⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-05-24 更新
From EduVisBench to EduVisAgent: A Benchmark and Multi-Agent Framework for Pedagogical Visualization
Authors:Haonian Ji, Shi Qiu, Siyang Xin, Siwei Han, Zhaorun Chen, Hongyi Wang, Dake Zhang, Huaxiu Yao
While foundation models (FMs), such as diffusion models and large vision-language models (LVLMs), have been widely applied in educational contexts, their ability to generate pedagogically effective visual explanations remains limited. Most existing approaches focus primarily on textual reasoning, overlooking the critical role of structured and interpretable visualizations in supporting conceptual understanding. To better assess the visual reasoning capabilities of FMs in educational settings, we introduce EduVisBench, a multi-domain, multi-level benchmark. EduVisBench features diverse STEM problem sets requiring visually grounded solutions, along with a fine-grained evaluation rubric informed by pedagogical theory. Our empirical analysis reveals that existing models frequently struggle with the inherent challenge of decomposing complex reasoning and translating it into visual representations aligned with human cognitive processes. To address these limitations, we propose EduVisAgent, a multi-agent collaborative framework that coordinates specialized agents for instructional planning, reasoning decomposition, metacognitive prompting, and visualization design. Experimental results show that EduVisAgent substantially outperforms all baselines, achieving a 40.2% improvement and delivering more educationally aligned visualizations. EduVisBench and EduVisAgent are available at https://github.com/aiming-lab/EduVisBench and https://github.com/aiming-lab/EduVisAgent.
尽管扩散模型等大型基础模型(FMs)和大型视觉语言模型(LVLMs)在教育环境中得到了广泛应用,它们在生成教学有效的视觉解释方面的能力仍然有限。目前大多数方法主要关注文本推理,忽视了结构化、可解释的视觉支持在促进概念理解方面的关键作用。为了更好地评估教育环境中基础模型的视觉推理能力,我们引入了EduVisBench,这是一个多领域、多层次的基准测试。EduVisBench包含多样化的STEM问题集,需要视觉解决方案,以及由教学理论支持的精细评估标准。我们的实证分析表明,现有模型在分解复杂推理并将其转化为与人类认知过程相符的视觉表示方面存在固有的挑战。为了解决这些局限性,我们提出了EduVisAgent,这是一个多智能体协作框架,协调专门用于教学规划的智能体,进行推理分解、元认知提示和可视化设计。实验结果表明,EduVisAgent显著优于所有基线模型,实现了40.2%的改进,并提供了更符合教育要求的可视化。EduVisBench和EduVisAgent可在以下网站访问:https://github.com/aiming-lab/EduVisBench 和 https://github.com/aiming-lab/EduVisAgent。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 16 pages; 7 figures
Summary
该文探讨了基础模型(如扩散模型和大型视觉语言模型)在教育背景下的应用及其生成有效视觉解释的局限性。为此,文章引入了一个多领域、多层次的基准测试EduVisBench,通过实证分析和精细化评估标准来评估模型在视觉推理方面的能力。针对现有模型的不足,文章提出了EduVisAgent多代理协作框架,通过专业化的代理来协调教学规划、推理分解、元认知提示和可视化设计。实验结果显示,EduVisAgent显著优于所有基线模型,实现了40.2%的改进,并提供了更符合教育需求的数据可视化。
Key Takeaways
- 基础模型在教育领域应用广泛,但在生成有效的视觉解释方面存在局限性。
- 现有模型主要关注文本推理,忽视了结构化、可解释的视觉支持在概念理解中的重要性。
- 引入EduVisBench基准测试,旨在评估模型在教育环境中的视觉推理能力。
- 实证分析显示现有模型在分解复杂推理和转化为与人类认知过程对齐的视觉表示方面存在挑战。
- 提出EduVisAgent多代理协作框架,包含教学规划、推理分解、元认知提示和可视化设计等功能。
- 实验结果显示EduVisAgent显著优于基线模型,实现了教育视觉化的改进。
点此查看论文截图




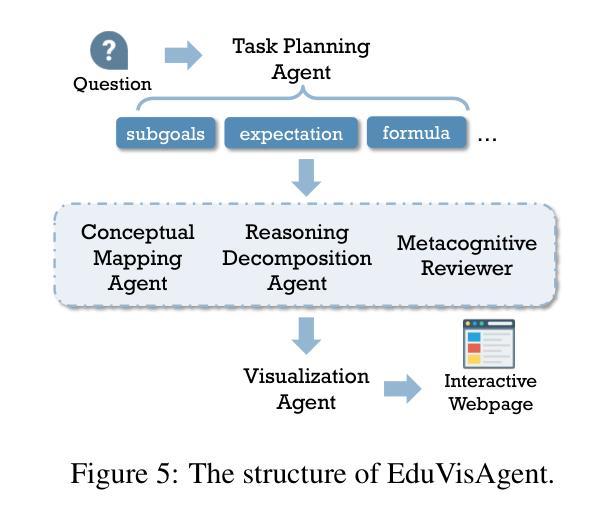

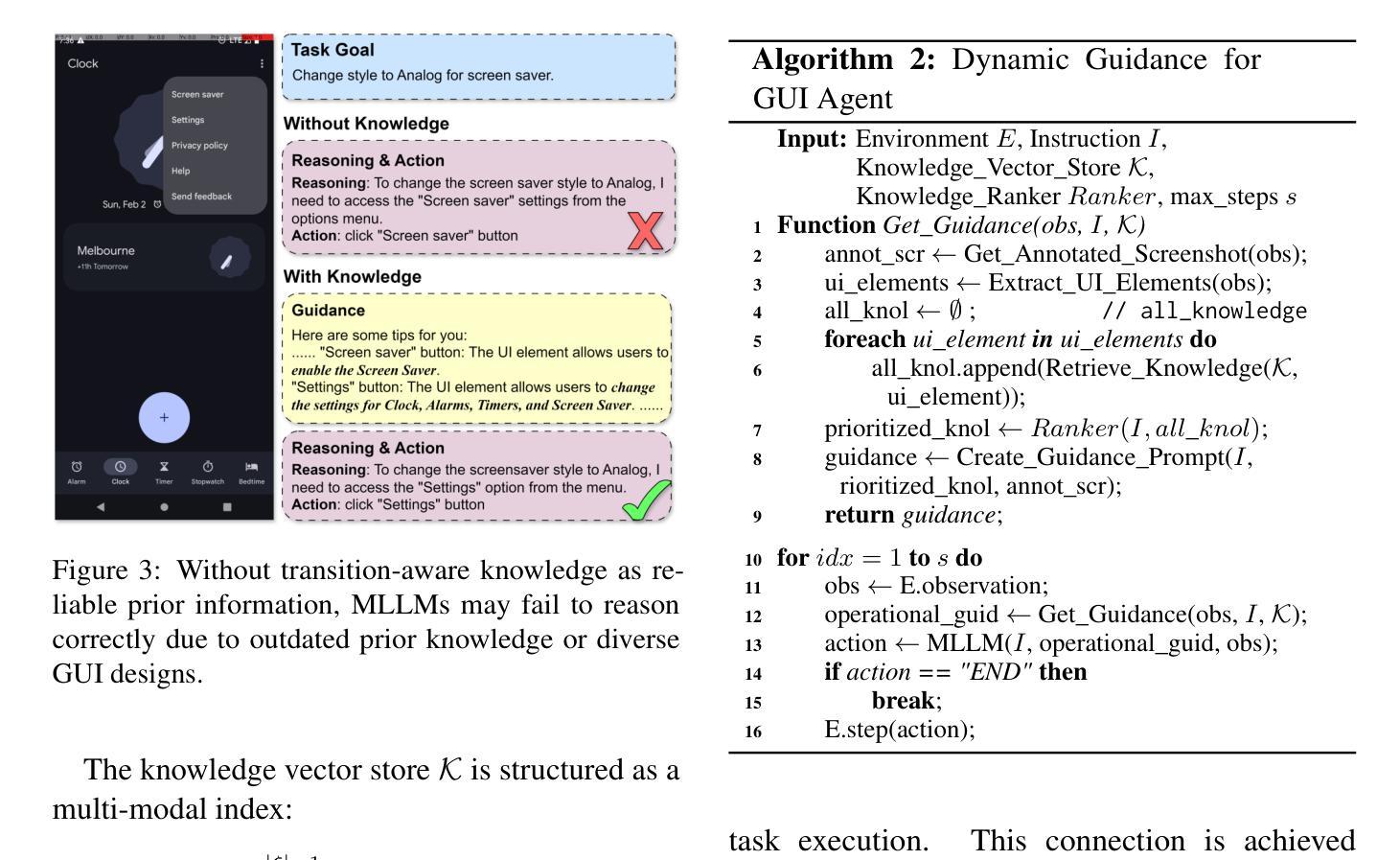
GUI-explorer: Autonomous Exploration and Mining of Transition-aware Knowledge for GUI Agent
Authors:Bin Xie, Rui Shao, Gongwei Chen, Kaiwen Zhou, Yinchuan Li, Jie Liu, Min Zhang, Liqiang Nie
GUI automation faces critical challenges in dynamic environments. MLLMs suffer from two key issues: misinterpreting UI components and outdated knowledge. Traditional fine-tuning methods are costly for app-specific knowledge updates. We propose GUI-explorer, a training-free GUI agent that incorporates two fundamental mechanisms: (1) Autonomous Exploration of Function-aware Trajectory. To comprehensively cover all application functionalities, we design a Function-aware Task Goal Generator that automatically constructs exploration goals by analyzing GUI structural information (e.g., screenshots and activity hierarchies). This enables systematic exploration to collect diverse trajectories. (2) Unsupervised Mining of Transition-aware Knowledge. To establish precise screen-operation logic, we develop a Transition-aware Knowledge Extractor that extracts effective screen-operation logic through unsupervised analysis the state transition of structured interaction triples (observation, action, outcome). This eliminates the need for human involvement in knowledge extraction. With a task success rate of 53.7% on SPA-Bench and 47.4% on AndroidWorld, GUI-explorer shows significant improvements over SOTA agents. It requires no parameter updates for new apps. GUI-explorer is open-sourced and publicly available at https://github.com/JiuTian-VL/GUI-explorer.
图形用户界面(GUI)自动化在动态环境中面临重大挑战。MLLMs面临两个关键问题:误解UI组件和知识储备过时。传统的微调方法对于特定应用程序的知识更新成本高昂。我们提出了GUI-explorer,这是一款无需训练的GUI代理,它包含两种基本机制:(1)功能感知轨迹的自主探索。为了全面覆盖所有应用程序功能,我们设计了一个功能感知任务目标生成器,它通过自动分析GUI结构信息(例如截图和活动层次结构)来构建探索目标。这能够实现系统的探索并收集各种轨迹。(2)过渡感知知识的无监督挖掘。为了建立精确的屏幕操作逻辑,我们开发了一个过渡感知知识提取器,它通过无监督分析结构化交互三元组(观察、行动、结果)的状态过渡来提取有效的屏幕操作逻辑。这消除了人类在知识提取中的参与。在SPA-Bench上,GUI-explorer的任务成功率为53.7%,在AndroidWorld上为47.4%,较其他最新代理有明显改进。GUI-explorer无需更新参数即可适应新应用程序。GUI-explorer已开源并可在https://github.com/JiuTian-VL/GUI-explorer公开访问。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF ACL 2025. Github: https://github.com/JiuTian-VL/GUI-explorer
摘要
自动化图形用户界面(GUI)面临动态环境中的关键挑战。MLLM面临两大问题:误解UI组件和知识过时。传统的微调方法对于应用程序特定知识的更新成本高昂。我们提出了GUI探索器,一种无需训练的GUI代理,它结合了两种基本机制:(1)功能感知轨迹的自主探索。为了全面覆盖所有应用程序功能,我们设计了一种功能感知任务目标生成器,它通过自动分析GUI结构信息(如截图和活动层次结构)来构建探索目标。这可以通过系统探索收集多样化的轨迹。(2)过渡感知知识的无监督挖掘。为了建立精确的屏幕操作逻辑,我们开发了一种过渡感知知识提取器,它通过无监督分析结构化交互三元组(观察、行动、结果)的状态转换来提取有效的屏幕操作逻辑。这消除了知识提取中人类参与的需要。在SPA-Bench上GUI探索器的任务成功率为53.7%,在AndroidWorld上为47.4%,相较于其他最先进代理有明显改进。GUI探索器无需针对新应用程序更新参数。GUI探索器已开源并可在https://github.com/JiuTian-VL/GUI-explorer获取。
关键见解
- GUI自动化在动态环境中面临挑战,包括误解UI组件和知识过时问题。
- 提出了一种名为GUI-explorer的无需训练的新GUI代理,解决传统方法的局限性。
- GUI-explorer通过自主探索和过渡感知知识挖掘两种基本机制工作。
- 功能感知任务目标生成器通过分析GUI结构信息自动构建探索目标,实现全面的应用功能覆盖。
- 过渡感知知识提取器通过无监督分析结构化交互三元组的状态转换来提取屏幕操作逻辑,无需人工参与。
- GUI-explorer在SPA-Bench和AndroidWorld上的任务成功率超过其他最先进代理。
点此查看论文截图



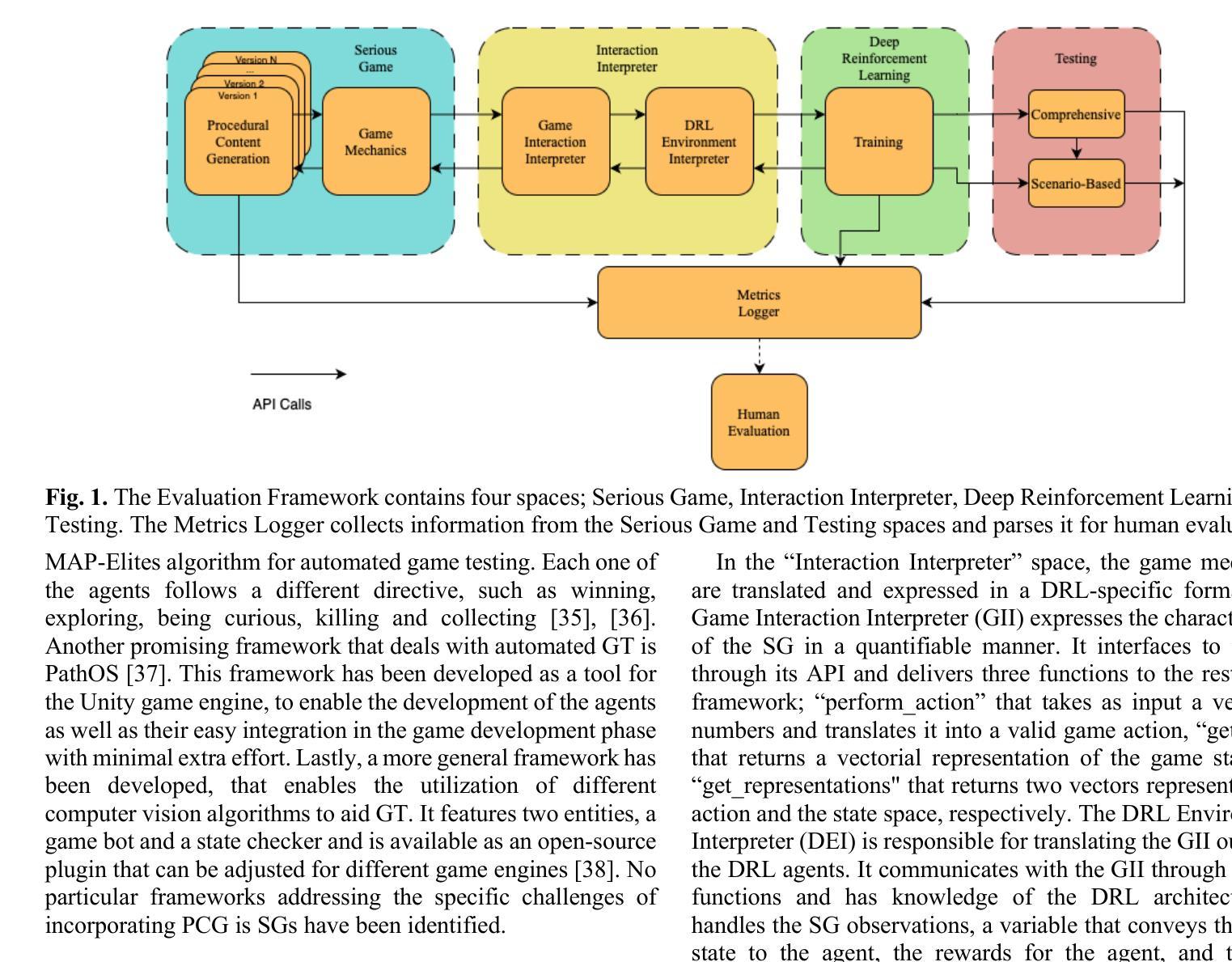
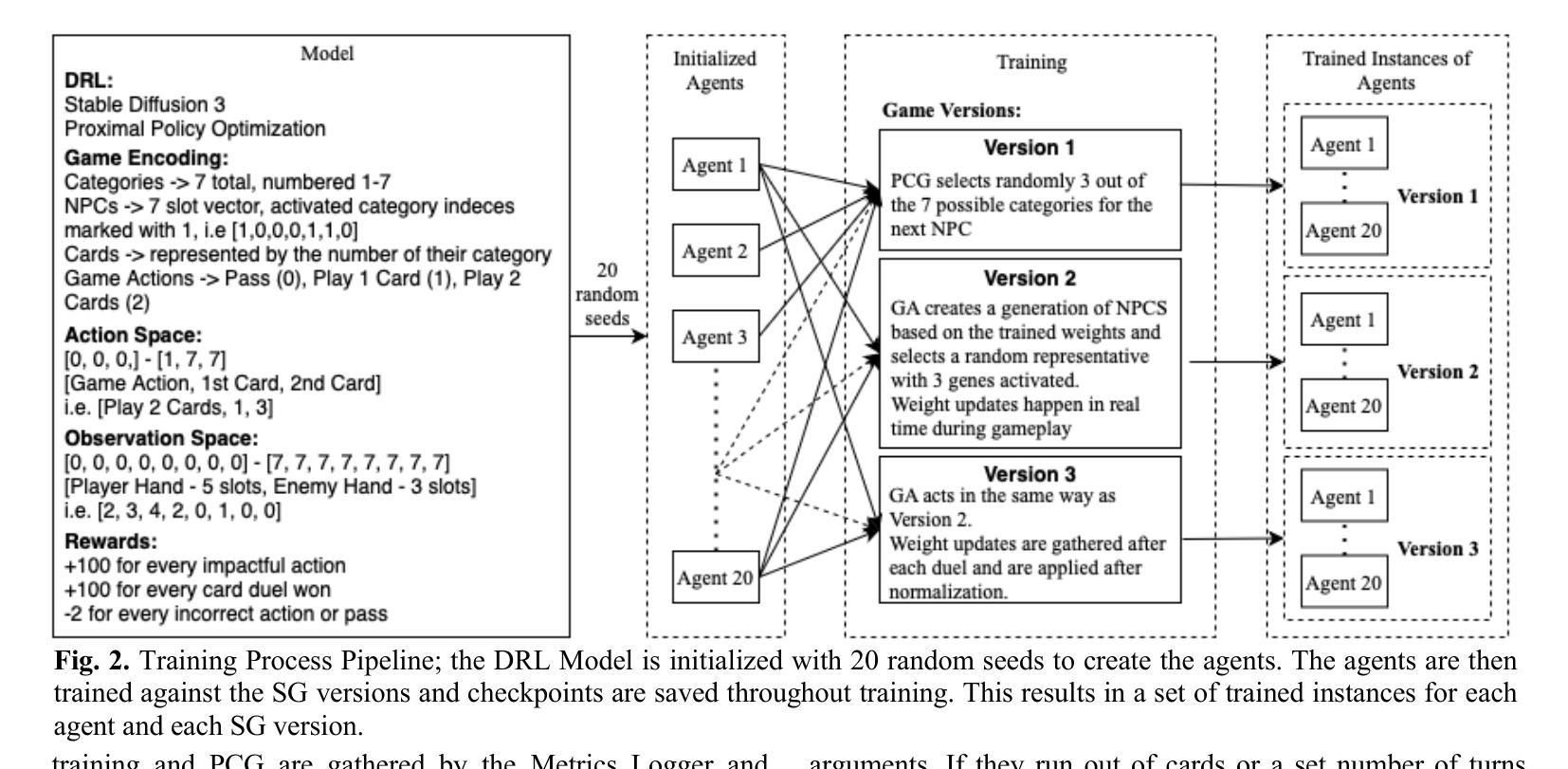
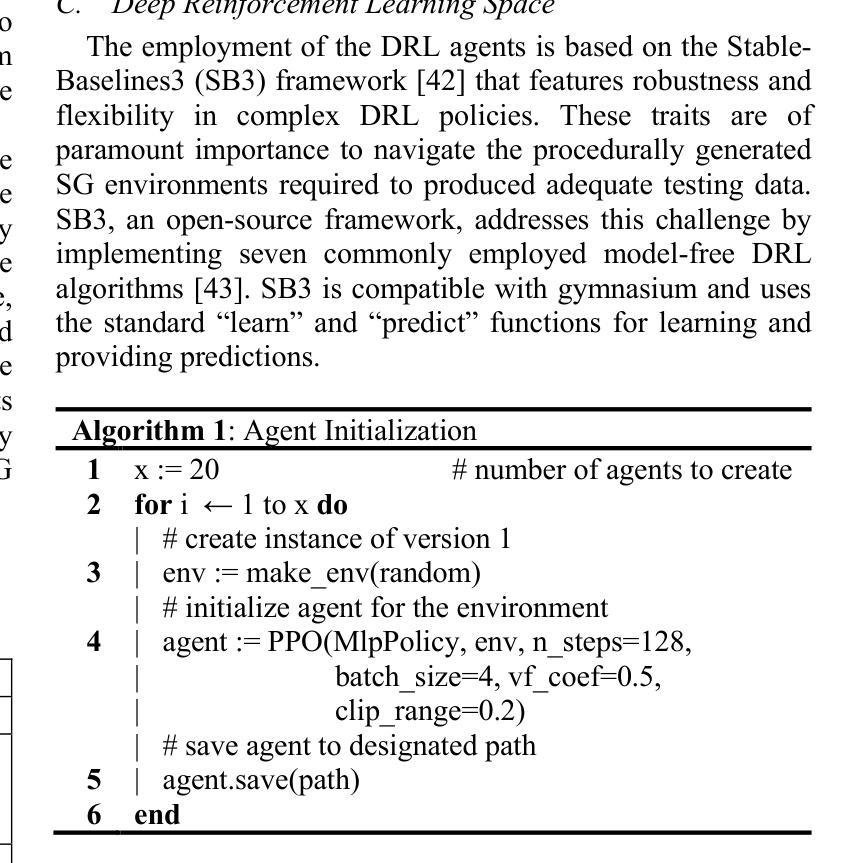
A modular framework for automated evaluation of procedural content generation in serious games with deep reinforcement learning agents
Authors:Eleftherios Kalafatis, Konstantinos Mitsis, Konstantia Zarkogianni, Maria Athanasiou, Konstantina Nikita
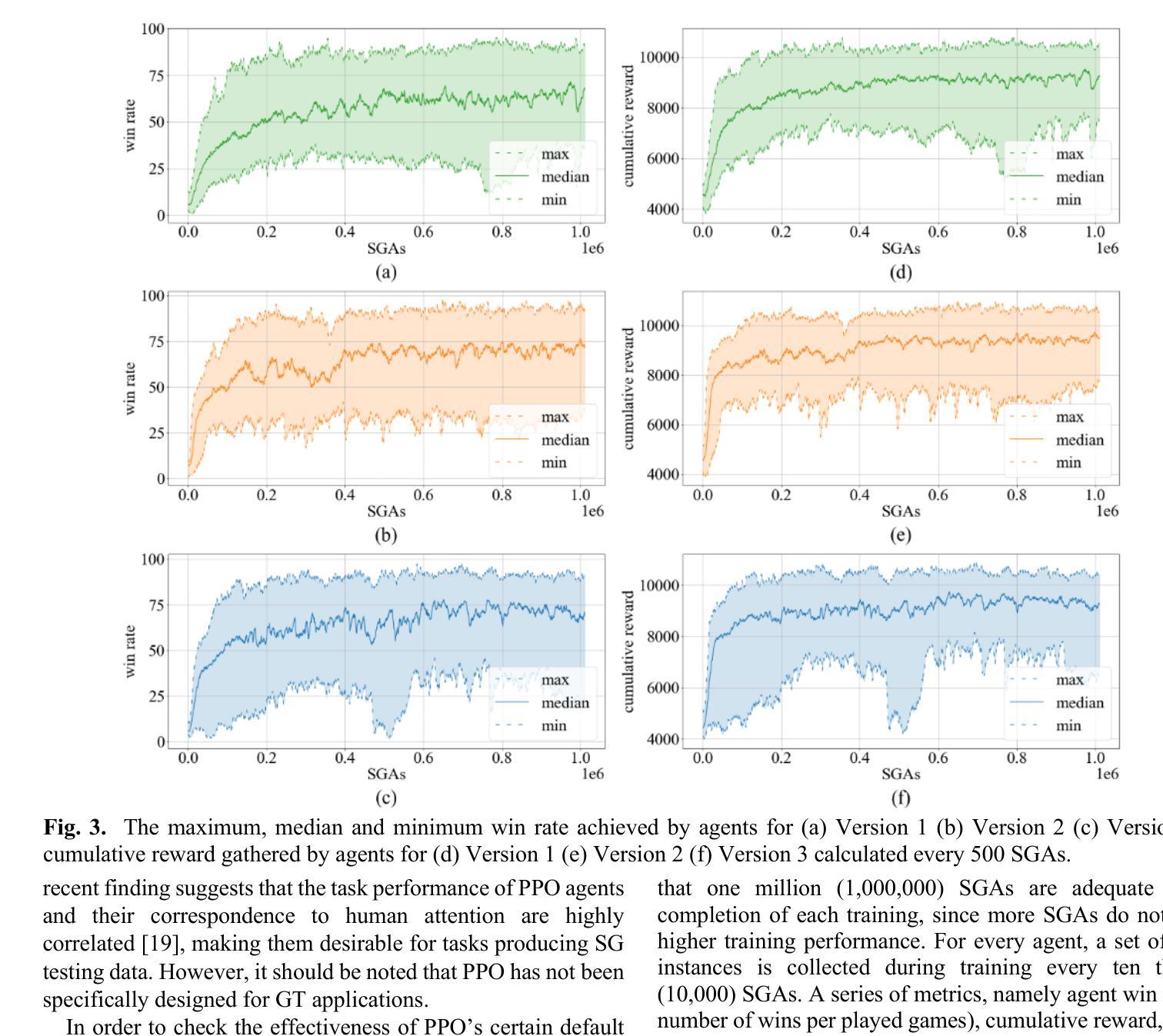
Serious Games (SGs) are nowadays shifting focus to include procedural content generation (PCG) in the development process as a means of offering personalized and enhanced player experience. However, the development of a framework to assess the impact of PCG techniques when integrated into SGs remains particularly challenging. This study proposes a methodology for automated evaluation of PCG integration in SGs, incorporating deep reinforcement learning (DRL) game testing agents. To validate the proposed framework, a previously introduced SG featuring card game mechanics and incorporating three different versions of PCG for nonplayer character (NPC) creation has been deployed. Version 1 features random NPC creation, while versions 2 and 3 utilize a genetic algorithm approach. These versions are used to test the impact of different dynamic SG environments on the proposed framework’s agents. The obtained results highlight the superiority of the DRL game testing agents trained on Versions 2 and 3 over those trained on Version 1 in terms of win rate (i.e. number of wins per played games) and training time. More specifically, within the execution of a test emulating regular gameplay, both Versions 2 and 3 peaked at a 97% win rate and achieved statistically significant higher (p=0009) win rates compared to those achieved in Version 1 that peaked at 94%. Overall, results advocate towards the proposed framework’s capability to produce meaningful data for the evaluation of procedurally generated content in SGs.
如今,严肃游戏(SGs)正将焦点转向在开发过程中包含程序内容生成(PCG),以提供个性化的增强玩家体验。然而,建立一个框架来评估PCG技术在SGs中的影响仍然是一个特别大的挑战。本研究提出了一种自动化评估SG中PCG集成的方法,该方法结合了深度强化学习(DRL)游戏测试代理。为了验证所提出的框架,已经部署了一款之前引入的采用卡牌游戏机制的SG,并融入了三种不同版本的PCG来进行非玩家角色(NPC)的创建。版本1具有随机NPC创建功能,而版本2和版本3则采用遗传算法方法。这些版本被用来测试不同的动态SG环境对所提出框架的代理的影响。获得的结果突显了版本2和版本3训练的DRL游戏测试代理在胜率(即每场游戏的获胜次数)和训练时间上优于版本1训练的代理。更具体地说,在一个模拟常规游戏玩法的测试中,版本2和版本3的胜率达到了峰值,为97%,并且其胜率在统计学上显著高于版本1(p=0.0009),版本1的峰值胜率为94%。总体而言,结果支持所提出框架在评估SG中程序生成内容方面的能力,能够产生有意义的数据。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文探讨了将程序化内容生成(PCG)技术集成到严肃游戏(SGs)中,并应用深度强化学习(DRL)游戏测试代理进行自动化评估的方法论。通过部署一款采用卡牌游戏机制的严肃游戏,并设计三种不同版本的PCG NPC创建技术进行测试验证,发现版本2和版本3中应用的遗传算法在训练出的DRL游戏测试代理性能上表现出优越性,具体体现在胜率和训练时间上。结果支持该框架对程序化生成内容进行有意义评估的能力。
Key Takeaways
- 严肃游戏现在将焦点转向在开发过程中加入程序化内容生成(PCG),以提供个性化的增强游戏体验。
- 提出了一种自动化评估PCG集成在SGs中的方法论,利用深度强化学习(DRL)游戏测试代理。
- 通过部署一款严肃游戏并设计三个版本的PCG NPC创建技术进行测试验证,发现版本2和版本3的遗传算法表现更优秀。
- DRL游戏测试代理在版本2和版本3中的胜率和训练时间均优于版本1。
- 结果支持该框架对程序化生成内容进行有意义评估的能力。
点此查看论文截图

O$^2$-Searcher: A Searching-based Agent Model for Open-Domain Open-Ended Question Answering
Authors:Jianbiao Mei, Tao Hu, Daocheng Fu, Licheng Wen, Xuemeng Yang, Rong Wu, Pinlong Cai, Xing Gao, Yu Yang, Chengjun Xie, Botian Shi, Yong Liu, Yu Qiao
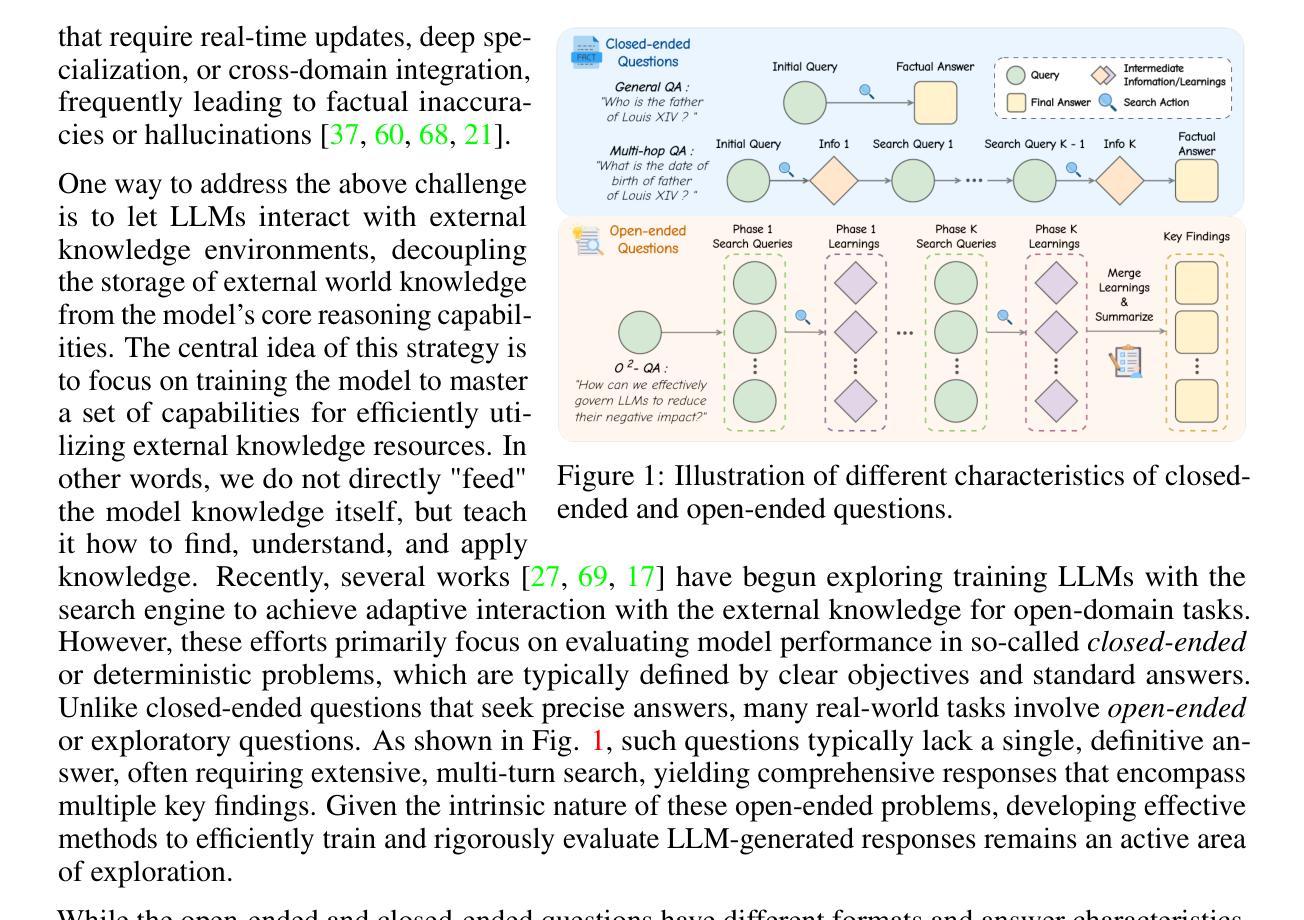
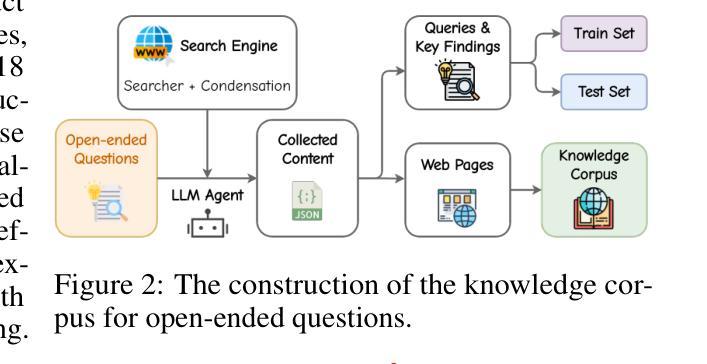
Large Language Models (LLMs), despite their advancements, are fundamentally limited by their static parametric knowledge, hindering performance on tasks requiring open-domain up-to-date information. While enabling LLMs to interact with external knowledge environments is a promising solution, current efforts primarily address closed-end problems. Open-ended questions, which characterized by lacking a standard answer or providing non-unique and diverse answers, remain underexplored. To bridge this gap, we present O$^2$-Searcher, a novel search agent leveraging reinforcement learning to effectively tackle both open-ended and closed-ended questions in the open domain. O$^2$-Searcher leverages an efficient, locally simulated search environment for dynamic knowledge acquisition, effectively decoupling the external world knowledge from model’s sophisticated reasoning processes. It employs a unified training mechanism with meticulously designed reward functions, enabling the agent to identify problem types and adapt different answer generation strategies. Furthermore, to evaluate performance on complex open-ended tasks, we construct O$^2$-QA, a high-quality benchmark featuring 300 manually curated, multi-domain open-ended questions with associated web page caches. Extensive experiments show that O$^2$-Searcher, using only a 3B model, significantly surpasses leading LLM agents on O$^2$-QA. It also achieves SOTA results on various closed-ended QA benchmarks against similarly-sized models, while performing on par with much larger ones.
尽管大型语言模型(LLMs)取得了进展,但它们仍受到静态参数知识的根本限制,这阻碍了它们在需要开放领域最新信息的任务上的表现。虽然让LLMs与外部环境进行交互是一个有前景的解决方案,但目前的努力主要侧重于解决封闭式问题。开放式问题缺乏标准答案或提供非唯一和多样化的答案,仍然被探索得不够。为了弥补这一差距,我们提出了O$^2$-Searcher,这是一个新的搜索代理,利用强化学习有效地解决开放式和封闭式问题在开放领域的问题。O$^2$-Searcher利用高效、局部模拟的搜索环境进行动态知识获取,有效地将外部世界的知识从模型的复杂推理过程中解耦出来。它采用统一的训练机制和精心设计的奖励函数,使代理能够识别问题类型并适应不同的答案生成策略。此外,为了评估在复杂开放式任务上的性能,我们构建了O$^2$-QA,这是一个高质量的标准,包含300个手动整理、多领域的开放式问题以及与相关网页缓存相关的内容。大量实验表明,仅使用3B模型的O$^2$-Searcher在O$^2$-QA上显著超越了领先的大型语言模型代理。它在各种封闭式问答基准测试上也取得了最新结果,在与同类规模的模型中表现突出,同时在与更大的模型的表现上持平。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 25 pages, 9 figures
Summary
本文探讨了大型语言模型在处理开放领域、实时信息的任务时的局限性,尤其是在处理开放性问题方面存在不足。为解决这一问题,文章提出了一种名为O$^2$-Searcher的新型搜索代理,该代理利用强化学习有效应对开放性和封闭性问题。它通过高效的本地模拟搜索环境实现动态知识获取,将外部世界知识与模型的复杂推理过程解耦。此外,为评估在复杂开放性任务上的性能,文章构建了一个高质量基准测试O$^2$-QA。实验表明,O$^2$-Searcher在O$^2$-QA上的表现显著超越了领先的大型语言模型代理,同时在各种封闭性问答基准测试上达到了顶尖水平。
Key Takeaways
- 大型语言模型在处理需要开放领域实时信息的任务时存在局限性。
- O$^2$-Searcher是一种新型搜索代理,能处理开放性和封闭性问题。
- O$^2$-Searcher利用强化学习,在本地模拟搜索环境实现动态知识获取。
- O$^2$-Searcher将外部世界知识与模型的推理过程解耦。
- 为评估在开放性任务上的性能,构建了基准测试O$^2$-QA。
- O$^2$-Searcher在O$^2$-QA上的表现超越了其他大型语言模型代理。
点此查看论文截图

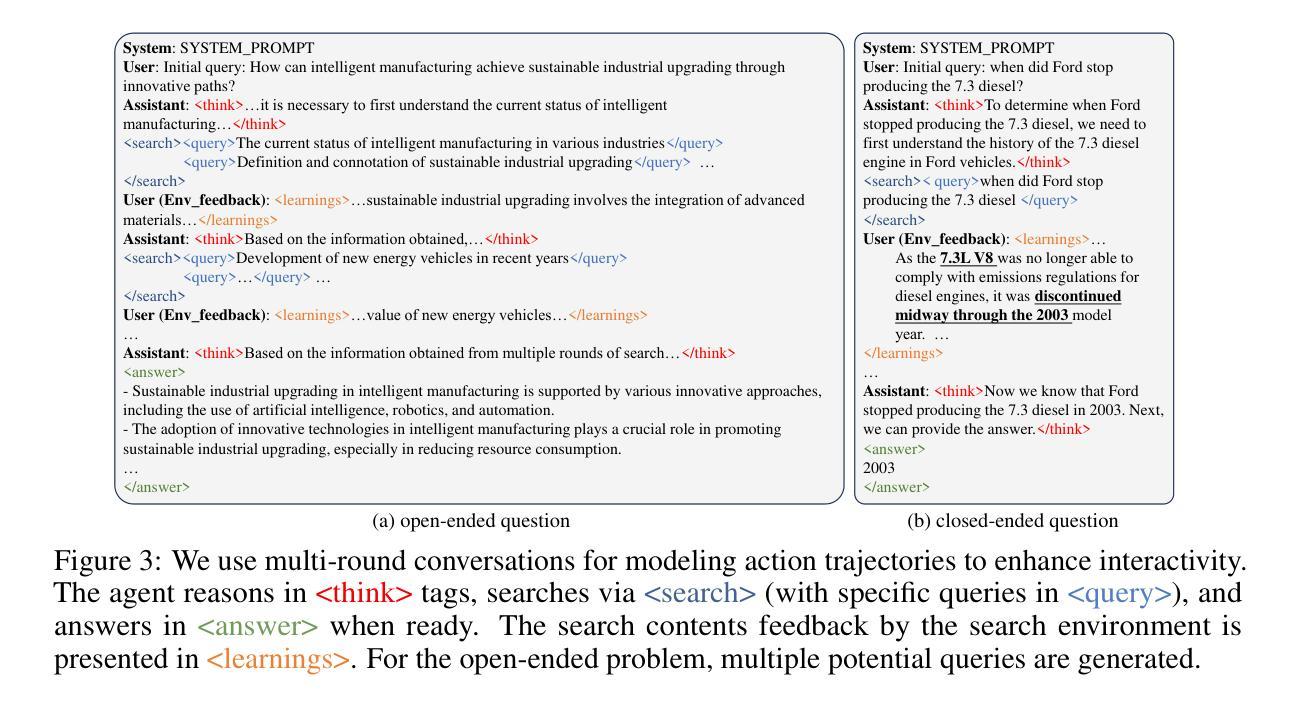
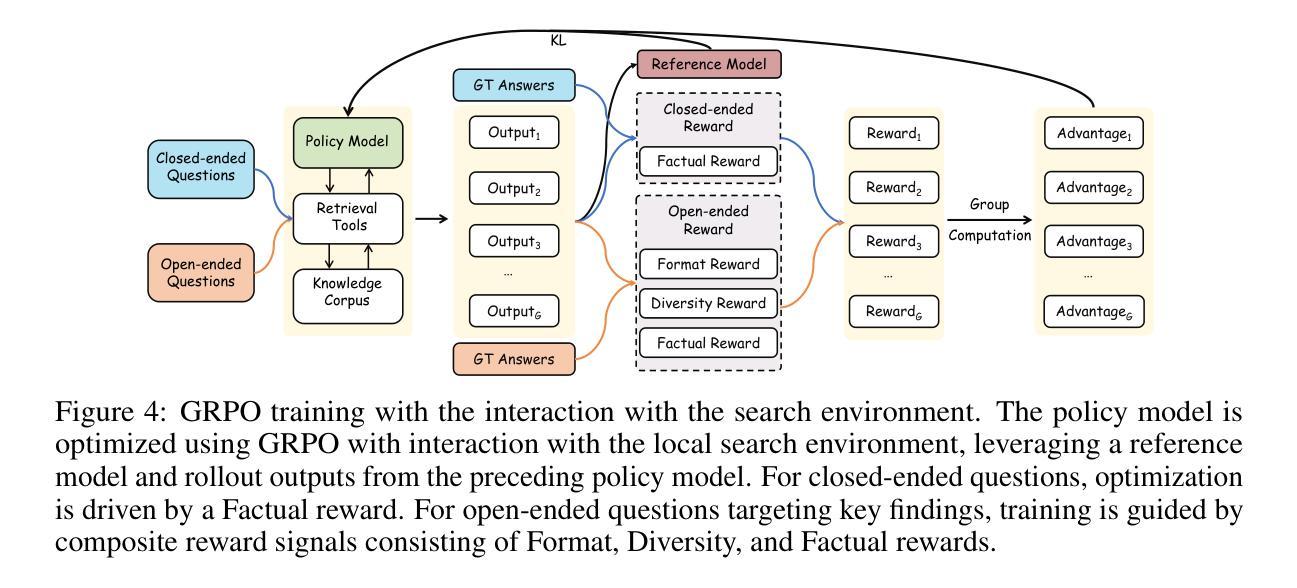
Psychology-driven LLM Agents for Explainable Panic Prediction on Social Media during Sudden Disaster Events
Authors:Mengzhu Liu, Zhengqiu Zhu, Chuan Ai, Chen Gao, Xinghong Li, Lingnan He, Kaisheng Lai, Yingfeng Chen, Xin Lu, Yong Li, Quanjun Yin
During sudden disaster events, accurately predicting public panic sentiment on social media is crucial for proactive governance and crisis management. Current efforts on this problem face three main challenges: lack of finely annotated data hinders emotion prediction studies, unmodeled risk perception causes prediction inaccuracies, and insufficient interpretability of panic formation mechanisms. We address these issues by proposing a Psychology-driven generative Agent framework (PsychoAgent) for explainable panic prediction based on emotion arousal theory. Specifically, we first construct a fine-grained open panic emotion dataset (namely COPE) via human-large language models (LLMs) collaboration to mitigate semantic bias. Then, we develop a framework integrating cross-domain heterogeneous data grounded in psychological mechanisms to model risk perception and cognitive differences in emotion generation. To enhance interpretability, we design an LLM-based role-playing agent that simulates individual psychological chains through dedicatedly designed prompts. Experimental results on our annotated dataset show that PsychoAgent improves panic emotion prediction performance by 12.6% to 21.7% compared to baseline models. Furthermore, the explainability and generalization of our approach is validated. Crucially, this represents a paradigm shift from opaque “data-driven fitting” to transparent “role-based simulation with mechanistic interpretation” for panic emotion prediction during emergencies. Our implementation is publicly available at: https://anonymous.4open.science/r/PsychoAgent-19DD.
在突发灾难事件中,准确预测社交媒体上的公众恐慌情绪对于积极治理和危机管理至关重要。目前,针对这个问题的研究面临三大挑战:缺乏精细标注的数据阻碍了情绪预测研究,未建模的风险感知导致预测不准确,以及恐慌形成机制的解释性不足。我们通过提出基于情绪激发理论的心理学驱动生成代理框架(PsychoAgent)来解决这些问题,以实现可解释的恐慌预测。具体而言,我们首先通过人类与大型语言模型(LLM)的合作,构建了一个精细的开放恐慌情绪数据集(名为COPE),以减轻语义偏见。然后,我们开发了一个整合跨域异构数据的框架,基于心理机制来模拟风险感知和情绪产生的认知差异。为了提高解释性,我们设计了一个基于LLM的角色扮演代理,通过专门设计的提示来模拟个体心理链。在我们标注的数据集上的实验结果表明,与基准模型相比,PsychoAgent提高了12.6%至21.7%的恐慌情绪预测性能。此外,我们的方法的可解释性和通用性得到了验证。重要的是,这代表了从隐蔽的“数据驱动拟合”到透明的“基于角色的模拟与机制解释”的范式转变,为紧急情况下的恐慌情绪预测提供了新的视角。我们的实现公开可用:https://anonymous.4open.science/r/PsychoAgent-19DD。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
基于情绪激发理论的心理驱动生成Agent框架(PsychoAgent)可实现解释性的恐慌预测。该研究构建了精细开放的恐慌情绪数据集COPE,开发了一个整合跨域异构数据的框架,模拟个体心理链,提高预测的可解释性。实验结果表明,PsychoAgent相较于基准模型,在恐慌情绪预测性能上提高了12.6%至21.7%。该研究的实施已公开。
Key Takeaways
- 在突发灾难事件中,准确预测社交媒体上的公众恐慌情绪对积极治理和危机管理至关重要。
- 当前研究面临三大挑战:缺乏精细标注的数据、未建模的风险感知导致预测不准确以及恐慌形成机制的解释性不足。
- 提出心理驱动生成Agent框架(PsychoAgent)进行解释性恐慌预测,基于情绪激发理论。
- 构建了一个精细开放的恐慌情绪数据集(COPE),通过人与大型语言模型(LLMs)的合作减少语义偏见。
- 集成跨域异构数据,基于心理机制建模风险感知和情绪产生的认知差异。
- 设计了基于LLM的角色扮演agent,模拟个体心理链,提高预测的可解释性。
点此查看论文截图

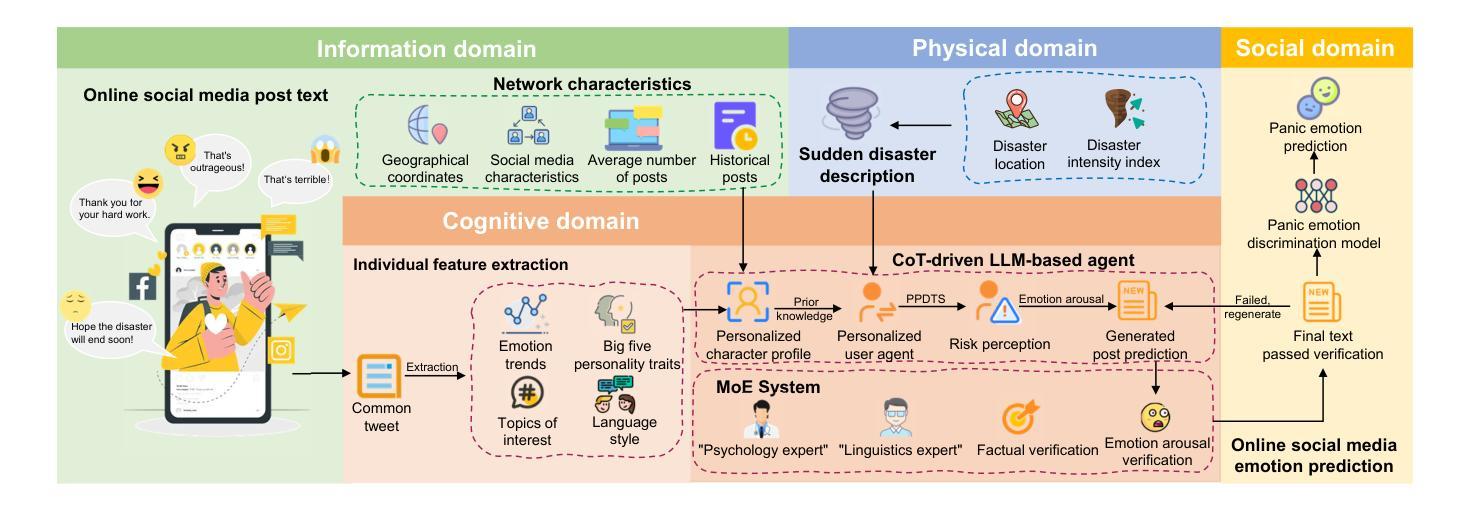
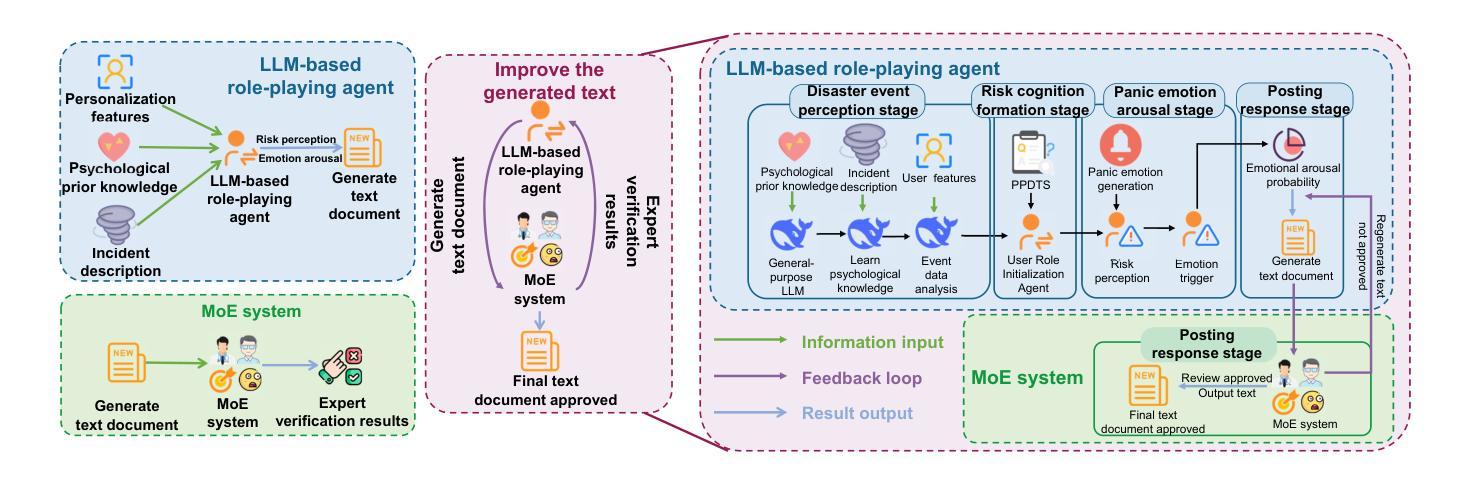
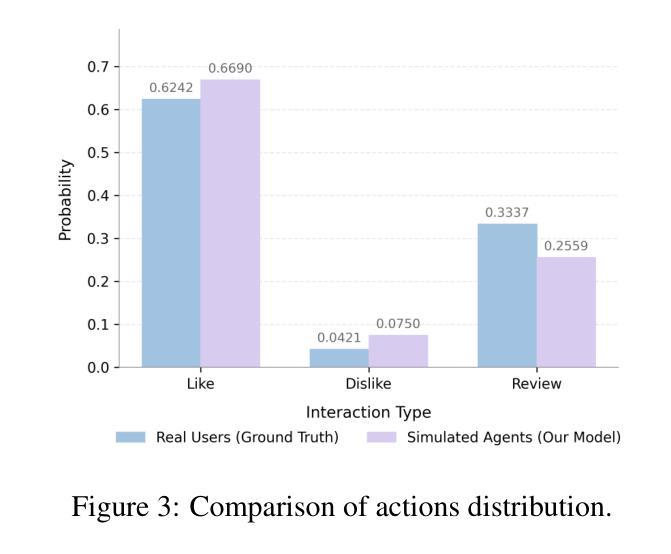
Beyond Static Testbeds: An Interaction-Centric Agent Simulation Platform for Dynamic Recommender Systems
Authors:Song Jin, Juntian Zhang, Yuhan Liu, Xun Zhang, Yufei Zhang, Guojun Yin, Fei Jiang, Wei Lin, Rui Yan
Evaluating and iterating upon recommender systems is crucial, yet traditional A/B testing is resource-intensive, and offline methods struggle with dynamic user-platform interactions. While agent-based simulation is promising, existing platforms often lack a mechanism for user actions to dynamically reshape the environment. To bridge this gap, we introduce RecInter, a novel agent-based simulation platform for recommender systems featuring a robust interaction mechanism. In RecInter platform, simulated user actions (e.g., likes, reviews, purchases) dynamically update item attributes in real-time, and introduced Merchant Agents can reply, fostering a more realistic and evolving ecosystem. High-fidelity simulation is ensured through Multidimensional User Profiling module, Advanced Agent Architecture, and LLM fine-tuned on Chain-of-Thought (CoT) enriched interaction data. Our platform achieves significantly improved simulation credibility and successfully replicates emergent phenomena like Brand Loyalty and the Matthew Effect. Experiments demonstrate that this interaction mechanism is pivotal for simulating realistic system evolution, establishing our platform as a credible testbed for recommender systems research.
评估并迭代推荐系统至关重要,然而传统的A/B测试资源消耗大,且离线方法在动态用户平台交互方面表现挣扎。虽然基于代理的模拟很有前景,但现有平台通常缺乏一种机制,使用户行为能够动态地重塑环境。为了弥补这一差距,我们引入了RecInter,这是一个新型的基于代理的推荐系统模拟平台,具有稳健的交互机制。在RecInter平台上,模拟的用户行为(例如喜欢、评论、购买)会实时动态更新物品属性,引入的商户代理可以做出回应,营造更加真实和不断演化的生态系统。通过多维度用户分析模块、高级代理架构以及在大规模预训练模型上微调的大型语言模型(LLM),确保了高保真模拟。我们的平台大大提高了模拟的可信度,并成功复制了品牌忠诚度和马太效应等突发现象。实验表明,这种交互机制对于模拟真实系统演变至关重要,使我们的平台成为推荐系统研究的可信测试平台。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
模拟用户行为在推荐系统中的交互,特别是实时动态更新的功能正在获得关注。然而传统的AB测试方式成本高昂,现有仿真平台的互动能力不强。为了解决此问题,本文引入了一个新型仿真平台RecInter,它通过用户模拟行为动态更新商品属性,并引入商户代理进行响应,从而构建更真实和动态的生态系统。RecInter平台通过多维度用户画像模块、先进的代理架构和微调的大型语言模型保证高保真模拟,并成功复制了品牌忠诚和马太效应等现实现象。平台建立的互动机制为模拟系统提供了真实可靠的测试环境。
Key Takeaways
- 推荐系统的评估和迭代至关重要,但传统AB测试成本高且离线方法难以应对动态的用户-平台交互。
- 为解决这些问题,引入了一种新型的基于代理的仿真平台RecInter。
- RecInter平台通过模拟用户行为实时更新商品属性,并引入商户代理进行响应,构建更真实和动态的生态系统。
- 平台采用了多维度用户画像模块、先进的代理架构和大型语言模型保证高保真模拟。
- 平台成功复制了品牌忠诚和马太效应等现实现象,证明了其模拟系统的真实性和可靠性。
点此查看论文截图


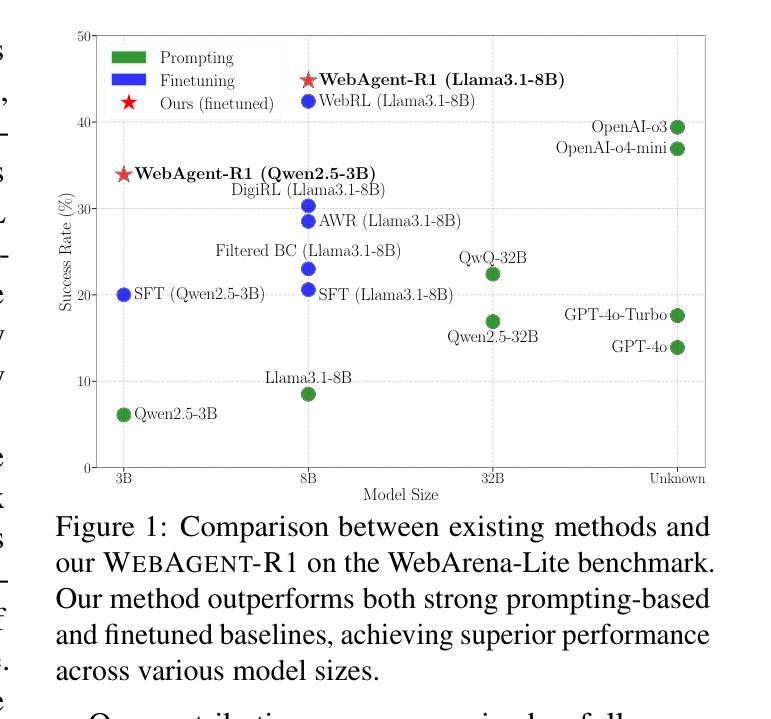
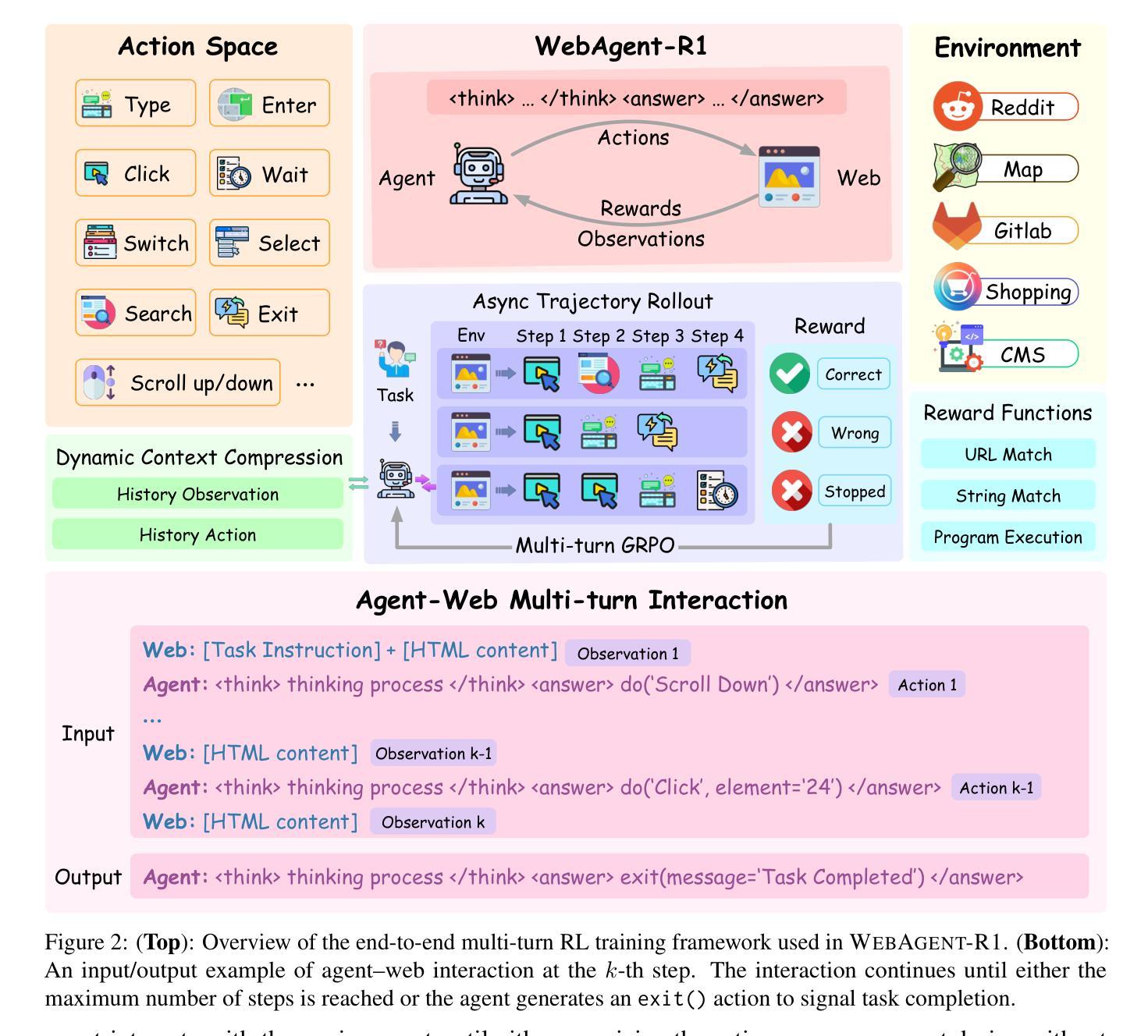
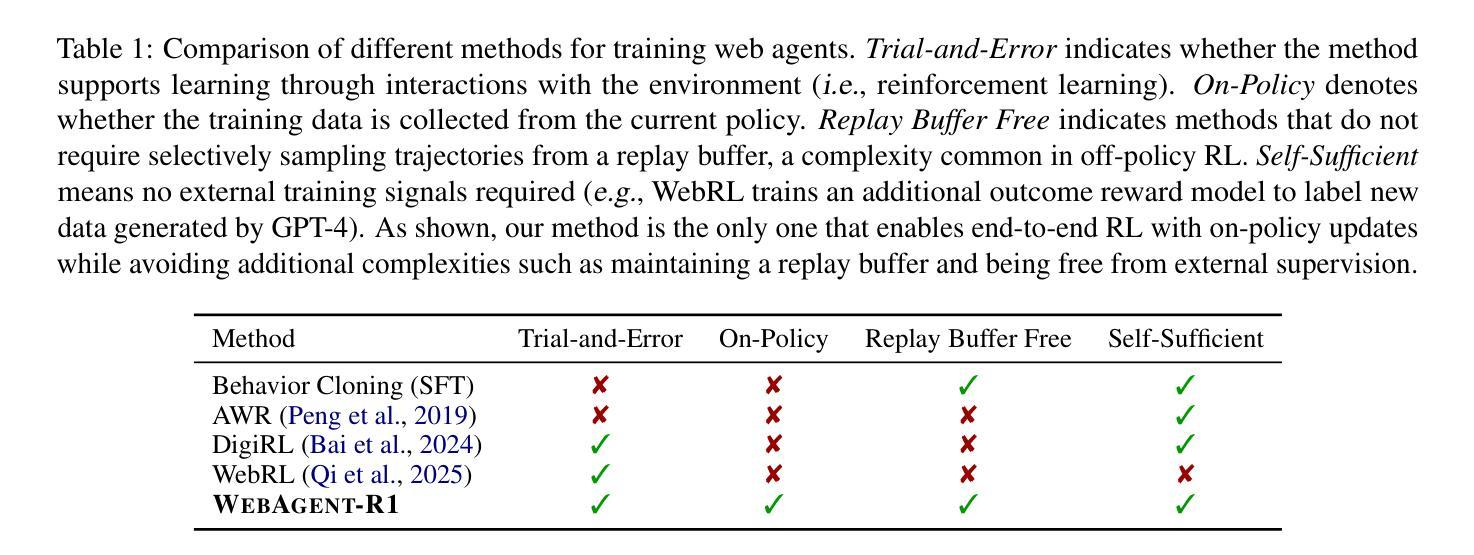
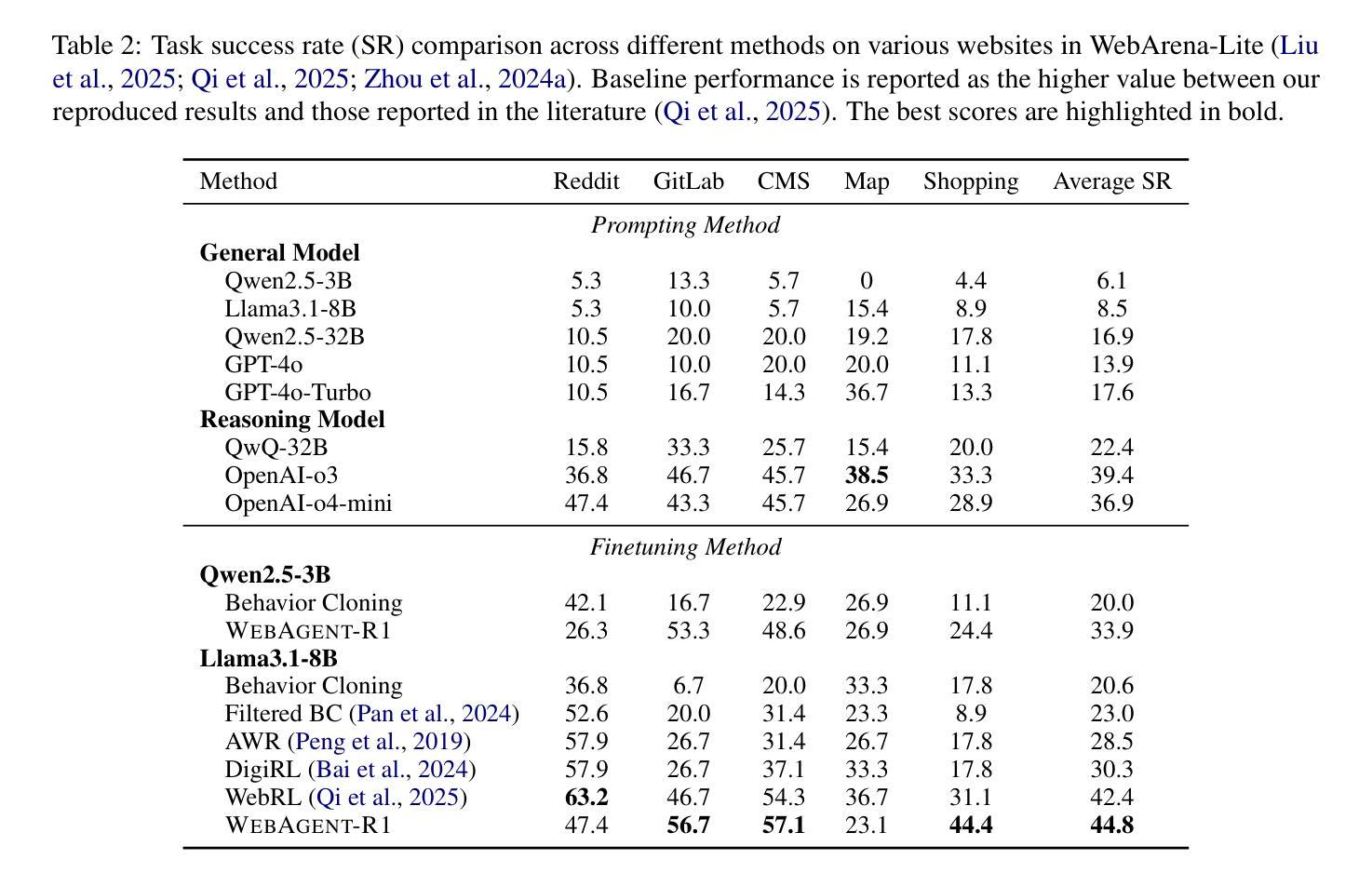
WebAgent-R1: Training Web Agents via End-to-End Multi-Turn Reinforcement Learning
Authors:Zhepei Wei, Wenlin Yao, Yao Liu, Weizhi Zhang, Qin Lu, Liang Qiu, Changlong Yu, Puyang Xu, Chao Zhang, Bing Yin, Hyokun Yun, Lihong Li
While reinforcement learning (RL) has demonstrated remarkable success in enhancing large language models (LLMs), it has primarily focused on single-turn tasks such as solving math problems. Training effective web agents for multi-turn interactions remains challenging due to the complexity of long-horizon decision-making across dynamic web interfaces. In this work, we present WebAgent-R1, a simple yet effective end-to-end multi-turn RL framework for training web agents. It learns directly from online interactions with web environments by asynchronously generating diverse trajectories, entirely guided by binary rewards depending on task success. Experiments on the WebArena-Lite benchmark demonstrate the effectiveness of WebAgent-R1, boosting the task success rate of Qwen-2.5-3B from 6.1% to 33.9% and Llama-3.1-8B from 8.5% to 44.8%, significantly outperforming existing state-of-the-art methods and strong proprietary models such as OpenAI o3. In-depth analyses reveal the effectiveness of the thinking-based prompting strategy and test-time scaling through increased interactions for web tasks. We further investigate different RL initialization policies by introducing two variants, namely WebAgent-R1-Zero and WebAgent-R1-CoT, which highlight the importance of the warm-up training stage (i.e., behavior cloning) and provide insights on incorporating long chain-of-thought (CoT) reasoning in web agents.
虽然强化学习(RL)在提升大型语言模型(LLM)方面取得了显著的成就,但它主要关注于如解决数学问题等单轮任务。由于跨动态网页界面的长周期决策复杂性,训练用于多轮交互的有效网络代理仍然具有挑战性。在这项工作中,我们提出了WebAgent-R1,这是一个简单但有效的端到端多轮强化学习框架,用于训练网络代理。它直接从与在线网络环境的交互中学习,通过异步生成多样的轨迹,完全由任务成功与否决定的二元奖励来引导。在WebArena-Lite基准测试上的实验证明了WebAgent-R1的有效性,它将Qwen-2.5-3B的任务成功率从6.1%提高到33.9%,将Llama-3.1-8B的任务成功率从8.5%提高到44.8%,显著优于现有的最先进的方法和强大的专有模型,如OpenAI o3。深入分析揭示了基于思考的提示策略和通过增加交互来进行测试时间缩放对于网络任务的有效性。我们进一步通过引入两种变体,即WebAgent-R1-Zero和WebAgent-R1-CoT,来探讨不同的RL初始化策略,这突出了热身训练阶段(即行为克隆)的重要性,并提供了将长链思维(CoT)推理融入网络代理的见解。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Preprint
Summary
强化学习在提升大型语言模型方面已展现显著成效,尤其在单回合任务如数学问题求解中。然而,在训练用于多回合交互的网页代理时仍面临挑战。本研究提出WebAgent-R1,一个简洁有效的多回合强化学习框架,能直接从与网页环境的在线交互中学习,通过异步生成多样化轨迹,仅根据任务成功与否提供二元奖励。在WebArena-Lite基准测试上的实验显示,WebAgent-R1显著提升任务成功率,相较于Qwen-2.5-3B模型提升从6.1%至33.9%,Llama-3.1-8B模型从8.5%提升至44.8%,显著超越现有先进方法与强大专有模型如OpenAI o3。深入分析显示基于思考提示策略的有效性以及通过增加交互的测试时间缩放对网页任务的效果。此外,研究引入两种强化学习初始化策略变体,突显热身训练阶段(行为克隆)的重要性,并提供将长链思维融入网页代理的见解。
Key Takeaways
- WebAgent-R1是一个用于训练网页代理的多回合强化学习框架,可从与网页环境的在线交互中直接学习。
- 该框架通过异步生成多样化轨迹,仅依据任务成功与否提供二元奖励。
- 在WebArena-Lite基准测试上,WebAgent-R1显著提升任务成功率,相较其他模型有显著优势。
- 基于思考提示策略在网页任务中展现出有效性。
- 增加交互的测试时间缩放能够提高网页代理的性能。
- 引入的两种RL初始化策略变体突显热身训练阶段的重要性。
点此查看论文截图


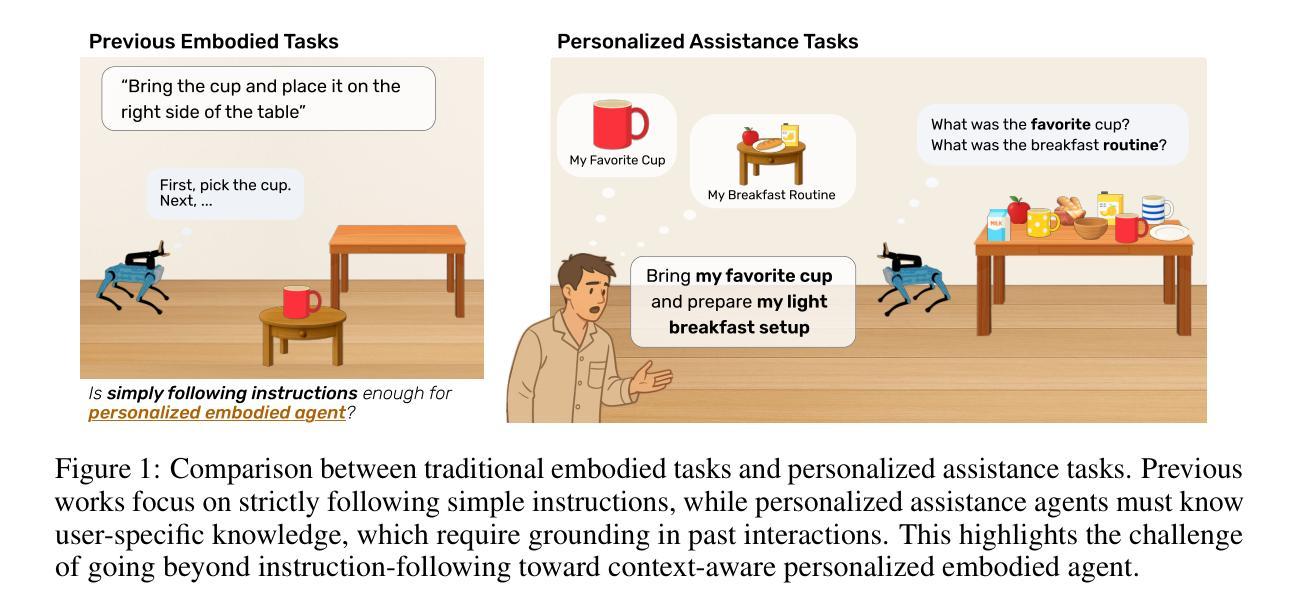
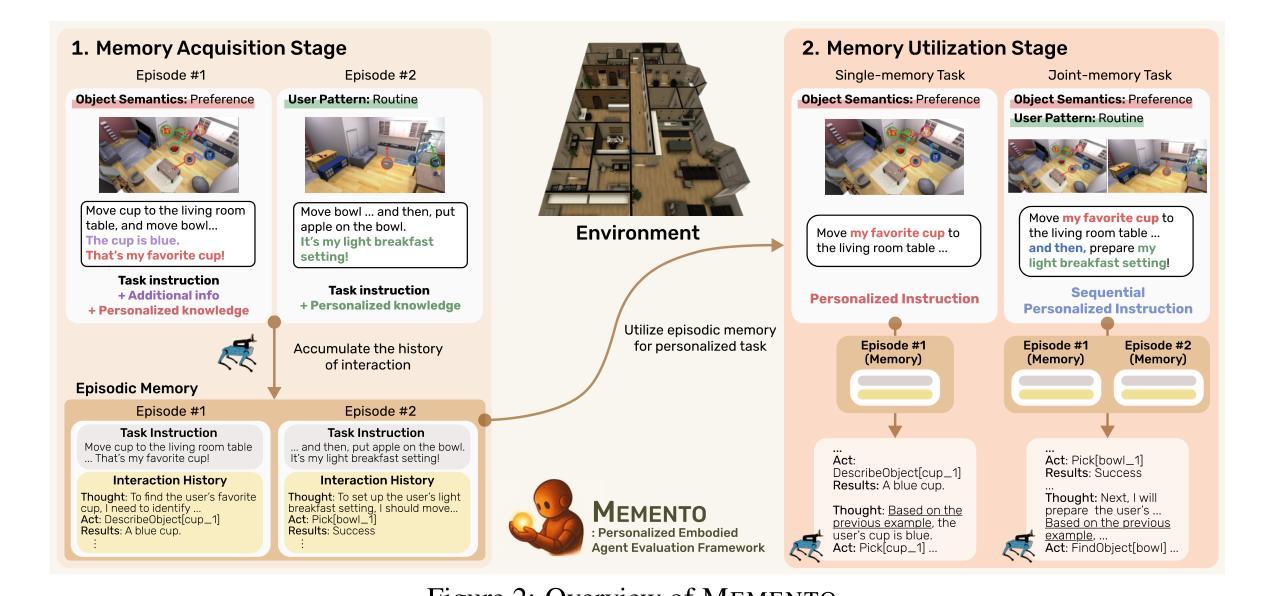
Embodied Agents Meet Personalization: Exploring Memory Utilization for Personalized Assistance
Authors:Taeyoon Kwon, Dongwook Choi, Sunghwan Kim, Hyojun Kim, Seungjun Moon, Beong-woo Kwak, Kuan-Hao Huang, Jinyoung Yeo
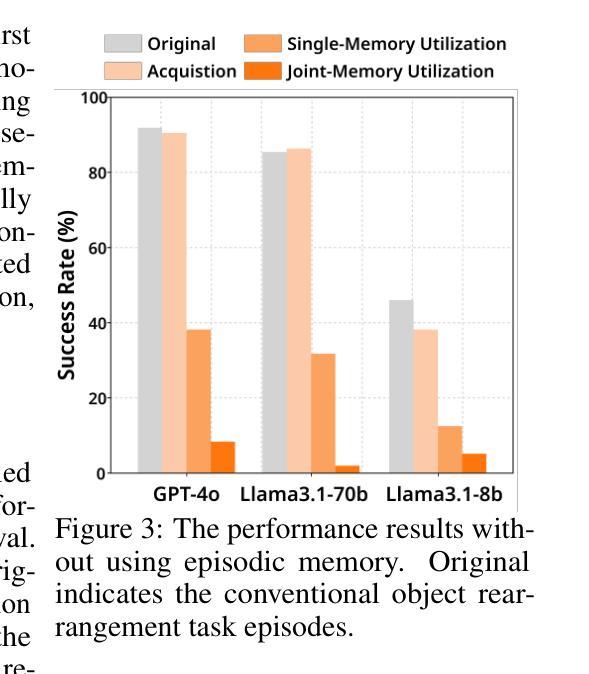
Embodied agents empowered by large language models (LLMs) have shown strong performance in household object rearrangement tasks. However, these tasks primarily focus on single-turn interactions with simplified instructions, which do not truly reflect the challenges of providing meaningful assistance to users. To provide personalized assistance, embodied agents must understand the unique semantics that users assign to the physical world (e.g., favorite cup, breakfast routine) by leveraging prior interaction history to interpret dynamic, real-world instructions. Yet, the effectiveness of embodied agents in utilizing memory for personalized assistance remains largely underexplored. To address this gap, we present MEMENTO, a personalized embodied agent evaluation framework designed to comprehensively assess memory utilization capabilities to provide personalized assistance. Our framework consists of a two-stage memory evaluation process design that enables quantifying the impact of memory utilization on task performance. This process enables the evaluation of agents’ understanding of personalized knowledge in object rearrangement tasks by focusing on its role in goal interpretation: (1) the ability to identify target objects based on personal meaning (object semantics), and (2) the ability to infer object-location configurations from consistent user patterns, such as routines (user patterns). Our experiments across various LLMs reveal significant limitations in memory utilization, with even frontier models like GPT-4o experiencing a 30.5% performance drop when required to reference multiple memories, particularly in tasks involving user patterns. These findings, along with our detailed analyses and case studies, provide valuable insights for future research in developing more effective personalized embodied agents. Project website: https://connoriginal.github.io/MEMENTO
由大型语言模型(LLMs)赋能的实体代理人在家庭物品重新布置任务中表现出强大的性能。然而,这些任务主要侧重于与简化指令的单轮交互,并不能真正反映为用户提供有意义帮助的挑战。为了提供个性化的帮助,实体代理人必须利用先前的交互历史来理解用户赋予物理世界的独特语义(例如,最喜欢的杯子、早餐例行程序),以解释动态、现实世界的指令。然而,实体代理人在利用记忆提供个性化帮助方面的有效性在很大程度上尚未被探索。为了弥补这一空白,我们推出了MEMENTO,这是一个个性化的实体代理人评估框架,旨在全面评估利用记忆提供个性化帮助的能力。我们的框架由两阶段记忆评估过程设计组成,能够量化记忆利用对任务性能的影响。这个过程通过关注记忆在目标解释中的重要作用,来评估代理人在物品重新布置任务中对个性化知识的理解能力:(1)基于个人意义(对象语义)识别目标对象的能力;(2)从一致的用户模式中推断对象位置配置的能力,例如例行程序(用户模式)。我们在各种LLMs上的实验揭示了记忆利用的显著局限性,甚至像GPT-4o这样的前沿模型在需要参考多条记忆时性能下降了30.5%,特别是在涉及用户模式的任务中。这些发现,以及我们的详细分析和案例研究,为未来研究开发更有效的个性化实体代理人提供了宝贵的见解。项目网站:https://connoriginal.github.io/MEMENTO
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Work in progress
Summary
大型语言模型赋能的实体智能代理在家庭物体重新布置任务中展现出强大性能,但现有研究主要集中在简单的单回合交互任务上,无法真正反映为用户提供的个性化服务的挑战。为用户提供个性化服务,实体智能代理需要理解用户赋予物理世界的独特语义,并利用过去的交互历史来解读动态、真实世界的指令。然而,实体智能代理在利用记忆提供个性化服务方面的有效性尚未得到充分研究。为解决这一空白,本文提出了MEMENTO个性化实体智能代理评估框架,旨在全面评估记忆利用能力以提供个性化服务。实验结果显示,大型语言模型在记忆利用方面存在显著局限,即使是最先进的模型如GPT-4o在需要参考多个记忆的任务中性能下降30.5%,特别是在涉及用户模式的任务中。
Key Takeaways
- 大型语言模型赋能的实体智能代理在家庭物体重新布置任务中表现出强大的性能。
- 当前研究主要集中在简单的单回合交互任务上,忽略了为用户提供个性化服务的挑战。
- 为提供个性化服务,实体智能代理需要理解用户赋予的物理世界的独特语义,并利用过去的交互历史解读真实世界的指令。
- MEMENTO框架用于评估实体智能代理的记忆利用能力以提供个性化服务。
- 实验发现大型语言模型在记忆利用方面存在局限,尤其在涉及用户模式的任务中性能显著下降。
- 多个记忆参考的任务中,即使是先进的模型如GPT-4o也面临性能挑战。
点此查看论文截图

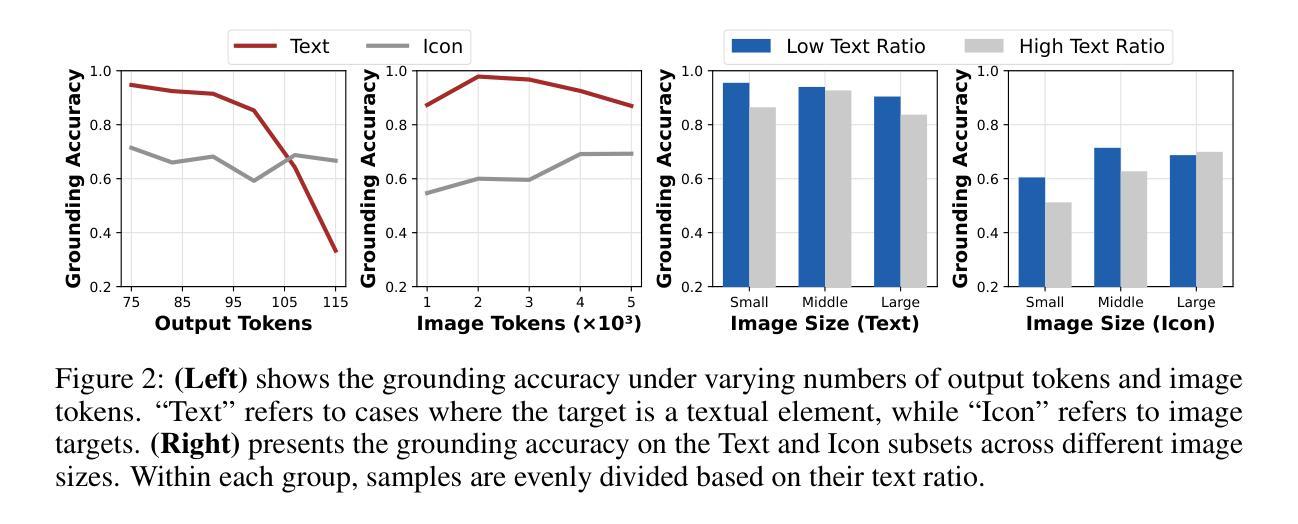
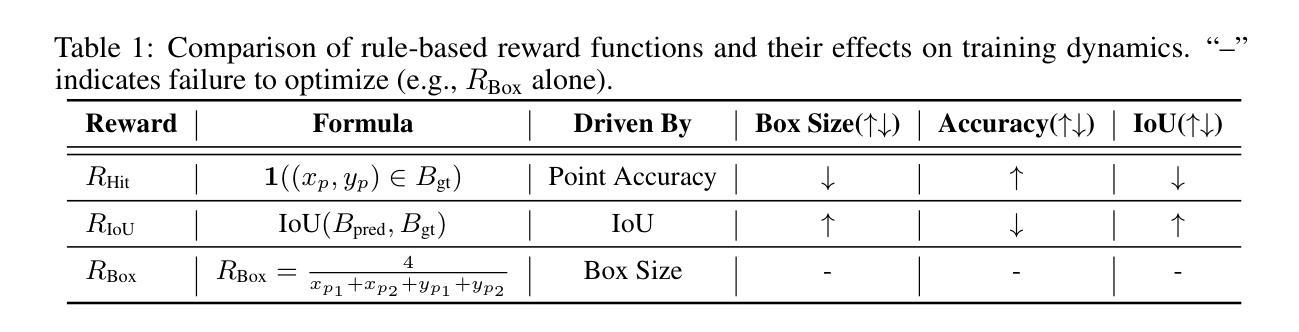
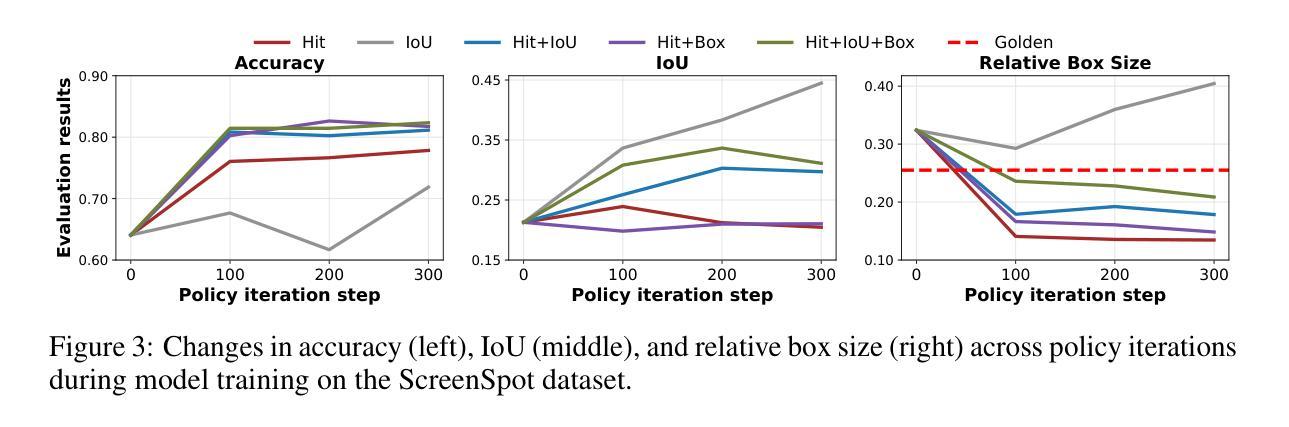
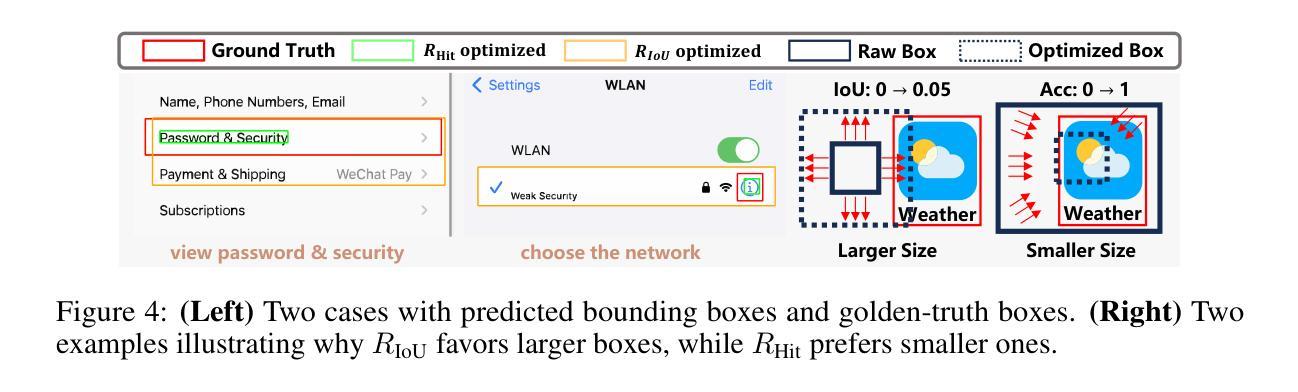
GUI-G1: Understanding R1-Zero-Like Training for Visual Grounding in GUI Agents
Authors:Yuqi Zhou, Sunhao Dai, Shuai Wang, Kaiwen Zhou, Qinglin Jia, Jun Xu
Recent Graphical User Interface (GUI) agents replicate the R1-Zero paradigm, coupling online Reinforcement Learning (RL) with explicit chain-of-thought reasoning prior to object grounding and thereby achieving substantial performance gains. In this paper, we first conduct extensive analysis experiments of three key components of that training pipeline: input design, output evaluation, and policy update-each revealing distinct challenges arising from blindly applying general-purpose RL without adapting to GUI grounding tasks. Input design: Current templates encourage the model to generate chain-of-thought reasoning, but longer chains unexpectedly lead to worse grounding performance. Output evaluation: Reward functions based on hit signals or box area allow models to exploit box size, leading to reward hacking and poor localization quality. Policy update: Online RL tends to overfit easy examples due to biases in length and sample difficulty, leading to under-optimization on harder cases. To address these issues, we propose three targeted solutions. First, we adopt a Fast Thinking Template that encourages direct answer generation, reducing excessive reasoning during training. Second, we incorporate a box size constraint into the reward function to mitigate reward hacking. Third, we revise the RL objective by adjusting length normalization and adding a difficulty-aware scaling factor, enabling better optimization on hard samples. Our GUI-G1-3B, trained on 17K public samples with Qwen2.5-VL-3B-Instruct, achieves 90.3% accuracy on ScreenSpot and 37.1% on ScreenSpot-Pro. This surpasses all prior models of similar size and even outperforms the larger UI-TARS-7B, establishing a new state-of-the-art in GUI agent grounding. The project repository is available at https://github.com/Yuqi-Zhou/GUI-G1.
最近的图形用户界面(GUI)代理复制了R1-Zero范式,将在线强化学习(RL)与对象接地之前的显式思维链推理相结合,从而实现了显著的性能提升。在本文中,我们首先对该训练管道的三个关键组件进行了广泛的分析实验:输入设计、输出评估和策略更新——每一个都揭示了盲目应用通用RL而不适应GUI接地任务所产生的独特挑战。输入设计:当前模板鼓励模型生成思维链推理,但更长的链条出乎意料地导致更差的接地性能。输出评估:基于命中信号或框区域的奖励函数允许模型利用框大小,从而导致奖励作弊和定位质量差。策略更新:由于长度和样本难度的偏见,在线RL往往会对简单示例进行过度拟合,导致在更复杂情况下的优化不足。为了解决这些问题,我们提出了三种有针对性的解决方案。首先,我们采用快速思考模板,鼓励直接答案生成,减少训练过程中的过度推理。其次,我们将框大小约束纳入奖励函数,以减轻奖励作弊。第三,我们通过调整长度归一化并添加一个难度感知缩放因子来修订RL目标,从而在困难样本上实现更好的优化。我们的GUI-G1-3B在17K公共样本上使用Qwen2.5-VL-3B-Instruct进行训练,在ScreenSpot上达到90.3%的准确率,在ScreenSpot-Pro上达到37.1%的准确率。这超越了类似大小的所有先前模型,甚至超越了更大的UI-TARS-7B,在GUI代理接地领域创造了新的最先进的水平。项目仓库可在https://github.com/Yuqi-Zhou/GUI-G1找到。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文分析了当前图形用户界面(GUI)代理在训练过程中所面临的挑战,并提出了针对性的解决方案。研究发现在输入设计、输出评价和策略更新三个方面存在挑战。为解决这些问题,提出了快速思考模板、引入盒尺寸约束和调整RL目标等措施。经过改进,GUI-G1-3B模型在ScreenSpot和ScreenSpot-Pro上取得了显著的成绩,达到了同类模型中的最佳水平。
Key Takeaways
- GUI代理在训练过程中面临输入设计、输出评价和策略更新的挑战。
- 现有模板鼓励生成链式思考推理,但过长的链会导致定位性能下降。
- 基于命中信号或框面积的奖励函数可能导致模型利用框大小,从而产生奖励黑客行为和低定位质量。
- 在线RL倾向于对简单样本过度拟合,导致在更复杂案例上的优化不足。
- 为解决这些问题,采取了快速思考模板、引入盒尺寸约束和调整RL目标等针对性措施。
点此查看论文截图

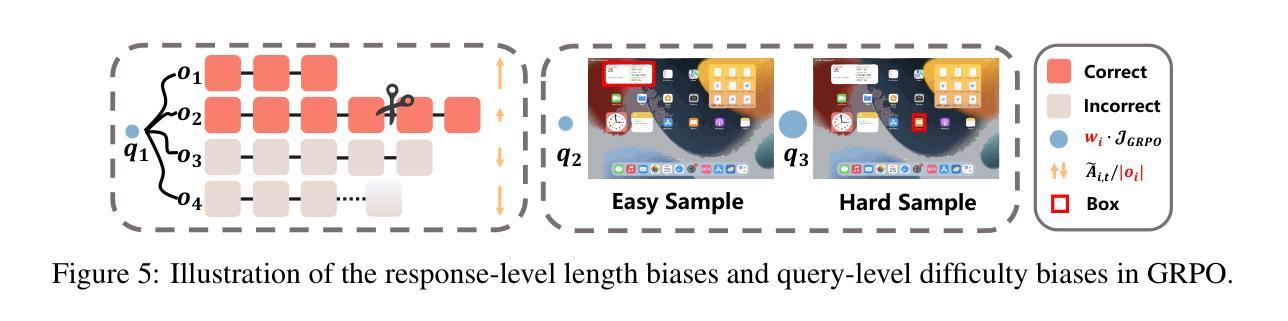

Multiple Weaks Win Single Strong: Large Language Models Ensemble Weak Reinforcement Learning Agents into a Supreme One
Authors:Yiwen Song, Qianyue Hao, Qingmin Liao, Jian Yuan, Yong Li
Model ensemble is a useful approach in reinforcement learning (RL) for training effective agents. Despite wide success of RL, training effective agents remains difficult due to the multitude of factors requiring careful tuning, such as algorithm selection, hyperparameter settings, and even random seed choices, all of which can significantly influence an agent’s performance. Model ensemble helps overcome this challenge by combining multiple weak agents into a single, more powerful one, enhancing overall performance. However, existing ensemble methods, such as majority voting and Boltzmann addition, are designed as fixed strategies and lack a semantic understanding of specific tasks, limiting their adaptability and effectiveness. To address this, we propose LLM-Ens, a novel approach that enhances RL model ensemble with task-specific semantic understandings driven by large language models (LLMs). Given a task, we first design an LLM to categorize states in this task into distinct ‘situations’, incorporating high-level descriptions of the task conditions. Then, we statistically analyze the strengths and weaknesses of each individual agent to be used in the ensemble in each situation. During the inference time, LLM-Ens dynamically identifies the changing task situation and switches to the agent that performs best in the current situation, ensuring dynamic model selection in the evolving task condition. Our approach is designed to be compatible with agents trained with different random seeds, hyperparameter settings, and various RL algorithms. Extensive experiments on the Atari benchmark show that LLM-Ens significantly improves the RL model ensemble, surpassing well-known baselines by up to 20.9%. For reproducibility, our code is open-source at https://anonymous.4open.science/r/LLM4RLensemble-F7EE.
模型集成是一种在强化学习(RL)中训练有效代理的有用方法。尽管强化学习取得了广泛的成功,但由于算法选择、超参数设置甚至随机种子选择等需要仔细调整的多重因素,训练有效代理仍然很困难,所有这些因素都可能显著影响代理的性能。模型集成通过把多个弱代理合并成一个更强大的单一代理,提高整体性能,从而克服这一挑战。然而,现有的集成方法,如多数投票和玻尔兹曼加法,被设计为固定策略,缺乏对特定任务的语义理解,限制了它们的适应性和有效性。为了解决这一问题,我们提出了LLM-Ens,这是一种结合大型语言模型(LLM)驱动的任务特定语义理解,增强RL模型集成的新型方法。给定一个任务,我们首先对LLM进行设计,将这个任务的状态分类为不同的“情境”,并融入任务条件的高级描述。然后,我们对集成中每种情境下每个个体代理的优势和劣势进行统计分析。在推理过程中,LLM-Ens动态识别任务情境的变化,并切换到当前情境下表现最佳的代理,确保在变化的任务条件下进行动态模型选择。我们的方法旨在与用不同随机种子、超参数设置和各种RL算法训练的代理兼容。在Atari基准测试的大量实验表明,LLM-Ens显著改进了RL模型集成,超越了知名基准测试达20.9%。为了可重复性,我们的代码已开源在https://anonymous.4open.science/r/LLM4RLensemble-F7EE。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
强化学习中的模型集成是一种训练有效代理的有用方法。训练有效的代理具有挑战性,因为它涉及到多个因素的微调,如算法选择、超参数设置甚至随机种子选择。模型集成通过结合多个弱代理为一个强大的单一代理来克服这一挑战,从而提高整体性能。然而,现有的集成方法如多数投票和波尔兹曼加法被设计为固定策略,缺乏特定任务的语义理解,限制了其适应性和有效性。为解决此问题,我们提出LLM-Ens,一种结合大型语言模型(LLM)驱动的特定任务语义理解的强化学习模型集成新方法。给定任务时,我们首先设计LLM将任务状态分类为不同的“情境”,并融入任务条件的高级描述。然后,我们统计分析了集成中每个个体代理在每个情境中的优势和劣势。在推理过程中,LLM-Ens动态识别任务情境的变化,并切换到当前情境下表现最佳的代理,确保在变化的任务条件下动态选择模型。我们的方法与使用不同随机种子、超参数设置和各种RL算法训练的代理兼容。在Atari基准测试上的大量实验表明,LLM-Ens显著提高了强化学习模型集成效果,超过知名基线高达20.9%。相关代码已开源于https://anonymous.4open.science/r/LLM4RLensemble-F7EE。
Key Takeaways
- 模型集成在强化学习中是一种有效的训练代理方法,通过结合多个代理来提高整体性能。
- 现有集成方法缺乏特定任务的语义理解,限制了其适应性和有效性。
- LLM-Ens方法利用大型语言模型(LLM)来驱动任务特定语义理解,将任务状态分类为不同的情境。
- LLM-Ens通过统计分析每个代理在每种情境中的表现来优化集成。
- 在推理过程中,LLM-Ens能动态识别任务情境变化,并选择最佳代理应对。
- LLM-Ens与不同设置和算法训练的代理兼容。
点此查看论文截图

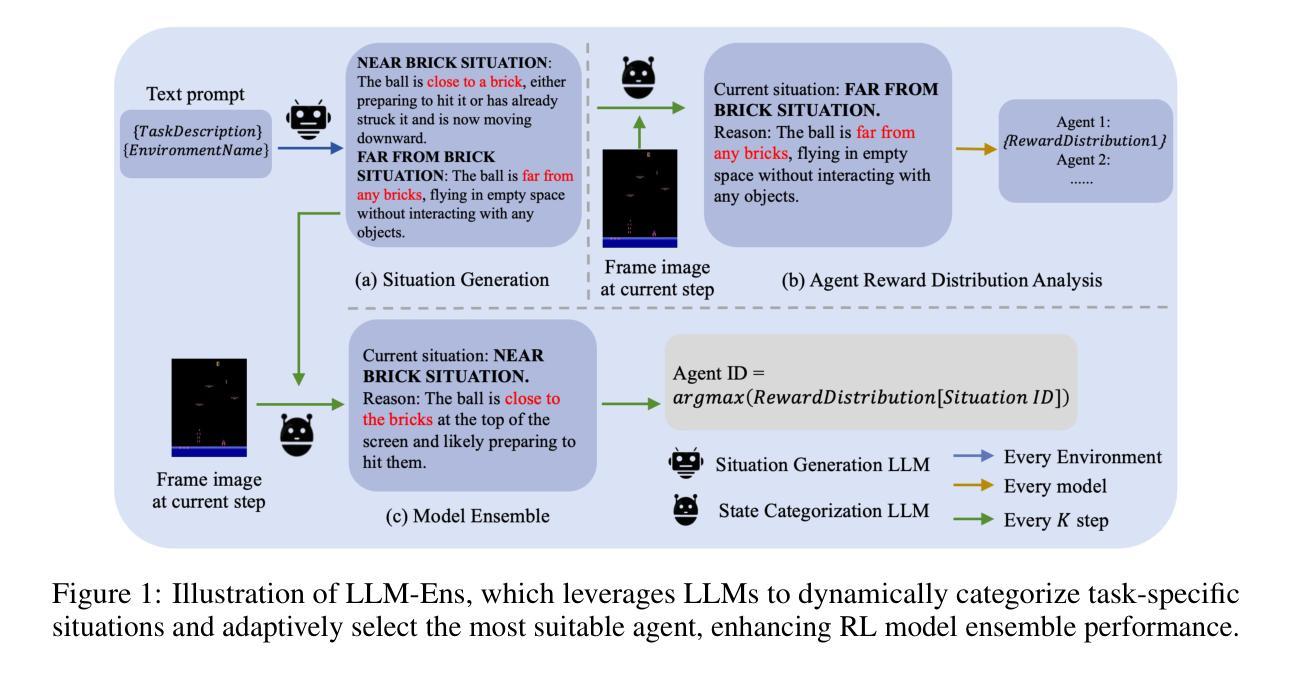

Adaptive Thinking via Mode Policy Optimization for Social Language Agents
Authors:Minzheng Wang, Yongbin Li, Haobo Wang, Xinghua Zhang, Nan Xu, Bingli Wu, Fei Huang, Haiyang Yu, Wenji Mao
Effective social intelligence simulation requires language agents to dynamically adjust reasoning depth, a capability notably absent in current studies. Existing methods either lack this kind of reasoning capability or enforce Long Chain-of-Thought reasoning uniformly across all scenarios, resulting in excessive token usage and inflexible social simulation. To address this, we propose an $\textbf{A}$daptive $\textbf{M}$ode $\textbf{L}$earning ($\textbf{AML}$) framework in this paper, aiming to improve the adaptive thinking ability of language agents in dynamic social interactions. To this end, we first identify hierarchical thinking modes ranging from intuitive response to deep deliberation based on the cognitive control theory. We then develop the $\textbf{A}$daptive $\textbf{M}$ode $\textbf{P}$olicy $\textbf{O}$ptimization ($\textbf{AMPO}$) algorithm to optimize the context-aware mode switching and reasoning. Our framework advances existing research in three key aspects: (1) Multi-granular thinking mode design, (2) Context-aware mode switching across social interaction, and (3) Token-efficient reasoning via depth-adaptive processing. Extensive experiments on social intelligence benchmarks verify that AML achieves 15.6% higher task performance than GPT-4o. Notably, our AMPO outperforms GRPO by 7.0% with 32.8% shorter reasoning chains, demonstrating the advantage of adaptive thinking mode selection and optimization mechanism in AMPO over GRPO’s fixed-depth solution.
有效的社会智能模拟需要语言代理动态调整推理深度,而当前的研究中普遍缺乏这种能力。现有的方法要么不具备这种推理能力,要么在所有场景中强制实施长链思维推理,导致过度使用标记(tokens)和灵活度不足的社会模拟。针对这一问题,本文提出了自适应模式学习(AML)框架,旨在提高语言代理在动态社会交互中的自适应思维能力。为此,我们首先基于认知控制理论,识别了从直觉反应到深思熟虑的不同层次思维模式。然后,我们开发了自适应模式策略优化(AMPO)算法,以优化基于上下文的模式切换和推理。我们的框架在三个方面推动了现有研究:(1)多粒度思维模式设计,(2)社会交互中的基于上下文模式切换,(3)通过深度自适应处理实现高效的标记推理。在社会智能基准测试上的大量实验证明,AML的任务性能比GPT-4o高出15.6%。值得注意的是,我们的AMPO在性能上优于GRPO,任务完成度高出7.0%,且推理链缩短32.8%,这显示了AMPO中自适应思维模式选择和优化机制的优势,超越了GRPO的固定深度解决方案。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Work in Progress. The code and data are available, see https://github.com/MozerWang/AMPO
Summary
基于现有研究中语言代理在动态社会交互中缺乏适应性思考能力的现状,本文提出了一个名为AML的适应模式学习框架,旨在提高语言代理在动态社会交互中的适应性思考能力。该框架通过设计多层次思考模式、实现语境感知模式切换和深度自适应处理,优化了语言代理的推理过程。实验证明,AML在社交智能基准测试中实现了优于GPT-4o的任务性能表现。
Key Takeaways
- 语言代理在动态社会交互中需要动态调整推理深度。
- 现有研究缺乏适应性思考能力或统一采用长链思维,导致过度使用标记和不灵活的社会模拟。
- AML框架旨在提高语言代理在动态社会交互中的适应性思考能力。
- AML框架包括设计多层次思考模式、实现语境感知模式切换和优化深度自适应处理。
- AMPO算法用于优化语境感知模式切换和推理过程。
- 实验证明AML在社交智能基准测试中表现优于GPT-4o和GRPO。
点此查看论文截图



Agentic AI Software Engineers: Programming with Trust
Authors:Abhik Roychoudhury, Corina Pasareanu, Michael Pradel, Baishakhi Ray
Large Language Models (LLMs) have shown surprising proficiency in generating code snippets, promising to automate large parts of software engineering via artificial intelligence (AI). We argue that successfully deploying AI software engineers requires a level of trust equal to or even greater than the trust established by human-driven software engineering practices. The recent trend toward LLM agents offers a path toward integrating the power of LLMs to create new code with the power of analysis tools to increase trust in the code. This opinion piece comments on whether LLM agents could dominate software engineering workflows in the future and whether the focus of programming will shift from programming at scale to programming with trust.
大型语言模型(LLMs)在生成代码片段方面表现出了惊人的熟练程度,有望通过人工智能(AI)自动化软件工程的很大一部分工作。我们主张,成功部署AI软件工程师需要建立与人类驱动的软件工程实践相当的甚至更高的信任度。最近对LLM代理的趋势提供了一个将LLMs的力量与分析工具的力量相结合来创建新代码的路径,以增加对代码的信任。本文作者认为,未来的软件工作流程中LLM代理是否会占据主导地位,编程的重点是否会从规模化编程转向可信编程,都是值得探讨的问题。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 5 pages
Summary
大型语言模型(LLMs)在生成代码片段方面表现出惊人的能力,预示着人工智能(AI)可能自动化软件工程的很大一部分工作。成功部署AI软件工程师需要建立与人类驱动的软件工程实践相当的信任水平,甚至更高。最近出现的LLM代理趋势为整合LLMs生成新代码的能力与分析工具增加代码信任的能力提供了途径。本评论文章探讨了LLM代理是否可能在未来主导软件工程工作流程,以及编程的焦点是否会从大规模编程转向具有信任的编程。
Key Takeaways
- 大型语言模型(LLMs)能生成代码片段,预示AI在软件工程中的潜在作用。
- 成功部署AI软件工程师需要建立高信任度,与人类驱动的软件工程实践相当。
- LLM代理的出现为整合LLMs的能力和分析工具增加了对代码的信心。
- LLM代理可能在未来主导软件工程工作流程。
- 编程的焦点可能会从大规模编程转向具有信任的编程。
- 需要进一步研究和探索如何在软件工程中平衡人工智能与人类角色的协作。
点此查看论文截图


InSTA: Towards Internet-Scale Training For Agents
Authors:Brandon Trabucco, Gunnar Sigurdsson, Robinson Piramuthu, Ruslan Salakhutdinov
The predominant approach for training web navigation agents is to gather human demonstrations for a set of popular websites and hand-written tasks, but it is becoming clear that human data is an inefficient resource. We develop a pipeline to facilitate internet-scale training for agents without laborious human annotations. In the first stage, an LLM annotates 150k sites with agentic tasks. In the next stage, LLM agents complete tasks and produce trajectories. In the final stage, an LLM filters trajectories by judging their success. Language models are powerful data curation tools, identifying harmful content with an accuracy of 97%, judging successful trajectories with an accuracy of 82.6%, and producing effective data. We train agents based on Qwen 3 1.7B that are competitive with frontier LLMs as web agents, while being smaller and faster. Our top agent reaches a success rate of 56.9%, outperforming the data collection policy Qwen 3 235B, a 235 times larger Llama 4 Maverick, and reaching 94.7% of the performance of Gemini 2.5 Flash. We are releasing code, models and data at: https://data-for-agents.github.io.
训练网络导航代理的主流方法是为流行网站和手写任务收集人类演示,但越来越明显的是,人类数据是一种低效的资源。我们开发了一个流程,以在没有繁琐的人类注释的情况下促进代理的互联网规模训练。在第一阶段,大型语言模型(LLM)为15万个网站注释了任务。在下一阶段,LLM代理完成任务并产生轨迹。在最后一个阶段,LLM通过判断其成功与否来过滤轨迹。语言模型是强大的数据整理工具,它们能准确地识别有害内容(准确率为97%),准确地判断成功的轨迹(准确率为82.6%),并能产生有效的数据。我们以Qwen 3 1.7B为基础训练代理,作为网络代理,我们的代理与前沿LLM具有竞争力,而且更小、更快。我们的顶级代理成功率达到56.9%,超过了数据采集策略Qwen 3 235B,一个体积大得多的Llama 4 Maverick,并达到了Gemini 2.5 Flash性能的94.7%。我们在以下网址发布代码、模型和数:https://data-for-agents.github.io。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Improved results, zero-shot transfer to Web Voyager
Summary
基于LLM的管道训练网络导航代理,无需繁琐的人工注释。通过LLM标注网站、完成代理任务和过滤轨迹,成功训练出竞争前沿的小型快速网络导航代理。该代理性能优异,成功率高,且可识别有害内容。相关代码、模型和数据已发布在相关网站。
Key Takeaways
- 使用LLM(大型语言模型)构建管道训练网络导航代理,提高了效率并降低了人工参与成本。
- LLM用于标注网站、完成代理任务和过滤轨迹,简化了训练过程。
- 成功训练出性能优异、成功率高的网络导航代理,达到了前沿水平。
- LLM能准确识别有害内容,展现了其在数据筛选方面的强大能力。
- 训练出的代理基于较小的模型(Qwen 3 1.7B),相较于大型模型(如Qwen 3 235B和Llama 4 Maverick)更为高效。
- 训练出的最佳代理性能达到了高成功率(56.9%),并接近Gemini 2.5 Flash的性能(达到其94.7%)。
点此查看论文截图





My Words Imply Your Opinion: Reader Agent-based Propagation Enhancement for Personalized Implicit Emotion Analysis
Authors:Jian Liao, Yu Feng, Yujin Zheng, Jun Zhao, Suge Wang, Jianxing Zheng
The subtlety of emotional expressions makes implicit emotion analysis (IEA) particularly sensitive to user-specific characteristics. Current studies personalize emotion analysis by focusing on the author but neglect the impact of the intended reader on implicit emotional feedback. In this paper, we introduce Personalized IEA (PIEA) and present the RAPPIE model, which addresses subjective variability by incorporating reader feedback. In particular, (1) we create reader agents based on large language models to simulate reader feedback, overcoming the issue of ``spiral of silence effect’’ and data incompleteness of real reader reaction. (2) We develop a role-aware multi-view graph learning to model the emotion interactive propagation process in scenarios with sparse reader information. (3) We construct two new PIEA datasets covering English and Chinese social media with detailed user metadata, addressing the text-centric limitation of existing datasets. Extensive experiments show that RAPPIE significantly outperforms state-of-the-art baselines, demonstrating the value of incorporating reader feedback in PIEA.
情感表达的细微之处使得隐式情感分析(IEA)特别关注用户特定特征。当前的研究通过关注作者来实现情感分析的个性化,但忽视了目标读者对隐式情感反馈的影响。在本文中,我们介绍了个性化IEA(PIEA)并提出了RAPPIE模型,该模型通过融入读者反馈来解决主观变化性的问题。具体来说,(1)我们基于大型语言模型创建读者代理来模拟读者反馈,从而克服“沉默螺旋效应”和真实读者反应数据不完整的问题。(2)我们开发了一种角色感知多视图图学习,以在读者信息稀疏的场景中建立情感交互传播过程。 (3)我们构建了两个新的PIEA数据集,涵盖了英语和中文社交媒体,并包含详细的用户元数据,解决了现有数据集以文本为中心的局限性。大量实验表明,RAPPIE在融入读者反馈后显著超越了最新基线,表现出其优越性。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
文本提出个性化隐式情感分析(PIEA)的新概念,并介绍RAPPIE模型。该模型通过模拟读者反馈克服真实读者反应的“沉默螺旋效应”和数据不完整性问题,并构建读者代理来捕捉读者信息对情绪表达的影响。通过角色感知的多视图图学习,建模情感交互传播过程。同时,创建覆盖英文和中文社交媒体的新数据集,包含详细的用户元数据。实验证明RAPPIE模型显著优于现有基线模型,证明了在PIEA中融入读者反馈的价值。
Key Takeaways
- 文本强调情感表达的微妙性使得隐式情感分析(IEA)对用户特定特性特别敏感。
- 当前研究个性化情感分析主要集中在作者上,但忽略了预期读者对隐式情感反馈的影响。
- 引入个性化隐式情感分析(PIEA)和RAPPIE模型,通过模拟读者反馈解决主观变异性问题。
- 创建基于大型语言模型的读者代理来模拟读者反馈,克服真实读者反应的“沉默螺旋效应”和数据不完整性问题。
- 发展角色感知的多视图图学习,建模情感交互传播过程,以处理稀疏的读者信息场景。
- 构建涵盖英文和中文社交媒体的新PIEA数据集,包含详细的用户元数据,解决现有数据集文本为中心的限制。
点此查看论文截图


HyperMARL: Adaptive Hypernetworks for Multi-Agent RL
Authors:Kale-ab Abebe Tessera, Arrasy Rahman, Amos Storkey, Stefano V. Albrecht
Adaptability to specialised or homogeneous behaviours is critical in cooperative multi-agent reinforcement learning (MARL). Parameter sharing (PS) techniques, common for efficient adaptation, often limit behavioural diversity due to cross-agent gradient interference, which we show can be exacerbated by the coupling of observations and agent IDs. Current remedies typically add complexity through altered objectives, manual preset diversity levels, or sequential updates. We ask: can shared policies adapt without these complexities? We propose HyperMARL, a PS approach using hypernetworks for dynamic agent-specific parameters, without altering the RL objective or requiring preset diversity levels. HyperMARL’s explicit decoupling of observation- and agent-conditioned gradients empirically reduces policy gradient variance, facilitates shared-policy adaptation (including specialisation), and helps mitigate cross-agent interference. Across diverse MARL benchmarks (up to 20 agents), requiring homogeneous, heterogeneous, or mixed behaviours, HyperMARL achieves competitive performance against key baselines – fully shared, non-parameter sharing, and three diversity-promoting methods – while preserving behavioural diversity comparable to non-parameter sharing. These findings establish HyperMARL as a versatile approach for adaptive MARL. The code is publicly available at https://github.com/KaleabTessera/HyperMARL.
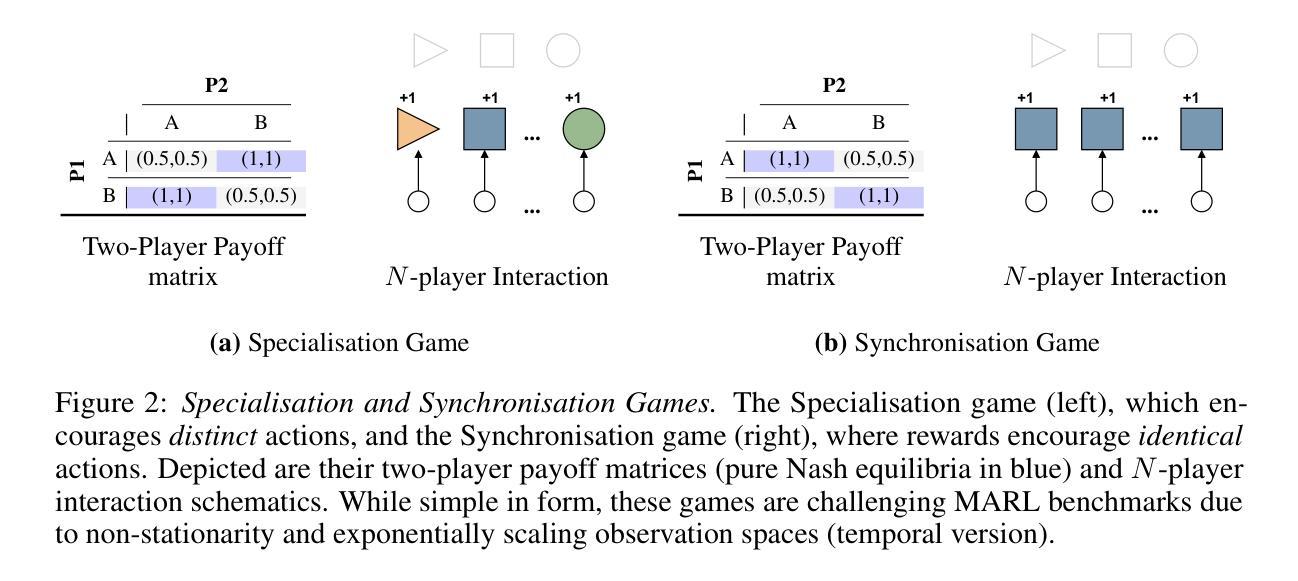
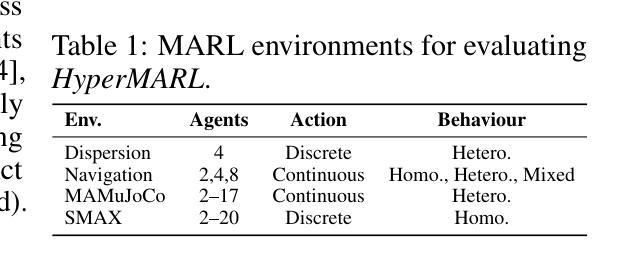
适应特殊或同质行为在合作多智能体强化学习(MARL)中至关重要。参数共享(PS)技术,常用于高效适应,但由于跨智能体梯度干扰,通常会限制行为多样性,我们表明观察和智能体ID的耦合会加剧这一问题。当前的补救措施通常通过改变目标、手动预设多样性水平或顺序更新来增加复杂性。我们的问题是:共享政策能否在没有这些复杂性的情况下适应?我们提出了HyperMARL,这是一种使用超网络进行动态特定于智能体的参数共享方法,无需改变RL目标或要求预设多样性水平。HyperMARL对观察和智能体条件下的梯度进行显式解耦,这实际上减少了政策梯度方差,促进了共享政策的适应(包括专业化),并有助于缓解跨智能体干扰。在多种MARL基准测试(最多20个智能体)中,需要同质、异质或混合行为,HyperMARL在关键基准线上实现了竞争性能——完全共享、非参数共享和三种促进多样性的方法,同时保持与非参数共享相当的行为多样性。这些发现证明HyperMARL是适应性MARL的通用方法。代码公开在https://github.com/KaleabTessera/HyperMARL。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
适应特定或同质化行为在合作多智能体强化学习(MARL)中至关重要。共享参数(PS)技术因对自适应的适应效率而普遍应用,但往往限制了行为多样性,因为存在跨智能体梯度干扰问题。我们提出了一种名为HyperMARL的新方法,使用超网络进行动态智能体特定参数化,无需改变强化学习目标或预设多样性级别。HyperMARL能够降低策略梯度方差、适应共享策略、减少跨智能体干扰等。在多种MARL基准测试上,HyperMARL实现了与关键基线相比具有竞争力的性能,同时保持与无参数共享相近的行为多样性。这表明HyperMARL是适应性MARL的一种通用方法。代码公开于:https://github.com/KaleabTessera/HyperMARL。
Key Takeaways
- 适应特定或同质化行为在多智能体强化学习中的重要性。
- 参数共享技术在多智能体强化学习中可能限制行为多样性,导致跨智能体梯度干扰问题。
- 提出HyperMARL方法,使用超网络进行动态智能体特定参数化,无需改变强化学习目标或预设多样性级别。
- HyperMARL能够降低策略梯度方差,促进共享策略适应,并有助于减少跨智能体干扰。
- 在多种MARL基准测试中,HyperMARL表现出与关键基线相比的竞争力,同时保持行为多样性。
- HyperMARL在保持行为多样性的同时,实现了较高的性能,证明了其作为适应性MARL通用方法的潜力。
点此查看论文截图



MLLM as Retriever: Interactively Learning Multimodal Retrieval for Embodied Agents
Authors:Junpeng Yue, Xinrun Xu, Börje F. Karlsson, Zongqing Lu
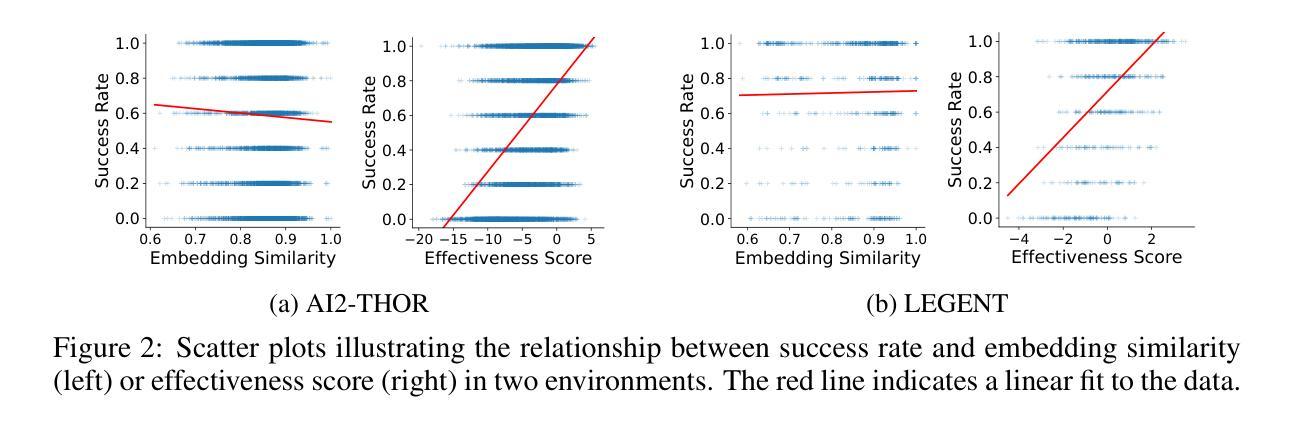
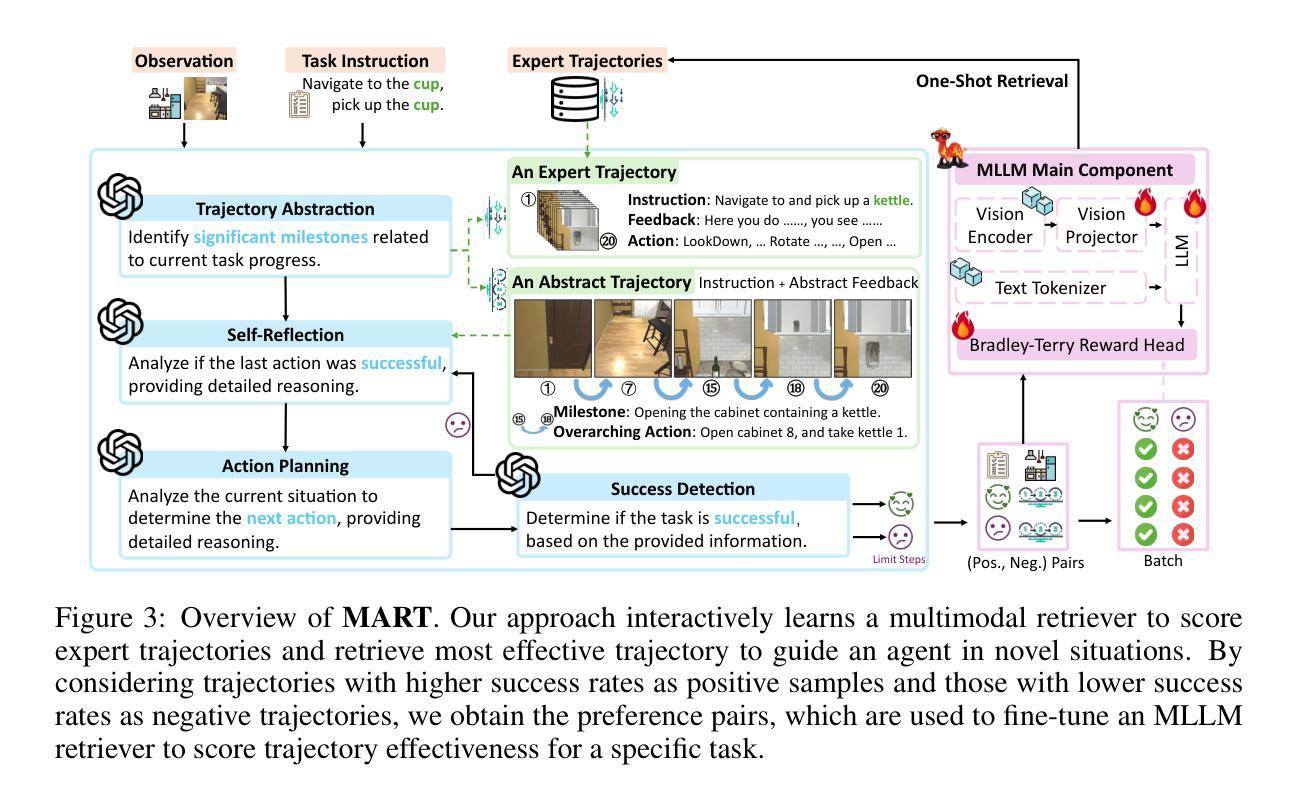
MLLM agents demonstrate potential for complex embodied tasks by retrieving multimodal task-relevant trajectory data. However, current retrieval methods primarily focus on surface-level similarities of textual or visual cues in trajectories, neglecting their effectiveness for the specific task at hand. To address this issue, we propose a novel method, MLLM As ReTriever (MART), which enhances the performance of embodied agents by utilizing interaction data to fine-tune an MLLM retriever based on preference learning, such that the retriever fully considers the effectiveness of trajectories and prioritizes them for unseen tasks. We also introduce Trajectory Abstraction, a mechanism that leverages MLLMs’ summarization capabilities to represent trajectories with fewer tokens while preserving key information, enabling agents to better comprehend milestones in the trajectory. Experimental results across various environments demonstrate our method significantly improves task success rates in unseen scenes compared to baseline methods. This work presents a new paradigm for multimodal retrieval in embodied agents, by fine-tuning a general-purpose MLLM as the retriever to assess trajectory effectiveness. All the code for benchmark tasks, simulator modifications, and the MLLM retriever is available at https://github.com/PKU-RL/MART.
MLLM代理通过检索多模式任务相关轨迹数据,展现出执行复杂实体任务潜力。然而,当前检索方法主要关注轨迹中文字或视觉线索的表面相似性,忽视了它们在特定任务中的有效性。为了解决这一问题,我们提出了一种新方法,名为MLLM作为检索器(MART),通过利用交互数据对基于偏好学习的MLLM检索器进行微调,提高实体代理的性能,使检索器全面考虑轨迹的有效性并优先用于未见任务。我们还引入了轨迹抽象机制,该机制利用MLLM的总结能力以较少的标记表示轨迹,同时保留关键信息,使代理能够更好地理解轨迹中的里程碑。在多种环境下的实验结果表明,与基准方法相比,我们的方法在未见场景中的任务成功率显著提高。这项工作通过微调通用MLLM作为检索器来评估轨迹的有效性,为实体代理中的多模式检索提供了新的范例。所有基准任务、模拟器修改和MLLM检索器的代码可在https://github.com/PKU-RL/ MART找到。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF ICLR 2025
Summary
MLLM代理在复杂的实体任务中展现出潜力,通过检索多模态任务相关轨迹数据来完成任务。然而,当前检索方法主要关注轨迹的文本或视觉线索的表面相似性,忽视了它们对特定任务的有效性。为此,我们提出了一种新方法MLLM As ReTriever(MART),通过利用交互数据对基于偏好学习的MLLM检索器进行微调,提高实体代理的性能,使检索器充分考虑轨迹的有效性并优先处理未见任务。我们还引入了轨迹抽象机制,利用MLLM的总结能力以更少的令牌表示轨迹,同时保留关键信息,使代理更好地理解轨迹中的里程碑。实验结果表明,与基准方法相比,我们的方法在未见场景中的任务成功率显著提高。本研究为实体代理中的多模态检索提供了新的范例,即通过微调通用MLLM作为检索器来评估轨迹的有效性。
Key Takeaways
- MLLM代理在复杂实体任务中展现潜力,可通过检索多模态轨迹数据完成任务。
- 当前检索方法主要关注表面相似性,忽视轨迹对特定任务的有效性。
- 提出新方法MLLM As ReTriever(MART),利用交互数据微调MLLM检索器,使其充分考虑轨迹有效性并优先处理未见任务。
- 引入轨迹抽象机制,用更少令牌表示轨迹同时保留关键信息。
- 实验结果显示,与基准方法相比,MART在未见场景的任务成功率上显著提高。
- 该研究为实体代理中的多模态检索提供了新的范例。
点此查看论文截图