⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-05-24 更新
Temporal Object Captioning for Street Scene Videos from LiDAR Tracks
Authors:Vignesh Gopinathan, Urs Zimmermann, Michael Arnold, Matthias Rottmann
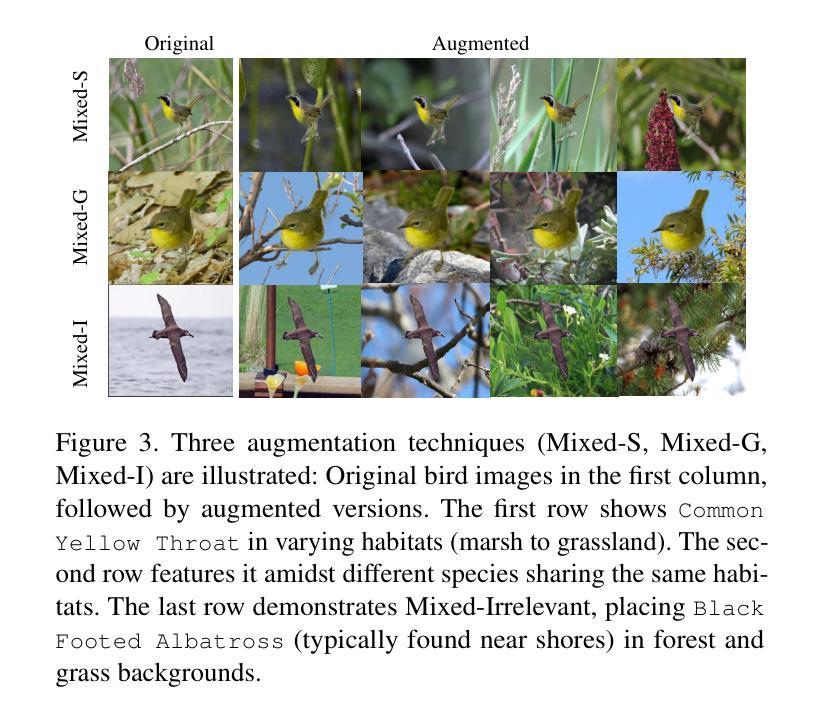
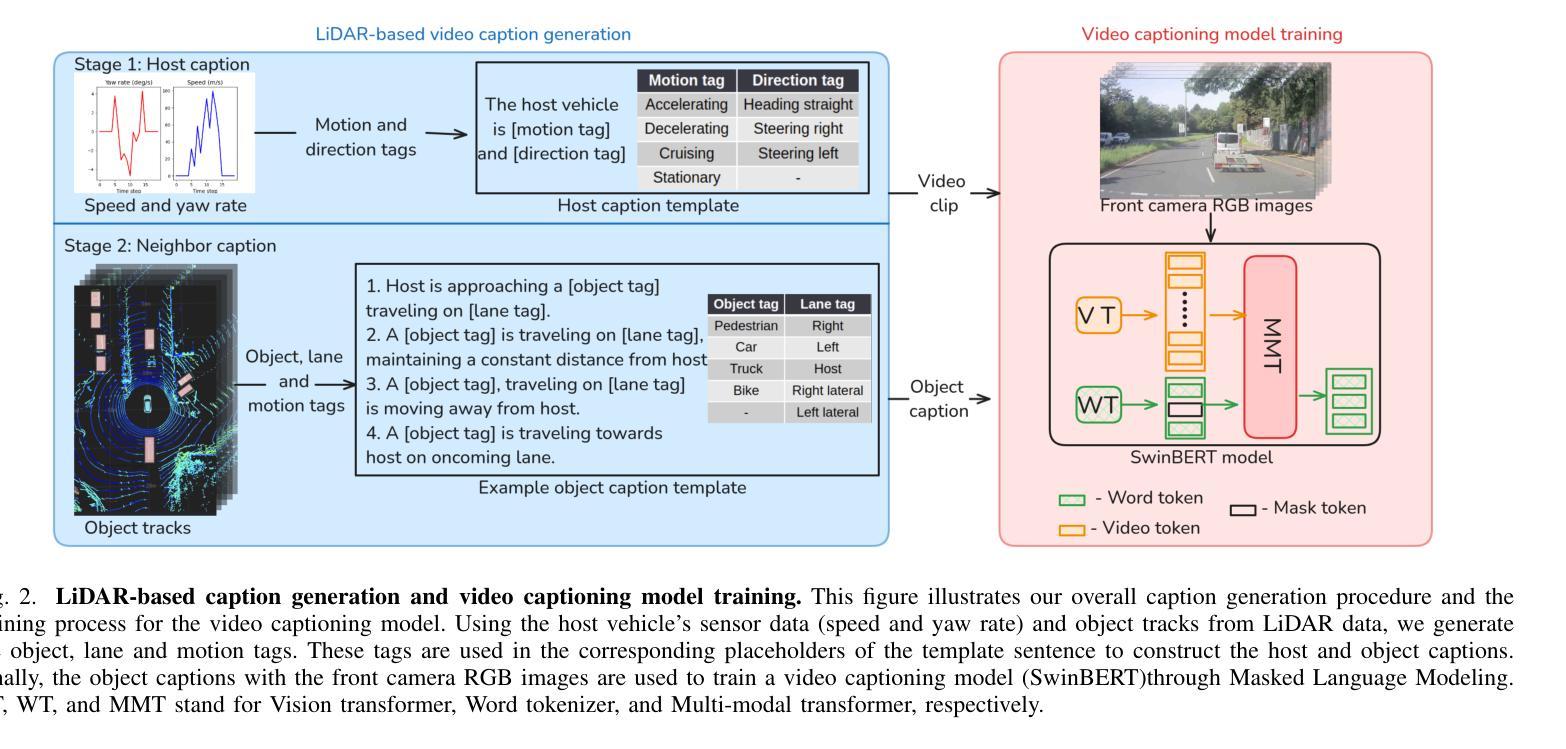
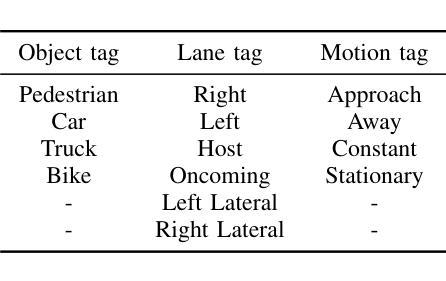
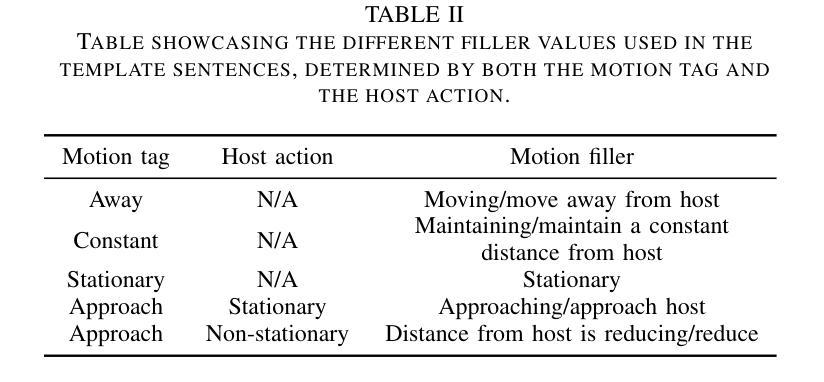
Video captioning models have seen notable advancements in recent years, especially with regard to their ability to capture temporal information. While many research efforts have focused on architectural advancements, such as temporal attention mechanisms, there remains a notable gap in understanding how models capture and utilize temporal semantics for effective temporal feature extraction, especially in the context of Advanced Driver Assistance Systems. We propose an automated LiDAR-based captioning procedure that focuses on the temporal dynamics of traffic participants. Our approach uses a rule-based system to extract essential details such as lane position and relative motion from object tracks, followed by a template-based caption generation. Our findings show that training SwinBERT, a video captioning model, using only front camera images and supervised with our template-based captions, specifically designed to encapsulate fine-grained temporal behavior, leads to improved temporal understanding consistently across three datasets. In conclusion, our results clearly demonstrate that integrating LiDAR-based caption supervision significantly enhances temporal understanding, effectively addressing and reducing the inherent visual/static biases prevalent in current state-of-the-art model architectures.
视频字幕生成模型在近年来取得了显著的进展,尤其是在捕捉时序信息方面。虽然许多研究工作都集中在架构的改进上,如时序注意力机制,但对于模型如何捕捉和利用时序语义进行有效时序特征提取的理解仍存在明显差距,特别是在高级驾驶辅助系统背景下。我们提出了一种基于激光雷达的自动字幕生成程序,它专注于交通参与者的时序动态。我们的方法使用基于规则的系统从物体轨迹中提取重要细节,如车道位置和相对运动,然后进行基于模板的字幕生成。我们的研究发现,仅使用前摄像头图像训练SwinBERT视频字幕生成模型,并使用我们专门设计用于包含精细时序行为的基于模板的字幕进行监督,可在三个数据集上持续提高时序理解能力。总之,我们的结果清楚地表明,结合基于激光雷达的字幕监督显著提高了时序理解能力,有效解决了当前最先进模型架构中普遍存在的视觉/静态偏见问题。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary:近年来,视频描述模型在捕捉时序信息方面取得了显著进展。尽管许多研究集中在架构改进上,如时序注意机制,但在理解模型如何捕获和利用时序语义进行有效时序特征提取方面仍存在差距,特别是在高级驾驶辅助系统上下文中。本文提出了一种基于激光雷达的自动描述程序,侧重于交通参与者的时序动态。该研究使用基于规则的系统提取车道位置和相对运动等关键细节,然后通过基于模板的描述生成。研究发现,使用仅来自前摄像头的图像训练SwinBERT视频描述模型,并结合专门针对精细时间行为的模板描述进行监督,可以持续改善时间理解。总的来说,结果清晰地证明,整合激光雷达描述的监督显着提高了时间理解能力,有效解决并减少了当前最先进的模型架构中普遍存在的视觉/静态偏见。
Key Takeaways:
- 视频描述模型在捕捉时序信息方面取得显著进展。
- 尽管存在许多关于架构改进的研究,但对模型如何捕获和利用时序语义的理解仍存在差距。
- 提出了一种基于激光雷达的自动描述程序,侧重于交通参与者的时序动态。
- 使用基于规则的系统提取关键信息,如车道位置和相对运动。
- 通过基于模板的描述生成进行描述。
- 使用仅前摄像头图像训练的SwinBERT模型结合模板描述监督可以提高时间理解能力。
点此查看论文截图

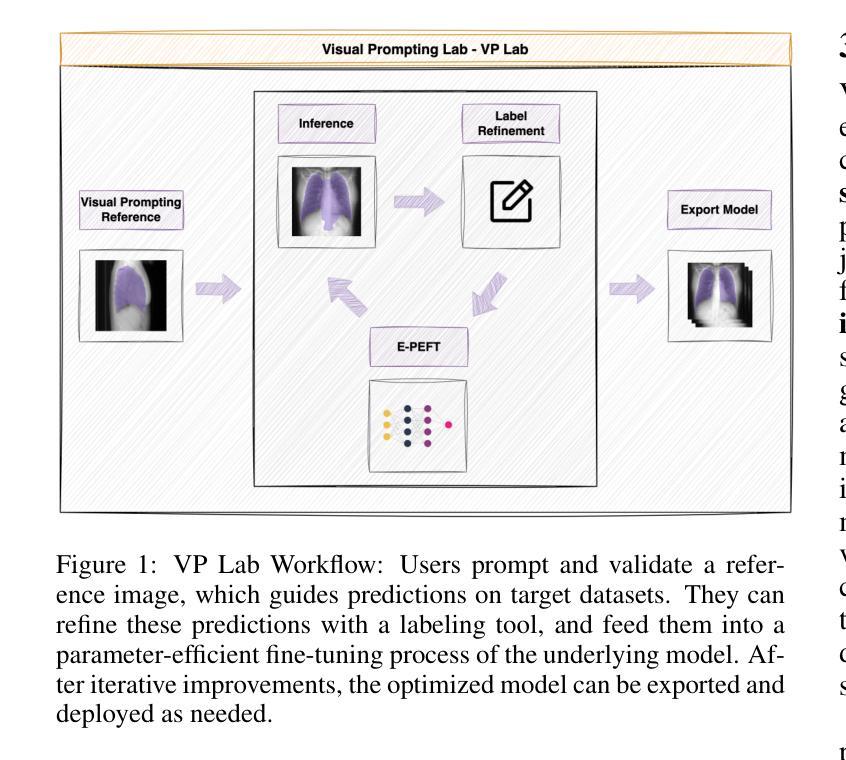
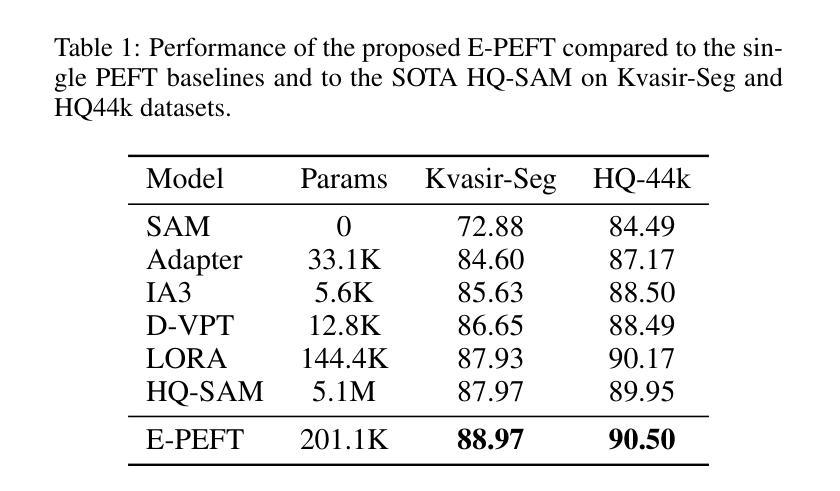
VP Lab: a PEFT-Enabled Visual Prompting Laboratory for Semantic Segmentation
Authors:Niccolo Avogaro, Thomas Frick, Yagmur G. Cinar, Daniel Caraballo, Cezary Skura, Filip M. Janicki, Piotr Kluska, Brown Ebouky, Nicola Farronato, Florian Scheidegger, Cristiano Malossi, Konrad Schindler, Andrea Bartezzaghi, Roy Assaf, Mattia Rigotti
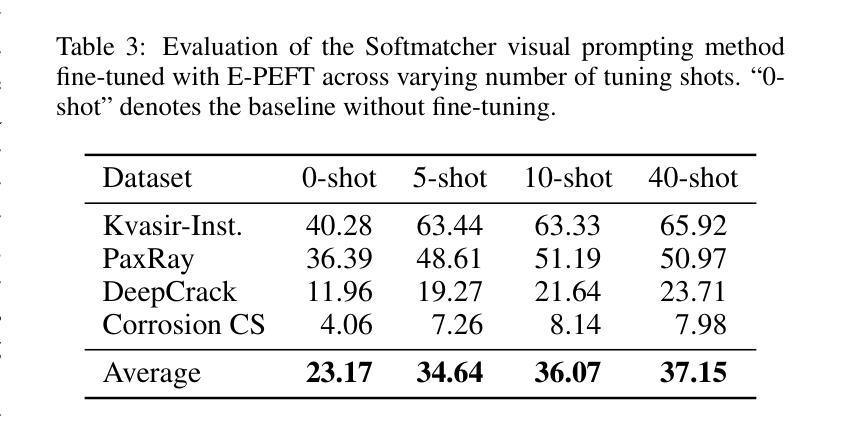
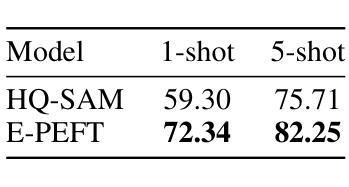
Large-scale pretrained vision backbones have transformed computer vision by providing powerful feature extractors that enable various downstream tasks, including training-free approaches like visual prompting for semantic segmentation. Despite their success in generic scenarios, these models often fall short when applied to specialized technical domains where the visual features differ significantly from their training distribution. To bridge this gap, we introduce VP Lab, a comprehensive iterative framework that enhances visual prompting for robust segmentation model development. At the core of VP Lab lies E-PEFT, a novel ensemble of parameter-efficient fine-tuning techniques specifically designed to adapt our visual prompting pipeline to specific domains in a manner that is both parameter- and data-efficient. Our approach not only surpasses the state-of-the-art in parameter-efficient fine-tuning for the Segment Anything Model (SAM), but also facilitates an interactive, near-real-time loop, allowing users to observe progressively improving results as they experiment within the framework. By integrating E-PEFT with visual prompting, we demonstrate a remarkable 50% increase in semantic segmentation mIoU performance across various technical datasets using only 5 validated images, establishing a new paradigm for fast, efficient, and interactive model deployment in new, challenging domains. This work comes in the form of a demonstration.
大规模预训练的视觉主干网络通过提供强大的特征提取器,为包括无训练方法(如语义分割的视觉提示)在内的各种下游任务提供了强大的支持,从而彻底改变了计算机视觉领域。尽管这些模型在通用场景中的表现非常出色,但当应用于特定技术域时,由于视觉特征与训练分布存在显著差异,这些模型往往无法达到预期效果。为了弥补这一差距,我们引入了VP Lab这一全面的迭代框架,用于增强视觉提示的稳健性分割模型开发。VP Lab的核心是E-PEFT,这是一种新型的参数高效微调技术集合,旨在以参数和数据效率高的方式调整我们的视觉提示管道,以适应特定领域。我们的方法不仅超越了针对分割任何模型(SAM)的参数高效微调的最先进水平,还促进了交互式近实时循环,使用户能够在框架内实验时观察到逐步改进的结果。通过将E-PEFT与视觉提示相结合,我们在各种技术数据集上实现了语义分割mIoU性能的显著提升。仅使用5张经过验证的图像,便实现了令人印象深刻的50%提升,为快速、高效、交互式模型在新挑战领域部署建立了新的范例。本工作以演示的形式呈现。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary:
大规模预训练视觉模型为计算机视觉提供了强大的特征提取器,可应用于多种下游任务,包括无需训练的视觉提示语义分割方法。然而,这些模型在应用于特定技术域时常常表现不佳,因为其与训练数据分布差异较大。为解决这一问题,我们推出VP Lab,一个全面的迭代框架,用于增强视觉提示的稳健分割模型开发。其核心是E-PEFT,一种参数效率高的微调技术集合,专门设计以适应特定的视觉提示管道,既参数高效又数据高效。我们的方法不仅超越了针对Segment Anything Model(SAM)的参数高效微调的最先进水平,而且提供了一个交互式、近实时的循环,使用户可以在框架内实验时观察到逐步改进的结果。通过整合E-PEFT与视觉提示,我们在各种技术数据集上实现了语义分割mIoU性能的50%提升,仅使用5张验证图像,为快速、高效、交互式模型在新挑战域中的部署建立了新范例。
Key Takeaways:
- 大规模预训练视觉模型已成为计算机视觉领域的强大工具,广泛应用于多种下游任务。
- 这些模型在特定技术域的应用中常面临挑战,因为其与训练数据分布存在差异。
- VP Lab是一个全面的迭代框架,旨在增强视觉提示的稳健分割模型开发。
- E-PEFT是专为适应特定域的视觉提示管道而设计的参数高效微调技术集合。
- E-PEFT不仅提高了参数效率,而且提高了数据效率。
- 通过整合E-PEFT与视觉提示,我们在多个技术数据集上实现了显著的语义分割性能提升。
点此查看论文截图

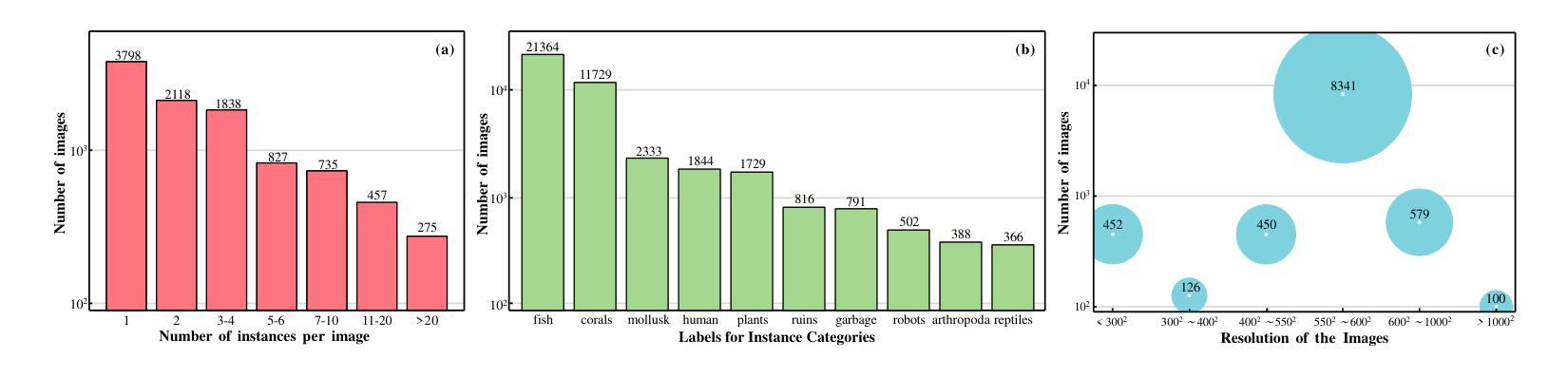
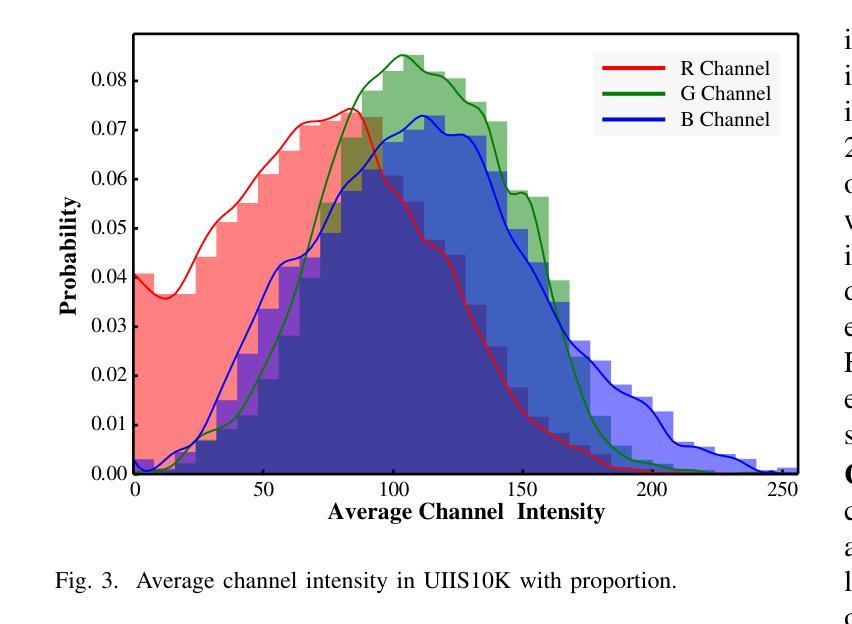
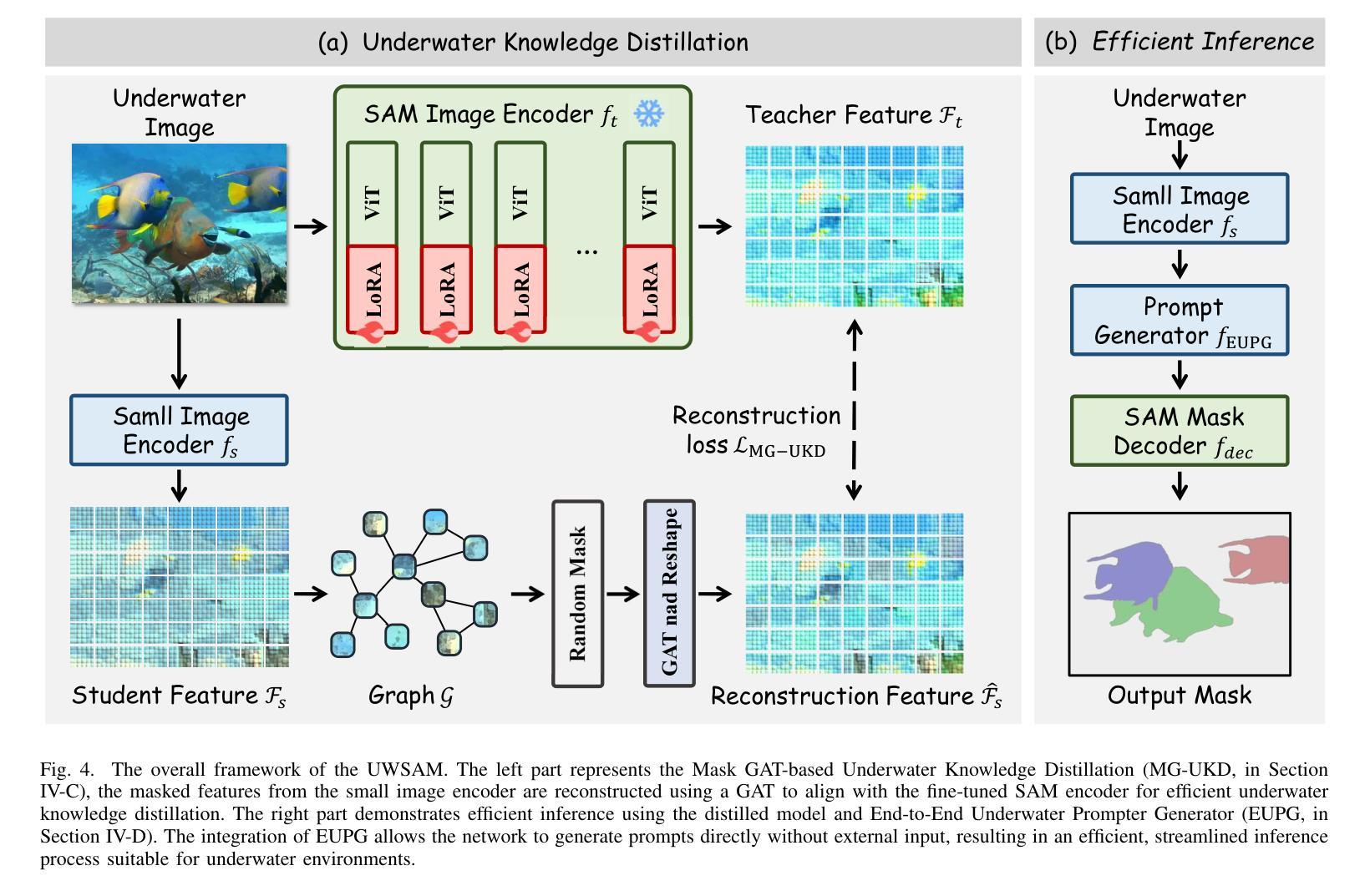
UWSAM: Segment Anything Model Guided Underwater Instance Segmentation and A Large-scale Benchmark Dataset
Authors:Hua Li, Shijie Lian, Zhiyuan Li, Runmin Cong, Sam Kwong
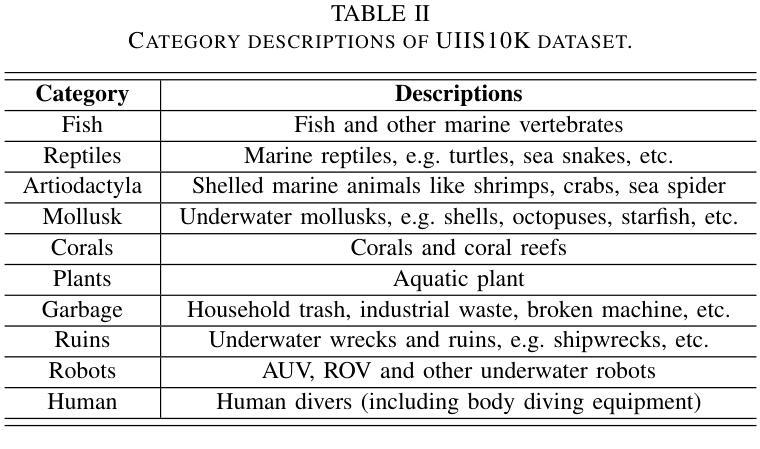
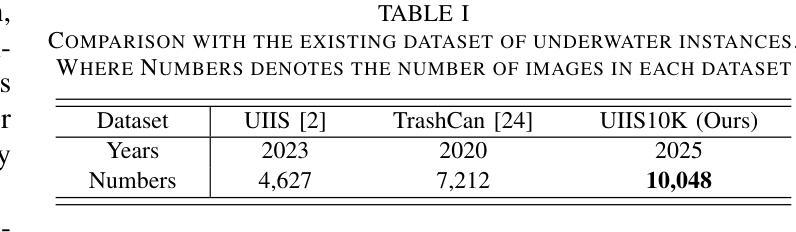
With recent breakthroughs in large-scale modeling, the Segment Anything Model (SAM) has demonstrated significant potential in a variety of visual applications. However, due to the lack of underwater domain expertise, SAM and its variants face performance limitations in end-to-end underwater instance segmentation tasks, while their higher computational requirements further hinder their application in underwater scenarios. To address this challenge, we propose a large-scale underwater instance segmentation dataset, UIIS10K, which includes 10,048 images with pixel-level annotations for 10 categories. Then, we introduce UWSAM, an efficient model designed for automatic and accurate segmentation of underwater instances. UWSAM efficiently distills knowledge from the SAM ViT-Huge image encoder into the smaller ViT-Small image encoder via the Mask GAT-based Underwater Knowledge Distillation (MG-UKD) method for effective visual representation learning. Furthermore, we design an End-to-end Underwater Prompt Generator (EUPG) for UWSAM, which automatically generates underwater prompts instead of explicitly providing foreground points or boxes as prompts, thus enabling the network to locate underwater instances accurately for efficient segmentation. Comprehensive experimental results show that our model is effective, achieving significant performance improvements over state-of-the-art methods on multiple underwater instance datasets. Datasets and codes are available at https://github.com/LiamLian0727/UIIS10K.
随着大规模建模领域的最新突破,Segment Anything Model(SAM)在各种视觉应用中表现出了巨大的潜力。然而,由于缺乏水下领域的专业知识,SAM及其变体在端到端的水下实例分割任务中面临性能限制,而它们较高的计算要求进一步阻碍了在水下场景中的应用。为了应对这一挑战,我们提出了大规模水下实例分割数据集UIIS10K,其中包含10,048张具有10类像素级注释的图像。接着,我们介绍了UWSAM,这是一个专为水下实例自动准确分割而设计的高效模型。UWSAM通过基于Mask GAT的水下知识蒸馏(MG-UKD)方法,有效地从SAM的ViT-Huge图像编码器提炼知识,并将其运用到较小的ViT-Small图像编码器上,从而实现有效的视觉表征学习。此外,我们还为UWSAM设计了端到端水下提示生成器(EUPG),它会自动生成水下提示,而不是显式提供前景点或框作为提示,从而能够准确定位水下实例,实现高效的分割。综合实验结果表明,我们的模型是有效的,在多个水下实例数据集上较最新方法实现了显著的性能提升。数据集和代码可在https://github.com/LiamLian0727/UIIS10K获取。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary:随着大规模建模的突破,Segment Anything Model(SAM)在多种视觉应用中展现出巨大潜力。然而,由于缺乏水下领域专业知识,SAM及其变体在端到端水下实例分割任务中的性能受到限制。为此,我们提出了大规模水下实例分割数据集UIIS10K,包含10,048张带有像素级注释的10类图像。同时,我们引入了专为水下自动精确实例分割设计的UWSAM模型。UWSAM通过基于Mask GAT的水下知识蒸馏(MG-UKD)方法,有效地从SAM的ViT-Huge图像编码器蒸馏知识到较小的ViT-Small图像编码器,实现有效的视觉表示学习。此外,我们还为UWSAM设计了端到端水下提示生成器(EUPG),可自动生成水下提示,而无需明确提供前景点或框作为提示,从而使网络能够准确定位水下实例,实现高效分割。
Key Takeaways:
- SAM模型在视觉应用中有巨大潜力,但在水下实例分割方面存在性能限制。
- 缺乏水下领域专业知识是影响SAM在水下任务中性能的主要原因之一。
- UIIS10K数据集包含大量水下实例分割的图像和像素级注释。
- UWSAM模型专为水下自动精确实例分割设计。
- UWSAM通过Mask GAT的水下知识蒸馏方法提升视觉表示学习。
- 端到端水下提示生成器(EUPG)能自动生成水下提示,提高网络定位水下实例的准确性。
- UWSAM模型在多个水下实例数据集上的性能显著,超越现有方法。
点此查看论文截图


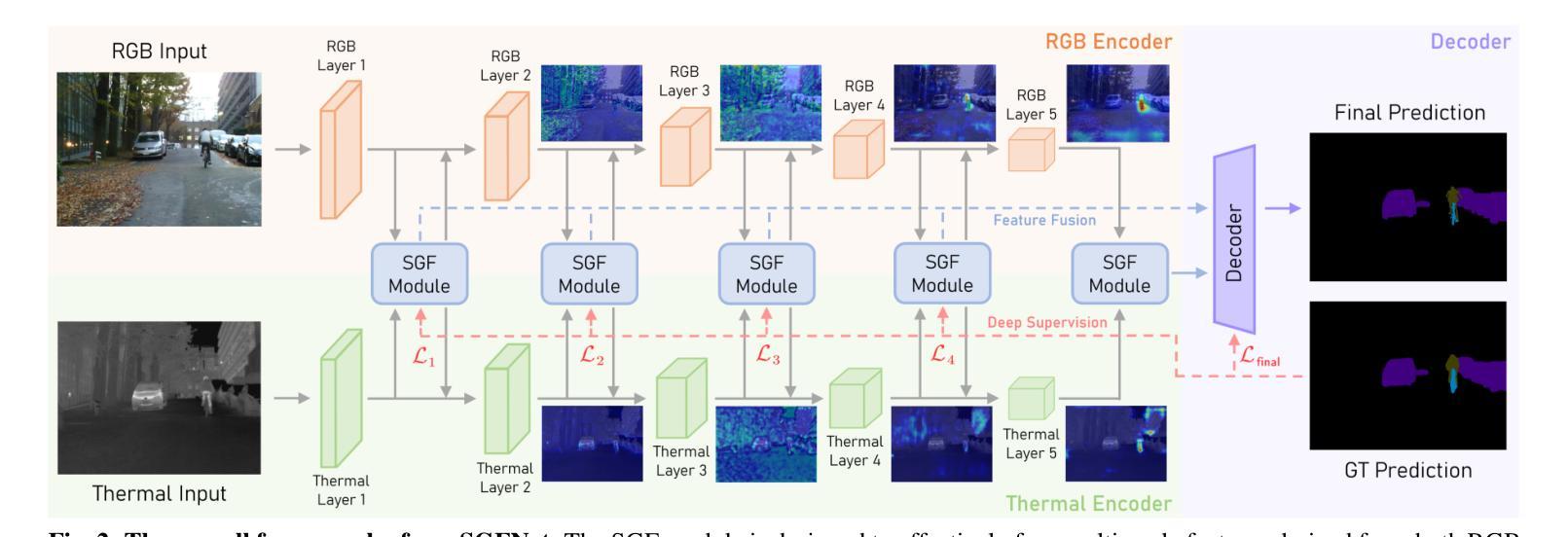
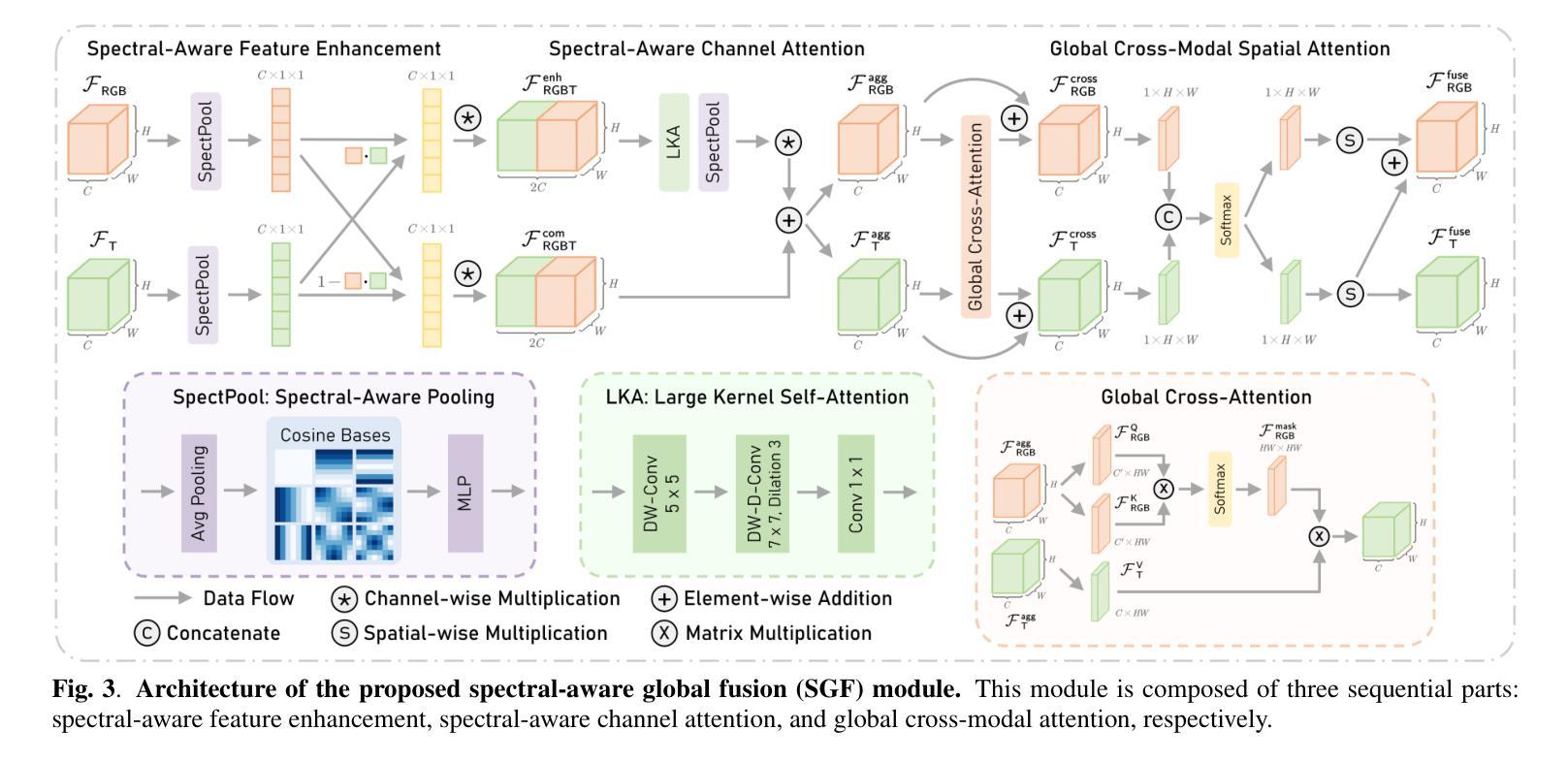
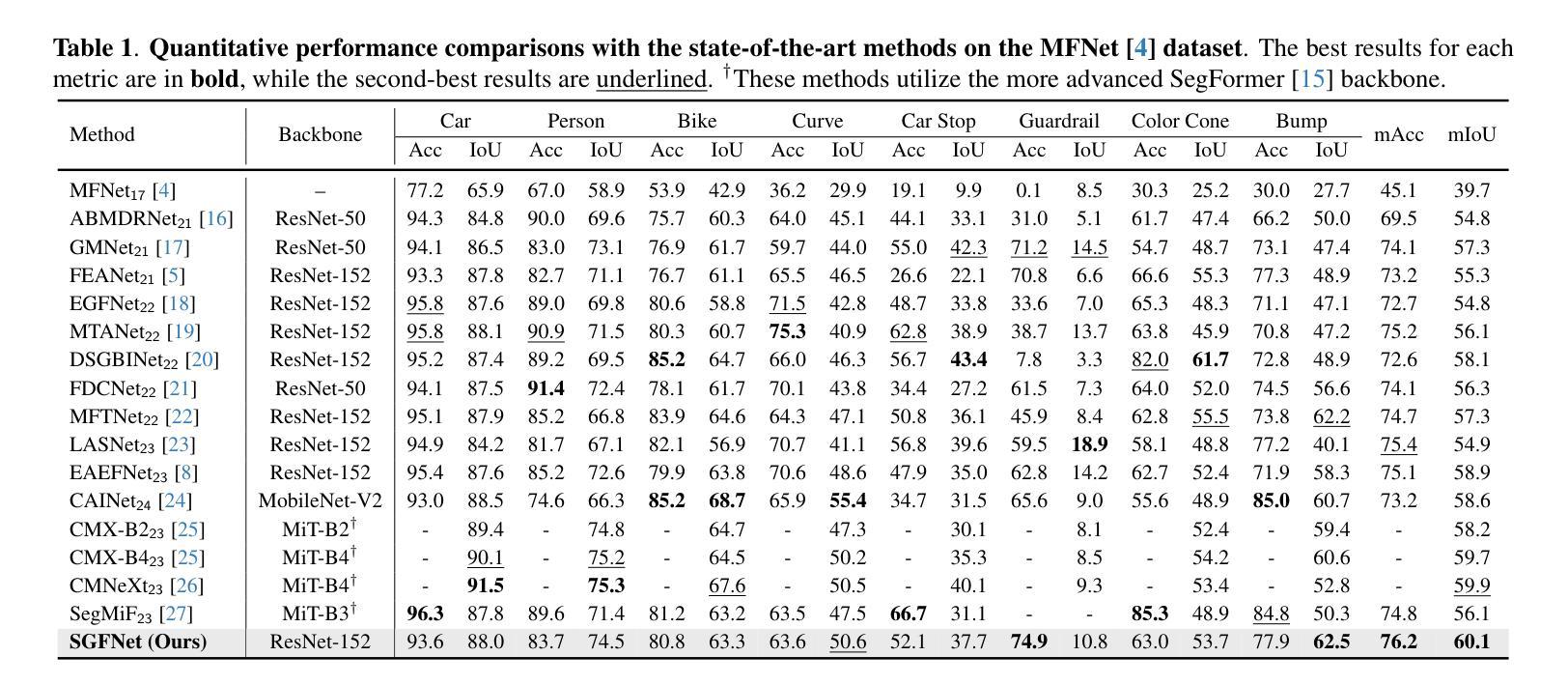
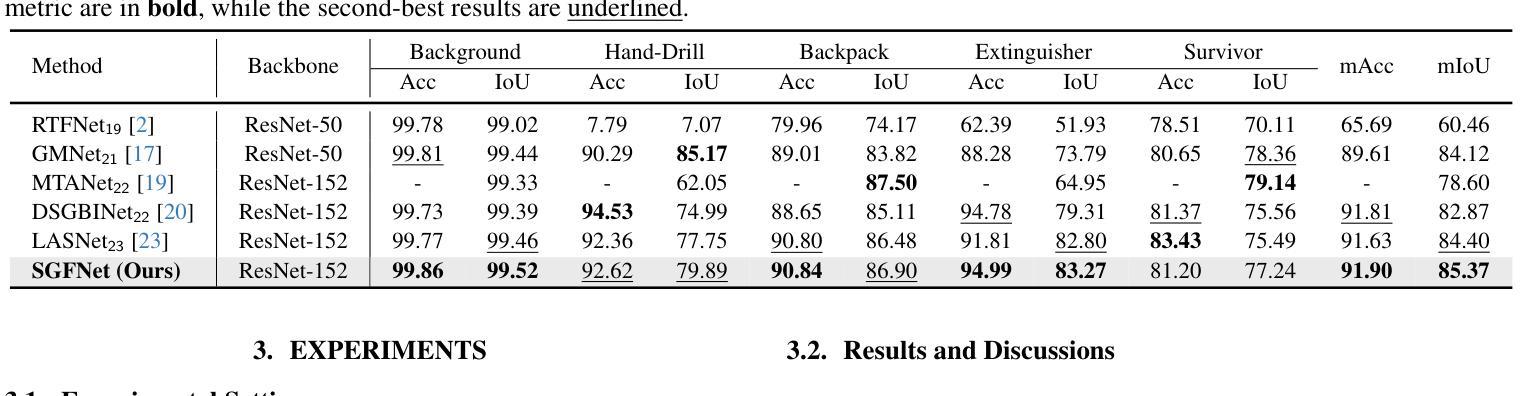
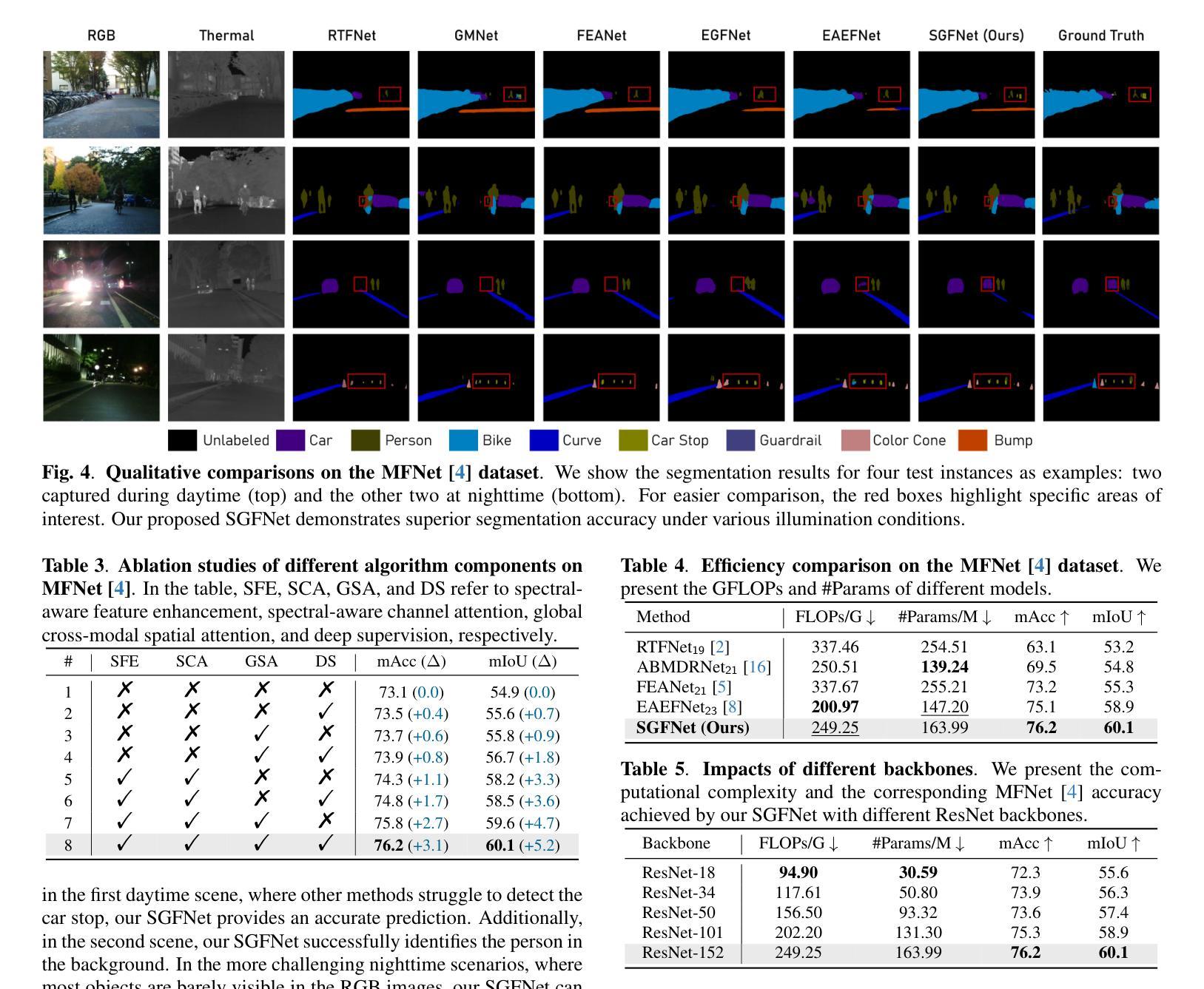
Spectral-Aware Global Fusion for RGB-Thermal Semantic Segmentation
Authors:Ce Zhang, Zifu Wan, Simon Stepputtis, Katia Sycara, Yaqi Xie
Semantic segmentation relying solely on RGB data often struggles in challenging conditions such as low illumination and obscured views, limiting its reliability in critical applications like autonomous driving. To address this, integrating additional thermal radiation data with RGB images demonstrates enhanced performance and robustness. However, how to effectively reconcile the modality discrepancies and fuse the RGB and thermal features remains a well-known challenge. In this work, we address this challenge from a novel spectral perspective. We observe that the multi-modal features can be categorized into two spectral components: low-frequency features that provide broad scene context, including color variations and smooth areas, and high-frequency features that capture modality-specific details such as edges and textures. Inspired by this, we propose the Spectral-aware Global Fusion Network (SGFNet) to effectively enhance and fuse the multi-modal features by explicitly modeling the interactions between the high-frequency, modality-specific features. Our experimental results demonstrate that SGFNet outperforms the state-of-the-art methods on the MFNet and PST900 datasets.
仅依赖RGB数据进行语义分割在挑战条件下(例如低光照和遮挡视图)往往表现不佳,这限制了其在自动驾驶等关键应用中的可靠性。为了解决这个问题,将额外的热辐射数据与RGB图像相结合,显示出更高的性能和稳健性。然而,如何有效地协调不同模态之间的差异并融合RGB和热特征仍然是一个公认的挑战。在这项工作中,我们从全新的光谱角度来解决这一挑战。我们发现多模态特征可以划分为两个光谱成分:提供广泛场景上下文的低频特征,包括颜色变化和平滑区域;以及捕捉特定模态细节(如边缘和纹理)的高频特征。受此启发,我们提出了Spectral-aware Global Fusion Network(SGFNet)网络,通过显式建模高频和特定模态特征之间的交互,有效地增强和融合多模态特征。我们的实验结果表明,在MFNet和PST900数据集上,SGFNet的性能超过了最先进的方法。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by ICIP 2025
Summary
本文指出,在挑战条件下,如低光照和遮挡视图中,仅依赖RGB数据的语义分割存在局限性。为解决这一问题,整合额外的热辐射数据与RGB图像能提高性能和稳健性。然而,如何有效协调不同模态之间的差异并融合RGB和热特征仍是一大挑战。本文从新的光谱视角出发,观察到多模态特征可分为两种光谱成分:提供场景广泛背景的低频特征,以及捕捉边缘和纹理等特定模态细节的高频特征。受此启发,本文提出谱感知全局融合网络(SGFNet),通过显式建模高频和特定模态特征之间的相互作用,有效增强和融合多模态特征。实验结果表明,SGFNet在MFNet和PST900数据集上的表现优于最新方法。
Key Takeaways
- 在低光照和遮挡等挑战条件下,仅依赖RGB数据的语义分割存在局限性。
- 整合RGB与热辐射数据可以提高语义分割的性能和稳健性。
- 存在协调不同模态之间的差异并融合RGB和热特征的技术挑战。
- 本文从新的光谱视角分析多模态特征,分为低频和高频特征。
- 低频特征提供场景背景信息,高频特征捕捉特定模态的细节(如边缘和纹理)。
- 提出谱感知全局融合网络(SGFNet),通过建模高频和特定模态特征之间的相互作用来增强和融合多模态特征。
点此查看论文截图

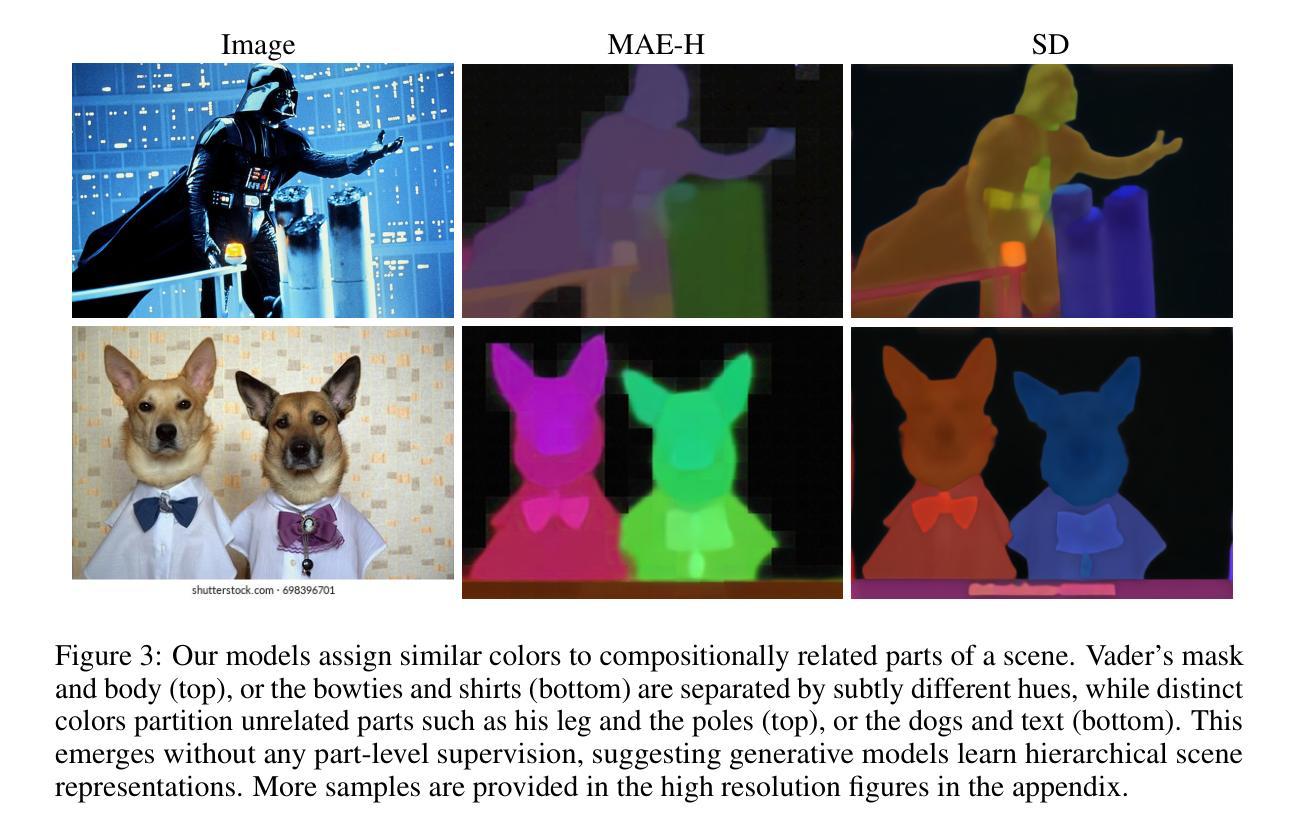
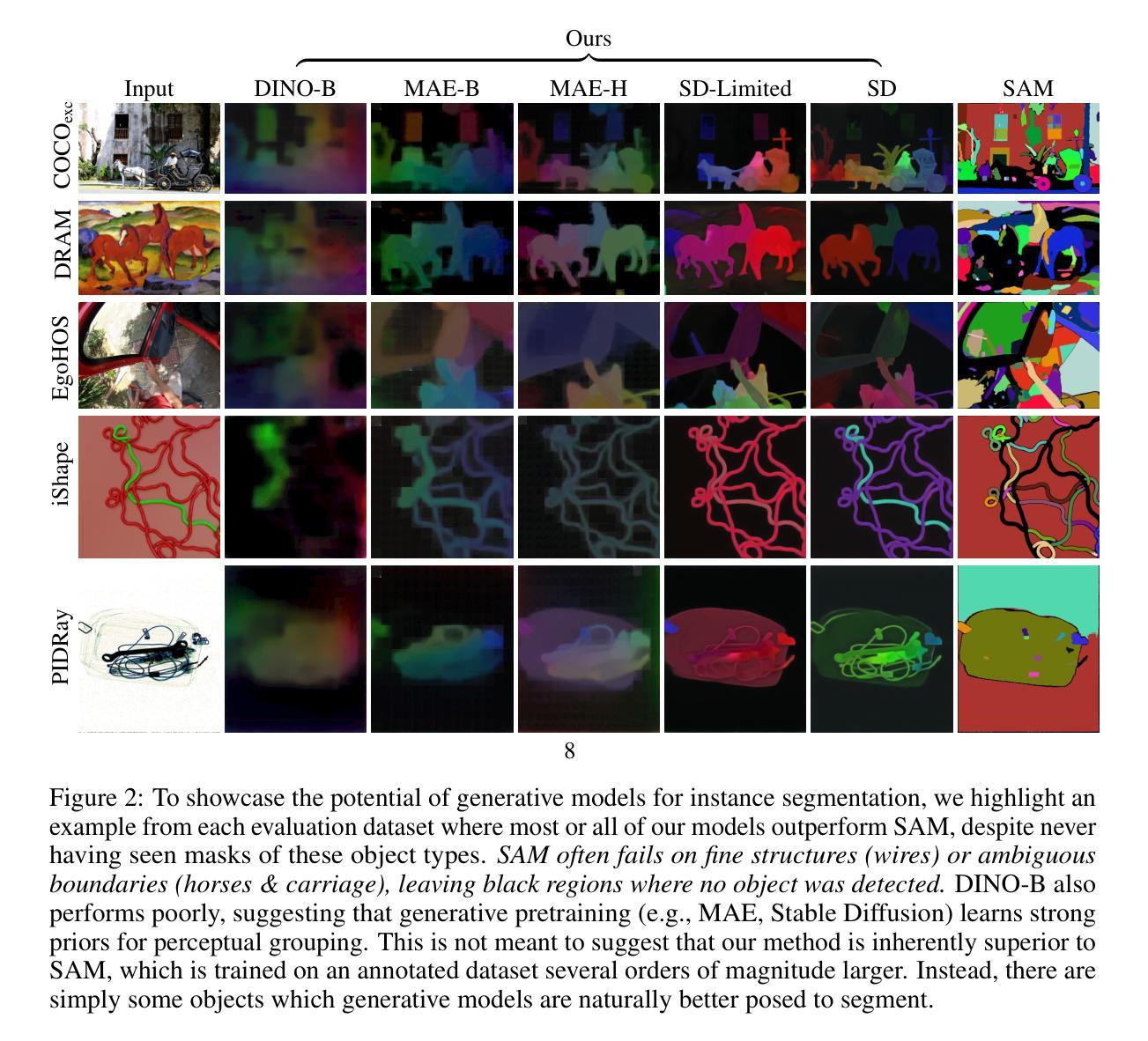
gen2seg: Generative Models Enable Generalizable Instance Segmentation
Authors:Om Khangaonkar, Hamed Pirsiavash
By pretraining to synthesize coherent images from perturbed inputs, generative models inherently learn to understand object boundaries and scene compositions. How can we repurpose these generative representations for general-purpose perceptual organization? We finetune Stable Diffusion and MAE (encoder+decoder) for category-agnostic instance segmentation using our instance coloring loss exclusively on a narrow set of object types (indoor furnishings and cars). Surprisingly, our models exhibit strong zero-shot generalization, accurately segmenting objects of types and styles unseen in finetuning (and in many cases, MAE’s ImageNet-1K pretraining too). Our best-performing models closely approach the heavily supervised SAM when evaluated on unseen object types and styles, and outperform it when segmenting fine structures and ambiguous boundaries. In contrast, existing promptable segmentation architectures or discriminatively pretrained models fail to generalize. This suggests that generative models learn an inherent grouping mechanism that transfers across categories and domains, even without internet-scale pretraining. Code, pretrained models, and demos are available on our website.
通过预训练从受扰输入中合成连贯的图像,生成模型本质上学会了理解对象边界和场景组成。我们如何将这些生成表示重新用于通用感知组织呢?我们对室内家具和汽车等少数对象类型,使用实例着色损失对Stable Diffusion和MAE(编码器+解码器)进行微调,用于类别无关的实例分割。令人惊讶的是,我们的模型表现出强大的零样本泛化能力,能够准确分割微调中未见过的对象类型和风格(并且在许多情况下,MAE的ImageNet-1K预训练也是如此)。在未见过的对象类型和风格进行评估时,我们表现最佳的模型接近高度监督的SAM,在分割精细结构和模糊边界时则表现优于它。相比之下,现有的可提示分割架构或判别预训练模型无法泛化。这表明生成模型学习了一种固有的分组机制,可以在类别和领域之间转移,即使不使用互联网规模的预训练也是如此。代码、预训练模型和演示可在我们的网站上找到。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Website: https://reachomk.github.io/gen2seg/
Summary
预训练生成模型从扰动输入中合成连贯图像,从而学习物体边界和场景组合。如何通过微调用于通用感知组织?我们对Stable Diffusion和MAE(编码器+解码器)进行类别无关的实例分割,使用实例染色损失仅针对少量物体类型(室内家具和汽车)。令人惊讶的是,模型表现出强大的零样本泛化能力,准确分割在微调中未见过的物体类型和风格(并且在许多情况下,MAE的ImageNet-1K预训练亦是如此)。最佳性能的模型在未见过的物体类型和风格上的评估接近高度监督的SAM,在分割精细结构和模糊边界时表现更优。这表明生成模型学习了一种固有的分组机制,可跨类别和领域迁移,即使无需互联网规模的预训练。
Key Takeaways
- 生成模型通过预训练学习合成连贯图像,从而掌握物体边界和场景组合的理解。
- 通过实例染色损失对特定物体类型(如室内家具和汽车)进行微调,模型表现出强大的零样本泛化能力。
- 最佳性能的模型在未见过的物体类型和风格上接近或优于高度监督的SAM。
- 生成模型在分割精细结构和模糊边界时表现优越。
- 相比其他可提示的分割架构或判别预训练模型,生成模型具有更好的泛化能力。
- 生成模型学习到一种固有的分组机制,可跨类别和领域迁移。
点此查看论文截图




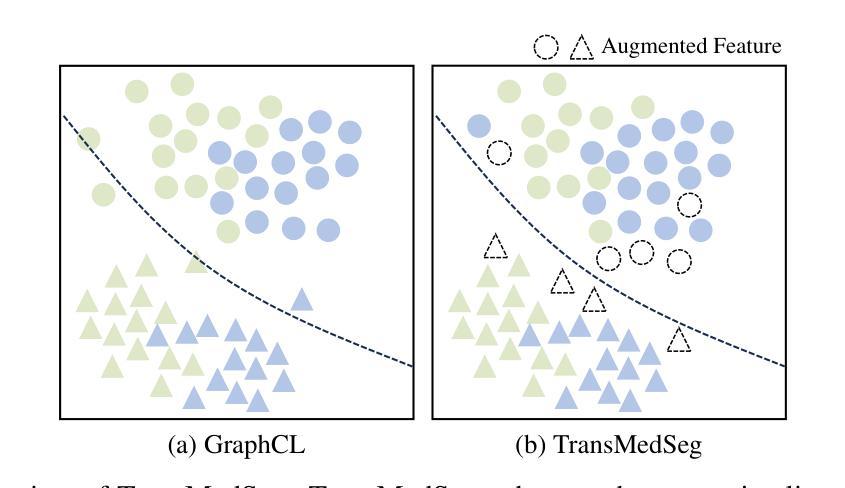
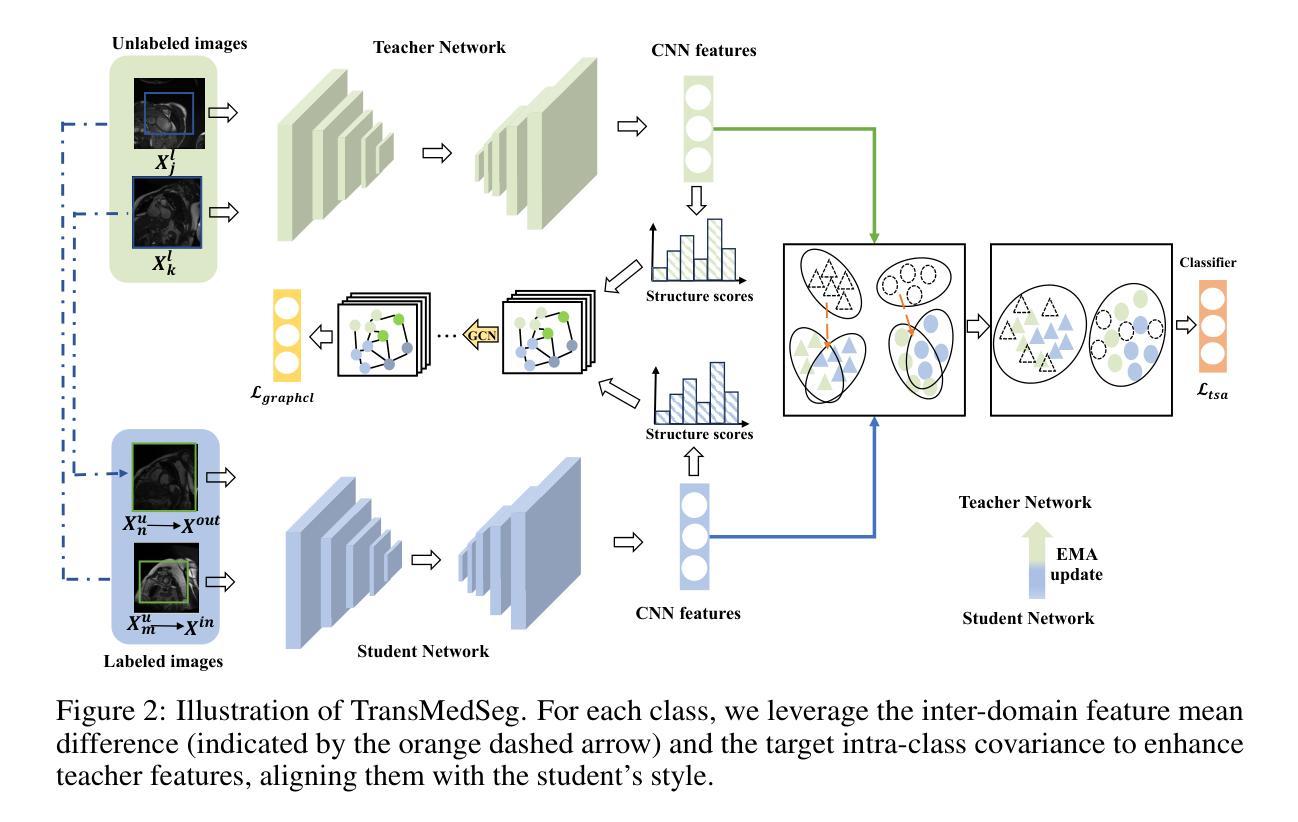
TransMedSeg: A Transferable Semantic Framework for Semi-Supervised Medical Image Segmentation
Authors:Mengzhu Wang, Jiao Li, Shanshan Wang, Long Lan, Huibin Tan, Liang Yang, Guoli Yang
Semi-supervised learning (SSL) has achieved significant progress in medical image segmentation (SSMIS) through effective utilization of limited labeled data. While current SSL methods for medical images predominantly rely on consistency regularization and pseudo-labeling, they often overlook transferable semantic relationships across different clinical domains and imaging modalities. To address this, we propose TransMedSeg, a novel transferable semantic framework for semi-supervised medical image segmentation. Our approach introduces a Transferable Semantic Augmentation (TSA) module, which implicitly enhances feature representations by aligning domain-invariant semantics through cross-domain distribution matching and intra-domain structural preservation. Specifically, TransMedSeg constructs a unified feature space where teacher network features are adaptively augmented towards student network semantics via a lightweight memory module, enabling implicit semantic transformation without explicit data generation. Interestingly, this augmentation is implicitly realized through an expected transferable cross-entropy loss computed over the augmented teacher distribution. An upper bound of the expected loss is theoretically derived and minimized during training, incurring negligible computational overhead. Extensive experiments on medical image datasets demonstrate that TransMedSeg outperforms existing semi-supervised methods, establishing a new direction for transferable representation learning in medical image analysis.
半监督学习(SSL)在医学图像分割(SSMIS)中通过有效利用有限标记数据取得了显著进展。虽然当前的医学图像SSL方法主要依赖于一致性正则化和伪标签,但它们往往忽视了不同临床域和成像模式之间的可转移语义关系。为了解决这一问题,我们提出了TransMedSeg,这是一种用于半监督医学图像分割的新型可转移语义框架。我们的方法引入了一个可转移语义增强(TSA)模块,该模块通过跨域分布匹配和域内结构保留来对齐域不变语义,从而隐式地增强特征表示。具体来说,TransMedSeg构建了一个统一的特征空间,其中教师网络特征通过轻量级内存模块向学生网络语义进行自适应增强,实现隐式语义转换而无需显式数据生成。有趣的是,这种增强是通过在教师分布上计算的预期可转移交叉熵损失来实现的。理论上推导了预期损失的上界,并在训练过程中进行最小化,几乎不会增加计算开销。在医学图像数据集上的广泛实验表明,TransMedSeg优于现有的半监督方法,为医学图像分析中的可转移表示学习指明了新的方向。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
在半监督学习(SSL)在医学图像分割(SSMIS)中利用有限标记数据取得显著进展的背景下,当前SSL方法主要依赖一致性正则化和伪标签,忽略了不同临床域和成像模式之间的可转移语义关系。为解决此问题,我们提出TransMedSeg,一种新型可转移语义框架,用于半监督医学图像分割。它引入可转移语义增强(TSA)模块,通过跨域分布匹配和域内结构保留,隐式地增强特征表示并对齐域不变语义。TransMedSeg构建统一特征空间,通过轻量级内存模块自适应增强教师网络特征向学生网络语义,实现隐式语义转换,无需显式数据生成。通过最小化理论推导的预期损失上限,在训练中引入的计算开销微乎其微。在医学图像数据集上的广泛实验表明,TransMedSeg优于现有半监督方法,为医学图像分析中的可转移表示学习指明了新方向。
Key Takeaways
- 当前SSL方法在医学图像分割中主要依赖一致性正则化和伪标签,但忽略了不同临床域和成像模式间的可转移语义关系。
- TransMedSeg是一种新型可转移语义框架,旨在解决这一问题。
- TransMedSeg引入TSA模块,隐式地增强特征表示并通过对齐域不变语义来改善SSL在医学图像分割中的性能。
- TransMedSeg构建统一特征空间,通过轻量级内存模块实现教师网络和学生网络之间的隐式语义转换。
- TransMedSeg利用预期的跨熵损失来实现可转移语义增强,该损失是通过教师分布增强来计算的。
- TransMedSeg通过最小化理论推导的预期损失上限来训练模型,同时保持计算开销微小。
点此查看论文截图

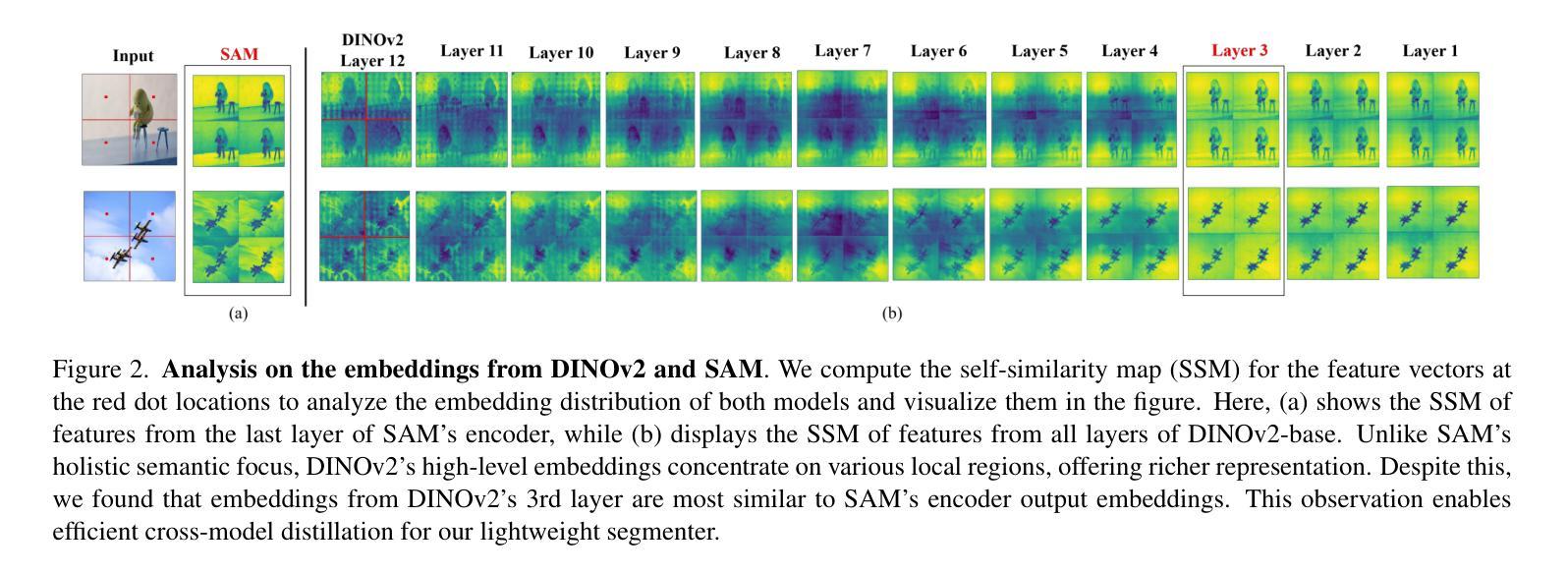
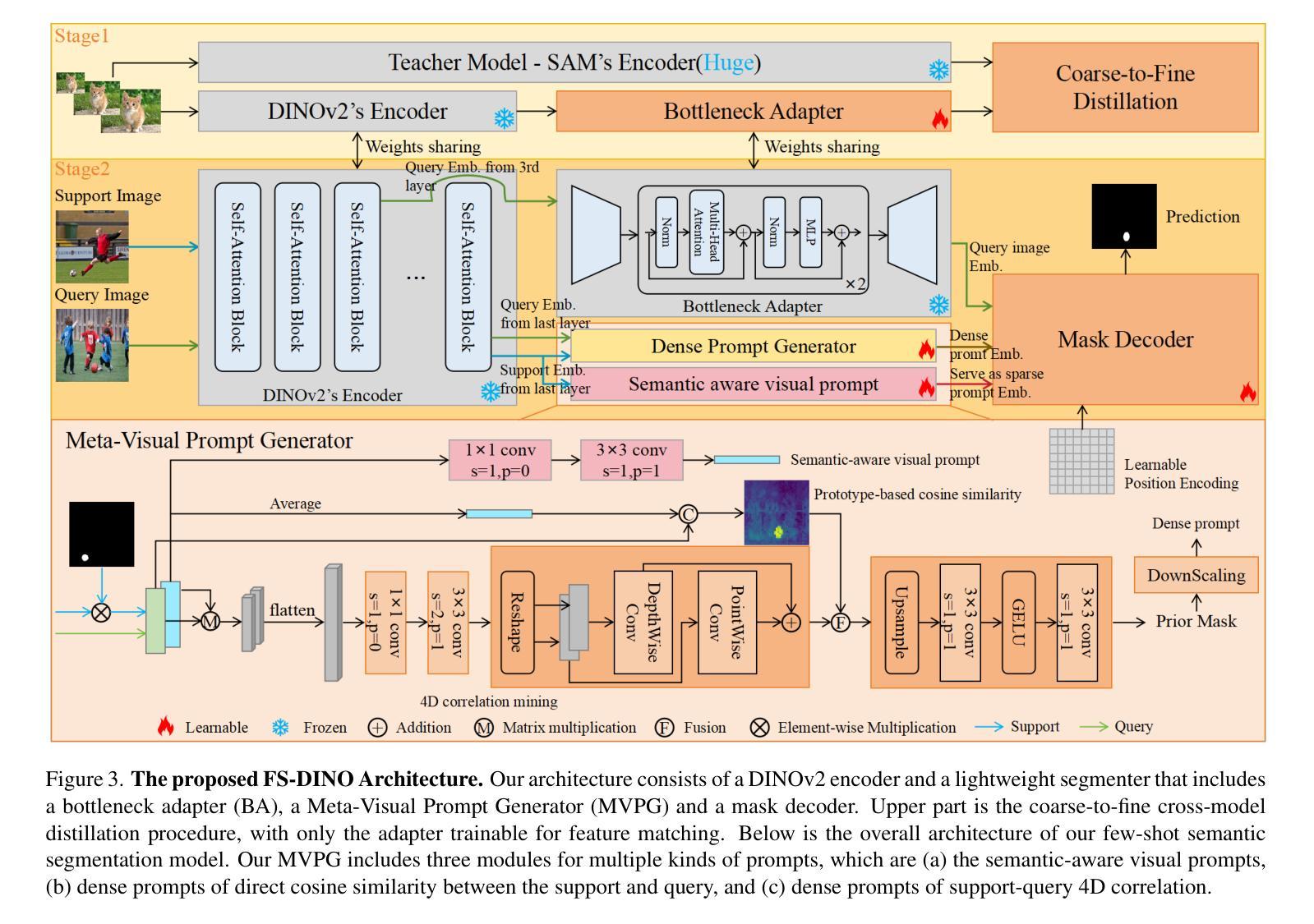
DINOv2-powered Few-Shot Semantic Segmentation: A Unified Framework via Cross-Model Distillation and 4D Correlation Mining
Authors:Wei Zhuo, Zhiyue Tang, Wufeng Xue, Hao Ding, Linlin Shen
Few-shot semantic segmentation has gained increasing interest due to its generalization capability, i.e., segmenting pixels of novel classes requiring only a few annotated images. Prior work has focused on meta-learning for support-query matching, with extensive development in both prototype-based and aggregation-based methods. To address data scarcity, recent approaches have turned to foundation models to enhance representation transferability for novel class segmentation. Among them, a hybrid dual-modal framework including both DINOv2 and SAM has garnered attention due to their complementary capabilities. We wonder “can we build a unified model with knowledge from both foundation models?” To this end, we propose FS-DINO, with only DINOv2’s encoder and a lightweight segmenter. The segmenter features a bottleneck adapter, a meta-visual prompt generator based on dense similarities and semantic embeddings, and a decoder. Through coarse-to-fine cross-model distillation, we effectively integrate SAM’s knowledge into our lightweight segmenter, which can be further enhanced by 4D correlation mining on support-query pairs. Extensive experiments on COCO-20i, PASCAL-5i, and FSS-1000 demonstrate the effectiveness and superiority of our method.
少样本语义分割因其泛化能力而受到越来越多的关注,即对新型类别进行像素分割时只需要很少标注的图像即可。先前的研究主要聚焦于基于支持集查询匹配的元学习,并在基于原型和基于聚合的方法上进行了大量开发。为了解决数据稀缺问题,近期的方法转向使用基础模型以增强新型类别分割的表示迁移能力。其中,一种混合双模态框架,包括DINOv2和SAM在内,因其互补能力而受到关注。我们想知道“我们能否建立一个融合两种基础模型知识的统一模型?”为此,我们提出了FS-DINO,仅采用DINOv2的编码器和轻量级分割器。分割器特点包括瓶颈适配器、基于密集相似性和语义嵌入的元视觉提示生成器以及解码器。通过粗到细的跨模型蒸馏,我们有效地将SAM的知识集成到我们的轻量级分割器中,通过支持查询对上的4D相关性挖掘可以进一步增强其性能。在COCO-20i、PASCAL-5i和FSS-1000上的大量实验证明了我们方法的有效性和优越性。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
这是一篇关于少样本语义分割技术的文章,主要介绍了如何借助基础模型来提升模型对新型类别的泛化能力。文章提出了一种名为FS-DINO的统一模型,该模型仅使用DINOv2的编码器和一个轻量级分割器。通过粗到细的跨模型蒸馏和4D关联挖掘技术,该模型能够有效地整合SAM的知识,进一步提升性能。在COCO-20i、PASCAL-5i和FSS-1000等数据集上的实验证明了该方法的有效性和优越性。
Key Takeaways
- 少样本语义分割技术因其在新型类别上的泛化能力而受到关注。
- 现有方法主要关注基于元学习的支持查询匹配技术。
- 基础模型被用来增强对新型类别分割的表示迁移能力。
- 提出了一个名为FS-DINO的统一模型,该模型结合了DINOv2的编码器和轻量级分割器。
- 通过粗到细的跨模型蒸馏技术整合了SAM的知识。
- 4D关联挖掘技术用于增强模型性能。
点此查看论文截图


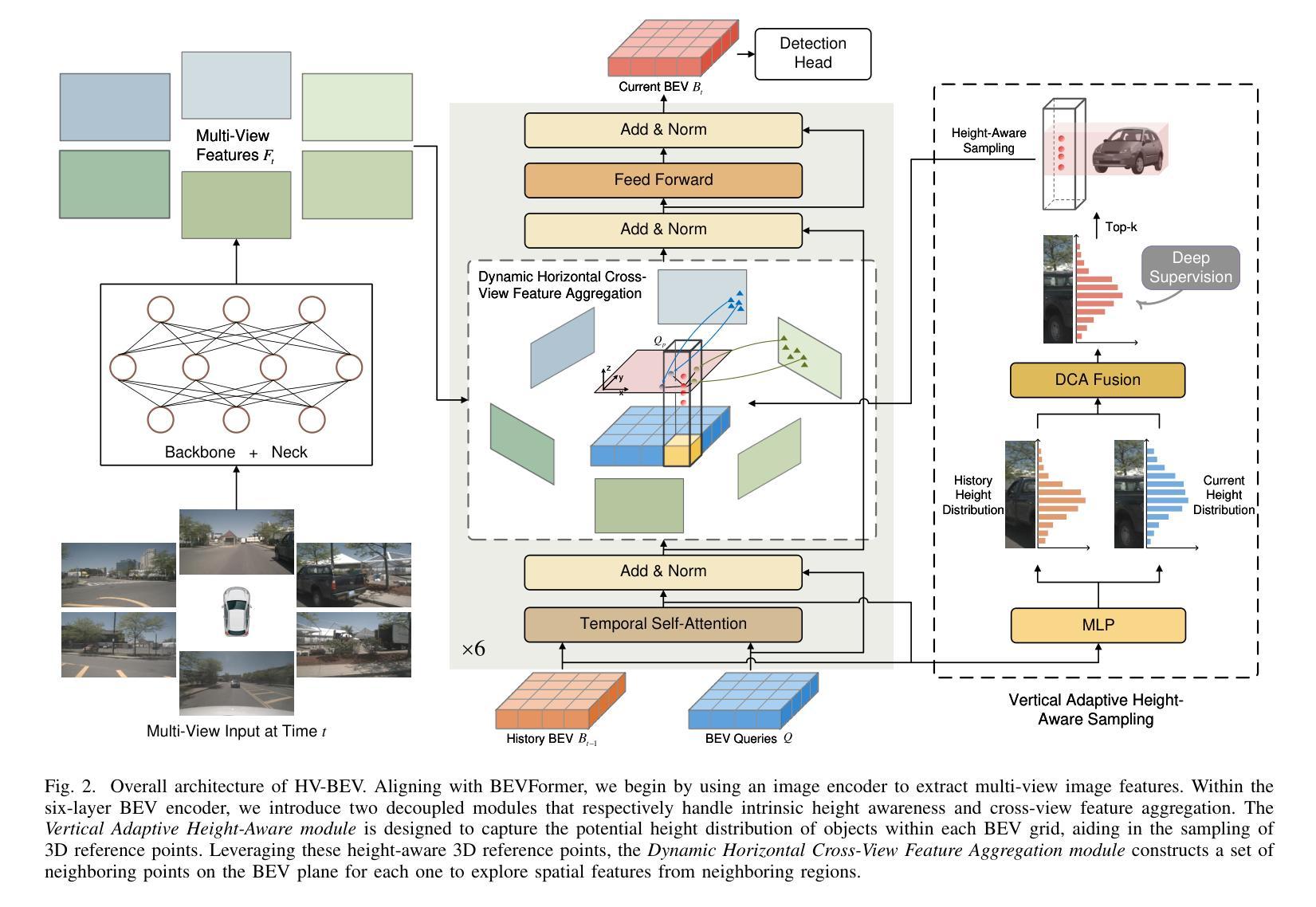
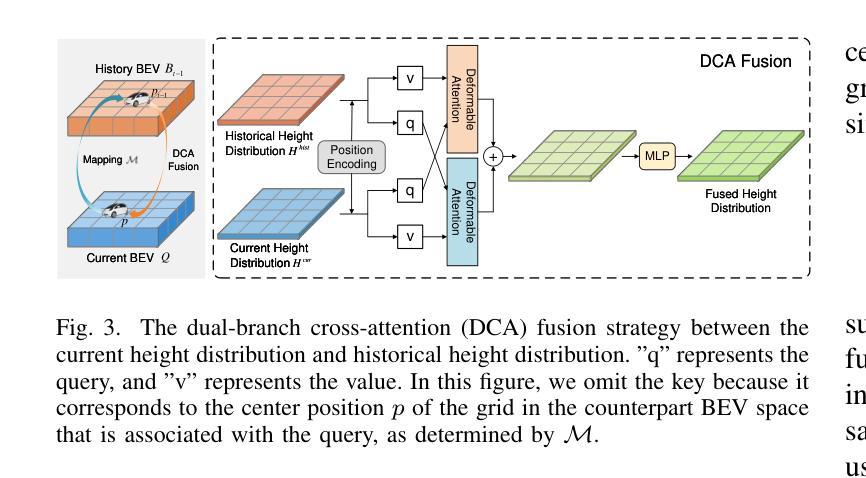
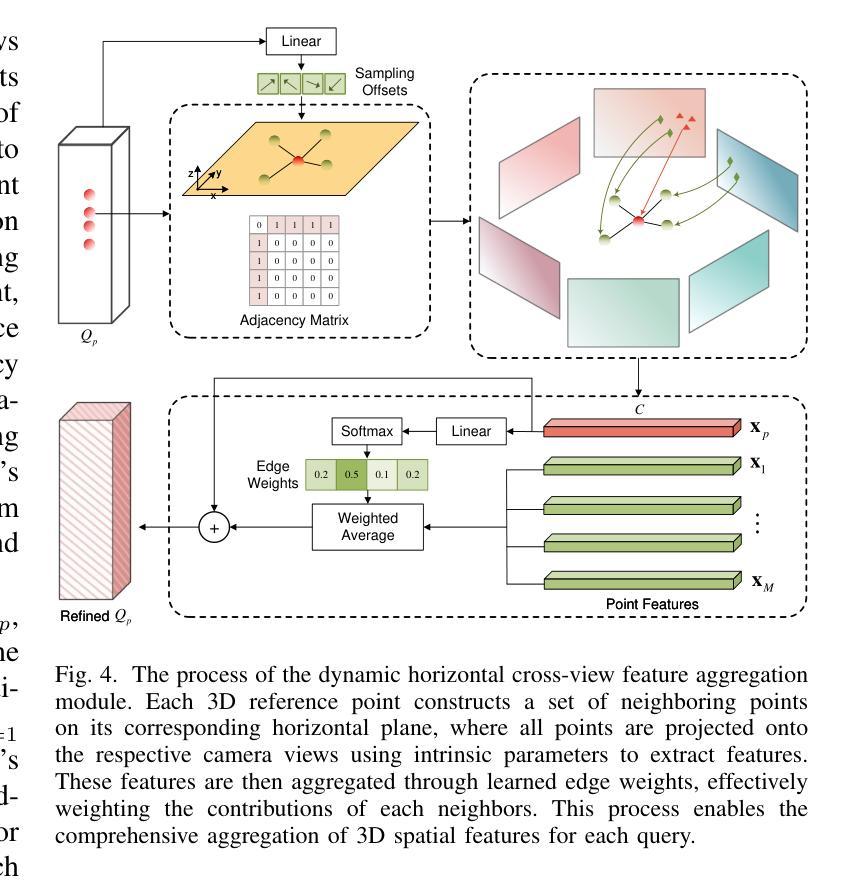
HV-BEV: Decoupling Horizontal and Vertical Feature Sampling for Multi-View 3D Object Detection
Authors:Di Wu, Feng Yang, Benlian Xu, Pan Liao, Wenhui Zhao, Dingwen Zhang
The application of vision-based multi-view environmental perception system has been increasingly recognized in autonomous driving technology, especially the BEV-based models. Current state-of-the-art solutions primarily encode image features from each camera view into the BEV space through explicit or implicit depth prediction. However, these methods often overlook the structured correlations among different parts of objects in 3D space and the fact that different categories of objects often occupy distinct local height ranges. For example, trucks appear at higher elevations, whereas traffic cones are near the ground. In this work, we propose a novel approach that decouples feature sampling in the \textbf{BEV} grid queries paradigm into \textbf{H}orizontal feature aggregation and \textbf{V}ertical adaptive height-aware reference point sampling (HV-BEV), aiming to improve both the aggregation of objects’ complete information and awareness of diverse objects’ height distribution. Specifically, a set of relevant neighboring points is dynamically constructed for each 3D reference point on the ground-aligned horizontal plane, enhancing the association of the same instance across different BEV grids, especially when the instance spans multiple image views around the vehicle. Additionally, instead of relying on uniform sampling within a fixed height range, we introduce a height-aware module that incorporates historical information, enabling the reference points to adaptively focus on the varying heights at which objects appear in different scenes. Extensive experiments validate the effectiveness of our proposed method, demonstrating its superior performance over the baseline across the nuScenes dataset. Moreover, our best-performing model achieves a remarkable 50.5% mAP and 59.8% NDS on the nuScenes testing set. The code is available at https://github.com/Uddd821/HV-BEV.
基于视觉的多视角环境感知系统在自动驾驶技术中的应用日益受到重视,尤其是基于鸟瞰视图(BEV)的模型。目前最先进的解决方案主要通过显式或隐式的深度预测,将每个相机视角的图像特征编码到鸟瞰视图空间中。然而,这些方法往往忽视了物体不同部分在三维空间中的结构化关联以及不同类别的物体通常占据不同的局部高度范围这一事实。例如,卡车出现在较高的地方,而交通锥则接近地面。在这项工作中,我们提出了一种新方法,将鸟瞰视图网格查询范式中的特征采样解耦为水平特征聚合和垂直自适应高度感知参考点采样(HV-BEV),旨在改进物体完整信息的聚合和不同物体高度分布的感知。具体来说,对于地面上对齐的水平平面上的每个三维参考点,动态构建了一组相关的邻近点,增强了同一实例在不同鸟瞰视图网格中的关联,特别是在实例跨越车辆周围多个图像视图时。此外,我们引入了高度感知模块,该模块利用历史信息,而不是在固定高度范围内进行均匀采样,使参考点能够自适应地关注不同场景中物体出现的高度变化。大量实验验证了我们所提出方法的有效性,在nuScenes数据集上相对于基线方法表现出卓越的性能。而且,我们表现最佳的模型在nuScenes测试集上取得了50.5%的mAP和59.8%的NDS。代码可在https://github.com/Uddd821/HV-BEV上找到。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 13 pages, 7 figures, submitted to T-ITS
Summary
基于视觉的多视角环境感知系统在自动驾驶技术中得到了广泛应用,特别是基于BEV的模型。本文提出了一种新的方法,将特征采样在BEV网格查询范式中解耦为水平特征聚合和垂直自适应高度感知参考点采样(HV-BEV),旨在改进对象完整信息的聚合和不同对象高度分布的感知。该方法在nuScenes数据集上的实验结果表明,该方法在基线方法上具有优异性能。同时,我们最好的模型在nuScenes测试集上达到了令人瞩目的50.5%的mAP和59.8%的NDS。代码可在GitHub上找到:https://github.com/Uddd821/HV-BEV。
Key Takeaways
- 自动驾驶技术中,基于视觉的多视角环境感知系统得到广泛应用,特别是BEV模型。
- 当前主流方法主要通过显式或隐式深度预测将各相机视角的图像特征编码到BEV空间。
- 本文提出的新方法HV-BEV,将特征采样解耦为水平特征聚合和垂直自适应高度感知参考点采样,以改进对象的完整信息聚合和不同对象的高度分布感知。
- HV-BEV方法通过动态构建相关邻近点,增强了同一实例在不同BEV网格之间的关联,特别是当实例跨越车辆周围的多个图像视图时。
- 该方法引入了一个自适应高度感知模块,该模块结合了历史信息,使参考点能够自适应地关注不同场景中对象出现的高度变化。
- 在nuScenes数据集上的实验验证了该方法的有效性,其性能优于基线方法。
点此查看论文截图