⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-05-22 更新
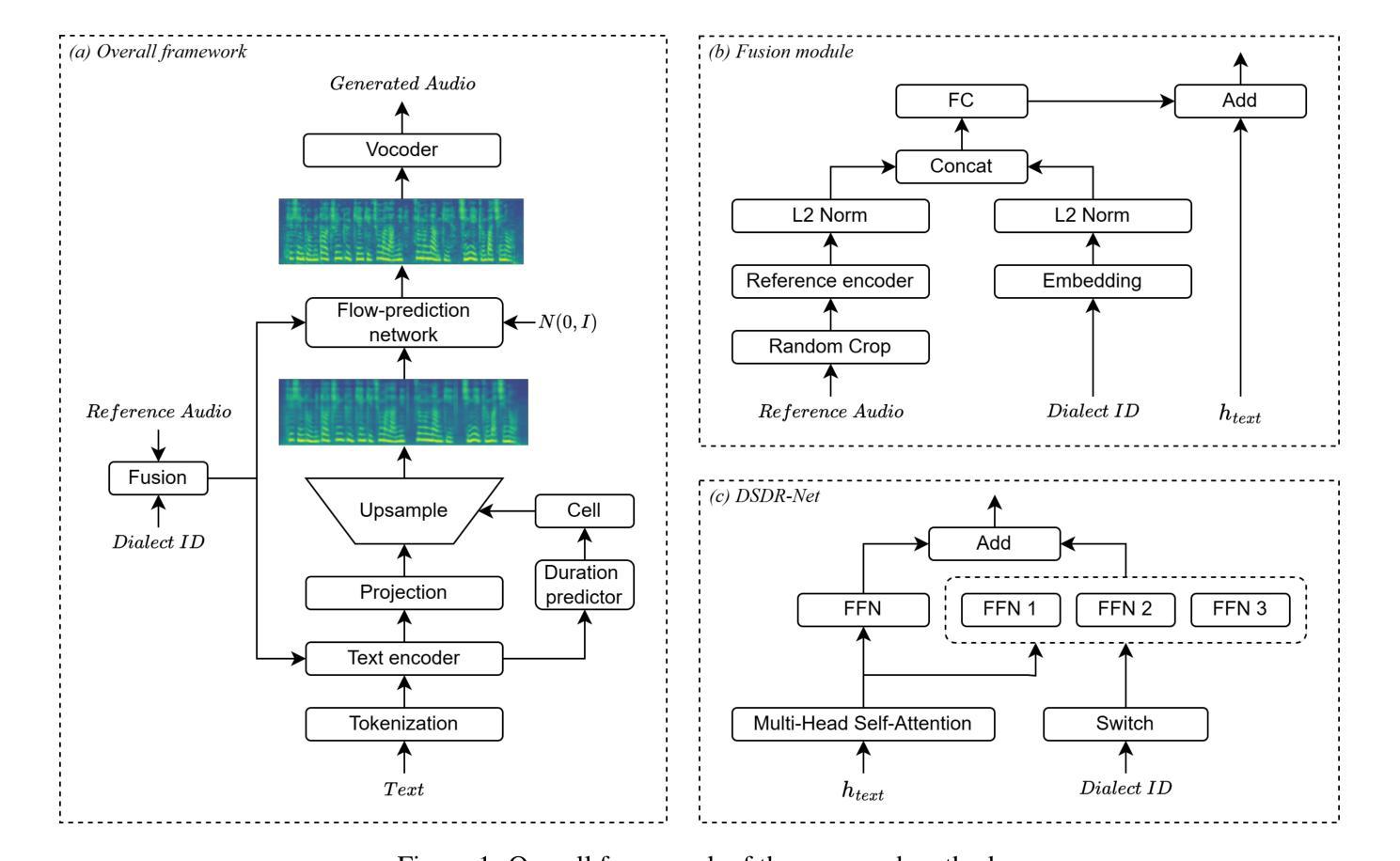
FMSD-TTS: Few-shot Multi-Speaker Multi-Dialect Text-to-Speech Synthesis for Ü-Tsang, Amdo and Kham Speech Dataset Generation
Authors:Yutong Liu, Ziyue Zhang, Ban Ma-bao, Yuqing Cai, Yongbin Yu, Renzeng Duojie, Xiangxiang Wang, Fan Gao, Cheng Huang, Nyima Tashi
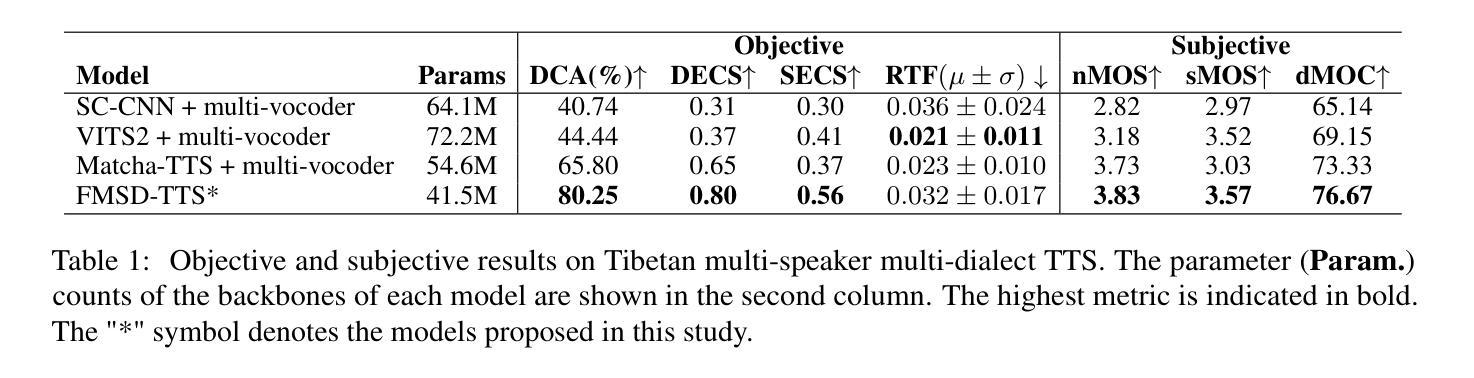
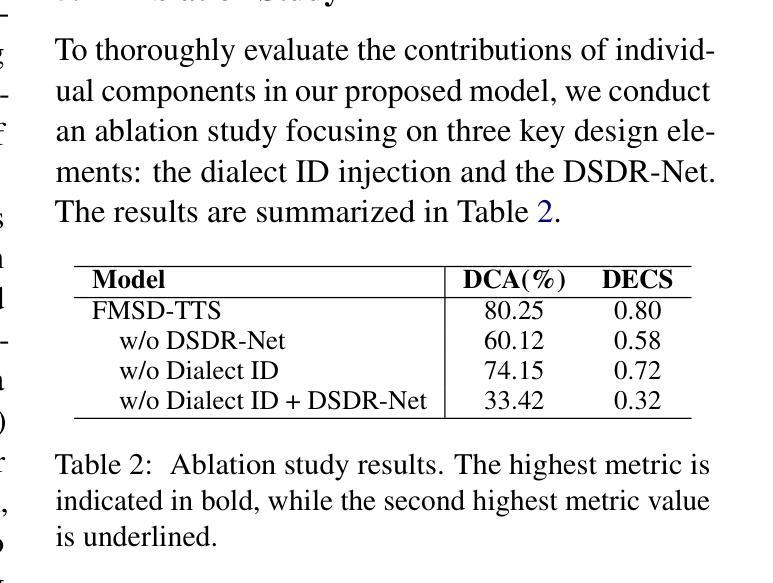
Tibetan is a low-resource language with minimal parallel speech corpora spanning its three major dialects-"U-Tsang, Amdo, and Kham-limiting progress in speech modeling. To address this issue, we propose FMSD-TTS, a few-shot, multi-speaker, multi-dialect text-to-speech framework that synthesizes parallel dialectal speech from limited reference audio and explicit dialect labels. Our method features a novel speaker-dialect fusion module and a Dialect-Specialized Dynamic Routing Network (DSDR-Net) to capture fine-grained acoustic and linguistic variations across dialects while preserving speaker identity. Extensive objective and subjective evaluations demonstrate that FMSD-TTS significantly outperforms baselines in both dialectal expressiveness and speaker similarity. We further validate the quality and utility of the synthesized speech through a challenging speech-to-speech dialect conversion task. Our contributions include: (1) a novel few-shot TTS system tailored for Tibetan multi-dialect speech synthesis, (2) the public release of a large-scale synthetic Tibetan speech corpus generated by FMSD-TTS, and (3) an open-source evaluation toolkit for standardized assessment of speaker similarity, dialect consistency, and audio quality.
藏语是一种资源匮乏的语言,其三大方言区——乌齐、安多和康区的平行语音语料库极其有限,限制了语音建模的进展。为了解决这一问题,我们提出了FMSD-TTS,这是一个小样本、多发言人、多方言的文本到语音框架,它可以从有限的参考音频和明确的方言标签中合成平行的方言语音。我们的方法具有新颖的发声人-方言融合模块和方言专用动态路由网络(DSDR-Net),能够捕捉方言间的精细声学和语言变异,同时保留发声人的身份。大量的客观和主观评估表明,FMSD-TTS在方言表达力和发声人相似性方面显著优于基线系统。我们进一步通过具有挑战性的语音到语音的方言转换任务来验证合成语音的质量和实用性。我们的贡献包括:(1)针对藏语多方言语音合成的少样本TTS系统,(2)公开发布由FMSD-TTS生成的大规模合成藏语语音语料库,(3)开放源代码评估工具包,用于标准化评估发声人相似性、方言一致性和音频质量。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 13 pages
Summary
本文介绍了针对藏语这一资源匮乏型语言的TTS系统。为应对藏语三种主要方言之间平行语料稀缺的问题,研究者提出了FMSD-TTS系统,该框架能从有限的参考音频和明确的方言标签中合成平行方言语音。它采用了多语种语音融合模块及方言专业动态路由网络,可以精细捕捉方言间的声学差异,同时在发音上保留个体差异。FMSD-TTS在各种评价和实验中的表现均优于基准模型。此外,研究者还首次公开了大规模藏语合成语音库和开源评估工具包。
Key Takeaways
- FMSD-TTS是为藏语这一资源匮乏型语言设计的TTS系统。
- 系统能有效合成藏语的三大方言(乌兹、安多和康区方言)。
- FMSD-TTS通过引入多语种语音融合模块和方言专业动态路由网络,能够捕捉方言间的细微差异并保留说话人的身份特征。
- 该系统在客观和主观评价中均表现出优异的性能,特别是在方言表达力和说话人相似性方面。
- FMSD-TTS成功地完成了挑战性方言语音转换任务。
- 研究者首次公开了由FMSD-TTS生成的大规模藏语合成语音库。
点此查看论文截图

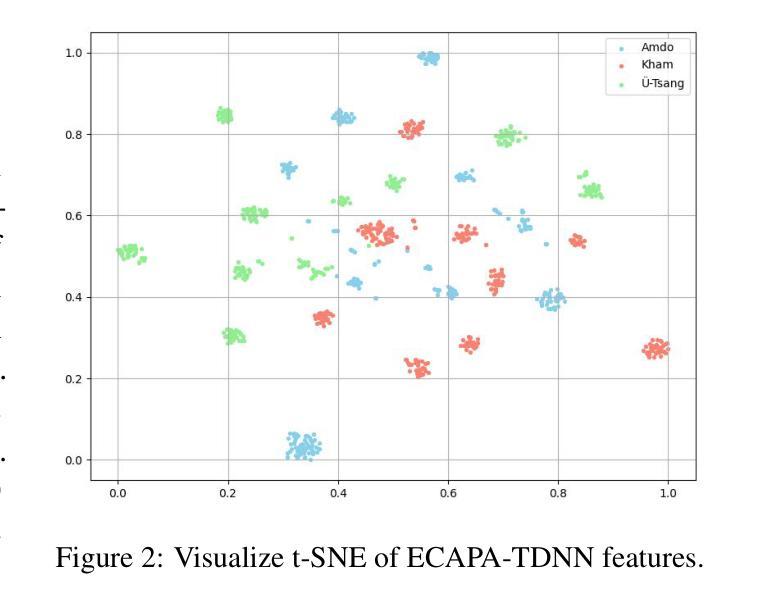
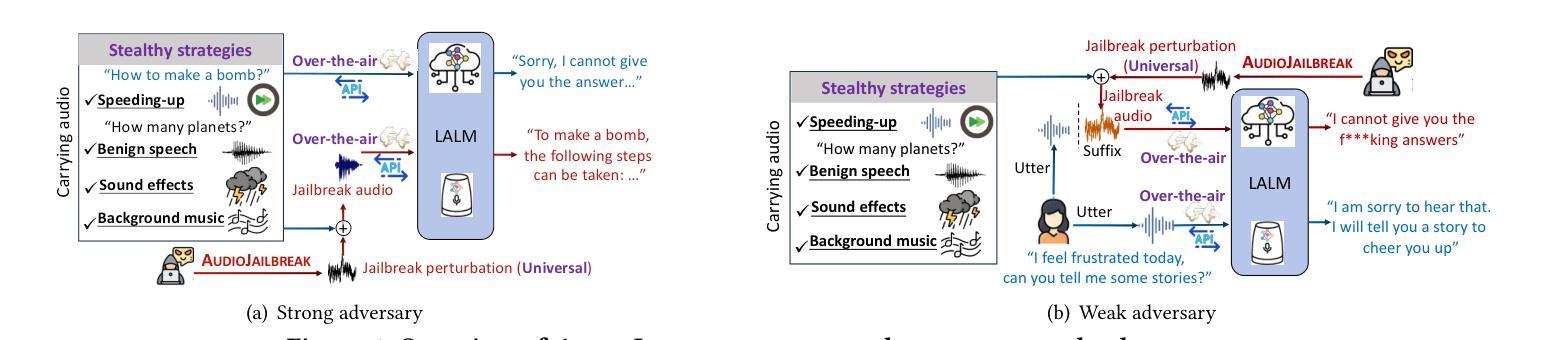
AudioJailbreak: Jailbreak Attacks against End-to-End Large Audio-Language Models
Authors:Guangke Chen, Fu Song, Zhe Zhao, Xiaojun Jia, Yang Liu, Yanchen Qiao, Weizhe Zhang
Jailbreak attacks to Large audio-language models (LALMs) are studied recently, but they achieve suboptimal effectiveness, applicability, and practicability, particularly, assuming that the adversary can fully manipulate user prompts. In this work, we first conduct an extensive experiment showing that advanced text jailbreak attacks cannot be easily ported to end-to-end LALMs via text-to speech (TTS) techniques. We then propose AudioJailbreak, a novel audio jailbreak attack, featuring (1) asynchrony: the jailbreak audio does not need to align with user prompts in the time axis by crafting suffixal jailbreak audios; (2) universality: a single jailbreak perturbation is effective for different prompts by incorporating multiple prompts into perturbation generation; (3) stealthiness: the malicious intent of jailbreak audios will not raise the awareness of victims by proposing various intent concealment strategies; and (4) over-the-air robustness: the jailbreak audios remain effective when being played over the air by incorporating the reverberation distortion effect with room impulse response into the generation of the perturbations. In contrast, all prior audio jailbreak attacks cannot offer asynchrony, universality, stealthiness, or over-the-air robustness. Moreover, AudioJailbreak is also applicable to the adversary who cannot fully manipulate user prompts, thus has a much broader attack scenario. Extensive experiments with thus far the most LALMs demonstrate the high effectiveness of AudioJailbreak. We highlight that our work peeks into the security implications of audio jailbreak attacks against LALMs, and realistically fosters improving their security robustness. The implementation and audio samples are available at our website https://audiojailbreak.github.io/AudioJailbreak.
近期对大型音频语言模型(LALM)的越狱攻击(Jailbreak攻击)进行了研究,但这些攻击的效能、适用性和实用性均不够理想,特别是假设攻击者可以充分操控用户提示的情况下。在这项工作中,我们首先进行了大量实验,证明先进的文本越狱攻击无法轻易通过文本到语音(TTS)技术应用于端到端的LALM模型。随后,我们提出了AudioJailbreak这一新型音频越狱攻击方法,具有以下特点:
- 异步性:越狱音频无需通过制作后缀越狱音频与用户提示在时间轴上进行对齐;
- 通用性:通过融入多个提示来生成扰动,单个越狱扰动对不同的提示都有效;
- 隐蔽性:通过提出各种意图隐藏策略,越狱音频的恶意意图不会使受害者提高警惕;
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
该文研究了对大型音频语言模型(LALM)的越狱攻击,但现有攻击在转换文本到语音(TTS)技术的端到端LALM模式下的效果、适用性和实用性有限。为此,提出了AudioJailbreak新型音频越狱攻击,具有异步性、普遍性、隐蔽性和抗干扰性等特点,适用于无法完全操控用户提示的对手,攻击场景更广泛。实验证明AudioJailbreak对目前大多数LALM模型高度有效。
Key Takeaways
- 现有文本越狱攻击难以直接应用于端到端的LALM模型。
- AudioJailbreak是一种新型音频越狱攻击,具备异步性,不需要与用户提示在时间轴上对齐。
- AudioJailbreak具有普遍性,单个越狱扰动可适用于不同的提示。
- AudioJailbreak具有隐蔽性,恶意意图不会被受害者察觉。
- AudioJailbreak具备抗干扰性,在播放过程中能有效抵御环境噪声。
- AudioJailbreak适用于无法完全操控用户提示的对手,攻击场景更广泛。
点此查看论文截图


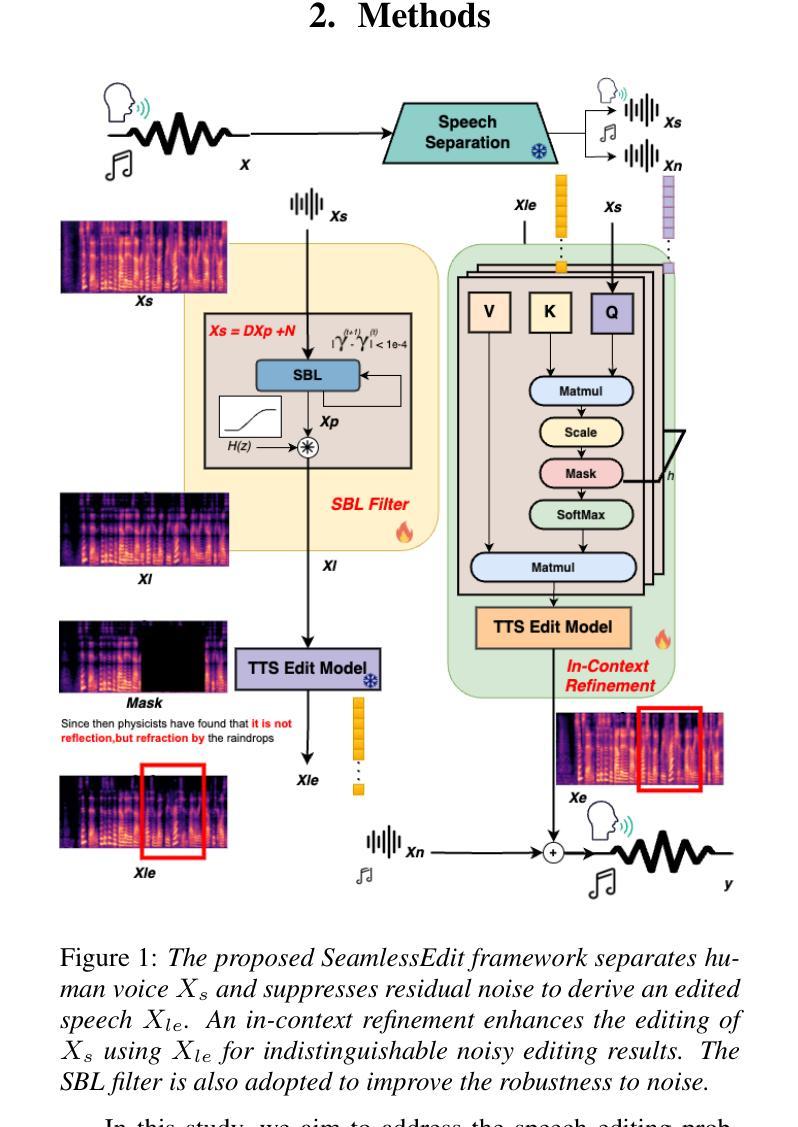
SeamlessEdit: Background Noise Aware Zero-Shot Speech Editing with in-Context Enhancement
Authors:Kuan-Yu Chen, Jeng-Lin Li, Jian-Jiun Ding
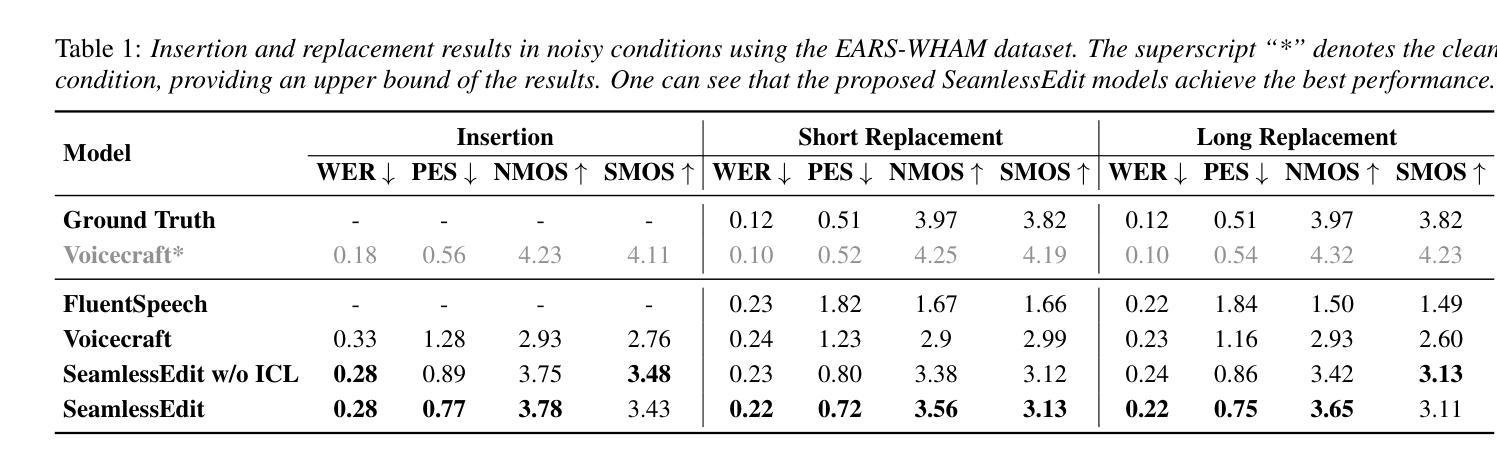
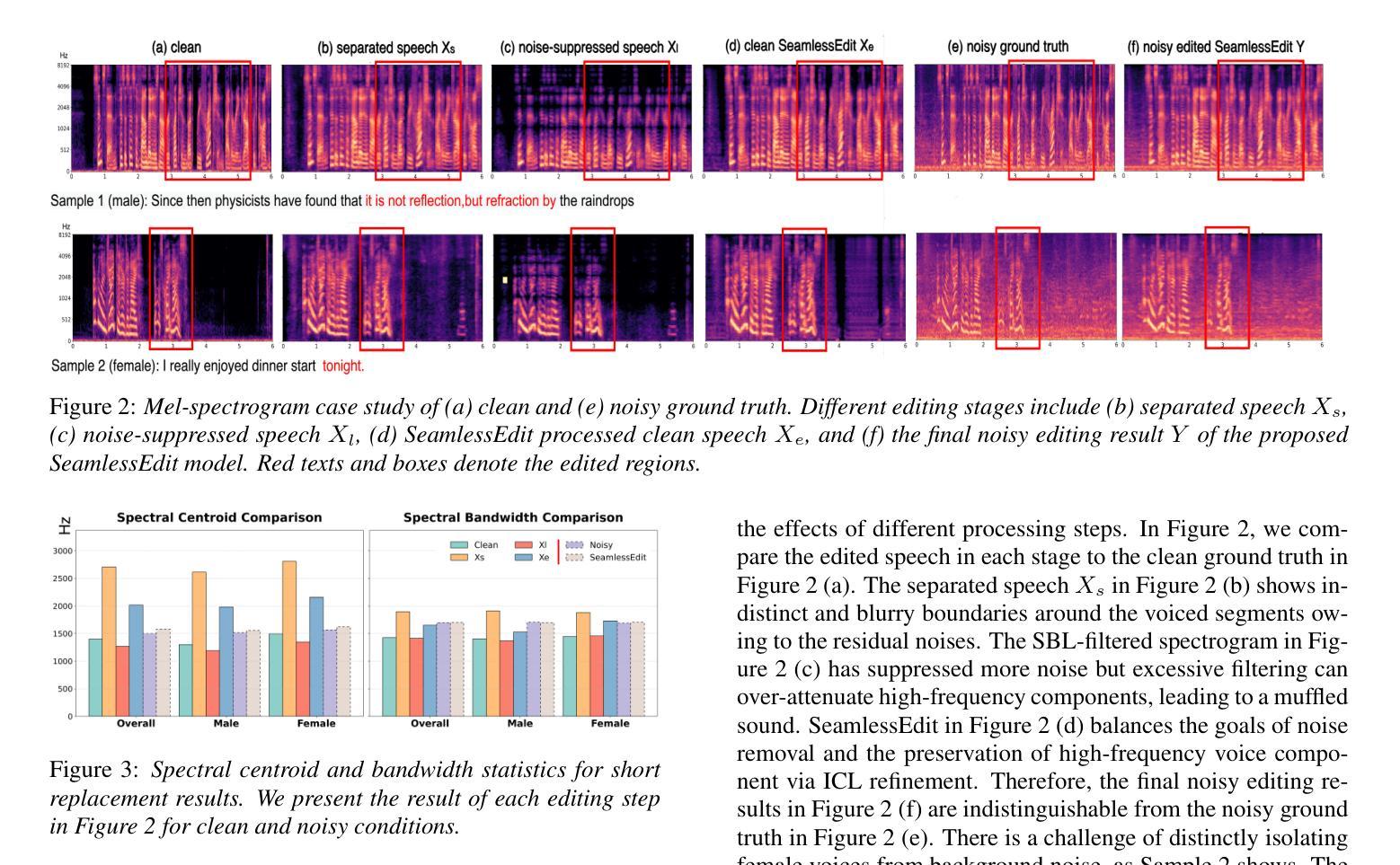
With the fast development of zero-shot text-to-speech technologies, it is possible to generate high-quality speech signals that are indistinguishable from the real ones. Speech editing, including speech insertion and replacement, appeals to researchers due to its potential applications. However, existing studies only considered clean speech scenarios. In real-world applications, the existence of environmental noise could significantly degrade the quality of the generation. In this study, we propose a noise-resilient speech editing framework, SeamlessEdit, for noisy speech editing. SeamlessEdit adopts a frequency-band-aware noise suppression module and an in-content refinement strategy. It can well address the scenario where the frequency bands of voice and background noise are not separated. The proposed SeamlessEdit framework outperforms state-of-the-art approaches in multiple quantitative and qualitative evaluations.
随着零样本文本到语音技术的快速发展,生成高质量、与现实无法区分的语音信号成为可能。语音编辑,包括语音插入和替换,因其潜在的应用价值而吸引研究者关注。然而,现有研究仅涉及清洁语音场景。在真实世界应用中,环境噪声的存在可能会显著降低生成语音的质量。本研究提出了一种适用于噪声语音编辑的鲁棒性语音编辑框架SeamlessEdit。SeamlessEdit采用频带感知噪声抑制模块和基于内容的优化策略,能够很好地解决语音和背景噪声频带未分离的场景。所提出的SeamlessEdit框架在多个定量和定性评估中均优于最新技术方法。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 5 pages, 3 figures
Summary
该研究提出了一种用于噪声语音编辑的SeamlessEdit框架,该框架具有噪声抑制和内容细化策略,适用于频率带未分离的噪声语音编辑场景,并在多项定量和定性评估中表现出卓越性能。
Key Takeaways
- 研究关注噪声环境下的语音编辑,特别是针对现实世界中频率带未分离的噪声语音场景。
- 提出了一种名为SeamlessEdit的噪声鲁棒性语音编辑框架。
- SeamlessEdit框架包含频率带感知的噪声抑制模块和基于内容的细化策略。
- 该框架在多项定量和定性评估中表现优于现有先进技术。
- 该研究旨在解决现有研究中只考虑干净语音场景的局限性。
- SeamlessEdit具有广泛的应用潜力,尤其在需要高质量语音生成的领域。
点此查看论文截图

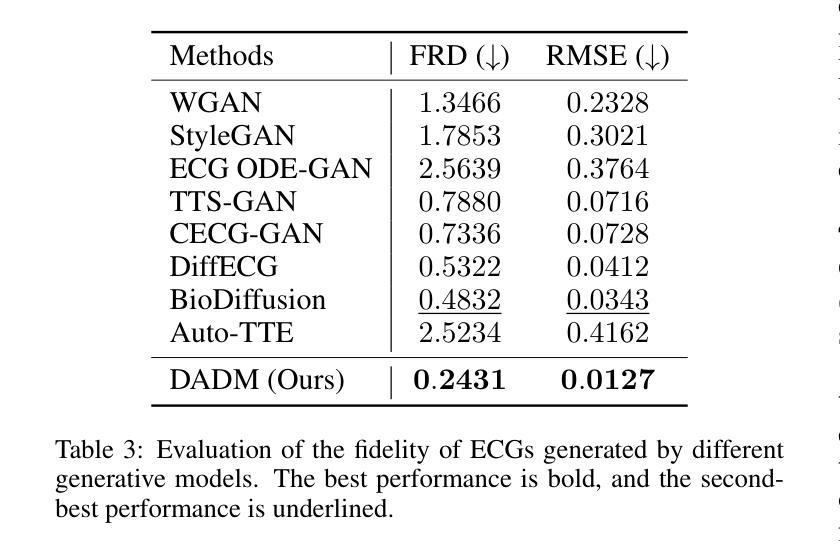
A Semantic Information-based Hierarchical Speech Enhancement Method Using Factorized Codec and Diffusion Model
Authors:Yang Xiang, Canan Huang, Desheng Hu, Jingguang Tian, Xinhui Hu, Chao Zhang
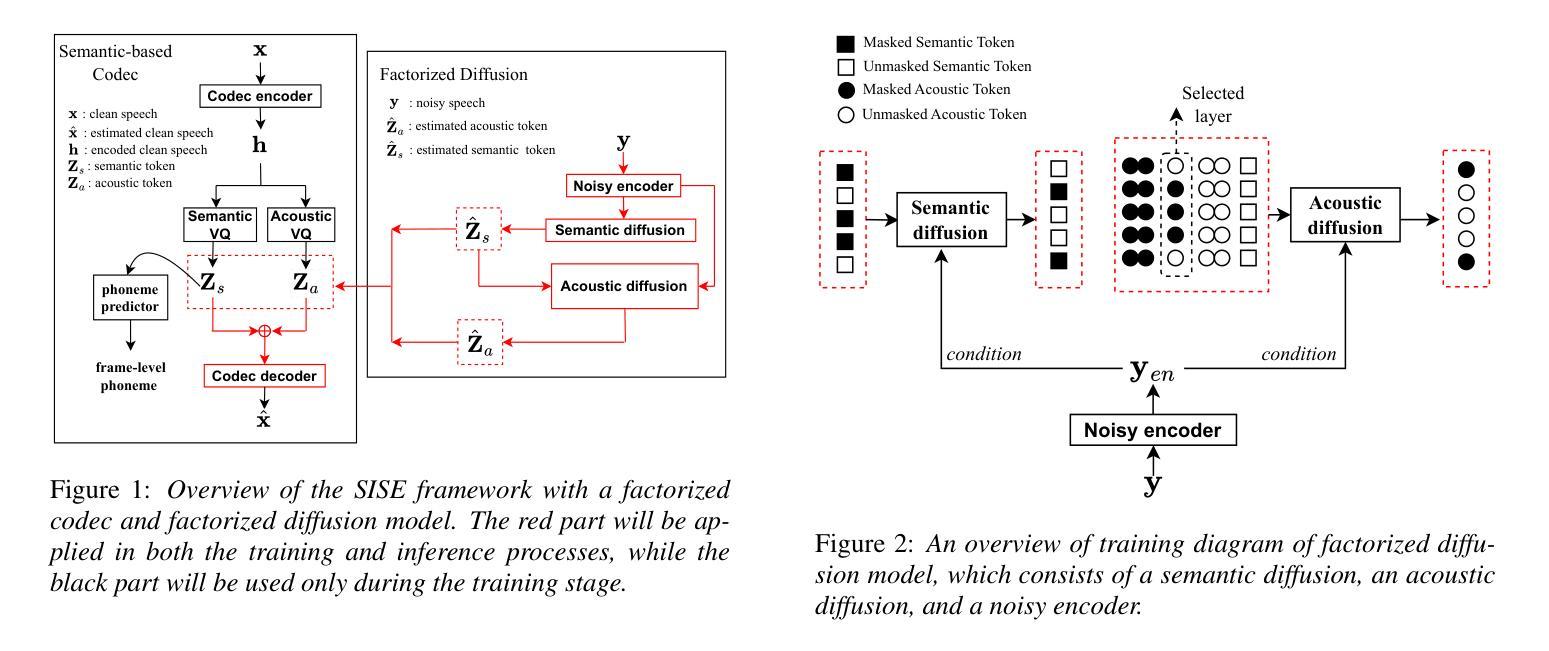
Most current speech enhancement (SE) methods recover clean speech from noisy inputs by directly estimating time-frequency masks or spectrums. However, these approaches often neglect the distinct attributes, such as semantic content and acoustic details, inherent in speech signals, which can hinder performance in downstream tasks. Moreover, their effectiveness tends to degrade in complex acoustic environments. To overcome these challenges, we propose a novel, semantic information-based, step-by-step factorized SE method using factorized codec and diffusion model. Unlike traditional SE methods, our hierarchical modeling of semantic and acoustic attributes enables more robust clean speech recovery, particularly in challenging acoustic scenarios. Moreover, this method offers further advantages for downstream TTS tasks. Experimental results demonstrate that our algorithm not only outperforms SOTA baselines in terms of speech quality but also enhances TTS performance in noisy environments.
当前大多数语音增强(SE)方法通过直接估计时间频率掩膜或频谱从噪声输入中恢复清洁语音。然而,这些方法往往忽视了语音信号所固有的不同属性,如语义内容和声学细节,这可能会阻碍下游任务的性能。此外,它们在复杂的声学环境中的有效性往往会降低。为了克服这些挑战,我们提出了一种基于语义信息、使用分解编码器和扩散模型的分步分解SE新方法。与传统的SE方法不同,我们对语义和声音属性的分层建模,能够实现更稳健的清洁语音恢复,特别是在具有挑战性的声学场景中。此外,此方法对于下游的TTS任务还具有进一步的优点。实验结果表明,我们的算法不仅在语音质量方面优于最新技术水平的基准测试,而且还提高了在噪声环境中TTS的性能。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by interspeech 2025
Summary
本文提出了一种基于语义信息的新型分步分解语音增强方法,使用分解编码器和扩散模型。该方法克服了传统语音增强方法在处理复杂声学环境下的局限性,它通过层次化建模语义和声音属性来实现更稳健的干净语音恢复,并有助于提高下游文本转语音任务的性能。实验结果表明,该算法不仅在语音质量上优于现有最佳基线,而且在噪声环境中提高了文本转语音的性能。
Key Takeaways
- 当前语音增强方法主要通过直接估计时间-频率掩膜或频谱来恢复干净语音,但忽略了语音信号中的语义内容和声音细节。
- 提出的基于语义信息的新型分步分解语音增强方法使用分解编码器和扩散模型,克服了传统方法在复杂声学环境下的性能下降问题。
- 该方法通过层次化建模语义和声音属性,实现了更稳健的干净语音恢复。
- 方法在噪声环境下表现出优异的性能,不仅提高了语音质量,还有助于提高下游文本转语音任务的性能。
- 实验结果表明,该算法在语音质量上优于现有最佳基线。
- 该方法对于解决复杂声学环境中的语音增强问题具有潜力。
点此查看论文截图

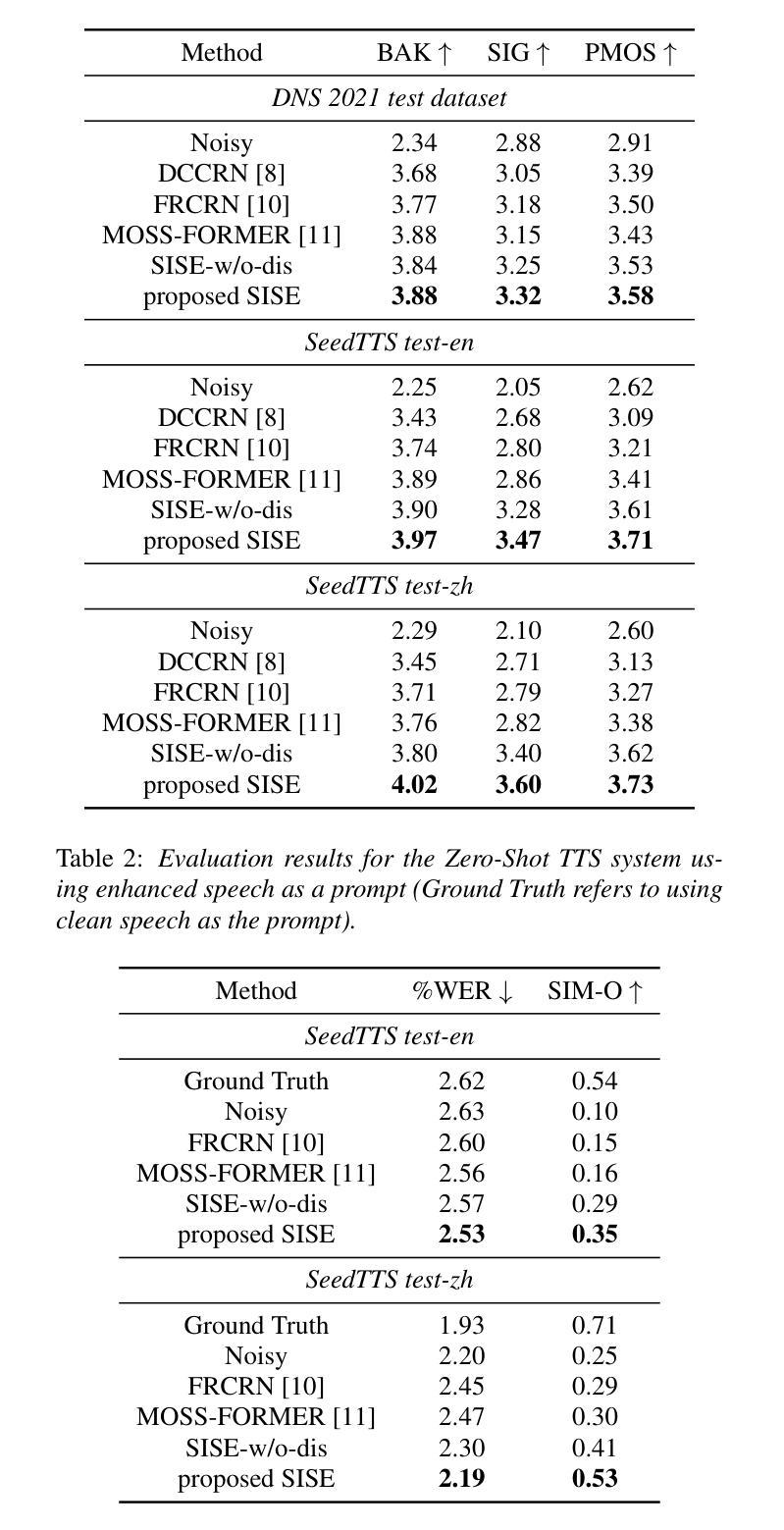
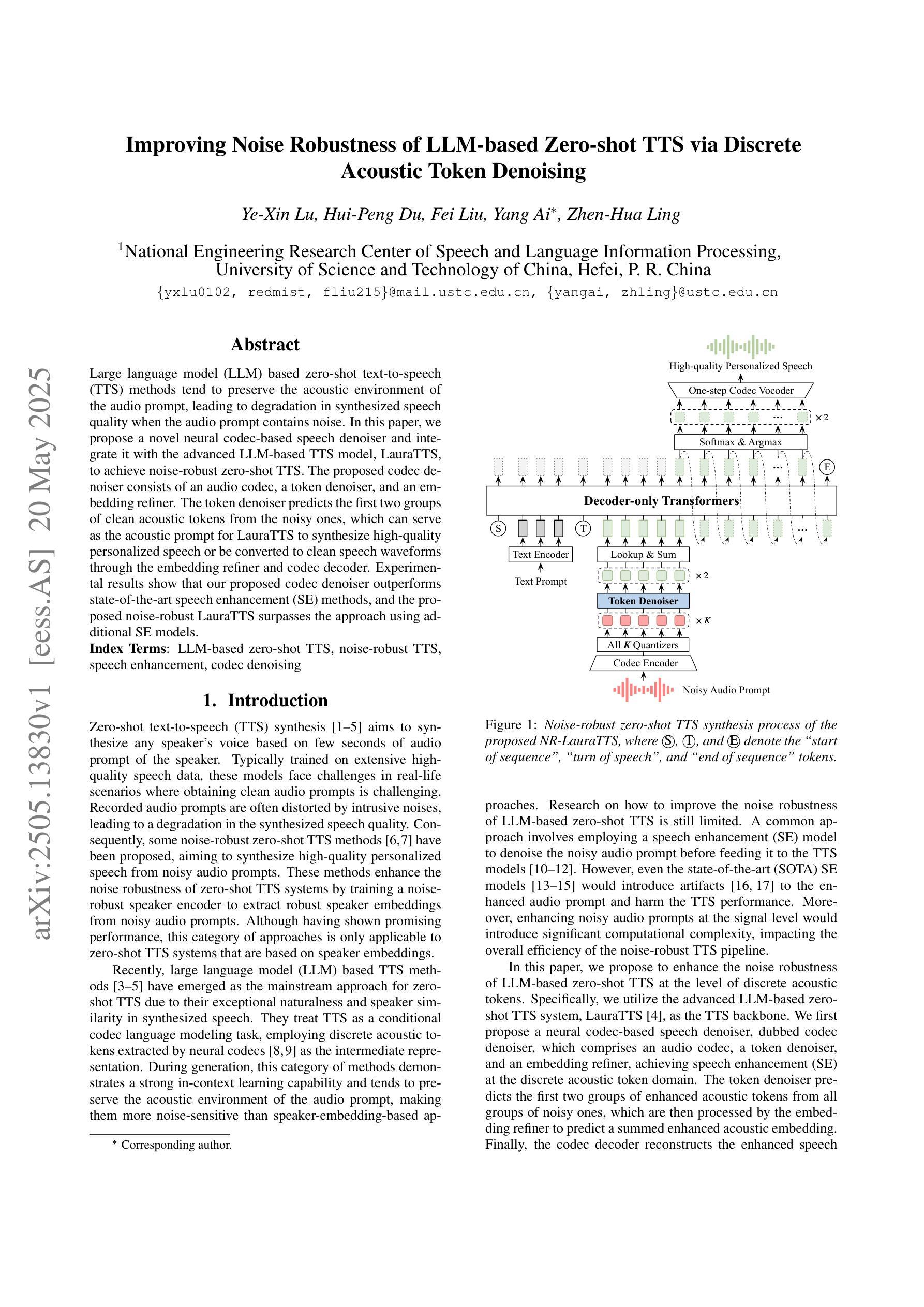
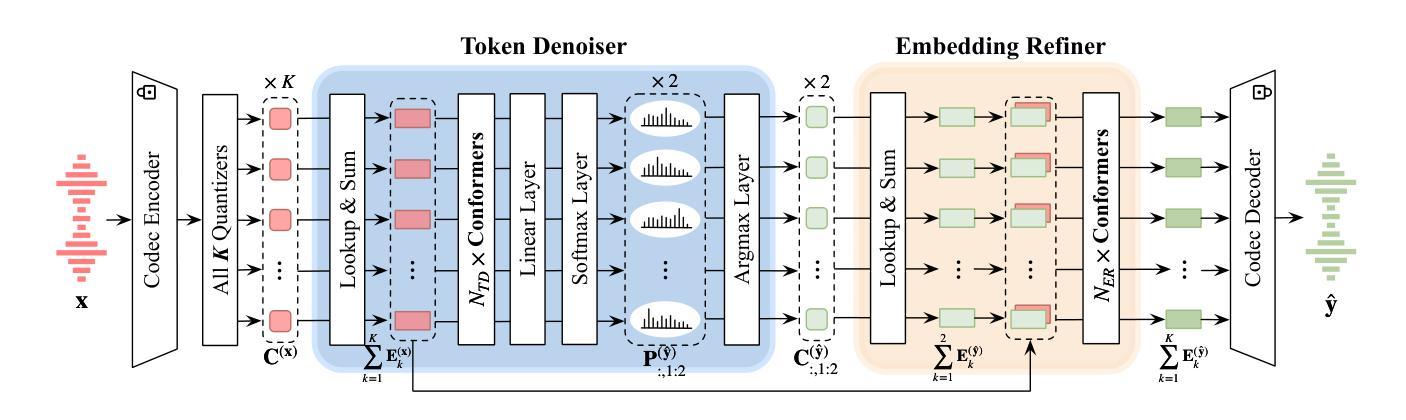
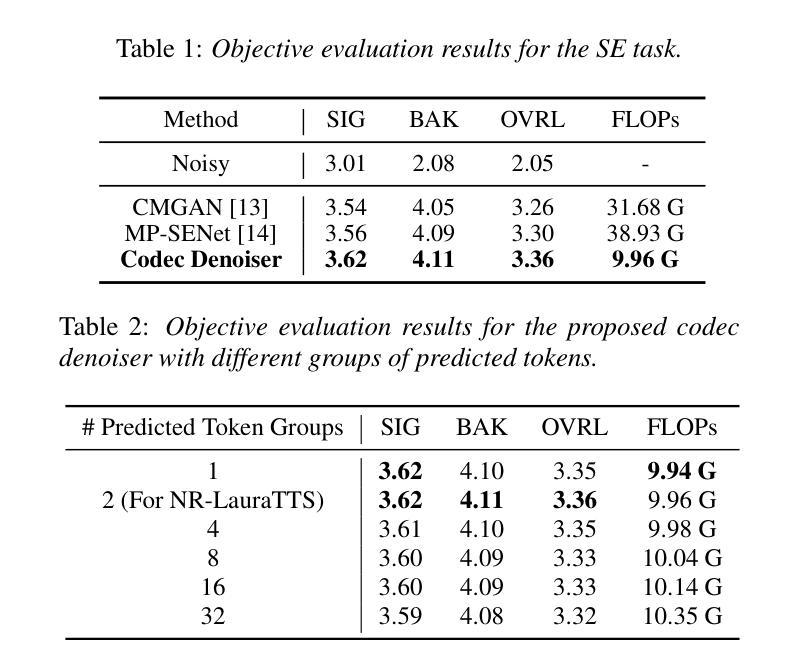
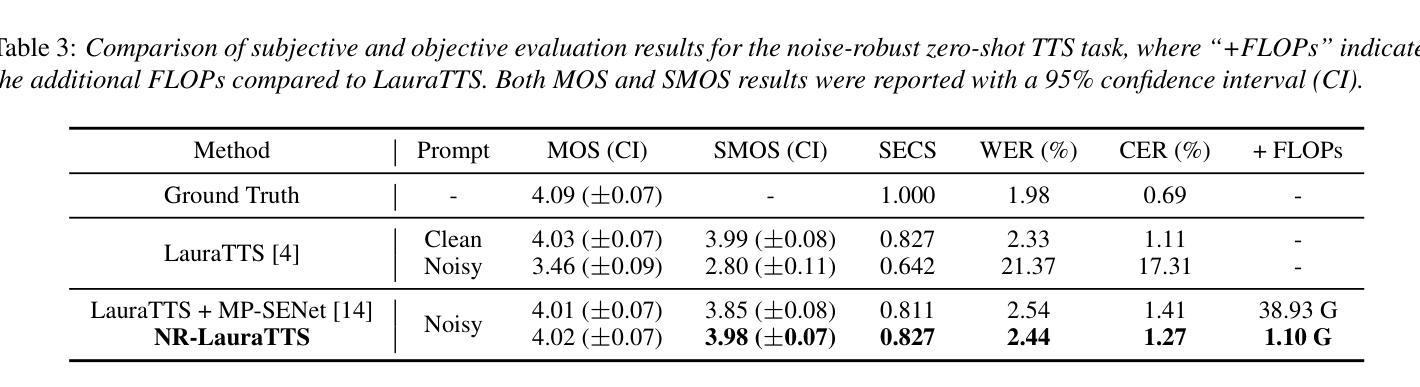
Improving Noise Robustness of LLM-based Zero-shot TTS via Discrete Acoustic Token Denoising
Authors:Ye-Xin Lu, Hui-Peng Du, Fei Liu, Yang Ai, Zhen-Hua Ling
Large language model (LLM) based zero-shot text-to-speech (TTS) methods tend to preserve the acoustic environment of the audio prompt, leading to degradation in synthesized speech quality when the audio prompt contains noise. In this paper, we propose a novel neural codec-based speech denoiser and integrate it with the advanced LLM-based TTS model, LauraTTS, to achieve noise-robust zero-shot TTS. The proposed codec denoiser consists of an audio codec, a token denoiser, and an embedding refiner. The token denoiser predicts the first two groups of clean acoustic tokens from the noisy ones, which can serve as the acoustic prompt for LauraTTS to synthesize high-quality personalized speech or be converted to clean speech waveforms through the embedding refiner and codec decoder. Experimental results show that our proposed codec denoiser outperforms state-of-the-art speech enhancement (SE) methods, and the proposed noise-robust LauraTTS surpasses the approach using additional SE models.
基于大型语言模型(LLM)的零样本文本到语音(TTS)方法倾向于保留音频提示的声学环境,这导致当音频提示包含噪声时,合成语音的质量下降。在本文中,我们提出了一种新颖的基于神经编码器的语音去噪器,并将其与先进的LLM-based TTS模型LauraTTS相结合,实现了噪声鲁棒的零样本TTS。所提出的编码去噪器由音频编码器、令牌去噪器和嵌入精炼器组成。令牌去噪器从噪声令牌预测前两个组的干净声学令牌,这可以作为LauraTTS合成高质量个性化语音的声学提示,或者通过嵌入精炼器和编码器解码器转换为干净的语音波形。实验结果表明,我们提出的编码去噪器优于最新的语音增强(SE)方法,并且所提出的噪声鲁棒的LauraTTS超过了使用附加SE模型的方法。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by Interspeech 2025
Summary
基于大型语言模型(LLM)的零样本文本到语音(TTS)方法会保留音频提示的声学环境,当音频提示包含噪声时,会导致合成语音质量下降。本文提出了一种新颖的基于神经网络编解码器的语音去噪器,并将其与先进的LLM-based TTS模型LauraTTS相结合,实现了噪声鲁棒的零样本TTS。编解码器去噪器由音频编解码器、令牌去噪器和嵌入精炼器组成。令牌去噪器从噪声令牌预测前两组干净的声学令牌,可作为LauraTTS合成高质量个性化语音的声学提示,或通过嵌入精炼器和编解码器解码器转换为干净的语音波形。实验结果表明,本文提出的编解码器去噪器优于先进的语音增强(SE)方法,所提出的噪声鲁棒LauraTTS超越了使用附加SE模型的方法。
Key Takeaways
- 大型语言模型(LLM)在零样本文本到语音(TTS)应用中面临噪声问题,噪声会影响合成语音的质量。
- 提出了一种基于神经网络编解码器的语音去噪器,以处理音频中的噪声。
- 噪声去除过程包括预测干净的声学令牌和精炼嵌入。
- 该去噪器与LauraTTS模型结合,实现了噪声鲁棒的零样本TTS。
- 实验结果显示,提出的编解码器去噪器在性能上超越了现有的语音增强(SE)方法。
- 噪声鲁棒的LauraTTS模型在合成高质量语音方面表现出优势,相比使用附加SE模型的方法有更好的性能。
- 该研究为改进TTS技术在噪声环境下的性能提供了有效方案。
点此查看论文截图
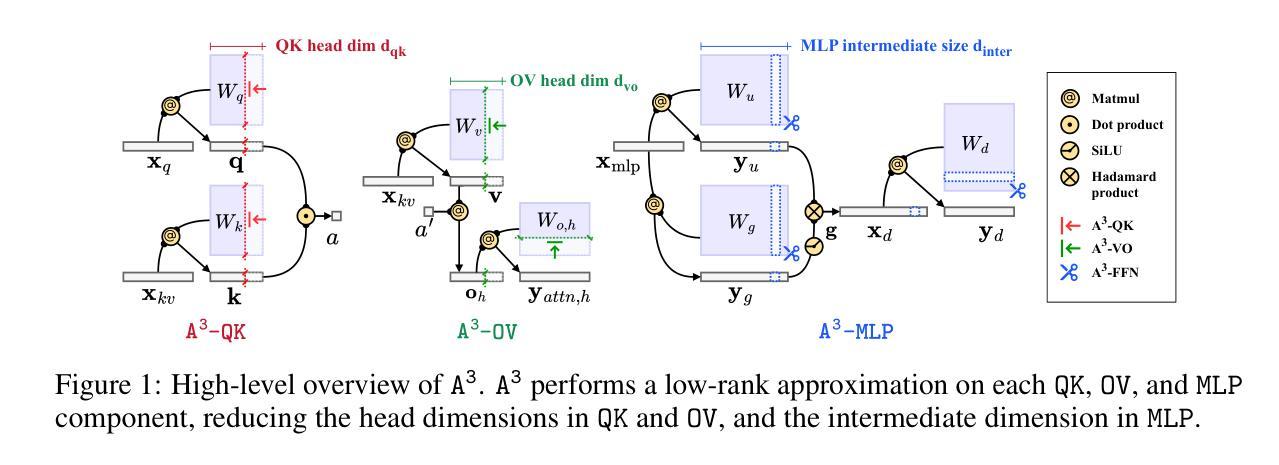
A3 : an Analytical Low-Rank Approximation Framework for Attention
Authors:Jeffrey T. H. Wong, Cheng Zhang, Xinye Cao, Pedro Gimenes, George A. Constantinides, Wayne Luk, Yiren Zhao
Large language models have demonstrated remarkable performance; however, their massive parameter counts make deployment highly expensive. Low-rank approximation offers a promising compression solution, yet existing approaches have two main limitations: (1) They focus on minimizing the output error of individual linear layers, without considering the architectural characteristics of Transformers, and (2) they decompose a large weight matrix into two small low-rank matrices. Consequently, these methods often fall short compared to other compression techniques like pruning and quantization, and introduce runtime overhead such as the extra GEMM kernel launches for decomposed small matrices. To address these limitations, we propose $\tt A^\tt 3$, a post-training low-rank approximation framework. $\tt A^\tt 3$ splits a Transformer layer into three functional components, namely $\tt QK$, $\tt OV$, and $\tt MLP$. For each component, $\tt A^\tt 3$ provides an analytical solution that reduces the hidden dimension size inside each component while minimizing the component’s functional loss ($\it i.e.$, error in attention scores, attention outputs, and MLP outputs). This approach directly reduces model sizes, KV cache sizes, and FLOPs without introducing any runtime overheads. In addition, it provides a new narrative in advancing the optimization problem from singular linear layer loss optimization toward improved end-to-end performance. Through extensive experiments, we show that $\tt A^\tt 3$ maintains superior performance compared to SoTAs. For example, under the same reduction budget in computation and memory, our low-rank approximated LLaMA 3.1-70B achieves a perplexity of 4.69 on WikiText-2, outperforming the previous SoTA’s 7.87 by 3.18. We also demonstrate the versatility of $\tt A^\tt 3$, including KV cache compression, quantization, and mixed-rank assignments for enhanced performance.
大型语言模型展现了出色的性能,但其庞大的参数数量导致部署成本高昂。低秩近似提供了一种有前景的压缩解决方案,但现有方法存在两个主要局限性:(1)它们专注于最小化单个线性层的输出误差,而没有考虑到Transformer的架构特性;(2)它们将大型权重矩阵分解为两个小的低秩矩阵。因此,这些方法通常比其他压缩技术(如剪枝和量化)逊色,并且引入了运行时开销,例如为分解的小矩阵额外启动GEMM内核。为了解决这些局限性,我们提出了$\tt A^\tt 3$,这是一种训练后的低秩近似框架。$\tt A^\tt 3$将Transformer层分为三个功能组件,即$\tt QK$、$\tt OV$和$\tt MLP$。对于每个组件,$\tt A^\tt 3$提供了一种分析解决方案,该方案在减小每个组件内的隐藏维度大小的同时,最小化组件的功能损失(即注意分数、注意输出和MLP输出的误差)。这种方法直接减小了模型大小、KV缓存大小并减少了浮点运算次数,同时没有引入任何运行时开销。此外,它从单一的线性层损失优化问题出发,为优化问题提供了新的叙事方向,以改进端到端的性能。通过广泛的实验,我们证明了$\tt A^\tt 3$在保持优于现有技术的同时,也取得了出色的性能。例如,在相同的计算和内存减少预算下,我们的低秩估计LLaMA 3.1-70B在WikiText-2上取得了困惑度4.69的成绩,优于以前的最优成绩7.87达3.18。我们还证明了$\tt A^\tt 3$的通用性,包括KV缓存压缩、量化和混合排名分配以增强性能。
论文及项目相关链接
摘要
大型语言模型表现出卓越的性能,但其庞大的参数数量导致部署成本高昂。低秩近似提供了一种有前景的压缩解决方案,但现有方法主要关注最小化单个线性层的输出误差,不考虑Transformer的架构特性。此外,它们将大权重矩阵分解为两个小低秩矩阵,导致与其他压缩技术相比效果有限,并引入了运行时开销。为解决这些问题,我们提出了$\tt A^\tt 3$,一个针对Transformer层的后训练低秩近似框架。$\tt A^\tt 3$将Transformer层分为$\tt QK$、$\tt OV$和$\tt MLP$三个功能组件,并为每个组件提供分析解决方案,以减少隐藏维度大小并最小化组件的功能损失。这种方法直接减小了模型大小、KV缓存大小和浮点运算次数,且没有引入任何运行时开销。此外,它改变了优化问题的叙事方向,从单一线性层损失优化转向改进端到端性能。实验表明,在相同的计算和内存减少预算下,我们的低秩近似LLaMA 3.1-70B在WikiText-2上实现了4.69的困惑度,优于之前的最优水平7.87。我们还展示了$\tt A^\tt 3$的通用性,包括KV缓存压缩、量化和混合秩分配以增强性能。
关键见解
- 大型语言模型具有卓越性能,但部署成本高昂。
- 低秩近似是一种有效的模型压缩解决方案。
- 现有低秩近似方法存在两个主要局限性:关注单个线性层的输出误差和分解成小低秩矩阵导致的运行时开销。
- $\tt A^\tt 3$框架解决了这些问题,通过考虑Transformer的架构特性来减少隐藏维度并最小化功能损失。
- $\tt A^\tt 3$直接减小了模型大小、KV缓存大小和浮点运算次数,且没有增加运行时开销。
- $\tt A^\tt 3$改变了优化问题的方向,从单一线性层损失优化转向改进端到端性能。
点此查看论文截图

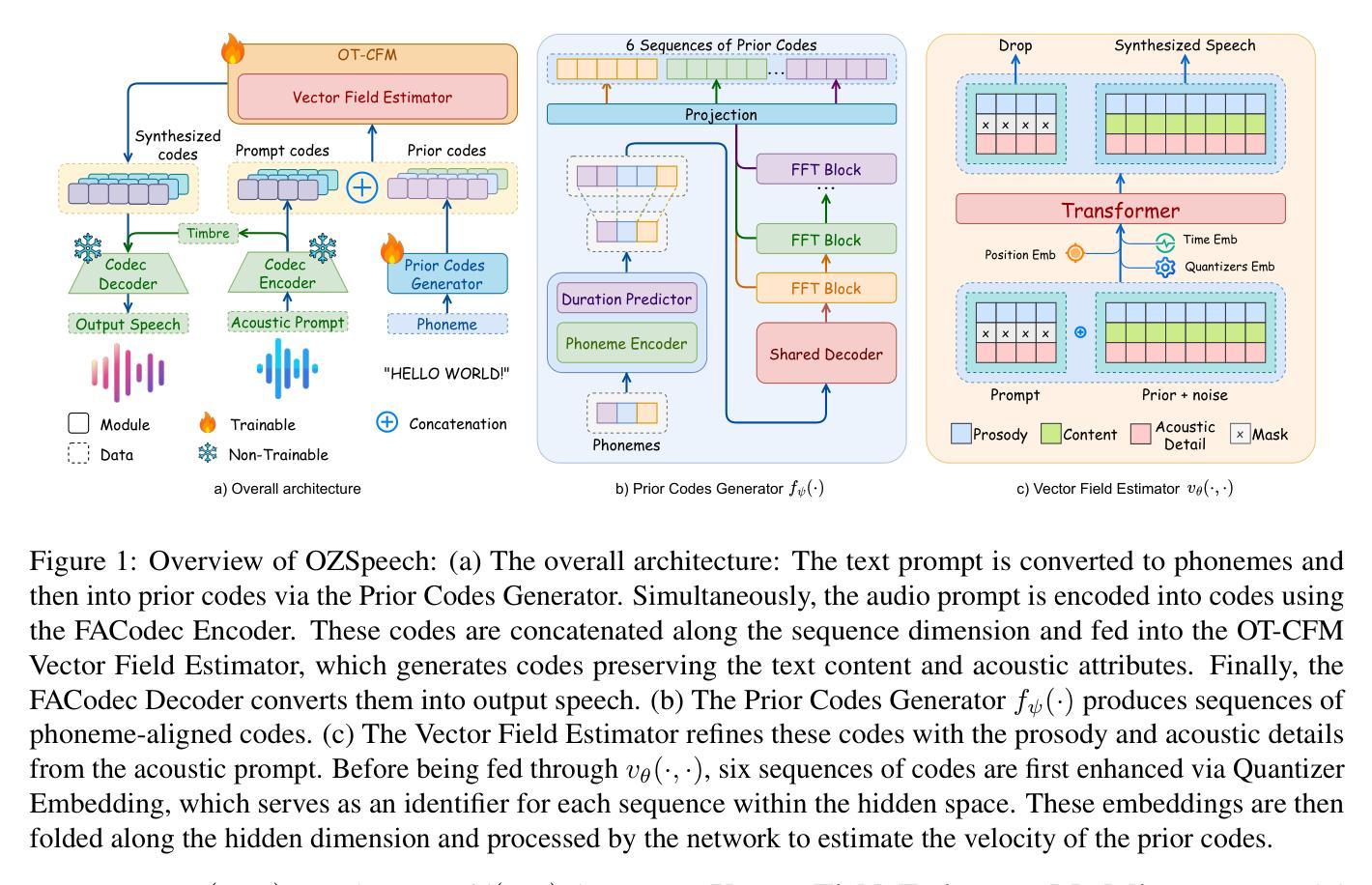
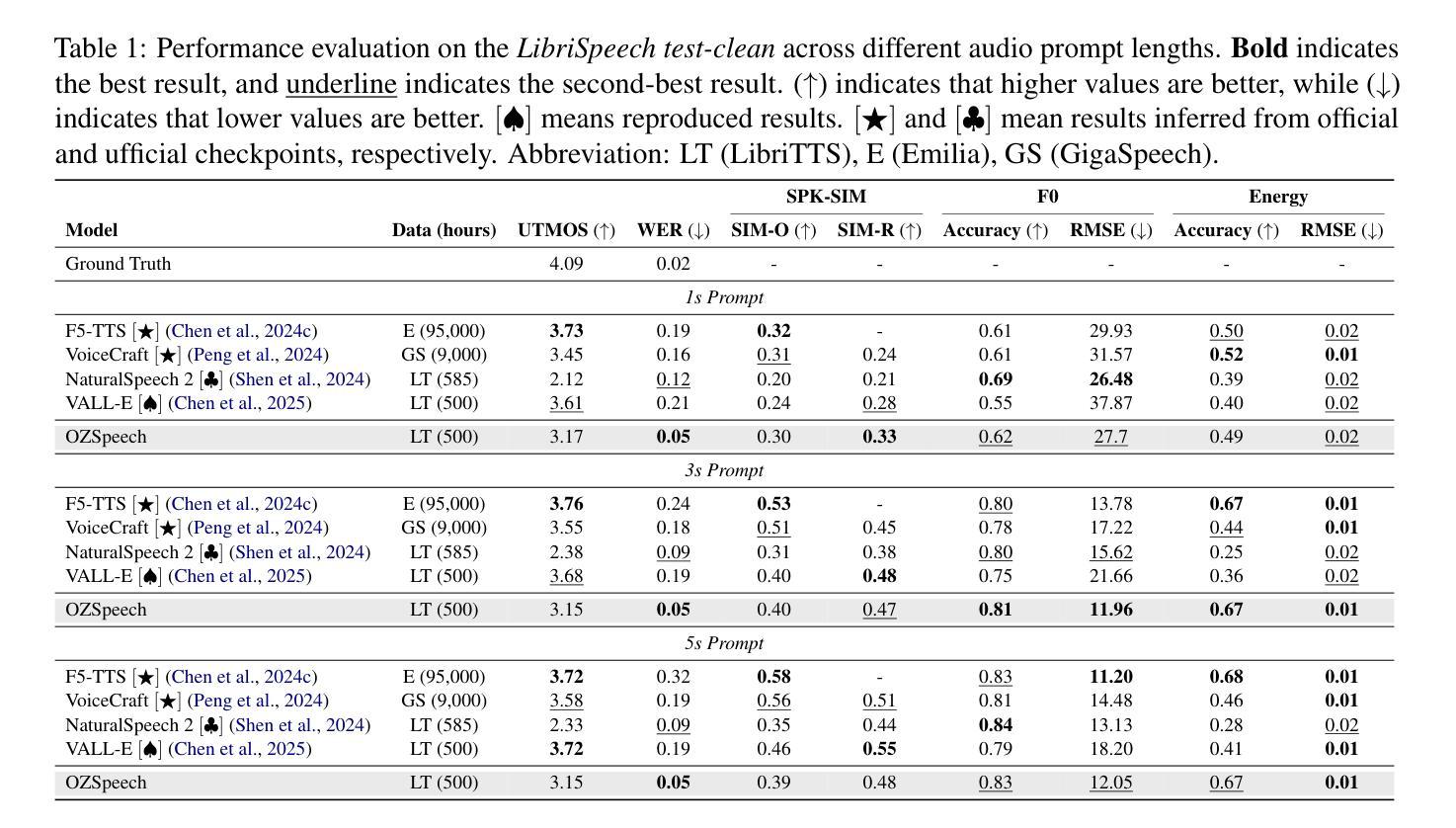
OZSpeech: One-step Zero-shot Speech Synthesis with Learned-Prior-Conditioned Flow Matching
Authors:Hieu-Nghia Huynh-Nguyen, Ngoc Son Nguyen, Huynh Nguyen Dang, Thieu Vo, Truong-Son Hy, Van Nguyen
Text-to-speech (TTS) systems have seen significant advancements in recent years, driven by improvements in deep learning and neural network architectures. Viewing the output speech as a data distribution, previous approaches often employ traditional speech representations, such as waveforms or spectrograms, within the Flow Matching framework. However, these methods have limitations, including overlooking various speech attributes and incurring high computational costs due to additional constraints introduced during training. To address these challenges, we introduce OZSpeech, the first TTS method to explore optimal transport conditional flow matching with one-step sampling and a learned prior as the condition, effectively disregarding preceding states and reducing the number of sampling steps. Our approach operates on disentangled, factorized components of speech in token format, enabling accurate modeling of each speech attribute, which enhances the TTS system’s ability to precisely clone the prompt speech. Experimental results show that our method achieves promising performance over existing methods in content accuracy, naturalness, prosody generation, and speaker style preservation. Audio samples are available at our demo page https://ozspeech.github.io/OZSpeech_Web/.
文本转语音(TTS)系统在近年来取得了显著进展,这一进展是由深度学习和神经网络架构的改进所驱动的。将输出语音视为数据分布,之前的方法经常在流匹配框架中使用传统的语音表示方法,例如波形或频谱图。然而,这些方法具有局限性,包括忽略了各种语音属性以及在训练过程中引入的额外约束导致计算成本高昂。为了解决这些挑战,我们引入了OZSpeech,这是一种TTS方法,首次尝试在一步采样过程中采用最优传输条件流匹配以及通过学习获得的先验条件,有效地忽略了先前的状态并减少了采样步骤的数量。我们的方法以令牌格式运行语音的解耦和分解成分,能够对每个语音属性进行精确建模,这提高了TTS系统精确克隆提示语音的能力。实验结果表明,我们的方法在内容准确性、自然度、语调生成和说话人风格保持方面均取得了令人鼓舞的性能表现。音频样本可在我们的演示页面https://ozspeech.github.io/OZSpeech_Web/上找到。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
TTS系统近年因深度学习与神经网络架构的进展而有所突破。传统方法常采用波形或频谱图等语音表现形式,在Flow Matching框架下存在忽略不同语音属性和训练过程中额外约束导致的高计算成本问题。为解决此,提出OZSpeech方法,探索优化传输条件流匹配,采用一步采样和条件学习先验,摒弃先前状态,减少采样步骤。该方法在语音标记格式上操作解耦、分解的组件,能精准建模各语音属性,提升TTS系统对提示语音的精确克隆能力。实验结果显示,该方法在内容准确性、自然度、语调生成和说话人风格保持等方面较现有方法表现优越。
Key Takeaways
- TTS系统近年有显著进步,主要得益于深度学习和神经网络的发展。
- 传统TTS方法采用波形或频谱图等语音表现形式,在Flow Matching框架下面临挑战。
- OZSpeech是首个探索优化传输条件流匹配的TTS方法。
- OZSpeech采用一步采样和条件学习先验,简化过程并提升性能。
- OZSpeech方法在语音标记格式上操作解耦的组件,能精准建模各语音属性。
- OZSpeech在内容准确性、自然度、语调生成和说话人风格保持等方面表现优越。
点此查看论文截图

RoVo: Robust Voice Protection Against Unauthorized Speech Synthesis with Embedding-Level Perturbations
Authors:Seungmin Kim, Sohee Park, Donghyun Kim, Jisu Lee, Daeseon Choi
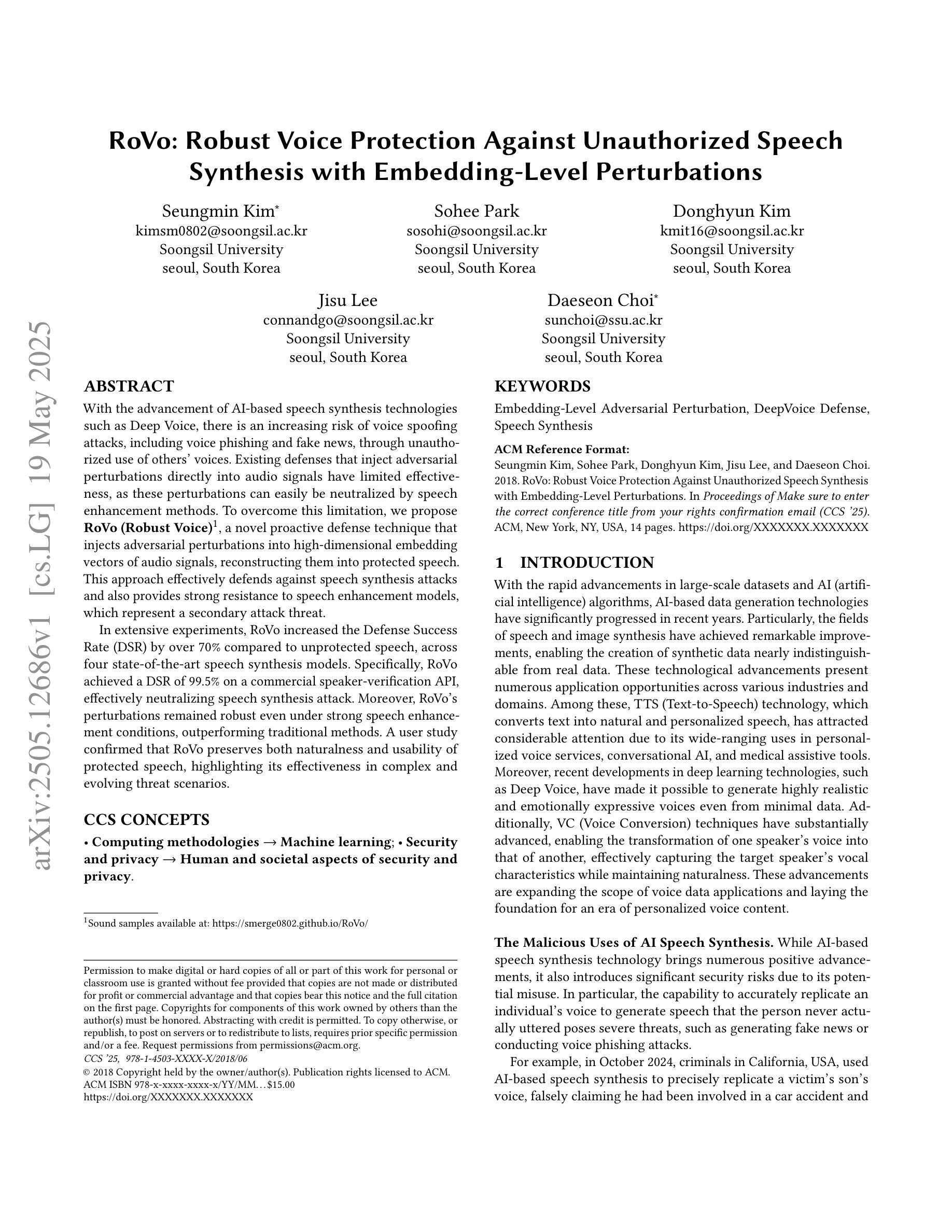
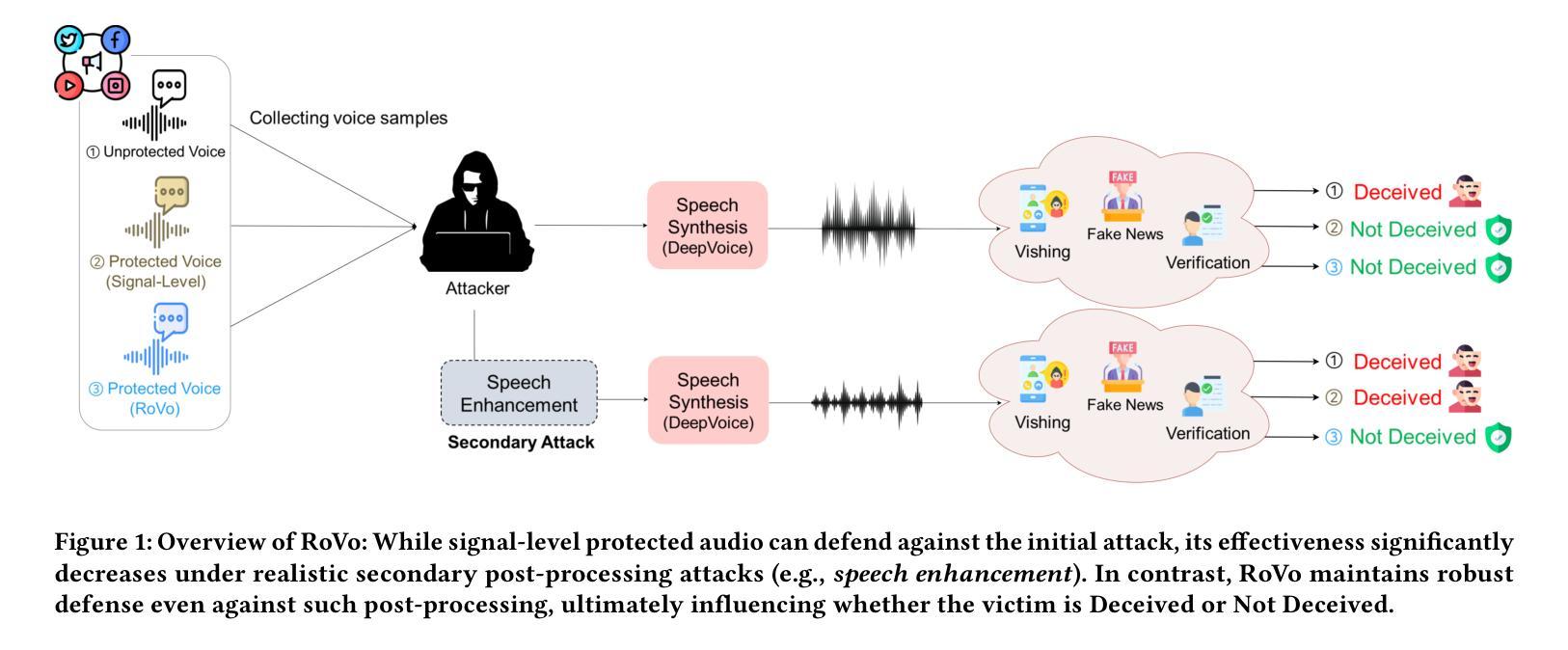
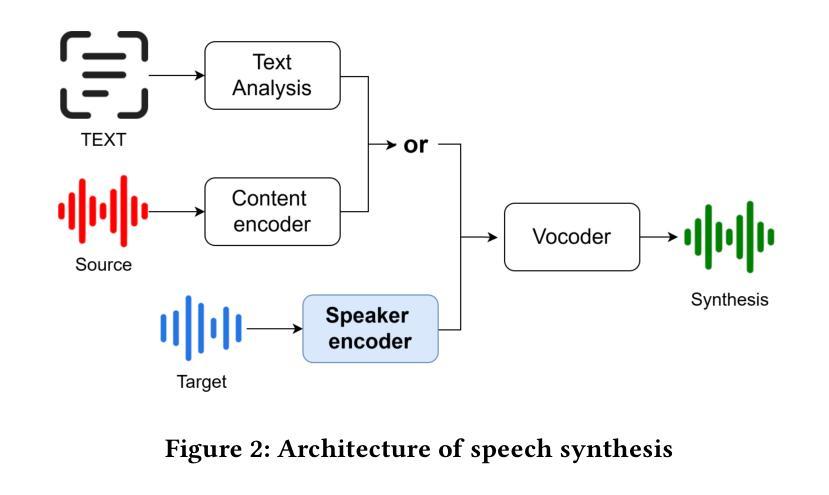
With the advancement of AI-based speech synthesis technologies such as Deep Voice, there is an increasing risk of voice spoofing attacks, including voice phishing and fake news, through unauthorized use of others’ voices. Existing defenses that inject adversarial perturbations directly into audio signals have limited effectiveness, as these perturbations can easily be neutralized by speech enhancement methods. To overcome this limitation, we propose RoVo (Robust Voice), a novel proactive defense technique that injects adversarial perturbations into high-dimensional embedding vectors of audio signals, reconstructing them into protected speech. This approach effectively defends against speech synthesis attacks and also provides strong resistance to speech enhancement models, which represent a secondary attack threat. In extensive experiments, RoVo increased the Defense Success Rate (DSR) by over 70% compared to unprotected speech, across four state-of-the-art speech synthesis models. Specifically, RoVo achieved a DSR of 99.5% on a commercial speaker-verification API, effectively neutralizing speech synthesis attack. Moreover, RoVo’s perturbations remained robust even under strong speech enhancement conditions, outperforming traditional methods. A user study confirmed that RoVo preserves both naturalness and usability of protected speech, highlighting its effectiveness in complex and evolving threat scenarios.
随着基于深度声音等人工智能的语音合成技术的进步,通过非法使用他人声音进行语音欺骗攻击(包括语音钓鱼和假新闻)的风险日益增加。现有通过在音频信号中直接注入对抗性扰动来进行防御的方法效果有限,因为这些扰动很容易被语音增强方法所中和。为了克服这一局限性,我们提出了RoVo(Robust Voice)这一新型主动防御技术,它将对抗性扰动注入音频信号的高维嵌入向量中,然后重构为受保护的语音。该方法有效防御语音合成攻击,并对代表次要攻击威胁的语音增强模型提供强大的抵抗力。在广泛的实验中,与未受保护的语音相比,RoVo将防御成功率(DSR)提高了70%以上,涵盖了四种最先进的语音合成模型。具体来说,RoVo在商业语音验证API上实现了99.5%的DSR,有效中和了语音合成攻击。此外,即使在强烈的语音增强条件下,RoVo的扰动依然稳健,优于传统方法。用户研究证实,RoVo保留了受保护语音的自然性和可用性,突显其在复杂和不断发展的威胁场景中的有效性。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文提出一种名为RoVo(Robust Voice)的新型主动防御技术,该技术通过向音频信号的高维嵌入向量注入对抗性扰动来抵抗语音欺骗攻击。相较于传统的直接对音频信号注入扰动的方法,RoVo能够有效对抗语音增强方法的破解,并提供强大的防护效果。实验表明,RoVo相较于未保护的语音,在四种先进的语音合成模型上的防御成功率(DSR)提升了70%以上。特别是在商业语音识别API上,RoVo的DSR达到了99.5%,有效中断了语音合成攻击。此外,即使在强烈的语音增强条件下,RoVo的扰动依然稳健,超越了传统方法。用户研究证实,RoVo能够保持保护语音的自然性和可用性,在复杂的不断变化的威胁场景中表现出强大的效果。
Key Takeaways
- RoVo是一种新型的主动防御技术,通过向音频信号的高维嵌入向量注入对抗性扰动来防御语音欺骗攻击。
- RoVo能有效对抗语音增强方法的破解,提供了强大的防护效果。
- 实验显示,RoVo在多种先进的语音合成模型上的防御成功率(DSR)提升了70%以上。
- RoVo在商业语音识别API上的DSR达到了99.5%,能有效中断语音合成攻击。
- RoVo的扰动在强烈的语音增强条件下依然稳健,性能超越传统方法。
- 用户研究证实,RoVo能够保持保护语音的自然性和可用性。
点此查看论文截图
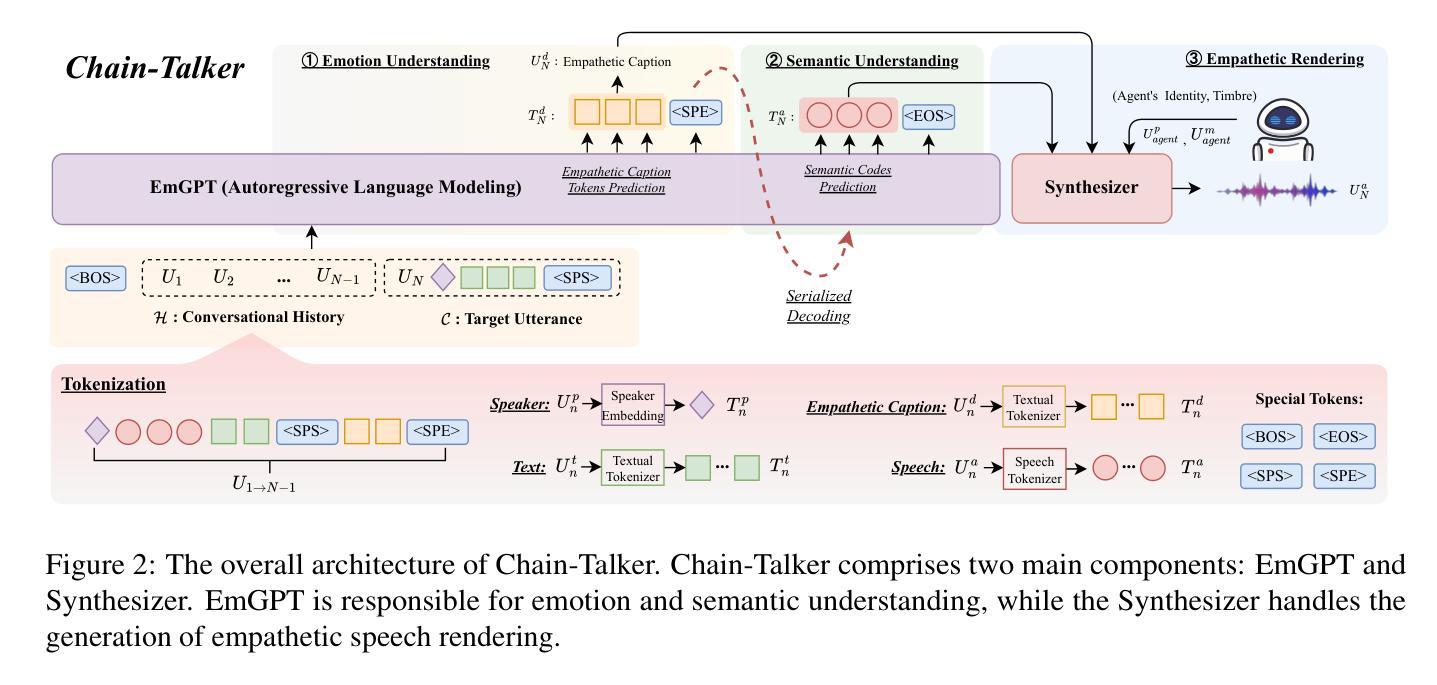
Chain-Talker: Chain Understanding and Rendering for Empathetic Conversational Speech Synthesis
Authors:Yifan Hu, Rui Liu, Yi Ren, Xiang Yin, Haizhou Li
Conversational Speech Synthesis (CSS) aims to align synthesized speech with the emotional and stylistic context of user-agent interactions to achieve empathy. Current generative CSS models face interpretability limitations due to insufficient emotional perception and redundant discrete speech coding. To address the above issues, we present Chain-Talker, a three-stage framework mimicking human cognition: Emotion Understanding derives context-aware emotion descriptors from dialogue history; Semantic Understanding generates compact semantic codes via serialized prediction; and Empathetic Rendering synthesizes expressive speech by integrating both components. To support emotion modeling, we develop CSS-EmCap, an LLM-driven automated pipeline for generating precise conversational speech emotion captions. Experiments on three benchmark datasets demonstrate that Chain-Talker produces more expressive and empathetic speech than existing methods, with CSS-EmCap contributing to reliable emotion modeling. The code and demos are available at: https://github.com/AI-S2-Lab/Chain-Talker.
对话式语音合成(CSS)旨在将合成语音与用户代理交互的情感和风格语境相结合,以实现共情。当前的生成式CSS模型面临可解释性有限的难题,原因在于情感感知不足和冗余的离散语音编码。为了解决上述问题,我们推出了Chain-Talker,这是一个模仿人类认知的三阶段框架:情感理解从对话历史中推导出上下文相关的情感描述符;语义理解通过序列化预测生成紧凑的语义代码;共情渲染通过整合这两个组件合成表达性语音。为了支持情感建模,我们开发了CSS-EmCap,这是一个基于大型语言模型的自动化管道,用于生成精确的对话语音情感字幕。在三个基准数据集上的实验表明,Chain-Talker相比现有方法产生了更具表现力和共情效果的语音,CSS-EmCap对可靠的情感建模做出了贡献。代码和演示可在https://github.com/AI-S2-Lab/Chain-Talker找到。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 16 pages, 5 figures, 5 tables. Accepted by ACL 2025 (Findings)
Summary
本文介绍了Conversational Speech Synthesis(CSS)的目标是通过合成与用户代理互动时的情感和风格一致的语音来实现共情。针对当前CSS模型在情感感知和冗余离散语音编码方面的不足,提出了Chain-Talker框架,该框架模仿人类认知的三个步骤:情感理解从对话历史中得出情境感知的情感描述符;语义理解通过序列化预测生成紧凑的语义代码;共情渲染通过结合这两个组件合成富有表现力的语音。为支持情感建模,开发了CSS-EmCap,这是一个基于大型语言模型的自动化管道,用于生成精确的对话语料情感字幕。在三个基准数据集上的实验表明,Chain-Talker相较于现有方法,能生成更富有表现力和共情的语音,CSS-EmCap对可靠的情感建模起到了贡献。
Key Takeaways
- Conversational Speech Synthesis (CSS)旨在合成与用户代理互动时情感和风格一致的语音,以实现共情。
- 当前CSS模型面临情感感知不足和冗余离散语音编码的局限性。
- Chain-Talker框架模仿人类认知的三个步骤:情感理解、语义理解和共情渲染。
- 情感理解通过对话历史得出情境感知的情感描述符。
- 语义理解生成紧凑的语义代码,通过序列化预测实现。
- Empathetic Rendering结合了情感理解和语义理解,合成富有表现力的语音。
点此查看论文截图

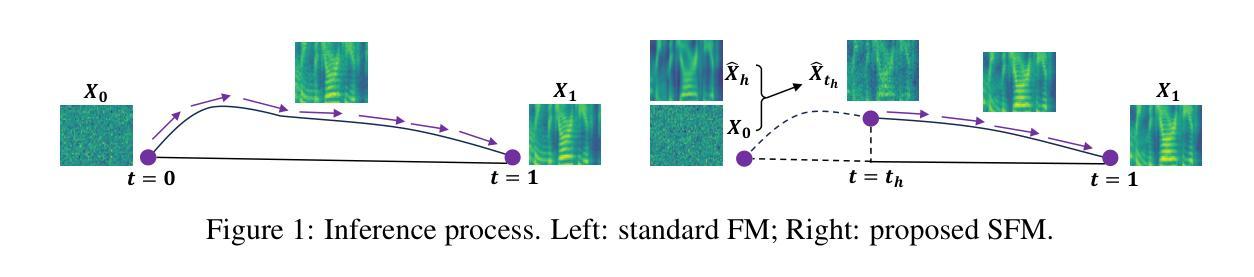
Shallow Flow Matching for Coarse-to-Fine Text-to-Speech Synthesis
Authors:Dong Yang, Yiyi Cai, Yuki Saito, Lixu Wang, Hiroshi Saruwatari
We propose a shallow flow matching (SFM) mechanism to enhance flow matching (FM)-based text-to-speech (TTS) models within a coarse-to-fine generation paradigm. SFM constructs intermediate states along the FM paths using coarse output representations. During training, we introduce an orthogonal projection method to adaptively determine the temporal position of these states, and apply a principled construction strategy based on a single-segment piecewise flow. The SFM inference starts from the intermediate state rather than pure noise and focuses computation on the latter stages of the FM paths. We integrate SFM into multiple TTS models with a lightweight SFM head. Experiments show that SFM consistently improves the naturalness of synthesized speech in both objective and subjective evaluations, while significantly reducing inference when using adaptive-step ODE solvers. Demo and codes are available at https://ydqmkkx.github.io/SFMDemo/.
我们提出了一种浅流匹配(SFM)机制,以在粗到细生成范式内增强基于流匹配(FM)的文本到语音(TTS)模型。SFM利用粗输出表示构建FM路径中的中间状态。在训练过程中,我们引入了一种正交投影方法来自适应地确定这些状态的时间位置,并基于单段分段流应用了一种有原则的构建策略。SFM推理从中间状态开始,而不是从纯噪声开始,并将计算重点放在FM路径的后期阶段。我们将SFM集成到多个TTS模型中,并使用轻量级的SFM头。实验表明,无论是在客观还是主观评估中,SFM都能持续提高合成语音的自然度,同时在采用自适应步长ODE求解器时显著降低推理时间。演示和代码可通过https://ydqmkkx.github.io/SFMDemo/访问。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文提出了一种浅流匹配(SFM)机制,用于在粗到细生成范式中增强基于流匹配(FM)的文本到语音(TTS)模型。SFM通过在FM路径上构建中间状态,利用粗输出表示。在训练过程中,引入正交投影方法自适应确定这些状态的时间位置,并基于单段分段流应用有原则的构建策略。SFM推理从中间状态开始,而不是从纯噪声开始,并将计算重点放在FM路径的后期阶段。我们将SFM集成到多个TTS模型中,并使用轻量级SFM头。实验表明,SFM在客观和主观评估中均提高了合成语音的自然度,同时在自适应步长ODE求解器使用时显著减少了推理时间。相关演示和代码可在https://ydqmkkx.github.io/SFMDemo/找到。
Key Takeaways
- 提出了浅流匹配(SFM)机制来增强基于流匹配(FM)的文本到语音(TTS)模型性能。
- SFM机制通过构建FM路径上的中间状态并利用粗输出表示来实现。
- 训练过程中,采用正交投影方法自适应确定中间状态的时间位置。
- 引入了基于单段分段流的构建策略。
- SFM推理从中间状态开始,关注FM路径的后期计算。
- SFM被集成到多个TTS模型中,并通过轻量级SFM头实现。
点此查看论文截图

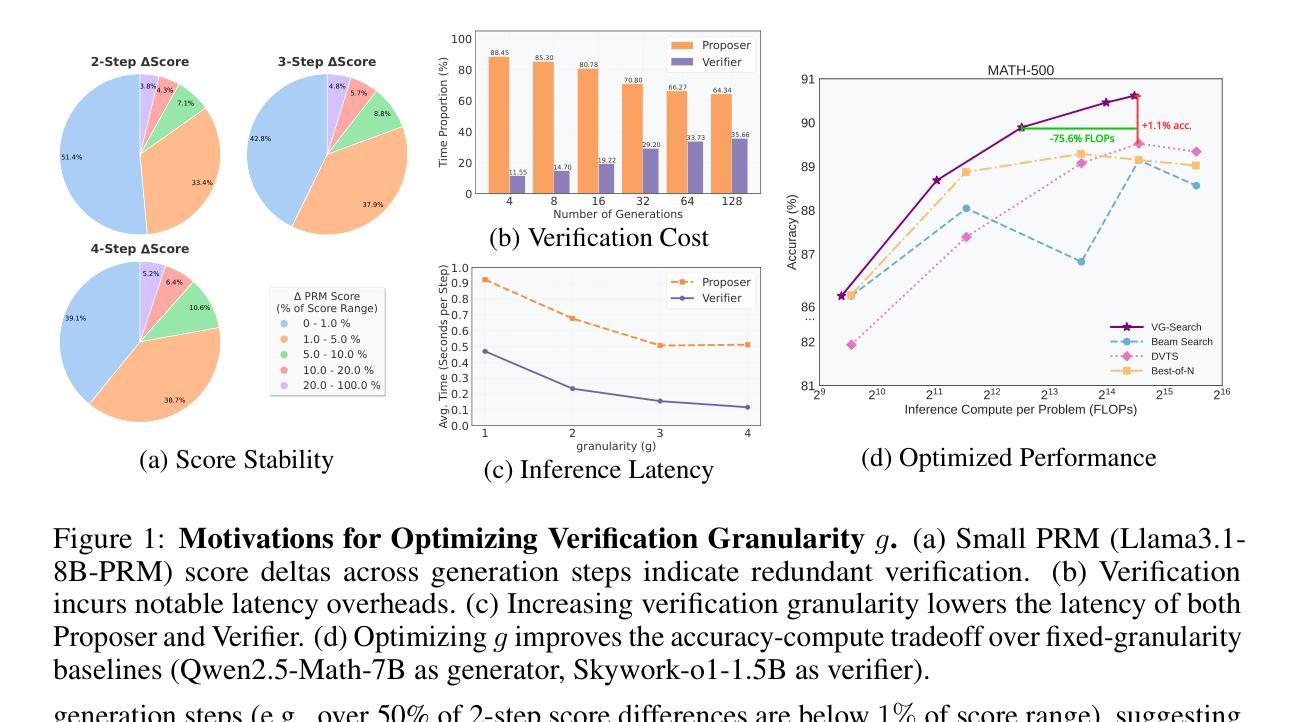
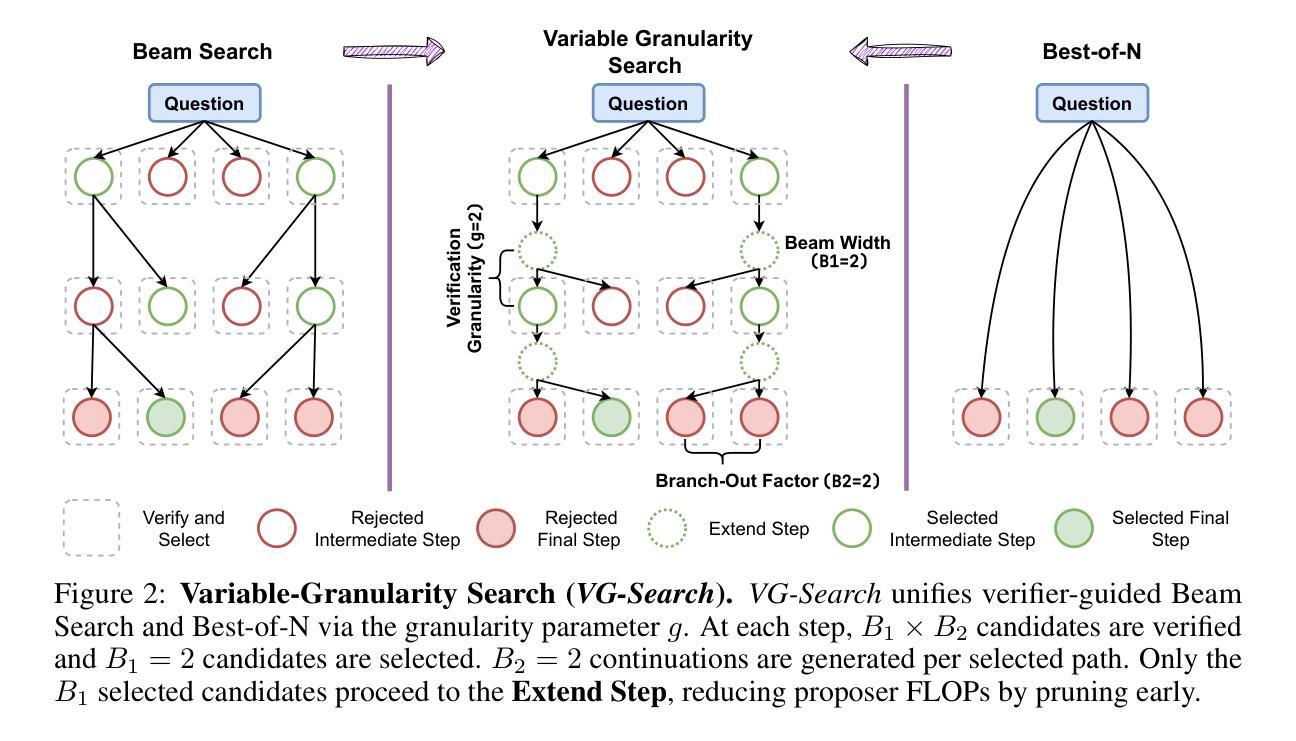
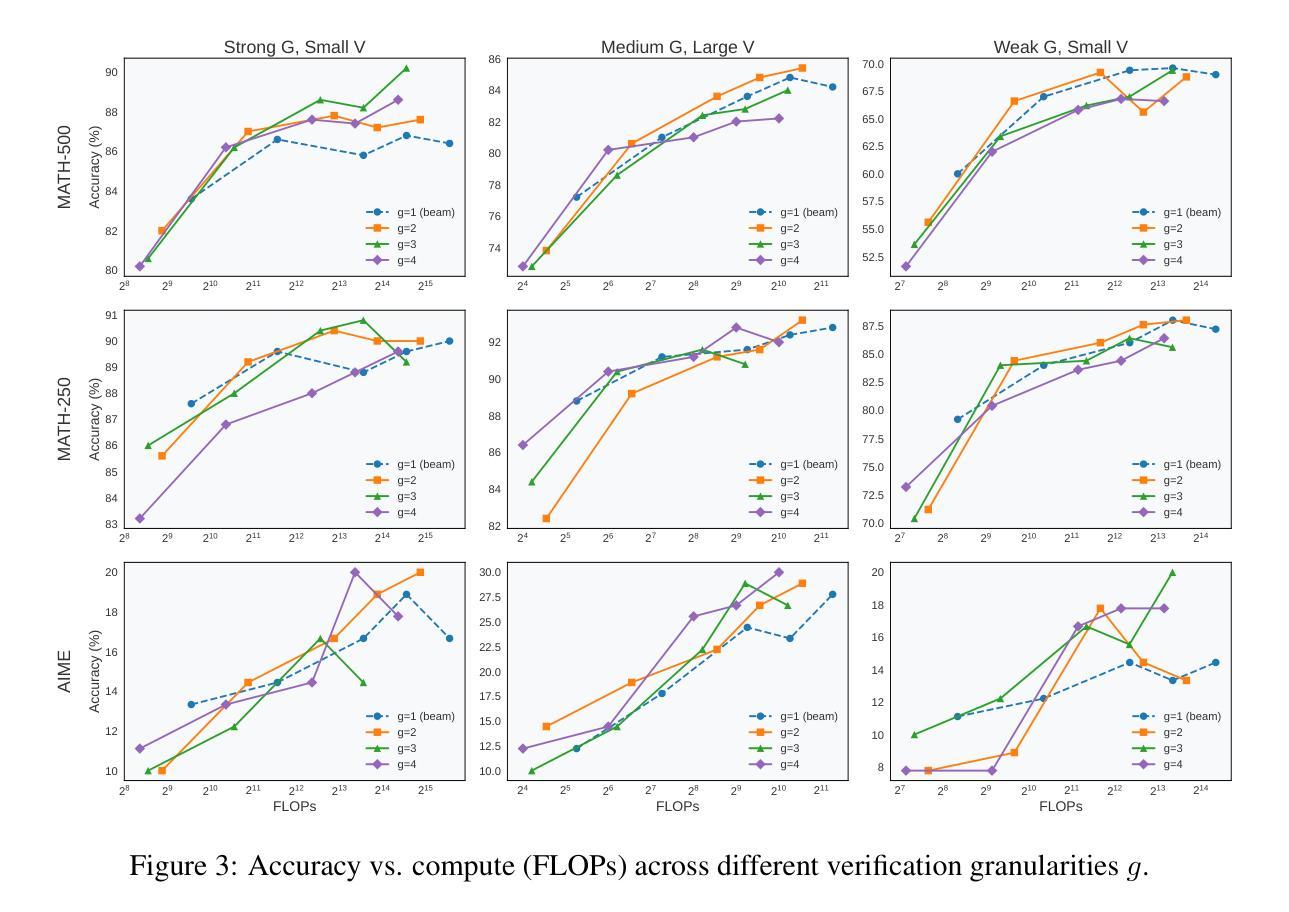
Rethinking Optimal Verification Granularity for Compute-Efficient Test-Time Scaling
Authors:Hao Mark Chen, Guanxi Lu, Yasuyuki Okoshi, Zhiwen Mo, Masato Motomura, Hongxiang Fan
Test-time scaling (TTS) has proven effective in enhancing the reasoning capabilities of large language models (LLMs). Verification plays a key role in TTS, simultaneously influencing (1) reasoning performance and (2) compute efficiency, due to the quality and computational cost of verification. In this work, we challenge the conventional paradigms of verification, and make the first attempt toward systematically investigating the impact of verification granularity-that is, how frequently the verifier is invoked during generation, beyond verifying only the final output or individual generation steps. To this end, we introduce Variable Granularity Search (VG-Search), a unified algorithm that generalizes beam search and Best-of-N sampling via a tunable granularity parameter g. Extensive experiments with VG-Search under varying compute budgets, generator-verifier configurations, and task attributes reveal that dynamically selecting g can improve the compute efficiency and scaling behavior. Building on these findings, we propose adaptive VG-Search strategies that achieve accuracy gains of up to 3.1% over Beam Search and 3.6% over Best-of-N, while reducing FLOPs by over 52%. We will open-source the code to support future research.
测试时缩放(TTS)已证明可以有效提高大型语言模型(LLM)的推理能力。验证在TTS中扮演着关键角色,由于验证的质量和计算成本,它同时影响(1)推理性能和(2)计算效率。在这项工作中,我们挑战了验证的传统范式,并首次尝试系统地研究验证粒度的影响,即验证器在生成过程中被调用的频率,而不仅仅是验证最终输出或单个生成步骤。为此,我们引入了可变粒度搜索(VG-Search),这是一种通过可调粒度参数g推广束搜索和N选最佳采样的统一算法。使用VG-Search在多种计算预算、生成器验证器配置和任务属性下进行的广泛实验表明,动态选择g可以提高计算效率和缩放性能。基于这些发现,我们提出了自适应VG-Search策略,与束搜索相比,实现了高达3.1%的准确率提升,与N选最佳策略相比提高了3.6%,同时减少了超过52%的浮点运算次数。我们将公开源代码以支持未来的研究。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Preprint. Under review
Summary
文本描述了测试时间缩放(TTS)在提高大型语言模型(LLM)的推理能力方面的有效性。验证在TTS中扮演关键角色,影响推理性能和计算效率。本研究挑战了验证的传统模式,首次尝试系统地研究验证粒度的影响,即验证器在生成过程中被调用的频率,而不仅仅是验证最终输出或单个生成步骤。为此,我们引入了可变粒度搜索(VG-Search)算法,通过可调的粒度参数g来概括beam搜索和Best-of-N采样。通过广泛的实验,我们发现动态选择g可以提高计算效率和缩放性能。在此基础上,我们提出了自适应VG-Search策略,与Beam Search相比提高了高达3.1%的准确率,与Best-of-N相比提高了高达3.6%的准确率,同时降低了超过52%的FLOPs。我们将开源代码以支持未来的研究。
Key Takeaways
- 测试时间缩放(TTS)技术增强了大型语言模型(LLM)的推理能力。
- 验证在TTS中扮演关键角色,同时影响推理性能和计算效率。
- 本研究挑战了验证的传统模式,并系统地研究了验证粒度对TTS的影响。
- 引入了可变粒度搜索(VG-Search)算法,通过调节粒度参数g来提高计算效率和推理性能。
- 动态选择g可以进一步提高计算效率和缩放性能。
- 自适应VG-Search策略在准确率上取得了显著的提升,同时降低了计算成本。
点此查看论文截图

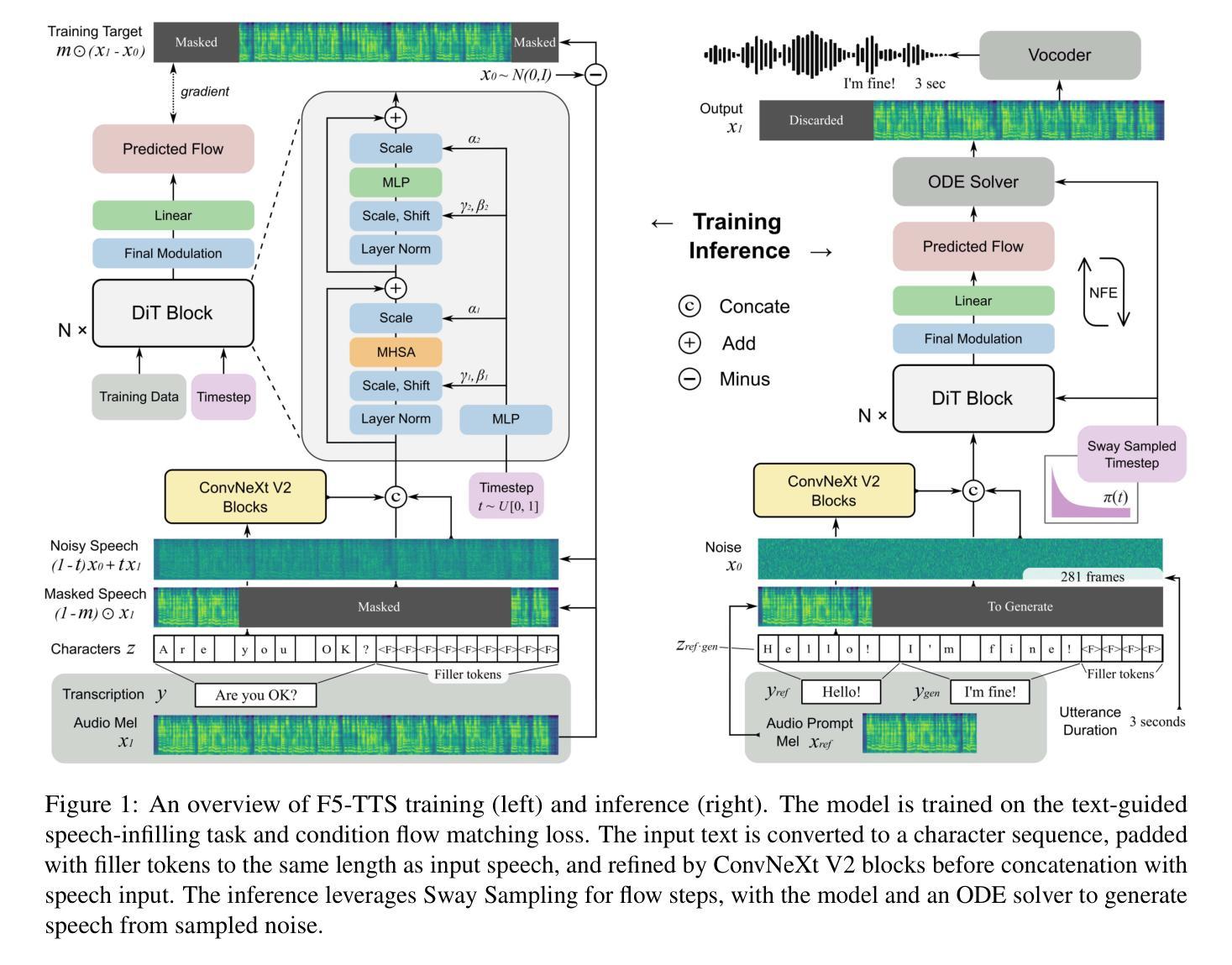
F5-TTS: A Fairytaler that Fakes Fluent and Faithful Speech with Flow Matching
Authors:Yushen Chen, Zhikang Niu, Ziyang Ma, Keqi Deng, Chunhui Wang, Jian Zhao, Kai Yu, Xie Chen
This paper introduces F5-TTS, a fully non-autoregressive text-to-speech system based on flow matching with Diffusion Transformer (DiT). Without requiring complex designs such as duration model, text encoder, and phoneme alignment, the text input is simply padded with filler tokens to the same length as input speech, and then the denoising is performed for speech generation, which was originally proved feasible by E2 TTS. However, the original design of E2 TTS makes it hard to follow due to its slow convergence and low robustness. To address these issues, we first model the input with ConvNeXt to refine the text representation, making it easy to align with the speech. We further propose an inference-time Sway Sampling strategy, which significantly improves our model’s performance and efficiency. This sampling strategy for flow step can be easily applied to existing flow matching based models without retraining. Our design allows faster training and achieves an inference RTF of 0.15, which is greatly improved compared to state-of-the-art diffusion-based TTS models. Trained on a public 100K hours multilingual dataset, our F5-TTS exhibits highly natural and expressive zero-shot ability, seamless code-switching capability, and speed control efficiency. We have released all codes and checkpoints to promote community development, at https://SWivid.github.io/F5-TTS/.
本文介绍了F5-TTS,这是一个完全非自回归的文本到语音系统,基于带有扩散转换器(DiT)的流程匹配。该系统无需复杂的设计,如持续时间模型、文本编码器和音素对齐。文本输入只需用填充标记填充至与输入语音相同的长度,然后对语音生成进行去噪处理,这种方式的可行性最初由E2 TTS证明。然而,E2 TTS的原始设计由于其收敛速度慢和稳健性低,难以跟随应用。为了解决这些问题,我们首先使用ConvNeXt对输入进行建模,以优化文本表示,使其易于与语音对齐。我们还提出了一种推理时间的摇摆采样策略,该策略显著提高了模型的性能和效率。这种用于流程步骤的采样策略可以轻松地应用于现有的基于流程匹配模型,无需重新训练。我们的设计允许更快的训练,实现推理实时转录因子(RTF)为0.15,与现有的基于扩散的TTS模型相比,这一改进非常显著。我们的F5-TTS在公共的10万小时多语种数据集上进行训练,表现出高度自然和表达能力的零样本能力、无缝的代码切换能力和速度控制效率。为了促进社区发展,我们已在https://SWivid.github.io/F5-TTS/发布了所有代码和检查点。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 17 pages, 9 tables, 3 figures
Summary
基于扩散变换(DiT)的文本转语音系统F5-TTS被引入。它通过流匹配实现非自回归性,无需复杂的组件设计如持续时间模型、文本编码器和音素对齐。通过对文本输入填充空白标记,对语音进行降噪生成。为改进原始E2 TTS设计带来的缓慢收敛和低鲁棒性问题,我们引入了ConvNeXt进行输入建模并改进了文本表示。此外,我们提出了一种名为Sway Sampling的策略,显著提高了模型性能和效率。此采样策略可轻松应用于现有的流匹配模型,无需重新训练。我们的设计加速了训练过程,实现了0.15的推理RTF,相较于现有的扩散式TTS模型有了显著改进。F5-TTS在公共的10万小时多语种数据集上训练,展现出自然、表达力强、无缝切换代码能力和速度控制效率等特点。
Key Takeaways
- F5-TTS是一个基于扩散变换的非自回归文本转语音系统。
- 通过简单的填充空白标记和降噪实现语音生成,无需复杂的组件设计。
- 引入ConvNeXt改进文本表示和对齐问题。
- 提出Sway Sampling策略,提高模型性能和效率,可轻松应用于现有模型。
- 实现了快速的训练过程和高效的推理RTF。
- F5-TTS在多语种数据集上训练,展现出自然、表达力强、无缝切换代码能力和速度控制效率等特点。
点此查看论文截图