⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-05-24 更新
Pursuing Temporal-Consistent Video Virtual Try-On via Dynamic Pose Interaction
Authors:Dong Li, Wenqi Zhong, Wei Yu, Yingwei Pan, Dingwen Zhang, Ting Yao, Junwei Han, Tao Mei
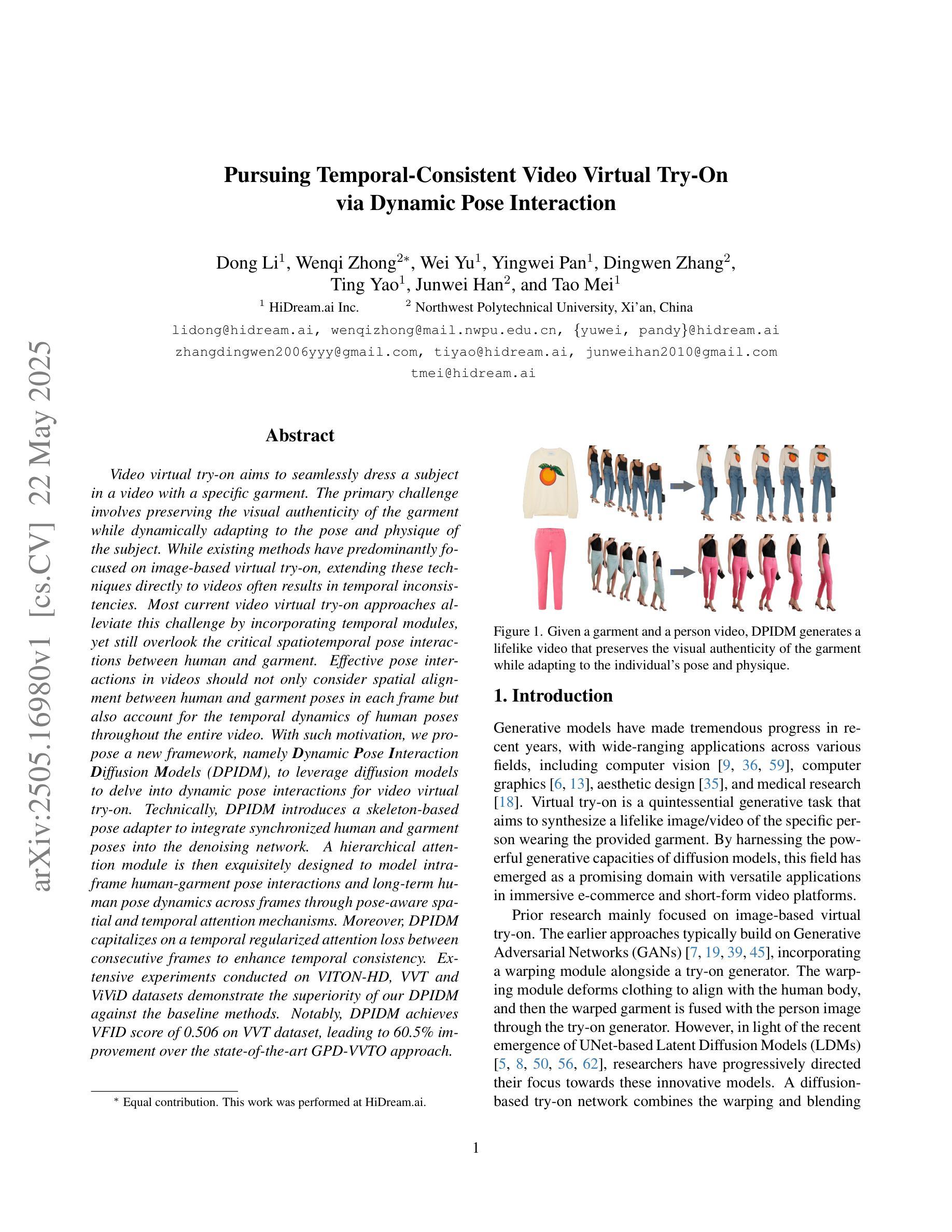
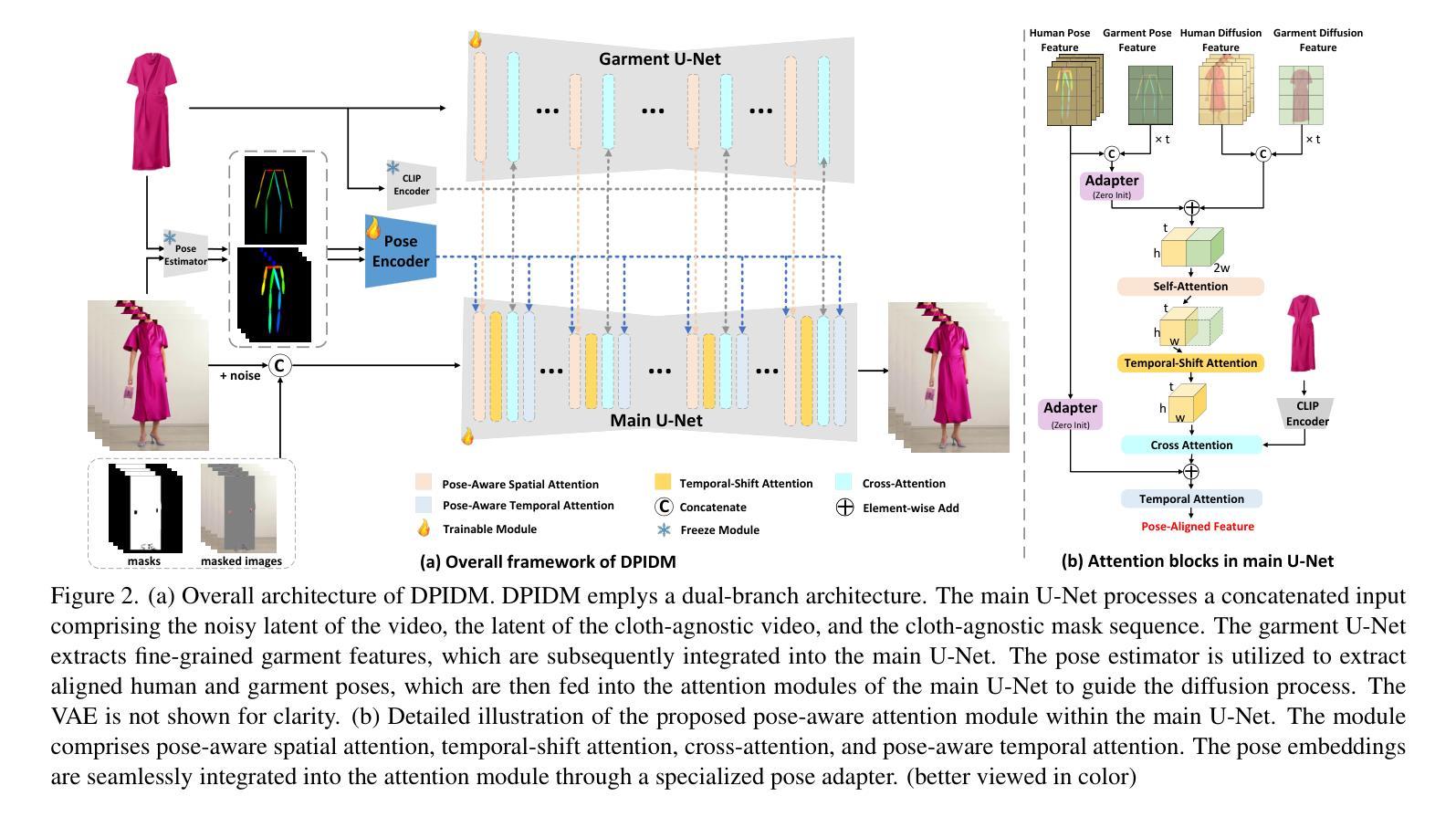
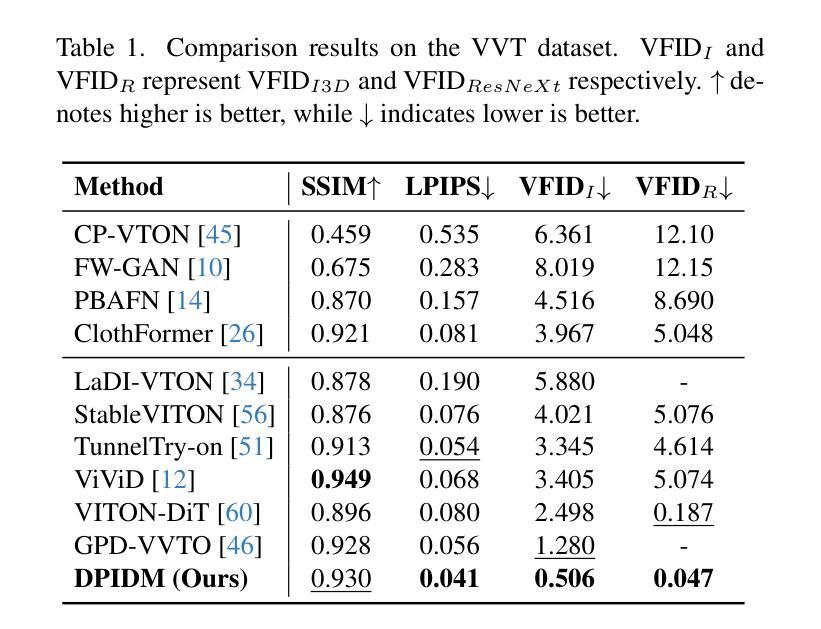
Video virtual try-on aims to seamlessly dress a subject in a video with a specific garment. The primary challenge involves preserving the visual authenticity of the garment while dynamically adapting to the pose and physique of the subject. While existing methods have predominantly focused on image-based virtual try-on, extending these techniques directly to videos often results in temporal inconsistencies. Most current video virtual try-on approaches alleviate this challenge by incorporating temporal modules, yet still overlook the critical spatiotemporal pose interactions between human and garment. Effective pose interactions in videos should not only consider spatial alignment between human and garment poses in each frame but also account for the temporal dynamics of human poses throughout the entire video. With such motivation, we propose a new framework, namely Dynamic Pose Interaction Diffusion Models (DPIDM), to leverage diffusion models to delve into dynamic pose interactions for video virtual try-on. Technically, DPIDM introduces a skeleton-based pose adapter to integrate synchronized human and garment poses into the denoising network. A hierarchical attention module is then exquisitely designed to model intra-frame human-garment pose interactions and long-term human pose dynamics across frames through pose-aware spatial and temporal attention mechanisms. Moreover, DPIDM capitalizes on a temporal regularized attention loss between consecutive frames to enhance temporal consistency. Extensive experiments conducted on VITON-HD, VVT and ViViD datasets demonstrate the superiority of our DPIDM against the baseline methods. Notably, DPIDM achieves VFID score of 0.506 on VVT dataset, leading to 60.5% improvement over the state-of-the-art GPD-VVTO approach.
视频虚拟试穿旨在无缝地将特定服装添加到视频中的主体上。主要挑战在于在动态适应主体的姿势和体型的同时,保持服装的视觉真实性。虽然现有方法主要集中在基于图像的虚拟试穿上,但直接将这些技术扩展到视频通常会导致时间上的不一致。当前大多数视频虚拟试穿方法通过引入时间模块来缓解这一挑战,但仍然忽略了人与服装之间关键的空间时间姿势交互。视频中的有效姿势交互不仅要考虑每一帧中人与服装姿势的空间对齐,还要考虑整个视频中人的姿势的动态变化。基于这样的动机,我们提出了一种新的框架,即动态姿势交互扩散模型(DPIDM),利用扩散模型深入研究视频虚拟试穿中的动态姿势交互。技术上,DPIDM引入了一个基于骨架的姿势适配器,将同步的人类和服装姿势集成到去噪网络中。然后精心设计了一个分层注意力模块,以通过姿势感知的空间和时间注意力机制对帧内的人与服装姿势交互以及跨帧的长期人类姿势动态进行建模。此外,DPIDM利用相邻帧之间的时间正则化注意力损失来增强时间一致性。在VITON-HD、VVT和ViViD数据集上进行的广泛实验证明了我们的DPIDM相对于基准方法的优越性。值得注意的是,DPIDM在VVT数据集上的VFID得分达到0.506,相较于目前最先进的GPD-VVTO方法,提升了60.5%。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF CVPR 2025
Summary
本文介绍了一种新的视频虚拟试穿框架——动态姿态交互扩散模型(DPIDM),该模型利用扩散模型深入探究视频中的动态姿态交互。DPIDM通过引入基于骨架的姿态适配器和层次注意力模块,实现了对帧内人与衣物姿态的精细建模,并考虑了跨帧的长期人体姿态动态。此外,DPIDM采用临时正则化注意力损失来增强时序一致性,在多个数据集上的实验表明其优越性。
Key Takeaways
- 视频虚拟试穿旨在无缝地将特定服装添加到视频中的主体上。
- 主要挑战在于在动态适应主体姿势和体型的同时保持服装的视觉真实性。
- 尽管图像虚拟试穿方法很受欢迎,但直接应用于视频会导致时序不一致性。
- 当前视频虚拟试穿方法虽然加入时序模块来缓解这个问题,但仍然忽略了关键的空间时间姿态交互。
- DPIDM框架利用扩散模型处理动态姿态交互进行视频虚拟试穿。
- DPIDM通过引入骨架基于的姿态适配器和层次注意力模块进行精细建模。
- DPIDM采用临时正则化注意力损失以增强时序一致性,并在多个数据集上实现了优越的性能。
点此查看论文截图

Incorporating Visual Correspondence into Diffusion Model for Virtual Try-On
Authors:Siqi Wan, Jingwen Chen, Yingwei Pan, Ting Yao, Tao Mei
Diffusion models have shown preliminary success in virtual try-on (VTON) task. The typical dual-branch architecture comprises two UNets for implicit garment deformation and synthesized image generation respectively, and has emerged as the recipe for VTON task. Nevertheless, the problem remains challenging to preserve the shape and every detail of the given garment due to the intrinsic stochasticity of diffusion model. To alleviate this issue, we novelly propose to explicitly capitalize on visual correspondence as the prior to tame diffusion process instead of simply feeding the whole garment into UNet as the appearance reference. Specifically, we interpret the fine-grained appearance and texture details as a set of structured semantic points, and match the semantic points rooted in garment to the ones over target person through local flow warping. Such 2D points are then augmented into 3D-aware cues with depth/normal map of target person. The correspondence mimics the way of putting clothing on human body and the 3D-aware cues act as semantic point matching to supervise diffusion model training. A point-focused diffusion loss is further devised to fully take the advantage of semantic point matching. Extensive experiments demonstrate strong garment detail preservation of our approach, evidenced by state-of-the-art VTON performances on both VITON-HD and DressCode datasets. Code is publicly available at: https://github.com/HiDream-ai/SPM-Diff.
扩散模型在虚拟试穿(VTON)任务中初步取得了成功。典型的双分支架构包含两个U网,分别用于隐式服装变形和合成图像生成,已成为VTON任务的配方。然而,由于扩散模型的固有随机性,保持给定服装的形状和每一个细节仍然是一个挑战。为了缓解这个问题,我们创新地提出明确利用视觉对应作为先验来驯服扩散过程,而不是简单地将整个服装输入U网作为外观参考。具体来说,我们将细致的外观和纹理细节解释为一组结构化语义点,并通过局部流扭曲将服装中的语义点与目标人物上的语义点相匹配。这些二维点然后通过目标人物的深度/法线图增强为三维感知线索。这种对应关系模仿了将衣服穿在人体上的方式,三维感知线索作为语义点匹配来监督扩散模型的训练。进一步设计了一种点聚焦扩散损失,以充分利用语义点匹配的优势。大量实验表明,我们的方法在服装细节保护方面具有优势,在VITON-HD和DressCode数据集上的VTON性能均达到了最新水平。代码公开在:HiDream-ai/SPM-Diff。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF ICLR 2025. Code is publicly available at: https://github.com/HiDream-ai/SPM-Diff
Summary
扩散模型在虚拟试穿(VTON)任务中取得初步成功。文章提出一种新型的双分支架构,使用两个UNet分别处理衣物变形和图像生成。为解决扩散模型内在随机性导致的衣物形状和细节保留问题,文章创新地提出利用视觉对应性作为扩散过程的先验信息,而非简单地将整个衣物输入UNet作为外观参考。通过匹配衣物中的语义点与目标人物上的点,实现精细外观和纹理细节的解读。此外,将这些2D点增强为具有目标人物深度/法线图的3D感知线索。视觉对应模仿了衣物穿在人体上的方式,而3D感知线索则作为语义点匹配来监督扩散模型的训练。实验证明,该方法在保持衣物细节方面表现出色,在VITON-HD和DressCode数据集上的虚拟试穿性能达到最新水平。
Key Takeaways
- 扩散模型在虚拟试穿任务中取得初步成功。
- 传统的双分支架构包括两个UNet,分别用于隐式衣物变形和合成图像生成。
- 提出的新方法利用视觉对应性作为扩散过程的先验信息,以提高衣物形状和细节的保留效果。
- 通过匹配衣物中的语义点与目标人物上的点,实现精细外观和纹理细节的解读。
- 2D点被增强为具有目标人物深度/法线图的3D感知线索。
- 视觉对应模仿衣物穿在人体上的方式。
点此查看论文截图


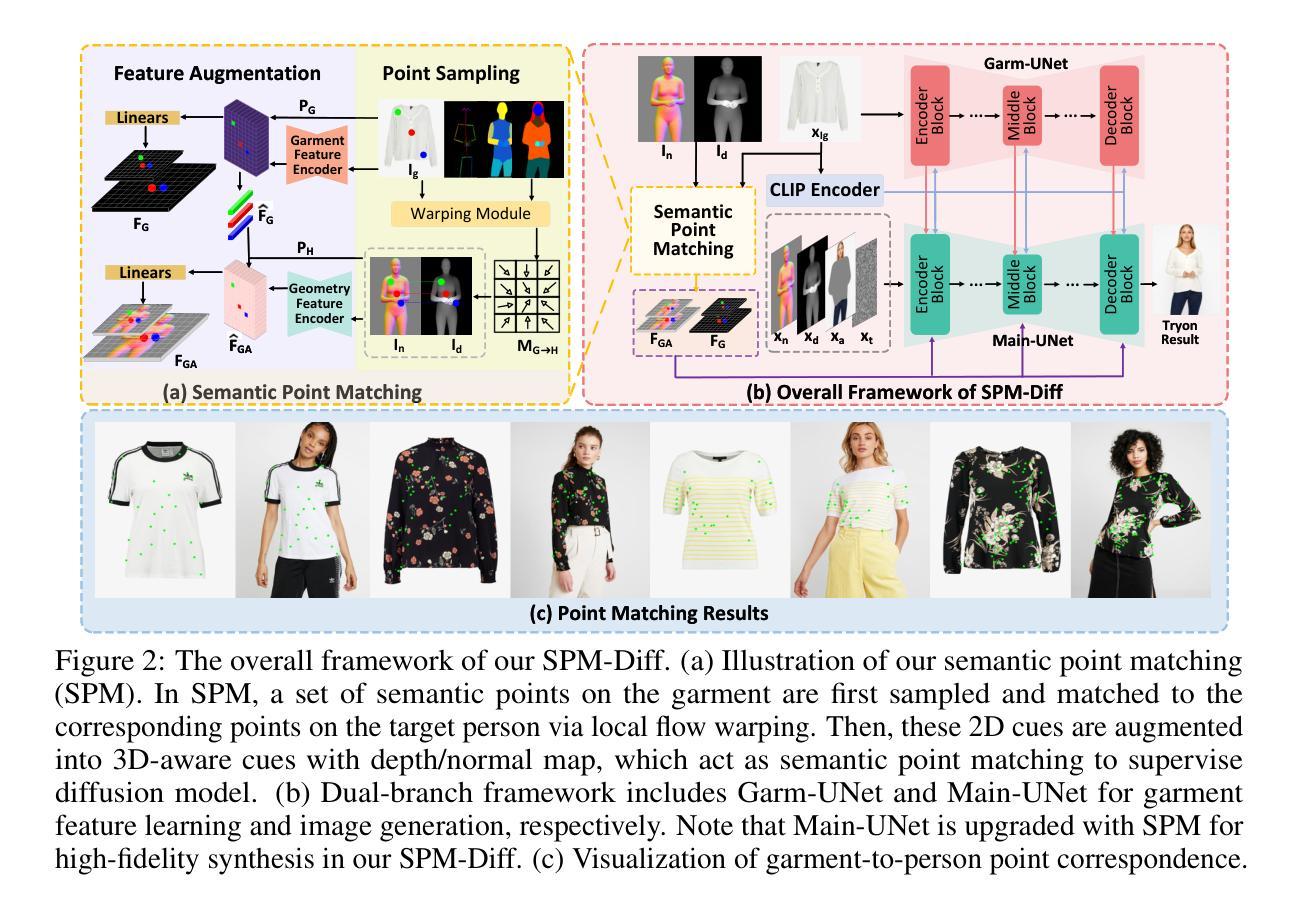
Creatively Upscaling Images with Global-Regional Priors
Authors:Yurui Qian, Qi Cai, Yingwei Pan, Ting Yao, Tao Mei
Contemporary diffusion models show remarkable capability in text-to-image generation, while still being limited to restricted resolutions (e.g., 1,024 X 1,024). Recent advances enable tuning-free higher-resolution image generation by recycling pre-trained diffusion models and extending them via regional denoising or dilated sampling/convolutions. However, these models struggle to simultaneously preserve global semantic structure and produce creative regional details in higher-resolution images. To address this, we present C-Upscale, a new recipe of tuning-free image upscaling that pivots on global-regional priors derived from given global prompt and estimated regional prompts via Multimodal LLM. Technically, the low-frequency component of low-resolution image is recognized as global structure prior to encourage global semantic consistency in high-resolution generation. Next, we perform regional attention control to screen cross-attention between global prompt and each region during regional denoising, leading to regional attention prior that alleviates object repetition issue. The estimated regional prompts containing rich descriptive details further act as regional semantic prior to fuel the creativity of regional detail generation. Both quantitative and qualitative evaluations demonstrate that our C-Upscale manages to generate ultra-high-resolution images (e.g., 4,096 X 4,096 and 8,192 X 8,192) with higher visual fidelity and more creative regional details.
当前扩散模型在文本到图像生成方面显示出显著的能力,但受限于较低分辨率(例如,1,024 X 1,024)。最近的进展通过回收预训练的扩散模型并通过区域去噪或膨胀采样/卷积对其进行扩展,实现了无需调整的高分辨率图像生成。然而,这些模型在保持全局语义结构的同时,在高分辨率图像中产生创造性区域细节方面遇到困难。为了解决这一问题,我们提出了C-Upscale,这是一种无需调整的图像超分辨率新方法,它依赖于基于给定全局提示和通过多模态大型语言模型估计的区域提示所派生的全局-区域先验知识。技术上,我们识别低分辨率图像的低频成分作为全局结构先验,以鼓励高分辨率生成中的全局语义一致性。接下来,我们对区域去噪过程中的全局提示和每个区域之间的交叉注意力进行筛选,形成区域注意力先验,缓解了对象重复问题。估计的区域提示富含描述性细节,进一步作为区域语义先验,为区域细节生成提供创造力。定量和定性评估均表明,我们的C-Upscale能够生成超高分辨率图像(例如,4,096 X 4,096和8,192 X 8,192),具有更高的视觉保真度和更富有创造力的区域细节。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF International Journal of Computer Vision (IJCV) 2025
Summary
本文介绍了当代扩散模型在文本转图像生成中的显著能力,但仍受限于低分辨率。近期发展通过再利用预训练扩散模型并借助区域去噪或膨胀采样/卷积进行扩展,实现了无调整高分辨率图像生成。然而,这些模型在保持全局语义结构和生成创意区域细节方面存在挑战。为此,本文提出了C-Upscale,一种无需调整的新图像超分辨率方案,基于全局和区域先验进行工作。该方案可从给定的全局提示和通过多模态大型语言模型估计的区域提示中派生出来。通过识别低分辨率图像的低频成分作为全局结构先验,鼓励在生成高分辨率图像时保持全局语义一致性。接着,对区域去噪过程中的全局提示和每个区域之间的交叉注意力进行筛选,形成区域注意力先验,减轻了对象重复问题。包含丰富描述性细节的区域提示估计进一步作为区域语义先验,促进区域细节生成的创造力。评估证明,C-Upscale成功生成了超高分辨率图像,具有更高的视觉保真度和更富有创造力的区域细节。
Key Takeaways
- 当代扩散模型虽擅长文本转图像生成,但分辨率受限。
- 近期发展通过扩展预训练扩散模型实现无调整高分辨率图像生成。
- 扩散模型在保持全局语义结构和生成创意区域细节方面存在挑战。
- C-Upscale是一种无需调整的新图像超分辨率方案,基于全局和区域先验。
- C-Upscale通过识别低分辨率图像的低频成分作为全局结构先验,促进全局语义一致性。
- C-Upscale采用区域注意力控制,减轻对象重复问题,并包含丰富细节的区域语义先验,促进区域细节创造力。
点此查看论文截图


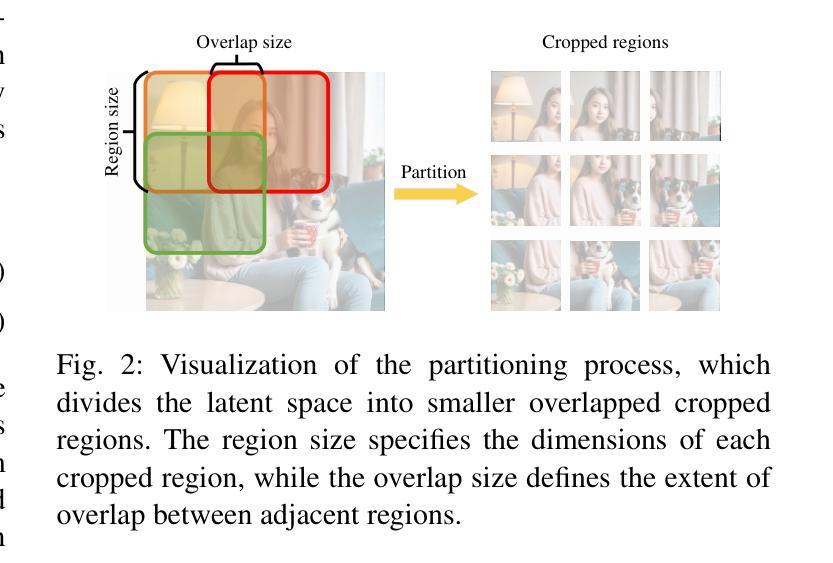
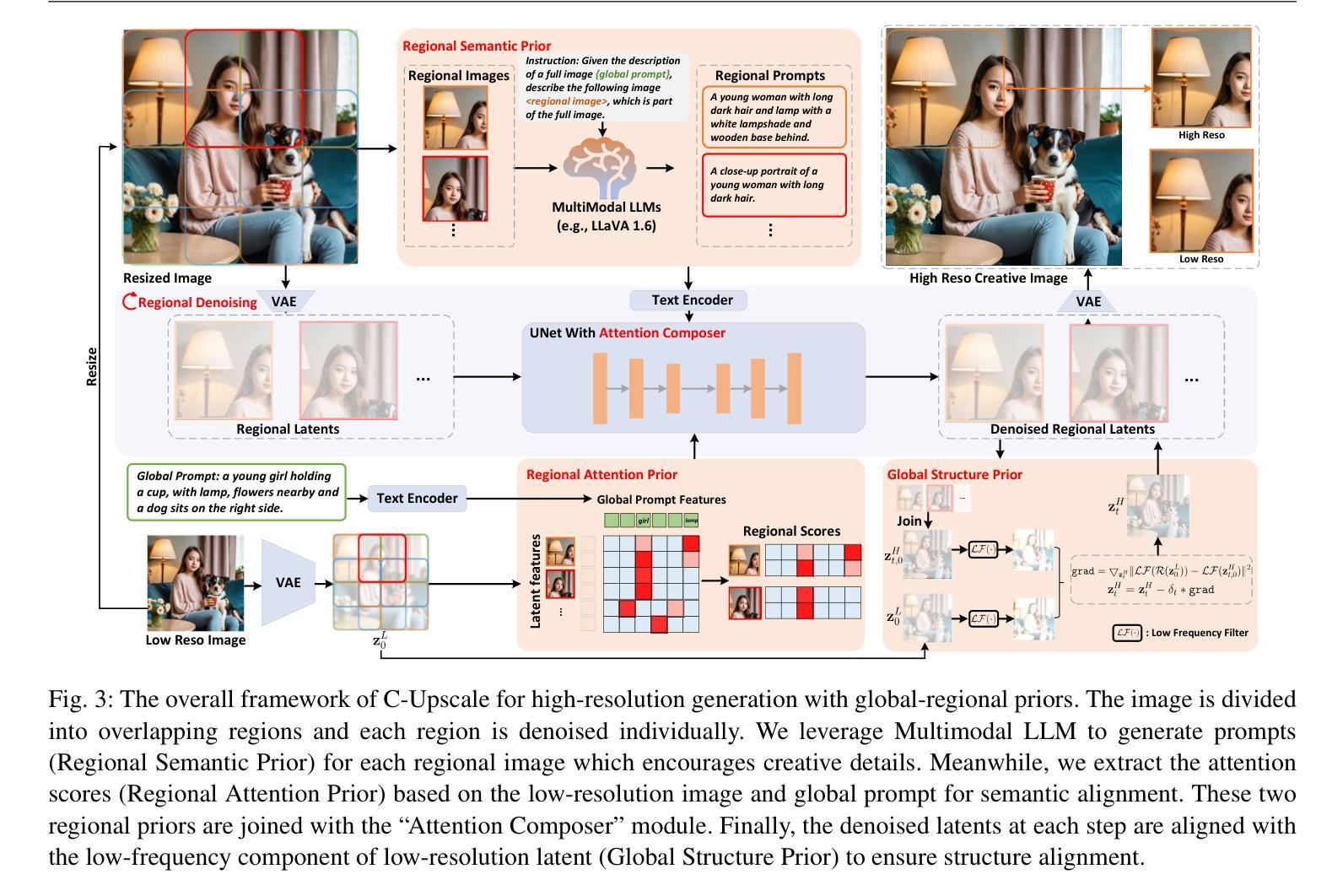
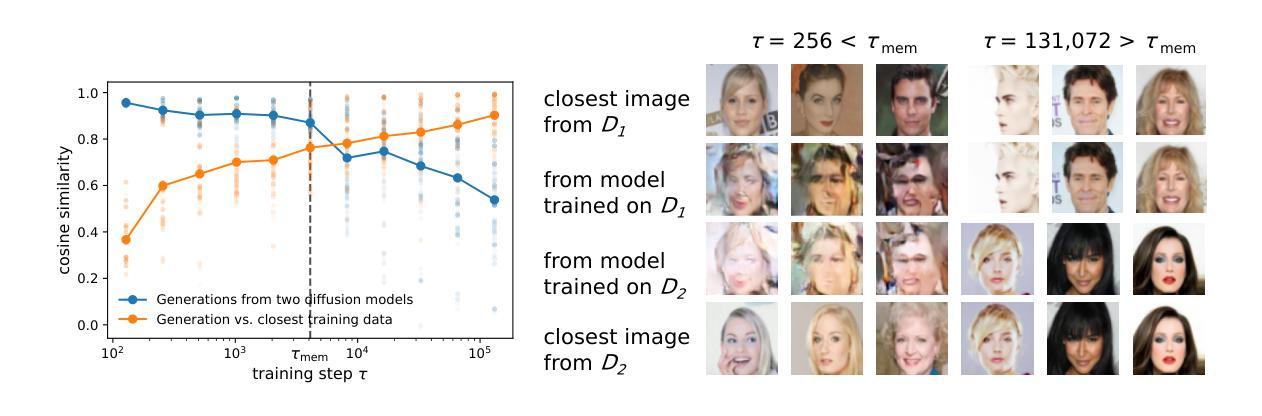
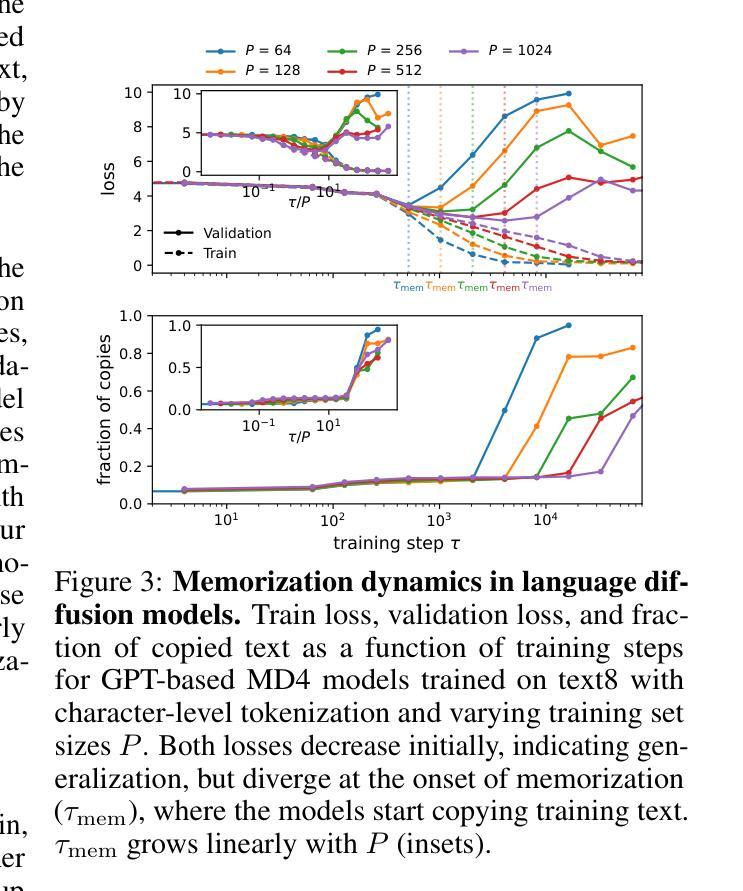
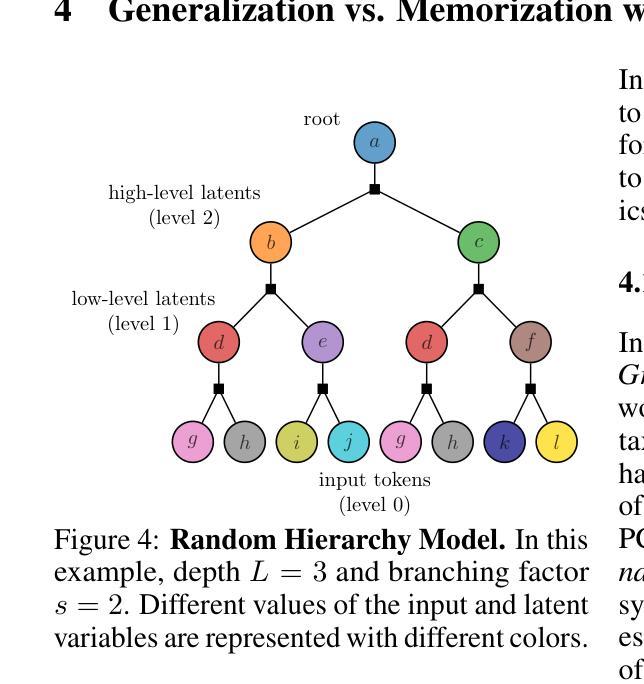
Bigger Isn’t Always Memorizing: Early Stopping Overparameterized Diffusion Models
Authors:Alessandro Favero, Antonio Sclocchi, Matthieu Wyart
Diffusion probabilistic models have become a cornerstone of modern generative AI, yet the mechanisms underlying their generalization remain poorly understood. In fact, if these models were perfectly minimizing their training loss, they would just generate data belonging to their training set, i.e., memorize, as empirically found in the overparameterized regime. We revisit this view by showing that, in highly overparameterized diffusion models, generalization in natural data domains is progressively achieved during training before the onset of memorization. Our results, ranging from image to language diffusion models, systematically support the empirical law that memorization time is proportional to the dataset size. Generalization vs. memorization is then best understood as a competition between time scales. We show that this phenomenology is recovered in diffusion models learning a simple probabilistic context-free grammar with random rules, where generalization corresponds to the hierarchical acquisition of deeper grammar rules as training time grows, and the generalization cost of early stopping can be characterized. We summarize these results in a phase diagram. Overall, our results support that a principled early-stopping criterion - scaling with dataset size - can effectively optimize generalization while avoiding memorization, with direct implications for hyperparameter transfer and privacy-sensitive applications.
扩散概率模型已成为现代生成式人工智能的基石,但其背后的泛化机制仍知之甚少。事实上,如果这些模型能够完美地最小化其训练损失,它们只会生成属于其训练集的数据,即进行记忆,正如在超参数范围内所发现的那样。我们通过展示高度超参数的扩散模型在记忆开始前,在自然数据领域泛化是在训练过程中逐步实现的,重新审视了这一观点。我们的结果涵盖了图像到语言扩散模型,系统地支持了经验法则,即记忆时间与数据集大小成正比。泛化与记忆之间的最佳理解是时间尺度的竞争。我们展示了在扩散模型学习具有随机规则的简单无上下文概率语法时恢复了这种现象,其中泛化对应于随着训练时间的增长层次地获取更深的语法规则,早期停止的泛化成本可以得到表征。我们在相图中总结了这些结果。总的来说,我们的结果支持一个原则性的早期停止准则——与数据集大小成比例——可以有效地优化泛化同时避免记忆,对超参数转移和隐私敏感应用有直接的影响。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
扩散概率模型是现代生成人工智能的核心,但其泛化机制尚不清楚。事实上,如果这些模型完美最小化其训练损失,它们只会生成属于其训练集的数据,即存在记忆现象,这在过度参数化状态下已被经验发现。我们重新审视这一观点,发现高度过度参数化的扩散模型中,在自然数据领域的泛化是在训练过程中逐渐实现的,且在记忆出现之前。我们的结果从图像到语言扩散模型都有系统支持,实证规律是记忆时间与数据集大小成正比。泛化与记忆之间的最佳理解是时间尺度的竞争。我们展示了这一现象在扩散模型学习简单的无上下文概率语法与随机规则时得以恢复,其中泛化对应于随着训练时间的增长层次地获取更深的语法规则,早期停止的泛化成本可以得到特征描述。总体而言,我们的结果支持一个原则性的早期停止准则——与数据集大小成比例——可以有效地优化泛化同时避免记忆现象,对超参数转移和隐私敏感应用有直接意义。
Key Takeaways
- 扩散概率模型是现代生成AI的核心,但其泛化机制尚未完全理解。
- 在过度参数化的扩散模型中,泛化过程是在训练过程中逐渐实现的,而非一开始就能达到。
- 记忆现象在扩散模型中也存在,尤其是在过度参数化状态下。
- 记忆时间与数据集大小成正比,这是一个实证规律。
- 泛化与记忆之间的平衡可以理解为时间尺度的竞争。
- 在学习简单的无上下文概率语法时,扩散模型的泛化过程与获取更深层次的语法规则相关。
点此查看论文截图

Forward-only Diffusion Probabilistic Models
Authors:Ziwei Luo, Fredrik K. Gustafsson, Jens Sjölund, Thomas B. Schön
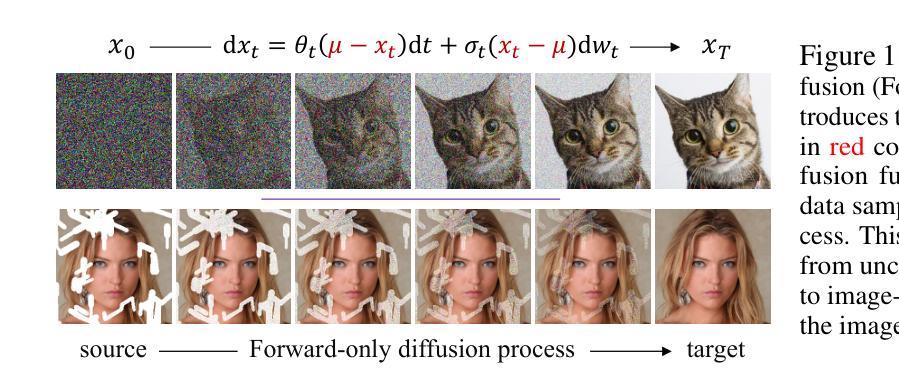
This work presents a forward-only diffusion (FoD) approach for generative modelling. In contrast to traditional diffusion models that rely on a coupled forward-backward diffusion scheme, FoD directly learns data generation through a single forward diffusion process, yielding a simple yet efficient generative framework. The core of FoD is a state-dependent linear stochastic differential equation that involves a mean-reverting term in both the drift and diffusion functions. This mean-reversion property guarantees the convergence to clean data, naturally simulating a stochastic interpolation between source and target distributions. More importantly, FoD is analytically tractable and is trained using a simple stochastic flow matching objective, enabling a few-step non-Markov chain sampling during inference. The proposed FoD model, despite its simplicity, achieves competitive performance on various image-conditioned (e.g., image restoration) and unconditional generation tasks, demonstrating its effectiveness in generative modelling. Our code is available at https://github.com/Algolzw/FoD.
本文提出了一种只前向扩散(FoD)的方法,用于生成建模。与传统的依赖于耦合的前向-后向扩散方案的扩散模型不同,FoD通过单一的前向扩散过程直接学习数据生成,从而构建了一个简单而高效的生成框架。FoD的核心是一个与状态相关的线性随机微分方程,该方程在漂移和扩散函数中涉及均值回复项。这种均值回归属性保证了向干净数据的收敛,自然地模拟了源分布和目标分布之间的随机插值。更重要的是,FoD分析上是可行的,并且使用简单的随机流匹配目标进行训练,在推理期间实现几步非马尔可夫链采样。尽管FoD模型简单,但在各种图像条件(例如图像恢复)和无条件生成任务上实现了具有竞争力的性能,证明了其在生成建模中的有效性。我们的代码位于https://github.com/Algolzw/FoD。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Project page: https://algolzw.github.io/fod
Summary
本文提出了一种仅前向扩散(FoD)的方法用于生成建模。与传统的依赖于耦合前向-后向扩散方案的扩散模型不同,FoD通过单一的前向扩散过程直接学习数据生成,提供了一个简洁而高效的生成框架。FoD的核心是一个涉及均值反转项的依赖于状态的非线性随机微分方程,这一特性保证了向清洁数据的收敛,自然地模拟了源分布和目标分布之间的随机插值。更重要的是,FoD具有分析上的可追踪性,并使用简单的随机流匹配目标进行训练,在推理期间实现少数非马尔可夫链采样步骤。尽管其简单性,提出的FoD模型在图像条件(如图像恢复)和无条件生成任务上取得了具有竞争力的表现,证明了其在生成建模中的有效性。
Key Takeaways
- 提出了一种仅前向扩散(FoD)的生成建模方法。
- 与传统扩散模型不同,FoD通过单一的前向扩散过程进行学习。
- FoD的核心是一个涉及均值反转的依赖于状态的非线性随机微分方程。
- 均值反转特性保证了向清洁数据的收敛,模拟了源分布与目标分布之间的随机插值。
- FoD具有分析上的可追踪性,并使用简单的随机流匹配目标进行训练。
- FoD模型在图像条件和无条件生成任务上取得了具有竞争力的表现。
点此查看论文截图


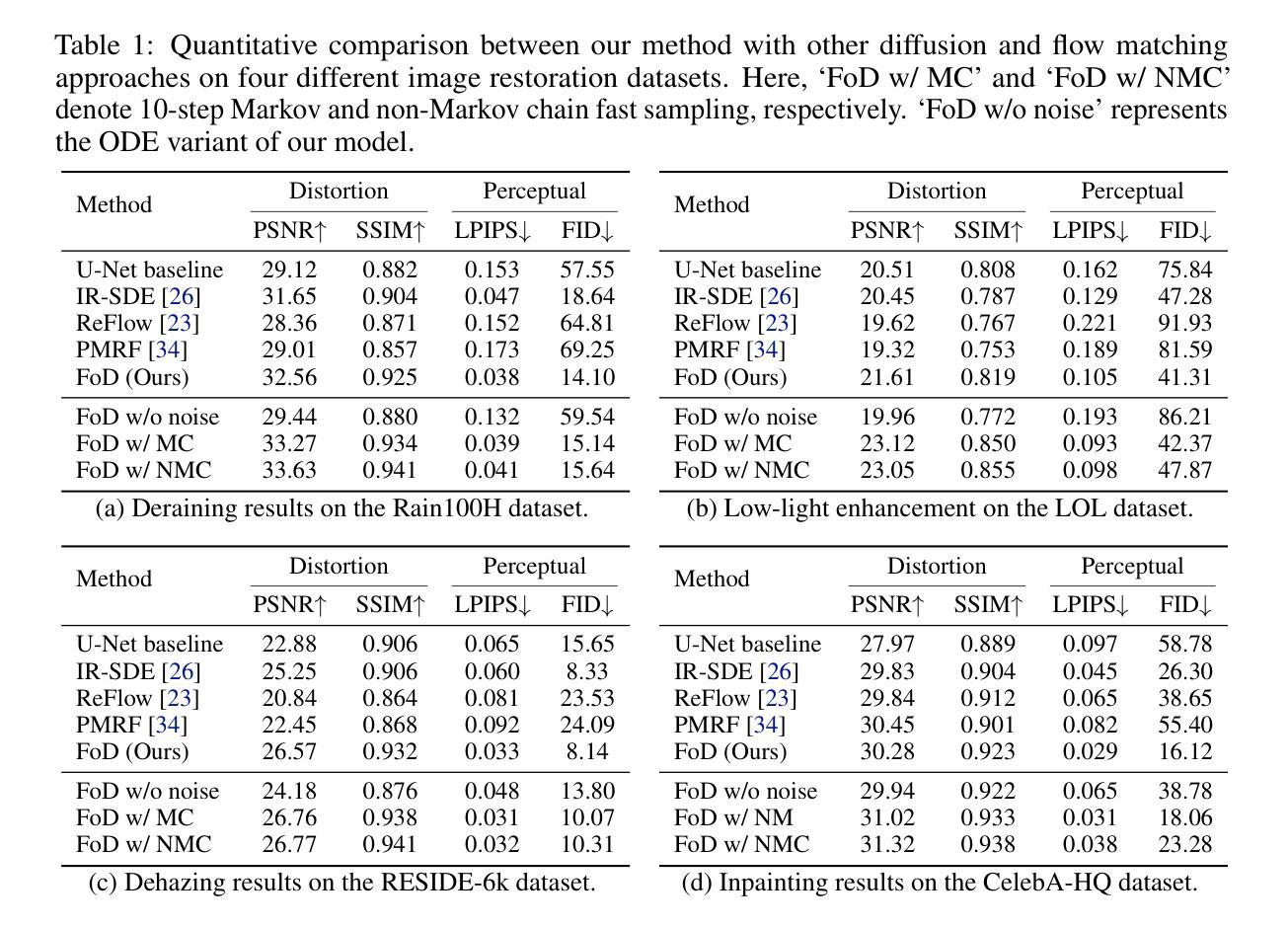
MAGIC: Motion-Aware Generative Inference via Confidence-Guided LLM
Authors:Siwei Meng, Yawei Luo, Ping Liu
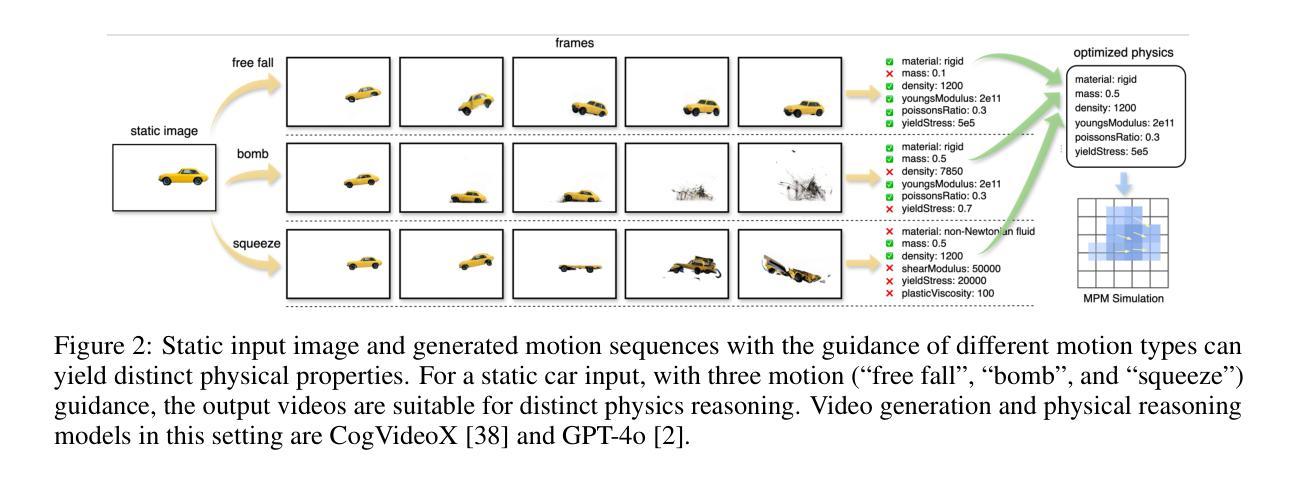
Recent advances in static 3D generation have intensified the demand for physically consistent dynamic 3D content. However, existing video generation models, including diffusion-based methods, often prioritize visual realism while neglecting physical plausibility, resulting in implausible object dynamics. Prior approaches for physics-aware dynamic generation typically rely on large-scale annotated datasets or extensive model fine-tuning, which imposes significant computational and data collection burdens and limits scalability across scenarios. To address these challenges, we present MAGIC, a training-free framework for single-image physical property inference and dynamic generation, integrating pretrained image-to-video diffusion models with iterative LLM-based reasoning. Our framework generates motion-rich videos from a static image and closes the visual-to-physical gap through a confidence-driven LLM feedback loop that adaptively steers the diffusion model toward physics-relevant motion. To translate visual dynamics into controllable physical behavior, we further introduce a differentiable MPM simulator operating directly on 3D Gaussians reconstructed from the single image, enabling physically grounded, simulation-ready outputs without any supervision or model tuning. Experiments show that MAGIC outperforms existing physics-aware generative methods in inference accuracy and achieves greater temporal coherence than state-of-the-art video diffusion models.
近期静态3D生成的进展加剧了对物理一致性动态3D内容的需求。然而,现有的视频生成模型,包括基于扩散的方法,通常优先考虑视觉真实性而忽视物理可行性,导致物体动态不可信。之前针对物理感知动态生成的方法通常依赖于大规模标注数据集或模型精细调整,这带来了显著的计算和数据收集负担,并限制了跨场景的扩展性。为了应对这些挑战,我们提出了MAGIC,这是一个无需训练的单图像物理属性推断和动态生成框架,它整合了预训练的图像到视频的扩散模型与基于迭代的大型语言模型(LLM)推理。我们的框架从静态图像生成运动丰富的视频,并通过信心驱动的LLM反馈循环缩小视觉到物理的差距,该循环自适应地引导扩散模型朝向物理相关的运动。为了将视觉动态转化为可控的物理行为,我们进一步引入了一个可直接在单图像重建的3D高斯上运行的可微分MPM模拟器,无需监督或模型调整即可实现物理基础、模拟就绪的输出。实验表明,MAGIC在推理准确性方面超越了现有的物理感知生成方法,并且在时间连贯性方面优于最先进的视频扩散模型。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
基于静态图像生成动态内容的物理一致性挑战。现有视频生成模型忽视物理合理性,导致物体动态不合理。MAGIC框架结合预训练的图像到视频的扩散模型与基于LLM的推理,无需训练即可进行单图像物理属性推断和动态生成。通过置信度驱动的LLM反馈循环和可微分的MPM模拟器,MAGIC实现了从静态图像生成运动丰富视频,并关闭了视觉到物理的差距。实验表明,MAGIC在推理准确性方面优于现有的物理感知生成方法,并且在时间连贯性方面达到了最先进的视频扩散模型的水平。
Key Takeaways
- 现有视频生成模型在生成动态内容时忽视了物理一致性,导致物体动态不合理。
- MAGIC框架是一个无需训练的框架,用于单图像物理属性推断和动态生成。
- MAGIC结合了预训练的图像到视频的扩散模型和基于LLM的推理。
- 通过置信度驱动的LLM反馈循环,MAGIC实现了自适应引导扩散模型向物理相关运动方向。
- MAGIC引入了一个可微分的MPM模拟器,直接在3D高斯上操作,生成物理上合理且模拟就绪的输出。
- 无需监督或模型调整,MAGIC能够从单个静态图像生成物理上丰富的视频内容。
点此查看论文截图

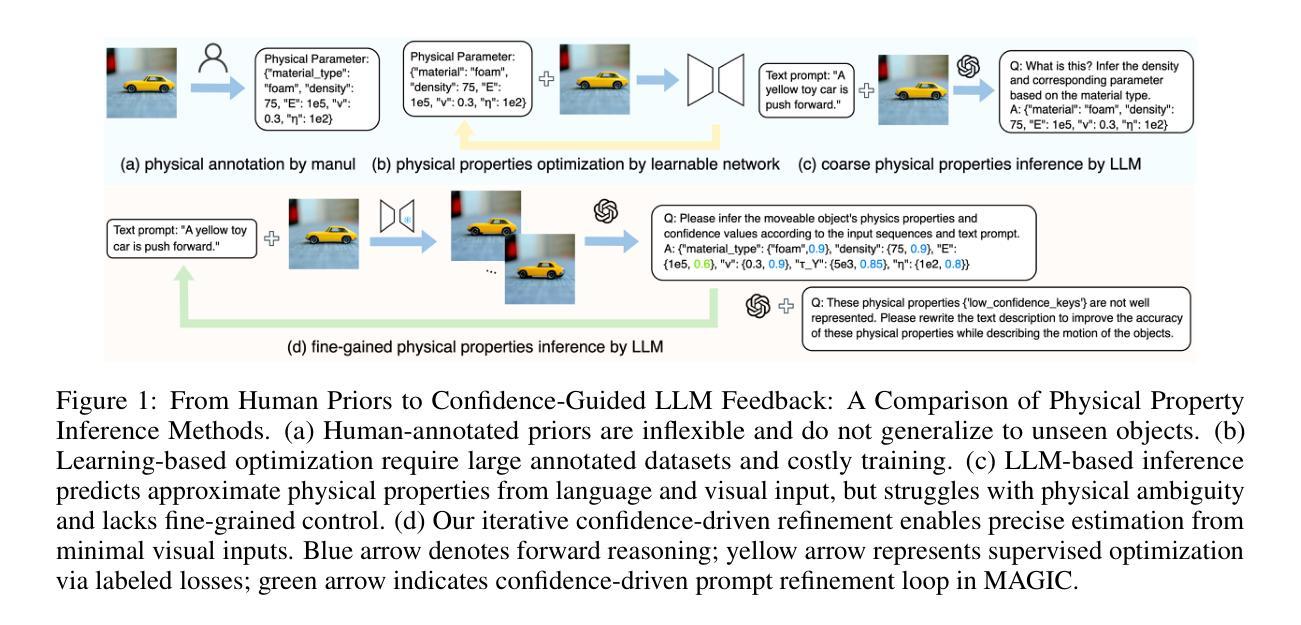

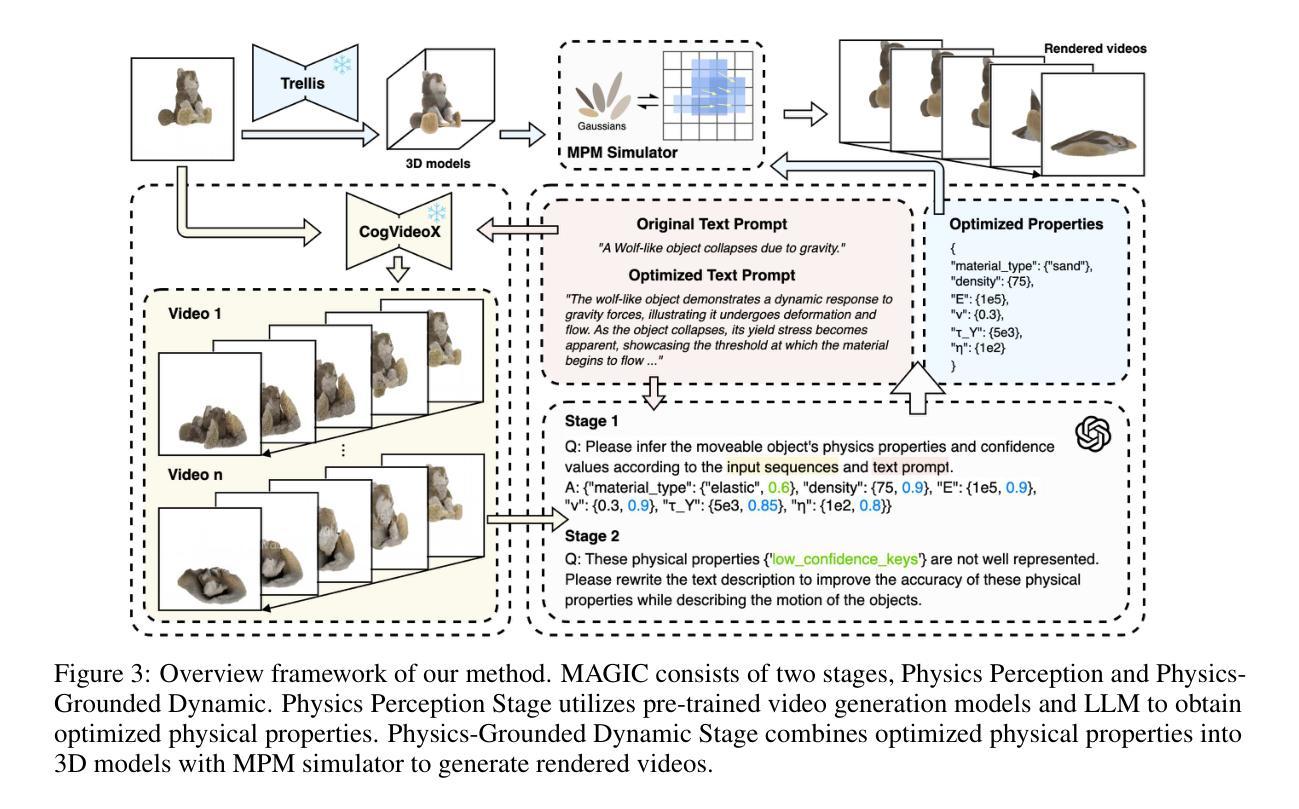

Style Transfer with Diffusion Models for Synthetic-to-Real Domain Adaptation
Authors:Estelle Chigot, Dennis G. Wilson, Meriem Ghrib, Thomas Oberlin
Semantic segmentation models trained on synthetic data often perform poorly on real-world images due to domain gaps, particularly in adverse conditions where labeled data is scarce. Yet, recent foundation models enable to generate realistic images without any training. This paper proposes to leverage such diffusion models to improve the performance of vision models when learned on synthetic data. We introduce two novel techniques for semantically consistent style transfer using diffusion models: Class-wise Adaptive Instance Normalization and Cross-Attention (CACTI) and its extension with selective attention Filtering (CACTIF). CACTI applies statistical normalization selectively based on semantic classes, while CACTIF further filters cross-attention maps based on feature similarity, preventing artifacts in regions with weak cross-attention correspondences. Our methods transfer style characteristics while preserving semantic boundaries and structural coherence, unlike approaches that apply global transformations or generate content without constraints. Experiments using GTA5 as source and Cityscapes/ACDC as target domains show that our approach produces higher quality images with lower FID scores and better content preservation. Our work demonstrates that class-aware diffusion-based style transfer effectively bridges the synthetic-to-real domain gap even with minimal target domain data, advancing robust perception systems for challenging real-world applications. The source code is available at: https://github.com/echigot/cactif.
利用合成数据训练的语义分割模型在真实世界图像上的表现往往较差,这主要是由于领域差距造成的,特别是在标记数据稀缺的不利条件下。然而,最近的基础模型能够在无需任何训练的情况下生成逼真的图像。本文提出利用这种扩散模型来改善在合成数据上学习的视觉模型的性能。我们介绍两种利用扩散模型进行语义一致风格转移的新技术:基于类别的自适应实例归一化和交叉注意力(CACTI),以及基于选择性注意力过滤的扩展(CACTIF)。CACTI根据语义类别有选择地应用统计归一化,而CACTIF则进一步根据特征相似性过滤交叉注意力图,防止在交叉注意力对应较弱的区域出现伪影。我们的方法在转移风格特征的同时,保留了语义边界和结构一致性,不同于那些应用全局变换或无约束生成内容的方法。使用GTA5作为源域,Cityscapes/ACDC作为目标域的实验表明,我们的方法生成了质量更高、FID得分更低、内容保存更好的图像。我们的工作证明,类感知扩散风格转移有效地缩短了合成到真实的领域差距,即使目标领域的数据最少,也为具有挑战性的真实世界应用提供了稳健的感知系统。源代码可在https://github.com/echigot/cactif获取。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Under review
Summary
基于扩散模型利用生成图像的方法能有效缩减合成图像与现实图像之间的差距,提高语义分割模型在真实世界图像上的性能。文中提出了两种新颖的语义一致性风格转移技术——基于分类自适应实例归一化和交叉注意力机制(CACTI)和其选择性注意力滤波扩展(CACTIF)。CACTI能够针对语义类别选择性应用统计归一化,而CACTIF则进一步根据特征相似性过滤交叉注意力映射,避免了弱交叉注意力对应区域的伪影。实验表明,该方法在GTA5作为源域和Cityscapes/ACDC作为目标域的场景下,生成图像质量更高、FID得分更低且内容保留更好。该研究证明了基于类别感知的扩散风格转移即使在目标域数据很少的情况下也能有效地弥合合成域与现实域之间的鸿沟,为应对挑战性的真实世界应用提供了先进的感知系统。
Key Takeaways
- 语义分割模型在真实世界图像上的性能可以通过利用扩散模型生成的图像来提高。
- 提出了两种新的语义一致性风格转移技术:CACTI和CACTIF。
- CACTI能够针对语义类别进行选择性统计归一化。
- CACTIF通过过滤交叉注意力映射来避免伪影,特别是在弱交叉注意力的区域。
- 实验结果显示,该方法在生成图像质量、FID得分和内容保留方面表现优异。
- 该方法有效地缩小了合成域与现实域之间的差距,尤其是使用较少的真实世界数据。
点此查看论文截图

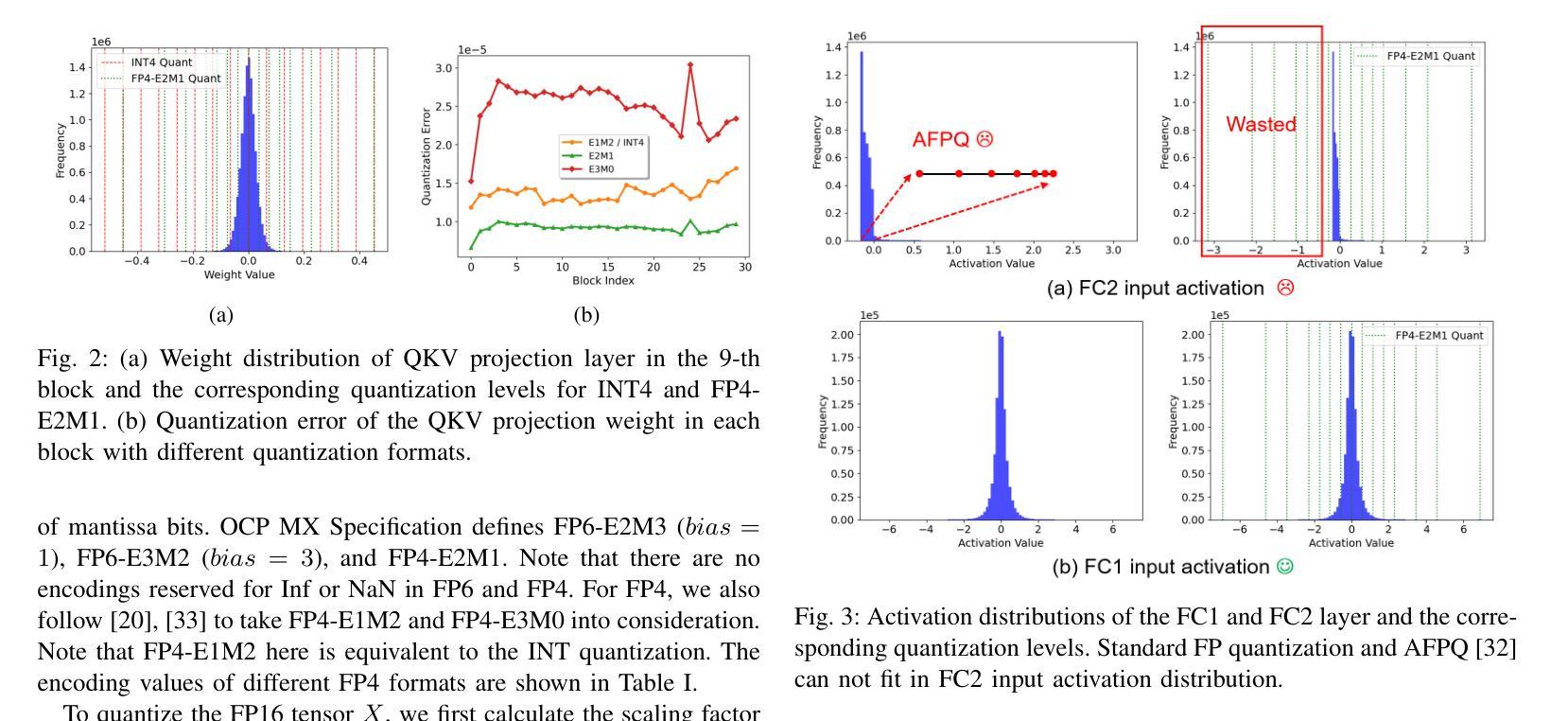
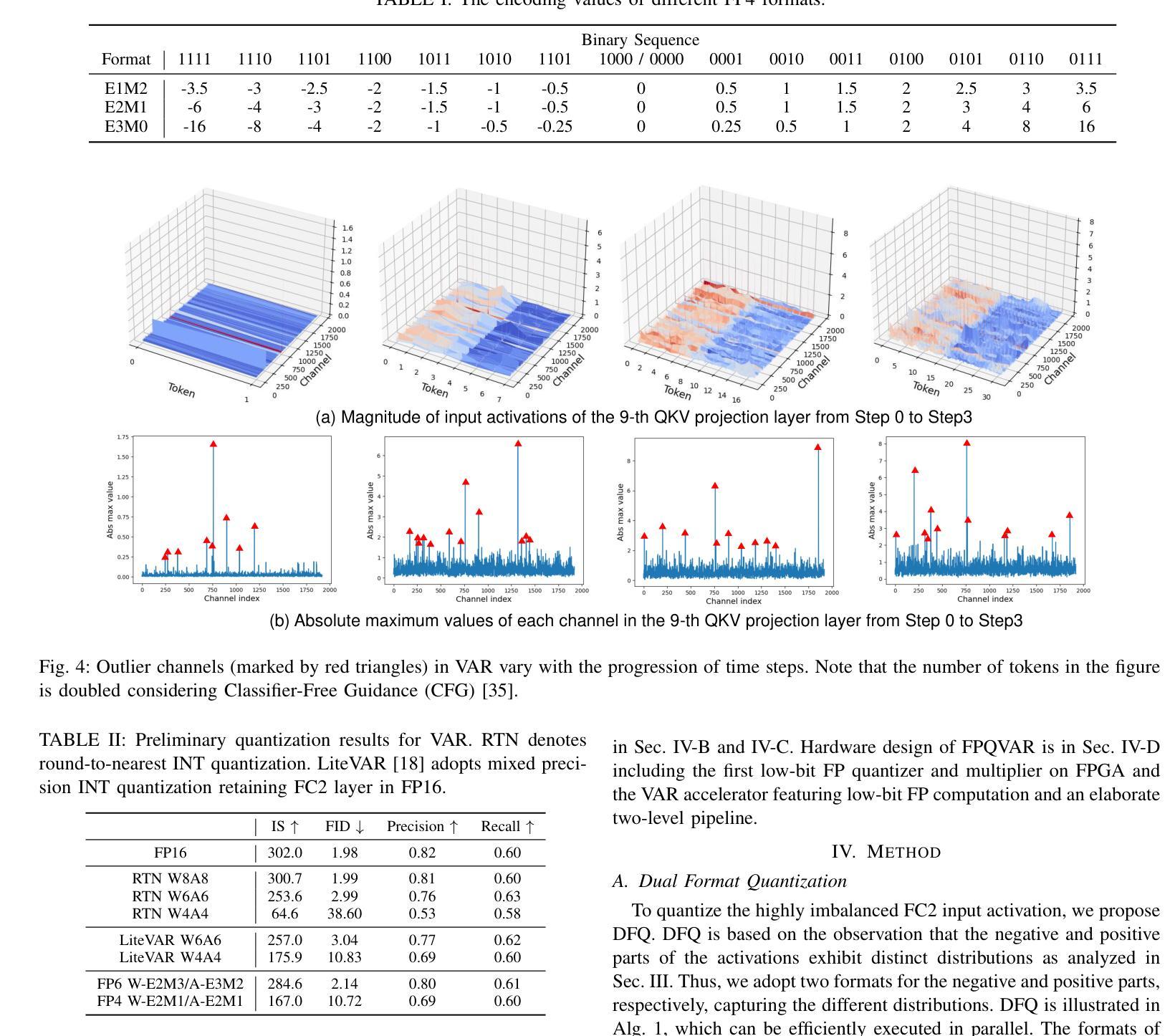
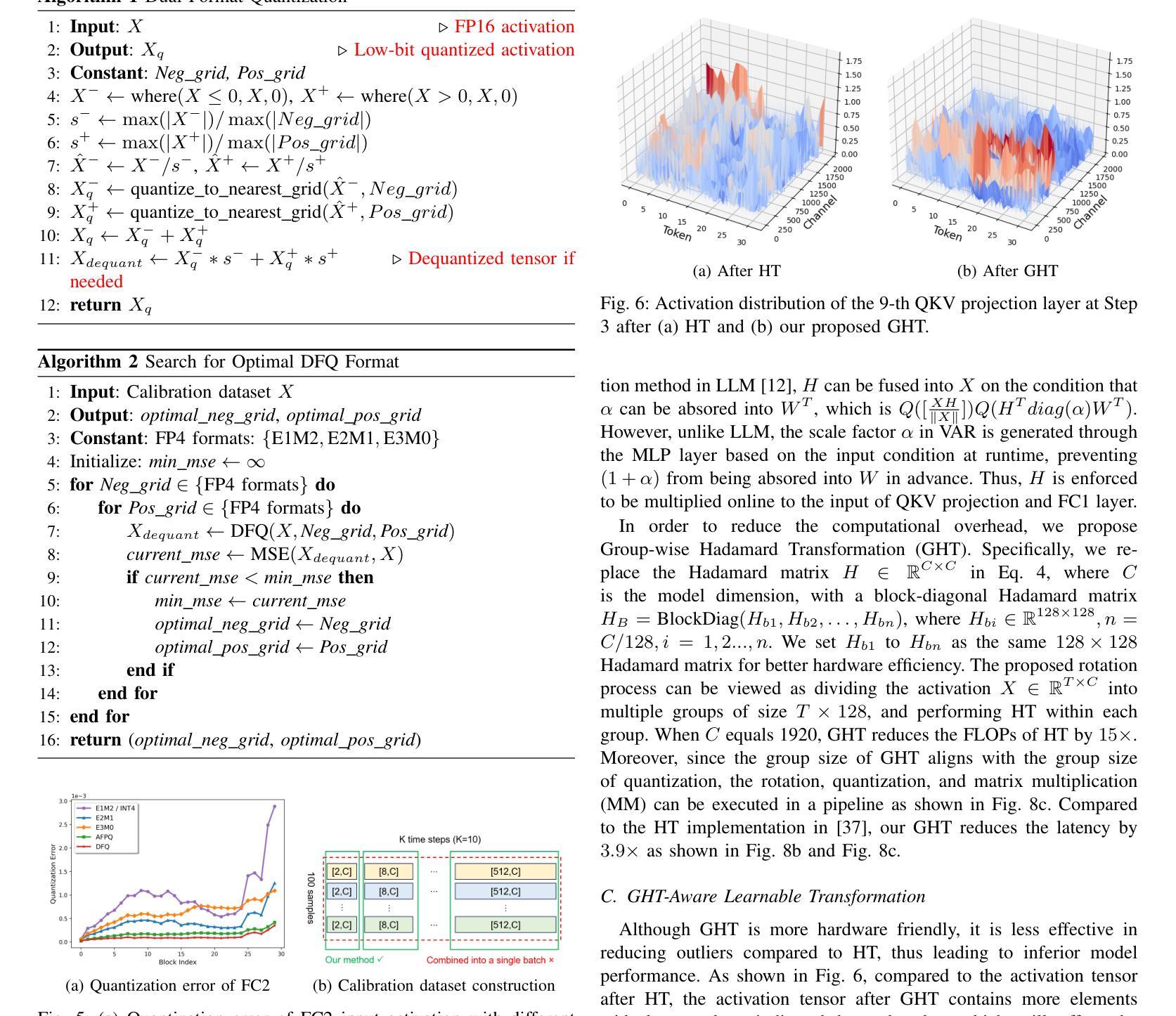
FPQVAR: Floating Point Quantization for Visual Autoregressive Model with FPGA Hardware Co-design
Authors:Renjie Wei, Songqiang Xu, Qingyu Guo, Meng Li
Visual autoregressive (VAR) modeling has marked a paradigm shift in image generation from next-token prediction to next-scale prediction. VAR predicts a set of tokens at each step from coarse to fine scale, leading to better image quality and faster inference speed compared to existing diffusion models. However, the large parameter size and computation cost hinder its deployment on edge devices. To reduce the memory and computation cost, we propose FPQVAR, an efficient post-training floating-point (FP) quantization framework for VAR featuring algorithm and hardware co-design. At the algorithm level, we first identify the challenges of quantizing VAR. To address them, we propose Dual Format Quantization for the highly imbalanced input activation. We further propose Group-wise Hadamard Transformation and GHT-Aware Learnable Transformation to address the time-varying outlier channels. At the hardware level, we design the first low-bit FP quantizer and multiplier with lookup tables on FPGA and propose the first FPGA-based VAR accelerator featuring low-bit FP computation and an elaborate two-level pipeline. Extensive experiments show that compared to the state-of-the-art quantization method, our proposed FPQVAR significantly improves Fr'echet Inception Distance (FID) from 10.83 to 3.58, Inception Score (IS) from 175.9 to 241.5 under 4-bit quantization. FPQVAR also significantly improves the performance of 6-bit quantized VAR, bringing it on par with the FP16 model. Our accelerator on AMD-Xilinx VCK190 FPGA achieves a throughput of 1.1 image/s, which is 3.1x higher than the integer-based accelerator. It also demonstrates 3.6x and 2.8x higher energy efficiency compared to the integer-based accelerator and GPU baseline, respectively.
视觉自回归(VAR)建模标志着图像生成从下一个词预测到下一个尺度预测的范式转变。VAR通过从粗略到精细尺度的每一步预测一系列标记(tokens),与现有的扩散模型相比,产生了更高质量的图像和更快的推理速度。然而,其庞大的参数大小和计算成本阻碍了其在边缘设备上的部署。为了降低内存和计算成本,我们提出了FPQVAR,这是一种用于VAR的后训练浮点(FP)量化框架,融合了算法和硬件协同设计。在算法层面,我们首先确定了量化VAR的挑战。为了解决这些问题,我们提出了用于高度不平衡输入激活的双重格式量化。我们还提出了分组哈达玛变换和GHT感知可学习变换,以解决时变异常通道的问题。在硬件层面,我们设计了基于FPGA的首个低位浮点量化和乘法器查找表,并提出了基于FPGA的VAR加速器,该加速器具有低位浮点计算和精心设计的两级流水线。大量实验表明,与最新的量化方法相比,我们提出的FPQVAR在4位量化下将Fréchet Inception Distance (FID)从10.83显著改进到3.58,Inception Score (IS)从175.9提高到241.5。FPQVAR还显著提高了6位量化VAR的性能,使其与FP16模型相当。我们的加速器在AMD-Xilinx VCK190 FPGA上的吞吐量达到1.1图像/秒,比整数加速器高出3.1倍。它还表现出比整数加速器和GPU基准测试高3.6倍和2.8倍的能效。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
视觉自回归(VAR)模型在图像生成领域实现了从下一个标记预测到下一个尺度预测的范式转变。VAR通过从粗到细的尺度预测一系列标记,提高了图像质量和推理速度。为降低内存和计算成本,便于在边缘设备部署,本文提出了FPQVAR,这是一个针对VAR的后训练浮点(FP)量化框架,融合了算法和硬件协同设计。在算法层面,提出双格式量化解决输入激活的不平衡问题,以及分组哈达玛变换和GHT感知可学习变换应对时变异常通道。在硬件层面,设计了低比特FP量化和乘法器,采用FPGA查找表,并推出基于FPGA的VAR加速器,实现低比特FP计算和两级精细管道。实验表明,与最新量化方法相比,FPQVAR在4位量化下将Fréchet Inception Distance (FID)从10.83大幅改善至3.58,Inception Score (IS)从175.9提升至241.5。在6位量化方面,FPQVAR的表现与FP16模型相当。在AMD-Xilinx VCK190 FPGA上,加速器吞吐量达1.1图像/秒,是整数加速器的3.1倍。此外,与整数加速器和GPU基准测试相比,其能效分别提高了3.6倍和2.8倍。
Key Takeaways
- 视觉自回归(VAR)模型实现了图像生成中的尺度预测转变,从粗到细提高图像质量和推理速度。
- FPQVAR是首个针对VAR的后训练浮点(FP)量化框架,包含算法和硬件协同设计。
- 在算法层面,FPQVAR通过双格式量化解决输入激活不平衡问题,通过分组哈达玛变换和GHT感知可学习变换应对异常通道。
- 在硬件层面,设计了低比特FP量化和乘法器,并推出基于FPGA的VAR加速器。
- FPQVAR显著提高了图像生成质量,同时在4位和6位量化方面表现出优异性能。
- 实验结果显示,FPQVAR在图像质量指标Fréchet Inception Distance (FID)和Inception Score (IS)上有显著改善。
点此查看论文截图


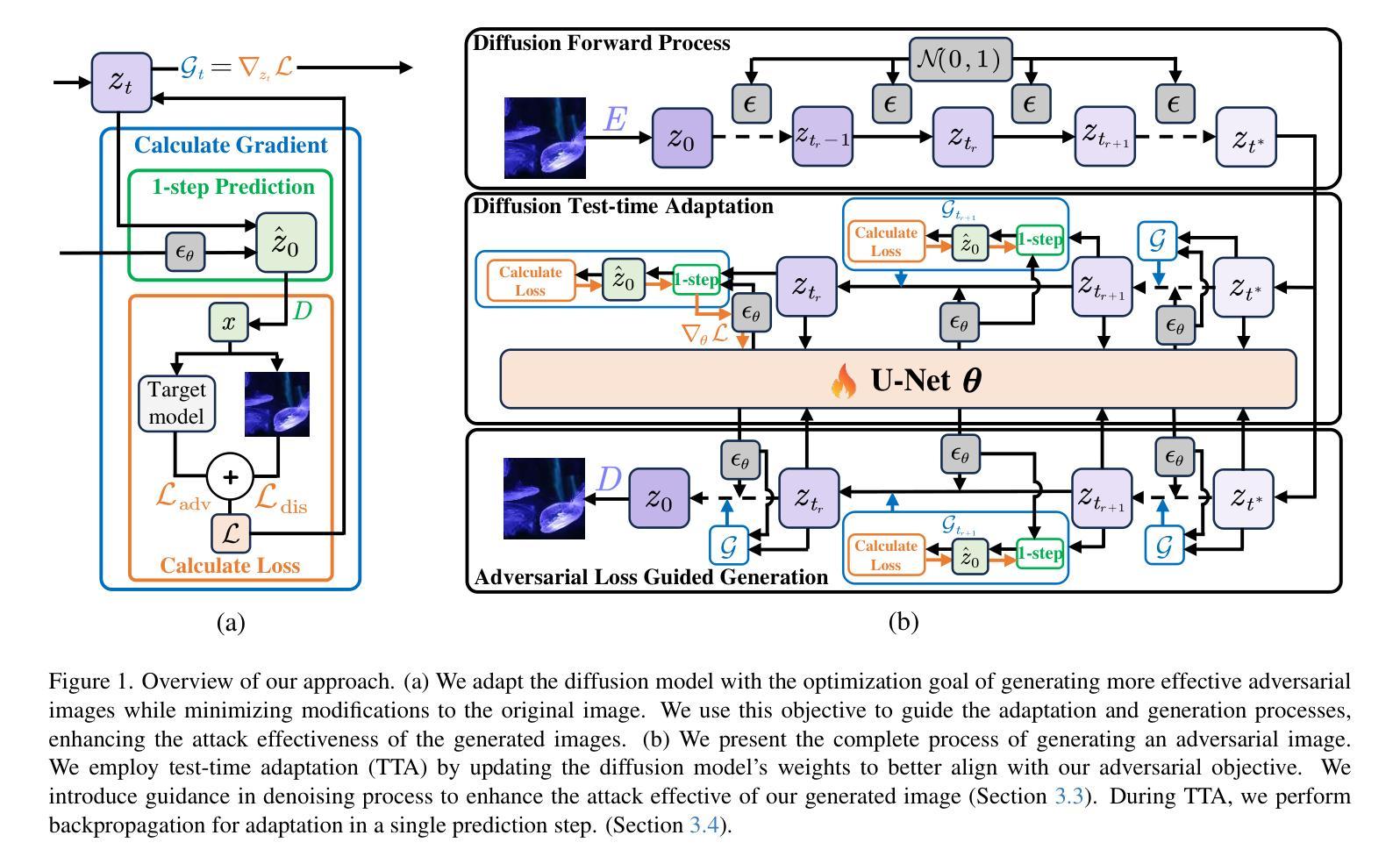
TRAIL: Transferable Robust Adversarial Images via Latent diffusion
Authors:Yuhao Xue, Zhifei Zhang, Xinyang Jiang, Yifei Shen, Junyao Gao, Wentao Gu, Jiale Zhao, Miaojing Shi, Cairong Zhao
Adversarial attacks exploiting unrestricted natural perturbations present severe security risks to deep learning systems, yet their transferability across models remains limited due to distribution mismatches between generated adversarial features and real-world data. While recent works utilize pre-trained diffusion models as adversarial priors, they still encounter challenges due to the distribution shift between the distribution of ideal adversarial samples and the natural image distribution learned by the diffusion model. To address the challenge, we propose Transferable Robust Adversarial Images via Latent Diffusion (TRAIL), a test-time adaptation framework that enables the model to generate images from a distribution of images with adversarial features and closely resembles the target images. To mitigate the distribution shift, during attacks, TRAIL updates the diffusion U-Net’s weights by combining adversarial objectives (to mislead victim models) and perceptual constraints (to preserve image realism). The adapted model then generates adversarial samples through iterative noise injection and denoising guided by these objectives. Experiments demonstrate that TRAIL significantly outperforms state-of-the-art methods in cross-model attack transferability, validating that distribution-aligned adversarial feature synthesis is critical for practical black-box attacks.
利用不受限制的自然扰动进行的对抗性攻击对深度学习系统构成了严重的安全风险。然而,由于生成的对抗性特征与现实世界数据之间的分布不匹配,这些攻击在不同模型之间的可转移性仍然有限。虽然最近的研究利用预训练的扩散模型作为对抗性先验,但由于理想对抗样本的分布与扩散模型学到的自然图像分布之间存在分布偏移,它们仍然面临挑战。为了应对这一挑战,我们提出了通过潜在扩散生成可转移稳健对抗图像(TRAIL)的方法,这是一种测试时间适应框架,使模型能够从具有对抗特征的图像分布中生成图像,并紧密模拟目标图像。为了缓解分布偏移,在攻击过程中,TRAIL通过结合对抗目标(以误导目标模型)和感知约束(以保持图像的真实性)来更新扩散U-Net的权重。适应后的模型然后通过迭代噪声注入和去噪,在这些目标的指导下生成对抗样本。实验表明,与传统的先进方法相比,TRAIL在跨模型攻击转移方面表现出显著的优势,验证了与实际黑箱攻击中对齐分布的对抗特征合成的重要性。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文提出一种名为TRAIL的测试时适应性框架,利用预训练的扩散模型作为对抗性先验,生成具有对抗性特征的图像分布,并紧密模拟目标图像。该框架通过结合对抗性目标和感知约束来减轻分布转移问题,从而更新扩散U-Net的权重。实验证明,TRAIL在跨模型攻击转移方面显著优于现有方法,验证了分布对齐对抗性特征合成对于实际黑盒攻击的重要性。
Key Takeaways
- 对抗攻击对深度学习系统构成严重安全风险,但其在模型间的传输性因生成对抗特征与真实世界数据分布不匹配而受限。
- 近期工作利用预训练的扩散模型作为对抗性先验,但仍面临挑战,即理想对抗样本分布与扩散模型学到的自然图像分布之间的分布转移问题。
- TRAIL框架通过测试时适应性,使模型能够从具有对抗性特征的图像分布中生成图像,并紧密模拟目标图像。
- TRAIL结合对抗性目标和感知约束来更新扩散U-Net的权重,以减轻分布转移问题。
- 对抗性目标旨在误导受害者模型,而感知约束则旨在保持图像的真实性。
- 通过迭代噪声注入和去噪过程,生成受目标引导的对抗样本。
点此查看论文截图

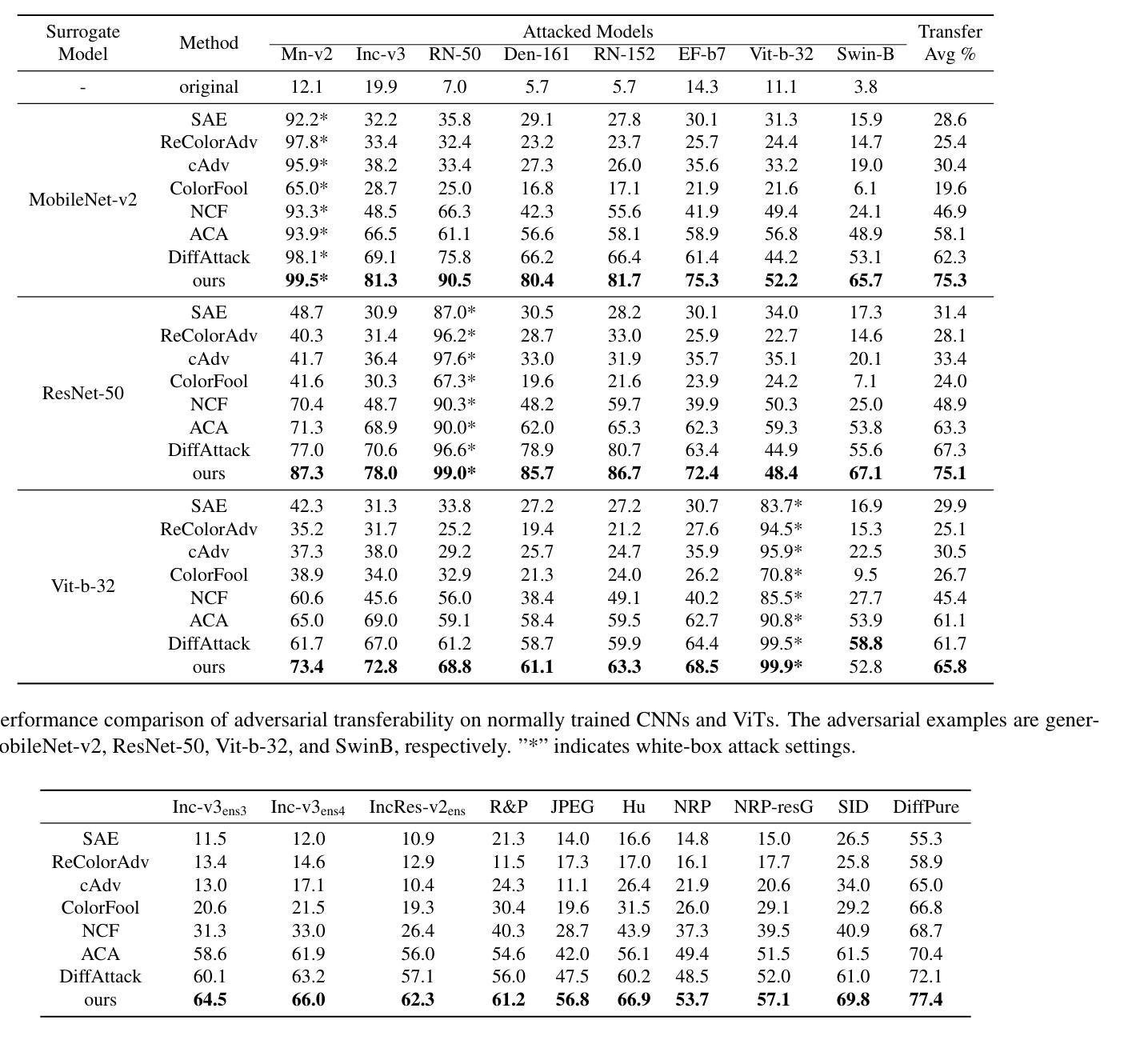
OSCAR: One-Step Diffusion Codec Across Multiple Bit-rates
Authors:Jinpei Guo, Yifei Ji, Zheng Chen, Kai Liu, Min Liu, Wang Rao, Wenbo Li, Yong Guo, Yulun Zhang
Pretrained latent diffusion models have shown strong potential for lossy image compression, owing to their powerful generative priors. Most existing diffusion-based methods reconstruct images by iteratively denoising from random noise, guided by compressed latent representations. While these approaches have achieved high reconstruction quality, their multi-step sampling process incurs substantial computational overhead. Moreover, they typically require training separate models for different compression bit-rates, leading to significant training and storage costs. To address these challenges, we propose a one-step diffusion codec across multiple bit-rates. termed OSCAR. Specifically, our method views compressed latents as noisy variants of the original latents, where the level of distortion depends on the bit-rate. This perspective allows them to be modeled as intermediate states along a diffusion trajectory. By establishing a mapping from the compression bit-rate to a pseudo diffusion timestep, we condition a single generative model to support reconstructions at multiple bit-rates. Meanwhile, we argue that the compressed latents retain rich structural information, thereby making one-step denoising feasible. Thus, OSCAR replaces iterative sampling with a single denoising pass, significantly improving inference efficiency. Extensive experiments demonstrate that OSCAR achieves superior performance in both quantitative and visual quality metrics. The code and models will be released at https://github.com/jp-guo/OSCAR.
预训练的潜在扩散模型在有损图像压缩方面显示出强大的潜力,这得益于其强大的生成先验。大多数现有的基于扩散的方法通过迭代去噪从随机噪声中重建图像,由压缩的潜在表示引导。虽然这些方法达到了较高的重建质量,但它们的多步采样过程产生了大量的计算开销。此外,它们通常需要针对不同的压缩比特率训练不同的模型,从而导致显著的训练和存储成本。为了解决这些挑战,我们提出了一种跨多个比特率的扩散编解码器(OSCAR)。具体来说,我们的方法将压缩潜在表示视为原始潜在表示的噪声版本,其中失真程度取决于比特率。这个视角允许将它们建模为沿扩散轨迹的中间状态。通过建立从压缩比特率到伪扩散时间步长的映射,我们将单一生成模型调整为支持多个比特率的重建。同时,我们认为压缩的潜在表示保留了丰富的结构信息,从而使得一步去噪成为可能。因此,OSCAR用单个去噪过程取代了迭代采样,大大提高了推理效率。大量实验表明,OSCAR在定量和视觉质量指标上均取得了卓越的性能。代码和模型将在https://github.com/jp-guo/OSCAR上发布。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
预训练潜在扩散模型在无损图像压缩领域展现出强大潜力,其生成先验具有显著优势。现有扩散方法主要通过迭代去噪从随机噪声中重建图像,这一过程由压缩潜在表示引导。虽然这些方法重建质量高,但多步采样过程带来较大计算开销,且通常需要针对不同压缩比特率训练不同模型,导致训练和存储成本增加。针对这些挑战,我们提出一种跨多比特率的单步扩散编解码器OSCAR。我们将压缩潜在视作原始潜在的噪声版本,其失真程度取决于比特率,将其作为扩散轨迹的中间状态建模。通过建立从压缩比特率到伪扩散时间步长的映射,我们使单一生成模型支持多比特率的重建。同时,我们认为压缩潜在保留了丰富的结构信息,使得一步去噪成为可能。因此,OSCAR用一步去噪过程替代了迭代采样,显著提高了推理效率。实验表明,OSCAR在定量和视觉质量指标上均实现优越性能。
Key Takeaways
- 预训练潜在扩散模型在无损图像压缩领域具有强大潜力。
- 现有扩散方法存在计算开销大、需要针对多种比特率训练不同模型的问题。
- OSCAR提出一种跨多比特率的单步扩散编解码器方法。
- OSCAR将压缩潜在视作原始潜在的噪声版本,并建立其与扩散轨迹中间状态的映射。
- OSCAR利用单一生成模型支持多比特率的图像重建。
- OSCAR通过一步去噪过程提高了推理效率。
点此查看论文截图


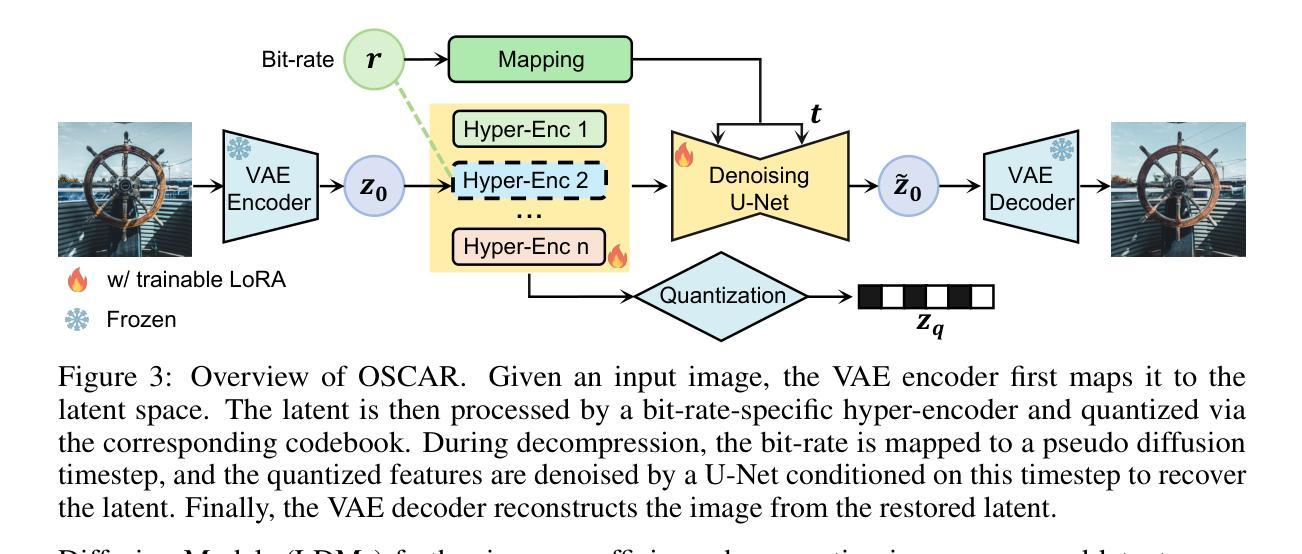
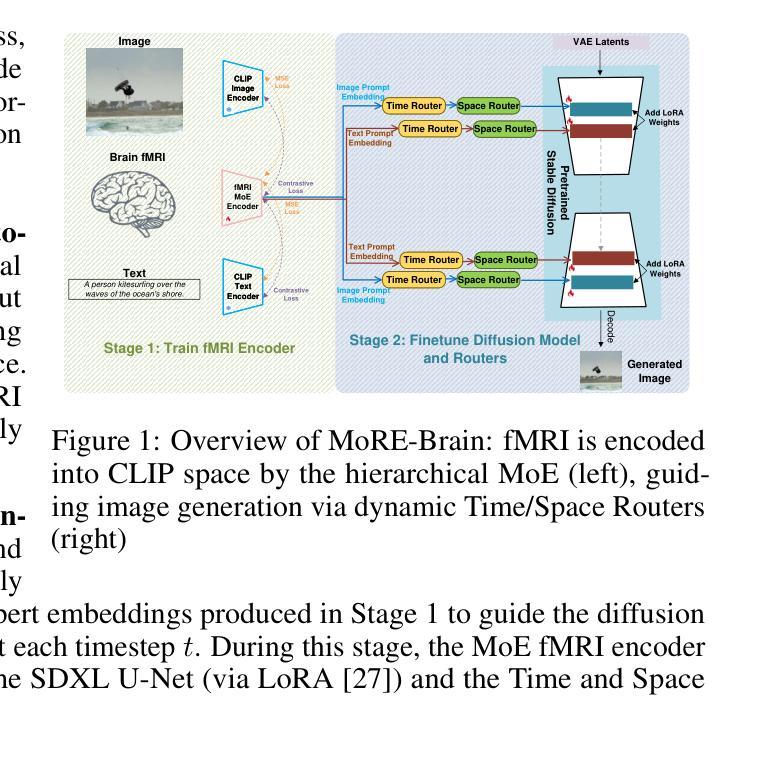
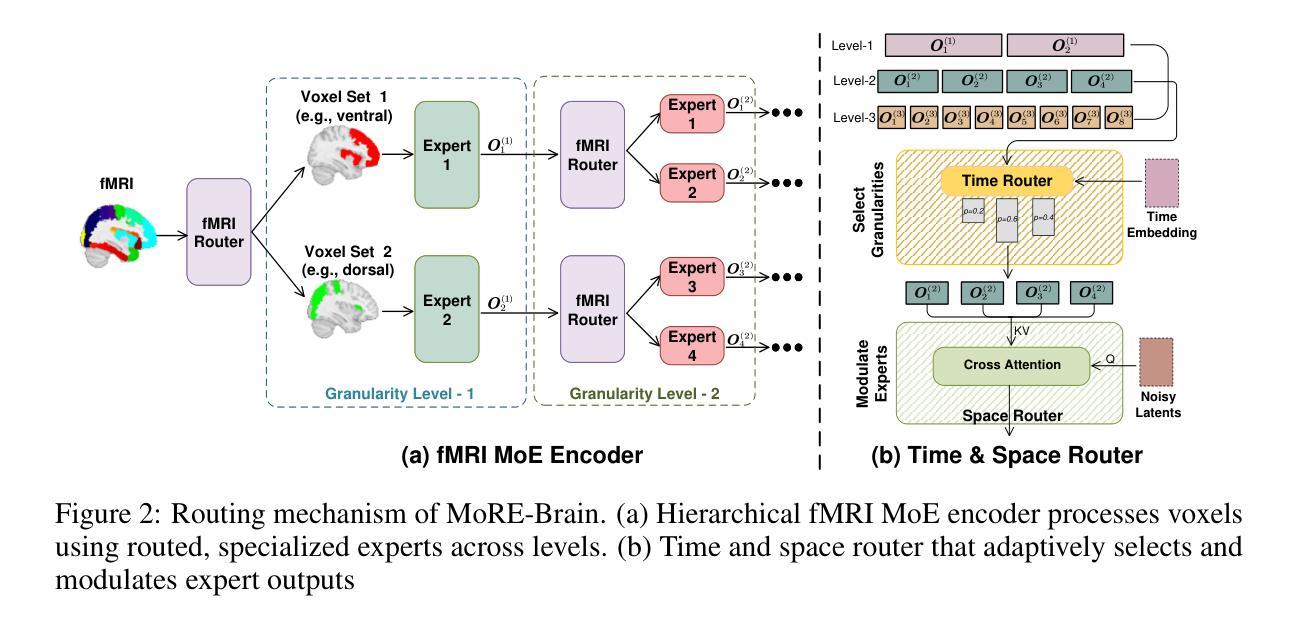
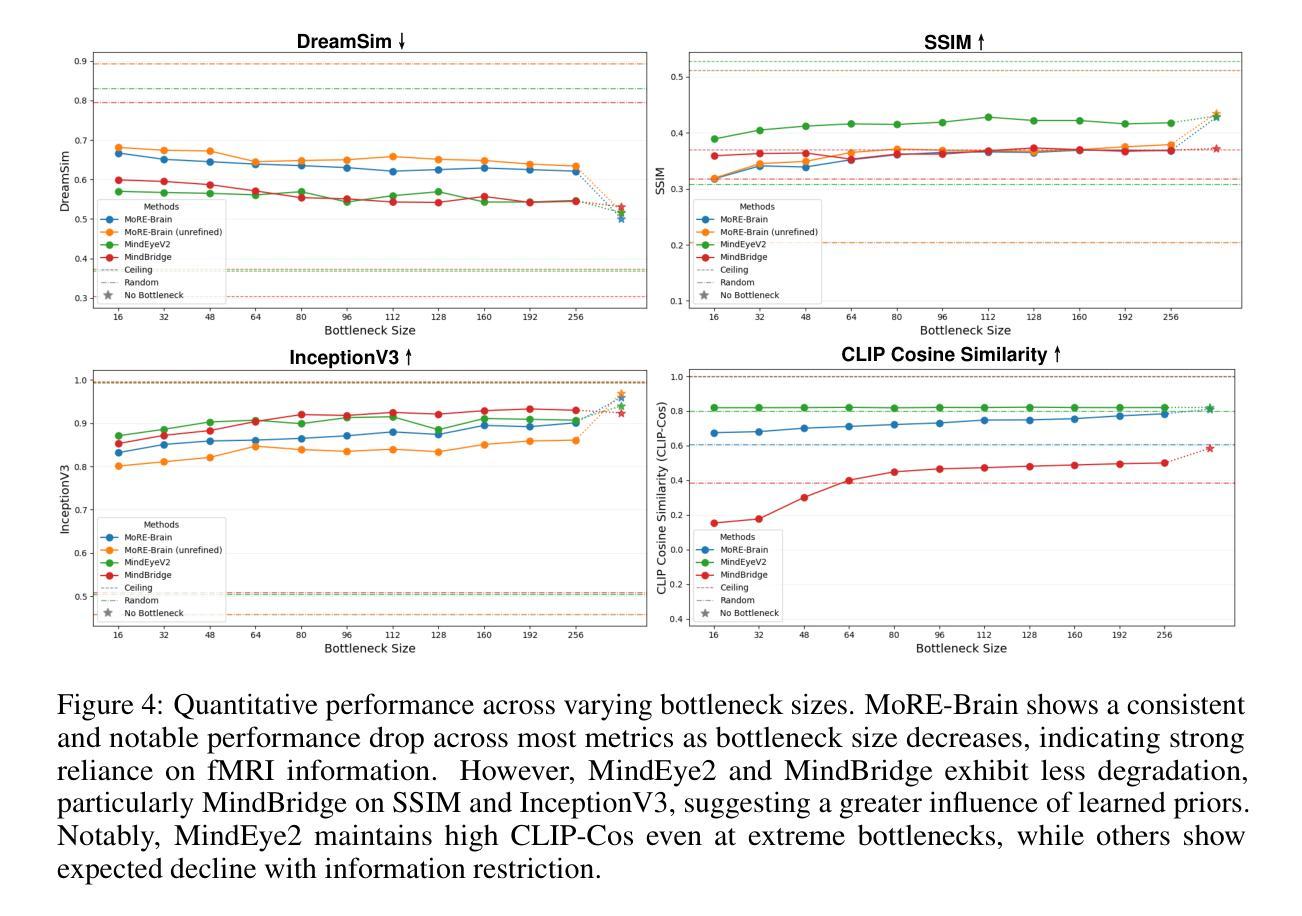
MoRE-Brain: Routed Mixture of Experts for Interpretable and Generalizable Cross-Subject fMRI Visual Decoding
Authors:Yuxiang Wei, Yanteng Zhang, Xi Xiao, Tianyang Wang, Xiao Wang, Vince D. Calhoun
Decoding visual experiences from fMRI offers a powerful avenue to understand human perception and develop advanced brain-computer interfaces. However, current progress often prioritizes maximizing reconstruction fidelity while overlooking interpretability, an essential aspect for deriving neuroscientific insight. To address this gap, we propose MoRE-Brain, a neuro-inspired framework designed for high-fidelity, adaptable, and interpretable visual reconstruction. MoRE-Brain uniquely employs a hierarchical Mixture-of-Experts architecture where distinct experts process fMRI signals from functionally related voxel groups, mimicking specialized brain networks. The experts are first trained to encode fMRI into the frozen CLIP space. A finetuned diffusion model then synthesizes images, guided by expert outputs through a novel dual-stage routing mechanism that dynamically weighs expert contributions across the diffusion process. MoRE-Brain offers three main advancements: First, it introduces a novel Mixture-of-Experts architecture grounded in brain network principles for neuro-decoding. Second, it achieves efficient cross-subject generalization by sharing core expert networks while adapting only subject-specific routers. Third, it provides enhanced mechanistic insight, as the explicit routing reveals precisely how different modeled brain regions shape the semantic and spatial attributes of the reconstructed image. Extensive experiments validate MoRE-Brain’s high reconstruction fidelity, with bottleneck analyses further demonstrating its effective utilization of fMRI signals, distinguishing genuine neural decoding from over-reliance on generative priors. Consequently, MoRE-Brain marks a substantial advance towards more generalizable and interpretable fMRI-based visual decoding. Code will be publicly available soon: https://github.com/yuxiangwei0808/MoRE-Brain.
从功能性磁共振成像(fMRI)中解码视觉经验提供了一种强大的方法来理解人类感知并开发先进的脑机接口。然而,目前的进展往往优先最大化重建保真度,而忽视了解释性这一对于获取神经科学洞察力的关键方面。为了解决这一差距,我们提出了MoRE-Brain,这是一个神经启发的框架,旨在实现高保真、可适应和可解释的视觉重建。MoRE-Brain独特地采用了一种层次化的混合专家架构,其中不同的专家处理来自功能相关体素组的fMRI信号,模仿专门的脑网络。专家首先被训练将fMRI编码到固定的CLIP空间中。然后,经过微调扩散模型由专家输出通过一种新型的双阶段路由机制合成图像,该机制在扩散过程中动态权衡专家的贡献。MoRE-Brain提供了三个主要进步:首先,它引入了一种基于脑网络原理的新型混合专家架构来进行神经解码。其次,通过共享核心专家网络并仅适应特定于主题的路由器,它实现了跨主题的有效泛化。第三,它提供了增强的机械洞察力,因为明确的路由机制揭示了不同建模的脑区域如何塑造重建图像的语义和空间属性。大量实验验证了MoRE-Brain的高重建保真度,瓶颈分析进一步证明了它有效利用fMRI信号的能力,区分了真正的神经解码和过度依赖生成先验知识。因此,MoRE-Brain标志着朝着更具通用性和可解释的基于fMRI的视觉解码迈出了重大的一步。代码将于近期在https://github.com/yuxiangwei0808/MoRE-Brain公开。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
利用功能性磁共振成像解码视觉体验是理解人类感知和发展先进脑机接口的有力途径。当前方法往往重视重建保真度的最大化而忽视了解释性,这对于获取神经科学洞察至关重要。为解决这一差距,我们提出MoRE-Brain框架,旨在实现高保真、可适应和可解释的视觉重建。该框架采用神经启发的层次化混合专家架构,处理功能相关体素组的fMRI信号,模仿专门化的脑网络。专家首先被训练将fMRI编码到固定的CLIP空间。随后通过微调扩散模型并借助新颖的双重阶段路由机制合成图像,该机制在扩散过程中动态权衡专家的贡献。MoRE-Brain具有三项主要优势:一是引入基于脑网络原理的混合专家架构用于神经解码;二是通过共享核心专家网络并仅适应特定主体路由器来实现跨主体高效概括;三是提供增强机制洞察力,显式路由揭示了不同模拟脑区域如何精确塑造重建图像的语义和空间属性。实验验证MoRE-Brain高重建保真度,瓶颈分析进一步证明其有效利用fMRI信号,区分真正的神经解码与过度依赖生成先验。因此,MoRE-Brain标志着在更具通用性和可解释的fMRI视觉解码方面取得重大进展。
Key Takeaways
- 利用解码视觉体验的fMRI是理解人类感知和开发先进脑机接口的有效方法。
- 当前方法偏重于重建保真度而忽视了解释性,MoRE-Brain框架旨在解决这一问题。
- MoRE-Brain采用混合专家架构处理fMRI信号,模仿脑网络工作方式。
- 该框架实现了高保真、可适应和可解释的视觉重建。
- MoRE-Brain具有跨主体概括能力,通过共享核心专家网络并适应特定主体路由器实现。
- 框架提供了增强的机制洞察力,展示了不同模拟脑区域如何影响重建图像的语义和空间属性。
点此查看论文截图


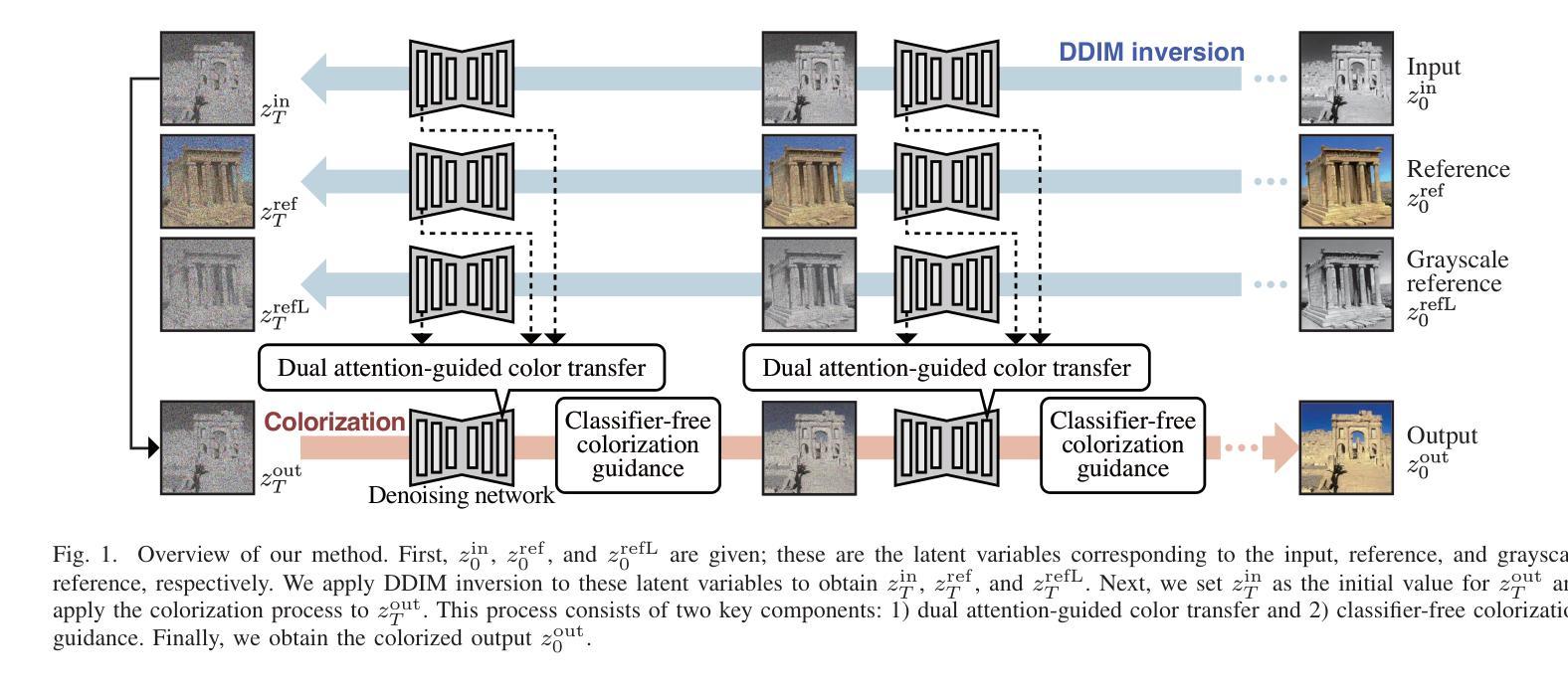
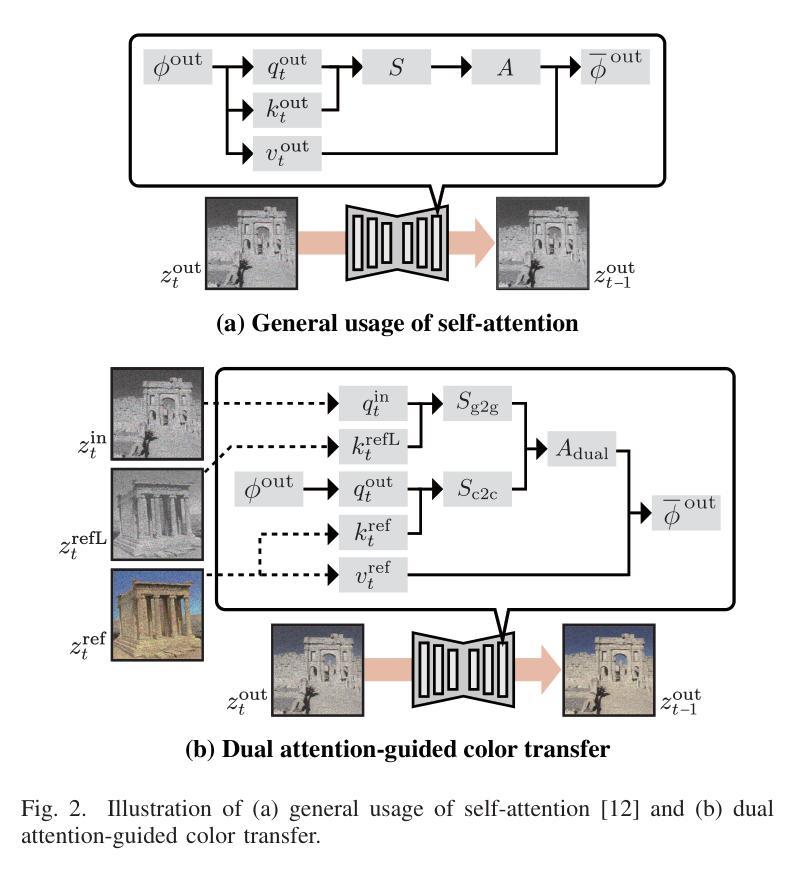
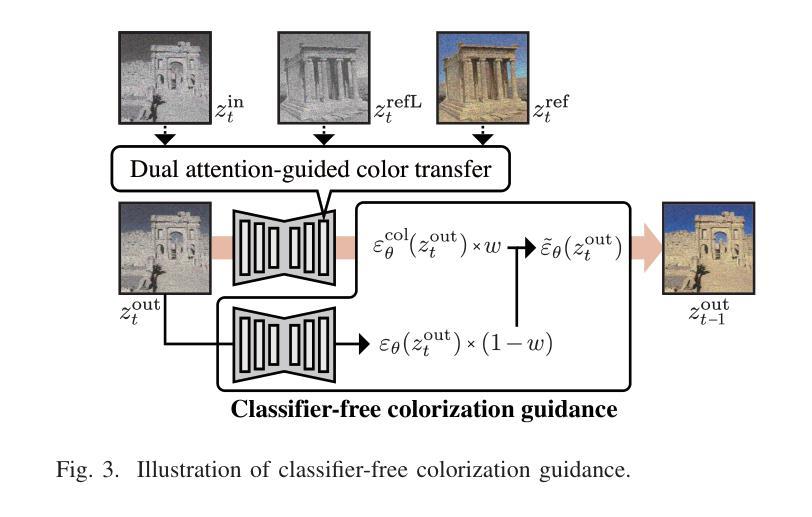
Leveraging the Powerful Attention of a Pre-trained Diffusion Model for Exemplar-based Image Colorization
Authors:Satoshi Kosugi
Exemplar-based image colorization aims to colorize a grayscale image using a reference color image, ensuring that reference colors are applied to corresponding input regions based on their semantic similarity. To achieve accurate semantic matching between regions, we leverage the self-attention module of a pre-trained diffusion model, which is trained on a large dataset and exhibits powerful attention capabilities. To harness this power, we propose a novel, fine-tuning-free approach based on a pre-trained diffusion model, making two key contributions. First, we introduce dual attention-guided color transfer. We utilize the self-attention module to compute an attention map between the input and reference images, effectively capturing semantic correspondences. The color features from the reference image is then transferred to the semantically matching regions of the input image, guided by this attention map, and finally, the grayscale features are replaced with the corresponding color features. Notably, we utilize dual attention to calculate attention maps separately for the grayscale and color images, achieving more precise semantic alignment. Second, we propose classifier-free colorization guidance, which enhances the transferred colors by combining color-transferred and non-color-transferred outputs. This process improves the quality of colorization. Our experimental results demonstrate that our method outperforms existing techniques in terms of image quality and fidelity to the reference. Specifically, we use 335 input-reference pairs from previous research, achieving an FID of 95.27 (image quality) and an SI-FID of 5.51 (fidelity to the reference). Our source code is available at https://github.com/satoshi-kosugi/powerful-attention.
基于范例的图像彩色化旨在使用参考彩色图像对灰度图像进行彩色化,确保参考颜色根据语义相似性应用于相应的输入区域。为了实现区域之间的准确语义匹配,我们利用预训练扩散模型的自注意力模块,该模块在大规模数据集上进行训练,展现出强大的注意力功能。为了利用这种能力,我们提出了一种基于预训练扩散模型的新型无需微调的方法,做出两个主要贡献。首先,我们引入双重注意力引导色彩转移。我们利用自注意力模块计算输入图像和参考图像之间的注意力图,有效地捕捉语义对应关系。然后,来自参考图像的颜色特征被转移到输入图像的语义匹配区域,由注意力图引导,最后,灰度特征被相应的颜色特征所替代。值得注意的是,我们使用双重注意力分别为灰度图像和彩色图像计算注意力图,实现更精确的语义对齐。其次,我们提出了无分类色彩化指导方法,通过结合色彩转移和非色彩转移的输出,增强转移的色彩。这一过程提高了彩色化的质量。我们的实验结果证明,我们的方法在图像质量和参考忠实度方面超越了现有技术。具体来说,我们使用335个输入-参考对来自之前的研究,达到FID(图像质量)为95.27,SI-FID(对参考的忠实度)为5.51。我们的源代码可在https://github.com/satoshi-kosugi/powerful-attention找到。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted to IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems for Video Technology (TCSVT)
Summary
彩色化图像的目标是利用参考彩色图像对灰度图像进行着色,确保参考颜色根据语义相似性应用于对应的输入区域。为了实现区域之间的准确语义匹配,我们利用预训练扩散模型的自注意力模块,该模块在大规模数据集上训练,展现出强大的注意力功能。我们提出了一种基于预训练扩散模型的无需微调的新方法,该方法做出了两个关键贡献。首先,我们引入了双注意力引导色彩转移。利用自注意力模块计算输入图像和参考图像之间的注意力图,有效地捕捉语义对应关系。参考图像的颜色特征被转移到输入图像的语义匹配区域,由注意力图引导,最后灰度特征被相应的颜色特征所替代。其次,我们提出了无分类色彩化指导方法,通过结合色彩转移和非色彩转移的输出,提高了转移颜色的质量。实验结果表明,我们的方法在图像质量和保持对参考图像的忠实度方面均优于现有技术。具体地,我们从之前的研究中使用了335个输入-参考对,实现了95.27的FID(图像质量)和5.51的SI-FID(对参考的忠实度)。我们的源代码可在https://github.com/satoshi-kosugi/powerful-attention上找到。
Key Takeaways
- 方法使用参考彩色图像来为灰度图像着色,并基于语义相似性匹配输入区域和参考颜色。
- 利用预训练扩散模型的自注意力模块实现精确语义匹配。
- 提出无需微调的新方法,利用双注意力引导色彩转移,通过注意力图捕捉语义对应关系并实现颜色转移。
- 引入无分类色彩化指导方法,结合色彩转移和非色彩转移的输出提高颜色质量。
- 方法在图像质量和忠实于参考方面优于现有技术。
- 使用335个输入-参考对进行实验验证方法的有效性。
点此查看论文截图
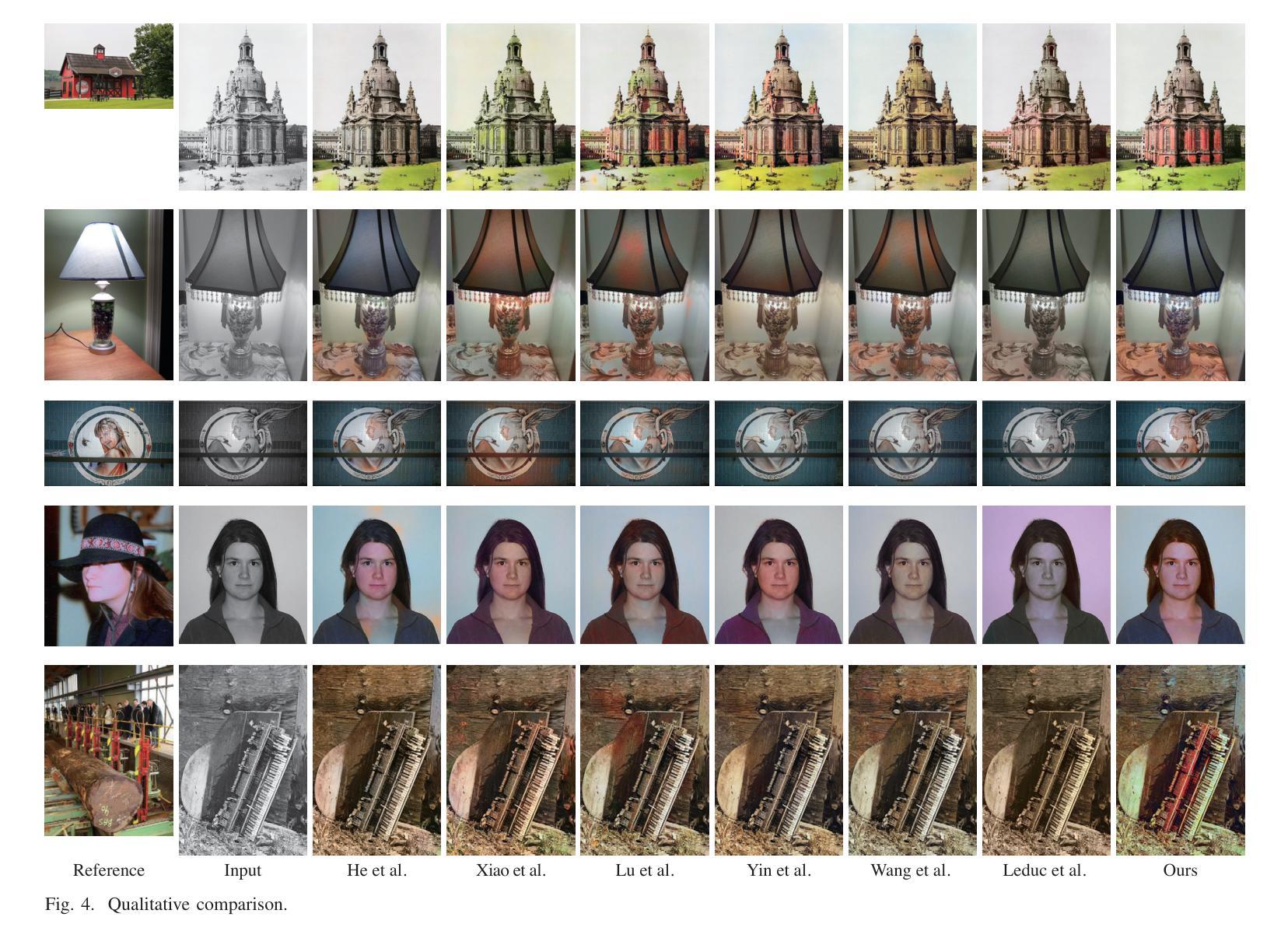


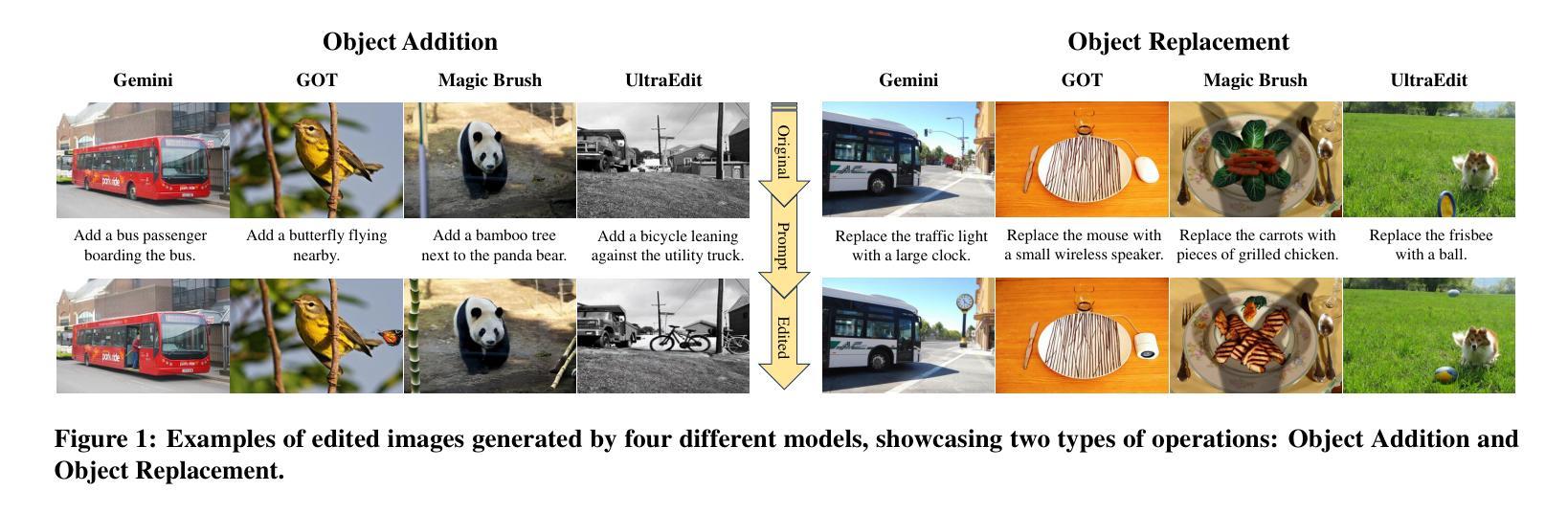
FragFake: A Dataset for Fine-Grained Detection of Edited Images with Vision Language Models
Authors:Zhen Sun, Ziyi Zhang, Zeren Luo, Zeyang Sha, Tianshuo Cong, Zheng Li, Shiwen Cui, Weiqiang Wang, Jiaheng Wei, Xinlei He, Qi Li, Qian Wang
Fine-grained edited image detection of localized edits in images is crucial for assessing content authenticity, especially given that modern diffusion models and image editing methods can produce highly realistic manipulations. However, this domain faces three challenges: (1) Binary classifiers yield only a global real-or-fake label without providing localization; (2) Traditional computer vision methods often rely on costly pixel-level annotations; and (3) No large-scale, high-quality dataset exists for modern image-editing detection techniques. To address these gaps, we develop an automated data-generation pipeline to create FragFake, the first dedicated benchmark dataset for edited image detection, which includes high-quality images from diverse editing models and a wide variety of edited objects. Based on FragFake, we utilize Vision Language Models (VLMs) for the first time in the task of edited image classification and edited region localization. Experimental results show that fine-tuned VLMs achieve higher average Object Precision across all datasets, significantly outperforming pretrained models. We further conduct ablation and transferability analyses to evaluate the detectors across various configurations and editing scenarios. To the best of our knowledge, this work is the first to reformulate localized image edit detection as a vision-language understanding task, establishing a new paradigm for the field. We anticipate that this work will establish a solid foundation to facilitate and inspire subsequent research endeavors in the domain of multimodal content authenticity.
精细编辑图像的图像检测对于评估内容真实性至关重要,尤其是考虑到现代扩散模型和图像编辑方法可以产生高度逼真的操纵。然而,此领域面临三个挑战:(1)二元分类器只产生全局真实或虚假的标签,无法提供定位;(2)传统计算机视觉方法通常依赖于昂贵的像素级注释;(3)对于现代图像编辑检测技术,尚不存在大规模高质量的数据集。为解决这些空白,我们开发了一个自动化的数据生成管道来创建FragFake,这是专门用于编辑图像检测的第一个基准数据集,包括来自各种编辑模型的高质量图像和多种编辑对象。基于FragFake,我们首次在编辑图像分类和编辑区域定位任务中使用视觉语言模型(VLMs)。实验结果表明,经过微调的VLMs在所有数据集上达到了更高的对象精度平均值,显著优于预训练模型。我们进一步进行了消融和可转移性分析,以评估检测器在各种配置和编辑场景中的表现。据我们所知,这项工作首次将局部图像编辑检测重新定位为视觉语言理解任务,为该领域建立了新的范式。我们预计这项工作将为多模式内容真实性的后续研究工作和提供灵感。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 14pages,15 figures
Summary
本文介绍了图像编辑检测的重要性及其所面临的挑战,包括分类器无法提供局部化信息、依赖高成本像素级标注以及缺乏针对现代图像编辑检测技术的大规模高质量数据集。为解决这些问题,研究团队开发了一个自动化数据生成管道,创建了FragFake数据集,用于编辑图像检测任务。基于该数据集,研究首次利用视觉语言模型(VLMs)进行图像分类和编辑区域定位任务,并取得了优异的结果。此研究开创性地将其改革为视觉语言理解任务,为领域中的后续研究提供了一个新方向。同时强调了其对多媒体内容真实性的重要性。
Key Takeaways
- 图像编辑检测对于评估内容真实性至关重要,尤其是考虑到现代扩散模型和图像编辑方法可以产生高度逼真的操作。
- 此领域面临三大挑战:分类器无法定位编辑区域、依赖昂贵的像素级标注以及缺乏针对现代图像编辑检测的大规模高质量数据集。
- 提出并创建FragFake数据集,这是一个专门针对编辑图像检测任务的高质量数据集,包含从不同编辑模型生成的各种高质量图像和多种编辑对象。
- 研究首次使用视觉语言模型(VLMs)进行图像分类和编辑区域定位任务,实验结果显示其性能优于预训练模型。
点此查看论文截图

Learning Joint ID-Textual Representation for ID-Preserving Image Synthesis
Authors:Zichuan Liu, Liming Jiang, Qing Yan, Yumin Jia, Hao Kang, Xin Lu
We propose a novel framework for ID-preserving generation using a multi-modal encoding strategy rather than injecting identity features via adapters into pre-trained models. Our method treats identity and text as a unified conditioning input. To achieve this, we introduce FaceCLIP, a multi-modal encoder that learns a joint embedding space for both identity and textual semantics. Given a reference face and a text prompt, FaceCLIP produces a unified representation that encodes both identity and text, which conditions a base diffusion model to generate images that are identity-consistent and text-aligned. We also present a multi-modal alignment algorithm to train FaceCLIP, using a loss that aligns its joint representation with face, text, and image embedding spaces. We then build FaceCLIP-SDXL, an ID-preserving image synthesis pipeline by integrating FaceCLIP with Stable Diffusion XL (SDXL). Compared to prior methods, FaceCLIP-SDXL enables photorealistic portrait generation with better identity preservation and textual relevance. Extensive experiments demonstrate its quantitative and qualitative superiority.
我们提出了一种新的ID保留生成框架,采用多模态编码策略,而不是通过适配器向预训练模型注入身份特征。我们的方法将身份和文本视为统一的条件输入。为了实现这一点,我们引入了FaceCLIP,这是一个多模态编码器,它学习身份和文本语义的联合嵌入空间。给定参考人脸和文本提示,FaceCLIP生成一个统一表示,该表示编码身份和文本,使基础扩散模型生成身份一致且文本对齐的图像。我们还提出了一种使用损失函数对齐其联合表示与面部、文本和图像嵌入空间的多模态对齐算法来训练FaceCLIP。然后,我们将FaceCLIP与Stable Diffusion XL(SDXL)相结合,构建了FaceCLIP-SDXL,一个ID保留图像合成管道。与之前的方法相比,FaceCLIP-SDXL能够实现具有更好身份保留和文本相关性的照片级肖像生成。大量实验证明了其在数量和质量上的优越性。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文提出了一种新颖的ID保留生成框架,采用多模态编码策略,而非通过适配器注入身份特征到预训练模型中。该方法将身份和文本视为统一的条件输入。为此,引入了FaceCLIP多模态编码器,学习身份和文本语义的联合嵌入空间。给定参考人脸和文本提示,FaceCLIP产生统一表示,编码身份和文本,以条件基础扩散模型生成一致身份和文本对齐的图像。还提出了一种多模态对齐算法来训练FaceCLIP,使用损失函数将其联合表示与面部、文本和图像嵌入空间对齐。通过与Stable Diffusion XL(SDXL)集成,构建了FaceCLIP-SDXL身份保留图像合成管道,实现了具有更好身份保留和文本相关性的逼真肖像生成。实验证明其定量和定性优势。
Key Takeaways
- 引入了一种新颖的ID保留生成框架,利用多模态编码策略。
- 提出了FaceCLIP多模态编码器,可以学习身份和文本语义的联合嵌入空间。
- FaceCLIP能够产生统一表示,编码身份和文本,为扩散模型提供条件。
- 介绍了多模态对齐算法来训练FaceCLIP,通过损失函数实现面部、文本和图像嵌入空间的对齐。
- 构建了FaceCLIP-SDXL身份保留图像合成管道,集成了FaceCLIP与Stable Diffusion XL(SDXL)。
- 该方法能够实现逼真肖像生成,具有更好的身份保留和文本相关性。
点此查看论文截图

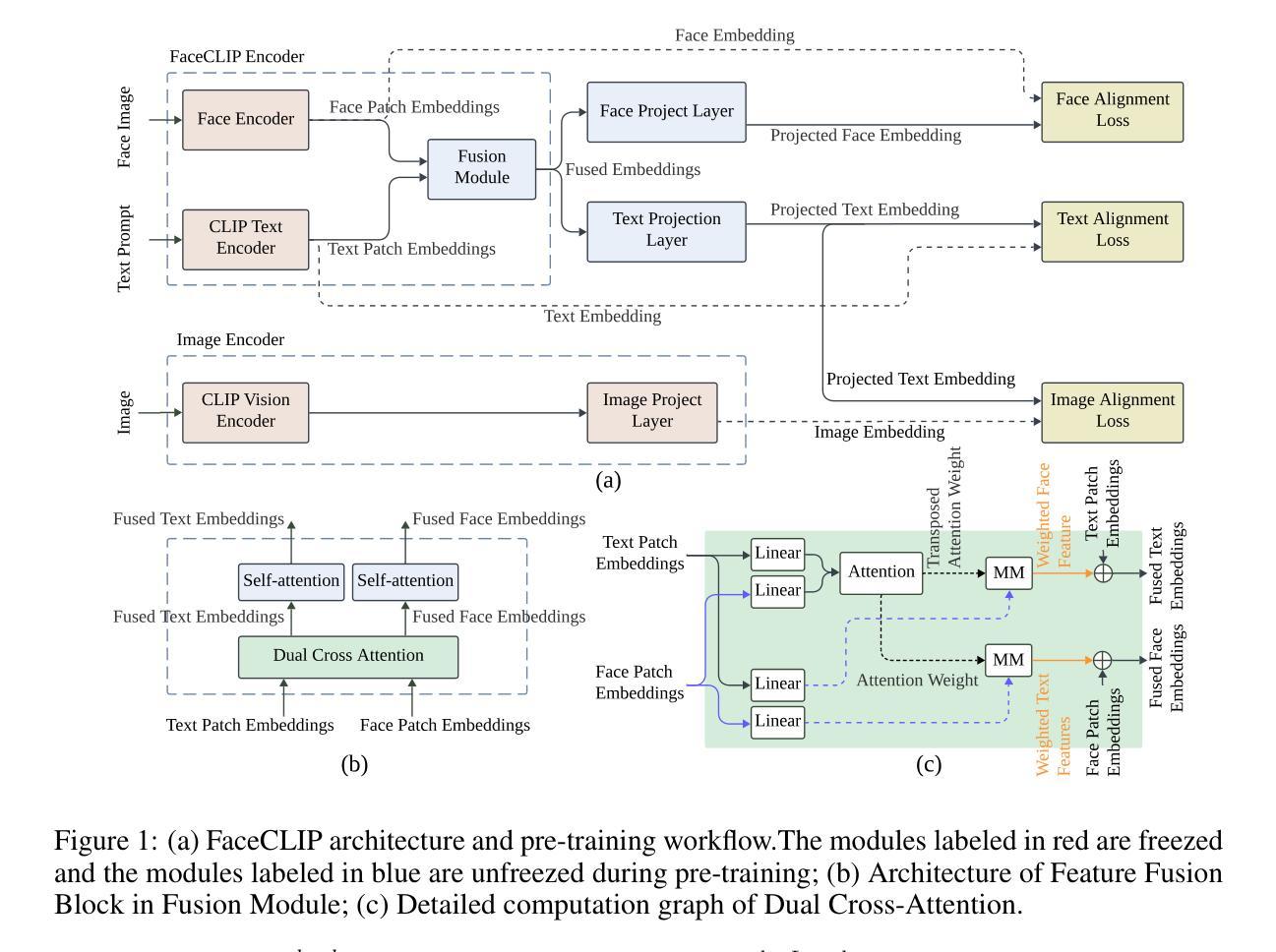
Split Gibbs Discrete Diffusion Posterior Sampling
Authors:Wenda Chu, Zihui Wu, Yifan Chen, Yang Song, Yisong Yue
We study the problem of posterior sampling in discrete-state spaces using discrete diffusion models. While posterior sampling methods for continuous diffusion models have achieved remarkable progress, analogous methods for discrete diffusion models remain challenging. In this work, we introduce a principled plug-and-play discrete diffusion posterior sampling algorithm based on split Gibbs sampling, which we call SGDD. Our algorithm enables reward-guided generation and solving inverse problems in discrete-state spaces. We demonstrate the convergence of SGDD to the target posterior distribution and verify this through controlled experiments on synthetic benchmarks. Our method enjoys state-of-the-art posterior sampling performance on a range of benchmarks for discrete data, including DNA sequence design, discrete image inverse problems, and music infilling, achieving more than 30% improved performance compared to existing baselines.
我们研究了离散状态空间中后采样的问题,使用了离散扩散模型。虽然连续扩散模型的后采样方法已经取得了显著的进步,但离散扩散模型的后采样方法仍然具有挑战性。在这项工作中,我们基于分割Gibbs采样引入了一种原则性的即插即用离散扩散后采样算法,我们称之为SGDD。我们的算法能够实现奖励引导生成和离散状态空间中的反问题求解。我们证明了SGDD能够收敛到目标后验分布,并通过合成基准的有控制实验验证了这一点。我们的方法在离散数据的一系列基准测试中享有最先进的后采样性能,包括DNA序列设计、离散图像反问题和音乐填充,与现有基线相比,性能提高了30%以上。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文研究了离散状态空间中的后采样问题,采用离散扩散模型进行研究。尽管连续扩散模型的后采样方法已经取得了显著进展,但离散扩散模型的后采样方法仍然具有挑战性。本文提出了一种基于分裂Gibbs采样的离散扩散后采样算法SGDD,该算法可实现奖励引导生成和解决离散状态空间中的逆问题。实验证明SGDD能收敛到目标后验分布,并在合成基准测试上得到验证。该方法在离散数据的一系列基准测试中表现出卓越的后采样性能,包括DNA序列设计、离散图像逆问题和音乐填充,相较于现有基线性能提升超过30%。
Key Takeaways
- 研究了离散状态空间中的后采样问题,这是离散扩散模型中的一个挑战。
- 提出了一种基于分裂Gibbs采样的离散扩散后采样算法SGDD。
- SGDD算法能够执行奖励引导生成和解决离散状态空间中的逆问题。
- 实验证明了SGDD能收敛到目标后验分布。
- SGDD在合成基准测试上表现出卓越性能。
- 在一系列基准测试中,SGDD在DNA序列设计、离散图像逆问题和音乐填充等方面表现出比现有基线更好的性能。
点此查看论文截图

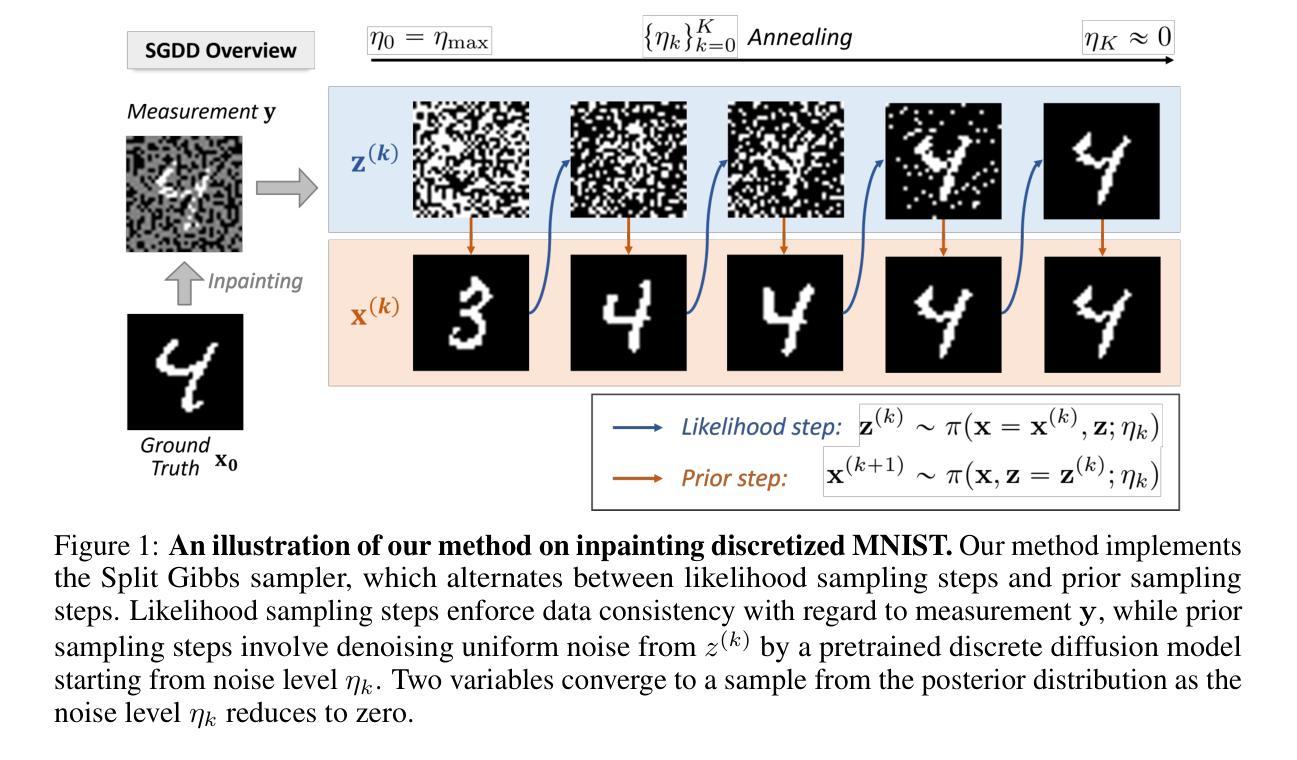
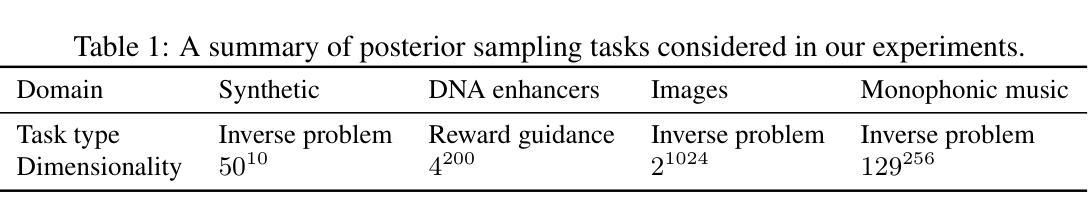
Remasking Discrete Diffusion Models with Inference-Time Scaling
Authors:Guanghan Wang, Yair Schiff, Subham Sekhar Sahoo, Volodymyr Kuleshov
Part of the success of diffusion models stems from their ability to perform iterative refinement, i.e., repeatedly correcting outputs during generation. However, modern masked discrete diffusion lacks this capability: when a token is generated, it cannot be updated again, even when it introduces an error. Here, we address this limitation by introducing the remasking diffusion model (ReMDM) sampler, a method that can be applied to pretrained masked diffusion models in a principled way and that is derived from a discrete diffusion model with a custom remasking backward process. Most interestingly, ReMDM endows discrete diffusion with a form of inference-time compute scaling. By increasing the number of sampling steps, ReMDM generates natural language outputs that approach the quality of autoregressive models, whereas when the computation budget is limited, ReMDM better maintains quality. ReMDM also improves sample quality of masked diffusion models for discretized images, and in scientific domains such as molecule design, ReMDM facilitates diffusion guidance and pushes the Pareto frontier of controllability relative to classical masking and uniform noise diffusion. We provide the code along with a blog post on the project page: https://remdm.github.io
扩散模型的部分成功源于其进行迭代优化的能力,即生成过程中反复修正输出。然而,现代掩码离散扩散缺乏这种能力:一旦生成标记,即使出现错误,也无法再次更新。在这里,我们通过引入重掩码扩散模型(ReMDM)采样器来解决这一限制,这是一种可以原则性地应用于预训练掩码扩散模型的方法,它来源于具有自定义反向重掩码过程的离散扩散模型。最有趣的是,ReMDM为离散扩散赋予了推理时间计算缩放的形式。通过增加采样步骤的数量,ReMDM生成的自然语言输出接近自回归模型的质量,而当计算预算有限时,ReMDM能更好地保持质量。ReMDM还提高了离散图像、分子设计等科学领域的掩码扩散模型的样本质量,并推动了相对于传统掩码和均匀噪声扩散的可控性的帕累托前沿。我们已提供项目页面上的代码及博客文章:https://remdm.github.io。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Project page: https://remdm.github.io
Summary
扩散模型的一部分成功源于其能够进行迭代优化的能力,即生成过程中不断修正输出。然而,现代掩码离散扩散缺乏这种能力:一旦生成令牌,即使出现错误,也不能再次更新。我们通过引入重掩码扩散模型(ReMDM)采样器来解决这一问题,该方法可以原则性地应用于预训练的掩码扩散模型,源于离散扩散模型,具有自定义的重掩码逆向过程。ReMDM使离散扩散具有一种推理时间计算缩放形式。通过增加采样步骤的数量,ReMDM生成的自然语言输出接近自回归模型的质量,而在计算预算有限时,ReMDM能更好地保持质量。此外,ReMDM还提高了掩码扩散模型在离散图像以及科学领域(如分子设计)的样本质量,推动了可控性的帕累托前沿,相对于传统的掩码和均匀噪声扩散有所突破。
Key Takeaways
- 扩散模型能够通过迭代优化生成结果。
- 现代掩码离散扩散无法更新已生成的令牌。
- ReMDM采样器解决了这一限制,提高了离散扩散模型的性能。
- ReMDM能够在有限的计算预算内生成高质量的自然语言输出。
- ReMDM提高了掩码扩散模型在图像科学领域的样本质量。
- ReMDM在分子设计等领域推动了扩散指导的帕累托前沿。
点此查看论文截图

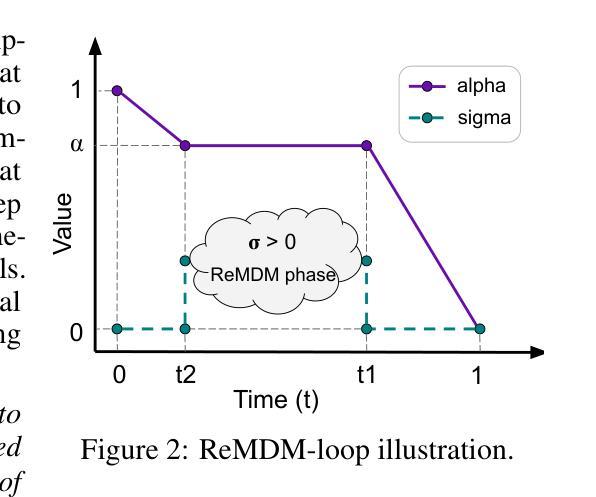
Dress-1-to-3: Single Image to Simulation-Ready 3D Outfit with Diffusion Prior and Differentiable Physics
Authors:Xuan Li, Chang Yu, Wenxin Du, Ying Jiang, Tianyi Xie, Yunuo Chen, Yin Yang, Chenfanfu Jiang
Recent advances in large models have significantly advanced image-to-3D reconstruction. However, the generated models are often fused into a single piece, limiting their applicability in downstream tasks. This paper focuses on 3D garment generation, a key area for applications like virtual try-on with dynamic garment animations, which require garments to be separable and simulation-ready. We introduce Dress-1-to-3, a novel pipeline that reconstructs physics-plausible, simulation-ready separated garments with sewing patterns and humans from an in-the-wild image. Starting with the image, our approach combines a pre-trained image-to-sewing pattern generation model for creating coarse sewing patterns with a pre-trained multi-view diffusion model to produce multi-view images. The sewing pattern is further refined using a differentiable garment simulator based on the generated multi-view images. Versatile experiments demonstrate that our optimization approach substantially enhances the geometric alignment of the reconstructed 3D garments and humans with the input image. Furthermore, by integrating a texture generation module and a human motion generation module, we produce customized physics-plausible and realistic dynamic garment demonstrations. Project page: https://dress-1-to-3.github.io/
近期大型模型的进展极大地推动了图像到3D重建的技术。然而,生成的模型通常被融合成单个部分,这在下游任务中的应用受到局限。本文重点关注3D服装生成,这是虚拟试穿等应用的关键领域,要求服装可分离且可模拟动态服装动画。我们引入了Dress-1-to-3,这是一个新型管道,可以从野生图像中重建物理可行的、可模拟的分离服装,包括缝纫图案和人类。从图像开始,我们的方法结合预训练的图像到缝纫图案生成模型来创建粗略的缝纫图案,以及与预训练的多视角扩散模型来生成多视角图像。缝纫图案进一步使用基于生成的多视角图像的可微分服装模拟器进行细化。多种实验表明,我们的优化方法极大地提高了重建的3D服装和人体与输入图像的几何对齐。此外,通过集成纹理生成模块和人体运动生成模块,我们生成了定制的、物理可行的和逼真的动态服装演示。项目页面:https://dress-1-to-3.github.io/
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Project page: https://dress-1-to-3.github.io/
Summary
本文介绍了Dress-1-to-3项目,该项目专注于从图像重建物理仿真可用的分离衣物模型。通过使用预训练图像到缝纫图案生成模型和多视角扩散模型,结合可微分的衣物模拟器,实现从单张图像重建出具有物理仿真效果的分离衣物。此方法提高了重建的3D衣物与输入图像几何对齐的精确度,并可通过集成纹理生成模块和运动生成模块,产生逼真的动态衣物演示。
Key Takeaways
- Dress-1-to-3项目实现从单张图像重建物理仿真可用的分离衣物模型。
- 使用预训练图像到缝纫图案生成模型创建粗缝纫图案。
- 利用预训练的多视角扩散模型生成多视角图像。
- 缝纫图案基于生成的多视角图像使用可微分的衣物模拟器进行精细调整。
- 优化方法提高了重建的3D衣物与输入图像的几何对齐精度。
- 通过集成纹理生成模块,产生定制的、物理仿真的动态衣物演示。
点此查看论文截图

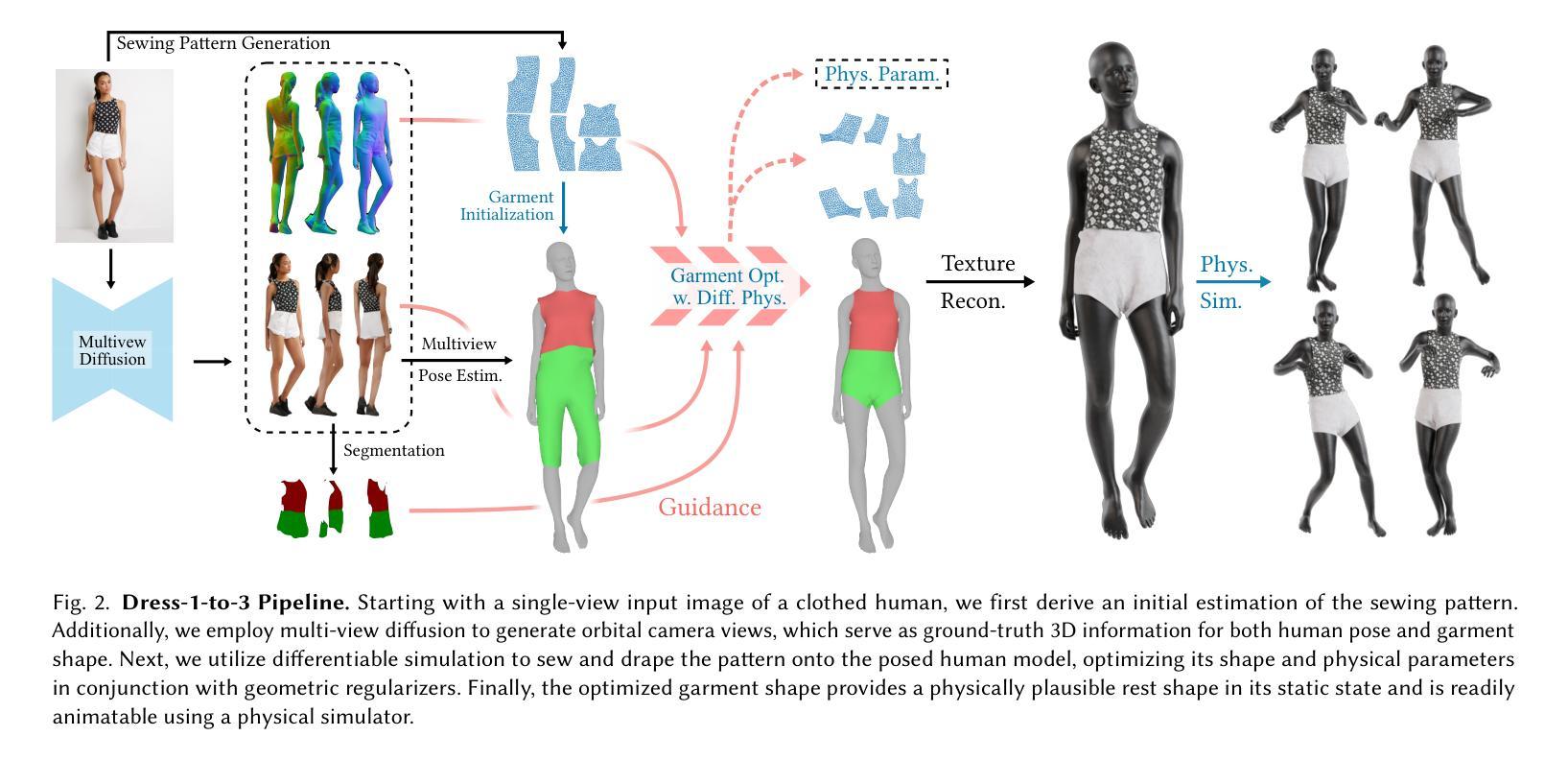
SAeUron: Interpretable Concept Unlearning in Diffusion Models with Sparse Autoencoders
Authors:Bartosz Cywiński, Kamil Deja
Diffusion models, while powerful, can inadvertently generate harmful or undesirable content, raising significant ethical and safety concerns. Recent machine unlearning approaches offer potential solutions but often lack transparency, making it difficult to understand the changes they introduce to the base model. In this work, we introduce SAeUron, a novel method leveraging features learned by sparse autoencoders (SAEs) to remove unwanted concepts in text-to-image diffusion models. First, we demonstrate that SAEs, trained in an unsupervised manner on activations from multiple denoising timesteps of the diffusion model, capture sparse and interpretable features corresponding to specific concepts. Building on this, we propose a feature selection method that enables precise interventions on model activations to block targeted content while preserving overall performance. Our evaluation shows that SAeUron outperforms existing approaches on the UnlearnCanvas benchmark for concepts and style unlearning, and effectively eliminates nudity when evaluated with I2P. Moreover, we show that with a single SAE, we can remove multiple concepts simultaneously and that in contrast to other methods, SAeUron mitigates the possibility of generating unwanted content under adversarial attack. Code and checkpoints are available at https://github.com/cywinski/SAeUron.
扩散模型虽然强大,但可能无意中生成有害或不良内容,引发严重的伦理和安全担忧。最近的机器非学习技术提供了新的解决方案,但往往缺乏透明度,使得难以了解它们对基础模型所做的改变。在这项研究中,我们介绍了SAeUron,这是一种利用稀疏自动编码器(SAE)学习到的特性来消除文本到图像扩散模型中不需要概念的新方法。首先,我们证明了在扩散模型的多个去噪时间步长的激活上采用无监督方式训练的SAE可以捕获对应于特定概念的稀疏和可解释的特性。在此基础上,我们提出了一种特征选择方法,能够对模型激活进行精确干预,以阻止目标内容,同时保留整体性能。我们的评估显示,在概念和风格非学习的UnlearnCanvas基准测试中,SAeUron优于现有方法,在评估裸体内容时与I2P结合使用可以有效消除其存在。此外,我们还表明,使用一个单一的SAE可以同时消除多个概念,而且与其他方法相比,SAeUron减轻了生成对抗攻击下可能产生的不必要内容的可能性。代码和检查点可在https://github.com/cywinski/SAeUron找到。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了Diffusion模型可能产生的伦理和安全问题,即可能生成有害或不受欢迎的内容。尽管现有的机器遗忘法提供了一种可能的解决方案,但它们往往缺乏透明度,难以了解对基础模型所做的改变。本文提出了一种新方法SAeUron,它利用稀疏自编码器(SAE)的特性来消除文本到图像扩散模型中的不需要的概念。实验表明,SAeUron在概念与风格遗忘的基准测试中表现优于现有方法,能够有效消除图像中的裸体内容。此外,我们还展示了单个SAE可以同时消除多个概念的能力,并且与其他方法相比,SAeUron减轻了生成对抗性攻击下产生的不必要内容的可能性。
Key Takeaways
- Diffusion模型可能会生成有害或不受欢迎的内容,引发伦理和安全担忧。
- 现有机器遗忘法解决此问题但缺乏透明度。
- SAeUron方法利用稀疏自编码器(SAE)的特性消除扩散模型中的不需要的概念。
- SAeUron在概念与风格遗忘的测试中表现优异,有效消除特定内容。
- SAeUron能同时消除多个概念。
- SAeUron降低了生成对抗性攻击下产生不必要内容的可能性。
点此查看论文截图
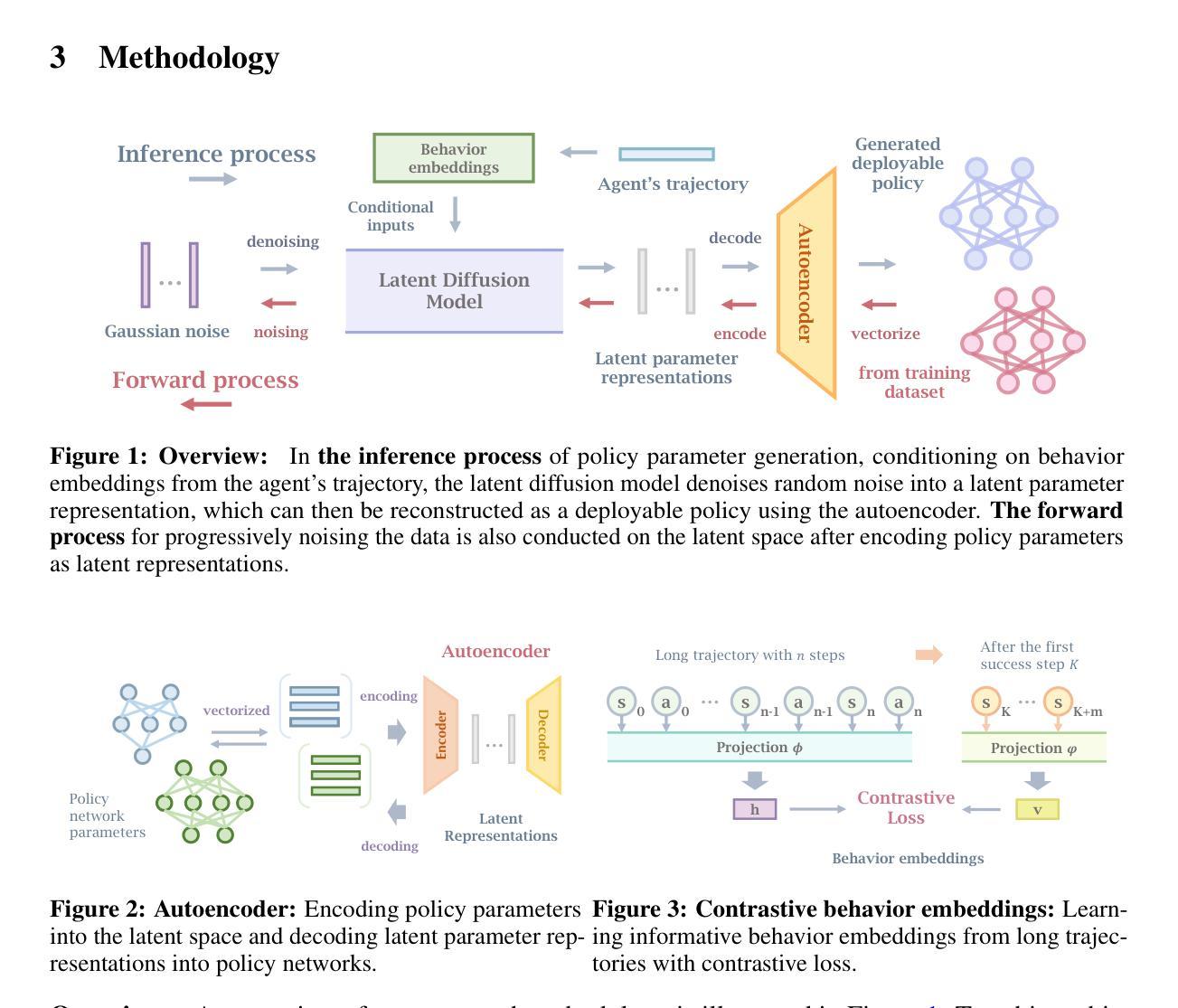
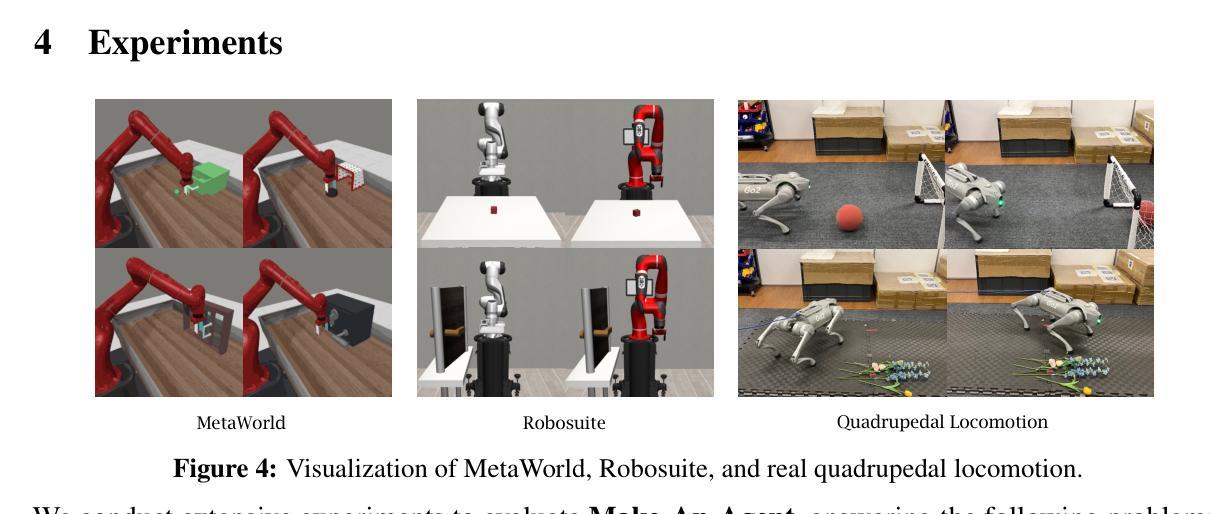
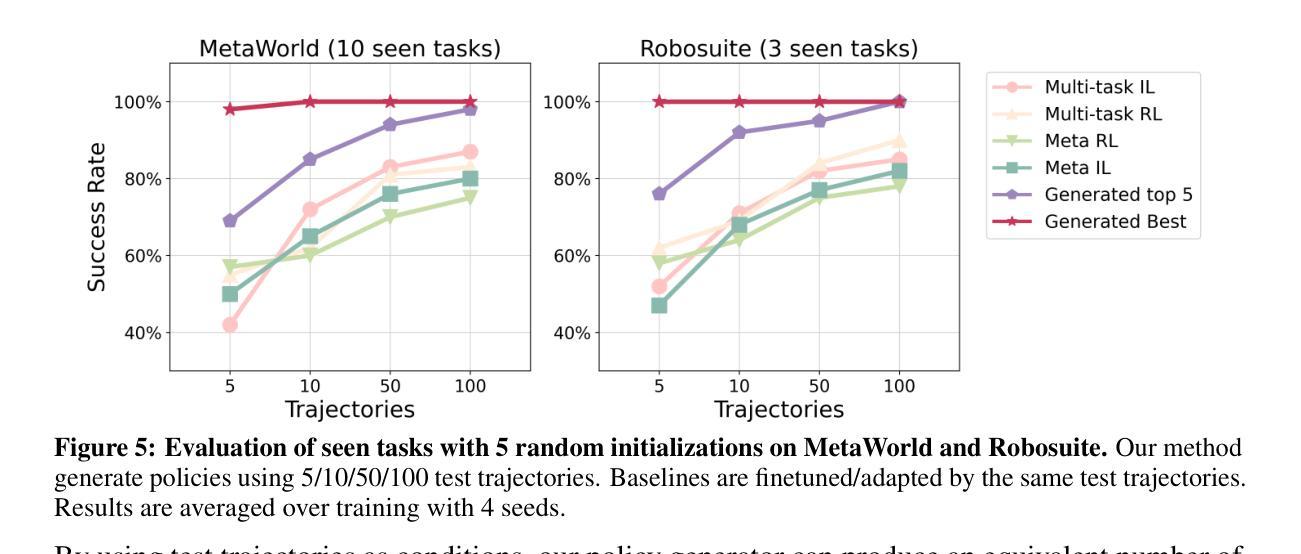
Make-An-Agent: A Generalizable Policy Network Generator with Behavior-Prompted Diffusion
Authors:Yongyuan Liang, Tingqiang Xu, Kaizhe Hu, Guangqi Jiang, Furong Huang, Huazhe Xu
Can we generate a control policy for an agent using just one demonstration of desired behaviors as a prompt, as effortlessly as creating an image from a textual description? In this paper, we present Make-An-Agent, a novel policy parameter generator that leverages the power of conditional diffusion models for behavior-to-policy generation. Guided by behavior embeddings that encode trajectory information, our policy generator synthesizes latent parameter representations, which can then be decoded into policy networks. Trained on policy network checkpoints and their corresponding trajectories, our generation model demonstrates remarkable versatility and scalability on multiple tasks and has a strong generalization ability on unseen tasks to output well-performed policies with only few-shot demonstrations as inputs. We showcase its efficacy and efficiency on various domains and tasks, including varying objectives, behaviors, and even across different robot manipulators. Beyond simulation, we directly deploy policies generated by Make-An-Agent onto real-world robots on locomotion tasks. Project page: https://cheryyunl.github.io/make-an-agent/
我们可以像从文本描述中创建图像一样,仅使用一个期望行为的演示来提示为智能体生成控制策略吗?在本文中,我们介绍了Make-An-Agent,这是一种新型的策略参数生成器,它利用条件扩散模型的力量进行行为到策略的生成。在行为嵌入的指导下(这些嵌入编码了轨迹信息),我们的策略生成器合成潜在参数表示,然后可以将其解码为策略网络。我们的生成模型在多个任务上表现出卓越的通用性和可扩展性,在未见过的新任务上具有很强的泛化能力,仅使用少数演示作为输入即可输出表现良好的策略。我们在各种领域和任务中展示了它的功效和效率,包括不同的目标、行为和甚至不同的机器人操纵器。除了模拟之外,我们还直接将Make-An-Agent生成的策略部署到现实世界中的机器人上进行运动任务。项目页面:https://cheryyunl.github.io/make-an-agent/
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Annual Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems 38
Summary
使用单一演示行为生成代理控制策略,如同根据文字描述生成图像一样简单便捷。本研究提出了Make-An-Agent,这是一种新型策略参数生成器,利用条件扩散模型实现行为到策略的生成。该策略生成器通过行为嵌入编码轨迹信息,合成潜在参数表示,然后解码为策略网络。在策略网络检查点及其对应轨迹的训练下,该生成模型在多个任务上表现出卓越的多功能性和可扩展性,并且对未见任务的策略输出具有较强的泛化能力,仅使用少量演示作为输入。它在各种领域和任务中展示了有效性和高效性,包括不同的目标、行为和机器人操作器。此外,我们将Make-An-Agent生成的策略直接部署到真实世界机器人上执行运动任务。
Key Takeaways
- Make-An-Agent利用条件扩散模型实现了从行为到策略的生成。
- 该策略生成器通过行为嵌入编码轨迹信息,进而合成潜在参数表示。
- 策略生成器可以解码为策略网络,具备卓越的多功能性和可扩展性。
- 生成模型在少量演示作为输入的情况下,对未见任务具有强泛化能力。
- Make-An-Agent在各种领域和任务中表现出有效性和高效性,包括不同的目标、行为和机器人操作器。
- Make-An-Agent可以直接将生成的策略部署到真实世界的机器人上。
点此查看论文截图