⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-05-24 更新
Tracking the Flight: Exploring a Computational Framework for Analyzing Escape Responses in Plains Zebra (Equus quagga)
Authors:Isla Duporge, Sofia Minano, Nikoloz Sirmpilatze, Igor Tatarnikov, Scott Wolf, Adam L. Tyson, Daniel Rubenstein
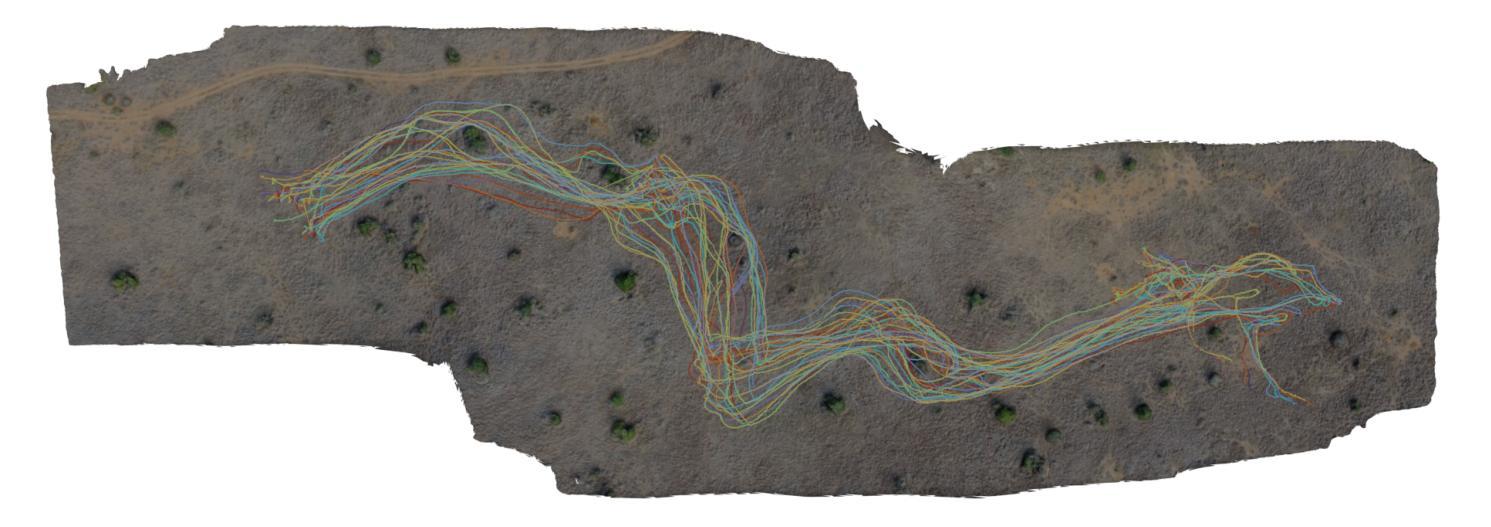
Ethological research increasingly benefits from the growing affordability and accessibility of drones, which enable the capture of high-resolution footage of animal movement at fine spatial and temporal scales. However, analyzing such footage presents the technical challenge of separating animal movement from drone motion. While non-trivial, computer vision techniques such as image registration and Structure-from-Motion (SfM) offer practical solutions. For conservationists, open-source tools that are user-friendly, require minimal setup, and deliver timely results are especially valuable for efficient data interpretation. This study evaluates three approaches: a bioimaging-based registration technique, an SfM pipeline, and a hybrid interpolation method. We apply these to a recorded escape event involving 44 plains zebras, captured in a single drone video. Using the best-performing method, we extract individual trajectories and identify key behavioral patterns: increased alignment (polarization) during escape, a brief widening of spacing just before stopping, and tighter coordination near the group’s center. These insights highlight the method’s effectiveness and its potential to scale to larger datasets, contributing to broader investigations of collective animal behavior.
生态学研究日益受益于无人机日益可负担的性价比和普及性,无人机能够捕捉到动物运动的高分辨率影像,精细的空间和时间尺度上都能观察到。然而,分析这样的影像面临技术挑战,即如何将动物运动与无人机运动区分开来。虽然有一定的难度,但计算机视觉技术,如图像配准和从运动结构(SfM),提供了实用的解决方案。对于保护主义者来说,用户友好的开源工具、需要最少的设置并且能及时反馈结果,对于高效的数据解读尤其有价值。本研究评估了三种方法:一种基于生物成像的配准技术、一个SfM管道和一个混合插值方法。我们将这些方法应用在一个涉及44只斑马逃跑事件的记录上,该视频由单架无人机拍摄。使用表现最好的方法,我们提取了单个轨迹并识别出了关键的行为模式:逃跑时增加对齐(极化)、逃跑前短暂扩大间距以及在群体中心附近更紧密的协调。这些见解凸显了该方法的有效性以及其扩展到更大数据集的潜力,为更广泛的群体动物行为研究做出了贡献。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted to the CV4Animals workshop at CVPR 2025
Summary
随着无人机成本和技术的普及,其被广泛应用于动物行为学研究中,能够捕捉动物行为的高分辨率影像。然而,如何区分动物行为和无人机运动的分析是一大技术挑战。计算机视觉技术如图像配准和运动结构技术为此提供了解决方案。本研究评估了三种方法,并应用于记录的一次涉及44只斑马逃离事件的分析。通过最佳方法的应用,提取了个体轨迹并识别了关键行为模式,如逃跑时的增加对齐、逃跑前的短暂间距扩大以及靠近群体中心的紧密协调。这为集体动物行为研究提供了有效方法和潜在的大规模数据集应用前景。
Key Takeaways
- 无人机在动物行为学研究中得到广泛应用,可捕捉高清晰度影像。
- 分析无人机影像时,区分动物行为与无人机运动是一大技术挑战。
- 计算机视觉技术如图像配准和运动结构技术为解决此挑战提供了方法。
- 本研究评估了三种方法,并成功应用于斑马逃离事件的分析。
- 通过最佳方法的应用,可以提取个体轨迹并识别关键行为模式。
- 这些方法对于研究集体动物行为有效,并有望应用于大规模数据集。
点此查看论文截图


Improvement of H$_2$O$_2$ electrogeneration using a Vulcan XC72 carbon-based electrocatalyst modified with Ce-doped Nb$_2$O$_5$
Authors:Aline B. Trench, João Paulo C. Moura, Vanessa S. Antonin, Caio Machado Fernandes, Liying Liu, Mauro C. Santos
The use of the oxygen reduction reaction (ORR) for in-situ production of H$_2$O$_2$ is an attractive alternative to replace the methods based on anthraquinone oxidation. This study investigates the modification of Vulcan XC72 carbon with Ce-doped Nb$_2$O$_5$ in different molar proportions and its application as electrocatalysts in the ORR. One performed the characterization of the electrocatalysts using X-ray diffraction, Raman spectroscopy, scanning electron microscopy, transmission electron microscopy, contact angle measurements, and X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy. Subsequently, the electrocatalysts were analyzed for the ORR and the Nb$_2$O$_5$ doped with 0.5% Ce showing the highest electrocatalytic response. This electrocatalyst was also employed as a gas diffusion electrode and exhibited more significant H$_2$O$_2$ production at all potentials than the Vulcan XC72 carbon modified solely with Nb$_2$O$_5$. At the applied potentials of -1.3 V and -1.9 V, it produced 105% and 86% more H$_2$O$_2$, respectively, than the Vulcan XC72 carbon modified only with Nb$_2$O$_5$. These results can be attributed to the doping of Nb$_2$O$_5$ with 0.5% Ce, which induces local distortions in the crystal lattice of Nb$_2$O$_5$ due to the difference in ionic radius between Nb$^{5+}$ and Ce$^{3+}$, which combined with increased hydrophilicity and wetting properties, may have facilitated electron transfer and O$_2$ transport, favoring the ORR.
使用氧还原反应(ORR)进行H2O2的原位生产是一种吸引人的替代方法,取代了基于蒽醌氧化的方法。本研究对Vulcan XC72碳进行了不同摩尔比例的铈掺杂的Nb2O5改性,并探讨了其在ORR中的电催化作用。利用X射线衍射、拉曼光谱、扫描电子显微镜、透射电子显微镜、接触角测量和X射线光电子能谱对电催化剂进行了表征。随后,对电催化剂进行了ORR分析,发现掺杂了0.5% Ce的Nb2O5表现出最高的电催化响应。该电催化剂还被用作气体扩散电极,在所有的电位下都表现出比仅用Nb2O5改性的Vulcan XC72碳更大的H2O2生产效率。在-1.3 V和-1.9 V的施加电位下,它产生的H2O2分别比仅用Nb2O5改性的Vulcan XC72碳多105%和86%。这些结果可归因于Nb2O5的掺杂,其中掺杂了0.5%的Ce,由于Nb5+和Ce3+之间的离子半径差异,会在Nb2O5的晶格中产生局部畸变。这种畸变与增加的亲水性和润湿性能相结合,可能促进了电子转移和氧气的传输,有利于氧还原反应。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
基于氧还原反应(ORR)的现场生产过氧化氢(H$_2$O$_2$)方法对替代基于蒽醌氧化法具有吸引力。本研究通过不同摩尔比例的Ce掺杂Nb$_2$O$_5$改性Vulcan XC72碳,并将其用作ORR中的电催化剂。经过一系列表征方法后,发现掺杂有0.5% Ce的Nb$_2$O$_5$表现最佳,其在所有电位下的过氧化氢产量显著高于仅使用Nb$_2$O$_5$改性的Vulcan XC72碳。此成果归因于掺杂Ce导致Nb$_2$O$_5$晶体晶格扭曲等改变,促进电子转移和氧输送。
Key Takeaways
- 研究采用氧还原反应(ORR)生产过氧化氢(H$_2$O$_2$)作为替代基于蒽醌氧化法的新方法。
- 通过掺杂不同比例的Ce到Nb$_2$O$_5$来改性Vulcan XC72碳,用作电催化剂。
- 掺杂有0.5% Ce的Nb$_2$O$_5$在ORR中表现最佳,其电催化响应最高。
- 该电催化剂在作为气体扩散电极应用时,在所有电位下的过氧化氢产量显著高于仅使用Nb$_2$O$_5$改性的Vulcan XC72碳。
- 在-1.3V和-1.9V的应用电位下,其分别产生了105%和86%更多的过氧化氢。
- 掺杂Ce导致Nb$_2$O$_5$晶体晶格扭曲,可能促进了电子转移和氧输送,从而有利于ORR。
点此查看论文截图

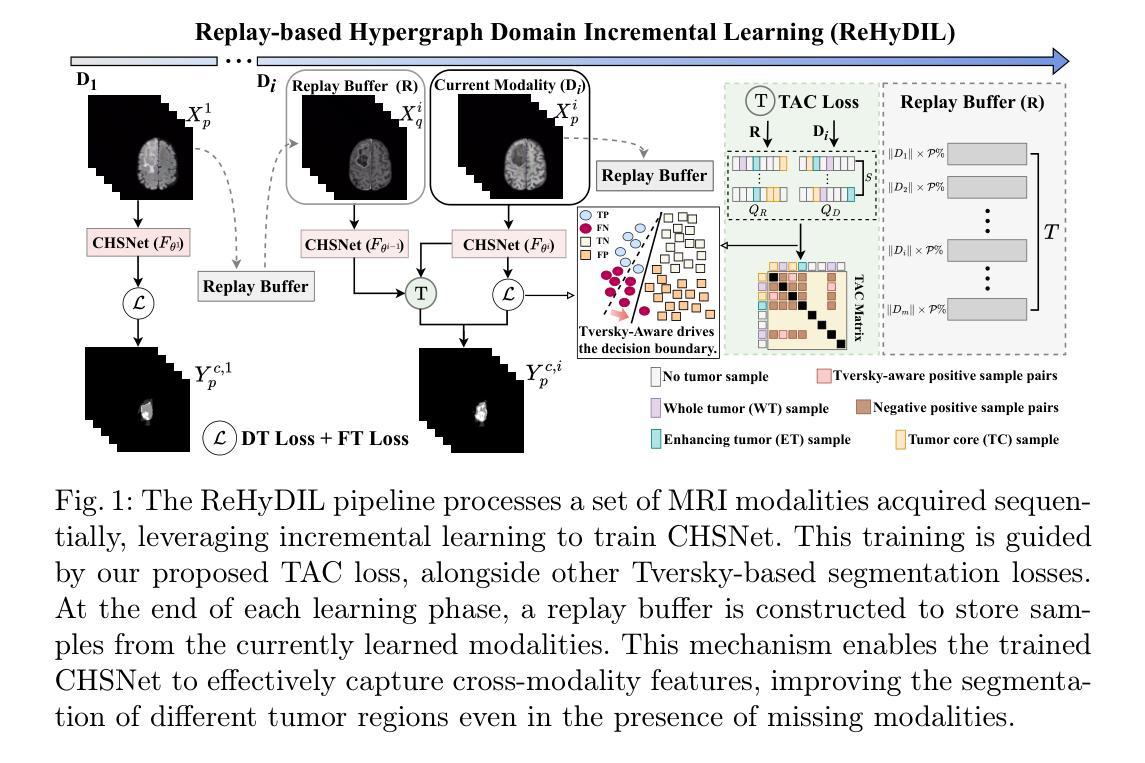
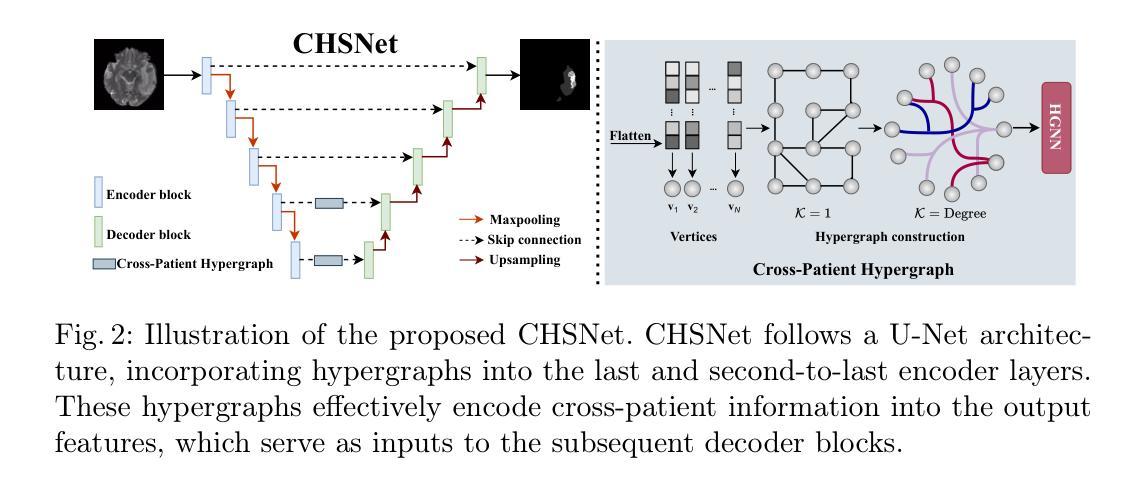
Hypergraph Tversky-Aware Domain Incremental Learning for Brain Tumor Segmentation with Missing Modalities
Authors:Junze Wang, Lei Fan, Weipeng Jing, Donglin Di, Yang Song, Sidong Liu, Cong Cong
Existing methods for multimodal MRI segmentation with missing modalities typically assume that all MRI modalities are available during training. However, in clinical practice, some modalities may be missing due to the sequential nature of MRI acquisition, leading to performance degradation. Furthermore, retraining models to accommodate newly available modalities can be inefficient and may cause overfitting, potentially compromising previously learned knowledge. To address these challenges, we propose Replay-based Hypergraph Domain Incremental Learning (ReHyDIL) for brain tumor segmentation with missing modalities. ReHyDIL leverages Domain Incremental Learning (DIL) to enable the segmentation model to learn from newly acquired MRI modalities without forgetting previously learned information. To enhance segmentation performance across diverse patient scenarios, we introduce the Cross-Patient Hypergraph Segmentation Network (CHSNet), which utilizes hypergraphs to capture high-order associations between patients. Additionally, we incorporate Tversky-Aware Contrastive (TAC) loss to effectively mitigate information imbalance both across and within different modalities. Extensive experiments on the BraTS2019 dataset demonstrate that ReHyDIL outperforms state-of-the-art methods, achieving an improvement of over 2% in the Dice Similarity Coefficient across various tumor regions. Our code is available at ReHyDIL.
现有针对缺失模态的多模态MRI分割方法通常假设在训练过程中所有MRI模态都是可用的。然而,在临床实践中,由于MRI采集的序列性,某些模态可能会缺失,导致性能下降。此外,为了容纳新可用的模态而重新训练模型可能效率低下,并可能导致过度拟合,从而可能损害之前学到的知识。为了解决这些挑战,我们提出了基于回放和超图域增量学习(ReHyDIL)的脑肿瘤分割方法,用于处理缺失模态的情况。ReHyDIL利用域增量学习(DIL)使分割模型能够从新获取的MRI模态中学习,而不会忘记之前学到的信息。为了提高不同患者场景下的分割性能,我们引入了跨患者超图分割网络(CHSNet),该网络利用超图来捕捉患者之间的高阶关联。此外,我们结合了Tversky感知对比(TAC)损失,以有效缓解不同模态之间和内部的信息不平衡问题。在BraTS2019数据集上的广泛实验表明,ReHyDIL优于最先进的方法,在各种肿瘤区域的Dice相似系数上提高了2%以上。我们的代码可在ReHyDIL网站上找到。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文提出一种基于回放和超图域的增量学习(ReHyDIL)方法,用于处理MRI图像中缺失模态的情况下的脑肿瘤分割问题。该方法结合了领域增量学习(DIL)和跨患者超图分割网络(CHSNet),以应对缺失模态导致的训练问题。同时,通过引入Tversky意识对比损失(TAC损失),提高跨不同模态的信息平衡性。在BraTS2019数据集上的实验表明,ReHyDIL较其他前沿方法有更出色的表现,在Dice相似系数上提高了超过2%。
Key Takeaways
- ReHyDIL方法结合了领域增量学习(DIL)来处理MRI图像中缺失模态的问题。
- CHSNet网络用于增强分割性能,适应不同的患者场景。
- ReHyDIL引入TAC损失以缓解不同模态之间的信息不平衡问题。
- 相比现有方法,ReHyDIL在BraTS2019数据集上的表现更优,Dice相似系数提高了超过2%。
- ReHyDIL能够适应新获取的MRI模态,同时保留之前学习的知识。
- ReHyDIL通过利用超图捕捉患者之间的高阶关联,提高了分割准确性。
- 该方法的代码已公开可用。
点此查看论文截图

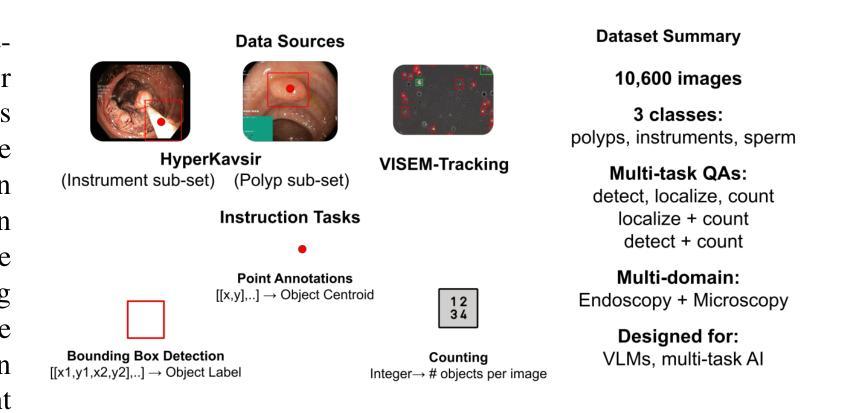
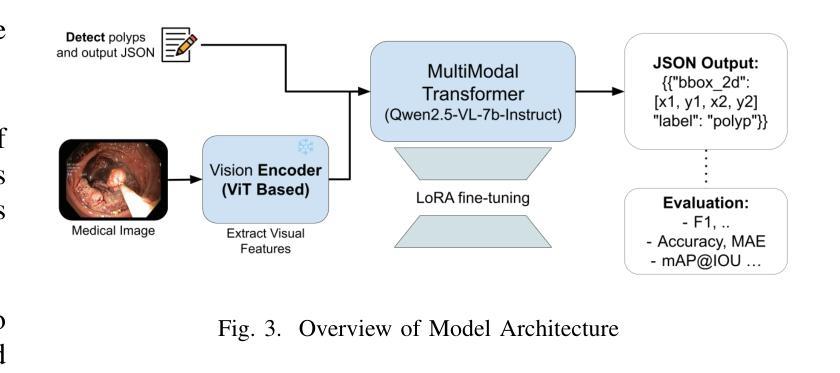
Point, Detect, Count: Multi-Task Medical Image Understanding with Instruction-Tuned Vision-Language Models
Authors:Sushant Gautam, Michael A. Riegler, Pål Halvorsen
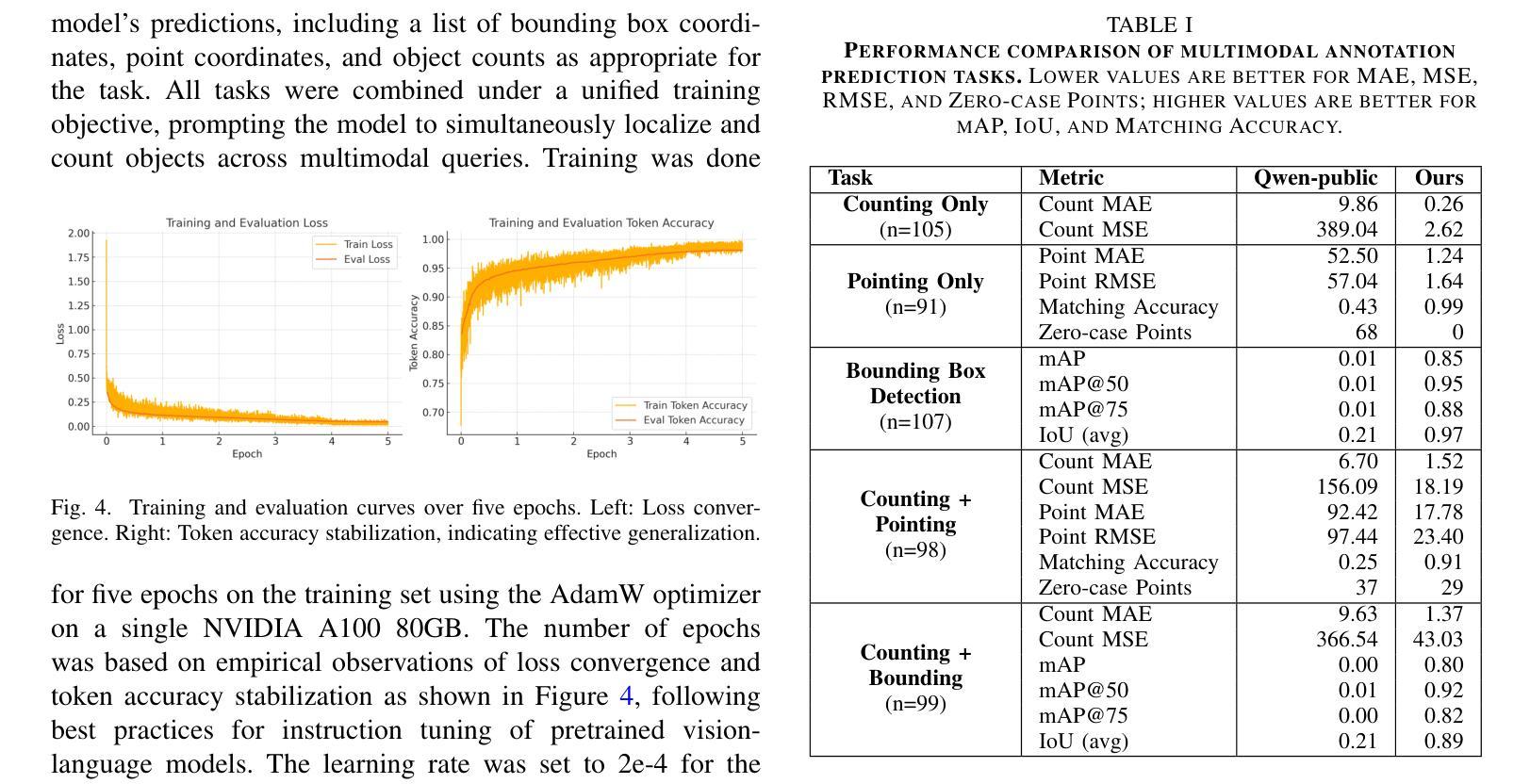
We investigate fine-tuning Vision-Language Models (VLMs) for multi-task medical image understanding, focusing on detection, localization, and counting of findings in medical images. Our objective is to evaluate whether instruction-tuned VLMs can simultaneously improve these tasks, with the goal of enhancing diagnostic accuracy and efficiency. Using MedMultiPoints, a multimodal dataset with annotations from endoscopy (polyps and instruments) and microscopy (sperm cells), we reformulate each task into instruction-based prompts suitable for vision-language reasoning. We fine-tune Qwen2.5-VL-7B-Instruct using Low-Rank Adaptation (LoRA) across multiple task combinations. Results show that multi-task training improves robustness and accuracy. For example, it reduces the Count Mean Absolute Error (MAE) and increases Matching Accuracy in the Counting + Pointing task. However, trade-offs emerge, such as more zero-case point predictions, indicating reduced reliability in edge cases despite overall performance gains. Our study highlights the potential of adapting general-purpose VLMs to specialized medical tasks via prompt-driven fine-tuning. This approach mirrors clinical workflows, where radiologists simultaneously localize, count, and describe findings - demonstrating how VLMs can learn composite diagnostic reasoning patterns. The model produces interpretable, structured outputs, offering a promising step toward explainable and versatile medical AI. Code, model weights, and scripts will be released for reproducibility at https://github.com/simula/PointDetectCount.
我们研究了针对多任务医学影像理解的视觉语言模型(VLMs)微调技术,重点聚焦于医学影像中的检测结果识别、定位以及计数。我们的目标是评估指令调整后的VLMs是否能够同时改进这些任务,旨在提高诊断和效率的准确性。我们使用MedMultiPoints这一包含内窥镜(息肉和仪器)和显微镜(精子细胞)注释的多模式数据集,将每个任务重新制定为适应视觉语言推理的指令提示。我们利用低秩自适应(LoRA)技术微调Qwen2.5-VL-7B-Instruct模型,适应多种任务组合。结果显示,多任务训练提高了稳健性和准确性。例如,它减少了计数平均绝对误差(MAE),并提高了计数+定位任务的匹配准确率。然而,也出现了一些权衡情况,比如更多的零案例点预测,这表明在整体性能提升的同时,边缘案例的可靠性有所降低。我们的研究突出了通过提示驱动微调将通用VLMs适应专业医疗任务的潜力。这种方法反映了临床工作流程,放射科医生同时定位、计数和描述发现结果,展示了VLMs如何学习复合诊断推理模式。该模型产生可解释的结构化输出,为向可解释和通用医疗人工智能迈出了一步,具有广阔的发展前景。相关代码、模型权重和脚本将在https://github.com/simula/PointDetectCount上发布,以促进研究的可重复性。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted as a full paper at the 38th IEEE International Symposium on Computer-Based Medical Systems (CBMS) 2025
Summary
本文探索了针对多任务医学图像理解的视觉语言模型(VLMs)的微调研究。文章重点介绍了如何使用MedMultiPoints数据集对模型进行训练,旨在通过多任务训练提高模型的稳健性和准确性,旨在提高诊断的准确性和效率。通过指令微调VLMs,文章展示了一种可能的方法来适应特殊医学任务,这种方法能够模拟医生同时定位、计数和描述病灶点的临床工作流程。此研究展示了利用结构化输出进行解释的潜力,对于推动医学人工智能的透明性和通用性具有重要意义。更多细节和数据将在相关代码和模型权重中公开。
Key Takeaways
- 研究关注多任务医学图像理解,特别是检测、定位和计数任务。
- 使用MedMultiPoints数据集进行训练,旨在提高诊断准确性和效率。
- 通过指令微调VLMs以适应特殊医学任务,展示了一种可能的方法。
- 多任务训练能提高模型的稳健性和准确性。例如,在计数和指向任务中减少了平均绝对误差(MAE),提高了匹配准确率。
- 研究发现存在权衡问题,如零案例点预测增多,边缘情况可靠性降低。
- 模型模拟医生临床工作流程,展示学习复合诊断推理模式的潜力。
点此查看论文截图
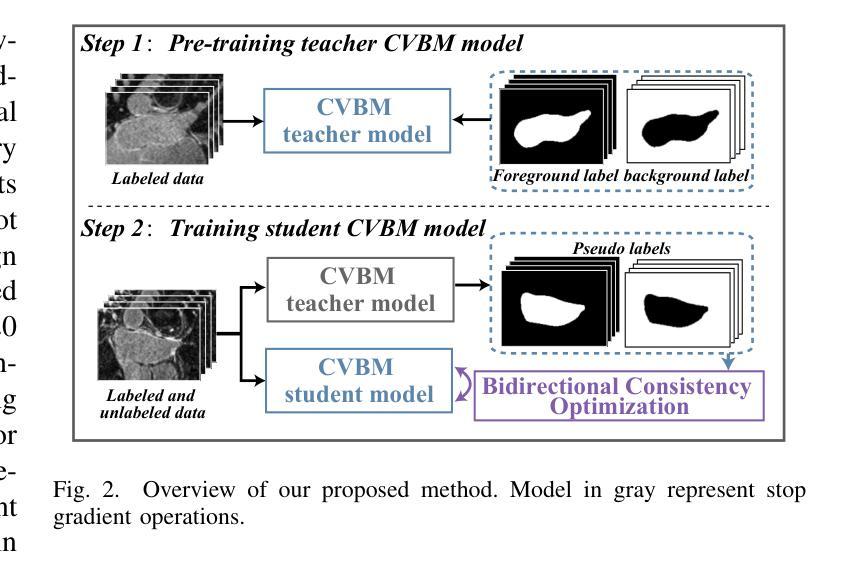
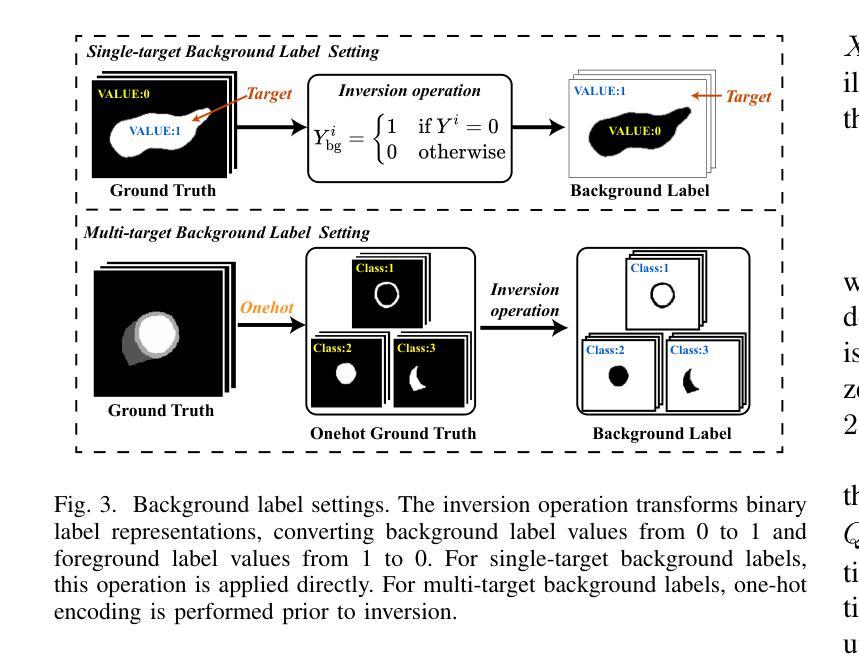
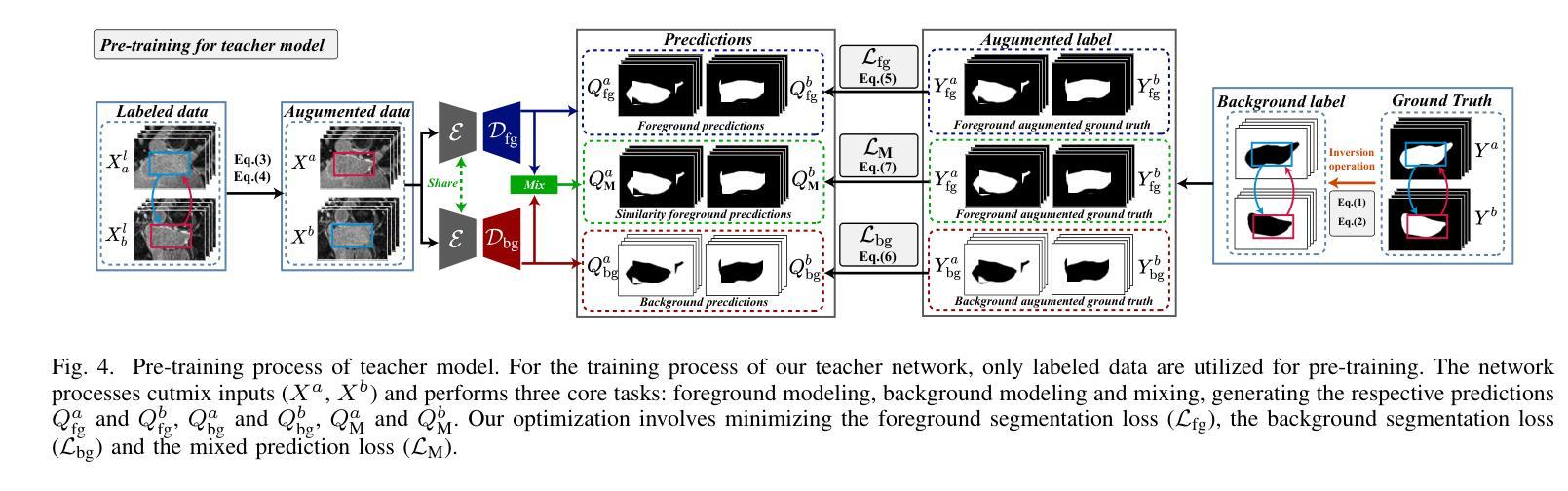
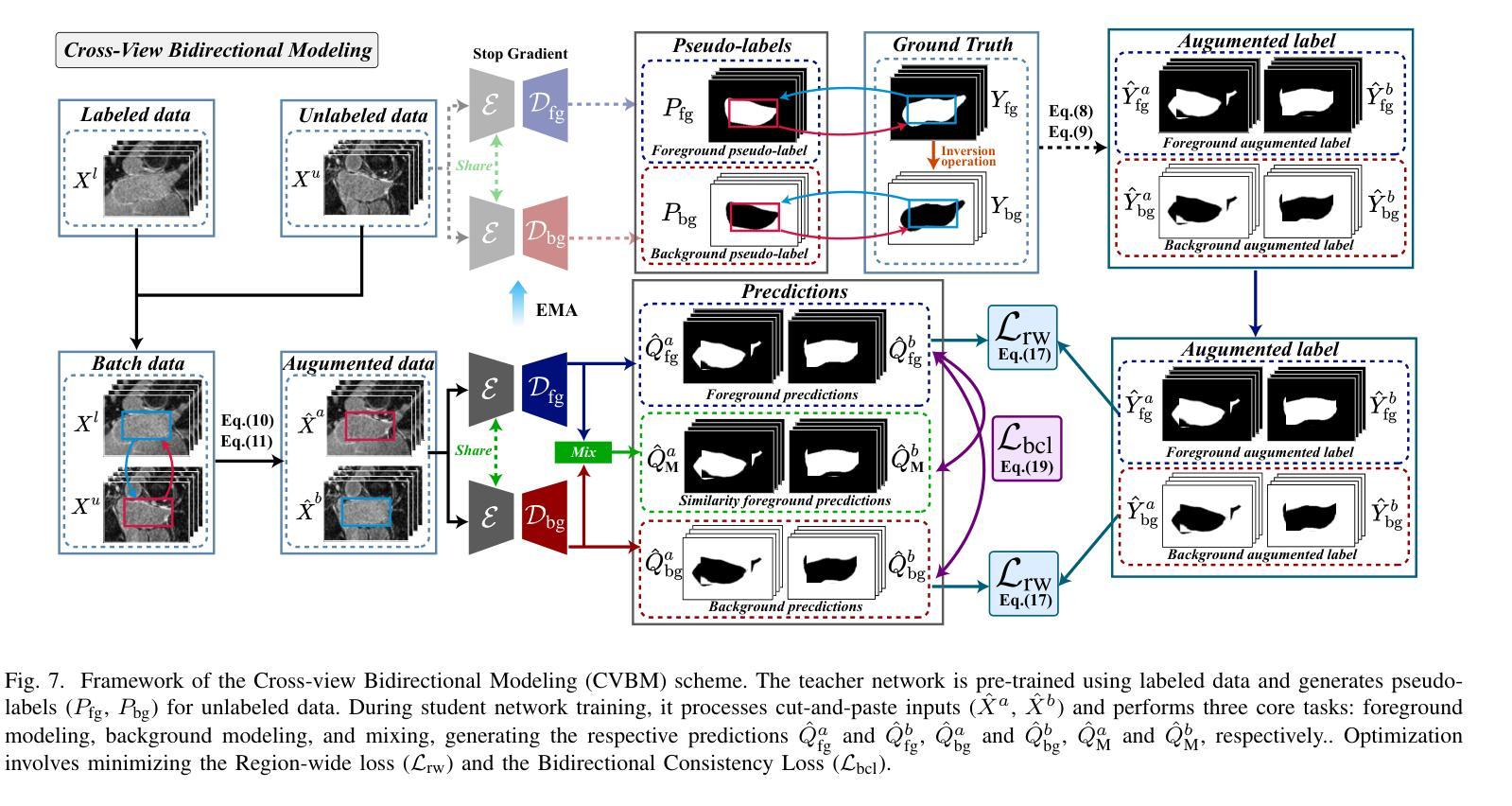
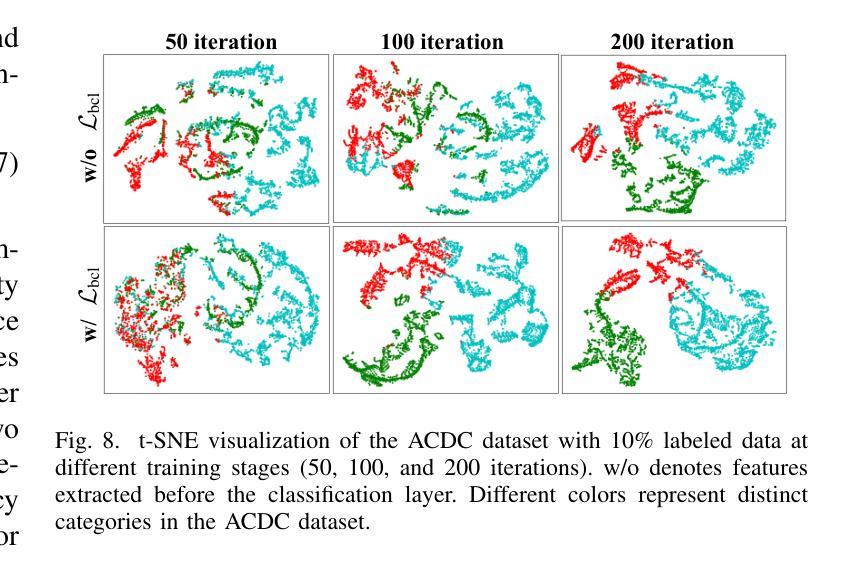
Background Matters: A Cross-view Bidirectional Modeling Framework for Semi-supervised Medical Image Segmentation
Authors:Luyang Cao, Jianwei Li, Yinghuan Shi
Semi-supervised medical image segmentation (SSMIS) leverages unlabeled data to reduce reliance on manually annotated images. However, current SOTA approaches predominantly focus on foreground-oriented modeling (i.e., segmenting only the foreground region) and have largely overlooked the potential benefits of explicitly modeling the background region. Our study theoretically and empirically demonstrates that highly certain predictions in background modeling enhance the confidence of corresponding foreground modeling. Building on this insight, we propose the Cross-view Bidirectional Modeling (CVBM) framework, which introduces a novel perspective by incorporating background modeling to improve foreground modeling performance. Within CVBM, background modeling serves as an auxiliary perspective, providing complementary supervisory signals to enhance the confidence of the foreground model. Additionally, CVBM introduces an innovative bidirectional consistency mechanism, which ensures mutual alignment between foreground predictions and background-guided predictions. Extensive experiments demonstrate that our approach achieves SOTA performance on the LA, Pancreas, ACDC, and HRF datasets. Notably, on the Pancreas dataset, CVBM outperforms fully supervised methods (i.e., DSC: 84.57% vs. 83.89%) while utilizing only 20% of the labeled data. Our code is publicly available at https://github.com/caoluyang0830/CVBM.git.
半监督医学图像分割(SSMIS)利用无标签数据减少了对手动标注图像的依赖。然而,当前的最先进方法主要关注前景导向建模(即只分割前景区域),并大多忽略了显式建模背景区域的潜在优势。我们的研究从理论和实证上证明,背景建模中的高确定性预测增强了对应前景建模的置信度。基于这一见解,我们提出了跨视图双向建模(CVBM)框架,通过引入背景建模来改善前景建模性能,提供了一种新颖的视角。在CVBM中,背景建模作为一个辅助视角,提供补充监督信号,增强前景模型的置信度。此外,CVBM引入了一种创新的双向一致性机制,确保前景预测和背景引导预测之间的相互对齐。大量实验表明,我们的方法在LA、胰腺、ACDC和HRF数据集上达到了最先进的性能。尤其在胰腺数据集上,CVBM在仅使用20%标记数据的情况下,超越了全监督方法(DSC:84.57%对83.89%)。我们的代码公开在https://github.com/caoluyang0830/CVBM.git。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by IEEE Transactions on Image Processing
Summary
医学图像分割中的半监督学习利用未标记数据减少对手动标注图像的依赖。然而,现有技术主要集中在前景建模上,忽视了背景建模的潜在优势。研究证明背景建模的确定性预测可以提高前景建模的置信度。基于此,提出Cross-view Bidirectional Modeling(CVBM)框架,通过引入背景建模改善前景建模性能。CVBM利用背景建模作为辅助视角,提供额外的监督信号,同时引入双向一致性机制确保预测间的相互对齐。实验表明,该方法在多个数据集上实现最佳性能,尤其在胰腺数据集上,CVBM在仅使用20%标记数据的情况下便超越全监督方法(DSC:84.57% vs. 83.89%)。代码已公开。
Key Takeaways
- SSMIS利用未标记数据减少标注图像的依赖。
- 当前方法主要关注前景建模,忽略背景建模的潜在优势。
- 背景建模的确定性预测能提高前景建模的置信度。
- 提出CVBM框架结合背景建模改善前景建模性能。
- CVBM利用背景建模作为辅助视角,提供额外的监督信号。
- 双向一致性机制确保前景和背景预测间的相互对齐。
- 实验表明CVBM在多个数据集上实现最佳性能,尤其在胰腺数据集上表现突出。
- 仅使用少量标记数据便超越全监督方法。
点此查看论文截图


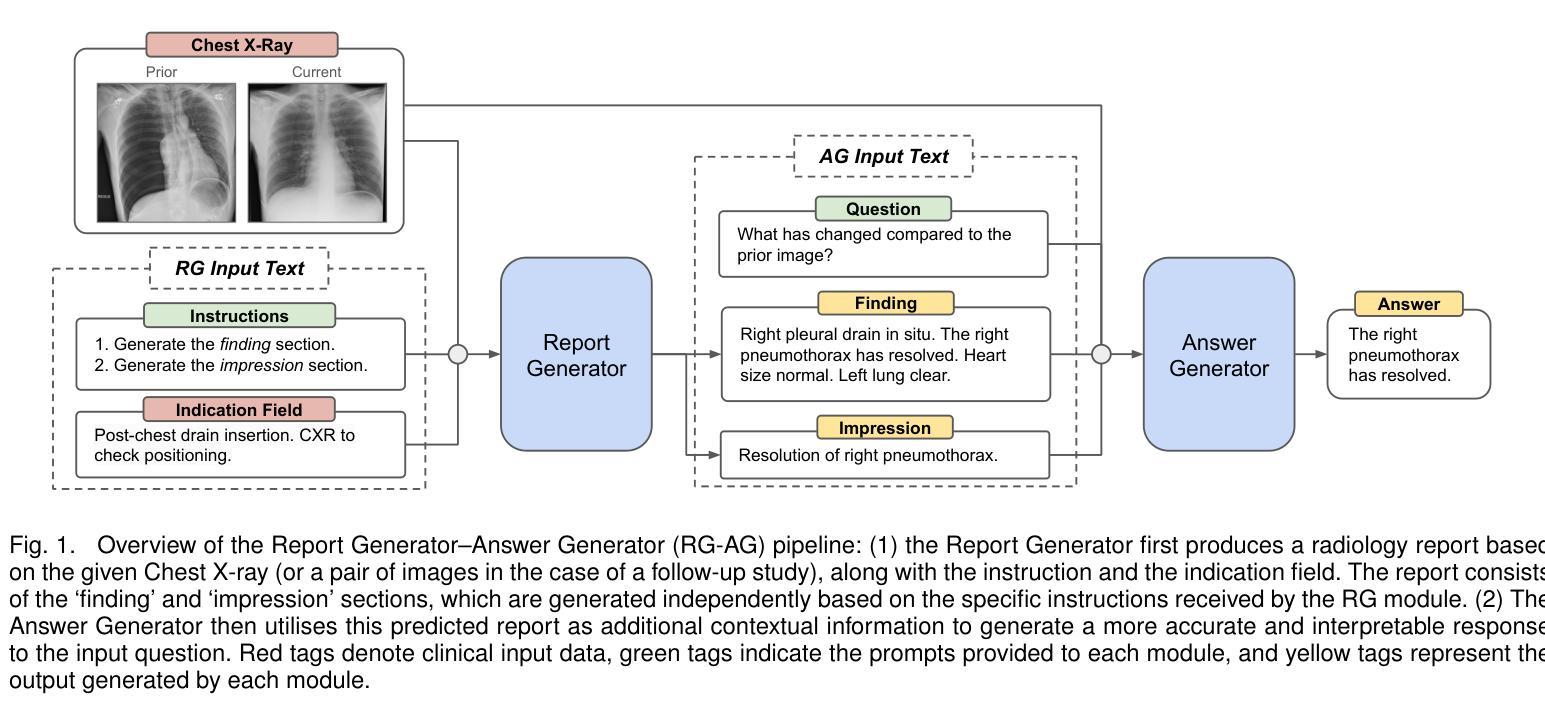
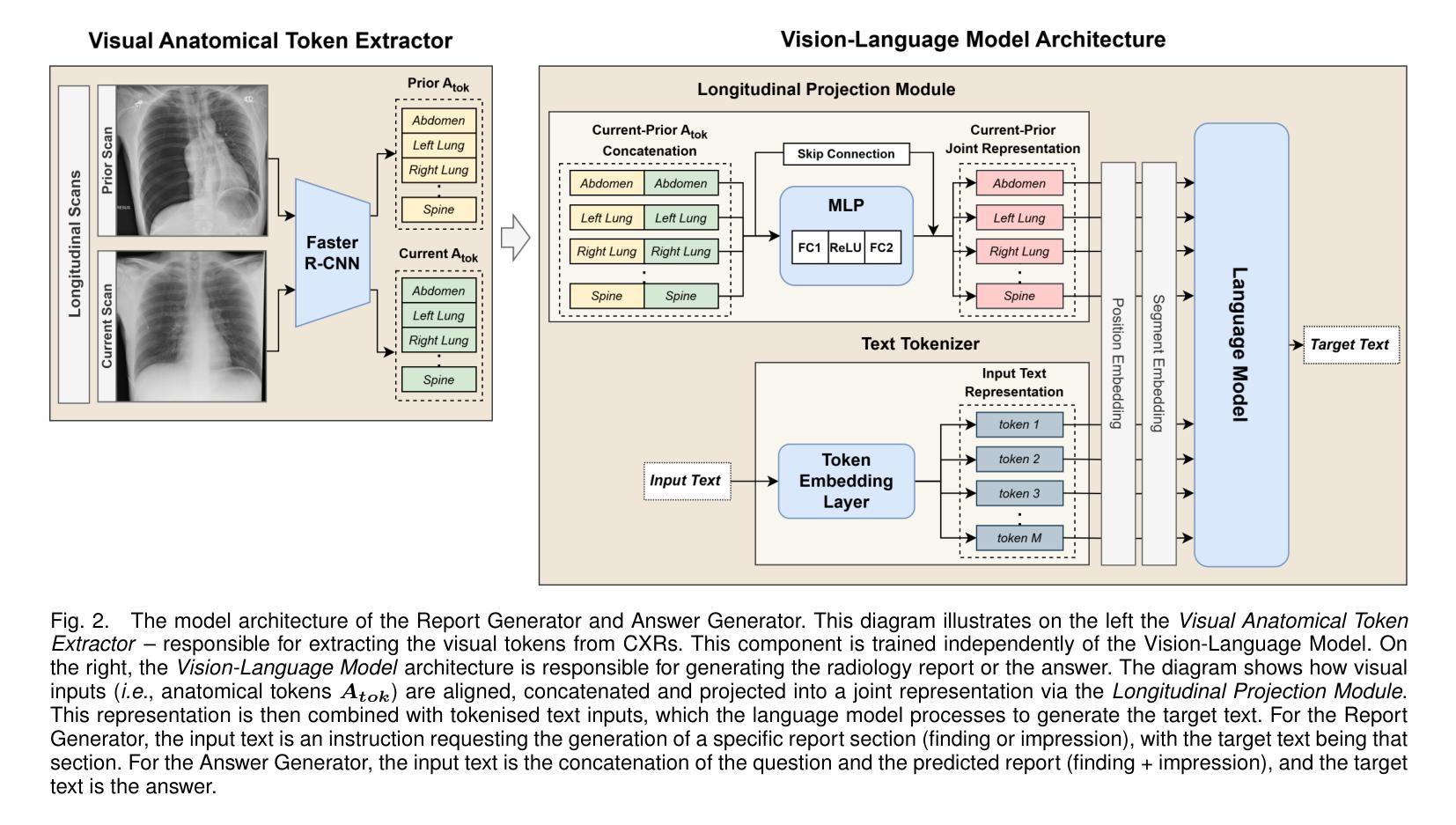
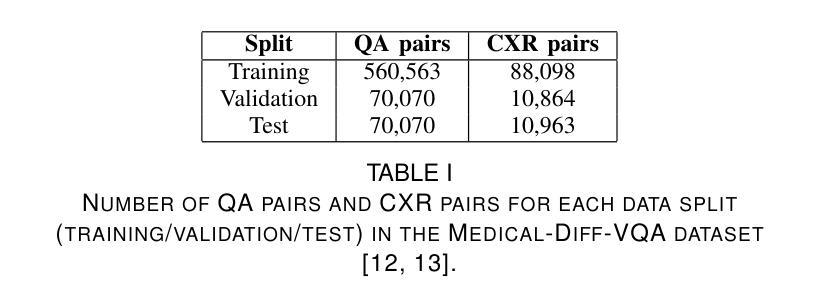
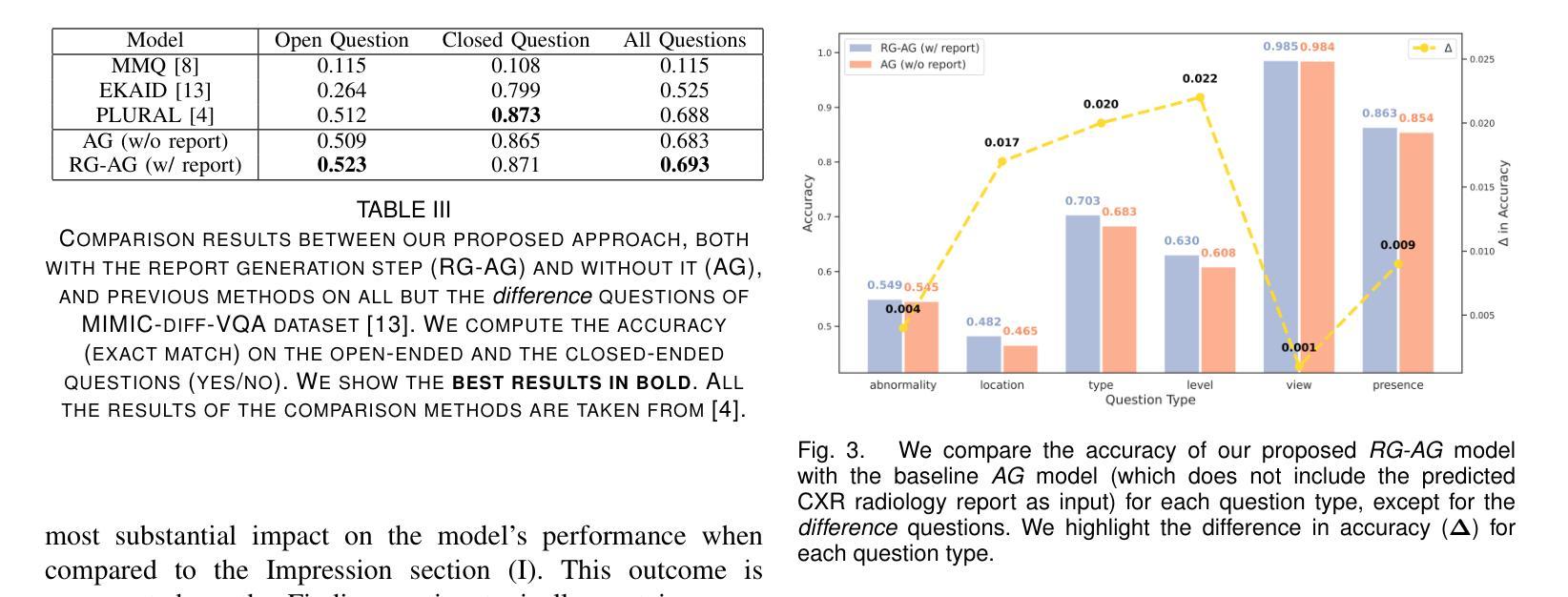
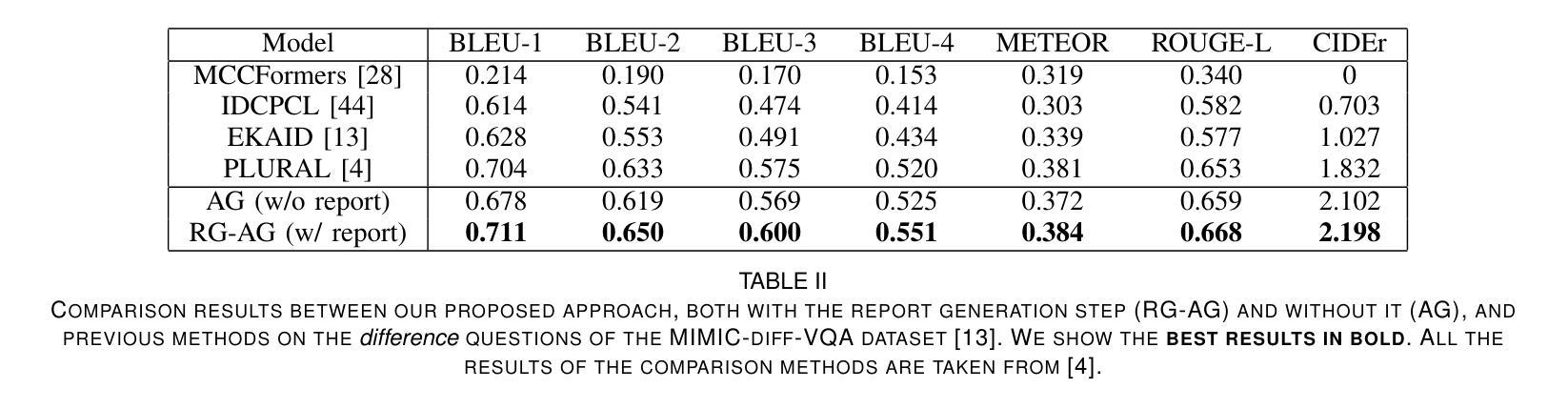
Grounding Chest X-Ray Visual Question Answering with Generated Radiology Reports
Authors:Francesco Dalla Serra, Patrick Schrempf, Chaoyang Wang, Zaiqiao Meng, Fani Deligianni, Alison Q. O’Neil
We present a novel approach to Chest X-ray (CXR) Visual Question Answering (VQA), addressing both single-image image-difference questions. Single-image questions focus on abnormalities within a specific CXR (“What abnormalities are seen in image X?”), while image-difference questions compare two longitudinal CXRs acquired at different time points (“What are the differences between image X and Y?”). We further explore how the integration of radiology reports can enhance the performance of VQA models. While previous approaches have demonstrated the utility of radiology reports during the pre-training phase, we extend this idea by showing that the reports can also be leveraged as additional input to improve the VQA model’s predicted answers. First, we propose a unified method that handles both types of questions and auto-regressively generates the answers. For single-image questions, the model is provided with a single CXR. For image-difference questions, the model is provided with two CXRs from the same patient, captured at different time points, enabling the model to detect and describe temporal changes. Taking inspiration from ‘Chain-of-Thought reasoning’, we demonstrate that performance on the CXR VQA task can be improved by grounding the answer generator module with a radiology report predicted for the same CXR. In our approach, the VQA model is divided into two steps: i) Report Generation (RG) and ii) Answer Generation (AG). Our results demonstrate that incorporating predicted radiology reports as evidence to the AG model enhances performance on both single-image and image-difference questions, achieving state-of-the-art results on the Medical-Diff-VQA dataset.
我们提出了一种针对胸部X光(CXR)视觉问答(VQA)的新型方法,该方法解决了单图像图像差异问题。单图像问题侧重于CXR内的异常现象(“图像X中看到了哪些异常?”),而图像差异问题则比较在不同时间点采集的两个纵向CXR(“图像X和Y之间的差异是什么?”)。我们进一步探讨了集成放射学报告如何增强VQA模型的表现。虽然以前的方法在预训练阶段展示了放射学报告的有用性,但我们通过展示报告还可以作为额外输入来改善VQA模型的预测答案,从而扩展了这一想法。首先,我们提出了一种统一的方法,该方法可以处理这两种类型的问题,并自动生成答案。对于单图像问题,模型会接收一张CXR。对于图像差异问题,模型会接收来自同一患者在不同时间点捕获的两张CXR,使模型能够检测和描述时间变化。我们从“思维链推理”中汲取灵感,证明通过把答案生成模块建立在为同一CXR预测的放射学报告上,可以改善CXR VQA任务的表现。在我们的方法中,VQA模型分为两个阶段:i)报告生成(RG)和ii)答案生成(AG)。我们的结果表明,将预测的放射学报告作为证据融入AG模型,提高了在单图像和图像差异问题上的性能,在Medical-Diff-VQA数据集上达到了最新水平。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了一种针对胸部X光(CXR)视觉问答(VQA)的新型方法,该方法能够处理单图像差异问题。单图像问题关注特定CXR中的异常,而图像差异问题则比较在不同时间点采集的两个纵向CXRs之间的差异。文章还探讨了将放射学报告融入VQA模型的方式,不仅可以用于预训练阶段,还可以作为额外输入来改善模型的预测答案。通过统一的处理方法,模型可以处理两种类型的问题,并自动生成答案。该方法分为报告生成和答案生成两个步骤,通过将预测的放射学报告作为证据融入答案生成模型,提高了在单图像和图像差异问题上的性能,实现了在Medical-Diff-VQA数据集上的最新结果。
Key Takeaways
- 介绍了处理胸部X光视觉问答的新型方法,涵盖单图像问题和图像差异问题。
- 探讨了将放射学报告融入VQA模型的多种方式,包括预训练和作为额外输入改善预测答案。
- 采用统一方法处理两种类型的问题,并自动生成答案。
- 模型分为报告生成和答案生成两个步骤。
- 预测的放射学报告作为证据融入答案生成模型,提高在单图像和图像差异问题上的性能。
- 该方法在Medical-Diff-VQA数据集上实现了最新结果。
点此查看论文截图

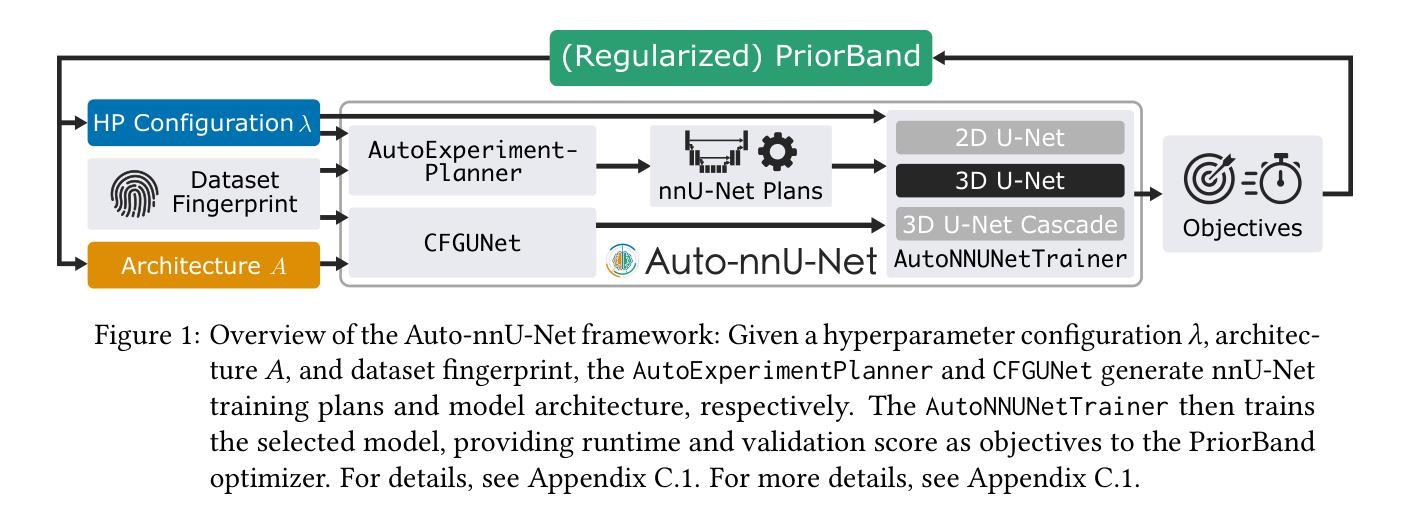
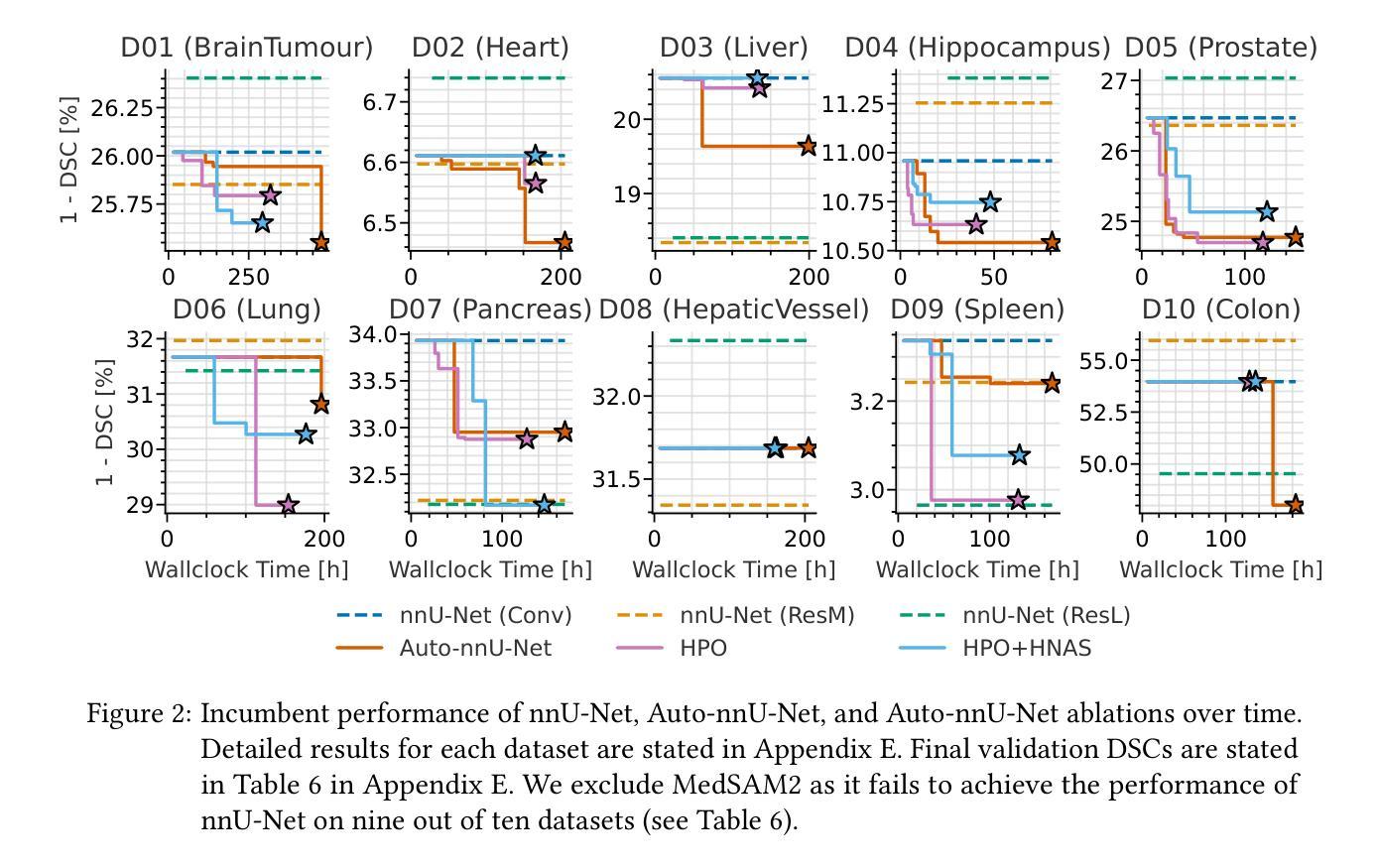
Auto-nnU-Net: Towards Automated Medical Image Segmentation
Authors:Jannis Becktepe, Leona Hennig, Steffen Oeltze-Jafra, Marius Lindauer
Medical Image Segmentation (MIS) includes diverse tasks, from bone to organ segmentation, each with its own challenges in finding the best segmentation model. The state-of-the-art AutoML-related MIS-framework nnU-Net automates many aspects of model configuration but remains constrained by fixed hyperparameters and heuristic design choices. As a full-AutoML framework for MIS, we propose Auto-nnU-Net, a novel nnU-Net variant enabling hyperparameter optimization (HPO), neural architecture search (NAS), and hierarchical NAS (HNAS). Additionally, we propose Regularized PriorBand to balance model accuracy with the computational resources required for training, addressing the resource constraints often faced in real-world medical settings that limit the feasibility of extensive training procedures. We evaluate our approach across diverse MIS datasets from the well-established Medical Segmentation Decathlon, analyzing the impact of AutoML techniques on segmentation performance, computational efficiency, and model design choices. The results demonstrate that our AutoML approach substantially improves the segmentation performance of nnU-Net on 6 out of 10 datasets and is on par on the other datasets while maintaining practical resource requirements. Our code is available at https://github.com/LUH-AI/AutonnUNet.
医学图像分割(MIS)涵盖了从骨骼到器官分割等多样化任务,在寻找最佳分割模型时每个任务都面临自己的挑战。最先进的与AutoML相关的MIS框架nnU-Net能够自动化模型配置的许多方面,但仍受到固定超参数和启发式设计选择的限制。作为MIS的全自动ML框架,我们提出了Auto-nnU-Net,这是一种新型的nnU-Net变体,能够实现超参数优化(HPO)、神经网络架构搜索(NAS)和分层NAS(HNAS)。此外,我们提出了正则化PriorBand,以平衡模型精度与训练所需的计算资源,解决现实医疗环境中经常面临的资源约束问题,这些资源约束限制了广泛训练程序的可行性。我们在经过良好验证的医学分割十项全能赛中的多样化MIS数据集上评估了我们的方法,分析了AutoML技术对分割性能、计算效率和模型设计选择的影响。结果表明,我们的AutoML方法在6个数据集上显著提高了nnU-Net的分割性能,在其他数据集上表现相当,同时保持了实际的资源需求。我们的代码可在[https://github.com/LUH-AI/AutonnUNet获取。]
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 31 pages, 19 figures. Accepted for publication at AutoML 2025
摘要
本研究针对医疗图像分割(MIS)中的多样任务挑战,提出了Auto-nnU-Net,这是一个全自动的MIS框架,改进了现有的nnU-Net模型。新框架引入超参数优化(HPO)、神经网络架构搜索(NAS)和分层NAS(HNAS),有效解决了固定超参数和启发式设计选择带来的限制。此外,该研究提出了Regularized PriorBand,旨在平衡模型精度和计算资源需求,以解决现实医疗环境中资源约束的问题。研究在Medical Segmentation Decathlon的不同MIS数据集上评估了新方法的影响,证明了AutoML技术在分割性能、计算效率和模型设计选择上的优势。Auto-nnU-Net在10个数据集中的6个上显著提高了nnU-Net的分割性能,其余数据集表现相当,同时满足了实际资源需求。相关代码已公开。
关键见解
- Auto-nnU-Net是一个全自动的医疗图像分割框架,扩展了现有的nnU-Net模型,支持超参数优化、神经网络架构搜索和分层NAS。
- Regularized PriorBand解决了模型精度和计算资源之间的平衡问题,尤其适用于资源受限的现实医疗环境。
- 在多个数据集上的评估表明,Auto-nnU-Net显著提高了分割性能,特别是在6个数据集上的表现优于nnU-Net。
- Auto-nnU-Net在保持实际资源需求的同时,其余数据集上的表现与nnU-Net相当。
- 该研究提供了一个有效的解决方案,以解决医疗图像分割中面临的多样任务挑战和计算资源限制问题。
- AutoML技术在医疗图像分割领域具有巨大的潜力,有望推动该领域的进一步发展。
点此查看论文截图

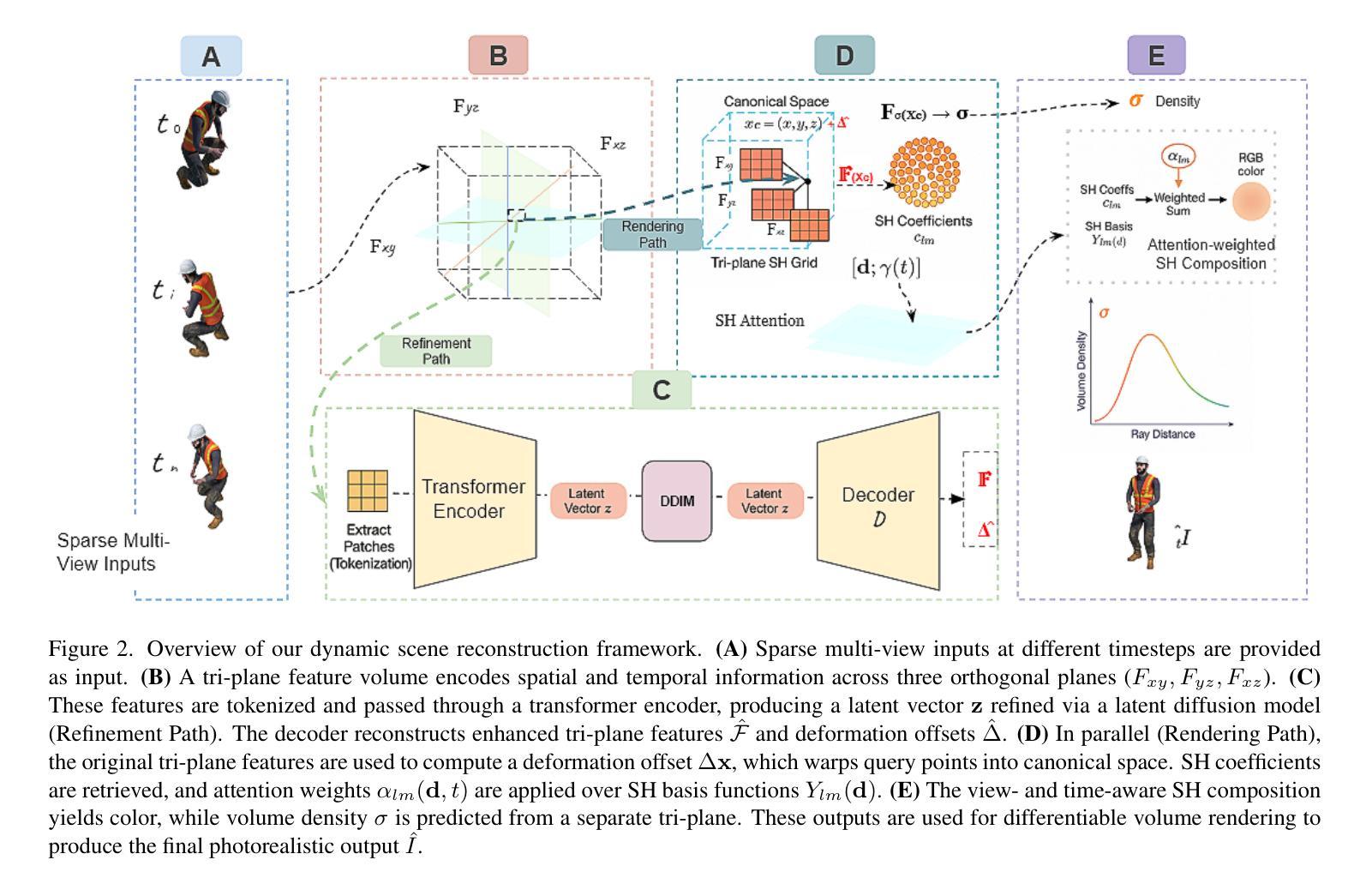
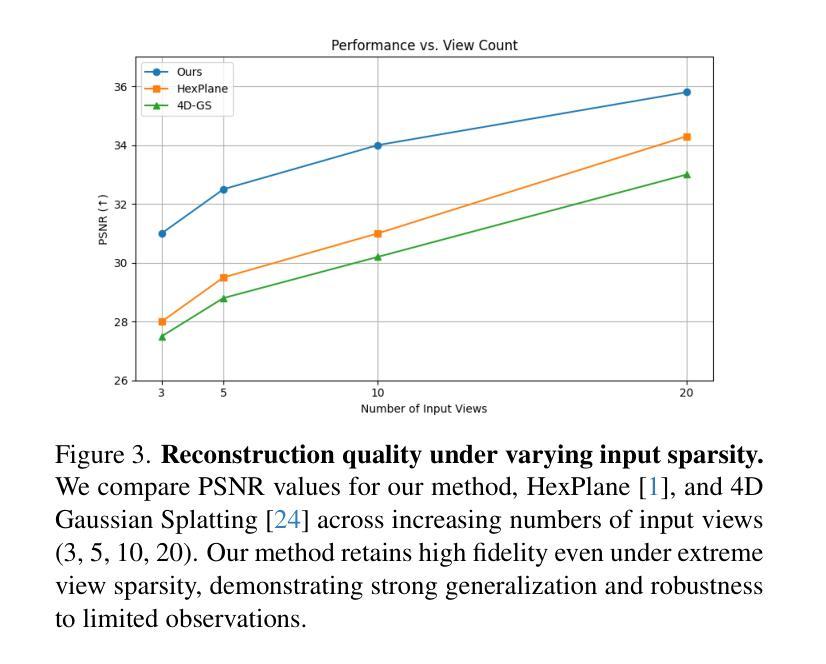
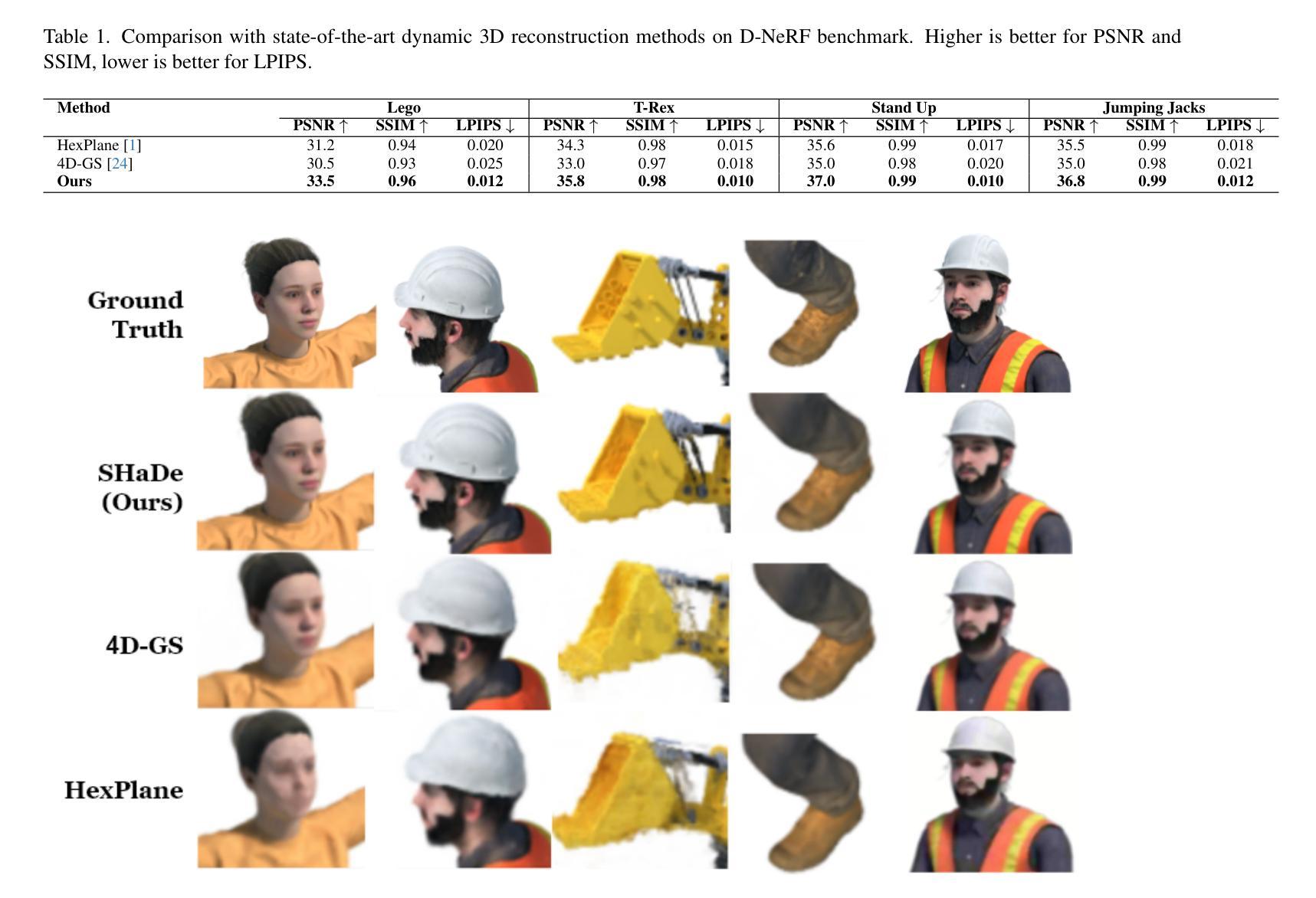
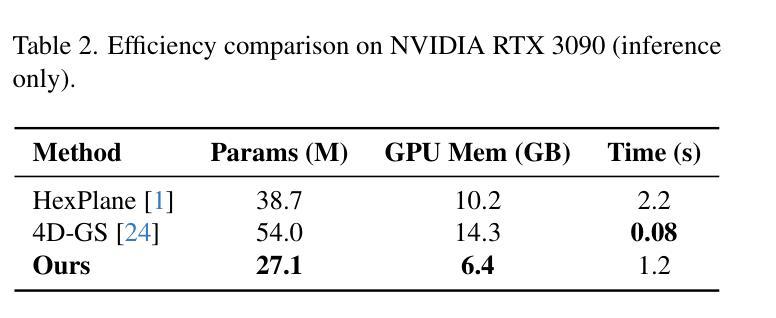
SHaDe: Compact and Consistent Dynamic 3D Reconstruction via Tri-Plane Deformation and Latent Diffusion
Authors:Asrar Alruwayqi
We present a novel framework for dynamic 3D scene reconstruction that integrates three key components: an explicit tri-plane deformation field, a view-conditioned canonical radiance field with spherical harmonics (SH) attention, and a temporally-aware latent diffusion prior. Our method encodes 4D scenes using three orthogonal 2D feature planes that evolve over time, enabling efficient and compact spatiotemporal representation. These features are explicitly warped into a canonical space via a deformation offset field, eliminating the need for MLP-based motion modeling. In canonical space, we replace traditional MLP decoders with a structured SH-based rendering head that synthesizes view-dependent color via attention over learned frequency bands improving both interpretability and rendering efficiency. To further enhance fidelity and temporal consistency, we introduce a transformer-guided latent diffusion module that refines the tri-plane and deformation features in a compressed latent space. This generative module denoises scene representations under ambiguous or out-of-distribution (OOD) motion, improving generalization. Our model is trained in two stages: the diffusion module is first pre-trained independently, and then fine-tuned jointly with the full pipeline using a combination of image reconstruction, diffusion denoising, and temporal consistency losses. We demonstrate state-of-the-art results on synthetic benchmarks, surpassing recent methods such as HexPlane and 4D Gaussian Splatting in visual quality, temporal coherence, and robustness to sparse-view dynamic inputs.
我们提出了一种新颖的动态3D场景重建框架,它集成了三个关键组件:显式三平面变形场、受视图条件约束的带有球面谐波(SH)注意力的规范辐射场,以及时间感知潜在扩散先验。我们的方法使用随时间变化的三个正交2D特征平面对4D场景进行编码,从而实现高效且紧凑的时空表示。这些特征通过一个变形偏移场显式地映射到规范空间,从而无需基于MLP的运动建模。在规范空间中,我们用结构化的SH渲染头替换传统的MLP解码器,通过关注学习到的频率带,合成与视图相关的颜色,提高了可解释性和渲染效率。为了进一步提高保真度和时间一致性,我们引入了一个基于变压器的潜在扩散模块,该模块在压缩的潜在空间中细化三平面和变形特征。这一生成模块在模糊或离群分布(OOD)运动的情况下对场景表示进行去噪,提高了泛化能力。我们的模型分为两个阶段进行训练:首先独立地预训练扩散模块,然后使用图像重建、扩散去噪和时间一致性损失的组合对完整管道进行微调。我们在合成基准测试上展示了卓越的结果,在视觉质量、时间连贯性和对稀疏视图动态输入的鲁棒性方面超越了最近的HexPlane和4D高斯拼贴方法。
论文及项目相关链接
摘要
本文提出了一种新的动态3D场景重建框架,集成了三个关键组件:显式三平面变形场、视条件规范辐射场和具有球面谐波(SH)注意力的时间感知潜在扩散先验。该方法通过三个随时间变化的正交二维特征平面编码四维场景,然后通过变形偏移场将这些特征显式地变换到规范空间,从而无需使用MLP基运动建模。在规范空间中,我们采用结构化SH渲染头代替传统MLP解码器,通过关注学习频率波段来合成视图相关的颜色,提高了可解释性和渲染效率。为了进一步改善保真度和时间一致性,我们引入了一个基于变压器的潜在扩散模块,该模块在压缩的潜在空间中细化三平面和变形特征。该生成模块减少了模糊或离群值运动下的场景表示的噪声,提高了泛化能力。该模型分为两个阶段进行训练:首先独立地预训练扩散模块,然后使用图像重建、扩散去噪和时间一致性损失的组合联合微调整个管道。我们在合成基准测试上展示了卓越的结果,在视觉质量、时间连贯性和对稀疏动态输入的鲁棒性方面超越了最近的HexPlane和四维高斯平版印刷等方法。
关键见解
一、提出了一个集成三关键组件的新型动态3D场景重建框架,包括显式三平面变形场、视条件规范辐射场和具有球面谐波(SH)注意力的时间感知潜在扩散先验。
二、采用三个随时间变化的正交二维特征平面编码四维场景,并借助变形偏移场将这些特征映射到规范空间。
三、使用结构化SH渲染头代替传统MLP解码器,实现高效渲染并提高模型的可解释性。
四、引入了基于变压器的潜在扩散模块,提高了场景表示的保真度和时间一致性,增强了模型对模糊或离群值运动的处理能力。
五、模型训练分为两个阶段:预训练扩散模块,然后结合多种损失对整个管道进行微调。
六、在合成基准测试上取得了卓越的结果,超越了现有的动态重建方法。本方法在视觉质量、时间连贯性和对稀疏输入信号的鲁棒性方面具有优势。
点此查看论文截图

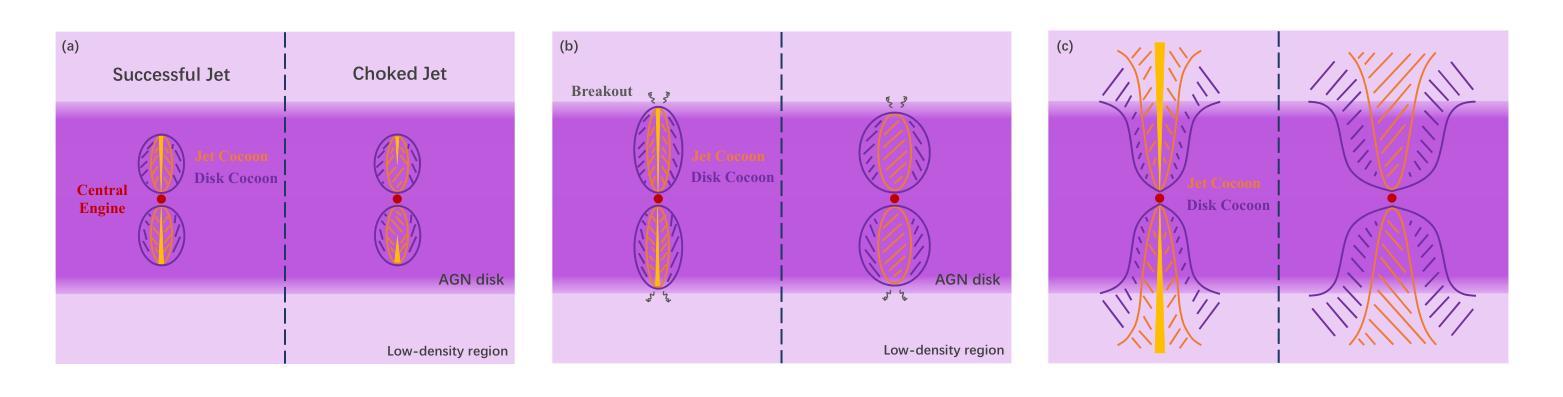
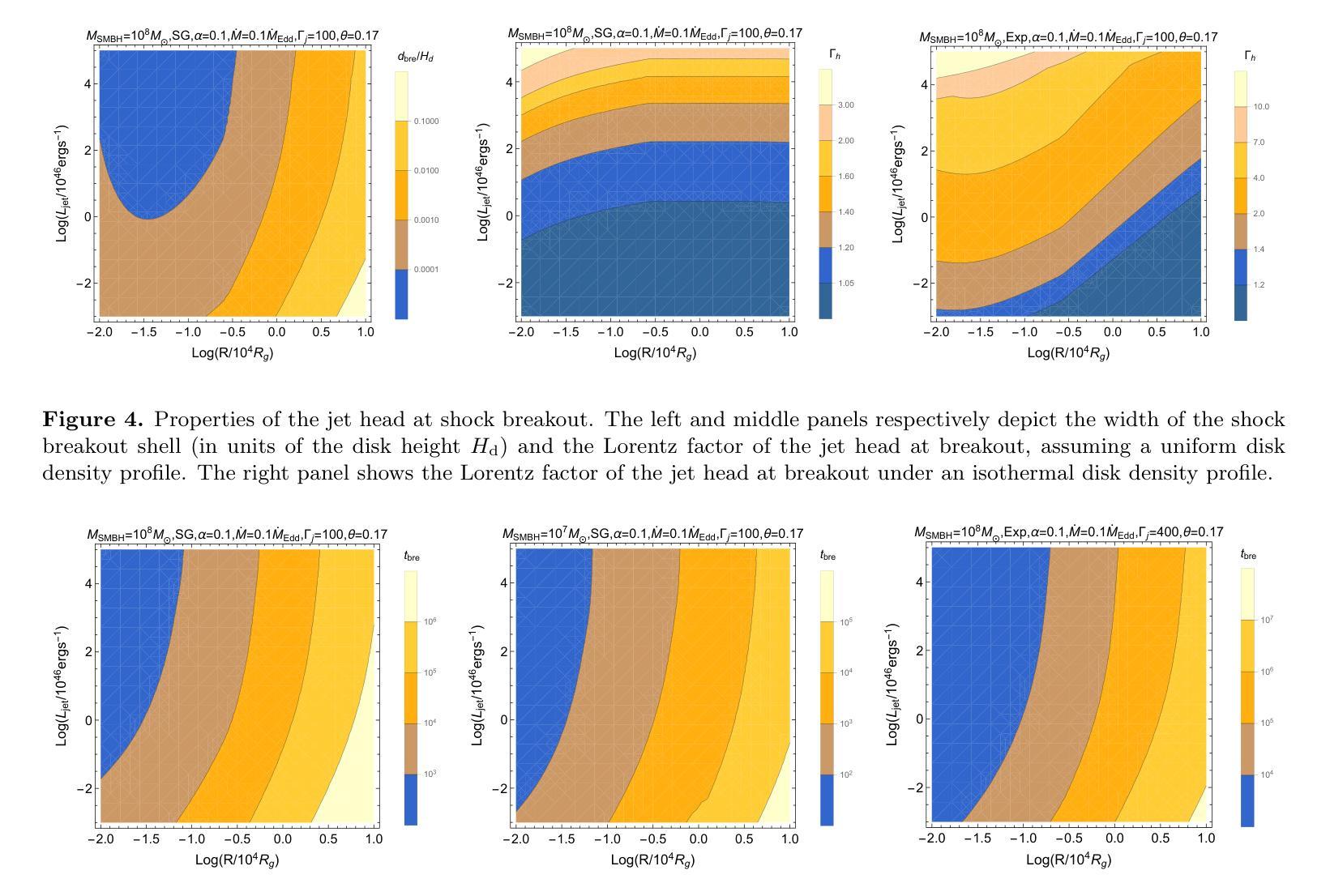
Observational Properties of Thermal Emission from Relativistic Jets Embedded in AGN Disks
Authors:Ken Chen, Zi-Gao Dai
Relativistic jets can be produced within the accretion disk of an active galactic nucleus (AGN), leading to distinct thermal emission as they propagate through a dense disk environment. In this paper, we present a comprehensive study of dynamical evolution of jets embedded in an AGN disk and their associated observational properties, focusing on scenarios in which jets either successfully break out of the disk or become choked. By modeling the jet-cocoon system propagation, we calculate the thermal emission contributions from the jet-head shock breakout, disk cocoon, and jet cocoon components. Our results reveal that soft X-ray flares are the most prominent observable signatures, with duration ranging from O(10^2) s to O(10^5) s, occasionally exhibiting double-peaked light curves, whereas UV/optical flares are detectable only for powerful jets, persisting for several days to tens of days. This thermal emission serves as a critical electromagnetic counterpart to jet-producing events and provide insights into jet dynamics and AGN disk properties. Our findings highlight the importance of multi-wavelength follow-up observations to establish a diagnostic paradigm for candidate electromagnetic counterpart identification to AGN-embedded events and to distinguish thermal flares from AGN background variability.
在活动星系核(AGN)的吸积盘中可以产生相对论性喷流,它们在稠密的盘环境中传播时会产生独特的热辐射。本文全面研究了嵌入在AGN盘中的喷流的动态演化及其相关的观测特性,重点关注喷流成功突破磁盘或受阻的场景。通过模拟喷流-茧状系统传播,我们计算了喷流头部冲击突破、盘茧和喷流茧组件的热辐射贡献。我们的结果表明,软X射线耀斑是最突出的可观测特征,持续时间从O(10^2)秒到O(10^5)秒不等,偶尔表现出双峰状光曲线,而紫外/光学耀斑仅对强大的喷流可检测,持续数天至数十天。这种热辐射是喷流产生事件的重要电磁对应物,为理解喷流动力和AGN盘特性提供了见解。我们的研究强调了多波长后续观测的重要性,以建立对候选电磁对应物的诊断范式,区分热闪与AGN背景变化。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 29 pages, 12 figures, 2 tables, accepted for publication in ApJ
Summary
活动星系核(AGN)喷流在致密盘环境中传播时,会产生特殊的热辐射。本文研究了喷流在AGN盘中的动态演化及其观测特性,重点研究喷流成功突破圆盘或被阻止的情境。模拟喷流-茧状物系统的传播过程,计算了喷流头部冲击突破、盘茧状物和喷流茧状物组件的热辐射贡献。结果显示软X射线耀斑是最显著的可观测特征,持续时间从几秒到数万秒不等,偶尔会出现双峰光变曲线,而紫外/光学耀斑只对于强大的喷流可检测到,持续数天至数十天。这种热辐射作为喷流产生事件的关键电磁对应体,为理解喷流动力学和AGN盘属性提供了见解。强调多波长后续观测的重要性,为识别与嵌入在AGN中的事件的电磁对应体并建立诊断范式以及区分热耀斑与背景活动星系核的变异性至关重要。
Key Takeaways
- 活动星系核(AGN)喷流在致密盘环境中传播时会产生独特的热辐射。
- 喷流的动态演化及其观测特性是研究重点,包括成功突破圆盘或被阻止的情境。
- 模拟喷流系统的传播以计算不同组件的热辐射贡献。
- 软X射线耀斑是最显著的可观测特征,持续时间从几秒到数万秒不等,偶尔出现双峰光变曲线。
- 紫外/光学耀斑仅对强大的喷流可检测到,持续数天至数十天。
- 热辐射为理解喷流动力学和AGN盘属性提供关键信息。
点此查看论文截图

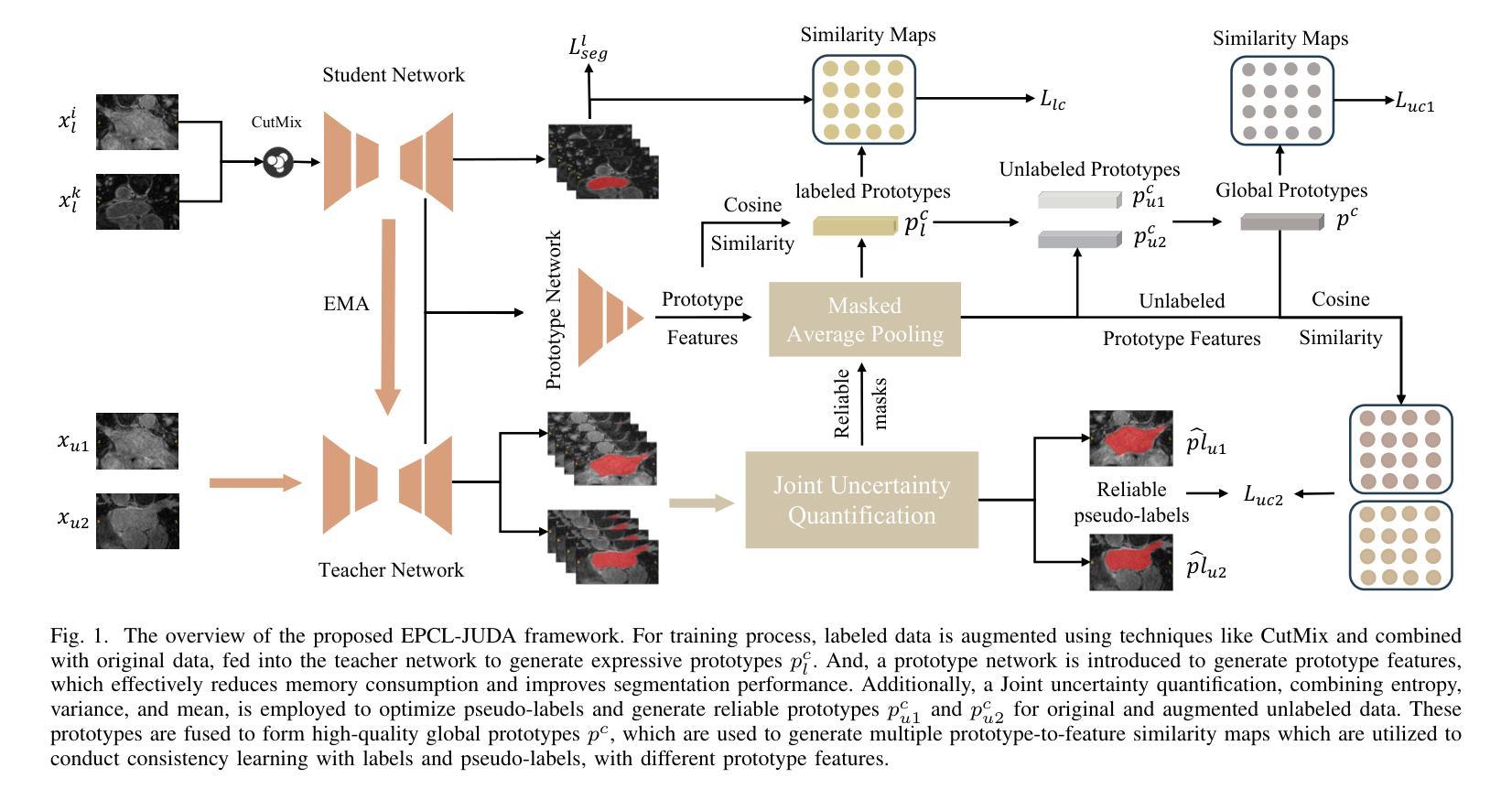
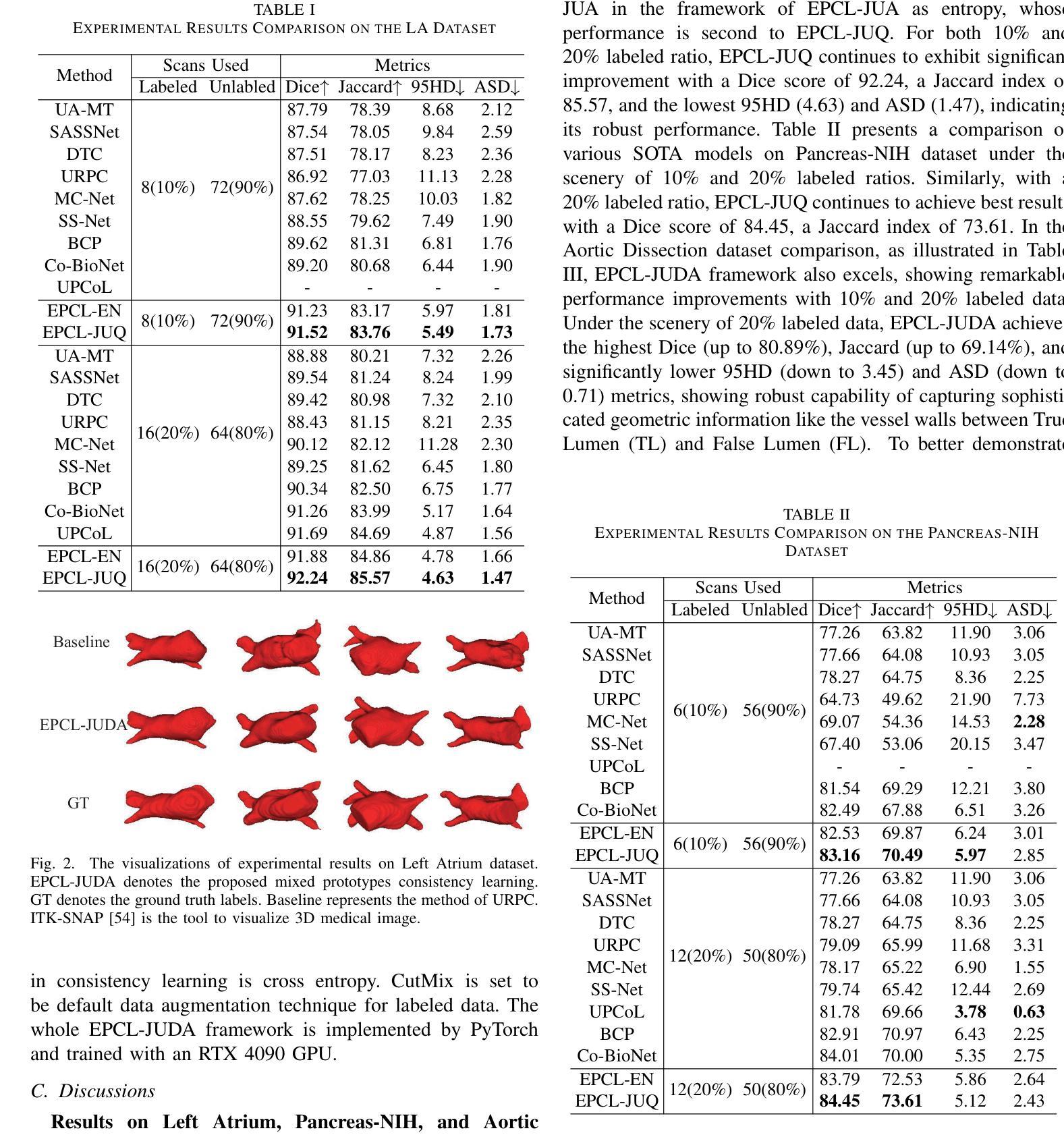
Efficient Prototype Consistency Learning in Medical Image Segmentation via Joint Uncertainty and Data Augmentation
Authors:Lijian Li, Yuanpeng He, Chi-Man Pun
Recently, prototype learning has emerged in semi-supervised medical image segmentation and achieved remarkable performance. However, the scarcity of labeled data limits the expressiveness of prototypes in previous methods, potentially hindering the complete representation of prototypes for class embedding. To overcome this issue, we propose an efficient prototype consistency learning via joint uncertainty quantification and data augmentation (EPCL-JUDA) to enhance the semantic expression of prototypes based on the framework of Mean-Teacher. The concatenation of original and augmented labeled data is fed into student network to generate expressive prototypes. Then, a joint uncertainty quantification method is devised to optimize pseudo-labels and generate reliable prototypes for original and augmented unlabeled data separately. High-quality global prototypes for each class are formed by fusing labeled and unlabeled prototypes, which are utilized to generate prototype-to-features to conduct consistency learning. Notably, a prototype network is proposed to reduce high memory requirements brought by the introduction of augmented data. Extensive experiments on Left Atrium, Pancreas-NIH, Type B Aortic Dissection datasets demonstrate EPCL-JUDA’s superiority over previous state-of-the-art approaches, confirming the effectiveness of our framework. The code will be released soon.
近期,原型学习在半监督医学图像分割中崭露头角,并获得了显著的性能。然而,标注数据的稀缺性限制了之前方法中原型的表达力,这可能阻碍了原型的完全表示为类嵌入。为了解决这个问题,我们提出了通过联合不确定性量化和数据增强(EPCL-JUDA)的有效原型一致性学习方法,以增强基于Mean-Teacher框架的原型语义表达。原始和增强后的标注数据的组合被输入到学生网络中以生成表达性原型。然后,设计了一种联合不确定性量化方法来优化伪标签并为原始和增强后的无标签数据分别生成可靠原型。通过融合有标签和无标签的原型,形成每个类的高质量全局原型,用于生成原型到特征进行一致性学习。值得注意的是,为了减少由引入增强数据带来的高内存要求,提出了一个原型网络。在左心房、胰腺NIH、B型主动脉夹层数据集上的大量实验表明,EPCL-JUDA优于之前的最新方法,证实了我们的框架的有效性。代码将很快发布。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF arXiv admin note: substantial text overlap with arXiv:2404.10717
Summary
近期,原型学习在医学图像分割的半监督学习中取得了显著成效。但之前的方法受限于标记数据的稀缺性,影响了原型的表达能力。为此,我们提出了基于Mean-Teacher框架的有效原型一致性学习方法EPCL-JUDA。通过联合不确定性量化进行数据增强,增强了原型的语义表达。将原始和增强后的标记数据合并输入学生网络以生成表达性原型。随后,设计了一种联合不确定性量化方法,以优化伪标签并为原始和增强后的未标记数据分别生成可靠的原型。通过融合标记和无标记原型形成高质量的全局原型,用于生成特征并进行一致性学习。此外,还提出了原型网络以降低增强数据带来的高内存需求。在Left Atrium、Pancreas-NIH和Type B Aortic Dissection数据集上的实验证明了EPCL-JUDA的优越性。
Key Takeaways
- 原型学习在医学图像分割的半监督学习中表现出显著成效。
- 现有方法受限于标记数据的稀缺性,影响了原型的表达能力。
- 提出了基于Mean-Teacher框架的有效原型一致性学习方法EPCL-JUDA,增强原型的语义表达。
- 通过联合不确定性量化优化伪标签,为原始和增强后的未标记数据生成可靠原型。
- 通过融合标记和无标记原型形成高质量全局原型,用于特征生成和一致性学习。
- 引入原型网络降低高内存需求。
点此查看论文截图

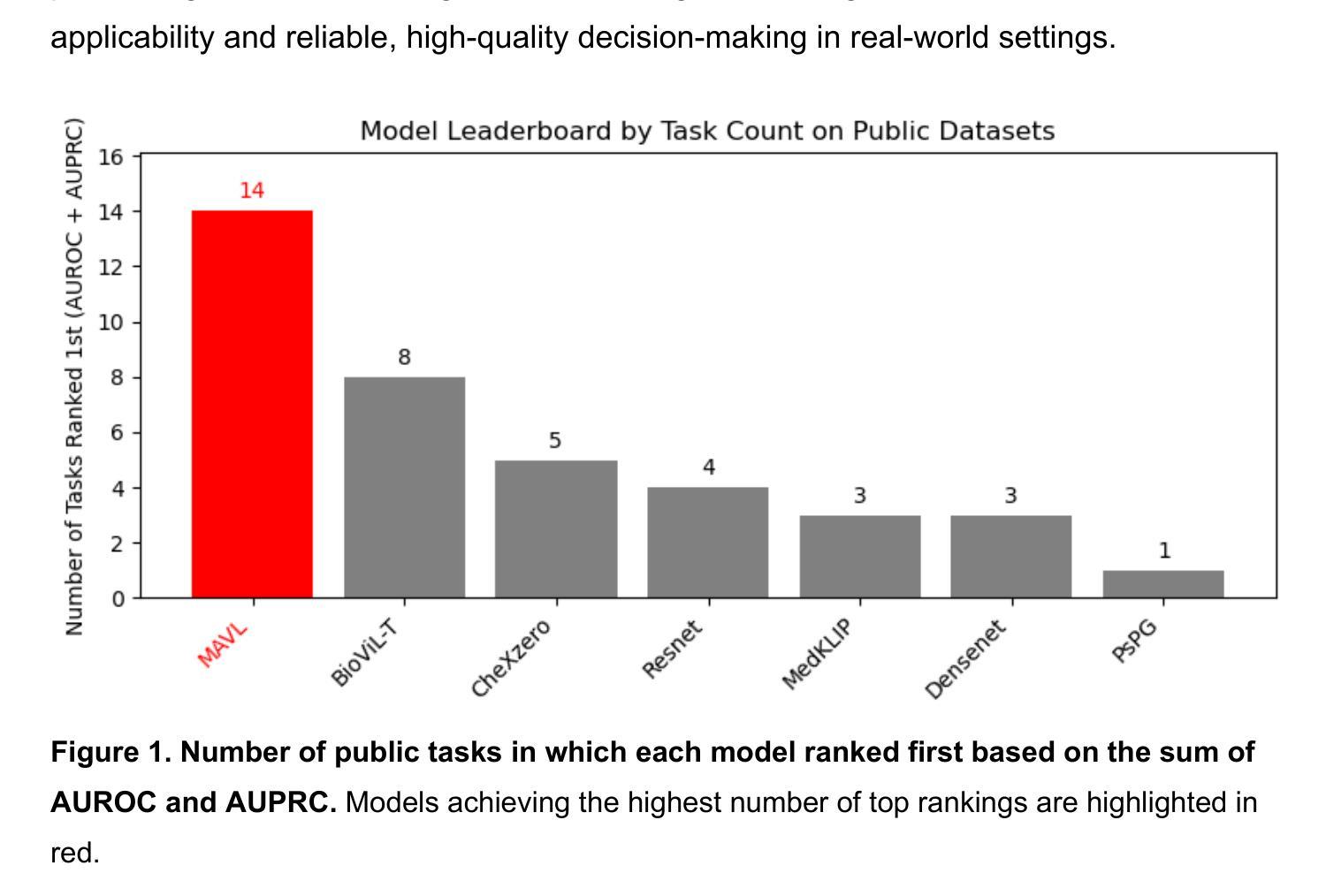
Benchmarking Chest X-ray Diagnosis Models Across Multinational Datasets
Authors:Qinmei Xu, Yiheng Li, Xianghao Zhan, Ahmet Gorkem Er, Brittany Dashevsky, Chuanjun Xu, Mohammed Alawad, Mengya Yang, Liu Ya, Changsheng Zhou, Xiao Li, Haruka Itakura, Olivier Gevaert
Foundation models leveraging vision-language pretraining have shown promise in chest X-ray (CXR) interpretation, yet their real-world performance across diverse populations and diagnostic tasks remains insufficiently evaluated. This study benchmarks the diagnostic performance and generalizability of foundation models versus traditional convolutional neural networks (CNNs) on multinational CXR datasets. We evaluated eight CXR diagnostic models - five vision-language foundation models and three CNN-based architectures - across 37 standardized classification tasks using six public datasets from the USA, Spain, India, and Vietnam, and three private datasets from hospitals in China. Performance was assessed using AUROC, AUPRC, and other metrics across both shared and dataset-specific tasks. Foundation models outperformed CNNs in both accuracy and task coverage. MAVL, a model incorporating knowledge-enhanced prompts and structured supervision, achieved the highest performance on public (mean AUROC: 0.82; AUPRC: 0.32) and private (mean AUROC: 0.95; AUPRC: 0.89) datasets, ranking first in 14 of 37 public and 3 of 4 private tasks. All models showed reduced performance on pediatric cases, with average AUROC dropping from 0.88 +/- 0.18 in adults to 0.57 +/- 0.29 in children (p = 0.0202). These findings highlight the value of structured supervision and prompt design in radiologic AI and suggest future directions including geographic expansion and ensemble modeling for clinical deployment. Code for all evaluated models is available at https://drive.google.com/drive/folders/1B99yMQm7bB4h1sVMIBja0RfUu8gLktCE
利用视觉语言预训练的基石模型在胸部X射线(CXR)解读方面显示出潜力,然而它们在多样人群和诊断任务中的现实世界性能仍评价不足。本研究在多国CXR数据集上,对基石模型与传统卷积神经网络(CNN)的诊断性能和泛化能力进行了评估。我们评估了8种CXR诊断模型(5种视觉语言基石模型和3种基于CNN的架构)在37个标准化分类任务上的表现,这些任务使用了来自美国、西班牙、印度和越南的六个公开数据集以及来自中国三家医院的三个私有数据集。性能评估采用AUROC、AUPRC和其他指标,包括共享任务和特定数据集的任务。基石模型在准确度和任务覆盖方面都优于CNN。MAVL模型结合了知识增强提示和结构化监督,在公开数据集(平均AUROC:0.82;AUPRC:0.32)和私有数据集(平均AUROC:0.95;AUPRC:0.89)上取得了最高性能,在37个公开任务中排名第一14个,在4个私有任务中排名第一3个。所有模型在儿科病例中的表现都有所下降,成年人和儿童的平均AUROC分别从0.88 +/- 0.18下降到0.57 +/- 0.29(p = 0.0202)。这些发现突显了结构化监督和提示设计在放射学人工智能中的价值,并提示未来的方向包括地理扩张和集成建模以用于临床部署。所有评估模型的代码可在https://drive.google.com/drive/folders/1B99yMQm7bB4h1sVMIBja0RfUu8gLktCE处获得。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 78 pages, 7 figures, 2 tabeles
Summary
本文研究了基于视觉语言预训练的模型在跨国胸部X射线(CXR)数据集上的诊断性能与泛化能力。对比了五种视觉语言基础模型和三种卷积神经网络(CNN)架构的八个CXR诊断模型,发现基础模型在准确度和任务覆盖方面都优于CNN。其中,结合了知识增强提示和结构化监督的MAVL模型在公共数据集和私有数据集上表现最佳。所有模型在儿科病例中的表现都有所下降,这表明未来需要进一步研究如何改进模型处理儿科病例的能力。代码可在Google Drive找到。
Key Takeaways
- 基于视觉语言预训练的模型在胸部X射线(CXR)解读中展现出潜力。
- 研究对比了八种CXR诊断模型(五种基础模型和三种CNN架构)在跨国数据集上的性能。
- 基础模型在准确度和任务覆盖方面优于CNN。
- MAVL模型结合了知识增强提示和结构化监督,在多数任务中表现最佳。
- 所有模型在儿科病例中的表现下降,提示需要改进模型处理儿科病例的能力。
- 研究强调了结构化监督和提示设计在放射学人工智能中的重要性。
点此查看论文截图

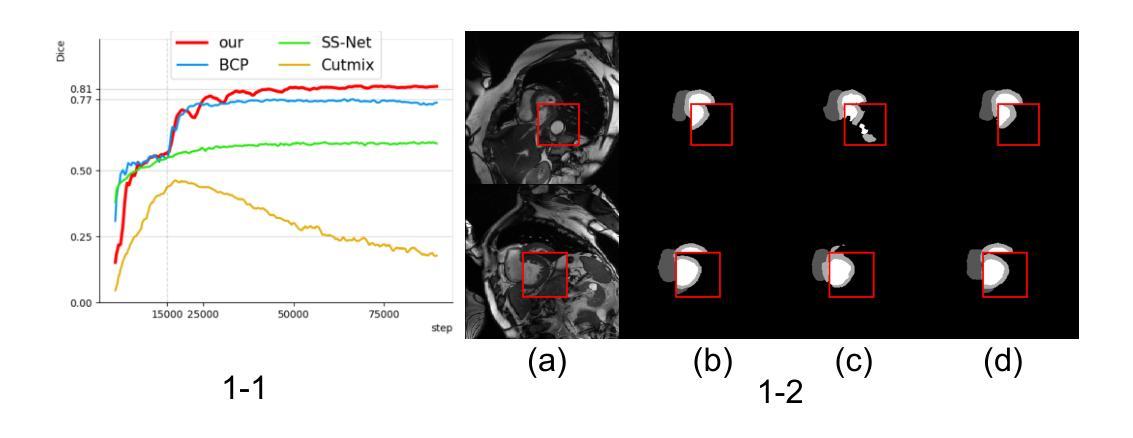
P3Net: Progressive and Periodic Perturbation for Semi-Supervised Medical Image Segmentation
Authors:Zhenyan Yao, Miao Zhang, Lanhu Wu, Yongri Piao, Feng Tian, Weibing Sun, Huchuan Lu
Perturbation with diverse unlabeled data has proven beneficial for semi-supervised medical image segmentation (SSMIS). While many works have successfully used various perturbation techniques, a deeper understanding of learning perturbations is needed. Excessive or inappropriate perturbation can have negative effects, so we aim to address two challenges: how to use perturbation mechanisms to guide the learning of unlabeled data through labeled data, and how to ensure accurate predictions in boundary regions. Inspired by human progressive and periodic learning, we propose a progressive and periodic perturbation mechanism (P3M) and a boundary-focused loss. P3M enables dynamic adjustment of perturbations, allowing the model to gradually learn them. Our boundary-focused loss encourages the model to concentrate on boundary regions, enhancing sensitivity to intricate details and ensuring accurate predictions. Experimental results demonstrate that our method achieves state-of-the-art performance on two 2D and 3D datasets. Moreover, P3M is extendable to other methods, and the proposed loss serves as a universal tool for improving existing methods, highlighting the scalability and applicability of our approach.
扰动技术在半监督医学图像分割(SSMIS)中,应用多样化的无标签数据已经证明是有益的。虽然许多工作已经成功地使用了各种扰动技术,但对学习扰动的理解仍然不够深入。过度的或不适当的扰动会产生负面影响,因此,我们旨在解决两个挑战:一是如何使用扰动机制通过有标签数据引导无标签数据的学习,二是如何确保边界区域的准确预测。受人类渐进式和周期性学习过程的启发,我们提出了一种渐进式和周期性扰动机制(P3M)和一种边界聚焦损失。P3M能够动态调整扰动,使模型能够逐步学习它们。我们的边界聚焦损失鼓励模型专注于边界区域,提高对复杂细节的敏感性,并确保准确预测。实验结果表明,我们的方法在二维和三维数据集上达到了最先进的性能。此外,P3M可扩展到其他方法,所提出的损失可作为改进现有方法的通用工具,突出了我们方法的可扩展性和适用性。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
半监督医学图像分割中利用多样无标签数据的扰动已证明有益。本文提出一种渐进式周期扰动机制(P3M)和边界聚焦损失,旨在解决如何利用扰动机制通过有标签数据引导无标签数据学习,以及如何在边界区域确保准确预测的挑战。该机制可动态调整扰动,使模型逐步学习。边界聚焦损失鼓励模型关注边界区域,提高敏感度和预测准确性。实验结果表明,该方法在二维和三维数据集上均达到最新技术水平。此外,P3M可扩展到其他方法,所提出的损失可作为改进现有方法的通用工具,凸显了方法的可扩展性和适用性。
Key Takeaways
- 多样无标签数据的扰动对半监督医学图像分割有益。
- 提出渐进式周期扰动机制(P3M)以动态调整扰动,使模型逐步学习。
- 引入边界聚焦损失,以提高模型对边界区域的敏感度和预测准确性。
- 实验结果显示该方法在二维和三维数据集上表现优异。
- P3M可扩展到其他方法,显示出其适用性。
- 所提出的损失函数可作为改进现有方法的通用工具。
点此查看论文截图

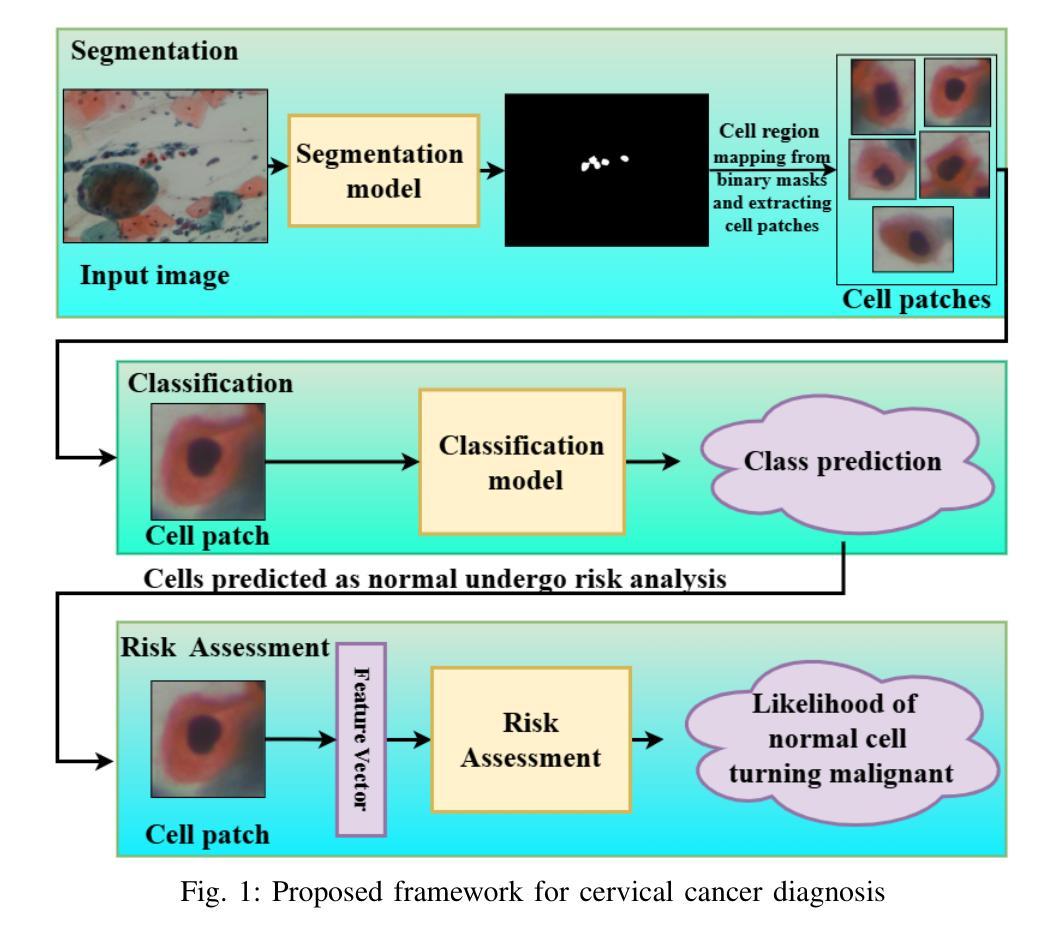
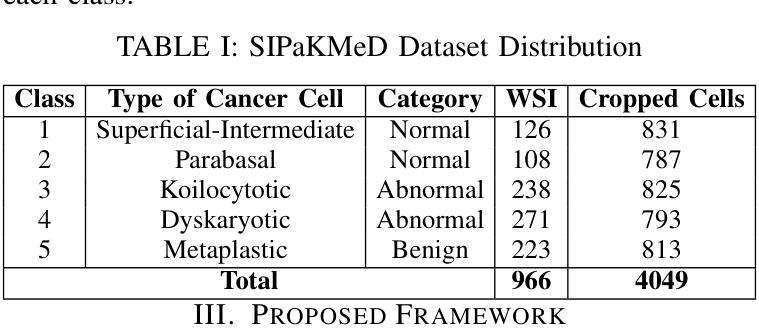
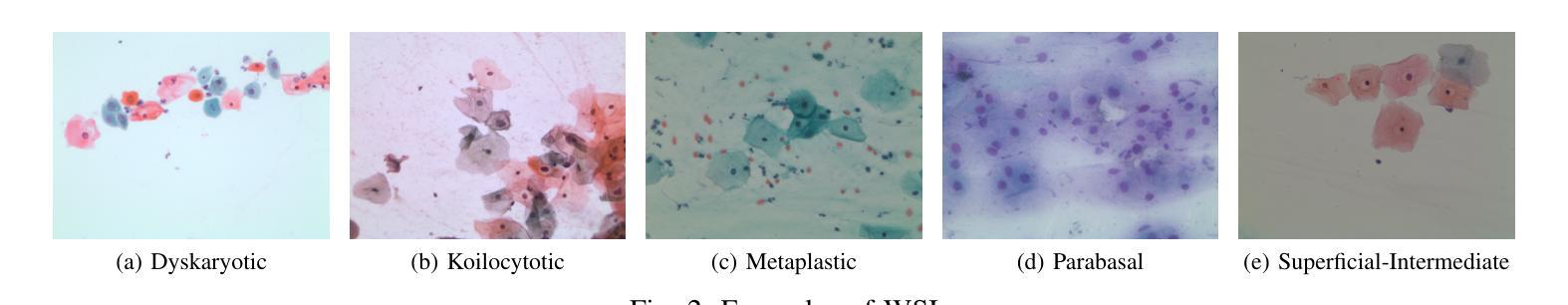
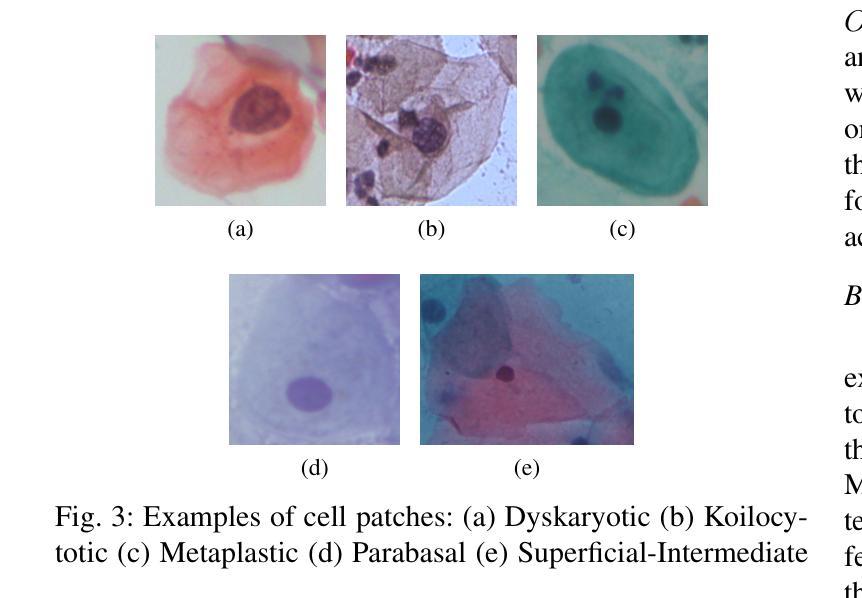
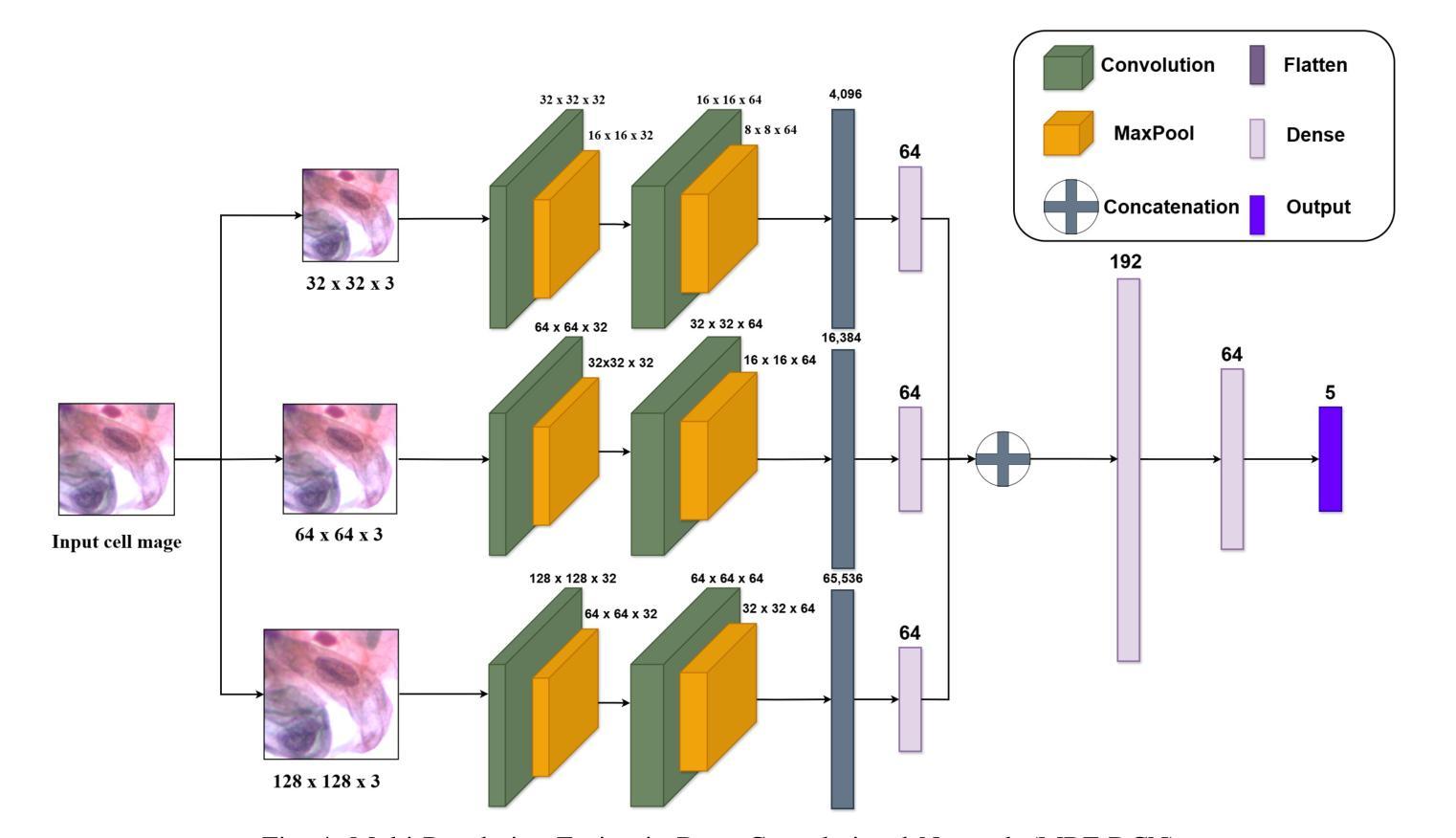
Deep Learning Enabled Segmentation, Classification and Risk Assessment of Cervical Cancer
Authors:Abdul Samad Shaik, Shashaank Mattur Aswatha, Rahul Jashvantbhai Pandya
Cervical cancer, the fourth leading cause of cancer in women globally, requires early detection through Pap smear tests to identify precancerous changes and prevent disease progression. In this study, we performed a focused analysis by segmenting the cellular boundaries and drawing bounding boxes to isolate the cancer cells. A novel Deep Learning (DL) architecture, the ``Multi-Resolution Fusion Deep Convolutional Network”, was proposed to effectively handle images with varying resolutions and aspect ratios, with its efficacy showcased using the SIPaKMeD dataset. The performance of this DL model was observed to be similar to the state-of-the-art models, with accuracy variations of a mere 2% to 3%, achieved using just 1.7 million learnable parameters, which is approximately 85 times less than the VGG-19 model. Furthermore, we introduced a multi-task learning technique that simultaneously performs segmentation and classification tasks and begets an Intersection over Union score of 0.83 and a classification accuracy of 90%. The final stage of the workflow employs a probabilistic approach for risk assessment, extracting feature vectors to predict the likelihood of normal cells progressing to malignant states, which can be utilized for the prognosis of cervical cancer.
宫颈癌是全球女性第四大常见癌症,需要通过涂片检查进行早期检测,以识别癌前病变并防止疾病进展。本研究中,我们通过分割细胞边界和绘制边界框来进行有针对性的分析,以隔离癌细胞。我们提出了一种新的深度学习(DL)架构——“多分辨率融合深度卷积网络”,该架构能够有效处理不同分辨率和长宽比的图像,其效能通过使用SIPaKMeD数据集得到了展示。此DL模型的表现与最先进的模型相似,仅使用170万可学习参数就达到了仅相差2%至3%的准确率,大约是VGG-19模型的85分之一。此外,我们引入了一种多任务学习技术,可以同时执行分割和分类任务,达到0.83的交并比和90%的分类准确率。工作流程的最后阶段采用概率方法进行风险评估,通过提取特征向量来预测正常细胞发展为恶性状态的可能性,这可用于宫颈癌的预后。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 11 pages, 10 figures
Summary
该研究利用深度学习技术,通过细胞边界分割和包围盒绘制来识别宫颈癌细胞。提出一种新颖的多分辨率融合深度卷积神经网络架构,有效处理不同分辨率和长宽比的图像,并使用SIPaKMeD数据集验证了其有效性。该模型性能与最新模型相似,仅使用约170万个可学习参数便实现了仅相差百分之二至三的精度,约为VGG-19模型的85倍。此外,引入多任务学习技术同时执行分割和分类任务,获得交并比分数为0.83和分类准确度为百分之九十。最后阶段采用概率方法进行风险评估,通过提取特征向量预测正常细胞发展为恶性状态的可能性,可用于预测宫颈癌的预后。
Key Takeaways
- 宫颈癌是全球女性第四大常见癌症,早期检测至关重要,可通过涂片检查发现癌前病变。
- 研究采用深度学习技术识别宫颈癌细胞,通过细胞边界分割和包围盒绘制进行细致分析。
- 提出一种新颖的多分辨率融合深度卷积神经网络架构,能有效处理不同分辨率和长宽比的图像。
- 该深度学习模型性能与最新技术相当,使用较少的可学习参数实现了高准确率。
- 多任务学习技术同时执行分割和分类任务,获得良好的交并比分数和分类准确度。
- 概率方法用于风险评估,可预测正常细胞转变为恶性状态的可能性。
点此查看论文截图

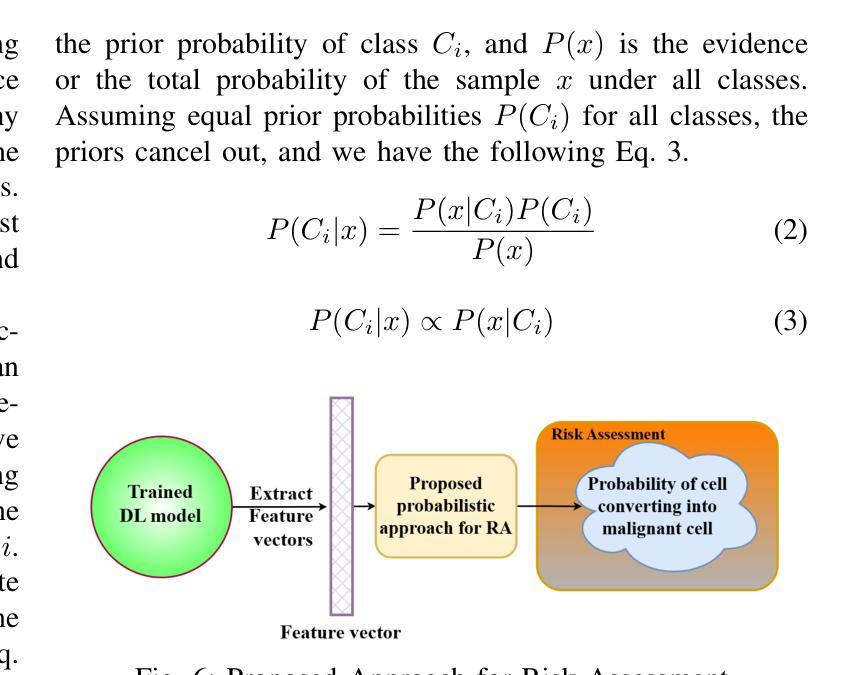
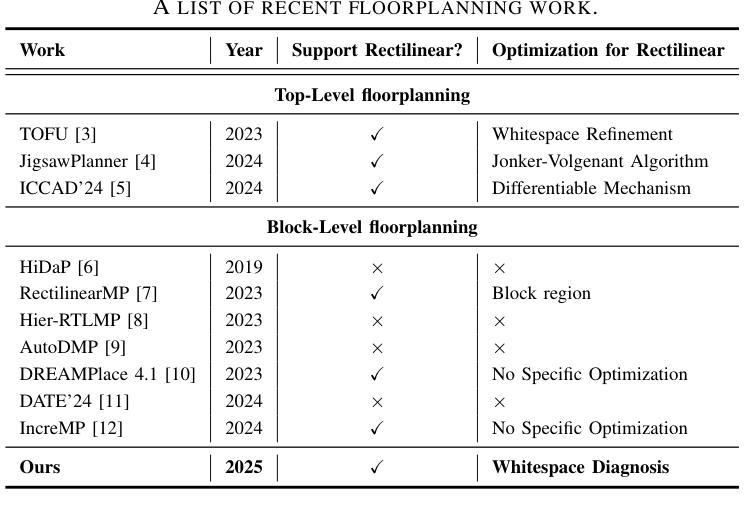
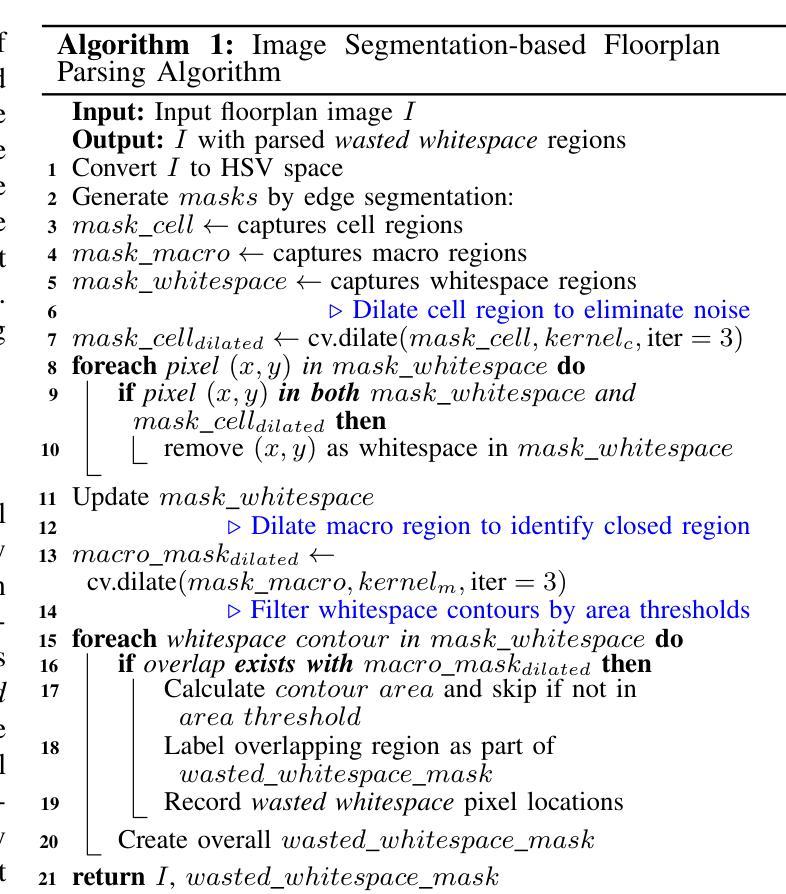
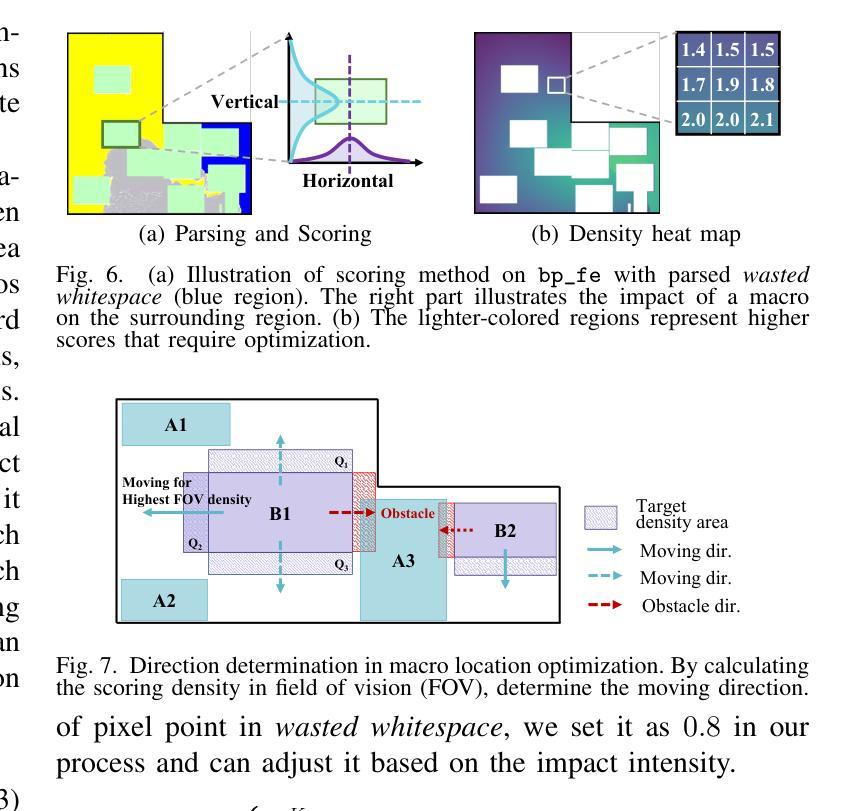
WISP: Image Segmentation-Based Whitespace Diagnosis for Optimal Rectilinear Floorplanning
Authors:Xiaotian Zhao, Zixuan Li, Yichen Cai, Xinfei Guo
The increasing number of rectilinear floorplans in modern chip designs presents significant challenges for traditional macro placers due to the additional complexity introduced by blocked corners. Particularly, the widely adopted wirelength model Half-Perimeter Wirelength (HPWL) struggles to accurately handle rectilinear boundaries, highlighting the need for additional objectives tailored to rectilinear floorplan optimization. In this paper, we identify the necessity for whitespace diagnosis in rectilinear floorplanning, an aspect often overlooked in past research. We introduce WISP, a novel framework that analyzes and scores whitespace regions to guide placement optimization. WISP leverages image segmentation techniques for whitespace parsing, a lightweight probabilistic model to score whitespace regions based on macro distribution, a Gaussian Mixture Model (GMM) for whitespace density scoring and direction-aware macro relocation to iteratively refine macro placement, reduce wasted whitespace, and enhance design quality. The proposed diagnostic technique also enables the reclamation of block-level unused area and its return to the top level, maximizing overall area utilization. When compared against state-of-the-art academia placer DREAMPlace 4.1, our method achieves an average improvement of 5.4% in routing wirelength, with a maximum of 11.4% across widely-used benchmarks. This yields an average of 41.5% and 43.7% improvement in Worst Negative Slack (WNS) and Total Negative Slack (TNS), respectively. Additionally, WISP recycles an average of 16.2% area at the block level, contributing to more efficient top-level area distribution.
在现代芯片设计中,矩形平面设计数量的增加给传统宏放置器带来了重大挑战,因为由于阻塞角落的引入而增加了复杂性。尤其是广泛采用的线长模型半周长线长(HPWL)很难准确处理矩形边界,这突显了需要针对矩形平面设计优化的附加目标。在本文中,我们确定了矩形平面规划中空白区域诊断的必要性,这是过去研究中经常被忽视的一个方面。我们介绍了WISP,这是一个新的框架,它分析和评估空白区域以引导放置优化。WISP利用图像分割技术进行空白区域解析,采用轻量级概率模型根据宏分布对空白区域进行评分,使用高斯混合模型(GMM)进行空白区域密度评分,并提供方向感知宏重新定位,以迭代地优化宏放置、减少浪费的空白区域并提高设计质量。所提出的诊断技术还启用了块级未使用区域的回收并将其返回到顶层,从而最大限度地提高了整体区域利用率。与最新的学术放置器DREAMPlace 4.1相比,我们的方法在路由线长上平均提高了5.4%,在广泛使用的基准测试中最高提高了11.4%。这导致最坏负时差(WNS)和总负时差(TNS)平均分别提高了41.5%和43.7%。此外,WISP在块级别平均回收了16.2%的区域,有助于更有效地分配顶层区域。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
针对现代芯片设计中矩形布局不断增加所带来的复杂性挑战,传统宏放置器面临困境。本文提出一种名为WISP的新型框架,用于分析和评分空白区域,以指导放置优化。WISP利用图像分割技术进行空白区域解析,采用轻量级概率模型对空白区域进行评分,并利用高斯混合模型进行空白区域密度评分和方向感知宏移位,以迭代优化宏放置、减少浪费的空白区域并提高设计质量。此外,该技术还能回收块级未使用的区域并将其返回给顶层,以实现最大面积利用率。与现有的最先进的学术界放置器DREAMPlace 4.1相比,WISP在路由线长上平均提高了5.4%,在最常用的基准测试中最高提高了11.4%。此外,WISP在块级别平均回收了16.2%的面积,有助于提高顶层面积分布的利用率。
Key Takeaways
- 现代芯片设计的矩形布局给传统宏放置器带来了挑战,需要针对矩形布局优化的新策略。
- WISP框架通过分析并评分空白区域来优化宏放置。
- WISP利用图像分割技术、概率模型和高斯混合模型进行空白区域解析、评分和密度评估。
- WISP通过迭代优化宏放置,减少了空白区域的浪费,提高了设计质量。
- WISP能够实现块级未使用区域的回收,并最大化整体面积利用率。
- 与DREAMPlace 4.1相比,WISP在路由线长上有所改进,平均提高了5.4%,在某些基准测试中最高达到了11.4%的提升。
点此查看论文截图


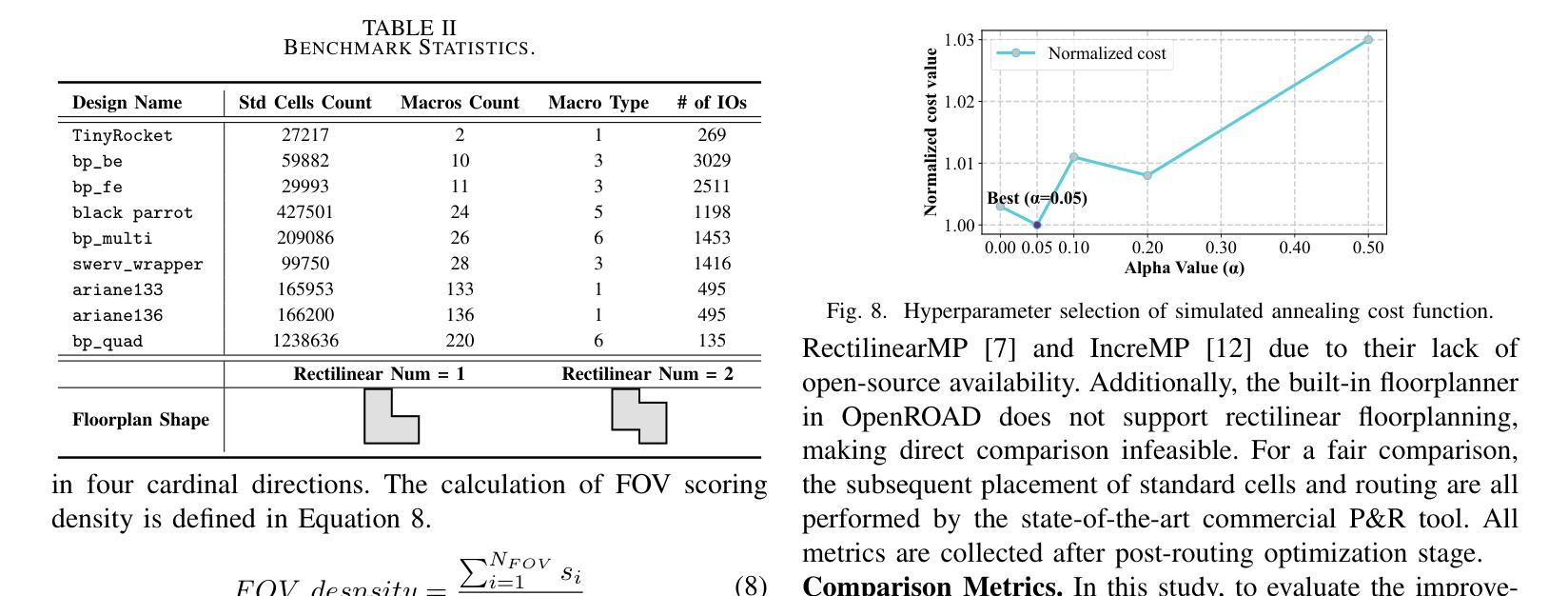
Zero-Shot Gaze-based Volumetric Medical Image Segmentation
Authors:Tatyana Shmykova, Leila Khaertdinova, Ilya Pershin
Accurate segmentation of anatomical structures in volumetric medical images is crucial for clinical applications, including disease monitoring and cancer treatment planning. Contemporary interactive segmentation models, such as Segment Anything Model 2 (SAM-2) and its medical variant (MedSAM-2), rely on manually provided prompts like bounding boxes and mouse clicks. In this study, we introduce eye gaze as a novel informational modality for interactive segmentation, marking the application of eye-tracking for 3D medical image segmentation. We evaluate the performance of using gaze-based prompts with SAM-2 and MedSAM-2 using both synthetic and real gaze data. Compared to bounding boxes, gaze-based prompts offer a time-efficient interaction approach with slightly lower segmentation quality. Our findings highlight the potential of using gaze as a complementary input modality for interactive 3D medical image segmentation.
在三维医学图像中对解剖结构进行精确分割对于临床应用至关重要,包括疾病监测和癌症治疗计划。当代的交互式分割模型,如Segment Anything Model 2(SAM-2)及其医学变体(MedSAM-2),依赖于手动提供的提示信息,如边界框和鼠标点击。在这项研究中,我们引入眼动追踪作为一种新型信息交互模式,用于交互式分割,标志着眼动追踪在三维医学图像分割中的应用。我们使用合成和真实眼动数据评估了基于眼动提示的SAM-2和MedSAM-2的性能。与边界框相比,基于眼动提示的方法提供了一种时间效率更高的交互方式,但分割质量略有下降。我们的研究结果表明,眼动作为一种补充输入模式在交互式三维医学图像分割中具有潜在应用价值。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted to MMFM-BIOMED Workshop @ CVPR 2025
Summary
本文介绍了在医学图像领域中使用眼动追踪技术进行交互式分割研究的重要性及其应用场景。通过对SAM-2和MedSAM-2等模型的研究,将眼动作为新的信息模式用于交互式分割,使用合成和真实眼动数据对基于眼动的提示进行性能评估。结果显示,相较于边界框提示,基于眼动的提示能提高交互效率并稍微降低分割质量,证明了其在交互式三维医学图像分割中的潜在应用价值。
Key Takeaways
- 医学图像分割在临床应用如疾病监测和癌症治疗规划中非常重要。
- 现有的交互式分割模型依赖于手动提示如边界框和鼠标点击。
- 研究引入了眼动追踪作为一种新的交互式分割的信息模式。
- 通过合成和真实眼动数据对眼动提示性能进行评估。
- 基于眼动的提示能提高交互效率。
- 基于眼动的提示对分割质量的影响略低于传统方法。
点此查看论文截图

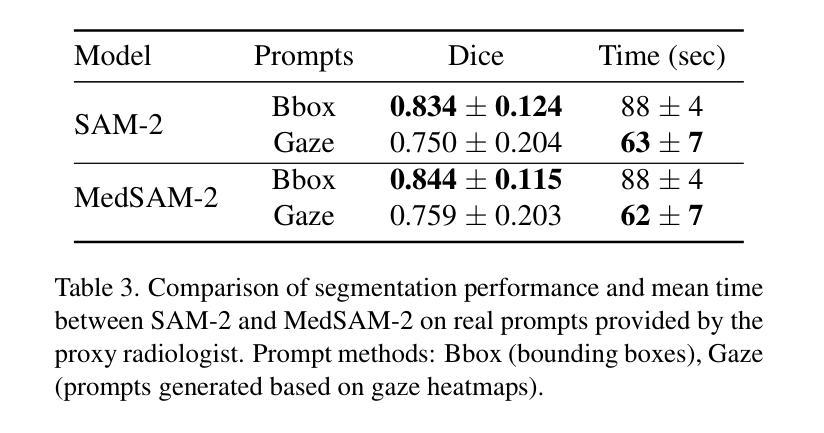
CAD: A General Multimodal Framework for Video Deepfake Detection via Cross-Modal Alignment and Distillation
Authors:Yuxuan Du, Zhendong Wang, Yuhao Luo, Caiyong Piao, Zhiyuan Yan, Hao Li, Li Yuan
The rapid emergence of multimodal deepfakes (visual and auditory content are manipulated in concert) undermines the reliability of existing detectors that rely solely on modality-specific artifacts or cross-modal inconsistencies. In this work, we first demonstrate that modality-specific forensic traces (e.g., face-swap artifacts or spectral distortions) and modality-shared semantic misalignments (e.g., lip-speech asynchrony) offer complementary evidence, and that neglecting either aspect limits detection performance. Existing approaches either naively fuse modality-specific features without reconciling their conflicting characteristics or focus predominantly on semantic misalignment at the expense of modality-specific fine-grained artifact cues. To address these shortcomings, we propose a general multimodal framework for video deepfake detection via Cross-Modal Alignment and Distillation (CAD). CAD comprises two core components: 1) Cross-modal alignment that identifies inconsistencies in high-level semantic synchronization (e.g., lip-speech mismatches); 2) Cross-modal distillation that mitigates feature conflicts during fusion while preserving modality-specific forensic traces (e.g., spectral distortions in synthetic audio). Extensive experiments on both multimodal and unimodal (e.g., image-only/video-only)deepfake benchmarks demonstrate that CAD significantly outperforms previous methods, validating the necessity of harmonious integration of multimodal complementary information.
多媒体深度伪造(视觉和听觉内容同步操纵)的迅速出现破坏了现有检测器的可靠性,这些检测器要么依赖于特定模态的伪迹,要么依赖于跨模态的不一致性。在这项工作中,我们首先证明特定模态的法医痕迹(例如面部替换伪迹或光谱失真)和模态共享的语义不匹配(例如唇语不同步)提供了互补证据,忽略任何一方面都会限制检测性能。现有方法要么简单地融合特定模态的特征,而没有解决其冲突特征,要么主要关注语义不匹配而忽略了特定模态的精细伪迹线索。为了解决这些不足,我们提出了一种基于跨模态对齐和蒸馏(CAD)的视频深度伪造检测通用多模态框架。CAD包含两个核心组件:1)跨模态对齐,用于识别高级语义同步中的不一致(例如唇语不匹配);2)跨模态蒸馏,在融合过程中缓解特征冲突,同时保留特定模态的法医痕迹(例如合成音频中的光谱失真)。在多媒体和单模态(例如仅图像/仅视频)深度伪造基准测试上的广泛实验表明,CAD显著优于以前的方法,验证了和谐整合多模态互补信息的必要性。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
多媒体深度伪造技术快速发展,对现有检测器提出挑战。本研究提出一种基于跨模态对齐和蒸馏(CAD)的通用多媒体框架,通过结合模态特定痕迹和模态共享语义不一致,实现视频深度伪造检测。CAD包含两个核心组件:跨模态对齐和跨模态蒸馏。前者识别高级语义同步的不一致性,后者在融合时缓解特征冲突并保留模态特定痕迹。
Key Takeaways
- 多模态深度伪造技术迅速崛起,对现有检测器构成挑战。
- 模态特定痕迹(例如面部替换痕迹或光谱失真)和模态共享语义不一致(例如唇音不同步)提供互补证据。
- 跨模态对齐是识别高级语义同步不一致性的关键。
- 跨模态蒸馏有助于在融合时缓解特征冲突并保留模态特定细节。
- 提出的CAD框架包含两个核心组件:跨模态对齐和跨模态蒸馏。
- CAD框架显著优于以前的方法,验证了和谐整合多媒体互补信息的必要性。
点此查看论文截图


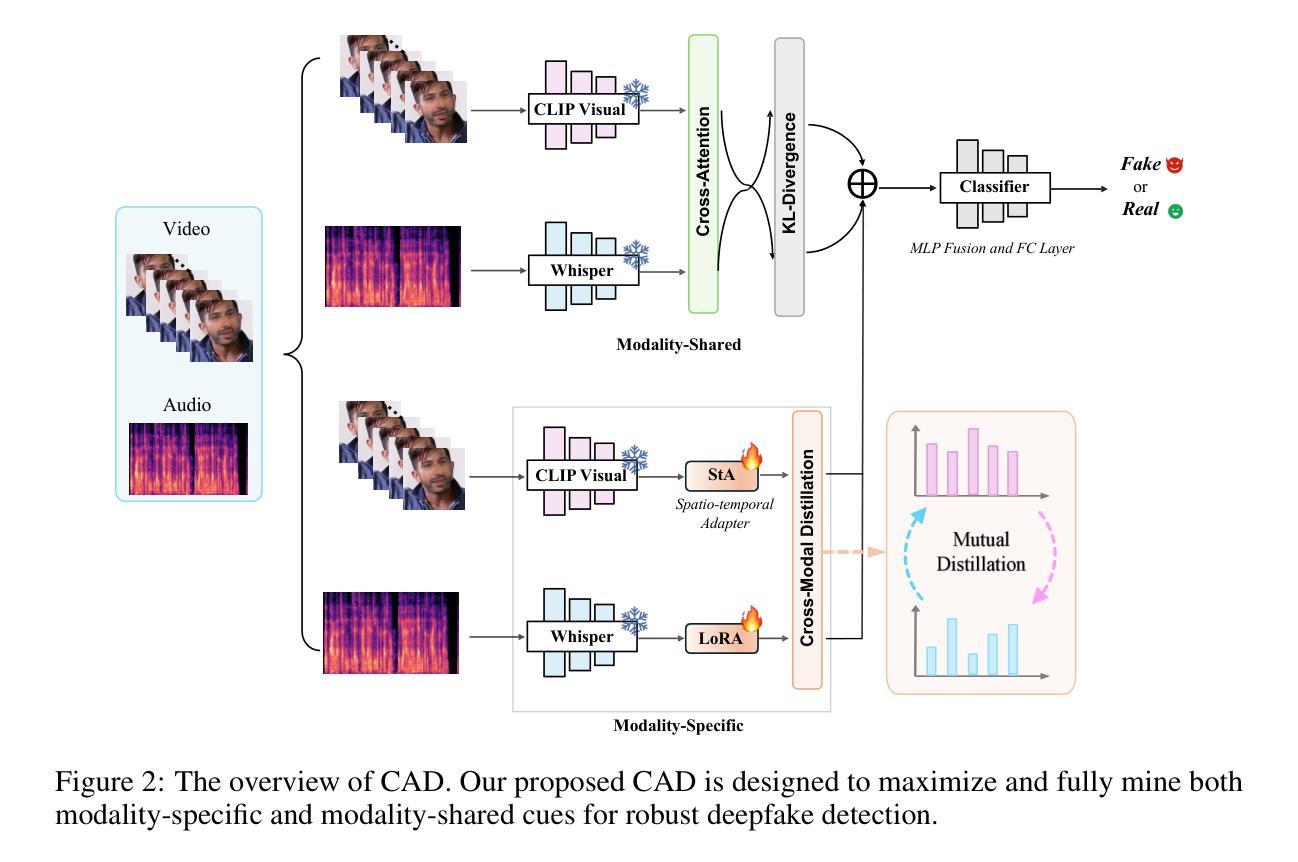
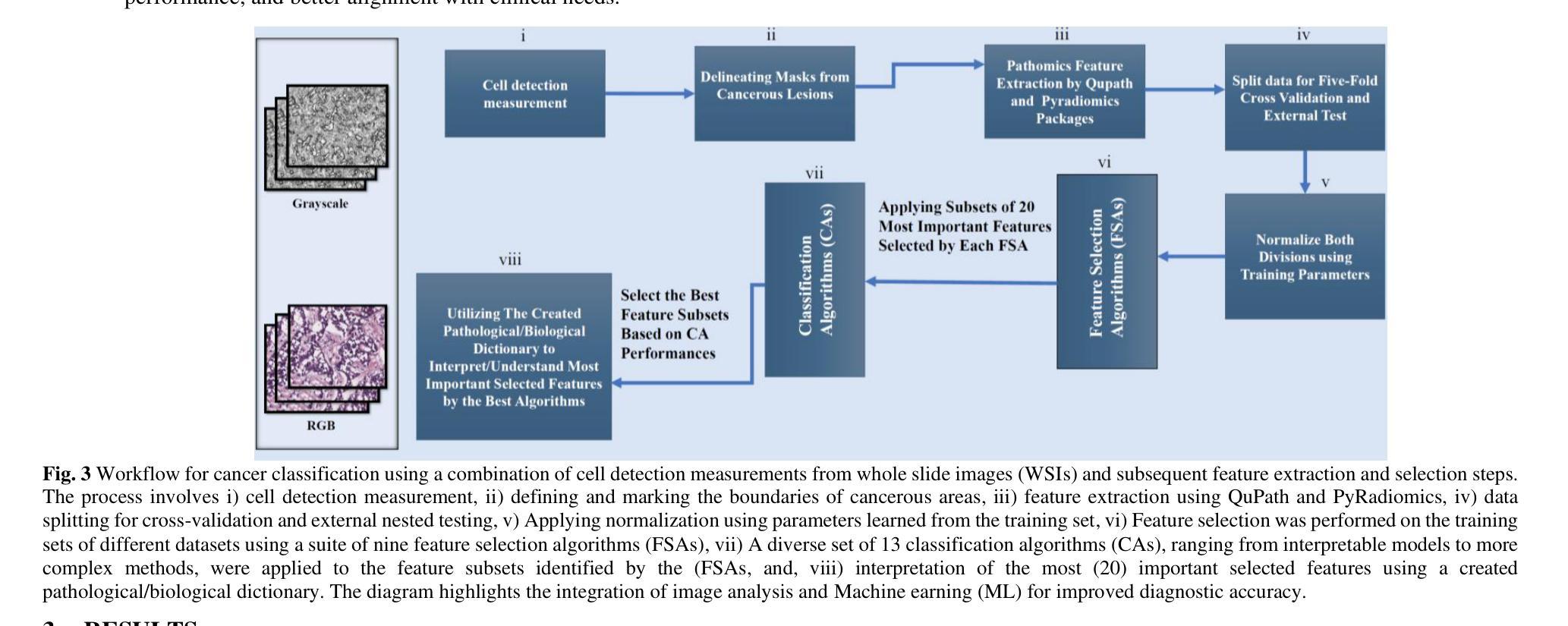
Pathobiological Dictionary Defining Pathomics and Texture Features: Addressing Understandable AI Issues in Personalized Liver Cancer; Dictionary Version LCP1.0
Authors:Mohammad R. Salmanpour, Seyed Mohammad Piri, Somayeh Sadat Mehrnia, Ahmad Shariftabrizi, Masume Allahmoradi, Venkata SK. Manem, Arman Rahmim, Ilker Hacihaliloglu
Artificial intelligence (AI) holds strong potential for medical diagnostics, yet its clinical adoption is limited by a lack of interpretability and generalizability. This study introduces the Pathobiological Dictionary for Liver Cancer (LCP1.0), a practical framework designed to translate complex Pathomics and Radiomics Features (PF and RF) into clinically meaningful insights aligned with existing diagnostic workflows. QuPath and PyRadiomics, standardized according to IBSI guidelines, were used to extract 333 imaging features from hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) tissue samples, including 240 PF-based-cell detection/intensity, 74 RF-based texture, and 19 RF-based first-order features. Expert-defined ROIs from the public dataset excluded artifact-prone areas, and features were aggregated at the case level. Their relevance to the WHO grading system was assessed using multiple classifiers linked with feature selectors. The resulting dictionary was validated by 8 experts in oncology and pathology. In collaboration with 10 domain experts, we developed a Pathobiological dictionary of imaging features such as PFs and RF. In our study, the Variable Threshold feature selection algorithm combined with the SVM model achieved the highest accuracy (0.80, P-value less than 0.05), selecting 20 key features, primarily clinical and pathomics traits such as Centroid, Cell Nucleus, and Cytoplasmic characteristics. These features, particularly nuclear and cytoplasmic, were strongly associated with tumor grading and prognosis, reflecting atypia indicators like pleomorphism, hyperchromasia, and cellular orientation.The LCP1.0 provides a clinically validated bridge between AI outputs and expert interpretation, enhancing model transparency and usability. Aligning AI-derived features with clinical semantics supports the development of interpretable, trustworthy diagnostic tools for liver cancer pathology.
人工智能(AI)在医学诊断方面拥有巨大潜力,但其临床应用受限于缺乏可解释性和泛化能力。本研究引入了肝癌生物病理学词典(LCP1.0),这是一个实用框架,旨在将复杂的病理学和放射学特征(PF和RF)转化为与现有诊断工作流相一致的、具有临床意义的见解。根据IBSI指南进行标准化的QuPath和PyRadiomics被用来从肝细胞癌(HCC)组织样本中提取333个成像特征,包括基于PF的细胞检测/强度特征240个,基于RF的纹理特征74个,基于RF的一阶特征19个。来自公共数据集的专家定义ROI排除了易产生伪影的区域,特征在病例层面进行了汇总。它们与WHO分级系统的相关性通过使用与特征选择器相关联的多重分类器进行评估。该词典得到了8名肿瘤学和病理学专家的验证。我们与10名领域专家合作,开发了病理生物学词典,包括成像特征,如PFs和RFs。在我们的研究中,结合支持向量机(SVM)模型的变量阈值特征选择算法达到了最高的准确性(0.80,P值小于0.05),选择了20个关键特征,主要是临床和病理特征,如质心、细胞核和细胞质特性。这些特征,尤其是细胞核和细胞质特征与肿瘤分级和预后密切相关,反映了诸如异型性、超染色和细胞方向等不典型的指标。LCP1.0为AI输出和专家解释之间提供了临床验证的桥梁,提高了模型的透明度和可用性。将AI衍生的特征与临床语义相结合,为肝癌病理开发可解释、可信赖的诊断工具提供了支持。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 29 pages, 4 figures and 1 table
Summary
本文介绍了人工智能在医学诊断中的潜力及限制,并提出了一种名为LCP1.0的实用框架。该框架能将复杂的Pathmics和Radiomics特征转化为具有临床意义的见解,与现有诊断流程相结合。研究使用QuPath和PyRadiomics提取了肝癌组织样本的333个成像特征,并通过多分类器评估其与WHO分级系统的相关性。最终开发出Pathobiological Dictionary(LCP1.0),实现了AI输出与专家解读之间的桥梁,增强了模型的透明度和可用性。此框架有利于开发可解释、可信赖的肝癌病理诊断工具。
Key Takeaways
- 人工智能在医学诊断中具有潜力,但缺乏解释性和通用性限制了其临床应用。
- LCP1.0框架用于将复杂的Pathmics和Radiomics特征转化为临床意义的见解。
- 研究使用QuPath和PyRadiomics提取肝癌样本的成像特征,包括基于PF的细胞检测和强度、基于RF的纹理和基于RF的一阶特征。
- 特征选择与分类器结合评估特征与WHO分级系统的相关性。
- 通过8位肿瘤学和病理学专家验证Pathobiological Dictionary(LCP1.0)。
- Variable Threshold特征选择算法结合SVM模型取得最高准确度(0.80),选出与肿瘤分级和预后密切相关的关键特征。这些特征主要包括临床和病理特征,如质心、细胞核和细胞质特性。
点此查看论文截图

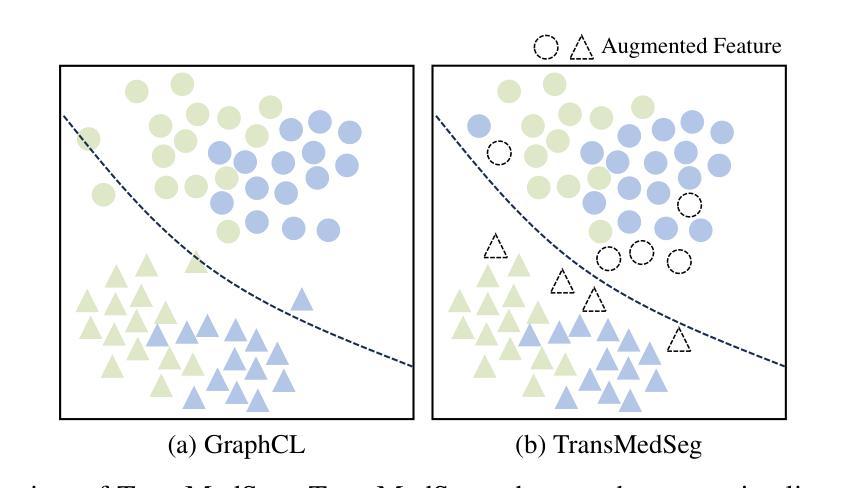
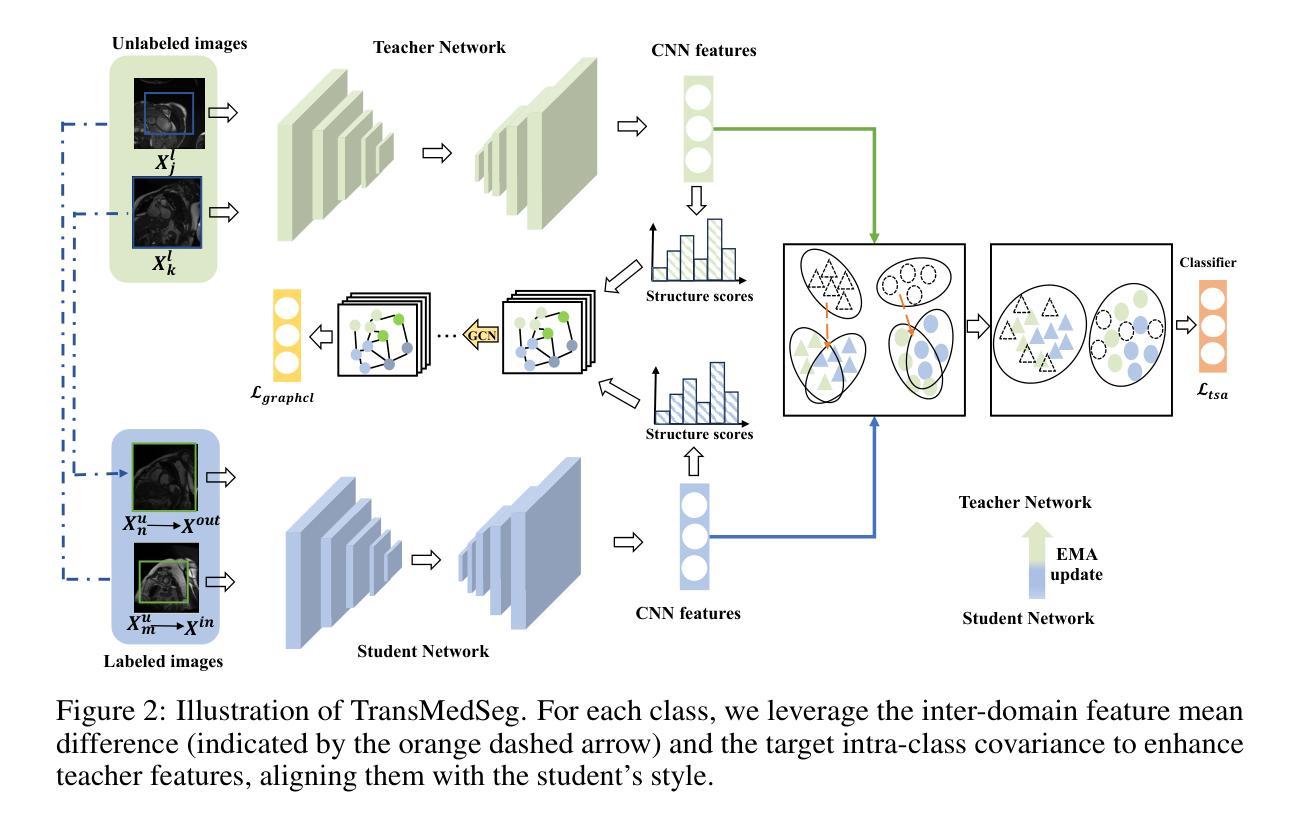
TransMedSeg: A Transferable Semantic Framework for Semi-Supervised Medical Image Segmentation
Authors:Mengzhu Wang, Jiao Li, Shanshan Wang, Long Lan, Huibin Tan, Liang Yang, Guoli Yang
Semi-supervised learning (SSL) has achieved significant progress in medical image segmentation (SSMIS) through effective utilization of limited labeled data. While current SSL methods for medical images predominantly rely on consistency regularization and pseudo-labeling, they often overlook transferable semantic relationships across different clinical domains and imaging modalities. To address this, we propose TransMedSeg, a novel transferable semantic framework for semi-supervised medical image segmentation. Our approach introduces a Transferable Semantic Augmentation (TSA) module, which implicitly enhances feature representations by aligning domain-invariant semantics through cross-domain distribution matching and intra-domain structural preservation. Specifically, TransMedSeg constructs a unified feature space where teacher network features are adaptively augmented towards student network semantics via a lightweight memory module, enabling implicit semantic transformation without explicit data generation. Interestingly, this augmentation is implicitly realized through an expected transferable cross-entropy loss computed over the augmented teacher distribution. An upper bound of the expected loss is theoretically derived and minimized during training, incurring negligible computational overhead. Extensive experiments on medical image datasets demonstrate that TransMedSeg outperforms existing semi-supervised methods, establishing a new direction for transferable representation learning in medical image analysis.
半监督学习(SSL)在医学图像分割(SSMIS)中通过有效利用有限的标记数据取得了显著进展。虽然当前用于医学图像的SSL方法主要依赖于一致性正则化和伪标签,但它们常常忽视了不同临床域和成像模式之间的可转移语义关系。为了解决这一问题,我们提出了TransMedSeg,这是一种用于半监督医学图像分割的可转移语义框架。我们的方法引入了一个可转移语义增强(TSA)模块,该模块通过跨域分布匹配和域内结构保留来对齐域不变语义,从而隐式地增强特征表示。具体来说,TransMedSeg构建了一个统一的特征空间,其中教师网络特征通过轻量级内存模块自适应地增强向学生网络语义,实现了隐式语义转换,无需显式数据生成。有趣的是,这种增强是通过在增强教师分布上计算的预期可转移交叉熵损失来隐式实现的。理论上推导了预期损失的上界,并在训练过程中进行最小化,几乎不会引起计算开销的增加。在医学图像数据集上的广泛实验表明,TransMedSeg优于现有的半监督方法,为医学图像分析中的可转移表示学习提供了新的方向。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
医学图像半监督学习(SSMIS)已经取得显著进展,但仍存在忽视跨不同临床领域和成像模态的可转移语义关系的问题。为此,提出了TransMedSeg,一种用于医学图像分割的新型可转移语义框架。它引入了一个可转移语义增强(TSA)模块,通过跨域分布匹配和域内结构保留隐式增强特征表示。TransMedSeg构建了一个统一特征空间,通过轻量级内存模块自适应增强教师网络特征向学生网络语义对齐,实现隐式语义转换。此外,通过预期的跨熵损失计算教师分布的增强版,实现隐性增强。理论推导预期损失的上界,并在训练过程中最小化,计算开销小。在医学图像数据集上的实验表明,TransMedSeg优于现有半监督方法,为医学图像分析中的可转移表示学习指明了新方向。
Key Takeaways
- TransMedSeg是一种针对医学图像分割的半监督学习新方法,旨在解决现有方法忽视跨不同临床领域和成像模态的可转移语义关系的问题。
- TransMedSeg引入TSA模块,通过跨域分布匹配和域内结构保留隐式增强特征表示,构建统一特征空间。
- 教师网络特征通过轻量级内存模块自适应地向学生网络语义对齐,实现隐式语义转换。
- TransMedSeg利用预期的跨熵损失计算教师分布的增强版,实现隐性增强,最小化理论推导的预期损失上界。
- TransMedSeg相对于现有半监督方法表现出优越性,为医学图像分析的可转移表示学习提供新的方向。
- TransMedSeg在处理医学图像分割任务时能有效利用有限的标注数据。
点此查看论文截图

MedBLIP: Fine-tuning BLIP for Medical Image Captioning
Authors:Manshi Limbu, Diwita Banerjee
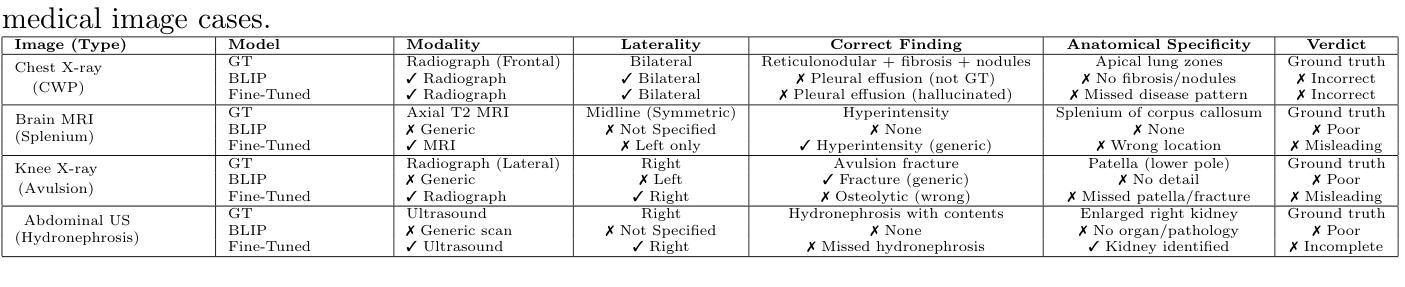
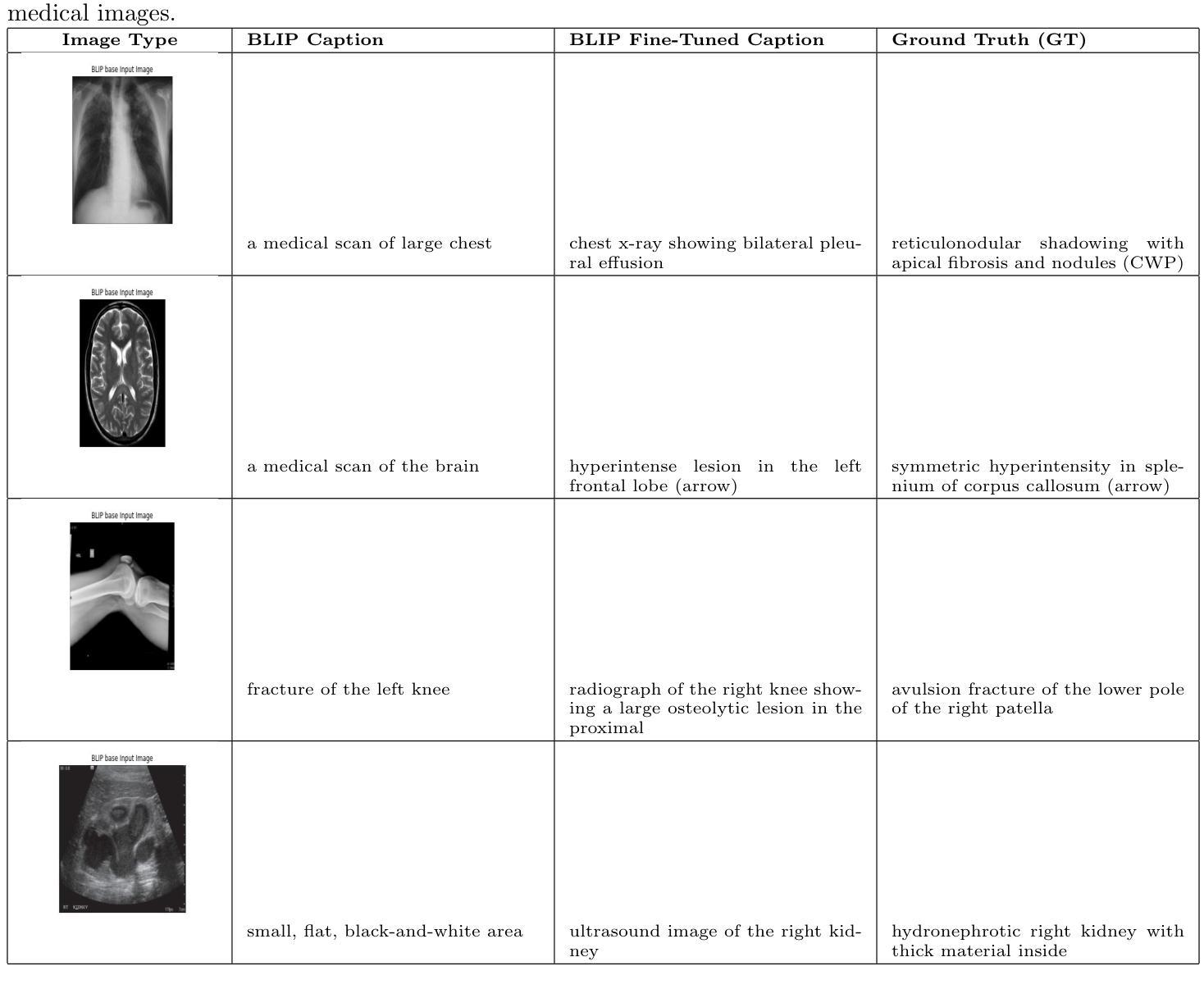
Medical image captioning is a challenging task that requires generating clinically accurate and semantically meaningful descriptions of radiology images. While recent vision-language models (VLMs) such as BLIP, BLIP2, Gemini and ViT-GPT2 show strong performance on natural image datasets, they often produce generic or imprecise captions when applied to specialized medical domains. In this project, we explore the effectiveness of fine-tuning the BLIP model on the ROCO dataset for improved radiology captioning. We compare the fine-tuned BLIP against its zero-shot version, BLIP-2 base, BLIP-2 Instruct and a ViT-GPT2 transformer baseline. Our results demonstrate that domain-specific fine-tuning on BLIP significantly improves performance across both quantitative and qualitative evaluation metrics. We also visualize decoder cross-attention maps to assess interpretability and conduct an ablation study to evaluate the contributions of encoder-only and decoder-only fine-tuning. Our findings highlight the importance of targeted adaptation for medical applications and suggest that decoder-only fine-tuning (encoder-frozen) offers a strong performance baseline with 5% lower training time than full fine-tuning, while full model fine-tuning still yields the best results overall.
医学图像标注是一项具有挑战性的任务,需要生成临床准确且语义明确的放射学图像描述。虽然最近的视觉语言模型(VLMs),如BLIP、BLIP2、Gemini和ViT-GPT2在自然图像数据集上表现出强大的性能,但它们应用于专业医学领域时,通常会产生通用或不够精确的标注。在本项目中,我们探讨了使用ROCO数据集对BLIP模型进行微调以改进放射学标注的有效性。我们将微调后的BLIP与其零样本版本、BLIP-2基础版、BLIP-2指令版和ViT-GPT2转换器基线进行了比较。我们的结果表明,在BLIP上进行特定领域的微调显著提高了定量和定性评估指标的性能。我们还通过可视化解码器交叉注意力图来评估可解释性,并进行了一项消融研究,以评估仅编码器微调与仅解码器微调各自的贡献。我们的研究强调了针对医学应用进行有针对性的适应性的重要性,并表明仅对解码器进行微调(冻结编码器)提供了一个强大的性能基准,其训练时间比完全微调低5%,而全模型微调仍然总体上表现最佳。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
医学图像描述是一项挑战任务,需要为放射学图像生成临床准确且语义有意义的描述。本研究通过微调BLIP模型在ROCO数据集上,提高了医学影像描述的效果。对比了微调后的BLIP与零样本版本的BLIP-2基础版、BLIP-2指导版以及ViT-GPT2转换器基线,发现微调BLIP模型在定量和定性评估指标上都有显著提高。同时,本研究还通过可视化解码器交叉注意力图来评估模型的可解释性,并通过消融研究评估了仅编码器或仅解码器微调的影响。结果表明,有针对性的适应对于医学应用至关重要,而仅解码器微调在训练时间上比全模型微调低5%,但仍表现出强大的性能基线。全模型微调仍然是目前最佳选择。
Key Takeaways
- 医学图像描述是一项需要生成临床准确和语义有意义的描述的挑战性任务。
- 研究通过对BLIP模型进行微调,提高了在ROCO数据集上的医学影像描述效果。
- 相比零样本版本的BLIP和其他模型,微调后的BLIP模型在定量和定性评估指标上都有显著提高。
- 可视化解码器交叉注意力图有助于评估模型的可解释性。
- 消融研究结果显示,仅解码器微调在训练时间上具有优势,而全模型微调则表现最佳。
- 针对性的模型适应对于医学应用至关重要。
点此查看论文截图

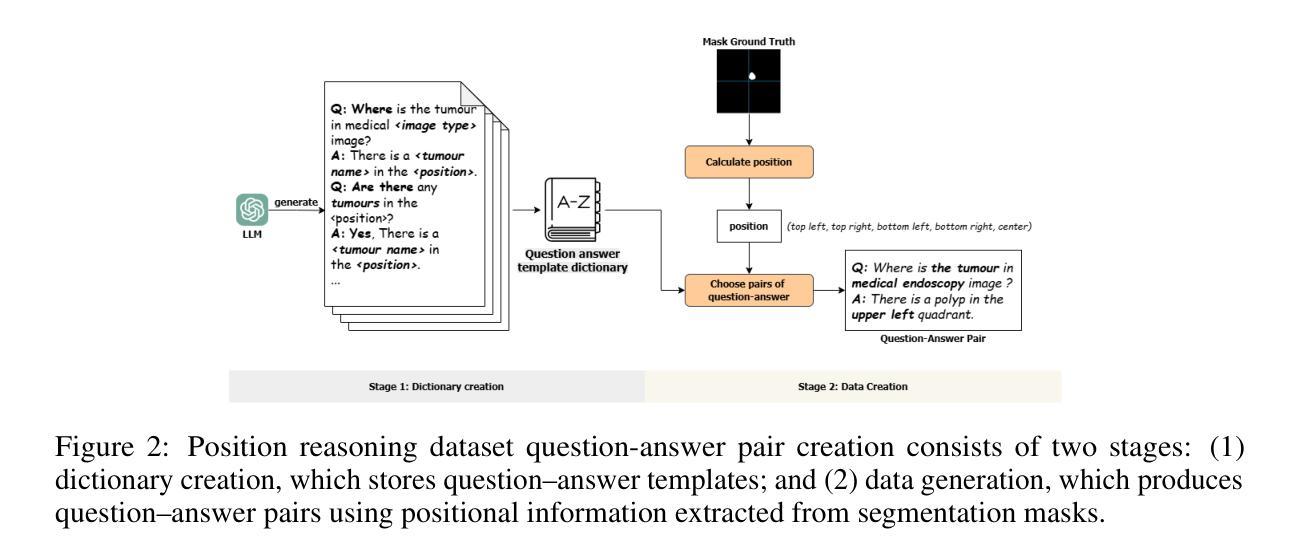
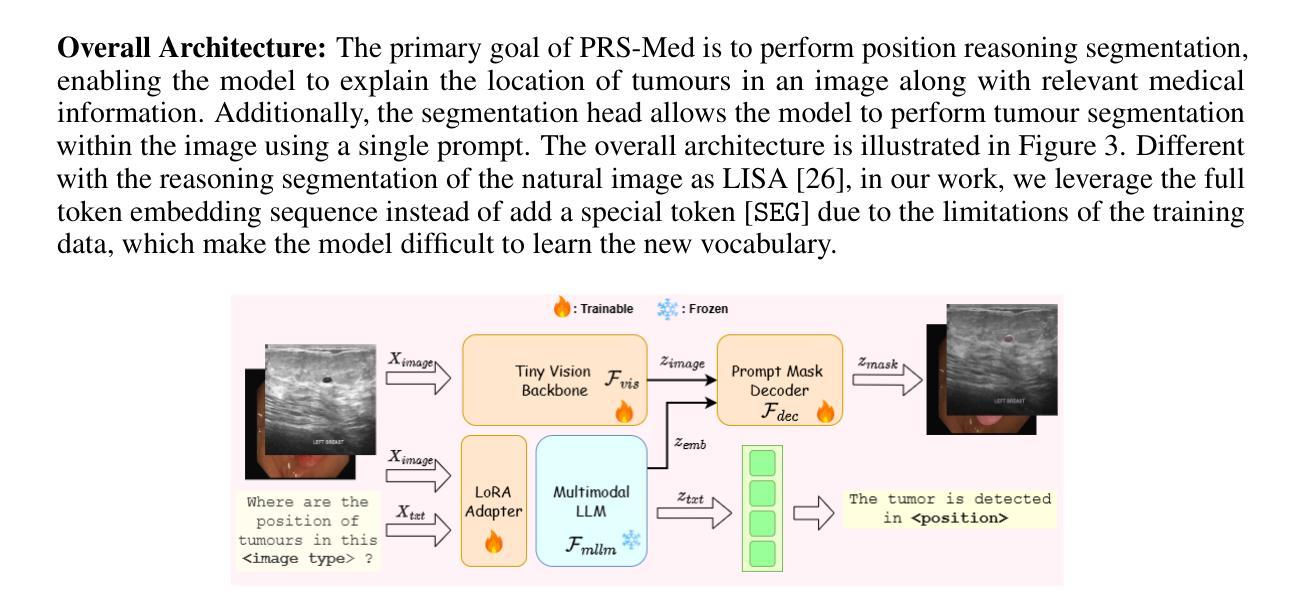
PRS-Med: Position Reasoning Segmentation with Vision-Language Model in Medical Imaging
Authors:Quoc-Huy Trinh, Minh-Van Nguyen, Jung Peng, Ulas Bagci, Debesh Jha
Recent advancements in prompt-based medical image segmentation have enabled clinicians to identify tumors using simple input like bounding boxes or text prompts. However, existing methods face challenges when doctors need to interact through natural language or when position reasoning is required - understanding spatial relationships between anatomical structures and pathologies. We present PRS-Med, a framework that integrates vision-language models with segmentation capabilities to generate both accurate segmentation masks and corresponding spatial reasoning outputs. Additionally, we introduce the MMRS dataset (Multimodal Medical in Positional Reasoning Segmentation), which provides diverse, spatially-grounded question-answer pairs to address the lack of position reasoning data in medical imaging. PRS-Med demonstrates superior performance across six imaging modalities (CT, MRI, X-ray, ultrasound, endoscopy, RGB), significantly outperforming state-of-the-art methods in both segmentation accuracy and position reasoning. Our approach enables intuitive doctor-system interaction through natural language, facilitating more efficient diagnoses. Our dataset pipeline, model, and codebase will be released to foster further research in spatially-aware multimodal reasoning for medical applications.
在基于提示的医疗图像分割方面的最新进展,已经使临床医生能够使用简单的输入,如边界框或文本提示来识别肿瘤。然而,当医生需要通过自然语言进行交互或需要位置推理(即理解解剖结构和病理之间的空间关系)时,现有方法面临挑战。我们提出了PRS-Med框架,它融合了视觉语言模型与分割能力,能够生成准确的分割掩膜和相应的空间推理输出。此外,我们还介绍了MMRS数据集(定位推理分割中的多模态医疗数据),该数据集提供了多样且基于空间的问题答案对,以解决医疗成像中位置推理数据的缺乏。PRS-Med在六种成像模式(CT、MRI、X光、超声、内窥镜、RGB)下表现出卓越的性能,在分割精度和位置推理方面都大大优于最先进的方法。我们的方法能够通过自然语言实现直观的医生系统交互,促进更高效的诊断。我们的数据集流程、模型和代码库将予以发布,以促进在空间感知多模式推理医疗应用方面的进一步研究。
论文及项目相关链接
摘要
最近,基于提示的医疗图像分割技术的进展,使得临床医生可以通过简单的输入,如边界框或文本提示,来识别肿瘤。然而,当医生需要通过自然语言进行交互或需要位置推理(即理解解剖结构和病理之间的空间关系)时,现有方法面临挑战。我们提出了PRS-Med框架,它结合了视觉语言模型和分割能力,能够生成准确的分割掩膜和相应的空间推理输出。此外,我们还介绍了MMRS数据集(位置推理分割中的多模态医疗图像),该数据集提供了多样且空间定位的问答对,以解决医疗影像中位置推理数据的缺乏。PRS-Med在六种成像模式(CT、MRI、X光、超声、内窥镜、RGB)下表现出卓越的性能,在分割准确性和位置推理方面都大大优于最新方法。我们的方法通过自然语言实现了医生与系统之间的直观交互,有助于更高效的诊断。我们的数据集管道、模型和源代码将予以公开,以促进空间感知多模态推理在医疗应用中的进一步研究。
关键见解
- PRS-Med框架结合了视觉语言模型和分割能力,能够生成准确的分割掩膜和相应的空间推理输出。
- 引入MMRS数据集,提供多样且空间定位的问答对,解决医疗影像中位置推理数据的缺乏问题。
- PRS-Med在六种不同的成像模式下表现出卓越性能,大大优于现有方法。
- 该方法通过自然语言实现了医生与系统之间的直观交互。
- PRS-Med框架有助于更高效的诊断。
- 数据集管道、模型和源代码将公开,以促进进一步研究。
点此查看论文截图