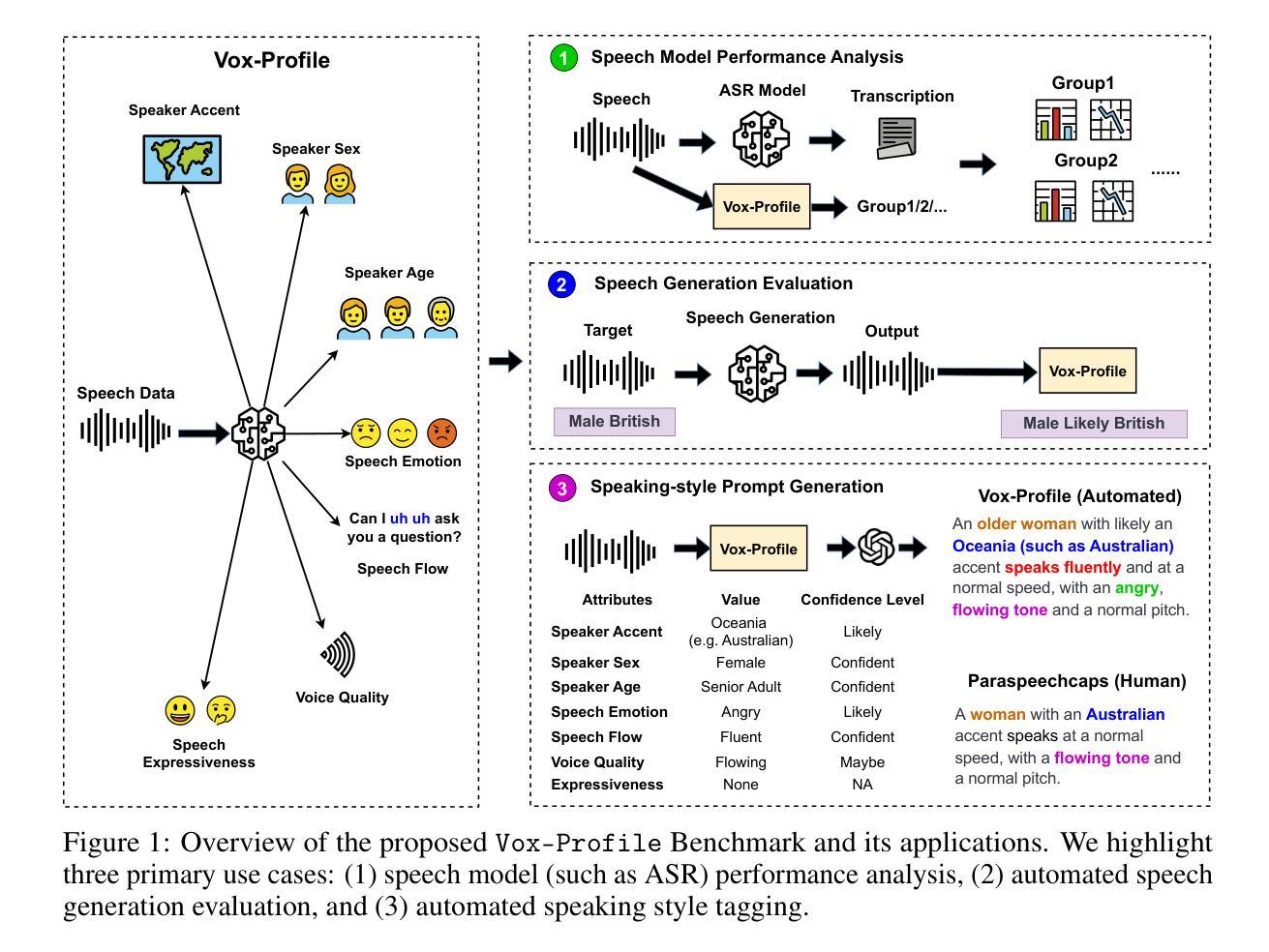
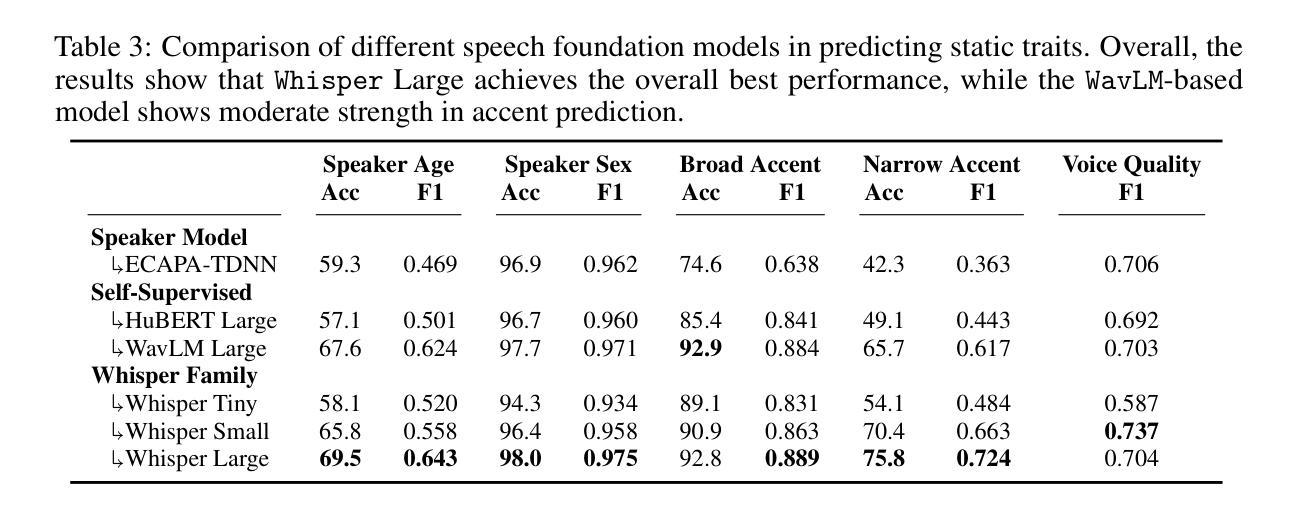
We introduce Vox-Profile, a comprehensive benchmark to characterize rich speaker and speech traits using speech foundation models. Unlike existing works that focus on a single dimension of speaker traits, Vox-Profile provides holistic and multi-dimensional profiles that reflect both static speaker traits (e.g., age, sex, accent) and dynamic speech properties (e.g., emotion, speech flow). This benchmark is grounded in speech science and linguistics, developed with domain experts to accurately index speaker and speech characteristics. We report benchmark experiments using over 15 publicly available speech datasets and several widely used speech foundation models that target various static and dynamic speaker and speech properties. In addition to benchmark experiments, we showcase several downstream applications supported by Vox-Profile. First, we show that Vox-Profile can augment existing speech recognition datasets to analyze ASR performance variability. Vox-Profile is also used as a tool to evaluate the performance of speech generation systems. Finally, we assess the quality of our automated profiles through comparison with human evaluation and show convergent validity. Vox-Profile is publicly available at: https://github.com/tiantiaf0627/vox-profile-release.
我们介绍了Vox-Profile,这是一个全面的基准测试,利用语音基础模型来表征丰富的说话人和语音特征。与现有专注于单一维度说话人特征的工作不同,Vox-Profile提供了全面且多维度的特征描述,这些描述既反映了静态的说话人特征(如年龄、性别、口音),也反映了动态的语音属性(如情感、语速)。该基准测试建立在语音科学和语言学的基础上,与领域专家合作开发,以准确索引说话人和语音特征。我们使用超过15个公开可用的语音数据集和几个针对各种静态和动态说话人和语音属性的广泛使用的基础模型进行基准测试实验。除了基准测试实验外,我们还展示了Vox-Profile支持的几个下游应用。首先,我们证明Vox-Profile可以扩充现有的语音识别数据集,分析ASR性能变化。Vox-Profile还被用作评估语音生成系统性能的工具。最后,我们通过与人类评估的比较来评估我们的自动分析结果的准确性,并展示其收敛有效性。Vox-Profile可在https://github.com/tiantiaf0627/vox-profile-release获得。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
Vox-Profile是一个全面的基准测试,用于利用语音基础模型来刻画丰富的说话人和语音特征。它不同于现有专注于单一维度的说话人特征的工作,而是提供反映静态说话人特征(如年龄、性别、口音)和动态语音属性(如情感、语速)的全方位多维度的分析。该基准测试建立在语音科学和语言学的基础上,与领域专家合作开发,以准确索引说话人和语音特征。使用超过15个公开可用的语音数据集和几个针对各种静态和动态说话人和语音属性的广泛使用的语音基础模型进行了基准测试实验。此外,还展示了Vox-Profile支持的几个下游应用,如增强现有语音识别数据集的分析能力、评估语音生成系统的性能以及通过与人类评估比较来评估自动化分析的质量。
Key Takeaways
- Vox-Profile是一个全面的基准测试,旨在利用语音基础模型表征丰富的说话人和语音特征。
- 它提供静态(如年龄、性别、口音)和动态(如情感、语速)的多维度分析。
- 该基准测试建立在语音科学和语言学的基础上,与领域专家合作开发。
- 使用多个公开数据集和广泛使用的语音基础模型进行了基准测试实验。
- Vox-Profile可增强现有语音识别数据集的分析能力。
- 它被用来评估语音生成系统的性能。
点此查看论文截图

Dual Precision Quantization for Efficient and Accurate Deep Neural Networks Inference
Authors:Tomer Gafni, Asaf Karnieli, Yair Hanani
Deep neural networks have achieved state-of-the-art results in a wide range of applications, from natural language processing and computer vision to speech recognition. However, as tasks become increasingly complex, model sizes continue to grow, posing challenges in latency and memory efficiency. To meet these constraints, post-training quantization has emerged as a promising solution. In this paper, we propose a novel hardware-efficient quantization and inference scheme that exploits hardware advantages with minimal accuracy degradation. Specifically, we introduce a W4A8 scheme, where weights are quantized and stored using 4-bit integer precision, and inference computations are performed using 8-bit floating-point arithmetic, demonstrating significant speedups and improved memory utilization compared to 16-bit operations, applicable on various modern accelerators. To mitigate accuracy loss, we develop a novel quantization algorithm, dubbed Dual Precision Quantization (DPQ), that leverages the unique structure of our scheme without introducing additional inference overhead. Experimental results demonstrate improved performance (i.e., increased throughput) while maintaining tolerable accuracy degradation relative to the full-precision model.
深度神经网络在众多应用中实现了最先进的成果,包括自然语言处理、计算机视觉和语音识别。然而,随着任务的复杂性不断增加,模型规模持续扩大,这对延迟和内存效率提出了挑战。为了应对这些约束,训练后量化作为一种具有前景的解决方案而出现。在本文中,我们提出了一种新型的硬件高效量化和推理方案,该方案利用硬件优势,以最小的精度损失为目标。具体来说,我们引入了W4A8方案,其中权重使用4位整数精度进行量化和存储,推理计算使用8位浮点算术执行,与16位操作相比,该方案在多种现代加速器上实现了显著的速度提升和内存利用率改善。为了缓解精度损失,我们开发了一种新型量化算法,称为双精度量化(DPQ),该算法利用了我们方案的独特结构,而没有引入额外的推理开销。实验结果证明,在提高性能(即提高吞吐量)的同时,相对于全精度模型,精度损失的容忍度得到了保持。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted at eLVM Workshop, CVPR, 2025
总结
本文提出一种新型硬件高效量化及推理方案,利用硬件优势实现最低精度损失。通过W4A8方案,权重以4位整数精度量化存储,推理计算则采用8位浮点运算,相较于传统的16位操作,显著提升了运算速度和内存利用率。同时,本文开发了一种新型量化算法——双精度量化(DPQ),能在不增加推理开销的前提下,充分利用该方案的独特结构。实验结果显示,在提高性能(即提升吞吐量)的同时,相较于全精度模型,精度损失在可接受范围内。
关键见解
- 深度神经网络在多个应用领域中实现了最先进的成果,但随着任务复杂性的增加,模型规模的增长带来了延迟和内存效率的挑战。
- 为应对这些挑战,训练后量化作为一种有前途的解决方案出现。
- 本文提出了一种硬件高效量化及推理方案,利用硬件优势实现最低精度损失。
- 引入W4A8方案,权重以4位整数精度量化存储,推理计算采用8位浮点运算。
- 开发了一种新型量化算法——双精度量化(DPQ),充分利用该方案的独特结构且无需增加额外的推理开销。
- 该方案在多种现代加速器上可实现显著的速度提升和内存利用改善。
- 实验结果显示在提高性能的同时,相较于全精度模型,精度损失较小。
点此查看论文截图

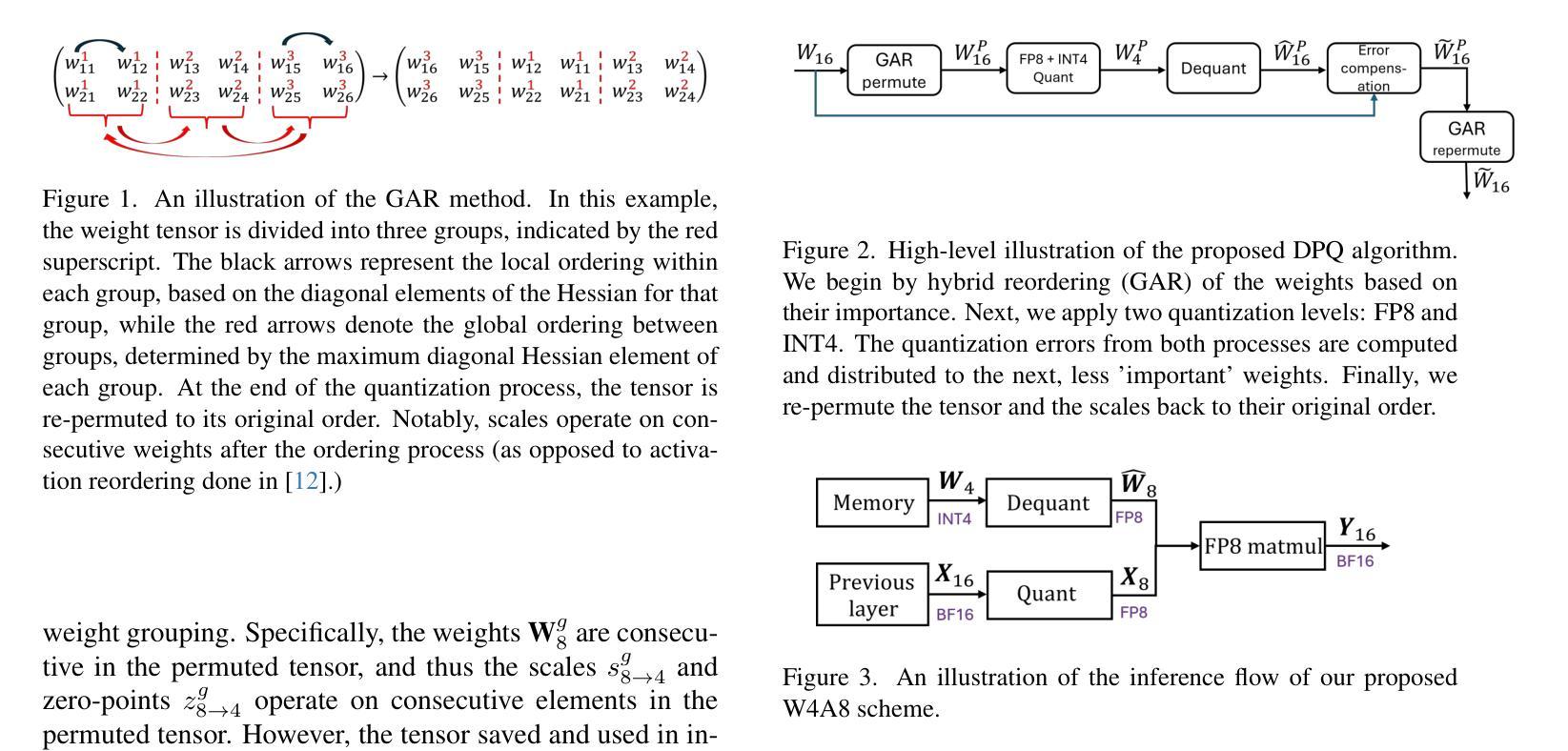
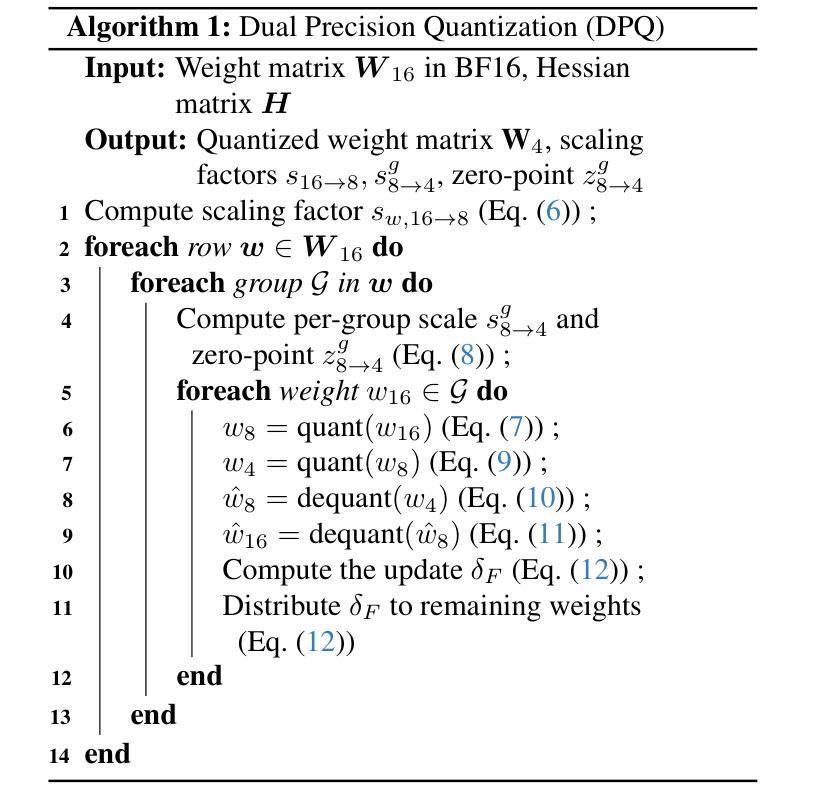
Mitigating Subgroup Disparities in Multi-Label Speech Emotion Recognition: A Pseudo-Labeling and Unsupervised Learning Approach
Authors:Yi-Cheng Lin, Huang-Cheng Chou, Hung-yi Lee
While subgroup disparities and performance bias are increasingly studied in computational research, fairness in categorical Speech Emotion Recognition (SER) remains underexplored. Existing methods often rely on explicit demographic labels, which are difficult to obtain due to privacy concerns. To address this limitation, we introduce an Implicit Demography Inference (IDI) module that leverages pseudo-labeling from a pre-trained model and unsupervised learning using k-means clustering to mitigate bias in SER. Our experiments show that pseudo-labeling IDI reduces subgroup disparities, improving fairness metrics by over 33% with less than a 3% decrease in SER accuracy. Also, the unsupervised IDI yields more than a 26% improvement in fairness metrics with a drop of less than 4% in SER performance. Further analyses reveal that the unsupervised IDI consistently mitigates race and age disparities, demonstrating its potential in scenarios where explicit demographic information is unavailable.
虽然子群体差异和性能偏差在计算研究中得到了越来越多的研究,但在分类语音情感识别(SER)中的公平性仍然被忽视。现有方法通常依赖于明确的人口统计标签,但由于隐私担忧,这些标签很难获得。为了解决这一局限性,我们引入了一个隐式人口统计推断(IDI)模块,该模块利用预训练模型的伪标签和通过k-means聚类进行的无监督学习来减轻SER中的偏见。我们的实验表明,伪标签IDI减少了子群体差异,公平度指标提高了33%以上,而SER准确率下降了不到3%。此外,无监督的IDI在公平度指标上提高了超过2.6%,同时SER性能下降了不到4%。进一步的分析表明,无监督的IDI始终在种族和年龄差异方面有所缓解,这显示了其在无法使用明确的人口统计信息的情况下具有潜力。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by InterSpeech 2025. 7 pages including 2 pages of appendix
Summary
该研究关注计算研究中日益突出的子群体差异和性能偏见问题,探讨了分类语音情感识别(SER)中的公平性。针对现有方法依赖难以获得的明确人口统计标签的问题,该研究引入了一种隐性人口统计推断(IDI)模块,该模块利用预训练模型的伪标签和k均值聚类的无监督学习来减轻SER中的偏见。实验表明,伪标签IDI减少了子群体差异,公平度指标提高了33%以上,而SER准确率仅下降不到3%。此外,无监督的IDI在公平度指标上提高了超过26%,SER性能下降不到4%。进一步分析表明,无监督的IDI持续缓解了种族和年龄差异,表明在缺乏明确人口统计信息的情况下,其具有潜在应用价值。
Key Takeaways
- 该研究关注语音情感识别(SER)中的公平性问题,特别是子群体差异和性能偏见。
- 现有方法依赖难以获取的人口统计标签,该研究引入隐性人口统计推断(IDI)模块来解决这一问题。
- 伪标签IDI方法能够减少子群体差异,公平度指标提高显著,同时保持较高的SER准确率。
- 无监督的IDI方法在公平度指标上也有显著改进,且在缺乏明确人口统计信息的情况下表现出潜力。
- 实验结果显示,这两种IDI方法都有效缓解了种族和年龄差异。
- 该研究通过引入IDI模块,提供了一种新的解决SER中偏见问题的方法。
点此查看论文截图

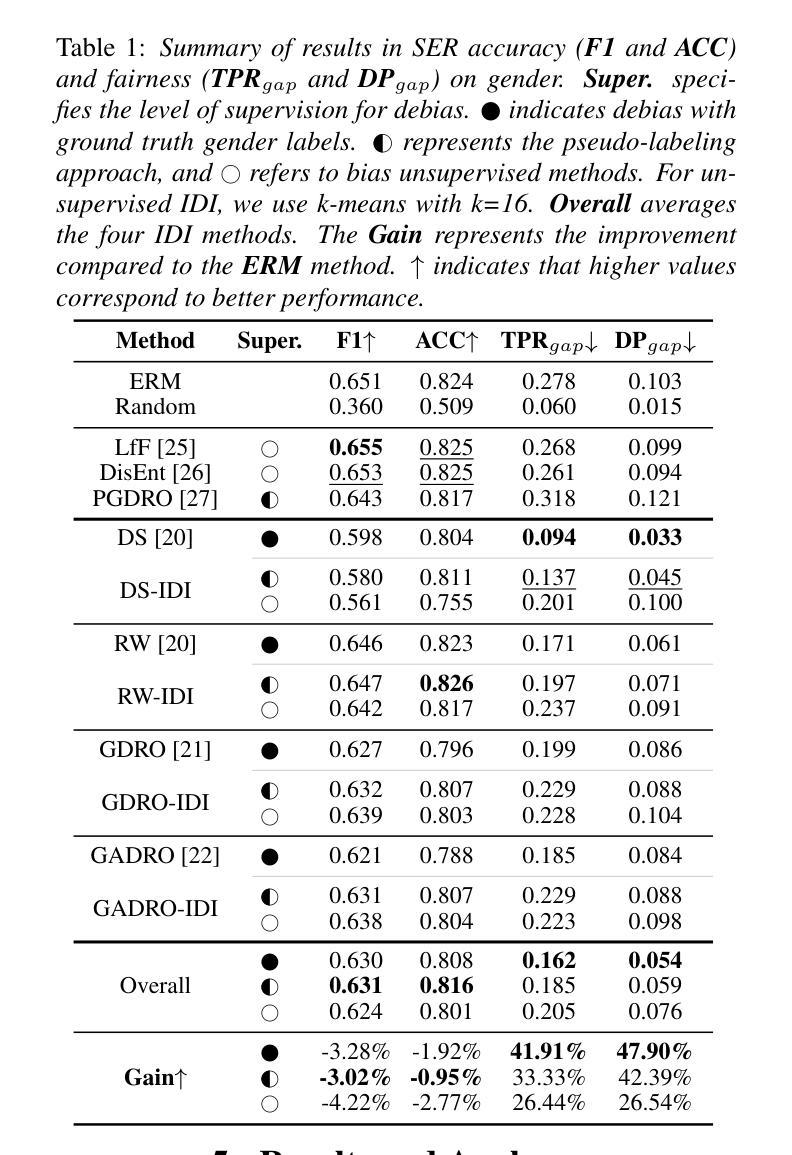
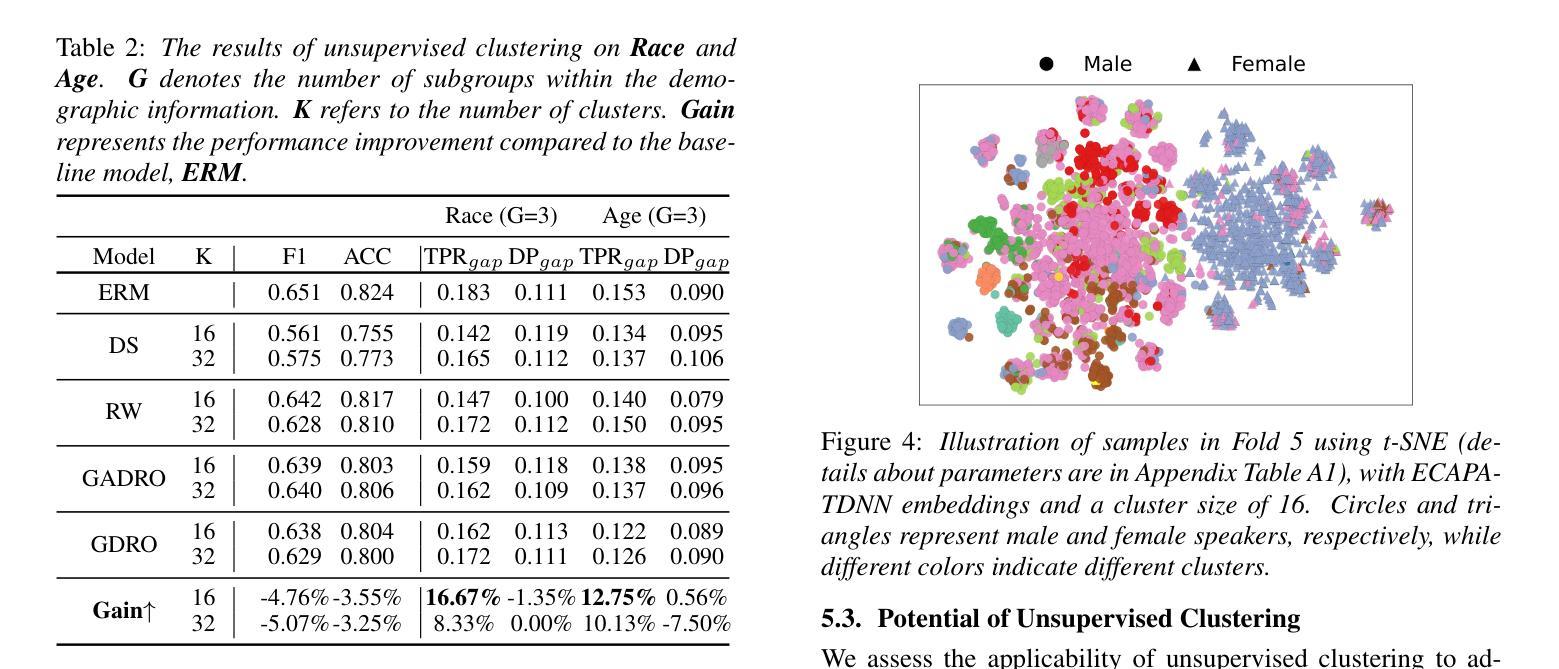
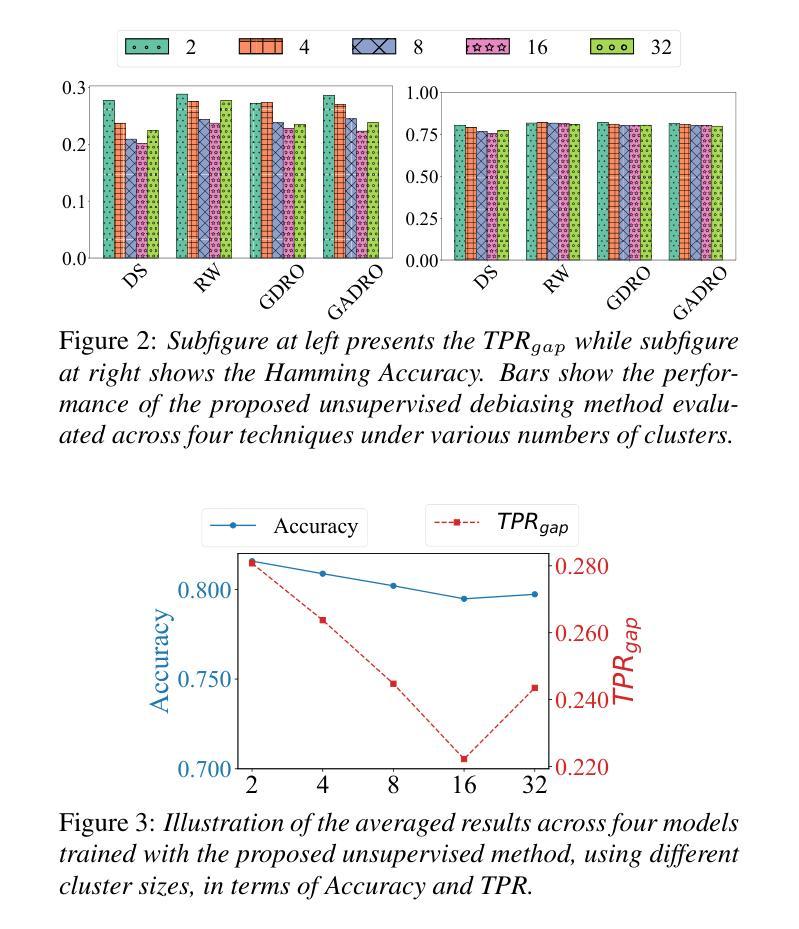
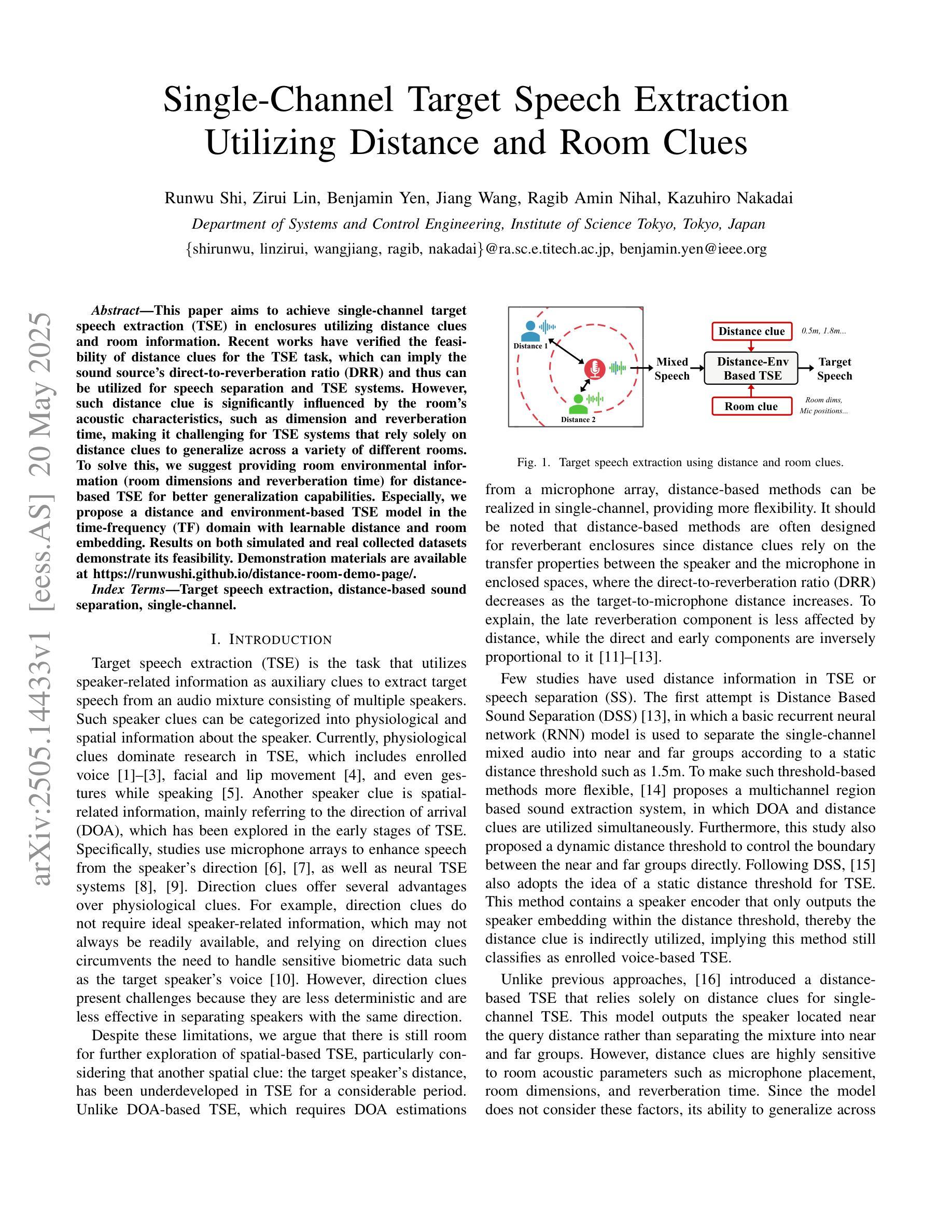
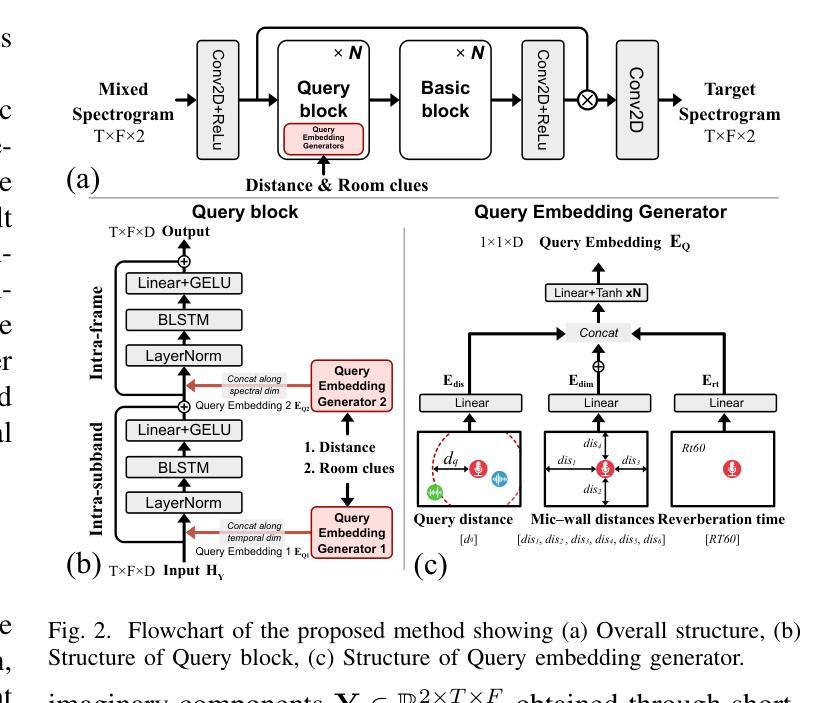
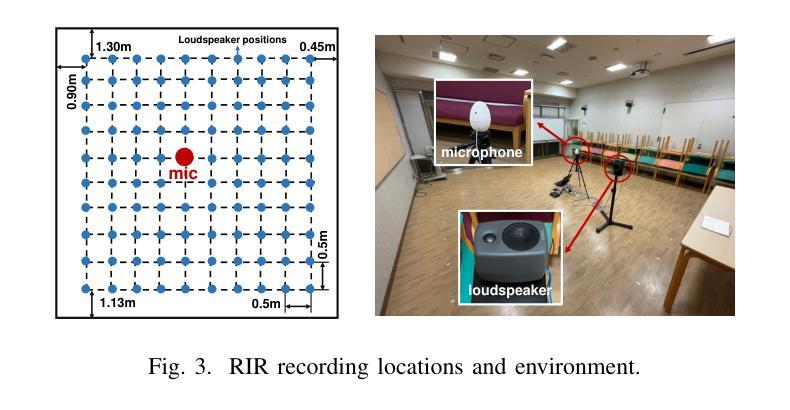
Single-Channel Target Speech Extraction Utilizing Distance and Room Clues
Authors:Runwu Shi, Zirui Lin, Benjamin Yen, Jiang Wang, Ragib Amin Nihal, Kazuhiro Nakadai
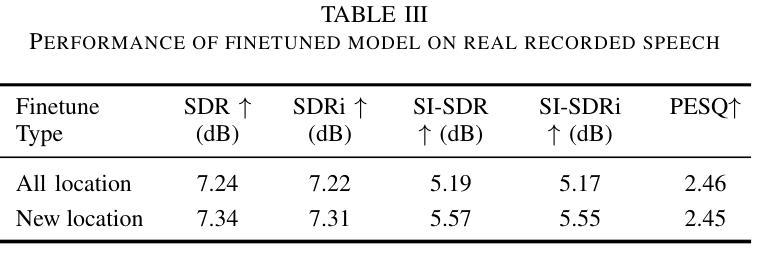
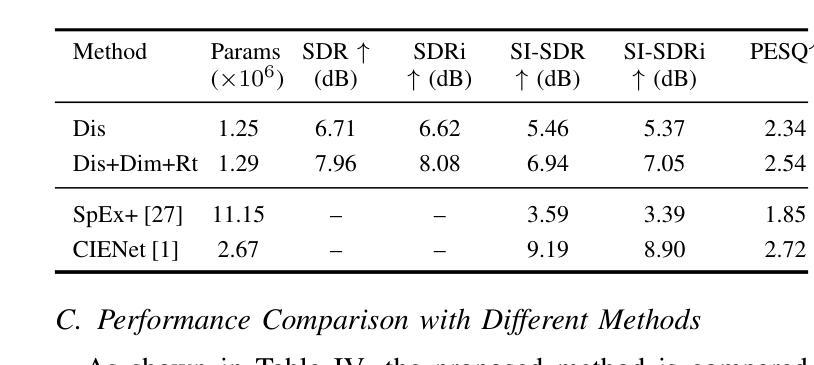
This paper aims to achieve single-channel target speech extraction (TSE) in enclosures utilizing distance clues and room information. Recent works have verified the feasibility of distance clues for the TSE task, which can imply the sound source’s direct-to-reverberation ratio (DRR) and thus can be utilized for speech separation and TSE systems. However, such distance clue is significantly influenced by the room’s acoustic characteristics, such as dimension and reverberation time, making it challenging for TSE systems that rely solely on distance clues to generalize across a variety of different rooms. To solve this, we suggest providing room environmental information (room dimensions and reverberation time) for distance-based TSE for better generalization capabilities. Especially, we propose a distance and environment-based TSE model in the time-frequency (TF) domain with learnable distance and room embedding. Results on both simulated and real collected datasets demonstrate its feasibility. Demonstration materials are available at https://runwushi.github.io/distance-room-demo-page/.
本文旨在利用距离线索和房间信息实现封闭环境下的单通道目标语音提取(TSE)。近期的研究已经验证了距离线索对于TSE任务的可行性,距离线索可以暗示声源的直达声与混响声比(DRR),因此可以用于语音分离和TSE系统。然而,这样的距离线索会受到房间声学特性的很大影响,如房间尺寸和混响时间,对于仅依赖距离线索的TSE系统来说,在不同的房间之间进行推广具有挑战性。为解决这一问题,我们建议在基于距离的TSE中提供房间环境信息(房间尺寸和混响时间),以提高其泛化能力。特别是,我们提出了一个基于时间和频率(TF)域的距离和环境TSE模型,具有可学习的距离和房间嵌入。在模拟和实际收集的数据集上的结果证明了其可行性。演示材料可在https://runwushi.github.io/distance-room-demo-page/找到。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 5 pages, 3 figures, accepted by Eusipco 2025
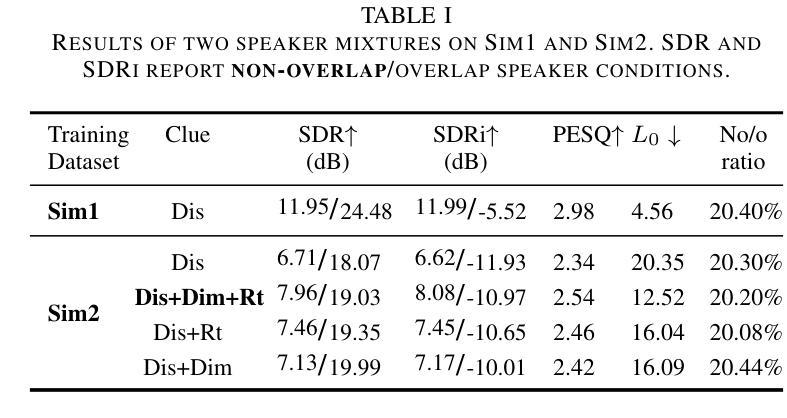
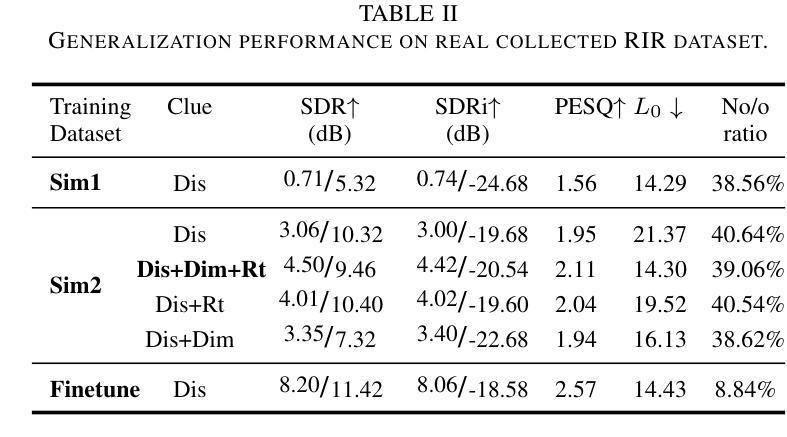
Summary
本文旨在利用距离线索和房间信息实现封闭环境下的单通道目标语音提取(TSE)。虽然距离线索可以暗示声源的直达声与混响声比(DRR),并用于语音分离和TSE系统,但其受房间声学特性(如尺寸和混响时间)的影响很大。为解决此问题,我们提议为基于距离的TSE提供房间环境信息(房间尺寸和混响时间),以提高其跨不同房间的泛化能力。我们提出一个基于时间和频率域的距离和环境TSE模型,具有可学习的距离和房间嵌入。在模拟和实际收集的数据集上的结果证明了其可行性。
Key Takeaways
- 该论文致力于在封闭环境中实现单通道目标语音提取(TSE)。
- 距离线索对于TSE任务具有可行性,能够暗示声源的直达声与混响声比(DRR)。
- 距离线索受到房间声学特性的影响,如房间尺寸和混响时间。
- 单纯依赖距离线索的TSE系统在面对不同房间时泛化能力有限。
- 为提高TSE系统的泛化能力,建议提供房间环境信息(如房间尺寸和混响时间)。
- 论文提出了一种基于时间和频率域的距离和环境TSE模型,具有可学习的距离和房间嵌入。
点此查看论文截图
HausaNLP: Current Status, Challenges and Future Directions for Hausa Natural Language Processing
Authors:Shamsuddeen Hassan Muhammad, Ibrahim Said Ahmad, Idris Abdulmumin, Falalu Ibrahim Lawan, Babangida Sani, Sukairaj Hafiz Imam, Yusuf Aliyu, Sani Abdullahi Sani, Ali Usman Umar, Kenneth Church, Vukosi Marivate
Hausa Natural Language Processing (NLP) has gained increasing attention in recent years, yet remains understudied as a low-resource language despite having over 120 million first-language (L1) and 80 million second-language (L2) speakers worldwide. While significant advances have been made in high-resource languages, Hausa NLP faces persistent challenges, including limited open-source datasets and inadequate model representation. This paper presents an overview of the current state of Hausa NLP, systematically examining existing resources, research contributions, and gaps across fundamental NLP tasks: text classification, machine translation, named entity recognition, speech recognition, and question answering. We introduce HausaNLP (https://catalog.hausanlp.org), a curated catalog that aggregates datasets, tools, and research works to enhance accessibility and drive further development. Furthermore, we discuss challenges in integrating Hausa into large language models (LLMs), addressing issues of suboptimal tokenization and dialectal variation. Finally, we propose strategic research directions emphasizing dataset expansion, improved language modeling approaches, and strengthened community collaboration to advance Hausa NLP. Our work provides both a foundation for accelerating Hausa NLP progress and valuable insights for broader multilingual NLP research.
近年来,豪萨自然语言处理(NLP)越来越受到关注,尽管全球有超过1.2亿的第一语言(L1)和8千万的第二语言(L2)使用者,但它仍然是一个资源匮乏的语言领域,相关研究相对较少。尽管在高资源语言方面取得了重大进展,但豪萨NLP仍然面临持续挑战,包括有限的开源数据集和不足的模型表示。本文概述了豪萨NLP的当前状态,系统地检查了现有资源、研究贡献以及基础NLP任务中的空白领域,包括文本分类、机器翻译、命名实体识别、语音识别和问答。我们介绍了豪萨NLP目录(https://catalog.hausanlp.org),该目录汇集了数据集、工具和研究成果,以提高可访问性并推动进一步发展。此外,我们讨论了将豪萨语集成到大型语言模型(LLM)中的挑战,解决次优分词和方言变化的问题。最后,我们提出了战略研究方向,强调扩大数据集、改进语言建模方法和加强社区合作,以推动豪萨NLP的发展。我们的工作为加速豪萨NLP的进步提供了基础,并为更广泛的多语言NLP研究提供了宝贵的见解。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
Hausa自然语言处理(NLP)虽然拥有超过一亿使用者,但作为低资源语言仍受到忽视。尽管在高资源语言方面取得了重大进展,但Hausa NLP仍面临开放数据集有限和模型表示不足等挑战。本文概述了Hausa NLP的现状,系统检查基本NLP任务的现有资源、研究贡献和差距,如文本分类、机器翻译、命名实体识别、语音识别和问题回答等。此外,介绍了HausaNLP(https://catalog.hausanlp.org),一个汇集数据集、工具和研究成果的目录,以提高可用性和推动进一步发展。文章还讨论了将Hausa融入大型语言模型(LLM)的挑战,并强调数据集扩展、改进的语言建模方法和加强社区协作的战略研究方向。本文既为加速Hausa NLP的发展提供了基础,也为更广泛的多元语言NLP研究提供了有价值的见解。
Key Takeaways
- Hausa NLP虽受到重视,但作为低资源语言仍存在诸多挑战。
- 缺乏开放数据集和模型表示是Hausa NLP面临的主要问题。
- 当前系统研究了Hausa NLP的基本任务,包括文本分类、机器翻译等。
- 介绍了HausaNLP目录,旨在提高资源的可用性和推动进一步发展。
- Hausa融入大型语言模型的挑战包括次优的分词和方言差异。
- 需要扩展数据集、改进语言建模方法并加强社区协作。
点此查看论文截图

Data-Efficient Hate Speech Detection via Cross-Lingual Nearest Neighbor Retrieval with Limited Labeled Data
Authors:Faeze Ghorbanpour, Daryna Dementieva, Alexander Fraser
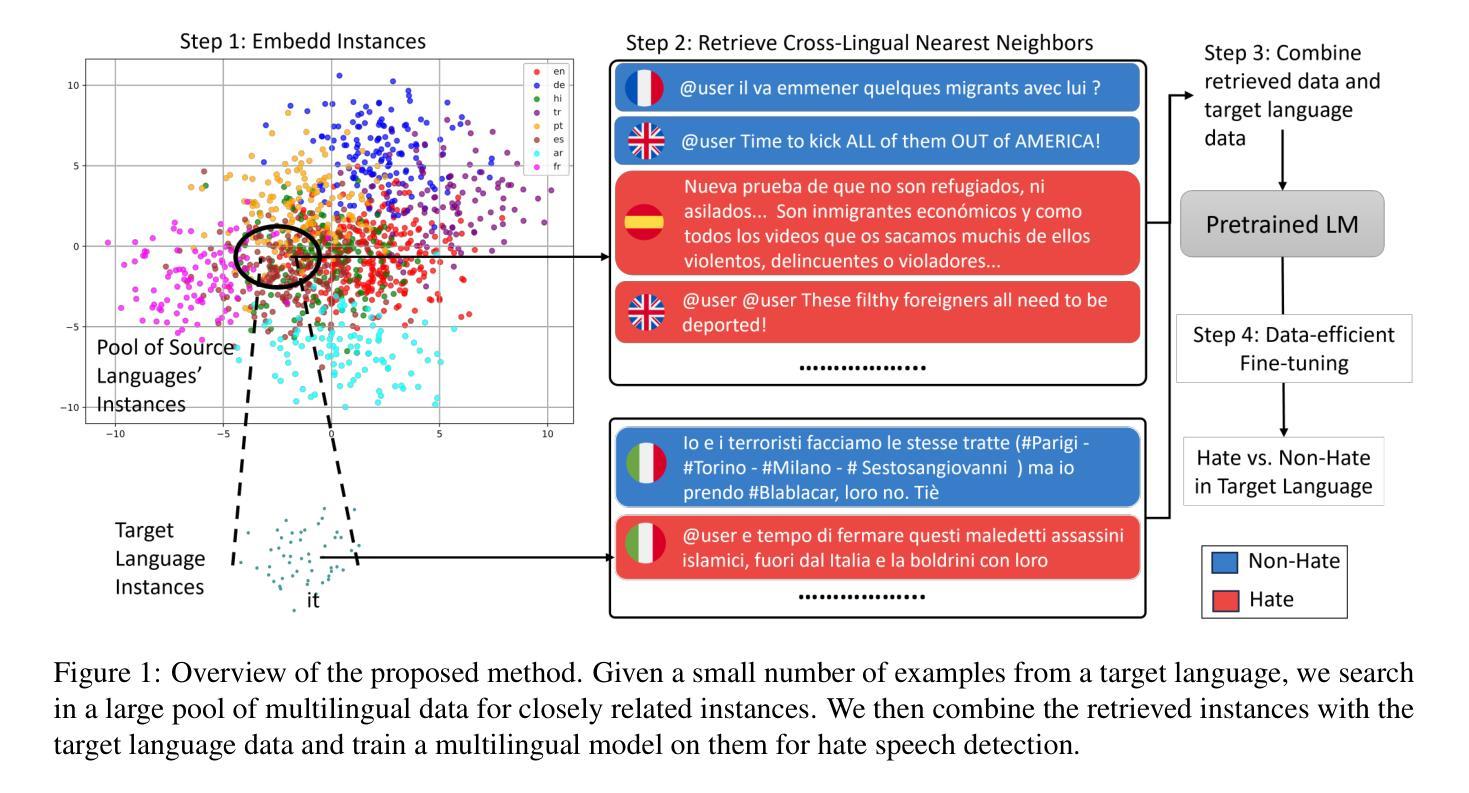
Considering the importance of detecting hateful language, labeled hate speech data is expensive and time-consuming to collect, particularly for low-resource languages. Prior work has demonstrated the effectiveness of cross-lingual transfer learning and data augmentation in improving performance on tasks with limited labeled data. To develop an efficient and scalable cross-lingual transfer learning approach, we leverage nearest-neighbor retrieval to augment minimal labeled data in the target language, thereby enhancing detection performance. Specifically, we assume access to a small set of labeled training instances in the target language and use these to retrieve the most relevant labeled examples from a large multilingual hate speech detection pool. We evaluate our approach on eight languages and demonstrate that it consistently outperforms models trained solely on the target language data. Furthermore, in most cases, our method surpasses the current state-of-the-art. Notably, our approach is highly data-efficient, retrieving as small as 200 instances in some cases while maintaining superior performance. Moreover, it is scalable, as the retrieval pool can be easily expanded, and the method can be readily adapted to new languages and tasks. We also apply maximum marginal relevance to mitigate redundancy and filter out highly similar retrieved instances, resulting in improvements in some languages.
考虑到检测仇恨性言论的重要性,标注仇恨言论的数据收集既昂贵又耗时,特别是针对低资源语言。先前的工作已经证明了跨语言迁移学习和数据增强在改善有限标记数据任务性能方面的有效性。为了开发一种高效且可扩展的跨语言迁移学习方法,我们利用最近邻检索来增强目标语言中的少量标记数据,从而提高检测性能。具体来说,我们假设目标语言中有少量标记训练实例可供访问,并利用这些实例从大型多语言仇恨言论检测池中检索最相关的标记示例。我们在八种语言上评估了我们的方法,并证明其性能始终优于仅使用目标语言数据训练的模型。此外,在大多数情况下,我们的方法超过了当前的最佳水平。值得注意的是,我们的方法非常注重数据效率,在某些情况下只需检索200个实例即可保持卓越性能。而且,它是可扩展的,因为检索池可以很容易地扩展,并且该方法可以轻松地适应新语言和任务。我们还应用最大边缘相关性来缓解冗余并过滤掉高度相似的检索实例,从而在某些语言中取得了改进。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
高效率、可拓展的跨语言迁移学习方法用于增强目标语言的少量标签数据,提高仇恨言论检测的准确性。通过最近邻检索从多语言仇恨言论检测池中获取最相关的实例。在多语言测试中表现出超越单一训练模型及当前最优方法的性能。此方法具备高效性、可拓展性,可适应新语言和任务。使用最大边缘相关性减少冗余和过滤高度相似的检索实例,进一步提升性能。
Key Takeaways
- 跨语言迁移学习方法用于增强目标语言的少量标签数据,提高仇恨言论检测的准确性。
- 采用最近邻检索从多语言仇恨言论检测池中获取相关实例。
- 方法在多语言测试中表现优越,超越单一训练模型及当前最优方法。
- 方法具备高效性和可拓展性,可适应新语言和任务。
- 使用最大边缘相关性减少冗余实例,提高检测性能。
- 只需少量目标语言数据即可进行高效的仇恨言论检测。
点此查看论文截图

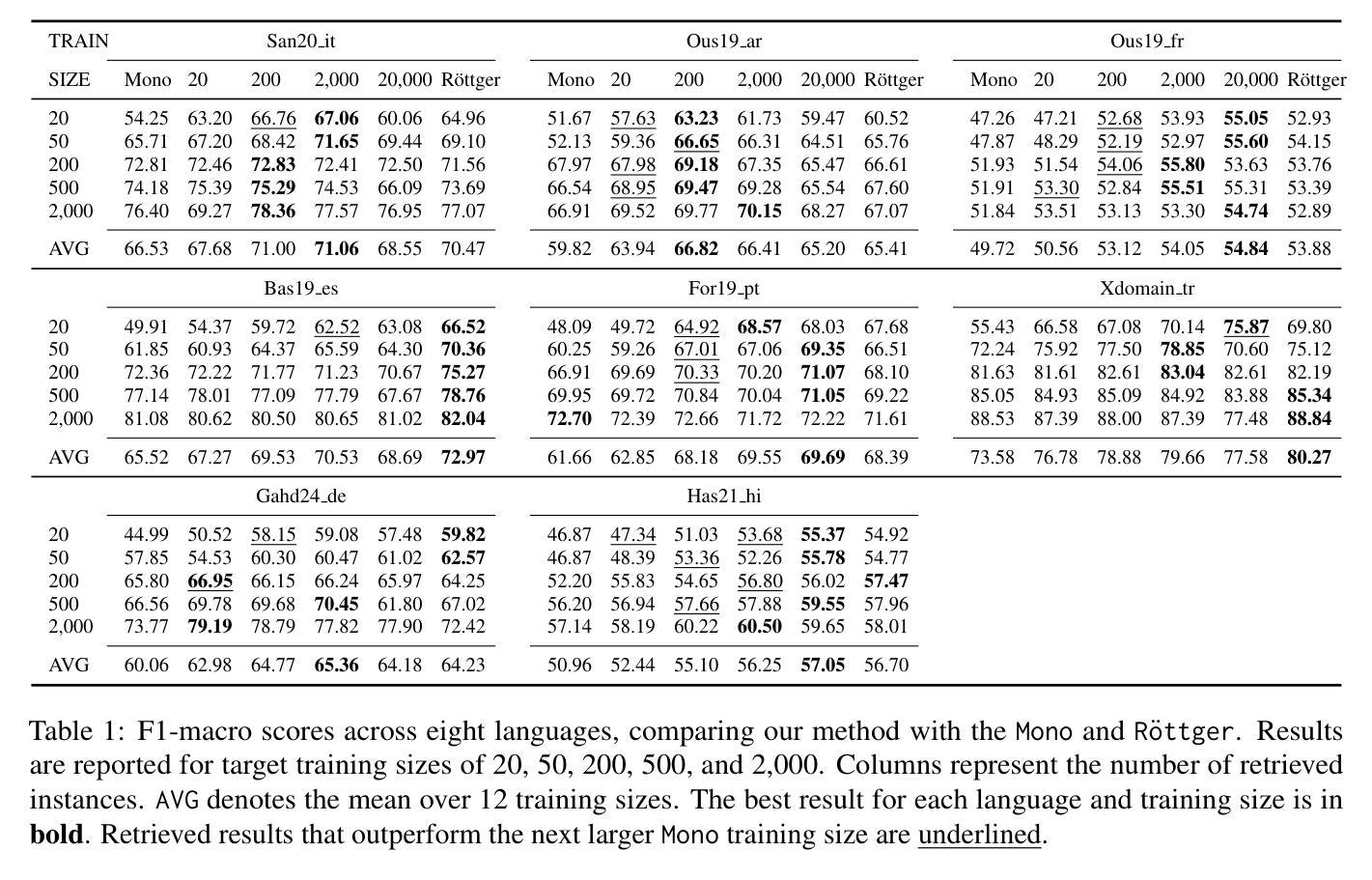
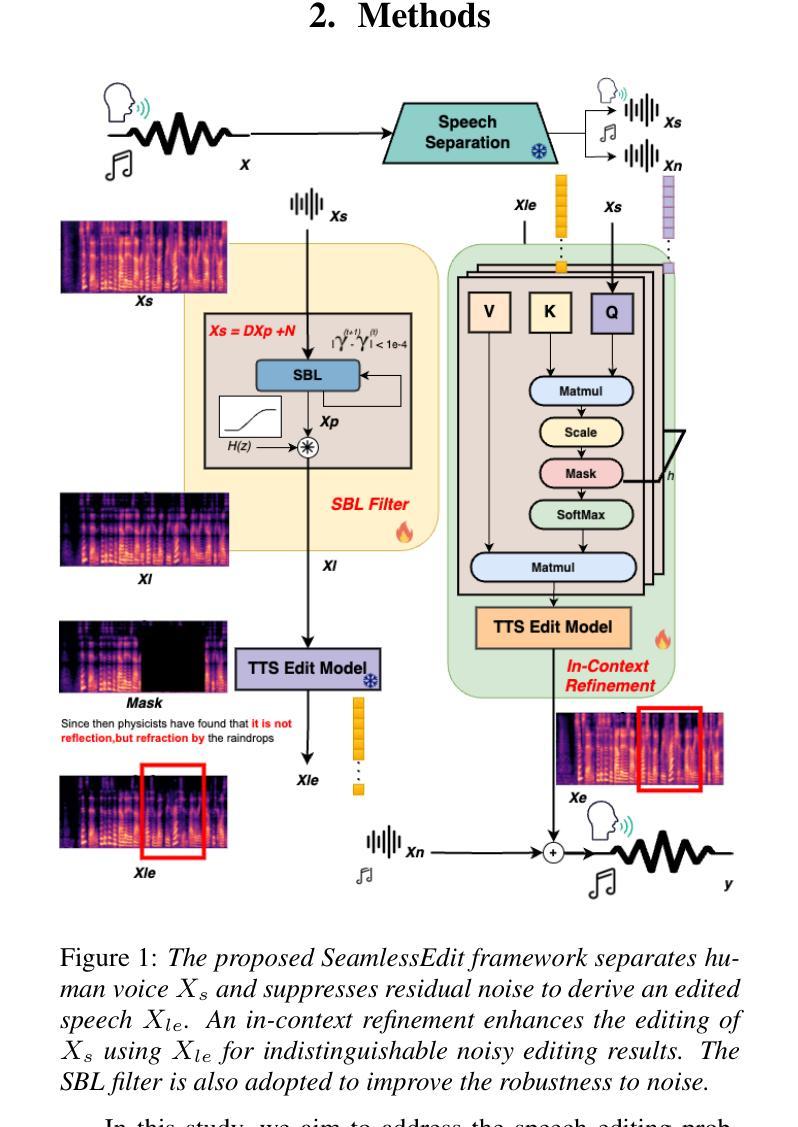
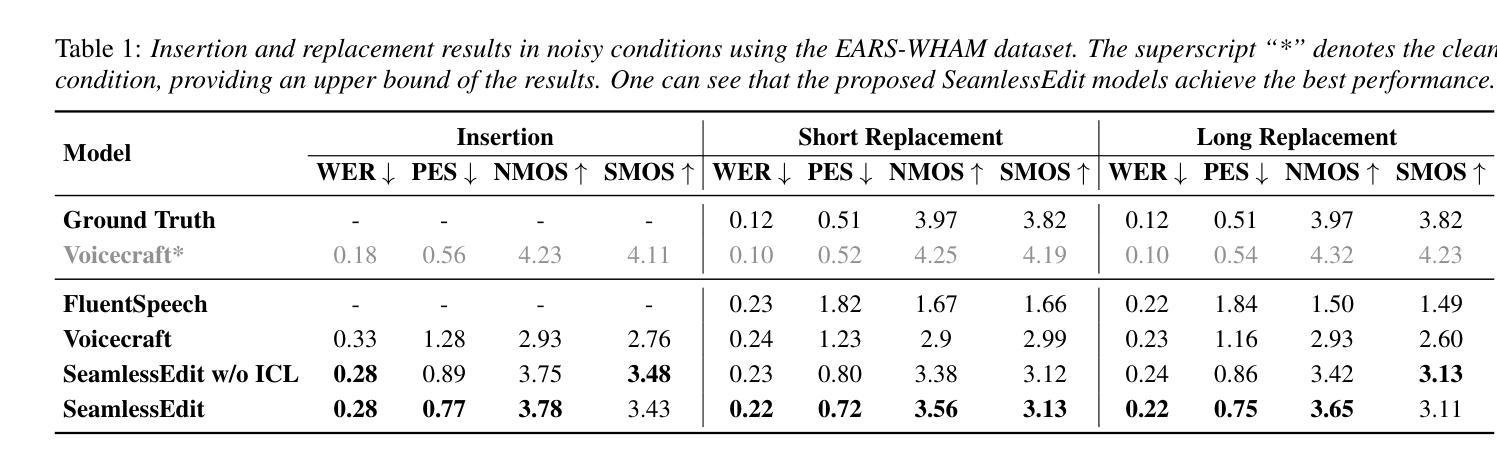
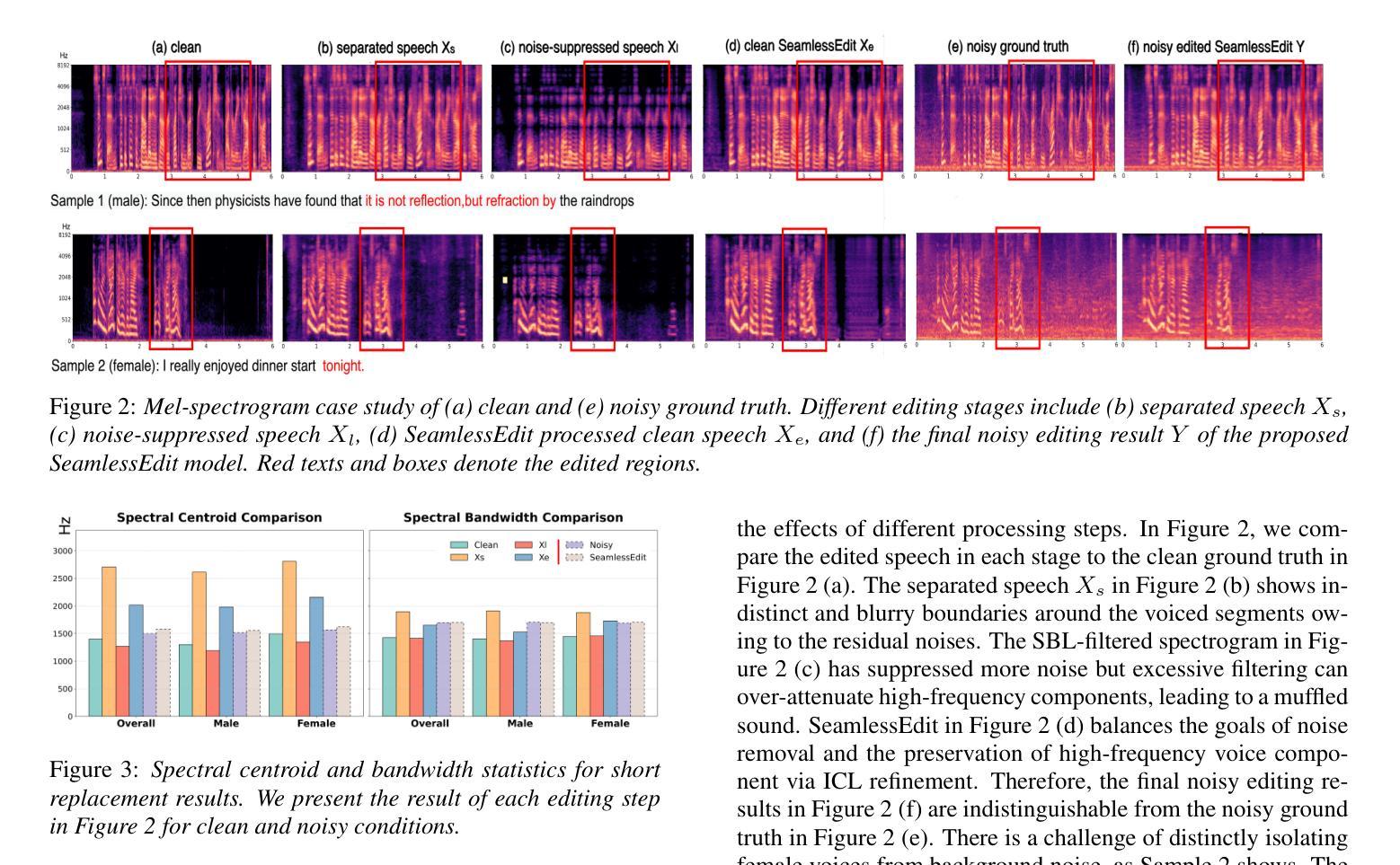
SeamlessEdit: Background Noise Aware Zero-Shot Speech Editing with in-Context Enhancement
Authors:Kuan-Yu Chen, Jeng-Lin Li, Jian-Jiun Ding
With the fast development of zero-shot text-to-speech technologies, it is possible to generate high-quality speech signals that are indistinguishable from the real ones. Speech editing, including speech insertion and replacement, appeals to researchers due to its potential applications. However, existing studies only considered clean speech scenarios. In real-world applications, the existence of environmental noise could significantly degrade the quality of the generation. In this study, we propose a noise-resilient speech editing framework, SeamlessEdit, for noisy speech editing. SeamlessEdit adopts a frequency-band-aware noise suppression module and an in-content refinement strategy. It can well address the scenario where the frequency bands of voice and background noise are not separated. The proposed SeamlessEdit framework outperforms state-of-the-art approaches in multiple quantitative and qualitative evaluations.
随着零起步文本到语音技术的快速发展,生成高质量、与真实语音难以区分的语音信号成为可能。语音编辑,包括语音插入和替换,因其潜在的应用价值而吸引研究者关注。然而,现有研究仅涉及干净语音场景。在真实世界应用中,环境噪声的存在可能会显著降低生成语音的质量。在这项研究中,我们提出了一个用于噪声语音编辑的噪声鲁棒性语音编辑框架,无缝编辑(SeamlessEdit)。SeamlessEdit采用频带感知噪声抑制模块和基于内容的细化策略,能够很好地解决语音和背景噪声频带未分离的场景。所提出的无缝编辑框架在多个定量和定性评估中均优于最新技术方法。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 5 pages, 3 figures
Summary
随着零样本文本转语音技术的快速发展,生成高质量、与现实无法区分的语音信号成为可能。尽管语音编辑,包括语音插入和替换,在潜在应用方面颇具吸引力,但现有研究主要集中在清洁语音场景上。实际应用中,环境噪声的存在会严重影响生成语音的质量。本研究提出了一种用于噪声语音编辑的稳健框架SeamlessEdit,它采用频带感知噪声抑制模块和内容内优化策略,能够很好地处理语音和背景噪声频带未分离的场景。SeamlessEdit框架在多项定量和定性评估中表现出超越现有先进方法的效果。
Key Takeaways
- 零样本文本转语音技术快速发展,可生成高质量与现实无法区分的语音信号。
- 语音编辑具有潜在应用价值,但现有研究主要集中在清洁语音场景。
- 实际应用中,环境噪声会严重影响生成语音的质量。
- 提出了一种用于噪声语音编辑的稳健框架SeamlessEdit。
- SeamlessEdit采用频带感知噪声抑制模块。
- SeamlessEdit采用内容内优化策略,能处理语音和背景噪声频带未分离的场景。
点此查看论文截图

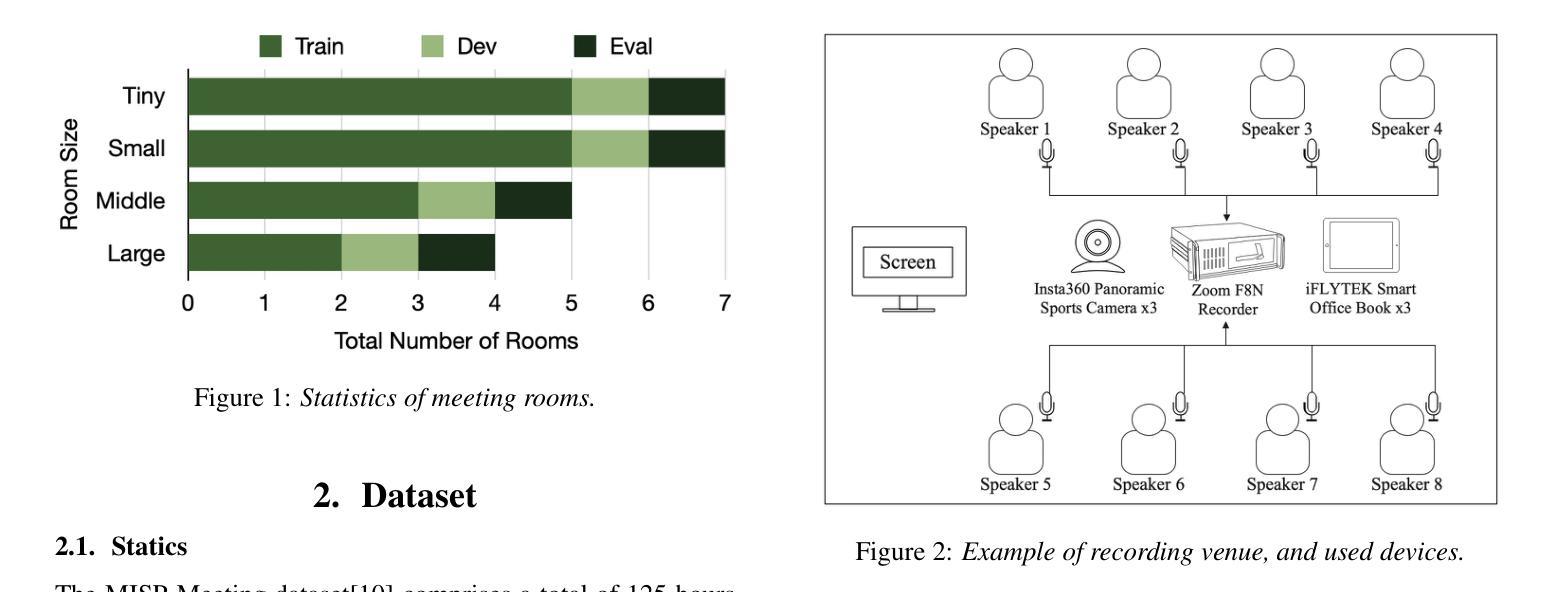
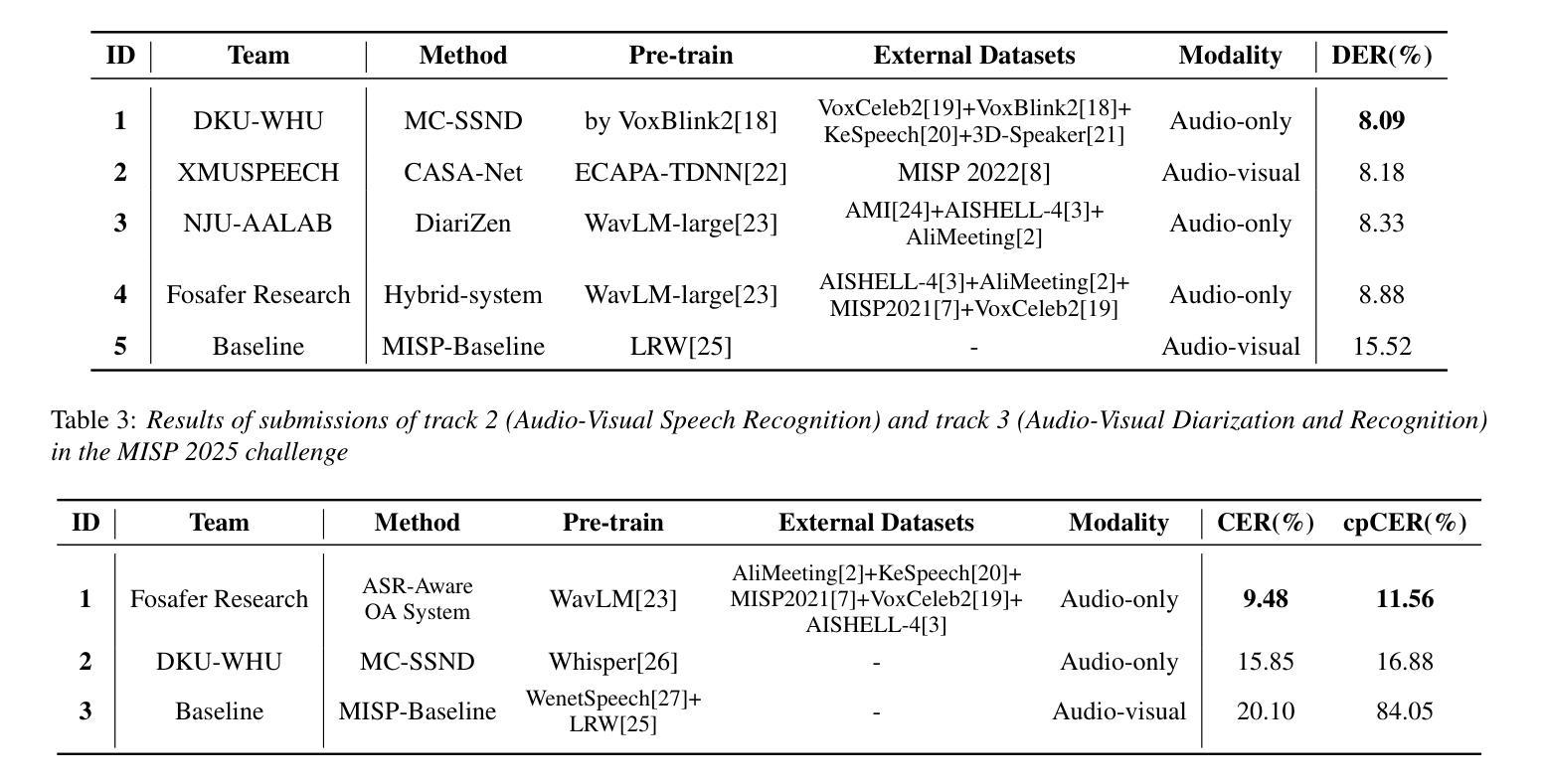
The Multimodal Information Based Speech Processing (MISP) 2025 Challenge: Audio-Visual Diarization and Recognition
Authors:Ming Gao, Shilong Wu, Hang Chen, Jun Du, Chin-Hui Lee, Shinji Watanabe, Jingdong Chen, Siniscalchi Sabato Marco, Odette Scharenborg
Meetings are a valuable yet challenging scenario for speech applications due to complex acoustic conditions. This paper summarizes the outcomes of the MISP 2025 Challenge, hosted at Interspeech 2025, which focuses on multi-modal, multi-device meeting transcription by incorporating video modality alongside audio. The tasks include Audio-Visual Speaker Diarization (AVSD), Audio-Visual Speech Recognition (AVSR), and Audio-Visual Diarization and Recognition (AVDR). We present the challenge’s objectives, tasks, dataset, baseline systems, and solutions proposed by participants. The best-performing systems achieved significant improvements over the baseline: the top AVSD model achieved a Diarization Error Rate (DER) of 8.09%, improving by 7.43%; the top AVSR system achieved a Character Error Rate (CER) of 9.48%, improving by 10.62%; and the best AVDR system achieved a concatenated minimum-permutation Character Error Rate (cpCER) of 11.56%, improving by 72.49%.
会议是语音应用的有价值但具有挑战性的场景,原因在于其复杂的声学条件。本文总结了MISP 2025挑战的结果,该挑战由Interspeech 2025主办,聚焦于多模态、多设备会议转录,除了音频外还纳入了视频模态。任务包括音频-视觉说话人识别(AVSD)、音频-视觉语音识别(AVSR)和音频-视觉说话人识别和语音识别(AVDR)。我们介绍了挑战的目标、任务、数据集、基线系统和参与者提出的解决方案。表现最佳的系统在基线的基础上取得了重大改进:最佳AVSD模型的聚类错误率(DER)达到了8.09%,提高了7.43%;最佳AVSR系统的字符错误率(CER)达到了9.48%,提高了10.62%;最佳AVDR系统的组合最小排列字符错误率(cpCER)达到了11.56%,提高了72.49%。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by Interspeech 2025. Camera-ready version
Summary
本文总结了MISP 2025挑战的成果,该挑战关注多模态、多设备的会议转录,结合了视频模态和音频。包括音视频演讲者识别、音视频语音识别和音视频识别和录音任务。提出挑战的目标、任务、数据集、基准系统和参与者解决方案。最佳系统相比基线有显著改善:最佳音视频演讲者识别模型的对数似然误差降低至8.09%,最佳音视频语音识别系统的字符错误率降至9.48%,最佳音视频识别和录音系统的字符错误率也有所降低。
Key Takeaways
- MISP 2025挑战关注多模态、多设备的会议转录,结合了视频模态和音频。
- 包括音视频演讲者识别(AVSD)、音视频语音识别(AVSR)和音视频识别和录音(AVDR)三大任务。
- 挑战提供了数据集供参与者使用。
- 最佳系统在三大任务中都取得了显著的改善成果。
- 最佳AVSD模型的Diarization Error Rate(DER)降低至8.09%。
- 最佳AVSR系统的Character Error Rate(CER)降低至9.48%。
点此查看论文截图

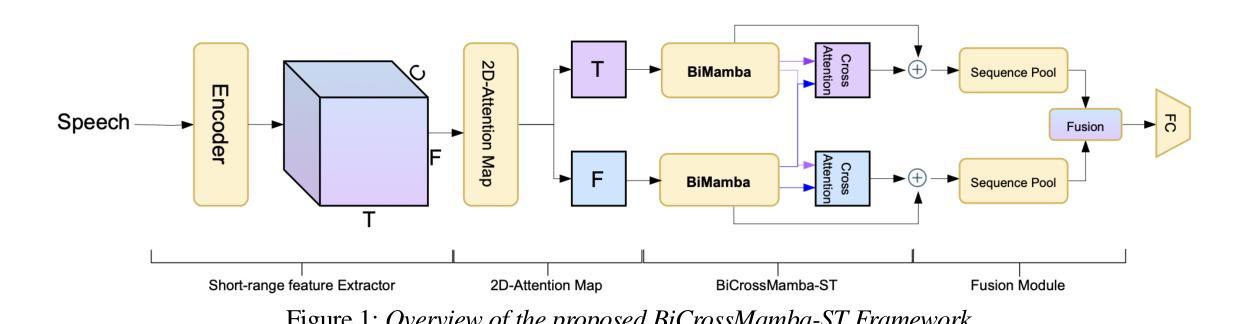
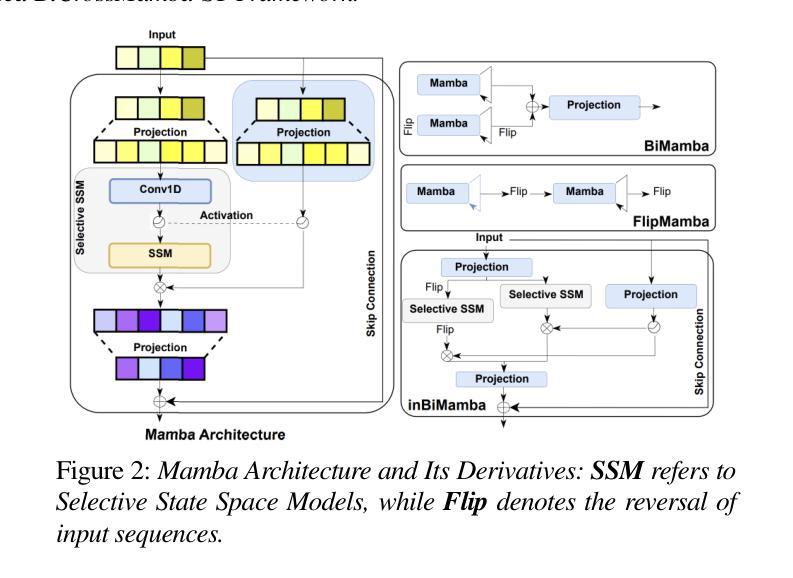
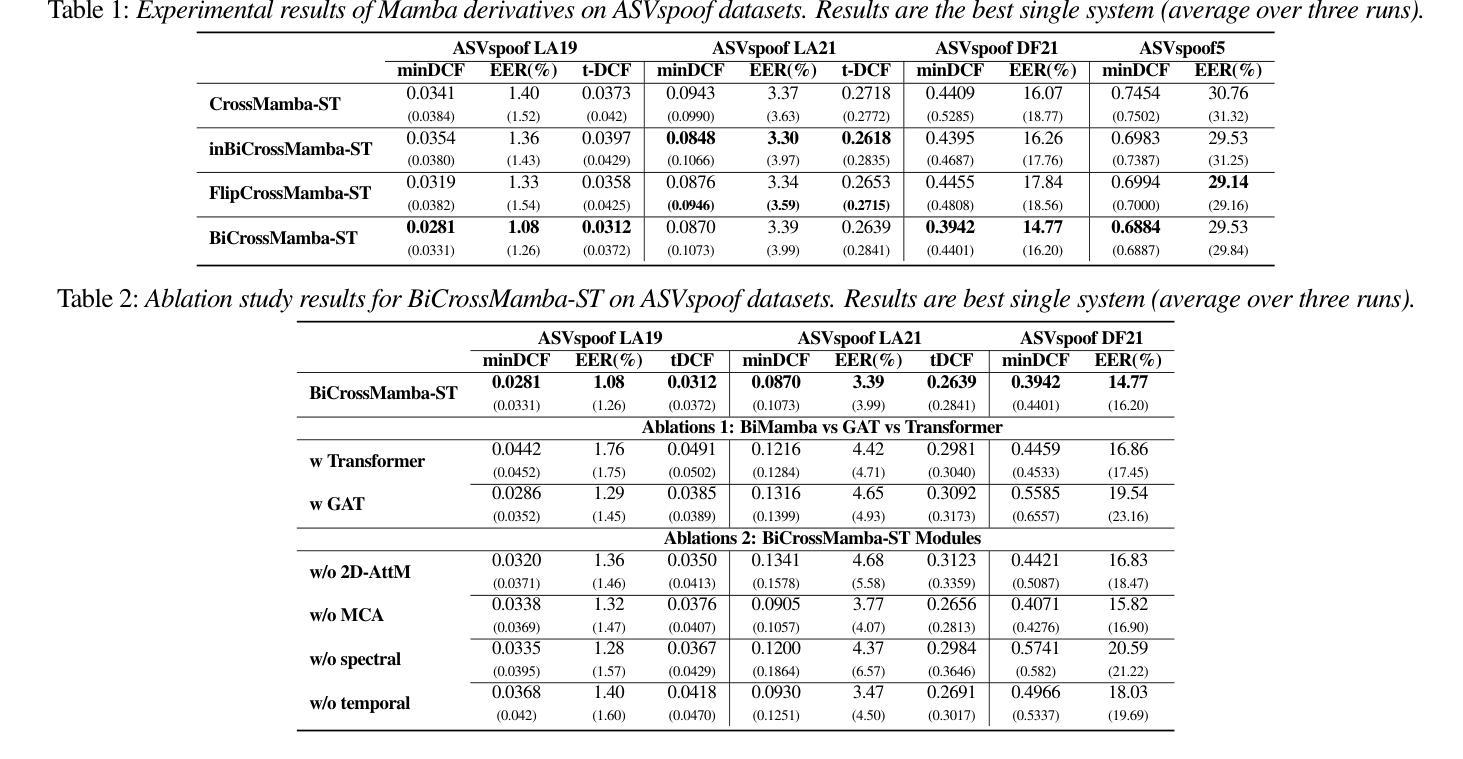
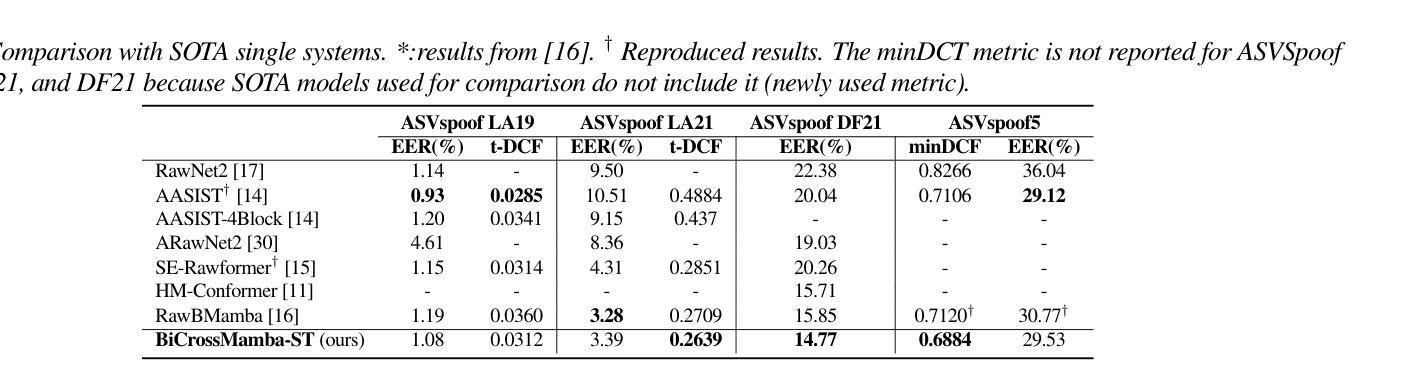
BiCrossMamba-ST: Speech Deepfake Detection with Bidirectional Mamba Spectro-Temporal Cross-Attention
Authors:Yassine El Kheir, Tim Polzehl, Sebastian Möller
We propose BiCrossMamba-ST, a robust framework for speech deepfake detection that leverages a dual-branch spectro-temporal architecture powered by bidirectional Mamba blocks and mutual cross-attention. By processing spectral sub-bands and temporal intervals separately and then integrating their representations, BiCrossMamba-ST effectively captures the subtle cues of synthetic speech. In addition, our proposed framework leverages a convolution-based 2D attention map to focus on specific spectro-temporal regions, enabling robust deepfake detection. Operating directly on raw features, BiCrossMamba-ST achieves significant performance improvements, a 67.74% and 26.3% relative gain over state-of-the-art AASIST on ASVSpoof LA21 and ASVSpoof DF21 benchmarks, respectively, and a 6.80% improvement over RawBMamba on ASVSpoof DF21. Code and models will be made publicly available.
我们提出了BiCrossMamba-ST这一稳健的语音深度伪造检测框架,它采用双分支时空架构,借助双向Mamba块和交叉互注意力机制。通过对光谱子带和时间段进行分别处理,然后整合它们的表示,BiCrossMamba-ST可以有效地捕捉合成语音的细微线索。此外,我们提出的框架利用基于卷积的二维注意力图来关注特定的时空区域,从而实现稳健的深度伪造检测。直接在原始特征上操作,BiCrossMamba-ST在ASVSpoof LA21和ASVSpoof DF21基准测试上相对于最新技术AASIST取得了显著的性能提升,相对增益分别为67.74%和26.3%,并且在ASVSpoof DF21上的原始BMamba模型也有6.80%的提升。代码和模型将公开发布。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted Interspeech 2025
Summary
本文提出了BiCrossMamba-ST这一稳健的语音深度伪造检测框架。它采用双分支光谱时间架构,结合双向Mamba块和交叉互注意力机制。通过分别处理频谱子带和时间间隔并整合其表示,有效捕捉合成语音的细微线索。此外,该框架利用基于卷积的2D注意力图,关注特定的光谱时间区域,从而实现稳健的深度伪造检测。直接在原始特征上操作,BiCrossMamba-ST在ASVSpoof LA21和ASVSpoof DF21基准测试上较先进方法AASIST有67.74%和26.3%的相对增益,并在ASVSpoof DF21上较RawBMamba有6.80%的改进。
Key Takeaways
- BiCrossMamba-ST是一个用于语音深度伪造检测的稳健框架。
- 采用双分支光谱时间架构,结合双向Mamba块和交叉互注意力机制。
- 通过处理频谱子带和时间间隔,有效捕捉合成语音的细微特征。
- 利用基于卷积的2D注意力图,关注特定光谱时间区域。
- 在ASVSpoof LA21和ASVSpoof DF21基准测试上较现有方法有明显性能提升。
- BiCrossMamba-ST直接在原始特征上操作,实现更高效的检测。
- 公开提供代码和模型。
点此查看论文截图

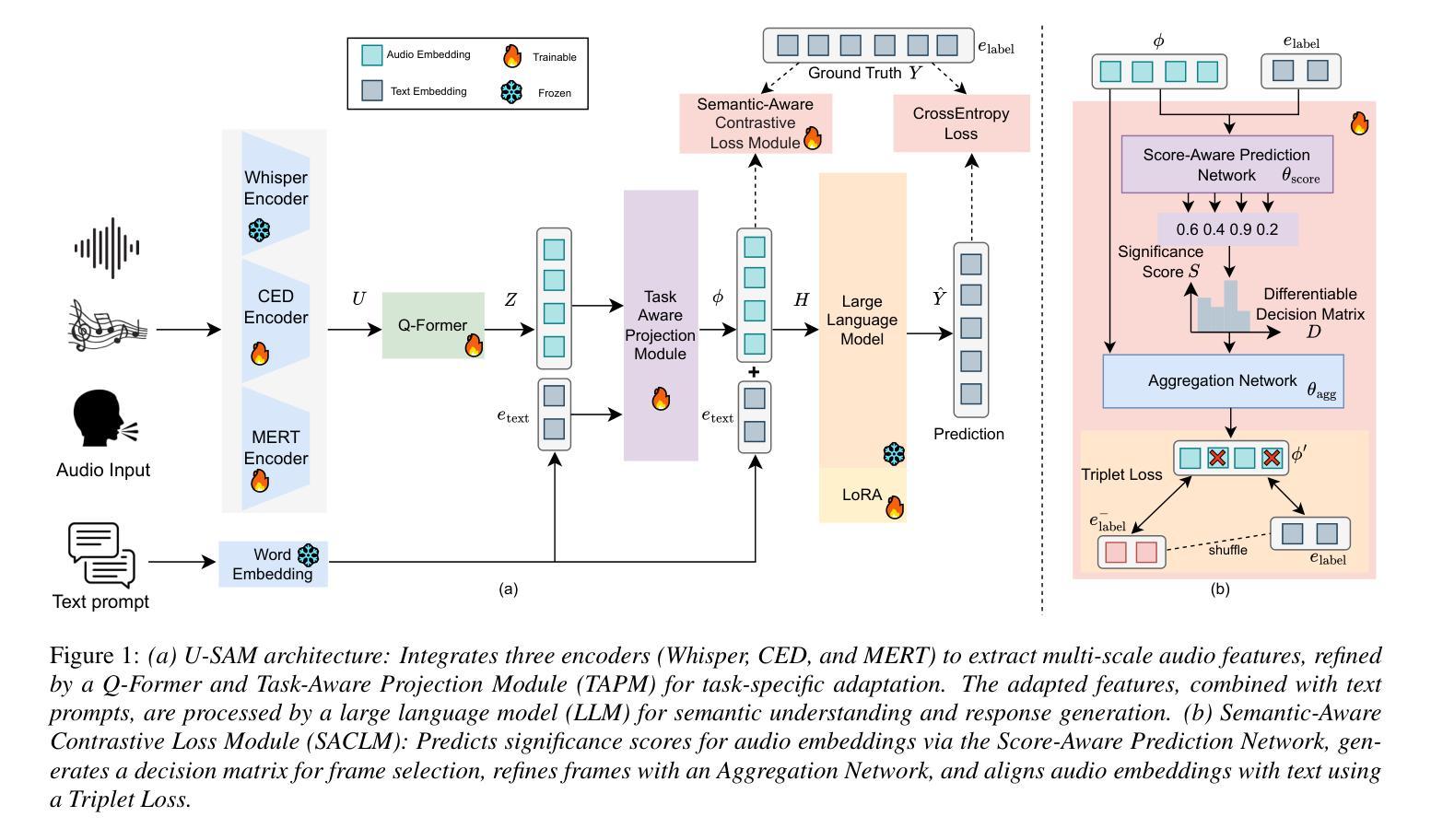
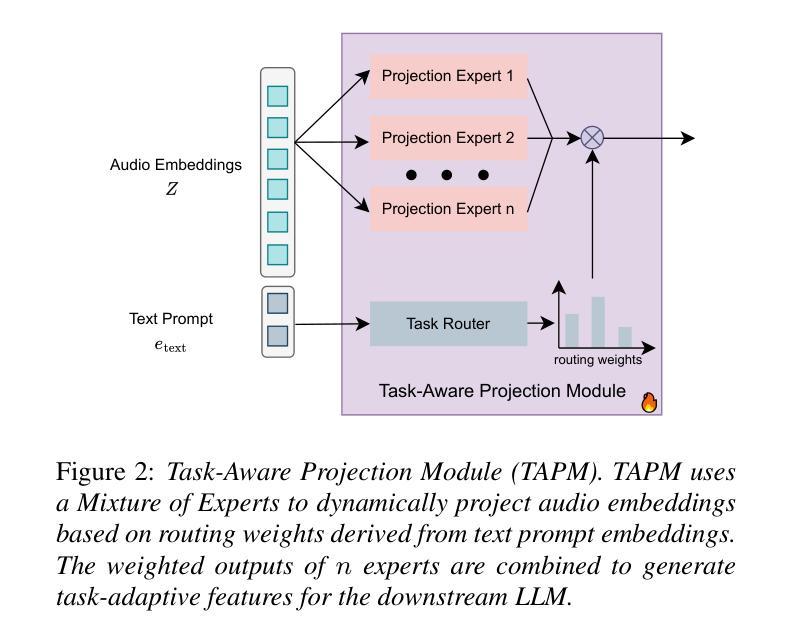
U-SAM: An audio language Model for Unified Speech, Audio, and Music Understanding
Authors:Ziqian Wang, Xianjun Xia, Xinfa Zhu, Lei Xie
The text generation paradigm for audio tasks has opened new possibilities for unified audio understanding. However, existing models face significant challenges in achieving a comprehensive understanding across diverse audio types, such as speech, general audio events, and music. Furthermore, their exclusive reliance on cross-entropy loss for alignment often falls short, as it treats all tokens equally and fails to account for redundant audio features, leading to weaker cross-modal alignment. To deal with the above challenges, this paper introduces U-SAM, an advanced audio language model that integrates specialized encoders for speech, audio, and music with a pre-trained large language model (LLM). U-SAM employs a Mixture of Experts (MoE) projector for task-aware feature fusion, dynamically routing and integrating the domain-specific encoder outputs. Additionally, U-SAM incorporates a Semantic-Aware Contrastive Loss Module, which explicitly identifies redundant audio features under language supervision and rectifies their semantic and spectral representations to enhance cross-modal alignment. Extensive experiments demonstrate that U-SAM consistently outperforms both specialized models and existing audio language models across multiple benchmarks. Moreover, it exhibits emergent capabilities on unseen tasks, showcasing its generalization potential. Code is available (https://github.com/Honee-W/U-SAM/).
音频任务的文本生成范式为统一音频理解提供了新的可能性。然而,现有模型在实现不同类型音频的全面理解方面面临重大挑战,如语音、通用音频事件和音乐。此外,它们对交叉熵损失的过度依赖往往难以实现良好的对齐,因为交叉熵损失平等对待所有标记,无法处理冗余的音频特征,导致跨模态对齐较弱。为了应对上述挑战,本文引入了U-SAM,这是一种先进的音频语言模型,它结合了针对语音、音频和音乐的专用编码器以及预训练的大型语言模型(LLM)。U-SAM采用混合专家(MoE)投影仪进行任务感知特征融合,动态路由和集成特定领域的编码器输出。此外,U-SAM还采用了语义感知对比损失模块,该模块在语言学监督下明确识别冗余音频特征,并纠正其语义和光谱表示,以增强跨模态对齐。大量实验表明,U-SAM在多个基准测试中始终优于专业模型和现有音频语言模型。而且,它在未见过的任务上展现出潜在能力,展示了其泛化潜力。代码可用(https://github.com/Honee-W/U-SAM/)。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted to Interspeech 2025
Summary
该文本介绍了针对音频任务的新型文本生成范式,并指出其在统一音频理解方面的新可能性。现有模型在处理多样化音频类型时面临挑战,如语音、通用音频事件和音乐等。为解决这些挑战,本文引入U-SAM模型,该模型集成了针对语音、音频和音乐的专用编码器,并结合预训练的大型语言模型(LLM)。U-SAM使用混合专家投影技术实现任务感知特征融合,同时动态路由和集成特定领域编码器的输出。此外,U-SAM还包含语义感知对比损失模块,该模块在语言学监督下明确识别冗余音频特征,并纠正其语义和光谱表示,以提高跨模态对齐能力。实验证明,U-SAM在多个基准测试中表现优于专业模型和现有音频语言模型。此外,它在未见任务上展现出潜力。代码已公开。
Key Takeaways
- 音频任务的文本生成范式带来了新的统一音频理解的可能性。
- 现有模型在处理多样化音频类型时面临挑战。
- U-SAM模型集成了专用编码器以处理语音、音频和音乐等不同类型的数据。
- U-SAM采用混合专家投影技术实现任务感知特征融合。
- U-SAM包含语义感知对比损失模块,以提高跨模态对齐能力。
- U-SAM在多个基准测试中表现优异,且在实际应用中具有潜在优势。
点此查看论文截图

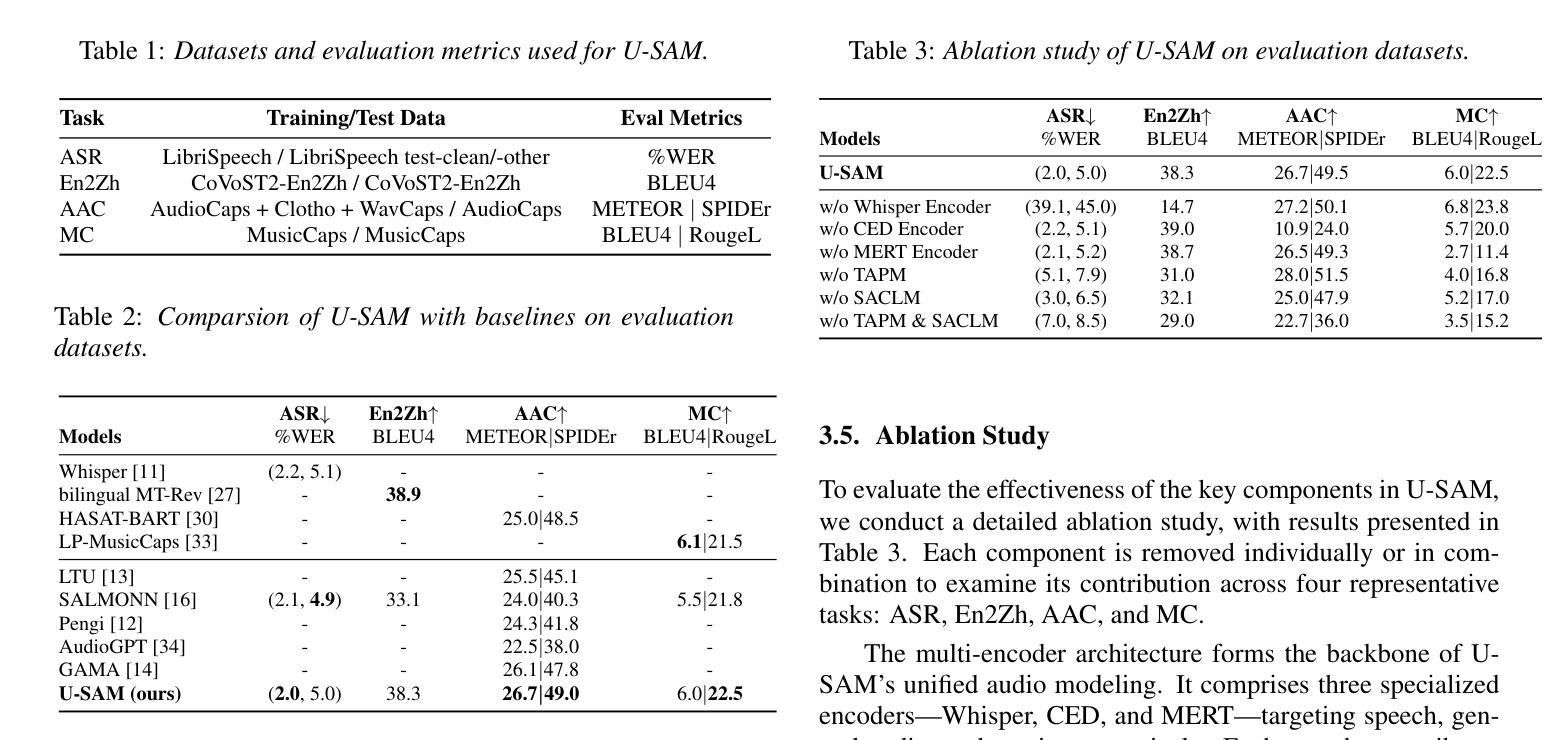
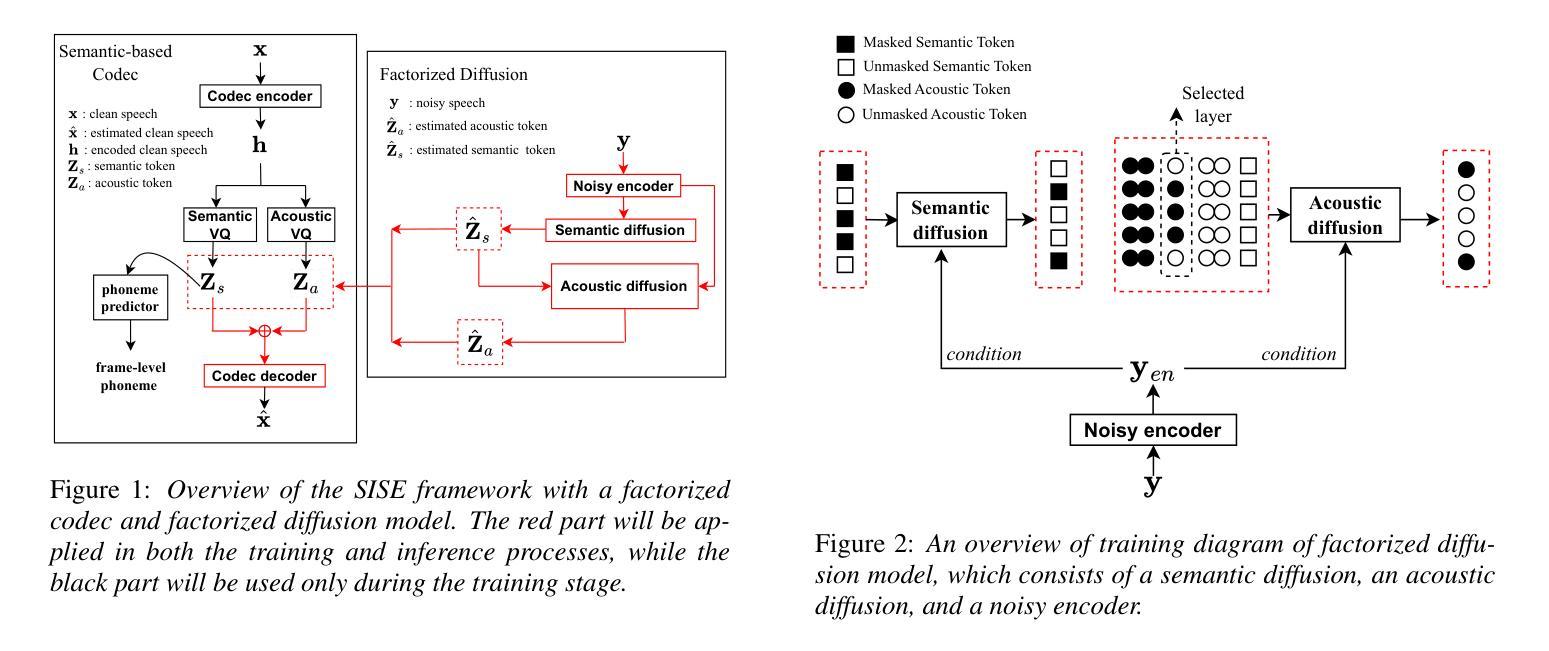
A Semantic Information-based Hierarchical Speech Enhancement Method Using Factorized Codec and Diffusion Model
Authors:Yang Xiang, Canan Huang, Desheng Hu, Jingguang Tian, Xinhui Hu, Chao Zhang
Most current speech enhancement (SE) methods recover clean speech from noisy inputs by directly estimating time-frequency masks or spectrums. However, these approaches often neglect the distinct attributes, such as semantic content and acoustic details, inherent in speech signals, which can hinder performance in downstream tasks. Moreover, their effectiveness tends to degrade in complex acoustic environments. To overcome these challenges, we propose a novel, semantic information-based, step-by-step factorized SE method using factorized codec and diffusion model. Unlike traditional SE methods, our hierarchical modeling of semantic and acoustic attributes enables more robust clean speech recovery, particularly in challenging acoustic scenarios. Moreover, this method offers further advantages for downstream TTS tasks. Experimental results demonstrate that our algorithm not only outperforms SOTA baselines in terms of speech quality but also enhances TTS performance in noisy environments.
当前大多数语音增强(SE)方法通过直接估计时间频率掩膜或频谱从噪声输入中恢复清洁语音。然而,这些方法往往忽视了语音信号中固有的不同属性,如语义内容和声音细节,这可能会阻碍下游任务的性能。此外,它们在复杂的声学环境中的有效性往往会降低。为了克服这些挑战,我们提出了一种新的基于语义信息的逐步分解的SE方法,该方法使用分解编码器和扩散模型。与传统的SE方法不同,我们对语义和声音属性的分层建模,能够实现更稳健的清洁语音恢复,特别是在具有挑战性的声学场景中。此外,此方法对于下游的TTS任务还具有进一步的优点。实验结果表明,我们的算法不仅在语音质量方面优于最新技术水平的基准测试,而且在有噪音的环境下提高了TTS的性能。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by interspeech 2025
Summary:
当前大多数语音增强方法通过直接估计时频掩模或频谱来从噪声输入中恢复清洁语音。然而,这些方法忽略了语音信号中的不同属性,如语义内容和声音细节,这可能会影响下游任务的表现。针对这些挑战,我们提出了一种基于语义信息的新颖、逐步分解的语音增强方法,使用分解编码器和扩散模型。与传统的语音增强方法不同,我们对语义和声音属性的分层建模能够实现更稳健的清洁语音恢复,特别是在复杂的声学场景中。此外,此方法对下游文本转语音任务具有优势。实验结果表明,我们的算法不仅在语音质量方面优于最新基线,还能提高噪声环境下的文本转语音性能。
Key Takeaways:
- 当前语音增强方法主要通过估计时频掩模或频谱来恢复清洁语音。
- 传统方法忽略了语音信号的语义内容和声音细节等独特属性。
- 所提方法采用基于语义信息的逐步分解语音增强策略,结合分解编码器和扩散模型。
- 分层建模语义和声音属性使该方法在复杂声学环境下实现更稳健的语音恢复。
- 所提方法不仅提高了语音质量,还提升了噪声环境下的文本转语音任务性能。
- 实验结果表明该方法在恢复清洁语音方面优于现有最新基线。
点此查看论文截图

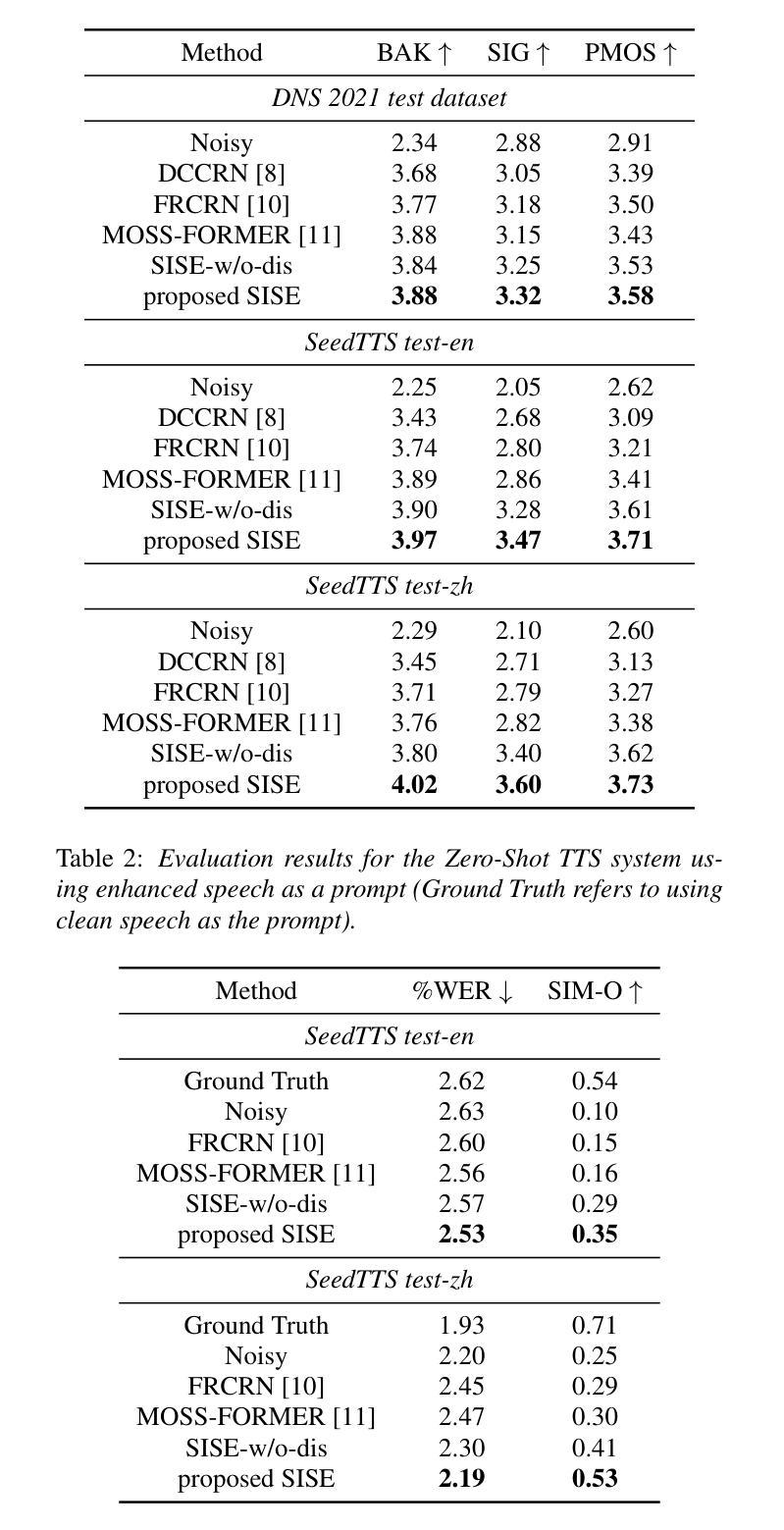
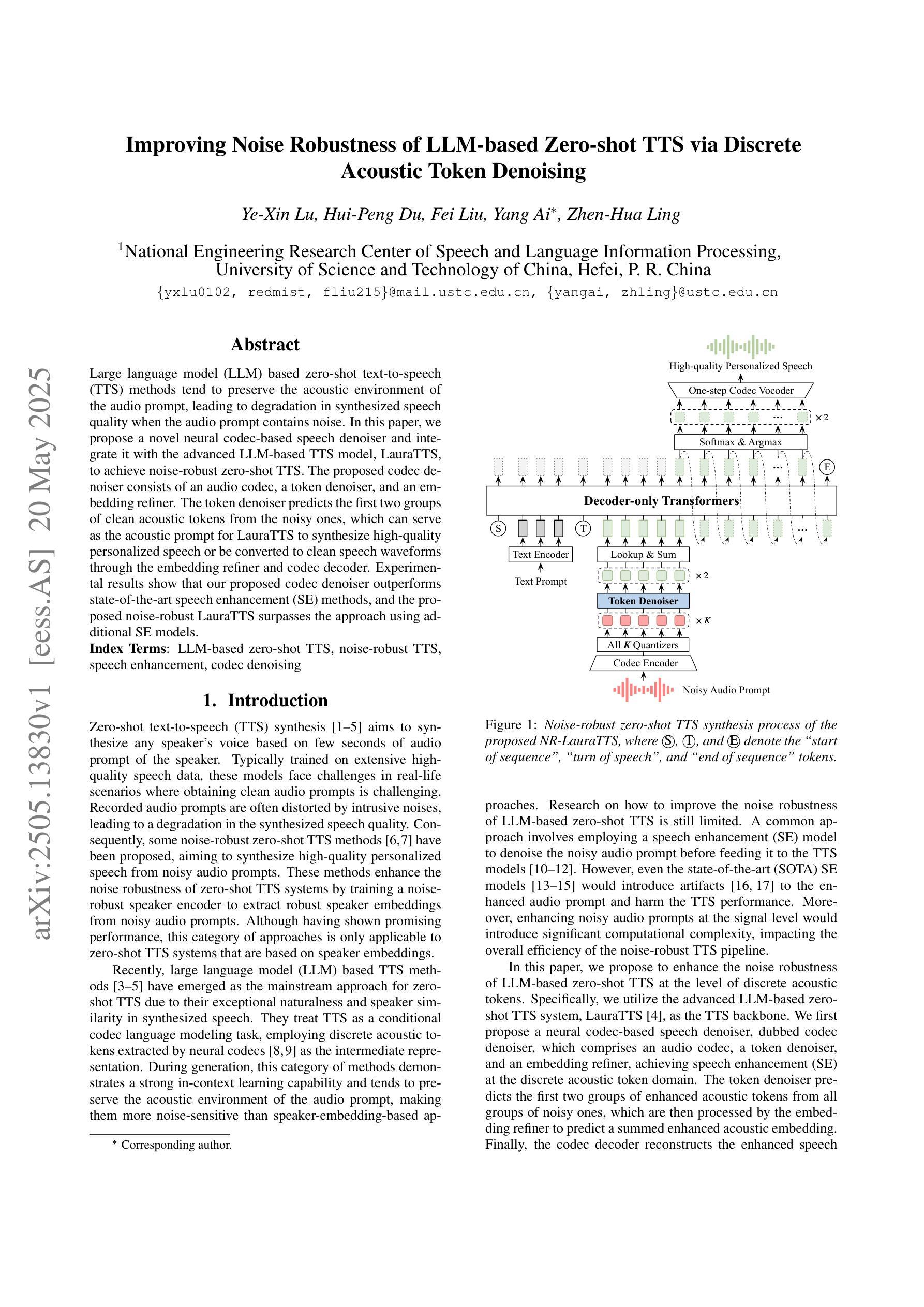
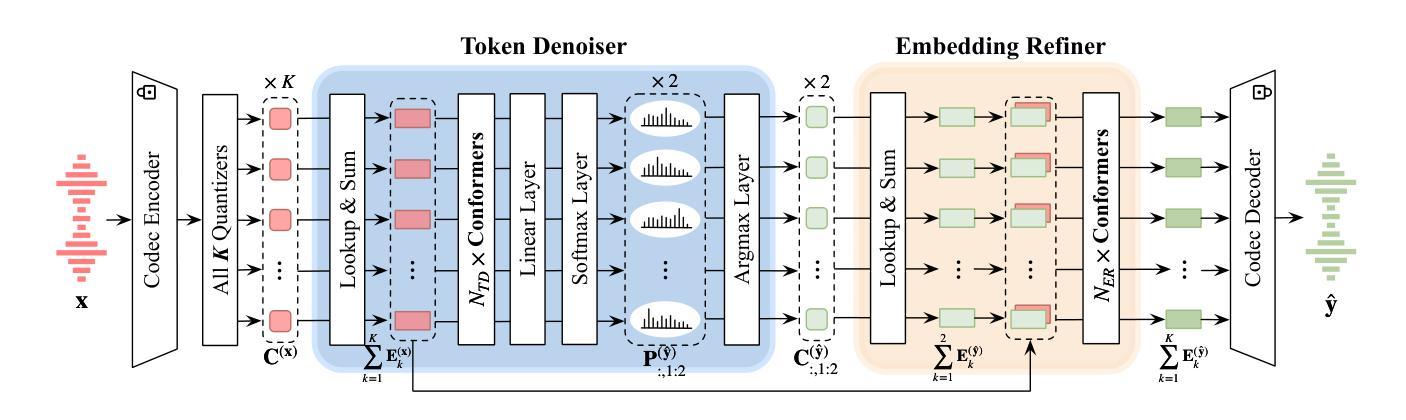
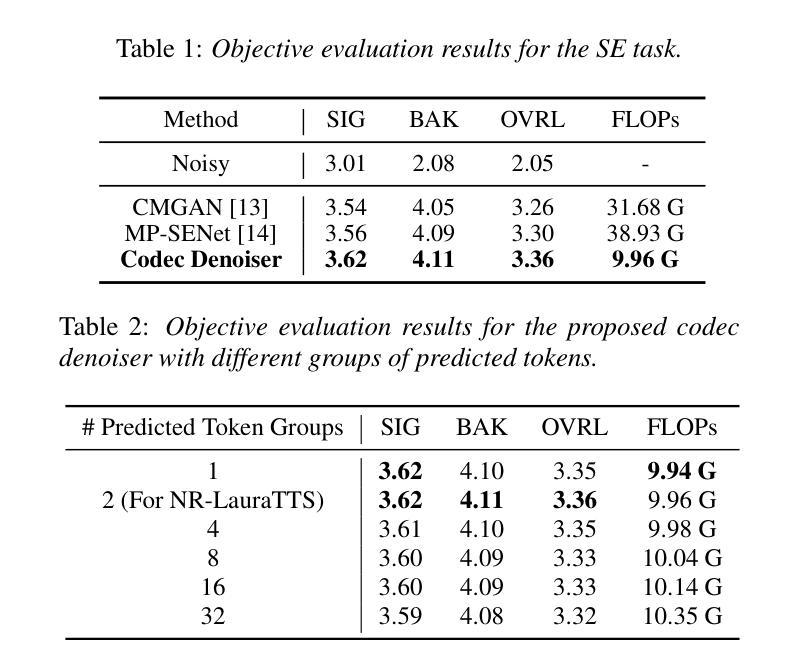
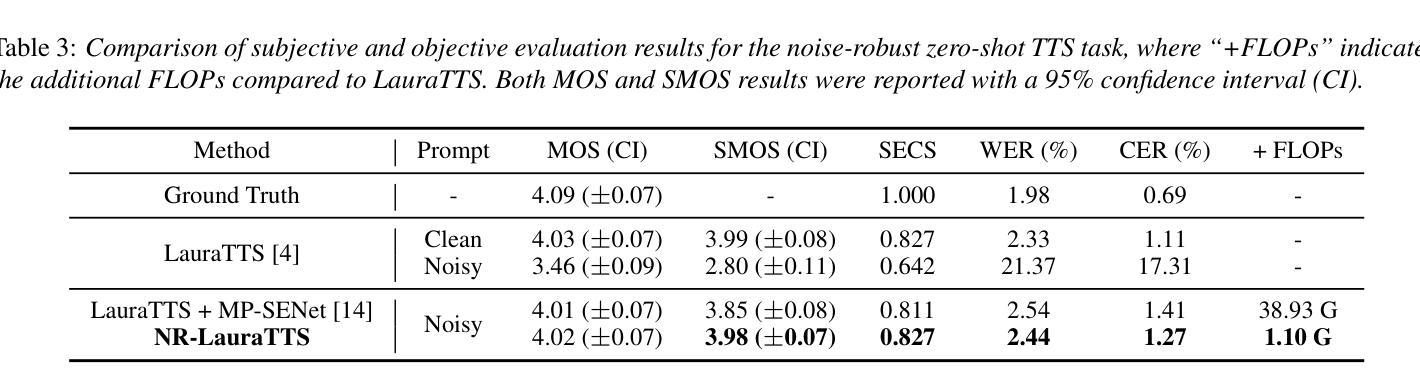
Improving Noise Robustness of LLM-based Zero-shot TTS via Discrete Acoustic Token Denoising
Authors:Ye-Xin Lu, Hui-Peng Du, Fei Liu, Yang Ai, Zhen-Hua Ling
Large language model (LLM) based zero-shot text-to-speech (TTS) methods tend to preserve the acoustic environment of the audio prompt, leading to degradation in synthesized speech quality when the audio prompt contains noise. In this paper, we propose a novel neural codec-based speech denoiser and integrate it with the advanced LLM-based TTS model, LauraTTS, to achieve noise-robust zero-shot TTS. The proposed codec denoiser consists of an audio codec, a token denoiser, and an embedding refiner. The token denoiser predicts the first two groups of clean acoustic tokens from the noisy ones, which can serve as the acoustic prompt for LauraTTS to synthesize high-quality personalized speech or be converted to clean speech waveforms through the embedding refiner and codec decoder. Experimental results show that our proposed codec denoiser outperforms state-of-the-art speech enhancement (SE) methods, and the proposed noise-robust LauraTTS surpasses the approach using additional SE models.
基于大型语言模型(LLM)的零样本文本到语音(TTS)方法倾向于保留音频提示的声学环境,但当音频提示包含噪声时,会导致合成语音质量下降。在本文中,我们提出了一种新型的基于神经网络编解码器的语音去噪器,并将其与先进的LLM-based TTS模型LauraTTS相结合,实现了噪声鲁棒的零样本TTS。所提出的编解码器去噪器由音频编解码器、令牌去噪器和嵌入精炼器组成。令牌去噪器从噪声令牌预测前两个组的干净声学令牌,这可以作为LauraTTS合成高质量个性化语音的声学提示,或通过嵌入精炼器和编解码器解码器转换为干净的语音波形。实验结果表明,我们提出的编解码器去噪器优于最新的语音增强(SE)方法,并且所提出的噪声鲁棒的LauraTTS超过了使用附加SE模型的方法。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by Interspeech 2025
Summary
本文提出了一种基于神经网络编解码器的语音去噪器,并将其与先进的LLM基TTS模型LauraTTS相结合,实现了噪声鲁棒的零样本TTS。该方法能够通过对噪声音频进行去噪处理,提高合成语音的质量。
Key Takeaways
- LLM基TTS方法在文本转语音过程中存在噪声问题,导致合成语音质量下降。
- 提出了一种新型的基于神经网络编解码器的语音去噪器,包括音频编解码器、令牌去噪器和嵌入精炼器。
- 令牌去噪器能够从含噪声的音频中预测出前两组干净的声学令牌,为LauraTTS合成高质量个性化语音提供声学提示。
- 嵌入精炼器和编解码器解码器可以将声学令牌转换为干净的语音波形。
- 实验结果表明,所提出的编解码器去噪器在语音增强方面的性能优于现有技术。
- 结合噪声鲁棒的LauraTTS模型,无需额外的语音增强模型即可实现更好的性能。
点此查看论文截图
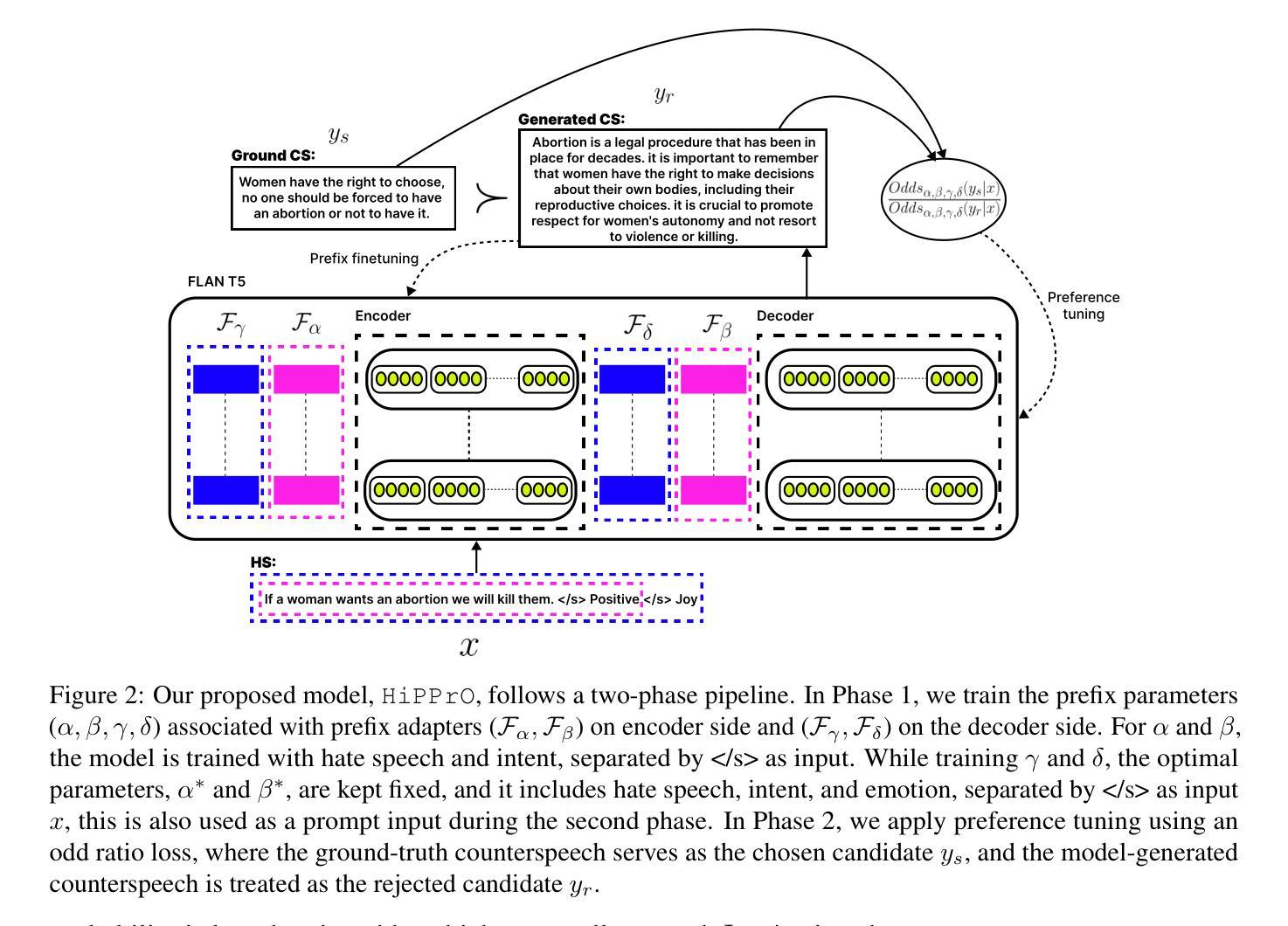
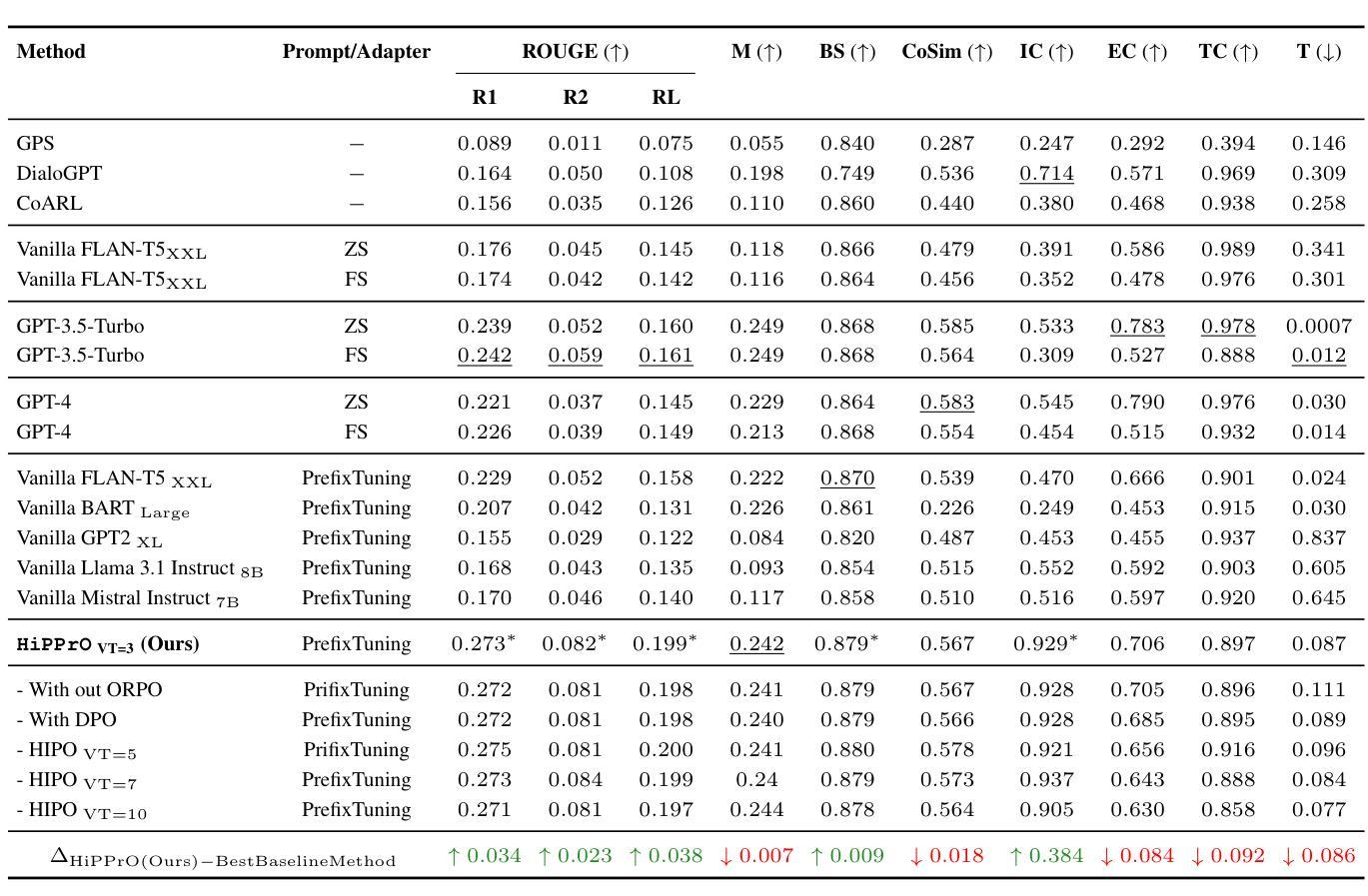
Counterspeech the ultimate shield! Multi-Conditioned Counterspeech Generation through Attributed Prefix Learning
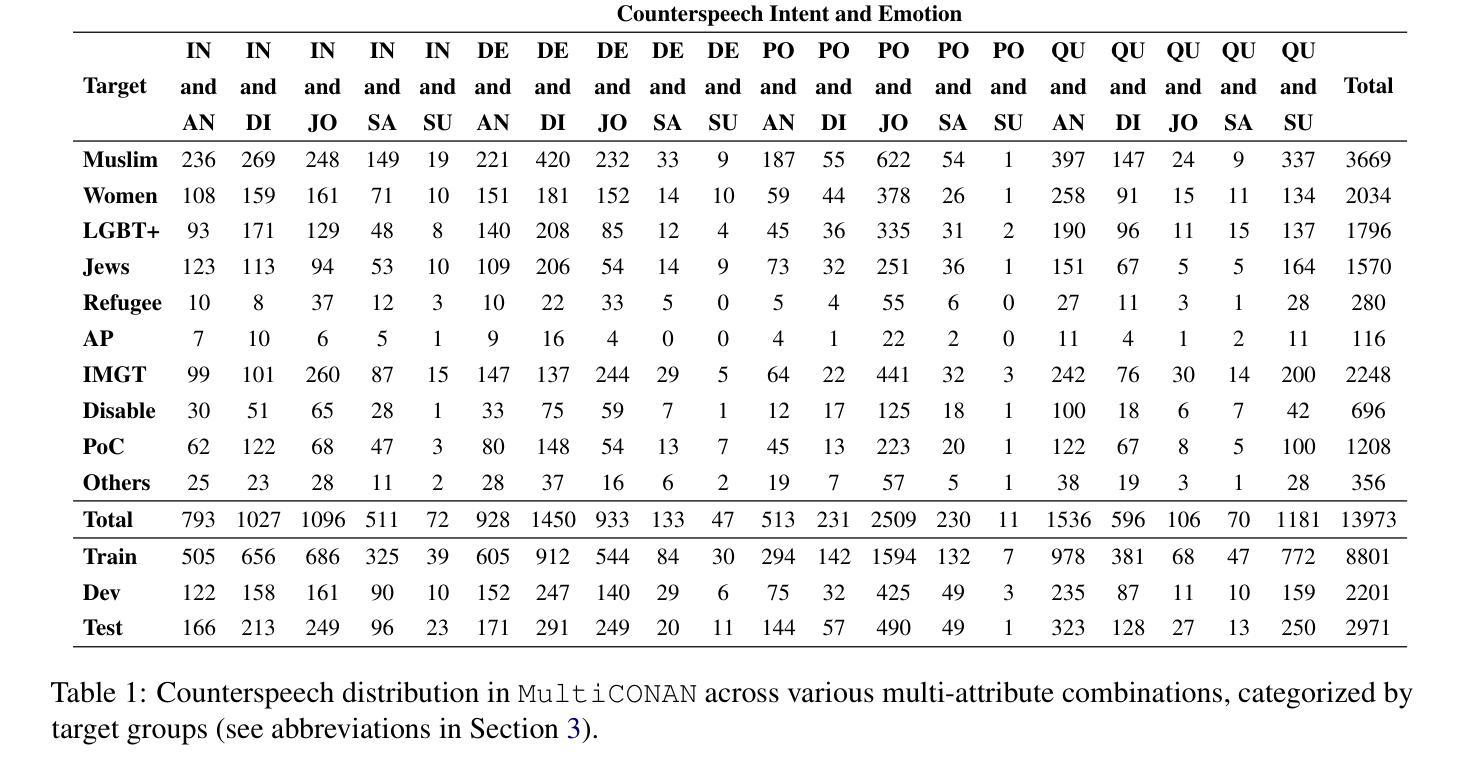
Authors:Aswini Kumar Padhi, Anil Bandhakavi, Tanmoy Chakraborty
Counterspeech has proven to be a powerful tool to combat hate speech online. Previous studies have focused on generating counterspeech conditioned only on specific intents (single attributed). However, a holistic approach considering multiple attributes simultaneously can yield more nuanced and effective responses. Here, we introduce HiPPrO, Hierarchical Prefix learning with Preference Optimization, a novel two-stage framework that utilizes the effectiveness of attribute-specific prefix embedding spaces hierarchically optimized during the counterspeech generation process in the first phase. Thereafter, we incorporate both reference and reward-free preference optimization to generate more constructive counterspeech. Furthermore, we extend IntentCONANv2 by annotating all 13,973 counterspeech instances with emotion labels by five annotators. HiPPrO leverages hierarchical prefix optimization to integrate these dual attributes effectively. An extensive evaluation demonstrates that HiPPrO achieves a ~38 % improvement in intent conformity and a ~3 %, ~2 %, ~3 % improvement in Rouge-1, Rouge-2, and Rouge-L, respectively, compared to several baseline models. Human evaluations further substantiate the superiority of our approach, highlighting the enhanced relevance and appropriateness of the generated counterspeech. This work underscores the potential of multi-attribute conditioning in advancing the efficacy of counterspeech generation systems.
反语已被证明是打击网络仇恨言论的有力工具。以往的研究主要集中在仅针对特定意图(单一属性)生成反语。然而,考虑多个属性同时的整体方法可以产生更精细和有效的响应。在这里,我们介绍了HiPPrO,即带有偏好优化的分层前缀学习,这是一种新的两阶段框架,它利用属性特定前缀嵌入空间在反语生成过程中的分层优化效果。之后,我们结合了参考和无奖励偏好优化,以生成更有建设性的反语。此外,我们扩展了IntentCONANv2,通过五位注释者对13973个反语实例进行情绪标签注释。HiPPrO利用分层前缀优化有效地整合了这些双重属性。大量评估表明,与几种基线模型相比,HiPPrO在意图一致性方面实现了约38%的改进,在Rouge-1、Rouge-2和Rouge-L方面分别实现了约3%、2%、3%的改进。人类评估进一步证实了我们方法的优越性,突出了生成反语的相关性和适当性的提高。这项工作强调了多属性条件在提升反语生成系统效率方面的潜力。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted in ACL 2025 Main Conference
Summary
本文介绍了对抗网络仇恨言论的强有力工具——反话术(counterspeech)。以往研究多侧重于生成特定意图的反话术,而全面考虑多个属性的方法能生成更精细和有效的回应。本文提出HiPPrO框架,利用属性特定前缀嵌入空间的层次优化生成反话术,并通过参考和无奖励偏好优化生成更具建设性的内容。此外,扩展了IntentCONANv2数据集,标注了带有情感标签的反话术实例。评估结果显示HiPPrO在意图符合度上提高了约38%,在Rouge-1、Rouge-2和Rouge-L上分别提高了约3%、2%、3%。人类评估进一步证实了其优越性,强调生成的反话术相关性和适当性得到提高。该研究突显了多属性条件在提升反话术生成系统效能方面的潜力。
Key Takeaways
- 反话术是打击网络仇恨言论的有效工具。
- 以往研究多关注特定意图的反话术生成,但全面考虑多个属性可生成更精细和有效的回应。
- HiPPrO框架利用属性特定前缀嵌入空间的层次优化生成反话术。
- 采用了参考和无奖励偏好优化方法,提升反话术的建设性。
- 扩展了IntentCONANv2数据集,包含情感标签的反话术实例。
- HiPPrO在多个评估指标上表现优越,尤其在意图符合度和内容评估上。
点此查看论文截图

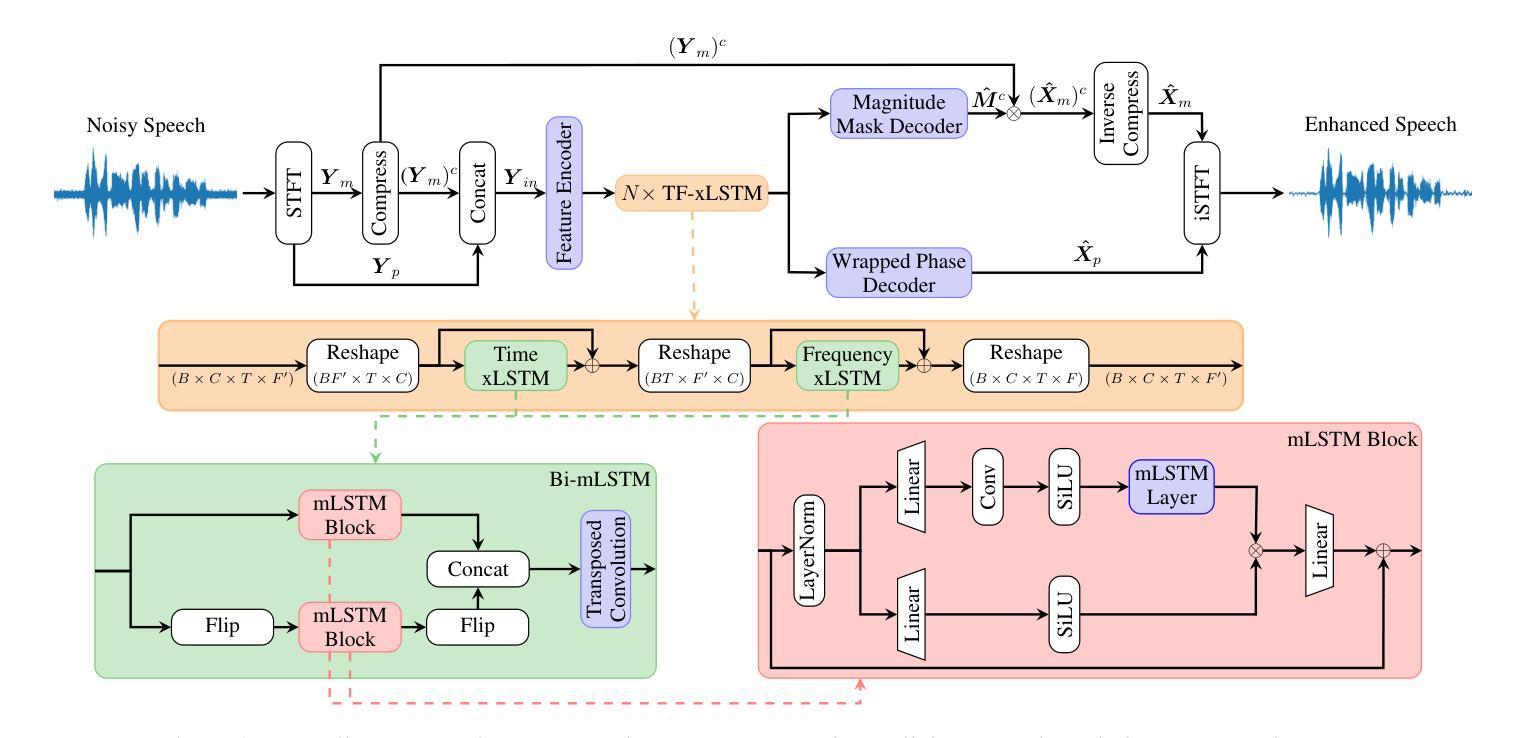
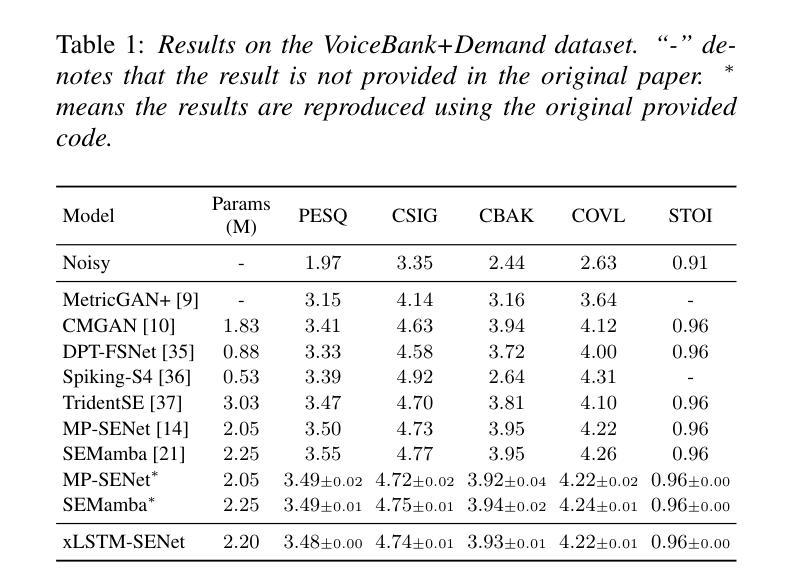
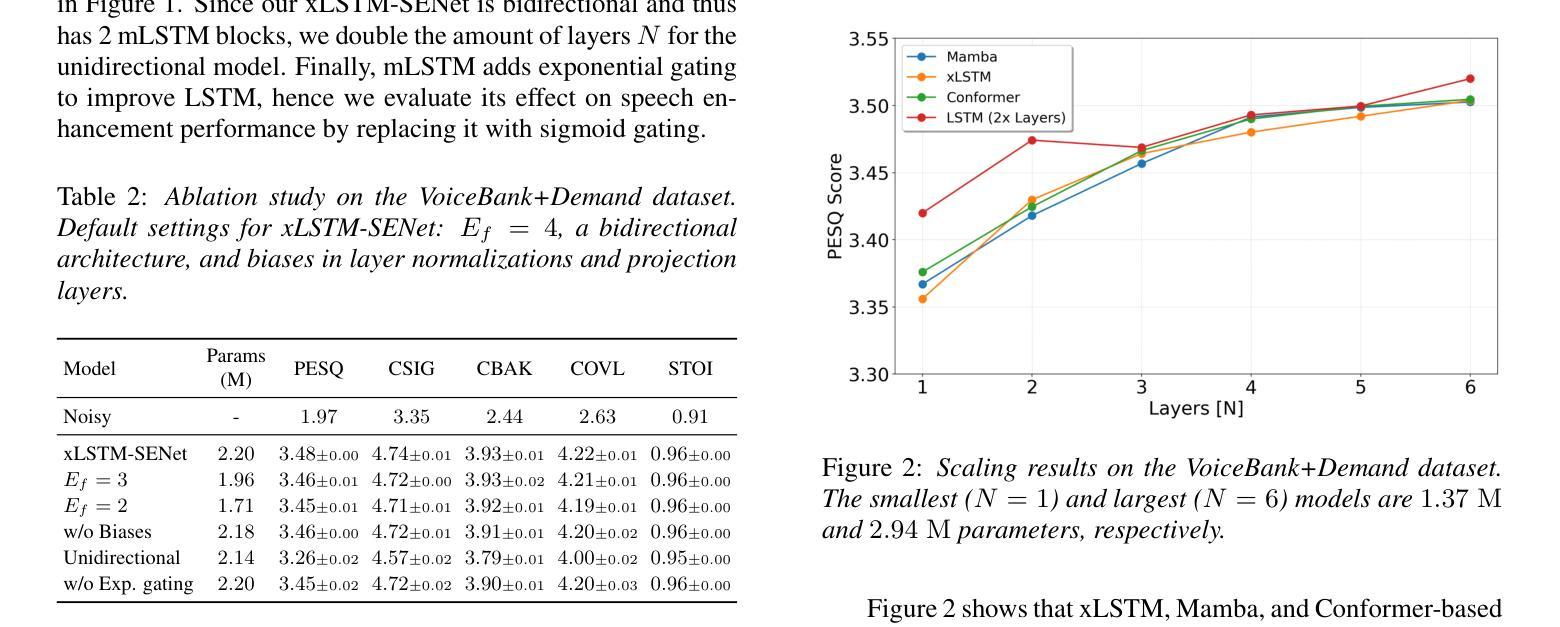
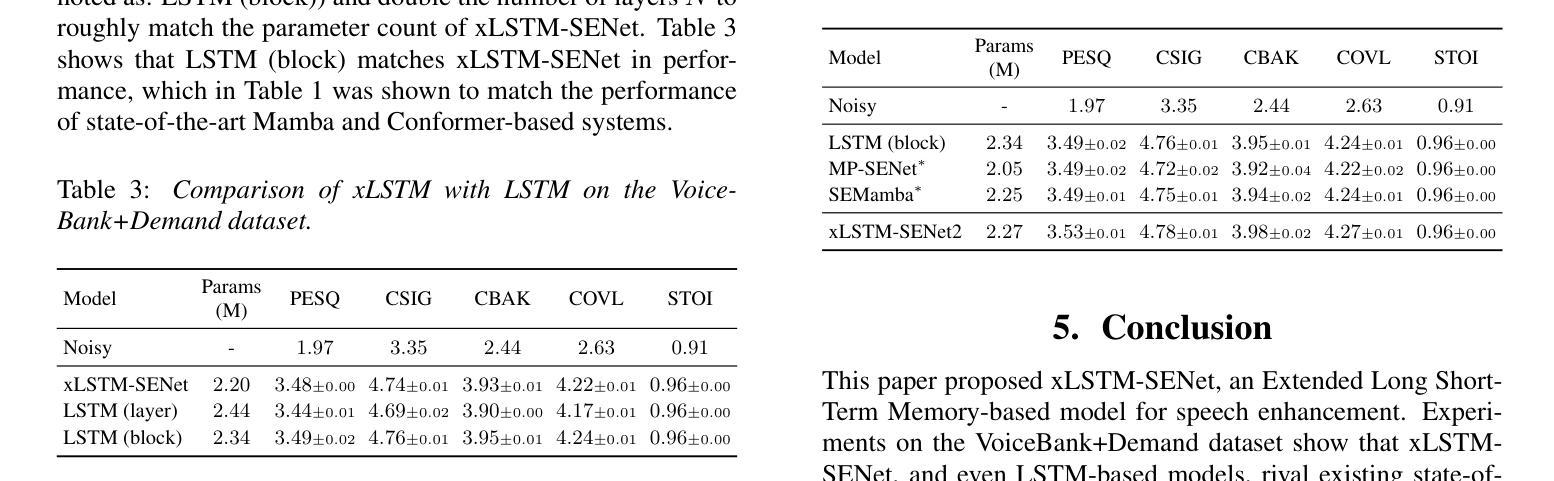
xLSTM-SENet: xLSTM for Single-Channel Speech Enhancement
Authors:Nikolai Lund Kühne, Jan Østergaard, Jesper Jensen, Zheng-Hua Tan
While attention-based architectures, such as Conformers, excel in speech enhancement, they face challenges such as scalability with respect to input sequence length. In contrast, the recently proposed Extended Long Short-Term Memory (xLSTM) architecture offers linear scalability. However, xLSTM-based models remain unexplored for speech enhancement. This paper introduces xLSTM-SENet, the first xLSTM-based single-channel speech enhancement system. A comparative analysis reveals that xLSTM-and notably, even LSTM-can match or outperform state-of-the-art Mamba- and Conformer-based systems across various model sizes in speech enhancement on the VoiceBank+Demand dataset. Through ablation studies, we identify key architectural design choices such as exponential gating and bidirectionality contributing to its effectiveness. Our best xLSTM-based model, xLSTM-SENet2, outperforms state-of-the-art Mamba- and Conformer-based systems of similar complexity on the Voicebank+DEMAND dataset.
基于注意力的架构,如Conformers,在语音增强方面表现出色,但它们面临着输入序列长度方面的可扩展性挑战。相比之下,最近提出的扩展长短期记忆(xLSTM)架构提供了线性可扩展性。然而,基于xLSTM的模型在语音增强方面尚未被探索。本文介绍了xLSTM-SENet,这是第一个基于xLSTM的单通道语音增强系统。对比分析表明,xLSTM(值得注意的是,甚至是LSTM)在VoiceBank+Demand数据集上的语音增强方面,可以匹配或优于最新的Mamba和Conformer系统,并且适用于各种模型大小。通过消融研究,我们确定了关键的设计选择,如指数门控和双向性,这些选择对模型的有效性有所贡献。我们最好的基于xLSTM的模型xLSTM-SENet2在Voicebank+DEMAND数据集上优于具有相似复杂度的最新Mamba和Conformer系统。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted at INTERSPEECH 2025
Summary
本文介绍了基于xLSTM的语音增强系统xLSTM-SENet。相较于传统的注意力机制架构如Conformers,xLSTM架构具有线性可扩展性优势,在语音增强方面表现优异。本文通过对比分析发现,xLSTM(尤其是LSTM)在VoiceBank+Demand数据集上的语音增强效果可与当前先进的Mamba和Conformer系统相媲美或更优秀。通过消去研究,确定了关键架构设计选择如指数门控和双向性对其性能的影响。其中,最佳模型xLSTM-SENet2在相似复杂度的条件下,性能优于当前先进的Mamba和Conformer系统。
Key Takeaways
- xLSTM架构具有线性可扩展性优势,适用于语音增强任务。
- 引入的xLSTM-SENet系统是首个基于xLSTM的单通道语音增强系统。
- xLSTM(包括LSTM)在VoiceBank+Demand数据集上的语音增强效果与当前先进技术相当或更优。
- 对比分析显示,xLSTM-based模型在各类模型大小上均有良好表现。
- 消去研究确定了指数门控和双向性等关键架构设计对系统性能的影响。
- 最佳模型xLSTM-SENet2在相似复杂度条件下,性能优于其他先进技术。
点此查看论文截图

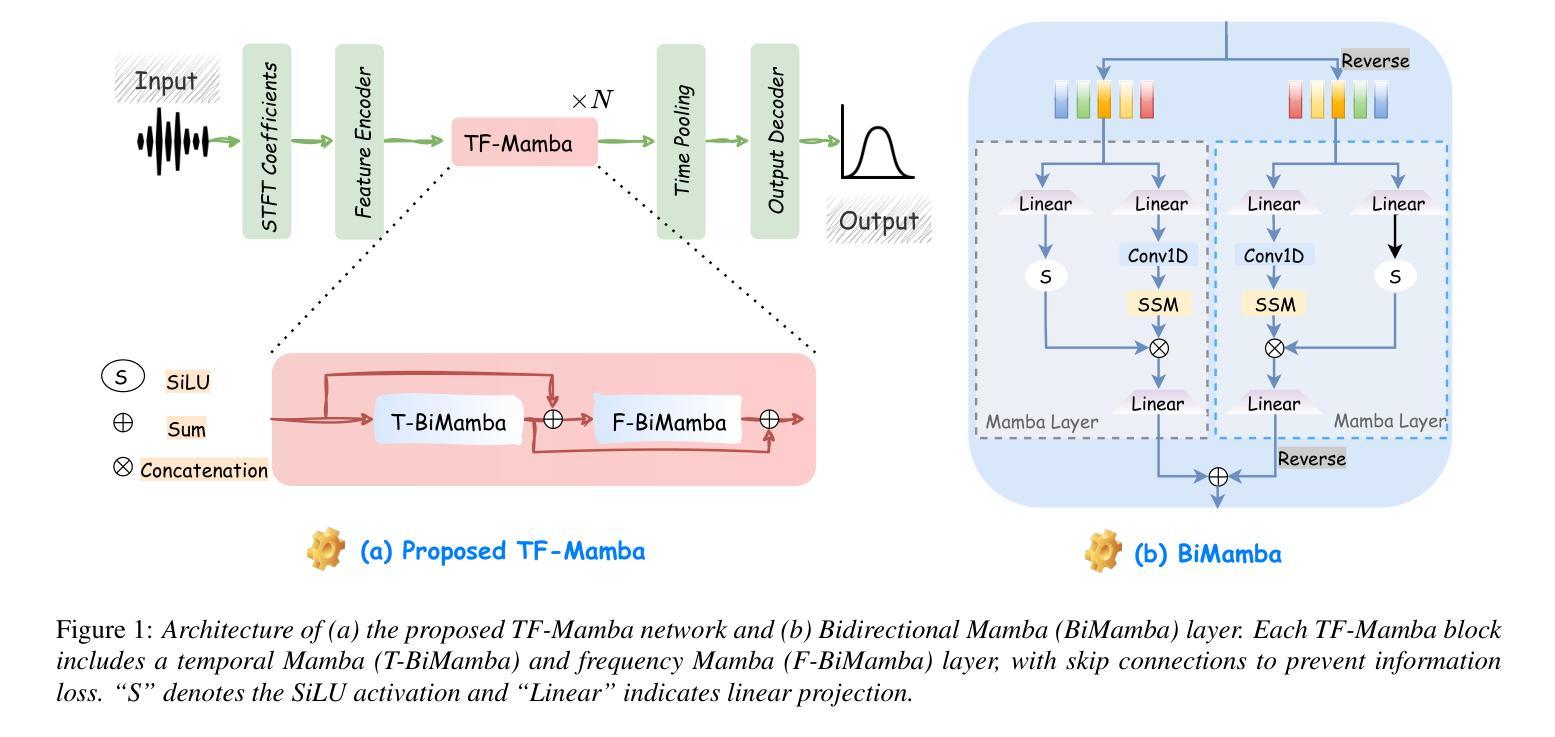
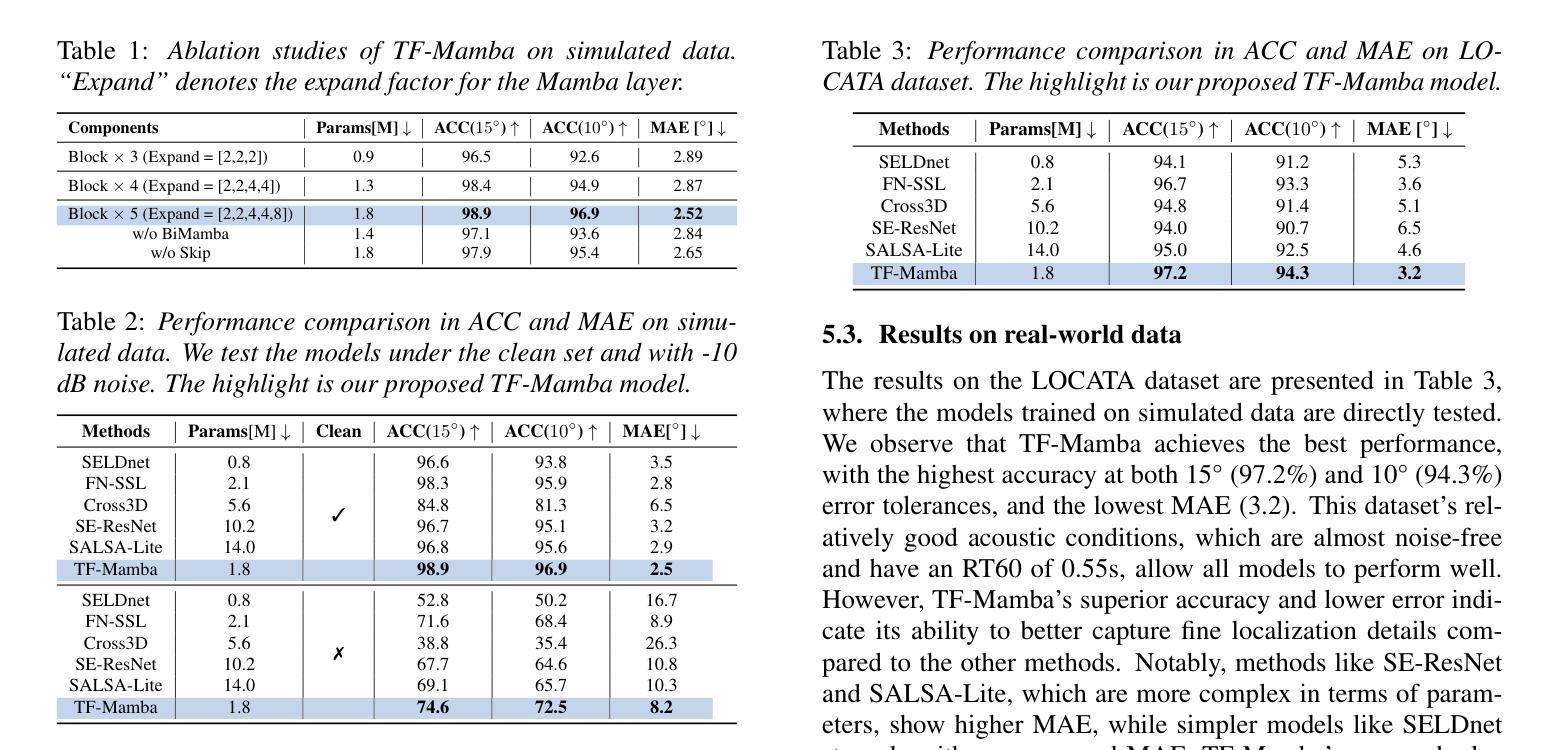
TF-Mamba: A Time-Frequency Network for Sound Source Localization
Authors:Yang Xiao, Rohan Kumar Das
Sound source localization (SSL) determines the position of sound sources using multi-channel audio data. It is commonly used to improve speech enhancement and separation. Extracting spatial features is crucial for SSL, especially in challenging acoustic environments. Recently, a novel structure referred to as Mamba demonstrated notable performance across various sequence-based modalities. This study introduces the Mamba for SSL tasks. We consider the Mamba-based model to analyze spatial features from speech signals by fusing both time and frequency features, and we develop an SSL system called TF-Mamba. This system integrates time and frequency fusion, with Bidirectional Mamba managing both time-wise and frequency-wise processing. We conduct the experiments on the simulated and real datasets. Experiments show that TF-Mamba significantly outperforms other advanced methods. The code will be publicly released in due course.
声源定位(SSL)使用多通道音频数据来确定声源的位置。它通常用于改进语音增强和分离。提取空间特征对于SSL至关重要,尤其在具有挑战性的声学环境中更是如此。最近,一种新型结构Mamba在各种基于序列的模态上表现出了显著的性能。本研究将Mamba引入SSL任务。我们考虑基于Mamba的模型,通过融合时间和频率特征来分析语音信号中的空间特征,并开发了一个名为TF-Mamba的SSL系统。该系统结合了时间和频率融合,双向Mamba负责管理时间和频率方面的处理。我们在模拟和真实数据集上进行了实验。实验表明,TF-Mamba显著优于其他先进方法。代码将在适当的时候公开发布。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by Interspeech 2025
Summary
本文介绍了声音源定位(SSL)技术,该技术利用多通道音频数据确定声音源的位置,用于提高语音增强和分离。文章重点介绍了名为Mamba的新型结构在SSL任务中的应用,通过融合时间和频率特征分析语音信号的空间特征。文章开发了一个名为TF-Mamba的SSL系统,该系统结合了时间和频率融合,使用双向Mamba管理时间和频率处理。实验表明,TF-Mamba显著优于其他先进方法。
Key Takeaways
- 声音源定位(SSL)技术利用多通道音频数据确定声音源位置,常用于语音增强和分离。
- Mamba是一种新型结构,在SSL任务中表现出显著性能。
- TF-Mamba系统结合了时间和频率融合,使用双向Mamba管理时间和频率处理。
- TF-Mamba系统在模拟和真实数据集上的实验表现优异,显著优于其他先进方法。
- 文中强调了提取空间特征在SSL中的重要性,尤其是在具有挑战性的声学环境中。
- Mamba结构在分析和处理语音信号的空间特征方面具有优势。
点此查看论文截图

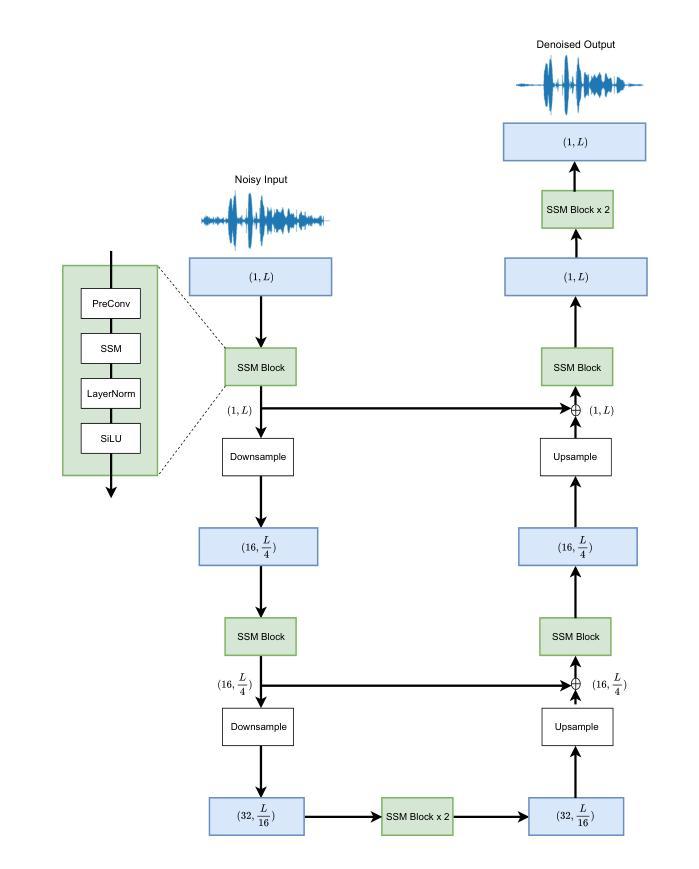
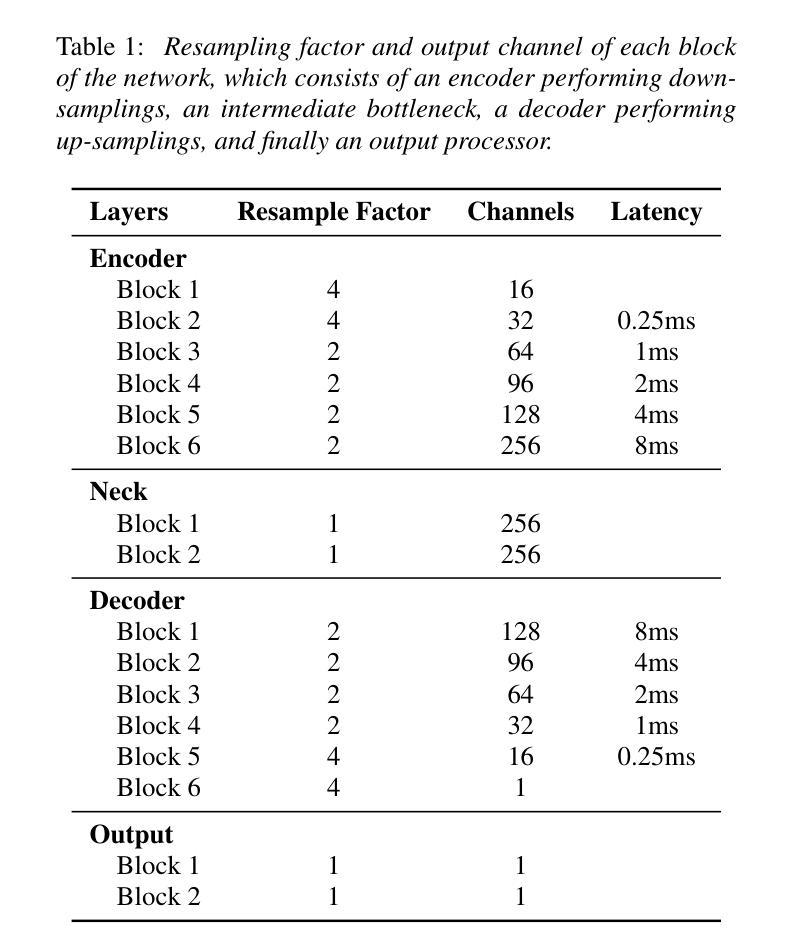
aTENNuate: Optimized Real-time Speech Enhancement with Deep SSMs on Raw Audio
Authors:Yan Ru Pei, Ritik Shrivastava, FNU Sidharth
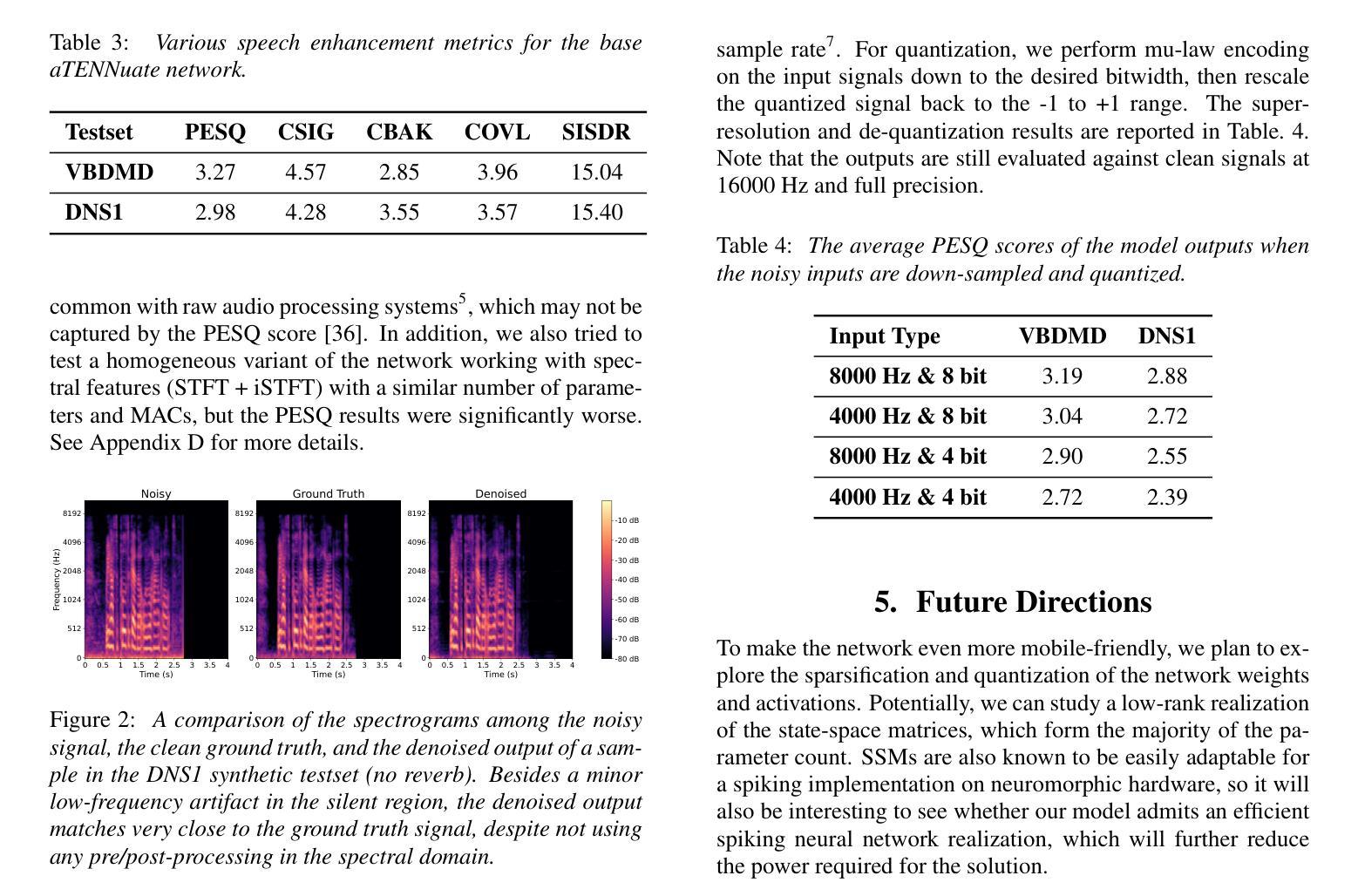
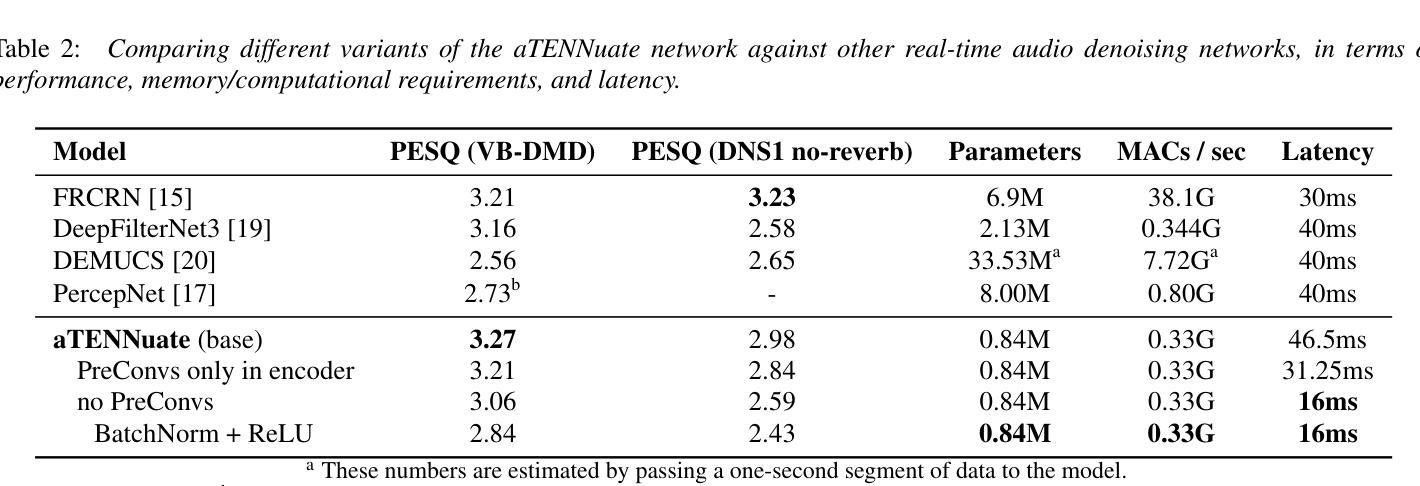
We present aTENNuate, a simple deep state-space autoencoder configured for efficient online raw speech enhancement in an end-to-end fashion. The network’s performance is primarily evaluated on raw speech denoising, with additional assessments on tasks such as super-resolution and de-quantization. We benchmark aTENNuate on the VoiceBank + DEMAND and the Microsoft DNS1 synthetic test sets. The network outperforms previous real-time denoising models in terms of PESQ score, parameter count, MACs, and latency. Even as a raw waveform processing model, the model maintains high fidelity to the clean signal with minimal audible artifacts. In addition, the model remains performant even when the noisy input is compressed down to 4000Hz and 4 bits, suggesting general speech enhancement capabilities in low-resource environments. Try it out by pip install attenuate
我们提出了aTENNuate,这是一个配置简单的深度状态空间自编码器,以端到端的方式实现高效的在线原始语音增强。该网络的主要评估指标是原始语音去噪,此外还对其他任务如超分辨率和去量化进行了评估。我们在VoiceBank + DEMAND和Microsoft DNS1合成测试集上对aTENNuate进行了基准测试。该网络在PESQ得分、参数计数、MACs和延迟方面优于之前的实时去噪模型。即使作为原始波形处理模型,该模型对清洁信号的保真度也很高,几乎听不到任何杂音。此外,即使嘈杂的输入压缩到4000Hz和4位,该模型仍然表现良好,这表明其在低资源环境下的通用语音增强能力。可以通过pip install attenuate来尝试使用它。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 7 pages, 2 figures
Summary
aTENNuate是一款针对在线原始语音增强设计的简单深度状态空间自编码器。它采用端到端的方式,主要用于原始语音降噪,并额外用于超分辨率和去量化任务。在VoiceBank + DEMAND和Microsoft DNS1合成测试集上进行的基准测试表明,该网络在PESQ分数、参数计数、MACs和延迟方面优于之前的实时降噪模型。此外,即使作为原始波形处理模型,该模型对清洁信号的保真度也很高,几乎听不到失真。即使在将嘈杂的输入压缩到4000Hz和4位的情况下,该模型在低资源环境中仍具有出色的语音增强能力。
Key Takeaways
- aTENNuate是一个用于在线原始语音增强的深度状态空间自编码器。
- 它主要用于原始语音降噪,并在VoiceBank + DEMAND和Microsoft DNS1测试集上进行了基准测试。
- aTENNuate在PESQ分数、参数计数、MACs和延迟方面优于其他实时降噪模型。
- 该模型对清洁语音信号的保真度高,产生的音频几乎无失真。
- aTENNuate在低资源环境中(如使用低频率和低比特率的输入)仍具有良好的性能。
- 安装aTENNuate只需通过pip install attenuate即可完成。
点此查看论文截图

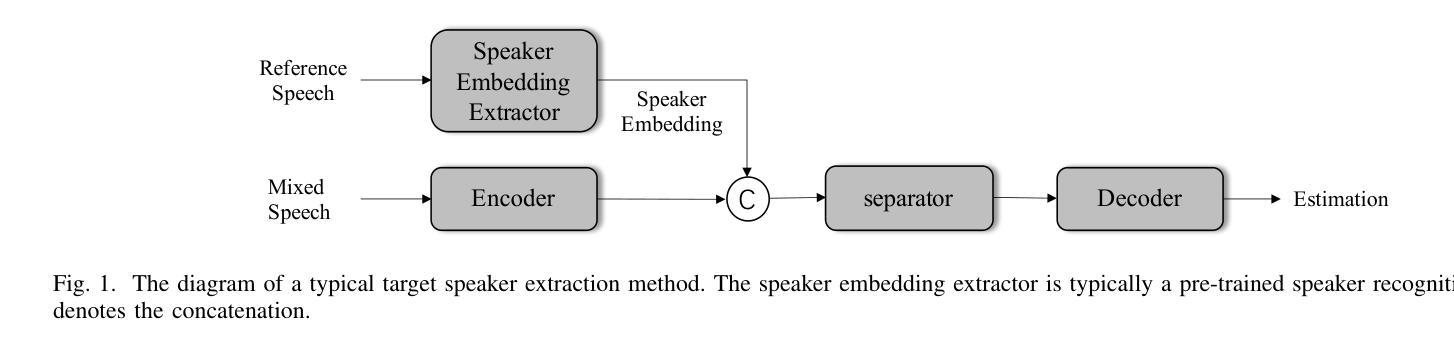
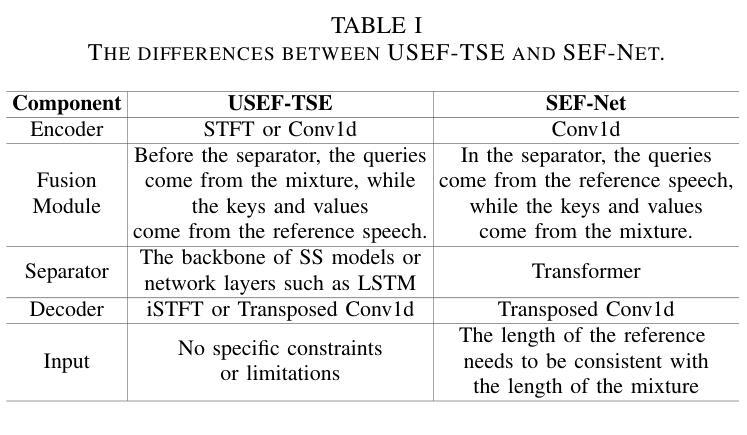
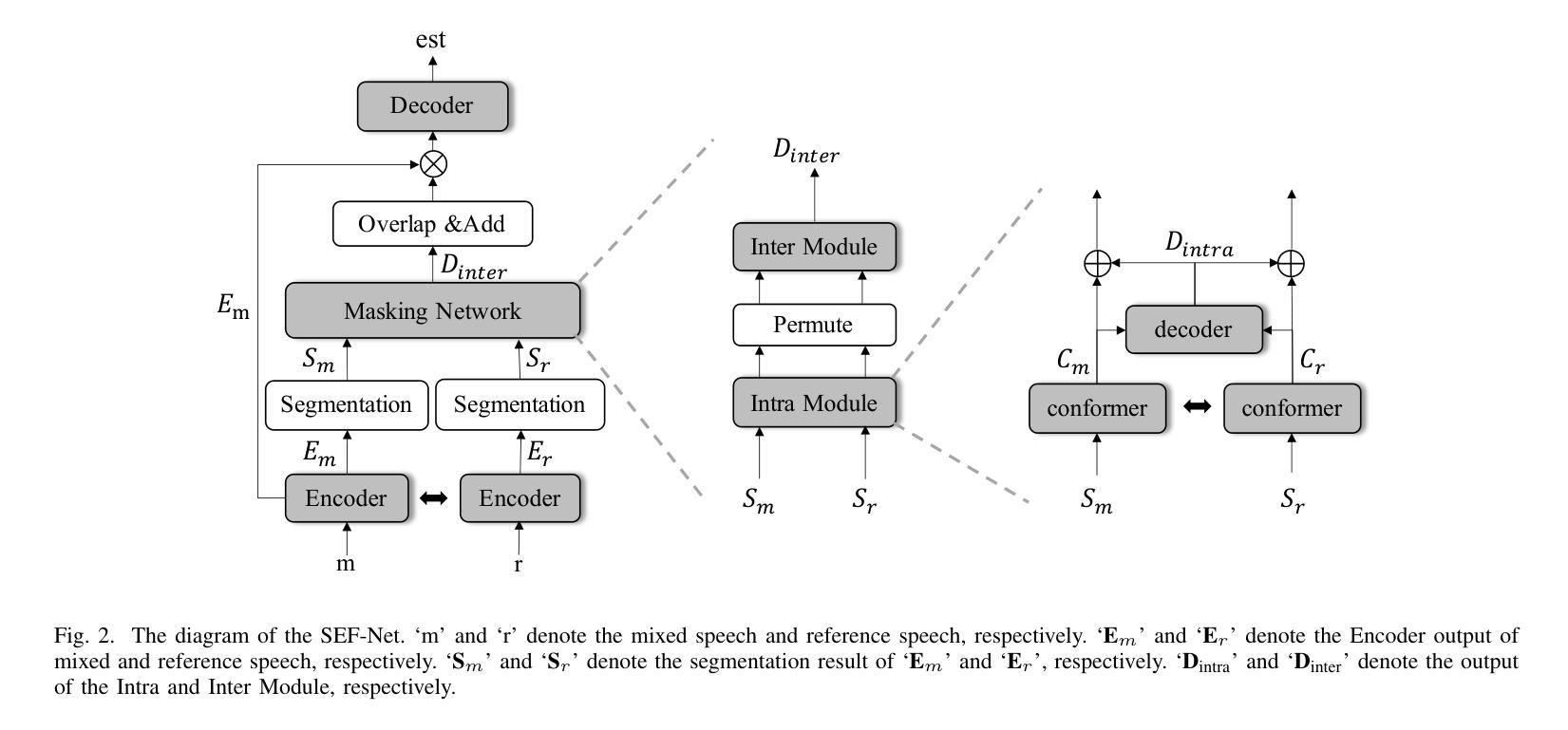
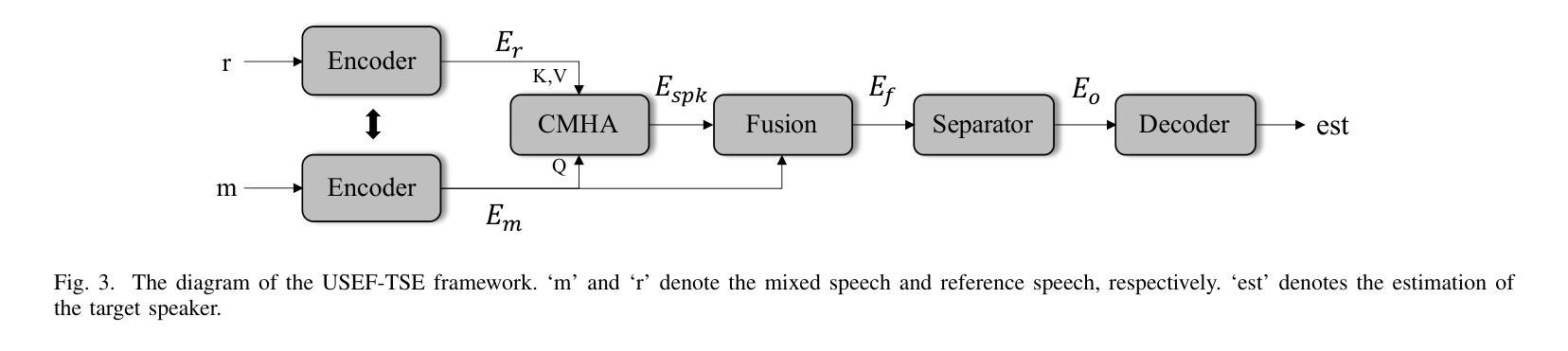
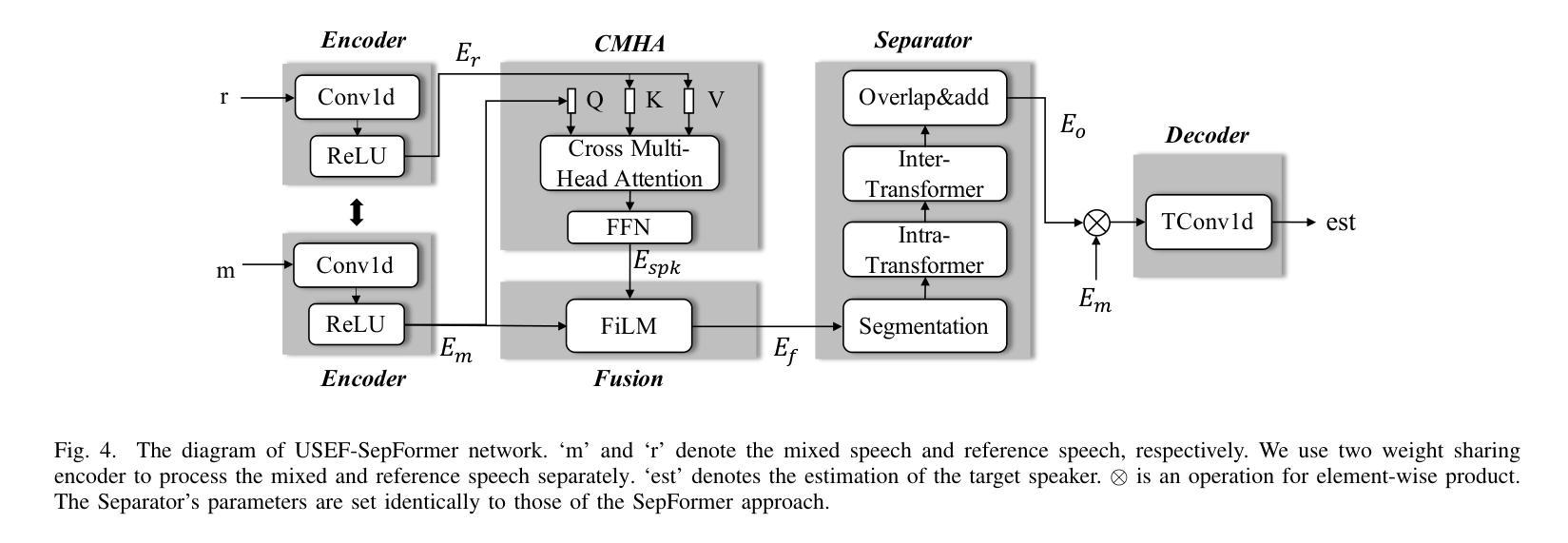
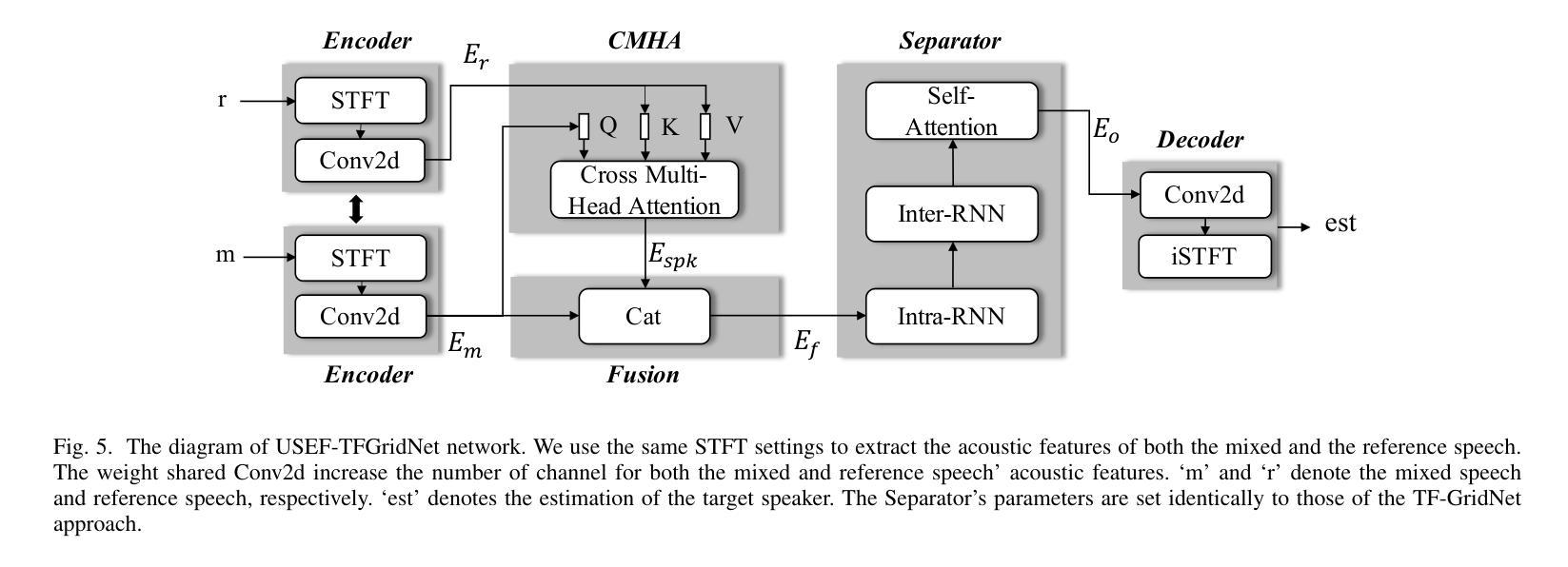
USEF-TSE: Universal Speaker Embedding Free Target Speaker Extraction
Authors:Bang Zeng, Ming Li
Target speaker extraction aims to separate the voice of a specific speaker from mixed speech. Traditionally, this process has relied on extracting a speaker embedding from a reference speech, in which a speaker recognition model is required. However, identifying an appropriate speaker recognition model can be challenging, and using the target speaker embedding as reference information may not be optimal for target speaker extraction tasks. This paper introduces a Universal Speaker Embedding-Free Target Speaker Extraction (USEF-TSE) framework that operates without relying on speaker embeddings. USEF-TSE utilizes a multi-head cross-attention mechanism as a frame-level target speaker feature extractor. This innovative approach allows mainstream speaker extraction solutions to bypass the dependency on speaker recognition models and better leverage the information available in the enrollment speech, including speaker characteristics and contextual details. Additionally, USEF-TSE can seamlessly integrate with other time-domain or time-frequency domain speech separation models to achieve effective speaker extraction. Experimental results show that our proposed method achieves state-of-the-art (SOTA) performance in terms of Scale-Invariant Signal-to-Distortion Ratio (SI-SDR) on the WSJ0-2mix, WHAM!, and WHAMR! datasets, which are standard benchmarks for monaural anechoic, noisy and noisy-reverberant two-speaker speech separation and speaker extraction. The results on the LibriMix and the blind test set of the ICASSP 2023 DNS Challenge demonstrate that the model performs well on more diverse and out-of-domain data. For access to the source code, please visit: https://github.com/ZBang/USEF-TSE.
目标说话人提取旨在从混合语音中分离出特定说话人的声音。传统上,这一过程依赖于从参考语音中提取说话人嵌入,这需要说话人识别模型。然而,识别合适的说话人识别模型可能具有挑战性,并且使用目标说话人嵌入作为参考信息可能不是针对目标说话人提取任务的最佳选择。本文介绍了一种无通用说话人嵌入目标说话人提取(USEF-TSE)框架,该框架无需依赖说话人嵌入即可运行。USEF-TSE利用多头交叉注意机制作为帧级目标说话人特征提取器。这种创新方法允许主流说话人提取解决方案绕过对说话人识别模型的依赖,并更好地利用注册语音中可用的信息,包括说话人特征和上下文细节。此外,USEF-TSE可以无缝集成到其他时域或时频域语音分离模型,以实现有效的说话人提取。实验结果表明,我们提出的方法在WSJ0-2mix、WHAM!和WHAMR!数据集上的尺度不变信号失真比(SI-SDR)方面达到了最新技术水平,这些数据集是单声道无回声、嘈杂和嘈杂混响两说话人语音分离和说话人提取的标准基准测试。在LibriMix和ICASSP 2023 DNS挑战的盲测试集上的结果证明,该模型在更多样化和领域外的数据上表现良好。如需访问源代码,请访问:https://github.com/ZBang/USEF-TSE。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by IEEE Transactions on Audio, Speech and Language Processing (TASLP)
摘要
目标说话人提取旨在从混合语音中分离特定说话人的声音。本文提出了一种无通用说话人嵌入目标说话人提取(USEF-TSE)框架,该框架无需依赖说话人嵌入即可运行。USEF-TSE利用多头交叉注意机制作为帧级目标说话人特征提取器,使主流说话人提取解决方案能够绕过对说话人识别模型的依赖,更好地利用报名语音中的信息,包括说话人特征和上下文细节。实验结果表明,该方法在WSJ0-2mix、WHAM!和WHAMR!数据集上的尺度不变信号失真比(SI-SDR)方面达到了最新水平。该模型在更多样化和非域数据的LibriMix和ICASSP 2023 DNS Challenge的盲测试集上表现良好。
关键见解
- 目标说话人提取旨在从混合语音中分离特定说话人的声音。
- 传统的说话人提取方法依赖于从参考语音中提取说话人嵌入,这需要使用说话人识别模型,但识别合适的模型具有挑战性。
- USEF-TSE框架无需依赖通用说话人嵌入进行目标说话人提取。
- USEF-TSE使用多头交叉注意机制作为帧级目标说话人特征提取器,能更有效地利用报名语音中的信息。
- USEF-TSE可以与其他时域或时频域语音分离模型无缝集成,以实现有效的说话人提取。
- 实验结果表明,USEF-TSE在多个标准数据集上达到了最新水平的性能。
点此查看论文截图